User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Low vitamin D linked to increased COVID-19 risk
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerobic exercise may up brain-training benefits in schizophrenia
Recent research has shown that social cognition training can benefit patients with schizophrenia, and a new study suggests that adding regular aerobic exercise sessions substantially increases the improvements in a dose-response manner.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 47 patients with schizophrenia, improvement in cognition tripled after adding an aerobic exercise program to cognitive training (CT) compared with CT alone.
Investigators, led by Keith H. Nuechterlein, PhD, professor of psychology, University of California, Los Angeles, note that there is “increasing evidence” to support the use of aerobic exercise to improve cognition and functioning in schizophrenia.
However, the “extent to which these gains are dependent on the amount of aerobic exercise completed remains unclear, although variability in adherence to intended exercise regiments is evident,” they write.
They also point out that
The findings were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society (SIRS) 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Body Circuit Training
In the study, 47 patients with first-episode schizophrenia were randomly assigned to receive 6 months of CT alone or 6 months of CT plus exercise (CT+E).
All participants underwent 4 hours per week of computerized CT with BrainHQ and SocialVille programs (PositScience).
Patients in the CT+E group also took part in total body circuit training. Two aerobic exercise sessions per week were held at the clinic and two were to be completed at home. The goal was 150 minutes of exercise per week in total.
Exercise intensity was titrated to the individual, at a target of 60% to 80% of heart rate reserve.
Both the CT and CT+E groups showed cognitive gains on the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) test, as well as work/school functioning gains on the Global Assessment Scale: Role.
However, results showed that the improvements in the CT+E group were three times greater than those shown in the CT group (P < .02 for the MCCB overall composite score).
Cognitive Gain Predictors
Because there were also substantial differences in the magnitude of cognitive improvement between the CT+E patients, the investigators sought to identify predictors of cognitive gain.
They found that patients in the CT+E group completed, on average, 85% of their in-clinic exercise sessions but only 39% of their home exercise sessions.
Those who completed a higher overall proportion of the exercise sessions had the largest cognitive gains (P = .03). This relationship was even stronger for patients who completed home exercise sessions (P = .02).
“Thus, aerobic exercise showed a dose-response relationship to cognitive improvement,” the researchers report.
To improve completion rates for home sessions, the investigators tried paying the patients $5 for each session completed, which was “helpful” but did not iron out the variability in adherence.
They also tried assigning points for completing the most exercise sessions in the desired heart rate. They awarded a monthly winner and divided the patients into two completion groups. However, there were “mixed” results.
“Development of systematic incentive strategies to encourage regular aerobic exercise will be critical to successful dissemination of exercise programs as part of the treatment of schizophrenia,” the researchers write.
They add that “pilot work with smartphone reminder systems is underway.”
Effective, but Intensity Is Key
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, David Kimhy, PhD, program leader for New Interventions in Schizophrenia, Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the results are consistent with previous research.
Aerobic exercise is “highly effective in improving neurocognitive functioning” in patients with schizophrenia, said Kimhy, who was not involved in the research.
“Many individuals with schizophrenia tend to have a highly sedentary lifestyle resulting in poor aerobic fitness,” he said. “Thus, aerobic fitness may represent one of the few modifiable risk factors for ameliorating poor neurocognitive functioning.”
He noted that those benefits are in addition to “the many cardiovascular and health benefits aerobic exercise provide, which are nearly nonexistent for cognitive training and pharmacological interventions.”
However, even if patients do take part in exercise sessions, “an important issue is in-session fidelity with training goals, as individuals may attend scheduled sessions but exercise very lightly,” Kimhy noted.
He pointed out that the proportion of time these patients exercise at their designated target training intensity is highly correlated with neurocognitive improvement. Consequently, “exercising with a trainer may increase both attendance and in-session training fidelity.”
Overall, although the current study suggests that in-clinic exercise sessions can be advantageous, “the recent COVID-19 pandemic made such options very challenging,” Kimhy said.
“To address this issue, our research group and others are currently examining employment of aerobic exercise training at home, connected with trainers via live two-way telehealth video calls,” he added.
Plasticity-Based Training
Two recent studies also indicate that remotely administered training programs can improve social cognition.
In the first study, published online July 2 in Schizophrenia Bulletin, 147 outpatients with schizophrenia were randomly assigned to complete 40 sessions of either SocialVille plasticity-based social cognition training or computer-based games such as crossword puzzles and solitaire.
“To develop these social cognition training exercises, we analyzed a tremendous amount of prior research about how the brain processes social information,” lead author Mor Nahum, PhD, School of Occupational Therapy, Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel, said in a press release.
“It turns out that social cognition requires fast and accurate brain information processing, so we developed exercises that trained the brain to process social stimuli, like faces and emotions, quickly and accurately,” Nahum added.
The interventions were conducted at home, with 55 participants completing the cognitive training and 53 completing the computer game sessions. (The remaining 39 either dropped out or withdrew.)
An average of 28 hours of social cognition training over 3 months was associated with a significant improvement on social cognitive composite scores compared with computer games (P < .001), but not on the UCSD Performance-Based Skills Assessment.
Further analysis suggested that more time spent on the cognitive training was associated with greater improvements in social cognition and social functioning, as well as on a motivation subscale.
The results “provide support for the efficacy of a remote, plasticity-based social cognitive training program,” the investigators write.
Such programs “may serve as a cost-effective adjunct to existing psychosocial treatments,” they add.
Auditory vs Visual Training
In the other study, published online May 21 in Schizophrenia Research, investigators led by Rogerio Panizzutti, MD, PhD, Instituto de Ciencias Biomedicas, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, randomly assigned 79 patients with schizophrenia to 40 hours of auditory or visual computerized training.
The exercises were dynamically equivalent between the two types of training, and their difficulty increased as the training progressed.
Both groups showed improvements in reasoning, problem-solving, and reported symptoms. However, the group receiving visual training also had greater improvement in global cognition and attention than the group receiving auditory training.
All studies were supported by Posit Science Corporation. The study authors and Kimhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent research has shown that social cognition training can benefit patients with schizophrenia, and a new study suggests that adding regular aerobic exercise sessions substantially increases the improvements in a dose-response manner.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 47 patients with schizophrenia, improvement in cognition tripled after adding an aerobic exercise program to cognitive training (CT) compared with CT alone.
Investigators, led by Keith H. Nuechterlein, PhD, professor of psychology, University of California, Los Angeles, note that there is “increasing evidence” to support the use of aerobic exercise to improve cognition and functioning in schizophrenia.
However, the “extent to which these gains are dependent on the amount of aerobic exercise completed remains unclear, although variability in adherence to intended exercise regiments is evident,” they write.
They also point out that
The findings were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society (SIRS) 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Body Circuit Training
In the study, 47 patients with first-episode schizophrenia were randomly assigned to receive 6 months of CT alone or 6 months of CT plus exercise (CT+E).
All participants underwent 4 hours per week of computerized CT with BrainHQ and SocialVille programs (PositScience).
Patients in the CT+E group also took part in total body circuit training. Two aerobic exercise sessions per week were held at the clinic and two were to be completed at home. The goal was 150 minutes of exercise per week in total.
Exercise intensity was titrated to the individual, at a target of 60% to 80% of heart rate reserve.
Both the CT and CT+E groups showed cognitive gains on the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) test, as well as work/school functioning gains on the Global Assessment Scale: Role.
However, results showed that the improvements in the CT+E group were three times greater than those shown in the CT group (P < .02 for the MCCB overall composite score).
Cognitive Gain Predictors
Because there were also substantial differences in the magnitude of cognitive improvement between the CT+E patients, the investigators sought to identify predictors of cognitive gain.
They found that patients in the CT+E group completed, on average, 85% of their in-clinic exercise sessions but only 39% of their home exercise sessions.
Those who completed a higher overall proportion of the exercise sessions had the largest cognitive gains (P = .03). This relationship was even stronger for patients who completed home exercise sessions (P = .02).
“Thus, aerobic exercise showed a dose-response relationship to cognitive improvement,” the researchers report.
To improve completion rates for home sessions, the investigators tried paying the patients $5 for each session completed, which was “helpful” but did not iron out the variability in adherence.
They also tried assigning points for completing the most exercise sessions in the desired heart rate. They awarded a monthly winner and divided the patients into two completion groups. However, there were “mixed” results.
“Development of systematic incentive strategies to encourage regular aerobic exercise will be critical to successful dissemination of exercise programs as part of the treatment of schizophrenia,” the researchers write.
They add that “pilot work with smartphone reminder systems is underway.”
Effective, but Intensity Is Key
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, David Kimhy, PhD, program leader for New Interventions in Schizophrenia, Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the results are consistent with previous research.
Aerobic exercise is “highly effective in improving neurocognitive functioning” in patients with schizophrenia, said Kimhy, who was not involved in the research.
“Many individuals with schizophrenia tend to have a highly sedentary lifestyle resulting in poor aerobic fitness,” he said. “Thus, aerobic fitness may represent one of the few modifiable risk factors for ameliorating poor neurocognitive functioning.”
He noted that those benefits are in addition to “the many cardiovascular and health benefits aerobic exercise provide, which are nearly nonexistent for cognitive training and pharmacological interventions.”
However, even if patients do take part in exercise sessions, “an important issue is in-session fidelity with training goals, as individuals may attend scheduled sessions but exercise very lightly,” Kimhy noted.
He pointed out that the proportion of time these patients exercise at their designated target training intensity is highly correlated with neurocognitive improvement. Consequently, “exercising with a trainer may increase both attendance and in-session training fidelity.”
Overall, although the current study suggests that in-clinic exercise sessions can be advantageous, “the recent COVID-19 pandemic made such options very challenging,” Kimhy said.
“To address this issue, our research group and others are currently examining employment of aerobic exercise training at home, connected with trainers via live two-way telehealth video calls,” he added.
Plasticity-Based Training
Two recent studies also indicate that remotely administered training programs can improve social cognition.
In the first study, published online July 2 in Schizophrenia Bulletin, 147 outpatients with schizophrenia were randomly assigned to complete 40 sessions of either SocialVille plasticity-based social cognition training or computer-based games such as crossword puzzles and solitaire.
“To develop these social cognition training exercises, we analyzed a tremendous amount of prior research about how the brain processes social information,” lead author Mor Nahum, PhD, School of Occupational Therapy, Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel, said in a press release.
“It turns out that social cognition requires fast and accurate brain information processing, so we developed exercises that trained the brain to process social stimuli, like faces and emotions, quickly and accurately,” Nahum added.
The interventions were conducted at home, with 55 participants completing the cognitive training and 53 completing the computer game sessions. (The remaining 39 either dropped out or withdrew.)
An average of 28 hours of social cognition training over 3 months was associated with a significant improvement on social cognitive composite scores compared with computer games (P < .001), but not on the UCSD Performance-Based Skills Assessment.
Further analysis suggested that more time spent on the cognitive training was associated with greater improvements in social cognition and social functioning, as well as on a motivation subscale.
The results “provide support for the efficacy of a remote, plasticity-based social cognitive training program,” the investigators write.
Such programs “may serve as a cost-effective adjunct to existing psychosocial treatments,” they add.
Auditory vs Visual Training
In the other study, published online May 21 in Schizophrenia Research, investigators led by Rogerio Panizzutti, MD, PhD, Instituto de Ciencias Biomedicas, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, randomly assigned 79 patients with schizophrenia to 40 hours of auditory or visual computerized training.
The exercises were dynamically equivalent between the two types of training, and their difficulty increased as the training progressed.
Both groups showed improvements in reasoning, problem-solving, and reported symptoms. However, the group receiving visual training also had greater improvement in global cognition and attention than the group receiving auditory training.
All studies were supported by Posit Science Corporation. The study authors and Kimhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent research has shown that social cognition training can benefit patients with schizophrenia, and a new study suggests that adding regular aerobic exercise sessions substantially increases the improvements in a dose-response manner.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 47 patients with schizophrenia, improvement in cognition tripled after adding an aerobic exercise program to cognitive training (CT) compared with CT alone.
Investigators, led by Keith H. Nuechterlein, PhD, professor of psychology, University of California, Los Angeles, note that there is “increasing evidence” to support the use of aerobic exercise to improve cognition and functioning in schizophrenia.
However, the “extent to which these gains are dependent on the amount of aerobic exercise completed remains unclear, although variability in adherence to intended exercise regiments is evident,” they write.
They also point out that
The findings were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society (SIRS) 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Body Circuit Training
In the study, 47 patients with first-episode schizophrenia were randomly assigned to receive 6 months of CT alone or 6 months of CT plus exercise (CT+E).
All participants underwent 4 hours per week of computerized CT with BrainHQ and SocialVille programs (PositScience).
Patients in the CT+E group also took part in total body circuit training. Two aerobic exercise sessions per week were held at the clinic and two were to be completed at home. The goal was 150 minutes of exercise per week in total.
Exercise intensity was titrated to the individual, at a target of 60% to 80% of heart rate reserve.
Both the CT and CT+E groups showed cognitive gains on the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) test, as well as work/school functioning gains on the Global Assessment Scale: Role.
However, results showed that the improvements in the CT+E group were three times greater than those shown in the CT group (P < .02 for the MCCB overall composite score).
Cognitive Gain Predictors
Because there were also substantial differences in the magnitude of cognitive improvement between the CT+E patients, the investigators sought to identify predictors of cognitive gain.
They found that patients in the CT+E group completed, on average, 85% of their in-clinic exercise sessions but only 39% of their home exercise sessions.
Those who completed a higher overall proportion of the exercise sessions had the largest cognitive gains (P = .03). This relationship was even stronger for patients who completed home exercise sessions (P = .02).
“Thus, aerobic exercise showed a dose-response relationship to cognitive improvement,” the researchers report.
To improve completion rates for home sessions, the investigators tried paying the patients $5 for each session completed, which was “helpful” but did not iron out the variability in adherence.
They also tried assigning points for completing the most exercise sessions in the desired heart rate. They awarded a monthly winner and divided the patients into two completion groups. However, there were “mixed” results.
“Development of systematic incentive strategies to encourage regular aerobic exercise will be critical to successful dissemination of exercise programs as part of the treatment of schizophrenia,” the researchers write.
They add that “pilot work with smartphone reminder systems is underway.”
Effective, but Intensity Is Key
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, David Kimhy, PhD, program leader for New Interventions in Schizophrenia, Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the results are consistent with previous research.
Aerobic exercise is “highly effective in improving neurocognitive functioning” in patients with schizophrenia, said Kimhy, who was not involved in the research.
“Many individuals with schizophrenia tend to have a highly sedentary lifestyle resulting in poor aerobic fitness,” he said. “Thus, aerobic fitness may represent one of the few modifiable risk factors for ameliorating poor neurocognitive functioning.”
He noted that those benefits are in addition to “the many cardiovascular and health benefits aerobic exercise provide, which are nearly nonexistent for cognitive training and pharmacological interventions.”
However, even if patients do take part in exercise sessions, “an important issue is in-session fidelity with training goals, as individuals may attend scheduled sessions but exercise very lightly,” Kimhy noted.
He pointed out that the proportion of time these patients exercise at their designated target training intensity is highly correlated with neurocognitive improvement. Consequently, “exercising with a trainer may increase both attendance and in-session training fidelity.”
Overall, although the current study suggests that in-clinic exercise sessions can be advantageous, “the recent COVID-19 pandemic made such options very challenging,” Kimhy said.
“To address this issue, our research group and others are currently examining employment of aerobic exercise training at home, connected with trainers via live two-way telehealth video calls,” he added.
Plasticity-Based Training
Two recent studies also indicate that remotely administered training programs can improve social cognition.
In the first study, published online July 2 in Schizophrenia Bulletin, 147 outpatients with schizophrenia were randomly assigned to complete 40 sessions of either SocialVille plasticity-based social cognition training or computer-based games such as crossword puzzles and solitaire.
“To develop these social cognition training exercises, we analyzed a tremendous amount of prior research about how the brain processes social information,” lead author Mor Nahum, PhD, School of Occupational Therapy, Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel, said in a press release.
“It turns out that social cognition requires fast and accurate brain information processing, so we developed exercises that trained the brain to process social stimuli, like faces and emotions, quickly and accurately,” Nahum added.
The interventions were conducted at home, with 55 participants completing the cognitive training and 53 completing the computer game sessions. (The remaining 39 either dropped out or withdrew.)
An average of 28 hours of social cognition training over 3 months was associated with a significant improvement on social cognitive composite scores compared with computer games (P < .001), but not on the UCSD Performance-Based Skills Assessment.
Further analysis suggested that more time spent on the cognitive training was associated with greater improvements in social cognition and social functioning, as well as on a motivation subscale.
The results “provide support for the efficacy of a remote, plasticity-based social cognitive training program,” the investigators write.
Such programs “may serve as a cost-effective adjunct to existing psychosocial treatments,” they add.
Auditory vs Visual Training
In the other study, published online May 21 in Schizophrenia Research, investigators led by Rogerio Panizzutti, MD, PhD, Instituto de Ciencias Biomedicas, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, randomly assigned 79 patients with schizophrenia to 40 hours of auditory or visual computerized training.
The exercises were dynamically equivalent between the two types of training, and their difficulty increased as the training progressed.
Both groups showed improvements in reasoning, problem-solving, and reported symptoms. However, the group receiving visual training also had greater improvement in global cognition and attention than the group receiving auditory training.
All studies were supported by Posit Science Corporation. The study authors and Kimhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosing and Managing Tardive Dyskinesia

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.
Microbiome research ‘opening doors’ to new Alzheimer’s disease treatments
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
FROM CP/AACP PSYCHIATRY UPDATE
A better tau blood test for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease?
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2020
Flu and pneumonia vaccination tied to lower dementia risk
In a cohort study of more than 9,000 older adults, receiving a single influenza vaccination was associated with a 17% lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease compared with not receiving the vaccine. In addition, for those who were vaccinated more than once over the years, there was an additional 13% reduction in Alzheimer’s disease incidence.
In another study, which included more than 5,000 older participants, being vaccinated against pneumonia between the ages of 65 and 75 reduced the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease by 30%.
The subject of vaccines “is obviously very topical with the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association. “While these are very preliminary data, these studies do suggest that with vaccination against both respiratory illnesses, there is the potential to lower risk for developing cognitive decline and dementia,” said Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved in the research.
The findings of both studies were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Lower Alzheimer’s disease prevalence
The influenza vaccine study was presented by Albert Amran, a fourth-year medical student at McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. The researchers used electronic health record data to create a propensity-matched cohort of 9,066 vaccinated and unvaccinated adults ages 60 and older.
Influenza vaccination, increased frequency of administration, and younger age at time of vaccination were all associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease, Mr. Amran reported.
Being vaccinated for influenza was significantly linked to a lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (odds ratio [OR], 0.83; P < .0001) in comparison with not being vaccinated. Receiving more than one vaccination over the years was associated with an additional reduction in AD incidence (OR, 0.87; P = .0342). The protection appeared to be strongest for those who received their first vaccination at a younger age, for example, at age 60 versus 70.
Mr. Amran and research colleagues have two theories as to why influenza vaccination may protect the brain.
One is that vaccination may aid the immune system as people age. “As people get older, their immune systems become less able to control infection. We’ve seen this with the ongoing pandemic, with older people at much higher risk for dying. Giving people the vaccine once a year may help keep the immune system in shape,” Mr. Amran said.
Another theory is that the prevention of influenza itself may be relevant. “Flu infections can be extremely deadly in older patients. Maybe the results of our study will give another reason for people to get vaccinated,” Mr. Amran said.
Pneumonia vaccine
The other study was presented by Svetlana Ukraintseva, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Ukraintseva and colleagues investigated associations between pneumococcal vaccine, with and without an accompanying influenza vaccine, and the risk for Alzheimer’s disease among 5,146 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Covariates included sex, race, birth cohort, education, smoking, and a known genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: the rs2075650 G allele in the TOMM40 gene.
In a logistic model with all covariates, vaccination against pneumonia between ages 65 and 75 was significantly associated with reduced risk of developing AD (OR, 0.70; P < .04). The largest reduction in Alzheimer’s disease risk (OR, 0.62; P < .04) was among those vaccinated against pneumonia who were noncarriers of the rs2075650 G allele.
Total number of vaccinations against pneumonia and influenza between ages 65 and 75 was also associated with a lower risk for Alzheimer’s disease (OR, 0.88; P < .01). However, the effect was not evident for the influenza vaccination alone.
“The fact that very different pathogens – viral, bacterial, fungal – have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease indicates a possibility that compromised host immunity may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease through increasing overall brain’s vulnerability to various microbes,” said Dr. Ukraintseva.
The current findings support further investigation of pneumococcal vaccine as a “reasonable candidate for repurposing in personalized AD prevention,” she noted. “These results also support the important role of boosting overall immune robustness/resilience in preventing Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Ukraintseva added.
Her group is currently working on confirming the findings in another population.
Brain protective?
“Neither study can prove that the benefit is directly related to the vaccine itself, but what they can indicate is that potentially, vaccines are a way to protect your health and brain,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
In a statement, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that more research is needed.
The new data call “for further studies in large, diverse clinical trials to inform whether vaccinations as a public health strategy decrease our risk for developing dementia as we age,” Dr. Carillo said.
Funding for the influenza vaccine study was provided by the Christopher Sarofim Family Professorship in Biomedical Informatics and Bioengineering, a UT STARs Award, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and the National Institutes of Health. Funding for the pneumonia study was provided by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Amran, Dr. Ukraintseva, Dr. Edelmayer, and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort study of more than 9,000 older adults, receiving a single influenza vaccination was associated with a 17% lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease compared with not receiving the vaccine. In addition, for those who were vaccinated more than once over the years, there was an additional 13% reduction in Alzheimer’s disease incidence.
In another study, which included more than 5,000 older participants, being vaccinated against pneumonia between the ages of 65 and 75 reduced the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease by 30%.
The subject of vaccines “is obviously very topical with the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association. “While these are very preliminary data, these studies do suggest that with vaccination against both respiratory illnesses, there is the potential to lower risk for developing cognitive decline and dementia,” said Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved in the research.
The findings of both studies were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Lower Alzheimer’s disease prevalence
The influenza vaccine study was presented by Albert Amran, a fourth-year medical student at McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. The researchers used electronic health record data to create a propensity-matched cohort of 9,066 vaccinated and unvaccinated adults ages 60 and older.
Influenza vaccination, increased frequency of administration, and younger age at time of vaccination were all associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease, Mr. Amran reported.
Being vaccinated for influenza was significantly linked to a lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (odds ratio [OR], 0.83; P < .0001) in comparison with not being vaccinated. Receiving more than one vaccination over the years was associated with an additional reduction in AD incidence (OR, 0.87; P = .0342). The protection appeared to be strongest for those who received their first vaccination at a younger age, for example, at age 60 versus 70.
Mr. Amran and research colleagues have two theories as to why influenza vaccination may protect the brain.
One is that vaccination may aid the immune system as people age. “As people get older, their immune systems become less able to control infection. We’ve seen this with the ongoing pandemic, with older people at much higher risk for dying. Giving people the vaccine once a year may help keep the immune system in shape,” Mr. Amran said.
Another theory is that the prevention of influenza itself may be relevant. “Flu infections can be extremely deadly in older patients. Maybe the results of our study will give another reason for people to get vaccinated,” Mr. Amran said.
Pneumonia vaccine
The other study was presented by Svetlana Ukraintseva, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Ukraintseva and colleagues investigated associations between pneumococcal vaccine, with and without an accompanying influenza vaccine, and the risk for Alzheimer’s disease among 5,146 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Covariates included sex, race, birth cohort, education, smoking, and a known genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: the rs2075650 G allele in the TOMM40 gene.
In a logistic model with all covariates, vaccination against pneumonia between ages 65 and 75 was significantly associated with reduced risk of developing AD (OR, 0.70; P < .04). The largest reduction in Alzheimer’s disease risk (OR, 0.62; P < .04) was among those vaccinated against pneumonia who were noncarriers of the rs2075650 G allele.
Total number of vaccinations against pneumonia and influenza between ages 65 and 75 was also associated with a lower risk for Alzheimer’s disease (OR, 0.88; P < .01). However, the effect was not evident for the influenza vaccination alone.
“The fact that very different pathogens – viral, bacterial, fungal – have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease indicates a possibility that compromised host immunity may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease through increasing overall brain’s vulnerability to various microbes,” said Dr. Ukraintseva.
The current findings support further investigation of pneumococcal vaccine as a “reasonable candidate for repurposing in personalized AD prevention,” she noted. “These results also support the important role of boosting overall immune robustness/resilience in preventing Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Ukraintseva added.
Her group is currently working on confirming the findings in another population.
Brain protective?
“Neither study can prove that the benefit is directly related to the vaccine itself, but what they can indicate is that potentially, vaccines are a way to protect your health and brain,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
In a statement, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that more research is needed.
The new data call “for further studies in large, diverse clinical trials to inform whether vaccinations as a public health strategy decrease our risk for developing dementia as we age,” Dr. Carillo said.
Funding for the influenza vaccine study was provided by the Christopher Sarofim Family Professorship in Biomedical Informatics and Bioengineering, a UT STARs Award, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and the National Institutes of Health. Funding for the pneumonia study was provided by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Amran, Dr. Ukraintseva, Dr. Edelmayer, and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort study of more than 9,000 older adults, receiving a single influenza vaccination was associated with a 17% lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease compared with not receiving the vaccine. In addition, for those who were vaccinated more than once over the years, there was an additional 13% reduction in Alzheimer’s disease incidence.
In another study, which included more than 5,000 older participants, being vaccinated against pneumonia between the ages of 65 and 75 reduced the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease by 30%.
The subject of vaccines “is obviously very topical with the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association. “While these are very preliminary data, these studies do suggest that with vaccination against both respiratory illnesses, there is the potential to lower risk for developing cognitive decline and dementia,” said Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved in the research.
The findings of both studies were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Lower Alzheimer’s disease prevalence
The influenza vaccine study was presented by Albert Amran, a fourth-year medical student at McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. The researchers used electronic health record data to create a propensity-matched cohort of 9,066 vaccinated and unvaccinated adults ages 60 and older.
Influenza vaccination, increased frequency of administration, and younger age at time of vaccination were all associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease, Mr. Amran reported.
Being vaccinated for influenza was significantly linked to a lower prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (odds ratio [OR], 0.83; P < .0001) in comparison with not being vaccinated. Receiving more than one vaccination over the years was associated with an additional reduction in AD incidence (OR, 0.87; P = .0342). The protection appeared to be strongest for those who received their first vaccination at a younger age, for example, at age 60 versus 70.
Mr. Amran and research colleagues have two theories as to why influenza vaccination may protect the brain.
One is that vaccination may aid the immune system as people age. “As people get older, their immune systems become less able to control infection. We’ve seen this with the ongoing pandemic, with older people at much higher risk for dying. Giving people the vaccine once a year may help keep the immune system in shape,” Mr. Amran said.
Another theory is that the prevention of influenza itself may be relevant. “Flu infections can be extremely deadly in older patients. Maybe the results of our study will give another reason for people to get vaccinated,” Mr. Amran said.
Pneumonia vaccine
The other study was presented by Svetlana Ukraintseva, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Ukraintseva and colleagues investigated associations between pneumococcal vaccine, with and without an accompanying influenza vaccine, and the risk for Alzheimer’s disease among 5,146 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Covariates included sex, race, birth cohort, education, smoking, and a known genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: the rs2075650 G allele in the TOMM40 gene.
In a logistic model with all covariates, vaccination against pneumonia between ages 65 and 75 was significantly associated with reduced risk of developing AD (OR, 0.70; P < .04). The largest reduction in Alzheimer’s disease risk (OR, 0.62; P < .04) was among those vaccinated against pneumonia who were noncarriers of the rs2075650 G allele.
Total number of vaccinations against pneumonia and influenza between ages 65 and 75 was also associated with a lower risk for Alzheimer’s disease (OR, 0.88; P < .01). However, the effect was not evident for the influenza vaccination alone.
“The fact that very different pathogens – viral, bacterial, fungal – have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease indicates a possibility that compromised host immunity may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease through increasing overall brain’s vulnerability to various microbes,” said Dr. Ukraintseva.
The current findings support further investigation of pneumococcal vaccine as a “reasonable candidate for repurposing in personalized AD prevention,” she noted. “These results also support the important role of boosting overall immune robustness/resilience in preventing Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Ukraintseva added.
Her group is currently working on confirming the findings in another population.
Brain protective?
“Neither study can prove that the benefit is directly related to the vaccine itself, but what they can indicate is that potentially, vaccines are a way to protect your health and brain,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
In a statement, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that more research is needed.
The new data call “for further studies in large, diverse clinical trials to inform whether vaccinations as a public health strategy decrease our risk for developing dementia as we age,” Dr. Carillo said.
Funding for the influenza vaccine study was provided by the Christopher Sarofim Family Professorship in Biomedical Informatics and Bioengineering, a UT STARs Award, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and the National Institutes of Health. Funding for the pneumonia study was provided by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Amran, Dr. Ukraintseva, Dr. Edelmayer, and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2020
Pandemic-related stress causing health issues in many Americans
Over the last 2 months, more than half of Americans have experienced some sort of adverse effect caused by stress related to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF).
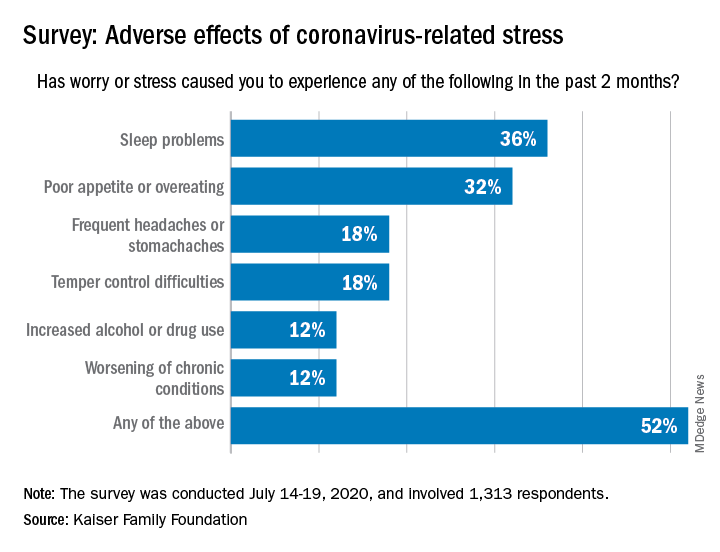
More than a third (36%) of the 1,313 respondents said they either had difficulty sleeping, falling asleep, or sleeping too much, KFF said in its latest Health Tracking Poll, conducted July 14-19, 2020. That was followed by poor appetite or overeating, which was mentioned by 32% of those surveyed.
Other adverse effects included frequent headaches or stomachaches (18%), temper-control issues (18%), increased drug or alcohol use (12%), and worsening of chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension (12%). Altogether, 52% of Americans have had at least one of these issues in the past 2 months, Liz Hamel and associates at KFF reported.
breaking down to 26% reporting a major impact and 28% reporting a minor impact (figures have been rounded), they said.
“As life with the coronavirus pandemic wears on, Americans increasingly say it is taking a negative toll on their mental health,” the investigators wrote. Earlier polls showed that pandemic-related stress was having an impact on mental health for 39% of respondents in May, compared with 45% in early April and 32% in March.
In the July poll, Black adults were much more likely to report a negative mental health impact (68%) than were Hispanics or Whites, who were both at 51%. Age was also a factor: The youngest group of respondents (ages 18-29 years) had the highest negative-impact rate (62%), and the oldest group (65 years and older) had the lowest (47%), they said.
When it came to reporting the adverse effects of stress or worry, however, the situation was somewhat different. Hispanics had the highest rate of such effects at 63%, while Blacks had a rate of 57% and 47% of Whites reported issues with sleep, eating, temper, and other problems, Ms. Hamel and associates reported.
Over the last 2 months, more than half of Americans have experienced some sort of adverse effect caused by stress related to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF).

More than a third (36%) of the 1,313 respondents said they either had difficulty sleeping, falling asleep, or sleeping too much, KFF said in its latest Health Tracking Poll, conducted July 14-19, 2020. That was followed by poor appetite or overeating, which was mentioned by 32% of those surveyed.
Other adverse effects included frequent headaches or stomachaches (18%), temper-control issues (18%), increased drug or alcohol use (12%), and worsening of chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension (12%). Altogether, 52% of Americans have had at least one of these issues in the past 2 months, Liz Hamel and associates at KFF reported.
breaking down to 26% reporting a major impact and 28% reporting a minor impact (figures have been rounded), they said.
“As life with the coronavirus pandemic wears on, Americans increasingly say it is taking a negative toll on their mental health,” the investigators wrote. Earlier polls showed that pandemic-related stress was having an impact on mental health for 39% of respondents in May, compared with 45% in early April and 32% in March.
In the July poll, Black adults were much more likely to report a negative mental health impact (68%) than were Hispanics or Whites, who were both at 51%. Age was also a factor: The youngest group of respondents (ages 18-29 years) had the highest negative-impact rate (62%), and the oldest group (65 years and older) had the lowest (47%), they said.
When it came to reporting the adverse effects of stress or worry, however, the situation was somewhat different. Hispanics had the highest rate of such effects at 63%, while Blacks had a rate of 57% and 47% of Whites reported issues with sleep, eating, temper, and other problems, Ms. Hamel and associates reported.
Over the last 2 months, more than half of Americans have experienced some sort of adverse effect caused by stress related to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF).

More than a third (36%) of the 1,313 respondents said they either had difficulty sleeping, falling asleep, or sleeping too much, KFF said in its latest Health Tracking Poll, conducted July 14-19, 2020. That was followed by poor appetite or overeating, which was mentioned by 32% of those surveyed.
Other adverse effects included frequent headaches or stomachaches (18%), temper-control issues (18%), increased drug or alcohol use (12%), and worsening of chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension (12%). Altogether, 52% of Americans have had at least one of these issues in the past 2 months, Liz Hamel and associates at KFF reported.
breaking down to 26% reporting a major impact and 28% reporting a minor impact (figures have been rounded), they said.
“As life with the coronavirus pandemic wears on, Americans increasingly say it is taking a negative toll on their mental health,” the investigators wrote. Earlier polls showed that pandemic-related stress was having an impact on mental health for 39% of respondents in May, compared with 45% in early April and 32% in March.
In the July poll, Black adults were much more likely to report a negative mental health impact (68%) than were Hispanics or Whites, who were both at 51%. Age was also a factor: The youngest group of respondents (ages 18-29 years) had the highest negative-impact rate (62%), and the oldest group (65 years and older) had the lowest (47%), they said.
When it came to reporting the adverse effects of stress or worry, however, the situation was somewhat different. Hispanics had the highest rate of such effects at 63%, while Blacks had a rate of 57% and 47% of Whites reported issues with sleep, eating, temper, and other problems, Ms. Hamel and associates reported.
MIS-C is a serious immune-mediated response to COVID-19 infection
One of the take-away messages from a review of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is that clinicians treating this condition “need to be comfortable with uncertainty,” Melissa Hazen, MD, said at a synthesis of multiple published case series and personal experience summarized at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting.
She emphasized MIS-C patient care “requires flexibility,” and she advised clinicians managing these patients to open the lines of communication with the many specialists who often are required to deal with complications affecting an array of organ systems.
MIS-C might best be understood as the most serious manifestation of an immune-mediated response to COVID-19 infection that ranges from transient mild symptoms to the life-threatening multiple organ involvement that characterizes this newly recognized threat. Although “most children who encounter this pathogen only develop mild disease,” the spectrum of the disease can move in a subset of patients to a “Kawasaki-like illness” without hemodynamic instability and then to MIS-C “with highly elevated systemic inflammatory markers and multiple organ involvement,” explained Dr. Hazen, an attending physician in the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital.
most of which have only recently reached publication, according to Dr. Hazen. In general, the description of the most common symptoms and their course has been relatively consistent.
In 186 cases of MIS-C collected in a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 148 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 90 patients (48%) received vasoactive support, 37 (20%) received mechanical ventilation, and 4 (2%) died.1 The median age was 8 years (range, 3-13 years) in this study. The case definition was fever for at least 24 hours, laboratory evidence of inflammation, multisystem organ involvement, and evidence of COVID-19 infection. In this cohort of 186 children, 92% had gastrointestinal, 80% had cardiovascular, 76% had hematologic, and 70% had respiratory system involvement.
In a different series of 95 cases collected in New York State, 79 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 61 (62%) received vasoactive support, 10 (10%) received mechanical ventilation, 4 (4%) received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and 2 (2%) died. 2 Thirty-one percent patients were aged 0-5 years, 42% were 6-12 years, and 26% were 13-20 years of age. In that series, for which the case definition was elevation of two or more inflammatory markers, virologic evidence of COVID-19 infection, 80% had gastrointestinal system involvement, and 53% had evidence of myocarditis.
In both of these series, as well as others published and unpublished, the peak in MIS-C cases has occurred about 3 to 4 weeks after peak COVID-19 activity, according to Diana Lee, MD, a pediatrician at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This pattern, reported by others, was observed in New York State, where 230 cases of MIS-C were collected from the beginning of May until the end of June, which reflected this 3- to 4-week delay in peak incidence.
“This does seem to be a rare syndrome since this [group of] 230 cases is amongst the entire population of children in New York State. So, yes, we should be keeping this in mind in our differential, but we should not forget all the other reasons that children can have a fever,” she said.
Both Dr. Hazen and Dr. Lee cautioned that MIS-C, despite a general consistency among published studies, remains a moving target in regard to how it is being characterized. In a 2-day period in May, the CDC, the World Health Organization, and New York State all issued descriptions of MIS-C, employing compatible but slightly different terminology and diagnostic criteria. Many questions regarding optimal methods of diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up remain unanswered.
Questions regarding the risk to the cardiovascular system, one of the organs most commonly affected in MIS-C, are among the most urgent. It is not now clear how best to monitor cardiovascular involvement, how to intervene, and how to follow patients in the postinfection period, according to Kevin G. Friedman, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and an attending physician in the department of cardiology at Boston Children’s Hospital.
“The most frequent complication we have seen is ventricular dysfunction, which occurs in about half of these patients,” he reported. “Usually it is in the mild to moderate range, but occasionally patients have an ejection fraction of less than 40%.”
Coronary abnormalities, typically in the form of dilations or small aneurysms, occur in 10%-20% of children with MIS-C, according to Dr. Friedman. Giant aneurysms have been reported.
“Some of these findings can progress including in both the acute phase and, particularly for the coronary aneurysms, in the subacute phase. We recommend echocardiograms and EKGs at diagnosis and at 1-2 weeks to recheck coronary size or sooner if there are clinical indications,” Dr. Friedman advised.
Protocols like these are constantly under review as more information becomes available. There are as yet no guidelines, and practice differs across institutions, according to the investigators summarizing this information.
None of the speakers had any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Feldstein LR et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-46.
2. Dufort EM et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State. N Engl J Med 2020;383:347-58.
One of the take-away messages from a review of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is that clinicians treating this condition “need to be comfortable with uncertainty,” Melissa Hazen, MD, said at a synthesis of multiple published case series and personal experience summarized at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting.
She emphasized MIS-C patient care “requires flexibility,” and she advised clinicians managing these patients to open the lines of communication with the many specialists who often are required to deal with complications affecting an array of organ systems.
MIS-C might best be understood as the most serious manifestation of an immune-mediated response to COVID-19 infection that ranges from transient mild symptoms to the life-threatening multiple organ involvement that characterizes this newly recognized threat. Although “most children who encounter this pathogen only develop mild disease,” the spectrum of the disease can move in a subset of patients to a “Kawasaki-like illness” without hemodynamic instability and then to MIS-C “with highly elevated systemic inflammatory markers and multiple organ involvement,” explained Dr. Hazen, an attending physician in the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital.
most of which have only recently reached publication, according to Dr. Hazen. In general, the description of the most common symptoms and their course has been relatively consistent.
In 186 cases of MIS-C collected in a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 148 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 90 patients (48%) received vasoactive support, 37 (20%) received mechanical ventilation, and 4 (2%) died.1 The median age was 8 years (range, 3-13 years) in this study. The case definition was fever for at least 24 hours, laboratory evidence of inflammation, multisystem organ involvement, and evidence of COVID-19 infection. In this cohort of 186 children, 92% had gastrointestinal, 80% had cardiovascular, 76% had hematologic, and 70% had respiratory system involvement.
In a different series of 95 cases collected in New York State, 79 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 61 (62%) received vasoactive support, 10 (10%) received mechanical ventilation, 4 (4%) received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and 2 (2%) died. 2 Thirty-one percent patients were aged 0-5 years, 42% were 6-12 years, and 26% were 13-20 years of age. In that series, for which the case definition was elevation of two or more inflammatory markers, virologic evidence of COVID-19 infection, 80% had gastrointestinal system involvement, and 53% had evidence of myocarditis.
In both of these series, as well as others published and unpublished, the peak in MIS-C cases has occurred about 3 to 4 weeks after peak COVID-19 activity, according to Diana Lee, MD, a pediatrician at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This pattern, reported by others, was observed in New York State, where 230 cases of MIS-C were collected from the beginning of May until the end of June, which reflected this 3- to 4-week delay in peak incidence.
“This does seem to be a rare syndrome since this [group of] 230 cases is amongst the entire population of children in New York State. So, yes, we should be keeping this in mind in our differential, but we should not forget all the other reasons that children can have a fever,” she said.
Both Dr. Hazen and Dr. Lee cautioned that MIS-C, despite a general consistency among published studies, remains a moving target in regard to how it is being characterized. In a 2-day period in May, the CDC, the World Health Organization, and New York State all issued descriptions of MIS-C, employing compatible but slightly different terminology and diagnostic criteria. Many questions regarding optimal methods of diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up remain unanswered.
Questions regarding the risk to the cardiovascular system, one of the organs most commonly affected in MIS-C, are among the most urgent. It is not now clear how best to monitor cardiovascular involvement, how to intervene, and how to follow patients in the postinfection period, according to Kevin G. Friedman, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and an attending physician in the department of cardiology at Boston Children’s Hospital.
“The most frequent complication we have seen is ventricular dysfunction, which occurs in about half of these patients,” he reported. “Usually it is in the mild to moderate range, but occasionally patients have an ejection fraction of less than 40%.”
Coronary abnormalities, typically in the form of dilations or small aneurysms, occur in 10%-20% of children with MIS-C, according to Dr. Friedman. Giant aneurysms have been reported.
“Some of these findings can progress including in both the acute phase and, particularly for the coronary aneurysms, in the subacute phase. We recommend echocardiograms and EKGs at diagnosis and at 1-2 weeks to recheck coronary size or sooner if there are clinical indications,” Dr. Friedman advised.
Protocols like these are constantly under review as more information becomes available. There are as yet no guidelines, and practice differs across institutions, according to the investigators summarizing this information.
None of the speakers had any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Feldstein LR et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-46.
2. Dufort EM et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State. N Engl J Med 2020;383:347-58.
One of the take-away messages from a review of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is that clinicians treating this condition “need to be comfortable with uncertainty,” Melissa Hazen, MD, said at a synthesis of multiple published case series and personal experience summarized at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting.
She emphasized MIS-C patient care “requires flexibility,” and she advised clinicians managing these patients to open the lines of communication with the many specialists who often are required to deal with complications affecting an array of organ systems.
MIS-C might best be understood as the most serious manifestation of an immune-mediated response to COVID-19 infection that ranges from transient mild symptoms to the life-threatening multiple organ involvement that characterizes this newly recognized threat. Although “most children who encounter this pathogen only develop mild disease,” the spectrum of the disease can move in a subset of patients to a “Kawasaki-like illness” without hemodynamic instability and then to MIS-C “with highly elevated systemic inflammatory markers and multiple organ involvement,” explained Dr. Hazen, an attending physician in the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital.
most of which have only recently reached publication, according to Dr. Hazen. In general, the description of the most common symptoms and their course has been relatively consistent.
In 186 cases of MIS-C collected in a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 148 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 90 patients (48%) received vasoactive support, 37 (20%) received mechanical ventilation, and 4 (2%) died.1 The median age was 8 years (range, 3-13 years) in this study. The case definition was fever for at least 24 hours, laboratory evidence of inflammation, multisystem organ involvement, and evidence of COVID-19 infection. In this cohort of 186 children, 92% had gastrointestinal, 80% had cardiovascular, 76% had hematologic, and 70% had respiratory system involvement.
In a different series of 95 cases collected in New York State, 79 (80%) were admitted to intensive care, 61 (62%) received vasoactive support, 10 (10%) received mechanical ventilation, 4 (4%) received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and 2 (2%) died. 2 Thirty-one percent patients were aged 0-5 years, 42% were 6-12 years, and 26% were 13-20 years of age. In that series, for which the case definition was elevation of two or more inflammatory markers, virologic evidence of COVID-19 infection, 80% had gastrointestinal system involvement, and 53% had evidence of myocarditis.
In both of these series, as well as others published and unpublished, the peak in MIS-C cases has occurred about 3 to 4 weeks after peak COVID-19 activity, according to Diana Lee, MD, a pediatrician at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This pattern, reported by others, was observed in New York State, where 230 cases of MIS-C were collected from the beginning of May until the end of June, which reflected this 3- to 4-week delay in peak incidence.
“This does seem to be a rare syndrome since this [group of] 230 cases is amongst the entire population of children in New York State. So, yes, we should be keeping this in mind in our differential, but we should not forget all the other reasons that children can have a fever,” she said.
Both Dr. Hazen and Dr. Lee cautioned that MIS-C, despite a general consistency among published studies, remains a moving target in regard to how it is being characterized. In a 2-day period in May, the CDC, the World Health Organization, and New York State all issued descriptions of MIS-C, employing compatible but slightly different terminology and diagnostic criteria. Many questions regarding optimal methods of diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up remain unanswered.
Questions regarding the risk to the cardiovascular system, one of the organs most commonly affected in MIS-C, are among the most urgent. It is not now clear how best to monitor cardiovascular involvement, how to intervene, and how to follow patients in the postinfection period, according to Kevin G. Friedman, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and an attending physician in the department of cardiology at Boston Children’s Hospital.
“The most frequent complication we have seen is ventricular dysfunction, which occurs in about half of these patients,” he reported. “Usually it is in the mild to moderate range, but occasionally patients have an ejection fraction of less than 40%.”
Coronary abnormalities, typically in the form of dilations or small aneurysms, occur in 10%-20% of children with MIS-C, according to Dr. Friedman. Giant aneurysms have been reported.
“Some of these findings can progress including in both the acute phase and, particularly for the coronary aneurysms, in the subacute phase. We recommend echocardiograms and EKGs at diagnosis and at 1-2 weeks to recheck coronary size or sooner if there are clinical indications,” Dr. Friedman advised.
Protocols like these are constantly under review as more information becomes available. There are as yet no guidelines, and practice differs across institutions, according to the investigators summarizing this information.
None of the speakers had any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Feldstein LR et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-46.
2. Dufort EM et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State. N Engl J Med 2020;383:347-58.
FROM PHM20 VIRTUAL
Physician recruitment drops by 30% because of pandemic
the firm reported.
“Rather than having many practice opportunities to choose from, physicians now may have to compete to secure practice opportunities that meet their needs,” the authors wrote in Merritt Hawkins’ report on the impact of COVID-19.
Most of the report concerns physician recruitment from April 1, 2019, to March 31, 2020. The data were mostly derived from searches that Merritt Hawkins conducted before the effects of the pandemic was fully felt.
Family medicine was again the most sought-after specialty, as it has been for the past 14 years. But demand for primary care doctors – including family physicians, internists, and pediatricians – leveled off, and average starting salaries for primary care doctors dropped during 2019-2020. In contrast, the number of searches conducted for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) increased by 54%, and their salaries increased slightly.
To explain the lackluster prospects for primary care before the pandemic, the authors cited research showing that patients were turning away from the traditional office visit model. At the same time, there was a rise in visits to NPs and PAs, including those in urgent care centers and retail clinics.
As a result of decreased demand for primary care physicians and the rising prevalence of telehealth, Merritt Hawkins expects primary care salaries to drop overall. With telehealth generating a larger portion of revenues, “it is uncertain whether primary care physicians will be able to sustain levels of reimbursement that were prevalent pre-COVID even at such time as the economy is improved and utilization increases,” the authors reported.
Demand for specialists was increasing prior to the COVID-19 crisis, partly as a result of the aging of the population. Seventy-eight percent of all searches were for medical specialists, compared with 67% 5 years ago. However, the pandemic has set back specialist searches. “Demand and compensation for specialists also will change as a result of COVID-19 in response to declines in the volume of medical procedures,” according to the authors.
In contrast, the recruitment of doctors who are on the front line of COVID-19 care is expected to increase. Among the fields anticipated to be in demand are emergency department specialists, infectious disease specialists, and pulmonology/critical care physicians. Travis Singleton, executive vice president of Merritt Hawkins, said in an interview that this trend is already happening and will accelerate as COVID-19 hot spots arise across the country.
Specialists in different fields received either higher or lower offers than during the previous year. Starting salaries for noninvasive cardiologists, for example, dropped 7.3%; gastroenterologists earned 7.7% less; and neurologists, 6.9% less. In contrast, orthopedic surgeons saw offers surge 16.7%; radiologists, 9.3%; and pulmonologists/critical care specialists, 7.7%.
Physicians were offered salaries plus bonuses in three-quarters of searches. Relative value unit–based production remained the most common basis for bonuses. Quality/value-based metrics were used in computing 64% of bonuses – up from 56% the previous year – but still determined only 11% of total physician compensation.
Pandemic outlook
Whereas health care helped drive the U.S. economy in 2018-2019, the pace of job growth in health care has decreased since March. As a result of the pandemic, health care spending in the United States declined by 18% in the first quarter of 2020. Physician practice revenue dropped by 55% during the first quarter, and many small and solo practices are still struggling.
In a 2018 Merritt Hawkins survey, 18% of physicians said they had used telehealth to treat patients. Because of the pandemic, that percentage jumped to 48% in April 2020. But telehealth hasn’t made up for the loss of patient revenue from in-office procedures, tests, and other services, and it still isn’t being reimbursed at the same level as in-office visits.
With practices under severe financial strain, the authors explained, “A majority of private practices have curtailed most physician recruiting activity since the virus emerged.”
In some states, many specialty practices have been adversely affected by the suspension of elective procedures, and specialty practices that rely on nonessential procedures are unlikely to recruit additional physicians.
One-third of practices could close
The survival of many private practices is now in question. “Based on the losses physician practices have sustained as a result of COVID-19, some markets could lose up to 35% or more of their most vulnerable group practices while a large percent of others will be acquired,” the authors wrote.
Hospitals and health systems will acquire the bulk of these practices, in many cases at fire-sale prices, Mr. Singleton predicted. This enormous shift from private practice to employment, he added, “will have as much to do with the [physician] income levels we’re going to see as the demand for the specialties themselves.”
Right now, he said, Merritt Hawkins is fielding a huge number of requests from doctors seeking employment, but there aren’t many jobs out there. “We haven’t seen an employer-friendly market like this since the 1970s,” he noted. “Before the pandemic, a physician might have had five to 10 jobs to choose from. Now it’s the opposite: We have one job, and 5 to 10 physicians are applying for it.”
Singleton believes the market will adjust by the second quarter of next year. Even if the pandemic worsens, he said, the system will have made the necessary corrections and adjustments “because we have to start seeing patients again, both in terms of demand and economics. So these doctors will be in demand again and will have work.”
Contingent employment
Although the COVID-related falloff in revenue has hit private practices the hardest, some employed physicians have also found themselves in a bind. According to a Merritt Hawkins/Physicians Foundation survey conducted in April, 21% of physicians said they had been furloughed or had taken a pay cut.
Mr. Singleton views this trend as part of hospitals’ reassessment of how they’re going to deal with labor going forward. To cope with utilization ebbs and flows in response to the virus, hospitals are now considering what the report calls a “contingent labor/flex staffing model.”
Under this type of arrangement, which some hospitals have already adopted, physicians may no longer work full time in a single setting, Mr. Singleton said. They may be asked to conduct telehealth visits on nights and weekends and work 20 hours a week in the clinic, or they may have shifts in multiple hospitals or clinics.
“You can make as much or more on a temporary basis as on a permanent basis,” he said. “But you have to be more flexible. You may have to travel or do a different scope of work, or work in different settings.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
the firm reported.
“Rather than having many practice opportunities to choose from, physicians now may have to compete to secure practice opportunities that meet their needs,” the authors wrote in Merritt Hawkins’ report on the impact of COVID-19.
Most of the report concerns physician recruitment from April 1, 2019, to March 31, 2020. The data were mostly derived from searches that Merritt Hawkins conducted before the effects of the pandemic was fully felt.
Family medicine was again the most sought-after specialty, as it has been for the past 14 years. But demand for primary care doctors – including family physicians, internists, and pediatricians – leveled off, and average starting salaries for primary care doctors dropped during 2019-2020. In contrast, the number of searches conducted for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) increased by 54%, and their salaries increased slightly.
To explain the lackluster prospects for primary care before the pandemic, the authors cited research showing that patients were turning away from the traditional office visit model. At the same time, there was a rise in visits to NPs and PAs, including those in urgent care centers and retail clinics.
As a result of decreased demand for primary care physicians and the rising prevalence of telehealth, Merritt Hawkins expects primary care salaries to drop overall. With telehealth generating a larger portion of revenues, “it is uncertain whether primary care physicians will be able to sustain levels of reimbursement that were prevalent pre-COVID even at such time as the economy is improved and utilization increases,” the authors reported.
Demand for specialists was increasing prior to the COVID-19 crisis, partly as a result of the aging of the population. Seventy-eight percent of all searches were for medical specialists, compared with 67% 5 years ago. However, the pandemic has set back specialist searches. “Demand and compensation for specialists also will change as a result of COVID-19 in response to declines in the volume of medical procedures,” according to the authors.
In contrast, the recruitment of doctors who are on the front line of COVID-19 care is expected to increase. Among the fields anticipated to be in demand are emergency department specialists, infectious disease specialists, and pulmonology/critical care physicians. Travis Singleton, executive vice president of Merritt Hawkins, said in an interview that this trend is already happening and will accelerate as COVID-19 hot spots arise across the country.
Specialists in different fields received either higher or lower offers than during the previous year. Starting salaries for noninvasive cardiologists, for example, dropped 7.3%; gastroenterologists earned 7.7% less; and neurologists, 6.9% less. In contrast, orthopedic surgeons saw offers surge 16.7%; radiologists, 9.3%; and pulmonologists/critical care specialists, 7.7%.
Physicians were offered salaries plus bonuses in three-quarters of searches. Relative value unit–based production remained the most common basis for bonuses. Quality/value-based metrics were used in computing 64% of bonuses – up from 56% the previous year – but still determined only 11% of total physician compensation.
Pandemic outlook
Whereas health care helped drive the U.S. economy in 2018-2019, the pace of job growth in health care has decreased since March. As a result of the pandemic, health care spending in the United States declined by 18% in the first quarter of 2020. Physician practice revenue dropped by 55% during the first quarter, and many small and solo practices are still struggling.
In a 2018 Merritt Hawkins survey, 18% of physicians said they had used telehealth to treat patients. Because of the pandemic, that percentage jumped to 48% in April 2020. But telehealth hasn’t made up for the loss of patient revenue from in-office procedures, tests, and other services, and it still isn’t being reimbursed at the same level as in-office visits.
With practices under severe financial strain, the authors explained, “A majority of private practices have curtailed most physician recruiting activity since the virus emerged.”
In some states, many specialty practices have been adversely affected by the suspension of elective procedures, and specialty practices that rely on nonessential procedures are unlikely to recruit additional physicians.
One-third of practices could close
The survival of many private practices is now in question. “Based on the losses physician practices have sustained as a result of COVID-19, some markets could lose up to 35% or more of their most vulnerable group practices while a large percent of others will be acquired,” the authors wrote.
Hospitals and health systems will acquire the bulk of these practices, in many cases at fire-sale prices, Mr. Singleton predicted. This enormous shift from private practice to employment, he added, “will have as much to do with the [physician] income levels we’re going to see as the demand for the specialties themselves.”
Right now, he said, Merritt Hawkins is fielding a huge number of requests from doctors seeking employment, but there aren’t many jobs out there. “We haven’t seen an employer-friendly market like this since the 1970s,” he noted. “Before the pandemic, a physician might have had five to 10 jobs to choose from. Now it’s the opposite: We have one job, and 5 to 10 physicians are applying for it.”
Singleton believes the market will adjust by the second quarter of next year. Even if the pandemic worsens, he said, the system will have made the necessary corrections and adjustments “because we have to start seeing patients again, both in terms of demand and economics. So these doctors will be in demand again and will have work.”
Contingent employment
Although the COVID-related falloff in revenue has hit private practices the hardest, some employed physicians have also found themselves in a bind. According to a Merritt Hawkins/Physicians Foundation survey conducted in April, 21% of physicians said they had been furloughed or had taken a pay cut.
Mr. Singleton views this trend as part of hospitals’ reassessment of how they’re going to deal with labor going forward. To cope with utilization ebbs and flows in response to the virus, hospitals are now considering what the report calls a “contingent labor/flex staffing model.”
Under this type of arrangement, which some hospitals have already adopted, physicians may no longer work full time in a single setting, Mr. Singleton said. They may be asked to conduct telehealth visits on nights and weekends and work 20 hours a week in the clinic, or they may have shifts in multiple hospitals or clinics.
“You can make as much or more on a temporary basis as on a permanent basis,” he said. “But you have to be more flexible. You may have to travel or do a different scope of work, or work in different settings.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
the firm reported.
“Rather than having many practice opportunities to choose from, physicians now may have to compete to secure practice opportunities that meet their needs,” the authors wrote in Merritt Hawkins’ report on the impact of COVID-19.
Most of the report concerns physician recruitment from April 1, 2019, to March 31, 2020. The data were mostly derived from searches that Merritt Hawkins conducted before the effects of the pandemic was fully felt.
Family medicine was again the most sought-after specialty, as it has been for the past 14 years. But demand for primary care doctors – including family physicians, internists, and pediatricians – leveled off, and average starting salaries for primary care doctors dropped during 2019-2020. In contrast, the number of searches conducted for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) increased by 54%, and their salaries increased slightly.
To explain the lackluster prospects for primary care before the pandemic, the authors cited research showing that patients were turning away from the traditional office visit model. At the same time, there was a rise in visits to NPs and PAs, including those in urgent care centers and retail clinics.
As a result of decreased demand for primary care physicians and the rising prevalence of telehealth, Merritt Hawkins expects primary care salaries to drop overall. With telehealth generating a larger portion of revenues, “it is uncertain whether primary care physicians will be able to sustain levels of reimbursement that were prevalent pre-COVID even at such time as the economy is improved and utilization increases,” the authors reported.
Demand for specialists was increasing prior to the COVID-19 crisis, partly as a result of the aging of the population. Seventy-eight percent of all searches were for medical specialists, compared with 67% 5 years ago. However, the pandemic has set back specialist searches. “Demand and compensation for specialists also will change as a result of COVID-19 in response to declines in the volume of medical procedures,” according to the authors.
In contrast, the recruitment of doctors who are on the front line of COVID-19 care is expected to increase. Among the fields anticipated to be in demand are emergency department specialists, infectious disease specialists, and pulmonology/critical care physicians. Travis Singleton, executive vice president of Merritt Hawkins, said in an interview that this trend is already happening and will accelerate as COVID-19 hot spots arise across the country.
Specialists in different fields received either higher or lower offers than during the previous year. Starting salaries for noninvasive cardiologists, for example, dropped 7.3%; gastroenterologists earned 7.7% less; and neurologists, 6.9% less. In contrast, orthopedic surgeons saw offers surge 16.7%; radiologists, 9.3%; and pulmonologists/critical care specialists, 7.7%.
Physicians were offered salaries plus bonuses in three-quarters of searches. Relative value unit–based production remained the most common basis for bonuses. Quality/value-based metrics were used in computing 64% of bonuses – up from 56% the previous year – but still determined only 11% of total physician compensation.
Pandemic outlook
Whereas health care helped drive the U.S. economy in 2018-2019, the pace of job growth in health care has decreased since March. As a result of the pandemic, health care spending in the United States declined by 18% in the first quarter of 2020. Physician practice revenue dropped by 55% during the first quarter, and many small and solo practices are still struggling.
In a 2018 Merritt Hawkins survey, 18% of physicians said they had used telehealth to treat patients. Because of the pandemic, that percentage jumped to 48% in April 2020. But telehealth hasn’t made up for the loss of patient revenue from in-office procedures, tests, and other services, and it still isn’t being reimbursed at the same level as in-office visits.
With practices under severe financial strain, the authors explained, “A majority of private practices have curtailed most physician recruiting activity since the virus emerged.”
In some states, many specialty practices have been adversely affected by the suspension of elective procedures, and specialty practices that rely on nonessential procedures are unlikely to recruit additional physicians.
One-third of practices could close
The survival of many private practices is now in question. “Based on the losses physician practices have sustained as a result of COVID-19, some markets could lose up to 35% or more of their most vulnerable group practices while a large percent of others will be acquired,” the authors wrote.
Hospitals and health systems will acquire the bulk of these practices, in many cases at fire-sale prices, Mr. Singleton predicted. This enormous shift from private practice to employment, he added, “will have as much to do with the [physician] income levels we’re going to see as the demand for the specialties themselves.”
Right now, he said, Merritt Hawkins is fielding a huge number of requests from doctors seeking employment, but there aren’t many jobs out there. “We haven’t seen an employer-friendly market like this since the 1970s,” he noted. “Before the pandemic, a physician might have had five to 10 jobs to choose from. Now it’s the opposite: We have one job, and 5 to 10 physicians are applying for it.”
Singleton believes the market will adjust by the second quarter of next year. Even if the pandemic worsens, he said, the system will have made the necessary corrections and adjustments “because we have to start seeing patients again, both in terms of demand and economics. So these doctors will be in demand again and will have work.”
Contingent employment
Although the COVID-related falloff in revenue has hit private practices the hardest, some employed physicians have also found themselves in a bind. According to a Merritt Hawkins/Physicians Foundation survey conducted in April, 21% of physicians said they had been furloughed or had taken a pay cut.
Mr. Singleton views this trend as part of hospitals’ reassessment of how they’re going to deal with labor going forward. To cope with utilization ebbs and flows in response to the virus, hospitals are now considering what the report calls a “contingent labor/flex staffing model.”
Under this type of arrangement, which some hospitals have already adopted, physicians may no longer work full time in a single setting, Mr. Singleton said. They may be asked to conduct telehealth visits on nights and weekends and work 20 hours a week in the clinic, or they may have shifts in multiple hospitals or clinics.
“You can make as much or more on a temporary basis as on a permanent basis,” he said. “But you have to be more flexible. You may have to travel or do a different scope of work, or work in different settings.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
NFL’s only physician player opts out of 2020 season over COVID
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.






