User login
Physicians urged to write indications on drug scripts as methotrexate users face new barriers with SCOTUS decision
.
The Court’s 5-4 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which halted abortion procedures across the country, also appears to be affecting certain drug regimens. Reports have emerged that pharmacies are denying access to methotrexate (MTX), a drug often used in patients with arthritis or cancer, as well as psoriasis and other skin diseases. In very high doses, MTX it is used to terminate an ectopic pregnancy after miscarriage. The drug can also lead to birth defects.
“It’s happening all over,” Donald Miller, PharmD, professor of pharmacy practice at North Dakota State University, Fargo, said in an interview. “Pharmacists are reluctant to dispense it, and rheumatologists are reluctant to prescribe it because they’re afraid of going to jail.”
Becky Schwartz, a patient who takes MTX for lupus, recently tweeted that her physician’s office stopped prescribing the drug because it is considered an abortifacient. “I had care that made my disabled life easier, and [the Supreme Court] took that from me,” Ms. Schwartz wrote.
Prior to the Supreme Court’s ruling, physicians were concerned about the impact an overturning of the 1973 law would have on patient access to MTX and other prescription medications with abortifacient properties. Doctors in general are becoming afraid of prescribing anything that’s a teratogen, said Dr. Miller.
MTX is used far more often for autoimmune disease than as an abortifacient, said rheumatologist Kristen Young, MD, clinical assistant professor at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix. It’s a slippery slope if states reacting to the Supreme Court ruling start regulating oral abortifacients, she added. Specifically, this will have a significant impact on patients with rheumatic disease.
Texas pharmacies target two drugs
MTX denials have caught the attention of health care organizations. “Uncertainty in financial and criminal liability for health care professionals in certain state laws and regulations are possibly compromising continuity of care and access [to] medications proven to be safe and effective by the Food and Drug Administration for these indications,” warned the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) in a statement to this news organization.
The APhA said that it was monitoring this situation to assess the effect on patients and pharmacists.
The Arthritis Foundation was made aware of challenges from patients in accessing their MTX prescription for managing their arthritis and shared a statement on the Foundation’s website.
In Texas, pharmacists can refuse to fill scripts for misoprostol and MTX, a combination used for medical abortions. According to the foundation, “Already there are reports that people in Texas who miscarry or take methotrexate for arthritis [are] having trouble getting their prescriptions filled.”
MTX, approved by the FDA in 1985, “is the absolute cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis. We cannot deny our patients this incredibly valuable drug,” said John Reveille, MD, vice-chair for the department of medicine at the University of Texas McGovern School of Medicine and a member of the Arthritis Foundation expert panel, in an interview.
“While it’s true that methotrexate can be lethal to the fetus, misoprostol is much more likely to cause a spontaneous abortion, and the combination is especially effective,” he said.
“If you look at Cochrane clinical studies, the dose of misoprostol contained in certain combinations with NSAIDs [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] can induce spontaneous abortions. It’s surprising that pharmacists are targeting methotrexate, an essential drug in arthritis treatment, when there are medications available that do not have this benefit that can by themselves cause loss of the fetus, such as mifepristone,” added Dr. Reveille.
The Dobbs ruling could also affect the ability of oncologists to provide lifesaving cancer care, according to Jason Westin, MD, an oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the department of lymphoma and myeloma.
“We have heard of medications with multiple indications, such as methotrexate, not being dispensed by pharmacies due to confusion regarding the intended use and potential consequences for the health care team,” he said in an interview.
Conflicting laws pose challenges for physicians
In North Dakota, inconsistencies in several laws are making it difficult for physicians and pharmacists to make decisions. “Lots of confusion can result when people pass laws against abortion. There’s sometimes no insight into the ramifications of those laws,” said Dr. Miller.
North Dakota approved a trigger law several years ago that makes abortion illegal 30 days after an overturning of Roe. However, another law that regulates abortion conflicts with the trigger law. “Some of the language will need clarification in the next legislative session,” he said.
APhA and other pharmacy associations strongly favor not interfering with the doctor- or pharmacist-patient relationship. The law needs to defer to appropriate care between doctor and patient, said Dr. Miller. State pharmacy associations in North Dakota are working with legislatures to clarify any exceptions in the law, he added.
Arizona lawmakers are trying to reconcile two abortion laws on the books. One, based on an 1864 territorial law, deems abortion illegal. In addition, a newly approved law bans abortions after 15 weeks. The latter will go into effect in September 2022. In both laws, a risk to the mother’s life is the only exception for abortion, said Dr. Young.
Denials aren’t widespread
Not all doctors are seeing MTX denials, but they’re worried about the future. “To date, we have not encountered difficulty in obtaining methotrexate based upon state abortion restrictions but are concerned that this could occur and result in dangerous delays in care,” said Dr. Westin.
Dr. Reveille, who practices rheumatology in Houston, has not yet received any complaints from patients. Things may be different in more rural parts of Texas, where pharmacists could be denying prescriptions based on religious issues, he offered.
It’s a little soon to see what repercussions may result from the Supreme Court ruling and state actions, said Dr. Reveille. “In Texas, we’re a bit ahead of the tidal wave.”
Access problems also haven’t shown up at the university clinic where Dr. Young practices. “In Arizona, it’s unclear if there would be a legal basis to refuse a person methotrexate on the basis that it can be used as an abortifacient,” she said.
Specificity is key in writing Rx scripts
Physicians can make things easier for patients by writing the indication and dose for the drug on the prescription slip. For example, a 10-mg script for MTX is not going to be used for an abortion, said Dr. Miller.
Rheumatologists in Texas have been doing this for some time, even before the Supreme Court ruling, said Fehmida Zahabi, MD, FACR, president of the Society of Texas Association of Rheumatology. For MTX prescriptions in premenopausal women, “patients are told their doctor needs to call the pharmacist. In the small print, we are asked to give a diagnosis to make sure we aren’t using it to terminate pregnancies,” said Dr. Zahabi.
She further noted that if the diagnosis is already indicated on the script, pharmacies generally won’t give patients a hard time.
Patients can also ask their physicians for a letter of medical necessity that confirms a drug’s use for a specific medical condition.
Mail order is another option if a local pharmacy won’t fill a prescription, said Dr. Miller. “This is legal unless a state makes it illegal to send an abortifacient across state lines,” he added.
Many medications used in rheumatic diseases are harmful in pregnancy, and it’s important to routinely discuss pregnancy risk and planning in the rheumatology clinic, said Dr. Young. This should include a thorough discussion and referral for long-acting reversible contraception in most cases, she suggested.
Actions at the federal, state level
President Joe Biden recently signed an executive order prompting federal regulators to protect access to medication abortions, among other steps to safeguard access to reproductive services.
In a statement on Twitter, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) said that it was “ ... following this issue closely to determine if rheumatology providers and patients are experiencing any widespread difficulty accessing methotrexate or if any initial disruptions are potentially temporary and due to the independent actions of pharmacists trying to figure out what is and isn’t allowed where they practice.”
ACR has assembled a task force of medical and policy experts to determine the best course of action for patients.
The Arthritis Foundation also continues to monitor the situation, encouraging patients to call its hotline, said Steven Schultz, director of state legislative affairs, in an interview.
“We are analyzing how medication abortion could cause confusion on the part of providers or pharmacists dispensing the medication and what this means for specific patients,” said Mr. Schultz. Through a survey, the foundation hopes to get a better idea of what’s going on in the states at a macro level.
This may take some time, as states go through a process of lawsuits, injunctions, or coming into session to do something that may affect access to MTX, said Mr. Schultz.
Being involved in local advocacy is more important than ever, stressed Dr. Young. “Additionally, being plugged into what the ACR and other advocacy groups are doing on the national level is helpful as well to know the status of these medication access issues.”
Rheumatologists have a unique voice in this discussion, she added. “We guide our patients to stability for a safe pregnancy, and even with careful planning, we see patients who become critically ill during pregnancy and require lifesaving treatment, which at times can mean an abortion is necessary.”
Oncologists also advocate for their patients on a regular basis to make sure they have access to the care they need, said Dr. Westin. This situation with Roe is no different, he added. “We will continue to use our unique expertise to advocate for policies that assure access to high-quality, evidence-based care – and to help our patients overcome barriers that may interfere.”
Dr. Reveille participated on an advisory board with Eli Lilly in October 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The Court’s 5-4 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which halted abortion procedures across the country, also appears to be affecting certain drug regimens. Reports have emerged that pharmacies are denying access to methotrexate (MTX), a drug often used in patients with arthritis or cancer, as well as psoriasis and other skin diseases. In very high doses, MTX it is used to terminate an ectopic pregnancy after miscarriage. The drug can also lead to birth defects.
“It’s happening all over,” Donald Miller, PharmD, professor of pharmacy practice at North Dakota State University, Fargo, said in an interview. “Pharmacists are reluctant to dispense it, and rheumatologists are reluctant to prescribe it because they’re afraid of going to jail.”
Becky Schwartz, a patient who takes MTX for lupus, recently tweeted that her physician’s office stopped prescribing the drug because it is considered an abortifacient. “I had care that made my disabled life easier, and [the Supreme Court] took that from me,” Ms. Schwartz wrote.
Prior to the Supreme Court’s ruling, physicians were concerned about the impact an overturning of the 1973 law would have on patient access to MTX and other prescription medications with abortifacient properties. Doctors in general are becoming afraid of prescribing anything that’s a teratogen, said Dr. Miller.
MTX is used far more often for autoimmune disease than as an abortifacient, said rheumatologist Kristen Young, MD, clinical assistant professor at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix. It’s a slippery slope if states reacting to the Supreme Court ruling start regulating oral abortifacients, she added. Specifically, this will have a significant impact on patients with rheumatic disease.
Texas pharmacies target two drugs
MTX denials have caught the attention of health care organizations. “Uncertainty in financial and criminal liability for health care professionals in certain state laws and regulations are possibly compromising continuity of care and access [to] medications proven to be safe and effective by the Food and Drug Administration for these indications,” warned the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) in a statement to this news organization.
The APhA said that it was monitoring this situation to assess the effect on patients and pharmacists.
The Arthritis Foundation was made aware of challenges from patients in accessing their MTX prescription for managing their arthritis and shared a statement on the Foundation’s website.
In Texas, pharmacists can refuse to fill scripts for misoprostol and MTX, a combination used for medical abortions. According to the foundation, “Already there are reports that people in Texas who miscarry or take methotrexate for arthritis [are] having trouble getting their prescriptions filled.”
MTX, approved by the FDA in 1985, “is the absolute cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis. We cannot deny our patients this incredibly valuable drug,” said John Reveille, MD, vice-chair for the department of medicine at the University of Texas McGovern School of Medicine and a member of the Arthritis Foundation expert panel, in an interview.
“While it’s true that methotrexate can be lethal to the fetus, misoprostol is much more likely to cause a spontaneous abortion, and the combination is especially effective,” he said.
“If you look at Cochrane clinical studies, the dose of misoprostol contained in certain combinations with NSAIDs [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] can induce spontaneous abortions. It’s surprising that pharmacists are targeting methotrexate, an essential drug in arthritis treatment, when there are medications available that do not have this benefit that can by themselves cause loss of the fetus, such as mifepristone,” added Dr. Reveille.
The Dobbs ruling could also affect the ability of oncologists to provide lifesaving cancer care, according to Jason Westin, MD, an oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the department of lymphoma and myeloma.
“We have heard of medications with multiple indications, such as methotrexate, not being dispensed by pharmacies due to confusion regarding the intended use and potential consequences for the health care team,” he said in an interview.
Conflicting laws pose challenges for physicians
In North Dakota, inconsistencies in several laws are making it difficult for physicians and pharmacists to make decisions. “Lots of confusion can result when people pass laws against abortion. There’s sometimes no insight into the ramifications of those laws,” said Dr. Miller.
North Dakota approved a trigger law several years ago that makes abortion illegal 30 days after an overturning of Roe. However, another law that regulates abortion conflicts with the trigger law. “Some of the language will need clarification in the next legislative session,” he said.
APhA and other pharmacy associations strongly favor not interfering with the doctor- or pharmacist-patient relationship. The law needs to defer to appropriate care between doctor and patient, said Dr. Miller. State pharmacy associations in North Dakota are working with legislatures to clarify any exceptions in the law, he added.
Arizona lawmakers are trying to reconcile two abortion laws on the books. One, based on an 1864 territorial law, deems abortion illegal. In addition, a newly approved law bans abortions after 15 weeks. The latter will go into effect in September 2022. In both laws, a risk to the mother’s life is the only exception for abortion, said Dr. Young.
Denials aren’t widespread
Not all doctors are seeing MTX denials, but they’re worried about the future. “To date, we have not encountered difficulty in obtaining methotrexate based upon state abortion restrictions but are concerned that this could occur and result in dangerous delays in care,” said Dr. Westin.
Dr. Reveille, who practices rheumatology in Houston, has not yet received any complaints from patients. Things may be different in more rural parts of Texas, where pharmacists could be denying prescriptions based on religious issues, he offered.
It’s a little soon to see what repercussions may result from the Supreme Court ruling and state actions, said Dr. Reveille. “In Texas, we’re a bit ahead of the tidal wave.”
Access problems also haven’t shown up at the university clinic where Dr. Young practices. “In Arizona, it’s unclear if there would be a legal basis to refuse a person methotrexate on the basis that it can be used as an abortifacient,” she said.
Specificity is key in writing Rx scripts
Physicians can make things easier for patients by writing the indication and dose for the drug on the prescription slip. For example, a 10-mg script for MTX is not going to be used for an abortion, said Dr. Miller.
Rheumatologists in Texas have been doing this for some time, even before the Supreme Court ruling, said Fehmida Zahabi, MD, FACR, president of the Society of Texas Association of Rheumatology. For MTX prescriptions in premenopausal women, “patients are told their doctor needs to call the pharmacist. In the small print, we are asked to give a diagnosis to make sure we aren’t using it to terminate pregnancies,” said Dr. Zahabi.
She further noted that if the diagnosis is already indicated on the script, pharmacies generally won’t give patients a hard time.
Patients can also ask their physicians for a letter of medical necessity that confirms a drug’s use for a specific medical condition.
Mail order is another option if a local pharmacy won’t fill a prescription, said Dr. Miller. “This is legal unless a state makes it illegal to send an abortifacient across state lines,” he added.
Many medications used in rheumatic diseases are harmful in pregnancy, and it’s important to routinely discuss pregnancy risk and planning in the rheumatology clinic, said Dr. Young. This should include a thorough discussion and referral for long-acting reversible contraception in most cases, she suggested.
Actions at the federal, state level
President Joe Biden recently signed an executive order prompting federal regulators to protect access to medication abortions, among other steps to safeguard access to reproductive services.
In a statement on Twitter, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) said that it was “ ... following this issue closely to determine if rheumatology providers and patients are experiencing any widespread difficulty accessing methotrexate or if any initial disruptions are potentially temporary and due to the independent actions of pharmacists trying to figure out what is and isn’t allowed where they practice.”
ACR has assembled a task force of medical and policy experts to determine the best course of action for patients.
The Arthritis Foundation also continues to monitor the situation, encouraging patients to call its hotline, said Steven Schultz, director of state legislative affairs, in an interview.
“We are analyzing how medication abortion could cause confusion on the part of providers or pharmacists dispensing the medication and what this means for specific patients,” said Mr. Schultz. Through a survey, the foundation hopes to get a better idea of what’s going on in the states at a macro level.
This may take some time, as states go through a process of lawsuits, injunctions, or coming into session to do something that may affect access to MTX, said Mr. Schultz.
Being involved in local advocacy is more important than ever, stressed Dr. Young. “Additionally, being plugged into what the ACR and other advocacy groups are doing on the national level is helpful as well to know the status of these medication access issues.”
Rheumatologists have a unique voice in this discussion, she added. “We guide our patients to stability for a safe pregnancy, and even with careful planning, we see patients who become critically ill during pregnancy and require lifesaving treatment, which at times can mean an abortion is necessary.”
Oncologists also advocate for their patients on a regular basis to make sure they have access to the care they need, said Dr. Westin. This situation with Roe is no different, he added. “We will continue to use our unique expertise to advocate for policies that assure access to high-quality, evidence-based care – and to help our patients overcome barriers that may interfere.”
Dr. Reveille participated on an advisory board with Eli Lilly in October 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The Court’s 5-4 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which halted abortion procedures across the country, also appears to be affecting certain drug regimens. Reports have emerged that pharmacies are denying access to methotrexate (MTX), a drug often used in patients with arthritis or cancer, as well as psoriasis and other skin diseases. In very high doses, MTX it is used to terminate an ectopic pregnancy after miscarriage. The drug can also lead to birth defects.
“It’s happening all over,” Donald Miller, PharmD, professor of pharmacy practice at North Dakota State University, Fargo, said in an interview. “Pharmacists are reluctant to dispense it, and rheumatologists are reluctant to prescribe it because they’re afraid of going to jail.”
Becky Schwartz, a patient who takes MTX for lupus, recently tweeted that her physician’s office stopped prescribing the drug because it is considered an abortifacient. “I had care that made my disabled life easier, and [the Supreme Court] took that from me,” Ms. Schwartz wrote.
Prior to the Supreme Court’s ruling, physicians were concerned about the impact an overturning of the 1973 law would have on patient access to MTX and other prescription medications with abortifacient properties. Doctors in general are becoming afraid of prescribing anything that’s a teratogen, said Dr. Miller.
MTX is used far more often for autoimmune disease than as an abortifacient, said rheumatologist Kristen Young, MD, clinical assistant professor at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix. It’s a slippery slope if states reacting to the Supreme Court ruling start regulating oral abortifacients, she added. Specifically, this will have a significant impact on patients with rheumatic disease.
Texas pharmacies target two drugs
MTX denials have caught the attention of health care organizations. “Uncertainty in financial and criminal liability for health care professionals in certain state laws and regulations are possibly compromising continuity of care and access [to] medications proven to be safe and effective by the Food and Drug Administration for these indications,” warned the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) in a statement to this news organization.
The APhA said that it was monitoring this situation to assess the effect on patients and pharmacists.
The Arthritis Foundation was made aware of challenges from patients in accessing their MTX prescription for managing their arthritis and shared a statement on the Foundation’s website.
In Texas, pharmacists can refuse to fill scripts for misoprostol and MTX, a combination used for medical abortions. According to the foundation, “Already there are reports that people in Texas who miscarry or take methotrexate for arthritis [are] having trouble getting their prescriptions filled.”
MTX, approved by the FDA in 1985, “is the absolute cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis. We cannot deny our patients this incredibly valuable drug,” said John Reveille, MD, vice-chair for the department of medicine at the University of Texas McGovern School of Medicine and a member of the Arthritis Foundation expert panel, in an interview.
“While it’s true that methotrexate can be lethal to the fetus, misoprostol is much more likely to cause a spontaneous abortion, and the combination is especially effective,” he said.
“If you look at Cochrane clinical studies, the dose of misoprostol contained in certain combinations with NSAIDs [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] can induce spontaneous abortions. It’s surprising that pharmacists are targeting methotrexate, an essential drug in arthritis treatment, when there are medications available that do not have this benefit that can by themselves cause loss of the fetus, such as mifepristone,” added Dr. Reveille.
The Dobbs ruling could also affect the ability of oncologists to provide lifesaving cancer care, according to Jason Westin, MD, an oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the department of lymphoma and myeloma.
“We have heard of medications with multiple indications, such as methotrexate, not being dispensed by pharmacies due to confusion regarding the intended use and potential consequences for the health care team,” he said in an interview.
Conflicting laws pose challenges for physicians
In North Dakota, inconsistencies in several laws are making it difficult for physicians and pharmacists to make decisions. “Lots of confusion can result when people pass laws against abortion. There’s sometimes no insight into the ramifications of those laws,” said Dr. Miller.
North Dakota approved a trigger law several years ago that makes abortion illegal 30 days after an overturning of Roe. However, another law that regulates abortion conflicts with the trigger law. “Some of the language will need clarification in the next legislative session,” he said.
APhA and other pharmacy associations strongly favor not interfering with the doctor- or pharmacist-patient relationship. The law needs to defer to appropriate care between doctor and patient, said Dr. Miller. State pharmacy associations in North Dakota are working with legislatures to clarify any exceptions in the law, he added.
Arizona lawmakers are trying to reconcile two abortion laws on the books. One, based on an 1864 territorial law, deems abortion illegal. In addition, a newly approved law bans abortions after 15 weeks. The latter will go into effect in September 2022. In both laws, a risk to the mother’s life is the only exception for abortion, said Dr. Young.
Denials aren’t widespread
Not all doctors are seeing MTX denials, but they’re worried about the future. “To date, we have not encountered difficulty in obtaining methotrexate based upon state abortion restrictions but are concerned that this could occur and result in dangerous delays in care,” said Dr. Westin.
Dr. Reveille, who practices rheumatology in Houston, has not yet received any complaints from patients. Things may be different in more rural parts of Texas, where pharmacists could be denying prescriptions based on religious issues, he offered.
It’s a little soon to see what repercussions may result from the Supreme Court ruling and state actions, said Dr. Reveille. “In Texas, we’re a bit ahead of the tidal wave.”
Access problems also haven’t shown up at the university clinic where Dr. Young practices. “In Arizona, it’s unclear if there would be a legal basis to refuse a person methotrexate on the basis that it can be used as an abortifacient,” she said.
Specificity is key in writing Rx scripts
Physicians can make things easier for patients by writing the indication and dose for the drug on the prescription slip. For example, a 10-mg script for MTX is not going to be used for an abortion, said Dr. Miller.
Rheumatologists in Texas have been doing this for some time, even before the Supreme Court ruling, said Fehmida Zahabi, MD, FACR, president of the Society of Texas Association of Rheumatology. For MTX prescriptions in premenopausal women, “patients are told their doctor needs to call the pharmacist. In the small print, we are asked to give a diagnosis to make sure we aren’t using it to terminate pregnancies,” said Dr. Zahabi.
She further noted that if the diagnosis is already indicated on the script, pharmacies generally won’t give patients a hard time.
Patients can also ask their physicians for a letter of medical necessity that confirms a drug’s use for a specific medical condition.
Mail order is another option if a local pharmacy won’t fill a prescription, said Dr. Miller. “This is legal unless a state makes it illegal to send an abortifacient across state lines,” he added.
Many medications used in rheumatic diseases are harmful in pregnancy, and it’s important to routinely discuss pregnancy risk and planning in the rheumatology clinic, said Dr. Young. This should include a thorough discussion and referral for long-acting reversible contraception in most cases, she suggested.
Actions at the federal, state level
President Joe Biden recently signed an executive order prompting federal regulators to protect access to medication abortions, among other steps to safeguard access to reproductive services.
In a statement on Twitter, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) said that it was “ ... following this issue closely to determine if rheumatology providers and patients are experiencing any widespread difficulty accessing methotrexate or if any initial disruptions are potentially temporary and due to the independent actions of pharmacists trying to figure out what is and isn’t allowed where they practice.”
ACR has assembled a task force of medical and policy experts to determine the best course of action for patients.
The Arthritis Foundation also continues to monitor the situation, encouraging patients to call its hotline, said Steven Schultz, director of state legislative affairs, in an interview.
“We are analyzing how medication abortion could cause confusion on the part of providers or pharmacists dispensing the medication and what this means for specific patients,” said Mr. Schultz. Through a survey, the foundation hopes to get a better idea of what’s going on in the states at a macro level.
This may take some time, as states go through a process of lawsuits, injunctions, or coming into session to do something that may affect access to MTX, said Mr. Schultz.
Being involved in local advocacy is more important than ever, stressed Dr. Young. “Additionally, being plugged into what the ACR and other advocacy groups are doing on the national level is helpful as well to know the status of these medication access issues.”
Rheumatologists have a unique voice in this discussion, she added. “We guide our patients to stability for a safe pregnancy, and even with careful planning, we see patients who become critically ill during pregnancy and require lifesaving treatment, which at times can mean an abortion is necessary.”
Oncologists also advocate for their patients on a regular basis to make sure they have access to the care they need, said Dr. Westin. This situation with Roe is no different, he added. “We will continue to use our unique expertise to advocate for policies that assure access to high-quality, evidence-based care – and to help our patients overcome barriers that may interfere.”
Dr. Reveille participated on an advisory board with Eli Lilly in October 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and more linked to lower CRC risk
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing posttraumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
High deductible insurance linked to delayed advanced cancer diagnosis
In oncology, delayed care may result in a failed opportunity to achieve remission. Delays in diagnosis can result in patients having to undergo more extensive surgery, radiation exposure, or more intensive drug therapy than if their disease had been detected at an early stage.
Now, researchers at Harvard Medical School, Boston, report that
Using national insurance claims data, the authors conducted an observational study to examine what happened when some workers with employer-based insurance were switched from low-deductible to high-deductible plans, compared with a control group of workers who remained on low-deductible plans.
After the switch, workers shunted into high-deductible plans had a longer time to first diagnosis of a metastatic cancer, indicating delayed detection of advanced disease, compared with controls. The difference translated into a delay in diagnosis of metastatic disease of nearly 5 months, reported Nico Trad, BA, a fourth-year medical student at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
“The takeaway here is that these plans were associated with delayed detection of metastatic cancer. We did not assess the mechanism, but it’s a reasonable assumption to make that increased cost-sharing is having some adverse impacts on people’s willingness to seek care. And although we didn’t study potential impacts, we might anticipate that a delayed diagnosis might also lead to delayed engagement with palliative care,” he said in an oral abstract presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“A delay in initiation of symptom-relieving therapies and a delayed presentation might also lead to greater dissemination of disease throughout the body, which also has the potential to limit therapeutic options,” he added.
‘Deductible relief day’
Mr. Trad said that in 2022 more than half of employees are covered by high-deductible health plans, compared with only about 10% in 2006.
This major shift in cost burden coincided with President Joseph Biden’s announcement in early 2022 of the “Cancer Moonshot,” program with the goal of reducing cancer mortality by 50% over the next 25 years.
“Part of that is cancer prevention and control, which involves timely detection of cancer so that we can treat it early and have better outcomes,” he said.
High-deductible health plans ostensibly provide motivation for patients to shop for lower-priced care and avoid unnecessary or low-quality care, but making patients shell out more upfront before their insurance kicks in, while it reduced health care utilization, can also reduce the quality of care, he said.
In 2022, “Deductible Relief Day,” the day in which the average patient has satisfied the deductible and insurance starts to pick up more of the tab, occurred in mid-May, compared with late February in 2006.
Insurance claims data
Mr. Trad and colleagues used health insurance claims data from a nationally representative cohort of privately insured patients in a national commercial and Medicare Advantage database. They excluded patients 65 and older who were eligible for Medicare because it does not have high-deductible options.
The study cohort included 345,401 adults from the ages of 18 to 64 whose employers mandated a switch from a low-deductible plan which was defined as $500 or less, to a high-deductible plan defined as $1,000 or more. Controls were 1,654,775 contemporaneous adults whose employers offered only low-deductible plans. Both groups had a 1-year baseline period when all members were enrolled in low deductible plans.
To minimize the possibility of confounding, the investigators matched the participants by age, gender, race/ethnicity, morbidity according to Adjusted Clinical Group score, poverty level, geographic region, employer size, baseline primary cancer, baseline medical and pharmacy costs, and follow-up duration.
During the baseline period, the hazard ratio for time to a first observed metastatic cancer diagnosis in the main cohort, compared with controls, was 0.96 with a nonsignificant P value, indicating no difference in the time to diagnosis between the groups.
During a maximum 13.5 years of follow-up, however, the participants who had been switched after a year to a high-deductible plan had a significantly longer time to first metastatic diagnosis (HR, 0.88; P = .01), indicating delayed diagnosis relative to controls. This difference translated to a delay of 4.6 months associated with the higher out-of-pocket costs plans.
According to a systematic review and meta-analysis published online in 2020, a 1-month delay in treatment for many types of cancer can translate into a 6% to 13% higher risk for death, a risk that continues to increase with further delays.
The investigators acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of retrospective claims-based data, which not contain information on how the patients fared after diagnosis.
“I would say in terms of policy relevance that this really points to the need for new and innovative insurance models that, No. 1, reduce the cost-sharing burden for patients so that they’re not deterred from seeking care, and No. 2, that align rather than contradict the goal of improving population-level survival from cancer,” Mr. Trad said.
Further evidence of a flawed system
The study adds to an already strong body of evidence showing that high-deductible plans can have a negative impact on health, said Sara R. Collins, vice president for health care coverage and access at the Commonwealth Fund, a New York–based private foundation dedicated to improving health care.
“This is really the latest evidence on top of years of research that shows that high-deductible health plans lead people to make decisions that are not in the best interest of their health,” said Ms. Collins, who is not affiliated with the study presented at ASCO.
“We have a health care cost problem in the United States that far exceeds that of other high-income countries. Insurers try to solve it by shifting the costs to consumers and using other measures to restrict people’s use of health care, and often needed health care like this. The result is less access to needed care, and long-term adverse health consequences and their associated costs to patients and the health system generally,” she said.
The real driver of health care costs is not utilization, but the prices that insurers and providers negotiate in their service contracts, she explained.
“Prices are the central problem, insurers have control over those prices in their negotiations with providers. So unless we can gain control of that driver, patients are going to continue to suffer unnecessarily from both the short- and long-term effects of insurers who use tools to reduce their access to care,” she said.
In oncology, delayed care may result in a failed opportunity to achieve remission. Delays in diagnosis can result in patients having to undergo more extensive surgery, radiation exposure, or more intensive drug therapy than if their disease had been detected at an early stage.
Now, researchers at Harvard Medical School, Boston, report that
Using national insurance claims data, the authors conducted an observational study to examine what happened when some workers with employer-based insurance were switched from low-deductible to high-deductible plans, compared with a control group of workers who remained on low-deductible plans.
After the switch, workers shunted into high-deductible plans had a longer time to first diagnosis of a metastatic cancer, indicating delayed detection of advanced disease, compared with controls. The difference translated into a delay in diagnosis of metastatic disease of nearly 5 months, reported Nico Trad, BA, a fourth-year medical student at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
“The takeaway here is that these plans were associated with delayed detection of metastatic cancer. We did not assess the mechanism, but it’s a reasonable assumption to make that increased cost-sharing is having some adverse impacts on people’s willingness to seek care. And although we didn’t study potential impacts, we might anticipate that a delayed diagnosis might also lead to delayed engagement with palliative care,” he said in an oral abstract presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“A delay in initiation of symptom-relieving therapies and a delayed presentation might also lead to greater dissemination of disease throughout the body, which also has the potential to limit therapeutic options,” he added.
‘Deductible relief day’
Mr. Trad said that in 2022 more than half of employees are covered by high-deductible health plans, compared with only about 10% in 2006.
This major shift in cost burden coincided with President Joseph Biden’s announcement in early 2022 of the “Cancer Moonshot,” program with the goal of reducing cancer mortality by 50% over the next 25 years.
“Part of that is cancer prevention and control, which involves timely detection of cancer so that we can treat it early and have better outcomes,” he said.
High-deductible health plans ostensibly provide motivation for patients to shop for lower-priced care and avoid unnecessary or low-quality care, but making patients shell out more upfront before their insurance kicks in, while it reduced health care utilization, can also reduce the quality of care, he said.
In 2022, “Deductible Relief Day,” the day in which the average patient has satisfied the deductible and insurance starts to pick up more of the tab, occurred in mid-May, compared with late February in 2006.
Insurance claims data
Mr. Trad and colleagues used health insurance claims data from a nationally representative cohort of privately insured patients in a national commercial and Medicare Advantage database. They excluded patients 65 and older who were eligible for Medicare because it does not have high-deductible options.
The study cohort included 345,401 adults from the ages of 18 to 64 whose employers mandated a switch from a low-deductible plan which was defined as $500 or less, to a high-deductible plan defined as $1,000 or more. Controls were 1,654,775 contemporaneous adults whose employers offered only low-deductible plans. Both groups had a 1-year baseline period when all members were enrolled in low deductible plans.
To minimize the possibility of confounding, the investigators matched the participants by age, gender, race/ethnicity, morbidity according to Adjusted Clinical Group score, poverty level, geographic region, employer size, baseline primary cancer, baseline medical and pharmacy costs, and follow-up duration.
During the baseline period, the hazard ratio for time to a first observed metastatic cancer diagnosis in the main cohort, compared with controls, was 0.96 with a nonsignificant P value, indicating no difference in the time to diagnosis between the groups.
During a maximum 13.5 years of follow-up, however, the participants who had been switched after a year to a high-deductible plan had a significantly longer time to first metastatic diagnosis (HR, 0.88; P = .01), indicating delayed diagnosis relative to controls. This difference translated to a delay of 4.6 months associated with the higher out-of-pocket costs plans.
According to a systematic review and meta-analysis published online in 2020, a 1-month delay in treatment for many types of cancer can translate into a 6% to 13% higher risk for death, a risk that continues to increase with further delays.
The investigators acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of retrospective claims-based data, which not contain information on how the patients fared after diagnosis.
“I would say in terms of policy relevance that this really points to the need for new and innovative insurance models that, No. 1, reduce the cost-sharing burden for patients so that they’re not deterred from seeking care, and No. 2, that align rather than contradict the goal of improving population-level survival from cancer,” Mr. Trad said.
Further evidence of a flawed system
The study adds to an already strong body of evidence showing that high-deductible plans can have a negative impact on health, said Sara R. Collins, vice president for health care coverage and access at the Commonwealth Fund, a New York–based private foundation dedicated to improving health care.
“This is really the latest evidence on top of years of research that shows that high-deductible health plans lead people to make decisions that are not in the best interest of their health,” said Ms. Collins, who is not affiliated with the study presented at ASCO.
“We have a health care cost problem in the United States that far exceeds that of other high-income countries. Insurers try to solve it by shifting the costs to consumers and using other measures to restrict people’s use of health care, and often needed health care like this. The result is less access to needed care, and long-term adverse health consequences and their associated costs to patients and the health system generally,” she said.
The real driver of health care costs is not utilization, but the prices that insurers and providers negotiate in their service contracts, she explained.
“Prices are the central problem, insurers have control over those prices in their negotiations with providers. So unless we can gain control of that driver, patients are going to continue to suffer unnecessarily from both the short- and long-term effects of insurers who use tools to reduce their access to care,” she said.
In oncology, delayed care may result in a failed opportunity to achieve remission. Delays in diagnosis can result in patients having to undergo more extensive surgery, radiation exposure, or more intensive drug therapy than if their disease had been detected at an early stage.
Now, researchers at Harvard Medical School, Boston, report that
Using national insurance claims data, the authors conducted an observational study to examine what happened when some workers with employer-based insurance were switched from low-deductible to high-deductible plans, compared with a control group of workers who remained on low-deductible plans.
After the switch, workers shunted into high-deductible plans had a longer time to first diagnosis of a metastatic cancer, indicating delayed detection of advanced disease, compared with controls. The difference translated into a delay in diagnosis of metastatic disease of nearly 5 months, reported Nico Trad, BA, a fourth-year medical student at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
“The takeaway here is that these plans were associated with delayed detection of metastatic cancer. We did not assess the mechanism, but it’s a reasonable assumption to make that increased cost-sharing is having some adverse impacts on people’s willingness to seek care. And although we didn’t study potential impacts, we might anticipate that a delayed diagnosis might also lead to delayed engagement with palliative care,” he said in an oral abstract presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“A delay in initiation of symptom-relieving therapies and a delayed presentation might also lead to greater dissemination of disease throughout the body, which also has the potential to limit therapeutic options,” he added.
‘Deductible relief day’
Mr. Trad said that in 2022 more than half of employees are covered by high-deductible health plans, compared with only about 10% in 2006.
This major shift in cost burden coincided with President Joseph Biden’s announcement in early 2022 of the “Cancer Moonshot,” program with the goal of reducing cancer mortality by 50% over the next 25 years.
“Part of that is cancer prevention and control, which involves timely detection of cancer so that we can treat it early and have better outcomes,” he said.
High-deductible health plans ostensibly provide motivation for patients to shop for lower-priced care and avoid unnecessary or low-quality care, but making patients shell out more upfront before their insurance kicks in, while it reduced health care utilization, can also reduce the quality of care, he said.
In 2022, “Deductible Relief Day,” the day in which the average patient has satisfied the deductible and insurance starts to pick up more of the tab, occurred in mid-May, compared with late February in 2006.
Insurance claims data
Mr. Trad and colleagues used health insurance claims data from a nationally representative cohort of privately insured patients in a national commercial and Medicare Advantage database. They excluded patients 65 and older who were eligible for Medicare because it does not have high-deductible options.
The study cohort included 345,401 adults from the ages of 18 to 64 whose employers mandated a switch from a low-deductible plan which was defined as $500 or less, to a high-deductible plan defined as $1,000 or more. Controls were 1,654,775 contemporaneous adults whose employers offered only low-deductible plans. Both groups had a 1-year baseline period when all members were enrolled in low deductible plans.
To minimize the possibility of confounding, the investigators matched the participants by age, gender, race/ethnicity, morbidity according to Adjusted Clinical Group score, poverty level, geographic region, employer size, baseline primary cancer, baseline medical and pharmacy costs, and follow-up duration.
During the baseline period, the hazard ratio for time to a first observed metastatic cancer diagnosis in the main cohort, compared with controls, was 0.96 with a nonsignificant P value, indicating no difference in the time to diagnosis between the groups.
During a maximum 13.5 years of follow-up, however, the participants who had been switched after a year to a high-deductible plan had a significantly longer time to first metastatic diagnosis (HR, 0.88; P = .01), indicating delayed diagnosis relative to controls. This difference translated to a delay of 4.6 months associated with the higher out-of-pocket costs plans.
According to a systematic review and meta-analysis published online in 2020, a 1-month delay in treatment for many types of cancer can translate into a 6% to 13% higher risk for death, a risk that continues to increase with further delays.
The investigators acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of retrospective claims-based data, which not contain information on how the patients fared after diagnosis.
“I would say in terms of policy relevance that this really points to the need for new and innovative insurance models that, No. 1, reduce the cost-sharing burden for patients so that they’re not deterred from seeking care, and No. 2, that align rather than contradict the goal of improving population-level survival from cancer,” Mr. Trad said.
Further evidence of a flawed system
The study adds to an already strong body of evidence showing that high-deductible plans can have a negative impact on health, said Sara R. Collins, vice president for health care coverage and access at the Commonwealth Fund, a New York–based private foundation dedicated to improving health care.
“This is really the latest evidence on top of years of research that shows that high-deductible health plans lead people to make decisions that are not in the best interest of their health,” said Ms. Collins, who is not affiliated with the study presented at ASCO.
“We have a health care cost problem in the United States that far exceeds that of other high-income countries. Insurers try to solve it by shifting the costs to consumers and using other measures to restrict people’s use of health care, and often needed health care like this. The result is less access to needed care, and long-term adverse health consequences and their associated costs to patients and the health system generally,” she said.
The real driver of health care costs is not utilization, but the prices that insurers and providers negotiate in their service contracts, she explained.
“Prices are the central problem, insurers have control over those prices in their negotiations with providers. So unless we can gain control of that driver, patients are going to continue to suffer unnecessarily from both the short- and long-term effects of insurers who use tools to reduce their access to care,” she said.
FROM ASCO 2022
New KRAS inhibitor shows promise in NSCLC
In a phase 2 cohort study, who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and immune therapy.
Adagrasib targets KRAS (G12C), which had long been thought undruggable until research published in 2013 revealed a new binding pocket that did not compete directly against the protein’s natural binding partner. The new trial further validates the approach. “It supports that clinically effective targeted therapies can be developed for patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC,” said Pasi Jänne, MD, PhD, who is the lead author of the study describing the new results published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
KRAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in human cancers. A mutated form is found in about 25% of NSCLCs. KRAS plays a key role in cell signaling governing growth, maturation, and cell death. The mutated form is linked to cancer growth and spread. Patients with mutated KRAS have few effective treatment options.
Adagrasib is currently under study and not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, sotorasib (Lumakras, Amgen), which also inhibits KRAS (G12C), was approved in May 2021 by the FDA for KRAS (G12C)–mutated NSCLC. There are some key differences between the drugs. Adagrasib has a half-life of 23 hours versus 5 hours for sotorasib, and the newer drug has the potential to penetrate the central nervous system. That could be an important consideration in NSCLC since it often metastasizes to the brain. “Having pharmacological approaches to treat brain metastases is a wonderful new therapeutic option for lung cancer patients,” said Dr. Jänne, who is director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Adagrasib is being investigated as part of the KRYSTAL-1 study, alone and as part of combinations in various solid tumors. Previously treated NSCLC KRAS (G12C) patients are also being enrolled in a phase 3 study of adagrasib combined with docetaxel, as well as another phase 2 study of adagrasib combined with pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for NSCLC KRAS (G12C).
Adagrasib is likely to remain a second-line therapy following chemotherapy and immunotherapy. “The activity by itself at the moment is not sufficient to be a first-line treatment. That may change in the future in combination with a standard of care agent or in a subset of patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC, although no subset with higher efficacy has been identified to date. Identification of predictive biomarkers for patients likely to benefit from single agent or an adagrasib combination treatment remains a high priority,” Dr. Jänne said.
The study included 116 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and anti–programmed death 1 or programmed death–ligand 1 therapy. They received 600 mg oral adagrasib twice per day over a median follow-up period of 12.9 months. About 42.9% (95% confidence interval, 33.5%-52.6%) experienced a confirmed objective response with a median duration of 8.5 months (95% CI, 6.2-13.8 months). The median progression-free survival was 6.5 months (95% CI, 4.7-8.4 months). After a median follow-up of 15.6 months, the median overall survival was 12.6 months (95% CI, 9.2-19.2 months). The estimated overall survival at 1 year was 50.8% (95% CI, 40.9%-60.0%).
33 patients had stable central nervous system metastases that had been previously treated. About 33.3% had an intracranial confirmed objective response (95% CI, 18.0-51.8%) with a median duration of response of 11.2 months (95% CI, 2.99 months to not available).
Adverse events are similar to what is seen with other targeted therapies, according to Dr. Jänne. 97.4% of patient reported a treatment-related adverse event; 52.6% had grade 1-2 adverse events, and 44.8% had grade 3 adverse events. 6.9% discontinued the drug as a result.
Dr. Jänne has consulted for Mirati Therapeutics and is a member of its scientific advisory board. The study was funded by Mirati Therapeutics.
In a phase 2 cohort study, who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and immune therapy.
Adagrasib targets KRAS (G12C), which had long been thought undruggable until research published in 2013 revealed a new binding pocket that did not compete directly against the protein’s natural binding partner. The new trial further validates the approach. “It supports that clinically effective targeted therapies can be developed for patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC,” said Pasi Jänne, MD, PhD, who is the lead author of the study describing the new results published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
KRAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in human cancers. A mutated form is found in about 25% of NSCLCs. KRAS plays a key role in cell signaling governing growth, maturation, and cell death. The mutated form is linked to cancer growth and spread. Patients with mutated KRAS have few effective treatment options.
Adagrasib is currently under study and not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, sotorasib (Lumakras, Amgen), which also inhibits KRAS (G12C), was approved in May 2021 by the FDA for KRAS (G12C)–mutated NSCLC. There are some key differences between the drugs. Adagrasib has a half-life of 23 hours versus 5 hours for sotorasib, and the newer drug has the potential to penetrate the central nervous system. That could be an important consideration in NSCLC since it often metastasizes to the brain. “Having pharmacological approaches to treat brain metastases is a wonderful new therapeutic option for lung cancer patients,” said Dr. Jänne, who is director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Adagrasib is being investigated as part of the KRYSTAL-1 study, alone and as part of combinations in various solid tumors. Previously treated NSCLC KRAS (G12C) patients are also being enrolled in a phase 3 study of adagrasib combined with docetaxel, as well as another phase 2 study of adagrasib combined with pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for NSCLC KRAS (G12C).
Adagrasib is likely to remain a second-line therapy following chemotherapy and immunotherapy. “The activity by itself at the moment is not sufficient to be a first-line treatment. That may change in the future in combination with a standard of care agent or in a subset of patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC, although no subset with higher efficacy has been identified to date. Identification of predictive biomarkers for patients likely to benefit from single agent or an adagrasib combination treatment remains a high priority,” Dr. Jänne said.
The study included 116 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and anti–programmed death 1 or programmed death–ligand 1 therapy. They received 600 mg oral adagrasib twice per day over a median follow-up period of 12.9 months. About 42.9% (95% confidence interval, 33.5%-52.6%) experienced a confirmed objective response with a median duration of 8.5 months (95% CI, 6.2-13.8 months). The median progression-free survival was 6.5 months (95% CI, 4.7-8.4 months). After a median follow-up of 15.6 months, the median overall survival was 12.6 months (95% CI, 9.2-19.2 months). The estimated overall survival at 1 year was 50.8% (95% CI, 40.9%-60.0%).
33 patients had stable central nervous system metastases that had been previously treated. About 33.3% had an intracranial confirmed objective response (95% CI, 18.0-51.8%) with a median duration of response of 11.2 months (95% CI, 2.99 months to not available).
Adverse events are similar to what is seen with other targeted therapies, according to Dr. Jänne. 97.4% of patient reported a treatment-related adverse event; 52.6% had grade 1-2 adverse events, and 44.8% had grade 3 adverse events. 6.9% discontinued the drug as a result.
Dr. Jänne has consulted for Mirati Therapeutics and is a member of its scientific advisory board. The study was funded by Mirati Therapeutics.
In a phase 2 cohort study, who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and immune therapy.
Adagrasib targets KRAS (G12C), which had long been thought undruggable until research published in 2013 revealed a new binding pocket that did not compete directly against the protein’s natural binding partner. The new trial further validates the approach. “It supports that clinically effective targeted therapies can be developed for patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC,” said Pasi Jänne, MD, PhD, who is the lead author of the study describing the new results published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
KRAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in human cancers. A mutated form is found in about 25% of NSCLCs. KRAS plays a key role in cell signaling governing growth, maturation, and cell death. The mutated form is linked to cancer growth and spread. Patients with mutated KRAS have few effective treatment options.
Adagrasib is currently under study and not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, sotorasib (Lumakras, Amgen), which also inhibits KRAS (G12C), was approved in May 2021 by the FDA for KRAS (G12C)–mutated NSCLC. There are some key differences between the drugs. Adagrasib has a half-life of 23 hours versus 5 hours for sotorasib, and the newer drug has the potential to penetrate the central nervous system. That could be an important consideration in NSCLC since it often metastasizes to the brain. “Having pharmacological approaches to treat brain metastases is a wonderful new therapeutic option for lung cancer patients,” said Dr. Jänne, who is director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Adagrasib is being investigated as part of the KRYSTAL-1 study, alone and as part of combinations in various solid tumors. Previously treated NSCLC KRAS (G12C) patients are also being enrolled in a phase 3 study of adagrasib combined with docetaxel, as well as another phase 2 study of adagrasib combined with pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for NSCLC KRAS (G12C).
Adagrasib is likely to remain a second-line therapy following chemotherapy and immunotherapy. “The activity by itself at the moment is not sufficient to be a first-line treatment. That may change in the future in combination with a standard of care agent or in a subset of patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC, although no subset with higher efficacy has been identified to date. Identification of predictive biomarkers for patients likely to benefit from single agent or an adagrasib combination treatment remains a high priority,” Dr. Jänne said.
The study included 116 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and anti–programmed death 1 or programmed death–ligand 1 therapy. They received 600 mg oral adagrasib twice per day over a median follow-up period of 12.9 months. About 42.9% (95% confidence interval, 33.5%-52.6%) experienced a confirmed objective response with a median duration of 8.5 months (95% CI, 6.2-13.8 months). The median progression-free survival was 6.5 months (95% CI, 4.7-8.4 months). After a median follow-up of 15.6 months, the median overall survival was 12.6 months (95% CI, 9.2-19.2 months). The estimated overall survival at 1 year was 50.8% (95% CI, 40.9%-60.0%).
33 patients had stable central nervous system metastases that had been previously treated. About 33.3% had an intracranial confirmed objective response (95% CI, 18.0-51.8%) with a median duration of response of 11.2 months (95% CI, 2.99 months to not available).
Adverse events are similar to what is seen with other targeted therapies, according to Dr. Jänne. 97.4% of patient reported a treatment-related adverse event; 52.6% had grade 1-2 adverse events, and 44.8% had grade 3 adverse events. 6.9% discontinued the drug as a result.
Dr. Jänne has consulted for Mirati Therapeutics and is a member of its scientific advisory board. The study was funded by Mirati Therapeutics.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
FDA approves combination pegloticase and methotrexate for refractory gout
Pegloticase, which has been available for 12 years, is a pegylated uric acid specific enzyme that lowers sUA by converting it to allantoin.
Though pegloticase is effective in treating chronic gout in patients refractory to conventional treatment, approximately 92% of patients develop antibodies against the drug, resulting in reduced efficacy.
Based on the immunomodulatory effects of methotrexate, researchers of the randomized, placebo-controlled MIRROR trial sought to determine whether combination treatment of pegloticase with methotrexate (multiple brands) would prevent the development of anti-drug antibodies.
Findings from the phase 4 trial found that co-administration of pegloticase and methotrexate reduced the formation of new anti-PEG antibodies. In the group receiving methotrexate and pegloticase, 23.2% (22 out of 95) of patients had an increase in anti-PEG antibodies, compared with 50% (24 of 48) in the pegloticase plus placebo group, according to a recent company press release.
Nearly three-quarters (71%) of participants in the group pretreated with methotrexate, followed by combination pegloticase-methotrexate, had sUA levels that dopped to below 6 mg/dL during the 52-week study. By comparison, 38.5% of participants in the pegloticase and placebo group reached the endpoint. Though gout flare occurred in both groups, methotrexate did not appear to increase the risk for adverse events or gout flare.
The study, led by John Botson, MD, RPh, CCD, a rheumatologist in Anchorage, Alaska, concluded that these measurements demonstrated a significant improvement from traditional pegloticase-only treatment of gout. “This trial confirms not only improved efficacy but improved safety in patients treated with pegloticase in combination with methotrexate 15 mg orally once weekly,” Dr. Botson said last month in an interview with this news organization.
The study was funded by Horizon. Dr. Botson reports receiving research support from Horizon and Radius Health and speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Aurinia, ChemoCentryx, Horizon, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pegloticase, which has been available for 12 years, is a pegylated uric acid specific enzyme that lowers sUA by converting it to allantoin.
Though pegloticase is effective in treating chronic gout in patients refractory to conventional treatment, approximately 92% of patients develop antibodies against the drug, resulting in reduced efficacy.
Based on the immunomodulatory effects of methotrexate, researchers of the randomized, placebo-controlled MIRROR trial sought to determine whether combination treatment of pegloticase with methotrexate (multiple brands) would prevent the development of anti-drug antibodies.
Findings from the phase 4 trial found that co-administration of pegloticase and methotrexate reduced the formation of new anti-PEG antibodies. In the group receiving methotrexate and pegloticase, 23.2% (22 out of 95) of patients had an increase in anti-PEG antibodies, compared with 50% (24 of 48) in the pegloticase plus placebo group, according to a recent company press release.
Nearly three-quarters (71%) of participants in the group pretreated with methotrexate, followed by combination pegloticase-methotrexate, had sUA levels that dopped to below 6 mg/dL during the 52-week study. By comparison, 38.5% of participants in the pegloticase and placebo group reached the endpoint. Though gout flare occurred in both groups, methotrexate did not appear to increase the risk for adverse events or gout flare.
The study, led by John Botson, MD, RPh, CCD, a rheumatologist in Anchorage, Alaska, concluded that these measurements demonstrated a significant improvement from traditional pegloticase-only treatment of gout. “This trial confirms not only improved efficacy but improved safety in patients treated with pegloticase in combination with methotrexate 15 mg orally once weekly,” Dr. Botson said last month in an interview with this news organization.
The study was funded by Horizon. Dr. Botson reports receiving research support from Horizon and Radius Health and speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Aurinia, ChemoCentryx, Horizon, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pegloticase, which has been available for 12 years, is a pegylated uric acid specific enzyme that lowers sUA by converting it to allantoin.
Though pegloticase is effective in treating chronic gout in patients refractory to conventional treatment, approximately 92% of patients develop antibodies against the drug, resulting in reduced efficacy.
Based on the immunomodulatory effects of methotrexate, researchers of the randomized, placebo-controlled MIRROR trial sought to determine whether combination treatment of pegloticase with methotrexate (multiple brands) would prevent the development of anti-drug antibodies.
Findings from the phase 4 trial found that co-administration of pegloticase and methotrexate reduced the formation of new anti-PEG antibodies. In the group receiving methotrexate and pegloticase, 23.2% (22 out of 95) of patients had an increase in anti-PEG antibodies, compared with 50% (24 of 48) in the pegloticase plus placebo group, according to a recent company press release.
Nearly three-quarters (71%) of participants in the group pretreated with methotrexate, followed by combination pegloticase-methotrexate, had sUA levels that dopped to below 6 mg/dL during the 52-week study. By comparison, 38.5% of participants in the pegloticase and placebo group reached the endpoint. Though gout flare occurred in both groups, methotrexate did not appear to increase the risk for adverse events or gout flare.
The study, led by John Botson, MD, RPh, CCD, a rheumatologist in Anchorage, Alaska, concluded that these measurements demonstrated a significant improvement from traditional pegloticase-only treatment of gout. “This trial confirms not only improved efficacy but improved safety in patients treated with pegloticase in combination with methotrexate 15 mg orally once weekly,” Dr. Botson said last month in an interview with this news organization.
The study was funded by Horizon. Dr. Botson reports receiving research support from Horizon and Radius Health and speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Aurinia, ChemoCentryx, Horizon, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical gel for epidermolysis bullosa shows ongoing benefit
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Vaccination a harder sell in the summer
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.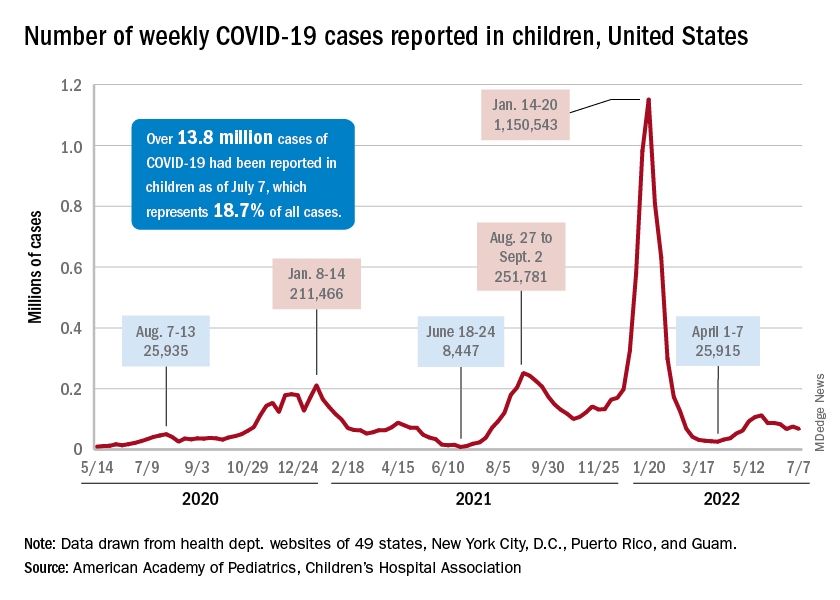
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
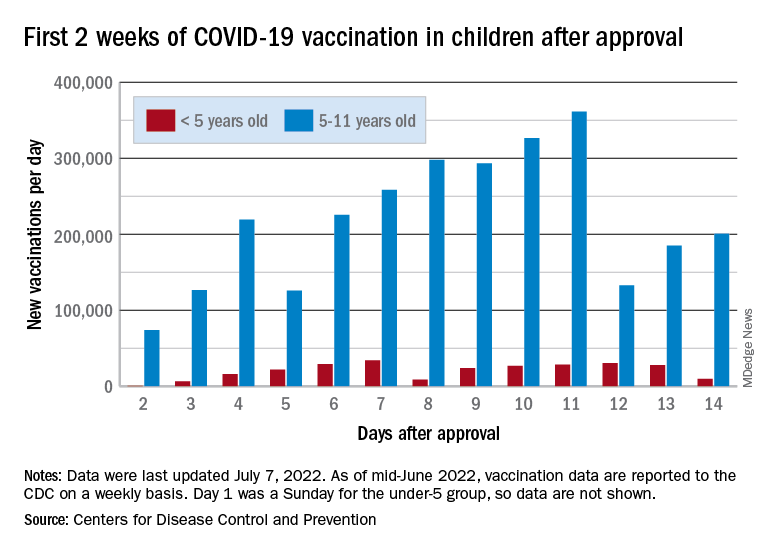
Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
Medical management of miscarriage curbs costs and maintains quality of care
Medical management of early pregnancy loss costs less and offers similar quality of life to uterine aspiration, based on data from an analytical model.
Early pregnancy loss (EPL) occurs in more than 1 million women in the United States each year, and many patients are diagnosed before they show symptoms, wrote Divyah Nagendra, MD, of Cambridge Health Alliance, Mass., and colleagues.
A 2018 study showed that medical management of EPL with mifepristone added to misoprostol increased effectiveness and reduced the need for additional medication or subsequent uterine procedures, but the cost of mifepristone is perceived as a barrier, and the cost-effectiveness of its use, compared with surgical or expectant management, has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
“We already know that adding mifepristone to the medical management of early pregnancy loss increases the effectiveness of the regimen,” coauthor Courtney A. Schreiber, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Procedural uterine aspiration is highly effective as well, so patients and providers may consider the cost when deciding on a treatment strategy,” she added.
“If medication management is preferred by many patients, decreases the need to access in-person clinical care during a pandemic, and is found to be cost-effective, clinicians and policymakers should increase efforts to improve mifepristone availability and reduce access burdens,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers created a decision-analytic model using data from published literature and the Pregnancy Failure Regiments Trial (PreFaiR) to compare office-based uterine aspiration to medical management with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol for EPL.
The PrFaiR study randomized 300 women who experienced EPL before 12 weeks’ gestation to medication management with 800 mcg misoprostol vaginally, with or without pretreatment of 200 mg mifeprestone orally. The average age of the participants was 30.7 years, and demographics were similar between the groups.
The researchers used the PrFaiR data for medical management and patient-level data from published literature for uterine aspiration.
The primary outcome was the cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained. QALY was based on a modified utility score from the published literature. Effectiveness was based on QALY gained and the rate of complete expulsion of the gestational sac without additional intervention.
Overall, the mean costs per person were significantly higher for uterine aspiration, compared with medical management ($828 vs. $661, P = .004). Uterine aspiration was significantly more effective for complete gestational sac expulsion (97.3% vs. 83.8%, P = .0001). However, the QALYs were significantly higher for medical management, compared with uterine aspiration (0.082 vs. 0.079, P < .0001).
Cost-effectiveness was greater for medical management from a health care sector perspective, with lower costs and higher QALYs than uterine aspiration, the researchers noted.
They also evaluated the effect of mifepristone pretreatment on cost-effectiveness and found that medical management would remain cost effective, compared with uterine aspiration even if uterine aspiration procedures decreased in cost and mifepristone increased in cost, and even if medication management had a decreased completion rate and utility score, compared with uterine aspiration.
“Our analysis demonstrates that the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for medical management is well below the maximum willingness-to-pay threshold of approximately $100,000 per QALY gained,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings.
Potential savings, uncertain access
Despite the potential savings and patient benefits, access to mifepristone remains a barrier, the researchers said.
Although the FDA lifted some restrictions on mifepristone in 2021 in the wake of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the effect of new abortion-related restrictions remains to be seen.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 2018 National Medicare reimbursement rates to calculate costs, though actual costs vary by region and payer, the researchers noted. Other limitations include variations in cost of mifepristone by region and time and the differences in data sources between the uterine aspiration and medical management groups. More research is needed to assess QALYs for early pregnancy loss to establish standard measures and to assess the societal perspective of ESL as well as the health care perspective, they added.
However, the current results support medical management of EPL with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol as a “high-value care alternative” to office-based uterine aspiration, they said. “Increasing access to mifepristone and eliminating unnecessary restrictions will improve early pregnancy care,” they concluded.
“Given how effective procedural management is, we were slightly surprised that medical management remains cost effective,” Dr. Schreiber said in an interview.
Looking ahead in the wake of new restrictions on use for abortion, “patients may have difficulty accessing either medical or procedural management for early pregnancy loss,” Dr. Schreiber noted. “We support the accessibility of all evidence-based care and hope that our data will help overcome perceived financial barriers,” she said. Additional research needs include improved implementation and access to evidence-based early pregnancy loss care, she added.
Reasons to lift regulations
“Given the recent overturning of Roe v. Wade, any medications that are associated with abortion have increased scrutiny, especially mifepristone and misoprostol, even though these medications are also used for managing early pregnancy loss,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “Demonstrating that medication management of EPL with mifepristone/misoprostol is less expensive and has increased QALYs associated with it is yet another reason to deregulate mifepristone so it can also be more accessible for management of EPL,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Prager said she was not surprised by the findings, as effective medication should be less expensive than a procedure. “I would caution that the increased QALYs found in this study should not be interpreted as a reason to restrict surgical management of EPL but to increase access also to medication management, even though medication has a slightly lower rate of complete gestational sac expulsion,” she noted. “Mode of management should be up to the patient, unless there is a clear medical reason for one or the other.”
Going forward, “the FDA has it in its power to remove the REMS, which would immediately make mifepristone a medication that can be prescribed through a pharmacy and therefore much more available,” said Dr. Prager. “Restrictions for both medication and surgical management of EPL will likely increase in states where abortion is illegal, and it could possibly lead to patients having less choice as to mode of management,” she explained.
“There are many studies showing that all modes of EPL management are safe and effective and should be supported with respect to patient choice,” Dr. Prager noted. “There are also substantial data supporting the overall safety of mifepristone, and there are no scientific or medical data suggesting the REMS increases safety in any way. Frankly, there are no good, evidence-based reasons to continue to keep the REMS in place,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health and a Society of Family Planning Research Fund Midcareer Mentor Award. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Prager had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Ob.Gyn. News.
Medical management of early pregnancy loss costs less and offers similar quality of life to uterine aspiration, based on data from an analytical model.
Early pregnancy loss (EPL) occurs in more than 1 million women in the United States each year, and many patients are diagnosed before they show symptoms, wrote Divyah Nagendra, MD, of Cambridge Health Alliance, Mass., and colleagues.
A 2018 study showed that medical management of EPL with mifepristone added to misoprostol increased effectiveness and reduced the need for additional medication or subsequent uterine procedures, but the cost of mifepristone is perceived as a barrier, and the cost-effectiveness of its use, compared with surgical or expectant management, has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
“We already know that adding mifepristone to the medical management of early pregnancy loss increases the effectiveness of the regimen,” coauthor Courtney A. Schreiber, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Procedural uterine aspiration is highly effective as well, so patients and providers may consider the cost when deciding on a treatment strategy,” she added.
“If medication management is preferred by many patients, decreases the need to access in-person clinical care during a pandemic, and is found to be cost-effective, clinicians and policymakers should increase efforts to improve mifepristone availability and reduce access burdens,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers created a decision-analytic model using data from published literature and the Pregnancy Failure Regiments Trial (PreFaiR) to compare office-based uterine aspiration to medical management with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol for EPL.
The PrFaiR study randomized 300 women who experienced EPL before 12 weeks’ gestation to medication management with 800 mcg misoprostol vaginally, with or without pretreatment of 200 mg mifeprestone orally. The average age of the participants was 30.7 years, and demographics were similar between the groups.
The researchers used the PrFaiR data for medical management and patient-level data from published literature for uterine aspiration.
The primary outcome was the cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained. QALY was based on a modified utility score from the published literature. Effectiveness was based on QALY gained and the rate of complete expulsion of the gestational sac without additional intervention.
Overall, the mean costs per person were significantly higher for uterine aspiration, compared with medical management ($828 vs. $661, P = .004). Uterine aspiration was significantly more effective for complete gestational sac expulsion (97.3% vs. 83.8%, P = .0001). However, the QALYs were significantly higher for medical management, compared with uterine aspiration (0.082 vs. 0.079, P < .0001).
Cost-effectiveness was greater for medical management from a health care sector perspective, with lower costs and higher QALYs than uterine aspiration, the researchers noted.
They also evaluated the effect of mifepristone pretreatment on cost-effectiveness and found that medical management would remain cost effective, compared with uterine aspiration even if uterine aspiration procedures decreased in cost and mifepristone increased in cost, and even if medication management had a decreased completion rate and utility score, compared with uterine aspiration.
“Our analysis demonstrates that the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for medical management is well below the maximum willingness-to-pay threshold of approximately $100,000 per QALY gained,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings.
Potential savings, uncertain access
Despite the potential savings and patient benefits, access to mifepristone remains a barrier, the researchers said.
Although the FDA lifted some restrictions on mifepristone in 2021 in the wake of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the effect of new abortion-related restrictions remains to be seen.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 2018 National Medicare reimbursement rates to calculate costs, though actual costs vary by region and payer, the researchers noted. Other limitations include variations in cost of mifepristone by region and time and the differences in data sources between the uterine aspiration and medical management groups. More research is needed to assess QALYs for early pregnancy loss to establish standard measures and to assess the societal perspective of ESL as well as the health care perspective, they added.
However, the current results support medical management of EPL with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol as a “high-value care alternative” to office-based uterine aspiration, they said. “Increasing access to mifepristone and eliminating unnecessary restrictions will improve early pregnancy care,” they concluded.
“Given how effective procedural management is, we were slightly surprised that medical management remains cost effective,” Dr. Schreiber said in an interview.
Looking ahead in the wake of new restrictions on use for abortion, “patients may have difficulty accessing either medical or procedural management for early pregnancy loss,” Dr. Schreiber noted. “We support the accessibility of all evidence-based care and hope that our data will help overcome perceived financial barriers,” she said. Additional research needs include improved implementation and access to evidence-based early pregnancy loss care, she added.
Reasons to lift regulations
“Given the recent overturning of Roe v. Wade, any medications that are associated with abortion have increased scrutiny, especially mifepristone and misoprostol, even though these medications are also used for managing early pregnancy loss,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “Demonstrating that medication management of EPL with mifepristone/misoprostol is less expensive and has increased QALYs associated with it is yet another reason to deregulate mifepristone so it can also be more accessible for management of EPL,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Prager said she was not surprised by the findings, as effective medication should be less expensive than a procedure. “I would caution that the increased QALYs found in this study should not be interpreted as a reason to restrict surgical management of EPL but to increase access also to medication management, even though medication has a slightly lower rate of complete gestational sac expulsion,” she noted. “Mode of management should be up to the patient, unless there is a clear medical reason for one or the other.”
Going forward, “the FDA has it in its power to remove the REMS, which would immediately make mifepristone a medication that can be prescribed through a pharmacy and therefore much more available,” said Dr. Prager. “Restrictions for both medication and surgical management of EPL will likely increase in states where abortion is illegal, and it could possibly lead to patients having less choice as to mode of management,” she explained.
“There are many studies showing that all modes of EPL management are safe and effective and should be supported with respect to patient choice,” Dr. Prager noted. “There are also substantial data supporting the overall safety of mifepristone, and there are no scientific or medical data suggesting the REMS increases safety in any way. Frankly, there are no good, evidence-based reasons to continue to keep the REMS in place,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health and a Society of Family Planning Research Fund Midcareer Mentor Award. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Prager had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Ob.Gyn. News.
Medical management of early pregnancy loss costs less and offers similar quality of life to uterine aspiration, based on data from an analytical model.
Early pregnancy loss (EPL) occurs in more than 1 million women in the United States each year, and many patients are diagnosed before they show symptoms, wrote Divyah Nagendra, MD, of Cambridge Health Alliance, Mass., and colleagues.
A 2018 study showed that medical management of EPL with mifepristone added to misoprostol increased effectiveness and reduced the need for additional medication or subsequent uterine procedures, but the cost of mifepristone is perceived as a barrier, and the cost-effectiveness of its use, compared with surgical or expectant management, has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
“We already know that adding mifepristone to the medical management of early pregnancy loss increases the effectiveness of the regimen,” coauthor Courtney A. Schreiber, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Procedural uterine aspiration is highly effective as well, so patients and providers may consider the cost when deciding on a treatment strategy,” she added.
“If medication management is preferred by many patients, decreases the need to access in-person clinical care during a pandemic, and is found to be cost-effective, clinicians and policymakers should increase efforts to improve mifepristone availability and reduce access burdens,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers created a decision-analytic model using data from published literature and the Pregnancy Failure Regiments Trial (PreFaiR) to compare office-based uterine aspiration to medical management with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol for EPL.
The PrFaiR study randomized 300 women who experienced EPL before 12 weeks’ gestation to medication management with 800 mcg misoprostol vaginally, with or without pretreatment of 200 mg mifeprestone orally. The average age of the participants was 30.7 years, and demographics were similar between the groups.
The researchers used the PrFaiR data for medical management and patient-level data from published literature for uterine aspiration.
The primary outcome was the cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained. QALY was based on a modified utility score from the published literature. Effectiveness was based on QALY gained and the rate of complete expulsion of the gestational sac without additional intervention.
Overall, the mean costs per person were significantly higher for uterine aspiration, compared with medical management ($828 vs. $661, P = .004). Uterine aspiration was significantly more effective for complete gestational sac expulsion (97.3% vs. 83.8%, P = .0001). However, the QALYs were significantly higher for medical management, compared with uterine aspiration (0.082 vs. 0.079, P < .0001).
Cost-effectiveness was greater for medical management from a health care sector perspective, with lower costs and higher QALYs than uterine aspiration, the researchers noted.
They also evaluated the effect of mifepristone pretreatment on cost-effectiveness and found that medical management would remain cost effective, compared with uterine aspiration even if uterine aspiration procedures decreased in cost and mifepristone increased in cost, and even if medication management had a decreased completion rate and utility score, compared with uterine aspiration.
“Our analysis demonstrates that the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for medical management is well below the maximum willingness-to-pay threshold of approximately $100,000 per QALY gained,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings.
Potential savings, uncertain access
Despite the potential savings and patient benefits, access to mifepristone remains a barrier, the researchers said.
Although the FDA lifted some restrictions on mifepristone in 2021 in the wake of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the effect of new abortion-related restrictions remains to be seen.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 2018 National Medicare reimbursement rates to calculate costs, though actual costs vary by region and payer, the researchers noted. Other limitations include variations in cost of mifepristone by region and time and the differences in data sources between the uterine aspiration and medical management groups. More research is needed to assess QALYs for early pregnancy loss to establish standard measures and to assess the societal perspective of ESL as well as the health care perspective, they added.
However, the current results support medical management of EPL with mifepristone pretreatment followed by misoprostol as a “high-value care alternative” to office-based uterine aspiration, they said. “Increasing access to mifepristone and eliminating unnecessary restrictions will improve early pregnancy care,” they concluded.
“Given how effective procedural management is, we were slightly surprised that medical management remains cost effective,” Dr. Schreiber said in an interview.
Looking ahead in the wake of new restrictions on use for abortion, “patients may have difficulty accessing either medical or procedural management for early pregnancy loss,” Dr. Schreiber noted. “We support the accessibility of all evidence-based care and hope that our data will help overcome perceived financial barriers,” she said. Additional research needs include improved implementation and access to evidence-based early pregnancy loss care, she added.
Reasons to lift regulations
“Given the recent overturning of Roe v. Wade, any medications that are associated with abortion have increased scrutiny, especially mifepristone and misoprostol, even though these medications are also used for managing early pregnancy loss,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “Demonstrating that medication management of EPL with mifepristone/misoprostol is less expensive and has increased QALYs associated with it is yet another reason to deregulate mifepristone so it can also be more accessible for management of EPL,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Prager said she was not surprised by the findings, as effective medication should be less expensive than a procedure. “I would caution that the increased QALYs found in this study should not be interpreted as a reason to restrict surgical management of EPL but to increase access also to medication management, even though medication has a slightly lower rate of complete gestational sac expulsion,” she noted. “Mode of management should be up to the patient, unless there is a clear medical reason for one or the other.”
Going forward, “the FDA has it in its power to remove the REMS, which would immediately make mifepristone a medication that can be prescribed through a pharmacy and therefore much more available,” said Dr. Prager. “Restrictions for both medication and surgical management of EPL will likely increase in states where abortion is illegal, and it could possibly lead to patients having less choice as to mode of management,” she explained.
“There are many studies showing that all modes of EPL management are safe and effective and should be supported with respect to patient choice,” Dr. Prager noted. “There are also substantial data supporting the overall safety of mifepristone, and there are no scientific or medical data suggesting the REMS increases safety in any way. Frankly, there are no good, evidence-based reasons to continue to keep the REMS in place,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health and a Society of Family Planning Research Fund Midcareer Mentor Award. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Prager had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Ob.Gyn. News.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
New insights into worldwide biliary tract cancer incidence, mortality
Incidence and mortality for biliary tract cancer (BTC) are both on the rise worldwide, according to a new analysis of data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer and the World Health Organization.
This diverse group of hepatic and perihepatic cancers include gallbladder cancer (GBC), intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC and ECC), and ampulla of Vater cancer. Although BTC is considered rare, incidence of its subtypes can vary significantly by geographic region. Because BTC is typically asymptomatic in its early stage, diagnosis is often made after tumors have spread, when there are few therapeutic options available. In the United States and Europe, 5-year survival is less than 20%.
Although previous studies have examined worldwide BTC incidence, few looked at multiple global regions or at all subtypes. Instead, subtypes may be grouped together and reported as composites, or BTC is lumped together with primary liver cancer. “To our knowledge, this is the first report combining data on worldwide incidence and mortality of all BTC subtypes per the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision,” the authors wrote in the study, published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
The researchers pointed out that classification coding systems have improved at defining BTC subtypes, so that studies using older coding subtypes could cause misinterpretation of incidence rates.
BTC subtypes also have unique sets of risk factors and different prognoses and treatment outcomes. “Thus, there is a need to define accurate epidemiologic trends that will allow specific risk factors to be identified, guiding experts in implementing policies to improve diagnosis and survival,” the authors wrote.
The study included data from 22 countries. BTC incidence ranged from 1.12 cases per 100,000 person-years in Vietnam to 12.42 in Chile. As expected, incidence rates were higher in the Asia-Pacific region (1.12-9.00) and South America (2.73-12.42), compared with Europe (2.00-3.59) and North America (2.33-2.35). Within the United States, Asian Americans had a higher BTC incidence than the general population (2.99 vs. 2.33).
In most countries, new cases were dominated by GBC, while ICC was the most common cause of death.
In each country, older patients were 5-10 times more likely to die than BTC patients generally. The sixth and seventh decades of life are the most common time of diagnosis, and treatment options may be limited in older patients.
Risk factors for BTC may include common comorbidities like obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and diabetes. Each is increasing individually, which may in turn contribute to rising BTC incidence. Observational analyses suggest that obesity may contribute to risk of ECC and gallbladder cancer, while diabetes and obesity may raise the risk of ICC. Smoking is associated with increased risk of all BTC subtypes except GBC, and alcohol consumption is associated with ICC.
“This study highlights how each subtype may be vulnerable to specific risk factors and emphasizes the value of separating epidemiologic data by subtype in order to better understand disease etiology,” the researchers wrote.
Risk factors associated with incidence and mortality from BTC aren’t limited to clinical characteristics. Genetic susceptibility may also play a role in incidence and mortality of different subtypes. There is also a relationship between gallstones and BTC risk. In Chile, about 50% of women have gallstones versus 17% of women in the United States. The cancer incidence is 27 per 100,000 person-years in Chile and 2 per 100,000 person-years in the United States. BTC is also the leading cause of cancer death among women in Chile.
The authors also highlighted the high rates of gallbladder cancer in India, despite a low prevalence of gallstones. Incidences can vary with geography along the flow of the Ganges River, which might reflect varying risks from contamination caused by agricultural runoff or industrial or human waste.
Worldwide BTC incidence and mortality was generally higher among women than men, with the exception of ampulla of Vater cancer, which was more common in men.
The study is limited by quality of data, which varied significantly between countries. Mortality data was missing from some countries know to have high BTC incidence. The databases had little survival data, which could have provided insights into treatment efficacy.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The authors have extensive financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are understudied malignancies with poor prognoses. A major impediment to a deeper understanding of BTC epidemiology is that the term BTC encompasses a heterogeneous group of cancers including cholangiocarcinoma (both intrahepatic and extrahepatic), as well as ampullary and gallbladder cancer. Studies have often lumped all BTC subgroups together despite differences in their geographic distribution, risk factors, and underlying pathogenesis. Furthermore, epidemiological reporting has often grouped “intrahepatic liver and bile duct cancers” which include hepatocellular carcinoma, a biologically different entity requiring a separate management strategy.
The study highlights the importance of future policy work to address the risk factors for BTCs that vary by region and that will likely evolve over time. It also stresses the urgent need for both early diagnostic strategies and improved biomarker-driven medical therapy, areas of ongoing research requiring accelerated development.
Irun Bhan, MD, is a transplant hepatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has no relevant conflicts.
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are understudied malignancies with poor prognoses. A major impediment to a deeper understanding of BTC epidemiology is that the term BTC encompasses a heterogeneous group of cancers including cholangiocarcinoma (both intrahepatic and extrahepatic), as well as ampullary and gallbladder cancer. Studies have often lumped all BTC subgroups together despite differences in their geographic distribution, risk factors, and underlying pathogenesis. Furthermore, epidemiological reporting has often grouped “intrahepatic liver and bile duct cancers” which include hepatocellular carcinoma, a biologically different entity requiring a separate management strategy.
The study highlights the importance of future policy work to address the risk factors for BTCs that vary by region and that will likely evolve over time. It also stresses the urgent need for both early diagnostic strategies and improved biomarker-driven medical therapy, areas of ongoing research requiring accelerated development.
Irun Bhan, MD, is a transplant hepatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has no relevant conflicts.
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are understudied malignancies with poor prognoses. A major impediment to a deeper understanding of BTC epidemiology is that the term BTC encompasses a heterogeneous group of cancers including cholangiocarcinoma (both intrahepatic and extrahepatic), as well as ampullary and gallbladder cancer. Studies have often lumped all BTC subgroups together despite differences in their geographic distribution, risk factors, and underlying pathogenesis. Furthermore, epidemiological reporting has often grouped “intrahepatic liver and bile duct cancers” which include hepatocellular carcinoma, a biologically different entity requiring a separate management strategy.
The study highlights the importance of future policy work to address the risk factors for BTCs that vary by region and that will likely evolve over time. It also stresses the urgent need for both early diagnostic strategies and improved biomarker-driven medical therapy, areas of ongoing research requiring accelerated development.
Irun Bhan, MD, is a transplant hepatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has no relevant conflicts.
Incidence and mortality for biliary tract cancer (BTC) are both on the rise worldwide, according to a new analysis of data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer and the World Health Organization.
This diverse group of hepatic and perihepatic cancers include gallbladder cancer (GBC), intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC and ECC), and ampulla of Vater cancer. Although BTC is considered rare, incidence of its subtypes can vary significantly by geographic region. Because BTC is typically asymptomatic in its early stage, diagnosis is often made after tumors have spread, when there are few therapeutic options available. In the United States and Europe, 5-year survival is less than 20%.
Although previous studies have examined worldwide BTC incidence, few looked at multiple global regions or at all subtypes. Instead, subtypes may be grouped together and reported as composites, or BTC is lumped together with primary liver cancer. “To our knowledge, this is the first report combining data on worldwide incidence and mortality of all BTC subtypes per the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision,” the authors wrote in the study, published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
The researchers pointed out that classification coding systems have improved at defining BTC subtypes, so that studies using older coding subtypes could cause misinterpretation of incidence rates.
BTC subtypes also have unique sets of risk factors and different prognoses and treatment outcomes. “Thus, there is a need to define accurate epidemiologic trends that will allow specific risk factors to be identified, guiding experts in implementing policies to improve diagnosis and survival,” the authors wrote.
The study included data from 22 countries. BTC incidence ranged from 1.12 cases per 100,000 person-years in Vietnam to 12.42 in Chile. As expected, incidence rates were higher in the Asia-Pacific region (1.12-9.00) and South America (2.73-12.42), compared with Europe (2.00-3.59) and North America (2.33-2.35). Within the United States, Asian Americans had a higher BTC incidence than the general population (2.99 vs. 2.33).
In most countries, new cases were dominated by GBC, while ICC was the most common cause of death.
In each country, older patients were 5-10 times more likely to die than BTC patients generally. The sixth and seventh decades of life are the most common time of diagnosis, and treatment options may be limited in older patients.
Risk factors for BTC may include common comorbidities like obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and diabetes. Each is increasing individually, which may in turn contribute to rising BTC incidence. Observational analyses suggest that obesity may contribute to risk of ECC and gallbladder cancer, while diabetes and obesity may raise the risk of ICC. Smoking is associated with increased risk of all BTC subtypes except GBC, and alcohol consumption is associated with ICC.
“This study highlights how each subtype may be vulnerable to specific risk factors and emphasizes the value of separating epidemiologic data by subtype in order to better understand disease etiology,” the researchers wrote.
Risk factors associated with incidence and mortality from BTC aren’t limited to clinical characteristics. Genetic susceptibility may also play a role in incidence and mortality of different subtypes. There is also a relationship between gallstones and BTC risk. In Chile, about 50% of women have gallstones versus 17% of women in the United States. The cancer incidence is 27 per 100,000 person-years in Chile and 2 per 100,000 person-years in the United States. BTC is also the leading cause of cancer death among women in Chile.
The authors also highlighted the high rates of gallbladder cancer in India, despite a low prevalence of gallstones. Incidences can vary with geography along the flow of the Ganges River, which might reflect varying risks from contamination caused by agricultural runoff or industrial or human waste.
Worldwide BTC incidence and mortality was generally higher among women than men, with the exception of ampulla of Vater cancer, which was more common in men.
The study is limited by quality of data, which varied significantly between countries. Mortality data was missing from some countries know to have high BTC incidence. The databases had little survival data, which could have provided insights into treatment efficacy.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The authors have extensive financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
Incidence and mortality for biliary tract cancer (BTC) are both on the rise worldwide, according to a new analysis of data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer and the World Health Organization.
This diverse group of hepatic and perihepatic cancers include gallbladder cancer (GBC), intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC and ECC), and ampulla of Vater cancer. Although BTC is considered rare, incidence of its subtypes can vary significantly by geographic region. Because BTC is typically asymptomatic in its early stage, diagnosis is often made after tumors have spread, when there are few therapeutic options available. In the United States and Europe, 5-year survival is less than 20%.
Although previous studies have examined worldwide BTC incidence, few looked at multiple global regions or at all subtypes. Instead, subtypes may be grouped together and reported as composites, or BTC is lumped together with primary liver cancer. “To our knowledge, this is the first report combining data on worldwide incidence and mortality of all BTC subtypes per the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision,” the authors wrote in the study, published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
The researchers pointed out that classification coding systems have improved at defining BTC subtypes, so that studies using older coding subtypes could cause misinterpretation of incidence rates.
BTC subtypes also have unique sets of risk factors and different prognoses and treatment outcomes. “Thus, there is a need to define accurate epidemiologic trends that will allow specific risk factors to be identified, guiding experts in implementing policies to improve diagnosis and survival,” the authors wrote.
The study included data from 22 countries. BTC incidence ranged from 1.12 cases per 100,000 person-years in Vietnam to 12.42 in Chile. As expected, incidence rates were higher in the Asia-Pacific region (1.12-9.00) and South America (2.73-12.42), compared with Europe (2.00-3.59) and North America (2.33-2.35). Within the United States, Asian Americans had a higher BTC incidence than the general population (2.99 vs. 2.33).
In most countries, new cases were dominated by GBC, while ICC was the most common cause of death.
In each country, older patients were 5-10 times more likely to die than BTC patients generally. The sixth and seventh decades of life are the most common time of diagnosis, and treatment options may be limited in older patients.
Risk factors for BTC may include common comorbidities like obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and diabetes. Each is increasing individually, which may in turn contribute to rising BTC incidence. Observational analyses suggest that obesity may contribute to risk of ECC and gallbladder cancer, while diabetes and obesity may raise the risk of ICC. Smoking is associated with increased risk of all BTC subtypes except GBC, and alcohol consumption is associated with ICC.
“This study highlights how each subtype may be vulnerable to specific risk factors and emphasizes the value of separating epidemiologic data by subtype in order to better understand disease etiology,” the researchers wrote.
Risk factors associated with incidence and mortality from BTC aren’t limited to clinical characteristics. Genetic susceptibility may also play a role in incidence and mortality of different subtypes. There is also a relationship between gallstones and BTC risk. In Chile, about 50% of women have gallstones versus 17% of women in the United States. The cancer incidence is 27 per 100,000 person-years in Chile and 2 per 100,000 person-years in the United States. BTC is also the leading cause of cancer death among women in Chile.
The authors also highlighted the high rates of gallbladder cancer in India, despite a low prevalence of gallstones. Incidences can vary with geography along the flow of the Ganges River, which might reflect varying risks from contamination caused by agricultural runoff or industrial or human waste.
Worldwide BTC incidence and mortality was generally higher among women than men, with the exception of ampulla of Vater cancer, which was more common in men.
The study is limited by quality of data, which varied significantly between countries. Mortality data was missing from some countries know to have high BTC incidence. The databases had little survival data, which could have provided insights into treatment efficacy.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The authors have extensive financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES





