User login
New uterine compression technique controls postpartum hemorrhage
A newly described uterine compression technique that uses simple supplies and does not require hysterotomy was successful in controlling postpartum hemorrhage in 16 of 18 (89%) women in two teaching hospitals in Nigeria, averting the need for hysterectomy in these women.
Each of the women had severe postpartum hemorrhage attributable to uterine atony and had undergone local protocols for medical management “to no avail,” Chidi Ochu Uzoma Esike, MD, who developed the technique, wrote in a report published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The technique involves placing six polyglactin (Vicryl) #2 or chromic #2 sutures in the lower uterine segment – three anteriorly and three posteriorly – and could be particularly useful in developing countries, where many women die from postpartum hemorrhage “because most of the medical officers who attend the majority of births in health facilities can perform cesarean delivery but cannot perform hysterectomy and find existing compression suture techniques too complex to perform,” Dr. Esike wrote in the case series report.
In addition, “specialized sutures and needles required for some of the known compression techniques are not readily available,” said Dr. Esike of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Alex Ekwueme Federal University Hospital and Ebyonyi State University in Abakaliki, Nigeria.
Angela Martin, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that “having a quick and effective surgical technique [for uncontrollable postpartum hemorrhage] is essential.”
“I love that Esike’s technique uses polyglactin (Vicryl) or chromic sutures. These are familiar to most surgeons, cheap, and typically available even in most resource-deficient settings,” said Dr. Martin, who was asked to comment on the report, adding that several of the known surgical techniques for uterine atony require a skilled operator and are indeed not universally feasible.
“If successful,” Dr. Martin said in an interview, “compression sutures can be lifesaving and fertility preserving.”
The technique involves tying the two middle sutures (one placed anteriorly and one posteriorly) at the fundus as an assistant slowly and continuously compresses the uterus. The more laterally placed sutures are tied similarly, with each pair tied at about 4 cm from the lateral edge of the uterus. “As the uterus is compressed, the slack should be taken up by the sutures before tying,” said Dr. Esike, whose report features both diagrammatic and photographic representations of suture insertion and tying.
For patients who delivered vaginally – nine in this case series – the technique involves performing a laparotomy and exteriorizing the uterus. The technique’s “suture placement,” Dr. Esike wrote, “took 11-25 minutes from the onset of laparotomy to completion.” There were no short or long-term complications in any of the 18 patients.
B-Lynch compression sutures are more complex to perform and require a larger curved needle, Dr. Esike wrote, and the Hayman technique similarly requires a longer needle that may not be available in resource-constrained countries. The hysterotomy required in the B-Lynch technique, Dr. Esike added, “leads to the uterus not contracting maximally until it is repaired,” which increases blood loss from the procedure.
Dr. Martin said the small size of the case series is not discouraging. “The B-Lynch suture was widely adopted after it was described in five cases in 1997,” she said. There are no randomized controlled trials to suggest that one method of uterine compression sutures is better than another. “Ultimately,” she said, “the technique chosen will depend on the surgeon’s training and available supplies.”
Dr. Esike had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Martin had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Esike COU. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003947.
A newly described uterine compression technique that uses simple supplies and does not require hysterotomy was successful in controlling postpartum hemorrhage in 16 of 18 (89%) women in two teaching hospitals in Nigeria, averting the need for hysterectomy in these women.
Each of the women had severe postpartum hemorrhage attributable to uterine atony and had undergone local protocols for medical management “to no avail,” Chidi Ochu Uzoma Esike, MD, who developed the technique, wrote in a report published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The technique involves placing six polyglactin (Vicryl) #2 or chromic #2 sutures in the lower uterine segment – three anteriorly and three posteriorly – and could be particularly useful in developing countries, where many women die from postpartum hemorrhage “because most of the medical officers who attend the majority of births in health facilities can perform cesarean delivery but cannot perform hysterectomy and find existing compression suture techniques too complex to perform,” Dr. Esike wrote in the case series report.
In addition, “specialized sutures and needles required for some of the known compression techniques are not readily available,” said Dr. Esike of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Alex Ekwueme Federal University Hospital and Ebyonyi State University in Abakaliki, Nigeria.
Angela Martin, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that “having a quick and effective surgical technique [for uncontrollable postpartum hemorrhage] is essential.”
“I love that Esike’s technique uses polyglactin (Vicryl) or chromic sutures. These are familiar to most surgeons, cheap, and typically available even in most resource-deficient settings,” said Dr. Martin, who was asked to comment on the report, adding that several of the known surgical techniques for uterine atony require a skilled operator and are indeed not universally feasible.
“If successful,” Dr. Martin said in an interview, “compression sutures can be lifesaving and fertility preserving.”
The technique involves tying the two middle sutures (one placed anteriorly and one posteriorly) at the fundus as an assistant slowly and continuously compresses the uterus. The more laterally placed sutures are tied similarly, with each pair tied at about 4 cm from the lateral edge of the uterus. “As the uterus is compressed, the slack should be taken up by the sutures before tying,” said Dr. Esike, whose report features both diagrammatic and photographic representations of suture insertion and tying.
For patients who delivered vaginally – nine in this case series – the technique involves performing a laparotomy and exteriorizing the uterus. The technique’s “suture placement,” Dr. Esike wrote, “took 11-25 minutes from the onset of laparotomy to completion.” There were no short or long-term complications in any of the 18 patients.
B-Lynch compression sutures are more complex to perform and require a larger curved needle, Dr. Esike wrote, and the Hayman technique similarly requires a longer needle that may not be available in resource-constrained countries. The hysterotomy required in the B-Lynch technique, Dr. Esike added, “leads to the uterus not contracting maximally until it is repaired,” which increases blood loss from the procedure.
Dr. Martin said the small size of the case series is not discouraging. “The B-Lynch suture was widely adopted after it was described in five cases in 1997,” she said. There are no randomized controlled trials to suggest that one method of uterine compression sutures is better than another. “Ultimately,” she said, “the technique chosen will depend on the surgeon’s training and available supplies.”
Dr. Esike had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Martin had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Esike COU. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003947.
A newly described uterine compression technique that uses simple supplies and does not require hysterotomy was successful in controlling postpartum hemorrhage in 16 of 18 (89%) women in two teaching hospitals in Nigeria, averting the need for hysterectomy in these women.
Each of the women had severe postpartum hemorrhage attributable to uterine atony and had undergone local protocols for medical management “to no avail,” Chidi Ochu Uzoma Esike, MD, who developed the technique, wrote in a report published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The technique involves placing six polyglactin (Vicryl) #2 or chromic #2 sutures in the lower uterine segment – three anteriorly and three posteriorly – and could be particularly useful in developing countries, where many women die from postpartum hemorrhage “because most of the medical officers who attend the majority of births in health facilities can perform cesarean delivery but cannot perform hysterectomy and find existing compression suture techniques too complex to perform,” Dr. Esike wrote in the case series report.
In addition, “specialized sutures and needles required for some of the known compression techniques are not readily available,” said Dr. Esike of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Alex Ekwueme Federal University Hospital and Ebyonyi State University in Abakaliki, Nigeria.
Angela Martin, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that “having a quick and effective surgical technique [for uncontrollable postpartum hemorrhage] is essential.”
“I love that Esike’s technique uses polyglactin (Vicryl) or chromic sutures. These are familiar to most surgeons, cheap, and typically available even in most resource-deficient settings,” said Dr. Martin, who was asked to comment on the report, adding that several of the known surgical techniques for uterine atony require a skilled operator and are indeed not universally feasible.
“If successful,” Dr. Martin said in an interview, “compression sutures can be lifesaving and fertility preserving.”
The technique involves tying the two middle sutures (one placed anteriorly and one posteriorly) at the fundus as an assistant slowly and continuously compresses the uterus. The more laterally placed sutures are tied similarly, with each pair tied at about 4 cm from the lateral edge of the uterus. “As the uterus is compressed, the slack should be taken up by the sutures before tying,” said Dr. Esike, whose report features both diagrammatic and photographic representations of suture insertion and tying.
For patients who delivered vaginally – nine in this case series – the technique involves performing a laparotomy and exteriorizing the uterus. The technique’s “suture placement,” Dr. Esike wrote, “took 11-25 minutes from the onset of laparotomy to completion.” There were no short or long-term complications in any of the 18 patients.
B-Lynch compression sutures are more complex to perform and require a larger curved needle, Dr. Esike wrote, and the Hayman technique similarly requires a longer needle that may not be available in resource-constrained countries. The hysterotomy required in the B-Lynch technique, Dr. Esike added, “leads to the uterus not contracting maximally until it is repaired,” which increases blood loss from the procedure.
Dr. Martin said the small size of the case series is not discouraging. “The B-Lynch suture was widely adopted after it was described in five cases in 1997,” she said. There are no randomized controlled trials to suggest that one method of uterine compression sutures is better than another. “Ultimately,” she said, “the technique chosen will depend on the surgeon’s training and available supplies.”
Dr. Esike had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Martin had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Esike COU. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003947.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
‘The pandemic within the pandemic’
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.
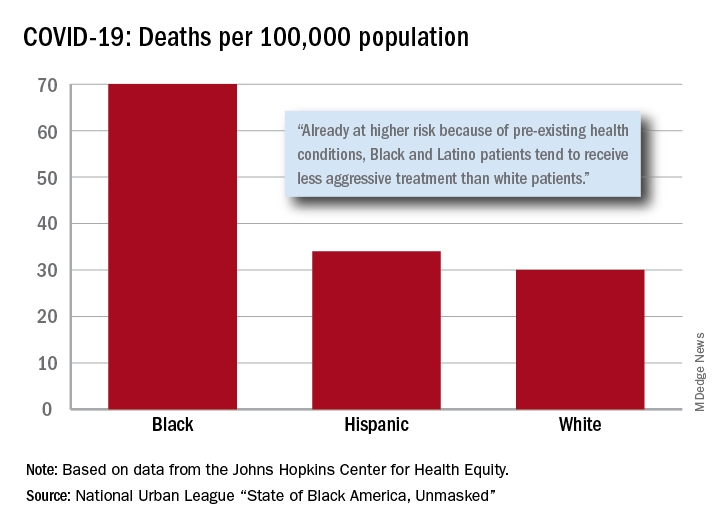
“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.

“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.

“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
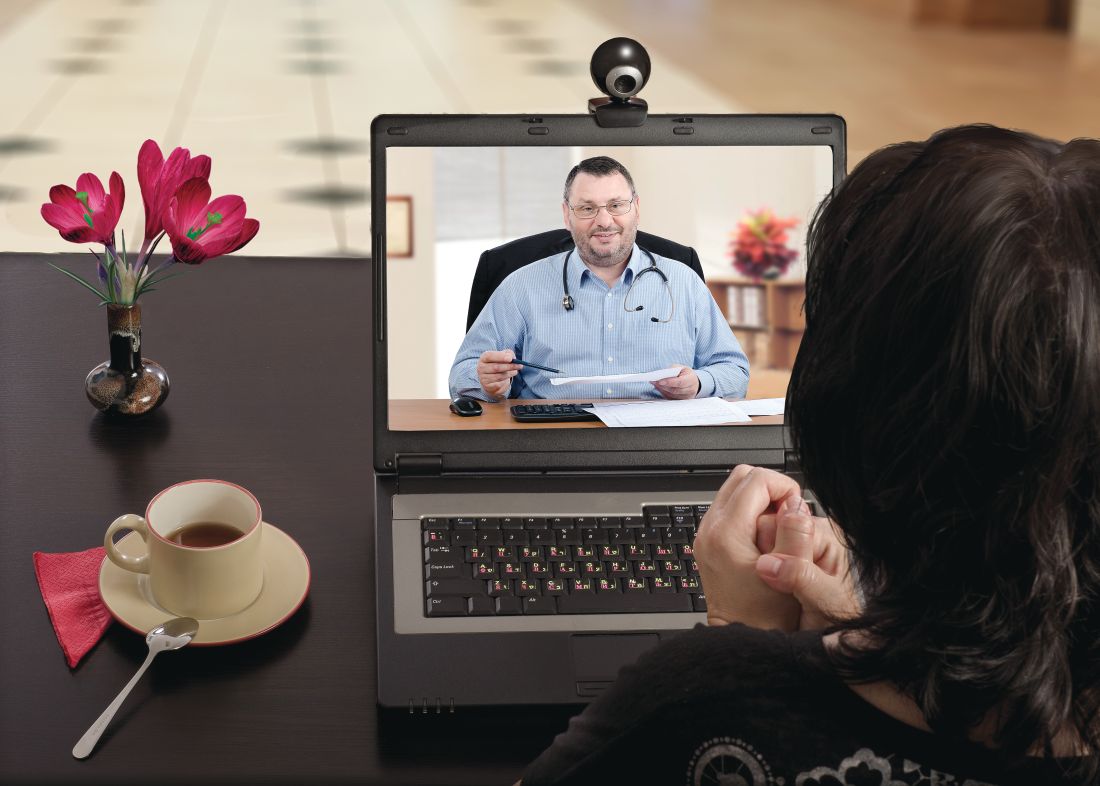
Patient visits post COVID-19
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Has telemedicine found its footing?
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Swab, spit, stay home? College coronavirus testing plans are all over the map
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
COVID-19 linked to development of myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ADHD and dyslexia may affect evaluation of concussion
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAN Sports Concussion Conference
Population health can improve postdischarge care
With the United States spending the most per capita on health care among industrialized nations but having the worst aggregate health outcomes, there’s a stark need for improvement, according to an expert at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Broadening the focus beyond the four walls of the hospital can bring better results while also saving money, said Adam Myers, MD, chief of population health at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Myers described the way his health system has begun to pay more careful attention to the needs of specific kinds of patients and tailoring posthospitalization care accordingly, with in-person and virtual home visits, and postdischarge clinics.
With an increasing attention to value, health care organizations have to change their structure or risk going the way of the Choluteca Bridge in Honduras, Dr. Myers said. The Choluteca Bridge was built to be hurricane proof, but was nonetheless rendered useless in 1998 after Hurricane Mitch shifted the very course of the river beneath it.
Similarly, the way health care is delivered often does not meet the needs of the population.
“Our national system has been focused almost entirely on inpatient care,” Dr. Myers said. “A lot of the transition in care is outside of facilities and outside the walls of our inpatient settings.”
Instead, he said a focus on population health – understanding and tending to the needs of people rather than just treating them when they show up at clinics – should involve more outpatient care that is less centralized, fees based on outcomes and patient experience rather than simply volume of services, team approaches rather than single-provider care, and a general attention to preserving health rather than treating sickness.
At Cleveland Clinic, care teams try to understand not just the care that is medically necessary, but what is wanted and justified, as well as how to deliver that care safely, reliably, and affordably with outcomes that patients and families desire.
The results are striking. After increasing the number of ambulatory patient “touches” for those with chronic disease, inpatient care – disliked by patients and costly to health centers – decreased. From the first quarter of 2018, outpatient visits increased 9%, while inpatient visits dropped 7.4%, Dr. Myers said.
“As we managed patients more effectively on an outpatient basis, their need for inpatient care diminished,” he said. “It works.”
Cleveland Clinic has also made changes designed to reduce costly readmissions, using virtual visits, house calls, time reserved for team meetings to identify patients with gaps in their care, and attention to nonmedical determinants of health, such as assessing fall risk at home and addressing lack of nutritious food options in a community.
The health system has seen a 28% reduction in the cost of care attributed to house calls, 12% cost reduction attributed to better care coordination, and a 49% decrease in hospital days for “superutilizers” of the ED, Dr. Myers said.
Postdischarge clinics – where patients can be seen for the first few visits after hospitalization – have also been valuable for many health systems, because they are closely in tune with what happened during the inpatient stay. These clinics are staffed by hospitalists, interns, residents, or ambulatory clinicians. Dr. Myers said hospitalists tend to have an improved perspective after working in a discharge clinic, with more concern about a patient’s needs once they leave the hospital bed.
“Those hospitalists that I know who have participated in programs like this start to act a bit more like primary care physicians,” he said.
In a Q&A session after Dr. Myers’ presentation, he discussed how hospitalists can affect the many layers of health care policy, factors that often overlap with population health.
He noted that medical care accounts for only about 20% of patient outcomes – the rest involve social and environmental factors.
“I don’t know about you , but I’m not satisfied only impacting 20% of health outcomes,” he said. First, physicians need to understand what is happening in their communities, and the health policies that are preventing improvement. Then, build partnerships to help fix these problems. He pointed to lead poisoning as an example.
“If you think about it, lead poisoning is a social housing problem that shows up as a health care issue. Unless we are getting out into the community and mitigating the root problem, we will have to treat it over and over again,” he said.
Dr. Myers reported no relevant financial disclosures.
With the United States spending the most per capita on health care among industrialized nations but having the worst aggregate health outcomes, there’s a stark need for improvement, according to an expert at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Broadening the focus beyond the four walls of the hospital can bring better results while also saving money, said Adam Myers, MD, chief of population health at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Myers described the way his health system has begun to pay more careful attention to the needs of specific kinds of patients and tailoring posthospitalization care accordingly, with in-person and virtual home visits, and postdischarge clinics.
With an increasing attention to value, health care organizations have to change their structure or risk going the way of the Choluteca Bridge in Honduras, Dr. Myers said. The Choluteca Bridge was built to be hurricane proof, but was nonetheless rendered useless in 1998 after Hurricane Mitch shifted the very course of the river beneath it.
Similarly, the way health care is delivered often does not meet the needs of the population.
“Our national system has been focused almost entirely on inpatient care,” Dr. Myers said. “A lot of the transition in care is outside of facilities and outside the walls of our inpatient settings.”
Instead, he said a focus on population health – understanding and tending to the needs of people rather than just treating them when they show up at clinics – should involve more outpatient care that is less centralized, fees based on outcomes and patient experience rather than simply volume of services, team approaches rather than single-provider care, and a general attention to preserving health rather than treating sickness.
At Cleveland Clinic, care teams try to understand not just the care that is medically necessary, but what is wanted and justified, as well as how to deliver that care safely, reliably, and affordably with outcomes that patients and families desire.
The results are striking. After increasing the number of ambulatory patient “touches” for those with chronic disease, inpatient care – disliked by patients and costly to health centers – decreased. From the first quarter of 2018, outpatient visits increased 9%, while inpatient visits dropped 7.4%, Dr. Myers said.
“As we managed patients more effectively on an outpatient basis, their need for inpatient care diminished,” he said. “It works.”
Cleveland Clinic has also made changes designed to reduce costly readmissions, using virtual visits, house calls, time reserved for team meetings to identify patients with gaps in their care, and attention to nonmedical determinants of health, such as assessing fall risk at home and addressing lack of nutritious food options in a community.
The health system has seen a 28% reduction in the cost of care attributed to house calls, 12% cost reduction attributed to better care coordination, and a 49% decrease in hospital days for “superutilizers” of the ED, Dr. Myers said.
Postdischarge clinics – where patients can be seen for the first few visits after hospitalization – have also been valuable for many health systems, because they are closely in tune with what happened during the inpatient stay. These clinics are staffed by hospitalists, interns, residents, or ambulatory clinicians. Dr. Myers said hospitalists tend to have an improved perspective after working in a discharge clinic, with more concern about a patient’s needs once they leave the hospital bed.
“Those hospitalists that I know who have participated in programs like this start to act a bit more like primary care physicians,” he said.
In a Q&A session after Dr. Myers’ presentation, he discussed how hospitalists can affect the many layers of health care policy, factors that often overlap with population health.
He noted that medical care accounts for only about 20% of patient outcomes – the rest involve social and environmental factors.
“I don’t know about you , but I’m not satisfied only impacting 20% of health outcomes,” he said. First, physicians need to understand what is happening in their communities, and the health policies that are preventing improvement. Then, build partnerships to help fix these problems. He pointed to lead poisoning as an example.
“If you think about it, lead poisoning is a social housing problem that shows up as a health care issue. Unless we are getting out into the community and mitigating the root problem, we will have to treat it over and over again,” he said.
Dr. Myers reported no relevant financial disclosures.
With the United States spending the most per capita on health care among industrialized nations but having the worst aggregate health outcomes, there’s a stark need for improvement, according to an expert at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Broadening the focus beyond the four walls of the hospital can bring better results while also saving money, said Adam Myers, MD, chief of population health at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Myers described the way his health system has begun to pay more careful attention to the needs of specific kinds of patients and tailoring posthospitalization care accordingly, with in-person and virtual home visits, and postdischarge clinics.
With an increasing attention to value, health care organizations have to change their structure or risk going the way of the Choluteca Bridge in Honduras, Dr. Myers said. The Choluteca Bridge was built to be hurricane proof, but was nonetheless rendered useless in 1998 after Hurricane Mitch shifted the very course of the river beneath it.
Similarly, the way health care is delivered often does not meet the needs of the population.
“Our national system has been focused almost entirely on inpatient care,” Dr. Myers said. “A lot of the transition in care is outside of facilities and outside the walls of our inpatient settings.”
Instead, he said a focus on population health – understanding and tending to the needs of people rather than just treating them when they show up at clinics – should involve more outpatient care that is less centralized, fees based on outcomes and patient experience rather than simply volume of services, team approaches rather than single-provider care, and a general attention to preserving health rather than treating sickness.
At Cleveland Clinic, care teams try to understand not just the care that is medically necessary, but what is wanted and justified, as well as how to deliver that care safely, reliably, and affordably with outcomes that patients and families desire.
The results are striking. After increasing the number of ambulatory patient “touches” for those with chronic disease, inpatient care – disliked by patients and costly to health centers – decreased. From the first quarter of 2018, outpatient visits increased 9%, while inpatient visits dropped 7.4%, Dr. Myers said.
“As we managed patients more effectively on an outpatient basis, their need for inpatient care diminished,” he said. “It works.”
Cleveland Clinic has also made changes designed to reduce costly readmissions, using virtual visits, house calls, time reserved for team meetings to identify patients with gaps in their care, and attention to nonmedical determinants of health, such as assessing fall risk at home and addressing lack of nutritious food options in a community.
The health system has seen a 28% reduction in the cost of care attributed to house calls, 12% cost reduction attributed to better care coordination, and a 49% decrease in hospital days for “superutilizers” of the ED, Dr. Myers said.
Postdischarge clinics – where patients can be seen for the first few visits after hospitalization – have also been valuable for many health systems, because they are closely in tune with what happened during the inpatient stay. These clinics are staffed by hospitalists, interns, residents, or ambulatory clinicians. Dr. Myers said hospitalists tend to have an improved perspective after working in a discharge clinic, with more concern about a patient’s needs once they leave the hospital bed.
“Those hospitalists that I know who have participated in programs like this start to act a bit more like primary care physicians,” he said.
In a Q&A session after Dr. Myers’ presentation, he discussed how hospitalists can affect the many layers of health care policy, factors that often overlap with population health.
He noted that medical care accounts for only about 20% of patient outcomes – the rest involve social and environmental factors.
“I don’t know about you , but I’m not satisfied only impacting 20% of health outcomes,” he said. First, physicians need to understand what is happening in their communities, and the health policies that are preventing improvement. Then, build partnerships to help fix these problems. He pointed to lead poisoning as an example.
“If you think about it, lead poisoning is a social housing problem that shows up as a health care issue. Unless we are getting out into the community and mitigating the root problem, we will have to treat it over and over again,” he said.
Dr. Myers reported no relevant financial disclosures.
How to get a position as a physician leader
The best ways to start
It’s been said that physicians tend to fall into leadership roles. Few physicians set out to become leaders, and then one day they realize that they desire to be a leader and an agent for change.
They may be rotating through the chairmanship of a clinical department or the management of a small practice and decide they like the work. In a large organization, doctors get assigned to committees, or specialists agree to run a new service line for a while, and it changes their lives.
Some physicians have a natural aptitude for managerial work. Often, colleagues tell them they are a good fit, but they may still have some reservations. In any case, it’s good to do a bit of soul-searching before taking the leap.
1. Weigh the pluses and minuses of a leadership role
When you stand at the precipice of a totally new career in physician leadership, it’s worthwhile to step back and consider the pluses and minuses of the work.
One plus is that there may be fewer work hours than on the clinical side, but being a physician leader is by no means a 9-to-5 job. In a large organization, a physician on the executive team can be on administrative call – dealing with institutional crises on off-hours – for a length of time. Board and strategic planning retreats tend to occur on weekends, and you may need to attend frequent dinner meetings.
Another plus is that the pay is pretty good. In 2016, physician leaders in large organizations earned an average of $350,000 a year, according to a survey by Cejka Executive Search and the American Association for Physician Leadership (AAPL).1
On the minus side, an executive probably won’t be as beloved as a clinician serving a host of grateful patients. And you will not have the kind of job security that most clinicians have. There may be frequent turnover among health care executives because of change of top leadership, pressure for more profitability, or a host of other reasons.
2. Try on different roles
To decide whether you want to make a career of being a physician leader, it’s useful to try out several different jobs. Volunteer for committees or take on a special project if it’s possible to do so in your organization.
You can also volunteer for posts outside the organization, such as joining the board of your local cancer or heart association or helping them out on a committee. You might volunteer for Little League or a school or civic organization. Your choices are wide open. The goal is to get a feel for directing an organization and whether that fits your lifestyle.
Also, talk to current physician leaders. Contact a cross-section of people, including those who are unhappy with their jobs and those who had to struggle with their new roles. This will give you some good perspective into whether the work is right for you, as well as tips on how to cope.
3. Find a mentor
This is also a good time to find a mentor for your new calling. Choose a seasoned physician leader who can help you over the long haul – someone who can get you up to speed and then advise you during crucial junctures in your career.
Good mentors should be willing to spend the time with you, have your best interests in mind, and be willing to provide honest assessments. They can also help you find opportunities for further learning and professional growth.
Some organizations assign mentors to physicians they want to develop for leadership roles. You can also choose specific mentors to help you in areas where you think you need more work, such as finance, quality improvement, or information systems.
Choose a path
There are many different paths you can take as a physician leader. In large organizations in particular, there are more leadership jobs open to physicians than ever before.
Jobs open to physicians can be found in the areas of clinical quality and safety, population health, managed care, and information technology. You can even look beyond these traditional roles to jobs that don’t usually attract physicians, such as in strategy, innovation, patient experience, and fundraising. In these roles, you are often expected to continue doing some clinical work.
Physician leaders now tend to have more influence than in the past. According to the Cejka-AAPL survey, 61% of physician executives said they had more strategic input currently than in the previous year.
A roster of potential physician leader jobs
1. Executive-level roles
Vice president for medical affairs. This is the traditional role for the physician executive, which involves acting as a liaison with the organization’s physicians. These officers oversee quality of care as well as hiring, training, and performance evaluation of physicians on staff.
Chief medical officer (CMO). This is now the typical term for the highest medical role in the organization. The CMO is part of the C-suite team and participates in governance, strategic planning, and business operation decisions. CMOs may be responsible for supporting value-based strategies and making sure that those strategies are efficient and medically necessary.
Physician-in-chief. This is a new term for the hospital’s top physician, who works with the senior leadership team to maintain standards of care and customer service. The physician-in-chief may also oversee operational efficiency and support organizational transformation.
Chief clinical officer (CCO). CCOs oversee patient engagement and clinical quality outcomes. They may lead initiatives to reduce waste and improve care quality, and they can be involved in implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) and data integration. They may also assist in medical staff development, clinical integration, and physician partnerships.
2. Quality, safety, and research roles
Chief patient safety officer (CPSO). CPSOs oversee the hospital or health system’s patient safety initiatives. Their goal is to reduce medical errors and near-misses.
Chief quality officer (CQO). CQOs are responsible for collecting quality data and supporting patient safety efforts. They advise on quality initiatives and hold clinicians accountable for meeting specific quality indicators. They may also be involved in developing a culture of continuous improvement in the organization.
Chief research officer (CRO). CROs oversee the organization’s research activities, including clinical trials, internal investigator-initiated research programs, and sponsored studies.
3. Technology
Chief medical information officer (CMIO). The CMIO is the information technology (IT) department’s liaison with the clinical staff, working on selection and improvement of EHR systems. The CMIO finds new ways for EHRs to improve healthcare delivery in the organization.
Chief health information officer (CHIO). CHIOs deal with EHR implementation and health informatics. They may report to the chief information officer, the chief operations officer, or another C-suite executive, and they manage health informatics, telehealth, business and clinical intelligence, and predictive analytics initiatives.
Chief technology officer (CTO). CTOs oversee the organization’s technology capabilities. They are responsible for leading the IT team and contributing to the organization’s strategic plan.
4. Jobs not usually for physicians
There are other leadership positions that may not traditionally appeal to physicians but could be worth considering:
Chief experience officer (CXO). This involves evaluating and improving the inpatient experience. CXOs work with physicians and staff on their performance in this area.
Chief innovation officer (CIO). CIOs keep up with industry trends, market disruptions, and new opportunities, and support policy innovations and training initiatives.
Chief transformation officer (CTO). CTOs are responsible for carrying out major changes in the organization. They are supposed to act as role models for change.
5. Salaries for selected physician executives
In addition to placing the average salary for a physician leader at $350,000, the 2016 Cejka-AAPL survey pinpointed average salaries for specific types of physician leaders. Chief medical officers earned $388,000, chief patient safety officers and chief quality officers $375,000, and chief medical information officers $372,500, the survey found.
Several emerging physician leader roles – physician-in-chief, chief strategy officer, chief transformation officer, chief innovation officer, and chief integration officer – earned on average $499,000 a year, according to the survey.
Those jobs provided even higher salaries than the $437,500 reported by Cejka-AAPL for physician CEOs. In comparison, a CEO at a medical group with fewer than 200 physicians had an average salary of $438,500 in 2018, according to SullivanCotter, a health care workforce strategy company.2
Some types of physician leaders have seen unusually high pay raises recently. From 2013 to 2016, the average salary for CMIOs rose 18%, and physician leaders working at the corporate level in a health system saw median compensation rise 67%, the Cejka-AAPL survey found.
Moving ahead
For physician leaders, moving up the ladder often means reinventing yourself. If you’re leaving clinical practice, be sure to develop a solid CV for your new role so that if your leadership position doesn’t work out, you are able to find an appropriate new position.
According to a 2003 assessment, CMOs typically lasted 18-24 months on the job.3
Expect to make mistakes and try to learn from them. If necessary, move on to the next job. There is always a market for seasoned physician executives who took a few punches, learned something from the experience, and found something new.
Start to network
One way to navigate the challenges of a new role is to have a strong network, a group of colleagues and mentors who can help you figure out your path forward. They can serve as sounding boards and contacts for new jobs in an industry that is constantly changing.
A well-functioning network takes constant maintenance.
You can find people for your network by attending a variety of different meetings that physician leaders and other healthcare executives attend. Make a point of keeping their contact information on file and periodically reaching out to them.
Learn in a dyad
Some healthcare organizations assign physician leaders to dyads, where they are matched with nonphysicians who have skills that the physician lacks, such as finance, data management, or organizational politics.
Dyads are less effective when the nonphysician has all the authority and the physician is basically a figurehead. But in an effective dyad, both partners share authority and they can teach skills to each other. While the physician in the dyad brings clinical insight, the nonphysician can provide managerial know-how.
Seek out coaching
There may be points in your leadership career when you become aware of areas where you need improvement. You may have gotten negative feedback on communication skills or political sensitivity. Consider hiring an executive coach; coaches provide concentrated sessions over limited periods of time.
Coaches can also help you prepare for the future. They can help you find ways to promote yourself for new projects or create a network of allies. They also can help you establish yourself as a thought leader in a particular field through writing and speaking engagements.
Some organizations provide in-house coaches. It is worthwhile to take advantage of this benefit. If you need to find a coach on your own, ask mentors or people in your network for recommendations.
Getting to the top
It can take years to rise to the level of the corporate C-suite or even to CEO of a large organization. At the top levels of management, you often have to cut back substantially on clinical work or even give it up entirely.
Becoming CEO of a hospital can be a logical fit for physicians. A physician CEO can relate to doctors on staff, who are a key constituency, and understands what clinical care is all about. However, physician CEOs also need to have a large degree of knowledge about finance, strategy, crisis management, quality improvement, and other nonclinical considerations, not to mention good people skills.
Physicians on boards
Some physicians would rather sit on the board of trustees than take the reins of CEO. Board membership allows you to continue practicing while still having a great deal of influence over the organization. Some physicians hold board seats for many years and enjoy a great deal of respect as the go-to person on clinical care.
Physicians are increasingly serving on the boards of hospitals and health systems. Trustees welcome physicians because they want more input from clinicians in decision-making. They tend to choose physicians who already have executive duties, such as having been a department head.
Which new skills should you learn?
Physician executives often put off learning business and management skills until after being appointed to a leadership position. Even then, they may prefer to take courses focused on a particular topic rather than earn a degree such as master of business administration (MBA).
Learning on the job
A number of executive skills can be learned on the job, such as dealing with quality measures, utilization, billing and coding, disease management, committees, and interpreting data. If you are not in a dyad model, you can ask someone knowledgeable in one of these skills to take you through the steps.
Many physicians could benefit from finance and business courses in order to learn some of the budgetary, accounting, and operational skills required to perform the job optimally.
In a survey of healthcare CEOs, only 30% said their most senior physician leader had a business or medical management degree, and only 21% required a degree.4
Taking classes
Physician executives who want to brush up on a particular topic can “mix and match,” taking short, focused classes on the particular topic whenever they feel the need. In addition to resources offered by SHM, courses are available from organizations such as the AAPL, American Hospital Association, the Medical Group Management Association, or the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, to name a few examples.
Pursuing degree programs
Degree programs like MBA, master of public health (MPH), and master of health care administration (MHA) are popular with many physician executives because they get a full overview of needed skills and the potential to earn more money with their new credentials. Physician leaders with an MBA earned 13% more in 2016 than did those with no MBA, according to the Cejka-AAPL survey.
Getting a master’s degree, however, takes time and money. For example, an MBA can cost $20,000 to as much as $100,000.5 MBA, MHA, and MPH degrees take 2 years to complete, while a master of medical management (MMM) and a physician-executive MBA – focusing specifically on what physician leaders need to learn – take 1 year.
Many part-time degree programs are available for those with full-time jobs. You can find them at nearby universities as well as far-off institutions. Much of the coursework is done online, but some on-site work is usually required. You’ll find that working directly with others enriches the learning experience and helps you build your network of colleagues.
Straight MBA or other degree?
In general, degree programs cover finance, communication, strategy, information systems, marketing, organizational behavior, operational management, and quality improvement. Straight MBA programs don’t focus on healthcare, but some physician executives still prefer this route, especially if it involves degrees from prestigious business schools.
MHA, MMM, physician-executive MBA, and other degree programs focused on healthcare are popular with many physicians on the executive track. The MPH is less business-oriented but may be preferable to some because of its focus on population-based health, which fits well with decision-making on health insurance and value-based care.
Conclusion
Physicians need to prepare for leadership because these roles are very different from clinical work. It’s easy to stumble and lose direction without mentors, a network of helpful colleagues, and at least some education in business principles.
Finding a mentor should start early in your new career. A seasoned physician executive can help you understand your options and point out your strengths and shortcomings. Beyond that, concentrated work with an executive coach can help you improve your skills and choose from among the many executive roles that are now available.
You can learn many skills on the job through dyads and other relationships with more seasoned colleagues, or take short classes on particular skills that need to be learned or sharpened. Many physician executives go a step further and get a master’s degree, such as an MBA, MHA, or MMM. This involves a year or two of study, but much of it can be done online.
This article is excerpted from the Medscape Physician Business Academy course “How to become an effective leader.” You can find more information on the course at www.medscape.com/courses/business/100018.
References
1. Cejka Executive Search. 2016 Physician Leadership Compensation Survey results released. Cejka and the American Association for Physician Leadership. Nov 3, 2016.
2. Knowles M. Salaries on upswing for physician executives. Becker’s Hospital Review. Sept 25, 2018.
3. Birrer RB. Becoming a physician executive. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. Jan-Feb 2003.
4. Witt/Kieffer. Transformation of physician executives: New accountability for quality, performance, integration. Fall 2010.
5. Jurica J. Does an executive salary stand up to a clinical salary? Vital Physician Executive. 2016.
The best ways to start
It’s been said that physicians tend to fall into leadership roles. Few physicians set out to become leaders, and then one day they realize that they desire to be a leader and an agent for change.
They may be rotating through the chairmanship of a clinical department or the management of a small practice and decide they like the work. In a large organization, doctors get assigned to committees, or specialists agree to run a new service line for a while, and it changes their lives.
Some physicians have a natural aptitude for managerial work. Often, colleagues tell them they are a good fit, but they may still have some reservations. In any case, it’s good to do a bit of soul-searching before taking the leap.
1. Weigh the pluses and minuses of a leadership role
When you stand at the precipice of a totally new career in physician leadership, it’s worthwhile to step back and consider the pluses and minuses of the work.
One plus is that there may be fewer work hours than on the clinical side, but being a physician leader is by no means a 9-to-5 job. In a large organization, a physician on the executive team can be on administrative call – dealing with institutional crises on off-hours – for a length of time. Board and strategic planning retreats tend to occur on weekends, and you may need to attend frequent dinner meetings.
Another plus is that the pay is pretty good. In 2016, physician leaders in large organizations earned an average of $350,000 a year, according to a survey by Cejka Executive Search and the American Association for Physician Leadership (AAPL).1
On the minus side, an executive probably won’t be as beloved as a clinician serving a host of grateful patients. And you will not have the kind of job security that most clinicians have. There may be frequent turnover among health care executives because of change of top leadership, pressure for more profitability, or a host of other reasons.
2. Try on different roles
To decide whether you want to make a career of being a physician leader, it’s useful to try out several different jobs. Volunteer for committees or take on a special project if it’s possible to do so in your organization.
You can also volunteer for posts outside the organization, such as joining the board of your local cancer or heart association or helping them out on a committee. You might volunteer for Little League or a school or civic organization. Your choices are wide open. The goal is to get a feel for directing an organization and whether that fits your lifestyle.
Also, talk to current physician leaders. Contact a cross-section of people, including those who are unhappy with their jobs and those who had to struggle with their new roles. This will give you some good perspective into whether the work is right for you, as well as tips on how to cope.
3. Find a mentor
This is also a good time to find a mentor for your new calling. Choose a seasoned physician leader who can help you over the long haul – someone who can get you up to speed and then advise you during crucial junctures in your career.
Good mentors should be willing to spend the time with you, have your best interests in mind, and be willing to provide honest assessments. They can also help you find opportunities for further learning and professional growth.
Some organizations assign mentors to physicians they want to develop for leadership roles. You can also choose specific mentors to help you in areas where you think you need more work, such as finance, quality improvement, or information systems.
Choose a path
There are many different paths you can take as a physician leader. In large organizations in particular, there are more leadership jobs open to physicians than ever before.
Jobs open to physicians can be found in the areas of clinical quality and safety, population health, managed care, and information technology. You can even look beyond these traditional roles to jobs that don’t usually attract physicians, such as in strategy, innovation, patient experience, and fundraising. In these roles, you are often expected to continue doing some clinical work.
Physician leaders now tend to have more influence than in the past. According to the Cejka-AAPL survey, 61% of physician executives said they had more strategic input currently than in the previous year.
A roster of potential physician leader jobs
1. Executive-level roles
Vice president for medical affairs. This is the traditional role for the physician executive, which involves acting as a liaison with the organization’s physicians. These officers oversee quality of care as well as hiring, training, and performance evaluation of physicians on staff.
Chief medical officer (CMO). This is now the typical term for the highest medical role in the organization. The CMO is part of the C-suite team and participates in governance, strategic planning, and business operation decisions. CMOs may be responsible for supporting value-based strategies and making sure that those strategies are efficient and medically necessary.
Physician-in-chief. This is a new term for the hospital’s top physician, who works with the senior leadership team to maintain standards of care and customer service. The physician-in-chief may also oversee operational efficiency and support organizational transformation.
Chief clinical officer (CCO). CCOs oversee patient engagement and clinical quality outcomes. They may lead initiatives to reduce waste and improve care quality, and they can be involved in implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) and data integration. They may also assist in medical staff development, clinical integration, and physician partnerships.
2. Quality, safety, and research roles
Chief patient safety officer (CPSO). CPSOs oversee the hospital or health system’s patient safety initiatives. Their goal is to reduce medical errors and near-misses.
Chief quality officer (CQO). CQOs are responsible for collecting quality data and supporting patient safety efforts. They advise on quality initiatives and hold clinicians accountable for meeting specific quality indicators. They may also be involved in developing a culture of continuous improvement in the organization.
Chief research officer (CRO). CROs oversee the organization’s research activities, including clinical trials, internal investigator-initiated research programs, and sponsored studies.
3. Technology
Chief medical information officer (CMIO). The CMIO is the information technology (IT) department’s liaison with the clinical staff, working on selection and improvement of EHR systems. The CMIO finds new ways for EHRs to improve healthcare delivery in the organization.
Chief health information officer (CHIO). CHIOs deal with EHR implementation and health informatics. They may report to the chief information officer, the chief operations officer, or another C-suite executive, and they manage health informatics, telehealth, business and clinical intelligence, and predictive analytics initiatives.
Chief technology officer (CTO). CTOs oversee the organization’s technology capabilities. They are responsible for leading the IT team and contributing to the organization’s strategic plan.
4. Jobs not usually for physicians
There are other leadership positions that may not traditionally appeal to physicians but could be worth considering:
Chief experience officer (CXO). This involves evaluating and improving the inpatient experience. CXOs work with physicians and staff on their performance in this area.
Chief innovation officer (CIO). CIOs keep up with industry trends, market disruptions, and new opportunities, and support policy innovations and training initiatives.
Chief transformation officer (CTO). CTOs are responsible for carrying out major changes in the organization. They are supposed to act as role models for change.
5. Salaries for selected physician executives
In addition to placing the average salary for a physician leader at $350,000, the 2016 Cejka-AAPL survey pinpointed average salaries for specific types of physician leaders. Chief medical officers earned $388,000, chief patient safety officers and chief quality officers $375,000, and chief medical information officers $372,500, the survey found.
Several emerging physician leader roles – physician-in-chief, chief strategy officer, chief transformation officer, chief innovation officer, and chief integration officer – earned on average $499,000 a year, according to the survey.
Those jobs provided even higher salaries than the $437,500 reported by Cejka-AAPL for physician CEOs. In comparison, a CEO at a medical group with fewer than 200 physicians had an average salary of $438,500 in 2018, according to SullivanCotter, a health care workforce strategy company.2
Some types of physician leaders have seen unusually high pay raises recently. From 2013 to 2016, the average salary for CMIOs rose 18%, and physician leaders working at the corporate level in a health system saw median compensation rise 67%, the Cejka-AAPL survey found.
Moving ahead
For physician leaders, moving up the ladder often means reinventing yourself. If you’re leaving clinical practice, be sure to develop a solid CV for your new role so that if your leadership position doesn’t work out, you are able to find an appropriate new position.
According to a 2003 assessment, CMOs typically lasted 18-24 months on the job.3
Expect to make mistakes and try to learn from them. If necessary, move on to the next job. There is always a market for seasoned physician executives who took a few punches, learned something from the experience, and found something new.
Start to network
One way to navigate the challenges of a new role is to have a strong network, a group of colleagues and mentors who can help you figure out your path forward. They can serve as sounding boards and contacts for new jobs in an industry that is constantly changing.
A well-functioning network takes constant maintenance.
You can find people for your network by attending a variety of different meetings that physician leaders and other healthcare executives attend. Make a point of keeping their contact information on file and periodically reaching out to them.
Learn in a dyad
Some healthcare organizations assign physician leaders to dyads, where they are matched with nonphysicians who have skills that the physician lacks, such as finance, data management, or organizational politics.
Dyads are less effective when the nonphysician has all the authority and the physician is basically a figurehead. But in an effective dyad, both partners share authority and they can teach skills to each other. While the physician in the dyad brings clinical insight, the nonphysician can provide managerial know-how.
Seek out coaching
There may be points in your leadership career when you become aware of areas where you need improvement. You may have gotten negative feedback on communication skills or political sensitivity. Consider hiring an executive coach; coaches provide concentrated sessions over limited periods of time.
Coaches can also help you prepare for the future. They can help you find ways to promote yourself for new projects or create a network of allies. They also can help you establish yourself as a thought leader in a particular field through writing and speaking engagements.
Some organizations provide in-house coaches. It is worthwhile to take advantage of this benefit. If you need to find a coach on your own, ask mentors or people in your network for recommendations.
Getting to the top
It can take years to rise to the level of the corporate C-suite or even to CEO of a large organization. At the top levels of management, you often have to cut back substantially on clinical work or even give it up entirely.
Becoming CEO of a hospital can be a logical fit for physicians. A physician CEO can relate to doctors on staff, who are a key constituency, and understands what clinical care is all about. However, physician CEOs also need to have a large degree of knowledge about finance, strategy, crisis management, quality improvement, and other nonclinical considerations, not to mention good people skills.
Physicians on boards
Some physicians would rather sit on the board of trustees than take the reins of CEO. Board membership allows you to continue practicing while still having a great deal of influence over the organization. Some physicians hold board seats for many years and enjoy a great deal of respect as the go-to person on clinical care.
Physicians are increasingly serving on the boards of hospitals and health systems. Trustees welcome physicians because they want more input from clinicians in decision-making. They tend to choose physicians who already have executive duties, such as having been a department head.
Which new skills should you learn?
Physician executives often put off learning business and management skills until after being appointed to a leadership position. Even then, they may prefer to take courses focused on a particular topic rather than earn a degree such as master of business administration (MBA).
Learning on the job
A number of executive skills can be learned on the job, such as dealing with quality measures, utilization, billing and coding, disease management, committees, and interpreting data. If you are not in a dyad model, you can ask someone knowledgeable in one of these skills to take you through the steps.
Many physicians could benefit from finance and business courses in order to learn some of the budgetary, accounting, and operational skills required to perform the job optimally.
In a survey of healthcare CEOs, only 30% said their most senior physician leader had a business or medical management degree, and only 21% required a degree.4
Taking classes
Physician executives who want to brush up on a particular topic can “mix and match,” taking short, focused classes on the particular topic whenever they feel the need. In addition to resources offered by SHM, courses are available from organizations such as the AAPL, American Hospital Association, the Medical Group Management Association, or the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, to name a few examples.
Pursuing degree programs
Degree programs like MBA, master of public health (MPH), and master of health care administration (MHA) are popular with many physician executives because they get a full overview of needed skills and the potential to earn more money with their new credentials. Physician leaders with an MBA earned 13% more in 2016 than did those with no MBA, according to the Cejka-AAPL survey.
Getting a master’s degree, however, takes time and money. For example, an MBA can cost $20,000 to as much as $100,000.5 MBA, MHA, and MPH degrees take 2 years to complete, while a master of medical management (MMM) and a physician-executive MBA – focusing specifically on what physician leaders need to learn – take 1 year.
Many part-time degree programs are available for those with full-time jobs. You can find them at nearby universities as well as far-off institutions. Much of the coursework is done online, but some on-site work is usually required. You’ll find that working directly with others enriches the learning experience and helps you build your network of colleagues.
Straight MBA or other degree?
In general, degree programs cover finance, communication, strategy, information systems, marketing, organizational behavior, operational management, and quality improvement. Straight MBA programs don’t focus on healthcare, but some physician executives still prefer this route, especially if it involves degrees from prestigious business schools.
MHA, MMM, physician-executive MBA, and other degree programs focused on healthcare are popular with many physicians on the executive track. The MPH is less business-oriented but may be preferable to some because of its focus on population-based health, which fits well with decision-making on health insurance and value-based care.
Conclusion
Physicians need to prepare for leadership because these roles are very different from clinical work. It’s easy to stumble and lose direction without mentors, a network of helpful colleagues, and at least some education in business principles.
Finding a mentor should start early in your new career. A seasoned physician executive can help you understand your options and point out your strengths and shortcomings. Beyond that, concentrated work with an executive coach can help you improve your skills and choose from among the many executive roles that are now available.
You can learn many skills on the job through dyads and other relationships with more seasoned colleagues, or take short classes on particular skills that need to be learned or sharpened. Many physician executives go a step further and get a master’s degree, such as an MBA, MHA, or MMM. This involves a year or two of study, but much of it can be done online.
This article is excerpted from the Medscape Physician Business Academy course “How to become an effective leader.” You can find more information on the course at www.medscape.com/courses/business/100018.
References
1. Cejka Executive Search. 2016 Physician Leadership Compensation Survey results released. Cejka and the American Association for Physician Leadership. Nov 3, 2016.
2. Knowles M. Salaries on upswing for physician executives. Becker’s Hospital Review. Sept 25, 2018.
3. Birrer RB. Becoming a physician executive. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. Jan-Feb 2003.
4. Witt/Kieffer. Transformation of physician executives: New accountability for quality, performance, integration. Fall 2010.
5. Jurica J. Does an executive salary stand up to a clinical salary? Vital Physician Executive. 2016.
The best ways to start
It’s been said that physicians tend to fall into leadership roles. Few physicians set out to become leaders, and then one day they realize that they desire to be a leader and an agent for change.
They may be rotating through the chairmanship of a clinical department or the management of a small practice and decide they like the work. In a large organization, doctors get assigned to committees, or specialists agree to run a new service line for a while, and it changes their lives.
Some physicians have a natural aptitude for managerial work. Often, colleagues tell them they are a good fit, but they may still have some reservations. In any case, it’s good to do a bit of soul-searching before taking the leap.
1. Weigh the pluses and minuses of a leadership role
When you stand at the precipice of a totally new career in physician leadership, it’s worthwhile to step back and consider the pluses and minuses of the work.
One plus is that there may be fewer work hours than on the clinical side, but being a physician leader is by no means a 9-to-5 job. In a large organization, a physician on the executive team can be on administrative call – dealing with institutional crises on off-hours – for a length of time. Board and strategic planning retreats tend to occur on weekends, and you may need to attend frequent dinner meetings.
Another plus is that the pay is pretty good. In 2016, physician leaders in large organizations earned an average of $350,000 a year, according to a survey by Cejka Executive Search and the American Association for Physician Leadership (AAPL).1
On the minus side, an executive probably won’t be as beloved as a clinician serving a host of grateful patients. And you will not have the kind of job security that most clinicians have. There may be frequent turnover among health care executives because of change of top leadership, pressure for more profitability, or a host of other reasons.
2. Try on different roles
To decide whether you want to make a career of being a physician leader, it’s useful to try out several different jobs. Volunteer for committees or take on a special project if it’s possible to do so in your organization.
You can also volunteer for posts outside the organization, such as joining the board of your local cancer or heart association or helping them out on a committee. You might volunteer for Little League or a school or civic organization. Your choices are wide open. The goal is to get a feel for directing an organization and whether that fits your lifestyle.
Also, talk to current physician leaders. Contact a cross-section of people, including those who are unhappy with their jobs and those who had to struggle with their new roles. This will give you some good perspective into whether the work is right for you, as well as tips on how to cope.
3. Find a mentor
This is also a good time to find a mentor for your new calling. Choose a seasoned physician leader who can help you over the long haul – someone who can get you up to speed and then advise you during crucial junctures in your career.
Good mentors should be willing to spend the time with you, have your best interests in mind, and be willing to provide honest assessments. They can also help you find opportunities for further learning and professional growth.
Some organizations assign mentors to physicians they want to develop for leadership roles. You can also choose specific mentors to help you in areas where you think you need more work, such as finance, quality improvement, or information systems.
Choose a path
There are many different paths you can take as a physician leader. In large organizations in particular, there are more leadership jobs open to physicians than ever before.
Jobs open to physicians can be found in the areas of clinical quality and safety, population health, managed care, and information technology. You can even look beyond these traditional roles to jobs that don’t usually attract physicians, such as in strategy, innovation, patient experience, and fundraising. In these roles, you are often expected to continue doing some clinical work.
Physician leaders now tend to have more influence than in the past. According to the Cejka-AAPL survey, 61% of physician executives said they had more strategic input currently than in the previous year.
A roster of potential physician leader jobs
1. Executive-level roles
Vice president for medical affairs. This is the traditional role for the physician executive, which involves acting as a liaison with the organization’s physicians. These officers oversee quality of care as well as hiring, training, and performance evaluation of physicians on staff.
Chief medical officer (CMO). This is now the typical term for the highest medical role in the organization. The CMO is part of the C-suite team and participates in governance, strategic planning, and business operation decisions. CMOs may be responsible for supporting value-based strategies and making sure that those strategies are efficient and medically necessary.
Physician-in-chief. This is a new term for the hospital’s top physician, who works with the senior leadership team to maintain standards of care and customer service. The physician-in-chief may also oversee operational efficiency and support organizational transformation.
Chief clinical officer (CCO). CCOs oversee patient engagement and clinical quality outcomes. They may lead initiatives to reduce waste and improve care quality, and they can be involved in implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) and data integration. They may also assist in medical staff development, clinical integration, and physician partnerships.
2. Quality, safety, and research roles
Chief patient safety officer (CPSO). CPSOs oversee the hospital or health system’s patient safety initiatives. Their goal is to reduce medical errors and near-misses.
Chief quality officer (CQO). CQOs are responsible for collecting quality data and supporting patient safety efforts. They advise on quality initiatives and hold clinicians accountable for meeting specific quality indicators. They may also be involved in developing a culture of continuous improvement in the organization.
Chief research officer (CRO). CROs oversee the organization’s research activities, including clinical trials, internal investigator-initiated research programs, and sponsored studies.
3. Technology
Chief medical information officer (CMIO). The CMIO is the information technology (IT) department’s liaison with the clinical staff, working on selection and improvement of EHR systems. The CMIO finds new ways for EHRs to improve healthcare delivery in the organization.
Chief health information officer (CHIO). CHIOs deal with EHR implementation and health informatics. They may report to the chief information officer, the chief operations officer, or another C-suite executive, and they manage health informatics, telehealth, business and clinical intelligence, and predictive analytics initiatives.
Chief technology officer (CTO). CTOs oversee the organization’s technology capabilities. They are responsible for leading the IT team and contributing to the organization’s strategic plan.
4. Jobs not usually for physicians
There are other leadership positions that may not traditionally appeal to physicians but could be worth considering:
Chief experience officer (CXO). This involves evaluating and improving the inpatient experience. CXOs work with physicians and staff on their performance in this area.
Chief innovation officer (CIO). CIOs keep up with industry trends, market disruptions, and new opportunities, and support policy innovations and training initiatives.
Chief transformation officer (CTO). CTOs are responsible for carrying out major changes in the organization. They are supposed to act as role models for change.
5. Salaries for selected physician executives
In addition to placing the average salary for a physician leader at $350,000, the 2016 Cejka-AAPL survey pinpointed average salaries for specific types of physician leaders. Chief medical officers earned $388,000, chief patient safety officers and chief quality officers $375,000, and chief medical information officers $372,500, the survey found.
Several emerging physician leader roles – physician-in-chief, chief strategy officer, chief transformation officer, chief innovation officer, and chief integration officer – earned on average $499,000 a year, according to the survey.
Those jobs provided even higher salaries than the $437,500 reported by Cejka-AAPL for physician CEOs. In comparison, a CEO at a medical group with fewer than 200 physicians had an average salary of $438,500 in 2018, according to SullivanCotter, a health care workforce strategy company.2
Some types of physician leaders have seen unusually high pay raises recently. From 2013 to 2016, the average salary for CMIOs rose 18%, and physician leaders working at the corporate level in a health system saw median compensation rise 67%, the Cejka-AAPL survey found.
Moving ahead
For physician leaders, moving up the ladder often means reinventing yourself. If you’re leaving clinical practice, be sure to develop a solid CV for your new role so that if your leadership position doesn’t work out, you are able to find an appropriate new position.
According to a 2003 assessment, CMOs typically lasted 18-24 months on the job.3
Expect to make mistakes and try to learn from them. If necessary, move on to the next job. There is always a market for seasoned physician executives who took a few punches, learned something from the experience, and found something new.
Start to network
One way to navigate the challenges of a new role is to have a strong network, a group of colleagues and mentors who can help you figure out your path forward. They can serve as sounding boards and contacts for new jobs in an industry that is constantly changing.
A well-functioning network takes constant maintenance.
You can find people for your network by attending a variety of different meetings that physician leaders and other healthcare executives attend. Make a point of keeping their contact information on file and periodically reaching out to them.
Learn in a dyad
Some healthcare organizations assign physician leaders to dyads, where they are matched with nonphysicians who have skills that the physician lacks, such as finance, data management, or organizational politics.
Dyads are less effective when the nonphysician has all the authority and the physician is basically a figurehead. But in an effective dyad, both partners share authority and they can teach skills to each other. While the physician in the dyad brings clinical insight, the nonphysician can provide managerial know-how.
Seek out coaching
There may be points in your leadership career when you become aware of areas where you need improvement. You may have gotten negative feedback on communication skills or political sensitivity. Consider hiring an executive coach; coaches provide concentrated sessions over limited periods of time.
Coaches can also help you prepare for the future. They can help you find ways to promote yourself for new projects or create a network of allies. They also can help you establish yourself as a thought leader in a particular field through writing and speaking engagements.
Some organizations provide in-house coaches. It is worthwhile to take advantage of this benefit. If you need to find a coach on your own, ask mentors or people in your network for recommendations.
Getting to the top
It can take years to rise to the level of the corporate C-suite or even to CEO of a large organization. At the top levels of management, you often have to cut back substantially on clinical work or even give it up entirely.
Becoming CEO of a hospital can be a logical fit for physicians. A physician CEO can relate to doctors on staff, who are a key constituency, and understands what clinical care is all about. However, physician CEOs also need to have a large degree of knowledge about finance, strategy, crisis management, quality improvement, and other nonclinical considerations, not to mention good people skills.
Physicians on boards
Some physicians would rather sit on the board of trustees than take the reins of CEO. Board membership allows you to continue practicing while still having a great deal of influence over the organization. Some physicians hold board seats for many years and enjoy a great deal of respect as the go-to person on clinical care.
Physicians are increasingly serving on the boards of hospitals and health systems. Trustees welcome physicians because they want more input from clinicians in decision-making. They tend to choose physicians who already have executive duties, such as having been a department head.
Which new skills should you learn?
Physician executives often put off learning business and management skills until after being appointed to a leadership position. Even then, they may prefer to take courses focused on a particular topic rather than earn a degree such as master of business administration (MBA).
Learning on the job
A number of executive skills can be learned on the job, such as dealing with quality measures, utilization, billing and coding, disease management, committees, and interpreting data. If you are not in a dyad model, you can ask someone knowledgeable in one of these skills to take you through the steps.
Many physicians could benefit from finance and business courses in order to learn some of the budgetary, accounting, and operational skills required to perform the job optimally.
In a survey of healthcare CEOs, only 30% said their most senior physician leader had a business or medical management degree, and only 21% required a degree.4
Taking classes
Physician executives who want to brush up on a particular topic can “mix and match,” taking short, focused classes on the particular topic whenever they feel the need. In addition to resources offered by SHM, courses are available from organizations such as the AAPL, American Hospital Association, the Medical Group Management Association, or the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, to name a few examples.
Pursuing degree programs
Degree programs like MBA, master of public health (MPH), and master of health care administration (MHA) are popular with many physician executives because they get a full overview of needed skills and the potential to earn more money with their new credentials. Physician leaders with an MBA earned 13% more in 2016 than did those with no MBA, according to the Cejka-AAPL survey.
Getting a master’s degree, however, takes time and money. For example, an MBA can cost $20,000 to as much as $100,000.5 MBA, MHA, and MPH degrees take 2 years to complete, while a master of medical management (MMM) and a physician-executive MBA – focusing specifically on what physician leaders need to learn – take 1 year.
Many part-time degree programs are available for those with full-time jobs. You can find them at nearby universities as well as far-off institutions. Much of the coursework is done online, but some on-site work is usually required. You’ll find that working directly with others enriches the learning experience and helps you build your network of colleagues.
Straight MBA or other degree?
In general, degree programs cover finance, communication, strategy, information systems, marketing, organizational behavior, operational management, and quality improvement. Straight MBA programs don’t focus on healthcare, but some physician executives still prefer this route, especially if it involves degrees from prestigious business schools.
MHA, MMM, physician-executive MBA, and other degree programs focused on healthcare are popular with many physicians on the executive track. The MPH is less business-oriented but may be preferable to some because of its focus on population-based health, which fits well with decision-making on health insurance and value-based care.
Conclusion
Physicians need to prepare for leadership because these roles are very different from clinical work. It’s easy to stumble and lose direction without mentors, a network of helpful colleagues, and at least some education in business principles.
Finding a mentor should start early in your new career. A seasoned physician executive can help you understand your options and point out your strengths and shortcomings. Beyond that, concentrated work with an executive coach can help you improve your skills and choose from among the many executive roles that are now available.
You can learn many skills on the job through dyads and other relationships with more seasoned colleagues, or take short classes on particular skills that need to be learned or sharpened. Many physician executives go a step further and get a master’s degree, such as an MBA, MHA, or MMM. This involves a year or two of study, but much of it can be done online.
This article is excerpted from the Medscape Physician Business Academy course “How to become an effective leader.” You can find more information on the course at www.medscape.com/courses/business/100018.
References
1. Cejka Executive Search. 2016 Physician Leadership Compensation Survey results released. Cejka and the American Association for Physician Leadership. Nov 3, 2016.
2. Knowles M. Salaries on upswing for physician executives. Becker’s Hospital Review. Sept 25, 2018.
3. Birrer RB. Becoming a physician executive. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. Jan-Feb 2003.
4. Witt/Kieffer. Transformation of physician executives: New accountability for quality, performance, integration. Fall 2010.
5. Jurica J. Does an executive salary stand up to a clinical salary? Vital Physician Executive. 2016.
More evidence links gum disease and dementia risk
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Managing acute pain in inpatients on OUD therapy
“This is something we’re going to see more frequently, and many of us already have,” Theresa E. Vettese, MD, said at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The drastic drop in prescriptions for opioid pain medications in the last several years hasn’t curtailed the current opioid epidemic. Instead, the epidemic has to a great extent morphed into expanded use of illicit heroin and fentanyl, noted Dr. Vettese, an internist, hospitalist, and palliative care physician at Emory University and Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta.
Mythbusting
Treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients on opioid agonist therapy for opioid use disorder (OUD) is actually pretty straightforward once a few common myths have been dispelled, she said.
One of these myths –common among both physicians and patients in treatment for OUD – is that prescribing opioids for management of acute pain will place such patients at risk for OUD relapse.
“In fact, the data really strongly suggest this is not the case,” Dr. Vettese said. “It will not worsen addiction. But if we don’t aggressively treat these patients’ acute pain, it puts them at higher risk for bad outcomes.”
Another myth – this one not uncommon among hospital pharmacy departments – is that only physicians with a special certification can prescribe methadone for inpatients.
“The federal laws are clear: Any physician who has a DEA license can prescribe methadone in the hospital acute care setting, not only for pain management, but also for treatment of opioid withdrawal. You can’t prescribe it in the outpatient setting for opioid withdrawal – that has to be dispensed through a federally regulated methadone outpatient treatment program. But in the hospital, we can feel safe that we can do so. You may need to educate your pharmacist about this,” she said.
Hospitalists also can prescribe buprenorphine in the acute care inpatient setting, both for pain and treatment of opioid withdrawal, without need for a DEA waiver.
“It’s useful to get some skills in using buprenorphine in the inpatient setting. You don’t need an X waiver, but I encourage everyone to do the X-waiver training because it’s a terrific educational session. It’s 8 hours for physicians and well worth it,” Dr. Vettese noted.
By federal law the inpatient physician also can prescribe 3 days of buprenorphine at discharge to get the patient to an outpatient provider.
Misconceptions also abound about NSAIDs as a nonopioid component of acute pain management in hospitalized patients. They actually are extremely effective for the treatment of musculoskeletal, orthopedic, procedural, migraine, and some types of cancer pain. The number needed to treat (NNT) for postoperative pain relief for ibuprofen or celecoxib is 2.5, and when used in conjunction with acetaminophen at 325 mg every 4 hours, that NNT drops to 1.5, similar to the NNT of 1.7 for oxycodone at 15 mg. It should be noted, however, that the bar defining effective pain relief in randomized studies is set rather low: A 50% greater reduction in pain than achieved with placebo.
Many hospitalists would like to use NSAIDs more often, but they’re leery of the associated risks of GI bleeding, ischemic cardiovascular events, and worsening kidney function. Dr. Vettese offered several risk-mitigation strategies to increase the use of NSAIDs as opioid-sparing agents for acute pain management.
She has changed her own clinical practice with regard to using NSAIDs in patients with chronic kidney disease in response to a 2019 systematic review by investigators at the University of Ottawa.
“This was a game changer for me because in this review, low-dose NSAIDs were safe in that they didn’t significantly increase the risk of worsening kidney failure even in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease. So this has expanded my use of NSAIDs in this population through stage 3 CKD. With a creatinine clearance below 30, however, kidney failure worsened rapidly, so I don’t do it in patients with CKD stage 4,” Dr. Vettese said.
Gastroenterologists categorize patients as being at high risk of GI bleeding related to NSAID use if they have a history of a complicated ulcer or they have at least three of the following risk factors: Age above 65 years, history of an uncomplicated ulcer, being on high-dose NSAID therapy, or concurrent use of aspirin, glucocorticoids, or anticoagulants. Patients are considered at moderate risk if they have one or two of the risk factors, and low risk if they have none. Dr. Vettese said that, while NSAIDs clearly should be avoided in the high-risk group, moderate-risk patients are a different matter.
“Many avoid the use of NSAIDs with moderate risk, but I think we can expand their use if we use the right NSAID and we use protective strategies,” Dr. Vettese said.
Celecoxib is the safest drug in terms of upper GI bleeding risk, but ibuprofen is close. They are associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk of bleeding when compared with risk in patients not on an NSAID. Naproxen or indeomethacin use carries a fourfold to fivefold increased risk.
“Celecoxib with a proton pump inhibitor is safest, followed by celecoxib alone, followed by ibuprofen with a proton pump inhibitor. So I advocate using NSAIDs more frequently in people who are at moderate risk by using them with a PPI,” she said.
There is persuasive evidence of increased cardiovascular risk in association with even short-duration NSAIDs, as the drugs are utilized in the treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients. That being said, Dr. Vettese believes hospitalists can use these drugs safely in more patients by following a thoughtful cardiovascular risk-mitigation strategy developed by Italian investigators.
Communicating about pain management
“Communication is always the key to effective pain management in every situation,” Dr. Vettese emphasized.
“I talk to the patient about the goals of effective pain management. I’ll discourage the use of the 1-10 pain scale, and instead, I’ll be honest about expectations, saying, ‘You have a problem that will cause acute pain, and it’s unlikely that I will be able to completely relieve your pain. The goal is to improve your function so that you can get up and go the bathroom by yourself, and so that you can sleep for a few hours. That’s how we’re going to measure the efficacy of our pain-management program.’ ”
She explains to the patient that she’ll be using nonopioid medications and nondrug therapies along with oral opioid pain medications, which are less risky than IV opioids. She offers reassurance that this treatment strategy won’t cause an OUD relapse. She lets the patient know up-front that the opioids will be tapered as the acute pain improves.
For the patient who comes into the hospital on buprenorphine for OUD, she immediately checks with the state prescription drug monitoring program to make sure everything is above board and there’s no indication of doctor shopping for prescriptions. For in-hospital acute pain, it’s safe and effective to continue the outpatient dose. On an outpatient basis, however, the drug is given once daily. On that dosing schedule both the euphoric effect as well as the analgesic effect are lost, so for acute pain management in the hospital it’s recommended to split the dose into twice- or thrice-daily doses to achieve an analgesic effect.
Oral NSAIDs are part of the treatment strategy whenever possible. For severe acute pain, Dr. Vettese will prescribe an immediate-release opioid having a high affinity to the mu opioid receptor, such as oral hydromorphone, on an as-needed basis. The drug has onset of effect in 30 minutes, peak effect in 1 hour, and a duration of effect of 4-6 hours, although she recommends going with 4 hours to provide adequate analgesia.
“These patients will require much higher doses than the patients who are opioid naive,” she advised.
For the patient with acute pain who is admitted while on methadone for OUD, it’s important to call the outpatient treatment program to verify the dosage.
“You can split the dose of methadone to try to get better analgesia, although I can tell you that patients who are treated with methadone for OUD frequently don’t want to do that. And if they don’t want to, then I don’t,” the hospitalist said.
As with the patient on buprenorphine for OUD, she’ll use additional oral immediate-release opioids as needed for acute severe pain in a patient on methadone for medication-assisted OUD treatment.
Dr. Vettese reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
“This is something we’re going to see more frequently, and many of us already have,” Theresa E. Vettese, MD, said at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The drastic drop in prescriptions for opioid pain medications in the last several years hasn’t curtailed the current opioid epidemic. Instead, the epidemic has to a great extent morphed into expanded use of illicit heroin and fentanyl, noted Dr. Vettese, an internist, hospitalist, and palliative care physician at Emory University and Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta.
Mythbusting
Treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients on opioid agonist therapy for opioid use disorder (OUD) is actually pretty straightforward once a few common myths have been dispelled, she said.
One of these myths –common among both physicians and patients in treatment for OUD – is that prescribing opioids for management of acute pain will place such patients at risk for OUD relapse.
“In fact, the data really strongly suggest this is not the case,” Dr. Vettese said. “It will not worsen addiction. But if we don’t aggressively treat these patients’ acute pain, it puts them at higher risk for bad outcomes.”
Another myth – this one not uncommon among hospital pharmacy departments – is that only physicians with a special certification can prescribe methadone for inpatients.
“The federal laws are clear: Any physician who has a DEA license can prescribe methadone in the hospital acute care setting, not only for pain management, but also for treatment of opioid withdrawal. You can’t prescribe it in the outpatient setting for opioid withdrawal – that has to be dispensed through a federally regulated methadone outpatient treatment program. But in the hospital, we can feel safe that we can do so. You may need to educate your pharmacist about this,” she said.
Hospitalists also can prescribe buprenorphine in the acute care inpatient setting, both for pain and treatment of opioid withdrawal, without need for a DEA waiver.
“It’s useful to get some skills in using buprenorphine in the inpatient setting. You don’t need an X waiver, but I encourage everyone to do the X-waiver training because it’s a terrific educational session. It’s 8 hours for physicians and well worth it,” Dr. Vettese noted.
By federal law the inpatient physician also can prescribe 3 days of buprenorphine at discharge to get the patient to an outpatient provider.
Misconceptions also abound about NSAIDs as a nonopioid component of acute pain management in hospitalized patients. They actually are extremely effective for the treatment of musculoskeletal, orthopedic, procedural, migraine, and some types of cancer pain. The number needed to treat (NNT) for postoperative pain relief for ibuprofen or celecoxib is 2.5, and when used in conjunction with acetaminophen at 325 mg every 4 hours, that NNT drops to 1.5, similar to the NNT of 1.7 for oxycodone at 15 mg. It should be noted, however, that the bar defining effective pain relief in randomized studies is set rather low: A 50% greater reduction in pain than achieved with placebo.
Many hospitalists would like to use NSAIDs more often, but they’re leery of the associated risks of GI bleeding, ischemic cardiovascular events, and worsening kidney function. Dr. Vettese offered several risk-mitigation strategies to increase the use of NSAIDs as opioid-sparing agents for acute pain management.
She has changed her own clinical practice with regard to using NSAIDs in patients with chronic kidney disease in response to a 2019 systematic review by investigators at the University of Ottawa.
“This was a game changer for me because in this review, low-dose NSAIDs were safe in that they didn’t significantly increase the risk of worsening kidney failure even in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease. So this has expanded my use of NSAIDs in this population through stage 3 CKD. With a creatinine clearance below 30, however, kidney failure worsened rapidly, so I don’t do it in patients with CKD stage 4,” Dr. Vettese said.
Gastroenterologists categorize patients as being at high risk of GI bleeding related to NSAID use if they have a history of a complicated ulcer or they have at least three of the following risk factors: Age above 65 years, history of an uncomplicated ulcer, being on high-dose NSAID therapy, or concurrent use of aspirin, glucocorticoids, or anticoagulants. Patients are considered at moderate risk if they have one or two of the risk factors, and low risk if they have none. Dr. Vettese said that, while NSAIDs clearly should be avoided in the high-risk group, moderate-risk patients are a different matter.
“Many avoid the use of NSAIDs with moderate risk, but I think we can expand their use if we use the right NSAID and we use protective strategies,” Dr. Vettese said.
Celecoxib is the safest drug in terms of upper GI bleeding risk, but ibuprofen is close. They are associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk of bleeding when compared with risk in patients not on an NSAID. Naproxen or indeomethacin use carries a fourfold to fivefold increased risk.
“Celecoxib with a proton pump inhibitor is safest, followed by celecoxib alone, followed by ibuprofen with a proton pump inhibitor. So I advocate using NSAIDs more frequently in people who are at moderate risk by using them with a PPI,” she said.
There is persuasive evidence of increased cardiovascular risk in association with even short-duration NSAIDs, as the drugs are utilized in the treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients. That being said, Dr. Vettese believes hospitalists can use these drugs safely in more patients by following a thoughtful cardiovascular risk-mitigation strategy developed by Italian investigators.
Communicating about pain management
“Communication is always the key to effective pain management in every situation,” Dr. Vettese emphasized.
“I talk to the patient about the goals of effective pain management. I’ll discourage the use of the 1-10 pain scale, and instead, I’ll be honest about expectations, saying, ‘You have a problem that will cause acute pain, and it’s unlikely that I will be able to completely relieve your pain. The goal is to improve your function so that you can get up and go the bathroom by yourself, and so that you can sleep for a few hours. That’s how we’re going to measure the efficacy of our pain-management program.’ ”
She explains to the patient that she’ll be using nonopioid medications and nondrug therapies along with oral opioid pain medications, which are less risky than IV opioids. She offers reassurance that this treatment strategy won’t cause an OUD relapse. She lets the patient know up-front that the opioids will be tapered as the acute pain improves.
For the patient who comes into the hospital on buprenorphine for OUD, she immediately checks with the state prescription drug monitoring program to make sure everything is above board and there’s no indication of doctor shopping for prescriptions. For in-hospital acute pain, it’s safe and effective to continue the outpatient dose. On an outpatient basis, however, the drug is given once daily. On that dosing schedule both the euphoric effect as well as the analgesic effect are lost, so for acute pain management in the hospital it’s recommended to split the dose into twice- or thrice-daily doses to achieve an analgesic effect.
Oral NSAIDs are part of the treatment strategy whenever possible. For severe acute pain, Dr. Vettese will prescribe an immediate-release opioid having a high affinity to the mu opioid receptor, such as oral hydromorphone, on an as-needed basis. The drug has onset of effect in 30 minutes, peak effect in 1 hour, and a duration of effect of 4-6 hours, although she recommends going with 4 hours to provide adequate analgesia.
“These patients will require much higher doses than the patients who are opioid naive,” she advised.
For the patient with acute pain who is admitted while on methadone for OUD, it’s important to call the outpatient treatment program to verify the dosage.
“You can split the dose of methadone to try to get better analgesia, although I can tell you that patients who are treated with methadone for OUD frequently don’t want to do that. And if they don’t want to, then I don’t,” the hospitalist said.
As with the patient on buprenorphine for OUD, she’ll use additional oral immediate-release opioids as needed for acute severe pain in a patient on methadone for medication-assisted OUD treatment.
Dr. Vettese reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
“This is something we’re going to see more frequently, and many of us already have,” Theresa E. Vettese, MD, said at HM20 Virtual, hosted by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The drastic drop in prescriptions for opioid pain medications in the last several years hasn’t curtailed the current opioid epidemic. Instead, the epidemic has to a great extent morphed into expanded use of illicit heroin and fentanyl, noted Dr. Vettese, an internist, hospitalist, and palliative care physician at Emory University and Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta.
Mythbusting
Treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients on opioid agonist therapy for opioid use disorder (OUD) is actually pretty straightforward once a few common myths have been dispelled, she said.
One of these myths –common among both physicians and patients in treatment for OUD – is that prescribing opioids for management of acute pain will place such patients at risk for OUD relapse.
“In fact, the data really strongly suggest this is not the case,” Dr. Vettese said. “It will not worsen addiction. But if we don’t aggressively treat these patients’ acute pain, it puts them at higher risk for bad outcomes.”
Another myth – this one not uncommon among hospital pharmacy departments – is that only physicians with a special certification can prescribe methadone for inpatients.
“The federal laws are clear: Any physician who has a DEA license can prescribe methadone in the hospital acute care setting, not only for pain management, but also for treatment of opioid withdrawal. You can’t prescribe it in the outpatient setting for opioid withdrawal – that has to be dispensed through a federally regulated methadone outpatient treatment program. But in the hospital, we can feel safe that we can do so. You may need to educate your pharmacist about this,” she said.
Hospitalists also can prescribe buprenorphine in the acute care inpatient setting, both for pain and treatment of opioid withdrawal, without need for a DEA waiver.
“It’s useful to get some skills in using buprenorphine in the inpatient setting. You don’t need an X waiver, but I encourage everyone to do the X-waiver training because it’s a terrific educational session. It’s 8 hours for physicians and well worth it,” Dr. Vettese noted.
By federal law the inpatient physician also can prescribe 3 days of buprenorphine at discharge to get the patient to an outpatient provider.
Misconceptions also abound about NSAIDs as a nonopioid component of acute pain management in hospitalized patients. They actually are extremely effective for the treatment of musculoskeletal, orthopedic, procedural, migraine, and some types of cancer pain. The number needed to treat (NNT) for postoperative pain relief for ibuprofen or celecoxib is 2.5, and when used in conjunction with acetaminophen at 325 mg every 4 hours, that NNT drops to 1.5, similar to the NNT of 1.7 for oxycodone at 15 mg. It should be noted, however, that the bar defining effective pain relief in randomized studies is set rather low: A 50% greater reduction in pain than achieved with placebo.
Many hospitalists would like to use NSAIDs more often, but they’re leery of the associated risks of GI bleeding, ischemic cardiovascular events, and worsening kidney function. Dr. Vettese offered several risk-mitigation strategies to increase the use of NSAIDs as opioid-sparing agents for acute pain management.
She has changed her own clinical practice with regard to using NSAIDs in patients with chronic kidney disease in response to a 2019 systematic review by investigators at the University of Ottawa.
“This was a game changer for me because in this review, low-dose NSAIDs were safe in that they didn’t significantly increase the risk of worsening kidney failure even in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease. So this has expanded my use of NSAIDs in this population through stage 3 CKD. With a creatinine clearance below 30, however, kidney failure worsened rapidly, so I don’t do it in patients with CKD stage 4,” Dr. Vettese said.
Gastroenterologists categorize patients as being at high risk of GI bleeding related to NSAID use if they have a history of a complicated ulcer or they have at least three of the following risk factors: Age above 65 years, history of an uncomplicated ulcer, being on high-dose NSAID therapy, or concurrent use of aspirin, glucocorticoids, or anticoagulants. Patients are considered at moderate risk if they have one or two of the risk factors, and low risk if they have none. Dr. Vettese said that, while NSAIDs clearly should be avoided in the high-risk group, moderate-risk patients are a different matter.
“Many avoid the use of NSAIDs with moderate risk, but I think we can expand their use if we use the right NSAID and we use protective strategies,” Dr. Vettese said.
Celecoxib is the safest drug in terms of upper GI bleeding risk, but ibuprofen is close. They are associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk of bleeding when compared with risk in patients not on an NSAID. Naproxen or indeomethacin use carries a fourfold to fivefold increased risk.
“Celecoxib with a proton pump inhibitor is safest, followed by celecoxib alone, followed by ibuprofen with a proton pump inhibitor. So I advocate using NSAIDs more frequently in people who are at moderate risk by using them with a PPI,” she said.
There is persuasive evidence of increased cardiovascular risk in association with even short-duration NSAIDs, as the drugs are utilized in the treatment of acute pain in hospitalized patients. That being said, Dr. Vettese believes hospitalists can use these drugs safely in more patients by following a thoughtful cardiovascular risk-mitigation strategy developed by Italian investigators.
Communicating about pain management
“Communication is always the key to effective pain management in every situation,” Dr. Vettese emphasized.
“I talk to the patient about the goals of effective pain management. I’ll discourage the use of the 1-10 pain scale, and instead, I’ll be honest about expectations, saying, ‘You have a problem that will cause acute pain, and it’s unlikely that I will be able to completely relieve your pain. The goal is to improve your function so that you can get up and go the bathroom by yourself, and so that you can sleep for a few hours. That’s how we’re going to measure the efficacy of our pain-management program.’ ”
She explains to the patient that she’ll be using nonopioid medications and nondrug therapies along with oral opioid pain medications, which are less risky than IV opioids. She offers reassurance that this treatment strategy won’t cause an OUD relapse. She lets the patient know up-front that the opioids will be tapered as the acute pain improves.
For the patient who comes into the hospital on buprenorphine for OUD, she immediately checks with the state prescription drug monitoring program to make sure everything is above board and there’s no indication of doctor shopping for prescriptions. For in-hospital acute pain, it’s safe and effective to continue the outpatient dose. On an outpatient basis, however, the drug is given once daily. On that dosing schedule both the euphoric effect as well as the analgesic effect are lost, so for acute pain management in the hospital it’s recommended to split the dose into twice- or thrice-daily doses to achieve an analgesic effect.
Oral NSAIDs are part of the treatment strategy whenever possible. For severe acute pain, Dr. Vettese will prescribe an immediate-release opioid having a high affinity to the mu opioid receptor, such as oral hydromorphone, on an as-needed basis. The drug has onset of effect in 30 minutes, peak effect in 1 hour, and a duration of effect of 4-6 hours, although she recommends going with 4 hours to provide adequate analgesia.
“These patients will require much higher doses than the patients who are opioid naive,” she advised.
For the patient with acute pain who is admitted while on methadone for OUD, it’s important to call the outpatient treatment program to verify the dosage.
“You can split the dose of methadone to try to get better analgesia, although I can tell you that patients who are treated with methadone for OUD frequently don’t want to do that. And if they don’t want to, then I don’t,” the hospitalist said.
As with the patient on buprenorphine for OUD, she’ll use additional oral immediate-release opioids as needed for acute severe pain in a patient on methadone for medication-assisted OUD treatment.
Dr. Vettese reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
FROM HM20 VIRTUAL