User login
‘A good and peaceful death’: Cancer hospice during the pandemic
Lillie Shockney, RN, MAS, a two-time breast cancer survivor and adjunct professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing in Baltimore, Maryland, mourns the many losses that her patients with advanced cancer now face in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. But in the void of the usual support networks and treatment plans, she sees the resurgence of something that has recently been crowded out: hospice.
The pandemic has forced patients and their physicians to reassess the risk/benefit balance of continuing or embarking on yet another cancer treatment.
“It’s one of the pearls that we will get out of this nightmare,” said Ms. Shockney, who recently retired as administrative director of the cancer survivorship programs at the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Physicians have been taught to treat the disease – so as long as there’s a treatment they give another treatment,” she told Medscape Medical News during a Zoom call from her home. “But for some patients with advanced disease, those treatments were making them very sick, so they were trading longevity over quality of life.”
Of course, longevity has never been a guarantee with cancer treatment, and even less so now, with the risk of COVID-19.
“This is going to bring them to some hard discussions,” says Brenda Nevidjon, RN, MSN, chief executive officer at the Oncology Nursing Society.
“We’ve known for a long time that there are patients who are on third- and fourth-round treatment options that have very little evidence of prolonging life or quality of life,” she told Medscape Medical News. “Do we bring these people out of their home to a setting where there could be a fair number of COVID-positive patients? Do we expose them to that?”
Across the world, these dilemmas are pushing cancer specialists to initiate discussions of hospice sooner with patients who have advanced disease, and with more clarity than before.
One of the reasons such conversations have often been avoided is that the concept of hospice is generally misunderstood, said Ms. Shockney.
“Patients think ‘you’re giving up on me, you’ve abandoned me’, but hospice is all about preserving the remainder of their quality of life and letting them have time with family and time to fulfill those elements of experiencing a good and peaceful death,” she said.
Indeed, hospice is “a benefit meant for somebody with at least a 6-month horizon,” agrees Ms. Nevidjon. Yet the average length of hospice in the United States is just 5 days. “It’s at the very, very end, and yet for some of these patients the 6 months they could get in hospice might be a better quality of life than the 4 months on another whole plan of chemotherapy. I can’t imagine that on the backside of this pandemic we will not have learned and we won’t start to change practices around initiating more of these conversations.”
Silver lining of this pandemic?
It’s too early into the pandemic to have hard data on whether hospice uptake has increased, but “it’s encouraging to hear that hospice is being discussed and offered sooner as an alternative to that third- or fourth-round chemo,” said Lori Bishop, MHA, RN, vice president of palliative and advanced care at the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
“I agree that improving informed-decision discussions and timely access to hospice is a silver lining of the pandemic,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But she points out that today’s hospice looks quite different than it did before the pandemic, with the immediate and very obvious difference being telehealth, which was not widely utilized previously.
In March, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth options for hospice providers, something that Ms. Bishop and other hospice providers hope will remain in place after the pandemic passes.
“Telehealth visits are offered to replace some in-home visits both to minimize risk of exposure to COVID-19 and reduce the drain on personal protective equipment,” Bishop explained.
“In-patient hospice programs are also finding unique ways to provide support and connect patients to their loved ones: visitors are allowed but limited to one or two. Music and pet therapy are being provided through the window or virtually and devices such as iPads are being used to help patients connect with loved ones,” she said.
Telehealth links patients out of loneliness, but the one thing it cannot do is provide the comfort of touch – an important part of any hospice program.
“Hand-holding ... I miss that a lot,” says Ms. Shockney, her eyes filling with tears. “When you take somebody’s hand, you don’t even have to speak; that connection, and eye contact, is all you need to help that person emotionally heal.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lillie Shockney, RN, MAS, a two-time breast cancer survivor and adjunct professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing in Baltimore, Maryland, mourns the many losses that her patients with advanced cancer now face in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. But in the void of the usual support networks and treatment plans, she sees the resurgence of something that has recently been crowded out: hospice.
The pandemic has forced patients and their physicians to reassess the risk/benefit balance of continuing or embarking on yet another cancer treatment.
“It’s one of the pearls that we will get out of this nightmare,” said Ms. Shockney, who recently retired as administrative director of the cancer survivorship programs at the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Physicians have been taught to treat the disease – so as long as there’s a treatment they give another treatment,” she told Medscape Medical News during a Zoom call from her home. “But for some patients with advanced disease, those treatments were making them very sick, so they were trading longevity over quality of life.”
Of course, longevity has never been a guarantee with cancer treatment, and even less so now, with the risk of COVID-19.
“This is going to bring them to some hard discussions,” says Brenda Nevidjon, RN, MSN, chief executive officer at the Oncology Nursing Society.
“We’ve known for a long time that there are patients who are on third- and fourth-round treatment options that have very little evidence of prolonging life or quality of life,” she told Medscape Medical News. “Do we bring these people out of their home to a setting where there could be a fair number of COVID-positive patients? Do we expose them to that?”
Across the world, these dilemmas are pushing cancer specialists to initiate discussions of hospice sooner with patients who have advanced disease, and with more clarity than before.
One of the reasons such conversations have often been avoided is that the concept of hospice is generally misunderstood, said Ms. Shockney.
“Patients think ‘you’re giving up on me, you’ve abandoned me’, but hospice is all about preserving the remainder of their quality of life and letting them have time with family and time to fulfill those elements of experiencing a good and peaceful death,” she said.
Indeed, hospice is “a benefit meant for somebody with at least a 6-month horizon,” agrees Ms. Nevidjon. Yet the average length of hospice in the United States is just 5 days. “It’s at the very, very end, and yet for some of these patients the 6 months they could get in hospice might be a better quality of life than the 4 months on another whole plan of chemotherapy. I can’t imagine that on the backside of this pandemic we will not have learned and we won’t start to change practices around initiating more of these conversations.”
Silver lining of this pandemic?
It’s too early into the pandemic to have hard data on whether hospice uptake has increased, but “it’s encouraging to hear that hospice is being discussed and offered sooner as an alternative to that third- or fourth-round chemo,” said Lori Bishop, MHA, RN, vice president of palliative and advanced care at the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
“I agree that improving informed-decision discussions and timely access to hospice is a silver lining of the pandemic,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But she points out that today’s hospice looks quite different than it did before the pandemic, with the immediate and very obvious difference being telehealth, which was not widely utilized previously.
In March, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth options for hospice providers, something that Ms. Bishop and other hospice providers hope will remain in place after the pandemic passes.
“Telehealth visits are offered to replace some in-home visits both to minimize risk of exposure to COVID-19 and reduce the drain on personal protective equipment,” Bishop explained.
“In-patient hospice programs are also finding unique ways to provide support and connect patients to their loved ones: visitors are allowed but limited to one or two. Music and pet therapy are being provided through the window or virtually and devices such as iPads are being used to help patients connect with loved ones,” she said.
Telehealth links patients out of loneliness, but the one thing it cannot do is provide the comfort of touch – an important part of any hospice program.
“Hand-holding ... I miss that a lot,” says Ms. Shockney, her eyes filling with tears. “When you take somebody’s hand, you don’t even have to speak; that connection, and eye contact, is all you need to help that person emotionally heal.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lillie Shockney, RN, MAS, a two-time breast cancer survivor and adjunct professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing in Baltimore, Maryland, mourns the many losses that her patients with advanced cancer now face in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. But in the void of the usual support networks and treatment plans, she sees the resurgence of something that has recently been crowded out: hospice.
The pandemic has forced patients and their physicians to reassess the risk/benefit balance of continuing or embarking on yet another cancer treatment.
“It’s one of the pearls that we will get out of this nightmare,” said Ms. Shockney, who recently retired as administrative director of the cancer survivorship programs at the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Physicians have been taught to treat the disease – so as long as there’s a treatment they give another treatment,” she told Medscape Medical News during a Zoom call from her home. “But for some patients with advanced disease, those treatments were making them very sick, so they were trading longevity over quality of life.”
Of course, longevity has never been a guarantee with cancer treatment, and even less so now, with the risk of COVID-19.
“This is going to bring them to some hard discussions,” says Brenda Nevidjon, RN, MSN, chief executive officer at the Oncology Nursing Society.
“We’ve known for a long time that there are patients who are on third- and fourth-round treatment options that have very little evidence of prolonging life or quality of life,” she told Medscape Medical News. “Do we bring these people out of their home to a setting where there could be a fair number of COVID-positive patients? Do we expose them to that?”
Across the world, these dilemmas are pushing cancer specialists to initiate discussions of hospice sooner with patients who have advanced disease, and with more clarity than before.
One of the reasons such conversations have often been avoided is that the concept of hospice is generally misunderstood, said Ms. Shockney.
“Patients think ‘you’re giving up on me, you’ve abandoned me’, but hospice is all about preserving the remainder of their quality of life and letting them have time with family and time to fulfill those elements of experiencing a good and peaceful death,” she said.
Indeed, hospice is “a benefit meant for somebody with at least a 6-month horizon,” agrees Ms. Nevidjon. Yet the average length of hospice in the United States is just 5 days. “It’s at the very, very end, and yet for some of these patients the 6 months they could get in hospice might be a better quality of life than the 4 months on another whole plan of chemotherapy. I can’t imagine that on the backside of this pandemic we will not have learned and we won’t start to change practices around initiating more of these conversations.”
Silver lining of this pandemic?
It’s too early into the pandemic to have hard data on whether hospice uptake has increased, but “it’s encouraging to hear that hospice is being discussed and offered sooner as an alternative to that third- or fourth-round chemo,” said Lori Bishop, MHA, RN, vice president of palliative and advanced care at the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
“I agree that improving informed-decision discussions and timely access to hospice is a silver lining of the pandemic,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But she points out that today’s hospice looks quite different than it did before the pandemic, with the immediate and very obvious difference being telehealth, which was not widely utilized previously.
In March, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth options for hospice providers, something that Ms. Bishop and other hospice providers hope will remain in place after the pandemic passes.
“Telehealth visits are offered to replace some in-home visits both to minimize risk of exposure to COVID-19 and reduce the drain on personal protective equipment,” Bishop explained.
“In-patient hospice programs are also finding unique ways to provide support and connect patients to their loved ones: visitors are allowed but limited to one or two. Music and pet therapy are being provided through the window or virtually and devices such as iPads are being used to help patients connect with loved ones,” she said.
Telehealth links patients out of loneliness, but the one thing it cannot do is provide the comfort of touch – an important part of any hospice program.
“Hand-holding ... I miss that a lot,” says Ms. Shockney, her eyes filling with tears. “When you take somebody’s hand, you don’t even have to speak; that connection, and eye contact, is all you need to help that person emotionally heal.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Germline testing in advanced cancer can lead to targeted treatment
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2020
MCC response varies based on immunosuppression type, especially CLL
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
FROM SID 2020
Oncologists’ income and satisfaction are up
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.
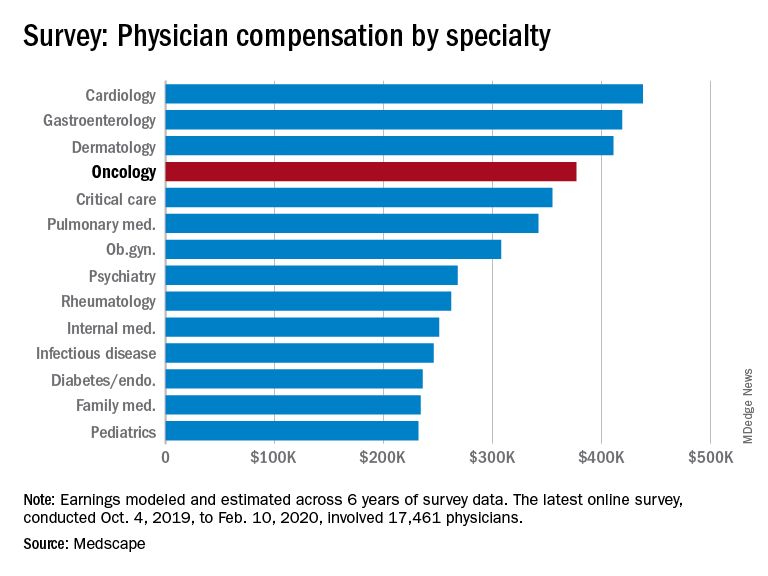
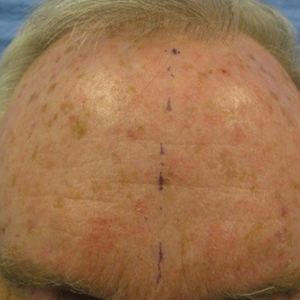
At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves pomalidomide for Kaposi sarcoma
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to pomalidomide (Pomalyst, Bristol-Myers Squibb) for the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that is resistant to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) or that occurs in HIV-negative patients.
Pomalidomide is the only oral agent and first new treatment option for Kaposi sarcoma in more than 20 years, according to the company.
The drug, a thalidomide analogue, is already marketed for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Pomalidomide has “shown positive results in Kaposi sarcoma patients, regardless of their HIV status,” said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch, National Cancer Institute, in a press statement.
The conditional approval is based on the 71% overall response rate observed in a phase 1/2 open-label, single-arm clinical trial that involved 28 patients, 18 of whom were HIV positive and 10 of whom were HIV negative.
Most of the responses were partial (57%; 16/28); 14% (4/28) were complete. Median duration of response was 12.1 months. Additionally, for half of the patients who showed a response, that response was maintained for more than 12 months.
Patients received 5 mg of pomalidomide once daily for 21 of 28-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
Permanent discontinuation because of an adverse reaction occurred in 11% (3/28) of patients.
Adverse reactions (≥20%) included maculopapular rash (71%), constipation (71%), fatigue (68%), nausea (36%), diarrhea (32%), cough (29%), dyspnea (29%), peripheral edema (29%), upper respiratory tract infection (29%), muscle spasms (25%), hypothyroidism (21%), dry skin (21%), and chills (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions included maculopapular rash (3.6%), diarrhea (3.6%), and peripheral edema (3.6%).
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥5%) that worsened from baseline included decreased absolute neutrophil count (50%), decreased phosphate level (25%), elevated glucose level (7%), and elevated creatine kinase level (7%).
As a thalidomide analogue, pomalidomide includes a boxed warning in the prescribing information; thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes severe birth defects or embryo-fetal death. Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke can occur in patients treated with pomalidomide; thromboprophylaxis is recommended.
Pomalidomide is available only through a restricted distribution program, Pomalyst REMS.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to pomalidomide (Pomalyst, Bristol-Myers Squibb) for the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that is resistant to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) or that occurs in HIV-negative patients.
Pomalidomide is the only oral agent and first new treatment option for Kaposi sarcoma in more than 20 years, according to the company.
The drug, a thalidomide analogue, is already marketed for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Pomalidomide has “shown positive results in Kaposi sarcoma patients, regardless of their HIV status,” said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch, National Cancer Institute, in a press statement.
The conditional approval is based on the 71% overall response rate observed in a phase 1/2 open-label, single-arm clinical trial that involved 28 patients, 18 of whom were HIV positive and 10 of whom were HIV negative.
Most of the responses were partial (57%; 16/28); 14% (4/28) were complete. Median duration of response was 12.1 months. Additionally, for half of the patients who showed a response, that response was maintained for more than 12 months.
Patients received 5 mg of pomalidomide once daily for 21 of 28-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
Permanent discontinuation because of an adverse reaction occurred in 11% (3/28) of patients.
Adverse reactions (≥20%) included maculopapular rash (71%), constipation (71%), fatigue (68%), nausea (36%), diarrhea (32%), cough (29%), dyspnea (29%), peripheral edema (29%), upper respiratory tract infection (29%), muscle spasms (25%), hypothyroidism (21%), dry skin (21%), and chills (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions included maculopapular rash (3.6%), diarrhea (3.6%), and peripheral edema (3.6%).
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥5%) that worsened from baseline included decreased absolute neutrophil count (50%), decreased phosphate level (25%), elevated glucose level (7%), and elevated creatine kinase level (7%).
As a thalidomide analogue, pomalidomide includes a boxed warning in the prescribing information; thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes severe birth defects or embryo-fetal death. Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke can occur in patients treated with pomalidomide; thromboprophylaxis is recommended.
Pomalidomide is available only through a restricted distribution program, Pomalyst REMS.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to pomalidomide (Pomalyst, Bristol-Myers Squibb) for the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that is resistant to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) or that occurs in HIV-negative patients.
Pomalidomide is the only oral agent and first new treatment option for Kaposi sarcoma in more than 20 years, according to the company.
The drug, a thalidomide analogue, is already marketed for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Pomalidomide has “shown positive results in Kaposi sarcoma patients, regardless of their HIV status,” said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch, National Cancer Institute, in a press statement.
The conditional approval is based on the 71% overall response rate observed in a phase 1/2 open-label, single-arm clinical trial that involved 28 patients, 18 of whom were HIV positive and 10 of whom were HIV negative.
Most of the responses were partial (57%; 16/28); 14% (4/28) were complete. Median duration of response was 12.1 months. Additionally, for half of the patients who showed a response, that response was maintained for more than 12 months.
Patients received 5 mg of pomalidomide once daily for 21 of 28-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
Permanent discontinuation because of an adverse reaction occurred in 11% (3/28) of patients.
Adverse reactions (≥20%) included maculopapular rash (71%), constipation (71%), fatigue (68%), nausea (36%), diarrhea (32%), cough (29%), dyspnea (29%), peripheral edema (29%), upper respiratory tract infection (29%), muscle spasms (25%), hypothyroidism (21%), dry skin (21%), and chills (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions included maculopapular rash (3.6%), diarrhea (3.6%), and peripheral edema (3.6%).
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥5%) that worsened from baseline included decreased absolute neutrophil count (50%), decreased phosphate level (25%), elevated glucose level (7%), and elevated creatine kinase level (7%).
As a thalidomide analogue, pomalidomide includes a boxed warning in the prescribing information; thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes severe birth defects or embryo-fetal death. Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke can occur in patients treated with pomalidomide; thromboprophylaxis is recommended.
Pomalidomide is available only through a restricted distribution program, Pomalyst REMS.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Video coaching may relieve anxiety and distress for long-distance cancer caregivers
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
FROM ASCO 2020
ASCO goes ahead online, as conference center is used as hospital
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neoadjuvant nivolumab ‘promising’ in Merkel cell carcinoma
Neoadjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) could improve outcomes for patients with high-risk resectable Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), say researchers reporting the first trial in this patient population.
The results come from a cohort of 39 patients with stage IIA-IV disease, all of whom received nivolumab 240 mg intravenously on days 1 and 15, with surgery planned for day 29. About half achieved a pathologic complete response (pCR) and/or a radiographic response. Recurrence-free survival was also prolonged among responders, and no relapses were observed at a median follow-up of 19.3 months.
“Additional investigation of these promising findings is warranted,” say the investigators.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy in MCC,” said lead author Suzanne Topalian, MD, professor of surgery at the Bloomberg-Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland. “While the results seem encouraging, I think that clinical trial experience with a greater number of patients and follow-up for a longer time period will be needed to assess whether this treatment approach should become standard for high-risk resectable MCC.”
The study was published online April 23 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Rare and Aggressive Skin Cancer
MCC is a rare and aggressive neuroendocrine skin cancer that is diagnosed in approximately 1600 people each year in the United States, note the authors.
The annual incidence of new MCC cases rose by 95% between 2000 and 2013, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
Although nearly two thirds of patients present with localized disease, regional and distant metastases often occur. Until recently, cytotoxic chemotherapy was the primary systemic therapy for advanced MCC. Although patients frequently respond to chemotherapy, the duration tends to be very limited, and 95% of patients experience disease progression within 1 year, the authors comment.
Growing evidence supports the hypothesis that MCC is an immunogenic cancer. Clinical trials of PD-L1 inhibitors have demonstrated increased progression-free and overall survival compared with chemotherapy when used either in the first-line or second-line setting, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 cancer therapy is still early in development, and there are many aspects deserving careful consideration,” Topalian told Medscape Medical News. “They are centered on balancing patient risk and benefit, finding an optimal presurgical treatment interval, exploring treatment combinations, determining if anti-PD-1 therapy should be continued after surgery, and defining biomarkers to guide treatment strategies for individual patients.”
Study Details
Topian and colleagues investigated neoadjuvant use of nivolumab in the CheckMate 358 study, which involved 39 patients with stage IIA-IV MCC (of whom 36 went on to surgery).
The median age of the patients was 68 years, and at enrollment, most patients (66.7%) had stage III disease. For 35 patients, tumors were evaluable for MCPyV status; 22 (62.9%) were positive. Quantifiable tumor cell PD-L1 expression occurred in 27 patients; expression was 1% or higher for seven of those patients (25.9%).
The primary endpoint for the neoadjuvant cohort was safety and tolerability of nivolumab, as measured by treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and surgical delays, defined as the proportion of patients who experienced TRAE-related delays of more than 4 weeks from the planned surgery date.
Exploratory endpoints included pCR, radiographic response, recurrence-free survival, overall survival, association of tumor MCPyV status, and PD-L1 expression with efficacy.
The median follow-up was 20.3 months. TRAEs of any grade were reported in 18 patients (46.2%). Three (7.7%) experienced a grade 3/4 event. TRAEs with potential immunologic causes occurred in six (15.4%) patients (two TRAEs were of grade 3/4).
Among those who underwent surgery, 17 (47.2%) achieved a pCR. Among patients who were radiographically evaluable (n = 33), 29 (87.9%) achieved some degree of radiographic tumor reduction. Within this group, 18 (54.5%) experienced tumor reductions of 30% or greater (the median change in tumor burden from baseline was −32.8%). Responses were observed regardless of tumor MCPyV, PD-L1, or TMB status.
Survival Outcomes
The median relapse-free survival was not reached for any of the patients who underwent surgery. At 12 and 24 months postoperatively, rates were 77.5% and 68.5%, respectively.
Among patients with pCR, relapse-free survival at 12 months was 100.0%, compared with 59.6% among those without pCR. At 24 months, it was 88.9% for those with pCR, vs 52.2% for those without pCR (hazard ratio [HR], 0.12; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01 – 0.93]).
Relapse-free survival was also higher for patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% in comparison with those with reduction of <30% or progression. At 12 months, it was 100.0%, vs 56.5%; at 24 months, it was 90.9%, vs 48.5% (HR, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01 – 0.87). No substantial difference was noted between patient subgroups with respect to tumor MCPyV status or PD-L1 expression.
Median overall survival was not reached in the entire cohort. At 12 and 24 months following the first dose of nivolumab, rates were 93.2% and 79.4%, respectively. For the patients who underwent surgery and were evaluable for pathologic response or radiographic response, 100.0% and 88.9% of patients with pCR and all patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% were alive at 12 and 24 months, respectively.
Overall survival rates among patients who underwent surgery were comparable in subgroups with regard to tumor MCPyV status and PD-L1 expression.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono, the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research, and the National Cancer Institute. Topalian reports relationships with Aduro, Potenza, Five Prime, Tizona, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, WindMIL, Dragonfly, ERVAXX, Trieza, Amgen, MedImmune, Merck, Compugen, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, Dynavax, Immunomic, Janssen Oncology, Immunocore, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Compugen Arbor, and NexImmune. Several coauthors have also disclosed relationships with industry.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neoadjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) could improve outcomes for patients with high-risk resectable Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), say researchers reporting the first trial in this patient population.
The results come from a cohort of 39 patients with stage IIA-IV disease, all of whom received nivolumab 240 mg intravenously on days 1 and 15, with surgery planned for day 29. About half achieved a pathologic complete response (pCR) and/or a radiographic response. Recurrence-free survival was also prolonged among responders, and no relapses were observed at a median follow-up of 19.3 months.
“Additional investigation of these promising findings is warranted,” say the investigators.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy in MCC,” said lead author Suzanne Topalian, MD, professor of surgery at the Bloomberg-Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland. “While the results seem encouraging, I think that clinical trial experience with a greater number of patients and follow-up for a longer time period will be needed to assess whether this treatment approach should become standard for high-risk resectable MCC.”
The study was published online April 23 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Rare and Aggressive Skin Cancer
MCC is a rare and aggressive neuroendocrine skin cancer that is diagnosed in approximately 1600 people each year in the United States, note the authors.
The annual incidence of new MCC cases rose by 95% between 2000 and 2013, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
Although nearly two thirds of patients present with localized disease, regional and distant metastases often occur. Until recently, cytotoxic chemotherapy was the primary systemic therapy for advanced MCC. Although patients frequently respond to chemotherapy, the duration tends to be very limited, and 95% of patients experience disease progression within 1 year, the authors comment.
Growing evidence supports the hypothesis that MCC is an immunogenic cancer. Clinical trials of PD-L1 inhibitors have demonstrated increased progression-free and overall survival compared with chemotherapy when used either in the first-line or second-line setting, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 cancer therapy is still early in development, and there are many aspects deserving careful consideration,” Topalian told Medscape Medical News. “They are centered on balancing patient risk and benefit, finding an optimal presurgical treatment interval, exploring treatment combinations, determining if anti-PD-1 therapy should be continued after surgery, and defining biomarkers to guide treatment strategies for individual patients.”
Study Details
Topian and colleagues investigated neoadjuvant use of nivolumab in the CheckMate 358 study, which involved 39 patients with stage IIA-IV MCC (of whom 36 went on to surgery).
The median age of the patients was 68 years, and at enrollment, most patients (66.7%) had stage III disease. For 35 patients, tumors were evaluable for MCPyV status; 22 (62.9%) were positive. Quantifiable tumor cell PD-L1 expression occurred in 27 patients; expression was 1% or higher for seven of those patients (25.9%).
The primary endpoint for the neoadjuvant cohort was safety and tolerability of nivolumab, as measured by treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and surgical delays, defined as the proportion of patients who experienced TRAE-related delays of more than 4 weeks from the planned surgery date.
Exploratory endpoints included pCR, radiographic response, recurrence-free survival, overall survival, association of tumor MCPyV status, and PD-L1 expression with efficacy.
The median follow-up was 20.3 months. TRAEs of any grade were reported in 18 patients (46.2%). Three (7.7%) experienced a grade 3/4 event. TRAEs with potential immunologic causes occurred in six (15.4%) patients (two TRAEs were of grade 3/4).
Among those who underwent surgery, 17 (47.2%) achieved a pCR. Among patients who were radiographically evaluable (n = 33), 29 (87.9%) achieved some degree of radiographic tumor reduction. Within this group, 18 (54.5%) experienced tumor reductions of 30% or greater (the median change in tumor burden from baseline was −32.8%). Responses were observed regardless of tumor MCPyV, PD-L1, or TMB status.
Survival Outcomes
The median relapse-free survival was not reached for any of the patients who underwent surgery. At 12 and 24 months postoperatively, rates were 77.5% and 68.5%, respectively.
Among patients with pCR, relapse-free survival at 12 months was 100.0%, compared with 59.6% among those without pCR. At 24 months, it was 88.9% for those with pCR, vs 52.2% for those without pCR (hazard ratio [HR], 0.12; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01 – 0.93]).
Relapse-free survival was also higher for patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% in comparison with those with reduction of <30% or progression. At 12 months, it was 100.0%, vs 56.5%; at 24 months, it was 90.9%, vs 48.5% (HR, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01 – 0.87). No substantial difference was noted between patient subgroups with respect to tumor MCPyV status or PD-L1 expression.
Median overall survival was not reached in the entire cohort. At 12 and 24 months following the first dose of nivolumab, rates were 93.2% and 79.4%, respectively. For the patients who underwent surgery and were evaluable for pathologic response or radiographic response, 100.0% and 88.9% of patients with pCR and all patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% were alive at 12 and 24 months, respectively.
Overall survival rates among patients who underwent surgery were comparable in subgroups with regard to tumor MCPyV status and PD-L1 expression.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono, the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research, and the National Cancer Institute. Topalian reports relationships with Aduro, Potenza, Five Prime, Tizona, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, WindMIL, Dragonfly, ERVAXX, Trieza, Amgen, MedImmune, Merck, Compugen, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, Dynavax, Immunomic, Janssen Oncology, Immunocore, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Compugen Arbor, and NexImmune. Several coauthors have also disclosed relationships with industry.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neoadjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) could improve outcomes for patients with high-risk resectable Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), say researchers reporting the first trial in this patient population.
The results come from a cohort of 39 patients with stage IIA-IV disease, all of whom received nivolumab 240 mg intravenously on days 1 and 15, with surgery planned for day 29. About half achieved a pathologic complete response (pCR) and/or a radiographic response. Recurrence-free survival was also prolonged among responders, and no relapses were observed at a median follow-up of 19.3 months.
“Additional investigation of these promising findings is warranted,” say the investigators.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy in MCC,” said lead author Suzanne Topalian, MD, professor of surgery at the Bloomberg-Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland. “While the results seem encouraging, I think that clinical trial experience with a greater number of patients and follow-up for a longer time period will be needed to assess whether this treatment approach should become standard for high-risk resectable MCC.”
The study was published online April 23 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Rare and Aggressive Skin Cancer
MCC is a rare and aggressive neuroendocrine skin cancer that is diagnosed in approximately 1600 people each year in the United States, note the authors.
The annual incidence of new MCC cases rose by 95% between 2000 and 2013, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
Although nearly two thirds of patients present with localized disease, regional and distant metastases often occur. Until recently, cytotoxic chemotherapy was the primary systemic therapy for advanced MCC. Although patients frequently respond to chemotherapy, the duration tends to be very limited, and 95% of patients experience disease progression within 1 year, the authors comment.
Growing evidence supports the hypothesis that MCC is an immunogenic cancer. Clinical trials of PD-L1 inhibitors have demonstrated increased progression-free and overall survival compared with chemotherapy when used either in the first-line or second-line setting, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 cancer therapy is still early in development, and there are many aspects deserving careful consideration,” Topalian told Medscape Medical News. “They are centered on balancing patient risk and benefit, finding an optimal presurgical treatment interval, exploring treatment combinations, determining if anti-PD-1 therapy should be continued after surgery, and defining biomarkers to guide treatment strategies for individual patients.”
Study Details
Topian and colleagues investigated neoadjuvant use of nivolumab in the CheckMate 358 study, which involved 39 patients with stage IIA-IV MCC (of whom 36 went on to surgery).
The median age of the patients was 68 years, and at enrollment, most patients (66.7%) had stage III disease. For 35 patients, tumors were evaluable for MCPyV status; 22 (62.9%) were positive. Quantifiable tumor cell PD-L1 expression occurred in 27 patients; expression was 1% or higher for seven of those patients (25.9%).
The primary endpoint for the neoadjuvant cohort was safety and tolerability of nivolumab, as measured by treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and surgical delays, defined as the proportion of patients who experienced TRAE-related delays of more than 4 weeks from the planned surgery date.
Exploratory endpoints included pCR, radiographic response, recurrence-free survival, overall survival, association of tumor MCPyV status, and PD-L1 expression with efficacy.
The median follow-up was 20.3 months. TRAEs of any grade were reported in 18 patients (46.2%). Three (7.7%) experienced a grade 3/4 event. TRAEs with potential immunologic causes occurred in six (15.4%) patients (two TRAEs were of grade 3/4).
Among those who underwent surgery, 17 (47.2%) achieved a pCR. Among patients who were radiographically evaluable (n = 33), 29 (87.9%) achieved some degree of radiographic tumor reduction. Within this group, 18 (54.5%) experienced tumor reductions of 30% or greater (the median change in tumor burden from baseline was −32.8%). Responses were observed regardless of tumor MCPyV, PD-L1, or TMB status.
Survival Outcomes
The median relapse-free survival was not reached for any of the patients who underwent surgery. At 12 and 24 months postoperatively, rates were 77.5% and 68.5%, respectively.
Among patients with pCR, relapse-free survival at 12 months was 100.0%, compared with 59.6% among those without pCR. At 24 months, it was 88.9% for those with pCR, vs 52.2% for those without pCR (hazard ratio [HR], 0.12; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01 – 0.93]).
Relapse-free survival was also higher for patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% in comparison with those with reduction of <30% or progression. At 12 months, it was 100.0%, vs 56.5%; at 24 months, it was 90.9%, vs 48.5% (HR, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01 – 0.87). No substantial difference was noted between patient subgroups with respect to tumor MCPyV status or PD-L1 expression.
Median overall survival was not reached in the entire cohort. At 12 and 24 months following the first dose of nivolumab, rates were 93.2% and 79.4%, respectively. For the patients who underwent surgery and were evaluable for pathologic response or radiographic response, 100.0% and 88.9% of patients with pCR and all patients with radiographic tumor reduction of ≥30% were alive at 12 and 24 months, respectively.
Overall survival rates among patients who underwent surgery were comparable in subgroups with regard to tumor MCPyV status and PD-L1 expression.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono, the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research, and the National Cancer Institute. Topalian reports relationships with Aduro, Potenza, Five Prime, Tizona, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, WindMIL, Dragonfly, ERVAXX, Trieza, Amgen, MedImmune, Merck, Compugen, DNAtrix, FLX Bio, Dynavax, Immunomic, Janssen Oncology, Immunocore, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Compugen Arbor, and NexImmune. Several coauthors have also disclosed relationships with industry.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Facial Malignancies in Patients Referred for Mohs Micrographic Surgery: A Retrospective Review of the Impact of Hair Growth on Tumor and Defect Size
Male facial hair trends are continuously changing and are influenced by culture, geography, religion, and ethnicity.1 Although the natural pattern of these hairs is largely androgen dependent, the phenotypic presentation often is a result of contemporary grooming practices that reflect prevailing trends.2 Beards are common throughout adulthood, and thus, preserving this facial hair pattern is considered with reconstructive techniques.3,4 Male facial skin physiology and beard hair biology are a dynamic interplay between both internal (eg, hormonal) and external (eg, shaving) variables. The density of beard hair follicles varies within different subunits, ranging between 20 and 80 follicles/cm2. Macroscopically, hairs vary in length, diameter, color, and growth rate across individuals and ethnicities.1,5
There is a paucity of literature assessing if male facial hair offers a protective role for external insults. One study utilized dosimetry to examine the effectiveness of facial hair on mannequins with varying lengths of hair in protecting against erythemal UV radiation (UVR). The authors concluded that, although facial hair provides protection from UVR, it is not significant.6 In a study of 200 male patients with
We sought to determine if facial hair growth is implicated in the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous malignancies. Specifically, we hypothesized that the presence of facial hair leads to a delay in diagnosis with increased subclinical growth given that tumors may be camouflaged and go undetected. Although there is a lack of literature, our anecdotal evidence suggests that male patients with facial hair have larger tumors compared to patients who do not regularly maintain any facial hair.
Methods
We performed a retrospective chart review following approval from the institutional review board at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. We identified all male patients with a cutaneous malignancy located on the face who were treated from January 2015 to December 2018. Photographs were reviewed and patients with tumors located within the following facial hair-bearing anatomic subunits were included: lip, melolabial fold, chin, mandible, preauricular cheek, buccal cheek, and parotid-masseteric cheek. Tumors located within the medial cheek were excluded.
Facial hair growth was determined via image review. Because biopsy photographs were not uploaded into the health record for patients who were referred externally, we reviewed all historical photographs for patients who had undergone prior Mohs micrographic surgery at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, preoperative photographs, and follow-up photographs as a proxy to determine facial hair status. Postoperative photographs taken within 2 weeks following surgery were not reviewed, as any facial hair growth was likely due to disinclination on behalf of the patient to shave near or over the incision. Age, number of days from biopsy to surgery, pathology, preoperative tumor size, number of Mohs layers, and defect size also were extrapolated from our chart review.
Statistical Analysis
Summary statistics were applied to describe demographic and clinical characteristics. An unpaired 2-tailed t test was utilized to test the null hypothesis that the mean difference was zero. The χ2 test was used for categorical variables. Results achieving P<.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
We reviewed medical records for 171 patients with facial hair and 336 patients without facial hair. The primary outcomes for this study assessed tumor and defect size in patients with facial hair compared to patients with no facial hair (Table 1). On average, patients who had facial hair were younger (67.5 years vs 74.0 years, P<.001). The median number of days from biopsy to surgery (43.0 vs 44.0 days) was comparable across both groups. The majority of patients (47%) exhibited a beard, while 30% had a mustache and 23% had a goatee. The most common tumor location was the preauricular cheek for both groups (29% and 28%, respectively). The mean preoperative tumor size in the facial hair cohort was 1.40 cm compared to 1.22 cm in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The mean number of Mohs layers in the facial hair cohort was 1.53 compared to 1.33 in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The facial hair cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (2.18 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.98 cm); however, this finding was not significant (P=.05).

We then stratified our data to analyze only lip tumors in patients with and without a mustache (Table 2). The mean preoperative tumor size in the mustache cohort was 1.10 cm compared to 0.82 cm in the group with no mustaches (P=.046). The mean number of Mohs layers in the mustache cohort was 1.57 compared to 1.42 in the group with no mustaches (P=.43). The mustache cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (1.63 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.33 cm), though this finding also did not reach significance (P=.13).

Comment
Our findings support anecdotal observations that tumors in men with facial hair are larger, require more Mohs layers, and result in larger defects compared with patients who are clean shaven. Similarly, in lip tumors, men with a mustache had a larger preoperative tumor size. Although these patients also required more Mohs layers to clear and a larger defect size, these parameters did not reach significance. These outcomes may, in part, be explained by a delay in diagnosis, as patients with facial hair may not notice any new suspicious lesions within the underlying skin as easily as patients with glabrous skin.
Although facial hair may shield skin from UVR, we agree with Parisi et al6 that this protection is marginal at best and that early persistent exposure to UVR plays a much more notable role in cutaneous carcinogenesis. As more men continue to grow facial hairstyles that emulate historical or contemporary trends, dermatologists should emphasize the risk for cutaneous malignancies within these sun-exposed areas of the face. Although some facial hair practices may reflect cultural or ethnic settings, the majority reflect a desired appearance that is achieved with grooming or otherwise.
Skin cancer screening in men with facial hair, particularly those with a strong history of UVR exposure and/or family history, should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose cutaneous tumors earlier. We encourage men with facial hair to be cognizant that cutaneous malignancies can arise within hair-bearing skin and to incorporate self–skin checks into grooming routines, which is particularly important in men with dense facial hair who forego regular self-care grooming or trim intermittently. Furthermore, we urge dermatologists to continue to thoroughly examine the underlying skin, especially in patients with full beards, during skin examinations. Diagnosing and treating cutaneous malignancies early is imperative to maximize ideal functional and cosmetic outcomes, particularly within perioral and lip subunits, where marginal millimeters can impact reconstructive complexity.
Conclusion
Men with facial hair who had cutaneous tumors in our study exhibited larger tumors, required more Mohs layers, and had a larger defect size compared to men without any facial hair growth. Similar findings also were noted when we stratified and compared lip tumors in patients with and without mustaches. Given these observations, patients and dermatologists should continue to have a high index of suspicion for any concerning lesion located within skin underlying facial hair. Regular screening in men with facial hair should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose and treat potential cutaneous tumors earlier.
- Wu Y, Konduru R, Deng D. Skin characteristics of Chinese men and their beard removal habits. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:17-21.
- Janif ZJ, Brooks RC, Dixson BJ. Negative frequency-dependent preferences and variation in male facial hair. Biol Lett. 2014;10:20130958.
- Benjegerdes KE, Jamerson J, Housewright CD. Repair of a large submental defect. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:141-143.
- Ninkovic M, Heidekruegger PI, Ehri D, et al. Beard reconstruction: a surgical algorithm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:E111-E118.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin–challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):3-9.
- Parisi AV, Turnbull DJ, Downs N, et al. Dosimetric investigation of the solar erythemal UV radiation protection provided by beards and moustaches. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2012;150:278-282.
- Liu DY, Gul MI, Wick J, et al. Long-term sheltering mustaches reduce incidence of lower lip actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1757-1758.e1.
Male facial hair trends are continuously changing and are influenced by culture, geography, religion, and ethnicity.1 Although the natural pattern of these hairs is largely androgen dependent, the phenotypic presentation often is a result of contemporary grooming practices that reflect prevailing trends.2 Beards are common throughout adulthood, and thus, preserving this facial hair pattern is considered with reconstructive techniques.3,4 Male facial skin physiology and beard hair biology are a dynamic interplay between both internal (eg, hormonal) and external (eg, shaving) variables. The density of beard hair follicles varies within different subunits, ranging between 20 and 80 follicles/cm2. Macroscopically, hairs vary in length, diameter, color, and growth rate across individuals and ethnicities.1,5
There is a paucity of literature assessing if male facial hair offers a protective role for external insults. One study utilized dosimetry to examine the effectiveness of facial hair on mannequins with varying lengths of hair in protecting against erythemal UV radiation (UVR). The authors concluded that, although facial hair provides protection from UVR, it is not significant.6 In a study of 200 male patients with
We sought to determine if facial hair growth is implicated in the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous malignancies. Specifically, we hypothesized that the presence of facial hair leads to a delay in diagnosis with increased subclinical growth given that tumors may be camouflaged and go undetected. Although there is a lack of literature, our anecdotal evidence suggests that male patients with facial hair have larger tumors compared to patients who do not regularly maintain any facial hair.
Methods
We performed a retrospective chart review following approval from the institutional review board at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. We identified all male patients with a cutaneous malignancy located on the face who were treated from January 2015 to December 2018. Photographs were reviewed and patients with tumors located within the following facial hair-bearing anatomic subunits were included: lip, melolabial fold, chin, mandible, preauricular cheek, buccal cheek, and parotid-masseteric cheek. Tumors located within the medial cheek were excluded.
Facial hair growth was determined via image review. Because biopsy photographs were not uploaded into the health record for patients who were referred externally, we reviewed all historical photographs for patients who had undergone prior Mohs micrographic surgery at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, preoperative photographs, and follow-up photographs as a proxy to determine facial hair status. Postoperative photographs taken within 2 weeks following surgery were not reviewed, as any facial hair growth was likely due to disinclination on behalf of the patient to shave near or over the incision. Age, number of days from biopsy to surgery, pathology, preoperative tumor size, number of Mohs layers, and defect size also were extrapolated from our chart review.
Statistical Analysis
Summary statistics were applied to describe demographic and clinical characteristics. An unpaired 2-tailed t test was utilized to test the null hypothesis that the mean difference was zero. The χ2 test was used for categorical variables. Results achieving P<.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
We reviewed medical records for 171 patients with facial hair and 336 patients without facial hair. The primary outcomes for this study assessed tumor and defect size in patients with facial hair compared to patients with no facial hair (Table 1). On average, patients who had facial hair were younger (67.5 years vs 74.0 years, P<.001). The median number of days from biopsy to surgery (43.0 vs 44.0 days) was comparable across both groups. The majority of patients (47%) exhibited a beard, while 30% had a mustache and 23% had a goatee. The most common tumor location was the preauricular cheek for both groups (29% and 28%, respectively). The mean preoperative tumor size in the facial hair cohort was 1.40 cm compared to 1.22 cm in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The mean number of Mohs layers in the facial hair cohort was 1.53 compared to 1.33 in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The facial hair cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (2.18 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.98 cm); however, this finding was not significant (P=.05).

We then stratified our data to analyze only lip tumors in patients with and without a mustache (Table 2). The mean preoperative tumor size in the mustache cohort was 1.10 cm compared to 0.82 cm in the group with no mustaches (P=.046). The mean number of Mohs layers in the mustache cohort was 1.57 compared to 1.42 in the group with no mustaches (P=.43). The mustache cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (1.63 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.33 cm), though this finding also did not reach significance (P=.13).

Comment
Our findings support anecdotal observations that tumors in men with facial hair are larger, require more Mohs layers, and result in larger defects compared with patients who are clean shaven. Similarly, in lip tumors, men with a mustache had a larger preoperative tumor size. Although these patients also required more Mohs layers to clear and a larger defect size, these parameters did not reach significance. These outcomes may, in part, be explained by a delay in diagnosis, as patients with facial hair may not notice any new suspicious lesions within the underlying skin as easily as patients with glabrous skin.
Although facial hair may shield skin from UVR, we agree with Parisi et al6 that this protection is marginal at best and that early persistent exposure to UVR plays a much more notable role in cutaneous carcinogenesis. As more men continue to grow facial hairstyles that emulate historical or contemporary trends, dermatologists should emphasize the risk for cutaneous malignancies within these sun-exposed areas of the face. Although some facial hair practices may reflect cultural or ethnic settings, the majority reflect a desired appearance that is achieved with grooming or otherwise.
Skin cancer screening in men with facial hair, particularly those with a strong history of UVR exposure and/or family history, should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose cutaneous tumors earlier. We encourage men with facial hair to be cognizant that cutaneous malignancies can arise within hair-bearing skin and to incorporate self–skin checks into grooming routines, which is particularly important in men with dense facial hair who forego regular self-care grooming or trim intermittently. Furthermore, we urge dermatologists to continue to thoroughly examine the underlying skin, especially in patients with full beards, during skin examinations. Diagnosing and treating cutaneous malignancies early is imperative to maximize ideal functional and cosmetic outcomes, particularly within perioral and lip subunits, where marginal millimeters can impact reconstructive complexity.
Conclusion
Men with facial hair who had cutaneous tumors in our study exhibited larger tumors, required more Mohs layers, and had a larger defect size compared to men without any facial hair growth. Similar findings also were noted when we stratified and compared lip tumors in patients with and without mustaches. Given these observations, patients and dermatologists should continue to have a high index of suspicion for any concerning lesion located within skin underlying facial hair. Regular screening in men with facial hair should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose and treat potential cutaneous tumors earlier.
Male facial hair trends are continuously changing and are influenced by culture, geography, religion, and ethnicity.1 Although the natural pattern of these hairs is largely androgen dependent, the phenotypic presentation often is a result of contemporary grooming practices that reflect prevailing trends.2 Beards are common throughout adulthood, and thus, preserving this facial hair pattern is considered with reconstructive techniques.3,4 Male facial skin physiology and beard hair biology are a dynamic interplay between both internal (eg, hormonal) and external (eg, shaving) variables. The density of beard hair follicles varies within different subunits, ranging between 20 and 80 follicles/cm2. Macroscopically, hairs vary in length, diameter, color, and growth rate across individuals and ethnicities.1,5
There is a paucity of literature assessing if male facial hair offers a protective role for external insults. One study utilized dosimetry to examine the effectiveness of facial hair on mannequins with varying lengths of hair in protecting against erythemal UV radiation (UVR). The authors concluded that, although facial hair provides protection from UVR, it is not significant.6 In a study of 200 male patients with
We sought to determine if facial hair growth is implicated in the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous malignancies. Specifically, we hypothesized that the presence of facial hair leads to a delay in diagnosis with increased subclinical growth given that tumors may be camouflaged and go undetected. Although there is a lack of literature, our anecdotal evidence suggests that male patients with facial hair have larger tumors compared to patients who do not regularly maintain any facial hair.
Methods
We performed a retrospective chart review following approval from the institutional review board at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. We identified all male patients with a cutaneous malignancy located on the face who were treated from January 2015 to December 2018. Photographs were reviewed and patients with tumors located within the following facial hair-bearing anatomic subunits were included: lip, melolabial fold, chin, mandible, preauricular cheek, buccal cheek, and parotid-masseteric cheek. Tumors located within the medial cheek were excluded.
Facial hair growth was determined via image review. Because biopsy photographs were not uploaded into the health record for patients who were referred externally, we reviewed all historical photographs for patients who had undergone prior Mohs micrographic surgery at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, preoperative photographs, and follow-up photographs as a proxy to determine facial hair status. Postoperative photographs taken within 2 weeks following surgery were not reviewed, as any facial hair growth was likely due to disinclination on behalf of the patient to shave near or over the incision. Age, number of days from biopsy to surgery, pathology, preoperative tumor size, number of Mohs layers, and defect size also were extrapolated from our chart review.
Statistical Analysis
Summary statistics were applied to describe demographic and clinical characteristics. An unpaired 2-tailed t test was utilized to test the null hypothesis that the mean difference was zero. The χ2 test was used for categorical variables. Results achieving P<.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
We reviewed medical records for 171 patients with facial hair and 336 patients without facial hair. The primary outcomes for this study assessed tumor and defect size in patients with facial hair compared to patients with no facial hair (Table 1). On average, patients who had facial hair were younger (67.5 years vs 74.0 years, P<.001). The median number of days from biopsy to surgery (43.0 vs 44.0 days) was comparable across both groups. The majority of patients (47%) exhibited a beard, while 30% had a mustache and 23% had a goatee. The most common tumor location was the preauricular cheek for both groups (29% and 28%, respectively). The mean preoperative tumor size in the facial hair cohort was 1.40 cm compared to 1.22 cm in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The mean number of Mohs layers in the facial hair cohort was 1.53 compared to 1.33 in the group with no facial hair (P=.03). The facial hair cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (2.18 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.98 cm); however, this finding was not significant (P=.05).

We then stratified our data to analyze only lip tumors in patients with and without a mustache (Table 2). The mean preoperative tumor size in the mustache cohort was 1.10 cm compared to 0.82 cm in the group with no mustaches (P=.046). The mean number of Mohs layers in the mustache cohort was 1.57 compared to 1.42 in the group with no mustaches (P=.43). The mustache cohort also had a larger mean postoperative defect size (1.63 cm) compared to the group with no facial hair (1.33 cm), though this finding also did not reach significance (P=.13).

Comment
Our findings support anecdotal observations that tumors in men with facial hair are larger, require more Mohs layers, and result in larger defects compared with patients who are clean shaven. Similarly, in lip tumors, men with a mustache had a larger preoperative tumor size. Although these patients also required more Mohs layers to clear and a larger defect size, these parameters did not reach significance. These outcomes may, in part, be explained by a delay in diagnosis, as patients with facial hair may not notice any new suspicious lesions within the underlying skin as easily as patients with glabrous skin.
Although facial hair may shield skin from UVR, we agree with Parisi et al6 that this protection is marginal at best and that early persistent exposure to UVR plays a much more notable role in cutaneous carcinogenesis. As more men continue to grow facial hairstyles that emulate historical or contemporary trends, dermatologists should emphasize the risk for cutaneous malignancies within these sun-exposed areas of the face. Although some facial hair practices may reflect cultural or ethnic settings, the majority reflect a desired appearance that is achieved with grooming or otherwise.
Skin cancer screening in men with facial hair, particularly those with a strong history of UVR exposure and/or family history, should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose cutaneous tumors earlier. We encourage men with facial hair to be cognizant that cutaneous malignancies can arise within hair-bearing skin and to incorporate self–skin checks into grooming routines, which is particularly important in men with dense facial hair who forego regular self-care grooming or trim intermittently. Furthermore, we urge dermatologists to continue to thoroughly examine the underlying skin, especially in patients with full beards, during skin examinations. Diagnosing and treating cutaneous malignancies early is imperative to maximize ideal functional and cosmetic outcomes, particularly within perioral and lip subunits, where marginal millimeters can impact reconstructive complexity.
Conclusion
Men with facial hair who had cutaneous tumors in our study exhibited larger tumors, required more Mohs layers, and had a larger defect size compared to men without any facial hair growth. Similar findings also were noted when we stratified and compared lip tumors in patients with and without mustaches. Given these observations, patients and dermatologists should continue to have a high index of suspicion for any concerning lesion located within skin underlying facial hair. Regular screening in men with facial hair should be discussed and encouraged to diagnose and treat potential cutaneous tumors earlier.
- Wu Y, Konduru R, Deng D. Skin characteristics of Chinese men and their beard removal habits. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:17-21.
- Janif ZJ, Brooks RC, Dixson BJ. Negative frequency-dependent preferences and variation in male facial hair. Biol Lett. 2014;10:20130958.
- Benjegerdes KE, Jamerson J, Housewright CD. Repair of a large submental defect. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:141-143.
- Ninkovic M, Heidekruegger PI, Ehri D, et al. Beard reconstruction: a surgical algorithm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:E111-E118.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin–challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):3-9.
- Parisi AV, Turnbull DJ, Downs N, et al. Dosimetric investigation of the solar erythemal UV radiation protection provided by beards and moustaches. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2012;150:278-282.
- Liu DY, Gul MI, Wick J, et al. Long-term sheltering mustaches reduce incidence of lower lip actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1757-1758.e1.
- Wu Y, Konduru R, Deng D. Skin characteristics of Chinese men and their beard removal habits. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:17-21.
- Janif ZJ, Brooks RC, Dixson BJ. Negative frequency-dependent preferences and variation in male facial hair. Biol Lett. 2014;10:20130958.
- Benjegerdes KE, Jamerson J, Housewright CD. Repair of a large submental defect. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:141-143.
- Ninkovic M, Heidekruegger PI, Ehri D, et al. Beard reconstruction: a surgical algorithm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:E111-E118.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin–challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):3-9.
- Parisi AV, Turnbull DJ, Downs N, et al. Dosimetric investigation of the solar erythemal UV radiation protection provided by beards and moustaches. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2012;150:278-282.
- Liu DY, Gul MI, Wick J, et al. Long-term sheltering mustaches reduce incidence of lower lip actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1757-1758.e1.
Practice Points
- In our study, men with cutaneous tumors who had facial hair exhibited larger tumors, required more Mohs layers, and had a larger defect size compared to men who do not have any facial hair growth.
- Both patients and dermatologists should have a high index of suspicion for any concerning lesion contained within skin underlying facial hair to ensure prompt diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous tumors.
CO2 Laser Ablative Fractional Resurfacing Photodynamic Therapy for Actinic Keratosis and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer: A Randomized Split-Side Study
Actinic keratosis (AK) is the most common cutaneous lesion and is regarded as a precursor to nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), particularly squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).1 Field cancerization refers to broad areas of chronically sun-exposed skin that show cumulative sun damage in the form of clinical and subclinical lesions. It is not feasible to treat large areas with multiple overt and subclinical lesions using surgical methods, and photodynamic therapy (PDT) has become a preferred method for treatment of field cancerization.2 Topical PDT uses the heme biosynthesis pathway precursors aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ALA (MAL), which localizes in the treatment area and is metabolized to protoporphyrin IX.3 After an incubation period, activation by a light source results in the formation of cytotoxic oxygen species,4 with reports of efficacy over large areas and excellent cosmetic outcomes.2
Laser ablative fractional resurfacing (AFR) also has been investigated as a treatment of AKs; CO2 laser AFR treatment resulted in a short-term reduction in the number of AK lesions and appeared to reduce the development of new lesions.5 However, case reports and small studies have indicated that pretreatment with laser AFR can increase the efficacy of PDT by creating microscopic vertical channels facilitating deeper penetration and uptake of the ALA.6 The use of erbium:YAG lasers in combination with PDT has demonstrated notable clinical and aesthetic improvements in treating basal cell carcinomas (BCCs)7 and AKs,8 with enhanced efficacy in moderate to thick AKs in particular. Hædersdal et al6 reported that CO2 laser AFR facilitated delivery of MAL into porcine skin, with AFR appearing to bypass the stratum corneum and deliver the treatment to the deep dermis.
The combination of CO2 laser AFR and PDT has shown statistically significant increases in efficacy for treatment of AKs compared to PDT alone (P<.001).9 In a small study, Alexiades10 reported a statistically significant improvement in AKs at 4 and 8 weeks posttreatment for 10 patients receiving CO2 laser AFR-PDT vs conventional PDT (P<.05). Studies of organ transplant recipients—who are at higher risk for AK and NMSC development—demonstrated favorable results for combined CO2 laser AFR and PDT vs either laser treatment11 or PDT9,12 alone, with significant reductions in the number of AKs (P=.002). Results were maintained for 3 to 4 months after treatment. Additional studies have shown that combining CO2 laser AFR and PDT may reduce the PDT incubation time or number of treatments required to achieve a response over conventional PDT.13,14
Our proof-of-concept study was designed to assess efficacy of CO2 laser AFR to enhance an approved drug delivery system in the treatment of AK and NMSC. The objective was to compare effect and durability of AFR-PDT vs standard ALA-PDT in the treatment of AK and NMSCs in a split-sided study of various body locations.
Methods
This randomized, split-sided study compared CO2 laser AFR-PDT to standard ALA-PDT for the treatment of AK and NMSC conducted at 1 site in Los Gatos, California. Patients who had a skin cancer screening and received a biopsy diagnosis of AK or NMSC were invited to attend an enrollment visit. Key inclusion criteria for enrollment were male or female patients aged 40 to 85 years with notable symmetrically comparable photodamage (at least 1 AK per square centimeter) in 1 or more skin areas—scalp, face, or distal extremities—with presence of clinically identifiable NMSCs proven by biopsy. Key exclusion criteria were patients who were pregnant; patients with epilepsy, seizures, or a photosensitive disorder; those taking photosensitizing medication (eg, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide); or immunocompromised patients. The study was approved by an institutional review board (Salus IRB [Austin, Texas]), and each participant underwent a complete and informed consent process.
Laterality for pretreatment with AFR followed by ALA-PDT vs ALA-PDT alone was determined at the time of treatment using a computer-based random number generator; even numbers resulted in pretreatment of the right side, and odd numbers resulted in pretreatment of the left side. Because of the difference in pretreatment methods for the 2 sides, it was not possible to perform the procedure under blinded conditions.
The treatment area was prepared by defatting the entire site with 70% isopropyl alcohol, followed by benzalkonium chloride antibacterial cleansing for the AFR pretreatment side. A 7% lidocaine/7% tetracaine ointment was applied under polyethylene wrap occlusion to the AFR pretreatment side for 20 minutes. Additionally, nerve blocks and field blocks with a mixture of 1.1% lidocaine with epinephrine/0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine were performed wherever feasible. After 20 minutes, the lidocaine-tetracaine ointment was removed with isopropanol, and AFR treatment commenced immediately with the SmartXide DOT laser (DEKA)(1 pass of 25 W, 1200-microsecond duration at 500-µm spacing, 200-µm spot size, achieving 12% surface area ablation). Hyperkeratotic treated areas were debrided with saline and received a second pass with the laser. Aminolevulinic acid solution 20% (Levulan Kerastick; DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc)15 was applied to both sides of the treatment area and allowed to absorb for a 1-hour incubation period, which was followed by blue-light exposure at a power density of 10 mW/cm2 for 16 minutes and 40 seconds using the BLU-U Photodynamic Therapy Illuminator (DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc). Areas treated with AFR were then covered with a layer of Aquaphor ointment (Beiersdorf, Inc) and an absorptive hydrogel dressing for48 to 96 hours, with continued application of the ointment until resolution of all crusting. After treatment, patients were instructed to avoid direct sun exposure, wear a hat or visor for the first 2 weeks posttreatment when outdoors, and apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor greater than 30 once skin had healed.
Follow-up was conducted at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the PDT procedure. The primary end points were clinical clearance of NMSC lesions at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment and histological clearance at 6 months. Secondary end points assessed quality of life and functional improvements.
Results
Twenty-four potential participants experiencing AKs and/or NMSCs were screened for the study, with 19 meeting inclusion criteria. All participants were white, non-Hispanic, and had Fitzpatrick skin types I or II. Treated areas for all participants had field cancerization defined as at least 1 AK per square centimeter. All 19 participants enrolled in the study completed the posttreatment evaluations up to 6 months. All AFR-pretreated sites showed superior results in reduction in number, size, or hyperkeratosis of AKs at all follow-up visits, with a complete absence of new AK formation at the 6-month follow-up (Table). Conversely, sites treated with standard PDT only showed some recurrence of AKs at 6 months. Of the 3 participants who had biopsy-confirmed BCCs on the AFR-pretreated side, there were 3 persistent lesions after treatment at the 6-month visit. Two participants experienced persistence of a confirmed SCC in situ that was on the laser-pretreated side only (1 on the forehead and 1 on the hand), whereas 1 participant with an SCC on the leg at baseline had no recurrence at 6 months. A participant who received treatment on the lower lip had persistence of actinic cheilitis on both the AFR- and non–AFR-treated sides of the lip.
Scalp and facial sites healed fully in an average of 7 days, whereas upper extremities—forearm and hands—took approximately 14 days to heal completely. Lower extremity AFR-pretreated sites exhibited substantial weeping, resulting in prolonged healing of approximately 21 days for resolution of all scabbing.
Comment
In this split-sided study in patients with field cancerization, the use of CO2 laser AFR before treatment with PDT increased AK lesion clearance compared to ALA-PDT alone. Prior studies of fractional laser–assisted drug delivery on porcine skin using topical MAL showed that laser channels approximately 3-mm apart were able to distribute protoporphyrin through the entire skin.6 The ablative nature of AFR theoretically provides deeper and more effusive penetration of the ALA solution than using conventional PDT or erbium:YAG lasers with PDT.7,8 Helsing et al11 applied CO2 laser AFR MAL-PDT to AKs in organ transplant recipients and obtained complete responses in 73% of patients compared to a complete response of 31% for AFR alone. The results reported in our study are consistent with Helsing et al,11 showing a complete clinical response for 14 of 19 patients (74%), of whom 4 (21%) had no recurrence of NMSC and 10 (53%) had no recurrence of AK on the AFR-PDT–treated side.
The pretreatment process required for the laser AFR added time to the initial visit compared to conventional PDT, which is balanced by a reduced PDT incubation time (1 hour vs the approved indication of 14–18 hours for face/scalp or 3 hours for upper extremities under occlusion). The use of microneedling as an alternative pretreatment procedure before PDT also has been investigated, with the aim of decreasing the optimum ALA absorption time. The mean reduction in AKs (89.3%) was significantly greater than for PDT alone (69.5%; P<.05) in a small study by Spencer and Freeman.18 Although microneedling is less time-intensive and labor-intensive than laser AFR, the photocoagulative effect and subsequent microhemorrhages resulting from AFR should result in much deeper penetration of ALA solution than for microneedling.
The limitations of this proof-of-concept study arose from the small sample size of 19 participants and the short follow-up period of 6 months. Furthermore, the unblinded nature of the study could create selection, detection, or reporting bias. Further follow-up appointments would aid in determining the longevity of results, which may encourage future use of this technique, despite the time-consuming preparation. A larger study with follow-up greater than 1 year would be beneficial, particularly for monitoring remission from SCCs and BCCs.
Conclusion
Pretreatment with CO2 laser AFR before ALA-PDT provided superior clearance of AKs and thin NMSCs at 6 months compared to ALA-PDT alone (Figure). Additionally, the incubation period for ALA absorption can be reduced before PDT, leading to a shorter treatment time overall. The benefits of AFR pretreatment on AK clearance demonstrated in this study warrant further investigation in a larger trial with a longer follow-up period to monitor maintenance of response.
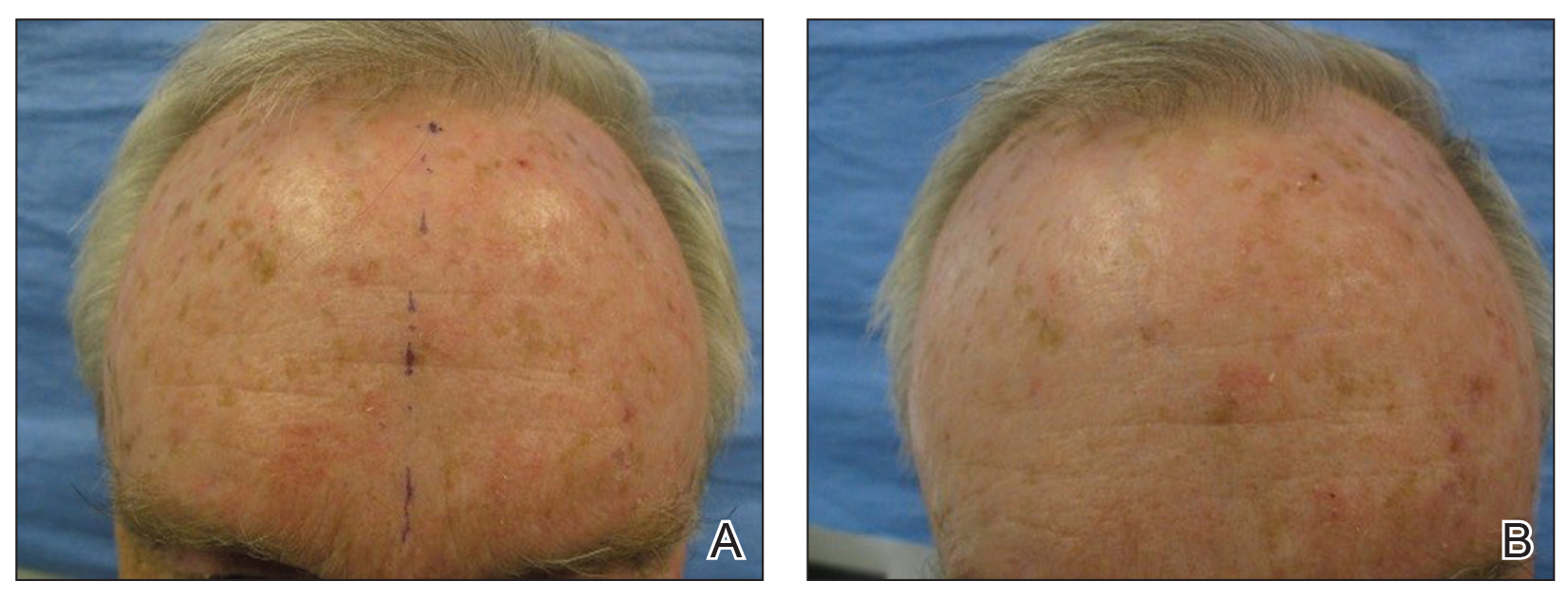
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who participated in this study. Editorial assistance was provided by Louise Gildea, PhD, of JK Associates Inc, part of the Fishawack Group of Companies (Fishawack, United Kingdom), funded by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Morton CA, McKenna KE, Rhodes LE. Guidelines for topical photodynamic therapy: update. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:1245-1266.
- Casas A, Fukuda H, Di Venosa G, et al. Photosensitization and mechanism of cytotoxicity induced by the use of ALA derivatives in photodynamic therapy. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:279-284.
- Klotz LO, Fritsch C, Briviba K, et al. Activation of JNK and p38 but not ERK MAP kinases in human skin cells by 5-aminolevulinate-photodynamic therapy. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4297-4300.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Hædersdal M, Sakamoto FH, Farinelli WA, et al. Fractional CO(2) laser-assisted drug delivery. Lasers Surg Med. 2010;42:113-122.
- Šmucler R, Vlk M. Combination of Er:YAG laser and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of nodular basal cell carcinoma. Lasers Surg Med. 2008;40:153-158.
- Ko DY, Jeon SY, Kim KH, et al. Fractional erbium:YAG laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for facial actinic keratoses: a randomized, comparative, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1529-1539.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Alexiades M. Randomized, controlled trial of fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing followed by ultrashort incubation aminolevulinic acid blue light photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1053-1064.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Jang YH, Lee DJ, Shin J, et al. Photodynamic therapy with ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser in treatment of actinic keratosis. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:417-422.
- Song HS, Jung SE, Jang YH, et al. Fractional carbon dioxide laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for patients with actinic keratosis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:296-301.
- ALA Kerastick (aminolevulinic acid HCl) for topical solution, 20% [package insert]. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2010.
- Data on file. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
- Campbell TM, Goldman MP. Adverse events of fractionated carbon dioxide laser: review of 373 treatments. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1645-1650.
- Spencer JM, Freeman SA. Microneedling prior to Levulan PDT for the treatment of actinic keratoses: a split-face, blinded trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1072-1074.
Actinic keratosis (AK) is the most common cutaneous lesion and is regarded as a precursor to nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), particularly squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).1 Field cancerization refers to broad areas of chronically sun-exposed skin that show cumulative sun damage in the form of clinical and subclinical lesions. It is not feasible to treat large areas with multiple overt and subclinical lesions using surgical methods, and photodynamic therapy (PDT) has become a preferred method for treatment of field cancerization.2 Topical PDT uses the heme biosynthesis pathway precursors aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ALA (MAL), which localizes in the treatment area and is metabolized to protoporphyrin IX.3 After an incubation period, activation by a light source results in the formation of cytotoxic oxygen species,4 with reports of efficacy over large areas and excellent cosmetic outcomes.2
Laser ablative fractional resurfacing (AFR) also has been investigated as a treatment of AKs; CO2 laser AFR treatment resulted in a short-term reduction in the number of AK lesions and appeared to reduce the development of new lesions.5 However, case reports and small studies have indicated that pretreatment with laser AFR can increase the efficacy of PDT by creating microscopic vertical channels facilitating deeper penetration and uptake of the ALA.6 The use of erbium:YAG lasers in combination with PDT has demonstrated notable clinical and aesthetic improvements in treating basal cell carcinomas (BCCs)7 and AKs,8 with enhanced efficacy in moderate to thick AKs in particular. Hædersdal et al6 reported that CO2 laser AFR facilitated delivery of MAL into porcine skin, with AFR appearing to bypass the stratum corneum and deliver the treatment to the deep dermis.
The combination of CO2 laser AFR and PDT has shown statistically significant increases in efficacy for treatment of AKs compared to PDT alone (P<.001).9 In a small study, Alexiades10 reported a statistically significant improvement in AKs at 4 and 8 weeks posttreatment for 10 patients receiving CO2 laser AFR-PDT vs conventional PDT (P<.05). Studies of organ transplant recipients—who are at higher risk for AK and NMSC development—demonstrated favorable results for combined CO2 laser AFR and PDT vs either laser treatment11 or PDT9,12 alone, with significant reductions in the number of AKs (P=.002). Results were maintained for 3 to 4 months after treatment. Additional studies have shown that combining CO2 laser AFR and PDT may reduce the PDT incubation time or number of treatments required to achieve a response over conventional PDT.13,14
Our proof-of-concept study was designed to assess efficacy of CO2 laser AFR to enhance an approved drug delivery system in the treatment of AK and NMSC. The objective was to compare effect and durability of AFR-PDT vs standard ALA-PDT in the treatment of AK and NMSCs in a split-sided study of various body locations.
Methods
This randomized, split-sided study compared CO2 laser AFR-PDT to standard ALA-PDT for the treatment of AK and NMSC conducted at 1 site in Los Gatos, California. Patients who had a skin cancer screening and received a biopsy diagnosis of AK or NMSC were invited to attend an enrollment visit. Key inclusion criteria for enrollment were male or female patients aged 40 to 85 years with notable symmetrically comparable photodamage (at least 1 AK per square centimeter) in 1 or more skin areas—scalp, face, or distal extremities—with presence of clinically identifiable NMSCs proven by biopsy. Key exclusion criteria were patients who were pregnant; patients with epilepsy, seizures, or a photosensitive disorder; those taking photosensitizing medication (eg, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide); or immunocompromised patients. The study was approved by an institutional review board (Salus IRB [Austin, Texas]), and each participant underwent a complete and informed consent process.
Laterality for pretreatment with AFR followed by ALA-PDT vs ALA-PDT alone was determined at the time of treatment using a computer-based random number generator; even numbers resulted in pretreatment of the right side, and odd numbers resulted in pretreatment of the left side. Because of the difference in pretreatment methods for the 2 sides, it was not possible to perform the procedure under blinded conditions.
The treatment area was prepared by defatting the entire site with 70% isopropyl alcohol, followed by benzalkonium chloride antibacterial cleansing for the AFR pretreatment side. A 7% lidocaine/7% tetracaine ointment was applied under polyethylene wrap occlusion to the AFR pretreatment side for 20 minutes. Additionally, nerve blocks and field blocks with a mixture of 1.1% lidocaine with epinephrine/0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine were performed wherever feasible. After 20 minutes, the lidocaine-tetracaine ointment was removed with isopropanol, and AFR treatment commenced immediately with the SmartXide DOT laser (DEKA)(1 pass of 25 W, 1200-microsecond duration at 500-µm spacing, 200-µm spot size, achieving 12% surface area ablation). Hyperkeratotic treated areas were debrided with saline and received a second pass with the laser. Aminolevulinic acid solution 20% (Levulan Kerastick; DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc)15 was applied to both sides of the treatment area and allowed to absorb for a 1-hour incubation period, which was followed by blue-light exposure at a power density of 10 mW/cm2 for 16 minutes and 40 seconds using the BLU-U Photodynamic Therapy Illuminator (DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc). Areas treated with AFR were then covered with a layer of Aquaphor ointment (Beiersdorf, Inc) and an absorptive hydrogel dressing for48 to 96 hours, with continued application of the ointment until resolution of all crusting. After treatment, patients were instructed to avoid direct sun exposure, wear a hat or visor for the first 2 weeks posttreatment when outdoors, and apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor greater than 30 once skin had healed.
Follow-up was conducted at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the PDT procedure. The primary end points were clinical clearance of NMSC lesions at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment and histological clearance at 6 months. Secondary end points assessed quality of life and functional improvements.
Results
Twenty-four potential participants experiencing AKs and/or NMSCs were screened for the study, with 19 meeting inclusion criteria. All participants were white, non-Hispanic, and had Fitzpatrick skin types I or II. Treated areas for all participants had field cancerization defined as at least 1 AK per square centimeter. All 19 participants enrolled in the study completed the posttreatment evaluations up to 6 months. All AFR-pretreated sites showed superior results in reduction in number, size, or hyperkeratosis of AKs at all follow-up visits, with a complete absence of new AK formation at the 6-month follow-up (Table). Conversely, sites treated with standard PDT only showed some recurrence of AKs at 6 months. Of the 3 participants who had biopsy-confirmed BCCs on the AFR-pretreated side, there were 3 persistent lesions after treatment at the 6-month visit. Two participants experienced persistence of a confirmed SCC in situ that was on the laser-pretreated side only (1 on the forehead and 1 on the hand), whereas 1 participant with an SCC on the leg at baseline had no recurrence at 6 months. A participant who received treatment on the lower lip had persistence of actinic cheilitis on both the AFR- and non–AFR-treated sides of the lip.

Scalp and facial sites healed fully in an average of 7 days, whereas upper extremities—forearm and hands—took approximately 14 days to heal completely. Lower extremity AFR-pretreated sites exhibited substantial weeping, resulting in prolonged healing of approximately 21 days for resolution of all scabbing.
Comment
In this split-sided study in patients with field cancerization, the use of CO2 laser AFR before treatment with PDT increased AK lesion clearance compared to ALA-PDT alone. Prior studies of fractional laser–assisted drug delivery on porcine skin using topical MAL showed that laser channels approximately 3-mm apart were able to distribute protoporphyrin through the entire skin.6 The ablative nature of AFR theoretically provides deeper and more effusive penetration of the ALA solution than using conventional PDT or erbium:YAG lasers with PDT.7,8 Helsing et al11 applied CO2 laser AFR MAL-PDT to AKs in organ transplant recipients and obtained complete responses in 73% of patients compared to a complete response of 31% for AFR alone. The results reported in our study are consistent with Helsing et al,11 showing a complete clinical response for 14 of 19 patients (74%), of whom 4 (21%) had no recurrence of NMSC and 10 (53%) had no recurrence of AK on the AFR-PDT–treated side.
The pretreatment process required for the laser AFR added time to the initial visit compared to conventional PDT, which is balanced by a reduced PDT incubation time (1 hour vs the approved indication of 14–18 hours for face/scalp or 3 hours for upper extremities under occlusion). The use of microneedling as an alternative pretreatment procedure before PDT also has been investigated, with the aim of decreasing the optimum ALA absorption time. The mean reduction in AKs (89.3%) was significantly greater than for PDT alone (69.5%; P<.05) in a small study by Spencer and Freeman.18 Although microneedling is less time-intensive and labor-intensive than laser AFR, the photocoagulative effect and subsequent microhemorrhages resulting from AFR should result in much deeper penetration of ALA solution than for microneedling.
The limitations of this proof-of-concept study arose from the small sample size of 19 participants and the short follow-up period of 6 months. Furthermore, the unblinded nature of the study could create selection, detection, or reporting bias. Further follow-up appointments would aid in determining the longevity of results, which may encourage future use of this technique, despite the time-consuming preparation. A larger study with follow-up greater than 1 year would be beneficial, particularly for monitoring remission from SCCs and BCCs.
Conclusion
Pretreatment with CO2 laser AFR before ALA-PDT provided superior clearance of AKs and thin NMSCs at 6 months compared to ALA-PDT alone (Figure). Additionally, the incubation period for ALA absorption can be reduced before PDT, leading to a shorter treatment time overall. The benefits of AFR pretreatment on AK clearance demonstrated in this study warrant further investigation in a larger trial with a longer follow-up period to monitor maintenance of response.

Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who participated in this study. Editorial assistance was provided by Louise Gildea, PhD, of JK Associates Inc, part of the Fishawack Group of Companies (Fishawack, United Kingdom), funded by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
Actinic keratosis (AK) is the most common cutaneous lesion and is regarded as a precursor to nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), particularly squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).1 Field cancerization refers to broad areas of chronically sun-exposed skin that show cumulative sun damage in the form of clinical and subclinical lesions. It is not feasible to treat large areas with multiple overt and subclinical lesions using surgical methods, and photodynamic therapy (PDT) has become a preferred method for treatment of field cancerization.2 Topical PDT uses the heme biosynthesis pathway precursors aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ALA (MAL), which localizes in the treatment area and is metabolized to protoporphyrin IX.3 After an incubation period, activation by a light source results in the formation of cytotoxic oxygen species,4 with reports of efficacy over large areas and excellent cosmetic outcomes.2
Laser ablative fractional resurfacing (AFR) also has been investigated as a treatment of AKs; CO2 laser AFR treatment resulted in a short-term reduction in the number of AK lesions and appeared to reduce the development of new lesions.5 However, case reports and small studies have indicated that pretreatment with laser AFR can increase the efficacy of PDT by creating microscopic vertical channels facilitating deeper penetration and uptake of the ALA.6 The use of erbium:YAG lasers in combination with PDT has demonstrated notable clinical and aesthetic improvements in treating basal cell carcinomas (BCCs)7 and AKs,8 with enhanced efficacy in moderate to thick AKs in particular. Hædersdal et al6 reported that CO2 laser AFR facilitated delivery of MAL into porcine skin, with AFR appearing to bypass the stratum corneum and deliver the treatment to the deep dermis.
The combination of CO2 laser AFR and PDT has shown statistically significant increases in efficacy for treatment of AKs compared to PDT alone (P<.001).9 In a small study, Alexiades10 reported a statistically significant improvement in AKs at 4 and 8 weeks posttreatment for 10 patients receiving CO2 laser AFR-PDT vs conventional PDT (P<.05). Studies of organ transplant recipients—who are at higher risk for AK and NMSC development—demonstrated favorable results for combined CO2 laser AFR and PDT vs either laser treatment11 or PDT9,12 alone, with significant reductions in the number of AKs (P=.002). Results were maintained for 3 to 4 months after treatment. Additional studies have shown that combining CO2 laser AFR and PDT may reduce the PDT incubation time or number of treatments required to achieve a response over conventional PDT.13,14
Our proof-of-concept study was designed to assess efficacy of CO2 laser AFR to enhance an approved drug delivery system in the treatment of AK and NMSC. The objective was to compare effect and durability of AFR-PDT vs standard ALA-PDT in the treatment of AK and NMSCs in a split-sided study of various body locations.
Methods
This randomized, split-sided study compared CO2 laser AFR-PDT to standard ALA-PDT for the treatment of AK and NMSC conducted at 1 site in Los Gatos, California. Patients who had a skin cancer screening and received a biopsy diagnosis of AK or NMSC were invited to attend an enrollment visit. Key inclusion criteria for enrollment were male or female patients aged 40 to 85 years with notable symmetrically comparable photodamage (at least 1 AK per square centimeter) in 1 or more skin areas—scalp, face, or distal extremities—with presence of clinically identifiable NMSCs proven by biopsy. Key exclusion criteria were patients who were pregnant; patients with epilepsy, seizures, or a photosensitive disorder; those taking photosensitizing medication (eg, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide); or immunocompromised patients. The study was approved by an institutional review board (Salus IRB [Austin, Texas]), and each participant underwent a complete and informed consent process.
Laterality for pretreatment with AFR followed by ALA-PDT vs ALA-PDT alone was determined at the time of treatment using a computer-based random number generator; even numbers resulted in pretreatment of the right side, and odd numbers resulted in pretreatment of the left side. Because of the difference in pretreatment methods for the 2 sides, it was not possible to perform the procedure under blinded conditions.
The treatment area was prepared by defatting the entire site with 70% isopropyl alcohol, followed by benzalkonium chloride antibacterial cleansing for the AFR pretreatment side. A 7% lidocaine/7% tetracaine ointment was applied under polyethylene wrap occlusion to the AFR pretreatment side for 20 minutes. Additionally, nerve blocks and field blocks with a mixture of 1.1% lidocaine with epinephrine/0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine were performed wherever feasible. After 20 minutes, the lidocaine-tetracaine ointment was removed with isopropanol, and AFR treatment commenced immediately with the SmartXide DOT laser (DEKA)(1 pass of 25 W, 1200-microsecond duration at 500-µm spacing, 200-µm spot size, achieving 12% surface area ablation). Hyperkeratotic treated areas were debrided with saline and received a second pass with the laser. Aminolevulinic acid solution 20% (Levulan Kerastick; DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc)15 was applied to both sides of the treatment area and allowed to absorb for a 1-hour incubation period, which was followed by blue-light exposure at a power density of 10 mW/cm2 for 16 minutes and 40 seconds using the BLU-U Photodynamic Therapy Illuminator (DUSA Pharmaceuticals, Inc). Areas treated with AFR were then covered with a layer of Aquaphor ointment (Beiersdorf, Inc) and an absorptive hydrogel dressing for48 to 96 hours, with continued application of the ointment until resolution of all crusting. After treatment, patients were instructed to avoid direct sun exposure, wear a hat or visor for the first 2 weeks posttreatment when outdoors, and apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor greater than 30 once skin had healed.
Follow-up was conducted at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the PDT procedure. The primary end points were clinical clearance of NMSC lesions at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment and histological clearance at 6 months. Secondary end points assessed quality of life and functional improvements.
Results
Twenty-four potential participants experiencing AKs and/or NMSCs were screened for the study, with 19 meeting inclusion criteria. All participants were white, non-Hispanic, and had Fitzpatrick skin types I or II. Treated areas for all participants had field cancerization defined as at least 1 AK per square centimeter. All 19 participants enrolled in the study completed the posttreatment evaluations up to 6 months. All AFR-pretreated sites showed superior results in reduction in number, size, or hyperkeratosis of AKs at all follow-up visits, with a complete absence of new AK formation at the 6-month follow-up (Table). Conversely, sites treated with standard PDT only showed some recurrence of AKs at 6 months. Of the 3 participants who had biopsy-confirmed BCCs on the AFR-pretreated side, there were 3 persistent lesions after treatment at the 6-month visit. Two participants experienced persistence of a confirmed SCC in situ that was on the laser-pretreated side only (1 on the forehead and 1 on the hand), whereas 1 participant with an SCC on the leg at baseline had no recurrence at 6 months. A participant who received treatment on the lower lip had persistence of actinic cheilitis on both the AFR- and non–AFR-treated sides of the lip.

Scalp and facial sites healed fully in an average of 7 days, whereas upper extremities—forearm and hands—took approximately 14 days to heal completely. Lower extremity AFR-pretreated sites exhibited substantial weeping, resulting in prolonged healing of approximately 21 days for resolution of all scabbing.
Comment
In this split-sided study in patients with field cancerization, the use of CO2 laser AFR before treatment with PDT increased AK lesion clearance compared to ALA-PDT alone. Prior studies of fractional laser–assisted drug delivery on porcine skin using topical MAL showed that laser channels approximately 3-mm apart were able to distribute protoporphyrin through the entire skin.6 The ablative nature of AFR theoretically provides deeper and more effusive penetration of the ALA solution than using conventional PDT or erbium:YAG lasers with PDT.7,8 Helsing et al11 applied CO2 laser AFR MAL-PDT to AKs in organ transplant recipients and obtained complete responses in 73% of patients compared to a complete response of 31% for AFR alone. The results reported in our study are consistent with Helsing et al,11 showing a complete clinical response for 14 of 19 patients (74%), of whom 4 (21%) had no recurrence of NMSC and 10 (53%) had no recurrence of AK on the AFR-PDT–treated side.
The pretreatment process required for the laser AFR added time to the initial visit compared to conventional PDT, which is balanced by a reduced PDT incubation time (1 hour vs the approved indication of 14–18 hours for face/scalp or 3 hours for upper extremities under occlusion). The use of microneedling as an alternative pretreatment procedure before PDT also has been investigated, with the aim of decreasing the optimum ALA absorption time. The mean reduction in AKs (89.3%) was significantly greater than for PDT alone (69.5%; P<.05) in a small study by Spencer and Freeman.18 Although microneedling is less time-intensive and labor-intensive than laser AFR, the photocoagulative effect and subsequent microhemorrhages resulting from AFR should result in much deeper penetration of ALA solution than for microneedling.
The limitations of this proof-of-concept study arose from the small sample size of 19 participants and the short follow-up period of 6 months. Furthermore, the unblinded nature of the study could create selection, detection, or reporting bias. Further follow-up appointments would aid in determining the longevity of results, which may encourage future use of this technique, despite the time-consuming preparation. A larger study with follow-up greater than 1 year would be beneficial, particularly for monitoring remission from SCCs and BCCs.
Conclusion
Pretreatment with CO2 laser AFR before ALA-PDT provided superior clearance of AKs and thin NMSCs at 6 months compared to ALA-PDT alone (Figure). Additionally, the incubation period for ALA absorption can be reduced before PDT, leading to a shorter treatment time overall. The benefits of AFR pretreatment on AK clearance demonstrated in this study warrant further investigation in a larger trial with a longer follow-up period to monitor maintenance of response.

Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who participated in this study. Editorial assistance was provided by Louise Gildea, PhD, of JK Associates Inc, part of the Fishawack Group of Companies (Fishawack, United Kingdom), funded by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Morton CA, McKenna KE, Rhodes LE. Guidelines for topical photodynamic therapy: update. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:1245-1266.
- Casas A, Fukuda H, Di Venosa G, et al. Photosensitization and mechanism of cytotoxicity induced by the use of ALA derivatives in photodynamic therapy. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:279-284.
- Klotz LO, Fritsch C, Briviba K, et al. Activation of JNK and p38 but not ERK MAP kinases in human skin cells by 5-aminolevulinate-photodynamic therapy. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4297-4300.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Hædersdal M, Sakamoto FH, Farinelli WA, et al. Fractional CO(2) laser-assisted drug delivery. Lasers Surg Med. 2010;42:113-122.
- Šmucler R, Vlk M. Combination of Er:YAG laser and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of nodular basal cell carcinoma. Lasers Surg Med. 2008;40:153-158.
- Ko DY, Jeon SY, Kim KH, et al. Fractional erbium:YAG laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for facial actinic keratoses: a randomized, comparative, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1529-1539.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Alexiades M. Randomized, controlled trial of fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing followed by ultrashort incubation aminolevulinic acid blue light photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1053-1064.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Jang YH, Lee DJ, Shin J, et al. Photodynamic therapy with ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser in treatment of actinic keratosis. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:417-422.
- Song HS, Jung SE, Jang YH, et al. Fractional carbon dioxide laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for patients with actinic keratosis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:296-301.
- ALA Kerastick (aminolevulinic acid HCl) for topical solution, 20% [package insert]. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2010.
- Data on file. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
- Campbell TM, Goldman MP. Adverse events of fractionated carbon dioxide laser: review of 373 treatments. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1645-1650.
- Spencer JM, Freeman SA. Microneedling prior to Levulan PDT for the treatment of actinic keratoses: a split-face, blinded trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1072-1074.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Morton CA, McKenna KE, Rhodes LE. Guidelines for topical photodynamic therapy: update. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:1245-1266.
- Casas A, Fukuda H, Di Venosa G, et al. Photosensitization and mechanism of cytotoxicity induced by the use of ALA derivatives in photodynamic therapy. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:279-284.
- Klotz LO, Fritsch C, Briviba K, et al. Activation of JNK and p38 but not ERK MAP kinases in human skin cells by 5-aminolevulinate-photodynamic therapy. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4297-4300.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Hædersdal M, Sakamoto FH, Farinelli WA, et al. Fractional CO(2) laser-assisted drug delivery. Lasers Surg Med. 2010;42:113-122.
- Šmucler R, Vlk M. Combination of Er:YAG laser and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of nodular basal cell carcinoma. Lasers Surg Med. 2008;40:153-158.
- Ko DY, Jeon SY, Kim KH, et al. Fractional erbium:YAG laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for facial actinic keratoses: a randomized, comparative, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1529-1539.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Alexiades M. Randomized, controlled trial of fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing followed by ultrashort incubation aminolevulinic acid blue light photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1053-1064.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Jang YH, Lee DJ, Shin J, et al. Photodynamic therapy with ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser in treatment of actinic keratosis. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:417-422.
- Song HS, Jung SE, Jang YH, et al. Fractional carbon dioxide laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for patients with actinic keratosis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:296-301.
- ALA Kerastick (aminolevulinic acid HCl) for topical solution, 20% [package insert]. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2010.
- Data on file. Wilmington, MA: DUSA Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
- Campbell TM, Goldman MP. Adverse events of fractionated carbon dioxide laser: review of 373 treatments. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1645-1650.
- Spencer JM, Freeman SA. Microneedling prior to Levulan PDT for the treatment of actinic keratoses: a split-face, blinded trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1072-1074.
Practice Points
- Pretreatment with CO2 laser ablative fractional resurfacing (AFR) before photodynamic therapy (PDT) provided efficient clearance of actinic keratosis (AK).
- Superior clearance of lesions was seen at 6 months for AK and thin nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) on pretreated sites compared to PDT alone, with no novel adverse events reported.
- A reduced incubation period for aminolevulinic acid (ALA) absorption before PDT was used, leading to a shorter overall treatment time.