User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Physicians Lament Over Reliance on Relative Value Units: Survey
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases, Type 2 Diabetes Reap GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Benefits, Too
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
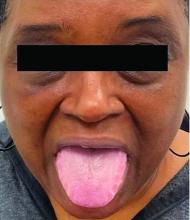
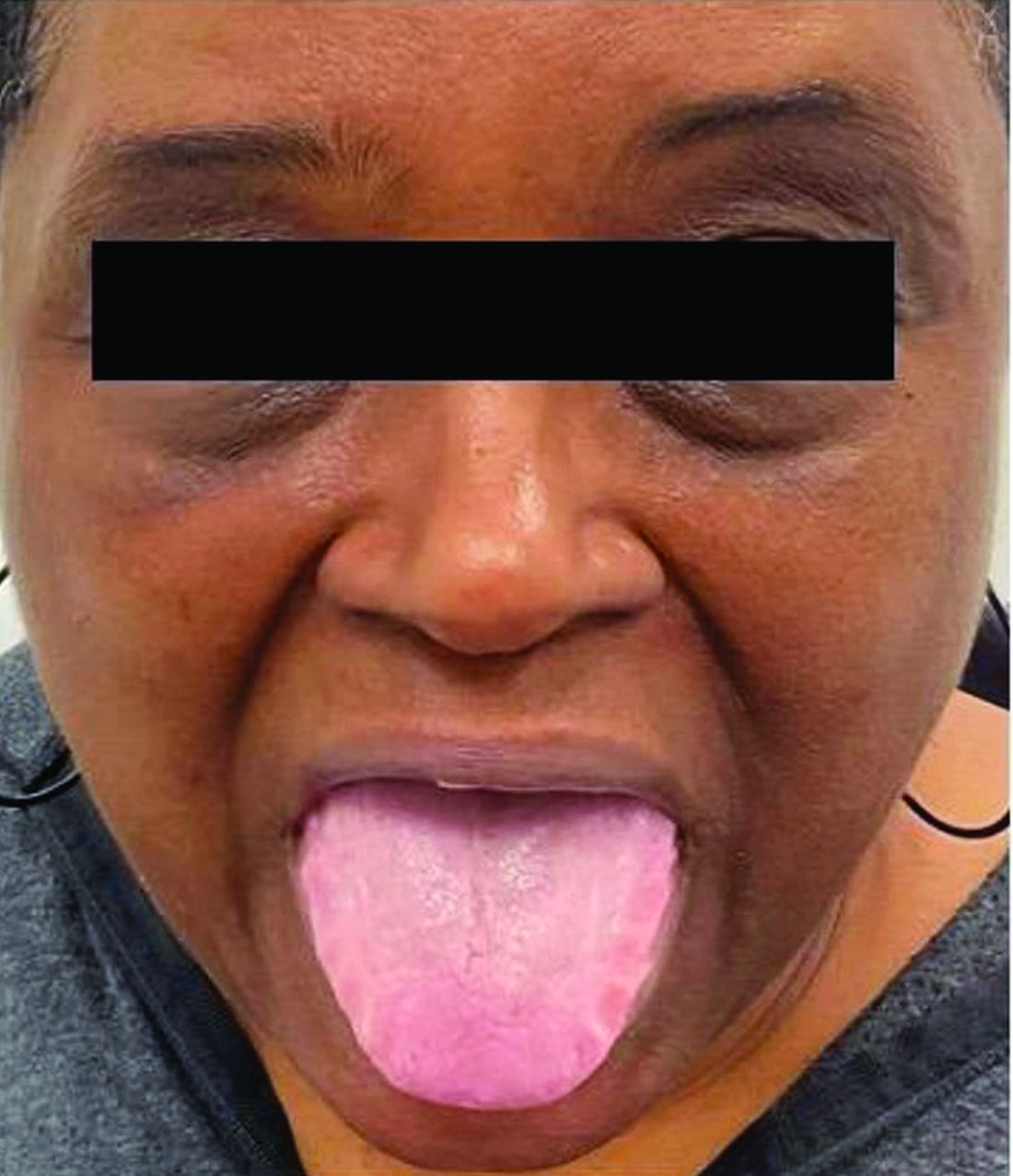
Necrotic Papules in a Pediatric Patient
The Diagnosis: Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta
Sectioned punch biopsies were performed on the patient’s right arm. Histopathology showed acanthosis and parakeratosis in the epidermis, with vacuolar degeneration and dyskeratosis in the basal layer. Dermal changes included extravasated red blood cells in the papillary dermis as well as perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in both the papillary and reticular dermis (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence of a perilesional biopsy using anti–human IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin conjugates showed no findings of immune deposition. Biopsy results were consistent with pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA), and the patient was treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin, triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily, and phototherapy with narrowband UVB 3 times weekly. Rapid improvement was noted at 2-month follow-up.
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta is a form of pityriasis lichenoides, a group of inflammatory dermatoses that are characterized clinically by successive crops of morphologically diverse lesions. Epidemiologic studies have shown a slight male predominance. It primarily affects children and young adults, with peak ages of 8 and 32 years in pediatric and adult populations, respectively.1
The pathogenesis of PLEVA remains unclear. An abnormal immune response to Toxoplasma, Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, and other pathogens has been suggested based on serologic evidence of concurrent disease activity with the onset of lesions as well as cutaneous improvement in some patients after treatment of the infection.1 A T-cell lymphoproliferative etiology also has been considered based on histopathologic similarities between PLEVA and lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) as well as findings of clonality in T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in many patients.1,2 Some clinicians consider LyP and PLEVA as separate entities on one disease spectrum.
Eruptions of PLEVA tend to favor the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions may begin as macules measuring 2 to 3 mm in diameter that quickly evolve into papules with fine scale that remains attached centrally. Ulcerations with hemorrhagic crusts also may be noted as the lesions progress in stage. The rash may persist for weeks to years, and overlapping crops of macules and papules at varying stages of development may be seen in the same patient.1
Histopathologic findings of PLEVA include spongiosis, dyskeratosis, parakeratosis, and focal keratinocyte necrosis within the epidermis, as well as vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer. Lymphocyte and erythrocyte extravasation may extend into the epidermis. Dermal findings may include edema and wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates extending into the reticular dermis.1

Important differential diagnoses to consider include LyP, mycosis fungoides (MF), pemphigus foliaceus, and varicella. Lymphomatoid papulosis is a benign CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent course of recurrent, often self-resolving papules that occur most frequently on the trunk, arms, and legs of older patients. There are several histologic subtypes of LyP, but the most common (type A) may manifest with wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in the dermis, similar to PLEVA. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies characteristically reveal clonality in LyP, and clonality has been reported in PLEVA. However, LyP demonstrates a higher cytologic grade and lacks the characteristic parakeratotic scale and superficial dermal microhemorrhage of PLEVA.3
Mycosis fungoides is a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent clinical course of persistent patches, plaques, or tumors of various sizes that often manifest in non–sun-exposed areas of the skin. Early stages of MF are difficult to detect histologically, but biopsies may show atypical lymphocytes with hyperchromatic, irregularly contoured nuclei arranged along the basal layer of the epidermis. Epidermal aggregates of atypical lymphocytes (also known as Pautrier microabscesses) are considered highly specific for MF. T-cell receptor and immunopathologic studies also are important adjuncts in the diagnosis of MF.4
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease caused by antibodies directed against desmoglein 1, which is found in the granular layer of the epidermis. It manifests with a subtle onset of scattered crusted lesions in the seborrheic areas, such as the scalp, face, chest, and upper back. Histopathologic findings of early blisters may include acantholysis and dyskeratosis in the stratum granulosum as well as vacuolization of the granular layer. The blisters may coalesce into superficial bullae containing fibrin and neutrophils. Immunofluorescence studies that demonstrate intraepidermal C3 and IgG deposition are key to the diagnosis of pemphigus.5
Varicella (also known as chickenpox) manifests with crops of vesicles on an erythematous base in a centripetal distribution favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. It often is preceded by prodromal fever, malaise, and myalgia. Histopathologic evaluation of varicella is uncommon but may reveal acantholysis, multinucleation, and nuclear margination of keratinocytes. Viral culture or nucleic acid amplification testing of lesions can be used to verify the diagnosis.6
Most cases of PLEVA resolve without intervention.7 Treatment is directed at speeding recovery, providing symptomatic relief, and limiting permanent sequelae. Topical steroids often are used to alleviate inflammation and pruritus. Systemic antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, and erythromycin have been used for their anti-inflammatory properties. Phototherapy of various wavelengths, including broadband and narrowband UVB as well as psoralen plus UVA, have led to improvements in affected patients. Refractory disease may warrant consideration of therapy with methotrexate, acitretin, dapsone, or cyclosporine.7
There have been rare reports of PLEVA evolving into its potentially lethal variant, febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, which is differentiated by the presence of systemic manifestations, including high fever, sore throat, diarrhea, central nervous system symptoms, abdominal pain, interstitial pneumonitis, splenomegaly, arthritis, sepsis, megaloblastic anemia, or conjunctival ulcers. The orogenital mucosa may be affected. Cutaneous lesions may rapidly progress to large, generalized, coalescent ulcers with necrotic crusts and vasculitic features on biopsy.8 Malignant transformation of PLEVA into LyP or MF rarely may occur and warrants continued follow-up of unresolved lesions.9
- Bowers S, Warshaw EM. Pityriasis lichenoides and its subtypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:557-572. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.07.058
- Teklehaimanot F, Gade A, Rubenstein R. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Martinez-Cabriales SA, Walsh S, Sade S, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis: an update and review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:59-73. doi:10.1111/jdv.15931
- Pimpinelli N, Olsen EA, Santucci M, et al. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1053-1063. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.057
- Lepe K, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. Pemphigus foliaceus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Ayoade F, Kumar S. Varicella zoster (chickenpox). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Bellinato F, Maurelli M, Gisondi P, et al. A systematic review of treatments for pityriasis lichenoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:2039-2049. doi:10.1111/jdv.15813
- Nofal A, Assaf M, Alakad R, et al. Febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease: proposed diagnostic criteria and therapeutic evaluation. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:729-738. doi:10.1111/ijd.13195
- Thomson KF, Whittaker SJ, Russell-Jones R, et al. Childhood cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in association with pityriasis lichenoides chronica. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:1136-1152. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.03232.x
The Diagnosis: Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta
Sectioned punch biopsies were performed on the patient’s right arm. Histopathology showed acanthosis and parakeratosis in the epidermis, with vacuolar degeneration and dyskeratosis in the basal layer. Dermal changes included extravasated red blood cells in the papillary dermis as well as perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in both the papillary and reticular dermis (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence of a perilesional biopsy using anti–human IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin conjugates showed no findings of immune deposition. Biopsy results were consistent with pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA), and the patient was treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin, triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily, and phototherapy with narrowband UVB 3 times weekly. Rapid improvement was noted at 2-month follow-up.
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta is a form of pityriasis lichenoides, a group of inflammatory dermatoses that are characterized clinically by successive crops of morphologically diverse lesions. Epidemiologic studies have shown a slight male predominance. It primarily affects children and young adults, with peak ages of 8 and 32 years in pediatric and adult populations, respectively.1
The pathogenesis of PLEVA remains unclear. An abnormal immune response to Toxoplasma, Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, and other pathogens has been suggested based on serologic evidence of concurrent disease activity with the onset of lesions as well as cutaneous improvement in some patients after treatment of the infection.1 A T-cell lymphoproliferative etiology also has been considered based on histopathologic similarities between PLEVA and lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) as well as findings of clonality in T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in many patients.1,2 Some clinicians consider LyP and PLEVA as separate entities on one disease spectrum.
Eruptions of PLEVA tend to favor the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions may begin as macules measuring 2 to 3 mm in diameter that quickly evolve into papules with fine scale that remains attached centrally. Ulcerations with hemorrhagic crusts also may be noted as the lesions progress in stage. The rash may persist for weeks to years, and overlapping crops of macules and papules at varying stages of development may be seen in the same patient.1
Histopathologic findings of PLEVA include spongiosis, dyskeratosis, parakeratosis, and focal keratinocyte necrosis within the epidermis, as well as vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer. Lymphocyte and erythrocyte extravasation may extend into the epidermis. Dermal findings may include edema and wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates extending into the reticular dermis.1

Important differential diagnoses to consider include LyP, mycosis fungoides (MF), pemphigus foliaceus, and varicella. Lymphomatoid papulosis is a benign CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent course of recurrent, often self-resolving papules that occur most frequently on the trunk, arms, and legs of older patients. There are several histologic subtypes of LyP, but the most common (type A) may manifest with wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in the dermis, similar to PLEVA. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies characteristically reveal clonality in LyP, and clonality has been reported in PLEVA. However, LyP demonstrates a higher cytologic grade and lacks the characteristic parakeratotic scale and superficial dermal microhemorrhage of PLEVA.3
Mycosis fungoides is a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent clinical course of persistent patches, plaques, or tumors of various sizes that often manifest in non–sun-exposed areas of the skin. Early stages of MF are difficult to detect histologically, but biopsies may show atypical lymphocytes with hyperchromatic, irregularly contoured nuclei arranged along the basal layer of the epidermis. Epidermal aggregates of atypical lymphocytes (also known as Pautrier microabscesses) are considered highly specific for MF. T-cell receptor and immunopathologic studies also are important adjuncts in the diagnosis of MF.4
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease caused by antibodies directed against desmoglein 1, which is found in the granular layer of the epidermis. It manifests with a subtle onset of scattered crusted lesions in the seborrheic areas, such as the scalp, face, chest, and upper back. Histopathologic findings of early blisters may include acantholysis and dyskeratosis in the stratum granulosum as well as vacuolization of the granular layer. The blisters may coalesce into superficial bullae containing fibrin and neutrophils. Immunofluorescence studies that demonstrate intraepidermal C3 and IgG deposition are key to the diagnosis of pemphigus.5
Varicella (also known as chickenpox) manifests with crops of vesicles on an erythematous base in a centripetal distribution favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. It often is preceded by prodromal fever, malaise, and myalgia. Histopathologic evaluation of varicella is uncommon but may reveal acantholysis, multinucleation, and nuclear margination of keratinocytes. Viral culture or nucleic acid amplification testing of lesions can be used to verify the diagnosis.6
Most cases of PLEVA resolve without intervention.7 Treatment is directed at speeding recovery, providing symptomatic relief, and limiting permanent sequelae. Topical steroids often are used to alleviate inflammation and pruritus. Systemic antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, and erythromycin have been used for their anti-inflammatory properties. Phototherapy of various wavelengths, including broadband and narrowband UVB as well as psoralen plus UVA, have led to improvements in affected patients. Refractory disease may warrant consideration of therapy with methotrexate, acitretin, dapsone, or cyclosporine.7
There have been rare reports of PLEVA evolving into its potentially lethal variant, febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, which is differentiated by the presence of systemic manifestations, including high fever, sore throat, diarrhea, central nervous system symptoms, abdominal pain, interstitial pneumonitis, splenomegaly, arthritis, sepsis, megaloblastic anemia, or conjunctival ulcers. The orogenital mucosa may be affected. Cutaneous lesions may rapidly progress to large, generalized, coalescent ulcers with necrotic crusts and vasculitic features on biopsy.8 Malignant transformation of PLEVA into LyP or MF rarely may occur and warrants continued follow-up of unresolved lesions.9
The Diagnosis: Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta
Sectioned punch biopsies were performed on the patient’s right arm. Histopathology showed acanthosis and parakeratosis in the epidermis, with vacuolar degeneration and dyskeratosis in the basal layer. Dermal changes included extravasated red blood cells in the papillary dermis as well as perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in both the papillary and reticular dermis (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence of a perilesional biopsy using anti–human IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin conjugates showed no findings of immune deposition. Biopsy results were consistent with pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA), and the patient was treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin, triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily, and phototherapy with narrowband UVB 3 times weekly. Rapid improvement was noted at 2-month follow-up.
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta is a form of pityriasis lichenoides, a group of inflammatory dermatoses that are characterized clinically by successive crops of morphologically diverse lesions. Epidemiologic studies have shown a slight male predominance. It primarily affects children and young adults, with peak ages of 8 and 32 years in pediatric and adult populations, respectively.1
The pathogenesis of PLEVA remains unclear. An abnormal immune response to Toxoplasma, Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, and other pathogens has been suggested based on serologic evidence of concurrent disease activity with the onset of lesions as well as cutaneous improvement in some patients after treatment of the infection.1 A T-cell lymphoproliferative etiology also has been considered based on histopathologic similarities between PLEVA and lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) as well as findings of clonality in T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in many patients.1,2 Some clinicians consider LyP and PLEVA as separate entities on one disease spectrum.
Eruptions of PLEVA tend to favor the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions may begin as macules measuring 2 to 3 mm in diameter that quickly evolve into papules with fine scale that remains attached centrally. Ulcerations with hemorrhagic crusts also may be noted as the lesions progress in stage. The rash may persist for weeks to years, and overlapping crops of macules and papules at varying stages of development may be seen in the same patient.1
Histopathologic findings of PLEVA include spongiosis, dyskeratosis, parakeratosis, and focal keratinocyte necrosis within the epidermis, as well as vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer. Lymphocyte and erythrocyte extravasation may extend into the epidermis. Dermal findings may include edema and wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates extending into the reticular dermis.1

Important differential diagnoses to consider include LyP, mycosis fungoides (MF), pemphigus foliaceus, and varicella. Lymphomatoid papulosis is a benign CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent course of recurrent, often self-resolving papules that occur most frequently on the trunk, arms, and legs of older patients. There are several histologic subtypes of LyP, but the most common (type A) may manifest with wedge-shaped perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates in the dermis, similar to PLEVA. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies characteristically reveal clonality in LyP, and clonality has been reported in PLEVA. However, LyP demonstrates a higher cytologic grade and lacks the characteristic parakeratotic scale and superficial dermal microhemorrhage of PLEVA.3
Mycosis fungoides is a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder that is characterized by an indolent clinical course of persistent patches, plaques, or tumors of various sizes that often manifest in non–sun-exposed areas of the skin. Early stages of MF are difficult to detect histologically, but biopsies may show atypical lymphocytes with hyperchromatic, irregularly contoured nuclei arranged along the basal layer of the epidermis. Epidermal aggregates of atypical lymphocytes (also known as Pautrier microabscesses) are considered highly specific for MF. T-cell receptor and immunopathologic studies also are important adjuncts in the diagnosis of MF.4
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease caused by antibodies directed against desmoglein 1, which is found in the granular layer of the epidermis. It manifests with a subtle onset of scattered crusted lesions in the seborrheic areas, such as the scalp, face, chest, and upper back. Histopathologic findings of early blisters may include acantholysis and dyskeratosis in the stratum granulosum as well as vacuolization of the granular layer. The blisters may coalesce into superficial bullae containing fibrin and neutrophils. Immunofluorescence studies that demonstrate intraepidermal C3 and IgG deposition are key to the diagnosis of pemphigus.5
Varicella (also known as chickenpox) manifests with crops of vesicles on an erythematous base in a centripetal distribution favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. It often is preceded by prodromal fever, malaise, and myalgia. Histopathologic evaluation of varicella is uncommon but may reveal acantholysis, multinucleation, and nuclear margination of keratinocytes. Viral culture or nucleic acid amplification testing of lesions can be used to verify the diagnosis.6
Most cases of PLEVA resolve without intervention.7 Treatment is directed at speeding recovery, providing symptomatic relief, and limiting permanent sequelae. Topical steroids often are used to alleviate inflammation and pruritus. Systemic antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, and erythromycin have been used for their anti-inflammatory properties. Phototherapy of various wavelengths, including broadband and narrowband UVB as well as psoralen plus UVA, have led to improvements in affected patients. Refractory disease may warrant consideration of therapy with methotrexate, acitretin, dapsone, or cyclosporine.7
There have been rare reports of PLEVA evolving into its potentially lethal variant, febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, which is differentiated by the presence of systemic manifestations, including high fever, sore throat, diarrhea, central nervous system symptoms, abdominal pain, interstitial pneumonitis, splenomegaly, arthritis, sepsis, megaloblastic anemia, or conjunctival ulcers. The orogenital mucosa may be affected. Cutaneous lesions may rapidly progress to large, generalized, coalescent ulcers with necrotic crusts and vasculitic features on biopsy.8 Malignant transformation of PLEVA into LyP or MF rarely may occur and warrants continued follow-up of unresolved lesions.9
- Bowers S, Warshaw EM. Pityriasis lichenoides and its subtypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:557-572. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.07.058
- Teklehaimanot F, Gade A, Rubenstein R. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Martinez-Cabriales SA, Walsh S, Sade S, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis: an update and review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:59-73. doi:10.1111/jdv.15931
- Pimpinelli N, Olsen EA, Santucci M, et al. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1053-1063. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.057
- Lepe K, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. Pemphigus foliaceus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Ayoade F, Kumar S. Varicella zoster (chickenpox). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Bellinato F, Maurelli M, Gisondi P, et al. A systematic review of treatments for pityriasis lichenoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:2039-2049. doi:10.1111/jdv.15813
- Nofal A, Assaf M, Alakad R, et al. Febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease: proposed diagnostic criteria and therapeutic evaluation. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:729-738. doi:10.1111/ijd.13195
- Thomson KF, Whittaker SJ, Russell-Jones R, et al. Childhood cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in association with pityriasis lichenoides chronica. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:1136-1152. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.03232.x
- Bowers S, Warshaw EM. Pityriasis lichenoides and its subtypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:557-572. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.07.058
- Teklehaimanot F, Gade A, Rubenstein R. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Martinez-Cabriales SA, Walsh S, Sade S, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis: an update and review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:59-73. doi:10.1111/jdv.15931
- Pimpinelli N, Olsen EA, Santucci M, et al. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1053-1063. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.057
- Lepe K, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. Pemphigus foliaceus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Ayoade F, Kumar S. Varicella zoster (chickenpox). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Bellinato F, Maurelli M, Gisondi P, et al. A systematic review of treatments for pityriasis lichenoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:2039-2049. doi:10.1111/jdv.15813
- Nofal A, Assaf M, Alakad R, et al. Febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease: proposed diagnostic criteria and therapeutic evaluation. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:729-738. doi:10.1111/ijd.13195
- Thomson KF, Whittaker SJ, Russell-Jones R, et al. Childhood cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in association with pityriasis lichenoides chronica. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:1136-1152. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.03232.x
A 7-year-old boy was referred to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a diffuse pruritic rash of 3 months’ duration. The rash began as scant erythematous papules on the face, and crops of similar lesions later erupted on the trunk, arms, and legs. He was treated previously by a pediatrician for scabies with topical permethrin followed by 2 doses of oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg without improvement. Physical examination revealed innumerable erythematous macules and papules with centrally adherent scaling distributed on the trunk, arms, and legs, as well as scant necrotic papules with a hemorrhagic crust and a peripheral rim of scale.

When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Will Compounding ‘Best Practices’ Guide Reassure Clinicians?
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 62-year-old Black female presented with an epidermal inclusion cyst on her left upper back
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
Diagnosing, Treating Rashes In Patients on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, Giant of Cancer Care, Dies
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Second Treatment for Prurigo Nodularis Approved by FDA
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.