User login
Psoriasiform Dermatitis Associated With the Moderna COVID-19 Messenger RNA Vaccine
To the Editor:
The Moderna COVID-19 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine was authorized for use on December 18, 2020, with the second dose beginning on January 15, 2021.1-3 Some individuals who received the Moderna vaccine experienced an intense rash known as “COVID arm,” a harmless but bothersome adverse effect that typically appears within a week and is a localized and transient immunogenic response.4 COVID arm differs from most vaccine adverse effects. The rash emerges not immediately but 5 to 9 days after the initial dose—on average, 1 week later. Apart from being itchy, the rash does not appear to be harmful and is not a reason to hesitate getting vaccinated.
Dermatologists and allergists have been studying this adverse effect, which has been formally termed delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity. Of potential clinical consequence is that the efficacy of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine may be harmed if postvaccination dermal reactions necessitate systemic corticosteroid therapy. Because this vaccine stimulates an immune response as viral RNA integrates in cells secondary to production of the spike protein of the virus, the skin may be affected secondarily and manifestations of any underlying disease may be aggravated.5 We report a patient who developed a psoriasiform dermatitis after the first dose of the Moderna vaccine.
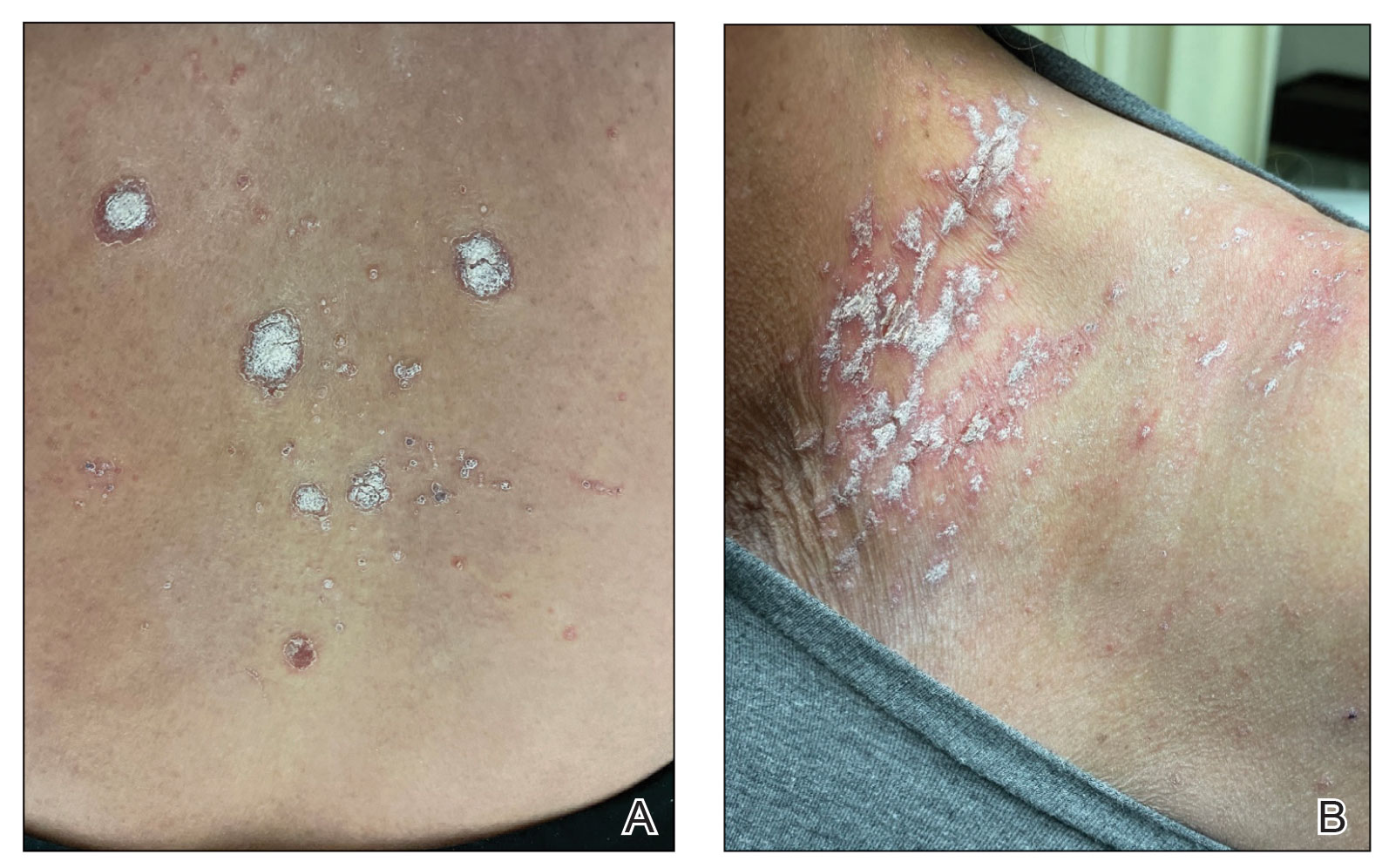
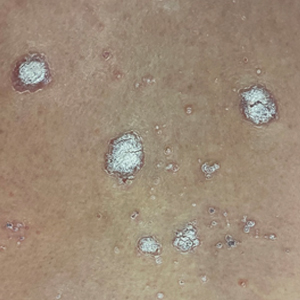
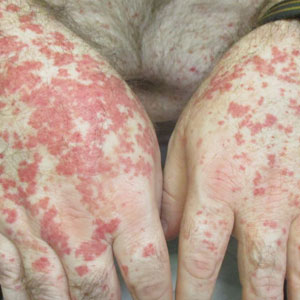
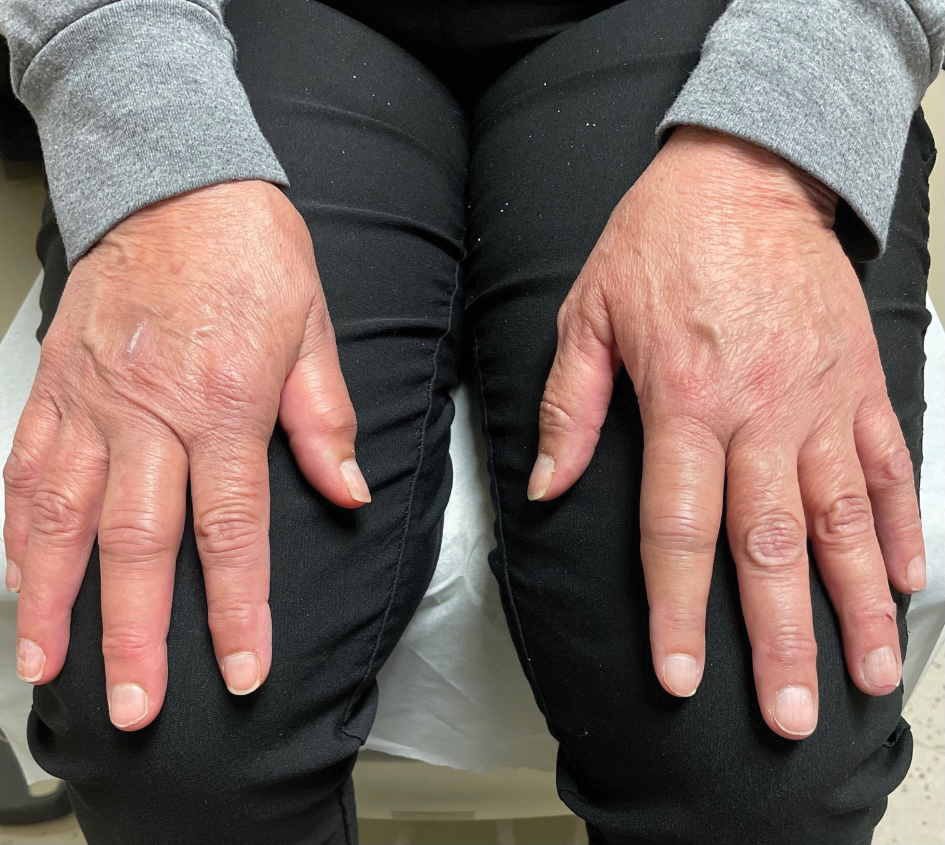
A 65-year-old woman presented to her primary care physician because of the severity of psoriasiform dermatitis that developed 5 days after she received the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. The patient had a medical history of Sjögren syndrome. Her medication history was negative, and her family history was negative for autoimmune disease. Physical examination by primary care revealed an erythematous scaly rash with plaques and papules on the neck and back (Figure 1). The patient presented again to primary care 2 days later with swollen, painful, discolored digits (Figure 2) and a stiff, sore neck.
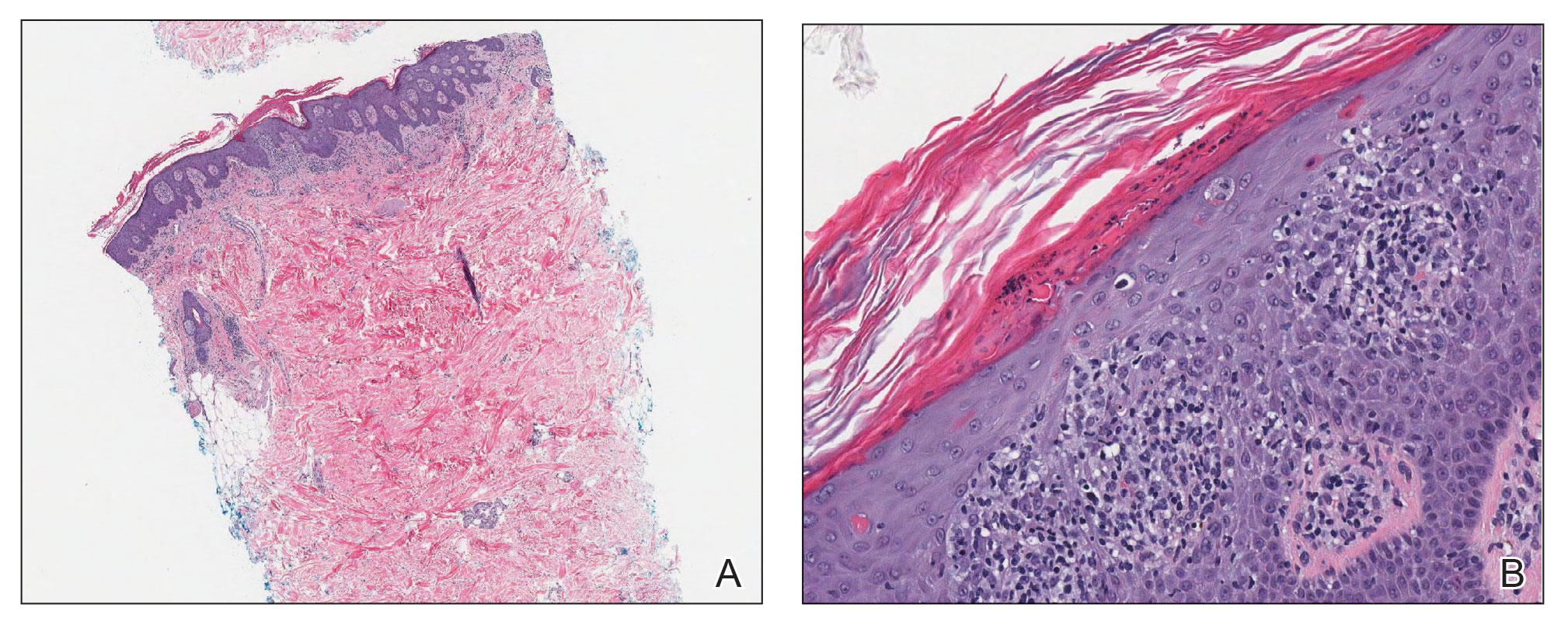
Laboratory results were positive for anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigens A and B. A complete blood cell count; comprehensive metabolic panel; erythrocyte sedimentation rate; and assays of rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, and anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide were within reference range. A biopsy of a lesion on the back showed psoriasiform dermatitis with confluent parakeratosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes. There was superficial perivascular inflammation with rare eosinophils (Figure 3).
The patient was treated with a course of systemic corticosteroids. The rash resolved in 1 week. She did not receive the second dose due to the rash.
Two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines—Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna—have been granted emergency use authorization by the US Food and Drug Administration.6 The safety profile of the mRNA-1273 vaccine for the median 2-month follow-up showed no safety concerns.3 Minor localized adverse effects (eg, pain, redness, swelling) have been observed more frequently with the vaccines than with placebo. Systemic symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, headache, and muscle and joint pain, also were seen somewhat more often with the vaccines than with placebo; most such effects occurred 24 to 48 hours after vaccination.3,6,7 The frequency of unsolicited adverse events and serious adverse events reported during the 28-day period after vaccination generally was similar among participants in the vaccine and placebo groups.3
There are 2 types of reactions to COVID-19 vaccination: immediate and delayed. Immediate reactions usually are due to anaphylaxis, requiring prompt recognition and treatment with epinephrine to stop rapid progression of life-threatening symptoms. Delayed reactions include localized reactions, such as urticaria and benign exanthema; serum sickness and serum sickness–like reactions; fever; and rare skin, organ, and neurologic sequelae.1,6-8
Cutaneous manifestations, present in 16% to 50% of patients with Sjögren syndrome, are considered one of the most common extraglandular presentations of the syndrome. They are classified as nonvascular (eg, xerosis, angular cheilitis, eyelid dermatitis, annular erythema) and vascular (eg, Raynaud phenomenon, vasculitis).9-11 Our patient did not have any of those findings. She had not taken any medications before the rash appeared, thereby ruling out a drug reaction.
The differential for our patient included post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash, which is not typical with Escherichia coli infection but is described with infection with Chlamydia species and Salmonella species. Moreover, post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash appear mostly on the palms and soles. Systemic lupus erythematosus–like rashes have a different histology and appear on sun-exposed areas; our patient’s rash was found mainly on unexposed areas.12
Because our patient received the Moderna vaccine 5 days before the rash appeared and later developed swelling of the digits with morning stiffness, a delayed serum sickness–like reaction secondary to COVID-19 vaccination was possible.3,6
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna incorporate a lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system that prevents rapid enzymatic degradation of mRNA and facilitates in vivo delivery of mRNA. This lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system is further stabilized by a polyethylene glycol 2000 lipid conjugate that provides a hydrophilic layer, thus prolonging half-life. The presence of lipid polyethylene glycol 2000 in mRNA vaccines has led to concern that this component could be implicated in anaphylaxis.6
COVID-19 antigens can give rise to varying clinical manifestations that are directly related to viral tissue damage or are indirectly induced by the antiviral immune response.13,14 Hyperactivation of the immune system to eradicate COVID-19 may trigger autoimmunity; several immune-mediated disorders have been described in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2. Dermal manifestations include cutaneous rash and vasculitis.13-16 Crucial immunologic steps occur during SARS-CoV-2 infection that may link autoimmunity to COVID-19.13,14 In preliminary published data on the efficacy of the Moderna vaccine on 45 trial enrollees, 3 did not receive the second dose of vaccination, including 1 who developed urticaria on both legs 5 days after the first dose.1
Introduction of viral RNA can induce autoimmunity that can be explained by various phenomena, including epitope spreading, molecular mimicry, cryptic antigen, and bystander activation. Remarkably, more than one-third of immunogenic proteins in SARS-CoV-2 have potentially problematic homology to proteins that are key to the human adaptive immune system.5
Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 seems to induce organ injury through alternative mechanisms beyond direct viral infection, including immunologic injury. In some situations, hyperactivation of the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 RNA can result in autoimmune disease. COVID-19 has been associated with immune-mediated systemic or organ-selective manifestations, some of which fulfill the diagnostic or classification criteria of specific autoimmune diseases. It is unclear whether those medical disorders are the result of transitory postinfectious epiphenomena.5
A few studies have shown that patients with rheumatic disease have an incidence and prevalence of COVID-19 that is similar to the general population. A similar pattern has been detected in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality rates, even among patients with an autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren syndrome.5,17 Furthermore, exacerbation of preexisting rheumatic symptoms may be due to hyperactivation of antiviral pathways in a person with an autoimmune disease.17-19 The findings in our patient suggested a direct role for the vaccine in skin manifestations, rather than for reactivation or development of new systemic autoimmune processes, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination has been described20; however, the case patient did not have a history of psoriasis. The mechanism(s) of such exacerbation remain unclear; COVID-19 vaccine–induced helper T cells (TH17) may play a role.21 Other skin manifestations encountered following COVID-19 vaccination include lichen planus, leukocytoclastic vasculitic rash, erythema multiforme–like rash, and pityriasis rosea–like rash.22-25 The immune mechanisms of these manifestations remain unclear.
The clinical presentation of delayed vaccination reactions can be attributed to the timing of symptoms and, in this case, the immune-mediated background of a psoriasiform reaction. Although adverse reactions to the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine are rare, more individuals should be studied after vaccination to confirm and better understand this phenomenon.
- Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, et al; . An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1920-1931. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022483
- Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, Widge AT, et al; . Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2427-2438. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028436
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, et al; COVE Study Group. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:403-416. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389
- Weise E. ‘COVID arm’ rash seen after Moderna vaccine annoying but harmless, doctors say. USA Today. January 27, 2021. Accessed September 4, 2022. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/health/2021/01/27/covid-arm-moderna-vaccine-rash-harmless-side-effect-doctors-say/4277725001/
- Talotta R, Robertson E. Autoimmunity as the comet tail of COVID-19 pandemic. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8:3621-3644. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i17.3621
- Castells MC, Phillips EJ. Maintaining safety with SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:643-649. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2035343
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al; . Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
- Dooling K, McClung N, Chamberland M, et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ interim recommendation for allocating initial supplies of COVID-19 vaccine—United States, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1857-1859. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6949e1
- Roguedas AM, Misery L, Sassolas B, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of primary Sjögren’s syndrome are underestimated. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22:632-636.
- Katayama I. Dry skin manifestations in Sjögren syndrome and atopic dermatitis related to aberrant sudomotor function in inflammatory allergic skin diseases. Allergol Int. 2018;67:448-454. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2018.07.001
- Generali E, Costanzo A, Mainetti C, et al. Cutaneous and mucosal manifestations of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:357-370. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8639-y
- Chanprapaph K, Tankunakorn J, Suchonwanit P, et al. Dermatologic manifestations, histologic features and disease progression among cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes: a prospective observational study in Asians. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:131-147. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00471-y
- Ortega-Quijano D, Jimenez-Cauhe J, Selda-Enriquez G, et al. Algorithm for the classification of COVID-19 rashes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e103-e104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.034
- Rahimi H, Tehranchinia Z. A comprehensive review of cutaneous manifestations associated with COVID-19. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1236520. doi:10.1155/2020/1236520
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Landa N, Mendieta-Eckert M, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Chilblain-like lesions on feet and hands during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:739-743. doi:10.1111/ijd.14937
- Dellavance A, Coelho Andrade LE. Immunologic derangement preceding clinical autoimmunity. Lupus. 2014;23:1305-1308. doi:10.1177/0961203314531346
- Parodi A, Gasparini G, Cozzani E. Could antiphospholipid antibodies contribute to coagulopathy in COVID-19? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e249. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.003
- Zhou Y, Han T, Chen J, et al. Clinical and autoimmune characteristics of severe and critical cases of COVID-19. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:1077-1086. doi:10.1111/cts.12805
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.812010
- Rouai M, Slimane MB, Sassi W, et al. Pustular rash triggered by Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022:e15465. doi:10.1111/dth.15465
- Altun E, Kuzucular E. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis after COVID-19 vaccination. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15279. doi:10.1111/dth.15279
- Buckley JE, Landis LN, Rapini RP. Pityriasis rosea-like rash after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2022;7:164-168. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.01.009
- Gökçek GE, Öksüm Solak E, Çölgeçen E. Pityriasis rosea like eruption: a dermatological manifestation of Coronavac-COVID-19 vaccine. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15256. doi:10.1111/dth.15256
- Kim MJ, Kim JW, Kim MS, et al. Generalized erythema multiforme-like skin rash following the first dose of COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:e98-e100. doi:10.1111/jdv.17757
To the Editor:
The Moderna COVID-19 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine was authorized for use on December 18, 2020, with the second dose beginning on January 15, 2021.1-3 Some individuals who received the Moderna vaccine experienced an intense rash known as “COVID arm,” a harmless but bothersome adverse effect that typically appears within a week and is a localized and transient immunogenic response.4 COVID arm differs from most vaccine adverse effects. The rash emerges not immediately but 5 to 9 days after the initial dose—on average, 1 week later. Apart from being itchy, the rash does not appear to be harmful and is not a reason to hesitate getting vaccinated.
Dermatologists and allergists have been studying this adverse effect, which has been formally termed delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity. Of potential clinical consequence is that the efficacy of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine may be harmed if postvaccination dermal reactions necessitate systemic corticosteroid therapy. Because this vaccine stimulates an immune response as viral RNA integrates in cells secondary to production of the spike protein of the virus, the skin may be affected secondarily and manifestations of any underlying disease may be aggravated.5 We report a patient who developed a psoriasiform dermatitis after the first dose of the Moderna vaccine.

A 65-year-old woman presented to her primary care physician because of the severity of psoriasiform dermatitis that developed 5 days after she received the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. The patient had a medical history of Sjögren syndrome. Her medication history was negative, and her family history was negative for autoimmune disease. Physical examination by primary care revealed an erythematous scaly rash with plaques and papules on the neck and back (Figure 1). The patient presented again to primary care 2 days later with swollen, painful, discolored digits (Figure 2) and a stiff, sore neck.

Laboratory results were positive for anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigens A and B. A complete blood cell count; comprehensive metabolic panel; erythrocyte sedimentation rate; and assays of rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, and anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide were within reference range. A biopsy of a lesion on the back showed psoriasiform dermatitis with confluent parakeratosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes. There was superficial perivascular inflammation with rare eosinophils (Figure 3).

The patient was treated with a course of systemic corticosteroids. The rash resolved in 1 week. She did not receive the second dose due to the rash.
Two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines—Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna—have been granted emergency use authorization by the US Food and Drug Administration.6 The safety profile of the mRNA-1273 vaccine for the median 2-month follow-up showed no safety concerns.3 Minor localized adverse effects (eg, pain, redness, swelling) have been observed more frequently with the vaccines than with placebo. Systemic symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, headache, and muscle and joint pain, also were seen somewhat more often with the vaccines than with placebo; most such effects occurred 24 to 48 hours after vaccination.3,6,7 The frequency of unsolicited adverse events and serious adverse events reported during the 28-day period after vaccination generally was similar among participants in the vaccine and placebo groups.3
There are 2 types of reactions to COVID-19 vaccination: immediate and delayed. Immediate reactions usually are due to anaphylaxis, requiring prompt recognition and treatment with epinephrine to stop rapid progression of life-threatening symptoms. Delayed reactions include localized reactions, such as urticaria and benign exanthema; serum sickness and serum sickness–like reactions; fever; and rare skin, organ, and neurologic sequelae.1,6-8
Cutaneous manifestations, present in 16% to 50% of patients with Sjögren syndrome, are considered one of the most common extraglandular presentations of the syndrome. They are classified as nonvascular (eg, xerosis, angular cheilitis, eyelid dermatitis, annular erythema) and vascular (eg, Raynaud phenomenon, vasculitis).9-11 Our patient did not have any of those findings. She had not taken any medications before the rash appeared, thereby ruling out a drug reaction.
The differential for our patient included post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash, which is not typical with Escherichia coli infection but is described with infection with Chlamydia species and Salmonella species. Moreover, post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash appear mostly on the palms and soles. Systemic lupus erythematosus–like rashes have a different histology and appear on sun-exposed areas; our patient’s rash was found mainly on unexposed areas.12
Because our patient received the Moderna vaccine 5 days before the rash appeared and later developed swelling of the digits with morning stiffness, a delayed serum sickness–like reaction secondary to COVID-19 vaccination was possible.3,6
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna incorporate a lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system that prevents rapid enzymatic degradation of mRNA and facilitates in vivo delivery of mRNA. This lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system is further stabilized by a polyethylene glycol 2000 lipid conjugate that provides a hydrophilic layer, thus prolonging half-life. The presence of lipid polyethylene glycol 2000 in mRNA vaccines has led to concern that this component could be implicated in anaphylaxis.6
COVID-19 antigens can give rise to varying clinical manifestations that are directly related to viral tissue damage or are indirectly induced by the antiviral immune response.13,14 Hyperactivation of the immune system to eradicate COVID-19 may trigger autoimmunity; several immune-mediated disorders have been described in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2. Dermal manifestations include cutaneous rash and vasculitis.13-16 Crucial immunologic steps occur during SARS-CoV-2 infection that may link autoimmunity to COVID-19.13,14 In preliminary published data on the efficacy of the Moderna vaccine on 45 trial enrollees, 3 did not receive the second dose of vaccination, including 1 who developed urticaria on both legs 5 days after the first dose.1
Introduction of viral RNA can induce autoimmunity that can be explained by various phenomena, including epitope spreading, molecular mimicry, cryptic antigen, and bystander activation. Remarkably, more than one-third of immunogenic proteins in SARS-CoV-2 have potentially problematic homology to proteins that are key to the human adaptive immune system.5
Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 seems to induce organ injury through alternative mechanisms beyond direct viral infection, including immunologic injury. In some situations, hyperactivation of the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 RNA can result in autoimmune disease. COVID-19 has been associated with immune-mediated systemic or organ-selective manifestations, some of which fulfill the diagnostic or classification criteria of specific autoimmune diseases. It is unclear whether those medical disorders are the result of transitory postinfectious epiphenomena.5
A few studies have shown that patients with rheumatic disease have an incidence and prevalence of COVID-19 that is similar to the general population. A similar pattern has been detected in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality rates, even among patients with an autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren syndrome.5,17 Furthermore, exacerbation of preexisting rheumatic symptoms may be due to hyperactivation of antiviral pathways in a person with an autoimmune disease.17-19 The findings in our patient suggested a direct role for the vaccine in skin manifestations, rather than for reactivation or development of new systemic autoimmune processes, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination has been described20; however, the case patient did not have a history of psoriasis. The mechanism(s) of such exacerbation remain unclear; COVID-19 vaccine–induced helper T cells (TH17) may play a role.21 Other skin manifestations encountered following COVID-19 vaccination include lichen planus, leukocytoclastic vasculitic rash, erythema multiforme–like rash, and pityriasis rosea–like rash.22-25 The immune mechanisms of these manifestations remain unclear.
The clinical presentation of delayed vaccination reactions can be attributed to the timing of symptoms and, in this case, the immune-mediated background of a psoriasiform reaction. Although adverse reactions to the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine are rare, more individuals should be studied after vaccination to confirm and better understand this phenomenon.
To the Editor:
The Moderna COVID-19 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine was authorized for use on December 18, 2020, with the second dose beginning on January 15, 2021.1-3 Some individuals who received the Moderna vaccine experienced an intense rash known as “COVID arm,” a harmless but bothersome adverse effect that typically appears within a week and is a localized and transient immunogenic response.4 COVID arm differs from most vaccine adverse effects. The rash emerges not immediately but 5 to 9 days after the initial dose—on average, 1 week later. Apart from being itchy, the rash does not appear to be harmful and is not a reason to hesitate getting vaccinated.
Dermatologists and allergists have been studying this adverse effect, which has been formally termed delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity. Of potential clinical consequence is that the efficacy of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine may be harmed if postvaccination dermal reactions necessitate systemic corticosteroid therapy. Because this vaccine stimulates an immune response as viral RNA integrates in cells secondary to production of the spike protein of the virus, the skin may be affected secondarily and manifestations of any underlying disease may be aggravated.5 We report a patient who developed a psoriasiform dermatitis after the first dose of the Moderna vaccine.

A 65-year-old woman presented to her primary care physician because of the severity of psoriasiform dermatitis that developed 5 days after she received the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. The patient had a medical history of Sjögren syndrome. Her medication history was negative, and her family history was negative for autoimmune disease. Physical examination by primary care revealed an erythematous scaly rash with plaques and papules on the neck and back (Figure 1). The patient presented again to primary care 2 days later with swollen, painful, discolored digits (Figure 2) and a stiff, sore neck.

Laboratory results were positive for anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigens A and B. A complete blood cell count; comprehensive metabolic panel; erythrocyte sedimentation rate; and assays of rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, and anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide were within reference range. A biopsy of a lesion on the back showed psoriasiform dermatitis with confluent parakeratosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes. There was superficial perivascular inflammation with rare eosinophils (Figure 3).

The patient was treated with a course of systemic corticosteroids. The rash resolved in 1 week. She did not receive the second dose due to the rash.
Two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines—Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna—have been granted emergency use authorization by the US Food and Drug Administration.6 The safety profile of the mRNA-1273 vaccine for the median 2-month follow-up showed no safety concerns.3 Minor localized adverse effects (eg, pain, redness, swelling) have been observed more frequently with the vaccines than with placebo. Systemic symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, headache, and muscle and joint pain, also were seen somewhat more often with the vaccines than with placebo; most such effects occurred 24 to 48 hours after vaccination.3,6,7 The frequency of unsolicited adverse events and serious adverse events reported during the 28-day period after vaccination generally was similar among participants in the vaccine and placebo groups.3
There are 2 types of reactions to COVID-19 vaccination: immediate and delayed. Immediate reactions usually are due to anaphylaxis, requiring prompt recognition and treatment with epinephrine to stop rapid progression of life-threatening symptoms. Delayed reactions include localized reactions, such as urticaria and benign exanthema; serum sickness and serum sickness–like reactions; fever; and rare skin, organ, and neurologic sequelae.1,6-8
Cutaneous manifestations, present in 16% to 50% of patients with Sjögren syndrome, are considered one of the most common extraglandular presentations of the syndrome. They are classified as nonvascular (eg, xerosis, angular cheilitis, eyelid dermatitis, annular erythema) and vascular (eg, Raynaud phenomenon, vasculitis).9-11 Our patient did not have any of those findings. She had not taken any medications before the rash appeared, thereby ruling out a drug reaction.
The differential for our patient included post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash, which is not typical with Escherichia coli infection but is described with infection with Chlamydia species and Salmonella species. Moreover, post–urinary tract infection immune-reactive arthritis and rash appear mostly on the palms and soles. Systemic lupus erythematosus–like rashes have a different histology and appear on sun-exposed areas; our patient’s rash was found mainly on unexposed areas.12
Because our patient received the Moderna vaccine 5 days before the rash appeared and later developed swelling of the digits with morning stiffness, a delayed serum sickness–like reaction secondary to COVID-19 vaccination was possible.3,6
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna incorporate a lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system that prevents rapid enzymatic degradation of mRNA and facilitates in vivo delivery of mRNA. This lipid-based nanoparticle carrier system is further stabilized by a polyethylene glycol 2000 lipid conjugate that provides a hydrophilic layer, thus prolonging half-life. The presence of lipid polyethylene glycol 2000 in mRNA vaccines has led to concern that this component could be implicated in anaphylaxis.6
COVID-19 antigens can give rise to varying clinical manifestations that are directly related to viral tissue damage or are indirectly induced by the antiviral immune response.13,14 Hyperactivation of the immune system to eradicate COVID-19 may trigger autoimmunity; several immune-mediated disorders have been described in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2. Dermal manifestations include cutaneous rash and vasculitis.13-16 Crucial immunologic steps occur during SARS-CoV-2 infection that may link autoimmunity to COVID-19.13,14 In preliminary published data on the efficacy of the Moderna vaccine on 45 trial enrollees, 3 did not receive the second dose of vaccination, including 1 who developed urticaria on both legs 5 days after the first dose.1
Introduction of viral RNA can induce autoimmunity that can be explained by various phenomena, including epitope spreading, molecular mimicry, cryptic antigen, and bystander activation. Remarkably, more than one-third of immunogenic proteins in SARS-CoV-2 have potentially problematic homology to proteins that are key to the human adaptive immune system.5
Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 seems to induce organ injury through alternative mechanisms beyond direct viral infection, including immunologic injury. In some situations, hyperactivation of the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 RNA can result in autoimmune disease. COVID-19 has been associated with immune-mediated systemic or organ-selective manifestations, some of which fulfill the diagnostic or classification criteria of specific autoimmune diseases. It is unclear whether those medical disorders are the result of transitory postinfectious epiphenomena.5
A few studies have shown that patients with rheumatic disease have an incidence and prevalence of COVID-19 that is similar to the general population. A similar pattern has been detected in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality rates, even among patients with an autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren syndrome.5,17 Furthermore, exacerbation of preexisting rheumatic symptoms may be due to hyperactivation of antiviral pathways in a person with an autoimmune disease.17-19 The findings in our patient suggested a direct role for the vaccine in skin manifestations, rather than for reactivation or development of new systemic autoimmune processes, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination has been described20; however, the case patient did not have a history of psoriasis. The mechanism(s) of such exacerbation remain unclear; COVID-19 vaccine–induced helper T cells (TH17) may play a role.21 Other skin manifestations encountered following COVID-19 vaccination include lichen planus, leukocytoclastic vasculitic rash, erythema multiforme–like rash, and pityriasis rosea–like rash.22-25 The immune mechanisms of these manifestations remain unclear.
The clinical presentation of delayed vaccination reactions can be attributed to the timing of symptoms and, in this case, the immune-mediated background of a psoriasiform reaction. Although adverse reactions to the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine are rare, more individuals should be studied after vaccination to confirm and better understand this phenomenon.
- Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, et al; . An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1920-1931. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022483
- Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, Widge AT, et al; . Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2427-2438. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028436
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, et al; COVE Study Group. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:403-416. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389
- Weise E. ‘COVID arm’ rash seen after Moderna vaccine annoying but harmless, doctors say. USA Today. January 27, 2021. Accessed September 4, 2022. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/health/2021/01/27/covid-arm-moderna-vaccine-rash-harmless-side-effect-doctors-say/4277725001/
- Talotta R, Robertson E. Autoimmunity as the comet tail of COVID-19 pandemic. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8:3621-3644. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i17.3621
- Castells MC, Phillips EJ. Maintaining safety with SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:643-649. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2035343
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al; . Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
- Dooling K, McClung N, Chamberland M, et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ interim recommendation for allocating initial supplies of COVID-19 vaccine—United States, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1857-1859. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6949e1
- Roguedas AM, Misery L, Sassolas B, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of primary Sjögren’s syndrome are underestimated. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22:632-636.
- Katayama I. Dry skin manifestations in Sjögren syndrome and atopic dermatitis related to aberrant sudomotor function in inflammatory allergic skin diseases. Allergol Int. 2018;67:448-454. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2018.07.001
- Generali E, Costanzo A, Mainetti C, et al. Cutaneous and mucosal manifestations of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:357-370. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8639-y
- Chanprapaph K, Tankunakorn J, Suchonwanit P, et al. Dermatologic manifestations, histologic features and disease progression among cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes: a prospective observational study in Asians. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:131-147. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00471-y
- Ortega-Quijano D, Jimenez-Cauhe J, Selda-Enriquez G, et al. Algorithm for the classification of COVID-19 rashes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e103-e104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.034
- Rahimi H, Tehranchinia Z. A comprehensive review of cutaneous manifestations associated with COVID-19. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1236520. doi:10.1155/2020/1236520
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Landa N, Mendieta-Eckert M, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Chilblain-like lesions on feet and hands during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:739-743. doi:10.1111/ijd.14937
- Dellavance A, Coelho Andrade LE. Immunologic derangement preceding clinical autoimmunity. Lupus. 2014;23:1305-1308. doi:10.1177/0961203314531346
- Parodi A, Gasparini G, Cozzani E. Could antiphospholipid antibodies contribute to coagulopathy in COVID-19? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e249. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.003
- Zhou Y, Han T, Chen J, et al. Clinical and autoimmune characteristics of severe and critical cases of COVID-19. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:1077-1086. doi:10.1111/cts.12805
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.812010
- Rouai M, Slimane MB, Sassi W, et al. Pustular rash triggered by Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022:e15465. doi:10.1111/dth.15465
- Altun E, Kuzucular E. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis after COVID-19 vaccination. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15279. doi:10.1111/dth.15279
- Buckley JE, Landis LN, Rapini RP. Pityriasis rosea-like rash after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2022;7:164-168. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.01.009
- Gökçek GE, Öksüm Solak E, Çölgeçen E. Pityriasis rosea like eruption: a dermatological manifestation of Coronavac-COVID-19 vaccine. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15256. doi:10.1111/dth.15256
- Kim MJ, Kim JW, Kim MS, et al. Generalized erythema multiforme-like skin rash following the first dose of COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:e98-e100. doi:10.1111/jdv.17757
- Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, et al; . An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1920-1931. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022483
- Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, Widge AT, et al; . Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2427-2438. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028436
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, et al; COVE Study Group. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:403-416. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389
- Weise E. ‘COVID arm’ rash seen after Moderna vaccine annoying but harmless, doctors say. USA Today. January 27, 2021. Accessed September 4, 2022. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/health/2021/01/27/covid-arm-moderna-vaccine-rash-harmless-side-effect-doctors-say/4277725001/
- Talotta R, Robertson E. Autoimmunity as the comet tail of COVID-19 pandemic. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8:3621-3644. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i17.3621
- Castells MC, Phillips EJ. Maintaining safety with SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:643-649. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2035343
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al; . Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
- Dooling K, McClung N, Chamberland M, et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ interim recommendation for allocating initial supplies of COVID-19 vaccine—United States, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1857-1859. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6949e1
- Roguedas AM, Misery L, Sassolas B, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of primary Sjögren’s syndrome are underestimated. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22:632-636.
- Katayama I. Dry skin manifestations in Sjögren syndrome and atopic dermatitis related to aberrant sudomotor function in inflammatory allergic skin diseases. Allergol Int. 2018;67:448-454. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2018.07.001
- Generali E, Costanzo A, Mainetti C, et al. Cutaneous and mucosal manifestations of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:357-370. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8639-y
- Chanprapaph K, Tankunakorn J, Suchonwanit P, et al. Dermatologic manifestations, histologic features and disease progression among cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes: a prospective observational study in Asians. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:131-147. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00471-y
- Ortega-Quijano D, Jimenez-Cauhe J, Selda-Enriquez G, et al. Algorithm for the classification of COVID-19 rashes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e103-e104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.034
- Rahimi H, Tehranchinia Z. A comprehensive review of cutaneous manifestations associated with COVID-19. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1236520. doi:10.1155/2020/1236520
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Landa N, Mendieta-Eckert M, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Chilblain-like lesions on feet and hands during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:739-743. doi:10.1111/ijd.14937
- Dellavance A, Coelho Andrade LE. Immunologic derangement preceding clinical autoimmunity. Lupus. 2014;23:1305-1308. doi:10.1177/0961203314531346
- Parodi A, Gasparini G, Cozzani E. Could antiphospholipid antibodies contribute to coagulopathy in COVID-19? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e249. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.003
- Zhou Y, Han T, Chen J, et al. Clinical and autoimmune characteristics of severe and critical cases of COVID-19. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:1077-1086. doi:10.1111/cts.12805
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.812010
- Rouai M, Slimane MB, Sassi W, et al. Pustular rash triggered by Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022:e15465. doi:10.1111/dth.15465
- Altun E, Kuzucular E. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis after COVID-19 vaccination. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15279. doi:10.1111/dth.15279
- Buckley JE, Landis LN, Rapini RP. Pityriasis rosea-like rash after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2022;7:164-168. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.01.009
- Gökçek GE, Öksüm Solak E, Çölgeçen E. Pityriasis rosea like eruption: a dermatological manifestation of Coronavac-COVID-19 vaccine. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:e15256. doi:10.1111/dth.15256
- Kim MJ, Kim JW, Kim MS, et al. Generalized erythema multiforme-like skin rash following the first dose of COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:e98-e100. doi:10.1111/jdv.17757
PRACTICE POINTS
- The differential diagnosis for a new-onset psoriasiform rash in an elderly patient should include a vaccine-related rash.
- A rash following vaccination that necessitates systemic corticosteroid therapy can decrease vaccine efficacy.
Practical pearls guide treatment of psoriasis in tricky areas
LAS VEGAS – With the right regimen, a majority of patients with psoriasis can achieve at least a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 score, Jennifer Soung, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
The array of treatment options includes mainstay topicals, new nonsteroidals, traditional oral systemics, new oral systemics, biologics, and light therapy, said Dr. Soung, director of clinical research at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Santa Ana, Calif. However, she said.
For these areas, make sure the diagnosis of psoriasis is correct, to avoid wasting time on the wrong course of treatment, Dr. Soung emphasized.
Scalp strategies
The scalp is often the first area of the body affected by psoriasis, and patients with severe scalp psoriasis may have minimal plaques on the body, Dr. Soung said. However, a differential diagnosis should include seborrheic dermatitis, she noted.
For most cases of scalp psoriasis, “start with localized topical treatment,” such as vitamin D and corticosteroid combination therapy, or excimer laser, Dr. Soung advised.
Systemic treatments with demonstrated effectiveness on scalp psoriasis in post hoc analyses of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis include adalimumab, etanercept, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Studies specifically focused on treatment of scalp psoriasis have shown success with secukinumab and apremilast, she noted.
Roflumilast foam, 0.3%, is in development and is an emerging option for scalp psoriasis. (A cream formulation of roflumilast, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was approved for treatment of plaque psoriasis in July 2022.) A phase 2b study of roflumilast foam showed that approximately one-third of patients with scalp psoriasis achieved a status of clear based on scalp-investigator global assessment, compared with approximately 3% of those on vehicle, and similar results were seen in a recently completed phase 3 trial for scalp and body psoriasis, she added.
Facial psoriasis
Patients with facial psoriasis tend to be younger, and they may have more severe disease overall, Dr. Soung said. Given the sensitivity of facial skin, “it is nice to have a nonsteroidal option,” she noted. Current novel nonsteroidal therapies include a cream formulation of tapinarof, an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, which was approved earlier this year for plaque psoriasis in adults, and roflumilast cream. Vitamin D and topical calcineurin inhibitors are options as well, she said.
Intertriginous tricks
Intertriginous (inverse) psoriasis is distinct from other areas in that the plaques are usually smooth and well-demarcated, with little or no scaling, Dr. Soung said. Erosions or signs of maceration may be present. The prevalence of inverse psoriasis is approximately 30%, but the prevalence on external genitalia is 80%, she noted. For inverse psoriasis, topical corticosteroids can result in adverse events such as poor wound healing and skin fragility, and some patients resist the idea of a steroid and don’t adhere to the medication, she added. Dr. Soung recommended topical corticosteroids for the short term, and topical calcineurin inhibitors or calcipotriol for the long term.
New topical options for inverse psoriasis include tapinarof and roflumilast, Dr. Soung said. For tapinarof, the phase 3 PSOARING program included assessment of tolerability in sensitive skin areas and found little to no irritation. Similarly, treatment with roflumilast cream was effective and well tolerated by patients with intertriginous plaque psoriasis in the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 studies, she said.
Genital psoriasis
Ask patients with psoriasis about genital psoriasis, because they often are too embarrassed to provide that information on their own, said Dr. Soung. In fact, 63% of patients with psoriasis report ever experiencing genital psoriasis, but it often goes undiagnosed and undertreated, which has a significant impact on patient quality of life and sexual health.
A differential diagnosis of genital psoriasis should include dermatitis, tinea or candidiasis, and even squamous cell carcinoma, she noted. Other considerations include fixed drug eruption, lichen nitidus, lichen sclerosus, and scabies.
Dr. Soung’s first line of treatment for genital psoriasis is low-potency topical corticosteroids for 2-4 weeks. If long-term topical therapy is needed, alternatives include calcineurin inhibitors and vitamin D analogs, she said. The new topicals roflumilast and tapinarof are options as well, she said.
For those patients with severe and extensive genital psoriasis, consider systemic therapy, possibly with ixekizumab or secukinumab, she added. Patients with moderate to severe genital psoriasis treated with apremilast have shown improvement at week 16, in an ongoing clinical trial, she noted.
Palmoplantar involvement
For patients with palmar plantar psoriasis, “don’t underestimate the impact on quality of life,” said Dr. Soung. Approximately 12%-16% of patients with psoriasis report palmoplantar involvement, she noted.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be stubborn, and many patients will need combination therapy with topicals and systemics, she said. “I am very curious about how well our new topical nonsteroidals will work in these areas,” she added.
Dr. Soung starts patients with palmoplantar psoriasis with a “potent to super-potent” twice daily topical corticosteroid, with or without occlusion. Her first-line systemic therapy is acitretin, 10-50 mg daily. However, keep in mind that acitretin is contraindicated in pregnancy, and also may cause side effects including cheilitis, alopecia, and peeling skin, she cautioned.
During the question and answer session, Dr. Soung was asked whether she routinely biopsies patients with palmoplantar psoriasis. “Not always,” was her answer. Instead, she looks for clues elsewhere on the body to confirm the diagnosis.
Nail know-how
Approximately 23%-27% of patients with psoriasis experience nail involvement, said Dr. Soung. Nail psoriasis can appear on the nail plate as pitting, onycholysis, or subungual hyperkeratosis, or in the nail bed as splinter hemorrhages or oil spots, she said.
For patients with psoriasis of the nails only, Dr. Soung described the use of high-potency topical corticosteroids, with or without calcipotriol. In her experience, she said that intralesional steroids for nail psoriasis are torturous to patients. For patients who have failed topical therapy or have psoriasis in other areas, with or without psoriatic arthritis, she advised the use of either IL-17 antagonists (secukinumab, ixekizumab, brodalumab) or IL-23 antagonists (risankizumab, guselkumab).
Dr. Soung disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Dermavant, and Novartis. She also disclosed serving as a speaker or member of the speakers’ bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, as well as research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, KoBio, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – With the right regimen, a majority of patients with psoriasis can achieve at least a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 score, Jennifer Soung, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
The array of treatment options includes mainstay topicals, new nonsteroidals, traditional oral systemics, new oral systemics, biologics, and light therapy, said Dr. Soung, director of clinical research at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Santa Ana, Calif. However, she said.
For these areas, make sure the diagnosis of psoriasis is correct, to avoid wasting time on the wrong course of treatment, Dr. Soung emphasized.
Scalp strategies
The scalp is often the first area of the body affected by psoriasis, and patients with severe scalp psoriasis may have minimal plaques on the body, Dr. Soung said. However, a differential diagnosis should include seborrheic dermatitis, she noted.
For most cases of scalp psoriasis, “start with localized topical treatment,” such as vitamin D and corticosteroid combination therapy, or excimer laser, Dr. Soung advised.
Systemic treatments with demonstrated effectiveness on scalp psoriasis in post hoc analyses of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis include adalimumab, etanercept, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Studies specifically focused on treatment of scalp psoriasis have shown success with secukinumab and apremilast, she noted.
Roflumilast foam, 0.3%, is in development and is an emerging option for scalp psoriasis. (A cream formulation of roflumilast, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was approved for treatment of plaque psoriasis in July 2022.) A phase 2b study of roflumilast foam showed that approximately one-third of patients with scalp psoriasis achieved a status of clear based on scalp-investigator global assessment, compared with approximately 3% of those on vehicle, and similar results were seen in a recently completed phase 3 trial for scalp and body psoriasis, she added.
Facial psoriasis
Patients with facial psoriasis tend to be younger, and they may have more severe disease overall, Dr. Soung said. Given the sensitivity of facial skin, “it is nice to have a nonsteroidal option,” she noted. Current novel nonsteroidal therapies include a cream formulation of tapinarof, an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, which was approved earlier this year for plaque psoriasis in adults, and roflumilast cream. Vitamin D and topical calcineurin inhibitors are options as well, she said.
Intertriginous tricks
Intertriginous (inverse) psoriasis is distinct from other areas in that the plaques are usually smooth and well-demarcated, with little or no scaling, Dr. Soung said. Erosions or signs of maceration may be present. The prevalence of inverse psoriasis is approximately 30%, but the prevalence on external genitalia is 80%, she noted. For inverse psoriasis, topical corticosteroids can result in adverse events such as poor wound healing and skin fragility, and some patients resist the idea of a steroid and don’t adhere to the medication, she added. Dr. Soung recommended topical corticosteroids for the short term, and topical calcineurin inhibitors or calcipotriol for the long term.
New topical options for inverse psoriasis include tapinarof and roflumilast, Dr. Soung said. For tapinarof, the phase 3 PSOARING program included assessment of tolerability in sensitive skin areas and found little to no irritation. Similarly, treatment with roflumilast cream was effective and well tolerated by patients with intertriginous plaque psoriasis in the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 studies, she said.
Genital psoriasis
Ask patients with psoriasis about genital psoriasis, because they often are too embarrassed to provide that information on their own, said Dr. Soung. In fact, 63% of patients with psoriasis report ever experiencing genital psoriasis, but it often goes undiagnosed and undertreated, which has a significant impact on patient quality of life and sexual health.
A differential diagnosis of genital psoriasis should include dermatitis, tinea or candidiasis, and even squamous cell carcinoma, she noted. Other considerations include fixed drug eruption, lichen nitidus, lichen sclerosus, and scabies.
Dr. Soung’s first line of treatment for genital psoriasis is low-potency topical corticosteroids for 2-4 weeks. If long-term topical therapy is needed, alternatives include calcineurin inhibitors and vitamin D analogs, she said. The new topicals roflumilast and tapinarof are options as well, she said.
For those patients with severe and extensive genital psoriasis, consider systemic therapy, possibly with ixekizumab or secukinumab, she added. Patients with moderate to severe genital psoriasis treated with apremilast have shown improvement at week 16, in an ongoing clinical trial, she noted.
Palmoplantar involvement
For patients with palmar plantar psoriasis, “don’t underestimate the impact on quality of life,” said Dr. Soung. Approximately 12%-16% of patients with psoriasis report palmoplantar involvement, she noted.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be stubborn, and many patients will need combination therapy with topicals and systemics, she said. “I am very curious about how well our new topical nonsteroidals will work in these areas,” she added.
Dr. Soung starts patients with palmoplantar psoriasis with a “potent to super-potent” twice daily topical corticosteroid, with or without occlusion. Her first-line systemic therapy is acitretin, 10-50 mg daily. However, keep in mind that acitretin is contraindicated in pregnancy, and also may cause side effects including cheilitis, alopecia, and peeling skin, she cautioned.
During the question and answer session, Dr. Soung was asked whether she routinely biopsies patients with palmoplantar psoriasis. “Not always,” was her answer. Instead, she looks for clues elsewhere on the body to confirm the diagnosis.
Nail know-how
Approximately 23%-27% of patients with psoriasis experience nail involvement, said Dr. Soung. Nail psoriasis can appear on the nail plate as pitting, onycholysis, or subungual hyperkeratosis, or in the nail bed as splinter hemorrhages or oil spots, she said.
For patients with psoriasis of the nails only, Dr. Soung described the use of high-potency topical corticosteroids, with or without calcipotriol. In her experience, she said that intralesional steroids for nail psoriasis are torturous to patients. For patients who have failed topical therapy or have psoriasis in other areas, with or without psoriatic arthritis, she advised the use of either IL-17 antagonists (secukinumab, ixekizumab, brodalumab) or IL-23 antagonists (risankizumab, guselkumab).
Dr. Soung disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Dermavant, and Novartis. She also disclosed serving as a speaker or member of the speakers’ bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, as well as research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, KoBio, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – With the right regimen, a majority of patients with psoriasis can achieve at least a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 score, Jennifer Soung, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
The array of treatment options includes mainstay topicals, new nonsteroidals, traditional oral systemics, new oral systemics, biologics, and light therapy, said Dr. Soung, director of clinical research at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Santa Ana, Calif. However, she said.
For these areas, make sure the diagnosis of psoriasis is correct, to avoid wasting time on the wrong course of treatment, Dr. Soung emphasized.
Scalp strategies
The scalp is often the first area of the body affected by psoriasis, and patients with severe scalp psoriasis may have minimal plaques on the body, Dr. Soung said. However, a differential diagnosis should include seborrheic dermatitis, she noted.
For most cases of scalp psoriasis, “start with localized topical treatment,” such as vitamin D and corticosteroid combination therapy, or excimer laser, Dr. Soung advised.
Systemic treatments with demonstrated effectiveness on scalp psoriasis in post hoc analyses of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis include adalimumab, etanercept, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Studies specifically focused on treatment of scalp psoriasis have shown success with secukinumab and apremilast, she noted.
Roflumilast foam, 0.3%, is in development and is an emerging option for scalp psoriasis. (A cream formulation of roflumilast, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was approved for treatment of plaque psoriasis in July 2022.) A phase 2b study of roflumilast foam showed that approximately one-third of patients with scalp psoriasis achieved a status of clear based on scalp-investigator global assessment, compared with approximately 3% of those on vehicle, and similar results were seen in a recently completed phase 3 trial for scalp and body psoriasis, she added.
Facial psoriasis
Patients with facial psoriasis tend to be younger, and they may have more severe disease overall, Dr. Soung said. Given the sensitivity of facial skin, “it is nice to have a nonsteroidal option,” she noted. Current novel nonsteroidal therapies include a cream formulation of tapinarof, an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, which was approved earlier this year for plaque psoriasis in adults, and roflumilast cream. Vitamin D and topical calcineurin inhibitors are options as well, she said.
Intertriginous tricks
Intertriginous (inverse) psoriasis is distinct from other areas in that the plaques are usually smooth and well-demarcated, with little or no scaling, Dr. Soung said. Erosions or signs of maceration may be present. The prevalence of inverse psoriasis is approximately 30%, but the prevalence on external genitalia is 80%, she noted. For inverse psoriasis, topical corticosteroids can result in adverse events such as poor wound healing and skin fragility, and some patients resist the idea of a steroid and don’t adhere to the medication, she added. Dr. Soung recommended topical corticosteroids for the short term, and topical calcineurin inhibitors or calcipotriol for the long term.
New topical options for inverse psoriasis include tapinarof and roflumilast, Dr. Soung said. For tapinarof, the phase 3 PSOARING program included assessment of tolerability in sensitive skin areas and found little to no irritation. Similarly, treatment with roflumilast cream was effective and well tolerated by patients with intertriginous plaque psoriasis in the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 studies, she said.
Genital psoriasis
Ask patients with psoriasis about genital psoriasis, because they often are too embarrassed to provide that information on their own, said Dr. Soung. In fact, 63% of patients with psoriasis report ever experiencing genital psoriasis, but it often goes undiagnosed and undertreated, which has a significant impact on patient quality of life and sexual health.
A differential diagnosis of genital psoriasis should include dermatitis, tinea or candidiasis, and even squamous cell carcinoma, she noted. Other considerations include fixed drug eruption, lichen nitidus, lichen sclerosus, and scabies.
Dr. Soung’s first line of treatment for genital psoriasis is low-potency topical corticosteroids for 2-4 weeks. If long-term topical therapy is needed, alternatives include calcineurin inhibitors and vitamin D analogs, she said. The new topicals roflumilast and tapinarof are options as well, she said.
For those patients with severe and extensive genital psoriasis, consider systemic therapy, possibly with ixekizumab or secukinumab, she added. Patients with moderate to severe genital psoriasis treated with apremilast have shown improvement at week 16, in an ongoing clinical trial, she noted.
Palmoplantar involvement
For patients with palmar plantar psoriasis, “don’t underestimate the impact on quality of life,” said Dr. Soung. Approximately 12%-16% of patients with psoriasis report palmoplantar involvement, she noted.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be stubborn, and many patients will need combination therapy with topicals and systemics, she said. “I am very curious about how well our new topical nonsteroidals will work in these areas,” she added.
Dr. Soung starts patients with palmoplantar psoriasis with a “potent to super-potent” twice daily topical corticosteroid, with or without occlusion. Her first-line systemic therapy is acitretin, 10-50 mg daily. However, keep in mind that acitretin is contraindicated in pregnancy, and also may cause side effects including cheilitis, alopecia, and peeling skin, she cautioned.
During the question and answer session, Dr. Soung was asked whether she routinely biopsies patients with palmoplantar psoriasis. “Not always,” was her answer. Instead, she looks for clues elsewhere on the body to confirm the diagnosis.
Nail know-how
Approximately 23%-27% of patients with psoriasis experience nail involvement, said Dr. Soung. Nail psoriasis can appear on the nail plate as pitting, onycholysis, or subungual hyperkeratosis, or in the nail bed as splinter hemorrhages or oil spots, she said.
For patients with psoriasis of the nails only, Dr. Soung described the use of high-potency topical corticosteroids, with or without calcipotriol. In her experience, she said that intralesional steroids for nail psoriasis are torturous to patients. For patients who have failed topical therapy or have psoriasis in other areas, with or without psoriatic arthritis, she advised the use of either IL-17 antagonists (secukinumab, ixekizumab, brodalumab) or IL-23 antagonists (risankizumab, guselkumab).
Dr. Soung disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Dermavant, and Novartis. She also disclosed serving as a speaker or member of the speakers’ bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, as well as research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, KoBio, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Two biologics equally effective for extraintestinal manifestations of IBD
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIGESTIVE AND LIVER DISEASE
IgA Vasculitis in the Setting of Biologic Therapy for Psoriasis and Recurrent Cutaneous Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Colonization
Case Report
A 47-year-old man presented with a sudden-onset rash consisting of red bumps on the abdomen and legs that had been ongoing for several days. He had known psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis that had been well controlled with adalimumab for the last 18 months. He reported concurrent onset of nausea but denied fevers, chills, night sweats, unintentional weight loss, abdominal pain, and pruritus. He endorsed prior cutaneous infections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). His medical history also included diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity. His other medications included oral losartan-hydrochlorothiazide, amlodipine, naproxen, and atorvastatin.
Physical examination revealed numerous thin purpuric papules—some with adherent scale—distributed on the lower legs, extensor forearms, and abdomen. Abdominal lesions were confined to weight-related striae (Figure 1). The palms, soles, oral mucosa, and face were spared. Three punch biopsies were performed, including 1 for direct immunofluorescence (DIF), and the patient was instructed to apply clobetasol to the affected areas twice daily until further notice.
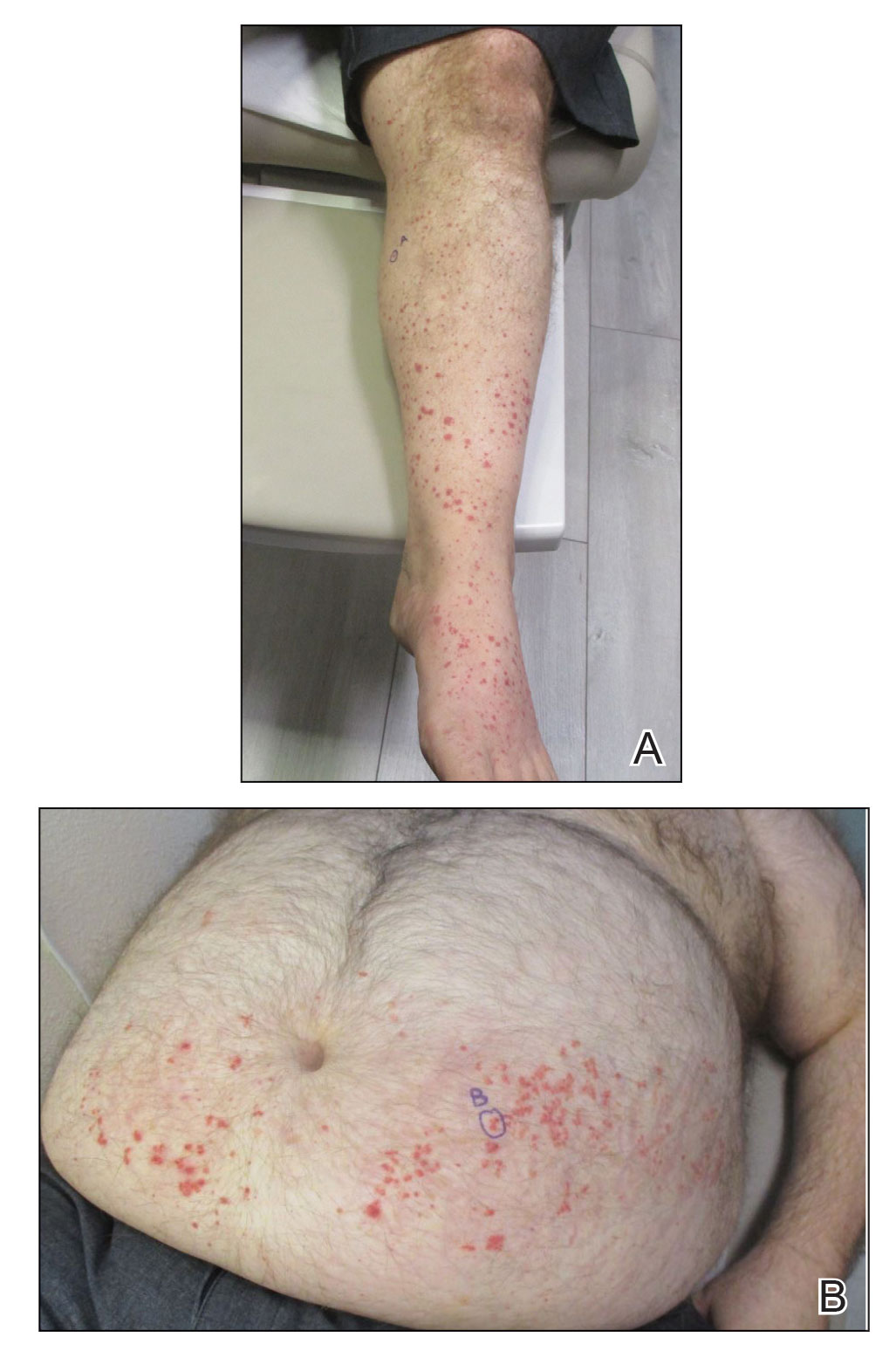
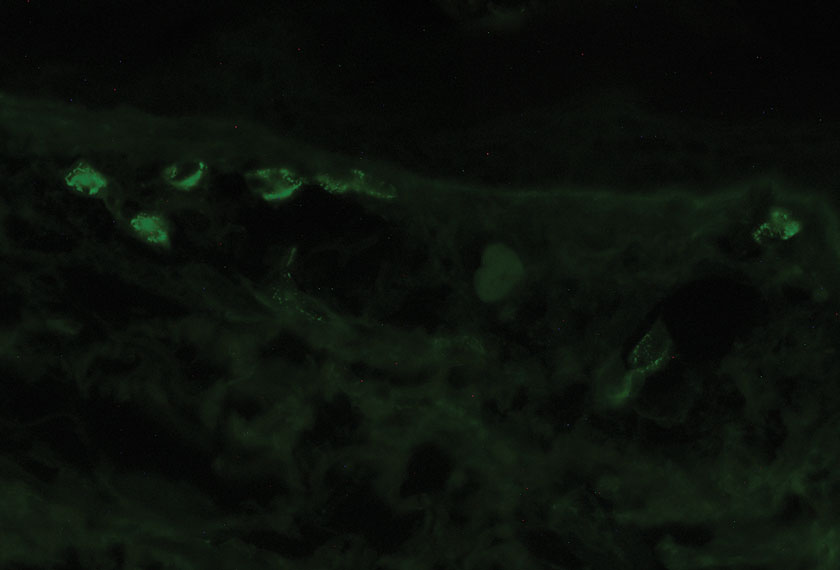
Pathology showed perivascular extravasation of erythrocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and leukocytoclasis surrounding blood vessels associated with fibrin (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence showed granular deposition of IgA, complement component 3, and fibrinogen in a superficial dermal vascular pattern (Figure 3). These results were consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. One specimen was consistent with the patient’s known psoriasis.
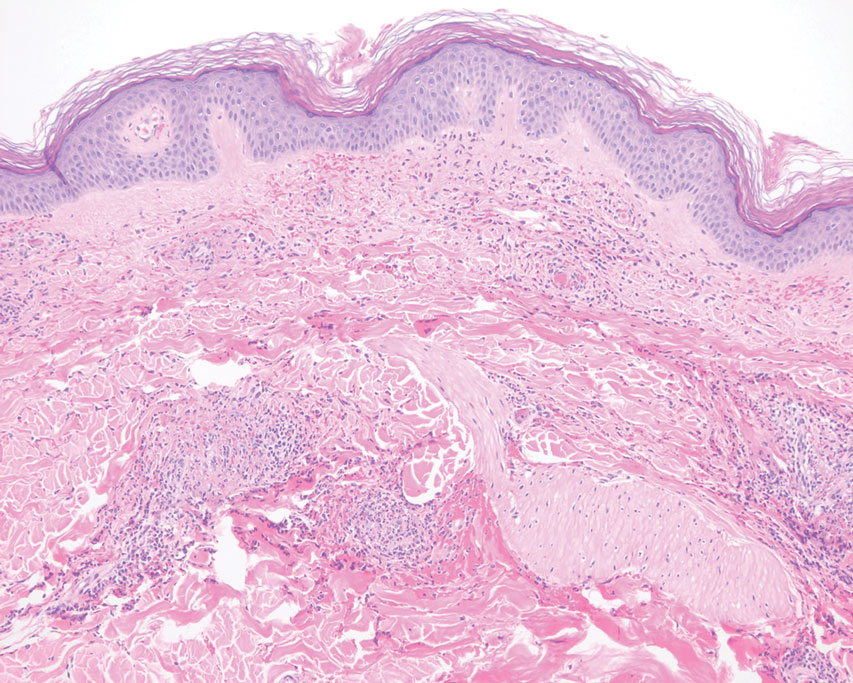
Urinalysis revealed moderate hemoglobinuria, and urine microscopy showed 174 red blood cells per high-power field. Creatinine was high at 1.87 mg/dL (reference range, <1.34 mg/dL; patient’s baseline, 0.81 mg/dL) and glomerular filtration rate was low (42 mL/min, patient’s baseline, >60 mL/min [reference range, 90–120 mL/min]). Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (21 mm/h [reference range, 0–22 mm/h]) and C-reactive protein were elevated (2.2 mg/dL [reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL]). Given his history of cutaneous MRSA infections, a bacterial culture swab was collected from the skin surface to check for colonization, which showed moderate growth of MRSA. Naproxen was discontinued over concern of worsening the patient’s renal status. The patient was instructed to rest at home with his legs elevated, wear compression socks when ambulatory, use chlorhexidine antiseptic daily as a body wash when showering, and apply mupirocin three times daily to the biopsy sites. He was referred to urology for his microhematuria, where cystoscopy revealed no abnormalities.A month passed with no improvement of the patient’s cutaneous vasculitis, and his psoriatic arthritis worsened without his usual use of naproxen. He developed abdominal pain and loss of appetite. A prednisone taper was ordered starting at 40 mg/d (28.8 mg/kg), which provided relief of the skin and joint symptoms only until the course was completed 12 days later.
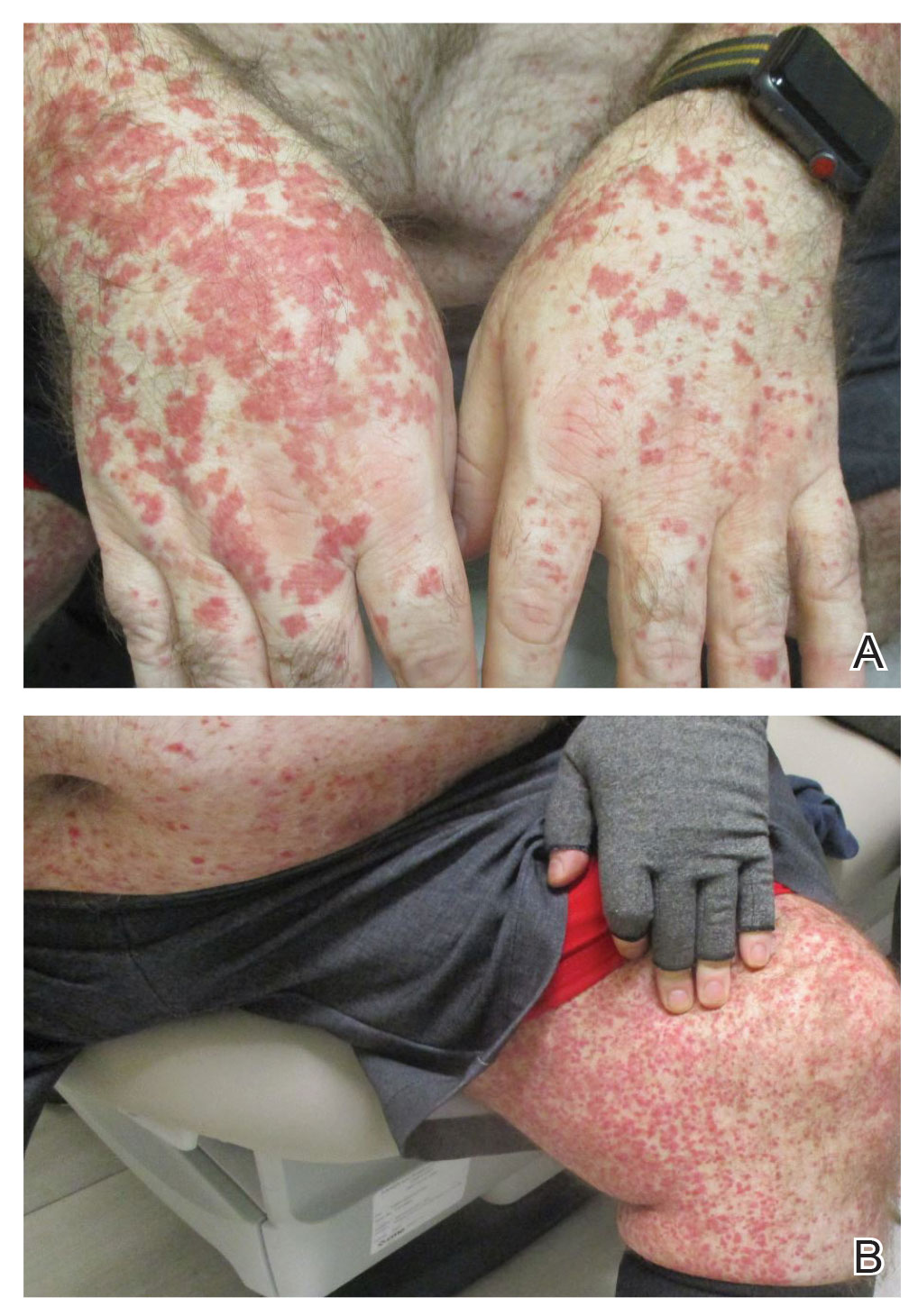
Five weeks after the initial presentation, the patient returned with a more severe eruption consisting of innumerable purpuric papules that coalesced in plaques on the abdomen, arms, and legs. He also had erythematous facial pustules and mild palmar petechiae (Figure 4). Three biopsies were performed, including 1 for DIF and 1 from a pustule on the forehead. Histology and DIF were again consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. The forehead biopsy was compatible with steroid acne (attributed to recent prednisone use) and psoriasis.
Rheumatology was consulted, and adalimumab was discontinued 6 weeks after the initial presentation out of concern for drug-induced cutaneous vasculitis. Vasculitis work-up was unremarkable, including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide, and serum protein electrophoresis. Oral dapsone was started at 100 mg/d, with the tentative plan of starting secukinumab if cutaneous symptoms improved. For 3 weeks, the patient’s cutaneous symptoms steadily improved.
Nine weeks after initial presentation to dermatology (3 weeks after discontinuing adalimumab) the patient self-administered his first dose of secukinumab at home. Several hours later, he reported sudden reappearance of vasculitis. He denied diarrhea, abdominal pain, bowel movement urgency, fevers, fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. Antistreptolysin O and hepatitis A antibodies were negative. He was instructed to hold secukinumab indefinitely.
Four weeks after his only secukinumab injection, the patient reported another episode of acute worsening cutaneous symptoms. A 4-week prednisone taper starting at 40 mg/d was ordered. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to rule out internal malignancy was unremarkable. Around this time, the patient reported major emotional distress related to an unexpected death in his family, which added to a gradual increase in his stress level related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Three weeks later, dapsone was increased to 100 mg twice daily on account of the patient’s adiposity and lack of cutaneous improvement on the lower dose. Subsequently, the vasculitis rapidly improved for 2 weeks. The patient then reported symptoms of headache, dizziness, and chills. He was tested for COVID-19 and was negative. Six weeks after increasing the dapsone dose (5 months after initial presentation), the skin was normalizing, showing only faintly hyperpigmented macules confined to areas of resolved vasculitis (forearms, abdomen, legs).
The patient had been on dapsone 100 mg twice daily for 3 months when he was started on ustekinumab (90 mg at weeks 0 and 4, with planned doses every 12 weeks) for psoriatic arthritis in hopes of withdrawing dapsone. His cutaneous symptoms have remained well controlled on this regimen for 18 months. Lowering of dapsone below 100 mg daily has resulted in recurrent mild vasculitis symptoms; he now maintains the once-daily dosing without negative side effects.
Comment
IgA vasculitis is a form of cutaneous small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) characterized by episodes of palpable purpura on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs that may be associated with arthritis, abdominal pain, and/or hematuria. Although vasculitis is a known potential adverse effect of anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α therapy, cases of adalimumab-induced IgA vasculitis are uncommon. As use of more targeted therapies for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, such as the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab, increases so do reports of associated adverse events. Of 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis, at least 4 were IgA vasculitis (Table).1-6 Another case described one patient with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing secukinumab treatment who experienced necrotizing glomerulonephritis; however, the authors concluded secukinumab likely was not causative in that case, as serologies and urinalyses suggested gradual onset of the process prior to initiating the medication.7
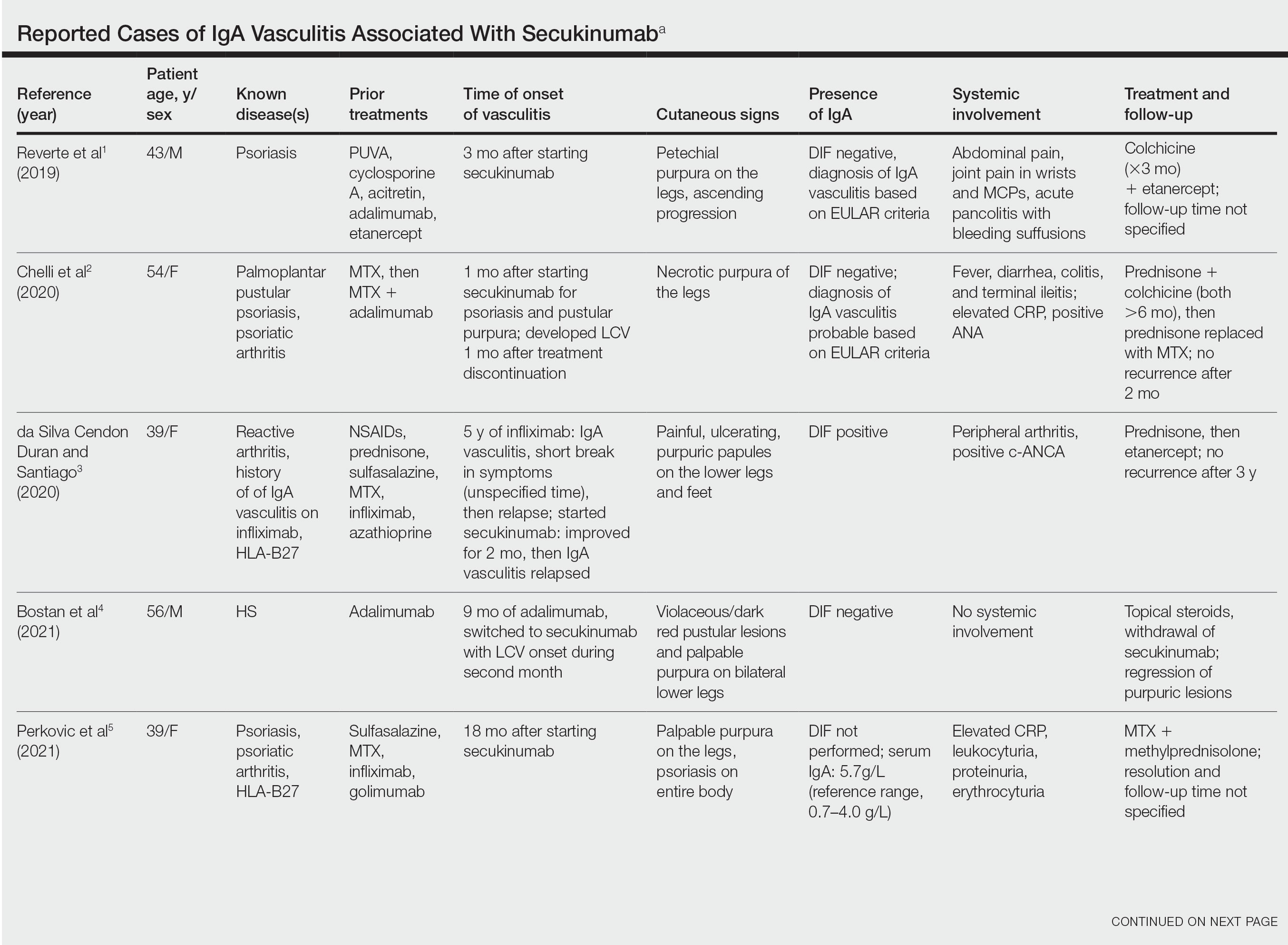
The exact pathogenesis of IgA vasculitis is unclear, but a prevailing theory involves the dysregulation of IgA synthesis and metabolism. Other than increased serum levels of transforming growth factor β, which is a major stimulating factor for IgA production, it also has been hypothesized that the presence of aberrantly hypoglycosylated IgA exposes an autoepitope for recognition by other pathogenic IgG and IgA, leading to the formation of large immune complexes that can readily deposit in postcapillary venules. The deposition of IgA immune complexes in postcapillary venules and the subsequent activation of the complement system causes direct damage to the endothelial cells of vessel walls. This complement activation is evidenced by vascular complement component 3 deposition on DIF (a nonspecific feature of LCV). Chemotaxis of neutrophils ensues, followed by their firm adherence and transendothelial migration (mediated by monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 [MCP-1]). Neutrophil degranulation releases reactive oxygen species and cytokines, which in turn recruit additional leukocytes to the area of inflammation, subsequently undergoing degeneration (leukocytoclasis). Microvascular permeability also is enhanced by MCP-1, allowing exudation of serum, erythrocytes, and fibrin. In the setting of elevated circulating TNF and IL-1, endothelium is stimulated to activate the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. This decreases endothelial fibrinolytic activity, leading to thrombosis. The high venous pressure and low fibrinolytic activity in the lower legs explains why vasculitic lesions often are confined to or begin in this distribution.1,8-10
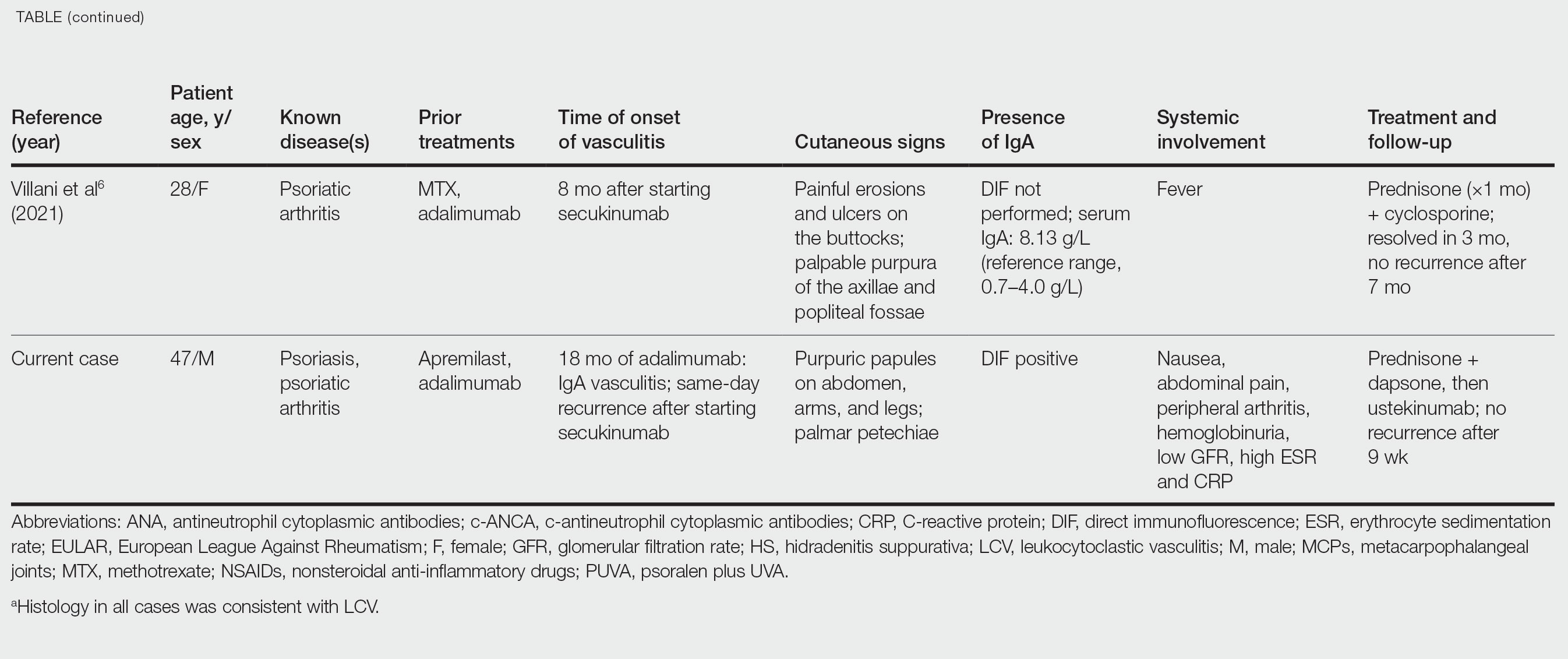
There also are noteworthy roles for cytokines in LCV. Circulating transforming growth factor β and IL-6—which are necessary for development of T helper 17 (TH17) cells and production of IL-17—are higher in patients with LCV compared to controls. Peripheral blood monocytes in patients with LCV demonstrate higher production of IL-17. Once TH17 cells develop, their survival and phenotype are maintained by IL-23 (considered the master regulator of TH17 differentiation). IL-17 is a potent chemoattractant of IL-8 (CXCL8) and MCP-1, both of which promote neutrophil-mediated perivascular inflammation. The IL-23 and IL-17 pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis also cause neutrophil activation and upregulate transcription of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α), which overlap with those implicated in LCV. Autoimmune disease generally entails some positive feedback loop of progressively severe self-recognition and tissue destruction by the immune system. These shared cytokinetic processes may explain how the internal environment of psoriasis could perpetuate IgA vasculitis.1,2,8,10-12
The mechanisms underlying vasculitis associated with adalimumab are unclear, but hypotheses involve direct toxicity on vessels, capillary deposition of anti-TNF/TNF immune complexes, or an inflammatory process resulting in autoantibodies. Similar hypotheses are posited for secukinumab-associated vasculitis, including deposition of secukinumab–IL-17 complexes. Anti–TNF-α medications may increase TH17 cell numbers, leading to increased production of IL-22 and a resultant immunologic microenvironment conducive to vasculitis. All 6 published cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis that we found had received prior treatment with a TNF-α blocker, but only 1 had occurrence of vasculitis during that treatment.1-6,10
In the 6 cases we reviewed, the time from starting secukinumab to onset of vasculitis ranged from 1 to 18 months. Our patient’s same-day re-emergence of vasculitis after his first secukinumab dose was so acute that we were skeptical of secukinumab as a potential trigger; this may simply have been coincident to the natural waxing and waning of the vasculitis (although onset of IgA vasculitis within 1 day of starting anti–TNF-α therapy has been reported).1-6,13
Specific associations of IgA vasculitis are many and can include bacterial organisms such as Helicobacter pylori, streptococci, and staphylococci. Although internal mucous membrane infections are considered more linked because of the surveillance role of IgA predominantly in mucosal tissues, it is possible that our patient with cutaneous MRSA harbored the same within the nasal mucosa. Our patient also received multiple vaccinations outside our department throughout his clinical course (2 hepatitis B and 1 pneumococcal conjugate), which are known potential triggers for vasculitis. Psychological stress is a known trigger for psoriasis, and given the cytokinetic relationship of psoriasis to vasculitis described previously, it may have indirectly contributed to vasculitis in our case. The anxiety associated with being immunosuppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic and bereavement of losing a family member may have contributed to the refractory nature of our patient’s condition. Renal involvement is relatively common in adults with IgA vasculitis and so should be ruled out, as should occult internal malignancy.8,10,14
It is unclear which of the above factors was causative in our case, but a multifactorial process is likely. Treatment of monoclonal antibody–associated vasculitis entails investigating for triggers and systemic involvement, removing the most likely culprit, quelling the vasculitis acutely, avoiding known potential exacerbators, and introducing an alternative long-term immunomodulant. In all 6 reported similar cases, discontinuation of secukinumab and initiation of prednisone or colchicine led to resolution.1-6 Dapsone also is acceptable for acute control of IgA vasculitis, although this medication is highly lipid soluble and penetrates well into various tissues.15 Thus, lower doses may prove ineffective for obese patients, as was demonstrated in our case. Given the known potential of vaccinations, infections, and other factors (eg, alcohol, penicillin) to trigger IgA vasculitis, these should be avoided.10
Blockade of IL-23 with ustekinumab has been suggested by other authors encountering secukinumab-associated vasculitis, as IL-23 is the main driver and sustainer of TH17 cell differentiation.8 Although 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis achieved resolution without long-term recurrence, none did so using an IL-23 inhibitor (nor had any of the described patients received IL-23 inhibitors previously).1-6 Given the established safety of IL-23 inhibitors and that they theoretically are well suited for this unique circumstance (by ceasing the main causative cytokine cascades “upstream”) and were efficacious in quickly resolving our patient’s vasculitis, we suggest that ustekinumab may represent
- Reverte M, Etienne M, Fouchard M, et al. Occurrence of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a patient treated with secukinumab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E455-E457.
- Chelli C, Loget J, Vanhaecke C, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis with gut involvement during secukinumab treatment for psoriatic arthritis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00077.
- da Silva Cendon Duran C, Santiago MB. Cutaneous vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020;7:001815.
- Bostan E, Gulseren D, Yalici-Armagan B, et al. Vasculitis during certolizumab pegol and secukinumab treatment: report of two cases. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E15007.
- Perkovic D, Simac P, Katic J. IgA vasculitis during secukinumab therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:2071-2073.
- Villani A, DE Fata Salvatores G, Nappa P, et al. Cutaneous leucocytoclastic vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Ital J Dermatol Venerol. 2021;156(suppl 1 to no. 6):9-10.
- Góis M, Messias A, Carvalho D, et al. MPO-ANCA-associated necrotizing glomerulonephritis in rheumatoid arthritis; a case report and review of literature. J Nephropathol. 2017;6:58-62.
- Jen HY, Chuang YH, Lin SC, et al. Increased serum interleukin-17 and peripheral Th17 cells in children with acute Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011;22:862-868.
- Hetland LE, Susrud KS, Lindahl KH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a literature review. Acta Derm Venereol 2017;97:1160-1166.
- Weedon D. The vasculopathic reaction pattern. In: Houston M, Davie B, eds. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier Limited; 2010:207-211.
- Puig L. Paradoxical reactions: anti-TNFα ants, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab, and others. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2018;53:49-63.
- Nestle F, Kaplan D, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509.
- Pinheiro RR, Lencastre A. Henoch-Schönlein purpura during anti-TNFα therapy: a fortuitous event or an indication to stop therapy? Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:304-305.
- Hello CL, Cohen P, Bousser MG, et al. Suspected hepatitis B vaccination related vasculitis. J Rheumatol. 1999;26:191-194.
- Wolverton SE. Dapsone. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier, Inc; 2021:222-231.
Case Report
A 47-year-old man presented with a sudden-onset rash consisting of red bumps on the abdomen and legs that had been ongoing for several days. He had known psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis that had been well controlled with adalimumab for the last 18 months. He reported concurrent onset of nausea but denied fevers, chills, night sweats, unintentional weight loss, abdominal pain, and pruritus. He endorsed prior cutaneous infections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). His medical history also included diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity. His other medications included oral losartan-hydrochlorothiazide, amlodipine, naproxen, and atorvastatin.
Physical examination revealed numerous thin purpuric papules—some with adherent scale—distributed on the lower legs, extensor forearms, and abdomen. Abdominal lesions were confined to weight-related striae (Figure 1). The palms, soles, oral mucosa, and face were spared. Three punch biopsies were performed, including 1 for direct immunofluorescence (DIF), and the patient was instructed to apply clobetasol to the affected areas twice daily until further notice.

Pathology showed perivascular extravasation of erythrocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and leukocytoclasis surrounding blood vessels associated with fibrin (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence showed granular deposition of IgA, complement component 3, and fibrinogen in a superficial dermal vascular pattern (Figure 3). These results were consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. One specimen was consistent with the patient’s known psoriasis.

Urinalysis revealed moderate hemoglobinuria, and urine microscopy showed 174 red blood cells per high-power field. Creatinine was high at 1.87 mg/dL (reference range, <1.34 mg/dL; patient’s baseline, 0.81 mg/dL) and glomerular filtration rate was low (42 mL/min, patient’s baseline, >60 mL/min [reference range, 90–120 mL/min]). Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (21 mm/h [reference range, 0–22 mm/h]) and C-reactive protein were elevated (2.2 mg/dL [reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL]). Given his history of cutaneous MRSA infections, a bacterial culture swab was collected from the skin surface to check for colonization, which showed moderate growth of MRSA. Naproxen was discontinued over concern of worsening the patient’s renal status. The patient was instructed to rest at home with his legs elevated, wear compression socks when ambulatory, use chlorhexidine antiseptic daily as a body wash when showering, and apply mupirocin three times daily to the biopsy sites. He was referred to urology for his microhematuria, where cystoscopy revealed no abnormalities.A month passed with no improvement of the patient’s cutaneous vasculitis, and his psoriatic arthritis worsened without his usual use of naproxen. He developed abdominal pain and loss of appetite. A prednisone taper was ordered starting at 40 mg/d (28.8 mg/kg), which provided relief of the skin and joint symptoms only until the course was completed 12 days later.

Five weeks after the initial presentation, the patient returned with a more severe eruption consisting of innumerable purpuric papules that coalesced in plaques on the abdomen, arms, and legs. He also had erythematous facial pustules and mild palmar petechiae (Figure 4). Three biopsies were performed, including 1 for DIF and 1 from a pustule on the forehead. Histology and DIF were again consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. The forehead biopsy was compatible with steroid acne (attributed to recent prednisone use) and psoriasis.

Rheumatology was consulted, and adalimumab was discontinued 6 weeks after the initial presentation out of concern for drug-induced cutaneous vasculitis. Vasculitis work-up was unremarkable, including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide, and serum protein electrophoresis. Oral dapsone was started at 100 mg/d, with the tentative plan of starting secukinumab if cutaneous symptoms improved. For 3 weeks, the patient’s cutaneous symptoms steadily improved.
Nine weeks after initial presentation to dermatology (3 weeks after discontinuing adalimumab) the patient self-administered his first dose of secukinumab at home. Several hours later, he reported sudden reappearance of vasculitis. He denied diarrhea, abdominal pain, bowel movement urgency, fevers, fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. Antistreptolysin O and hepatitis A antibodies were negative. He was instructed to hold secukinumab indefinitely.
Four weeks after his only secukinumab injection, the patient reported another episode of acute worsening cutaneous symptoms. A 4-week prednisone taper starting at 40 mg/d was ordered. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to rule out internal malignancy was unremarkable. Around this time, the patient reported major emotional distress related to an unexpected death in his family, which added to a gradual increase in his stress level related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Three weeks later, dapsone was increased to 100 mg twice daily on account of the patient’s adiposity and lack of cutaneous improvement on the lower dose. Subsequently, the vasculitis rapidly improved for 2 weeks. The patient then reported symptoms of headache, dizziness, and chills. He was tested for COVID-19 and was negative. Six weeks after increasing the dapsone dose (5 months after initial presentation), the skin was normalizing, showing only faintly hyperpigmented macules confined to areas of resolved vasculitis (forearms, abdomen, legs).
The patient had been on dapsone 100 mg twice daily for 3 months when he was started on ustekinumab (90 mg at weeks 0 and 4, with planned doses every 12 weeks) for psoriatic arthritis in hopes of withdrawing dapsone. His cutaneous symptoms have remained well controlled on this regimen for 18 months. Lowering of dapsone below 100 mg daily has resulted in recurrent mild vasculitis symptoms; he now maintains the once-daily dosing without negative side effects.
Comment
IgA vasculitis is a form of cutaneous small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) characterized by episodes of palpable purpura on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs that may be associated with arthritis, abdominal pain, and/or hematuria. Although vasculitis is a known potential adverse effect of anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α therapy, cases of adalimumab-induced IgA vasculitis are uncommon. As use of more targeted therapies for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, such as the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab, increases so do reports of associated adverse events. Of 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis, at least 4 were IgA vasculitis (Table).1-6 Another case described one patient with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing secukinumab treatment who experienced necrotizing glomerulonephritis; however, the authors concluded secukinumab likely was not causative in that case, as serologies and urinalyses suggested gradual onset of the process prior to initiating the medication.7

The exact pathogenesis of IgA vasculitis is unclear, but a prevailing theory involves the dysregulation of IgA synthesis and metabolism. Other than increased serum levels of transforming growth factor β, which is a major stimulating factor for IgA production, it also has been hypothesized that the presence of aberrantly hypoglycosylated IgA exposes an autoepitope for recognition by other pathogenic IgG and IgA, leading to the formation of large immune complexes that can readily deposit in postcapillary venules. The deposition of IgA immune complexes in postcapillary venules and the subsequent activation of the complement system causes direct damage to the endothelial cells of vessel walls. This complement activation is evidenced by vascular complement component 3 deposition on DIF (a nonspecific feature of LCV). Chemotaxis of neutrophils ensues, followed by their firm adherence and transendothelial migration (mediated by monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 [MCP-1]). Neutrophil degranulation releases reactive oxygen species and cytokines, which in turn recruit additional leukocytes to the area of inflammation, subsequently undergoing degeneration (leukocytoclasis). Microvascular permeability also is enhanced by MCP-1, allowing exudation of serum, erythrocytes, and fibrin. In the setting of elevated circulating TNF and IL-1, endothelium is stimulated to activate the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. This decreases endothelial fibrinolytic activity, leading to thrombosis. The high venous pressure and low fibrinolytic activity in the lower legs explains why vasculitic lesions often are confined to or begin in this distribution.1,8-10

There also are noteworthy roles for cytokines in LCV. Circulating transforming growth factor β and IL-6—which are necessary for development of T helper 17 (TH17) cells and production of IL-17—are higher in patients with LCV compared to controls. Peripheral blood monocytes in patients with LCV demonstrate higher production of IL-17. Once TH17 cells develop, their survival and phenotype are maintained by IL-23 (considered the master regulator of TH17 differentiation). IL-17 is a potent chemoattractant of IL-8 (CXCL8) and MCP-1, both of which promote neutrophil-mediated perivascular inflammation. The IL-23 and IL-17 pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis also cause neutrophil activation and upregulate transcription of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α), which overlap with those implicated in LCV. Autoimmune disease generally entails some positive feedback loop of progressively severe self-recognition and tissue destruction by the immune system. These shared cytokinetic processes may explain how the internal environment of psoriasis could perpetuate IgA vasculitis.1,2,8,10-12
The mechanisms underlying vasculitis associated with adalimumab are unclear, but hypotheses involve direct toxicity on vessels, capillary deposition of anti-TNF/TNF immune complexes, or an inflammatory process resulting in autoantibodies. Similar hypotheses are posited for secukinumab-associated vasculitis, including deposition of secukinumab–IL-17 complexes. Anti–TNF-α medications may increase TH17 cell numbers, leading to increased production of IL-22 and a resultant immunologic microenvironment conducive to vasculitis. All 6 published cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis that we found had received prior treatment with a TNF-α blocker, but only 1 had occurrence of vasculitis during that treatment.1-6,10
In the 6 cases we reviewed, the time from starting secukinumab to onset of vasculitis ranged from 1 to 18 months. Our patient’s same-day re-emergence of vasculitis after his first secukinumab dose was so acute that we were skeptical of secukinumab as a potential trigger; this may simply have been coincident to the natural waxing and waning of the vasculitis (although onset of IgA vasculitis within 1 day of starting anti–TNF-α therapy has been reported).1-6,13
Specific associations of IgA vasculitis are many and can include bacterial organisms such as Helicobacter pylori, streptococci, and staphylococci. Although internal mucous membrane infections are considered more linked because of the surveillance role of IgA predominantly in mucosal tissues, it is possible that our patient with cutaneous MRSA harbored the same within the nasal mucosa. Our patient also received multiple vaccinations outside our department throughout his clinical course (2 hepatitis B and 1 pneumococcal conjugate), which are known potential triggers for vasculitis. Psychological stress is a known trigger for psoriasis, and given the cytokinetic relationship of psoriasis to vasculitis described previously, it may have indirectly contributed to vasculitis in our case. The anxiety associated with being immunosuppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic and bereavement of losing a family member may have contributed to the refractory nature of our patient’s condition. Renal involvement is relatively common in adults with IgA vasculitis and so should be ruled out, as should occult internal malignancy.8,10,14
It is unclear which of the above factors was causative in our case, but a multifactorial process is likely. Treatment of monoclonal antibody–associated vasculitis entails investigating for triggers and systemic involvement, removing the most likely culprit, quelling the vasculitis acutely, avoiding known potential exacerbators, and introducing an alternative long-term immunomodulant. In all 6 reported similar cases, discontinuation of secukinumab and initiation of prednisone or colchicine led to resolution.1-6 Dapsone also is acceptable for acute control of IgA vasculitis, although this medication is highly lipid soluble and penetrates well into various tissues.15 Thus, lower doses may prove ineffective for obese patients, as was demonstrated in our case. Given the known potential of vaccinations, infections, and other factors (eg, alcohol, penicillin) to trigger IgA vasculitis, these should be avoided.10
Blockade of IL-23 with ustekinumab has been suggested by other authors encountering secukinumab-associated vasculitis, as IL-23 is the main driver and sustainer of TH17 cell differentiation.8 Although 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis achieved resolution without long-term recurrence, none did so using an IL-23 inhibitor (nor had any of the described patients received IL-23 inhibitors previously).1-6 Given the established safety of IL-23 inhibitors and that they theoretically are well suited for this unique circumstance (by ceasing the main causative cytokine cascades “upstream”) and were efficacious in quickly resolving our patient’s vasculitis, we suggest that ustekinumab may represent
Case Report
A 47-year-old man presented with a sudden-onset rash consisting of red bumps on the abdomen and legs that had been ongoing for several days. He had known psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis that had been well controlled with adalimumab for the last 18 months. He reported concurrent onset of nausea but denied fevers, chills, night sweats, unintentional weight loss, abdominal pain, and pruritus. He endorsed prior cutaneous infections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). His medical history also included diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity. His other medications included oral losartan-hydrochlorothiazide, amlodipine, naproxen, and atorvastatin.
Physical examination revealed numerous thin purpuric papules—some with adherent scale—distributed on the lower legs, extensor forearms, and abdomen. Abdominal lesions were confined to weight-related striae (Figure 1). The palms, soles, oral mucosa, and face were spared. Three punch biopsies were performed, including 1 for direct immunofluorescence (DIF), and the patient was instructed to apply clobetasol to the affected areas twice daily until further notice.

Pathology showed perivascular extravasation of erythrocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and leukocytoclasis surrounding blood vessels associated with fibrin (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence showed granular deposition of IgA, complement component 3, and fibrinogen in a superficial dermal vascular pattern (Figure 3). These results were consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. One specimen was consistent with the patient’s known psoriasis.

Urinalysis revealed moderate hemoglobinuria, and urine microscopy showed 174 red blood cells per high-power field. Creatinine was high at 1.87 mg/dL (reference range, <1.34 mg/dL; patient’s baseline, 0.81 mg/dL) and glomerular filtration rate was low (42 mL/min, patient’s baseline, >60 mL/min [reference range, 90–120 mL/min]). Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (21 mm/h [reference range, 0–22 mm/h]) and C-reactive protein were elevated (2.2 mg/dL [reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL]). Given his history of cutaneous MRSA infections, a bacterial culture swab was collected from the skin surface to check for colonization, which showed moderate growth of MRSA. Naproxen was discontinued over concern of worsening the patient’s renal status. The patient was instructed to rest at home with his legs elevated, wear compression socks when ambulatory, use chlorhexidine antiseptic daily as a body wash when showering, and apply mupirocin three times daily to the biopsy sites. He was referred to urology for his microhematuria, where cystoscopy revealed no abnormalities.A month passed with no improvement of the patient’s cutaneous vasculitis, and his psoriatic arthritis worsened without his usual use of naproxen. He developed abdominal pain and loss of appetite. A prednisone taper was ordered starting at 40 mg/d (28.8 mg/kg), which provided relief of the skin and joint symptoms only until the course was completed 12 days later.

Five weeks after the initial presentation, the patient returned with a more severe eruption consisting of innumerable purpuric papules that coalesced in plaques on the abdomen, arms, and legs. He also had erythematous facial pustules and mild palmar petechiae (Figure 4). Three biopsies were performed, including 1 for DIF and 1 from a pustule on the forehead. Histology and DIF were again consistent with IgA small-vessel vasculitis. The forehead biopsy was compatible with steroid acne (attributed to recent prednisone use) and psoriasis.

Rheumatology was consulted, and adalimumab was discontinued 6 weeks after the initial presentation out of concern for drug-induced cutaneous vasculitis. Vasculitis work-up was unremarkable, including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide, and serum protein electrophoresis. Oral dapsone was started at 100 mg/d, with the tentative plan of starting secukinumab if cutaneous symptoms improved. For 3 weeks, the patient’s cutaneous symptoms steadily improved.
Nine weeks after initial presentation to dermatology (3 weeks after discontinuing adalimumab) the patient self-administered his first dose of secukinumab at home. Several hours later, he reported sudden reappearance of vasculitis. He denied diarrhea, abdominal pain, bowel movement urgency, fevers, fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. Antistreptolysin O and hepatitis A antibodies were negative. He was instructed to hold secukinumab indefinitely.
Four weeks after his only secukinumab injection, the patient reported another episode of acute worsening cutaneous symptoms. A 4-week prednisone taper starting at 40 mg/d was ordered. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to rule out internal malignancy was unremarkable. Around this time, the patient reported major emotional distress related to an unexpected death in his family, which added to a gradual increase in his stress level related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Three weeks later, dapsone was increased to 100 mg twice daily on account of the patient’s adiposity and lack of cutaneous improvement on the lower dose. Subsequently, the vasculitis rapidly improved for 2 weeks. The patient then reported symptoms of headache, dizziness, and chills. He was tested for COVID-19 and was negative. Six weeks after increasing the dapsone dose (5 months after initial presentation), the skin was normalizing, showing only faintly hyperpigmented macules confined to areas of resolved vasculitis (forearms, abdomen, legs).
The patient had been on dapsone 100 mg twice daily for 3 months when he was started on ustekinumab (90 mg at weeks 0 and 4, with planned doses every 12 weeks) for psoriatic arthritis in hopes of withdrawing dapsone. His cutaneous symptoms have remained well controlled on this regimen for 18 months. Lowering of dapsone below 100 mg daily has resulted in recurrent mild vasculitis symptoms; he now maintains the once-daily dosing without negative side effects.
Comment
IgA vasculitis is a form of cutaneous small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) characterized by episodes of palpable purpura on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs that may be associated with arthritis, abdominal pain, and/or hematuria. Although vasculitis is a known potential adverse effect of anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α therapy, cases of adalimumab-induced IgA vasculitis are uncommon. As use of more targeted therapies for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, such as the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab, increases so do reports of associated adverse events. Of 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis, at least 4 were IgA vasculitis (Table).1-6 Another case described one patient with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing secukinumab treatment who experienced necrotizing glomerulonephritis; however, the authors concluded secukinumab likely was not causative in that case, as serologies and urinalyses suggested gradual onset of the process prior to initiating the medication.7

The exact pathogenesis of IgA vasculitis is unclear, but a prevailing theory involves the dysregulation of IgA synthesis and metabolism. Other than increased serum levels of transforming growth factor β, which is a major stimulating factor for IgA production, it also has been hypothesized that the presence of aberrantly hypoglycosylated IgA exposes an autoepitope for recognition by other pathogenic IgG and IgA, leading to the formation of large immune complexes that can readily deposit in postcapillary venules. The deposition of IgA immune complexes in postcapillary venules and the subsequent activation of the complement system causes direct damage to the endothelial cells of vessel walls. This complement activation is evidenced by vascular complement component 3 deposition on DIF (a nonspecific feature of LCV). Chemotaxis of neutrophils ensues, followed by their firm adherence and transendothelial migration (mediated by monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 [MCP-1]). Neutrophil degranulation releases reactive oxygen species and cytokines, which in turn recruit additional leukocytes to the area of inflammation, subsequently undergoing degeneration (leukocytoclasis). Microvascular permeability also is enhanced by MCP-1, allowing exudation of serum, erythrocytes, and fibrin. In the setting of elevated circulating TNF and IL-1, endothelium is stimulated to activate the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. This decreases endothelial fibrinolytic activity, leading to thrombosis. The high venous pressure and low fibrinolytic activity in the lower legs explains why vasculitic lesions often are confined to or begin in this distribution.1,8-10

There also are noteworthy roles for cytokines in LCV. Circulating transforming growth factor β and IL-6—which are necessary for development of T helper 17 (TH17) cells and production of IL-17—are higher in patients with LCV compared to controls. Peripheral blood monocytes in patients with LCV demonstrate higher production of IL-17. Once TH17 cells develop, their survival and phenotype are maintained by IL-23 (considered the master regulator of TH17 differentiation). IL-17 is a potent chemoattractant of IL-8 (CXCL8) and MCP-1, both of which promote neutrophil-mediated perivascular inflammation. The IL-23 and IL-17 pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis also cause neutrophil activation and upregulate transcription of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α), which overlap with those implicated in LCV. Autoimmune disease generally entails some positive feedback loop of progressively severe self-recognition and tissue destruction by the immune system. These shared cytokinetic processes may explain how the internal environment of psoriasis could perpetuate IgA vasculitis.1,2,8,10-12
The mechanisms underlying vasculitis associated with adalimumab are unclear, but hypotheses involve direct toxicity on vessels, capillary deposition of anti-TNF/TNF immune complexes, or an inflammatory process resulting in autoantibodies. Similar hypotheses are posited for secukinumab-associated vasculitis, including deposition of secukinumab–IL-17 complexes. Anti–TNF-α medications may increase TH17 cell numbers, leading to increased production of IL-22 and a resultant immunologic microenvironment conducive to vasculitis. All 6 published cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis that we found had received prior treatment with a TNF-α blocker, but only 1 had occurrence of vasculitis during that treatment.1-6,10
In the 6 cases we reviewed, the time from starting secukinumab to onset of vasculitis ranged from 1 to 18 months. Our patient’s same-day re-emergence of vasculitis after his first secukinumab dose was so acute that we were skeptical of secukinumab as a potential trigger; this may simply have been coincident to the natural waxing and waning of the vasculitis (although onset of IgA vasculitis within 1 day of starting anti–TNF-α therapy has been reported).1-6,13
Specific associations of IgA vasculitis are many and can include bacterial organisms such as Helicobacter pylori, streptococci, and staphylococci. Although internal mucous membrane infections are considered more linked because of the surveillance role of IgA predominantly in mucosal tissues, it is possible that our patient with cutaneous MRSA harbored the same within the nasal mucosa. Our patient also received multiple vaccinations outside our department throughout his clinical course (2 hepatitis B and 1 pneumococcal conjugate), which are known potential triggers for vasculitis. Psychological stress is a known trigger for psoriasis, and given the cytokinetic relationship of psoriasis to vasculitis described previously, it may have indirectly contributed to vasculitis in our case. The anxiety associated with being immunosuppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic and bereavement of losing a family member may have contributed to the refractory nature of our patient’s condition. Renal involvement is relatively common in adults with IgA vasculitis and so should be ruled out, as should occult internal malignancy.8,10,14
It is unclear which of the above factors was causative in our case, but a multifactorial process is likely. Treatment of monoclonal antibody–associated vasculitis entails investigating for triggers and systemic involvement, removing the most likely culprit, quelling the vasculitis acutely, avoiding known potential exacerbators, and introducing an alternative long-term immunomodulant. In all 6 reported similar cases, discontinuation of secukinumab and initiation of prednisone or colchicine led to resolution.1-6 Dapsone also is acceptable for acute control of IgA vasculitis, although this medication is highly lipid soluble and penetrates well into various tissues.15 Thus, lower doses may prove ineffective for obese patients, as was demonstrated in our case. Given the known potential of vaccinations, infections, and other factors (eg, alcohol, penicillin) to trigger IgA vasculitis, these should be avoided.10
Blockade of IL-23 with ustekinumab has been suggested by other authors encountering secukinumab-associated vasculitis, as IL-23 is the main driver and sustainer of TH17 cell differentiation.8 Although 6 previously reported cases of secukinumab-associated vasculitis achieved resolution without long-term recurrence, none did so using an IL-23 inhibitor (nor had any of the described patients received IL-23 inhibitors previously).1-6 Given the established safety of IL-23 inhibitors and that they theoretically are well suited for this unique circumstance (by ceasing the main causative cytokine cascades “upstream”) and were efficacious in quickly resolving our patient’s vasculitis, we suggest that ustekinumab may represent
- Reverte M, Etienne M, Fouchard M, et al. Occurrence of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a patient treated with secukinumab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E455-E457.
- Chelli C, Loget J, Vanhaecke C, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis with gut involvement during secukinumab treatment for psoriatic arthritis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00077.
- da Silva Cendon Duran C, Santiago MB. Cutaneous vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020;7:001815.
- Bostan E, Gulseren D, Yalici-Armagan B, et al. Vasculitis during certolizumab pegol and secukinumab treatment: report of two cases. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E15007.
- Perkovic D, Simac P, Katic J. IgA vasculitis during secukinumab therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:2071-2073.
- Villani A, DE Fata Salvatores G, Nappa P, et al. Cutaneous leucocytoclastic vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Ital J Dermatol Venerol. 2021;156(suppl 1 to no. 6):9-10.
- Góis M, Messias A, Carvalho D, et al. MPO-ANCA-associated necrotizing glomerulonephritis in rheumatoid arthritis; a case report and review of literature. J Nephropathol. 2017;6:58-62.
- Jen HY, Chuang YH, Lin SC, et al. Increased serum interleukin-17 and peripheral Th17 cells in children with acute Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011;22:862-868.
- Hetland LE, Susrud KS, Lindahl KH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a literature review. Acta Derm Venereol 2017;97:1160-1166.
- Weedon D. The vasculopathic reaction pattern. In: Houston M, Davie B, eds. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier Limited; 2010:207-211.
- Puig L. Paradoxical reactions: anti-TNFα ants, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab, and others. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2018;53:49-63.
- Nestle F, Kaplan D, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509.
- Pinheiro RR, Lencastre A. Henoch-Schönlein purpura during anti-TNFα therapy: a fortuitous event or an indication to stop therapy? Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:304-305.
- Hello CL, Cohen P, Bousser MG, et al. Suspected hepatitis B vaccination related vasculitis. J Rheumatol. 1999;26:191-194.
- Wolverton SE. Dapsone. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier, Inc; 2021:222-231.
- Reverte M, Etienne M, Fouchard M, et al. Occurrence of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a patient treated with secukinumab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E455-E457.
- Chelli C, Loget J, Vanhaecke C, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis with gut involvement during secukinumab treatment for psoriatic arthritis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00077.
- da Silva Cendon Duran C, Santiago MB. Cutaneous vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020;7:001815.
- Bostan E, Gulseren D, Yalici-Armagan B, et al. Vasculitis during certolizumab pegol and secukinumab treatment: report of two cases. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E15007.
- Perkovic D, Simac P, Katic J. IgA vasculitis during secukinumab therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:2071-2073.
- Villani A, DE Fata Salvatores G, Nappa P, et al. Cutaneous leucocytoclastic vasculitis during secukinumab treatment. Ital J Dermatol Venerol. 2021;156(suppl 1 to no. 6):9-10.
- Góis M, Messias A, Carvalho D, et al. MPO-ANCA-associated necrotizing glomerulonephritis in rheumatoid arthritis; a case report and review of literature. J Nephropathol. 2017;6:58-62.
- Jen HY, Chuang YH, Lin SC, et al. Increased serum interleukin-17 and peripheral Th17 cells in children with acute Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011;22:862-868.
- Hetland LE, Susrud KS, Lindahl KH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a literature review. Acta Derm Venereol 2017;97:1160-1166.
- Weedon D. The vasculopathic reaction pattern. In: Houston M, Davie B, eds. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier Limited; 2010:207-211.
- Puig L. Paradoxical reactions: anti-TNFα ants, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab, and others. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2018;53:49-63.
- Nestle F, Kaplan D, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509.
- Pinheiro RR, Lencastre A. Henoch-Schönlein purpura during anti-TNFα therapy: a fortuitous event or an indication to stop therapy? Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:304-305.
- Hello CL, Cohen P, Bousser MG, et al. Suspected hepatitis B vaccination related vasculitis. J Rheumatol. 1999;26:191-194.
- Wolverton SE. Dapsone. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier, Inc; 2021:222-231.
Practice Points
- Biologic medications including adalimumab and more rarely secukinumab may be associated with leukocytoclastic vasculitis; a smaller subset of patients may experience IgA vasculitis.
- The IL-23 blocker ustekinumab may represent an ideal therapeutic agent when secukinumabassociated vasculitis is suspected. Because IL-23 is the main driver and sustainer of TH17 cell differentiation, it may cease the main causative cytokine cascades “upstream.”
JAK inhibitors show no excess cardiovascular safety signal in French nationwide cohort
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Climate change: Commentary in four dermatology journals calls for emergency action
“moving beyond merely discussing skin-related impacts” and toward prioritizing both patient and planetary health.
Dermatologists must make emissions-saving changes in everyday practice, for instance, and the specialty must enlist key stakeholders in public health, nonprofits, and industry – that is, pharmaceutical and medical supply companies – in finding solutions to help mitigate and adapt to climate change, wrote Eva Rawlings Parker, MD, and Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD.
“We have an ethical imperative to act,” they wrote. “The time is now for dermatologists and our medical societies to collectively rise to meet this crisis.”
Their commentary was published online in the International Journal of Dermatology , Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, British Journal of Dermatology, and Pediatric Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Parker, assistant professor of dermatology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said that she and Dr. Boos, associate professor in the division of dermatology and department of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, were motivated to write the editorial upon finding that dermatology was not represented among more than 230 medical journals that published an editorial in September 2021 calling for emergency action to limit global warming and protect health. In addition to the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, the copublishing journals represented numerous specialties, from nursing and pediatrics, to cardiology, rheumatology, and gastroenterology.
The editorial was not published in any dermatology journals, Dr. Parker said. “It was incredibly disappointing for me along with many of my colleagues who advocate for climate action because we realized it was a missed opportunity for dermatology to align with other medical specialties and be on the forefront of leading climate action to protect health.”
‘A threat multiplier’
The impact of climate change on skin disease is “an incredibly important part of our conversation as dermatologists because many cutaneous diseases are climate sensitive and we’re often seeing the effects of climate change every day in our clinical practices,” Dr. Parker said.
In fact, the impact on skin disease needs to be explored much further through more robust research funding, so that dermatology can better understand not only the incidence and severity of climate-induced changes in skin diseases – including and beyond atopic dermatitis, acne, and psoriasis – but also the mechanisms and pathophysiology involved, she said.
However, the impacts are much broader, she and Dr. Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, maintain in their commentary. “An essential concept to broker among dermatologists is that the impacts of climate change extend well beyond skin disease by also placing broad pressure” on infrastructure, the economy, financial markets, global supply chains, food and water insecurity, and more, they wrote, noting the deep inequities of climate change.
Climate change is a “threat multiplier for public health, equity, and health systems,” the commentary says. “The confluence of these climate-related pressures should sound alarm bells as they place enormous jeopardy on the practice of dermatology across all scales and regions.”
Health care is among the most carbon-intensive service sectors worldwide, contributing to almost 5% of greenhouse gas emissions globally, the commentary says. And nationally, of the estimated greenhouse gas emissions from the United States, the health care sector contributes 10%, Dr. Parker said in the interview, referring to a 2016 report.
In addition, according to a 2019 report, the United States is the top contributor to health care’s global climate footprint, contributing 27% of health care’s global emissions, Dr. Parker noted.
In their commentary, she and Dr. Boos wrote that individually and practice wide, dermatologists can impact decarbonization through measures such as virtual attendance at medical meetings and greater utilization of telehealth services. Reductions in carbon emissions were demonstrated for virtual isotretinoin follow-up visits in a recent study, and these savings could be extrapolated to other routine follow-up visits for conditions such as rosacea, monitoring of biologics in patients with well-controlled disease, and postoperative wound checks, they said.
But when it comes to measures such as significantly reducing packaging and waste and “curating supply chains to make them more sustainable,” it is medical societies that have the “larger voice and broader relationship with the pharmaceutical industry” and with medical supply manufacturers and distributors, Dr. Parker explained in the interview, noting the potential for reducing the extensive amount of packaging used for drug samples.
Dr. Parker cochairs the American Academy of Dermatology’s Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues, which was established several years ago, and Dr. Boos is a member of the group’s executive committee.
AAD actions
In its 2018 Position Statement on Climate and Health, the American Academy of Dermatology resolved to raise awareness of the effects of climate change on the skin and educate patients about this, and to “work with other medical societies in ongoing and future efforts to educate the public and mitigate the effects of climate change on global health.”
Asked about the commentary’s call for more collaboration with industry and other stakeholders – and the impact that organized dermatology can have on planetary health – Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said in an email that the AAD is “first and foremost an organization focused on providing gold-standard educational resources for dermatologists.”
The academy recognizes that “there are many dermatologic consequences of climate change that will increasingly affect our patients and challenge our membership,” and it has provided education on climate change in forums such as articles, podcasts, and sessions at AAD meetings, said Dr. Kaufmann, clinical professor in the department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Regarding collaboration with other societies, he said that the AAD’s “focus to date has been on how to provide our members with educational resources to understand and prepare for how climate change may impact their practices and the dermatologic health of their patients,” he said.
The AAD has also sought to address its own carbon footprint and improve sustainability of its operations, including taking steps to reduce plastic and paper waste at its educational events, and to eliminate plastic waste associated with mailing resources like its member magazine, Dr. Kaufmann noted.
And in keeping with the Academy pledge – also articulated in the 2018 position statement – to support and facilitate dermatologists’ efforts to decrease their carbon footprint “in a cost effective (or cost-saving) manner,” Dr. Kaufmann said that the AAD has been offering a program called My Green Doctor as a free benefit of membership.
‘Be part of the solution’
In an interview, Mary E. Maloney, MD, professor of medicine and director of dermatologic surgery at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said her practice did an audit of their surgical area and found ways to increase the use of paper-packaged gauze – and decrease use of gauze in hard plastic containers – and otherwise decrease the amount of disposables, all of which take “huge amounts of resources” to create.
In the process, “we found significant savings,” she said. “Little things can turn out, in the long run, to be big things.”
Asked about the commentary, Dr. Maloney, who is involved in the AAD’s climate change resource group, said “the message is that yes, we need to be aware of the diseases affected by climate change. But our greater imperative is to be part of the solution and not part of the problem as far as doing things that affect climate change.”
Organized dermatology needs to broaden its advocacy, she said. “I don’t want us to stop advocating for things for our patients, but I do want us to start advocating for the world ... If we don’t try to [mitigate] climate change, we won’t have patients to advocate for.”
Dr. Parker, an associate editor of The Journal of Climate Change and Health, and Dr. Boos declared no conflicts of interest and no funding source for their commentary. Dr. Maloney said she has no conflicts of interest.
“moving beyond merely discussing skin-related impacts” and toward prioritizing both patient and planetary health.
Dermatologists must make emissions-saving changes in everyday practice, for instance, and the specialty must enlist key stakeholders in public health, nonprofits, and industry – that is, pharmaceutical and medical supply companies – in finding solutions to help mitigate and adapt to climate change, wrote Eva Rawlings Parker, MD, and Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD.
“We have an ethical imperative to act,” they wrote. “The time is now for dermatologists and our medical societies to collectively rise to meet this crisis.”
Their commentary was published online in the International Journal of Dermatology , Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, British Journal of Dermatology, and Pediatric Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Parker, assistant professor of dermatology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said that she and Dr. Boos, associate professor in the division of dermatology and department of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, were motivated to write the editorial upon finding that dermatology was not represented among more than 230 medical journals that published an editorial in September 2021 calling for emergency action to limit global warming and protect health. In addition to the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, the copublishing journals represented numerous specialties, from nursing and pediatrics, to cardiology, rheumatology, and gastroenterology.
The editorial was not published in any dermatology journals, Dr. Parker said. “It was incredibly disappointing for me along with many of my colleagues who advocate for climate action because we realized it was a missed opportunity for dermatology to align with other medical specialties and be on the forefront of leading climate action to protect health.”
‘A threat multiplier’
The impact of climate change on skin disease is “an incredibly important part of our conversation as dermatologists because many cutaneous diseases are climate sensitive and we’re often seeing the effects of climate change every day in our clinical practices,” Dr. Parker said.
In fact, the impact on skin disease needs to be explored much further through more robust research funding, so that dermatology can better understand not only the incidence and severity of climate-induced changes in skin diseases – including and beyond atopic dermatitis, acne, and psoriasis – but also the mechanisms and pathophysiology involved, she said.
However, the impacts are much broader, she and Dr. Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, maintain in their commentary. “An essential concept to broker among dermatologists is that the impacts of climate change extend well beyond skin disease by also placing broad pressure” on infrastructure, the economy, financial markets, global supply chains, food and water insecurity, and more, they wrote, noting the deep inequities of climate change.
Climate change is a “threat multiplier for public health, equity, and health systems,” the commentary says. “The confluence of these climate-related pressures should sound alarm bells as they place enormous jeopardy on the practice of dermatology across all scales and regions.”
Health care is among the most carbon-intensive service sectors worldwide, contributing to almost 5% of greenhouse gas emissions globally, the commentary says. And nationally, of the estimated greenhouse gas emissions from the United States, the health care sector contributes 10%, Dr. Parker said in the interview, referring to a 2016 report.
In addition, according to a 2019 report, the United States is the top contributor to health care’s global climate footprint, contributing 27% of health care’s global emissions, Dr. Parker noted.
In their commentary, she and Dr. Boos wrote that individually and practice wide, dermatologists can impact decarbonization through measures such as virtual attendance at medical meetings and greater utilization of telehealth services. Reductions in carbon emissions were demonstrated for virtual isotretinoin follow-up visits in a recent study, and these savings could be extrapolated to other routine follow-up visits for conditions such as rosacea, monitoring of biologics in patients with well-controlled disease, and postoperative wound checks, they said.
But when it comes to measures such as significantly reducing packaging and waste and “curating supply chains to make them more sustainable,” it is medical societies that have the “larger voice and broader relationship with the pharmaceutical industry” and with medical supply manufacturers and distributors, Dr. Parker explained in the interview, noting the potential for reducing the extensive amount of packaging used for drug samples.
Dr. Parker cochairs the American Academy of Dermatology’s Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues, which was established several years ago, and Dr. Boos is a member of the group’s executive committee.
AAD actions
In its 2018 Position Statement on Climate and Health, the American Academy of Dermatology resolved to raise awareness of the effects of climate change on the skin and educate patients about this, and to “work with other medical societies in ongoing and future efforts to educate the public and mitigate the effects of climate change on global health.”
Asked about the commentary’s call for more collaboration with industry and other stakeholders – and the impact that organized dermatology can have on planetary health – Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said in an email that the AAD is “first and foremost an organization focused on providing gold-standard educational resources for dermatologists.”
The academy recognizes that “there are many dermatologic consequences of climate change that will increasingly affect our patients and challenge our membership,” and it has provided education on climate change in forums such as articles, podcasts, and sessions at AAD meetings, said Dr. Kaufmann, clinical professor in the department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Regarding collaboration with other societies, he said that the AAD’s “focus to date has been on how to provide our members with educational resources to understand and prepare for how climate change may impact their practices and the dermatologic health of their patients,” he said.
The AAD has also sought to address its own carbon footprint and improve sustainability of its operations, including taking steps to reduce plastic and paper waste at its educational events, and to eliminate plastic waste associated with mailing resources like its member magazine, Dr. Kaufmann noted.
And in keeping with the Academy pledge – also articulated in the 2018 position statement – to support and facilitate dermatologists’ efforts to decrease their carbon footprint “in a cost effective (or cost-saving) manner,” Dr. Kaufmann said that the AAD has been offering a program called My Green Doctor as a free benefit of membership.
‘Be part of the solution’
In an interview, Mary E. Maloney, MD, professor of medicine and director of dermatologic surgery at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said her practice did an audit of their surgical area and found ways to increase the use of paper-packaged gauze – and decrease use of gauze in hard plastic containers – and otherwise decrease the amount of disposables, all of which take “huge amounts of resources” to create.
In the process, “we found significant savings,” she said. “Little things can turn out, in the long run, to be big things.”
Asked about the commentary, Dr. Maloney, who is involved in the AAD’s climate change resource group, said “the message is that yes, we need to be aware of the diseases affected by climate change. But our greater imperative is to be part of the solution and not part of the problem as far as doing things that affect climate change.”
Organized dermatology needs to broaden its advocacy, she said. “I don’t want us to stop advocating for things for our patients, but I do want us to start advocating for the world ... If we don’t try to [mitigate] climate change, we won’t have patients to advocate for.”
Dr. Parker, an associate editor of The Journal of Climate Change and Health, and Dr. Boos declared no conflicts of interest and no funding source for their commentary. Dr. Maloney said she has no conflicts of interest.
“moving beyond merely discussing skin-related impacts” and toward prioritizing both patient and planetary health.
Dermatologists must make emissions-saving changes in everyday practice, for instance, and the specialty must enlist key stakeholders in public health, nonprofits, and industry – that is, pharmaceutical and medical supply companies – in finding solutions to help mitigate and adapt to climate change, wrote Eva Rawlings Parker, MD, and Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD.
“We have an ethical imperative to act,” they wrote. “The time is now for dermatologists and our medical societies to collectively rise to meet this crisis.”
Their commentary was published online in the International Journal of Dermatology , Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, British Journal of Dermatology, and Pediatric Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Parker, assistant professor of dermatology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said that she and Dr. Boos, associate professor in the division of dermatology and department of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, were motivated to write the editorial upon finding that dermatology was not represented among more than 230 medical journals that published an editorial in September 2021 calling for emergency action to limit global warming and protect health. In addition to the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, the copublishing journals represented numerous specialties, from nursing and pediatrics, to cardiology, rheumatology, and gastroenterology.
The editorial was not published in any dermatology journals, Dr. Parker said. “It was incredibly disappointing for me along with many of my colleagues who advocate for climate action because we realized it was a missed opportunity for dermatology to align with other medical specialties and be on the forefront of leading climate action to protect health.”
‘A threat multiplier’
The impact of climate change on skin disease is “an incredibly important part of our conversation as dermatologists because many cutaneous diseases are climate sensitive and we’re often seeing the effects of climate change every day in our clinical practices,” Dr. Parker said.
In fact, the impact on skin disease needs to be explored much further through more robust research funding, so that dermatology can better understand not only the incidence and severity of climate-induced changes in skin diseases – including and beyond atopic dermatitis, acne, and psoriasis – but also the mechanisms and pathophysiology involved, she said.
However, the impacts are much broader, she and Dr. Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, maintain in their commentary. “An essential concept to broker among dermatologists is that the impacts of climate change extend well beyond skin disease by also placing broad pressure” on infrastructure, the economy, financial markets, global supply chains, food and water insecurity, and more, they wrote, noting the deep inequities of climate change.
Climate change is a “threat multiplier for public health, equity, and health systems,” the commentary says. “The confluence of these climate-related pressures should sound alarm bells as they place enormous jeopardy on the practice of dermatology across all scales and regions.”
Health care is among the most carbon-intensive service sectors worldwide, contributing to almost 5% of greenhouse gas emissions globally, the commentary says. And nationally, of the estimated greenhouse gas emissions from the United States, the health care sector contributes 10%, Dr. Parker said in the interview, referring to a 2016 report.
In addition, according to a 2019 report, the United States is the top contributor to health care’s global climate footprint, contributing 27% of health care’s global emissions, Dr. Parker noted.
In their commentary, she and Dr. Boos wrote that individually and practice wide, dermatologists can impact decarbonization through measures such as virtual attendance at medical meetings and greater utilization of telehealth services. Reductions in carbon emissions were demonstrated for virtual isotretinoin follow-up visits in a recent study, and these savings could be extrapolated to other routine follow-up visits for conditions such as rosacea, monitoring of biologics in patients with well-controlled disease, and postoperative wound checks, they said.
But when it comes to measures such as significantly reducing packaging and waste and “curating supply chains to make them more sustainable,” it is medical societies that have the “larger voice and broader relationship with the pharmaceutical industry” and with medical supply manufacturers and distributors, Dr. Parker explained in the interview, noting the potential for reducing the extensive amount of packaging used for drug samples.
Dr. Parker cochairs the American Academy of Dermatology’s Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues, which was established several years ago, and Dr. Boos is a member of the group’s executive committee.
AAD actions
In its 2018 Position Statement on Climate and Health, the American Academy of Dermatology resolved to raise awareness of the effects of climate change on the skin and educate patients about this, and to “work with other medical societies in ongoing and future efforts to educate the public and mitigate the effects of climate change on global health.”
Asked about the commentary’s call for more collaboration with industry and other stakeholders – and the impact that organized dermatology can have on planetary health – Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said in an email that the AAD is “first and foremost an organization focused on providing gold-standard educational resources for dermatologists.”
The academy recognizes that “there are many dermatologic consequences of climate change that will increasingly affect our patients and challenge our membership,” and it has provided education on climate change in forums such as articles, podcasts, and sessions at AAD meetings, said Dr. Kaufmann, clinical professor in the department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Regarding collaboration with other societies, he said that the AAD’s “focus to date has been on how to provide our members with educational resources to understand and prepare for how climate change may impact their practices and the dermatologic health of their patients,” he said.
The AAD has also sought to address its own carbon footprint and improve sustainability of its operations, including taking steps to reduce plastic and paper waste at its educational events, and to eliminate plastic waste associated with mailing resources like its member magazine, Dr. Kaufmann noted.
And in keeping with the Academy pledge – also articulated in the 2018 position statement – to support and facilitate dermatologists’ efforts to decrease their carbon footprint “in a cost effective (or cost-saving) manner,” Dr. Kaufmann said that the AAD has been offering a program called My Green Doctor as a free benefit of membership.
‘Be part of the solution’
In an interview, Mary E. Maloney, MD, professor of medicine and director of dermatologic surgery at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said her practice did an audit of their surgical area and found ways to increase the use of paper-packaged gauze – and decrease use of gauze in hard plastic containers – and otherwise decrease the amount of disposables, all of which take “huge amounts of resources” to create.
In the process, “we found significant savings,” she said. “Little things can turn out, in the long run, to be big things.”
Asked about the commentary, Dr. Maloney, who is involved in the AAD’s climate change resource group, said “the message is that yes, we need to be aware of the diseases affected by climate change. But our greater imperative is to be part of the solution and not part of the problem as far as doing things that affect climate change.”
Organized dermatology needs to broaden its advocacy, she said. “I don’t want us to stop advocating for things for our patients, but I do want us to start advocating for the world ... If we don’t try to [mitigate] climate change, we won’t have patients to advocate for.”
Dr. Parker, an associate editor of The Journal of Climate Change and Health, and Dr. Boos declared no conflicts of interest and no funding source for their commentary. Dr. Maloney said she has no conflicts of interest.
Dermatologists fear effects of Dobbs decision for patients on isotretinoin, methotrexate
More than 3 months after the Dobbs decision by the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade and revoked the constitutional right to an abortion, Some have beefed up their already stringent instructions and lengthy conversations about avoiding pregnancy while on the medication.
The major fear is that a patient who is taking contraceptive precautions, in accordance with the isotretinoin risk-management program, iPLEDGE, but still becomes pregnant while on isotretinoin may find out about the pregnancy too late to undergo an abortion in her own state and may not be able to travel to another state – or the patient may live in a state where abortions are entirely prohibited and is unable to travel to another state.
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane; its former brand name was Accutane.
As of Oct. 7, a total of 14 states have banned most abortions, while 4 others have bans at 6, 15, 18, or 20 weeks. Attempts to restrict abortion on several other states are underway.
“To date, we don’t know of any specific effects of the Dobbs decision on isotretinoin prescribing, but with abortion access banned in many states, we anticipate that this could be a very real issue for individuals who accidentally become pregnant while taking isotretinoin,” said Ilona Frieden, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s iPLEDGE Workgroup.
The iPLEDGE REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) is the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program that is in place to manage the risk of isotretinoin teratogenicity and minimize fetal exposure. The work group meets with the FDA and isotretinoin manufacturers to keep the program safe and operating smoothly. The iPLEDGE workgroup has not yet issued any specific statements on the implications of the Dobbs decision on prescribing isotretinoin.
But work on the issue is ongoing by the American Academy of Dermatology. In a statement issued in September, Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said that the academy “is continuing to work with its Patient Guidance for State Regulations Regarding Reproductive Health Task Force to help dermatologists best navigate state laws about how care should be implemented for patients who are or might become pregnant, and have been exposed to teratogenic medications.”
The task force, working with the academy, is “in the process of developing resources to help members better assist patients and have a productive and caring dialogue with them,” according to the statement. No specific timeline was given for when those resources might be available.
Methotrexate prescriptions
Also of concern are prescriptions for methotrexate, which is prescribed for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other skin diseases. Soon after the Dobbs decision was announced on June 24, pharmacies began to require pharmacists in states that banned abortions to verify that a prescription for methotrexate was not intended for an abortion, since methotrexate is used in combination with misoprostol for termination of an early pregnancy.
The action was taken, spokespersons for several major pharmacies said, to comply with state laws. According to Kara Page, a CVS spokesperson: “Pharmacists are caught in the middle on this issue.” Laws in some states, she told this news organization, “restrict the dispensing of medications for the purpose of inducing an abortion. These laws, some of which include criminal penalties, have forced us to require pharmacists in these states to validate that the intended indication is not to terminate a pregnancy before they can fill a prescription for methotrexate.”
“New laws in various states require additional steps for dispensing certain prescriptions and apply to all pharmacies, including Walgreens,” Fraser Engerman, a spokesperson for Walgreens, told this news organization. “In these states, our pharmacists work closely with prescribers as needed, to fill lawful, clinically appropriate prescriptions. We provide ongoing training and information to help our pharmacists understand the latest requirements in their area, and with these supports, the expectation is they are empowered to fill these prescriptions.”
The iPLEDGE program has numerous requirements before a patient can begin isotretinoin treatment. Patients capable of becoming pregnant must agree to use two effective forms of birth control during the entire treatment period, which typically lasts 4 or 5 months, as well as 1 month before and 1 month after treatment, or commit to total abstinence during that time.
Perspective: A Georgia dermatologist
Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, who sees patients regularly, practices in Georgia, where abortion is now banned at about 6 weeks of pregnancy. Dr. Yeung worries that some dermatologists in Georgia and elsewhere may not even want to take the risk of prescribing isotretinoin, although the results in treating resistant acne are well documented.
That isn’t his only concern. “Some may not want to prescribe it to a patient who reports they are abstinent and instead require them to go on two forms [of contraception].” Or some women who are not sexually active with anyone who can get them pregnant may also be asked to go on contraception, he said. Abstinence is an alternative option in iPLEDGE.
In the past, he said, well before the Dobbs decision, some doctors have argued that iPLEDGE should not include abstinence as an option. That 2020 report was challenged by others who pointed out that removing the abstinence option would pose ethical issues and may disproportionately affect minorities and others.
Before the Dobbs decision, Dr. Yeung noted, dermatologists prescribing isotretinoin focused on pregnancy prevention but knew that if pregnancy accidentally occurred, abortion was available as an option. “The reality after the decision is, it may or may not be available to all our patients.”
Of the 14 states banning most abortions, 10 are clustered within the South and Southeast. A woman living in Arkansas, which bans most abortions, for example, is surrounded by 6 other states that do the same.
Perspective: An Arizona dermatologist
Christina Kranc, MD, is a general dermatologist in Phoenix and Scottsdale. Arizona now bans most abortions. However, this has not changed her practice much when prescribing isotretinoin, she told this news organization, because when selecting appropriate candidates for the medication, she is strict on the contraceptive requirement, and only very rarely agrees to a patient relying on abstinence.
And if a patient capable of becoming pregnant was only having sex with another patient capable of becoming pregnant? Dr. Kranc said she would still require contraception unless it was impossible for pregnancy to occur.
Among the many scenarios a dermatologist might have to consider are a lesbian cisgender woman who is having, or has only had, sexual activity with another cisgender women.
Perspective: A Connecticut dermatologist
The concern is not only about isotretinoin but all teratogenic drugs, according to Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, vice chair of dermatology and professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics at the University of Connecticut, Farmington. She often prescribes methotrexate, which is also teratogenic.
Her advice for colleagues: “Whether you believe in abortion or not is irrelevant; it’s something you discuss with your patients.” She, too, fears that doctors in states banning abortions will stop prescribing these medications, “and that is very sad.”
For those practicing in states limiting or banning abortions, Dr. Grant-Kels said, “They need to have an even longer discussion with their patients about how serious this is.” Those doctors need to talk about not only two or three types of birth control, but also discuss with the patient about the potential need for travel, should pregnancy occur and abortion be the chosen option.
Although the newer biologics are an option for psoriasis, they are expensive. And, she said, many insurers require a step-therapy approach, and “want you to start with cheaper medications,” such as methotrexate. As a result, “in some states you won’t have access to the targeted therapies unless a patient fails something like methotrexate.”
Dr. Grant-Kels worries in particular about low-income women who may not have the means to travel to get an abortion.
Need for EC education
In a recent survey of 57 pediatric dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, only a third said they felt confident in their understanding of emergency contraception.
The authors of the study noted that the most common reasons for pregnancies during isotretinoin therapy reported to the FDA from 2011 to 2017 “included ineffective or inconsistent use” of contraceptives and “unsuccessful abstinence,” and recommended that physicians who prescribe isotretinoin update and increase their understanding of emergency contraception.
Dr. Yeung, Dr. Kranc, Dr. Grant-Kels, and Dr. Frieden reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 3 months after the Dobbs decision by the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade and revoked the constitutional right to an abortion, Some have beefed up their already stringent instructions and lengthy conversations about avoiding pregnancy while on the medication.
The major fear is that a patient who is taking contraceptive precautions, in accordance with the isotretinoin risk-management program, iPLEDGE, but still becomes pregnant while on isotretinoin may find out about the pregnancy too late to undergo an abortion in her own state and may not be able to travel to another state – or the patient may live in a state where abortions are entirely prohibited and is unable to travel to another state.
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane; its former brand name was Accutane.
As of Oct. 7, a total of 14 states have banned most abortions, while 4 others have bans at 6, 15, 18, or 20 weeks. Attempts to restrict abortion on several other states are underway.
“To date, we don’t know of any specific effects of the Dobbs decision on isotretinoin prescribing, but with abortion access banned in many states, we anticipate that this could be a very real issue for individuals who accidentally become pregnant while taking isotretinoin,” said Ilona Frieden, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s iPLEDGE Workgroup.
The iPLEDGE REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) is the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program that is in place to manage the risk of isotretinoin teratogenicity and minimize fetal exposure. The work group meets with the FDA and isotretinoin manufacturers to keep the program safe and operating smoothly. The iPLEDGE workgroup has not yet issued any specific statements on the implications of the Dobbs decision on prescribing isotretinoin.
But work on the issue is ongoing by the American Academy of Dermatology. In a statement issued in September, Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said that the academy “is continuing to work with its Patient Guidance for State Regulations Regarding Reproductive Health Task Force to help dermatologists best navigate state laws about how care should be implemented for patients who are or might become pregnant, and have been exposed to teratogenic medications.”
The task force, working with the academy, is “in the process of developing resources to help members better assist patients and have a productive and caring dialogue with them,” according to the statement. No specific timeline was given for when those resources might be available.
Methotrexate prescriptions
Also of concern are prescriptions for methotrexate, which is prescribed for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other skin diseases. Soon after the Dobbs decision was announced on June 24, pharmacies began to require pharmacists in states that banned abortions to verify that a prescription for methotrexate was not intended for an abortion, since methotrexate is used in combination with misoprostol for termination of an early pregnancy.
The action was taken, spokespersons for several major pharmacies said, to comply with state laws. According to Kara Page, a CVS spokesperson: “Pharmacists are caught in the middle on this issue.” Laws in some states, she told this news organization, “restrict the dispensing of medications for the purpose of inducing an abortion. These laws, some of which include criminal penalties, have forced us to require pharmacists in these states to validate that the intended indication is not to terminate a pregnancy before they can fill a prescription for methotrexate.”
“New laws in various states require additional steps for dispensing certain prescriptions and apply to all pharmacies, including Walgreens,” Fraser Engerman, a spokesperson for Walgreens, told this news organization. “In these states, our pharmacists work closely with prescribers as needed, to fill lawful, clinically appropriate prescriptions. We provide ongoing training and information to help our pharmacists understand the latest requirements in their area, and with these supports, the expectation is they are empowered to fill these prescriptions.”
The iPLEDGE program has numerous requirements before a patient can begin isotretinoin treatment. Patients capable of becoming pregnant must agree to use two effective forms of birth control during the entire treatment period, which typically lasts 4 or 5 months, as well as 1 month before and 1 month after treatment, or commit to total abstinence during that time.
Perspective: A Georgia dermatologist
Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, who sees patients regularly, practices in Georgia, where abortion is now banned at about 6 weeks of pregnancy. Dr. Yeung worries that some dermatologists in Georgia and elsewhere may not even want to take the risk of prescribing isotretinoin, although the results in treating resistant acne are well documented.
That isn’t his only concern. “Some may not want to prescribe it to a patient who reports they are abstinent and instead require them to go on two forms [of contraception].” Or some women who are not sexually active with anyone who can get them pregnant may also be asked to go on contraception, he said. Abstinence is an alternative option in iPLEDGE.
In the past, he said, well before the Dobbs decision, some doctors have argued that iPLEDGE should not include abstinence as an option. That 2020 report was challenged by others who pointed out that removing the abstinence option would pose ethical issues and may disproportionately affect minorities and others.
Before the Dobbs decision, Dr. Yeung noted, dermatologists prescribing isotretinoin focused on pregnancy prevention but knew that if pregnancy accidentally occurred, abortion was available as an option. “The reality after the decision is, it may or may not be available to all our patients.”
Of the 14 states banning most abortions, 10 are clustered within the South and Southeast. A woman living in Arkansas, which bans most abortions, for example, is surrounded by 6 other states that do the same.
Perspective: An Arizona dermatologist
Christina Kranc, MD, is a general dermatologist in Phoenix and Scottsdale. Arizona now bans most abortions. However, this has not changed her practice much when prescribing isotretinoin, she told this news organization, because when selecting appropriate candidates for the medication, she is strict on the contraceptive requirement, and only very rarely agrees to a patient relying on abstinence.
And if a patient capable of becoming pregnant was only having sex with another patient capable of becoming pregnant? Dr. Kranc said she would still require contraception unless it was impossible for pregnancy to occur.
Among the many scenarios a dermatologist might have to consider are a lesbian cisgender woman who is having, or has only had, sexual activity with another cisgender women.
Perspective: A Connecticut dermatologist
The concern is not only about isotretinoin but all teratogenic drugs, according to Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, vice chair of dermatology and professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics at the University of Connecticut, Farmington. She often prescribes methotrexate, which is also teratogenic.
Her advice for colleagues: “Whether you believe in abortion or not is irrelevant; it’s something you discuss with your patients.” She, too, fears that doctors in states banning abortions will stop prescribing these medications, “and that is very sad.”
For those practicing in states limiting or banning abortions, Dr. Grant-Kels said, “They need to have an even longer discussion with their patients about how serious this is.” Those doctors need to talk about not only two or three types of birth control, but also discuss with the patient about the potential need for travel, should pregnancy occur and abortion be the chosen option.
Although the newer biologics are an option for psoriasis, they are expensive. And, she said, many insurers require a step-therapy approach, and “want you to start with cheaper medications,” such as methotrexate. As a result, “in some states you won’t have access to the targeted therapies unless a patient fails something like methotrexate.”
Dr. Grant-Kels worries in particular about low-income women who may not have the means to travel to get an abortion.
Need for EC education
In a recent survey of 57 pediatric dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, only a third said they felt confident in their understanding of emergency contraception.
The authors of the study noted that the most common reasons for pregnancies during isotretinoin therapy reported to the FDA from 2011 to 2017 “included ineffective or inconsistent use” of contraceptives and “unsuccessful abstinence,” and recommended that physicians who prescribe isotretinoin update and increase their understanding of emergency contraception.
Dr. Yeung, Dr. Kranc, Dr. Grant-Kels, and Dr. Frieden reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 3 months after the Dobbs decision by the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade and revoked the constitutional right to an abortion, Some have beefed up their already stringent instructions and lengthy conversations about avoiding pregnancy while on the medication.
The major fear is that a patient who is taking contraceptive precautions, in accordance with the isotretinoin risk-management program, iPLEDGE, but still becomes pregnant while on isotretinoin may find out about the pregnancy too late to undergo an abortion in her own state and may not be able to travel to another state – or the patient may live in a state where abortions are entirely prohibited and is unable to travel to another state.
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane; its former brand name was Accutane.
As of Oct. 7, a total of 14 states have banned most abortions, while 4 others have bans at 6, 15, 18, or 20 weeks. Attempts to restrict abortion on several other states are underway.
“To date, we don’t know of any specific effects of the Dobbs decision on isotretinoin prescribing, but with abortion access banned in many states, we anticipate that this could be a very real issue for individuals who accidentally become pregnant while taking isotretinoin,” said Ilona Frieden, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s iPLEDGE Workgroup.
The iPLEDGE REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) is the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program that is in place to manage the risk of isotretinoin teratogenicity and minimize fetal exposure. The work group meets with the FDA and isotretinoin manufacturers to keep the program safe and operating smoothly. The iPLEDGE workgroup has not yet issued any specific statements on the implications of the Dobbs decision on prescribing isotretinoin.
But work on the issue is ongoing by the American Academy of Dermatology. In a statement issued in September, Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, president of the AAD, said that the academy “is continuing to work with its Patient Guidance for State Regulations Regarding Reproductive Health Task Force to help dermatologists best navigate state laws about how care should be implemented for patients who are or might become pregnant, and have been exposed to teratogenic medications.”
The task force, working with the academy, is “in the process of developing resources to help members better assist patients and have a productive and caring dialogue with them,” according to the statement. No specific timeline was given for when those resources might be available.
Methotrexate prescriptions
Also of concern are prescriptions for methotrexate, which is prescribed for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other skin diseases. Soon after the Dobbs decision was announced on June 24, pharmacies began to require pharmacists in states that banned abortions to verify that a prescription for methotrexate was not intended for an abortion, since methotrexate is used in combination with misoprostol for termination of an early pregnancy.
The action was taken, spokespersons for several major pharmacies said, to comply with state laws. According to Kara Page, a CVS spokesperson: “Pharmacists are caught in the middle on this issue.” Laws in some states, she told this news organization, “restrict the dispensing of medications for the purpose of inducing an abortion. These laws, some of which include criminal penalties, have forced us to require pharmacists in these states to validate that the intended indication is not to terminate a pregnancy before they can fill a prescription for methotrexate.”
“New laws in various states require additional steps for dispensing certain prescriptions and apply to all pharmacies, including Walgreens,” Fraser Engerman, a spokesperson for Walgreens, told this news organization. “In these states, our pharmacists work closely with prescribers as needed, to fill lawful, clinically appropriate prescriptions. We provide ongoing training and information to help our pharmacists understand the latest requirements in their area, and with these supports, the expectation is they are empowered to fill these prescriptions.”
The iPLEDGE program has numerous requirements before a patient can begin isotretinoin treatment. Patients capable of becoming pregnant must agree to use two effective forms of birth control during the entire treatment period, which typically lasts 4 or 5 months, as well as 1 month before and 1 month after treatment, or commit to total abstinence during that time.
Perspective: A Georgia dermatologist
Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, who sees patients regularly, practices in Georgia, where abortion is now banned at about 6 weeks of pregnancy. Dr. Yeung worries that some dermatologists in Georgia and elsewhere may not even want to take the risk of prescribing isotretinoin, although the results in treating resistant acne are well documented.
That isn’t his only concern. “Some may not want to prescribe it to a patient who reports they are abstinent and instead require them to go on two forms [of contraception].” Or some women who are not sexually active with anyone who can get them pregnant may also be asked to go on contraception, he said. Abstinence is an alternative option in iPLEDGE.
In the past, he said, well before the Dobbs decision, some doctors have argued that iPLEDGE should not include abstinence as an option. That 2020 report was challenged by others who pointed out that removing the abstinence option would pose ethical issues and may disproportionately affect minorities and others.
Before the Dobbs decision, Dr. Yeung noted, dermatologists prescribing isotretinoin focused on pregnancy prevention but knew that if pregnancy accidentally occurred, abortion was available as an option. “The reality after the decision is, it may or may not be available to all our patients.”
Of the 14 states banning most abortions, 10 are clustered within the South and Southeast. A woman living in Arkansas, which bans most abortions, for example, is surrounded by 6 other states that do the same.
Perspective: An Arizona dermatologist
Christina Kranc, MD, is a general dermatologist in Phoenix and Scottsdale. Arizona now bans most abortions. However, this has not changed her practice much when prescribing isotretinoin, she told this news organization, because when selecting appropriate candidates for the medication, she is strict on the contraceptive requirement, and only very rarely agrees to a patient relying on abstinence.
And if a patient capable of becoming pregnant was only having sex with another patient capable of becoming pregnant? Dr. Kranc said she would still require contraception unless it was impossible for pregnancy to occur.
Among the many scenarios a dermatologist might have to consider are a lesbian cisgender woman who is having, or has only had, sexual activity with another cisgender women.
Perspective: A Connecticut dermatologist
The concern is not only about isotretinoin but all teratogenic drugs, according to Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, vice chair of dermatology and professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics at the University of Connecticut, Farmington. She often prescribes methotrexate, which is also teratogenic.
Her advice for colleagues: “Whether you believe in abortion or not is irrelevant; it’s something you discuss with your patients.” She, too, fears that doctors in states banning abortions will stop prescribing these medications, “and that is very sad.”
For those practicing in states limiting or banning abortions, Dr. Grant-Kels said, “They need to have an even longer discussion with their patients about how serious this is.” Those doctors need to talk about not only two or three types of birth control, but also discuss with the patient about the potential need for travel, should pregnancy occur and abortion be the chosen option.
Although the newer biologics are an option for psoriasis, they are expensive. And, she said, many insurers require a step-therapy approach, and “want you to start with cheaper medications,” such as methotrexate. As a result, “in some states you won’t have access to the targeted therapies unless a patient fails something like methotrexate.”
Dr. Grant-Kels worries in particular about low-income women who may not have the means to travel to get an abortion.
Need for EC education
In a recent survey of 57 pediatric dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, only a third said they felt confident in their understanding of emergency contraception.
The authors of the study noted that the most common reasons for pregnancies during isotretinoin therapy reported to the FDA from 2011 to 2017 “included ineffective or inconsistent use” of contraceptives and “unsuccessful abstinence,” and recommended that physicians who prescribe isotretinoin update and increase their understanding of emergency contraception.
Dr. Yeung, Dr. Kranc, Dr. Grant-Kels, and Dr. Frieden reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A White female presented with pustules and erythematous macules on the left palm
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease characterized by well-demarcated, scaly, erythematous plaques. Those who present with the condition often have a family history, which supports recent research uncovering various genes implicated in its pathogenesis. The disease is also associated with other systemic complications, most notably cardiovascular disease.
This condition is found in a small percentage of patients with psoriasis and presentation varies from hyperkeratotic plaques to pustular lesions. The pustular form is known as palmoplantar pustulosis and is within the spectrum of palmoplantar psoriasis.
Psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis and its severity can be measured using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. If biopsy is performed, the histology demonstrates parakeratosis, orthokeratosis, loss of the stratum granulosum, and dilated vasculature with an inflammatory cell infiltrate. The keratinocytes present with abnormal differentiation and hyperplasia, and the presence of foci of neutrophils known as “Munro’s microabscesses” in the stratum corneum serve as the hallmark of histological diagnosis. However, it is important to note that appearance can vary based on the stage of the lesion and the subtype of psoriasis present.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be especially limiting and difficult to treat because of its distribution. Topical steroids, topical vitamin D analogues, and narrow band ultraviolet light therapy can be effective for less severe cases. Methotrexate, biologic treatments, and apremilast can be used for more extensive disease.
This patient is HLA-B27 positive and has uveitis. The presence of the HLA-B27 allele has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease, uveitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. It has also been reported to be associated with pustular psoriasis. She responded well to topical steroids and vitamin D analogues.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro at Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Psoriasis: Overview and Diagnosis, in “Evidence-Based Psoriasis. Updates in Clinical Dermatology.” (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International, 2018).
2. Merola JF et al. Dermatol Ther. 2018 May;31(3):e12589.
3. Chung J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):623-32.
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease characterized by well-demarcated, scaly, erythematous plaques. Those who present with the condition often have a family history, which supports recent research uncovering various genes implicated in its pathogenesis. The disease is also associated with other systemic complications, most notably cardiovascular disease.
This condition is found in a small percentage of patients with psoriasis and presentation varies from hyperkeratotic plaques to pustular lesions. The pustular form is known as palmoplantar pustulosis and is within the spectrum of palmoplantar psoriasis.
Psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis and its severity can be measured using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. If biopsy is performed, the histology demonstrates parakeratosis, orthokeratosis, loss of the stratum granulosum, and dilated vasculature with an inflammatory cell infiltrate. The keratinocytes present with abnormal differentiation and hyperplasia, and the presence of foci of neutrophils known as “Munro’s microabscesses” in the stratum corneum serve as the hallmark of histological diagnosis. However, it is important to note that appearance can vary based on the stage of the lesion and the subtype of psoriasis present.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be especially limiting and difficult to treat because of its distribution. Topical steroids, topical vitamin D analogues, and narrow band ultraviolet light therapy can be effective for less severe cases. Methotrexate, biologic treatments, and apremilast can be used for more extensive disease.
This patient is HLA-B27 positive and has uveitis. The presence of the HLA-B27 allele has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease, uveitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. It has also been reported to be associated with pustular psoriasis. She responded well to topical steroids and vitamin D analogues.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro at Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Psoriasis: Overview and Diagnosis, in “Evidence-Based Psoriasis. Updates in Clinical Dermatology.” (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International, 2018).
2. Merola JF et al. Dermatol Ther. 2018 May;31(3):e12589.
3. Chung J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):623-32.
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease characterized by well-demarcated, scaly, erythematous plaques. Those who present with the condition often have a family history, which supports recent research uncovering various genes implicated in its pathogenesis. The disease is also associated with other systemic complications, most notably cardiovascular disease.
This condition is found in a small percentage of patients with psoriasis and presentation varies from hyperkeratotic plaques to pustular lesions. The pustular form is known as palmoplantar pustulosis and is within the spectrum of palmoplantar psoriasis.
Psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis and its severity can be measured using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. If biopsy is performed, the histology demonstrates parakeratosis, orthokeratosis, loss of the stratum granulosum, and dilated vasculature with an inflammatory cell infiltrate. The keratinocytes present with abnormal differentiation and hyperplasia, and the presence of foci of neutrophils known as “Munro’s microabscesses” in the stratum corneum serve as the hallmark of histological diagnosis. However, it is important to note that appearance can vary based on the stage of the lesion and the subtype of psoriasis present.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can be especially limiting and difficult to treat because of its distribution. Topical steroids, topical vitamin D analogues, and narrow band ultraviolet light therapy can be effective for less severe cases. Methotrexate, biologic treatments, and apremilast can be used for more extensive disease.
This patient is HLA-B27 positive and has uveitis. The presence of the HLA-B27 allele has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease, uveitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. It has also been reported to be associated with pustular psoriasis. She responded well to topical steroids and vitamin D analogues.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro at Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Psoriasis: Overview and Diagnosis, in “Evidence-Based Psoriasis. Updates in Clinical Dermatology.” (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International, 2018).
2. Merola JF et al. Dermatol Ther. 2018 May;31(3):e12589.
3. Chung J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):623-32.
Medicare Part D Prescription Claims for Brodalumab: Analysis of Annual Trends for 2017-2019
To the Editor:
Brodalumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17RA, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. The drug is the only biologic agent available for the treatment of psoriasis for which a psoriasis area severity index score of 100 is a primary end point.1,2 Brodalumab is associated with an FDA boxed warning due to an increased risk for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB), including completed suicides, during clinical trials.
We sought to characterize national utilization of this effective yet underutilized drug among Medicare beneficiaries by surveying the Medicare Part D Prescriber dataset.3 We tabulated brodalumab utilization statistics and characteristics of high-volume prescribers who had 11 or more annual claims for brodalumab.
Despite its associated boxed warning, the number of Medicare D claims for brodalumab increased by 1756 from 2017 to 2019, surpassing $7 million in costs by 2019. The number of beneficiaries also increased from 11 to 292—a 415.2% annual increase in beneficiaries for whom brodalumab was prescribed (Table 1).
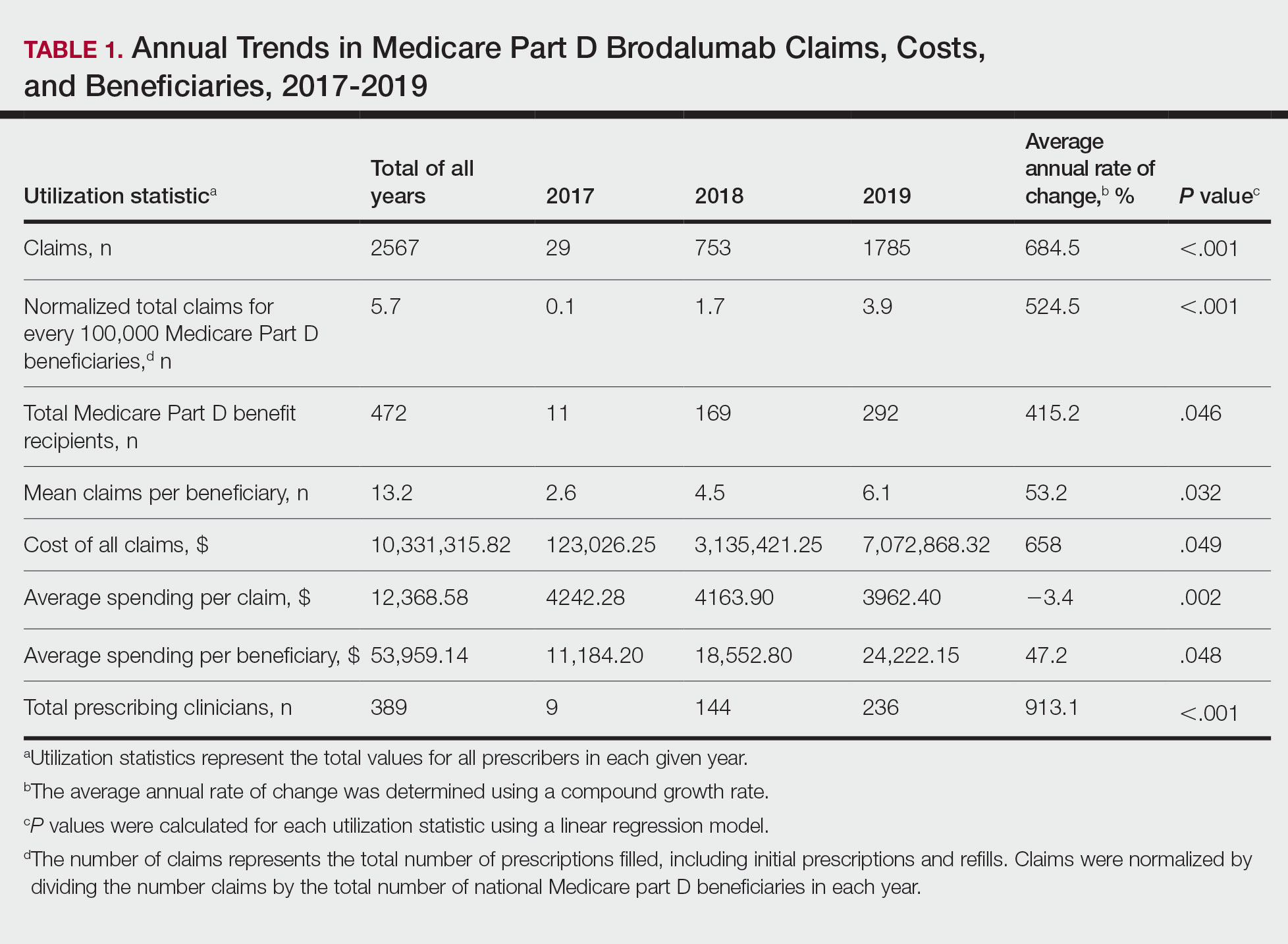
In addition, states in the West and South had the highest utilization rates of brodalumab in 2019. There also was an increasing trend toward high-volume prescribers of brodalumab, with private practice clinicians constituting the majority (Table 2).
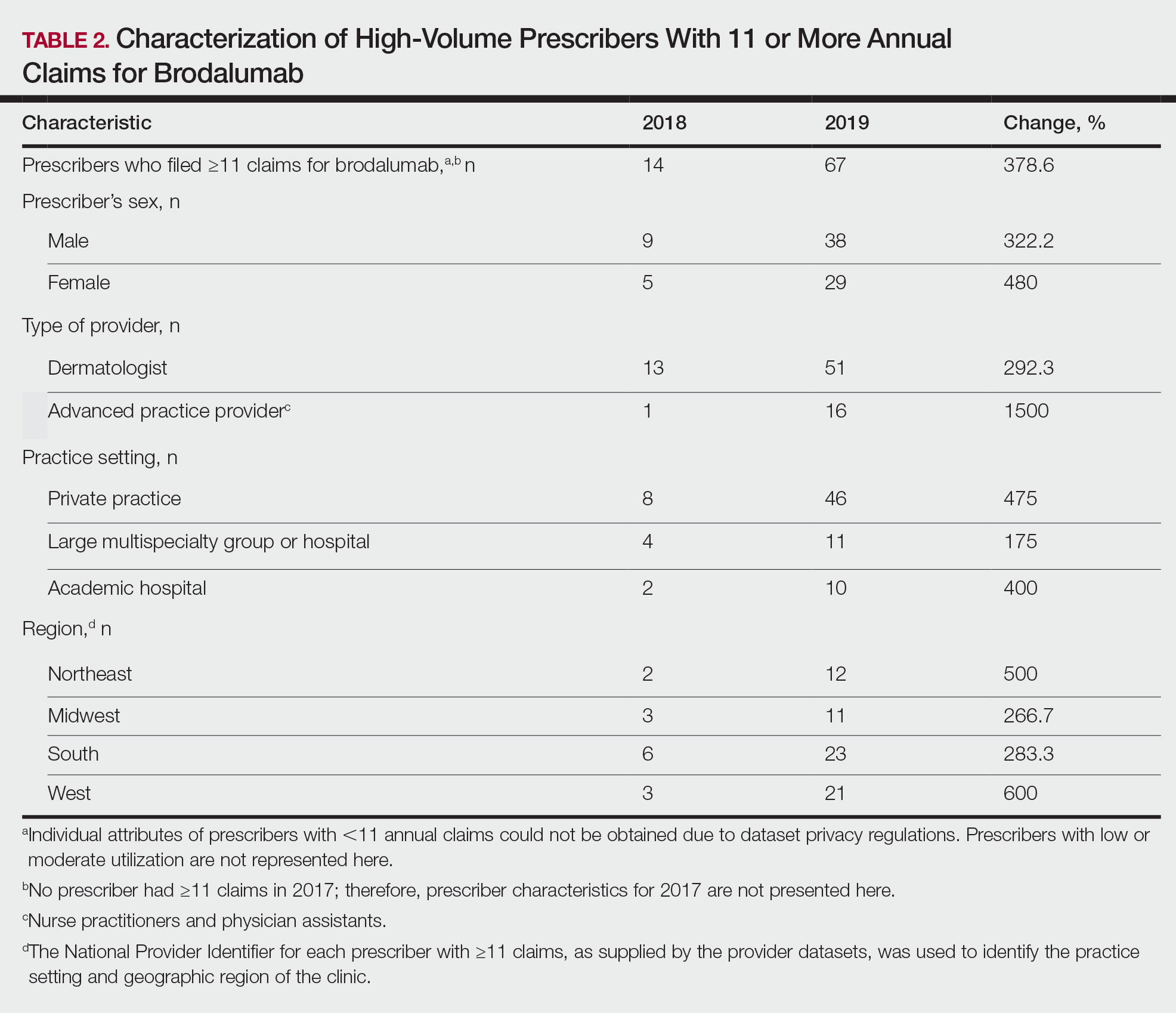
There was a substantial increase in advanced practice providers including nurse practitioners and physician assistants who were brodalumab prescribers. Although this trend might promote greater access to brodalumab, it is vital to ensure that advanced practice providers receive targeted training to properly understand the complexities of treatment with brodalumab.
Although the utilization of brodalumab has increased since 2017 (P<.001), it is still underutilized compared to the other IL-17 inhibitors secukinumab and ixekizumab. Secukinumab was FDA approved for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in 2015, followed by ixekizumab in 2016.4
According to the Medicare Part D database, both secukinumab and ixekizumab had a higher number of total claims and prescribers compared to brodalumab in the years of their debut.3 In 2015, there were 3593 claims for and 862 prescribers of secukinumab; in 2016, there were 1731 claims for and 681 prescribers of ixekizumab. In contrast, there were only 29 claims for and 11 prescribers of brodalumab in 2017, the year that the drug was approved by the FDA. During the same 3-year period, secukinumab and ixekizumab had a substantially greater number of claims—totals of 176,823 and 55,289, respectively—than brodalumab. The higher number of claims for secukinumab and ixekizumab compared to brodalumab may reflect clinicians’ increasing confidence in prescribing those drugs, given their long-term safety and efficacy. In addition, secukinumab and ixekizumab do not require completion of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which makes them more readily prescribable.3
Overall, most experts agree that there is no increase in the risk for suicide associated with brodalumab compared to the general population. A 2-year pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab supports the safety of this drug.5 All participants who completed suicide during the clinical trials harbored an underlying psychiatric disorder or stressor(s).6
Although causation between brodalumab and SIB has not been demonstrated, it remains imperative that prescribers diligently assess patients’ risk of SIB and subsequently their access to appropriate psychiatric services as a precaution, if necessary. This is particularly important for private practice prescribers, who constitute the majority of Medicare D brodalumab claims, because they must ensure collaboration with a multidisciplinary team involving mental health providers. Lastly, considering that the highest number of brodalumab Medicare D claims were in western and southern states, it is critical to note that those 2 regions also harbor comparatively fewer mental health facilities that accept Medicare than other regions of the country.7 Prescribers in western and southern states must be mindful of mental health coverage limitations when treating psoriasis patients with brodalumab.
The increase in the number of claims, beneficiaries, and prescribers of brodalumab during its first 3 years of availability might be attributed to its efficacy and safety. On the other hand, the boxed warning and REMS associated with brodalumab might have led to underutilization of this drug compared to other IL-17 inhibitors.
Our analysis is limited by its representative restriction to Medicare patients. There also are limited data on brodalumab given its novelty. Individual attributes of prescribers with fewer than 11 annual claims for brodalumab could not be obtained because of dataset regulations; however, aggregated utilization statistics provide an indication of brodalumab prescribing patterns among all providers. Furthermore, during this analysis, data on the Medicare D database were limited to 2013 through 2020. Studies are needed to determine prescribing patterns of brodalumab since this study period.
- Foulkes AC, Warren RB. Brodalumab in psoriasis: evidence to date and clinical potential. Drugs Context. 2019;8:212570. doi:10.7573/dic.212570
- Beck KM, Koo J. Brodalumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: up-to-date. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19:287-292. doi:10.1080/14712598.2019.1579794
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D Prescribers. Updated July 27, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider
- Drugs. US Food and Drug Administration website. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs
- Lebwohl M, Leonardi C, Wu JJ, et al. Two-year US pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:173-180. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00472-x
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.08.024
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Mental Health Services Survey (N-MHSS): 2019, Data On Mental Health Treatment Facilities. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; August 13, 2020. Accessed September 21, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/national-mental-health-services-survey-n-mhss-2019-data-mental-health-treatment-facilities
To the Editor:
Brodalumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17RA, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. The drug is the only biologic agent available for the treatment of psoriasis for which a psoriasis area severity index score of 100 is a primary end point.1,2 Brodalumab is associated with an FDA boxed warning due to an increased risk for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB), including completed suicides, during clinical trials.
We sought to characterize national utilization of this effective yet underutilized drug among Medicare beneficiaries by surveying the Medicare Part D Prescriber dataset.3 We tabulated brodalumab utilization statistics and characteristics of high-volume prescribers who had 11 or more annual claims for brodalumab.
Despite its associated boxed warning, the number of Medicare D claims for brodalumab increased by 1756 from 2017 to 2019, surpassing $7 million in costs by 2019. The number of beneficiaries also increased from 11 to 292—a 415.2% annual increase in beneficiaries for whom brodalumab was prescribed (Table 1).

In addition, states in the West and South had the highest utilization rates of brodalumab in 2019. There also was an increasing trend toward high-volume prescribers of brodalumab, with private practice clinicians constituting the majority (Table 2).

There was a substantial increase in advanced practice providers including nurse practitioners and physician assistants who were brodalumab prescribers. Although this trend might promote greater access to brodalumab, it is vital to ensure that advanced practice providers receive targeted training to properly understand the complexities of treatment with brodalumab.
Although the utilization of brodalumab has increased since 2017 (P<.001), it is still underutilized compared to the other IL-17 inhibitors secukinumab and ixekizumab. Secukinumab was FDA approved for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in 2015, followed by ixekizumab in 2016.4
According to the Medicare Part D database, both secukinumab and ixekizumab had a higher number of total claims and prescribers compared to brodalumab in the years of their debut.3 In 2015, there were 3593 claims for and 862 prescribers of secukinumab; in 2016, there were 1731 claims for and 681 prescribers of ixekizumab. In contrast, there were only 29 claims for and 11 prescribers of brodalumab in 2017, the year that the drug was approved by the FDA. During the same 3-year period, secukinumab and ixekizumab had a substantially greater number of claims—totals of 176,823 and 55,289, respectively—than brodalumab. The higher number of claims for secukinumab and ixekizumab compared to brodalumab may reflect clinicians’ increasing confidence in prescribing those drugs, given their long-term safety and efficacy. In addition, secukinumab and ixekizumab do not require completion of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which makes them more readily prescribable.3
Overall, most experts agree that there is no increase in the risk for suicide associated with brodalumab compared to the general population. A 2-year pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab supports the safety of this drug.5 All participants who completed suicide during the clinical trials harbored an underlying psychiatric disorder or stressor(s).6
Although causation between brodalumab and SIB has not been demonstrated, it remains imperative that prescribers diligently assess patients’ risk of SIB and subsequently their access to appropriate psychiatric services as a precaution, if necessary. This is particularly important for private practice prescribers, who constitute the majority of Medicare D brodalumab claims, because they must ensure collaboration with a multidisciplinary team involving mental health providers. Lastly, considering that the highest number of brodalumab Medicare D claims were in western and southern states, it is critical to note that those 2 regions also harbor comparatively fewer mental health facilities that accept Medicare than other regions of the country.7 Prescribers in western and southern states must be mindful of mental health coverage limitations when treating psoriasis patients with brodalumab.
The increase in the number of claims, beneficiaries, and prescribers of brodalumab during its first 3 years of availability might be attributed to its efficacy and safety. On the other hand, the boxed warning and REMS associated with brodalumab might have led to underutilization of this drug compared to other IL-17 inhibitors.
Our analysis is limited by its representative restriction to Medicare patients. There also are limited data on brodalumab given its novelty. Individual attributes of prescribers with fewer than 11 annual claims for brodalumab could not be obtained because of dataset regulations; however, aggregated utilization statistics provide an indication of brodalumab prescribing patterns among all providers. Furthermore, during this analysis, data on the Medicare D database were limited to 2013 through 2020. Studies are needed to determine prescribing patterns of brodalumab since this study period.
To the Editor:
Brodalumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17RA, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. The drug is the only biologic agent available for the treatment of psoriasis for which a psoriasis area severity index score of 100 is a primary end point.1,2 Brodalumab is associated with an FDA boxed warning due to an increased risk for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB), including completed suicides, during clinical trials.
We sought to characterize national utilization of this effective yet underutilized drug among Medicare beneficiaries by surveying the Medicare Part D Prescriber dataset.3 We tabulated brodalumab utilization statistics and characteristics of high-volume prescribers who had 11 or more annual claims for brodalumab.
Despite its associated boxed warning, the number of Medicare D claims for brodalumab increased by 1756 from 2017 to 2019, surpassing $7 million in costs by 2019. The number of beneficiaries also increased from 11 to 292—a 415.2% annual increase in beneficiaries for whom brodalumab was prescribed (Table 1).

In addition, states in the West and South had the highest utilization rates of brodalumab in 2019. There also was an increasing trend toward high-volume prescribers of brodalumab, with private practice clinicians constituting the majority (Table 2).

There was a substantial increase in advanced practice providers including nurse practitioners and physician assistants who were brodalumab prescribers. Although this trend might promote greater access to brodalumab, it is vital to ensure that advanced practice providers receive targeted training to properly understand the complexities of treatment with brodalumab.
Although the utilization of brodalumab has increased since 2017 (P<.001), it is still underutilized compared to the other IL-17 inhibitors secukinumab and ixekizumab. Secukinumab was FDA approved for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in 2015, followed by ixekizumab in 2016.4
According to the Medicare Part D database, both secukinumab and ixekizumab had a higher number of total claims and prescribers compared to brodalumab in the years of their debut.3 In 2015, there were 3593 claims for and 862 prescribers of secukinumab; in 2016, there were 1731 claims for and 681 prescribers of ixekizumab. In contrast, there were only 29 claims for and 11 prescribers of brodalumab in 2017, the year that the drug was approved by the FDA. During the same 3-year period, secukinumab and ixekizumab had a substantially greater number of claims—totals of 176,823 and 55,289, respectively—than brodalumab. The higher number of claims for secukinumab and ixekizumab compared to brodalumab may reflect clinicians’ increasing confidence in prescribing those drugs, given their long-term safety and efficacy. In addition, secukinumab and ixekizumab do not require completion of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which makes them more readily prescribable.3
Overall, most experts agree that there is no increase in the risk for suicide associated with brodalumab compared to the general population. A 2-year pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab supports the safety of this drug.5 All participants who completed suicide during the clinical trials harbored an underlying psychiatric disorder or stressor(s).6
Although causation between brodalumab and SIB has not been demonstrated, it remains imperative that prescribers diligently assess patients’ risk of SIB and subsequently their access to appropriate psychiatric services as a precaution, if necessary. This is particularly important for private practice prescribers, who constitute the majority of Medicare D brodalumab claims, because they must ensure collaboration with a multidisciplinary team involving mental health providers. Lastly, considering that the highest number of brodalumab Medicare D claims were in western and southern states, it is critical to note that those 2 regions also harbor comparatively fewer mental health facilities that accept Medicare than other regions of the country.7 Prescribers in western and southern states must be mindful of mental health coverage limitations when treating psoriasis patients with brodalumab.
The increase in the number of claims, beneficiaries, and prescribers of brodalumab during its first 3 years of availability might be attributed to its efficacy and safety. On the other hand, the boxed warning and REMS associated with brodalumab might have led to underutilization of this drug compared to other IL-17 inhibitors.
Our analysis is limited by its representative restriction to Medicare patients. There also are limited data on brodalumab given its novelty. Individual attributes of prescribers with fewer than 11 annual claims for brodalumab could not be obtained because of dataset regulations; however, aggregated utilization statistics provide an indication of brodalumab prescribing patterns among all providers. Furthermore, during this analysis, data on the Medicare D database were limited to 2013 through 2020. Studies are needed to determine prescribing patterns of brodalumab since this study period.
- Foulkes AC, Warren RB. Brodalumab in psoriasis: evidence to date and clinical potential. Drugs Context. 2019;8:212570. doi:10.7573/dic.212570
- Beck KM, Koo J. Brodalumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: up-to-date. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19:287-292. doi:10.1080/14712598.2019.1579794
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D Prescribers. Updated July 27, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider
- Drugs. US Food and Drug Administration website. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs
- Lebwohl M, Leonardi C, Wu JJ, et al. Two-year US pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:173-180. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00472-x
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.08.024
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Mental Health Services Survey (N-MHSS): 2019, Data On Mental Health Treatment Facilities. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; August 13, 2020. Accessed September 21, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/national-mental-health-services-survey-n-mhss-2019-data-mental-health-treatment-facilities
- Foulkes AC, Warren RB. Brodalumab in psoriasis: evidence to date and clinical potential. Drugs Context. 2019;8:212570. doi:10.7573/dic.212570
- Beck KM, Koo J. Brodalumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: up-to-date. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19:287-292. doi:10.1080/14712598.2019.1579794
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D Prescribers. Updated July 27, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider
- Drugs. US Food and Drug Administration website. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs
- Lebwohl M, Leonardi C, Wu JJ, et al. Two-year US pharmacovigilance report on brodalumab. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:173-180. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00472-x
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.08.024
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Mental Health Services Survey (N-MHSS): 2019, Data On Mental Health Treatment Facilities. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; August 13, 2020. Accessed September 21, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/national-mental-health-services-survey-n-mhss-2019-data-mental-health-treatment-facilities
Practice Points
- Brodalumab is associated with a boxed warning due to increased suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB), including completed suicides, during clinical trials.
- Brodalumab is underutilized compared to the other US Food and Drug Administration–approved IL-17 inhibitors used to treat psoriasis.
- Most experts agree that there is no increased risk for suicide associated with brodalumab. However, it remains imperative that prescribers assess patients’ risk of SIB and subsequently their access to appropriate psychiatric services prior to initiating and during treatment with brodalumab.
Apremilast may have some cardiometabolic benefits in patients with psoriasis
The trial, led by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, found that apremilast (Otezla) has a neutral effect on aortic vascular inflammation in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
It also had variable, but generally favorable, associations with 68 cardiometabolic biomarkers tested and associations with reductions in both visceral and subcutaneous fat. Findings of the study were published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Fat reductions maintained at 1-year mark
The researchers found a 5%-6% reduction in subcutaneous and visceral fat at week 16 of the study that was maintained at the 1-year mark. “The fact that it was rock stable a year later is pretty encouraging,” Dr. Gelfand told this news organization.
As for effects on vascular inflammation, Dr. Gelfand said, “The good news is we didn’t find any adverse effects on aortic vascular inflammation, but we didn’t find any beneficial effects either. That was a little disappointing.
“The most surprising thing was really the effects on visceral adiposity,” he added. “I’m not aware of any other drug having demonstrated that effect.”
Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist with NYU Langone Health in New York, who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization that despite seemingly good epidemiologic evidence in observational studies that by treating psoriasis surrogates of cardiovascular risk can be reduced, this trial, like others before it, failed to reduce aortic vascular inflammation.
The trial does help answer the question of whether apremilast can induce weight loss, he said, something that earlier trials suggested. “This trial confirms that, which is exciting,” he said. The reduction in both visceral and subcutaneous fat “deserves a lot further study.”
Several questions remain, Dr. Garshick said. Both he and Dr. Gelfand pointed to the need for large, placebo-controlled trials. “We still don’t know which medications may be preferrable in psoriasis to reduce [cardiovascular] risk if any at all,” Dr. Garshick said.
Seventy patients enrolled
In total, 70 patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were enrolled, 60 completed week 16, and 39 completed week 52 of the single-arm, open-label trial conducted between April 2017 and August 2021 at seven dermatology sites in the United States.
Participants took 30 mg of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitor approved for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, twice daily. Participants’ average age was 47.5 years; most were male (77.1%) and White (82.9%); almost 6% were Black. Average body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Patients could not have received biologics within 90 days of study baseline (or 180 days for ustekinumab [Stelara]).
There was no change in aortic vascular inflammation at week 16 (target to background ratio, −0.02; 95% confidence interval [CI], −0.08 to 0.05; P = .61) or week 52 (target to background ratio, −0.07; 95% CI, −0.15 to 0.01; P = .09) compared with baseline.
“At week 16, there were reductions in levels of interleukin-1b, fetuin A, valine, leucine, and isoleucine,” the authors wrote, adding that at week 52, compared with baseline, “there were reductions in levels of ferritin, cholesterol efflux capacity, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone, and ketone bodies, and an increase in levels of apolipoprotein A-1.”
This study highlights the importance of screening, Dr. Garshick said.
He and Dr. Gelfand said people with psoriatic disease tend to be vastly underscreened for cardiovascular risk factors.
Dr. Gelfand said, “If we did what we knew worked – meaning we screened them for diabetes, we screen their cholesterol, we check their blood pressure, and we adequately treated those traditional cardiovascular risk factors, we probably could narrow the gap quite a bit” in terms of the lower life expectancy people face when they have more significant psoriasis.
Celgene was the initial funding sponsor; sponsorship was then transferred to Amgen. The authors designed, executed, analyzed, and reported the study. Celgene provided nonbinding input into study design, and Amgen provided nonbinding input into the reporting of results. Dr. Gelfand reported numerous disclosures with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Garshick reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The trial, led by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, found that apremilast (Otezla) has a neutral effect on aortic vascular inflammation in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
It also had variable, but generally favorable, associations with 68 cardiometabolic biomarkers tested and associations with reductions in both visceral and subcutaneous fat. Findings of the study were published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Fat reductions maintained at 1-year mark
The researchers found a 5%-6% reduction in subcutaneous and visceral fat at week 16 of the study that was maintained at the 1-year mark. “The fact that it was rock stable a year later is pretty encouraging,” Dr. Gelfand told this news organization.
As for effects on vascular inflammation, Dr. Gelfand said, “The good news is we didn’t find any adverse effects on aortic vascular inflammation, but we didn’t find any beneficial effects either. That was a little disappointing.
“The most surprising thing was really the effects on visceral adiposity,” he added. “I’m not aware of any other drug having demonstrated that effect.”
Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist with NYU Langone Health in New York, who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization that despite seemingly good epidemiologic evidence in observational studies that by treating psoriasis surrogates of cardiovascular risk can be reduced, this trial, like others before it, failed to reduce aortic vascular inflammation.
The trial does help answer the question of whether apremilast can induce weight loss, he said, something that earlier trials suggested. “This trial confirms that, which is exciting,” he said. The reduction in both visceral and subcutaneous fat “deserves a lot further study.”
Several questions remain, Dr. Garshick said. Both he and Dr. Gelfand pointed to the need for large, placebo-controlled trials. “We still don’t know which medications may be preferrable in psoriasis to reduce [cardiovascular] risk if any at all,” Dr. Garshick said.
Seventy patients enrolled
In total, 70 patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were enrolled, 60 completed week 16, and 39 completed week 52 of the single-arm, open-label trial conducted between April 2017 and August 2021 at seven dermatology sites in the United States.
Participants took 30 mg of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitor approved for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, twice daily. Participants’ average age was 47.5 years; most were male (77.1%) and White (82.9%); almost 6% were Black. Average body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Patients could not have received biologics within 90 days of study baseline (or 180 days for ustekinumab [Stelara]).
There was no change in aortic vascular inflammation at week 16 (target to background ratio, −0.02; 95% confidence interval [CI], −0.08 to 0.05; P = .61) or week 52 (target to background ratio, −0.07; 95% CI, −0.15 to 0.01; P = .09) compared with baseline.
“At week 16, there were reductions in levels of interleukin-1b, fetuin A, valine, leucine, and isoleucine,” the authors wrote, adding that at week 52, compared with baseline, “there were reductions in levels of ferritin, cholesterol efflux capacity, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone, and ketone bodies, and an increase in levels of apolipoprotein A-1.”
This study highlights the importance of screening, Dr. Garshick said.
He and Dr. Gelfand said people with psoriatic disease tend to be vastly underscreened for cardiovascular risk factors.
Dr. Gelfand said, “If we did what we knew worked – meaning we screened them for diabetes, we screen their cholesterol, we check their blood pressure, and we adequately treated those traditional cardiovascular risk factors, we probably could narrow the gap quite a bit” in terms of the lower life expectancy people face when they have more significant psoriasis.
Celgene was the initial funding sponsor; sponsorship was then transferred to Amgen. The authors designed, executed, analyzed, and reported the study. Celgene provided nonbinding input into study design, and Amgen provided nonbinding input into the reporting of results. Dr. Gelfand reported numerous disclosures with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Garshick reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The trial, led by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, found that apremilast (Otezla) has a neutral effect on aortic vascular inflammation in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
It also had variable, but generally favorable, associations with 68 cardiometabolic biomarkers tested and associations with reductions in both visceral and subcutaneous fat. Findings of the study were published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Fat reductions maintained at 1-year mark
The researchers found a 5%-6% reduction in subcutaneous and visceral fat at week 16 of the study that was maintained at the 1-year mark. “The fact that it was rock stable a year later is pretty encouraging,” Dr. Gelfand told this news organization.
As for effects on vascular inflammation, Dr. Gelfand said, “The good news is we didn’t find any adverse effects on aortic vascular inflammation, but we didn’t find any beneficial effects either. That was a little disappointing.
“The most surprising thing was really the effects on visceral adiposity,” he added. “I’m not aware of any other drug having demonstrated that effect.”
Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist with NYU Langone Health in New York, who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization that despite seemingly good epidemiologic evidence in observational studies that by treating psoriasis surrogates of cardiovascular risk can be reduced, this trial, like others before it, failed to reduce aortic vascular inflammation.
The trial does help answer the question of whether apremilast can induce weight loss, he said, something that earlier trials suggested. “This trial confirms that, which is exciting,” he said. The reduction in both visceral and subcutaneous fat “deserves a lot further study.”
Several questions remain, Dr. Garshick said. Both he and Dr. Gelfand pointed to the need for large, placebo-controlled trials. “We still don’t know which medications may be preferrable in psoriasis to reduce [cardiovascular] risk if any at all,” Dr. Garshick said.
Seventy patients enrolled
In total, 70 patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were enrolled, 60 completed week 16, and 39 completed week 52 of the single-arm, open-label trial conducted between April 2017 and August 2021 at seven dermatology sites in the United States.
Participants took 30 mg of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitor approved for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, twice daily. Participants’ average age was 47.5 years; most were male (77.1%) and White (82.9%); almost 6% were Black. Average body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Patients could not have received biologics within 90 days of study baseline (or 180 days for ustekinumab [Stelara]).
There was no change in aortic vascular inflammation at week 16 (target to background ratio, −0.02; 95% confidence interval [CI], −0.08 to 0.05; P = .61) or week 52 (target to background ratio, −0.07; 95% CI, −0.15 to 0.01; P = .09) compared with baseline.
“At week 16, there were reductions in levels of interleukin-1b, fetuin A, valine, leucine, and isoleucine,” the authors wrote, adding that at week 52, compared with baseline, “there were reductions in levels of ferritin, cholesterol efflux capacity, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone, and ketone bodies, and an increase in levels of apolipoprotein A-1.”
This study highlights the importance of screening, Dr. Garshick said.
He and Dr. Gelfand said people with psoriatic disease tend to be vastly underscreened for cardiovascular risk factors.
Dr. Gelfand said, “If we did what we knew worked – meaning we screened them for diabetes, we screen their cholesterol, we check their blood pressure, and we adequately treated those traditional cardiovascular risk factors, we probably could narrow the gap quite a bit” in terms of the lower life expectancy people face when they have more significant psoriasis.
Celgene was the initial funding sponsor; sponsorship was then transferred to Amgen. The authors designed, executed, analyzed, and reported the study. Celgene provided nonbinding input into study design, and Amgen provided nonbinding input into the reporting of results. Dr. Gelfand reported numerous disclosures with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Garshick reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY