User login
STI update: Testing, treatment, and emerging threats
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
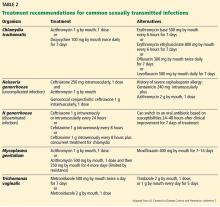
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
KEY POINTS
- Screen for gonorrhea and chlamydia annually—and more frequently for those at highest risk—in sexually active women age 25 and younger and in men who have sex with men, who should also be screened at the same time for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and syphilis.
- Test for Trichomonas vaginalis in women who have symptoms suggesting it, and routinely screen for this pathogen in women who are HIV-positive.
- Nucleic acid amplification is the preferred test for gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection; the use of urine specimens is acceptable.
- Consider M genitalium if therapy for gonorrhea and chlamydia fails or tests for those diseases are negative.
- Single-dose antibiotic therapy is preferred for chlamydia and uncomplicated gonorrhea. It is also available for trichomoniasis, although metronidazole 500 mg twice a day for 7 days has a higher cure rate.
Low-dose steroids for acute exacerbations of COPD in a non-ICU setting: Worth consideration
Despite guidelines recommending low-dose oral glucocorticoids over high-dose intravenous (IV) glucocorticoids for inpatient management of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), we have observed that most patients still receive high-dose IV therapy before being transitioned to low-dose oral therapy at discharge. Clinical inertia undoubtedly plays a significant role in the slow adoption of new recommendations, but in this era of evidence-based practice, the unfortunate lack of data supporting low over high steroid doses for acute exacerbations of COPD also contributes to hesitancy of physicians.
A SIGNIFICANT AND GROWING BURDEN
COPD is one of the most common pulmonary conditions managed by hospitalists today, and by the year 2030, it is predicted to become the third leading cause of death worldwide.1
COPD is also a significant economic burden, costing $50 billion to manage in the United States, most of that from the cost of lengthy hospital stays.2 COPD patients have 1 to 2 exacerbations per year.3 Bacterial and viral infections are responsible for most exacerbations, and 15% to 20% are from air pollution and other environmental causes of airway inflammation.3
CHALLENGES TO CHANGING PRACTICE
Glucocorticoids are the gold standard for treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. It is well-documented that compared with placebo, glucocorticoids reduce mortality risk, length of hospital stay, and exacerbation recurrence after 1 month.4 And while high-dose IV steroid therapy has been the standard approach, oral administration has been found to be noninferior to IV administration with regard to treatment and length of hospital stay.5
While adverse effects are more common at higher doses, the optimal dose and duration of systemic glucocorticoid therapy for acute exacerbations of COPD are still largely at the discretion of the physician. The 2019 report of the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) recommends low doses (40 mg) for no more than 5 to 7 days for exacerbations, based on reports that showed no worse outcomes with low-dose oral than with high-dose IV therapy.6,7 (In the 2010 study by Lindenauer et al,7 92% of nearly 80,000 patients received high-dose IV steroids, reflecting standard practice at that time.) However, the GOLD guidelines do not address mortality rates, length of stay, or readmission rates for either approach, as they are devised to direct treatment in patients with stable mild to advanced COPD, not exacerbations.
THE EVIDENCE FOR LOW-DOSE STEROIDS
Mortality rates
Aksoy et al8 established that, compared with placebo, low-dose steroids improved mortality rates in a subset of patients with acute exacerbations, specifically those with eosinophilic exacerbations. This study followed the 2013 Reduction in the Use of Corticosteroids in Exacerbated COPD (REDUCE) trial, which showed mortality rates were not lower with 14 days of low-dose prednisone treatment than with 5 days.9
Length of hospital stay
With regard to length of hospital stay, in 2011 Wang et al10 found no statistically significant difference between high- and low-dose steroid treatment.However, the REDUCE trial found that low-dose steroids shortened the median length of stay by 1 day compared with placebo.9
Hospital readmission rates
The REDUCE trial found no statistically significant difference in readmission rates when comparing 5 days of low-dose treatment vs 14 days.9 However, Aksoy et al8 found that readmission rates were significantly lower with low-dose treatment than with placebo.No study has yet examined readmission rates with high-dose vs low-dose steroid treatment.
What does the evidence tell us?
Low-dose oral glucocorticoid treatment shows definitive benefits in terms of lower mortality rates, shorter hospital length of stay, and lower readmission rates vs placebo in the treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. Furthermore, a 14-day course is no better than 5 days in terms of mortality rates. And low-dose glucocorticoid treatment shows reduced mortality rates in addition to similar hospital length of stay when compared to high-dose glucocorticoid treatment.
Together, these findings lend credibility to the current GOLD recommendations. However, we have observed that in sharp contrast to the leading clinical guidelines, most patients hospitalized for acute exacerbations of COPD are still treated initially with high-dose IV corticosteroids. Why?
Obstacles that perpetuate the use of high-dose over low-dose treatment include lack of knowledge of glucocorticoid pharmacokinetics among clinicians, use of outdated order sets, and the reflex notion that more of a drug is more efficacious in its desired effect. In addition, administrative obstacles include using high-dose IV steroids to justify an inpatient stay or continued hospitalization.
COUNTERING THE OBSTACLES: THE HOSPITALIST’S ROLE
To counter these obstacles, we propose standardization of inpatient treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD to include initial low-dose steroid treatment in accordance with the most recent GOLD guidelines.6 This would benefit the patient by reducing undesirable effects of high-dose steroids, and at the same time reduce the economic burden of managing COPD exacerbations. Considering the large number of hospitalizations for COPD exacerbation each year, hospitalists can play a large role in this effort by routinely incorporating the low-dose steroid recommendation into their clinical practice.
- World Health Organization. Chronic respiratory diseases: burden of COPD. www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Guarascio AJ, Ray SM, Finch CK, Self TH. The clinical and economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the USA. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res 2013; 5:235–245. doi:10.2147/CEOR.S34321
- Sethi S, Murphy TF. Infection in the pathogenesis and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359(22):2355–2365. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0800353
- Walters JA, Tan DJ, White CJ, Gibson PG, Wood-Baker R, Walters EH. Systemic corticosteroids for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (9):CD001288. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001288.pub4
- de Jong YP, Uil SM, Grotjohan HP, Postma DS, Kerstjens HA, van den Berg JW. Oral or IV prednisolone in the treatment of COPD exacerbations: a randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Chest 2007; 132(6):1741–1747. doi:10.1378/chest.07-0208
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 2019 report. www.goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/GOLD-2019-v1.7-FINAL-14Nov2018-WMS.pdf. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Lindenauer PK, Pekow PS, Lahti MC, Lee Y, Benjamin EM, Rothberg MB. Association of corticosteroid dose and route of administration with risk of treatment failure in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. JAMA 2010; 303(23):2359–2367. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.796
- Aksoy E, Güngör S, Agca MÇ, et al. A revised treatment approach for hospitalized patients with eosinophilic and neutrophilic exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Turk Thorac J 2018; 19(4):193–200. doi:10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2018.18004
- Leuppi JD, Schuetz P, Bingisser R, et al. Short-term vs conventional glucocorticoid therapy in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013; 309(21):2223–2231. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.5023
- Wang PH, Cheng SL, Wang HC, et al. Systemic steroids in acute exacerbation of COPD—from guidelines to bedside. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 49(11):705–708. doi:10.5414/cp201588
Despite guidelines recommending low-dose oral glucocorticoids over high-dose intravenous (IV) glucocorticoids for inpatient management of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), we have observed that most patients still receive high-dose IV therapy before being transitioned to low-dose oral therapy at discharge. Clinical inertia undoubtedly plays a significant role in the slow adoption of new recommendations, but in this era of evidence-based practice, the unfortunate lack of data supporting low over high steroid doses for acute exacerbations of COPD also contributes to hesitancy of physicians.
A SIGNIFICANT AND GROWING BURDEN
COPD is one of the most common pulmonary conditions managed by hospitalists today, and by the year 2030, it is predicted to become the third leading cause of death worldwide.1
COPD is also a significant economic burden, costing $50 billion to manage in the United States, most of that from the cost of lengthy hospital stays.2 COPD patients have 1 to 2 exacerbations per year.3 Bacterial and viral infections are responsible for most exacerbations, and 15% to 20% are from air pollution and other environmental causes of airway inflammation.3
CHALLENGES TO CHANGING PRACTICE
Glucocorticoids are the gold standard for treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. It is well-documented that compared with placebo, glucocorticoids reduce mortality risk, length of hospital stay, and exacerbation recurrence after 1 month.4 And while high-dose IV steroid therapy has been the standard approach, oral administration has been found to be noninferior to IV administration with regard to treatment and length of hospital stay.5
While adverse effects are more common at higher doses, the optimal dose and duration of systemic glucocorticoid therapy for acute exacerbations of COPD are still largely at the discretion of the physician. The 2019 report of the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) recommends low doses (40 mg) for no more than 5 to 7 days for exacerbations, based on reports that showed no worse outcomes with low-dose oral than with high-dose IV therapy.6,7 (In the 2010 study by Lindenauer et al,7 92% of nearly 80,000 patients received high-dose IV steroids, reflecting standard practice at that time.) However, the GOLD guidelines do not address mortality rates, length of stay, or readmission rates for either approach, as they are devised to direct treatment in patients with stable mild to advanced COPD, not exacerbations.
THE EVIDENCE FOR LOW-DOSE STEROIDS
Mortality rates
Aksoy et al8 established that, compared with placebo, low-dose steroids improved mortality rates in a subset of patients with acute exacerbations, specifically those with eosinophilic exacerbations. This study followed the 2013 Reduction in the Use of Corticosteroids in Exacerbated COPD (REDUCE) trial, which showed mortality rates were not lower with 14 days of low-dose prednisone treatment than with 5 days.9
Length of hospital stay
With regard to length of hospital stay, in 2011 Wang et al10 found no statistically significant difference between high- and low-dose steroid treatment.However, the REDUCE trial found that low-dose steroids shortened the median length of stay by 1 day compared with placebo.9
Hospital readmission rates
The REDUCE trial found no statistically significant difference in readmission rates when comparing 5 days of low-dose treatment vs 14 days.9 However, Aksoy et al8 found that readmission rates were significantly lower with low-dose treatment than with placebo.No study has yet examined readmission rates with high-dose vs low-dose steroid treatment.
What does the evidence tell us?
Low-dose oral glucocorticoid treatment shows definitive benefits in terms of lower mortality rates, shorter hospital length of stay, and lower readmission rates vs placebo in the treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. Furthermore, a 14-day course is no better than 5 days in terms of mortality rates. And low-dose glucocorticoid treatment shows reduced mortality rates in addition to similar hospital length of stay when compared to high-dose glucocorticoid treatment.
Together, these findings lend credibility to the current GOLD recommendations. However, we have observed that in sharp contrast to the leading clinical guidelines, most patients hospitalized for acute exacerbations of COPD are still treated initially with high-dose IV corticosteroids. Why?
Obstacles that perpetuate the use of high-dose over low-dose treatment include lack of knowledge of glucocorticoid pharmacokinetics among clinicians, use of outdated order sets, and the reflex notion that more of a drug is more efficacious in its desired effect. In addition, administrative obstacles include using high-dose IV steroids to justify an inpatient stay or continued hospitalization.
COUNTERING THE OBSTACLES: THE HOSPITALIST’S ROLE
To counter these obstacles, we propose standardization of inpatient treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD to include initial low-dose steroid treatment in accordance with the most recent GOLD guidelines.6 This would benefit the patient by reducing undesirable effects of high-dose steroids, and at the same time reduce the economic burden of managing COPD exacerbations. Considering the large number of hospitalizations for COPD exacerbation each year, hospitalists can play a large role in this effort by routinely incorporating the low-dose steroid recommendation into their clinical practice.
Despite guidelines recommending low-dose oral glucocorticoids over high-dose intravenous (IV) glucocorticoids for inpatient management of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), we have observed that most patients still receive high-dose IV therapy before being transitioned to low-dose oral therapy at discharge. Clinical inertia undoubtedly plays a significant role in the slow adoption of new recommendations, but in this era of evidence-based practice, the unfortunate lack of data supporting low over high steroid doses for acute exacerbations of COPD also contributes to hesitancy of physicians.
A SIGNIFICANT AND GROWING BURDEN
COPD is one of the most common pulmonary conditions managed by hospitalists today, and by the year 2030, it is predicted to become the third leading cause of death worldwide.1
COPD is also a significant economic burden, costing $50 billion to manage in the United States, most of that from the cost of lengthy hospital stays.2 COPD patients have 1 to 2 exacerbations per year.3 Bacterial and viral infections are responsible for most exacerbations, and 15% to 20% are from air pollution and other environmental causes of airway inflammation.3
CHALLENGES TO CHANGING PRACTICE
Glucocorticoids are the gold standard for treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. It is well-documented that compared with placebo, glucocorticoids reduce mortality risk, length of hospital stay, and exacerbation recurrence after 1 month.4 And while high-dose IV steroid therapy has been the standard approach, oral administration has been found to be noninferior to IV administration with regard to treatment and length of hospital stay.5
While adverse effects are more common at higher doses, the optimal dose and duration of systemic glucocorticoid therapy for acute exacerbations of COPD are still largely at the discretion of the physician. The 2019 report of the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) recommends low doses (40 mg) for no more than 5 to 7 days for exacerbations, based on reports that showed no worse outcomes with low-dose oral than with high-dose IV therapy.6,7 (In the 2010 study by Lindenauer et al,7 92% of nearly 80,000 patients received high-dose IV steroids, reflecting standard practice at that time.) However, the GOLD guidelines do not address mortality rates, length of stay, or readmission rates for either approach, as they are devised to direct treatment in patients with stable mild to advanced COPD, not exacerbations.
THE EVIDENCE FOR LOW-DOSE STEROIDS
Mortality rates
Aksoy et al8 established that, compared with placebo, low-dose steroids improved mortality rates in a subset of patients with acute exacerbations, specifically those with eosinophilic exacerbations. This study followed the 2013 Reduction in the Use of Corticosteroids in Exacerbated COPD (REDUCE) trial, which showed mortality rates were not lower with 14 days of low-dose prednisone treatment than with 5 days.9
Length of hospital stay
With regard to length of hospital stay, in 2011 Wang et al10 found no statistically significant difference between high- and low-dose steroid treatment.However, the REDUCE trial found that low-dose steroids shortened the median length of stay by 1 day compared with placebo.9
Hospital readmission rates
The REDUCE trial found no statistically significant difference in readmission rates when comparing 5 days of low-dose treatment vs 14 days.9 However, Aksoy et al8 found that readmission rates were significantly lower with low-dose treatment than with placebo.No study has yet examined readmission rates with high-dose vs low-dose steroid treatment.
What does the evidence tell us?
Low-dose oral glucocorticoid treatment shows definitive benefits in terms of lower mortality rates, shorter hospital length of stay, and lower readmission rates vs placebo in the treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD. Furthermore, a 14-day course is no better than 5 days in terms of mortality rates. And low-dose glucocorticoid treatment shows reduced mortality rates in addition to similar hospital length of stay when compared to high-dose glucocorticoid treatment.
Together, these findings lend credibility to the current GOLD recommendations. However, we have observed that in sharp contrast to the leading clinical guidelines, most patients hospitalized for acute exacerbations of COPD are still treated initially with high-dose IV corticosteroids. Why?
Obstacles that perpetuate the use of high-dose over low-dose treatment include lack of knowledge of glucocorticoid pharmacokinetics among clinicians, use of outdated order sets, and the reflex notion that more of a drug is more efficacious in its desired effect. In addition, administrative obstacles include using high-dose IV steroids to justify an inpatient stay or continued hospitalization.
COUNTERING THE OBSTACLES: THE HOSPITALIST’S ROLE
To counter these obstacles, we propose standardization of inpatient treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD to include initial low-dose steroid treatment in accordance with the most recent GOLD guidelines.6 This would benefit the patient by reducing undesirable effects of high-dose steroids, and at the same time reduce the economic burden of managing COPD exacerbations. Considering the large number of hospitalizations for COPD exacerbation each year, hospitalists can play a large role in this effort by routinely incorporating the low-dose steroid recommendation into their clinical practice.
- World Health Organization. Chronic respiratory diseases: burden of COPD. www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Guarascio AJ, Ray SM, Finch CK, Self TH. The clinical and economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the USA. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res 2013; 5:235–245. doi:10.2147/CEOR.S34321
- Sethi S, Murphy TF. Infection in the pathogenesis and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359(22):2355–2365. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0800353
- Walters JA, Tan DJ, White CJ, Gibson PG, Wood-Baker R, Walters EH. Systemic corticosteroids for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (9):CD001288. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001288.pub4
- de Jong YP, Uil SM, Grotjohan HP, Postma DS, Kerstjens HA, van den Berg JW. Oral or IV prednisolone in the treatment of COPD exacerbations: a randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Chest 2007; 132(6):1741–1747. doi:10.1378/chest.07-0208
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 2019 report. www.goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/GOLD-2019-v1.7-FINAL-14Nov2018-WMS.pdf. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Lindenauer PK, Pekow PS, Lahti MC, Lee Y, Benjamin EM, Rothberg MB. Association of corticosteroid dose and route of administration with risk of treatment failure in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. JAMA 2010; 303(23):2359–2367. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.796
- Aksoy E, Güngör S, Agca MÇ, et al. A revised treatment approach for hospitalized patients with eosinophilic and neutrophilic exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Turk Thorac J 2018; 19(4):193–200. doi:10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2018.18004
- Leuppi JD, Schuetz P, Bingisser R, et al. Short-term vs conventional glucocorticoid therapy in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013; 309(21):2223–2231. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.5023
- Wang PH, Cheng SL, Wang HC, et al. Systemic steroids in acute exacerbation of COPD—from guidelines to bedside. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 49(11):705–708. doi:10.5414/cp201588
- World Health Organization. Chronic respiratory diseases: burden of COPD. www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Guarascio AJ, Ray SM, Finch CK, Self TH. The clinical and economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the USA. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res 2013; 5:235–245. doi:10.2147/CEOR.S34321
- Sethi S, Murphy TF. Infection in the pathogenesis and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359(22):2355–2365. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0800353
- Walters JA, Tan DJ, White CJ, Gibson PG, Wood-Baker R, Walters EH. Systemic corticosteroids for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (9):CD001288. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001288.pub4
- de Jong YP, Uil SM, Grotjohan HP, Postma DS, Kerstjens HA, van den Berg JW. Oral or IV prednisolone in the treatment of COPD exacerbations: a randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Chest 2007; 132(6):1741–1747. doi:10.1378/chest.07-0208
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 2019 report. www.goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/GOLD-2019-v1.7-FINAL-14Nov2018-WMS.pdf. Accessed October 16, 2019.
- Lindenauer PK, Pekow PS, Lahti MC, Lee Y, Benjamin EM, Rothberg MB. Association of corticosteroid dose and route of administration with risk of treatment failure in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. JAMA 2010; 303(23):2359–2367. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.796
- Aksoy E, Güngör S, Agca MÇ, et al. A revised treatment approach for hospitalized patients with eosinophilic and neutrophilic exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Turk Thorac J 2018; 19(4):193–200. doi:10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2018.18004
- Leuppi JD, Schuetz P, Bingisser R, et al. Short-term vs conventional glucocorticoid therapy in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013; 309(21):2223–2231. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.5023
- Wang PH, Cheng SL, Wang HC, et al. Systemic steroids in acute exacerbation of COPD—from guidelines to bedside. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 49(11):705–708. doi:10.5414/cp201588
Correction: Diabetes management
Information was omitted from Table 1 on page 596 of the article, Makin V, Lansang MC. Diabetes management: beyond hemoglobin A1c (Cleve Clin J Med 2019; 86[9]:595–600, doi:10.3949/ccjm.86a.18031).
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors pose a low risk of hypoglyemia, and that should have been noted in the table. The corrected table appears below and online.
Information was omitted from Table 1 on page 596 of the article, Makin V, Lansang MC. Diabetes management: beyond hemoglobin A1c (Cleve Clin J Med 2019; 86[9]:595–600, doi:10.3949/ccjm.86a.18031).
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors pose a low risk of hypoglyemia, and that should have been noted in the table. The corrected table appears below and online.
Information was omitted from Table 1 on page 596 of the article, Makin V, Lansang MC. Diabetes management: beyond hemoglobin A1c (Cleve Clin J Med 2019; 86[9]:595–600, doi:10.3949/ccjm.86a.18031).
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors pose a low risk of hypoglyemia, and that should have been noted in the table. The corrected table appears below and online.
Get ready for changes in polypharmacy quality ratings
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – and managed care organizations should start preparing now for the shift.
Panelists at an Oct. 30 session at the annual meeting of the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy presented strategies for addressing the three areas of polypharmacy that will be tracked in the new rating system, which will replace the current high-risk medication measurement that is being retired this year.
Anticholinergic medications
The first area presented by the panelists was polypharmacy use of multiple anticholinergic medications in older adults (Poly-ACH). The new quality measure will examine the percentage of members aged 65 years or older who are using two or more anticholinergic medications concurrently.
“We know that anticholinergic burden increases the risk of cognitive decline in particular, but it’s also associated with a higher risk of falls, an increased number of hospitalizations, and [diminished] physical function,” said Marti Groeneweg, PharmD, supervisor of clinical pharmacy services at Kaiser Permanente.
Dr. Groeneweg noted that, in addition to using multiple drugs in this class, patients can also benefit from a decrease in the dosage of their drugs, so that should also be considered in managing the medication of beneficiaries.
She highlighted a program Kaiser Permanente started in the Northwest United States to reduce the concurrent use of these drugs. The program targeted tricyclic antidepressants – nortriptyline, in particular.
The company instituted a multipronged approach that included provider detailing of the risks of using multiple drugs and how they could taper schedules, as well as providing them with other supporting resources and a list of safer, alternative drugs. It also reached out to patients to educate them about the risks of their medications and why it was important for them to taper their medications. The third part of the approach was to use the EHR to provide doctors with the best-available information at the point of prescribing. And finally, there was a pharmacist review process put in place for more complex cases.
Dr. Groeneweg emphasized that this information was incorporated into existing programs.
The intervention, which is fairly new, has not been in place long enough to know exactly how well it is working, but early indicators suggest “we are on the right track,” she said, noting that to date there has been a decrease of 28% in the number of tricyclic antidepressant prescriptions per 1,000 Medicare members per month.
CNS medications
The second area the panelists addressed was the polypharmacy use of multiple CNS-active medications in older adults (Poly-CNS).
Rainelle Gaddy, PharmD, Rx clinical programs pharmacy lead at Humana Pharmacy Solutions, , noted that the clinical rationale for this measure was the “increased risk of falls and fractures when these medications are taken concurrently.”
She pointed out that taking one or more of the CNS medications can result in a 1.5-fold increase in the risk for falls, and that risk increases to 2.5-fold if two or more drugs are taken. In addition, a high-dose of these medications can lead to a threefold increase in risk of recurrent falls.
Dr. Gaddy highlighted a number of interventions that could be implemented when the managed care organization is not integrated in the way Kaiser Permanente is.
“Pharmacists can pay a pivotal role [in helping] patients who are receiving these Poly-CNS medications because they are able to interact and talk through the actual patient picture for all their medications ... because pharmacists have always been seen as being a trusted source,” she said.
Dr. Gaddy added that health plans can take a more direct role in reaching out to patients, for example, through telephone outreach, as well as direct mail, email, and newsletters.
“We want to make sure that members have as much information as possible,” she said.
She added that it is very important to include physicians and other prescribers in this process through faxes and information included in EHRs.
Opioids and benzodiazepines
The final measure highlighted during the session was the one measuring the concurrent use of opioids and benzodiazepines.
Dr. Gaddy noted that taking the two concurrently is associated with a fourfold increase in risk of opioid overdose and death, compared with opioid use without a benzodiazepine.
She noted that a black box warning on the risks of concurrent use was added to both opioids and benzodiazepines in August 2016 and that resulted in a 10% decrease in the concurrent use.
“This new measure is intended to ensure that the downward trend continues. CMS has indicated as such,” Dr. Gaddy said.
Most of the intervention strategies she highlighted were similar to those for the Poly-CNS category, including the use of medication therapy management programs and targeted interventions, telephone outreach to members, and provider detailing and outreach.
“Provider detailing is really key,” Dr. Gaddy said. “On any given day, it’s so easy for physicians to see 30 patients. The great thing about the provider detailing is that you are able to give the provider a ‘packet’ of their members, you can identify and/or aid in showing them the risk assessment associated with members taking these medications, and then equip them with pocket guides and [materials so they can] streamline the medications.”
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – and managed care organizations should start preparing now for the shift.
Panelists at an Oct. 30 session at the annual meeting of the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy presented strategies for addressing the three areas of polypharmacy that will be tracked in the new rating system, which will replace the current high-risk medication measurement that is being retired this year.
Anticholinergic medications
The first area presented by the panelists was polypharmacy use of multiple anticholinergic medications in older adults (Poly-ACH). The new quality measure will examine the percentage of members aged 65 years or older who are using two or more anticholinergic medications concurrently.
“We know that anticholinergic burden increases the risk of cognitive decline in particular, but it’s also associated with a higher risk of falls, an increased number of hospitalizations, and [diminished] physical function,” said Marti Groeneweg, PharmD, supervisor of clinical pharmacy services at Kaiser Permanente.
Dr. Groeneweg noted that, in addition to using multiple drugs in this class, patients can also benefit from a decrease in the dosage of their drugs, so that should also be considered in managing the medication of beneficiaries.
She highlighted a program Kaiser Permanente started in the Northwest United States to reduce the concurrent use of these drugs. The program targeted tricyclic antidepressants – nortriptyline, in particular.
The company instituted a multipronged approach that included provider detailing of the risks of using multiple drugs and how they could taper schedules, as well as providing them with other supporting resources and a list of safer, alternative drugs. It also reached out to patients to educate them about the risks of their medications and why it was important for them to taper their medications. The third part of the approach was to use the EHR to provide doctors with the best-available information at the point of prescribing. And finally, there was a pharmacist review process put in place for more complex cases.
Dr. Groeneweg emphasized that this information was incorporated into existing programs.
The intervention, which is fairly new, has not been in place long enough to know exactly how well it is working, but early indicators suggest “we are on the right track,” she said, noting that to date there has been a decrease of 28% in the number of tricyclic antidepressant prescriptions per 1,000 Medicare members per month.
CNS medications
The second area the panelists addressed was the polypharmacy use of multiple CNS-active medications in older adults (Poly-CNS).
Rainelle Gaddy, PharmD, Rx clinical programs pharmacy lead at Humana Pharmacy Solutions, , noted that the clinical rationale for this measure was the “increased risk of falls and fractures when these medications are taken concurrently.”
She pointed out that taking one or more of the CNS medications can result in a 1.5-fold increase in the risk for falls, and that risk increases to 2.5-fold if two or more drugs are taken. In addition, a high-dose of these medications can lead to a threefold increase in risk of recurrent falls.
Dr. Gaddy highlighted a number of interventions that could be implemented when the managed care organization is not integrated in the way Kaiser Permanente is.
“Pharmacists can pay a pivotal role [in helping] patients who are receiving these Poly-CNS medications because they are able to interact and talk through the actual patient picture for all their medications ... because pharmacists have always been seen as being a trusted source,” she said.
Dr. Gaddy added that health plans can take a more direct role in reaching out to patients, for example, through telephone outreach, as well as direct mail, email, and newsletters.
“We want to make sure that members have as much information as possible,” she said.
She added that it is very important to include physicians and other prescribers in this process through faxes and information included in EHRs.
Opioids and benzodiazepines
The final measure highlighted during the session was the one measuring the concurrent use of opioids and benzodiazepines.
Dr. Gaddy noted that taking the two concurrently is associated with a fourfold increase in risk of opioid overdose and death, compared with opioid use without a benzodiazepine.
She noted that a black box warning on the risks of concurrent use was added to both opioids and benzodiazepines in August 2016 and that resulted in a 10% decrease in the concurrent use.
“This new measure is intended to ensure that the downward trend continues. CMS has indicated as such,” Dr. Gaddy said.
Most of the intervention strategies she highlighted were similar to those for the Poly-CNS category, including the use of medication therapy management programs and targeted interventions, telephone outreach to members, and provider detailing and outreach.
“Provider detailing is really key,” Dr. Gaddy said. “On any given day, it’s so easy for physicians to see 30 patients. The great thing about the provider detailing is that you are able to give the provider a ‘packet’ of their members, you can identify and/or aid in showing them the risk assessment associated with members taking these medications, and then equip them with pocket guides and [materials so they can] streamline the medications.”
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – and managed care organizations should start preparing now for the shift.
Panelists at an Oct. 30 session at the annual meeting of the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy presented strategies for addressing the three areas of polypharmacy that will be tracked in the new rating system, which will replace the current high-risk medication measurement that is being retired this year.
Anticholinergic medications
The first area presented by the panelists was polypharmacy use of multiple anticholinergic medications in older adults (Poly-ACH). The new quality measure will examine the percentage of members aged 65 years or older who are using two or more anticholinergic medications concurrently.
“We know that anticholinergic burden increases the risk of cognitive decline in particular, but it’s also associated with a higher risk of falls, an increased number of hospitalizations, and [diminished] physical function,” said Marti Groeneweg, PharmD, supervisor of clinical pharmacy services at Kaiser Permanente.
Dr. Groeneweg noted that, in addition to using multiple drugs in this class, patients can also benefit from a decrease in the dosage of their drugs, so that should also be considered in managing the medication of beneficiaries.
She highlighted a program Kaiser Permanente started in the Northwest United States to reduce the concurrent use of these drugs. The program targeted tricyclic antidepressants – nortriptyline, in particular.
The company instituted a multipronged approach that included provider detailing of the risks of using multiple drugs and how they could taper schedules, as well as providing them with other supporting resources and a list of safer, alternative drugs. It also reached out to patients to educate them about the risks of their medications and why it was important for them to taper their medications. The third part of the approach was to use the EHR to provide doctors with the best-available information at the point of prescribing. And finally, there was a pharmacist review process put in place for more complex cases.
Dr. Groeneweg emphasized that this information was incorporated into existing programs.
The intervention, which is fairly new, has not been in place long enough to know exactly how well it is working, but early indicators suggest “we are on the right track,” she said, noting that to date there has been a decrease of 28% in the number of tricyclic antidepressant prescriptions per 1,000 Medicare members per month.
CNS medications
The second area the panelists addressed was the polypharmacy use of multiple CNS-active medications in older adults (Poly-CNS).
Rainelle Gaddy, PharmD, Rx clinical programs pharmacy lead at Humana Pharmacy Solutions, , noted that the clinical rationale for this measure was the “increased risk of falls and fractures when these medications are taken concurrently.”
She pointed out that taking one or more of the CNS medications can result in a 1.5-fold increase in the risk for falls, and that risk increases to 2.5-fold if two or more drugs are taken. In addition, a high-dose of these medications can lead to a threefold increase in risk of recurrent falls.
Dr. Gaddy highlighted a number of interventions that could be implemented when the managed care organization is not integrated in the way Kaiser Permanente is.
“Pharmacists can pay a pivotal role [in helping] patients who are receiving these Poly-CNS medications because they are able to interact and talk through the actual patient picture for all their medications ... because pharmacists have always been seen as being a trusted source,” she said.
Dr. Gaddy added that health plans can take a more direct role in reaching out to patients, for example, through telephone outreach, as well as direct mail, email, and newsletters.
“We want to make sure that members have as much information as possible,” she said.
She added that it is very important to include physicians and other prescribers in this process through faxes and information included in EHRs.
Opioids and benzodiazepines
The final measure highlighted during the session was the one measuring the concurrent use of opioids and benzodiazepines.
Dr. Gaddy noted that taking the two concurrently is associated with a fourfold increase in risk of opioid overdose and death, compared with opioid use without a benzodiazepine.
She noted that a black box warning on the risks of concurrent use was added to both opioids and benzodiazepines in August 2016 and that resulted in a 10% decrease in the concurrent use.
“This new measure is intended to ensure that the downward trend continues. CMS has indicated as such,” Dr. Gaddy said.
Most of the intervention strategies she highlighted were similar to those for the Poly-CNS category, including the use of medication therapy management programs and targeted interventions, telephone outreach to members, and provider detailing and outreach.
“Provider detailing is really key,” Dr. Gaddy said. “On any given day, it’s so easy for physicians to see 30 patients. The great thing about the provider detailing is that you are able to give the provider a ‘packet’ of their members, you can identify and/or aid in showing them the risk assessment associated with members taking these medications, and then equip them with pocket guides and [materials so they can] streamline the medications.”
REPORTING FROM AMCP NEXUS 2019
2019 at a glance: Hem-onc U.S. drug approvals
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.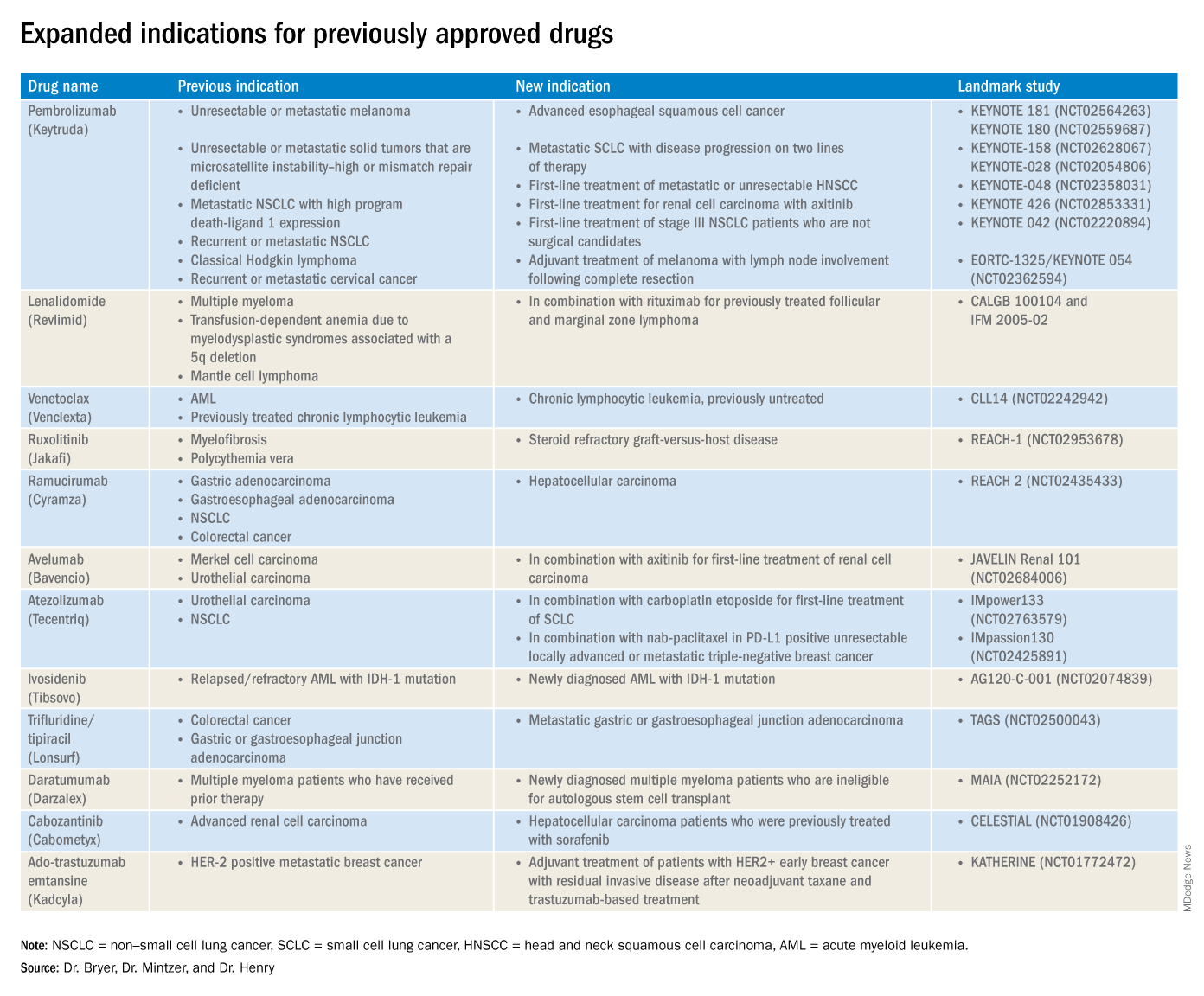
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
FDA approves diroximel fumarate for relapsing MS
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
SUSTAIN 10: Weight loss, glycemic control better with semaglutide than liraglutide
BARCELONA – Patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with semaglutide achieved greater reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and body weight, compared with those receiving liraglutide, according to results presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In the phase 3b SUSTAIN 10 trial, conducted in 11 European countries, mean glycated hemoglobin at 30 weeks decreased by 1.7% with once-weekly semaglutide and 1.0% for once-daily liraglutide, from the overall baseline level of 8.2%. The estimated treatment difference (ETD) between the two treatments was –0.69 percentage points (95% confidence interval, –0.82 to –0.56; P less than .0001).
Mean body weight decreased during the same period by 5.8 kg with semaglutide and 1.9 kg with liraglutide, from a baseline of 96.9 kg. The ETD was 3.83 kg (95% CI, –4.57 to –3.09; P less than .0001).
The doses of semaglutide and liraglutide used in the study were 1.0 mg and 1.2 mg, respectively, the latter being the dose that is used most commonly in clinical practice, study investigator Matthew Capehorn, MB, CAB, explained in an interview at the meeting.
“We know that at a dose of 1.8 mg, liraglutide is more effective than 1.2 mg, but it’s about whether it is deemed more cost effective,” said Dr. Capehorn, who is clinical manager at Rotherham (England) Institute for Obesity, Clifton Medical Centre. “Certainly, in the United Kingdom, we’re encouraged to use the 1.2-mg dose” according to guidance from the National Institute for Heath and Care Excellence, and “other European countries are the same.”
Dr. Capehorn noted that studies are being done with a higher dose of semaglutide to see if it has potential as a weight loss drug in its own right in patients who do not have type 2 diabetes. “I care as much about obesity and cardiovascular disease as I do about chasing the HbA1c level and getting that reduced, so I would rather pick an agent that covers all three [components], than just looking at the HbA1c,” he said.
In SUSTAIN 10,577 adults with type 2 diabetes and an HbA1c level of between 7.0% and 11.0% who were on stable doses of one to three oral antidiabetic drugs were randomized to receive semaglutide (n = 290) or liraglutide (n = 287) for 30 weeks.
The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c from baseline to week 30, and the secondary confirmatory endpoint was change in body weight over the same period.
In presenting the findings, which were simultaneously published in Diabetes & Metabolism, Dr. Capehorn noted that the efficacy results were consistent with those of other SUSTAIN trials that compared semaglutide with other glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor antagonists, notably SUSTAIN 3 (with exenatide extended release) and SUSTAIN 7 (with dulaglutide).
Other efficacy findings from SUSTAIN 10 were that semaglutide produced greater mean changes than did liraglutide in both fasting plasma glucose and in a 7-point, self-monitoring of blood glucose profile.
A greater percentage of people treated with semaglutide, compared with liraglutide, also achieved their glycemic targets of less than 7.0% (80% vs. 46%, respectively) and of 6.5% or less (58% vs. 25%), and their weight loss targets of 5% or more (56% vs. 18%) and 10% or more (19% vs. 4%).
In addition, more semaglutide- than liraglutide-treated patients achieved an HbA1c target of less than 7.0% without severe or blood glucose–confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, with or without weight gain (76% vs. 37%; P less than .0001). There were also more semaglutide patients who achieved an HbA1c reduction of 1% or more and a weight loss reduction of 10% or more (17% vs. 4% for liraglutide, P less than .0001).
The safety profiles were similar for semaglutide and liraglutide, Dr. Capehorn noted, but gastrointestinal adverse events were more prevalent in patients receiving semaglutide, compared with liraglutide (43.9% vs. 38.3%), and more patients receiving semaglutide discontinued treatment prematurely because of those adverse events (11.4% vs. 6.6% for liraglutide).
Novo Nordisk sponsored the study. Dr. Capehorn reported receiving research funding from, providing advisory board support to, and speaker fees from Novo Nordisk and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Capehorn M et al. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 53; Capehorn M et al. Diabetes Metab. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.101117.
BARCELONA – Patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with semaglutide achieved greater reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and body weight, compared with those receiving liraglutide, according to results presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In the phase 3b SUSTAIN 10 trial, conducted in 11 European countries, mean glycated hemoglobin at 30 weeks decreased by 1.7% with once-weekly semaglutide and 1.0% for once-daily liraglutide, from the overall baseline level of 8.2%. The estimated treatment difference (ETD) between the two treatments was –0.69 percentage points (95% confidence interval, –0.82 to –0.56; P less than .0001).
Mean body weight decreased during the same period by 5.8 kg with semaglutide and 1.9 kg with liraglutide, from a baseline of 96.9 kg. The ETD was 3.83 kg (95% CI, –4.57 to –3.09; P less than .0001).
The doses of semaglutide and liraglutide used in the study were 1.0 mg and 1.2 mg, respectively, the latter being the dose that is used most commonly in clinical practice, study investigator Matthew Capehorn, MB, CAB, explained in an interview at the meeting.
“We know that at a dose of 1.8 mg, liraglutide is more effective than 1.2 mg, but it’s about whether it is deemed more cost effective,” said Dr. Capehorn, who is clinical manager at Rotherham (England) Institute for Obesity, Clifton Medical Centre. “Certainly, in the United Kingdom, we’re encouraged to use the 1.2-mg dose” according to guidance from the National Institute for Heath and Care Excellence, and “other European countries are the same.”
Dr. Capehorn noted that studies are being done with a higher dose of semaglutide to see if it has potential as a weight loss drug in its own right in patients who do not have type 2 diabetes. “I care as much about obesity and cardiovascular disease as I do about chasing the HbA1c level and getting that reduced, so I would rather pick an agent that covers all three [components], than just looking at the HbA1c,” he said.
In SUSTAIN 10,577 adults with type 2 diabetes and an HbA1c level of between 7.0% and 11.0% who were on stable doses of one to three oral antidiabetic drugs were randomized to receive semaglutide (n = 290) or liraglutide (n = 287) for 30 weeks.
The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c from baseline to week 30, and the secondary confirmatory endpoint was change in body weight over the same period.
In presenting the findings, which were simultaneously published in Diabetes & Metabolism, Dr. Capehorn noted that the efficacy results were consistent with those of other SUSTAIN trials that compared semaglutide with other glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor antagonists, notably SUSTAIN 3 (with exenatide extended release) and SUSTAIN 7 (with dulaglutide).
Other efficacy findings from SUSTAIN 10 were that semaglutide produced greater mean changes than did liraglutide in both fasting plasma glucose and in a 7-point, self-monitoring of blood glucose profile.
A greater percentage of people treated with semaglutide, compared with liraglutide, also achieved their glycemic targets of less than 7.0% (80% vs. 46%, respectively) and of 6.5% or less (58% vs. 25%), and their weight loss targets of 5% or more (56% vs. 18%) and 10% or more (19% vs. 4%).
In addition, more semaglutide- than liraglutide-treated patients achieved an HbA1c target of less than 7.0% without severe or blood glucose–confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, with or without weight gain (76% vs. 37%; P less than .0001). There were also more semaglutide patients who achieved an HbA1c reduction of 1% or more and a weight loss reduction of 10% or more (17% vs. 4% for liraglutide, P less than .0001).
The safety profiles were similar for semaglutide and liraglutide, Dr. Capehorn noted, but gastrointestinal adverse events were more prevalent in patients receiving semaglutide, compared with liraglutide (43.9% vs. 38.3%), and more patients receiving semaglutide discontinued treatment prematurely because of those adverse events (11.4% vs. 6.6% for liraglutide).
Novo Nordisk sponsored the study. Dr. Capehorn reported receiving research funding from, providing advisory board support to, and speaker fees from Novo Nordisk and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Capehorn M et al. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 53; Capehorn M et al. Diabetes Metab. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.101117.
BARCELONA – Patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with semaglutide achieved greater reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and body weight, compared with those receiving liraglutide, according to results presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In the phase 3b SUSTAIN 10 trial, conducted in 11 European countries, mean glycated hemoglobin at 30 weeks decreased by 1.7% with once-weekly semaglutide and 1.0% for once-daily liraglutide, from the overall baseline level of 8.2%. The estimated treatment difference (ETD) between the two treatments was –0.69 percentage points (95% confidence interval, –0.82 to –0.56; P less than .0001).
Mean body weight decreased during the same period by 5.8 kg with semaglutide and 1.9 kg with liraglutide, from a baseline of 96.9 kg. The ETD was 3.83 kg (95% CI, –4.57 to –3.09; P less than .0001).
The doses of semaglutide and liraglutide used in the study were 1.0 mg and 1.2 mg, respectively, the latter being the dose that is used most commonly in clinical practice, study investigator Matthew Capehorn, MB, CAB, explained in an interview at the meeting.
“We know that at a dose of 1.8 mg, liraglutide is more effective than 1.2 mg, but it’s about whether it is deemed more cost effective,” said Dr. Capehorn, who is clinical manager at Rotherham (England) Institute for Obesity, Clifton Medical Centre. “Certainly, in the United Kingdom, we’re encouraged to use the 1.2-mg dose” according to guidance from the National Institute for Heath and Care Excellence, and “other European countries are the same.”
Dr. Capehorn noted that studies are being done with a higher dose of semaglutide to see if it has potential as a weight loss drug in its own right in patients who do not have type 2 diabetes. “I care as much about obesity and cardiovascular disease as I do about chasing the HbA1c level and getting that reduced, so I would rather pick an agent that covers all three [components], than just looking at the HbA1c,” he said.
In SUSTAIN 10,577 adults with type 2 diabetes and an HbA1c level of between 7.0% and 11.0% who were on stable doses of one to three oral antidiabetic drugs were randomized to receive semaglutide (n = 290) or liraglutide (n = 287) for 30 weeks.
The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c from baseline to week 30, and the secondary confirmatory endpoint was change in body weight over the same period.
In presenting the findings, which were simultaneously published in Diabetes & Metabolism, Dr. Capehorn noted that the efficacy results were consistent with those of other SUSTAIN trials that compared semaglutide with other glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor antagonists, notably SUSTAIN 3 (with exenatide extended release) and SUSTAIN 7 (with dulaglutide).
Other efficacy findings from SUSTAIN 10 were that semaglutide produced greater mean changes than did liraglutide in both fasting plasma glucose and in a 7-point, self-monitoring of blood glucose profile.
A greater percentage of people treated with semaglutide, compared with liraglutide, also achieved their glycemic targets of less than 7.0% (80% vs. 46%, respectively) and of 6.5% or less (58% vs. 25%), and their weight loss targets of 5% or more (56% vs. 18%) and 10% or more (19% vs. 4%).
In addition, more semaglutide- than liraglutide-treated patients achieved an HbA1c target of less than 7.0% without severe or blood glucose–confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, with or without weight gain (76% vs. 37%; P less than .0001). There were also more semaglutide patients who achieved an HbA1c reduction of 1% or more and a weight loss reduction of 10% or more (17% vs. 4% for liraglutide, P less than .0001).
The safety profiles were similar for semaglutide and liraglutide, Dr. Capehorn noted, but gastrointestinal adverse events were more prevalent in patients receiving semaglutide, compared with liraglutide (43.9% vs. 38.3%), and more patients receiving semaglutide discontinued treatment prematurely because of those adverse events (11.4% vs. 6.6% for liraglutide).
Novo Nordisk sponsored the study. Dr. Capehorn reported receiving research funding from, providing advisory board support to, and speaker fees from Novo Nordisk and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Capehorn M et al. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 53; Capehorn M et al. Diabetes Metab. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.101117.
REPORTING FROM EASD 2019
FDA approves onabotulinumtoxinA for pediatric lower limb spasticity
The Food and Drug Administration has approved onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) for treatment of pediatric lower limb spasticity in patients aged 2-17 years, excluding those in whom it is associated with cerebral palsy, according to an announcement from Allergan.
The approval is based on a phase 3 study evaluating safety and efficacy in more than 300 patients with lower limb spasticity. Although patients with cerebral palsy were included in the study, they’re excluded from this indication. Orphan Drug Exclusivity prevents it from being indicated for lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy because abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport) already has marketing exclusivity for the indication. Botox also is indicated for children aged 2-17 years of age with upper limb spasticity, as well as nine other indications.
OnabotulinumtoxinA comes with warnings, including problems of swallowing, speaking, or breathing and even risk of spread of the toxin. It also may cause loss of strength or general muscle weakness, vision problems, or dizziness within hours or weeks of administration. Serious and sometimes immediate allergic reactions have been reported. Patients and health care professionals should discuss various concerns before treatment, including whether the patient has recently received antibiotics by injection, or has taken muscle relaxants, allergy or cold medicine, sleep medicine, and aspirinlike products or blood thinners. It’s important to note that the dose of onabotulinumtoxinA is not the same as that for other botulinum toxin products. The full prescribing information is available on the Allergan website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) for treatment of pediatric lower limb spasticity in patients aged 2-17 years, excluding those in whom it is associated with cerebral palsy, according to an announcement from Allergan.
The approval is based on a phase 3 study evaluating safety and efficacy in more than 300 patients with lower limb spasticity. Although patients with cerebral palsy were included in the study, they’re excluded from this indication. Orphan Drug Exclusivity prevents it from being indicated for lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy because abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport) already has marketing exclusivity for the indication. Botox also is indicated for children aged 2-17 years of age with upper limb spasticity, as well as nine other indications.
OnabotulinumtoxinA comes with warnings, including problems of swallowing, speaking, or breathing and even risk of spread of the toxin. It also may cause loss of strength or general muscle weakness, vision problems, or dizziness within hours or weeks of administration. Serious and sometimes immediate allergic reactions have been reported. Patients and health care professionals should discuss various concerns before treatment, including whether the patient has recently received antibiotics by injection, or has taken muscle relaxants, allergy or cold medicine, sleep medicine, and aspirinlike products or blood thinners. It’s important to note that the dose of onabotulinumtoxinA is not the same as that for other botulinum toxin products. The full prescribing information is available on the Allergan website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) for treatment of pediatric lower limb spasticity in patients aged 2-17 years, excluding those in whom it is associated with cerebral palsy, according to an announcement from Allergan.
The approval is based on a phase 3 study evaluating safety and efficacy in more than 300 patients with lower limb spasticity. Although patients with cerebral palsy were included in the study, they’re excluded from this indication. Orphan Drug Exclusivity prevents it from being indicated for lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy because abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport) already has marketing exclusivity for the indication. Botox also is indicated for children aged 2-17 years of age with upper limb spasticity, as well as nine other indications.
OnabotulinumtoxinA comes with warnings, including problems of swallowing, speaking, or breathing and even risk of spread of the toxin. It also may cause loss of strength or general muscle weakness, vision problems, or dizziness within hours or weeks of administration. Serious and sometimes immediate allergic reactions have been reported. Patients and health care professionals should discuss various concerns before treatment, including whether the patient has recently received antibiotics by injection, or has taken muscle relaxants, allergy or cold medicine, sleep medicine, and aspirinlike products or blood thinners. It’s important to note that the dose of onabotulinumtoxinA is not the same as that for other botulinum toxin products. The full prescribing information is available on the Allergan website.
Hematopoietic cell transplant offers realistic cure in secondary AML
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
FROM BIOLOGY OF BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
FDA approves Trikafta for treatment of cystic fibrosis
in patients aged 12 years or older, the first triple-combination therapy approved for that indication.
Approval for Trikafta was based on results from two clinical trials in patients with cystic fibrosis with an F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. In the first trial, a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 403 patients, the mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased by 14% from baseline, compared with placebo. In the second trial, a 4-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study of 107 patients, mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second was increased 10% from baseline, compared with tezacaftor/ivacaftor, according to the FDA press release.
In the first trial, patients who received Trikafta also saw improvement in sweat chloride, reduction in the number of pulmonary exacerbations, and reduction of body mass index, compared with placebo.
The most common adverse events associated with Trikafta during the trials were headaches, upper respiratory tract infections, abdominal pains, diarrhea, rashes, and rhinorrhea, among others. The label includes a warning related to elevated liver function tests, use at the same time with products that induce or inhibit a liver enzyme called cytochrome P450 3A4, and cataract risk.
“At the FDA, we’re consistently looking for ways to help speed the development of new therapies for complex diseases, while maintaining our high standards of review. Today’s landmark approval is a testament to these efforts, making a novel treatment available to most cystic fibrosis patients, including adolescents, who previously had no options and giving others in the cystic fibrosis community access to an additional effective therapy,” said acting FDA Commissioner Ned Sharpless, MD.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
in patients aged 12 years or older, the first triple-combination therapy approved for that indication.
Approval for Trikafta was based on results from two clinical trials in patients with cystic fibrosis with an F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. In the first trial, a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 403 patients, the mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased by 14% from baseline, compared with placebo. In the second trial, a 4-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study of 107 patients, mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second was increased 10% from baseline, compared with tezacaftor/ivacaftor, according to the FDA press release.
In the first trial, patients who received Trikafta also saw improvement in sweat chloride, reduction in the number of pulmonary exacerbations, and reduction of body mass index, compared with placebo.
The most common adverse events associated with Trikafta during the trials were headaches, upper respiratory tract infections, abdominal pains, diarrhea, rashes, and rhinorrhea, among others. The label includes a warning related to elevated liver function tests, use at the same time with products that induce or inhibit a liver enzyme called cytochrome P450 3A4, and cataract risk.
“At the FDA, we’re consistently looking for ways to help speed the development of new therapies for complex diseases, while maintaining our high standards of review. Today’s landmark approval is a testament to these efforts, making a novel treatment available to most cystic fibrosis patients, including adolescents, who previously had no options and giving others in the cystic fibrosis community access to an additional effective therapy,” said acting FDA Commissioner Ned Sharpless, MD.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
in patients aged 12 years or older, the first triple-combination therapy approved for that indication.
Approval for Trikafta was based on results from two clinical trials in patients with cystic fibrosis with an F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. In the first trial, a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 403 patients, the mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased by 14% from baseline, compared with placebo. In the second trial, a 4-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study of 107 patients, mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second was increased 10% from baseline, compared with tezacaftor/ivacaftor, according to the FDA press release.
In the first trial, patients who received Trikafta also saw improvement in sweat chloride, reduction in the number of pulmonary exacerbations, and reduction of body mass index, compared with placebo.
The most common adverse events associated with Trikafta during the trials were headaches, upper respiratory tract infections, abdominal pains, diarrhea, rashes, and rhinorrhea, among others. The label includes a warning related to elevated liver function tests, use at the same time with products that induce or inhibit a liver enzyme called cytochrome P450 3A4, and cataract risk.
“At the FDA, we’re consistently looking for ways to help speed the development of new therapies for complex diseases, while maintaining our high standards of review. Today’s landmark approval is a testament to these efforts, making a novel treatment available to most cystic fibrosis patients, including adolescents, who previously had no options and giving others in the cystic fibrosis community access to an additional effective therapy,” said acting FDA Commissioner Ned Sharpless, MD.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.