User login
STOP-DAPT 2 ACS: 1 month of DAPT proves inadequate for patients with recent ACS
One month of dual antiplatelet therapy followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy failed to prove noninferiority to 12 unbroken months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a multicenter Japanese trial that randomized more than 4,000 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) after a recent acute coronary syndrome episode.
The outcomes showed that while truncating DAPT duration could, as expected, cut major bleeding episodes roughly in half, it also led to a significant near doubling of myocardial infarction and showed a strong trend toward also increasing a composite tally of several types of ischemic events. These data were reported this week by Hirotoshi Watanabe, MD, PhD, at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. All study patients had undergone PCI with cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting (CCEE) coronary stents (Xience).
These findings from the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial highlighted the limits of minimizing DAPT after PCI in patients at high ischemic risk, such as after an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) event.
It also was a counterpoint to a somewhat similar study also reported at the congress, MASTER DAPT, which showed that 1 month of DAPT was noninferior to 3 or more months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a distinctly different population of patients undergoing PCI (and using a different type of coronary stent) – those at high bleeding risk and with only about half the patients having had a recent ACS.
The results of STOPDAPT-2 ACS “do not support use of 1 month of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy with clopidogrel compared with standard DAPT,” commented Robert A. Byrne, MBBCh, PhD, designated discussant for the report and professor at the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences in Dublin.
“Although major bleeding was significantly reduced with this approach, there appeared to be a significant increase in adverse ischemic events, and there was a clear signal in relation to overall mortality, the ultimate arbiter of net clinical benefit,” added Dr. Byrne, who is also director of cardiology at Mater Private Hospital in Dublin.
He suggested that a mechanistic explanation for the signal of harm seem in STOPDAPT-2 ACS was the relatively low potency of clopidogrel (Plavix) as an antiplatelet agent, compared with other P2Y12 inhibitors such as prasugrel (Effient) and ticagrelor (Brilinta), as well as the genetically driven variability in response to clopidogrel that’s also absent with alternative agents.
These between-agent differences are of “particular clinical relevance in the early aftermath of an ACS event,” Dr. Byrne said.
12-month DAPT remains standard for PCI patients with recent ACS
The totality of clinical evidence “continues to support a standard 12-month duration of DAPT – using aspirin and either prasugrel or ticagrelor – as the preferred default approach,” Dr. Byrne concluded.
He acknowledged that an abbreviated duration of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy “might be considered as an alternative.” In patients following an ACS event who do not have high risk for bleeding, he said, the minimum duration of DAPT should be at least 3 months and with preferential use of a more potent P2Y12 inhibitor.
Twelve months of DAPT treatment with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor for patients following PCI “remains the standard of care in guidelines,” noted Marco Roffi, MD, a second discussant at the congress. But several questions remain, he added, such as which P2Y12 inhibitors work best and whether DAPT can be less than 12 months.
“The investigators [for STOPDAPT-2 ACS] pushed these questions to the limit with 1 month of DAPT and clopidogrel monotherapy,” said Dr. Roffi, professor and director of interventional cardiology at University Hospital, Geneva.
“This was a risky bet, and the investigators lost by not proving noninferiority and with excess ischemic events,” he commented.
First came STOPDAPT-2
Dr. Watanabe and colleagues designed STOPDAPT-2 ACS as a follow-up to their prior STOPDAPT-2 trial, which randomly assigned slightly more than 3000 patients at 90 Japanese centers to the identical two treatment options: 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy or 12 months of DAPT, except the trial enrolled all types of patients undergoing PCI. This meant that a minority, 38%, had a recent ACS event, while the remaining patients had chronic coronary artery disease. As in STOPDAPT-2 ACS, all patients in STOPDAPT-2 had received a CCEE stent.
STOPDAPT-2 also used the same primary endpoint to tally net clinical benefit as STOPDAPT-2 ACS: cardiovascular death, MI, stroke of any type, definite stent thrombosis, or TIMI major or minor bleeding classification.
In STOPDAPT-2, using the mixed population with both recent ACS and chronic coronary disease, the regimen of 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy was both noninferior to and superior to 12 months of DAPT, reducing the net adverse-event tally by 36% relative to 12-month DAPT and by an absolute reduction of 1.34%, as reported in 2019.
Despite this superiority, the results from STOPDAPT-2 had little impact on global practice, commented Kurt Huber, MD, professor and director of the cardiology ICU at the Medical University of Vienna.
“STOP-DAPT-2 did not give us a clear message with respect to reducing antiplatelet treatment after 1 month. I thought that for ACS patients 1 month might be too short,” Dr. Huber said during a press briefing.
Focusing on post-ACS
To directly address this issue, the investigators launched STOPDAPT-2 ACS, which used the same design as the preceding study but only enrolled patients soon after an ACS event. The trial included for its main analysis 3,008 newly enrolled patients with recent ACS, and 1,161 patients who had a recent ACS event and had been randomly assigned in STOPDAPT-2, creating a total study cohort for the new analysis of 4136 patients treated and followed for the study’s full 12 months.
The patients averaged 67 years old, 79% were men, and 30% had diabetes. About 56% had a recent ST-elevation MI, about 20% a recent non–ST-elevation MI, and the remaining 24% had unstable angina. For their unspecified P2Y12 inhibition, roughly half the patients received clopidogrel and the rest received prasugrel. Adherence to the two assigned treatment regimens was very good, with a very small number of patients not adhering to their assigned protocol.
The composite adverse event incidence over 12 months was 3.2% among those who received 1-month DAPT and 2.83% in those on DAPT for 12 months, a difference that failed to achieve the prespecified definition of noninferiority for 1-month DAPT, reported Dr. Watanabe, an interventional cardiologist at Kyoto University.
The ischemic event composite was 50% lower among those on 12-month DAPT, compared with 1 month of DAPT, a difference that just missed significance. The rate of MI was 91% higher with 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months, a significant difference.
One-month DAPT also significantly reduced the primary measure of bleeding events – the combination of TIMI major and minor bleeds – by a significant 54%, compared with 12-month DAPT. A second metric of clinically meaningful bleeds, those that meet either the type 3 or 5 definition of the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium, were reduced by a significant 59% by 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months of DAPT.
The new findings from STOPDAPT-2 ACS contrasted with those from MASTER DAPT, but in an explicable way that related to different patient types, different P2Y12 inhibitors, different treatment durations, and different stents.
“We’ve seen in MASTER DAPT that if you use the right stent and use ticagrelor for monotherapy there may be some ability to shorten DAPT, but we still do not know what would happen in patients with very high ischemic risk,” concluded Dr. Huber.
“A reduction in DAPT duration might work in patients without high bleeding risk, but I would exclude patients with very high ischemic risk,” he added. “I also can’t tell you whether 1 month or 3 months is the right approach, and I think clopidogrel is not the right drug to use for monotherapy after ACS.”
STOPDAPT-2 and STOPDAPT-2 ACS were both sponsored by Abbott Vascular, which markets the CCEE (Xience) stents used in both studies. Dr. Watanabe has received lecture fees from Abbott and from Daiichi-Sankyo. Dr. Byrne has received research funding from Abbott Vascular as well as from Biosensors, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific. Roffi has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, GE Healthcare, Medtronic, and Terumo. Dr. Huber has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One month of dual antiplatelet therapy followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy failed to prove noninferiority to 12 unbroken months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a multicenter Japanese trial that randomized more than 4,000 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) after a recent acute coronary syndrome episode.
The outcomes showed that while truncating DAPT duration could, as expected, cut major bleeding episodes roughly in half, it also led to a significant near doubling of myocardial infarction and showed a strong trend toward also increasing a composite tally of several types of ischemic events. These data were reported this week by Hirotoshi Watanabe, MD, PhD, at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. All study patients had undergone PCI with cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting (CCEE) coronary stents (Xience).
These findings from the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial highlighted the limits of minimizing DAPT after PCI in patients at high ischemic risk, such as after an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) event.
It also was a counterpoint to a somewhat similar study also reported at the congress, MASTER DAPT, which showed that 1 month of DAPT was noninferior to 3 or more months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a distinctly different population of patients undergoing PCI (and using a different type of coronary stent) – those at high bleeding risk and with only about half the patients having had a recent ACS.
The results of STOPDAPT-2 ACS “do not support use of 1 month of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy with clopidogrel compared with standard DAPT,” commented Robert A. Byrne, MBBCh, PhD, designated discussant for the report and professor at the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences in Dublin.
“Although major bleeding was significantly reduced with this approach, there appeared to be a significant increase in adverse ischemic events, and there was a clear signal in relation to overall mortality, the ultimate arbiter of net clinical benefit,” added Dr. Byrne, who is also director of cardiology at Mater Private Hospital in Dublin.
He suggested that a mechanistic explanation for the signal of harm seem in STOPDAPT-2 ACS was the relatively low potency of clopidogrel (Plavix) as an antiplatelet agent, compared with other P2Y12 inhibitors such as prasugrel (Effient) and ticagrelor (Brilinta), as well as the genetically driven variability in response to clopidogrel that’s also absent with alternative agents.
These between-agent differences are of “particular clinical relevance in the early aftermath of an ACS event,” Dr. Byrne said.
12-month DAPT remains standard for PCI patients with recent ACS
The totality of clinical evidence “continues to support a standard 12-month duration of DAPT – using aspirin and either prasugrel or ticagrelor – as the preferred default approach,” Dr. Byrne concluded.
He acknowledged that an abbreviated duration of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy “might be considered as an alternative.” In patients following an ACS event who do not have high risk for bleeding, he said, the minimum duration of DAPT should be at least 3 months and with preferential use of a more potent P2Y12 inhibitor.
Twelve months of DAPT treatment with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor for patients following PCI “remains the standard of care in guidelines,” noted Marco Roffi, MD, a second discussant at the congress. But several questions remain, he added, such as which P2Y12 inhibitors work best and whether DAPT can be less than 12 months.
“The investigators [for STOPDAPT-2 ACS] pushed these questions to the limit with 1 month of DAPT and clopidogrel monotherapy,” said Dr. Roffi, professor and director of interventional cardiology at University Hospital, Geneva.
“This was a risky bet, and the investigators lost by not proving noninferiority and with excess ischemic events,” he commented.
First came STOPDAPT-2
Dr. Watanabe and colleagues designed STOPDAPT-2 ACS as a follow-up to their prior STOPDAPT-2 trial, which randomly assigned slightly more than 3000 patients at 90 Japanese centers to the identical two treatment options: 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy or 12 months of DAPT, except the trial enrolled all types of patients undergoing PCI. This meant that a minority, 38%, had a recent ACS event, while the remaining patients had chronic coronary artery disease. As in STOPDAPT-2 ACS, all patients in STOPDAPT-2 had received a CCEE stent.
STOPDAPT-2 also used the same primary endpoint to tally net clinical benefit as STOPDAPT-2 ACS: cardiovascular death, MI, stroke of any type, definite stent thrombosis, or TIMI major or minor bleeding classification.
In STOPDAPT-2, using the mixed population with both recent ACS and chronic coronary disease, the regimen of 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy was both noninferior to and superior to 12 months of DAPT, reducing the net adverse-event tally by 36% relative to 12-month DAPT and by an absolute reduction of 1.34%, as reported in 2019.
Despite this superiority, the results from STOPDAPT-2 had little impact on global practice, commented Kurt Huber, MD, professor and director of the cardiology ICU at the Medical University of Vienna.
“STOP-DAPT-2 did not give us a clear message with respect to reducing antiplatelet treatment after 1 month. I thought that for ACS patients 1 month might be too short,” Dr. Huber said during a press briefing.
Focusing on post-ACS
To directly address this issue, the investigators launched STOPDAPT-2 ACS, which used the same design as the preceding study but only enrolled patients soon after an ACS event. The trial included for its main analysis 3,008 newly enrolled patients with recent ACS, and 1,161 patients who had a recent ACS event and had been randomly assigned in STOPDAPT-2, creating a total study cohort for the new analysis of 4136 patients treated and followed for the study’s full 12 months.
The patients averaged 67 years old, 79% were men, and 30% had diabetes. About 56% had a recent ST-elevation MI, about 20% a recent non–ST-elevation MI, and the remaining 24% had unstable angina. For their unspecified P2Y12 inhibition, roughly half the patients received clopidogrel and the rest received prasugrel. Adherence to the two assigned treatment regimens was very good, with a very small number of patients not adhering to their assigned protocol.
The composite adverse event incidence over 12 months was 3.2% among those who received 1-month DAPT and 2.83% in those on DAPT for 12 months, a difference that failed to achieve the prespecified definition of noninferiority for 1-month DAPT, reported Dr. Watanabe, an interventional cardiologist at Kyoto University.
The ischemic event composite was 50% lower among those on 12-month DAPT, compared with 1 month of DAPT, a difference that just missed significance. The rate of MI was 91% higher with 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months, a significant difference.
One-month DAPT also significantly reduced the primary measure of bleeding events – the combination of TIMI major and minor bleeds – by a significant 54%, compared with 12-month DAPT. A second metric of clinically meaningful bleeds, those that meet either the type 3 or 5 definition of the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium, were reduced by a significant 59% by 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months of DAPT.
The new findings from STOPDAPT-2 ACS contrasted with those from MASTER DAPT, but in an explicable way that related to different patient types, different P2Y12 inhibitors, different treatment durations, and different stents.
“We’ve seen in MASTER DAPT that if you use the right stent and use ticagrelor for monotherapy there may be some ability to shorten DAPT, but we still do not know what would happen in patients with very high ischemic risk,” concluded Dr. Huber.
“A reduction in DAPT duration might work in patients without high bleeding risk, but I would exclude patients with very high ischemic risk,” he added. “I also can’t tell you whether 1 month or 3 months is the right approach, and I think clopidogrel is not the right drug to use for monotherapy after ACS.”
STOPDAPT-2 and STOPDAPT-2 ACS were both sponsored by Abbott Vascular, which markets the CCEE (Xience) stents used in both studies. Dr. Watanabe has received lecture fees from Abbott and from Daiichi-Sankyo. Dr. Byrne has received research funding from Abbott Vascular as well as from Biosensors, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific. Roffi has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, GE Healthcare, Medtronic, and Terumo. Dr. Huber has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One month of dual antiplatelet therapy followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy failed to prove noninferiority to 12 unbroken months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a multicenter Japanese trial that randomized more than 4,000 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) after a recent acute coronary syndrome episode.
The outcomes showed that while truncating DAPT duration could, as expected, cut major bleeding episodes roughly in half, it also led to a significant near doubling of myocardial infarction and showed a strong trend toward also increasing a composite tally of several types of ischemic events. These data were reported this week by Hirotoshi Watanabe, MD, PhD, at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. All study patients had undergone PCI with cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting (CCEE) coronary stents (Xience).
These findings from the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial highlighted the limits of minimizing DAPT after PCI in patients at high ischemic risk, such as after an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) event.
It also was a counterpoint to a somewhat similar study also reported at the congress, MASTER DAPT, which showed that 1 month of DAPT was noninferior to 3 or more months of DAPT for net clinical benefit in a distinctly different population of patients undergoing PCI (and using a different type of coronary stent) – those at high bleeding risk and with only about half the patients having had a recent ACS.
The results of STOPDAPT-2 ACS “do not support use of 1 month of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy with clopidogrel compared with standard DAPT,” commented Robert A. Byrne, MBBCh, PhD, designated discussant for the report and professor at the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences in Dublin.
“Although major bleeding was significantly reduced with this approach, there appeared to be a significant increase in adverse ischemic events, and there was a clear signal in relation to overall mortality, the ultimate arbiter of net clinical benefit,” added Dr. Byrne, who is also director of cardiology at Mater Private Hospital in Dublin.
He suggested that a mechanistic explanation for the signal of harm seem in STOPDAPT-2 ACS was the relatively low potency of clopidogrel (Plavix) as an antiplatelet agent, compared with other P2Y12 inhibitors such as prasugrel (Effient) and ticagrelor (Brilinta), as well as the genetically driven variability in response to clopidogrel that’s also absent with alternative agents.
These between-agent differences are of “particular clinical relevance in the early aftermath of an ACS event,” Dr. Byrne said.
12-month DAPT remains standard for PCI patients with recent ACS
The totality of clinical evidence “continues to support a standard 12-month duration of DAPT – using aspirin and either prasugrel or ticagrelor – as the preferred default approach,” Dr. Byrne concluded.
He acknowledged that an abbreviated duration of DAPT followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy “might be considered as an alternative.” In patients following an ACS event who do not have high risk for bleeding, he said, the minimum duration of DAPT should be at least 3 months and with preferential use of a more potent P2Y12 inhibitor.
Twelve months of DAPT treatment with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor for patients following PCI “remains the standard of care in guidelines,” noted Marco Roffi, MD, a second discussant at the congress. But several questions remain, he added, such as which P2Y12 inhibitors work best and whether DAPT can be less than 12 months.
“The investigators [for STOPDAPT-2 ACS] pushed these questions to the limit with 1 month of DAPT and clopidogrel monotherapy,” said Dr. Roffi, professor and director of interventional cardiology at University Hospital, Geneva.
“This was a risky bet, and the investigators lost by not proving noninferiority and with excess ischemic events,” he commented.
First came STOPDAPT-2
Dr. Watanabe and colleagues designed STOPDAPT-2 ACS as a follow-up to their prior STOPDAPT-2 trial, which randomly assigned slightly more than 3000 patients at 90 Japanese centers to the identical two treatment options: 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy or 12 months of DAPT, except the trial enrolled all types of patients undergoing PCI. This meant that a minority, 38%, had a recent ACS event, while the remaining patients had chronic coronary artery disease. As in STOPDAPT-2 ACS, all patients in STOPDAPT-2 had received a CCEE stent.
STOPDAPT-2 also used the same primary endpoint to tally net clinical benefit as STOPDAPT-2 ACS: cardiovascular death, MI, stroke of any type, definite stent thrombosis, or TIMI major or minor bleeding classification.
In STOPDAPT-2, using the mixed population with both recent ACS and chronic coronary disease, the regimen of 1 month of DAPT followed by 11 months of clopidogrel monotherapy was both noninferior to and superior to 12 months of DAPT, reducing the net adverse-event tally by 36% relative to 12-month DAPT and by an absolute reduction of 1.34%, as reported in 2019.
Despite this superiority, the results from STOPDAPT-2 had little impact on global practice, commented Kurt Huber, MD, professor and director of the cardiology ICU at the Medical University of Vienna.
“STOP-DAPT-2 did not give us a clear message with respect to reducing antiplatelet treatment after 1 month. I thought that for ACS patients 1 month might be too short,” Dr. Huber said during a press briefing.
Focusing on post-ACS
To directly address this issue, the investigators launched STOPDAPT-2 ACS, which used the same design as the preceding study but only enrolled patients soon after an ACS event. The trial included for its main analysis 3,008 newly enrolled patients with recent ACS, and 1,161 patients who had a recent ACS event and had been randomly assigned in STOPDAPT-2, creating a total study cohort for the new analysis of 4136 patients treated and followed for the study’s full 12 months.
The patients averaged 67 years old, 79% were men, and 30% had diabetes. About 56% had a recent ST-elevation MI, about 20% a recent non–ST-elevation MI, and the remaining 24% had unstable angina. For their unspecified P2Y12 inhibition, roughly half the patients received clopidogrel and the rest received prasugrel. Adherence to the two assigned treatment regimens was very good, with a very small number of patients not adhering to their assigned protocol.
The composite adverse event incidence over 12 months was 3.2% among those who received 1-month DAPT and 2.83% in those on DAPT for 12 months, a difference that failed to achieve the prespecified definition of noninferiority for 1-month DAPT, reported Dr. Watanabe, an interventional cardiologist at Kyoto University.
The ischemic event composite was 50% lower among those on 12-month DAPT, compared with 1 month of DAPT, a difference that just missed significance. The rate of MI was 91% higher with 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months, a significant difference.
One-month DAPT also significantly reduced the primary measure of bleeding events – the combination of TIMI major and minor bleeds – by a significant 54%, compared with 12-month DAPT. A second metric of clinically meaningful bleeds, those that meet either the type 3 or 5 definition of the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium, were reduced by a significant 59% by 1-month DAPT, compared with 12 months of DAPT.
The new findings from STOPDAPT-2 ACS contrasted with those from MASTER DAPT, but in an explicable way that related to different patient types, different P2Y12 inhibitors, different treatment durations, and different stents.
“We’ve seen in MASTER DAPT that if you use the right stent and use ticagrelor for monotherapy there may be some ability to shorten DAPT, but we still do not know what would happen in patients with very high ischemic risk,” concluded Dr. Huber.
“A reduction in DAPT duration might work in patients without high bleeding risk, but I would exclude patients with very high ischemic risk,” he added. “I also can’t tell you whether 1 month or 3 months is the right approach, and I think clopidogrel is not the right drug to use for monotherapy after ACS.”
STOPDAPT-2 and STOPDAPT-2 ACS were both sponsored by Abbott Vascular, which markets the CCEE (Xience) stents used in both studies. Dr. Watanabe has received lecture fees from Abbott and from Daiichi-Sankyo. Dr. Byrne has received research funding from Abbott Vascular as well as from Biosensors, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific. Roffi has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, GE Healthcare, Medtronic, and Terumo. Dr. Huber has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Explaining Away Those Shades of Gray
ANSWER
The correct answer is that new hairs growing in to replace those lost from alopecia areata tend to be white (choice “b”). They usually regain their normal color, eventually.
DISCUSSION
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune phenomenon implying an increased tendency to develop other autoimmune diseases (eg, vitiligo [choice “a”], which can appear initially in the scalp).
This case turned out to be simple but had the potential to be far more serious. The biopsy of the dark patch showed benign seborrheic keratosis, but it was possible that another section could have demonstrated features of melanoma (choice “c”). When present, melanoma can occasionally trigger an immune response that destroys pigment cells in hair follicles, causing the hairs to lose their pigment. This is why the entire dark patch was later excised. Fortunately, the pathology report ruled out melanoma.
While it has been reported that stress can cause hair to turn gray (choice “d”), there were better (and more accurate) explanations for this patient’s presentation.
This case, though fairly straightforward, serves as a reminder that it is our job as clinicians to connect the dots to rule out worst-case scenarios.
Outcome
This patient’s hair all grew back, regaining its normal color, without any treatment.
ANSWER
The correct answer is that new hairs growing in to replace those lost from alopecia areata tend to be white (choice “b”). They usually regain their normal color, eventually.
DISCUSSION
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune phenomenon implying an increased tendency to develop other autoimmune diseases (eg, vitiligo [choice “a”], which can appear initially in the scalp).
This case turned out to be simple but had the potential to be far more serious. The biopsy of the dark patch showed benign seborrheic keratosis, but it was possible that another section could have demonstrated features of melanoma (choice “c”). When present, melanoma can occasionally trigger an immune response that destroys pigment cells in hair follicles, causing the hairs to lose their pigment. This is why the entire dark patch was later excised. Fortunately, the pathology report ruled out melanoma.
While it has been reported that stress can cause hair to turn gray (choice “d”), there were better (and more accurate) explanations for this patient’s presentation.
This case, though fairly straightforward, serves as a reminder that it is our job as clinicians to connect the dots to rule out worst-case scenarios.
Outcome
This patient’s hair all grew back, regaining its normal color, without any treatment.
ANSWER
The correct answer is that new hairs growing in to replace those lost from alopecia areata tend to be white (choice “b”). They usually regain their normal color, eventually.
DISCUSSION
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune phenomenon implying an increased tendency to develop other autoimmune diseases (eg, vitiligo [choice “a”], which can appear initially in the scalp).
This case turned out to be simple but had the potential to be far more serious. The biopsy of the dark patch showed benign seborrheic keratosis, but it was possible that another section could have demonstrated features of melanoma (choice “c”). When present, melanoma can occasionally trigger an immune response that destroys pigment cells in hair follicles, causing the hairs to lose their pigment. This is why the entire dark patch was later excised. Fortunately, the pathology report ruled out melanoma.
While it has been reported that stress can cause hair to turn gray (choice “d”), there were better (and more accurate) explanations for this patient’s presentation.
This case, though fairly straightforward, serves as a reminder that it is our job as clinicians to connect the dots to rule out worst-case scenarios.
Outcome
This patient’s hair all grew back, regaining its normal color, without any treatment.
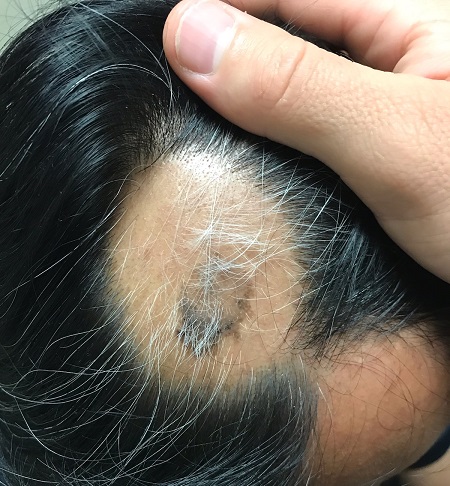
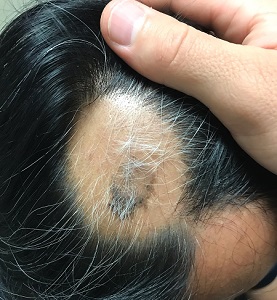
About 2 months ago, a 55-year-old man suddenly experienced complete hair loss in 1 confined area of his scalp. There were no accompanying symptoms. Some of the hair subsequently grew back, but it was partially gray—a phenomenon that greatly disturbed the patient.
In general, the patient’s health was quite good, although he reported that the initial hair loss occurred about 1 month after he lost his job and got divorced.
Most of the hair was missing from a roughly round, 5-cm, ill-defined area of the left parietal scalp. The few hairs left were gray. More disturbing, though, was a dark (brown, tan, and black), oddly shaped, 2.8-cm patch in the center of the alopecic area.
Punch biopsy from the bald area showed clear evidence of alopecia areata (T-cells surrounding hair follicles, and lack of features that would support other items in the differential). Shave biopsy of the dark patch showed seborrheic keratosis, with no atypia.
FDA inaction on hair loss drug’s suicide, depression, erectile dysfunction risk sparks lawsuit
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Will interchangeable insulin be more affordable in the U.S.?
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VARSITY: Better histologic outcomes with vedolizumab than adalimumab in UC
In patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (UC), treatment with vedolizumab leads to better histologic outcomes than treatment with adalimumab, according to findings from the VARSITY trial.
The findings come from an analysis in Gastroenterology of prespecified histologic exploratory endpoints from the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, controlled VARSITY trial, which was the first head-to-head comparison of two biologics in the treatment of UC. VARSITY demonstrated improved rates of clinical remission and endoscopic improvement at week 52 with vedolizumab.
The authors, led by Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet of the department of gastroenterology at Nancy (France) University Hospital, noted that there is general consensus that endoscopic improvement is considered the best endpoint for demonstrating effective maintenance therapy in UC. However, they added that “endoscopic changes do not necessarily reflect quiescent microscopic disease, and complete resolution of mucosal inflammation can only be confirmed by histologic assessment.” Still, histologic outcomes are not currently recommended as a goal of therapy in clinical practice, possibly due to a lack of standardized and validated scoring systems suitable for routine clinical use. Nevertheless, histologic outcomes have been shown to predict hospitalization, corticosteroid use, exacerbation, and the risk of advanced colorectal neoplasia.
To assess histologic outcomes in the two treatment regimens, the researchers included the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index (RHI) as two validated scoring systems.
During the 52-week study, 769 patients were assigned to vedolizumab (300 mg IV) or adalimumab (40 mg subcutaneously).
At week 14 and week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group achieved histologic remission as determined by Geboes Index score less than 2 (week 52, 29.2% vs. 8.3%; difference, 20.9%; 95% confidence interval, 15.6%-26.2%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 2 or less (week 52, 37.6% vs. 19.9%; difference, 17.6%; 95% CI, 11.3%-23.8%; P < .0001).
At week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group than in the adalimumab group achieved minimum histologic disease activity as determined by Geboes Index score of 3.1 or less (45.7% vs. 30.8%; difference, 14.8%; 95% CI, 8.0%-21.5%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 4 or less(42.3% vs. 25.6%; difference, 16.6%; 95% CI, 10.0%-23.1%; P < .0001).
The investigators performed post hoc analyses of mucosal healing, defined as a composite of the histologic and endoscopic outcomes, with the latter defined as Mayo endoscopic subscore of 1 or less. A greater proportion of patients treated with vedolizumab than with adalimumab met the composite of histologic remission on each score plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%), with similar findings for minimal histologic disease activity plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%).
The authors noted that the RHI scoring system revealed greater associations between histologic outcomes and endoscopic improvement than did the Geboes Index score, which is an important finding considering the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation’s stance recommending consideration of mucosal healing based on findings from endoscopy and histology.
Some study limitations included how the study design precluded dose escalation and a lack of long-term follow-up among these patients.
The researchers believe that the RHI score may be a better choice than the Geboes score for comparing efficacy in clinical trials because RHI is more reproducible, more sensitive to change, and is comparatively easy to interpret.
The study was funded by Takeda, which makes vedolizumab. The authors disclosed several relationships with industry, including some having stock options with or being employed by Takeda.
Another important element of this study was the exploration of association between endoscopic and histologic outcomes using two validated histologic indices (the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index). While both indices showed moderate agreement overall between histologic activity and endoscopic improvement, the Robarts score correlated better with endoscopic improvement. Therefore, the authors propose that the Robarts scoring system may be the better index for assessing histologic outcomes. This is important because standardized scoring systems would be needed to translate histologic outcomes as a goal in real clinical practice.
The landscape continues to evolve for treatment goals in UC. Symptom control is the tip of the iceberg and endoscopic along with histologic control may lead to a more durable remission.
Robin Dalal, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has nothing to disclose.
Another important element of this study was the exploration of association between endoscopic and histologic outcomes using two validated histologic indices (the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index). While both indices showed moderate agreement overall between histologic activity and endoscopic improvement, the Robarts score correlated better with endoscopic improvement. Therefore, the authors propose that the Robarts scoring system may be the better index for assessing histologic outcomes. This is important because standardized scoring systems would be needed to translate histologic outcomes as a goal in real clinical practice.
The landscape continues to evolve for treatment goals in UC. Symptom control is the tip of the iceberg and endoscopic along with histologic control may lead to a more durable remission.
Robin Dalal, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has nothing to disclose.
Another important element of this study was the exploration of association between endoscopic and histologic outcomes using two validated histologic indices (the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index). While both indices showed moderate agreement overall between histologic activity and endoscopic improvement, the Robarts score correlated better with endoscopic improvement. Therefore, the authors propose that the Robarts scoring system may be the better index for assessing histologic outcomes. This is important because standardized scoring systems would be needed to translate histologic outcomes as a goal in real clinical practice.
The landscape continues to evolve for treatment goals in UC. Symptom control is the tip of the iceberg and endoscopic along with histologic control may lead to a more durable remission.
Robin Dalal, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has nothing to disclose.
In patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (UC), treatment with vedolizumab leads to better histologic outcomes than treatment with adalimumab, according to findings from the VARSITY trial.
The findings come from an analysis in Gastroenterology of prespecified histologic exploratory endpoints from the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, controlled VARSITY trial, which was the first head-to-head comparison of two biologics in the treatment of UC. VARSITY demonstrated improved rates of clinical remission and endoscopic improvement at week 52 with vedolizumab.
The authors, led by Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet of the department of gastroenterology at Nancy (France) University Hospital, noted that there is general consensus that endoscopic improvement is considered the best endpoint for demonstrating effective maintenance therapy in UC. However, they added that “endoscopic changes do not necessarily reflect quiescent microscopic disease, and complete resolution of mucosal inflammation can only be confirmed by histologic assessment.” Still, histologic outcomes are not currently recommended as a goal of therapy in clinical practice, possibly due to a lack of standardized and validated scoring systems suitable for routine clinical use. Nevertheless, histologic outcomes have been shown to predict hospitalization, corticosteroid use, exacerbation, and the risk of advanced colorectal neoplasia.
To assess histologic outcomes in the two treatment regimens, the researchers included the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index (RHI) as two validated scoring systems.
During the 52-week study, 769 patients were assigned to vedolizumab (300 mg IV) or adalimumab (40 mg subcutaneously).
At week 14 and week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group achieved histologic remission as determined by Geboes Index score less than 2 (week 52, 29.2% vs. 8.3%; difference, 20.9%; 95% confidence interval, 15.6%-26.2%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 2 or less (week 52, 37.6% vs. 19.9%; difference, 17.6%; 95% CI, 11.3%-23.8%; P < .0001).
At week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group than in the adalimumab group achieved minimum histologic disease activity as determined by Geboes Index score of 3.1 or less (45.7% vs. 30.8%; difference, 14.8%; 95% CI, 8.0%-21.5%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 4 or less(42.3% vs. 25.6%; difference, 16.6%; 95% CI, 10.0%-23.1%; P < .0001).
The investigators performed post hoc analyses of mucosal healing, defined as a composite of the histologic and endoscopic outcomes, with the latter defined as Mayo endoscopic subscore of 1 or less. A greater proportion of patients treated with vedolizumab than with adalimumab met the composite of histologic remission on each score plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%), with similar findings for minimal histologic disease activity plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%).
The authors noted that the RHI scoring system revealed greater associations between histologic outcomes and endoscopic improvement than did the Geboes Index score, which is an important finding considering the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation’s stance recommending consideration of mucosal healing based on findings from endoscopy and histology.
Some study limitations included how the study design precluded dose escalation and a lack of long-term follow-up among these patients.
The researchers believe that the RHI score may be a better choice than the Geboes score for comparing efficacy in clinical trials because RHI is more reproducible, more sensitive to change, and is comparatively easy to interpret.
The study was funded by Takeda, which makes vedolizumab. The authors disclosed several relationships with industry, including some having stock options with or being employed by Takeda.
In patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (UC), treatment with vedolizumab leads to better histologic outcomes than treatment with adalimumab, according to findings from the VARSITY trial.
The findings come from an analysis in Gastroenterology of prespecified histologic exploratory endpoints from the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, controlled VARSITY trial, which was the first head-to-head comparison of two biologics in the treatment of UC. VARSITY demonstrated improved rates of clinical remission and endoscopic improvement at week 52 with vedolizumab.
The authors, led by Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet of the department of gastroenterology at Nancy (France) University Hospital, noted that there is general consensus that endoscopic improvement is considered the best endpoint for demonstrating effective maintenance therapy in UC. However, they added that “endoscopic changes do not necessarily reflect quiescent microscopic disease, and complete resolution of mucosal inflammation can only be confirmed by histologic assessment.” Still, histologic outcomes are not currently recommended as a goal of therapy in clinical practice, possibly due to a lack of standardized and validated scoring systems suitable for routine clinical use. Nevertheless, histologic outcomes have been shown to predict hospitalization, corticosteroid use, exacerbation, and the risk of advanced colorectal neoplasia.
To assess histologic outcomes in the two treatment regimens, the researchers included the Geboes Index score and the Robarts Histopathology Index (RHI) as two validated scoring systems.
During the 52-week study, 769 patients were assigned to vedolizumab (300 mg IV) or adalimumab (40 mg subcutaneously).
At week 14 and week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group achieved histologic remission as determined by Geboes Index score less than 2 (week 52, 29.2% vs. 8.3%; difference, 20.9%; 95% confidence interval, 15.6%-26.2%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 2 or less (week 52, 37.6% vs. 19.9%; difference, 17.6%; 95% CI, 11.3%-23.8%; P < .0001).
At week 52, more patients in the vedolizumab group than in the adalimumab group achieved minimum histologic disease activity as determined by Geboes Index score of 3.1 or less (45.7% vs. 30.8%; difference, 14.8%; 95% CI, 8.0%-21.5%; P < .0001) and RHI score of 4 or less(42.3% vs. 25.6%; difference, 16.6%; 95% CI, 10.0%-23.1%; P < .0001).
The investigators performed post hoc analyses of mucosal healing, defined as a composite of the histologic and endoscopic outcomes, with the latter defined as Mayo endoscopic subscore of 1 or less. A greater proportion of patients treated with vedolizumab than with adalimumab met the composite of histologic remission on each score plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%), with similar findings for minimal histologic disease activity plus endoscopic improvement (Geboes, 35.0% vs. 20.2%; RHI, 33.7% vs. 18.1%).
The authors noted that the RHI scoring system revealed greater associations between histologic outcomes and endoscopic improvement than did the Geboes Index score, which is an important finding considering the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation’s stance recommending consideration of mucosal healing based on findings from endoscopy and histology.
Some study limitations included how the study design precluded dose escalation and a lack of long-term follow-up among these patients.
The researchers believe that the RHI score may be a better choice than the Geboes score for comparing efficacy in clinical trials because RHI is more reproducible, more sensitive to change, and is comparatively easy to interpret.
The study was funded by Takeda, which makes vedolizumab. The authors disclosed several relationships with industry, including some having stock options with or being employed by Takeda.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Elderly mice receive the gift of warmth
Steal from the warm, give to the cold
If there’s one constant in life other than taxes, it’s elderly people moving to Florida. The Sunshine State’s reputation as a giant retirement home needs no elaboration, but why do senior citizens gravitate there? Well, many reasons, but a big one is that, the older you get, the more susceptible and sensitive you are to the cold. And now, according to a new study, we may have identified a culprit.
Researchers from Yale University examined a group of mice and found that the older ones lacked ICL2 cells in their fatty tissue. These cells, at least in younger mice, help restore body heat when exposed to cold temperatures. Lacking these cells meant that older mice had a limited ability to burn their fat and raise their temperature in response to cold.
Well, job done, all we need to do now is stimulate production of ICL2 cells in elderly people, and they’ll be able to go outside in 80-degree weather without a sweater again. Except there’s a problem. In a cruel twist of fate, when the elderly mice were given a molecule to boost ICL2 cell production, they actually became less tolerant of the cold than at baseline. Oops.
The scientists didn’t give up though, and gave their elderly mice ICL2 cells from young mice. This finally did the trick, though we have to admit, if that treatment does eventually scale up to humans, the prospect of a bunch of senior citizens taking ICL2 cells from young people to stay warm does sound a bit like a bad vampire movie premise. “I vant to suck your immune cell group 2 innate lymphoid cells!” Not the most pithy catch phrase in the world.
Grocery store tapping your subconscious? It’s a good thing
We all know there’s marketing and functionality elements to grocery stores and how they’re set up for your shopping pleasure. But what if I told you that the good old supermarket subconscious trick works on how healthy food decisions are?
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Southampton in England found that if you placed a wider selection of fruits and vegetables near the entrances and more nonfood items near checkouts, sales decreased on the sweets and increased on the produce. “The findings of our study suggest that a healthier store layout could lead to nearly 10,000 extra portions of fruit and vegetables and approximately 1,500 fewer portions of confectionery being sold on a weekly basis in each store,” lead author Dr. Christina Vogel explained.
You’re probably thinking that food placement studies aren’t new. That’s true, but this one went above and beyond. Instead of just looking at the influence placement has on purchase, this one took it further by trying to reduce the consumers’ “calorie opportunities” and examining the effect on sales. Also, customer loyalty, patterns, and diets were taken into account across multiple household members.
The researchers think shifting the layouts in grocery stores could shift people’s food choices, producing a domino effect on the population’s overall diet. With obesity, diabetes, and cardiology concerns always looming, swaying consumers toward healthier food choices makes for better public health overall.
So if you feel like you’re being subconsciously assaulted by veggies every time you walk into Trader Joe’s, just know it’s for your own good.
TikTokers take on tics
We know TikTok is what makes a lot of teens and young adults tick, but what if TikTokers are actually catching tic disorders from other TikTokers?
TikTok blew up during the pandemic. Many people were stuck at home and had nothing better to do than make and watch TikTok videos. The pandemic brought isolation, uncertainty, and anxiety. The stress that followed may have caused many people, mostly women and young girls, to develop tic disorders.
There’s a TikTok for everything, whether it’s a new dance or a recipe. Many people even use TikTok to speak out about their illnesses. Several TikTokers have Tourette’s syndrome and show their tics on their videos. It appears that some audience members actually “catch” the tics from watching the videos and are then unable to stop certain jerking movements or saying specific words.
Neurologists at the University of Calgary (Alta.), who were hearing from colleagues and getting referrals of such patients, called it “an epidemic within the pandemic.” The behavior is not actually Tourette’s, they told Vice, but the patients “cannot stop, and we have absolutely witnessed that.”
There is, of course, controversy over the issue. One individual with the condition said, “I feel like there’s a lot of really weird, backwards stigma on TikTok about tic disorders. Like, you aren’t allowed to have one unless it’s this one.”
Who would have guessed that people would disagree over stuff on the Internet?
Look on the bright side: Obesity edition
The pandemic may have postponed “Top Gun: Maverick” and “The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel” until who-knows-when, but we here at LOTME are happy to announce the nearly-as-anticipated return of Bacteria vs. the World.
As you may recall from our last edition of BVTW, bacteria battled the ghost of Charles Darwin, who had taken the earthly form of antibiotics capable of stopping bacterial evolution. Tonight, our prokaryotic protagonists take on an equally relentless and ubiquitous challenger: obesity.
Specifically, we’re putting bacteria up against the obesity survival paradox, that phenomenon in which obesity and overweight seem to protect against – yes, you guessed it – bacterial infections.
A Swedish research team observed a group of 2,196 individual adults who received care for suspected severe bacterial infection at Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde. One year after hospitalization, 26% of normal-weight (body mass index, 18.5-24.99) patients were dead, compared with 17% of overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.99), 16% of obese (BMI, 30.0-34.99), and 9% of very obese (BMI >35) patients.
These results confirm the obesity survival paradox, but “what we don’t know is how being overweight can benefit the patient with a bacterial infection, or whether it’s connected with functions in the immune system and how they’re regulated,” lead author Dr. Åsa Alsiö said in a written statement.
A spokes-cell for the bacteria disputed the results and challenged the legitimacy of the investigators. When asked if there should be some sort of reexamination of the findings, he/she/it replied: “You bet your flagella.” We then pointed out that humans don’t have flagellum, and the representative raised his/her/its flagella in what could only be considered an obscene gesture.
Steal from the warm, give to the cold
If there’s one constant in life other than taxes, it’s elderly people moving to Florida. The Sunshine State’s reputation as a giant retirement home needs no elaboration, but why do senior citizens gravitate there? Well, many reasons, but a big one is that, the older you get, the more susceptible and sensitive you are to the cold. And now, according to a new study, we may have identified a culprit.
Researchers from Yale University examined a group of mice and found that the older ones lacked ICL2 cells in their fatty tissue. These cells, at least in younger mice, help restore body heat when exposed to cold temperatures. Lacking these cells meant that older mice had a limited ability to burn their fat and raise their temperature in response to cold.
Well, job done, all we need to do now is stimulate production of ICL2 cells in elderly people, and they’ll be able to go outside in 80-degree weather without a sweater again. Except there’s a problem. In a cruel twist of fate, when the elderly mice were given a molecule to boost ICL2 cell production, they actually became less tolerant of the cold than at baseline. Oops.
The scientists didn’t give up though, and gave their elderly mice ICL2 cells from young mice. This finally did the trick, though we have to admit, if that treatment does eventually scale up to humans, the prospect of a bunch of senior citizens taking ICL2 cells from young people to stay warm does sound a bit like a bad vampire movie premise. “I vant to suck your immune cell group 2 innate lymphoid cells!” Not the most pithy catch phrase in the world.
Grocery store tapping your subconscious? It’s a good thing
We all know there’s marketing and functionality elements to grocery stores and how they’re set up for your shopping pleasure. But what if I told you that the good old supermarket subconscious trick works on how healthy food decisions are?
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Southampton in England found that if you placed a wider selection of fruits and vegetables near the entrances and more nonfood items near checkouts, sales decreased on the sweets and increased on the produce. “The findings of our study suggest that a healthier store layout could lead to nearly 10,000 extra portions of fruit and vegetables and approximately 1,500 fewer portions of confectionery being sold on a weekly basis in each store,” lead author Dr. Christina Vogel explained.
You’re probably thinking that food placement studies aren’t new. That’s true, but this one went above and beyond. Instead of just looking at the influence placement has on purchase, this one took it further by trying to reduce the consumers’ “calorie opportunities” and examining the effect on sales. Also, customer loyalty, patterns, and diets were taken into account across multiple household members.
The researchers think shifting the layouts in grocery stores could shift people’s food choices, producing a domino effect on the population’s overall diet. With obesity, diabetes, and cardiology concerns always looming, swaying consumers toward healthier food choices makes for better public health overall.
So if you feel like you’re being subconsciously assaulted by veggies every time you walk into Trader Joe’s, just know it’s for your own good.
TikTokers take on tics
We know TikTok is what makes a lot of teens and young adults tick, but what if TikTokers are actually catching tic disorders from other TikTokers?
TikTok blew up during the pandemic. Many people were stuck at home and had nothing better to do than make and watch TikTok videos. The pandemic brought isolation, uncertainty, and anxiety. The stress that followed may have caused many people, mostly women and young girls, to develop tic disorders.
There’s a TikTok for everything, whether it’s a new dance or a recipe. Many people even use TikTok to speak out about their illnesses. Several TikTokers have Tourette’s syndrome and show their tics on their videos. It appears that some audience members actually “catch” the tics from watching the videos and are then unable to stop certain jerking movements or saying specific words.
Neurologists at the University of Calgary (Alta.), who were hearing from colleagues and getting referrals of such patients, called it “an epidemic within the pandemic.” The behavior is not actually Tourette’s, they told Vice, but the patients “cannot stop, and we have absolutely witnessed that.”
There is, of course, controversy over the issue. One individual with the condition said, “I feel like there’s a lot of really weird, backwards stigma on TikTok about tic disorders. Like, you aren’t allowed to have one unless it’s this one.”
Who would have guessed that people would disagree over stuff on the Internet?
Look on the bright side: Obesity edition
The pandemic may have postponed “Top Gun: Maverick” and “The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel” until who-knows-when, but we here at LOTME are happy to announce the nearly-as-anticipated return of Bacteria vs. the World.
As you may recall from our last edition of BVTW, bacteria battled the ghost of Charles Darwin, who had taken the earthly form of antibiotics capable of stopping bacterial evolution. Tonight, our prokaryotic protagonists take on an equally relentless and ubiquitous challenger: obesity.
Specifically, we’re putting bacteria up against the obesity survival paradox, that phenomenon in which obesity and overweight seem to protect against – yes, you guessed it – bacterial infections.
A Swedish research team observed a group of 2,196 individual adults who received care for suspected severe bacterial infection at Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde. One year after hospitalization, 26% of normal-weight (body mass index, 18.5-24.99) patients were dead, compared with 17% of overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.99), 16% of obese (BMI, 30.0-34.99), and 9% of very obese (BMI >35) patients.
These results confirm the obesity survival paradox, but “what we don’t know is how being overweight can benefit the patient with a bacterial infection, or whether it’s connected with functions in the immune system and how they’re regulated,” lead author Dr. Åsa Alsiö said in a written statement.
A spokes-cell for the bacteria disputed the results and challenged the legitimacy of the investigators. When asked if there should be some sort of reexamination of the findings, he/she/it replied: “You bet your flagella.” We then pointed out that humans don’t have flagellum, and the representative raised his/her/its flagella in what could only be considered an obscene gesture.
Steal from the warm, give to the cold
If there’s one constant in life other than taxes, it’s elderly people moving to Florida. The Sunshine State’s reputation as a giant retirement home needs no elaboration, but why do senior citizens gravitate there? Well, many reasons, but a big one is that, the older you get, the more susceptible and sensitive you are to the cold. And now, according to a new study, we may have identified a culprit.
Researchers from Yale University examined a group of mice and found that the older ones lacked ICL2 cells in their fatty tissue. These cells, at least in younger mice, help restore body heat when exposed to cold temperatures. Lacking these cells meant that older mice had a limited ability to burn their fat and raise their temperature in response to cold.
Well, job done, all we need to do now is stimulate production of ICL2 cells in elderly people, and they’ll be able to go outside in 80-degree weather without a sweater again. Except there’s a problem. In a cruel twist of fate, when the elderly mice were given a molecule to boost ICL2 cell production, they actually became less tolerant of the cold than at baseline. Oops.
The scientists didn’t give up though, and gave their elderly mice ICL2 cells from young mice. This finally did the trick, though we have to admit, if that treatment does eventually scale up to humans, the prospect of a bunch of senior citizens taking ICL2 cells from young people to stay warm does sound a bit like a bad vampire movie premise. “I vant to suck your immune cell group 2 innate lymphoid cells!” Not the most pithy catch phrase in the world.
Grocery store tapping your subconscious? It’s a good thing
We all know there’s marketing and functionality elements to grocery stores and how they’re set up for your shopping pleasure. But what if I told you that the good old supermarket subconscious trick works on how healthy food decisions are?
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Southampton in England found that if you placed a wider selection of fruits and vegetables near the entrances and more nonfood items near checkouts, sales decreased on the sweets and increased on the produce. “The findings of our study suggest that a healthier store layout could lead to nearly 10,000 extra portions of fruit and vegetables and approximately 1,500 fewer portions of confectionery being sold on a weekly basis in each store,” lead author Dr. Christina Vogel explained.
You’re probably thinking that food placement studies aren’t new. That’s true, but this one went above and beyond. Instead of just looking at the influence placement has on purchase, this one took it further by trying to reduce the consumers’ “calorie opportunities” and examining the effect on sales. Also, customer loyalty, patterns, and diets were taken into account across multiple household members.
The researchers think shifting the layouts in grocery stores could shift people’s food choices, producing a domino effect on the population’s overall diet. With obesity, diabetes, and cardiology concerns always looming, swaying consumers toward healthier food choices makes for better public health overall.
So if you feel like you’re being subconsciously assaulted by veggies every time you walk into Trader Joe’s, just know it’s for your own good.
TikTokers take on tics
We know TikTok is what makes a lot of teens and young adults tick, but what if TikTokers are actually catching tic disorders from other TikTokers?
TikTok blew up during the pandemic. Many people were stuck at home and had nothing better to do than make and watch TikTok videos. The pandemic brought isolation, uncertainty, and anxiety. The stress that followed may have caused many people, mostly women and young girls, to develop tic disorders.
There’s a TikTok for everything, whether it’s a new dance or a recipe. Many people even use TikTok to speak out about their illnesses. Several TikTokers have Tourette’s syndrome and show their tics on their videos. It appears that some audience members actually “catch” the tics from watching the videos and are then unable to stop certain jerking movements or saying specific words.
Neurologists at the University of Calgary (Alta.), who were hearing from colleagues and getting referrals of such patients, called it “an epidemic within the pandemic.” The behavior is not actually Tourette’s, they told Vice, but the patients “cannot stop, and we have absolutely witnessed that.”
There is, of course, controversy over the issue. One individual with the condition said, “I feel like there’s a lot of really weird, backwards stigma on TikTok about tic disorders. Like, you aren’t allowed to have one unless it’s this one.”
Who would have guessed that people would disagree over stuff on the Internet?
Look on the bright side: Obesity edition
The pandemic may have postponed “Top Gun: Maverick” and “The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel” until who-knows-when, but we here at LOTME are happy to announce the nearly-as-anticipated return of Bacteria vs. the World.
As you may recall from our last edition of BVTW, bacteria battled the ghost of Charles Darwin, who had taken the earthly form of antibiotics capable of stopping bacterial evolution. Tonight, our prokaryotic protagonists take on an equally relentless and ubiquitous challenger: obesity.
Specifically, we’re putting bacteria up against the obesity survival paradox, that phenomenon in which obesity and overweight seem to protect against – yes, you guessed it – bacterial infections.
A Swedish research team observed a group of 2,196 individual adults who received care for suspected severe bacterial infection at Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde. One year after hospitalization, 26% of normal-weight (body mass index, 18.5-24.99) patients were dead, compared with 17% of overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.99), 16% of obese (BMI, 30.0-34.99), and 9% of very obese (BMI >35) patients.
These results confirm the obesity survival paradox, but “what we don’t know is how being overweight can benefit the patient with a bacterial infection, or whether it’s connected with functions in the immune system and how they’re regulated,” lead author Dr. Åsa Alsiö said in a written statement.
A spokes-cell for the bacteria disputed the results and challenged the legitimacy of the investigators. When asked if there should be some sort of reexamination of the findings, he/she/it replied: “You bet your flagella.” We then pointed out that humans don’t have flagellum, and the representative raised his/her/its flagella in what could only be considered an obscene gesture.
Modifier -25 and the New 2021 E/M Codes: Documentation of Separate and Distinct Just Got Easier
Insurers Target Modifier -25
Modifier -25 allows reporting of both a minor procedure (ie, one with a 0- or 10-day global period) and a separate and distinct evaluation and management (E/M) service on the same date of service.1 Because of the multicomplaint nature of dermatology, the ability to report a same-day procedure and an E/M service is critical for efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered dermatologic care. However, it is well known that the use of modifier -25 has been under notable insurer scrutiny and is a common reason for medical record audits.2,3 Some insurers have responded to increased utilization of modifier -25 by cutting reimbursement for claims that include both a procedure and an E/M service or by denying one of the services altogether.4-6 The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services also have expressed concern about this coding combination with proposed cuts to reimbursement.7 Moreover, the Office of Inspector General has announced a work plan to investigate the frequent utilization of E/M codes and minor procedures by dermatologists.8 Clearly, modifier -25 is a continued target by insurers and regulators; therefore, dermatologists will want to make sure their coding and documentation meet all requirements and are updated for the new E/M codes for 2021.
The American Medical Association’s Current Procedural Terminology indicates that modifier -25 allows reporting of a “significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management service by the same physician or other qualified health care professional on the same day of a procedure or other service.”1 Given that dermatology patients typically present with multiple concerns, dermatologists commonly evaluate and treat numerous conditions during one visit. Understanding what constitutes a separately identifiable E/M service is critical to bill accurately and to pass insurer audits.
Global Surgical Package
To appropriately bill both a procedure and an E/M service, the physician must indicate that the patient’s condition required an E/M service above and beyond the usual work of the procedure. The compilation of evaluation and work included in the payment for a procedure is called the global surgical package.9 In general, the global surgical package includes local or topical anesthesia; the surgical service/procedure itself; immediate postoperative care, including dictating the operative note; meeting/discussing the patient’s procedure with family and other physicians; and writing orders for the patient. For minor procedures (ie, those with either 0- or 10-day global periods), the surgical package also includes same-day E/M services associated with the decision to perform surgery. An appropriate history and physical examination as well as a discussion of the differential diagnosis, treatment options, and risk and benefits of treatment are all included in the payment of a minor procedure itself. Therefore, an evaluation to discuss a patient’s condition or change in condition, alternatives to treatment, or next steps after a diagnosis related to a treatment or diagnostic procedure should not be separately reported. Moreover, the fact that the patient is new to the physician is not in itself sufficient to allow reporting of an E/M service with these minor procedures. For major procedures (ie, those with 90-day postoperative periods), the decision for surgery is excluded from the global surgical package.
2021 E/M Codes Simplify Documentation
The biggest coding change of 2021 was the new E/M codes.10 Prior to this year, the descriptors of E/M services recognized 7 components to define the levels of E/M services11: history and nature of the presenting problem; physical examination; medical decision-making (MDM); counseling; coordination of care; and time. Furthermore, history, physical examination, and MDM were all broken down into more granular elements that were summed to determine the level for each component; for example, the history of the presenting problem was defined as a chronological description of the development of the patient’s present illness, including the following elements: location, quality, severity, duration, timing, context, modifying factors, and associated signs and symptoms. Each of these categories would constitute bullet points to be summed to determine the level of history. Physical examination and MDM bullet points also would be summed to determine a proper coding level.11 Understandably, this coding scheme was complicated and burdensome to medical providers.
The redefinition of the E/M codes for 2021 substantially simplified the determination of coding level and documentation.10 The revisions to the E/M office visit code descriptors and documentation standards are now centered around how physicians think and take care of patients and not on mandatory standards and checking boxes. The main changes involve MDM as the prime determinant of the coding level. Elements of MDM affecting coding for an outpatient or office visit now include only 3 components: the number and complexity of problems addressed in the encounter, the amount or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed, and the risk of complications or morbidity of patient management. Gone are the requirements from the earlier criteria requiring so many bullet points for the history, physical examination, and MDM.
Dermatologists may ask, “How does the new E/M coding structure affect reporting and documenting an E/M and a procedure on the same day?” The answer is that the determination of separate and distinct is basically unchanged with the new E/M codes; however, the documentation requirements for modifier -25 using the new E/M codes are simplified.
As always, the key to determining whether a separate and distinct E/M service was provided and subsequently documented is to deconstruct the medical note. All evaluation services associated with the procedure—making a clinical diagnosis or differential diagnosis, decision to perform surgery, and discussion of alternative treatments—should be removed from one’s documentation as shown in the example below. If a complete E/M service still exists, then an E/M may be billed in addition to the procedure. Physical examination of the treatment area is included in the surgical package. With the prior E/M criteria, physical examination of the procedural area could not be used again as a bullet point to count for the E/M level. However, with the new 2021 coding requirements, the documentation of a separate MDM will be sufficient to meet criteria because documentation of physical examination is not a requirement.
Modifier -25 Examples
Let’s examine a typical dermatologist medical note. An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. The patient also complains of a growing tender lesion on the left elbow of 2 months’ duration. Physical examination reveals a linear vesicular eruption on the left wrist and a tender hyperkeratotic papule on the left elbow. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed. The decision is made to perform a tangential biopsy of the lesion on the left elbow because of the suspicion for malignancy. The biopsy is performed the same day.
This case clearly illustrates performance of an E/M service in the treatment of rhus dermatitis, which is separate and distinct from the biopsy procedure; however, in evaluating whether the case meets the documentation requirements for modifier -25, the information in the medical note inclusive to the procedure’s global surgical package, including history associated with establishing the diagnosis, physical examination of the procedure area(s), and discussion of treatment options, is eliminated, leaving the following notes: An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed.
Because the physical examination of the body part (left arm) is included in the procedure’s global surgical package, the examination of the left wrist cannot be used as coding support for the E/M service. This makes a difference for coding level in the prior E/M coding requirements, which required examination bullet points. However, with the 2021 E/M codes, documentation of physical examination bullet points is irrelevant to the coding level. Therefore, qualifying for a modifier -25 claim is more straightforward in this case with the new code set. Because bullet points are not integral to the 2021 E/M codes, qualifying and properly documenting for a higher level of service will likely be more common in dermatology.
Final Thoughts
Frequent use of modifier -25 is a critical part of a high-quality and cost-effective dermatology practice. Same-day performance of minor procedures and E/M services allows for more rapid and efficient diagnosis and treatment of various conditions as well as minimizing unnecessary office visits. The new E/M codes for 2021 actually make the documentation of a separate and distinct E/M service less complicated because the bullet point requirements associated with the old E/M codes have been eliminated. Understanding how the new E/M code descriptors affect modifier -25 reporting and clear documentation of separate, distinct, and medically necessary E/M services will be needed due to increased insurer scrutiny and audits.
- Current Procedural Terminology 2021, Professional Edition. American Medical Association; 2020.
- Rogers HW. Modifier −25 victory, but the battle is not over. Cutis. 2018;101:409-410.
- Rogers HW. One diagnosis and modifier −25: appropriate or audit target? Cutis. 2017;99:165-166.
- Update regarding E/M with modifier −25—professional. Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield website. Published February 1, 2019. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://providernews.anthem.com/ohio/article/update-regarding-em-with-modifier-25-professional
- Payment policies—surgery. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care website. Updated May 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.harvardpilgrim.org/provider/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2020/07/H-6-Surgery-PM.pdf
- Modifier 25: frequently asked questions. Independence Blue Cross website. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://provcomm.ibx.com/ibc/archive/pages/A86603B03881756B8525817E00768006.aspx
- Huang G. CMS 2019 fee schedule takes modifier 25 cuts, runs with them. Doctors Management website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.doctors-management.com/cms-2019-feeschedule-modifier25/
- Dermatologist claims for evaluation and management services on the same day as minor surgical procedures. US Department of Health and Humans Services Office of Inspector General website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000577.asp
- Global surgery booklet. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated September 2018. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/outreach-and-education/medicare-learning-network-mln/mlnproducts/downloads/globallsurgery-icn907166.pdf
- American Medical Association. CPT® Evaluation and management (E/M)—office or other outpatient (99202-99215) and prolonged services (99354, 99355, 99356, 99417) code and guideline changes. Updated March 9, 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2019-06/cpt-office-prolonged-svs-code-changes.pdf
- 1997 documentation guidelines for evaluation and management services. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNEdWebGuide/Downloads/97Docguidelines.pdf
Insurers Target Modifier -25
Modifier -25 allows reporting of both a minor procedure (ie, one with a 0- or 10-day global period) and a separate and distinct evaluation and management (E/M) service on the same date of service.1 Because of the multicomplaint nature of dermatology, the ability to report a same-day procedure and an E/M service is critical for efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered dermatologic care. However, it is well known that the use of modifier -25 has been under notable insurer scrutiny and is a common reason for medical record audits.2,3 Some insurers have responded to increased utilization of modifier -25 by cutting reimbursement for claims that include both a procedure and an E/M service or by denying one of the services altogether.4-6 The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services also have expressed concern about this coding combination with proposed cuts to reimbursement.7 Moreover, the Office of Inspector General has announced a work plan to investigate the frequent utilization of E/M codes and minor procedures by dermatologists.8 Clearly, modifier -25 is a continued target by insurers and regulators; therefore, dermatologists will want to make sure their coding and documentation meet all requirements and are updated for the new E/M codes for 2021.
The American Medical Association’s Current Procedural Terminology indicates that modifier -25 allows reporting of a “significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management service by the same physician or other qualified health care professional on the same day of a procedure or other service.”1 Given that dermatology patients typically present with multiple concerns, dermatologists commonly evaluate and treat numerous conditions during one visit. Understanding what constitutes a separately identifiable E/M service is critical to bill accurately and to pass insurer audits.
Global Surgical Package
To appropriately bill both a procedure and an E/M service, the physician must indicate that the patient’s condition required an E/M service above and beyond the usual work of the procedure. The compilation of evaluation and work included in the payment for a procedure is called the global surgical package.9 In general, the global surgical package includes local or topical anesthesia; the surgical service/procedure itself; immediate postoperative care, including dictating the operative note; meeting/discussing the patient’s procedure with family and other physicians; and writing orders for the patient. For minor procedures (ie, those with either 0- or 10-day global periods), the surgical package also includes same-day E/M services associated with the decision to perform surgery. An appropriate history and physical examination as well as a discussion of the differential diagnosis, treatment options, and risk and benefits of treatment are all included in the payment of a minor procedure itself. Therefore, an evaluation to discuss a patient’s condition or change in condition, alternatives to treatment, or next steps after a diagnosis related to a treatment or diagnostic procedure should not be separately reported. Moreover, the fact that the patient is new to the physician is not in itself sufficient to allow reporting of an E/M service with these minor procedures. For major procedures (ie, those with 90-day postoperative periods), the decision for surgery is excluded from the global surgical package.
2021 E/M Codes Simplify Documentation
The biggest coding change of 2021 was the new E/M codes.10 Prior to this year, the descriptors of E/M services recognized 7 components to define the levels of E/M services11: history and nature of the presenting problem; physical examination; medical decision-making (MDM); counseling; coordination of care; and time. Furthermore, history, physical examination, and MDM were all broken down into more granular elements that were summed to determine the level for each component; for example, the history of the presenting problem was defined as a chronological description of the development of the patient’s present illness, including the following elements: location, quality, severity, duration, timing, context, modifying factors, and associated signs and symptoms. Each of these categories would constitute bullet points to be summed to determine the level of history. Physical examination and MDM bullet points also would be summed to determine a proper coding level.11 Understandably, this coding scheme was complicated and burdensome to medical providers.
The redefinition of the E/M codes for 2021 substantially simplified the determination of coding level and documentation.10 The revisions to the E/M office visit code descriptors and documentation standards are now centered around how physicians think and take care of patients and not on mandatory standards and checking boxes. The main changes involve MDM as the prime determinant of the coding level. Elements of MDM affecting coding for an outpatient or office visit now include only 3 components: the number and complexity of problems addressed in the encounter, the amount or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed, and the risk of complications or morbidity of patient management. Gone are the requirements from the earlier criteria requiring so many bullet points for the history, physical examination, and MDM.
Dermatologists may ask, “How does the new E/M coding structure affect reporting and documenting an E/M and a procedure on the same day?” The answer is that the determination of separate and distinct is basically unchanged with the new E/M codes; however, the documentation requirements for modifier -25 using the new E/M codes are simplified.
As always, the key to determining whether a separate and distinct E/M service was provided and subsequently documented is to deconstruct the medical note. All evaluation services associated with the procedure—making a clinical diagnosis or differential diagnosis, decision to perform surgery, and discussion of alternative treatments—should be removed from one’s documentation as shown in the example below. If a complete E/M service still exists, then an E/M may be billed in addition to the procedure. Physical examination of the treatment area is included in the surgical package. With the prior E/M criteria, physical examination of the procedural area could not be used again as a bullet point to count for the E/M level. However, with the new 2021 coding requirements, the documentation of a separate MDM will be sufficient to meet criteria because documentation of physical examination is not a requirement.
Modifier -25 Examples
Let’s examine a typical dermatologist medical note. An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. The patient also complains of a growing tender lesion on the left elbow of 2 months’ duration. Physical examination reveals a linear vesicular eruption on the left wrist and a tender hyperkeratotic papule on the left elbow. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed. The decision is made to perform a tangential biopsy of the lesion on the left elbow because of the suspicion for malignancy. The biopsy is performed the same day.
This case clearly illustrates performance of an E/M service in the treatment of rhus dermatitis, which is separate and distinct from the biopsy procedure; however, in evaluating whether the case meets the documentation requirements for modifier -25, the information in the medical note inclusive to the procedure’s global surgical package, including history associated with establishing the diagnosis, physical examination of the procedure area(s), and discussion of treatment options, is eliminated, leaving the following notes: An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed.
Because the physical examination of the body part (left arm) is included in the procedure’s global surgical package, the examination of the left wrist cannot be used as coding support for the E/M service. This makes a difference for coding level in the prior E/M coding requirements, which required examination bullet points. However, with the 2021 E/M codes, documentation of physical examination bullet points is irrelevant to the coding level. Therefore, qualifying for a modifier -25 claim is more straightforward in this case with the new code set. Because bullet points are not integral to the 2021 E/M codes, qualifying and properly documenting for a higher level of service will likely be more common in dermatology.
Final Thoughts
Frequent use of modifier -25 is a critical part of a high-quality and cost-effective dermatology practice. Same-day performance of minor procedures and E/M services allows for more rapid and efficient diagnosis and treatment of various conditions as well as minimizing unnecessary office visits. The new E/M codes for 2021 actually make the documentation of a separate and distinct E/M service less complicated because the bullet point requirements associated with the old E/M codes have been eliminated. Understanding how the new E/M code descriptors affect modifier -25 reporting and clear documentation of separate, distinct, and medically necessary E/M services will be needed due to increased insurer scrutiny and audits.
Insurers Target Modifier -25
Modifier -25 allows reporting of both a minor procedure (ie, one with a 0- or 10-day global period) and a separate and distinct evaluation and management (E/M) service on the same date of service.1 Because of the multicomplaint nature of dermatology, the ability to report a same-day procedure and an E/M service is critical for efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered dermatologic care. However, it is well known that the use of modifier -25 has been under notable insurer scrutiny and is a common reason for medical record audits.2,3 Some insurers have responded to increased utilization of modifier -25 by cutting reimbursement for claims that include both a procedure and an E/M service or by denying one of the services altogether.4-6 The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services also have expressed concern about this coding combination with proposed cuts to reimbursement.7 Moreover, the Office of Inspector General has announced a work plan to investigate the frequent utilization of E/M codes and minor procedures by dermatologists.8 Clearly, modifier -25 is a continued target by insurers and regulators; therefore, dermatologists will want to make sure their coding and documentation meet all requirements and are updated for the new E/M codes for 2021.
The American Medical Association’s Current Procedural Terminology indicates that modifier -25 allows reporting of a “significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management service by the same physician or other qualified health care professional on the same day of a procedure or other service.”1 Given that dermatology patients typically present with multiple concerns, dermatologists commonly evaluate and treat numerous conditions during one visit. Understanding what constitutes a separately identifiable E/M service is critical to bill accurately and to pass insurer audits.
Global Surgical Package
To appropriately bill both a procedure and an E/M service, the physician must indicate that the patient’s condition required an E/M service above and beyond the usual work of the procedure. The compilation of evaluation and work included in the payment for a procedure is called the global surgical package.9 In general, the global surgical package includes local or topical anesthesia; the surgical service/procedure itself; immediate postoperative care, including dictating the operative note; meeting/discussing the patient’s procedure with family and other physicians; and writing orders for the patient. For minor procedures (ie, those with either 0- or 10-day global periods), the surgical package also includes same-day E/M services associated with the decision to perform surgery. An appropriate history and physical examination as well as a discussion of the differential diagnosis, treatment options, and risk and benefits of treatment are all included in the payment of a minor procedure itself. Therefore, an evaluation to discuss a patient’s condition or change in condition, alternatives to treatment, or next steps after a diagnosis related to a treatment or diagnostic procedure should not be separately reported. Moreover, the fact that the patient is new to the physician is not in itself sufficient to allow reporting of an E/M service with these minor procedures. For major procedures (ie, those with 90-day postoperative periods), the decision for surgery is excluded from the global surgical package.
2021 E/M Codes Simplify Documentation
The biggest coding change of 2021 was the new E/M codes.10 Prior to this year, the descriptors of E/M services recognized 7 components to define the levels of E/M services11: history and nature of the presenting problem; physical examination; medical decision-making (MDM); counseling; coordination of care; and time. Furthermore, history, physical examination, and MDM were all broken down into more granular elements that were summed to determine the level for each component; for example, the history of the presenting problem was defined as a chronological description of the development of the patient’s present illness, including the following elements: location, quality, severity, duration, timing, context, modifying factors, and associated signs and symptoms. Each of these categories would constitute bullet points to be summed to determine the level of history. Physical examination and MDM bullet points also would be summed to determine a proper coding level.11 Understandably, this coding scheme was complicated and burdensome to medical providers.
The redefinition of the E/M codes for 2021 substantially simplified the determination of coding level and documentation.10 The revisions to the E/M office visit code descriptors and documentation standards are now centered around how physicians think and take care of patients and not on mandatory standards and checking boxes. The main changes involve MDM as the prime determinant of the coding level. Elements of MDM affecting coding for an outpatient or office visit now include only 3 components: the number and complexity of problems addressed in the encounter, the amount or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed, and the risk of complications or morbidity of patient management. Gone are the requirements from the earlier criteria requiring so many bullet points for the history, physical examination, and MDM.
Dermatologists may ask, “How does the new E/M coding structure affect reporting and documenting an E/M and a procedure on the same day?” The answer is that the determination of separate and distinct is basically unchanged with the new E/M codes; however, the documentation requirements for modifier -25 using the new E/M codes are simplified.
As always, the key to determining whether a separate and distinct E/M service was provided and subsequently documented is to deconstruct the medical note. All evaluation services associated with the procedure—making a clinical diagnosis or differential diagnosis, decision to perform surgery, and discussion of alternative treatments—should be removed from one’s documentation as shown in the example below. If a complete E/M service still exists, then an E/M may be billed in addition to the procedure. Physical examination of the treatment area is included in the surgical package. With the prior E/M criteria, physical examination of the procedural area could not be used again as a bullet point to count for the E/M level. However, with the new 2021 coding requirements, the documentation of a separate MDM will be sufficient to meet criteria because documentation of physical examination is not a requirement.
Modifier -25 Examples
Let’s examine a typical dermatologist medical note. An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. The patient also complains of a growing tender lesion on the left elbow of 2 months’ duration. Physical examination reveals a linear vesicular eruption on the left wrist and a tender hyperkeratotic papule on the left elbow. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed. The decision is made to perform a tangential biopsy of the lesion on the left elbow because of the suspicion for malignancy. The biopsy is performed the same day.
This case clearly illustrates performance of an E/M service in the treatment of rhus dermatitis, which is separate and distinct from the biopsy procedure; however, in evaluating whether the case meets the documentation requirements for modifier -25, the information in the medical note inclusive to the procedure’s global surgical package, including history associated with establishing the diagnosis, physical examination of the procedure area(s), and discussion of treatment options, is eliminated, leaving the following notes: An established patient presents to the dermatologist complaining of an itchy rash on the left wrist after a hiking trip. Treatment with topical hydrocortisone 1% did not help. No data is evaluated. A diagnosis of acute rhus dermatitis of the left wrist is made, and betamethasone cream is prescribed.
Because the physical examination of the body part (left arm) is included in the procedure’s global surgical package, the examination of the left wrist cannot be used as coding support for the E/M service. This makes a difference for coding level in the prior E/M coding requirements, which required examination bullet points. However, with the 2021 E/M codes, documentation of physical examination bullet points is irrelevant to the coding level. Therefore, qualifying for a modifier -25 claim is more straightforward in this case with the new code set. Because bullet points are not integral to the 2021 E/M codes, qualifying and properly documenting for a higher level of service will likely be more common in dermatology.
Final Thoughts
Frequent use of modifier -25 is a critical part of a high-quality and cost-effective dermatology practice. Same-day performance of minor procedures and E/M services allows for more rapid and efficient diagnosis and treatment of various conditions as well as minimizing unnecessary office visits. The new E/M codes for 2021 actually make the documentation of a separate and distinct E/M service less complicated because the bullet point requirements associated with the old E/M codes have been eliminated. Understanding how the new E/M code descriptors affect modifier -25 reporting and clear documentation of separate, distinct, and medically necessary E/M services will be needed due to increased insurer scrutiny and audits.
- Current Procedural Terminology 2021, Professional Edition. American Medical Association; 2020.
- Rogers HW. Modifier −25 victory, but the battle is not over. Cutis. 2018;101:409-410.
- Rogers HW. One diagnosis and modifier −25: appropriate or audit target? Cutis. 2017;99:165-166.
- Update regarding E/M with modifier −25—professional. Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield website. Published February 1, 2019. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://providernews.anthem.com/ohio/article/update-regarding-em-with-modifier-25-professional
- Payment policies—surgery. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care website. Updated May 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.harvardpilgrim.org/provider/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2020/07/H-6-Surgery-PM.pdf
- Modifier 25: frequently asked questions. Independence Blue Cross website. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://provcomm.ibx.com/ibc/archive/pages/A86603B03881756B8525817E00768006.aspx
- Huang G. CMS 2019 fee schedule takes modifier 25 cuts, runs with them. Doctors Management website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.doctors-management.com/cms-2019-feeschedule-modifier25/
- Dermatologist claims for evaluation and management services on the same day as minor surgical procedures. US Department of Health and Humans Services Office of Inspector General website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000577.asp
- Global surgery booklet. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated September 2018. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/outreach-and-education/medicare-learning-network-mln/mlnproducts/downloads/globallsurgery-icn907166.pdf
- American Medical Association. CPT® Evaluation and management (E/M)—office or other outpatient (99202-99215) and prolonged services (99354, 99355, 99356, 99417) code and guideline changes. Updated March 9, 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2019-06/cpt-office-prolonged-svs-code-changes.pdf
- 1997 documentation guidelines for evaluation and management services. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNEdWebGuide/Downloads/97Docguidelines.pdf
- Current Procedural Terminology 2021, Professional Edition. American Medical Association; 2020.
- Rogers HW. Modifier −25 victory, but the battle is not over. Cutis. 2018;101:409-410.
- Rogers HW. One diagnosis and modifier −25: appropriate or audit target? Cutis. 2017;99:165-166.
- Update regarding E/M with modifier −25—professional. Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield website. Published February 1, 2019. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://providernews.anthem.com/ohio/article/update-regarding-em-with-modifier-25-professional
- Payment policies—surgery. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care website. Updated May 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.harvardpilgrim.org/provider/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2020/07/H-6-Surgery-PM.pdf
- Modifier 25: frequently asked questions. Independence Blue Cross website. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://provcomm.ibx.com/ibc/archive/pages/A86603B03881756B8525817E00768006.aspx
- Huang G. CMS 2019 fee schedule takes modifier 25 cuts, runs with them. Doctors Management website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.doctors-management.com/cms-2019-feeschedule-modifier25/
- Dermatologist claims for evaluation and management services on the same day as minor surgical procedures. US Department of Health and Humans Services Office of Inspector General website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000577.asp
- Global surgery booklet. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated September 2018. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/outreach-and-education/medicare-learning-network-mln/mlnproducts/downloads/globallsurgery-icn907166.pdf
- American Medical Association. CPT® Evaluation and management (E/M)—office or other outpatient (99202-99215) and prolonged services (99354, 99355, 99356, 99417) code and guideline changes. Updated March 9, 2021. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2019-06/cpt-office-prolonged-svs-code-changes.pdf
- 1997 documentation guidelines for evaluation and management services. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Accessed August 17, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNEdWebGuide/Downloads/97Docguidelines.pdf
Practice Points
- Insurer scrutiny of same-day evaluation and management (E/M) and procedure services has increased, and dermatologists should be prepared for more frequent medical record reviews and audits.
- The new 2021 E/M codes actually reduce the hurdles for reporting a separate and distinct E/M service by eliminating the history and physical examination bullet points of the previous code set.
Increasing Skin of Color Publications in the Dermatology Literature: A Call to Action
The US population is becoming more diverse. By 2044, it is predicted that there will be a majority minority population in the United States.1 Therefore, it is imperative to continue to develop educational mechanisms for all dermatologists to increase and maintain competency in skin of color dermatology, which will contribute to the achievement of health equity for patients with all skin tones and hair types.
Not only is clinical skin of color education necessary, but diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) education for dermatologists also is critical. Clinical examination,2 diagnosis, and treatment of skin and hair disorders across the skin of color spectrum with cultural humility is essential to achieve health equity. If trainees, dermatologists, other specialists, and primary care clinicians are not frequently exposed to patients with darker skin tones and coily hair, the nuances in diagnosing and treating these patients must be learned in alternate ways.
To ready the nation’s physicians and clinicians to care for the growing diverse population, exposure to more images of dermatologic diseases in those with darker skin tones in journal articles, textbooks, conference lectures, and online dermatology image libraries is necessary to help close the skin of color training and practice gap.3,4 The following initiatives demonstrate how Cutis has sought to address these educational gaps and remains committed to improving DEI education in dermatology.
Collaboration With the Skin of Color Society
The Skin of Color Society (SOCS), which was founded in 2004 by Dr. Susan C. Taylor, is a dermatologic organization with more than 800 members representing 32 countries. Its mission includes promoting awareness and excellence within skin of color dermatology through research, education, and mentorship. The SOCS has utilized strategic partnerships with national and international dermatologists, as well as professional medical organizations and community, industry, and corporate groups, to ultimately ensure that patients with skin of color receive the expert care they deserve.5 In 2017, Cutis published the inaugural article in its collaboration with the SOCS,6 and more articles, which undergo regular peer review, continue to be published quarterly (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/skin-color).
Increase Number of Journal Articles on Skin of Color Topics
Increasing the number of journal articles on skin of color–related topics needs to be intentional, as it is a tool that has been identified as a necessary part of enhancing awareness and subsequently improving patient care. Wilson et al7 used stringent criteria to review all articles published from January 2018 to October 2020 in 52 dermatology journals for inclusion of topics on skin of color, hair in patients with skin of color, diversity and inclusion, and socioeconomic and health care disparities in the skin of color population. The journals they reviewed included publications based on continents with majority skin of color populations, such as Asia, as well as those with minority skin of color populations, such as Europe. During the study period, the percentage of articles covering skin of color ranged from 2.04% to 61.8%, with an average of 16.8%.7
The total number of Cutis articles published during the study period was 709, with 132 (18.62%) meeting the investigators’ criteria for articles on skin of color; these included case reports in which at least 1 patient with skin of color was featured.7 Overall, Cutis ranked 16th of the 52 journals for inclusion of skin of color content. Cutis was one of only a few journals based in North America, a non–skin-of-color–predominant continent, to make the top 16 in this study.7
Some of the 132 skin of color articles published in Cutis were the result of the journal’s collaboration with the SOCS. Through this collaboration, articles were published on a variety of skin of color topics, including DEI (6), alopecia and hair care (5), dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging (1), atopic dermatitis (1), cosmetics (1), hidradenitis suppurativa (1), pigmentation (1), rosacea (1), and skin cancer (2). These articles also resulted in a number of podcast discussions (https://www.mdedge.com/podcasts/dermatology-weekly), including one on dealing with DEI, one on pigmentation, and one on dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging. The latter featured the SOCS Scientific Symposium poster winners in 2020.
The number of articles published specifically through Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS accounted for only a small part of the journal’s 132 skin of color articles identified in the study by Wilson et al.7 We speculate that Cutis’s display of intentional commitment to supporting the inclusion of skin of color articles in the journal may in turn encourage its broader readership to submit more skin of color–focused articles for peer review.
Wilson et al7 specifically remarked that “Cutis’s [Skin of Color] section in each issue is a promising idea.” They also highlighted Clinics in Dermatology for committing an entire issue to skin of color; however, despite this initiative, Clinics in Dermatology still ranked 35th of 52 journals with regard to the overall percentage of skin of color articles published.7 This suggests that a journal publishing one special issue on skin of color annually is a helpful addition to the literature, but increasing the number of articles related to skin of color in each journal issue, similar to Cutis, will ultimately result in a higher overall number of skin of color articles in the dermatology literature.
Both Amuzie et al4 and Wilson et al7 concluded that the higher a journal’s impact factor, the lower the number of skin of color articles published.However, skin of color articles published in high-impact journals received a higher number of citations than those in other lower-impact journals.4 High-impact journals may use Cutis as a model for increasing the number of skin of color articles they publish, which will have a notable impact on increasing skin of color knowledge and educating dermatologists.
Coverage of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
In another study, Bray et al8 conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from January 2008 to July 2019 to quantify the number of articles specifically focused on DEI in a variety of medical specialties. The field of dermatology had the highest number of articles published on DEI (25) compared to the other specialties, including family medicine (23), orthopedic surgery (12), internal medicine (9), general surgery (7), radiology (6), ophthalmology (2), and anesthesiology (2).8 However, Wilson et al7 found that, out of all the categories of skin of color articles published in dermatology journals during their study period, those focused on DEI made up less than 1% of the total number of articles. Dermatology is off to a great start compared to other specialties, but there is still more work to do in dermatology for DEI. Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS has resulted in 6 DEI articles published since 2017.
Think Beyond Dermatology Education
The collaboration between Cutis and the SOCS was established to create a series of articles dedicated to increasing the skin of color dermatology knowledge base of the Cutis readership and beyond; however, increased readership and more citations are needed to amplify the reach of the articles published by these skin of color experts. Cutis’s collaboration with SOCS is one mechanism to increase the skin of color literature, but skin of color and DEI articles outside of this collaboration should continue to be published in each issue of Cutis.
The collaboration between SOCS and Cutis was and continues to be a forward-thinking step toward improving skin of color dermatology education, but there is still work to be done across the medical literature with regard to increasing intentional publication of skin of color articles. Nondermatologist clinicians in the Cutis readership benefit from knowledge of skin of color, as all specialties and primary care will see increased patient diversity in their examination rooms.
To further ensure that primary care is not left behind, Cutis has partnered with The Journal of Family Practice to produce a new column called Dx Across the Skin of Color Spectrum (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/dx-across-skin-color-spectrum), which is co-published in both journals.9,10 These one-page fact sheets highlight images of dermatologic conditions in skin of color as well as images of the same condition in lighter skin, a concept suggested by Cutis Associate Editor, Dr. Candrice R. Heath. The goal of this new column is to increase the accurate diagnosis of dermatologic conditions in skin of color and to highlight health disparities related to a particular condition in an easy-to-understand format. Uniquely, Dr. Heath co-authors this content with family physician Dr. Richard P. Usatine.
Final Thoughts
The entire community of medical journals should continue to develop creative ways to educate their readership. Medical professionals stay up-to-date on best practices through journal articles, textbooks, conferences, and even podcasts. Therefore, it is best to incorporate skin of color knowledge throughout all educational programming, particularly through enduring materials such as journal articles. Wilson et al7 suggested that a minimum of 16.8% of a dermatology journal’s articles in each issue should focus on skin of color in addition to special focus issues, as this will work toward more equitable dermatologic care.
Knowledge is only part of the equation; compassionate care with cultural humility is the other part. Publishing scientific facts about biology and structure, diagnosis, and treatment selection in skin of color, as well as committing to lifelong learning about the differences in our patients despite the absence of shared life or cultural experiences, may be the key to truly impacting health equity.11 We believe that together we will get there one journal article and one citation at a time.
- Colby SL, Ortman JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. Published March 2015. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Alvarado SM, Feng H. Representation of dark skin images of common dermatologic conditions in educational resources: a cross-sectional analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1427-1431. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.041
- Amuzie AU, Jia JL, Taylor SC, et al. Skin-of-color article representation in dermatology literature 2009-2019: higher citation counts and opportunities for inclusion [published online March 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.063
- Learn more about SOCS. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/
- Subash J, Tull R, McMichael A. Diversity in dermatology: a society devoted to skin of color. Cutis. 2017;99:322-324.
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of colorand diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action [published online April 20, 2021]. Int J Womens Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Bray JK, McMichael AJ, Huang WW, et al. Publication rates on the topic of racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology versus other specialties. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt094243gp.
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2021;107:332. doi:10.12788/cutis.0274
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:56. doi:10.12788/cutis.0298
- Jones N, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships [published online August 3, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14721
The US population is becoming more diverse. By 2044, it is predicted that there will be a majority minority population in the United States.1 Therefore, it is imperative to continue to develop educational mechanisms for all dermatologists to increase and maintain competency in skin of color dermatology, which will contribute to the achievement of health equity for patients with all skin tones and hair types.
Not only is clinical skin of color education necessary, but diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) education for dermatologists also is critical. Clinical examination,2 diagnosis, and treatment of skin and hair disorders across the skin of color spectrum with cultural humility is essential to achieve health equity. If trainees, dermatologists, other specialists, and primary care clinicians are not frequently exposed to patients with darker skin tones and coily hair, the nuances in diagnosing and treating these patients must be learned in alternate ways.
To ready the nation’s physicians and clinicians to care for the growing diverse population, exposure to more images of dermatologic diseases in those with darker skin tones in journal articles, textbooks, conference lectures, and online dermatology image libraries is necessary to help close the skin of color training and practice gap.3,4 The following initiatives demonstrate how Cutis has sought to address these educational gaps and remains committed to improving DEI education in dermatology.
Collaboration With the Skin of Color Society
The Skin of Color Society (SOCS), which was founded in 2004 by Dr. Susan C. Taylor, is a dermatologic organization with more than 800 members representing 32 countries. Its mission includes promoting awareness and excellence within skin of color dermatology through research, education, and mentorship. The SOCS has utilized strategic partnerships with national and international dermatologists, as well as professional medical organizations and community, industry, and corporate groups, to ultimately ensure that patients with skin of color receive the expert care they deserve.5 In 2017, Cutis published the inaugural article in its collaboration with the SOCS,6 and more articles, which undergo regular peer review, continue to be published quarterly (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/skin-color).
Increase Number of Journal Articles on Skin of Color Topics
Increasing the number of journal articles on skin of color–related topics needs to be intentional, as it is a tool that has been identified as a necessary part of enhancing awareness and subsequently improving patient care. Wilson et al7 used stringent criteria to review all articles published from January 2018 to October 2020 in 52 dermatology journals for inclusion of topics on skin of color, hair in patients with skin of color, diversity and inclusion, and socioeconomic and health care disparities in the skin of color population. The journals they reviewed included publications based on continents with majority skin of color populations, such as Asia, as well as those with minority skin of color populations, such as Europe. During the study period, the percentage of articles covering skin of color ranged from 2.04% to 61.8%, with an average of 16.8%.7
The total number of Cutis articles published during the study period was 709, with 132 (18.62%) meeting the investigators’ criteria for articles on skin of color; these included case reports in which at least 1 patient with skin of color was featured.7 Overall, Cutis ranked 16th of the 52 journals for inclusion of skin of color content. Cutis was one of only a few journals based in North America, a non–skin-of-color–predominant continent, to make the top 16 in this study.7
Some of the 132 skin of color articles published in Cutis were the result of the journal’s collaboration with the SOCS. Through this collaboration, articles were published on a variety of skin of color topics, including DEI (6), alopecia and hair care (5), dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging (1), atopic dermatitis (1), cosmetics (1), hidradenitis suppurativa (1), pigmentation (1), rosacea (1), and skin cancer (2). These articles also resulted in a number of podcast discussions (https://www.mdedge.com/podcasts/dermatology-weekly), including one on dealing with DEI, one on pigmentation, and one on dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging. The latter featured the SOCS Scientific Symposium poster winners in 2020.
The number of articles published specifically through Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS accounted for only a small part of the journal’s 132 skin of color articles identified in the study by Wilson et al.7 We speculate that Cutis’s display of intentional commitment to supporting the inclusion of skin of color articles in the journal may in turn encourage its broader readership to submit more skin of color–focused articles for peer review.
Wilson et al7 specifically remarked that “Cutis’s [Skin of Color] section in each issue is a promising idea.” They also highlighted Clinics in Dermatology for committing an entire issue to skin of color; however, despite this initiative, Clinics in Dermatology still ranked 35th of 52 journals with regard to the overall percentage of skin of color articles published.7 This suggests that a journal publishing one special issue on skin of color annually is a helpful addition to the literature, but increasing the number of articles related to skin of color in each journal issue, similar to Cutis, will ultimately result in a higher overall number of skin of color articles in the dermatology literature.
Both Amuzie et al4 and Wilson et al7 concluded that the higher a journal’s impact factor, the lower the number of skin of color articles published.However, skin of color articles published in high-impact journals received a higher number of citations than those in other lower-impact journals.4 High-impact journals may use Cutis as a model for increasing the number of skin of color articles they publish, which will have a notable impact on increasing skin of color knowledge and educating dermatologists.
Coverage of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
In another study, Bray et al8 conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from January 2008 to July 2019 to quantify the number of articles specifically focused on DEI in a variety of medical specialties. The field of dermatology had the highest number of articles published on DEI (25) compared to the other specialties, including family medicine (23), orthopedic surgery (12), internal medicine (9), general surgery (7), radiology (6), ophthalmology (2), and anesthesiology (2).8 However, Wilson et al7 found that, out of all the categories of skin of color articles published in dermatology journals during their study period, those focused on DEI made up less than 1% of the total number of articles. Dermatology is off to a great start compared to other specialties, but there is still more work to do in dermatology for DEI. Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS has resulted in 6 DEI articles published since 2017.
Think Beyond Dermatology Education
The collaboration between Cutis and the SOCS was established to create a series of articles dedicated to increasing the skin of color dermatology knowledge base of the Cutis readership and beyond; however, increased readership and more citations are needed to amplify the reach of the articles published by these skin of color experts. Cutis’s collaboration with SOCS is one mechanism to increase the skin of color literature, but skin of color and DEI articles outside of this collaboration should continue to be published in each issue of Cutis.
The collaboration between SOCS and Cutis was and continues to be a forward-thinking step toward improving skin of color dermatology education, but there is still work to be done across the medical literature with regard to increasing intentional publication of skin of color articles. Nondermatologist clinicians in the Cutis readership benefit from knowledge of skin of color, as all specialties and primary care will see increased patient diversity in their examination rooms.
To further ensure that primary care is not left behind, Cutis has partnered with The Journal of Family Practice to produce a new column called Dx Across the Skin of Color Spectrum (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/dx-across-skin-color-spectrum), which is co-published in both journals.9,10 These one-page fact sheets highlight images of dermatologic conditions in skin of color as well as images of the same condition in lighter skin, a concept suggested by Cutis Associate Editor, Dr. Candrice R. Heath. The goal of this new column is to increase the accurate diagnosis of dermatologic conditions in skin of color and to highlight health disparities related to a particular condition in an easy-to-understand format. Uniquely, Dr. Heath co-authors this content with family physician Dr. Richard P. Usatine.
Final Thoughts
The entire community of medical journals should continue to develop creative ways to educate their readership. Medical professionals stay up-to-date on best practices through journal articles, textbooks, conferences, and even podcasts. Therefore, it is best to incorporate skin of color knowledge throughout all educational programming, particularly through enduring materials such as journal articles. Wilson et al7 suggested that a minimum of 16.8% of a dermatology journal’s articles in each issue should focus on skin of color in addition to special focus issues, as this will work toward more equitable dermatologic care.
Knowledge is only part of the equation; compassionate care with cultural humility is the other part. Publishing scientific facts about biology and structure, diagnosis, and treatment selection in skin of color, as well as committing to lifelong learning about the differences in our patients despite the absence of shared life or cultural experiences, may be the key to truly impacting health equity.11 We believe that together we will get there one journal article and one citation at a time.
The US population is becoming more diverse. By 2044, it is predicted that there will be a majority minority population in the United States.1 Therefore, it is imperative to continue to develop educational mechanisms for all dermatologists to increase and maintain competency in skin of color dermatology, which will contribute to the achievement of health equity for patients with all skin tones and hair types.
Not only is clinical skin of color education necessary, but diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) education for dermatologists also is critical. Clinical examination,2 diagnosis, and treatment of skin and hair disorders across the skin of color spectrum with cultural humility is essential to achieve health equity. If trainees, dermatologists, other specialists, and primary care clinicians are not frequently exposed to patients with darker skin tones and coily hair, the nuances in diagnosing and treating these patients must be learned in alternate ways.
To ready the nation’s physicians and clinicians to care for the growing diverse population, exposure to more images of dermatologic diseases in those with darker skin tones in journal articles, textbooks, conference lectures, and online dermatology image libraries is necessary to help close the skin of color training and practice gap.3,4 The following initiatives demonstrate how Cutis has sought to address these educational gaps and remains committed to improving DEI education in dermatology.
Collaboration With the Skin of Color Society
The Skin of Color Society (SOCS), which was founded in 2004 by Dr. Susan C. Taylor, is a dermatologic organization with more than 800 members representing 32 countries. Its mission includes promoting awareness and excellence within skin of color dermatology through research, education, and mentorship. The SOCS has utilized strategic partnerships with national and international dermatologists, as well as professional medical organizations and community, industry, and corporate groups, to ultimately ensure that patients with skin of color receive the expert care they deserve.5 In 2017, Cutis published the inaugural article in its collaboration with the SOCS,6 and more articles, which undergo regular peer review, continue to be published quarterly (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/skin-color).
Increase Number of Journal Articles on Skin of Color Topics
Increasing the number of journal articles on skin of color–related topics needs to be intentional, as it is a tool that has been identified as a necessary part of enhancing awareness and subsequently improving patient care. Wilson et al7 used stringent criteria to review all articles published from January 2018 to October 2020 in 52 dermatology journals for inclusion of topics on skin of color, hair in patients with skin of color, diversity and inclusion, and socioeconomic and health care disparities in the skin of color population. The journals they reviewed included publications based on continents with majority skin of color populations, such as Asia, as well as those with minority skin of color populations, such as Europe. During the study period, the percentage of articles covering skin of color ranged from 2.04% to 61.8%, with an average of 16.8%.7
The total number of Cutis articles published during the study period was 709, with 132 (18.62%) meeting the investigators’ criteria for articles on skin of color; these included case reports in which at least 1 patient with skin of color was featured.7 Overall, Cutis ranked 16th of the 52 journals for inclusion of skin of color content. Cutis was one of only a few journals based in North America, a non–skin-of-color–predominant continent, to make the top 16 in this study.7
Some of the 132 skin of color articles published in Cutis were the result of the journal’s collaboration with the SOCS. Through this collaboration, articles were published on a variety of skin of color topics, including DEI (6), alopecia and hair care (5), dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging (1), atopic dermatitis (1), cosmetics (1), hidradenitis suppurativa (1), pigmentation (1), rosacea (1), and skin cancer (2). These articles also resulted in a number of podcast discussions (https://www.mdedge.com/podcasts/dermatology-weekly), including one on dealing with DEI, one on pigmentation, and one on dermoscopy/optical coherence tomography imaging. The latter featured the SOCS Scientific Symposium poster winners in 2020.
The number of articles published specifically through Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS accounted for only a small part of the journal’s 132 skin of color articles identified in the study by Wilson et al.7 We speculate that Cutis’s display of intentional commitment to supporting the inclusion of skin of color articles in the journal may in turn encourage its broader readership to submit more skin of color–focused articles for peer review.
Wilson et al7 specifically remarked that “Cutis’s [Skin of Color] section in each issue is a promising idea.” They also highlighted Clinics in Dermatology for committing an entire issue to skin of color; however, despite this initiative, Clinics in Dermatology still ranked 35th of 52 journals with regard to the overall percentage of skin of color articles published.7 This suggests that a journal publishing one special issue on skin of color annually is a helpful addition to the literature, but increasing the number of articles related to skin of color in each journal issue, similar to Cutis, will ultimately result in a higher overall number of skin of color articles in the dermatology literature.
Both Amuzie et al4 and Wilson et al7 concluded that the higher a journal’s impact factor, the lower the number of skin of color articles published.However, skin of color articles published in high-impact journals received a higher number of citations than those in other lower-impact journals.4 High-impact journals may use Cutis as a model for increasing the number of skin of color articles they publish, which will have a notable impact on increasing skin of color knowledge and educating dermatologists.
Coverage of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
In another study, Bray et al8 conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from January 2008 to July 2019 to quantify the number of articles specifically focused on DEI in a variety of medical specialties. The field of dermatology had the highest number of articles published on DEI (25) compared to the other specialties, including family medicine (23), orthopedic surgery (12), internal medicine (9), general surgery (7), radiology (6), ophthalmology (2), and anesthesiology (2).8 However, Wilson et al7 found that, out of all the categories of skin of color articles published in dermatology journals during their study period, those focused on DEI made up less than 1% of the total number of articles. Dermatology is off to a great start compared to other specialties, but there is still more work to do in dermatology for DEI. Cutis’s collaboration with the SOCS has resulted in 6 DEI articles published since 2017.
Think Beyond Dermatology Education
The collaboration between Cutis and the SOCS was established to create a series of articles dedicated to increasing the skin of color dermatology knowledge base of the Cutis readership and beyond; however, increased readership and more citations are needed to amplify the reach of the articles published by these skin of color experts. Cutis’s collaboration with SOCS is one mechanism to increase the skin of color literature, but skin of color and DEI articles outside of this collaboration should continue to be published in each issue of Cutis.
The collaboration between SOCS and Cutis was and continues to be a forward-thinking step toward improving skin of color dermatology education, but there is still work to be done across the medical literature with regard to increasing intentional publication of skin of color articles. Nondermatologist clinicians in the Cutis readership benefit from knowledge of skin of color, as all specialties and primary care will see increased patient diversity in their examination rooms.
To further ensure that primary care is not left behind, Cutis has partnered with The Journal of Family Practice to produce a new column called Dx Across the Skin of Color Spectrum (https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/dx-across-skin-color-spectrum), which is co-published in both journals.9,10 These one-page fact sheets highlight images of dermatologic conditions in skin of color as well as images of the same condition in lighter skin, a concept suggested by Cutis Associate Editor, Dr. Candrice R. Heath. The goal of this new column is to increase the accurate diagnosis of dermatologic conditions in skin of color and to highlight health disparities related to a particular condition in an easy-to-understand format. Uniquely, Dr. Heath co-authors this content with family physician Dr. Richard P. Usatine.
Final Thoughts
The entire community of medical journals should continue to develop creative ways to educate their readership. Medical professionals stay up-to-date on best practices through journal articles, textbooks, conferences, and even podcasts. Therefore, it is best to incorporate skin of color knowledge throughout all educational programming, particularly through enduring materials such as journal articles. Wilson et al7 suggested that a minimum of 16.8% of a dermatology journal’s articles in each issue should focus on skin of color in addition to special focus issues, as this will work toward more equitable dermatologic care.
Knowledge is only part of the equation; compassionate care with cultural humility is the other part. Publishing scientific facts about biology and structure, diagnosis, and treatment selection in skin of color, as well as committing to lifelong learning about the differences in our patients despite the absence of shared life or cultural experiences, may be the key to truly impacting health equity.11 We believe that together we will get there one journal article and one citation at a time.
- Colby SL, Ortman JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. Published March 2015. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Alvarado SM, Feng H. Representation of dark skin images of common dermatologic conditions in educational resources: a cross-sectional analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1427-1431. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.041
- Amuzie AU, Jia JL, Taylor SC, et al. Skin-of-color article representation in dermatology literature 2009-2019: higher citation counts and opportunities for inclusion [published online March 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.063
- Learn more about SOCS. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/
- Subash J, Tull R, McMichael A. Diversity in dermatology: a society devoted to skin of color. Cutis. 2017;99:322-324.
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of colorand diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action [published online April 20, 2021]. Int J Womens Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Bray JK, McMichael AJ, Huang WW, et al. Publication rates on the topic of racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology versus other specialties. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt094243gp.
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2021;107:332. doi:10.12788/cutis.0274
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:56. doi:10.12788/cutis.0298
- Jones N, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships [published online August 3, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14721
- Colby SL, Ortman JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. Published March 2015. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Alvarado SM, Feng H. Representation of dark skin images of common dermatologic conditions in educational resources: a cross-sectional analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1427-1431. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.041
- Amuzie AU, Jia JL, Taylor SC, et al. Skin-of-color article representation in dermatology literature 2009-2019: higher citation counts and opportunities for inclusion [published online March 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.063
- Learn more about SOCS. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 11, 2021. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/
- Subash J, Tull R, McMichael A. Diversity in dermatology: a society devoted to skin of color. Cutis. 2017;99:322-324.
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of colorand diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action [published online April 20, 2021]. Int J Womens Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Bray JK, McMichael AJ, Huang WW, et al. Publication rates on the topic of racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology versus other specialties. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt094243gp.
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2021;107:332. doi:10.12788/cutis.0274
- Heath CR, Usatine R. Psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:56. doi:10.12788/cutis.0298
- Jones N, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships [published online August 3, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14721
Practice Points
- Submitting more articles related to skin of color for peer review and publication will increase educational opportunities.
- Journals that publish skin of color articles play a critical role in reducing educational gaps and ultimately help improve patient care for those with skin of color.
Medical education must takes broader view of disabilities
“All physicians, regardless of specialty, will work with patients with disabilities,” Corrie Harris, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), said in a plenary session presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference.
Disabilities vary in their visibility, from cognitive and sensory impairments that are not immediately obvious to an obvious physical disability, she said.
One in four adults and one in six children in the United States has a disability, said Dr. Harris. The prevalence of disability increases with age, but occurs across the lifespan, and will likely increase in the future with greater improvements in health care overall.
Dr. Harris reviewed the current conceptual model that forms the basis for the World Health Organization definition of functioning disability. This “functional model” defines disability as caused by interactions between health conditions and the environment, and the response is to “prioritize function to meet patient goals,” Dr. Harris said at the meeting, sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
This model is based on collaboration between health care providers and their patients with disabilities, and training is important to help providers make this collaboration successful, said Dr. Harris. Without training, physicians may be ineffective in communicating with patients with disabilities by not speaking directly to the patient, not speaking in a way the patient can understand clearly, and not providing accessible patient education materials. Physicians also tend to minimize the extent of the patient’s expertise in their own condition based on their lived experiences, and tend to underestimate the abilities of patients with disabilities.
However, direct experience with disabled patients and an understanding of the health disparities they endure can help physicians look at these patients “through a more intersectional lens,” that also takes into account social determinants of health, Dr. Harris said. “I have found that people with disabilities are the best teachers about disability, because they have expertise that comes from their lived experience.”
Patients are the best teachers
Several initiatives are helping physicians to bridge this gap in understanding and reduce disparities in care. One such program is FRAME: Faces Redefining the Art of Medical Education. FRAME is a web-based film library designed to present medical information to health care providers in training, clinicians, families, and communities in a dignified and humanizing way. FRAME was developed in part by fashion photographer Rick Guidotti, who was inspired after meeting a young woman with albinism to create Positive Exposure, an ongoing project featuring children and adolescents with various disabilities.
FRAME films are “short films presenting all the basic hallmark characteristics of a certain genetic condition, but presented by somebody living with that condition,” said Mr. Guidotti in his presentation during the session.
The National Curriculum Initiative in Developmental Medicine (NCIDM) is designed to incorporate care for individuals with disabilities into medical education. NCIDM is a project created by the American Academy of Developmental Medicine and Dentistry (AADMD).
“The need for this program is that there is no U.S. requirement for medical schools to teach about intellectual and developmental disabilities,” Priya Chandan, MD, also of the University of Louisville, said in her presentation during the session. “Approximately 81% of graduating medical students have no training in caring for adults with disabilities,” said Dr. Chandan, who serves as director of the NCIDM.
The current NCIDM was created as a 5-year partnership between the AADMD and Special Olympics, supported in part by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Chandan said. The purpose was to provide training to medical students in the field of developmental medicine, meaning the care of individuals with intellectual/developmental disabilities (IDD) across the lifespan. The AADMD has expanded to 26 medical schools in the United States and will reach approximately 4,000 medical students by the conclusion of the current initiative.
One challenge in medical education is getting past the idea that people living with disabilities need to be fixed, said Dr. Chandan. The NCIDM approach reflects Mr. Guidotti’s approach in both the FRAME initiatives and his Positive Exposure foundation, with a focus on treating people as people, and letting individuals with disabilities represent themselves.
Dr. Chandan described the NCIDM curriculum as allowing for flexible teaching methodologies and materials, as long as they meet the NCIDM-created learning goals and objectives. The curriculum also includes standardized evaluations. Each NCIDM program in a participating medical school includes a faculty champion, and the curriculum supports meeting people with IDD not only inside medical settings, but also outside in the community.
NCIDM embraces the idea of community-engaged scholarship, which Dr. Chandan defined as “a form of scholarship that directly benefits the community and is consistent with university and unit missions.” This method combined teaching and conducting research while providing a service to the community.
The next steps for the current NCIDM initiative are to complete collection of data and course evaluations from participating schools by early 2022, followed by continued dissemination and collaboration through AADMD.
Overall, the content of the curriculum explores how and where IDD fits into clinical care, Dr. Chandan said, who also emphasized the implications of communication. “How we think affects how we communicate,” she added. Be mindful of the language used to talk to and about patients with disabilities, both to colleagues and to learners.
When talking to the patient, find something in common, beyond the diagnosis, said Dr. Chandan. Remember that some disabilities are visible and some are not. “Treat people with respect, because you won’t know what their functional level is just by looking,” she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“All physicians, regardless of specialty, will work with patients with disabilities,” Corrie Harris, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), said in a plenary session presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference.
Disabilities vary in their visibility, from cognitive and sensory impairments that are not immediately obvious to an obvious physical disability, she said.
One in four adults and one in six children in the United States has a disability, said Dr. Harris. The prevalence of disability increases with age, but occurs across the lifespan, and will likely increase in the future with greater improvements in health care overall.
Dr. Harris reviewed the current conceptual model that forms the basis for the World Health Organization definition of functioning disability. This “functional model” defines disability as caused by interactions between health conditions and the environment, and the response is to “prioritize function to meet patient goals,” Dr. Harris said at the meeting, sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
This model is based on collaboration between health care providers and their patients with disabilities, and training is important to help providers make this collaboration successful, said Dr. Harris. Without training, physicians may be ineffective in communicating with patients with disabilities by not speaking directly to the patient, not speaking in a way the patient can understand clearly, and not providing accessible patient education materials. Physicians also tend to minimize the extent of the patient’s expertise in their own condition based on their lived experiences, and tend to underestimate the abilities of patients with disabilities.
However, direct experience with disabled patients and an understanding of the health disparities they endure can help physicians look at these patients “through a more intersectional lens,” that also takes into account social determinants of health, Dr. Harris said. “I have found that people with disabilities are the best teachers about disability, because they have expertise that comes from their lived experience.”
Patients are the best teachers
Several initiatives are helping physicians to bridge this gap in understanding and reduce disparities in care. One such program is FRAME: Faces Redefining the Art of Medical Education. FRAME is a web-based film library designed to present medical information to health care providers in training, clinicians, families, and communities in a dignified and humanizing way. FRAME was developed in part by fashion photographer Rick Guidotti, who was inspired after meeting a young woman with albinism to create Positive Exposure, an ongoing project featuring children and adolescents with various disabilities.
FRAME films are “short films presenting all the basic hallmark characteristics of a certain genetic condition, but presented by somebody living with that condition,” said Mr. Guidotti in his presentation during the session.
The National Curriculum Initiative in Developmental Medicine (NCIDM) is designed to incorporate care for individuals with disabilities into medical education. NCIDM is a project created by the American Academy of Developmental Medicine and Dentistry (AADMD).
“The need for this program is that there is no U.S. requirement for medical schools to teach about intellectual and developmental disabilities,” Priya Chandan, MD, also of the University of Louisville, said in her presentation during the session. “Approximately 81% of graduating medical students have no training in caring for adults with disabilities,” said Dr. Chandan, who serves as director of the NCIDM.
The current NCIDM was created as a 5-year partnership between the AADMD and Special Olympics, supported in part by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Chandan said. The purpose was to provide training to medical students in the field of developmental medicine, meaning the care of individuals with intellectual/developmental disabilities (IDD) across the lifespan. The AADMD has expanded to 26 medical schools in the United States and will reach approximately 4,000 medical students by the conclusion of the current initiative.
One challenge in medical education is getting past the idea that people living with disabilities need to be fixed, said Dr. Chandan. The NCIDM approach reflects Mr. Guidotti’s approach in both the FRAME initiatives and his Positive Exposure foundation, with a focus on treating people as people, and letting individuals with disabilities represent themselves.
Dr. Chandan described the NCIDM curriculum as allowing for flexible teaching methodologies and materials, as long as they meet the NCIDM-created learning goals and objectives. The curriculum also includes standardized evaluations. Each NCIDM program in a participating medical school includes a faculty champion, and the curriculum supports meeting people with IDD not only inside medical settings, but also outside in the community.
NCIDM embraces the idea of community-engaged scholarship, which Dr. Chandan defined as “a form of scholarship that directly benefits the community and is consistent with university and unit missions.” This method combined teaching and conducting research while providing a service to the community.
The next steps for the current NCIDM initiative are to complete collection of data and course evaluations from participating schools by early 2022, followed by continued dissemination and collaboration through AADMD.
Overall, the content of the curriculum explores how and where IDD fits into clinical care, Dr. Chandan said, who also emphasized the implications of communication. “How we think affects how we communicate,” she added. Be mindful of the language used to talk to and about patients with disabilities, both to colleagues and to learners.
When talking to the patient, find something in common, beyond the diagnosis, said Dr. Chandan. Remember that some disabilities are visible and some are not. “Treat people with respect, because you won’t know what their functional level is just by looking,” she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“All physicians, regardless of specialty, will work with patients with disabilities,” Corrie Harris, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), said in a plenary session presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference.
Disabilities vary in their visibility, from cognitive and sensory impairments that are not immediately obvious to an obvious physical disability, she said.
One in four adults and one in six children in the United States has a disability, said Dr. Harris. The prevalence of disability increases with age, but occurs across the lifespan, and will likely increase in the future with greater improvements in health care overall.
Dr. Harris reviewed the current conceptual model that forms the basis for the World Health Organization definition of functioning disability. This “functional model” defines disability as caused by interactions between health conditions and the environment, and the response is to “prioritize function to meet patient goals,” Dr. Harris said at the meeting, sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
This model is based on collaboration between health care providers and their patients with disabilities, and training is important to help providers make this collaboration successful, said Dr. Harris. Without training, physicians may be ineffective in communicating with patients with disabilities by not speaking directly to the patient, not speaking in a way the patient can understand clearly, and not providing accessible patient education materials. Physicians also tend to minimize the extent of the patient’s expertise in their own condition based on their lived experiences, and tend to underestimate the abilities of patients with disabilities.
However, direct experience with disabled patients and an understanding of the health disparities they endure can help physicians look at these patients “through a more intersectional lens,” that also takes into account social determinants of health, Dr. Harris said. “I have found that people with disabilities are the best teachers about disability, because they have expertise that comes from their lived experience.”
Patients are the best teachers
Several initiatives are helping physicians to bridge this gap in understanding and reduce disparities in care. One such program is FRAME: Faces Redefining the Art of Medical Education. FRAME is a web-based film library designed to present medical information to health care providers in training, clinicians, families, and communities in a dignified and humanizing way. FRAME was developed in part by fashion photographer Rick Guidotti, who was inspired after meeting a young woman with albinism to create Positive Exposure, an ongoing project featuring children and adolescents with various disabilities.
FRAME films are “short films presenting all the basic hallmark characteristics of a certain genetic condition, but presented by somebody living with that condition,” said Mr. Guidotti in his presentation during the session.
The National Curriculum Initiative in Developmental Medicine (NCIDM) is designed to incorporate care for individuals with disabilities into medical education. NCIDM is a project created by the American Academy of Developmental Medicine and Dentistry (AADMD).
“The need for this program is that there is no U.S. requirement for medical schools to teach about intellectual and developmental disabilities,” Priya Chandan, MD, also of the University of Louisville, said in her presentation during the session. “Approximately 81% of graduating medical students have no training in caring for adults with disabilities,” said Dr. Chandan, who serves as director of the NCIDM.
The current NCIDM was created as a 5-year partnership between the AADMD and Special Olympics, supported in part by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Chandan said. The purpose was to provide training to medical students in the field of developmental medicine, meaning the care of individuals with intellectual/developmental disabilities (IDD) across the lifespan. The AADMD has expanded to 26 medical schools in the United States and will reach approximately 4,000 medical students by the conclusion of the current initiative.
One challenge in medical education is getting past the idea that people living with disabilities need to be fixed, said Dr. Chandan. The NCIDM approach reflects Mr. Guidotti’s approach in both the FRAME initiatives and his Positive Exposure foundation, with a focus on treating people as people, and letting individuals with disabilities represent themselves.
Dr. Chandan described the NCIDM curriculum as allowing for flexible teaching methodologies and materials, as long as they meet the NCIDM-created learning goals and objectives. The curriculum also includes standardized evaluations. Each NCIDM program in a participating medical school includes a faculty champion, and the curriculum supports meeting people with IDD not only inside medical settings, but also outside in the community.
NCIDM embraces the idea of community-engaged scholarship, which Dr. Chandan defined as “a form of scholarship that directly benefits the community and is consistent with university and unit missions.” This method combined teaching and conducting research while providing a service to the community.
The next steps for the current NCIDM initiative are to complete collection of data and course evaluations from participating schools by early 2022, followed by continued dissemination and collaboration through AADMD.
Overall, the content of the curriculum explores how and where IDD fits into clinical care, Dr. Chandan said, who also emphasized the implications of communication. “How we think affects how we communicate,” she added. Be mindful of the language used to talk to and about patients with disabilities, both to colleagues and to learners.
When talking to the patient, find something in common, beyond the diagnosis, said Dr. Chandan. Remember that some disabilities are visible and some are not. “Treat people with respect, because you won’t know what their functional level is just by looking,” she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PHM 2021
A Modified Anchor Taping Technique for Distal Onychocryptosis
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, colloquially known as an ingrown nail, most commonly affects the lateral folds of the toenails. It also can affect the fingernails and the distal aspect of the nail unit, though these presentations are not as well described in the literature. In onychocryptosis, the nail plate grows downward into the periungual skin, resulting in chronic pain and inflammation. Risk factors include overtrimming the nails with rounded edges, local trauma, nail surgery, wearing tight footwear, obesity, and onychomycosis.1
Although surgical intervention might be required for severe or refractory disease, conservative treatment options are first line and often curative. A variety of techniques have been designed to separate the ingrown portion of the nail plate from underlying skin, including placement of an intervening piece of dental floss, cotton, or plastic tubing.2
Anchor taping is another effective method of treating onychocryptosis; a strip of tape is used to gently pull and secure the affected nail fold away from the overlying nail plate. This technique has been well described for the treatment of onychocryptosis of the lateral toenail.3-5 In 2017, Arai and Haneke5 presented a modified technique for the treatment of distal disease.
We present a simplified method that was used successfully in a case of distal onychocryptosis of the thumbnail that occurred approximately 4 months after complete nail avulsion with a nail matrix biopsy (Figure 1).
The Technique
A strongly adhesive, soft cotton, elastic tape that is 1-inch wide, such as Elastikon Elastic Tape (Johnson & Johnson), is used to pull and secure the hyponychium away from the overlying nail plate. When this technique is used for lateral onychocryptosis, a single strip of tape is secured to the affected lateral nail fold, pulled obliquely and proximally, and secured to the base of the digit.3-5 In the Arai and Haneke5 method for the treatment of distal disease, a piece of tape is first placed at the distal nail fold, pulled proximally, and secured to the ventral aspect of the digit. Then, 1 or 2 additional strips of tape are applied to the lateral nail folds, pulled obliquely, and adhered to the base of the digit, as in the classic technique for lateral onychocryptosis.5
In our modification for the treatment of distal disease, only 2 strips of tape are required, each approximately 5-cm long. The first strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium parallel to the long axis of the finger, pulled away from the distal edge of the nail plate, and secured obliquely and proximally to the base of the finger on one side. The second strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium in the same manner, directly overlying the first strip, but is then pulled obliquely in the opposite direction and secured to the other side of the proximal finger (Figure 2). The 2 strips of tape are applied directly overlying each other at the distal nail fold but with opposing tension vectors to optimize pull on the distal nail fold. This modification eliminates the need to apply an initial strip of tape along the long axis of the digit, as described by Arai and Haneke.5
The patient is instructed on this method in the office and will change the tape at home daily for 2 to 6 weeks, until the nail plate has grown out over the hyponychium (Figure 3). This technique also can be combined with other modalities, such as dilute vinegar soaks performed daily after changing the tape to ease inflammation and prevent infection. Because strongly adhesive tape is used, it also is recommended that the patient soak the tape before removing it to prevent damage to underlying skin.
Practice Implications
Anchor taping is a common and effective treatment of onychocryptosis. Most techniques described in the literature are for lateral toenail cases, which often are managed by podiatry. A modification for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis has been previously described.5 We describe a similar modification using 2 tape strips pulled in opposite directions, which successfully resolved a case of distal onychocryptosis of the fingernail that developed following a nail procedure.
Because nail dystrophy is a relatively common complication of nail surgery, dermatologic surgeons should be aware of this simple, cost-effective, and noninvasive technique for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis.
- Geizhals S, Lipner SR. Review of onychocryptosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt9985w2n0
- Mayeaux EJ Jr, Carter C, Murphy TE. Ingrown toenail management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:158-164.
- Tsunoda M, Tsunoda K. Patient-controlled taping for the treatment of ingrown toenails. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:553-555. doi:10.1370/afm.1712
- Watabe A, Yamasaki K, Hashimoto A, et al. Retrospective evaluation of conservative treatment for 140 ingrown toenails with a novel taping procedure. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:822-825. doi:10.2340/00015555-2065
- Arai H, Haneke E. Noninvasive treatment for ingrown nails: anchor taping, acrylic affixed gutter splint, sculptured nail, and others. In: Baran R, Hadj-Rabia S, Silverman R, eds. Pediatric Nail Disorders. CRC Press; 2017:252-274.
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, colloquially known as an ingrown nail, most commonly affects the lateral folds of the toenails. It also can affect the fingernails and the distal aspect of the nail unit, though these presentations are not as well described in the literature. In onychocryptosis, the nail plate grows downward into the periungual skin, resulting in chronic pain and inflammation. Risk factors include overtrimming the nails with rounded edges, local trauma, nail surgery, wearing tight footwear, obesity, and onychomycosis.1
Although surgical intervention might be required for severe or refractory disease, conservative treatment options are first line and often curative. A variety of techniques have been designed to separate the ingrown portion of the nail plate from underlying skin, including placement of an intervening piece of dental floss, cotton, or plastic tubing.2
Anchor taping is another effective method of treating onychocryptosis; a strip of tape is used to gently pull and secure the affected nail fold away from the overlying nail plate. This technique has been well described for the treatment of onychocryptosis of the lateral toenail.3-5 In 2017, Arai and Haneke5 presented a modified technique for the treatment of distal disease.
We present a simplified method that was used successfully in a case of distal onychocryptosis of the thumbnail that occurred approximately 4 months after complete nail avulsion with a nail matrix biopsy (Figure 1).

The Technique
A strongly adhesive, soft cotton, elastic tape that is 1-inch wide, such as Elastikon Elastic Tape (Johnson & Johnson), is used to pull and secure the hyponychium away from the overlying nail plate. When this technique is used for lateral onychocryptosis, a single strip of tape is secured to the affected lateral nail fold, pulled obliquely and proximally, and secured to the base of the digit.3-5 In the Arai and Haneke5 method for the treatment of distal disease, a piece of tape is first placed at the distal nail fold, pulled proximally, and secured to the ventral aspect of the digit. Then, 1 or 2 additional strips of tape are applied to the lateral nail folds, pulled obliquely, and adhered to the base of the digit, as in the classic technique for lateral onychocryptosis.5
In our modification for the treatment of distal disease, only 2 strips of tape are required, each approximately 5-cm long. The first strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium parallel to the long axis of the finger, pulled away from the distal edge of the nail plate, and secured obliquely and proximally to the base of the finger on one side. The second strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium in the same manner, directly overlying the first strip, but is then pulled obliquely in the opposite direction and secured to the other side of the proximal finger (Figure 2). The 2 strips of tape are applied directly overlying each other at the distal nail fold but with opposing tension vectors to optimize pull on the distal nail fold. This modification eliminates the need to apply an initial strip of tape along the long axis of the digit, as described by Arai and Haneke.5

The patient is instructed on this method in the office and will change the tape at home daily for 2 to 6 weeks, until the nail plate has grown out over the hyponychium (Figure 3). This technique also can be combined with other modalities, such as dilute vinegar soaks performed daily after changing the tape to ease inflammation and prevent infection. Because strongly adhesive tape is used, it also is recommended that the patient soak the tape before removing it to prevent damage to underlying skin.

Practice Implications
Anchor taping is a common and effective treatment of onychocryptosis. Most techniques described in the literature are for lateral toenail cases, which often are managed by podiatry. A modification for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis has been previously described.5 We describe a similar modification using 2 tape strips pulled in opposite directions, which successfully resolved a case of distal onychocryptosis of the fingernail that developed following a nail procedure.
Because nail dystrophy is a relatively common complication of nail surgery, dermatologic surgeons should be aware of this simple, cost-effective, and noninvasive technique for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis.
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, colloquially known as an ingrown nail, most commonly affects the lateral folds of the toenails. It also can affect the fingernails and the distal aspect of the nail unit, though these presentations are not as well described in the literature. In onychocryptosis, the nail plate grows downward into the periungual skin, resulting in chronic pain and inflammation. Risk factors include overtrimming the nails with rounded edges, local trauma, nail surgery, wearing tight footwear, obesity, and onychomycosis.1
Although surgical intervention might be required for severe or refractory disease, conservative treatment options are first line and often curative. A variety of techniques have been designed to separate the ingrown portion of the nail plate from underlying skin, including placement of an intervening piece of dental floss, cotton, or plastic tubing.2
Anchor taping is another effective method of treating onychocryptosis; a strip of tape is used to gently pull and secure the affected nail fold away from the overlying nail plate. This technique has been well described for the treatment of onychocryptosis of the lateral toenail.3-5 In 2017, Arai and Haneke5 presented a modified technique for the treatment of distal disease.
We present a simplified method that was used successfully in a case of distal onychocryptosis of the thumbnail that occurred approximately 4 months after complete nail avulsion with a nail matrix biopsy (Figure 1).

The Technique
A strongly adhesive, soft cotton, elastic tape that is 1-inch wide, such as Elastikon Elastic Tape (Johnson & Johnson), is used to pull and secure the hyponychium away from the overlying nail plate. When this technique is used for lateral onychocryptosis, a single strip of tape is secured to the affected lateral nail fold, pulled obliquely and proximally, and secured to the base of the digit.3-5 In the Arai and Haneke5 method for the treatment of distal disease, a piece of tape is first placed at the distal nail fold, pulled proximally, and secured to the ventral aspect of the digit. Then, 1 or 2 additional strips of tape are applied to the lateral nail folds, pulled obliquely, and adhered to the base of the digit, as in the classic technique for lateral onychocryptosis.5
In our modification for the treatment of distal disease, only 2 strips of tape are required, each approximately 5-cm long. The first strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium parallel to the long axis of the finger, pulled away from the distal edge of the nail plate, and secured obliquely and proximally to the base of the finger on one side. The second strip of tape is applied to the hyponychium in the same manner, directly overlying the first strip, but is then pulled obliquely in the opposite direction and secured to the other side of the proximal finger (Figure 2). The 2 strips of tape are applied directly overlying each other at the distal nail fold but with opposing tension vectors to optimize pull on the distal nail fold. This modification eliminates the need to apply an initial strip of tape along the long axis of the digit, as described by Arai and Haneke.5

The patient is instructed on this method in the office and will change the tape at home daily for 2 to 6 weeks, until the nail plate has grown out over the hyponychium (Figure 3). This technique also can be combined with other modalities, such as dilute vinegar soaks performed daily after changing the tape to ease inflammation and prevent infection. Because strongly adhesive tape is used, it also is recommended that the patient soak the tape before removing it to prevent damage to underlying skin.

Practice Implications
Anchor taping is a common and effective treatment of onychocryptosis. Most techniques described in the literature are for lateral toenail cases, which often are managed by podiatry. A modification for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis has been previously described.5 We describe a similar modification using 2 tape strips pulled in opposite directions, which successfully resolved a case of distal onychocryptosis of the fingernail that developed following a nail procedure.
Because nail dystrophy is a relatively common complication of nail surgery, dermatologic surgeons should be aware of this simple, cost-effective, and noninvasive technique for the treatment of distal onychocryptosis.
- Geizhals S, Lipner SR. Review of onychocryptosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt9985w2n0
- Mayeaux EJ Jr, Carter C, Murphy TE. Ingrown toenail management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:158-164.
- Tsunoda M, Tsunoda K. Patient-controlled taping for the treatment of ingrown toenails. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:553-555. doi:10.1370/afm.1712
- Watabe A, Yamasaki K, Hashimoto A, et al. Retrospective evaluation of conservative treatment for 140 ingrown toenails with a novel taping procedure. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:822-825. doi:10.2340/00015555-2065
- Arai H, Haneke E. Noninvasive treatment for ingrown nails: anchor taping, acrylic affixed gutter splint, sculptured nail, and others. In: Baran R, Hadj-Rabia S, Silverman R, eds. Pediatric Nail Disorders. CRC Press; 2017:252-274.
- Geizhals S, Lipner SR. Review of onychocryptosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt9985w2n0
- Mayeaux EJ Jr, Carter C, Murphy TE. Ingrown toenail management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:158-164.
- Tsunoda M, Tsunoda K. Patient-controlled taping for the treatment of ingrown toenails. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:553-555. doi:10.1370/afm.1712
- Watabe A, Yamasaki K, Hashimoto A, et al. Retrospective evaluation of conservative treatment for 140 ingrown toenails with a novel taping procedure. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:822-825. doi:10.2340/00015555-2065
- Arai H, Haneke E. Noninvasive treatment for ingrown nails: anchor taping, acrylic affixed gutter splint, sculptured nail, and others. In: Baran R, Hadj-Rabia S, Silverman R, eds. Pediatric Nail Disorders. CRC Press; 2017:252-274.