User login
Healthy habits lower T2D microvascular risks: Cohort study
People with diabetes who adhere to a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and follow other healthy lifestyle practices have a significantly lower risk of microvascular complications from the disease, such as diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy, as well as foot disorders, than counterparts with diabetes who don’t, a prospective cohort study of more than 7,000 patients with type 2 diabetes has found.
“We believe this is one of the first large-scale analyses among diabetes patients that specifically examined an overall healthy lifestyle in relation to the risk of developing microvascular complications,” senior study author Qi Sun, MD, ScD, said in an interview. “The results are not surprising that the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk of developing these complications and the enhanced adherence to the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk as well. And these findings bear lots of public health significance as they suggest the important role of living a healthy lifestyle in the prevention of diabetes complications, on top of the clinical treatment.”
Dr. Sun is an associate professor of nutrition and epidemiology at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
The study stated that the findings “lend support” for the American Diabetes Association guidelines for healthy lifestyle practices in people with diabetes.
The study used a cohort from two large prospective cohort studies, the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), comprising 4,982 women and 2,095 men who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes during follow-up. They had no cardiovascular disease or cancer at the time of their diabetes diagnosis. Both NHS and HPFS used validated questionnaires to gather information on diet, lifestyle, medical history, and newly diagnosed diseases every 2-4 years. The latter study included NHS and HPFS participants who also completed supplementary questionnaires about their diabetes.
The latest study took into account five modifiable lifestyle-related factors: diet, body weight, smoking status, alcohol, and physical activity. For diet, both large studies used the 2010 Alternate Healthy Eating Index to assess diet quality; those in the upper 40th percentile of the study population were defined as healthy diet. Healthy body weight was defined at a body mass index of 18.5-25 kg/m2.
Among the latter study cohort, 2,878 incident cases of diabetic microvascular complications were documented during follow-up. Patients who adhered to a healthy lifestyle before their diabetes diagnosis, defined as having four or more low-risk lifestyle factors, had a 27% lower relative risk of developing any microvascular complication than counterparts with no low-risk lifestyle factors (relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.35-1; P = .006).
The study found similar outcomes for those who adopted a healthy lifestyle after their diabetes diagnosis, with a 32% reduction in relative risk compared with those who didn’t adopt any healthy lifestyle practices (RR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.55-0.83; P < .001).
Dr. Sun noted what was noteworthy about his group’s cohort study. “The unique design is truly the prospective follow-up over time so that we could examine the lifestyle at diabetes diagnosis as well as changes in lifestyle before and after diabetes in relation to the future risk of developing the complications,” he said.
A randomized trial would be a more rigorous way to evaluate the impact of a healthy lifestyle, he added, “although it’s much more expensive than a cohort study like what we did with this investigation.”
As for future research, Dr. Sun said, “It will be interesting to understand mechanisms underlying these observations. It’s also critical to understand why certain diabetes patients may not benefit from a healthy lifestyle, since some of them, even when living a healthy lifestyle, still develop the complications.”
This trial shows in a new light the benefits of healthy lifestyle practices on microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., and a professor at the University of Miami, said in a comment. “These benefits have always been surmised and demonstrated in a limited way in previous trials, but not subject to the level of analysis seen in this prospective cohort trial.”
He called the study design “excellent,” adding, “ ‘Validated’ self-reported questionnaires were used widely, although minimal detail is provided about the validation process.” One limitation, he noted, was “the homogeneity of the participants; all were health professionals.”
The study “affirms” and “quantitates” the benefits of a healthy lifestyle in type 2 diabetes. “The issue is not unawareness but rather application,” Dr. Jellinger said. “Modifying long-held lifestyle habits is a real challenge. Perhaps by ‘quantitating’ the benefit, as shown in this trial and hopefully additional studies, impetus will be provided to refocus on this approach, which is too often simply given lip service.”
The National Institutes of Health provided funding for the study. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Jellinger disclosed relationships with Amgen and Esperion.
People with diabetes who adhere to a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and follow other healthy lifestyle practices have a significantly lower risk of microvascular complications from the disease, such as diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy, as well as foot disorders, than counterparts with diabetes who don’t, a prospective cohort study of more than 7,000 patients with type 2 diabetes has found.
“We believe this is one of the first large-scale analyses among diabetes patients that specifically examined an overall healthy lifestyle in relation to the risk of developing microvascular complications,” senior study author Qi Sun, MD, ScD, said in an interview. “The results are not surprising that the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk of developing these complications and the enhanced adherence to the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk as well. And these findings bear lots of public health significance as they suggest the important role of living a healthy lifestyle in the prevention of diabetes complications, on top of the clinical treatment.”
Dr. Sun is an associate professor of nutrition and epidemiology at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
The study stated that the findings “lend support” for the American Diabetes Association guidelines for healthy lifestyle practices in people with diabetes.
The study used a cohort from two large prospective cohort studies, the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), comprising 4,982 women and 2,095 men who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes during follow-up. They had no cardiovascular disease or cancer at the time of their diabetes diagnosis. Both NHS and HPFS used validated questionnaires to gather information on diet, lifestyle, medical history, and newly diagnosed diseases every 2-4 years. The latter study included NHS and HPFS participants who also completed supplementary questionnaires about their diabetes.
The latest study took into account five modifiable lifestyle-related factors: diet, body weight, smoking status, alcohol, and physical activity. For diet, both large studies used the 2010 Alternate Healthy Eating Index to assess diet quality; those in the upper 40th percentile of the study population were defined as healthy diet. Healthy body weight was defined at a body mass index of 18.5-25 kg/m2.
Among the latter study cohort, 2,878 incident cases of diabetic microvascular complications were documented during follow-up. Patients who adhered to a healthy lifestyle before their diabetes diagnosis, defined as having four or more low-risk lifestyle factors, had a 27% lower relative risk of developing any microvascular complication than counterparts with no low-risk lifestyle factors (relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.35-1; P = .006).
The study found similar outcomes for those who adopted a healthy lifestyle after their diabetes diagnosis, with a 32% reduction in relative risk compared with those who didn’t adopt any healthy lifestyle practices (RR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.55-0.83; P < .001).
Dr. Sun noted what was noteworthy about his group’s cohort study. “The unique design is truly the prospective follow-up over time so that we could examine the lifestyle at diabetes diagnosis as well as changes in lifestyle before and after diabetes in relation to the future risk of developing the complications,” he said.
A randomized trial would be a more rigorous way to evaluate the impact of a healthy lifestyle, he added, “although it’s much more expensive than a cohort study like what we did with this investigation.”
As for future research, Dr. Sun said, “It will be interesting to understand mechanisms underlying these observations. It’s also critical to understand why certain diabetes patients may not benefit from a healthy lifestyle, since some of them, even when living a healthy lifestyle, still develop the complications.”
This trial shows in a new light the benefits of healthy lifestyle practices on microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., and a professor at the University of Miami, said in a comment. “These benefits have always been surmised and demonstrated in a limited way in previous trials, but not subject to the level of analysis seen in this prospective cohort trial.”
He called the study design “excellent,” adding, “ ‘Validated’ self-reported questionnaires were used widely, although minimal detail is provided about the validation process.” One limitation, he noted, was “the homogeneity of the participants; all were health professionals.”
The study “affirms” and “quantitates” the benefits of a healthy lifestyle in type 2 diabetes. “The issue is not unawareness but rather application,” Dr. Jellinger said. “Modifying long-held lifestyle habits is a real challenge. Perhaps by ‘quantitating’ the benefit, as shown in this trial and hopefully additional studies, impetus will be provided to refocus on this approach, which is too often simply given lip service.”
The National Institutes of Health provided funding for the study. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Jellinger disclosed relationships with Amgen and Esperion.
People with diabetes who adhere to a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and follow other healthy lifestyle practices have a significantly lower risk of microvascular complications from the disease, such as diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy, as well as foot disorders, than counterparts with diabetes who don’t, a prospective cohort study of more than 7,000 patients with type 2 diabetes has found.
“We believe this is one of the first large-scale analyses among diabetes patients that specifically examined an overall healthy lifestyle in relation to the risk of developing microvascular complications,” senior study author Qi Sun, MD, ScD, said in an interview. “The results are not surprising that the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk of developing these complications and the enhanced adherence to the healthy lifestyle is associated with lower risk as well. And these findings bear lots of public health significance as they suggest the important role of living a healthy lifestyle in the prevention of diabetes complications, on top of the clinical treatment.”
Dr. Sun is an associate professor of nutrition and epidemiology at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
The study stated that the findings “lend support” for the American Diabetes Association guidelines for healthy lifestyle practices in people with diabetes.
The study used a cohort from two large prospective cohort studies, the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), comprising 4,982 women and 2,095 men who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes during follow-up. They had no cardiovascular disease or cancer at the time of their diabetes diagnosis. Both NHS and HPFS used validated questionnaires to gather information on diet, lifestyle, medical history, and newly diagnosed diseases every 2-4 years. The latter study included NHS and HPFS participants who also completed supplementary questionnaires about their diabetes.
The latest study took into account five modifiable lifestyle-related factors: diet, body weight, smoking status, alcohol, and physical activity. For diet, both large studies used the 2010 Alternate Healthy Eating Index to assess diet quality; those in the upper 40th percentile of the study population were defined as healthy diet. Healthy body weight was defined at a body mass index of 18.5-25 kg/m2.
Among the latter study cohort, 2,878 incident cases of diabetic microvascular complications were documented during follow-up. Patients who adhered to a healthy lifestyle before their diabetes diagnosis, defined as having four or more low-risk lifestyle factors, had a 27% lower relative risk of developing any microvascular complication than counterparts with no low-risk lifestyle factors (relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.35-1; P = .006).
The study found similar outcomes for those who adopted a healthy lifestyle after their diabetes diagnosis, with a 32% reduction in relative risk compared with those who didn’t adopt any healthy lifestyle practices (RR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.55-0.83; P < .001).
Dr. Sun noted what was noteworthy about his group’s cohort study. “The unique design is truly the prospective follow-up over time so that we could examine the lifestyle at diabetes diagnosis as well as changes in lifestyle before and after diabetes in relation to the future risk of developing the complications,” he said.
A randomized trial would be a more rigorous way to evaluate the impact of a healthy lifestyle, he added, “although it’s much more expensive than a cohort study like what we did with this investigation.”
As for future research, Dr. Sun said, “It will be interesting to understand mechanisms underlying these observations. It’s also critical to understand why certain diabetes patients may not benefit from a healthy lifestyle, since some of them, even when living a healthy lifestyle, still develop the complications.”
This trial shows in a new light the benefits of healthy lifestyle practices on microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., and a professor at the University of Miami, said in a comment. “These benefits have always been surmised and demonstrated in a limited way in previous trials, but not subject to the level of analysis seen in this prospective cohort trial.”
He called the study design “excellent,” adding, “ ‘Validated’ self-reported questionnaires were used widely, although minimal detail is provided about the validation process.” One limitation, he noted, was “the homogeneity of the participants; all were health professionals.”
The study “affirms” and “quantitates” the benefits of a healthy lifestyle in type 2 diabetes. “The issue is not unawareness but rather application,” Dr. Jellinger said. “Modifying long-held lifestyle habits is a real challenge. Perhaps by ‘quantitating’ the benefit, as shown in this trial and hopefully additional studies, impetus will be provided to refocus on this approach, which is too often simply given lip service.”
The National Institutes of Health provided funding for the study. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Jellinger disclosed relationships with Amgen and Esperion.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Female doctors have higher infertility rates and riskier pregnancies: What can be done?
In 2021, Eugene Kim, MD, division director of pediatric surgery and vice chair in the department of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, gave his presidential address to the Association for Academic Surgery.
“Presidents tend to give a message of hope or inspiration; I probably took it in a different way,” he said.
Dr. Kim told the story of one of his clinical partners, Eveline Shue, who, after five rounds of in vitro fertilization (IVF), became pregnant with twins. A high-achiever in her field, Ms. Shue continued working the grueling hours required by her job throughout pregnancy until she noticed concerning symptoms – musculoskeletal issues, extreme swelling, and more. She and her group decided that she should step back from work in her third trimester. A few days later, Ms. Shue suffered a stroke. She was rushed to the hospital where her babies were delivered by emergency C-section. Ms. Shue underwent brain surgery but later recovered and is still practicing in Southern California.
“I remember being at her bedside thinking, ‘How could we have let this happen? How could we have prevented this?’ ”
Dr. Kim’s speech kicked off a firestorm of awareness about pregnancy complications among physicians. “I got scores of emails from women around the country, surgeons in particular, who felt like their issues had been seen. The conversation was long overdue,” he said.
Family planning issues, pregnancy complications, infertility, and pregnancy loss are common, pervasive, and often silent issues in medicine. In July 2021, Dr. Kim and a group of other researchers published a study in JAMA Surgery. It revealed staggering truths: When compared to non-surgeons, female surgeons were more likely to delay pregnancy, use assisted reproductive technology such as IVF, have non-elective C-sections, and suffer pregnancy loss. In the study, 42% of surgeons had experienced pregnancy loss – more than double the rate of the general population. Almost half had serious pregnancy complications.
Research has found that female physicians in general have a significantly greater incidence of miscarriage, infertility, and pregnancy complications than the general population. According to a 2016 survey in the Journal of Women’s Health, the infertility rate for physicians is nearly 1 in 4, about double the rate of the general public.
The barriers to starting a family
Physicians face significant professional barriers that impact family planning. Demanding jobs with exhausting and often unpredictable hours contribute to a culture that, traditionally, has been far from family friendly. As a result, many physicians start families later. “For a pediatric surgeon, you finish training at age 35 – minimum,” says Dr. Kim. “Simply being a surgeon makes you a high-risk pregnancy candidate just because of the career.”
In 2020, Ariela L. Marshall, MD, an associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman school of medicine, co-authored a commentary article in Academic Medicine titled “Physician Fertility: A Call to Action” which was based on her own experiences with infertility. Dr. Marshall was 34 when she and her husband decided to start a family, and she says her infertility diagnosis “came as a shock.”
“I never stopped to think about the consequences of a career path where I’m not going to be established until my 30s,” Dr. Marshall says. “I never thought about how long hours, overnight shifts, or working all the time could impact my fertility.”
It would take four cycles of IVF egg retrieval to create embryos and one failed implantation before Dr. Marshall became pregnant with her son.
When it comes to the timing of pregnancy, medical culture also plays a role. “There’s a lot of messaging around when it’s appropriate to carry a baby – and it’s not until after training is done,” says Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, a clinical associate professor and special advisor for DEI programs at Stanford (Calif.) University’s department of medicine.
There are always exceptions. Some institutions are more flexible than others about pregnancy during residency. But Dr. Salles notes that this attitude is “not universal,” partly because of the lack of a comprehensive approach to pregnancy or parenthood in the United States. “There’s no federal paid parental leave in this country,” reminds Dr. Salles. “That signals that we don’t value parenting.”
The trickle-down effect of this in medicine is more like a waterfall. Some physicians complain when other physicians are out on leave. There’s an additional burden of work when people take time away, and there are often no support structures in place for backup or fill-in care. Dr. Salles said doctors often tell her that they were responsible for finding coverage for any time off during pregnancy or after becoming a parent. A paper of hers published in JAMA Surgery found that, for physicians, a fear of burdening others was a major barrier to getting pregnant during residency in the first place.
The physical consequences
Although research supports the benefits of physical activity throughout pregnancy, a job such as surgery that requires being on your feet for long periods of time “is not the same as exercise,” explains Erika Lu Rangel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Dr. Kim’s lead author on the JAMA Surgery article.
Surgeons operating for more than 12 hours a week are at higher risk for pregnancy complications, the study found. Dr. Rangel also cites data suggesting that night shifts or swing shifts (the hours between day and night) put women at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
Equally alarming: Medical trainees appear to have “almost as high a rate of pregnancy complications as surgeons who have already completed their training,” said Dr. Rangel. It is a concerning finding since, as a younger cohort, they should have lower complication rates based on their age. But doctors in training may be on their feet even more than surgeons during long shifts.
Like Dr. Salles, Dr. Rangel sees these issues as part of a pervasive culture of “presenteeism” in medicine, and she points out that many surgeons don’t even take time off to grieve pregnancy loss or physically recover from it. “We work even when we’re sick and even when it’s not good for our health,” she said. “I think that’s an unhealthy behavior that we cultivate from the time that we’re trainees, and we carry it on through when we’re in practice.”
Penn Medicine’s Dr. Marshall remembers that her own maternity leave was “not an easy process to navigate.” From her hospital room on a magnesium drip for preeclampsia, she still attended Zoom meetings with her colleagues. “Nobody says, ‘Oh, you have to do this,’ ” Dr. Marshall explains, “but you wind up feeling guilty if you’re not there at all moments for everyone. That’s also something that needs to change.”
Dr. Rangel was pregnant with her oldest son as a fourth-year surgery resident. The day she gave birth to him she remembers waking up with a flu-like illness and a fever. She went to work anyway, because “you don’t call in sick as a resident.” She was barely able to complete her rounds and then had to lie down between cases. A co-resident found her and took her to labor and delivery. She had gone into premature labor at 37 weeks, and her son went into the NICU with complications.
“I remember feeling this enormous guilt,” says Dr. Rangel. “I’d been a mom for just a few minutes, and I felt like I had already failed him because I had prioritized what the residency thought of me above what I knew was necessary for his health.”
Hope for the future
Disturbed by the status quo, many physicians are pushing for change. “I think there’s a really important and positive conversation going on in the medical community right now about ways that we need to support new parent physicians,” said Dr. Rangel.
Parental leave is a key part of that support. Last year, The American Board of Medical Specialties enacted a mandate that all specialty boards 2 years or more in duration must provide at least 6 weeks of parental and caregiver leave. In 2023, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) required that all training programs match that policy. “This sends a message to policymakers and leaders in American medicine that this is a priority,” said Dr. Rangel.
In January 2022, a group from the University of Michigan also published an article in the Annals of Surgery called “Safe and Supported Pregnancy: A Call to Action for Surgery Chairs and Program Directors”. The essay urged leading groups such as the ACGME and the American Board of Surgery to “directly address the health and safety of pregnant trainees” and specifically, to “allow for further flexibility during training for pregnancy and peripartum periods,” calling these “fundamental necessities for cultural progress.”
Others have recommended allowing pregnant trainees more flexibility in their schedules or front-loading certain parts of the training that may be more difficult as a pregnancy progresses. Insurance coverage for fertility preservation and reproductive endocrinology services, and support for reentry (including lactation and childcare) are also issues that must be addressed, says Dr. Salles.
A new paper of Dr. Rangel’s, published in JAMA Surgery, suggests that things like mentorship for residents from faculty can also be important pieces of the puzzle.
Education about reproductive health must start earlier, too – as early as medical school. Research suggests only 8% of physicians receive education on the risks of delaying pregnancy. Those who do are significantly less likely to experience pregnancy loss or seek infertility treatment.
Dr. Salles recalls sitting in a classroom learning about advanced maternal age at a time when age 35 seemed unimaginably distant. “It was never taught – at least to my recollection – in a way that was like, ‘this could be your future,’ ” Dr. Salles says.” It was more like this abstract patient who might have advanced maternal age and what the consequences would be. Maybe some of my colleagues put two and two together, but I definitely didn’t.”
Dr. Marshall is the curriculum chair for the IGNITEMed Initiative, which aims to educate medical students about issues not discussed in traditional medical school curricula. Dr. Marshall and her colleague Julia Files, MD, talk with IGNITEMed students about reproductive life planning.
“Raising awareness is a very big thing. That’s not just true for medical students but for professionals at every level of medicine,” Dr. Marshall said. “Residency and fellowship training program directors, department chairs, and hospital CEOs all need to understand that these issues are very common in the people they oversee – and that they are medical issues, like any other medical issue, where people need time off and support.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2021, Eugene Kim, MD, division director of pediatric surgery and vice chair in the department of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, gave his presidential address to the Association for Academic Surgery.
“Presidents tend to give a message of hope or inspiration; I probably took it in a different way,” he said.
Dr. Kim told the story of one of his clinical partners, Eveline Shue, who, after five rounds of in vitro fertilization (IVF), became pregnant with twins. A high-achiever in her field, Ms. Shue continued working the grueling hours required by her job throughout pregnancy until she noticed concerning symptoms – musculoskeletal issues, extreme swelling, and more. She and her group decided that she should step back from work in her third trimester. A few days later, Ms. Shue suffered a stroke. She was rushed to the hospital where her babies were delivered by emergency C-section. Ms. Shue underwent brain surgery but later recovered and is still practicing in Southern California.
“I remember being at her bedside thinking, ‘How could we have let this happen? How could we have prevented this?’ ”
Dr. Kim’s speech kicked off a firestorm of awareness about pregnancy complications among physicians. “I got scores of emails from women around the country, surgeons in particular, who felt like their issues had been seen. The conversation was long overdue,” he said.
Family planning issues, pregnancy complications, infertility, and pregnancy loss are common, pervasive, and often silent issues in medicine. In July 2021, Dr. Kim and a group of other researchers published a study in JAMA Surgery. It revealed staggering truths: When compared to non-surgeons, female surgeons were more likely to delay pregnancy, use assisted reproductive technology such as IVF, have non-elective C-sections, and suffer pregnancy loss. In the study, 42% of surgeons had experienced pregnancy loss – more than double the rate of the general population. Almost half had serious pregnancy complications.
Research has found that female physicians in general have a significantly greater incidence of miscarriage, infertility, and pregnancy complications than the general population. According to a 2016 survey in the Journal of Women’s Health, the infertility rate for physicians is nearly 1 in 4, about double the rate of the general public.
The barriers to starting a family
Physicians face significant professional barriers that impact family planning. Demanding jobs with exhausting and often unpredictable hours contribute to a culture that, traditionally, has been far from family friendly. As a result, many physicians start families later. “For a pediatric surgeon, you finish training at age 35 – minimum,” says Dr. Kim. “Simply being a surgeon makes you a high-risk pregnancy candidate just because of the career.”
In 2020, Ariela L. Marshall, MD, an associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman school of medicine, co-authored a commentary article in Academic Medicine titled “Physician Fertility: A Call to Action” which was based on her own experiences with infertility. Dr. Marshall was 34 when she and her husband decided to start a family, and she says her infertility diagnosis “came as a shock.”
“I never stopped to think about the consequences of a career path where I’m not going to be established until my 30s,” Dr. Marshall says. “I never thought about how long hours, overnight shifts, or working all the time could impact my fertility.”
It would take four cycles of IVF egg retrieval to create embryos and one failed implantation before Dr. Marshall became pregnant with her son.
When it comes to the timing of pregnancy, medical culture also plays a role. “There’s a lot of messaging around when it’s appropriate to carry a baby – and it’s not until after training is done,” says Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, a clinical associate professor and special advisor for DEI programs at Stanford (Calif.) University’s department of medicine.
There are always exceptions. Some institutions are more flexible than others about pregnancy during residency. But Dr. Salles notes that this attitude is “not universal,” partly because of the lack of a comprehensive approach to pregnancy or parenthood in the United States. “There’s no federal paid parental leave in this country,” reminds Dr. Salles. “That signals that we don’t value parenting.”
The trickle-down effect of this in medicine is more like a waterfall. Some physicians complain when other physicians are out on leave. There’s an additional burden of work when people take time away, and there are often no support structures in place for backup or fill-in care. Dr. Salles said doctors often tell her that they were responsible for finding coverage for any time off during pregnancy or after becoming a parent. A paper of hers published in JAMA Surgery found that, for physicians, a fear of burdening others was a major barrier to getting pregnant during residency in the first place.
The physical consequences
Although research supports the benefits of physical activity throughout pregnancy, a job such as surgery that requires being on your feet for long periods of time “is not the same as exercise,” explains Erika Lu Rangel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Dr. Kim’s lead author on the JAMA Surgery article.
Surgeons operating for more than 12 hours a week are at higher risk for pregnancy complications, the study found. Dr. Rangel also cites data suggesting that night shifts or swing shifts (the hours between day and night) put women at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
Equally alarming: Medical trainees appear to have “almost as high a rate of pregnancy complications as surgeons who have already completed their training,” said Dr. Rangel. It is a concerning finding since, as a younger cohort, they should have lower complication rates based on their age. But doctors in training may be on their feet even more than surgeons during long shifts.
Like Dr. Salles, Dr. Rangel sees these issues as part of a pervasive culture of “presenteeism” in medicine, and she points out that many surgeons don’t even take time off to grieve pregnancy loss or physically recover from it. “We work even when we’re sick and even when it’s not good for our health,” she said. “I think that’s an unhealthy behavior that we cultivate from the time that we’re trainees, and we carry it on through when we’re in practice.”
Penn Medicine’s Dr. Marshall remembers that her own maternity leave was “not an easy process to navigate.” From her hospital room on a magnesium drip for preeclampsia, she still attended Zoom meetings with her colleagues. “Nobody says, ‘Oh, you have to do this,’ ” Dr. Marshall explains, “but you wind up feeling guilty if you’re not there at all moments for everyone. That’s also something that needs to change.”
Dr. Rangel was pregnant with her oldest son as a fourth-year surgery resident. The day she gave birth to him she remembers waking up with a flu-like illness and a fever. She went to work anyway, because “you don’t call in sick as a resident.” She was barely able to complete her rounds and then had to lie down between cases. A co-resident found her and took her to labor and delivery. She had gone into premature labor at 37 weeks, and her son went into the NICU with complications.
“I remember feeling this enormous guilt,” says Dr. Rangel. “I’d been a mom for just a few minutes, and I felt like I had already failed him because I had prioritized what the residency thought of me above what I knew was necessary for his health.”
Hope for the future
Disturbed by the status quo, many physicians are pushing for change. “I think there’s a really important and positive conversation going on in the medical community right now about ways that we need to support new parent physicians,” said Dr. Rangel.
Parental leave is a key part of that support. Last year, The American Board of Medical Specialties enacted a mandate that all specialty boards 2 years or more in duration must provide at least 6 weeks of parental and caregiver leave. In 2023, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) required that all training programs match that policy. “This sends a message to policymakers and leaders in American medicine that this is a priority,” said Dr. Rangel.
In January 2022, a group from the University of Michigan also published an article in the Annals of Surgery called “Safe and Supported Pregnancy: A Call to Action for Surgery Chairs and Program Directors”. The essay urged leading groups such as the ACGME and the American Board of Surgery to “directly address the health and safety of pregnant trainees” and specifically, to “allow for further flexibility during training for pregnancy and peripartum periods,” calling these “fundamental necessities for cultural progress.”
Others have recommended allowing pregnant trainees more flexibility in their schedules or front-loading certain parts of the training that may be more difficult as a pregnancy progresses. Insurance coverage for fertility preservation and reproductive endocrinology services, and support for reentry (including lactation and childcare) are also issues that must be addressed, says Dr. Salles.
A new paper of Dr. Rangel’s, published in JAMA Surgery, suggests that things like mentorship for residents from faculty can also be important pieces of the puzzle.
Education about reproductive health must start earlier, too – as early as medical school. Research suggests only 8% of physicians receive education on the risks of delaying pregnancy. Those who do are significantly less likely to experience pregnancy loss or seek infertility treatment.
Dr. Salles recalls sitting in a classroom learning about advanced maternal age at a time when age 35 seemed unimaginably distant. “It was never taught – at least to my recollection – in a way that was like, ‘this could be your future,’ ” Dr. Salles says.” It was more like this abstract patient who might have advanced maternal age and what the consequences would be. Maybe some of my colleagues put two and two together, but I definitely didn’t.”
Dr. Marshall is the curriculum chair for the IGNITEMed Initiative, which aims to educate medical students about issues not discussed in traditional medical school curricula. Dr. Marshall and her colleague Julia Files, MD, talk with IGNITEMed students about reproductive life planning.
“Raising awareness is a very big thing. That’s not just true for medical students but for professionals at every level of medicine,” Dr. Marshall said. “Residency and fellowship training program directors, department chairs, and hospital CEOs all need to understand that these issues are very common in the people they oversee – and that they are medical issues, like any other medical issue, where people need time off and support.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2021, Eugene Kim, MD, division director of pediatric surgery and vice chair in the department of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, gave his presidential address to the Association for Academic Surgery.
“Presidents tend to give a message of hope or inspiration; I probably took it in a different way,” he said.
Dr. Kim told the story of one of his clinical partners, Eveline Shue, who, after five rounds of in vitro fertilization (IVF), became pregnant with twins. A high-achiever in her field, Ms. Shue continued working the grueling hours required by her job throughout pregnancy until she noticed concerning symptoms – musculoskeletal issues, extreme swelling, and more. She and her group decided that she should step back from work in her third trimester. A few days later, Ms. Shue suffered a stroke. She was rushed to the hospital where her babies were delivered by emergency C-section. Ms. Shue underwent brain surgery but later recovered and is still practicing in Southern California.
“I remember being at her bedside thinking, ‘How could we have let this happen? How could we have prevented this?’ ”
Dr. Kim’s speech kicked off a firestorm of awareness about pregnancy complications among physicians. “I got scores of emails from women around the country, surgeons in particular, who felt like their issues had been seen. The conversation was long overdue,” he said.
Family planning issues, pregnancy complications, infertility, and pregnancy loss are common, pervasive, and often silent issues in medicine. In July 2021, Dr. Kim and a group of other researchers published a study in JAMA Surgery. It revealed staggering truths: When compared to non-surgeons, female surgeons were more likely to delay pregnancy, use assisted reproductive technology such as IVF, have non-elective C-sections, and suffer pregnancy loss. In the study, 42% of surgeons had experienced pregnancy loss – more than double the rate of the general population. Almost half had serious pregnancy complications.
Research has found that female physicians in general have a significantly greater incidence of miscarriage, infertility, and pregnancy complications than the general population. According to a 2016 survey in the Journal of Women’s Health, the infertility rate for physicians is nearly 1 in 4, about double the rate of the general public.
The barriers to starting a family
Physicians face significant professional barriers that impact family planning. Demanding jobs with exhausting and often unpredictable hours contribute to a culture that, traditionally, has been far from family friendly. As a result, many physicians start families later. “For a pediatric surgeon, you finish training at age 35 – minimum,” says Dr. Kim. “Simply being a surgeon makes you a high-risk pregnancy candidate just because of the career.”
In 2020, Ariela L. Marshall, MD, an associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman school of medicine, co-authored a commentary article in Academic Medicine titled “Physician Fertility: A Call to Action” which was based on her own experiences with infertility. Dr. Marshall was 34 when she and her husband decided to start a family, and she says her infertility diagnosis “came as a shock.”
“I never stopped to think about the consequences of a career path where I’m not going to be established until my 30s,” Dr. Marshall says. “I never thought about how long hours, overnight shifts, or working all the time could impact my fertility.”
It would take four cycles of IVF egg retrieval to create embryos and one failed implantation before Dr. Marshall became pregnant with her son.
When it comes to the timing of pregnancy, medical culture also plays a role. “There’s a lot of messaging around when it’s appropriate to carry a baby – and it’s not until after training is done,” says Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, a clinical associate professor and special advisor for DEI programs at Stanford (Calif.) University’s department of medicine.
There are always exceptions. Some institutions are more flexible than others about pregnancy during residency. But Dr. Salles notes that this attitude is “not universal,” partly because of the lack of a comprehensive approach to pregnancy or parenthood in the United States. “There’s no federal paid parental leave in this country,” reminds Dr. Salles. “That signals that we don’t value parenting.”
The trickle-down effect of this in medicine is more like a waterfall. Some physicians complain when other physicians are out on leave. There’s an additional burden of work when people take time away, and there are often no support structures in place for backup or fill-in care. Dr. Salles said doctors often tell her that they were responsible for finding coverage for any time off during pregnancy or after becoming a parent. A paper of hers published in JAMA Surgery found that, for physicians, a fear of burdening others was a major barrier to getting pregnant during residency in the first place.
The physical consequences
Although research supports the benefits of physical activity throughout pregnancy, a job such as surgery that requires being on your feet for long periods of time “is not the same as exercise,” explains Erika Lu Rangel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Dr. Kim’s lead author on the JAMA Surgery article.
Surgeons operating for more than 12 hours a week are at higher risk for pregnancy complications, the study found. Dr. Rangel also cites data suggesting that night shifts or swing shifts (the hours between day and night) put women at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
Equally alarming: Medical trainees appear to have “almost as high a rate of pregnancy complications as surgeons who have already completed their training,” said Dr. Rangel. It is a concerning finding since, as a younger cohort, they should have lower complication rates based on their age. But doctors in training may be on their feet even more than surgeons during long shifts.
Like Dr. Salles, Dr. Rangel sees these issues as part of a pervasive culture of “presenteeism” in medicine, and she points out that many surgeons don’t even take time off to grieve pregnancy loss or physically recover from it. “We work even when we’re sick and even when it’s not good for our health,” she said. “I think that’s an unhealthy behavior that we cultivate from the time that we’re trainees, and we carry it on through when we’re in practice.”
Penn Medicine’s Dr. Marshall remembers that her own maternity leave was “not an easy process to navigate.” From her hospital room on a magnesium drip for preeclampsia, she still attended Zoom meetings with her colleagues. “Nobody says, ‘Oh, you have to do this,’ ” Dr. Marshall explains, “but you wind up feeling guilty if you’re not there at all moments for everyone. That’s also something that needs to change.”
Dr. Rangel was pregnant with her oldest son as a fourth-year surgery resident. The day she gave birth to him she remembers waking up with a flu-like illness and a fever. She went to work anyway, because “you don’t call in sick as a resident.” She was barely able to complete her rounds and then had to lie down between cases. A co-resident found her and took her to labor and delivery. She had gone into premature labor at 37 weeks, and her son went into the NICU with complications.
“I remember feeling this enormous guilt,” says Dr. Rangel. “I’d been a mom for just a few minutes, and I felt like I had already failed him because I had prioritized what the residency thought of me above what I knew was necessary for his health.”
Hope for the future
Disturbed by the status quo, many physicians are pushing for change. “I think there’s a really important and positive conversation going on in the medical community right now about ways that we need to support new parent physicians,” said Dr. Rangel.
Parental leave is a key part of that support. Last year, The American Board of Medical Specialties enacted a mandate that all specialty boards 2 years or more in duration must provide at least 6 weeks of parental and caregiver leave. In 2023, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) required that all training programs match that policy. “This sends a message to policymakers and leaders in American medicine that this is a priority,” said Dr. Rangel.
In January 2022, a group from the University of Michigan also published an article in the Annals of Surgery called “Safe and Supported Pregnancy: A Call to Action for Surgery Chairs and Program Directors”. The essay urged leading groups such as the ACGME and the American Board of Surgery to “directly address the health and safety of pregnant trainees” and specifically, to “allow for further flexibility during training for pregnancy and peripartum periods,” calling these “fundamental necessities for cultural progress.”
Others have recommended allowing pregnant trainees more flexibility in their schedules or front-loading certain parts of the training that may be more difficult as a pregnancy progresses. Insurance coverage for fertility preservation and reproductive endocrinology services, and support for reentry (including lactation and childcare) are also issues that must be addressed, says Dr. Salles.
A new paper of Dr. Rangel’s, published in JAMA Surgery, suggests that things like mentorship for residents from faculty can also be important pieces of the puzzle.
Education about reproductive health must start earlier, too – as early as medical school. Research suggests only 8% of physicians receive education on the risks of delaying pregnancy. Those who do are significantly less likely to experience pregnancy loss or seek infertility treatment.
Dr. Salles recalls sitting in a classroom learning about advanced maternal age at a time when age 35 seemed unimaginably distant. “It was never taught – at least to my recollection – in a way that was like, ‘this could be your future,’ ” Dr. Salles says.” It was more like this abstract patient who might have advanced maternal age and what the consequences would be. Maybe some of my colleagues put two and two together, but I definitely didn’t.”
Dr. Marshall is the curriculum chair for the IGNITEMed Initiative, which aims to educate medical students about issues not discussed in traditional medical school curricula. Dr. Marshall and her colleague Julia Files, MD, talk with IGNITEMed students about reproductive life planning.
“Raising awareness is a very big thing. That’s not just true for medical students but for professionals at every level of medicine,” Dr. Marshall said. “Residency and fellowship training program directors, department chairs, and hospital CEOs all need to understand that these issues are very common in the people they oversee – and that they are medical issues, like any other medical issue, where people need time off and support.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Surgeon General says 13-year-olds shouldn’t be on social media
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Which populations should be screened for cervical cancer?
Montrouge, France – Whether you are a cisgender woman or a transgender man who has kept his uterus, regardless of the sex of your partner, and even if you are a woman who is no longer sexually active, you must take part in cervical cancer screening. This is the reminder issued by Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, at a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical-Vaginal Diseases Society (SFCPCV).
Cervical screening currently targets asymptomatic, immunocompetent, and sexually active women between ages 25 and 65 years.
Sex between women
There is a widely held belief that only men can transmit human papillomavirus (HPV). “If you are in a sexual relationship with a man, then yes, you can get HPV from him. But it’s also possible for HPV to be transmitted in a sexual relationship between two women via touch, bodily fluids, or sex toys,” said Dr. Maruani, who pointed out that 20% of lesbians and 30% of bisexual women are HPV carriers.
Because women who have sexual relationships with other women have the mistaken view that their demographic is less affected, they are less likely to take part in cervical screening. They also present more often with advanced lesions and with cancer because of the lack of screening in this group.
Transgender men
Dr. Maruani defines transgender men as “women who have changed gender and who have become men.” Why are they affected by cervical screening? Not all of them are. Those who’ve had their uterus removed no longer have a cervix, so this screening doesn’t affect them. But hysterectomies are rarely performed, as they’re not required in most European countries to legally change gender.
The figures are concerning: 27% of transgender men are screened versus 60% of cisgender females.
“For this demographic, specialist gynecology appointments are hard to come by. Sitting in a women’s waiting room is not easy,” said Dr. Maruani, recalling that often discussion about the transition phase takes up the entire appointment time. It’s also usually the case that any medical problems or health care prevention issues not related to the topic of transitioning are not discussed.
Moreover, the online appointment-booking software doesn’t allow transgender men who have kept their cervix and legally identify as men to make an appointment. “Gynecologists must disable this default option,” said Dr. Maruani.
Likewise, transgender men will not receive an invitation to take part in cervical or breast cancer screening, as they are identified as male by social security services and screening sites. Furthermore, in what Dr. Maruani referred to as an “administrative head-scratcher that needs to change,” some medical procedures are not funded for men.
Yet the risk of contracting HPV is higher among transgender men than in the rest of the population because of different sexual practices in this demographic, as well as the propensity to have multiple sexual partners. The risk of finding abnormalities on cytology screening is greater.
Although data regarding cancer are lacking, “if screening is inadequate but the risk of infection with HPV is great, logic tells us that there will be more lesions, more cancer” in this demographic, said Dr. Maruani.
Celibate women
Nowadays, screening drops with age in women, especially after menopause. This is especially true for women who are no longer sexually active. Another preconceived notion to be addressed is that women who are no longer sexually active no longer need screening. But this concept completely goes against the natural history of HPV infection. “There are years, at least 5, between infection and the development of precancerous lesions. There is a further 5 years between a precancerous lesion and cancer,” said Dr. Maruani.
A woman could still be at risk even 20 years after contracting HPV. Approximately 80% of women are exposed to HPV, and 5%-10% have a persistent infection that could lead to the development of precancerous lesions.
“So, a woman who is no longer sexually active can’t stop participating in cervical screening, especially since there aren’t any symptoms until a fairly advanced stage of cancer.” No longer having sex does not mean that screening can be stopped.
What treatment is appropriate for partners of a woman who is no longer sexually active? None. During the press conference, the specialists agreed that a positive HPV test would be of importance to her partner. Even so, they recalled that the infection would generally be an old one and that the woman’s partner (whether male or female) would therefore have probably already been exposed to it. Patients should also be reminded that, in the past, cytology testing did not look for HPV, so the virus could already have been there. According to these specialists, you don’t need to change your sexual habits, just continue to monitor yourself.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version first appeared on Medscape.com.
Montrouge, France – Whether you are a cisgender woman or a transgender man who has kept his uterus, regardless of the sex of your partner, and even if you are a woman who is no longer sexually active, you must take part in cervical cancer screening. This is the reminder issued by Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, at a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical-Vaginal Diseases Society (SFCPCV).
Cervical screening currently targets asymptomatic, immunocompetent, and sexually active women between ages 25 and 65 years.
Sex between women
There is a widely held belief that only men can transmit human papillomavirus (HPV). “If you are in a sexual relationship with a man, then yes, you can get HPV from him. But it’s also possible for HPV to be transmitted in a sexual relationship between two women via touch, bodily fluids, or sex toys,” said Dr. Maruani, who pointed out that 20% of lesbians and 30% of bisexual women are HPV carriers.
Because women who have sexual relationships with other women have the mistaken view that their demographic is less affected, they are less likely to take part in cervical screening. They also present more often with advanced lesions and with cancer because of the lack of screening in this group.
Transgender men
Dr. Maruani defines transgender men as “women who have changed gender and who have become men.” Why are they affected by cervical screening? Not all of them are. Those who’ve had their uterus removed no longer have a cervix, so this screening doesn’t affect them. But hysterectomies are rarely performed, as they’re not required in most European countries to legally change gender.
The figures are concerning: 27% of transgender men are screened versus 60% of cisgender females.
“For this demographic, specialist gynecology appointments are hard to come by. Sitting in a women’s waiting room is not easy,” said Dr. Maruani, recalling that often discussion about the transition phase takes up the entire appointment time. It’s also usually the case that any medical problems or health care prevention issues not related to the topic of transitioning are not discussed.
Moreover, the online appointment-booking software doesn’t allow transgender men who have kept their cervix and legally identify as men to make an appointment. “Gynecologists must disable this default option,” said Dr. Maruani.
Likewise, transgender men will not receive an invitation to take part in cervical or breast cancer screening, as they are identified as male by social security services and screening sites. Furthermore, in what Dr. Maruani referred to as an “administrative head-scratcher that needs to change,” some medical procedures are not funded for men.
Yet the risk of contracting HPV is higher among transgender men than in the rest of the population because of different sexual practices in this demographic, as well as the propensity to have multiple sexual partners. The risk of finding abnormalities on cytology screening is greater.
Although data regarding cancer are lacking, “if screening is inadequate but the risk of infection with HPV is great, logic tells us that there will be more lesions, more cancer” in this demographic, said Dr. Maruani.
Celibate women
Nowadays, screening drops with age in women, especially after menopause. This is especially true for women who are no longer sexually active. Another preconceived notion to be addressed is that women who are no longer sexually active no longer need screening. But this concept completely goes against the natural history of HPV infection. “There are years, at least 5, between infection and the development of precancerous lesions. There is a further 5 years between a precancerous lesion and cancer,” said Dr. Maruani.
A woman could still be at risk even 20 years after contracting HPV. Approximately 80% of women are exposed to HPV, and 5%-10% have a persistent infection that could lead to the development of precancerous lesions.
“So, a woman who is no longer sexually active can’t stop participating in cervical screening, especially since there aren’t any symptoms until a fairly advanced stage of cancer.” No longer having sex does not mean that screening can be stopped.
What treatment is appropriate for partners of a woman who is no longer sexually active? None. During the press conference, the specialists agreed that a positive HPV test would be of importance to her partner. Even so, they recalled that the infection would generally be an old one and that the woman’s partner (whether male or female) would therefore have probably already been exposed to it. Patients should also be reminded that, in the past, cytology testing did not look for HPV, so the virus could already have been there. According to these specialists, you don’t need to change your sexual habits, just continue to monitor yourself.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version first appeared on Medscape.com.
Montrouge, France – Whether you are a cisgender woman or a transgender man who has kept his uterus, regardless of the sex of your partner, and even if you are a woman who is no longer sexually active, you must take part in cervical cancer screening. This is the reminder issued by Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, at a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical-Vaginal Diseases Society (SFCPCV).
Cervical screening currently targets asymptomatic, immunocompetent, and sexually active women between ages 25 and 65 years.
Sex between women
There is a widely held belief that only men can transmit human papillomavirus (HPV). “If you are in a sexual relationship with a man, then yes, you can get HPV from him. But it’s also possible for HPV to be transmitted in a sexual relationship between two women via touch, bodily fluids, or sex toys,” said Dr. Maruani, who pointed out that 20% of lesbians and 30% of bisexual women are HPV carriers.
Because women who have sexual relationships with other women have the mistaken view that their demographic is less affected, they are less likely to take part in cervical screening. They also present more often with advanced lesions and with cancer because of the lack of screening in this group.
Transgender men
Dr. Maruani defines transgender men as “women who have changed gender and who have become men.” Why are they affected by cervical screening? Not all of them are. Those who’ve had their uterus removed no longer have a cervix, so this screening doesn’t affect them. But hysterectomies are rarely performed, as they’re not required in most European countries to legally change gender.
The figures are concerning: 27% of transgender men are screened versus 60% of cisgender females.
“For this demographic, specialist gynecology appointments are hard to come by. Sitting in a women’s waiting room is not easy,” said Dr. Maruani, recalling that often discussion about the transition phase takes up the entire appointment time. It’s also usually the case that any medical problems or health care prevention issues not related to the topic of transitioning are not discussed.
Moreover, the online appointment-booking software doesn’t allow transgender men who have kept their cervix and legally identify as men to make an appointment. “Gynecologists must disable this default option,” said Dr. Maruani.
Likewise, transgender men will not receive an invitation to take part in cervical or breast cancer screening, as they are identified as male by social security services and screening sites. Furthermore, in what Dr. Maruani referred to as an “administrative head-scratcher that needs to change,” some medical procedures are not funded for men.
Yet the risk of contracting HPV is higher among transgender men than in the rest of the population because of different sexual practices in this demographic, as well as the propensity to have multiple sexual partners. The risk of finding abnormalities on cytology screening is greater.
Although data regarding cancer are lacking, “if screening is inadequate but the risk of infection with HPV is great, logic tells us that there will be more lesions, more cancer” in this demographic, said Dr. Maruani.
Celibate women
Nowadays, screening drops with age in women, especially after menopause. This is especially true for women who are no longer sexually active. Another preconceived notion to be addressed is that women who are no longer sexually active no longer need screening. But this concept completely goes against the natural history of HPV infection. “There are years, at least 5, between infection and the development of precancerous lesions. There is a further 5 years between a precancerous lesion and cancer,” said Dr. Maruani.
A woman could still be at risk even 20 years after contracting HPV. Approximately 80% of women are exposed to HPV, and 5%-10% have a persistent infection that could lead to the development of precancerous lesions.
“So, a woman who is no longer sexually active can’t stop participating in cervical screening, especially since there aren’t any symptoms until a fairly advanced stage of cancer.” No longer having sex does not mean that screening can be stopped.
What treatment is appropriate for partners of a woman who is no longer sexually active? None. During the press conference, the specialists agreed that a positive HPV test would be of importance to her partner. Even so, they recalled that the infection would generally be an old one and that the woman’s partner (whether male or female) would therefore have probably already been exposed to it. Patients should also be reminded that, in the past, cytology testing did not look for HPV, so the virus could already have been there. According to these specialists, you don’t need to change your sexual habits, just continue to monitor yourself.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scalp ridges

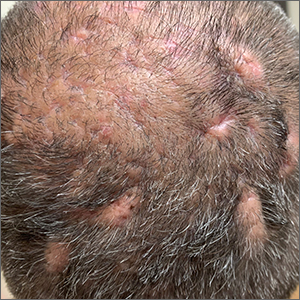
The gyrate or cerebriform pattern of inflammatory, often pus-filled, subcutaneous tracts of the scalp pointed to a diagnosis of dissecting cellulitis. This patient did not have the fluctuant tracts frequently seen in more active disease but did have the scarring and alopecia common with this disorder.
Dissecting cellulitis is similar to acne and hidradenitis suppurativa in that it starts with follicular plugging. This plugging leads to inflammation, dilation and rupture of the follicle, and purulent sinus tract formation. The sinus tracts of the scalp can be extensive. Dissecting cellulitis is most common in 18- to 40-year-olds and more common in Black individuals.1 When it occurs in conjunction with cystic acne and hidradenitis suppurativa, it is known as the follicular occlusion triad syndrome.
While oral antibiotics are an option for the treatment of dissecting cellulitis, oral isotretinoin is the first-line approach. Tumor necrosis factor alfa inhibitors have also been used with success, according to case reports.1
Given that this patient had a small area of current inflammation, he was started on oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 months. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months to reassess his progress and to explore treatment with isotretinoin if the condition worsened or did not improve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Federico A, Rossi A, Caro G, et al. Are dissecting cellulitis and hidradenitis suppurativa different diseases? Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:496-499. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.01.002

The gyrate or cerebriform pattern of inflammatory, often pus-filled, subcutaneous tracts of the scalp pointed to a diagnosis of dissecting cellulitis. This patient did not have the fluctuant tracts frequently seen in more active disease but did have the scarring and alopecia common with this disorder.
Dissecting cellulitis is similar to acne and hidradenitis suppurativa in that it starts with follicular plugging. This plugging leads to inflammation, dilation and rupture of the follicle, and purulent sinus tract formation. The sinus tracts of the scalp can be extensive. Dissecting cellulitis is most common in 18- to 40-year-olds and more common in Black individuals.1 When it occurs in conjunction with cystic acne and hidradenitis suppurativa, it is known as the follicular occlusion triad syndrome.
While oral antibiotics are an option for the treatment of dissecting cellulitis, oral isotretinoin is the first-line approach. Tumor necrosis factor alfa inhibitors have also been used with success, according to case reports.1
Given that this patient had a small area of current inflammation, he was started on oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 months. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months to reassess his progress and to explore treatment with isotretinoin if the condition worsened or did not improve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

The gyrate or cerebriform pattern of inflammatory, often pus-filled, subcutaneous tracts of the scalp pointed to a diagnosis of dissecting cellulitis. This patient did not have the fluctuant tracts frequently seen in more active disease but did have the scarring and alopecia common with this disorder.
Dissecting cellulitis is similar to acne and hidradenitis suppurativa in that it starts with follicular plugging. This plugging leads to inflammation, dilation and rupture of the follicle, and purulent sinus tract formation. The sinus tracts of the scalp can be extensive. Dissecting cellulitis is most common in 18- to 40-year-olds and more common in Black individuals.1 When it occurs in conjunction with cystic acne and hidradenitis suppurativa, it is known as the follicular occlusion triad syndrome.
While oral antibiotics are an option for the treatment of dissecting cellulitis, oral isotretinoin is the first-line approach. Tumor necrosis factor alfa inhibitors have also been used with success, according to case reports.1
Given that this patient had a small area of current inflammation, he was started on oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 months. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months to reassess his progress and to explore treatment with isotretinoin if the condition worsened or did not improve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Federico A, Rossi A, Caro G, et al. Are dissecting cellulitis and hidradenitis suppurativa different diseases? Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:496-499. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.01.002
1. Federico A, Rossi A, Caro G, et al. Are dissecting cellulitis and hidradenitis suppurativa different diseases? Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:496-499. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.01.002
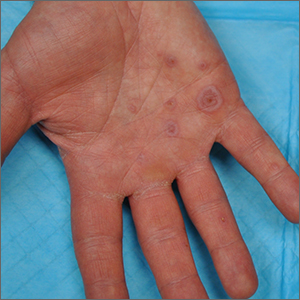
Palmar rash
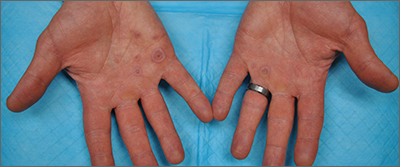
This patient’s targetoid and tingling skin lesions, in association with herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, are a classic presentation of erythema multiforme (EM).
EM is an acute, self-limited, immune-mediated process that most commonly arises in a symmetrical pattern on acral surfaces. These lesions may be accompanied by eruptions on oral, anogenital, or ocular mucosa. EM is classified into 2 subtypes: major and minor. EM major refers to EM with significant mucosal involvement on at least 2 mucosal sites; it may also manifest with a prodrome of fevers, arthralgias, and malaise. EM minor is used to classify EM with minimal mucosal involvement.1
The term “multiforme” denotes the varied dermatologic changes, including macules, papules, and targetoid lesions with 3 identifiable zones, which are pathognomonic for EM. The classic 3 zones consist of an inner dusky, vesicular, or necrotic center; a middle elevated edematous surrounding ring; and an outer ring of macular erythema. Patients may also present with an atypical macular target lesion, characterized by fewer than 3 zones with an ill-defined border between the zones. The lesions may be asymptomatic, or patients may describe an itchy or burning sensation.
The differential diagnosis of EM includes urticaria, fixed drug eruption, subacute lupus erythematosus, Kawasaki disease, erythema annulare centrifugum, vasculitis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Infections with HSV types 1 or 2 are the leading cause of EM and are thought to involve a cell-mediated immune process directed against viral antigens in skin.2 Other infectious causes include cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza virus, and—rarely—newer strains of coronavirus.3 Pharmacologic reactions are the cause in a small percentage of patients, and may involve nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, sulfonamides, antiepileptics, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Studies also link the development of EM to primary malignancy, autoimmune disease, and immunizations.1
The treatment of EM is dependent on the clinical course and severity of the disease. If a causative agent is identified, it should be discontinued (if a drug) or treated (if an infection). Topical antiseptic mouthwashes, antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids can be used to relieve cutaneous discomfort. Biologics and immunosuppressants can be used with patients who have severe symptoms or functional impairment. Patients who have recurrences associated with HSV should be given antiviral prophylaxis for 6 months consisting of oral acyclovir 10 mg/kg/d, valacyclovir 500 to 1000 mg/d, or famciclovir 250 mg twice daily.1
Given the recurrent nature of this patient’s disease, and its association with HSV outbreaks, he was prescribed prophylactic valacyclovir 1000 mg/d orally for 6 months to reduce HSV outbreaks and hopefully prevent future EM episodes.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Lynn Midani, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Trayes KP, Love G, Studdiford JS. Erythema multiforme: recognition and management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:82-88.
2. Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema multiforme. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 1, 2022. Accessed December 15, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470259/
3. Bennardo L, Nisticò SP, Dastoli S, et al. Erythema multiforme and COVID-19: what do we know? Medicina. 2021;57:828. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080828

This patient’s targetoid and tingling skin lesions, in association with herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, are a classic presentation of erythema multiforme (EM).
EM is an acute, self-limited, immune-mediated process that most commonly arises in a symmetrical pattern on acral surfaces. These lesions may be accompanied by eruptions on oral, anogenital, or ocular mucosa. EM is classified into 2 subtypes: major and minor. EM major refers to EM with significant mucosal involvement on at least 2 mucosal sites; it may also manifest with a prodrome of fevers, arthralgias, and malaise. EM minor is used to classify EM with minimal mucosal involvement.1
The term “multiforme” denotes the varied dermatologic changes, including macules, papules, and targetoid lesions with 3 identifiable zones, which are pathognomonic for EM. The classic 3 zones consist of an inner dusky, vesicular, or necrotic center; a middle elevated edematous surrounding ring; and an outer ring of macular erythema. Patients may also present with an atypical macular target lesion, characterized by fewer than 3 zones with an ill-defined border between the zones. The lesions may be asymptomatic, or patients may describe an itchy or burning sensation.
The differential diagnosis of EM includes urticaria, fixed drug eruption, subacute lupus erythematosus, Kawasaki disease, erythema annulare centrifugum, vasculitis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Infections with HSV types 1 or 2 are the leading cause of EM and are thought to involve a cell-mediated immune process directed against viral antigens in skin.2 Other infectious causes include cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza virus, and—rarely—newer strains of coronavirus.3 Pharmacologic reactions are the cause in a small percentage of patients, and may involve nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, sulfonamides, antiepileptics, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Studies also link the development of EM to primary malignancy, autoimmune disease, and immunizations.1
The treatment of EM is dependent on the clinical course and severity of the disease. If a causative agent is identified, it should be discontinued (if a drug) or treated (if an infection). Topical antiseptic mouthwashes, antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids can be used to relieve cutaneous discomfort. Biologics and immunosuppressants can be used with patients who have severe symptoms or functional impairment. Patients who have recurrences associated with HSV should be given antiviral prophylaxis for 6 months consisting of oral acyclovir 10 mg/kg/d, valacyclovir 500 to 1000 mg/d, or famciclovir 250 mg twice daily.1
Given the recurrent nature of this patient’s disease, and its association with HSV outbreaks, he was prescribed prophylactic valacyclovir 1000 mg/d orally for 6 months to reduce HSV outbreaks and hopefully prevent future EM episodes.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Lynn Midani, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

This patient’s targetoid and tingling skin lesions, in association with herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, are a classic presentation of erythema multiforme (EM).
EM is an acute, self-limited, immune-mediated process that most commonly arises in a symmetrical pattern on acral surfaces. These lesions may be accompanied by eruptions on oral, anogenital, or ocular mucosa. EM is classified into 2 subtypes: major and minor. EM major refers to EM with significant mucosal involvement on at least 2 mucosal sites; it may also manifest with a prodrome of fevers, arthralgias, and malaise. EM minor is used to classify EM with minimal mucosal involvement.1
The term “multiforme” denotes the varied dermatologic changes, including macules, papules, and targetoid lesions with 3 identifiable zones, which are pathognomonic for EM. The classic 3 zones consist of an inner dusky, vesicular, or necrotic center; a middle elevated edematous surrounding ring; and an outer ring of macular erythema. Patients may also present with an atypical macular target lesion, characterized by fewer than 3 zones with an ill-defined border between the zones. The lesions may be asymptomatic, or patients may describe an itchy or burning sensation.
The differential diagnosis of EM includes urticaria, fixed drug eruption, subacute lupus erythematosus, Kawasaki disease, erythema annulare centrifugum, vasculitis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Infections with HSV types 1 or 2 are the leading cause of EM and are thought to involve a cell-mediated immune process directed against viral antigens in skin.2 Other infectious causes include cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza virus, and—rarely—newer strains of coronavirus.3 Pharmacologic reactions are the cause in a small percentage of patients, and may involve nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, sulfonamides, antiepileptics, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Studies also link the development of EM to primary malignancy, autoimmune disease, and immunizations.1
The treatment of EM is dependent on the clinical course and severity of the disease. If a causative agent is identified, it should be discontinued (if a drug) or treated (if an infection). Topical antiseptic mouthwashes, antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids can be used to relieve cutaneous discomfort. Biologics and immunosuppressants can be used with patients who have severe symptoms or functional impairment. Patients who have recurrences associated with HSV should be given antiviral prophylaxis for 6 months consisting of oral acyclovir 10 mg/kg/d, valacyclovir 500 to 1000 mg/d, or famciclovir 250 mg twice daily.1
Given the recurrent nature of this patient’s disease, and its association with HSV outbreaks, he was prescribed prophylactic valacyclovir 1000 mg/d orally for 6 months to reduce HSV outbreaks and hopefully prevent future EM episodes.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Lynn Midani, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Trayes KP, Love G, Studdiford JS. Erythema multiforme: recognition and management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:82-88.
2. Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema multiforme. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 1, 2022. Accessed December 15, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470259/
3. Bennardo L, Nisticò SP, Dastoli S, et al. Erythema multiforme and COVID-19: what do we know? Medicina. 2021;57:828. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080828
1. Trayes KP, Love G, Studdiford JS. Erythema multiforme: recognition and management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:82-88.
2. Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema multiforme. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 1, 2022. Accessed December 15, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470259/
3. Bennardo L, Nisticò SP, Dastoli S, et al. Erythema multiforme and COVID-19: what do we know? Medicina. 2021;57:828. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080828
Annular Plaques Overlying Hyperpigmented Telangiectatic Patches on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).
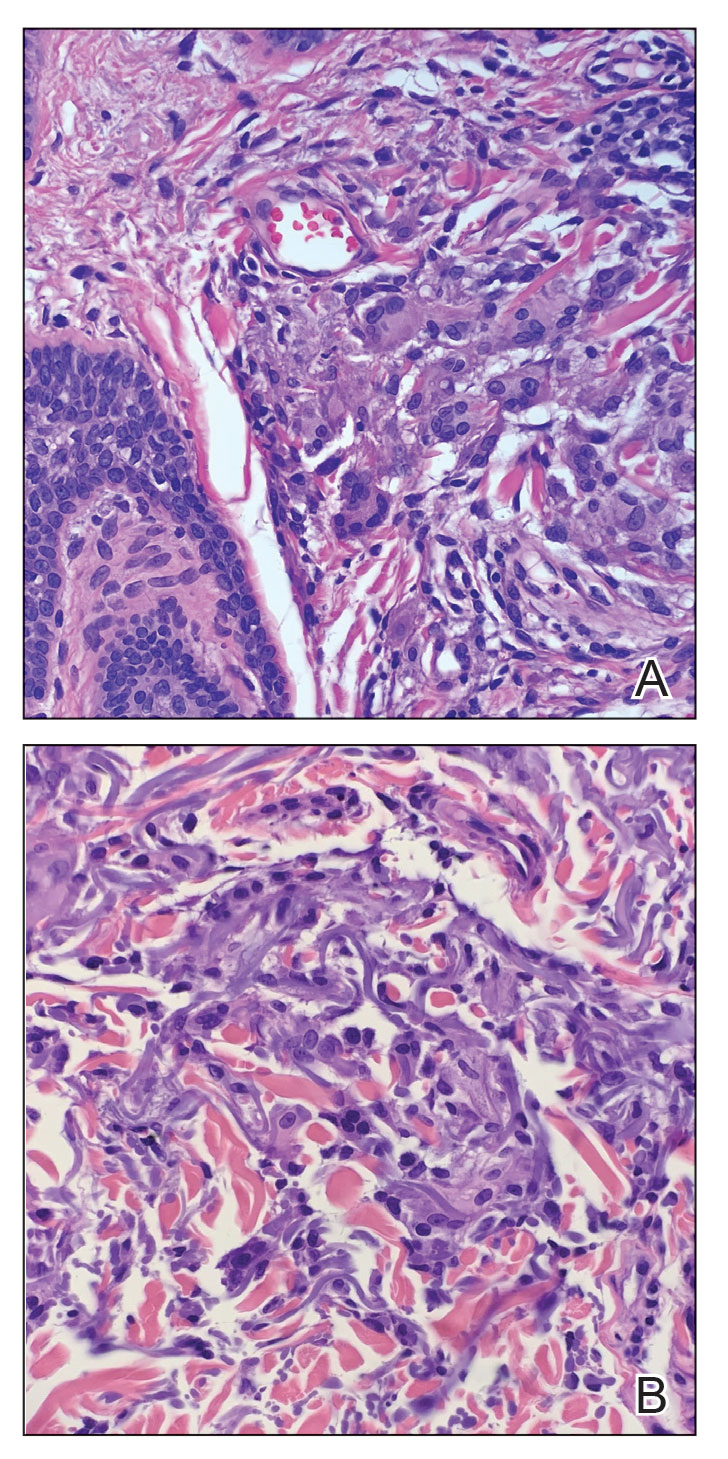
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
A 58-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, nephrolithiasis, hypovitaminosis D, and hypercholesterolemia presented to our dermatology clinic for a follow-up total-body skin examination after a prior diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma on the vertex of the scalp. Physical examination revealed extensive photodamage and annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches on the dorsal portion of the neck. The eruption persisted for 1 year and failed to improve with clotrimazole cream. His medications included simvastatin, metformin, chlorthalidone, vitamin D, and tamsulosin. Two shave biopsies from the posterior neck were performed.

Elevated PCSK9 levels associated with psoriasis suggest new treatment target
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
The ongoing search for answers
Hidden in the Dec. 1, 2022, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine was a small article on using deferiprone for Parkinson’s disease.
The idea behind it makes sense. A key factor in Parkinson’s disease is a loss of cells in the substantia nigra. The cells that have been lost have a build-up of iron content, suggesting that iron contributes to their demise. Therefore, maybe using an iron chelating agent to remove it may help.
Like I said, it makes sense.
Unfortunately, it didn’t quite work that way. In spite of a clear reduction of nigrostriatal iron, compared with the placebo group, the treated patients had worse MDS-UPDRS scores over 36 weeks than those on the placebo.
Back to the drawing board.
I’m not criticizing the people who did the study – it seemed like a reasonable hypothesis, and testing it is the only way we find out if it’s correct. We learn just as much, if not more, from a negative study as from a positive one, incrementally working toward the answer with each.
We face the same thing with the amyloid theory in Alzheimer’s disease. Getting rid of amyloid should fix the problem.
But it doesn’t, at least not completely. Even lecanemab, the latest-and-greatest of treatments, only shows a 27% slowing in disease progression. This is certainly meaningful – I’m not knocking it – but we’re still far from a cure. To date we haven’t even stopped disease progression, let alone reversed it.
Although the new drugs have a remarkable mechanism of action, the clinical results aren’t nearly as good as one would expect if amyloid was the whole issue.
Which, at this point, it probably isn’t, anymore than nigrostriatal iron deposition is the sole cause of Parkinson’s disease.
Right now we’re better able to find planets 27,700 light years away (SWEEPS-11) than we are at knowing the cause of neuronal changes in the person sitting across the desk from us. That’s not saying we won’t have the answers someday, it just means we don’t have them now.
I was in my 3rd year of medical school in January of 1992, (surgery rotation at the Omaha VA, to be specific) when the first definitive planet outside our solar system was identified. Today, 31 years later, the number of exoplanets stands at 5,297.
But the laws of physics are generally a lot more predictable than those of biology.
That doesn’t mean we won’t find the answers, or more effective treatments, eventually. But it will take more time, work, and studies – with both positive and negative results – to get there.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Hidden in the Dec. 1, 2022, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine was a small article on using deferiprone for Parkinson’s disease.
The idea behind it makes sense. A key factor in Parkinson’s disease is a loss of cells in the substantia nigra. The cells that have been lost have a build-up of iron content, suggesting that iron contributes to their demise. Therefore, maybe using an iron chelating agent to remove it may help.
Like I said, it makes sense.
Unfortunately, it didn’t quite work that way. In spite of a clear reduction of nigrostriatal iron, compared with the placebo group, the treated patients had worse MDS-UPDRS scores over 36 weeks than those on the placebo.
Back to the drawing board.
I’m not criticizing the people who did the study – it seemed like a reasonable hypothesis, and testing it is the only way we find out if it’s correct. We learn just as much, if not more, from a negative study as from a positive one, incrementally working toward the answer with each.
We face the same thing with the amyloid theory in Alzheimer’s disease. Getting rid of amyloid should fix the problem.
But it doesn’t, at least not completely. Even lecanemab, the latest-and-greatest of treatments, only shows a 27% slowing in disease progression. This is certainly meaningful – I’m not knocking it – but we’re still far from a cure. To date we haven’t even stopped disease progression, let alone reversed it.
Although the new drugs have a remarkable mechanism of action, the clinical results aren’t nearly as good as one would expect if amyloid was the whole issue.
Which, at this point, it probably isn’t, anymore than nigrostriatal iron deposition is the sole cause of Parkinson’s disease.
Right now we’re better able to find planets 27,700 light years away (SWEEPS-11) than we are at knowing the cause of neuronal changes in the person sitting across the desk from us. That’s not saying we won’t have the answers someday, it just means we don’t have them now.
I was in my 3rd year of medical school in January of 1992, (surgery rotation at the Omaha VA, to be specific) when the first definitive planet outside our solar system was identified. Today, 31 years later, the number of exoplanets stands at 5,297.
But the laws of physics are generally a lot more predictable than those of biology.
That doesn’t mean we won’t find the answers, or more effective treatments, eventually. But it will take more time, work, and studies – with both positive and negative results – to get there.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Hidden in the Dec. 1, 2022, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine was a small article on using deferiprone for Parkinson’s disease.
The idea behind it makes sense. A key factor in Parkinson’s disease is a loss of cells in the substantia nigra. The cells that have been lost have a build-up of iron content, suggesting that iron contributes to their demise. Therefore, maybe using an iron chelating agent to remove it may help.
Like I said, it makes sense.
Unfortunately, it didn’t quite work that way. In spite of a clear reduction of nigrostriatal iron, compared with the placebo group, the treated patients had worse MDS-UPDRS scores over 36 weeks than those on the placebo.
Back to the drawing board.
I’m not criticizing the people who did the study – it seemed like a reasonable hypothesis, and testing it is the only way we find out if it’s correct. We learn just as much, if not more, from a negative study as from a positive one, incrementally working toward the answer with each.
We face the same thing with the amyloid theory in Alzheimer’s disease. Getting rid of amyloid should fix the problem.
But it doesn’t, at least not completely. Even lecanemab, the latest-and-greatest of treatments, only shows a 27% slowing in disease progression. This is certainly meaningful – I’m not knocking it – but we’re still far from a cure. To date we haven’t even stopped disease progression, let alone reversed it.
Although the new drugs have a remarkable mechanism of action, the clinical results aren’t nearly as good as one would expect if amyloid was the whole issue.
Which, at this point, it probably isn’t, anymore than nigrostriatal iron deposition is the sole cause of Parkinson’s disease.
Right now we’re better able to find planets 27,700 light years away (SWEEPS-11) than we are at knowing the cause of neuronal changes in the person sitting across the desk from us. That’s not saying we won’t have the answers someday, it just means we don’t have them now.
I was in my 3rd year of medical school in January of 1992, (surgery rotation at the Omaha VA, to be specific) when the first definitive planet outside our solar system was identified. Today, 31 years later, the number of exoplanets stands at 5,297.
But the laws of physics are generally a lot more predictable than those of biology.
That doesn’t mean we won’t find the answers, or more effective treatments, eventually. But it will take more time, work, and studies – with both positive and negative results – to get there.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Six healthy lifestyle habits linked to slowed memory decline
Investigators found that a healthy diet, cognitive activity, regular physical exercise, not smoking, and abstaining from alcohol were significantly linked to slowed cognitive decline irrespective of APOE4 status.
After adjusting for health and socioeconomic factors, investigators found that each individual healthy behavior was associated with a slower-than-average decline in memory over a decade. A healthy diet emerged as the strongest deterrent, followed by cognitive activity and physical exercise.
“A healthy lifestyle is associated with slower memory decline, even in the presence of the APOE4 allele,” study investigators led by Jianping Jia, MD, PhD, of the Innovation Center for Neurological Disorders and the department of neurology, Xuan Wu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, write.
“This study might offer important information to protect older adults against memory decline,” they add.
The study was published online in the BMJ.
Preventing memory decline
Memory “continuously declines as people age,” but age-related memory decline is not necessarily a prodrome of dementia and can “merely be senescent forgetfulness,” the investigators note. This can be “reversed or [can] become stable,” instead of progressing to a pathologic state.
Factors affecting memory include aging, APOE4 genotype, chronic diseases, and lifestyle patterns, with lifestyle “receiving increasing attention as a modifiable behavior.”
Nevertheless, few studies have focused on the impact of lifestyle on memory, and those that have are mostly cross-sectional and also “did not consider the interaction between a healthy lifestyle and genetic risk,” the researchers note.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a longitudinal study, known as the China Cognition and Aging Study, that considered genetic risk as well as lifestyle factors.
The study began in 2009 and concluded in 2019. Participants were evaluated and underwent neuropsychological testing in 2012, 2014, 2016, and at the study’s conclusion.
Participants (n = 29,072; mean [SD] age, 72.23 [6.61] years; 48.54% women; 20.43% APOE4 carriers) were required to have normal cognitive function at baseline. Data on those whose condition progressed to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia during the follow-up period were excluded after their diagnosis.
The Mini–Mental State Examination was used to assess global cognitive function. Memory function was assessed using the World Health Organization/University of California, Los Angeles Auditory Verbal Learning Test.
“Lifestyle” consisted of six modifiable factors: physical exercise (weekly frequency and total time), smoking (current, former, or never-smokers), alcohol consumption (never drank, drank occasionally, low to excess drinking, and heavy drinking), diet (daily intake of 12 food items: fruits, vegetables, fish, meat, dairy products, salt, oil, eggs, cereals, legumes, nuts, tea), cognitive activity (writing, reading, playing cards, mahjong, other games), and social contact (participating in meetings, attending parties, visiting friends/relatives, traveling, chatting online).
Participants’ lifestyles were scored on the basis of the number of healthy factors they engaged in.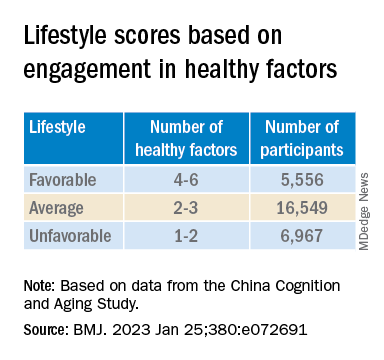
Participants were also stratified by APOE genotype into APOE4 carriers and noncarriers.
Demographic and other items of health information, including the presence of medical illness, were used as covariates. The researchers also included the “learning effect of each participant as a covariate, due to repeated cognitive assessments.”
Important for public health
During the 10-year period, 7,164 participants died, and 3,567 stopped participating.
Participants in the favorable and average groups showed slower memory decline per increased year of age (0.007 [0.005-0.009], P < .001; and 0.002 [0 .000-0.003], P = .033 points higher, respectively), compared with those in the unfavorable group.
Healthy diet had the strongest protective effect on memory.
Memory decline occurred faster in APOE4 vesus non-APOE4 carriers (0.002 points/year [95% confidence interval, 0.001-0.003]; P = .007).
But APOE4 carriers with favorable and average lifestyles showed slower memory decline (0.027 [0.023-0.031] and 0.014 [0.010-0.019], respectively), compared with those with unfavorable lifestyles. Similar findings were obtained in non-APOE4 carriers.
Those with favorable or average lifestyle were respectively almost 90% and 30% less likely to develop dementia or MCI, compared with those with an unfavorable lifestyle.
The authors acknowledge the study’s limitations, including its observational design and the potential for measurement errors, owing to self-reporting of lifestyle factors. Additionally, some participants did not return for follow-up evaluations, leading to potential selection bias.
Nevertheless, the findings “might offer important information for public health to protect older [people] against memory decline,” they note – especially since the study “provides evidence that these effects also include individuals with the APOE4 allele.”
‘Important, encouraging’ research
In a comment, Severine Sabia, PhD, a senior researcher at the Université Paris Cité, INSERM Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Medicalé, France, called the findings “important and encouraging.”
However, said Dr. Sabia, who was not involved with the study, “there remain important research questions that need to be investigated in order to identify key behaviors: which combination, the cutoff of risk, and when to intervene.”
Future research on prevention “should examine a wider range of possible risk factors” and should also “identify specific exposures associated with the greatest risk, while also considering the risk threshold and age at exposure for each one.”
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Sabia and co-author Archana Singh-Manoux, PhD, note that the risk of cognitive decline and dementia are probably determined by multiple factors.
They liken it to the “multifactorial risk paradigm introduced by the Framingham study,” which has “led to a substantial reduction in cardiovascular disease.” A similar approach could be used with dementia prevention, they suggest.
The authors received support from the Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University for the submitted work. One of the authors received a grant from the French National Research Agency. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sabia received grant funding from the French National Research Agency. Dr. Singh-Manoux received grants from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that a healthy diet, cognitive activity, regular physical exercise, not smoking, and abstaining from alcohol were significantly linked to slowed cognitive decline irrespective of APOE4 status.
After adjusting for health and socioeconomic factors, investigators found that each individual healthy behavior was associated with a slower-than-average decline in memory over a decade. A healthy diet emerged as the strongest deterrent, followed by cognitive activity and physical exercise.
“A healthy lifestyle is associated with slower memory decline, even in the presence of the APOE4 allele,” study investigators led by Jianping Jia, MD, PhD, of the Innovation Center for Neurological Disorders and the department of neurology, Xuan Wu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, write.
“This study might offer important information to protect older adults against memory decline,” they add.
The study was published online in the BMJ.
Preventing memory decline
Memory “continuously declines as people age,” but age-related memory decline is not necessarily a prodrome of dementia and can “merely be senescent forgetfulness,” the investigators note. This can be “reversed or [can] become stable,” instead of progressing to a pathologic state.
Factors affecting memory include aging, APOE4 genotype, chronic diseases, and lifestyle patterns, with lifestyle “receiving increasing attention as a modifiable behavior.”
Nevertheless, few studies have focused on the impact of lifestyle on memory, and those that have are mostly cross-sectional and also “did not consider the interaction between a healthy lifestyle and genetic risk,” the researchers note.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a longitudinal study, known as the China Cognition and Aging Study, that considered genetic risk as well as lifestyle factors.
The study began in 2009 and concluded in 2019. Participants were evaluated and underwent neuropsychological testing in 2012, 2014, 2016, and at the study’s conclusion.
Participants (n = 29,072; mean [SD] age, 72.23 [6.61] years; 48.54% women; 20.43% APOE4 carriers) were required to have normal cognitive function at baseline. Data on those whose condition progressed to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia during the follow-up period were excluded after their diagnosis.
The Mini–Mental State Examination was used to assess global cognitive function. Memory function was assessed using the World Health Organization/University of California, Los Angeles Auditory Verbal Learning Test.
“Lifestyle” consisted of six modifiable factors: physical exercise (weekly frequency and total time), smoking (current, former, or never-smokers), alcohol consumption (never drank, drank occasionally, low to excess drinking, and heavy drinking), diet (daily intake of 12 food items: fruits, vegetables, fish, meat, dairy products, salt, oil, eggs, cereals, legumes, nuts, tea), cognitive activity (writing, reading, playing cards, mahjong, other games), and social contact (participating in meetings, attending parties, visiting friends/relatives, traveling, chatting online).
Participants’ lifestyles were scored on the basis of the number of healthy factors they engaged in.
Participants were also stratified by APOE genotype into APOE4 carriers and noncarriers.
Demographic and other items of health information, including the presence of medical illness, were used as covariates. The researchers also included the “learning effect of each participant as a covariate, due to repeated cognitive assessments.”
Important for public health
During the 10-year period, 7,164 participants died, and 3,567 stopped participating.
Participants in the favorable and average groups showed slower memory decline per increased year of age (0.007 [0.005-0.009], P < .001; and 0.002 [0 .000-0.003], P = .033 points higher, respectively), compared with those in the unfavorable group.
Healthy diet had the strongest protective effect on memory.
Memory decline occurred faster in APOE4 vesus non-APOE4 carriers (0.002 points/year [95% confidence interval, 0.001-0.003]; P = .007).
But APOE4 carriers with favorable and average lifestyles showed slower memory decline (0.027 [0.023-0.031] and 0.014 [0.010-0.019], respectively), compared with those with unfavorable lifestyles. Similar findings were obtained in non-APOE4 carriers.
Those with favorable or average lifestyle were respectively almost 90% and 30% less likely to develop dementia or MCI, compared with those with an unfavorable lifestyle.
The authors acknowledge the study’s limitations, including its observational design and the potential for measurement errors, owing to self-reporting of lifestyle factors. Additionally, some participants did not return for follow-up evaluations, leading to potential selection bias.
Nevertheless, the findings “might offer important information for public health to protect older [people] against memory decline,” they note – especially since the study “provides evidence that these effects also include individuals with the APOE4 allele.”
‘Important, encouraging’ research
In a comment, Severine Sabia, PhD, a senior researcher at the Université Paris Cité, INSERM Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Medicalé, France, called the findings “important and encouraging.”
However, said Dr. Sabia, who was not involved with the study, “there remain important research questions that need to be investigated in order to identify key behaviors: which combination, the cutoff of risk, and when to intervene.”
Future research on prevention “should examine a wider range of possible risk factors” and should also “identify specific exposures associated with the greatest risk, while also considering the risk threshold and age at exposure for each one.”
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Sabia and co-author Archana Singh-Manoux, PhD, note that the risk of cognitive decline and dementia are probably determined by multiple factors.
They liken it to the “multifactorial risk paradigm introduced by the Framingham study,” which has “led to a substantial reduction in cardiovascular disease.” A similar approach could be used with dementia prevention, they suggest.
The authors received support from the Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University for the submitted work. One of the authors received a grant from the French National Research Agency. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sabia received grant funding from the French National Research Agency. Dr. Singh-Manoux received grants from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that a healthy diet, cognitive activity, regular physical exercise, not smoking, and abstaining from alcohol were significantly linked to slowed cognitive decline irrespective of APOE4 status.
After adjusting for health and socioeconomic factors, investigators found that each individual healthy behavior was associated with a slower-than-average decline in memory over a decade. A healthy diet emerged as the strongest deterrent, followed by cognitive activity and physical exercise.
“A healthy lifestyle is associated with slower memory decline, even in the presence of the APOE4 allele,” study investigators led by Jianping Jia, MD, PhD, of the Innovation Center for Neurological Disorders and the department of neurology, Xuan Wu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, write.
“This study might offer important information to protect older adults against memory decline,” they add.
The study was published online in the BMJ.
Preventing memory decline
Memory “continuously declines as people age,” but age-related memory decline is not necessarily a prodrome of dementia and can “merely be senescent forgetfulness,” the investigators note. This can be “reversed or [can] become stable,” instead of progressing to a pathologic state.
Factors affecting memory include aging, APOE4 genotype, chronic diseases, and lifestyle patterns, with lifestyle “receiving increasing attention as a modifiable behavior.”
Nevertheless, few studies have focused on the impact of lifestyle on memory, and those that have are mostly cross-sectional and also “did not consider the interaction between a healthy lifestyle and genetic risk,” the researchers note.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a longitudinal study, known as the China Cognition and Aging Study, that considered genetic risk as well as lifestyle factors.
The study began in 2009 and concluded in 2019. Participants were evaluated and underwent neuropsychological testing in 2012, 2014, 2016, and at the study’s conclusion.
Participants (n = 29,072; mean [SD] age, 72.23 [6.61] years; 48.54% women; 20.43% APOE4 carriers) were required to have normal cognitive function at baseline. Data on those whose condition progressed to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia during the follow-up period were excluded after their diagnosis.
The Mini–Mental State Examination was used to assess global cognitive function. Memory function was assessed using the World Health Organization/University of California, Los Angeles Auditory Verbal Learning Test.
“Lifestyle” consisted of six modifiable factors: physical exercise (weekly frequency and total time), smoking (current, former, or never-smokers), alcohol consumption (never drank, drank occasionally, low to excess drinking, and heavy drinking), diet (daily intake of 12 food items: fruits, vegetables, fish, meat, dairy products, salt, oil, eggs, cereals, legumes, nuts, tea), cognitive activity (writing, reading, playing cards, mahjong, other games), and social contact (participating in meetings, attending parties, visiting friends/relatives, traveling, chatting online).
Participants’ lifestyles were scored on the basis of the number of healthy factors they engaged in.
Participants were also stratified by APOE genotype into APOE4 carriers and noncarriers.
Demographic and other items of health information, including the presence of medical illness, were used as covariates. The researchers also included the “learning effect of each participant as a covariate, due to repeated cognitive assessments.”
Important for public health
During the 10-year period, 7,164 participants died, and 3,567 stopped participating.
Participants in the favorable and average groups showed slower memory decline per increased year of age (0.007 [0.005-0.009], P < .001; and 0.002 [0 .000-0.003], P = .033 points higher, respectively), compared with those in the unfavorable group.
Healthy diet had the strongest protective effect on memory.
Memory decline occurred faster in APOE4 vesus non-APOE4 carriers (0.002 points/year [95% confidence interval, 0.001-0.003]; P = .007).
But APOE4 carriers with favorable and average lifestyles showed slower memory decline (0.027 [0.023-0.031] and 0.014 [0.010-0.019], respectively), compared with those with unfavorable lifestyles. Similar findings were obtained in non-APOE4 carriers.
Those with favorable or average lifestyle were respectively almost 90% and 30% less likely to develop dementia or MCI, compared with those with an unfavorable lifestyle.
The authors acknowledge the study’s limitations, including its observational design and the potential for measurement errors, owing to self-reporting of lifestyle factors. Additionally, some participants did not return for follow-up evaluations, leading to potential selection bias.
Nevertheless, the findings “might offer important information for public health to protect older [people] against memory decline,” they note – especially since the study “provides evidence that these effects also include individuals with the APOE4 allele.”
‘Important, encouraging’ research
In a comment, Severine Sabia, PhD, a senior researcher at the Université Paris Cité, INSERM Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Medicalé, France, called the findings “important and encouraging.”
However, said Dr. Sabia, who was not involved with the study, “there remain important research questions that need to be investigated in order to identify key behaviors: which combination, the cutoff of risk, and when to intervene.”
Future research on prevention “should examine a wider range of possible risk factors” and should also “identify specific exposures associated with the greatest risk, while also considering the risk threshold and age at exposure for each one.”
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Sabia and co-author Archana Singh-Manoux, PhD, note that the risk of cognitive decline and dementia are probably determined by multiple factors.
They liken it to the “multifactorial risk paradigm introduced by the Framingham study,” which has “led to a substantial reduction in cardiovascular disease.” A similar approach could be used with dementia prevention, they suggest.
The authors received support from the Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University for the submitted work. One of the authors received a grant from the French National Research Agency. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sabia received grant funding from the French National Research Agency. Dr. Singh-Manoux received grants from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ