User login
Real-world data generate debate on definition of flare in axial spondyloarthritis
How best to define axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) flares in practice remains the subject of some debate as evidenced by the discussion that followed an abstract presentation at the 12th International Congress on Spondyloarthritides.
It’s an important topic, said Maxime Breban, MD, PhD, of Ambroise Paré Hospital in Paris, as flares can adversely affect patient outcomes. The absence of flares may also a useful measure of how well a patient is responding to treatment in clinical trials and whether a treatment can be tapered.
“There have been many ways to define flares in the past and there is no consensus,” he observed.
Although the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) devised 12 preliminary definitions of flare in 2016, “these were not that good when we moved to patients,” Dr. Breban suggested.
The ASAS definitions were based on patient vignettes, he explained, and used a combination of variables from the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), a visual analog scale (VAS) of pain, and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP).
The study that Dr. Breban presented looked at the performance of the ASAS preliminary definitions of axSpA flares in a real-life patient population, as well as prospectively determining how variations in BASDAI and VAS pain were associated with patient-perceived flares of disease.
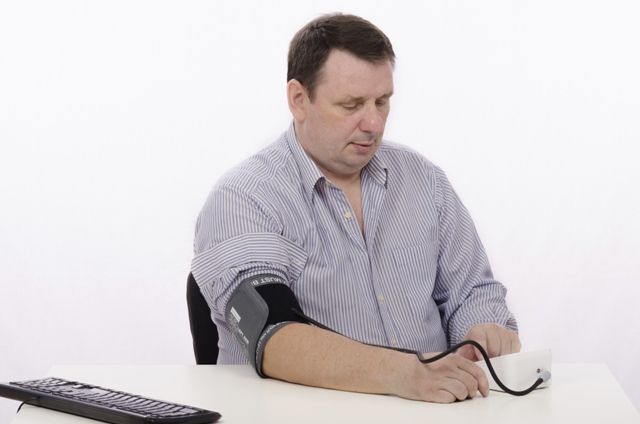
A total of 99 patients took part in the study, recruited through a secure e-health platform called SPONDY+. Once a week, patients completed the BASDAI questionnaire and the pain VAS, and stated whether their disease had flared in the past week.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated to see how well the BASDAI and pain VAS identified patients who were experiencing a flare or had a recently resolved flare of axSpA.
Dr. Breban reported that variation in the BASDAI “appears a suitable variable to monitor the occurrence and resolution of patient-reported flare in axial spondylarthritis.”
In predicting a flare, the area under the curve (AUC) was significantly higher for the change in BASDAI than for the change in pain VAS, at a respective 0.81 and 0.77 (P = .01). However, both variables were similarly accurate in predicting the resolution of a flare, with respective AUCs of 0.78 and 0.80 (P = .3).
A 0.22-point increase in BASDAI was reported to be the best balance between sensitivity (70%) and specificity (79%) for a flare. However, this is “outside of what is possible within a test–retest situation,” Désirée van der Heijde, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, said during discussion.
Dr. van der Heijde told Dr. Breban: “I understand that that comes out of your data, that that’s the best combination for sensitivity and specificity, but the next step is to decide if that makes sense.”
The ROC curves that Dr. Breban presented showed the range of sensitivities and specificities that could be achieved. If the specificity was increased to be 90% or higher, the specificity fell to 55%, with the change in BASDAI being an increase of 0.8 points. Conversely, bringing the sensitivity above 90% meant the specificity dropped to 39% and the change in BASDAI was a decrease of 0.1 point.
“So that means you can choose whatever you want as a cutoff,” Dr. Breban said. It depends on what you are aiming to do. “If you want to identify a flare, you can increase sensitivity, or specificity, according to what your purpose is,” he suggested.
“The next step, of course, is what to choose as a flare. Then it depends on how you want to use a flare if you want to use a flare to change the treatment,” agreed Dr. van der Heijde. “That was why, in the ASAS group, it was decided to have a high specificity so that you are not changing treatment all the time.”
In the data that Dr. Breban presented, the ASAS preliminary definitions were highly specific but lacked sensitivity. None of the ASAS definitions yielded sensitivity values higher than 37%, whereas specificity was higher than 95% for all of them.
The study’s design did not allow researchers to test the ASDAS-CRP as a definition of flare in its real-world patient sample. Thus, it is looking only at the patient’s perspective on flare, and there is a “huge discrepancy” between patient and physician-reported disease activity, Dr. van der Heijde noted. “So, I think before using your data to really choose the flare definition, I think we need to take it all into account.”
Maxime Dougados, MD, PhD, of Cochin Hospital in Paris, who has been “deeply involved in the elaboration of the definition of flare” added his thoughts: “Flare means for me, not a status, but a change,” he observed.
But if the aim of treating people with axSpA is to achieve a good or acceptable state of health, he questioned whether work should be continued to define the concept of a flare.
The definition of a flare was conceived for use in clinical trials mainly, Dr. van der Heijde noted. It helped to assess how changes in treatment might affect the outcomes of patients. In clinical practice, especially now with treat-to-target gaining more and more traction in axSpA, she agreed that perhaps the goal should be to focus more on the health status of patients.
Dr. Breban acknowledged that the SPONDY+ platform has been developed by bepatient with support from Merck Sharp & Dohme. No other disclosures were made.
How best to define axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) flares in practice remains the subject of some debate as evidenced by the discussion that followed an abstract presentation at the 12th International Congress on Spondyloarthritides.
It’s an important topic, said Maxime Breban, MD, PhD, of Ambroise Paré Hospital in Paris, as flares can adversely affect patient outcomes. The absence of flares may also a useful measure of how well a patient is responding to treatment in clinical trials and whether a treatment can be tapered.
“There have been many ways to define flares in the past and there is no consensus,” he observed.
Although the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) devised 12 preliminary definitions of flare in 2016, “these were not that good when we moved to patients,” Dr. Breban suggested.
The ASAS definitions were based on patient vignettes, he explained, and used a combination of variables from the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), a visual analog scale (VAS) of pain, and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP).
The study that Dr. Breban presented looked at the performance of the ASAS preliminary definitions of axSpA flares in a real-life patient population, as well as prospectively determining how variations in BASDAI and VAS pain were associated with patient-perceived flares of disease.
A total of 99 patients took part in the study, recruited through a secure e-health platform called SPONDY+. Once a week, patients completed the BASDAI questionnaire and the pain VAS, and stated whether their disease had flared in the past week.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated to see how well the BASDAI and pain VAS identified patients who were experiencing a flare or had a recently resolved flare of axSpA.
Dr. Breban reported that variation in the BASDAI “appears a suitable variable to monitor the occurrence and resolution of patient-reported flare in axial spondylarthritis.”
In predicting a flare, the area under the curve (AUC) was significantly higher for the change in BASDAI than for the change in pain VAS, at a respective 0.81 and 0.77 (P = .01). However, both variables were similarly accurate in predicting the resolution of a flare, with respective AUCs of 0.78 and 0.80 (P = .3).
A 0.22-point increase in BASDAI was reported to be the best balance between sensitivity (70%) and specificity (79%) for a flare. However, this is “outside of what is possible within a test–retest situation,” Désirée van der Heijde, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, said during discussion.
Dr. van der Heijde told Dr. Breban: “I understand that that comes out of your data, that that’s the best combination for sensitivity and specificity, but the next step is to decide if that makes sense.”
The ROC curves that Dr. Breban presented showed the range of sensitivities and specificities that could be achieved. If the specificity was increased to be 90% or higher, the specificity fell to 55%, with the change in BASDAI being an increase of 0.8 points. Conversely, bringing the sensitivity above 90% meant the specificity dropped to 39% and the change in BASDAI was a decrease of 0.1 point.
“So that means you can choose whatever you want as a cutoff,” Dr. Breban said. It depends on what you are aiming to do. “If you want to identify a flare, you can increase sensitivity, or specificity, according to what your purpose is,” he suggested.
“The next step, of course, is what to choose as a flare. Then it depends on how you want to use a flare if you want to use a flare to change the treatment,” agreed Dr. van der Heijde. “That was why, in the ASAS group, it was decided to have a high specificity so that you are not changing treatment all the time.”
In the data that Dr. Breban presented, the ASAS preliminary definitions were highly specific but lacked sensitivity. None of the ASAS definitions yielded sensitivity values higher than 37%, whereas specificity was higher than 95% for all of them.
The study’s design did not allow researchers to test the ASDAS-CRP as a definition of flare in its real-world patient sample. Thus, it is looking only at the patient’s perspective on flare, and there is a “huge discrepancy” between patient and physician-reported disease activity, Dr. van der Heijde noted. “So, I think before using your data to really choose the flare definition, I think we need to take it all into account.”
Maxime Dougados, MD, PhD, of Cochin Hospital in Paris, who has been “deeply involved in the elaboration of the definition of flare” added his thoughts: “Flare means for me, not a status, but a change,” he observed.
But if the aim of treating people with axSpA is to achieve a good or acceptable state of health, he questioned whether work should be continued to define the concept of a flare.
The definition of a flare was conceived for use in clinical trials mainly, Dr. van der Heijde noted. It helped to assess how changes in treatment might affect the outcomes of patients. In clinical practice, especially now with treat-to-target gaining more and more traction in axSpA, she agreed that perhaps the goal should be to focus more on the health status of patients.
Dr. Breban acknowledged that the SPONDY+ platform has been developed by bepatient with support from Merck Sharp & Dohme. No other disclosures were made.
How best to define axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) flares in practice remains the subject of some debate as evidenced by the discussion that followed an abstract presentation at the 12th International Congress on Spondyloarthritides.
It’s an important topic, said Maxime Breban, MD, PhD, of Ambroise Paré Hospital in Paris, as flares can adversely affect patient outcomes. The absence of flares may also a useful measure of how well a patient is responding to treatment in clinical trials and whether a treatment can be tapered.
“There have been many ways to define flares in the past and there is no consensus,” he observed.
Although the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) devised 12 preliminary definitions of flare in 2016, “these were not that good when we moved to patients,” Dr. Breban suggested.
The ASAS definitions were based on patient vignettes, he explained, and used a combination of variables from the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), a visual analog scale (VAS) of pain, and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP).
The study that Dr. Breban presented looked at the performance of the ASAS preliminary definitions of axSpA flares in a real-life patient population, as well as prospectively determining how variations in BASDAI and VAS pain were associated with patient-perceived flares of disease.
A total of 99 patients took part in the study, recruited through a secure e-health platform called SPONDY+. Once a week, patients completed the BASDAI questionnaire and the pain VAS, and stated whether their disease had flared in the past week.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated to see how well the BASDAI and pain VAS identified patients who were experiencing a flare or had a recently resolved flare of axSpA.
Dr. Breban reported that variation in the BASDAI “appears a suitable variable to monitor the occurrence and resolution of patient-reported flare in axial spondylarthritis.”
In predicting a flare, the area under the curve (AUC) was significantly higher for the change in BASDAI than for the change in pain VAS, at a respective 0.81 and 0.77 (P = .01). However, both variables were similarly accurate in predicting the resolution of a flare, with respective AUCs of 0.78 and 0.80 (P = .3).
A 0.22-point increase in BASDAI was reported to be the best balance between sensitivity (70%) and specificity (79%) for a flare. However, this is “outside of what is possible within a test–retest situation,” Désirée van der Heijde, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, said during discussion.
Dr. van der Heijde told Dr. Breban: “I understand that that comes out of your data, that that’s the best combination for sensitivity and specificity, but the next step is to decide if that makes sense.”
The ROC curves that Dr. Breban presented showed the range of sensitivities and specificities that could be achieved. If the specificity was increased to be 90% or higher, the specificity fell to 55%, with the change in BASDAI being an increase of 0.8 points. Conversely, bringing the sensitivity above 90% meant the specificity dropped to 39% and the change in BASDAI was a decrease of 0.1 point.
“So that means you can choose whatever you want as a cutoff,” Dr. Breban said. It depends on what you are aiming to do. “If you want to identify a flare, you can increase sensitivity, or specificity, according to what your purpose is,” he suggested.
“The next step, of course, is what to choose as a flare. Then it depends on how you want to use a flare if you want to use a flare to change the treatment,” agreed Dr. van der Heijde. “That was why, in the ASAS group, it was decided to have a high specificity so that you are not changing treatment all the time.”
In the data that Dr. Breban presented, the ASAS preliminary definitions were highly specific but lacked sensitivity. None of the ASAS definitions yielded sensitivity values higher than 37%, whereas specificity was higher than 95% for all of them.
The study’s design did not allow researchers to test the ASDAS-CRP as a definition of flare in its real-world patient sample. Thus, it is looking only at the patient’s perspective on flare, and there is a “huge discrepancy” between patient and physician-reported disease activity, Dr. van der Heijde noted. “So, I think before using your data to really choose the flare definition, I think we need to take it all into account.”
Maxime Dougados, MD, PhD, of Cochin Hospital in Paris, who has been “deeply involved in the elaboration of the definition of flare” added his thoughts: “Flare means for me, not a status, but a change,” he observed.
But if the aim of treating people with axSpA is to achieve a good or acceptable state of health, he questioned whether work should be continued to define the concept of a flare.
The definition of a flare was conceived for use in clinical trials mainly, Dr. van der Heijde noted. It helped to assess how changes in treatment might affect the outcomes of patients. In clinical practice, especially now with treat-to-target gaining more and more traction in axSpA, she agreed that perhaps the goal should be to focus more on the health status of patients.
Dr. Breban acknowledged that the SPONDY+ platform has been developed by bepatient with support from Merck Sharp & Dohme. No other disclosures were made.
FROM THE 2021 SPA CONGRESS
Flagellate Shiitake Mushroom Reaction With Histologic Features of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
To the Editor:
A 59-year-old man presented with a severely pruritic rash on the legs, arms, abdomen, groin, and buttocks of 3 days’ duration. He reported subjective fever and chills. Prior to the appearance of the rash, the patient and his family had eaten shiitake mushrooms daily for 3 days. He denied any new medications in the last several months or any recent upper respiratory or gastrointestinal tract illnesses. His medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetes-induced end-stage renal disease requiring home peritoneal dialysis. His long-term medications for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hyperlipidemia, and insomnia included amlodipine, atorvastatin, finasteride, gabapentin, insulin glargine, linagliptin, metoprolol, and mirtazapine.
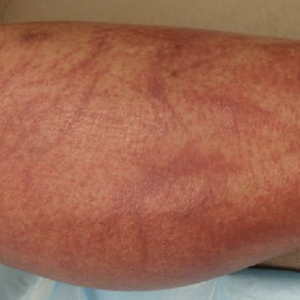
Physical examination revealed an afebrile man with medium brown skin tone and diffuse, bright red, erythematous patches on the lower legs, axillae, medial forearms, lateral trunk, lower abdomen, and groin. There were distinct flagellate, linear, red patches on the lower legs (Figure 1). In addition, small clusters of 1- to 2-mm superficial pustules were present on the right upper medial thigh and left forearm with micropapules grouped in the skin folds.

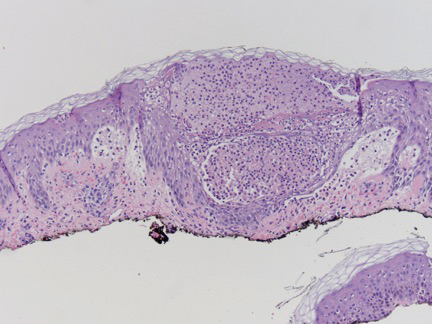
A shave biopsy specimen from a pustule on the right upper medial thigh revealed spongiotic dermatitis with neutrophilic subcorneal pustule formation and frequent eosinophils (Figure 2). The dermis contained scattered mixed inflammatory cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes (Figure 3). These histologic findings were consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). No biopsy was performed on the flagellate patches due to its clinically distinct presentation and well-established association with shiitake mushroom ingestion.

The patient was treated with triamcinolone ointment and systemic corticosteroids to reduce pruritus and quickly clear the lesions due to his comorbidities. He recovered completely within 1 week and had no evidence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from the flagellate dermatitis.
Flagellate dermatitis is an intensely pruritic dermatitis characterized by 1-mm, disseminated, erythematous papules in a linear grouped arrangement secondary to koebnerization due to the patient scratching. It was first described in 1977 by Nakamura.1 Although it rarely is seen outside of China and Japan, there are well-established associations of flagellate dermatitis with bleomycin and shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) ingestion. One key clinical difference between the two causes is that postinflammatory hyperpigmentation changes usually are seen with bleomycin-induced flagellate dermatitis and typically are not present with shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis.2 Following ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, the median time of onset of presentation typically is 24 hours but ranges from 12 hours to 5 days. Most patients completely recover by 3 weeks, with or without treatment.3 Although the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is not clear, the most common theory is a toxic reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide isolated from shiitake mushrooms. However, type I and IV allergic hypersensitivities also have been supported by the time of onset, clearance, severe pruritus, benefit from steroids and antihistamines, and lack of grouped outbreaks in people exposed to shared meals containing shiitake mushrooms.3,4 Furthermore, there is a case of patch test–confirmed allergic contact dermatitis to shiitake mushrooms, demonstrating a 1+ reaction at 96 hours to the cap of a shiitake mushroom but a negative pin-prick test at 20 minutes, suggesting type IV hypersensitivity.5 An additional case revealed a positive skin-prick test with formation of a 4-mm wheal and subsequent pruritic papules and vesicles appearing 48 to 72 hours later at the prick site.6 Subsequent cases have been reported in association with consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms, but cases have been reported after consumption of fully cooked mushrooms, which does not support a toxin-mediated theory, as cooking the mushroom before consumption likely would denature or change the structure of the suspected toxin.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a rare eruption that occurs due to ingestion of a causative agent, usually an antibiotic, and is characterized by the presence of fever and disseminated, erythematous, pinpoint, sterile pustules on the skin and mucous membranes. It affects 1 to 5 persons per million per year, with more than 90% of cases attributed to drug ingestion.7 Spontaneous resolution can be expected within 15 days of its onset; however, there is a mortality rate of up to 5% that occurs most often in those with severe comorbidities or in older patients, for whom systemic corticosteroid therapy may be justified.7,8 A multinational case-control study conducted to evaluate the risk of AGEP associated with certain drugs revealed macrolides (namely pristinamycin); β-lactam antibiotics including penicillin, aminopenicillin, and cephalosporin; quinolones; hydroxychloroquine; anti-infective sulfonamides; terbinafine; and diltiazem as the most strongly associated culprits.9 Our patient’s flagellate dermatitis was unique in that it also showed histologic features of AGEP. The pathogenesis of drug-induced AGEP has been partially elucidated and involves activation of drug-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that migrate to the skin and participate in apoptotic signaling of keratinocytes and recruitment of neutrophils and eosinophils, which form subcorneal sterile pustules.7 In a study of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, 50% (7/14) of patients with AGEP had positive patch tests to the causative agent.10 This T cell–dependent response explains why the condition responds to systemic corticosteroids. Additionally, our case report of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP suggests that the pathogenesis of flagellate dermatitis may be a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction. The time of onset, lack of grouped outbreaks in those sharing shiitake mushroom–containing meals, severe pruritus, lack of cases demonstrating an anaphylactic or wheal and flare response, benefit of steroids, and a case with histologic features of AGEP all lend support to this theory.
We report a case of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP. The time course, histologic features of AGEP, absence of new medications, and resolution with discontinuation of shiitake mushrooms lends support of the hypothesis that the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is similar to AGEP’s type IV hypersensitivity reaction. To further elucidate its pathogenesis, skin prick testing and patch testing with shiitake mushrooms in patients exhibiting shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis may prove to be beneficial.
- Nakamura T. Toxicoderma caused by shiitake (Lentinus edodes)[in Japanese]. Jpn J Clin Dermatol. 1977;31:65-68.
- Chu EY, Anand D, Dawn A, et al. Shiitake dermatitis: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Cutis. 2013;91:287-290.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
- Nakamura T. Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:65-70.
- Curnow P, Tam M. Contact dermatitis to shiitake mushroom. Australas J Dermatol. 2003;44:155-157.
- Lippert U, Martin V, Schwertfeger C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:178-179.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:113-119.
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:989-996.
- Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Flechet ML, et al. Patch testing in severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;35:234-236.
To the Editor:
A 59-year-old man presented with a severely pruritic rash on the legs, arms, abdomen, groin, and buttocks of 3 days’ duration. He reported subjective fever and chills. Prior to the appearance of the rash, the patient and his family had eaten shiitake mushrooms daily for 3 days. He denied any new medications in the last several months or any recent upper respiratory or gastrointestinal tract illnesses. His medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetes-induced end-stage renal disease requiring home peritoneal dialysis. His long-term medications for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hyperlipidemia, and insomnia included amlodipine, atorvastatin, finasteride, gabapentin, insulin glargine, linagliptin, metoprolol, and mirtazapine.
Physical examination revealed an afebrile man with medium brown skin tone and diffuse, bright red, erythematous patches on the lower legs, axillae, medial forearms, lateral trunk, lower abdomen, and groin. There were distinct flagellate, linear, red patches on the lower legs (Figure 1). In addition, small clusters of 1- to 2-mm superficial pustules were present on the right upper medial thigh and left forearm with micropapules grouped in the skin folds.

A shave biopsy specimen from a pustule on the right upper medial thigh revealed spongiotic dermatitis with neutrophilic subcorneal pustule formation and frequent eosinophils (Figure 2). The dermis contained scattered mixed inflammatory cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes (Figure 3). These histologic findings were consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). No biopsy was performed on the flagellate patches due to its clinically distinct presentation and well-established association with shiitake mushroom ingestion.

The patient was treated with triamcinolone ointment and systemic corticosteroids to reduce pruritus and quickly clear the lesions due to his comorbidities. He recovered completely within 1 week and had no evidence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from the flagellate dermatitis.

Flagellate dermatitis is an intensely pruritic dermatitis characterized by 1-mm, disseminated, erythematous papules in a linear grouped arrangement secondary to koebnerization due to the patient scratching. It was first described in 1977 by Nakamura.1 Although it rarely is seen outside of China and Japan, there are well-established associations of flagellate dermatitis with bleomycin and shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) ingestion. One key clinical difference between the two causes is that postinflammatory hyperpigmentation changes usually are seen with bleomycin-induced flagellate dermatitis and typically are not present with shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis.2 Following ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, the median time of onset of presentation typically is 24 hours but ranges from 12 hours to 5 days. Most patients completely recover by 3 weeks, with or without treatment.3 Although the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is not clear, the most common theory is a toxic reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide isolated from shiitake mushrooms. However, type I and IV allergic hypersensitivities also have been supported by the time of onset, clearance, severe pruritus, benefit from steroids and antihistamines, and lack of grouped outbreaks in people exposed to shared meals containing shiitake mushrooms.3,4 Furthermore, there is a case of patch test–confirmed allergic contact dermatitis to shiitake mushrooms, demonstrating a 1+ reaction at 96 hours to the cap of a shiitake mushroom but a negative pin-prick test at 20 minutes, suggesting type IV hypersensitivity.5 An additional case revealed a positive skin-prick test with formation of a 4-mm wheal and subsequent pruritic papules and vesicles appearing 48 to 72 hours later at the prick site.6 Subsequent cases have been reported in association with consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms, but cases have been reported after consumption of fully cooked mushrooms, which does not support a toxin-mediated theory, as cooking the mushroom before consumption likely would denature or change the structure of the suspected toxin.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a rare eruption that occurs due to ingestion of a causative agent, usually an antibiotic, and is characterized by the presence of fever and disseminated, erythematous, pinpoint, sterile pustules on the skin and mucous membranes. It affects 1 to 5 persons per million per year, with more than 90% of cases attributed to drug ingestion.7 Spontaneous resolution can be expected within 15 days of its onset; however, there is a mortality rate of up to 5% that occurs most often in those with severe comorbidities or in older patients, for whom systemic corticosteroid therapy may be justified.7,8 A multinational case-control study conducted to evaluate the risk of AGEP associated with certain drugs revealed macrolides (namely pristinamycin); β-lactam antibiotics including penicillin, aminopenicillin, and cephalosporin; quinolones; hydroxychloroquine; anti-infective sulfonamides; terbinafine; and diltiazem as the most strongly associated culprits.9 Our patient’s flagellate dermatitis was unique in that it also showed histologic features of AGEP. The pathogenesis of drug-induced AGEP has been partially elucidated and involves activation of drug-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that migrate to the skin and participate in apoptotic signaling of keratinocytes and recruitment of neutrophils and eosinophils, which form subcorneal sterile pustules.7 In a study of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, 50% (7/14) of patients with AGEP had positive patch tests to the causative agent.10 This T cell–dependent response explains why the condition responds to systemic corticosteroids. Additionally, our case report of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP suggests that the pathogenesis of flagellate dermatitis may be a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction. The time of onset, lack of grouped outbreaks in those sharing shiitake mushroom–containing meals, severe pruritus, lack of cases demonstrating an anaphylactic or wheal and flare response, benefit of steroids, and a case with histologic features of AGEP all lend support to this theory.
We report a case of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP. The time course, histologic features of AGEP, absence of new medications, and resolution with discontinuation of shiitake mushrooms lends support of the hypothesis that the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is similar to AGEP’s type IV hypersensitivity reaction. To further elucidate its pathogenesis, skin prick testing and patch testing with shiitake mushrooms in patients exhibiting shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis may prove to be beneficial.
To the Editor:
A 59-year-old man presented with a severely pruritic rash on the legs, arms, abdomen, groin, and buttocks of 3 days’ duration. He reported subjective fever and chills. Prior to the appearance of the rash, the patient and his family had eaten shiitake mushrooms daily for 3 days. He denied any new medications in the last several months or any recent upper respiratory or gastrointestinal tract illnesses. His medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetes-induced end-stage renal disease requiring home peritoneal dialysis. His long-term medications for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hyperlipidemia, and insomnia included amlodipine, atorvastatin, finasteride, gabapentin, insulin glargine, linagliptin, metoprolol, and mirtazapine.
Physical examination revealed an afebrile man with medium brown skin tone and diffuse, bright red, erythematous patches on the lower legs, axillae, medial forearms, lateral trunk, lower abdomen, and groin. There were distinct flagellate, linear, red patches on the lower legs (Figure 1). In addition, small clusters of 1- to 2-mm superficial pustules were present on the right upper medial thigh and left forearm with micropapules grouped in the skin folds.

A shave biopsy specimen from a pustule on the right upper medial thigh revealed spongiotic dermatitis with neutrophilic subcorneal pustule formation and frequent eosinophils (Figure 2). The dermis contained scattered mixed inflammatory cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes (Figure 3). These histologic findings were consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). No biopsy was performed on the flagellate patches due to its clinically distinct presentation and well-established association with shiitake mushroom ingestion.

The patient was treated with triamcinolone ointment and systemic corticosteroids to reduce pruritus and quickly clear the lesions due to his comorbidities. He recovered completely within 1 week and had no evidence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from the flagellate dermatitis.

Flagellate dermatitis is an intensely pruritic dermatitis characterized by 1-mm, disseminated, erythematous papules in a linear grouped arrangement secondary to koebnerization due to the patient scratching. It was first described in 1977 by Nakamura.1 Although it rarely is seen outside of China and Japan, there are well-established associations of flagellate dermatitis with bleomycin and shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) ingestion. One key clinical difference between the two causes is that postinflammatory hyperpigmentation changes usually are seen with bleomycin-induced flagellate dermatitis and typically are not present with shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis.2 Following ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, the median time of onset of presentation typically is 24 hours but ranges from 12 hours to 5 days. Most patients completely recover by 3 weeks, with or without treatment.3 Although the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is not clear, the most common theory is a toxic reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide isolated from shiitake mushrooms. However, type I and IV allergic hypersensitivities also have been supported by the time of onset, clearance, severe pruritus, benefit from steroids and antihistamines, and lack of grouped outbreaks in people exposed to shared meals containing shiitake mushrooms.3,4 Furthermore, there is a case of patch test–confirmed allergic contact dermatitis to shiitake mushrooms, demonstrating a 1+ reaction at 96 hours to the cap of a shiitake mushroom but a negative pin-prick test at 20 minutes, suggesting type IV hypersensitivity.5 An additional case revealed a positive skin-prick test with formation of a 4-mm wheal and subsequent pruritic papules and vesicles appearing 48 to 72 hours later at the prick site.6 Subsequent cases have been reported in association with consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms, but cases have been reported after consumption of fully cooked mushrooms, which does not support a toxin-mediated theory, as cooking the mushroom before consumption likely would denature or change the structure of the suspected toxin.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a rare eruption that occurs due to ingestion of a causative agent, usually an antibiotic, and is characterized by the presence of fever and disseminated, erythematous, pinpoint, sterile pustules on the skin and mucous membranes. It affects 1 to 5 persons per million per year, with more than 90% of cases attributed to drug ingestion.7 Spontaneous resolution can be expected within 15 days of its onset; however, there is a mortality rate of up to 5% that occurs most often in those with severe comorbidities or in older patients, for whom systemic corticosteroid therapy may be justified.7,8 A multinational case-control study conducted to evaluate the risk of AGEP associated with certain drugs revealed macrolides (namely pristinamycin); β-lactam antibiotics including penicillin, aminopenicillin, and cephalosporin; quinolones; hydroxychloroquine; anti-infective sulfonamides; terbinafine; and diltiazem as the most strongly associated culprits.9 Our patient’s flagellate dermatitis was unique in that it also showed histologic features of AGEP. The pathogenesis of drug-induced AGEP has been partially elucidated and involves activation of drug-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that migrate to the skin and participate in apoptotic signaling of keratinocytes and recruitment of neutrophils and eosinophils, which form subcorneal sterile pustules.7 In a study of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, 50% (7/14) of patients with AGEP had positive patch tests to the causative agent.10 This T cell–dependent response explains why the condition responds to systemic corticosteroids. Additionally, our case report of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP suggests that the pathogenesis of flagellate dermatitis may be a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction. The time of onset, lack of grouped outbreaks in those sharing shiitake mushroom–containing meals, severe pruritus, lack of cases demonstrating an anaphylactic or wheal and flare response, benefit of steroids, and a case with histologic features of AGEP all lend support to this theory.
We report a case of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis with histologic features of AGEP. The time course, histologic features of AGEP, absence of new medications, and resolution with discontinuation of shiitake mushrooms lends support of the hypothesis that the pathogenesis of shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis is similar to AGEP’s type IV hypersensitivity reaction. To further elucidate its pathogenesis, skin prick testing and patch testing with shiitake mushrooms in patients exhibiting shiitake mushroom–induced flagellate dermatitis may prove to be beneficial.
- Nakamura T. Toxicoderma caused by shiitake (Lentinus edodes)[in Japanese]. Jpn J Clin Dermatol. 1977;31:65-68.
- Chu EY, Anand D, Dawn A, et al. Shiitake dermatitis: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Cutis. 2013;91:287-290.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
- Nakamura T. Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:65-70.
- Curnow P, Tam M. Contact dermatitis to shiitake mushroom. Australas J Dermatol. 2003;44:155-157.
- Lippert U, Martin V, Schwertfeger C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:178-179.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:113-119.
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:989-996.
- Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Flechet ML, et al. Patch testing in severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;35:234-236.
- Nakamura T. Toxicoderma caused by shiitake (Lentinus edodes)[in Japanese]. Jpn J Clin Dermatol. 1977;31:65-68.
- Chu EY, Anand D, Dawn A, et al. Shiitake dermatitis: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Cutis. 2013;91:287-290.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
- Nakamura T. Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:65-70.
- Curnow P, Tam M. Contact dermatitis to shiitake mushroom. Australas J Dermatol. 2003;44:155-157.
- Lippert U, Martin V, Schwertfeger C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:178-179.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:113-119.
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:989-996.
- Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Flechet ML, et al. Patch testing in severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;35:234-236.
Practice Points
- Ingestion of shiitake mushrooms and bleomycin is associated with flagellate dermatitis.
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare condition associated with certain drug ingestion.
When children and teens with cancer get COVID-19
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 causes major interruption in global HIV progress
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New AHA guidance targets obesity-related hypertension
Whereas previous scientific statements from the American Heart Association have addressed how diet, physical activity, and weight control can help prevent and manage hypertension, a new AHA statement focuses on obesity-related hypertension.
The document, which was published online Sept. 20, 2021, in Hypertension, also identifies knowledge gaps and suggests future research directions.
“Given [that] obesity is a major risk factor for hypertension, and hypertension is one of the greatest (if not the greatest) attributable risk factors for most cardiovascular diseases, we thought it was important to focus on weight loss strategies and update what we know about the treatment options that are available to treat obesity hypertension,” writing group chair Michael E. Hall, MD, told this news organization.
“Medical and surgical strategies may help with long-term weight and blood pressure improvement, in addition to a heart-healthy diet and physical activity,” he noted in a press release from the AHA. “We often don’t consider medications or metabolic surgery until after there has been target organ damage, such as heart injury or having a stroke.”
However, by acting earlier, “we may be able to prevent these complications,” added Dr. Hall, associate division director for cardiovascular diseases at the University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson.
“This is not a call for greater use of one specific therapy,” he clarified. “However, we do know that more aggressive treatments including antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery are underutilized.”
According to Dr. Hall, “we treat the secondary problem [i.e., the hypertension or diabetes], but we are not treating the root cause [obesity] as aggressively.”
“Hopefully this statement will increase awareness that there are several [treatment] options [and] bring attention to this major health issue,” he said.
He added that the most important question, in his mind, is how best to tackle obesity among children and adolescents to lower their risk of hypertension and other associated complications.
The statement is aimed at both primary care providers and specialists.
Diet, physical activity help, but weight regain common
Losing 5%-10% of body weight can lead to a more than 5–mm Hg reduction in systolic blood pressure and a 4–mm Hg reduction in diastolic blood pressure, the statement notes. Losing 10 kg may lower systolic blood pressure by 5-20 mm Hg.
To manage weight, control hypertension, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, guidelines recommend the Mediterranean diet or the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which both emphasize fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds, with moderate intake of fish, seafood, poultry, and dairy, and low intake of red and processed meats and sweets. The Mediterranean diet also includes olive oil and moderate consumption of (mainly red) wine.
The effect of intermittent fasting on blood pressure control is not clear, the statement noted.
It added that typically 150-225 minutes and 225-420 minutes of physical activity per week can produce weight loss of 2-3 kg or 5-7.5 kg respectively, and 200-300 minutes of physical activity per week is needed to maintain this weight loss.
“Successful weight-loss maintenance over years therefore typically requires high levels of [physical activity] and limited sedentary time, frequent weight monitoring, and high levels of dietary restraint,” and weight regain is common, the authors summarize.
Other options to address obesity, hypertension
Weight-loss pharmacotherapies and metabolic surgery are other options to treat obesity and lower hypertension.
The statement reports that four drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for long-term weight loss: Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave), and liraglutide 3.0 mg (Saxenda). On June 4, the FDA approved a fifth drug, semaglutide (Wegovy).
The long-term effects of antiobesity medications on blood pressure are mixed.
However, “prescription rates for these drugs remain low, likely because of limited insurance coverage and low levels of clinical proficiency with treating obesity,” Dr. Hall and colleagues write.
Metabolic surgery could be a weight loss option for certain patients, and it is associated with blood pressure lowering.
In the 100-patient Gastric Bypass to Treat Obese Patients With Steady Hypertension (GATEWAY) trial, published in Circulation in 2018, more patients in the Roux-en-Y gastric-bypass group than the control group (84% vs. 13%) met the primary outcome of a 30% or greater reduction in the number of blood pressure-lowering medications at 12 months while maintaining an office blood pressure less than 140/90 mm Hg.
Unanswered questions, future research directions
In 2015-2016, an estimated 18.5% of U.S. children and adolescents aged 2-19 years had obesity, the statement notes. Children with obesity have a twofold increased risk of incident hypertension, and those with severe obesity have an over fourfold increased risk of this outcome, compared with children who have a healthy weight.
Dr. Hall and colleagues emphasized that, “as the prevalence of obesity continues to increase, hypertension and associated cardiorenal diseases will also increase unless more effective strategies to prevent and treat obesity are developed.”
They identified 17 unanswered questions (knowledge gaps) that can guide the direction of future research. These include:
- What new strategies and science-based guidelines are needed to curb the growing evidence of childhood obesity?
- Does intentional weight loss with pharmacotherapy or metabolic surgery in childhood and early adulthood prevent hypertension and subsequent target organ damage in later life?
- What is the optimal amount of time that clinicians should allow before recommending more aggressive weight management strategies (that is, antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery) or hypertension strategies beyond lifestyle changes?
“To me,” Dr. Hall said, “addressing childhood obesity hypertension and determining optimal timing of antiobesity therapies are the most important [issues]. Certainly, these therapies (i.e., diets, medications, surgeries) have some risks, but we don’t have a clear understanding if their benefits outweigh these risks in younger obese people or whether initiating these therapies before the onset of target organ damage such as heart failure” outweigh the risks.
Dr. Hall has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whereas previous scientific statements from the American Heart Association have addressed how diet, physical activity, and weight control can help prevent and manage hypertension, a new AHA statement focuses on obesity-related hypertension.
The document, which was published online Sept. 20, 2021, in Hypertension, also identifies knowledge gaps and suggests future research directions.
“Given [that] obesity is a major risk factor for hypertension, and hypertension is one of the greatest (if not the greatest) attributable risk factors for most cardiovascular diseases, we thought it was important to focus on weight loss strategies and update what we know about the treatment options that are available to treat obesity hypertension,” writing group chair Michael E. Hall, MD, told this news organization.
“Medical and surgical strategies may help with long-term weight and blood pressure improvement, in addition to a heart-healthy diet and physical activity,” he noted in a press release from the AHA. “We often don’t consider medications or metabolic surgery until after there has been target organ damage, such as heart injury or having a stroke.”
However, by acting earlier, “we may be able to prevent these complications,” added Dr. Hall, associate division director for cardiovascular diseases at the University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson.
“This is not a call for greater use of one specific therapy,” he clarified. “However, we do know that more aggressive treatments including antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery are underutilized.”
According to Dr. Hall, “we treat the secondary problem [i.e., the hypertension or diabetes], but we are not treating the root cause [obesity] as aggressively.”
“Hopefully this statement will increase awareness that there are several [treatment] options [and] bring attention to this major health issue,” he said.
He added that the most important question, in his mind, is how best to tackle obesity among children and adolescents to lower their risk of hypertension and other associated complications.
The statement is aimed at both primary care providers and specialists.
Diet, physical activity help, but weight regain common
Losing 5%-10% of body weight can lead to a more than 5–mm Hg reduction in systolic blood pressure and a 4–mm Hg reduction in diastolic blood pressure, the statement notes. Losing 10 kg may lower systolic blood pressure by 5-20 mm Hg.
To manage weight, control hypertension, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, guidelines recommend the Mediterranean diet or the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which both emphasize fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds, with moderate intake of fish, seafood, poultry, and dairy, and low intake of red and processed meats and sweets. The Mediterranean diet also includes olive oil and moderate consumption of (mainly red) wine.
The effect of intermittent fasting on blood pressure control is not clear, the statement noted.
It added that typically 150-225 minutes and 225-420 minutes of physical activity per week can produce weight loss of 2-3 kg or 5-7.5 kg respectively, and 200-300 minutes of physical activity per week is needed to maintain this weight loss.
“Successful weight-loss maintenance over years therefore typically requires high levels of [physical activity] and limited sedentary time, frequent weight monitoring, and high levels of dietary restraint,” and weight regain is common, the authors summarize.
Other options to address obesity, hypertension
Weight-loss pharmacotherapies and metabolic surgery are other options to treat obesity and lower hypertension.
The statement reports that four drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for long-term weight loss: Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave), and liraglutide 3.0 mg (Saxenda). On June 4, the FDA approved a fifth drug, semaglutide (Wegovy).
The long-term effects of antiobesity medications on blood pressure are mixed.
However, “prescription rates for these drugs remain low, likely because of limited insurance coverage and low levels of clinical proficiency with treating obesity,” Dr. Hall and colleagues write.
Metabolic surgery could be a weight loss option for certain patients, and it is associated with blood pressure lowering.
In the 100-patient Gastric Bypass to Treat Obese Patients With Steady Hypertension (GATEWAY) trial, published in Circulation in 2018, more patients in the Roux-en-Y gastric-bypass group than the control group (84% vs. 13%) met the primary outcome of a 30% or greater reduction in the number of blood pressure-lowering medications at 12 months while maintaining an office blood pressure less than 140/90 mm Hg.
Unanswered questions, future research directions
In 2015-2016, an estimated 18.5% of U.S. children and adolescents aged 2-19 years had obesity, the statement notes. Children with obesity have a twofold increased risk of incident hypertension, and those with severe obesity have an over fourfold increased risk of this outcome, compared with children who have a healthy weight.
Dr. Hall and colleagues emphasized that, “as the prevalence of obesity continues to increase, hypertension and associated cardiorenal diseases will also increase unless more effective strategies to prevent and treat obesity are developed.”
They identified 17 unanswered questions (knowledge gaps) that can guide the direction of future research. These include:
- What new strategies and science-based guidelines are needed to curb the growing evidence of childhood obesity?
- Does intentional weight loss with pharmacotherapy or metabolic surgery in childhood and early adulthood prevent hypertension and subsequent target organ damage in later life?
- What is the optimal amount of time that clinicians should allow before recommending more aggressive weight management strategies (that is, antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery) or hypertension strategies beyond lifestyle changes?
“To me,” Dr. Hall said, “addressing childhood obesity hypertension and determining optimal timing of antiobesity therapies are the most important [issues]. Certainly, these therapies (i.e., diets, medications, surgeries) have some risks, but we don’t have a clear understanding if their benefits outweigh these risks in younger obese people or whether initiating these therapies before the onset of target organ damage such as heart failure” outweigh the risks.
Dr. Hall has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whereas previous scientific statements from the American Heart Association have addressed how diet, physical activity, and weight control can help prevent and manage hypertension, a new AHA statement focuses on obesity-related hypertension.
The document, which was published online Sept. 20, 2021, in Hypertension, also identifies knowledge gaps and suggests future research directions.
“Given [that] obesity is a major risk factor for hypertension, and hypertension is one of the greatest (if not the greatest) attributable risk factors for most cardiovascular diseases, we thought it was important to focus on weight loss strategies and update what we know about the treatment options that are available to treat obesity hypertension,” writing group chair Michael E. Hall, MD, told this news organization.
“Medical and surgical strategies may help with long-term weight and blood pressure improvement, in addition to a heart-healthy diet and physical activity,” he noted in a press release from the AHA. “We often don’t consider medications or metabolic surgery until after there has been target organ damage, such as heart injury or having a stroke.”
However, by acting earlier, “we may be able to prevent these complications,” added Dr. Hall, associate division director for cardiovascular diseases at the University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson.
“This is not a call for greater use of one specific therapy,” he clarified. “However, we do know that more aggressive treatments including antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery are underutilized.”
According to Dr. Hall, “we treat the secondary problem [i.e., the hypertension or diabetes], but we are not treating the root cause [obesity] as aggressively.”
“Hopefully this statement will increase awareness that there are several [treatment] options [and] bring attention to this major health issue,” he said.
He added that the most important question, in his mind, is how best to tackle obesity among children and adolescents to lower their risk of hypertension and other associated complications.
The statement is aimed at both primary care providers and specialists.
Diet, physical activity help, but weight regain common
Losing 5%-10% of body weight can lead to a more than 5–mm Hg reduction in systolic blood pressure and a 4–mm Hg reduction in diastolic blood pressure, the statement notes. Losing 10 kg may lower systolic blood pressure by 5-20 mm Hg.
To manage weight, control hypertension, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, guidelines recommend the Mediterranean diet or the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which both emphasize fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds, with moderate intake of fish, seafood, poultry, and dairy, and low intake of red and processed meats and sweets. The Mediterranean diet also includes olive oil and moderate consumption of (mainly red) wine.
The effect of intermittent fasting on blood pressure control is not clear, the statement noted.
It added that typically 150-225 minutes and 225-420 minutes of physical activity per week can produce weight loss of 2-3 kg or 5-7.5 kg respectively, and 200-300 minutes of physical activity per week is needed to maintain this weight loss.
“Successful weight-loss maintenance over years therefore typically requires high levels of [physical activity] and limited sedentary time, frequent weight monitoring, and high levels of dietary restraint,” and weight regain is common, the authors summarize.
Other options to address obesity, hypertension
Weight-loss pharmacotherapies and metabolic surgery are other options to treat obesity and lower hypertension.
The statement reports that four drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for long-term weight loss: Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave), and liraglutide 3.0 mg (Saxenda). On June 4, the FDA approved a fifth drug, semaglutide (Wegovy).
The long-term effects of antiobesity medications on blood pressure are mixed.
However, “prescription rates for these drugs remain low, likely because of limited insurance coverage and low levels of clinical proficiency with treating obesity,” Dr. Hall and colleagues write.
Metabolic surgery could be a weight loss option for certain patients, and it is associated with blood pressure lowering.
In the 100-patient Gastric Bypass to Treat Obese Patients With Steady Hypertension (GATEWAY) trial, published in Circulation in 2018, more patients in the Roux-en-Y gastric-bypass group than the control group (84% vs. 13%) met the primary outcome of a 30% or greater reduction in the number of blood pressure-lowering medications at 12 months while maintaining an office blood pressure less than 140/90 mm Hg.
Unanswered questions, future research directions
In 2015-2016, an estimated 18.5% of U.S. children and adolescents aged 2-19 years had obesity, the statement notes. Children with obesity have a twofold increased risk of incident hypertension, and those with severe obesity have an over fourfold increased risk of this outcome, compared with children who have a healthy weight.
Dr. Hall and colleagues emphasized that, “as the prevalence of obesity continues to increase, hypertension and associated cardiorenal diseases will also increase unless more effective strategies to prevent and treat obesity are developed.”
They identified 17 unanswered questions (knowledge gaps) that can guide the direction of future research. These include:
- What new strategies and science-based guidelines are needed to curb the growing evidence of childhood obesity?
- Does intentional weight loss with pharmacotherapy or metabolic surgery in childhood and early adulthood prevent hypertension and subsequent target organ damage in later life?
- What is the optimal amount of time that clinicians should allow before recommending more aggressive weight management strategies (that is, antiobesity medications or metabolic surgery) or hypertension strategies beyond lifestyle changes?
“To me,” Dr. Hall said, “addressing childhood obesity hypertension and determining optimal timing of antiobesity therapies are the most important [issues]. Certainly, these therapies (i.e., diets, medications, surgeries) have some risks, but we don’t have a clear understanding if their benefits outweigh these risks in younger obese people or whether initiating these therapies before the onset of target organ damage such as heart failure” outweigh the risks.
Dr. Hall has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should hospitalists use albumin to treat non-SBP infections in patients with cirrhosis?
Caution is advised in patients at risk of pulmonary edema
Case
A 56 year-old male with hypertension, alcohol use disorder, stage II chronic kidney disease, and biopsy-proven cirrhosis presents with fever and chills, pyuria, flank pain, and an acute kidney injury concerning for pyelonephritis. Is there a benefit in treating with albumin in addition to guideline-based antibiotics?
Brief overview of the issue
Albumin is a negatively charged human protein produced by the liver. Albumin comprises 50% of plasma protein and over 75% of plasma oncotic pressure.1 It was first used at Walter Reed Hospital in 1940 and subsequently for burn injuries after the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941.2
Albumin serves several important physiologic functions including maintaining oncotic pressure, endothelial support, antioxidation, nitrogen oxide scavenging, and buffering and transport of solutes and drugs, including antibiotics. In cirrhosis, albumin is diluted due to sodium and water retention. There is increased redistribution, decreased synthesis by the liver, and impaired albumin molecule binding.3
For patients with liver disease, per the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), albumin should be administered to prevent post paracentesis circulatory dysfunction after large volume paracentesis, to prevent renal failure and mortality in the setting of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), and in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) type I to potentially improve mortality.4,5 Beyond these three guideline-based indications, other uses for albumin for patients with liver disease have been proposed, including treatment of hyponatremia, posttransplant fluid resuscitation, diuretic unresponsive ascites, and long-term management of cirrhosis. There has yet to be strong evidence supporting these additional indications. However, given the known benefits of albumin in patients with SBP, there has been recent research into treatment of non-SBP infections, including urinary tract infections.
Overview of the data
There have been three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding albumin administration for the treatment of non-SBP infections for hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. All three trials randomized patients to a treatment arm of albumin and antibiotics versus a control group of antibiotics alone. The treatment protocol prescribed 20% albumin with 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. The most common infections studied were pneumonia and urinary tract infection. These RCTs found that albumin administration was associated with improved renal and/or circulatory function, but not with a reduction in mortality.

First, there was a single center RCT by Guevara et al. in 2012 of 110 patients with cirrhosis and infection based on SIRS criteria.6 The primary outcome was 90-day survival with secondary outcomes of renal failure development, renal function at days 3,7 and 14, and circulatory function measured by plasma renin, aldosterone, and norepinephrine. Renal function and circulatory function improved in the albumin group, but not mortality. In a multivariable regression analysis, albumin was statistically predictive of survival (hazard ratio of 0.294).
Second, there was a multicenter RCT by Thévenot et al. in 2015 of 193 patients.7 The primary outcome was 90-day renal failure and the secondary outcome was 90-day survival. Renal failure was chosen as the primary endpoint because of its association with survival in this patient population. The treatment group had delayed onset of renal failure, but no difference in the development of 90-day renal failure or 90-day mortality rate. Notably, eight patients (8.3%) in the albumin group developed pulmonary edema with two deaths. This led the oversight committee to prematurely terminate the study.
Third and most recently, there was a multicenter RCT by Fernández et al. in 2019 of 118 patients.8 The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality, with secondary outcomes of circulatory dysfunction measured by plasma renin concentration, systemic inflammation measured by plasma IL-6 and biomarkers, complications including acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and nosocomial bacterial infections, and 90-day mortality. Between the albumin and control group, there were no differences in in-hospital mortality (13.1% vs. 10.5%, P > .66), inflammation, circulatory dysfunction, or liver severity. However, a significantly higher proportion of patients in the albumin group had resolution of their ACLF (82.3% vs. 33.3%, P = .003) and a lower proportion developed nosocomial infections (6.6% vs. 24.6%, P = .007). A major weakness of this study was that patients in the albumin group had a higher combined rate of ACLF and kidney dysfunction (44.3% vs. 24.6%, P = .02).
Beyond these three randomized controlled trials, there was a study on the long-term administration of albumin for patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Patients who received twice weekly albumin infusions had a lower 2-year mortality rate and a reduction in the incidence of both SBP and non-SBP infections.9 Another long-term study of albumin administration found similar results with greater 18-month survival and fewer non-SBP infections.10 A trial looking at inflammation in patients without bacterial infections and in biobanked samples from cirrhotic patients with bacterial infections found that treatment with albumin reduced systemic inflammation.11
In summary, the three RCTs looked at comparable patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection and all underwent similar treatment protocols with 20% albumin dosed at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. All studies evaluated mortality in either the primary or secondary outcome, and none found significant differences in mortality between treatment and control groups. Each study also evaluated and found improvement in renal and/or circulatory function. Fernández et al. also found increased resolution of ACLF, fewer nosocomial infections, and reduction in some inflammatory markers. However, all studies had relatively small sample sizes that were underpowered to detect mortality differences. Furthermore, randomization did not lead to well-matched groups, with the treatment group patients in the Fernández study having higher rates of ACLF and kidney dysfunction.
The data suggest that albumin may be beneficial in improving renal and circulatory function. In select patients with ACLF and elevated serum creatinine, albumin treatment may be considered. There has been discussion about the use of albumin preferentially in patients with subdiaphragmatic bacterial infections, most related to increased risk of renal failure such as biliary and urinary tract infections.12 The authors of these studies also note that albumin may be more beneficial in patients with higher baseline creatinine. Caution is warranted for patients with impaired cardiac function or poor respiratory status given the possibility of pulmonary edema. Finally, the high cost of albumin in many medical centers is a major limitation of this treatment approach.
Application of data to our patient
Our patient has cirrhosis and is acutely presenting with pyelonephritis and acute kidney injury. He has no baseline pulmonary disease or oxygen requirement. His recent transthoracic echocardiogram is reviewed and he has no evidence of cardiac disease.
Because he has an elevated creatinine, an infectious process associated with progressive renal failure, and is not at an elevated baseline risk of developing pulmonary edema, albumin would be reasonable to administer at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3 of hospitalization.
Bottom line
In certain patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, the use of albumin to help improve renal and circulatory function is reasonable. There is no evidence that albumin will improve mortality and caution is warranted for patients at risk for pulmonary edema.
Dr. Rambachan is an academic hospital medicine fellow at the University of California, San Francisco.
References
1. Caironi P and Gattinoni L. The clinical use of albumin: the point of view of a specialist in intensive care. Blood Transfus. 2009;7(4):259-67. doi: 10.2450/2009.0002-09.
2. Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
3. Walayat S et al. Role of albumin in cirrhosis: from a hospitalist’s perspective. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2017;7(1):8-14. 2017 Mar 31. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2017.1302704.
4. Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
5. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis [published correction appears in J Hepatol. 2018 Nov;69(5):1207]. J Hepatol. 2018 Aug;69(2):406-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024.
6. Guevara M et al. Albumin for bacterial infections other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. A randomized, controlled study. J Hepatol. 2012 Oct;57(4):759-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.06.013.
7. Thévenot T et al. Effect of albumin in cirrhotic patients with infection other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A randomized trial. J Hepatol. 2015 Apr;62(4):822-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.017.
8. Fernández J et al. Efficacy of albumin treatment for patients with cirrhosis and infections unrelated to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Apr;18(4):963-73.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.c gh.2019.07.055.
9. Di Pascoli M et al. Long-term administration of human albumin improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Liver Int. 2019 Jan;39(1):98-105. doi: 10.1111/liv.13968.
10. Caraceni P et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2018 Aug 4;392(10145):386]. Lancet. 2018 June;391(10138):2417-29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7.
11. Fernández J et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019 July;157(1):149-62. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021.
12. Fasolato S et al. Renal failure and bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis: Epidemiology and clinical features. Hepatology. 2007;45(1):223-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.21443.
Key points
- In patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, and for large volume paracentesis, albumin improves outcomes and is recommended by guidelines.
- In patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, there is some evidence that albumin may improve renal and circulatory function.
- Clinicians should be cautious about albumin use in patients at an elevated risk for development of pulmonary edema.
Quiz
Which of the following is not a guideline-recommended use of albumin for patients with cirrhosis?
A. Treatment of type 1 hepatorenal syndrome
B. Treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
C. To correct plasma albumin < 2.5 g/dL in nontransplant patients
D. Post large-volume paracentesis
The answer is C. Per the EASL and AASLD, A,B, and D are recommended. There is not strong evidence to support administering albumin to correct low plasma albumin.
Additional reading
- Bernardi M et al. Albumin in decompensated cirrhosis: new concepts and perspectives. Gut. 2020 June;69(6):1127-38. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318843.
- Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
- Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019 June;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
Caution is advised in patients at risk of pulmonary edema
Caution is advised in patients at risk of pulmonary edema
Case
A 56 year-old male with hypertension, alcohol use disorder, stage II chronic kidney disease, and biopsy-proven cirrhosis presents with fever and chills, pyuria, flank pain, and an acute kidney injury concerning for pyelonephritis. Is there a benefit in treating with albumin in addition to guideline-based antibiotics?
Brief overview of the issue
Albumin is a negatively charged human protein produced by the liver. Albumin comprises 50% of plasma protein and over 75% of plasma oncotic pressure.1 It was first used at Walter Reed Hospital in 1940 and subsequently for burn injuries after the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941.2
Albumin serves several important physiologic functions including maintaining oncotic pressure, endothelial support, antioxidation, nitrogen oxide scavenging, and buffering and transport of solutes and drugs, including antibiotics. In cirrhosis, albumin is diluted due to sodium and water retention. There is increased redistribution, decreased synthesis by the liver, and impaired albumin molecule binding.3
For patients with liver disease, per the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), albumin should be administered to prevent post paracentesis circulatory dysfunction after large volume paracentesis, to prevent renal failure and mortality in the setting of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), and in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) type I to potentially improve mortality.4,5 Beyond these three guideline-based indications, other uses for albumin for patients with liver disease have been proposed, including treatment of hyponatremia, posttransplant fluid resuscitation, diuretic unresponsive ascites, and long-term management of cirrhosis. There has yet to be strong evidence supporting these additional indications. However, given the known benefits of albumin in patients with SBP, there has been recent research into treatment of non-SBP infections, including urinary tract infections.
Overview of the data
There have been three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding albumin administration for the treatment of non-SBP infections for hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. All three trials randomized patients to a treatment arm of albumin and antibiotics versus a control group of antibiotics alone. The treatment protocol prescribed 20% albumin with 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. The most common infections studied were pneumonia and urinary tract infection. These RCTs found that albumin administration was associated with improved renal and/or circulatory function, but not with a reduction in mortality.

First, there was a single center RCT by Guevara et al. in 2012 of 110 patients with cirrhosis and infection based on SIRS criteria.6 The primary outcome was 90-day survival with secondary outcomes of renal failure development, renal function at days 3,7 and 14, and circulatory function measured by plasma renin, aldosterone, and norepinephrine. Renal function and circulatory function improved in the albumin group, but not mortality. In a multivariable regression analysis, albumin was statistically predictive of survival (hazard ratio of 0.294).
Second, there was a multicenter RCT by Thévenot et al. in 2015 of 193 patients.7 The primary outcome was 90-day renal failure and the secondary outcome was 90-day survival. Renal failure was chosen as the primary endpoint because of its association with survival in this patient population. The treatment group had delayed onset of renal failure, but no difference in the development of 90-day renal failure or 90-day mortality rate. Notably, eight patients (8.3%) in the albumin group developed pulmonary edema with two deaths. This led the oversight committee to prematurely terminate the study.
Third and most recently, there was a multicenter RCT by Fernández et al. in 2019 of 118 patients.8 The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality, with secondary outcomes of circulatory dysfunction measured by plasma renin concentration, systemic inflammation measured by plasma IL-6 and biomarkers, complications including acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and nosocomial bacterial infections, and 90-day mortality. Between the albumin and control group, there were no differences in in-hospital mortality (13.1% vs. 10.5%, P > .66), inflammation, circulatory dysfunction, or liver severity. However, a significantly higher proportion of patients in the albumin group had resolution of their ACLF (82.3% vs. 33.3%, P = .003) and a lower proportion developed nosocomial infections (6.6% vs. 24.6%, P = .007). A major weakness of this study was that patients in the albumin group had a higher combined rate of ACLF and kidney dysfunction (44.3% vs. 24.6%, P = .02).
Beyond these three randomized controlled trials, there was a study on the long-term administration of albumin for patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Patients who received twice weekly albumin infusions had a lower 2-year mortality rate and a reduction in the incidence of both SBP and non-SBP infections.9 Another long-term study of albumin administration found similar results with greater 18-month survival and fewer non-SBP infections.10 A trial looking at inflammation in patients without bacterial infections and in biobanked samples from cirrhotic patients with bacterial infections found that treatment with albumin reduced systemic inflammation.11
In summary, the three RCTs looked at comparable patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection and all underwent similar treatment protocols with 20% albumin dosed at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. All studies evaluated mortality in either the primary or secondary outcome, and none found significant differences in mortality between treatment and control groups. Each study also evaluated and found improvement in renal and/or circulatory function. Fernández et al. also found increased resolution of ACLF, fewer nosocomial infections, and reduction in some inflammatory markers. However, all studies had relatively small sample sizes that were underpowered to detect mortality differences. Furthermore, randomization did not lead to well-matched groups, with the treatment group patients in the Fernández study having higher rates of ACLF and kidney dysfunction.
The data suggest that albumin may be beneficial in improving renal and circulatory function. In select patients with ACLF and elevated serum creatinine, albumin treatment may be considered. There has been discussion about the use of albumin preferentially in patients with subdiaphragmatic bacterial infections, most related to increased risk of renal failure such as biliary and urinary tract infections.12 The authors of these studies also note that albumin may be more beneficial in patients with higher baseline creatinine. Caution is warranted for patients with impaired cardiac function or poor respiratory status given the possibility of pulmonary edema. Finally, the high cost of albumin in many medical centers is a major limitation of this treatment approach.
Application of data to our patient
Our patient has cirrhosis and is acutely presenting with pyelonephritis and acute kidney injury. He has no baseline pulmonary disease or oxygen requirement. His recent transthoracic echocardiogram is reviewed and he has no evidence of cardiac disease.
Because he has an elevated creatinine, an infectious process associated with progressive renal failure, and is not at an elevated baseline risk of developing pulmonary edema, albumin would be reasonable to administer at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3 of hospitalization.
Bottom line
In certain patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, the use of albumin to help improve renal and circulatory function is reasonable. There is no evidence that albumin will improve mortality and caution is warranted for patients at risk for pulmonary edema.
Dr. Rambachan is an academic hospital medicine fellow at the University of California, San Francisco.
References
1. Caironi P and Gattinoni L. The clinical use of albumin: the point of view of a specialist in intensive care. Blood Transfus. 2009;7(4):259-67. doi: 10.2450/2009.0002-09.
2. Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
3. Walayat S et al. Role of albumin in cirrhosis: from a hospitalist’s perspective. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2017;7(1):8-14. 2017 Mar 31. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2017.1302704.
4. Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
5. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis [published correction appears in J Hepatol. 2018 Nov;69(5):1207]. J Hepatol. 2018 Aug;69(2):406-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024.
6. Guevara M et al. Albumin for bacterial infections other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. A randomized, controlled study. J Hepatol. 2012 Oct;57(4):759-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.06.013.
7. Thévenot T et al. Effect of albumin in cirrhotic patients with infection other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A randomized trial. J Hepatol. 2015 Apr;62(4):822-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.017.
8. Fernández J et al. Efficacy of albumin treatment for patients with cirrhosis and infections unrelated to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Apr;18(4):963-73.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.c gh.2019.07.055.
9. Di Pascoli M et al. Long-term administration of human albumin improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Liver Int. 2019 Jan;39(1):98-105. doi: 10.1111/liv.13968.
10. Caraceni P et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2018 Aug 4;392(10145):386]. Lancet. 2018 June;391(10138):2417-29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7.
11. Fernández J et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019 July;157(1):149-62. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021.
12. Fasolato S et al. Renal failure and bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis: Epidemiology and clinical features. Hepatology. 2007;45(1):223-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.21443.
Key points
- In patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, and for large volume paracentesis, albumin improves outcomes and is recommended by guidelines.
- In patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, there is some evidence that albumin may improve renal and circulatory function.
- Clinicians should be cautious about albumin use in patients at an elevated risk for development of pulmonary edema.
Quiz
Which of the following is not a guideline-recommended use of albumin for patients with cirrhosis?
A. Treatment of type 1 hepatorenal syndrome
B. Treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
C. To correct plasma albumin < 2.5 g/dL in nontransplant patients
D. Post large-volume paracentesis
The answer is C. Per the EASL and AASLD, A,B, and D are recommended. There is not strong evidence to support administering albumin to correct low plasma albumin.
Additional reading
- Bernardi M et al. Albumin in decompensated cirrhosis: new concepts and perspectives. Gut. 2020 June;69(6):1127-38. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318843.
- Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
- Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019 June;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
Case
A 56 year-old male with hypertension, alcohol use disorder, stage II chronic kidney disease, and biopsy-proven cirrhosis presents with fever and chills, pyuria, flank pain, and an acute kidney injury concerning for pyelonephritis. Is there a benefit in treating with albumin in addition to guideline-based antibiotics?
Brief overview of the issue
Albumin is a negatively charged human protein produced by the liver. Albumin comprises 50% of plasma protein and over 75% of plasma oncotic pressure.1 It was first used at Walter Reed Hospital in 1940 and subsequently for burn injuries after the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941.2
Albumin serves several important physiologic functions including maintaining oncotic pressure, endothelial support, antioxidation, nitrogen oxide scavenging, and buffering and transport of solutes and drugs, including antibiotics. In cirrhosis, albumin is diluted due to sodium and water retention. There is increased redistribution, decreased synthesis by the liver, and impaired albumin molecule binding.3
For patients with liver disease, per the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), albumin should be administered to prevent post paracentesis circulatory dysfunction after large volume paracentesis, to prevent renal failure and mortality in the setting of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), and in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) type I to potentially improve mortality.4,5 Beyond these three guideline-based indications, other uses for albumin for patients with liver disease have been proposed, including treatment of hyponatremia, posttransplant fluid resuscitation, diuretic unresponsive ascites, and long-term management of cirrhosis. There has yet to be strong evidence supporting these additional indications. However, given the known benefits of albumin in patients with SBP, there has been recent research into treatment of non-SBP infections, including urinary tract infections.
Overview of the data
There have been three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding albumin administration for the treatment of non-SBP infections for hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. All three trials randomized patients to a treatment arm of albumin and antibiotics versus a control group of antibiotics alone. The treatment protocol prescribed 20% albumin with 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. The most common infections studied were pneumonia and urinary tract infection. These RCTs found that albumin administration was associated with improved renal and/or circulatory function, but not with a reduction in mortality.

First, there was a single center RCT by Guevara et al. in 2012 of 110 patients with cirrhosis and infection based on SIRS criteria.6 The primary outcome was 90-day survival with secondary outcomes of renal failure development, renal function at days 3,7 and 14, and circulatory function measured by plasma renin, aldosterone, and norepinephrine. Renal function and circulatory function improved in the albumin group, but not mortality. In a multivariable regression analysis, albumin was statistically predictive of survival (hazard ratio of 0.294).
Second, there was a multicenter RCT by Thévenot et al. in 2015 of 193 patients.7 The primary outcome was 90-day renal failure and the secondary outcome was 90-day survival. Renal failure was chosen as the primary endpoint because of its association with survival in this patient population. The treatment group had delayed onset of renal failure, but no difference in the development of 90-day renal failure or 90-day mortality rate. Notably, eight patients (8.3%) in the albumin group developed pulmonary edema with two deaths. This led the oversight committee to prematurely terminate the study.
Third and most recently, there was a multicenter RCT by Fernández et al. in 2019 of 118 patients.8 The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality, with secondary outcomes of circulatory dysfunction measured by plasma renin concentration, systemic inflammation measured by plasma IL-6 and biomarkers, complications including acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and nosocomial bacterial infections, and 90-day mortality. Between the albumin and control group, there were no differences in in-hospital mortality (13.1% vs. 10.5%, P > .66), inflammation, circulatory dysfunction, or liver severity. However, a significantly higher proportion of patients in the albumin group had resolution of their ACLF (82.3% vs. 33.3%, P = .003) and a lower proportion developed nosocomial infections (6.6% vs. 24.6%, P = .007). A major weakness of this study was that patients in the albumin group had a higher combined rate of ACLF and kidney dysfunction (44.3% vs. 24.6%, P = .02).
Beyond these three randomized controlled trials, there was a study on the long-term administration of albumin for patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Patients who received twice weekly albumin infusions had a lower 2-year mortality rate and a reduction in the incidence of both SBP and non-SBP infections.9 Another long-term study of albumin administration found similar results with greater 18-month survival and fewer non-SBP infections.10 A trial looking at inflammation in patients without bacterial infections and in biobanked samples from cirrhotic patients with bacterial infections found that treatment with albumin reduced systemic inflammation.11
In summary, the three RCTs looked at comparable patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection and all underwent similar treatment protocols with 20% albumin dosed at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3. All studies evaluated mortality in either the primary or secondary outcome, and none found significant differences in mortality between treatment and control groups. Each study also evaluated and found improvement in renal and/or circulatory function. Fernández et al. also found increased resolution of ACLF, fewer nosocomial infections, and reduction in some inflammatory markers. However, all studies had relatively small sample sizes that were underpowered to detect mortality differences. Furthermore, randomization did not lead to well-matched groups, with the treatment group patients in the Fernández study having higher rates of ACLF and kidney dysfunction.
The data suggest that albumin may be beneficial in improving renal and circulatory function. In select patients with ACLF and elevated serum creatinine, albumin treatment may be considered. There has been discussion about the use of albumin preferentially in patients with subdiaphragmatic bacterial infections, most related to increased risk of renal failure such as biliary and urinary tract infections.12 The authors of these studies also note that albumin may be more beneficial in patients with higher baseline creatinine. Caution is warranted for patients with impaired cardiac function or poor respiratory status given the possibility of pulmonary edema. Finally, the high cost of albumin in many medical centers is a major limitation of this treatment approach.
Application of data to our patient
Our patient has cirrhosis and is acutely presenting with pyelonephritis and acute kidney injury. He has no baseline pulmonary disease or oxygen requirement. His recent transthoracic echocardiogram is reviewed and he has no evidence of cardiac disease.
Because he has an elevated creatinine, an infectious process associated with progressive renal failure, and is not at an elevated baseline risk of developing pulmonary edema, albumin would be reasonable to administer at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1.0 g/kg on day 3 of hospitalization.
Bottom line
In certain patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, the use of albumin to help improve renal and circulatory function is reasonable. There is no evidence that albumin will improve mortality and caution is warranted for patients at risk for pulmonary edema.
Dr. Rambachan is an academic hospital medicine fellow at the University of California, San Francisco.
References
1. Caironi P and Gattinoni L. The clinical use of albumin: the point of view of a specialist in intensive care. Blood Transfus. 2009;7(4):259-67. doi: 10.2450/2009.0002-09.
2. Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
3. Walayat S et al. Role of albumin in cirrhosis: from a hospitalist’s perspective. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2017;7(1):8-14. 2017 Mar 31. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2017.1302704.
4. Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
5. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis [published correction appears in J Hepatol. 2018 Nov;69(5):1207]. J Hepatol. 2018 Aug;69(2):406-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024.
6. Guevara M et al. Albumin for bacterial infections other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. A randomized, controlled study. J Hepatol. 2012 Oct;57(4):759-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.06.013.
7. Thévenot T et al. Effect of albumin in cirrhotic patients with infection other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A randomized trial. J Hepatol. 2015 Apr;62(4):822-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.017.
8. Fernández J et al. Efficacy of albumin treatment for patients with cirrhosis and infections unrelated to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Apr;18(4):963-73.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.c gh.2019.07.055.
9. Di Pascoli M et al. Long-term administration of human albumin improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Liver Int. 2019 Jan;39(1):98-105. doi: 10.1111/liv.13968.
10. Caraceni P et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2018 Aug 4;392(10145):386]. Lancet. 2018 June;391(10138):2417-29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7.
11. Fernández J et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019 July;157(1):149-62. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021.
12. Fasolato S et al. Renal failure and bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis: Epidemiology and clinical features. Hepatology. 2007;45(1):223-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.21443.
Key points
- In patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, and for large volume paracentesis, albumin improves outcomes and is recommended by guidelines.
- In patients with cirrhosis and a non-SBP infection, there is some evidence that albumin may improve renal and circulatory function.
- Clinicians should be cautious about albumin use in patients at an elevated risk for development of pulmonary edema.
Quiz
Which of the following is not a guideline-recommended use of albumin for patients with cirrhosis?
A. Treatment of type 1 hepatorenal syndrome
B. Treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
C. To correct plasma albumin < 2.5 g/dL in nontransplant patients
D. Post large-volume paracentesis
The answer is C. Per the EASL and AASLD, A,B, and D are recommended. There is not strong evidence to support administering albumin to correct low plasma albumin.
Additional reading
- Bernardi M et al. Albumin in decompensated cirrhosis: new concepts and perspectives. Gut. 2020 June;69(6):1127-38. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318843.
- Runyon BA; AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline [for the] management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1651-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359.
- Paine CH et al. Albumin in cirrhosis: More than a colloid. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019 June;17(2):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00227-4.
FDA approves Abbott’s Portico valve for TAVR
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated USPSTF screening guidelines may reduce lung cancer deaths
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 50-year-old woman presents to your office for a well-woman exam. Her past medical history includes a 22-pack-year smoking history (she quit 5 years ago), well-controlled hypertension, and mild obesity. She has no family history of cancer, but she does have a family history of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Besides age- and risk-appropriate laboratory tests, cervical cancer screening, breast cancer screening, and initial colon cancer screening, are there any other preventive services you would offer her?
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women, and it is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States—regardless of gender. The American Cancer Society estimates that 235,760 people will be diagnosed with lung cancer and 131,880 people will die of the disease in 2021.2
In the 2015 National Cancer Institute report on the economic costs of cancer, direct and indirect costs of lung cancer totaled $21.1 billion annually. Lost productivity from lung cancer added another $36.1 billion in annual costs.3 The economic costs increased to $23.8 billion in 2020, with no data on lost productivity.4
Smoking tobacco is by far the primary risk factor for lung cancer, and it is estimated to account for 90% of all lung cancer cases. Compared with nonsmokers, the relative risk of lung cancer is approximately 20 times higher for smokers.5,6
Because the median age of lung cancer diagnosis is 70 years, increasing age is also considered a risk factor for lung cancer.2,7
Although lung cancer has a relatively poor prognosis—with an average 5-year survival rate of 20.5%—early-stage lung cancer is more amenable to treatment and has a better prognosis (as is true with many cancers).1
LDCT has a high sensitivity, as well as a reasonable specificity, for lung cancer detection. There is demonstrated benefit in screening patients who are at high risk for lung cancer.8-11 In 2013, the USPSTF recommended annual lung cancer screening (B recommendation) with LDCT in adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30-pack-year smoking history, and who currently smoke or quit within the past 15 years.1
Continue to: STUDY SUMMARY
STUDY SUMMARY
Broader eligibility for screening supports mortality benefit
This is an update to the 2013 clinical practice guideline on lung cancer screening. The USPSTF used 2 methods to provide the best possible evidence for the recommendations. The first method was a systematic review of the accuracy of screening for lung cancer with LDCT, evaluating both the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening. The systematic review examined various subgroups, the number and/or frequency of LDCT scans, and various approaches to reducing false-positive results. In addition to the systematic review, they used collaborative modeling studies to determine the optimal age for beginning and ending screening, the optimal screening interval, and the relative benefits and harms of various screening strategies. These modeling studies complemented the evidence review.
The review included 7 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), plus the modeling studies. Only the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST; N = 53,454) and the Nederlands-Leuvens Longkanker Screenings Onderzoek (NELSON) trial (N = 15,792) had adequate power to detect a mortality benefit from screening (NLST: relative risk reduction = 16%; 95% CI, 5%-25%; NELSON: incidence rate ratio = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.61-0.90) compared with no screening.
Screening intervals, from the NLST and NELSON trials as well as the modeling studies, revealed the greatest benefit from annual screening (statistics not shared). Evidence also showed that screening those with lighter smoking histories (< 30 pack-years) and at an earlier age (age 50) provided increased mortality benefit. No evidence was found for a benefit of screening past 80 years of age. The modeling studies concluded that the 2013 USPSTF screening program, using a starting age of 55 and a 30-pack-year smoking history, would reduce mortality by 9.8%, but by changing to a starting age of 50, a 20-pack-year smoking history, and annual screening, the mortality benefit was increased to 13%.1,11
Comparison with computer-based risk prediction models from the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) revealed insufficient evidence at this time to show that prediction model–based screening offered any benefit beyond that of the age and smoking history risk factor model.
The incidence of false-positive results was > 25% in the NLST at baseline and at 1 year. Use of a classification system such as the Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) could reduce that from 26.6% to 12.8%.2 Another potential harm from LDCT screening is radiation exposure. Evidence from several RCTs and cohort studies showed the exposure from 1 LDCT scan to be 0.65 to 2.36 mSv, whereas the annual background radiation in the United States is 2.4 mSv. The modeling studies estimated that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
Continue to: WHAT'S NEW
WHAT’S NEW
Expanded age range, reduced pack-year history
Annual lung cancer screening is now recommended to begin for patients at age 50 years with a 20-pack-year history instead of age 55 years with a 30-pack-year history. This would nearly double (87% overall) the number of people eligible for screening, and it would include more Black patients and women, who tend to smoke fewer cigarettes than their White male counterparts. The American College of Radiology estimates that the expanded screening criteria could save between 30,000 and 60,000 lives per year.12
CAVEATS
Screening criteria for upper age limit, years since smoking remain unchanged
For those patients who quit smoking, the guidelines apply only to those who have stopped smoking within the past 15 years. Furthermore, the benefit does not extend beyond age 80 or where other conditions reduce life expectancy. And, as noted earlier, modeling studies estimate that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Concerns about false-positives, radiation exposure may limit acceptance
Challenges would be based mostly on the need for greater, more detailed dialogue between physicians and patients at higher risk for lung cancer in a time-constrained environment. Also, LDCT may not be available in some areas, and patients and physicians may have concerns regarding repeated CT exposure. In addition, false-positive results increase patient stress and may adversely affect both patient and physician acceptance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. US Preventive Services Task Force. Lung cancer: screening. Final recommendation statement. March 9, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening
2. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for lung cancer. Updated January 12, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
3. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health; 2015.
4. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health. Updated July 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://progressreport.cancer.gov/after/economic_burden
5. Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Ford JG, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 suppl):e1S-e29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2345
6. Samet JM. Health benefits of smoking cessation. Clin Chest Med. 1991;12:669-679.
7. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5-29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21254
8. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
9. Pinsky PF, Church TR, Izmirlian G, et al. The National Lung Screening Trial: results stratified by demographics, smoking history, and lung cancer histology. Cancer. 2013;119:3976-3983. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28326
10. de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:503-513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793
11. Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the Benefits and Harms of Lung Cancer Screening With Low-Dose Computed Tomography: A Collaborative Modeling Study for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2021.
12. American College of Radiology. Updated USPSTF lung cancer screening guidelines would help save lives. July 7, 2020. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.acr.org/Media-Center/ACR-News-Releases/2020/Updated-USPSTF-Lung-Cancer-Screening-Guidelines-Would-Help-Save-Lives
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 50-year-old woman presents to your office for a well-woman exam. Her past medical history includes a 22-pack-year smoking history (she quit 5 years ago), well-controlled hypertension, and mild obesity. She has no family history of cancer, but she does have a family history of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Besides age- and risk-appropriate laboratory tests, cervical cancer screening, breast cancer screening, and initial colon cancer screening, are there any other preventive services you would offer her?
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women, and it is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States—regardless of gender. The American Cancer Society estimates that 235,760 people will be diagnosed with lung cancer and 131,880 people will die of the disease in 2021.2
In the 2015 National Cancer Institute report on the economic costs of cancer, direct and indirect costs of lung cancer totaled $21.1 billion annually. Lost productivity from lung cancer added another $36.1 billion in annual costs.3 The economic costs increased to $23.8 billion in 2020, with no data on lost productivity.4
Smoking tobacco is by far the primary risk factor for lung cancer, and it is estimated to account for 90% of all lung cancer cases. Compared with nonsmokers, the relative risk of lung cancer is approximately 20 times higher for smokers.5,6
Because the median age of lung cancer diagnosis is 70 years, increasing age is also considered a risk factor for lung cancer.2,7
Although lung cancer has a relatively poor prognosis—with an average 5-year survival rate of 20.5%—early-stage lung cancer is more amenable to treatment and has a better prognosis (as is true with many cancers).1
LDCT has a high sensitivity, as well as a reasonable specificity, for lung cancer detection. There is demonstrated benefit in screening patients who are at high risk for lung cancer.8-11 In 2013, the USPSTF recommended annual lung cancer screening (B recommendation) with LDCT in adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30-pack-year smoking history, and who currently smoke or quit within the past 15 years.1
Continue to: STUDY SUMMARY
STUDY SUMMARY
Broader eligibility for screening supports mortality benefit
This is an update to the 2013 clinical practice guideline on lung cancer screening. The USPSTF used 2 methods to provide the best possible evidence for the recommendations. The first method was a systematic review of the accuracy of screening for lung cancer with LDCT, evaluating both the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening. The systematic review examined various subgroups, the number and/or frequency of LDCT scans, and various approaches to reducing false-positive results. In addition to the systematic review, they used collaborative modeling studies to determine the optimal age for beginning and ending screening, the optimal screening interval, and the relative benefits and harms of various screening strategies. These modeling studies complemented the evidence review.
The review included 7 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), plus the modeling studies. Only the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST; N = 53,454) and the Nederlands-Leuvens Longkanker Screenings Onderzoek (NELSON) trial (N = 15,792) had adequate power to detect a mortality benefit from screening (NLST: relative risk reduction = 16%; 95% CI, 5%-25%; NELSON: incidence rate ratio = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.61-0.90) compared with no screening.
Screening intervals, from the NLST and NELSON trials as well as the modeling studies, revealed the greatest benefit from annual screening (statistics not shared). Evidence also showed that screening those with lighter smoking histories (< 30 pack-years) and at an earlier age (age 50) provided increased mortality benefit. No evidence was found for a benefit of screening past 80 years of age. The modeling studies concluded that the 2013 USPSTF screening program, using a starting age of 55 and a 30-pack-year smoking history, would reduce mortality by 9.8%, but by changing to a starting age of 50, a 20-pack-year smoking history, and annual screening, the mortality benefit was increased to 13%.1,11
Comparison with computer-based risk prediction models from the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) revealed insufficient evidence at this time to show that prediction model–based screening offered any benefit beyond that of the age and smoking history risk factor model.
The incidence of false-positive results was > 25% in the NLST at baseline and at 1 year. Use of a classification system such as the Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) could reduce that from 26.6% to 12.8%.2 Another potential harm from LDCT screening is radiation exposure. Evidence from several RCTs and cohort studies showed the exposure from 1 LDCT scan to be 0.65 to 2.36 mSv, whereas the annual background radiation in the United States is 2.4 mSv. The modeling studies estimated that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
Continue to: WHAT'S NEW
WHAT’S NEW
Expanded age range, reduced pack-year history
Annual lung cancer screening is now recommended to begin for patients at age 50 years with a 20-pack-year history instead of age 55 years with a 30-pack-year history. This would nearly double (87% overall) the number of people eligible for screening, and it would include more Black patients and women, who tend to smoke fewer cigarettes than their White male counterparts. The American College of Radiology estimates that the expanded screening criteria could save between 30,000 and 60,000 lives per year.12
CAVEATS
Screening criteria for upper age limit, years since smoking remain unchanged
For those patients who quit smoking, the guidelines apply only to those who have stopped smoking within the past 15 years. Furthermore, the benefit does not extend beyond age 80 or where other conditions reduce life expectancy. And, as noted earlier, modeling studies estimate that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Concerns about false-positives, radiation exposure may limit acceptance
Challenges would be based mostly on the need for greater, more detailed dialogue between physicians and patients at higher risk for lung cancer in a time-constrained environment. Also, LDCT may not be available in some areas, and patients and physicians may have concerns regarding repeated CT exposure. In addition, false-positive results increase patient stress and may adversely affect both patient and physician acceptance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 50-year-old woman presents to your office for a well-woman exam. Her past medical history includes a 22-pack-year smoking history (she quit 5 years ago), well-controlled hypertension, and mild obesity. She has no family history of cancer, but she does have a family history of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Besides age- and risk-appropriate laboratory tests, cervical cancer screening, breast cancer screening, and initial colon cancer screening, are there any other preventive services you would offer her?
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women, and it is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States—regardless of gender. The American Cancer Society estimates that 235,760 people will be diagnosed with lung cancer and 131,880 people will die of the disease in 2021.2
In the 2015 National Cancer Institute report on the economic costs of cancer, direct and indirect costs of lung cancer totaled $21.1 billion annually. Lost productivity from lung cancer added another $36.1 billion in annual costs.3 The economic costs increased to $23.8 billion in 2020, with no data on lost productivity.4
Smoking tobacco is by far the primary risk factor for lung cancer, and it is estimated to account for 90% of all lung cancer cases. Compared with nonsmokers, the relative risk of lung cancer is approximately 20 times higher for smokers.5,6
Because the median age of lung cancer diagnosis is 70 years, increasing age is also considered a risk factor for lung cancer.2,7
Although lung cancer has a relatively poor prognosis—with an average 5-year survival rate of 20.5%—early-stage lung cancer is more amenable to treatment and has a better prognosis (as is true with many cancers).1
LDCT has a high sensitivity, as well as a reasonable specificity, for lung cancer detection. There is demonstrated benefit in screening patients who are at high risk for lung cancer.8-11 In 2013, the USPSTF recommended annual lung cancer screening (B recommendation) with LDCT in adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30-pack-year smoking history, and who currently smoke or quit within the past 15 years.1
Continue to: STUDY SUMMARY
STUDY SUMMARY
Broader eligibility for screening supports mortality benefit
This is an update to the 2013 clinical practice guideline on lung cancer screening. The USPSTF used 2 methods to provide the best possible evidence for the recommendations. The first method was a systematic review of the accuracy of screening for lung cancer with LDCT, evaluating both the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening. The systematic review examined various subgroups, the number and/or frequency of LDCT scans, and various approaches to reducing false-positive results. In addition to the systematic review, they used collaborative modeling studies to determine the optimal age for beginning and ending screening, the optimal screening interval, and the relative benefits and harms of various screening strategies. These modeling studies complemented the evidence review.
The review included 7 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), plus the modeling studies. Only the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST; N = 53,454) and the Nederlands-Leuvens Longkanker Screenings Onderzoek (NELSON) trial (N = 15,792) had adequate power to detect a mortality benefit from screening (NLST: relative risk reduction = 16%; 95% CI, 5%-25%; NELSON: incidence rate ratio = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.61-0.90) compared with no screening.
Screening intervals, from the NLST and NELSON trials as well as the modeling studies, revealed the greatest benefit from annual screening (statistics not shared). Evidence also showed that screening those with lighter smoking histories (< 30 pack-years) and at an earlier age (age 50) provided increased mortality benefit. No evidence was found for a benefit of screening past 80 years of age. The modeling studies concluded that the 2013 USPSTF screening program, using a starting age of 55 and a 30-pack-year smoking history, would reduce mortality by 9.8%, but by changing to a starting age of 50, a 20-pack-year smoking history, and annual screening, the mortality benefit was increased to 13%.1,11
Comparison with computer-based risk prediction models from the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) revealed insufficient evidence at this time to show that prediction model–based screening offered any benefit beyond that of the age and smoking history risk factor model.
The incidence of false-positive results was > 25% in the NLST at baseline and at 1 year. Use of a classification system such as the Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) could reduce that from 26.6% to 12.8%.2 Another potential harm from LDCT screening is radiation exposure. Evidence from several RCTs and cohort studies showed the exposure from 1 LDCT scan to be 0.65 to 2.36 mSv, whereas the annual background radiation in the United States is 2.4 mSv. The modeling studies estimated that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
Continue to: WHAT'S NEW
WHAT’S NEW
Expanded age range, reduced pack-year history
Annual lung cancer screening is now recommended to begin for patients at age 50 years with a 20-pack-year history instead of age 55 years with a 30-pack-year history. This would nearly double (87% overall) the number of people eligible for screening, and it would include more Black patients and women, who tend to smoke fewer cigarettes than their White male counterparts. The American College of Radiology estimates that the expanded screening criteria could save between 30,000 and 60,000 lives per year.12
CAVEATS
Screening criteria for upper age limit, years since smoking remain unchanged
For those patients who quit smoking, the guidelines apply only to those who have stopped smoking within the past 15 years. Furthermore, the benefit does not extend beyond age 80 or where other conditions reduce life expectancy. And, as noted earlier, modeling studies estimate that there would be 1 death caused by LDCT for every 18.5 cancer deaths avoided.1,11
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Concerns about false-positives, radiation exposure may limit acceptance
Challenges would be based mostly on the need for greater, more detailed dialogue between physicians and patients at higher risk for lung cancer in a time-constrained environment. Also, LDCT may not be available in some areas, and patients and physicians may have concerns regarding repeated CT exposure. In addition, false-positive results increase patient stress and may adversely affect both patient and physician acceptance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. US Preventive Services Task Force. Lung cancer: screening. Final recommendation statement. March 9, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening
2. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for lung cancer. Updated January 12, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
3. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health; 2015.
4. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health. Updated July 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://progressreport.cancer.gov/after/economic_burden
5. Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Ford JG, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 suppl):e1S-e29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2345
6. Samet JM. Health benefits of smoking cessation. Clin Chest Med. 1991;12:669-679.
7. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5-29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21254
8. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
9. Pinsky PF, Church TR, Izmirlian G, et al. The National Lung Screening Trial: results stratified by demographics, smoking history, and lung cancer histology. Cancer. 2013;119:3976-3983. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28326
10. de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:503-513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793
11. Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the Benefits and Harms of Lung Cancer Screening With Low-Dose Computed Tomography: A Collaborative Modeling Study for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2021.
12. American College of Radiology. Updated USPSTF lung cancer screening guidelines would help save lives. July 7, 2020. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.acr.org/Media-Center/ACR-News-Releases/2020/Updated-USPSTF-Lung-Cancer-Screening-Guidelines-Would-Help-Save-Lives
1. US Preventive Services Task Force. Lung cancer: screening. Final recommendation statement. March 9, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening
2. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for lung cancer. Updated January 12, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
3. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health; 2015.
4. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Trends Progress Report—Financial Burden of Cancer Care. National Institutes of Health. Updated July 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://progressreport.cancer.gov/after/economic_burden
5. Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Ford JG, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 suppl):e1S-e29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2345
6. Samet JM. Health benefits of smoking cessation. Clin Chest Med. 1991;12:669-679.
7. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5-29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21254
8. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
9. Pinsky PF, Church TR, Izmirlian G, et al. The National Lung Screening Trial: results stratified by demographics, smoking history, and lung cancer histology. Cancer. 2013;119:3976-3983. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28326
10. de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:503-513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793
11. Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the Benefits and Harms of Lung Cancer Screening With Low-Dose Computed Tomography: A Collaborative Modeling Study for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2021.
12. American College of Radiology. Updated USPSTF lung cancer screening guidelines would help save lives. July 7, 2020. Accessed August 19, 2021. www.acr.org/Media-Center/ACR-News-Releases/2020/Updated-USPSTF-Lung-Cancer-Screening-Guidelines-Would-Help-Save-Lives
PRACTICE CHANGER
Start assessing risk and screening for lung cancer at age 50 in patients who have a 20-pack-year history of smoking, using low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scanning. This practice, based on a 2020 US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guideline update, is expected to reduce annual mortality from lung cancer by an additional 3% or more (from 9.8% to 13%).
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
A: Evidence-based clinical practice guideline1
US Preventive Services Task Force. Lung cancer: screening. Final recommendation statement. March 9, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening
Study supports add-on therapy for germline and wildtype BRCA mutations
The initial improvement that was seen in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates with the addition of carboplatin to paclitaxel and standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy translated into improved event-free survival (EFS) rates in patients with resectable TNBC more than 4 years after surgery.
The benefits of adding carboplatin to paclitaxel, followed by four cycles of AC (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) chemotherapy, were seen both in patients with germline BRCA mutations and those with wildtype BRCA.
The trial results also demonstrated, however, that there were no short- or long-term benefits to adding veliparib (ABT-888), a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, to the mix.
Although pCR and EFS rates were significantly improved with the combination of paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with paclitaxel alone, there were no significant differences when veliparib was added in either pCR, EFS, or overall survival (OS).
“These findings overall support the inclusion of carboplatin into neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage 2 and 3 triple-negative breast cancer patients, regardless of germline BRCA status,” concluded lead author Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, chief executive officer and chair of the German Breast Group.
She presented the new data during an oral session at the virtual European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2021.
The BrighTNess results show that “neoadjuvant carboplatin plus paclitaxel is superior to paclitaxel alone, with high pCR rates and benefit of event-free survival rates with manageable toxicity and no safety signals,” commented invited discussant Monica Arnedos, MD, PhD, head of the breast cancer research program at the Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France.
The findings also put to rest the notion that patients with germline BRCA mutations would not benefit from carboplatin treatment because of extreme sensitivity to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
“The BrighTNess study says otherwise,” Dr. Arnedos said. “Today we’ve seen that the pCR improved event-free survival regardless of the germline BRCA mutated status, so BRCA-mutated germline patients require neoadjuvant carboplatin.”
The new data may lead to changes in breast cancer guidelines, she suggested.
Prior to these results, the evidence was that “platinum salts as neoadjuvant chemotherapy increased pCR rates in triple-negative breast cancer patients, but this was associated with more toxicity, and with higher rates of treatment discontinuation and dose reduction, without strong evidence of long-term benefit. This led to a lack of consensus to recommend platinum salts in this setting between the different breast cancer guidelines.”
The new BrighTNess data showed that the improved pCR rates translated into an EFS benefit in both platinum-containing groups of the trial, a finding that is consistent with the KEYNOTE-522 trial, which showed that adding pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to chemotherapy improved pCR in patients with early TNBC.
The BrighTNess results suggest that patients with high- or moderate-risk TNBC could be treated in the neoadjuvant setting with paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by standard chemotherapy concurrently with pembrolizumab, followed by surgery, and adjuvant therapy with pembrolizumab plus olaparib (Lynparza) for patients with germline BRCA mutations, or capecitabine for patients without mutations, Dr. Arnedos proposed.
BrighTNess study details
The BrighTNess trial involved 634 patients with previously untreated histologically or cytologically confirmed stage 2-3 TNBC who were candidates for potentially curative surgery and had a good performance status. They were randomly assigned to receive either paclitaxel plus carboplatin and veliparib, paclitaxel plus carboplatin only, or paclitaxel alone prior to four cycles of chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (AC).
Initial results, published in 2018 in The Lancet Oncology, showed that the addition of veliparib to carboplatin and paclitaxel improved pCR rates compared with paclitaxel alone but not paclitaxel plus carboplatin. The trial data supported the addition of carboplatin to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy but not veliparib, the investigators stated at the time.
Now at the ESMO meeting, Dr. Loibl presented longer follow-up results.
After a median follow-up of 4.5 years, the hazard ratio (HR) for event-free survival with the paclitaxel/carboplatin/veliparib combination compared with paclitaxel alone was 0.63 (P = .016). In a post-hoc analysis, the adjusted HR was 0.57 (P = .018).
In a subgroup of 309 patients who had initial pCRs, the HR for EFS compared with patients without a pCR was 0.26 (P < .0001). Among patients with germline BRCA mutation, the HR for EFS for those who had a pCR was 0.14 (P = .0004), and among those with germline wildtype BRCA and a pCR the HR was 0.29 (P < .0001).
However, there were no significant differences in OS a median of 4.5 years after surgery.
An analysis of the frequency of myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia, or other second primary malignancies also showed no significant differences between the groups, Dr. Loibl noted.
Although there were higher rates of hematologic malignancies with the addition of carboplatin, with or without veliparib, these adverse events did not compromise either treatment delivery of the benefits of carboplatin on the primary pCR endpoint, she added.
The BrighTNess trial was supported by AbbVie. Dr. Loibl has reported receiving grants and honoraria from AbbVie and others, including Medscape. Dr. Arnedos has reported receiving honoraria, travel grants, and/or research grants from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The initial improvement that was seen in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates with the addition of carboplatin to paclitaxel and standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy translated into improved event-free survival (EFS) rates in patients with resectable TNBC more than 4 years after surgery.
The benefits of adding carboplatin to paclitaxel, followed by four cycles of AC (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) chemotherapy, were seen both in patients with germline BRCA mutations and those with wildtype BRCA.
The trial results also demonstrated, however, that there were no short- or long-term benefits to adding veliparib (ABT-888), a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, to the mix.
Although pCR and EFS rates were significantly improved with the combination of paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with paclitaxel alone, there were no significant differences when veliparib was added in either pCR, EFS, or overall survival (OS).
“These findings overall support the inclusion of carboplatin into neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage 2 and 3 triple-negative breast cancer patients, regardless of germline BRCA status,” concluded lead author Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, chief executive officer and chair of the German Breast Group.
She presented the new data during an oral session at the virtual European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2021.
The BrighTNess results show that “neoadjuvant carboplatin plus paclitaxel is superior to paclitaxel alone, with high pCR rates and benefit of event-free survival rates with manageable toxicity and no safety signals,” commented invited discussant Monica Arnedos, MD, PhD, head of the breast cancer research program at the Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France.
The findings also put to rest the notion that patients with germline BRCA mutations would not benefit from carboplatin treatment because of extreme sensitivity to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
“The BrighTNess study says otherwise,” Dr. Arnedos said. “Today we’ve seen that the pCR improved event-free survival regardless of the germline BRCA mutated status, so BRCA-mutated germline patients require neoadjuvant carboplatin.”
The new data may lead to changes in breast cancer guidelines, she suggested.
Prior to these results, the evidence was that “platinum salts as neoadjuvant chemotherapy increased pCR rates in triple-negative breast cancer patients, but this was associated with more toxicity, and with higher rates of treatment discontinuation and dose reduction, without strong evidence of long-term benefit. This led to a lack of consensus to recommend platinum salts in this setting between the different breast cancer guidelines.”
The new BrighTNess data showed that the improved pCR rates translated into an EFS benefit in both platinum-containing groups of the trial, a finding that is consistent with the KEYNOTE-522 trial, which showed that adding pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to chemotherapy improved pCR in patients with early TNBC.
The BrighTNess results suggest that patients with high- or moderate-risk TNBC could be treated in the neoadjuvant setting with paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by standard chemotherapy concurrently with pembrolizumab, followed by surgery, and adjuvant therapy with pembrolizumab plus olaparib (Lynparza) for patients with germline BRCA mutations, or capecitabine for patients without mutations, Dr. Arnedos proposed.
BrighTNess study details
The BrighTNess trial involved 634 patients with previously untreated histologically or cytologically confirmed stage 2-3 TNBC who were candidates for potentially curative surgery and had a good performance status. They were randomly assigned to receive either paclitaxel plus carboplatin and veliparib, paclitaxel plus carboplatin only, or paclitaxel alone prior to four cycles of chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (AC).
Initial results, published in 2018 in The Lancet Oncology, showed that the addition of veliparib to carboplatin and paclitaxel improved pCR rates compared with paclitaxel alone but not paclitaxel plus carboplatin. The trial data supported the addition of carboplatin to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy but not veliparib, the investigators stated at the time.
Now at the ESMO meeting, Dr. Loibl presented longer follow-up results.
After a median follow-up of 4.5 years, the hazard ratio (HR) for event-free survival with the paclitaxel/carboplatin/veliparib combination compared with paclitaxel alone was 0.63 (P = .016). In a post-hoc analysis, the adjusted HR was 0.57 (P = .018).
In a subgroup of 309 patients who had initial pCRs, the HR for EFS compared with patients without a pCR was 0.26 (P < .0001). Among patients with germline BRCA mutation, the HR for EFS for those who had a pCR was 0.14 (P = .0004), and among those with germline wildtype BRCA and a pCR the HR was 0.29 (P < .0001).
However, there were no significant differences in OS a median of 4.5 years after surgery.
An analysis of the frequency of myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia, or other second primary malignancies also showed no significant differences between the groups, Dr. Loibl noted.
Although there were higher rates of hematologic malignancies with the addition of carboplatin, with or without veliparib, these adverse events did not compromise either treatment delivery of the benefits of carboplatin on the primary pCR endpoint, she added.
The BrighTNess trial was supported by AbbVie. Dr. Loibl has reported receiving grants and honoraria from AbbVie and others, including Medscape. Dr. Arnedos has reported receiving honoraria, travel grants, and/or research grants from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The initial improvement that was seen in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates with the addition of carboplatin to paclitaxel and standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy translated into improved event-free survival (EFS) rates in patients with resectable TNBC more than 4 years after surgery.
The benefits of adding carboplatin to paclitaxel, followed by four cycles of AC (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) chemotherapy, were seen both in patients with germline BRCA mutations and those with wildtype BRCA.
The trial results also demonstrated, however, that there were no short- or long-term benefits to adding veliparib (ABT-888), a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, to the mix.
Although pCR and EFS rates were significantly improved with the combination of paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with paclitaxel alone, there were no significant differences when veliparib was added in either pCR, EFS, or overall survival (OS).
“These findings overall support the inclusion of carboplatin into neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage 2 and 3 triple-negative breast cancer patients, regardless of germline BRCA status,” concluded lead author Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, chief executive officer and chair of the German Breast Group.
She presented the new data during an oral session at the virtual European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2021.
The BrighTNess results show that “neoadjuvant carboplatin plus paclitaxel is superior to paclitaxel alone, with high pCR rates and benefit of event-free survival rates with manageable toxicity and no safety signals,” commented invited discussant Monica Arnedos, MD, PhD, head of the breast cancer research program at the Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France.
The findings also put to rest the notion that patients with germline BRCA mutations would not benefit from carboplatin treatment because of extreme sensitivity to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
“The BrighTNess study says otherwise,” Dr. Arnedos said. “Today we’ve seen that the pCR improved event-free survival regardless of the germline BRCA mutated status, so BRCA-mutated germline patients require neoadjuvant carboplatin.”
The new data may lead to changes in breast cancer guidelines, she suggested.
Prior to these results, the evidence was that “platinum salts as neoadjuvant chemotherapy increased pCR rates in triple-negative breast cancer patients, but this was associated with more toxicity, and with higher rates of treatment discontinuation and dose reduction, without strong evidence of long-term benefit. This led to a lack of consensus to recommend platinum salts in this setting between the different breast cancer guidelines.”
The new BrighTNess data showed that the improved pCR rates translated into an EFS benefit in both platinum-containing groups of the trial, a finding that is consistent with the KEYNOTE-522 trial, which showed that adding pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to chemotherapy improved pCR in patients with early TNBC.
The BrighTNess results suggest that patients with high- or moderate-risk TNBC could be treated in the neoadjuvant setting with paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by standard chemotherapy concurrently with pembrolizumab, followed by surgery, and adjuvant therapy with pembrolizumab plus olaparib (Lynparza) for patients with germline BRCA mutations, or capecitabine for patients without mutations, Dr. Arnedos proposed.
BrighTNess study details
The BrighTNess trial involved 634 patients with previously untreated histologically or cytologically confirmed stage 2-3 TNBC who were candidates for potentially curative surgery and had a good performance status. They were randomly assigned to receive either paclitaxel plus carboplatin and veliparib, paclitaxel plus carboplatin only, or paclitaxel alone prior to four cycles of chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (AC).
Initial results, published in 2018 in The Lancet Oncology, showed that the addition of veliparib to carboplatin and paclitaxel improved pCR rates compared with paclitaxel alone but not paclitaxel plus carboplatin. The trial data supported the addition of carboplatin to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy but not veliparib, the investigators stated at the time.
Now at the ESMO meeting, Dr. Loibl presented longer follow-up results.
After a median follow-up of 4.5 years, the hazard ratio (HR) for event-free survival with the paclitaxel/carboplatin/veliparib combination compared with paclitaxel alone was 0.63 (P = .016). In a post-hoc analysis, the adjusted HR was 0.57 (P = .018).
In a subgroup of 309 patients who had initial pCRs, the HR for EFS compared with patients without a pCR was 0.26 (P < .0001). Among patients with germline BRCA mutation, the HR for EFS for those who had a pCR was 0.14 (P = .0004), and among those with germline wildtype BRCA and a pCR the HR was 0.29 (P < .0001).
However, there were no significant differences in OS a median of 4.5 years after surgery.
An analysis of the frequency of myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia, or other second primary malignancies also showed no significant differences between the groups, Dr. Loibl noted.
Although there were higher rates of hematologic malignancies with the addition of carboplatin, with or without veliparib, these adverse events did not compromise either treatment delivery of the benefits of carboplatin on the primary pCR endpoint, she added.
The BrighTNess trial was supported by AbbVie. Dr. Loibl has reported receiving grants and honoraria from AbbVie and others, including Medscape. Dr. Arnedos has reported receiving honoraria, travel grants, and/or research grants from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.