User login
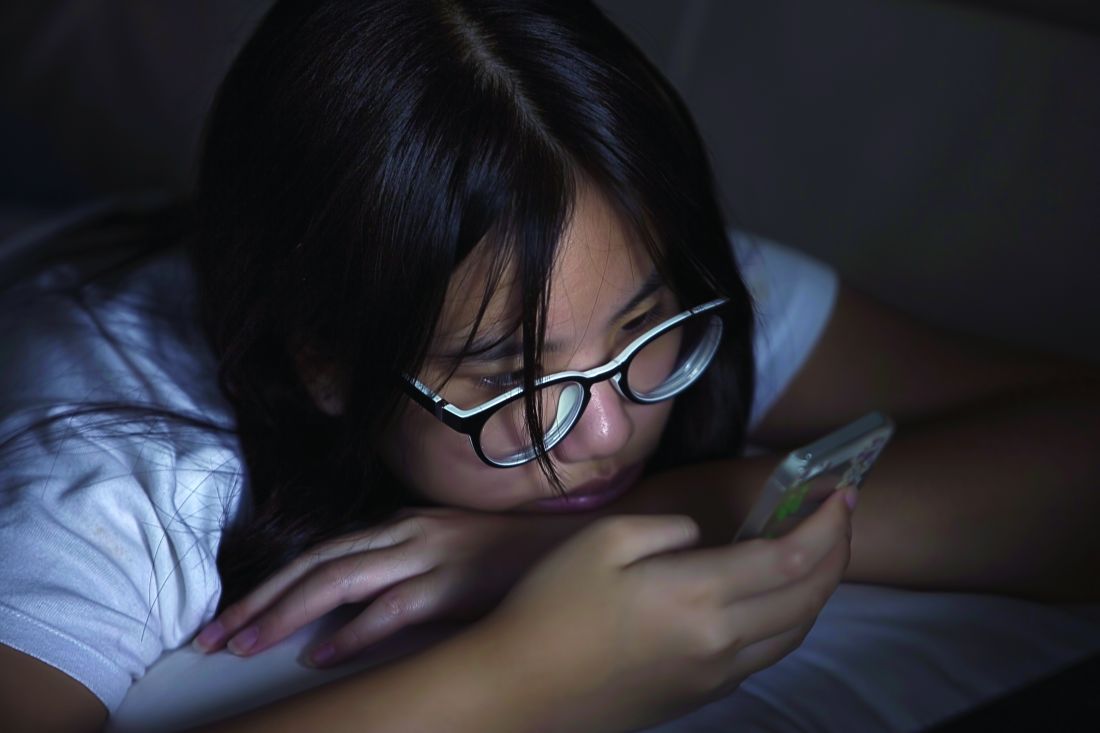
Smartphone ‘addiction’ tied to poor sleep in young adults
Smartphone “addiction” may explain poor sleep quality in a significant proportion of young adults, new research suggests.
Investigators found that almost 40% of adults aged 18-30 years who self-reported excessive smartphone use also reported poor sleep.
“Our study provides further support to the growing body of evidence that smartphone addiction has a deleterious impact on sleep,” wrote the researchers.
The study was published online March 2 in Frontiers of Psychiatry.
Not a clinical diagnosis
Smartphone addiction is not formally recognized as a clinical diagnosis, but it’s an “active” area of research, lead investigator Ben Carter, PhD, King’s College London, noted in the report.
In a cross-sectional survey, 1,043 college students (aged 18-30 years, 73% women) completed the 10-question validated Smartphone Addiction Scale Short Version (SAS-SV) and the adapted Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Score Index.
On the SAS-SV, 406 students (38.9%) reported “addiction” to their smartphones. This estimated prevalence is consistent with other reported studies in young adult populations globally, which is in the range of 30%-45%, the researchers noted.
Overall, 61.6% of participants surveyed reported poor sleep; among those who reported smartphone addiction, 68.7% had poor sleep quality, vs. 57.1% of those who did not report smartphone addiction.
In multivariable analysis that adjusted for a variety of relevant factors, among those for whom there was evidence of smartphone addiction, the odds of poor sleep were increased by 41% (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.41; 95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.87, P = .018).
The findings also suggest that a greater amount of time spent using the phone and greater use late at night can raise the risk for smartphone addiction.
“Should smartphone addiction become firmly established as a focus of clinical concern, those using their phones after midnight or using their phones for four or more hours per day are likely to be at high risk, and should guide administration of the SAS-SV,” the researchers wrote.
Caveats, cautions, and concerns
Reached for comment, Paul Weigle, MD, psychiatrist with Hartford HealthCare and Hartford (Conn.) Hospital, and member of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, said the finding of a relationship between addictive smartphone usage and poor sleep quality is not surprising.
“Great increases in adolescent screen media habits in recent decades have seen a concurrent increase in rates of insomnia among this population,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Weigle also noted that young people who use the phone excessively often do so in bed, “which decreases sleep onset by disrupting conditioning (the tendency for our bodies to relate bed with sleep) and by increasing physiological arousal, which makes it more difficult to fall asleep. The blue light from smartphones used at night disrupts our body’s natural circadian rhythms, confusing our brains regarding whether it is night or day, and further worsens sleep.”
Dr. Weigle said in an interview that some of his patients come to him seeking sleep medications, although the best treatment is to perform a “smartphone-ectomy” every evening.
Teenage patients will “beg, borrow, or steal” to be allowed to keep their phones by the bed with the promise not to use them overnight. Three-quarters of the time, when the parents are able to charge the phone in another room, “the sleep problem resolves,” Dr. Weigle said.
One caveat, he said, is that it’s “somewhat unclear whether this is best classified as an addiction or simply a seriously problematic habit. Either way, this type of habit causes a great deal of distress and dysfunction in the lives of those it affects, so it is important to understand,” he said.
In a statement, Bob Patton, PhD, lecturer in clinical psychology, University of Surrey, Guildford, England, noted that this is a cross-sectional study “and as such cannot lead to any firm conclusions about phone usage as the cause of reduced sleep quality.
“It does, however, provide some compelling evidence,” Dr. Patton said, “that the nature of smartphone usage and its related consequences are important considerations in addressing the emerging phenomenon of ‘smartphone addiction.’ ”
Also weighing in, Andrew Przybylski, PhD, director of research, Oxford (England) Internet Institute, University of Oxford, said by any global health body and is not a psychiatric disorder.
“The study is a correlational analysis of a sample of participants recruited on university campuses and therefore only reflects the experiences of those who had the purpose of the study explained to them. It can say nothing about behaviors in the general population,” Dr. Przybylski said in a statement.
“Readers should be cautious of making any firm conclusions about the impact of smartphone use in the general population, or the idea that they’re addictive in any objective sense, on the basis of this work,” he added. The study had no specific funding. Dr. Carter, Dr. Weigle, Dr. Patton, and Dr. Przybylski have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Smartphone “addiction” may explain poor sleep quality in a significant proportion of young adults, new research suggests.
Investigators found that almost 40% of adults aged 18-30 years who self-reported excessive smartphone use also reported poor sleep.
“Our study provides further support to the growing body of evidence that smartphone addiction has a deleterious impact on sleep,” wrote the researchers.
The study was published online March 2 in Frontiers of Psychiatry.
Not a clinical diagnosis
Smartphone addiction is not formally recognized as a clinical diagnosis, but it’s an “active” area of research, lead investigator Ben Carter, PhD, King’s College London, noted in the report.
In a cross-sectional survey, 1,043 college students (aged 18-30 years, 73% women) completed the 10-question validated Smartphone Addiction Scale Short Version (SAS-SV) and the adapted Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Score Index.
On the SAS-SV, 406 students (38.9%) reported “addiction” to their smartphones. This estimated prevalence is consistent with other reported studies in young adult populations globally, which is in the range of 30%-45%, the researchers noted.
Overall, 61.6% of participants surveyed reported poor sleep; among those who reported smartphone addiction, 68.7% had poor sleep quality, vs. 57.1% of those who did not report smartphone addiction.
In multivariable analysis that adjusted for a variety of relevant factors, among those for whom there was evidence of smartphone addiction, the odds of poor sleep were increased by 41% (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.41; 95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.87, P = .018).
The findings also suggest that a greater amount of time spent using the phone and greater use late at night can raise the risk for smartphone addiction.
“Should smartphone addiction become firmly established as a focus of clinical concern, those using their phones after midnight or using their phones for four or more hours per day are likely to be at high risk, and should guide administration of the SAS-SV,” the researchers wrote.
Caveats, cautions, and concerns
Reached for comment, Paul Weigle, MD, psychiatrist with Hartford HealthCare and Hartford (Conn.) Hospital, and member of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, said the finding of a relationship between addictive smartphone usage and poor sleep quality is not surprising.
“Great increases in adolescent screen media habits in recent decades have seen a concurrent increase in rates of insomnia among this population,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Weigle also noted that young people who use the phone excessively often do so in bed, “which decreases sleep onset by disrupting conditioning (the tendency for our bodies to relate bed with sleep) and by increasing physiological arousal, which makes it more difficult to fall asleep. The blue light from smartphones used at night disrupts our body’s natural circadian rhythms, confusing our brains regarding whether it is night or day, and further worsens sleep.”
Dr. Weigle said in an interview that some of his patients come to him seeking sleep medications, although the best treatment is to perform a “smartphone-ectomy” every evening.
Teenage patients will “beg, borrow, or steal” to be allowed to keep their phones by the bed with the promise not to use them overnight. Three-quarters of the time, when the parents are able to charge the phone in another room, “the sleep problem resolves,” Dr. Weigle said.
One caveat, he said, is that it’s “somewhat unclear whether this is best classified as an addiction or simply a seriously problematic habit. Either way, this type of habit causes a great deal of distress and dysfunction in the lives of those it affects, so it is important to understand,” he said.
In a statement, Bob Patton, PhD, lecturer in clinical psychology, University of Surrey, Guildford, England, noted that this is a cross-sectional study “and as such cannot lead to any firm conclusions about phone usage as the cause of reduced sleep quality.
“It does, however, provide some compelling evidence,” Dr. Patton said, “that the nature of smartphone usage and its related consequences are important considerations in addressing the emerging phenomenon of ‘smartphone addiction.’ ”
Also weighing in, Andrew Przybylski, PhD, director of research, Oxford (England) Internet Institute, University of Oxford, said by any global health body and is not a psychiatric disorder.
“The study is a correlational analysis of a sample of participants recruited on university campuses and therefore only reflects the experiences of those who had the purpose of the study explained to them. It can say nothing about behaviors in the general population,” Dr. Przybylski said in a statement.
“Readers should be cautious of making any firm conclusions about the impact of smartphone use in the general population, or the idea that they’re addictive in any objective sense, on the basis of this work,” he added. The study had no specific funding. Dr. Carter, Dr. Weigle, Dr. Patton, and Dr. Przybylski have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Smartphone “addiction” may explain poor sleep quality in a significant proportion of young adults, new research suggests.
Investigators found that almost 40% of adults aged 18-30 years who self-reported excessive smartphone use also reported poor sleep.
“Our study provides further support to the growing body of evidence that smartphone addiction has a deleterious impact on sleep,” wrote the researchers.
The study was published online March 2 in Frontiers of Psychiatry.
Not a clinical diagnosis
Smartphone addiction is not formally recognized as a clinical diagnosis, but it’s an “active” area of research, lead investigator Ben Carter, PhD, King’s College London, noted in the report.
In a cross-sectional survey, 1,043 college students (aged 18-30 years, 73% women) completed the 10-question validated Smartphone Addiction Scale Short Version (SAS-SV) and the adapted Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Score Index.
On the SAS-SV, 406 students (38.9%) reported “addiction” to their smartphones. This estimated prevalence is consistent with other reported studies in young adult populations globally, which is in the range of 30%-45%, the researchers noted.
Overall, 61.6% of participants surveyed reported poor sleep; among those who reported smartphone addiction, 68.7% had poor sleep quality, vs. 57.1% of those who did not report smartphone addiction.
In multivariable analysis that adjusted for a variety of relevant factors, among those for whom there was evidence of smartphone addiction, the odds of poor sleep were increased by 41% (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.41; 95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.87, P = .018).
The findings also suggest that a greater amount of time spent using the phone and greater use late at night can raise the risk for smartphone addiction.
“Should smartphone addiction become firmly established as a focus of clinical concern, those using their phones after midnight or using their phones for four or more hours per day are likely to be at high risk, and should guide administration of the SAS-SV,” the researchers wrote.
Caveats, cautions, and concerns
Reached for comment, Paul Weigle, MD, psychiatrist with Hartford HealthCare and Hartford (Conn.) Hospital, and member of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, said the finding of a relationship between addictive smartphone usage and poor sleep quality is not surprising.
“Great increases in adolescent screen media habits in recent decades have seen a concurrent increase in rates of insomnia among this population,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Weigle also noted that young people who use the phone excessively often do so in bed, “which decreases sleep onset by disrupting conditioning (the tendency for our bodies to relate bed with sleep) and by increasing physiological arousal, which makes it more difficult to fall asleep. The blue light from smartphones used at night disrupts our body’s natural circadian rhythms, confusing our brains regarding whether it is night or day, and further worsens sleep.”
Dr. Weigle said in an interview that some of his patients come to him seeking sleep medications, although the best treatment is to perform a “smartphone-ectomy” every evening.
Teenage patients will “beg, borrow, or steal” to be allowed to keep their phones by the bed with the promise not to use them overnight. Three-quarters of the time, when the parents are able to charge the phone in another room, “the sleep problem resolves,” Dr. Weigle said.
One caveat, he said, is that it’s “somewhat unclear whether this is best classified as an addiction or simply a seriously problematic habit. Either way, this type of habit causes a great deal of distress and dysfunction in the lives of those it affects, so it is important to understand,” he said.
In a statement, Bob Patton, PhD, lecturer in clinical psychology, University of Surrey, Guildford, England, noted that this is a cross-sectional study “and as such cannot lead to any firm conclusions about phone usage as the cause of reduced sleep quality.
“It does, however, provide some compelling evidence,” Dr. Patton said, “that the nature of smartphone usage and its related consequences are important considerations in addressing the emerging phenomenon of ‘smartphone addiction.’ ”
Also weighing in, Andrew Przybylski, PhD, director of research, Oxford (England) Internet Institute, University of Oxford, said by any global health body and is not a psychiatric disorder.
“The study is a correlational analysis of a sample of participants recruited on university campuses and therefore only reflects the experiences of those who had the purpose of the study explained to them. It can say nothing about behaviors in the general population,” Dr. Przybylski said in a statement.
“Readers should be cautious of making any firm conclusions about the impact of smartphone use in the general population, or the idea that they’re addictive in any objective sense, on the basis of this work,” he added. The study had no specific funding. Dr. Carter, Dr. Weigle, Dr. Patton, and Dr. Przybylski have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inpatient sodium imbalances linked to adverse COVID-19 outcomes
Both high and low serum sodium levels are associated with adverse outcomes for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, new research suggests.
In the retrospective study of 488 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at one of two London hospitals between February and May 2020, hypernatremia (defined as serum sodium level >145 mmol/L) at any time point during hospital stay was associated with a threefold increase in inpatient mortality.
Hyponatremia (serum sodium level <135 mmol/L) was associated with twice the likelihood of requiring advanced ventilatory support. In-hospital mortality was also increased among patients with hypovolemic hyponatremia.
“Serum sodium values could be used in clinical practice to identify patients with COVID-19 at high risk of poor outcomes who would benefit from more intensive monitoring and judicious rehydration,” Ploutarchos Tzoulis, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their article, which was published online on Feb. 24, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The findings will be presented at the upcoming news conference held by the Endocrine Society
Should sodium be included in a risk calculator for COVID-19?
Dr. Tzoulis, professor of endocrinology at the University College London Medical School, said in an interview that “sodium could be incorporated in risk calculators across other routine biomarkers, such as white cell count, lymphocytes, and CRP [C-reactive protein], in order to provide a tool for dynamic risk stratification throughout the clinical course of COVID-19 and assist clinical decision-making.”
Moreover, he said, “we should follow less conservative strategies in the rate and amount of fluid resuscitation in order to prevent hypernatremia, which is induced by negative fluid balance and can often be iatrogenic.”
Asked to comment, Steven Q. Simpson, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said that the article is missing key results that would assist in interpreting of the findings.
“Data regarding diuretic use and sparing of fluid administration are not in the paper. ... It is simply not possible to tell whether serum sodium is a ‘predictor’ ... or if it is a side effect of other issues or actions taken by physicians in patients who are progressing poorly.
“To say that sodium needs to be included in a risk calculator is to subtly suggest that there is some causal association with mortality, and that has quite clearly not been established,” stressed Dr. Simpson, who is president of the American College of Chest Physicians but was not speaking for the organization.
He added: “The data are interesting, but not actionable. It is common practice in critical care medicine to adjust water and salt intake to maintain serum sodium within the normal range, so the paper really doesn’t change any behavior.”
Dr. Tzoulis said in an interview that, despite not having electronic medical record data on diuretic use or fluid input and output, “our acute physicians and intensivists at both study sites have been adamant that they’ve not routinely used diuretics in COVID-19 patients. Diuretics have been sparingly used in our cohort, and also the frequency of pulmonary edema was reported as below 5%.”
Regarding volume of fluid intake, Dr. Tzoulis noted, “At our hospital sites, the strategy has been that of cautious fluid resuscitation. In fact, the amount of fluid given has been reported by our physicians and intensivists as ‘on purpose much more conservative than the usual one adopted in patients with community-acquired pneumonia at risk of respiratory failure.’ ”
Hyper- and hyponatremia linked to adverse COVID-19 outcomes
In the study, 5.3% of the 488 patients had hypernatremia at hospital presentation, and 24.6% had hyponatremia. Of note, only 19% of those with hyponatremia underwent laboratory workup to determine the etiology. Of those, three quarters had hypovolemic hyponatremia, determined on the basis of a urinary sodium cutoff of 30 mmol/L.
The total in-hospital mortality rate was 31.1%. There was a strong, although nonsignificant, trend toward higher mortality in association with sodium status at admission. Death rates were 28.4%, 30.8%, and 46.1% for those who were normonatremic, hyponatremic, and hypernatremic, respectively (P = .07). Baseline serum sodium levels didn’t differ between survivors (137 mmol/L) and nonsurvivors (138 mmol/L).
In multivariable analysis, the occurrence of hypernatremia at any point during the first 5 days in the hospital was among three independent risk factors for higher in-hospital mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.74; P = .02). The other risk factors were older age and higher CRP level.
Overall, hyponatremia was not associated with death (P = .41).
During hospitalization, 37.9% of patients remained normonatremic; 36.9% experienced hyponatremia; 10.9% had hypernatremia; and 14.3% had both conditions at some point during their stay.
In-hospital mortality was 21% among those with normonatremia, compared with 56.6% for those with hypernatremia (odds ratio, 3.05; P = .0038) and 45.7% for those with both (OR, 2.25; P < .0001).
The 28.3% mortality rate in the overall group that experienced hyponatremia didn’t differ significantly from the 21.1% in the normonatremic group (OR, 1.34; P = .16). However, the death rate was 40.9% among the subgroup that developed hypovolemic hyponatremia, significantly higher than the normonatremic group (OR, 2.59, P = .0017).
The incidence of hyponatremia decreased from 24.6% at admission to 14.1% 5 days later, whereas the frequency of hypernatremia rose from 5.3% to 13.8%.
Key finding: Link between hospital-acquired hypernatremia and death
“The key novel finding of our study was that hospital-acquired hypernatremia, rather than hypernatremia at admission, was a predictor for in-hospital mortality, with the worst prognosis being reported in patients with the largest increase in serum sodium in the first 5 days of hospitalization,” noted Dr. Tzoulis and colleagues.
Hypernatremia was present in 29.6% of nonsurvivors, compared with 5.2% in survivors.
Among 120 patients with hyponatremia at admission, 31.7% received advanced respiratory support, compared with 17.5% and 7.7% of those with normonatremia or hypernatremia, respectively (OR, 2.18; P = .0011).
In contrast, there was no difference in the proportions needing ventilatory support between those with hypernatremia and those with normonatremia (16.7% vs. 12.4%; OR, 1.44; P = .39).
Acute kidney injury occurred in 181 patients (37.1%). It was not related to serum sodium concentration at any time point.
Dr. Tzoulis and Dr. Simpson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Both high and low serum sodium levels are associated with adverse outcomes for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, new research suggests.
In the retrospective study of 488 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at one of two London hospitals between February and May 2020, hypernatremia (defined as serum sodium level >145 mmol/L) at any time point during hospital stay was associated with a threefold increase in inpatient mortality.
Hyponatremia (serum sodium level <135 mmol/L) was associated with twice the likelihood of requiring advanced ventilatory support. In-hospital mortality was also increased among patients with hypovolemic hyponatremia.
“Serum sodium values could be used in clinical practice to identify patients with COVID-19 at high risk of poor outcomes who would benefit from more intensive monitoring and judicious rehydration,” Ploutarchos Tzoulis, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their article, which was published online on Feb. 24, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The findings will be presented at the upcoming news conference held by the Endocrine Society
Should sodium be included in a risk calculator for COVID-19?
Dr. Tzoulis, professor of endocrinology at the University College London Medical School, said in an interview that “sodium could be incorporated in risk calculators across other routine biomarkers, such as white cell count, lymphocytes, and CRP [C-reactive protein], in order to provide a tool for dynamic risk stratification throughout the clinical course of COVID-19 and assist clinical decision-making.”
Moreover, he said, “we should follow less conservative strategies in the rate and amount of fluid resuscitation in order to prevent hypernatremia, which is induced by negative fluid balance and can often be iatrogenic.”
Asked to comment, Steven Q. Simpson, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said that the article is missing key results that would assist in interpreting of the findings.
“Data regarding diuretic use and sparing of fluid administration are not in the paper. ... It is simply not possible to tell whether serum sodium is a ‘predictor’ ... or if it is a side effect of other issues or actions taken by physicians in patients who are progressing poorly.
“To say that sodium needs to be included in a risk calculator is to subtly suggest that there is some causal association with mortality, and that has quite clearly not been established,” stressed Dr. Simpson, who is president of the American College of Chest Physicians but was not speaking for the organization.
He added: “The data are interesting, but not actionable. It is common practice in critical care medicine to adjust water and salt intake to maintain serum sodium within the normal range, so the paper really doesn’t change any behavior.”
Dr. Tzoulis said in an interview that, despite not having electronic medical record data on diuretic use or fluid input and output, “our acute physicians and intensivists at both study sites have been adamant that they’ve not routinely used diuretics in COVID-19 patients. Diuretics have been sparingly used in our cohort, and also the frequency of pulmonary edema was reported as below 5%.”
Regarding volume of fluid intake, Dr. Tzoulis noted, “At our hospital sites, the strategy has been that of cautious fluid resuscitation. In fact, the amount of fluid given has been reported by our physicians and intensivists as ‘on purpose much more conservative than the usual one adopted in patients with community-acquired pneumonia at risk of respiratory failure.’ ”
Hyper- and hyponatremia linked to adverse COVID-19 outcomes
In the study, 5.3% of the 488 patients had hypernatremia at hospital presentation, and 24.6% had hyponatremia. Of note, only 19% of those with hyponatremia underwent laboratory workup to determine the etiology. Of those, three quarters had hypovolemic hyponatremia, determined on the basis of a urinary sodium cutoff of 30 mmol/L.
The total in-hospital mortality rate was 31.1%. There was a strong, although nonsignificant, trend toward higher mortality in association with sodium status at admission. Death rates were 28.4%, 30.8%, and 46.1% for those who were normonatremic, hyponatremic, and hypernatremic, respectively (P = .07). Baseline serum sodium levels didn’t differ between survivors (137 mmol/L) and nonsurvivors (138 mmol/L).
In multivariable analysis, the occurrence of hypernatremia at any point during the first 5 days in the hospital was among three independent risk factors for higher in-hospital mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.74; P = .02). The other risk factors were older age and higher CRP level.
Overall, hyponatremia was not associated with death (P = .41).
During hospitalization, 37.9% of patients remained normonatremic; 36.9% experienced hyponatremia; 10.9% had hypernatremia; and 14.3% had both conditions at some point during their stay.
In-hospital mortality was 21% among those with normonatremia, compared with 56.6% for those with hypernatremia (odds ratio, 3.05; P = .0038) and 45.7% for those with both (OR, 2.25; P < .0001).
The 28.3% mortality rate in the overall group that experienced hyponatremia didn’t differ significantly from the 21.1% in the normonatremic group (OR, 1.34; P = .16). However, the death rate was 40.9% among the subgroup that developed hypovolemic hyponatremia, significantly higher than the normonatremic group (OR, 2.59, P = .0017).
The incidence of hyponatremia decreased from 24.6% at admission to 14.1% 5 days later, whereas the frequency of hypernatremia rose from 5.3% to 13.8%.
Key finding: Link between hospital-acquired hypernatremia and death
“The key novel finding of our study was that hospital-acquired hypernatremia, rather than hypernatremia at admission, was a predictor for in-hospital mortality, with the worst prognosis being reported in patients with the largest increase in serum sodium in the first 5 days of hospitalization,” noted Dr. Tzoulis and colleagues.
Hypernatremia was present in 29.6% of nonsurvivors, compared with 5.2% in survivors.
Among 120 patients with hyponatremia at admission, 31.7% received advanced respiratory support, compared with 17.5% and 7.7% of those with normonatremia or hypernatremia, respectively (OR, 2.18; P = .0011).
In contrast, there was no difference in the proportions needing ventilatory support between those with hypernatremia and those with normonatremia (16.7% vs. 12.4%; OR, 1.44; P = .39).
Acute kidney injury occurred in 181 patients (37.1%). It was not related to serum sodium concentration at any time point.
Dr. Tzoulis and Dr. Simpson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Both high and low serum sodium levels are associated with adverse outcomes for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, new research suggests.
In the retrospective study of 488 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at one of two London hospitals between February and May 2020, hypernatremia (defined as serum sodium level >145 mmol/L) at any time point during hospital stay was associated with a threefold increase in inpatient mortality.
Hyponatremia (serum sodium level <135 mmol/L) was associated with twice the likelihood of requiring advanced ventilatory support. In-hospital mortality was also increased among patients with hypovolemic hyponatremia.
“Serum sodium values could be used in clinical practice to identify patients with COVID-19 at high risk of poor outcomes who would benefit from more intensive monitoring and judicious rehydration,” Ploutarchos Tzoulis, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their article, which was published online on Feb. 24, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The findings will be presented at the upcoming news conference held by the Endocrine Society
Should sodium be included in a risk calculator for COVID-19?
Dr. Tzoulis, professor of endocrinology at the University College London Medical School, said in an interview that “sodium could be incorporated in risk calculators across other routine biomarkers, such as white cell count, lymphocytes, and CRP [C-reactive protein], in order to provide a tool for dynamic risk stratification throughout the clinical course of COVID-19 and assist clinical decision-making.”
Moreover, he said, “we should follow less conservative strategies in the rate and amount of fluid resuscitation in order to prevent hypernatremia, which is induced by negative fluid balance and can often be iatrogenic.”
Asked to comment, Steven Q. Simpson, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said that the article is missing key results that would assist in interpreting of the findings.
“Data regarding diuretic use and sparing of fluid administration are not in the paper. ... It is simply not possible to tell whether serum sodium is a ‘predictor’ ... or if it is a side effect of other issues or actions taken by physicians in patients who are progressing poorly.
“To say that sodium needs to be included in a risk calculator is to subtly suggest that there is some causal association with mortality, and that has quite clearly not been established,” stressed Dr. Simpson, who is president of the American College of Chest Physicians but was not speaking for the organization.
He added: “The data are interesting, but not actionable. It is common practice in critical care medicine to adjust water and salt intake to maintain serum sodium within the normal range, so the paper really doesn’t change any behavior.”
Dr. Tzoulis said in an interview that, despite not having electronic medical record data on diuretic use or fluid input and output, “our acute physicians and intensivists at both study sites have been adamant that they’ve not routinely used diuretics in COVID-19 patients. Diuretics have been sparingly used in our cohort, and also the frequency of pulmonary edema was reported as below 5%.”
Regarding volume of fluid intake, Dr. Tzoulis noted, “At our hospital sites, the strategy has been that of cautious fluid resuscitation. In fact, the amount of fluid given has been reported by our physicians and intensivists as ‘on purpose much more conservative than the usual one adopted in patients with community-acquired pneumonia at risk of respiratory failure.’ ”
Hyper- and hyponatremia linked to adverse COVID-19 outcomes
In the study, 5.3% of the 488 patients had hypernatremia at hospital presentation, and 24.6% had hyponatremia. Of note, only 19% of those with hyponatremia underwent laboratory workup to determine the etiology. Of those, three quarters had hypovolemic hyponatremia, determined on the basis of a urinary sodium cutoff of 30 mmol/L.
The total in-hospital mortality rate was 31.1%. There was a strong, although nonsignificant, trend toward higher mortality in association with sodium status at admission. Death rates were 28.4%, 30.8%, and 46.1% for those who were normonatremic, hyponatremic, and hypernatremic, respectively (P = .07). Baseline serum sodium levels didn’t differ between survivors (137 mmol/L) and nonsurvivors (138 mmol/L).
In multivariable analysis, the occurrence of hypernatremia at any point during the first 5 days in the hospital was among three independent risk factors for higher in-hospital mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.74; P = .02). The other risk factors were older age and higher CRP level.
Overall, hyponatremia was not associated with death (P = .41).
During hospitalization, 37.9% of patients remained normonatremic; 36.9% experienced hyponatremia; 10.9% had hypernatremia; and 14.3% had both conditions at some point during their stay.
In-hospital mortality was 21% among those with normonatremia, compared with 56.6% for those with hypernatremia (odds ratio, 3.05; P = .0038) and 45.7% for those with both (OR, 2.25; P < .0001).
The 28.3% mortality rate in the overall group that experienced hyponatremia didn’t differ significantly from the 21.1% in the normonatremic group (OR, 1.34; P = .16). However, the death rate was 40.9% among the subgroup that developed hypovolemic hyponatremia, significantly higher than the normonatremic group (OR, 2.59, P = .0017).
The incidence of hyponatremia decreased from 24.6% at admission to 14.1% 5 days later, whereas the frequency of hypernatremia rose from 5.3% to 13.8%.
Key finding: Link between hospital-acquired hypernatremia and death
“The key novel finding of our study was that hospital-acquired hypernatremia, rather than hypernatremia at admission, was a predictor for in-hospital mortality, with the worst prognosis being reported in patients with the largest increase in serum sodium in the first 5 days of hospitalization,” noted Dr. Tzoulis and colleagues.
Hypernatremia was present in 29.6% of nonsurvivors, compared with 5.2% in survivors.
Among 120 patients with hyponatremia at admission, 31.7% received advanced respiratory support, compared with 17.5% and 7.7% of those with normonatremia or hypernatremia, respectively (OR, 2.18; P = .0011).
In contrast, there was no difference in the proportions needing ventilatory support between those with hypernatremia and those with normonatremia (16.7% vs. 12.4%; OR, 1.44; P = .39).
Acute kidney injury occurred in 181 patients (37.1%). It was not related to serum sodium concentration at any time point.
Dr. Tzoulis and Dr. Simpson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mitochondrial DNA variant increases gallstone risk
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S rRNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S rRNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S rRNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Obesity: A ‘double hit’ in pregnant women with heart disease
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Stunning’ report shows eating disorders are vastly underestimated
A “stunning” new analysis of global data on eating disorders show that they are far more prevalent and disabling than previously reported.
Investigators found the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019 underestimated the prevalence of eating disorders by nearly 42 million cases, meaning these disorders are four times more common than previously reported.
“Our work highlights that eating disorders are far more prevalent and disabling than previously quantified,” lead author Damian F. Santomauro, PhD, University of Queensland and Center for Mental Health Research, Brisbane, Australia, said in an interview.
The study was published online March 3 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Policy implications
The GBD Study 2019 reports the prevalence and burden of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa under the umbrella of “eating disorders.”
However, binge-eating disorder (BED) and other specified feeding or eating disorder (OSFED) are more common, the investigators noted.
By excluding BED and OSFED, 41.9 million cases of eating disorders were not represented in the study.
The researchers calculate that the GBD 2019 overlooked 17.3 million people with BED and 24.6 million people with OSFED.
, bringing the total eating disorder DALYs to 6.6 million in 2019, they reported.
“When disorders are left out of the GBD, there is a risk that policymakers and service planners will interpret that these diseases are not prevalent or disabling and therefore not important to address,” said Dr. Santomauro.
“Our results show that the formal inclusion of binge-eating disorder and OSFED in GBD is both feasible and important and will lead to better representation of eating disorder burden globally.
“In turn, this will enhance recognition of the burden experienced by people living with these disorders and hopefully motivate increased investment in research, prevention, and treatment in future,” he added.
Landmark article, clarion call for action
In an accompanying commentary, Jennifer J. Thomas, PhD, and Kendra R. Becker, PhD, with the Eating Disorders Clinical and Research Program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that this “stunning” analysis highlights that eating disorders are four times more common than previously thought.
This “landmark” analysis also demonstrates that BED and OSFED are especially common with increasing age. It highlights the burden of eating disorders in men, “shattering the inaccurate but entrenched stereotype that eating disorders affect only thin, young, White women,” Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker pointed out.
This article, they wrote, is a “clarion call” for BED and OSFED to be included in future versions of the GBD Study.
Going a step further, Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker said the GBD Study should also include estimates of the prevalence of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder, rumination disorder, and pica and that the investigators should obtain direct measures of the disability associated with all feeding and eating disorders included in the DSM-5.
“If they do, the reported global burden will be even greater, underscoring the clear need for increased funding to study, prevent, and treat these debilitating illnesses,” they concluded.
The study was funded by Queensland Health, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the editorialists are listed with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “stunning” new analysis of global data on eating disorders show that they are far more prevalent and disabling than previously reported.
Investigators found the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019 underestimated the prevalence of eating disorders by nearly 42 million cases, meaning these disorders are four times more common than previously reported.
“Our work highlights that eating disorders are far more prevalent and disabling than previously quantified,” lead author Damian F. Santomauro, PhD, University of Queensland and Center for Mental Health Research, Brisbane, Australia, said in an interview.
The study was published online March 3 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Policy implications
The GBD Study 2019 reports the prevalence and burden of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa under the umbrella of “eating disorders.”
However, binge-eating disorder (BED) and other specified feeding or eating disorder (OSFED) are more common, the investigators noted.
By excluding BED and OSFED, 41.9 million cases of eating disorders were not represented in the study.
The researchers calculate that the GBD 2019 overlooked 17.3 million people with BED and 24.6 million people with OSFED.
, bringing the total eating disorder DALYs to 6.6 million in 2019, they reported.
“When disorders are left out of the GBD, there is a risk that policymakers and service planners will interpret that these diseases are not prevalent or disabling and therefore not important to address,” said Dr. Santomauro.
“Our results show that the formal inclusion of binge-eating disorder and OSFED in GBD is both feasible and important and will lead to better representation of eating disorder burden globally.
“In turn, this will enhance recognition of the burden experienced by people living with these disorders and hopefully motivate increased investment in research, prevention, and treatment in future,” he added.
Landmark article, clarion call for action
In an accompanying commentary, Jennifer J. Thomas, PhD, and Kendra R. Becker, PhD, with the Eating Disorders Clinical and Research Program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that this “stunning” analysis highlights that eating disorders are four times more common than previously thought.
This “landmark” analysis also demonstrates that BED and OSFED are especially common with increasing age. It highlights the burden of eating disorders in men, “shattering the inaccurate but entrenched stereotype that eating disorders affect only thin, young, White women,” Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker pointed out.
This article, they wrote, is a “clarion call” for BED and OSFED to be included in future versions of the GBD Study.
Going a step further, Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker said the GBD Study should also include estimates of the prevalence of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder, rumination disorder, and pica and that the investigators should obtain direct measures of the disability associated with all feeding and eating disorders included in the DSM-5.
“If they do, the reported global burden will be even greater, underscoring the clear need for increased funding to study, prevent, and treat these debilitating illnesses,” they concluded.
The study was funded by Queensland Health, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the editorialists are listed with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “stunning” new analysis of global data on eating disorders show that they are far more prevalent and disabling than previously reported.
Investigators found the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019 underestimated the prevalence of eating disorders by nearly 42 million cases, meaning these disorders are four times more common than previously reported.
“Our work highlights that eating disorders are far more prevalent and disabling than previously quantified,” lead author Damian F. Santomauro, PhD, University of Queensland and Center for Mental Health Research, Brisbane, Australia, said in an interview.
The study was published online March 3 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Policy implications
The GBD Study 2019 reports the prevalence and burden of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa under the umbrella of “eating disorders.”
However, binge-eating disorder (BED) and other specified feeding or eating disorder (OSFED) are more common, the investigators noted.
By excluding BED and OSFED, 41.9 million cases of eating disorders were not represented in the study.
The researchers calculate that the GBD 2019 overlooked 17.3 million people with BED and 24.6 million people with OSFED.
, bringing the total eating disorder DALYs to 6.6 million in 2019, they reported.
“When disorders are left out of the GBD, there is a risk that policymakers and service planners will interpret that these diseases are not prevalent or disabling and therefore not important to address,” said Dr. Santomauro.
“Our results show that the formal inclusion of binge-eating disorder and OSFED in GBD is both feasible and important and will lead to better representation of eating disorder burden globally.
“In turn, this will enhance recognition of the burden experienced by people living with these disorders and hopefully motivate increased investment in research, prevention, and treatment in future,” he added.
Landmark article, clarion call for action
In an accompanying commentary, Jennifer J. Thomas, PhD, and Kendra R. Becker, PhD, with the Eating Disorders Clinical and Research Program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that this “stunning” analysis highlights that eating disorders are four times more common than previously thought.
This “landmark” analysis also demonstrates that BED and OSFED are especially common with increasing age. It highlights the burden of eating disorders in men, “shattering the inaccurate but entrenched stereotype that eating disorders affect only thin, young, White women,” Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker pointed out.
This article, they wrote, is a “clarion call” for BED and OSFED to be included in future versions of the GBD Study.
Going a step further, Dr. Thomas and Dr. Becker said the GBD Study should also include estimates of the prevalence of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder, rumination disorder, and pica and that the investigators should obtain direct measures of the disability associated with all feeding and eating disorders included in the DSM-5.
“If they do, the reported global burden will be even greater, underscoring the clear need for increased funding to study, prevent, and treat these debilitating illnesses,” they concluded.
The study was funded by Queensland Health, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the editorialists are listed with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inclusivity needed in PHM fellowships
A year and a half ago, I found myself seated in a crowded hall at the national Pediatric Hospital Medicine (PHM) conference. Throughout the conference, trainees like me were warmly welcomed into small groups and lunch tables. I tried to keep my cool while PHM “celebrities” chatted with me in the elevator. Most sessions were prepared with plenty of chairs, and those that were not encouraged latecomers to grab a spot on the floor or the back wall – the more the merrier.
The intention of this “advice for applicants” meeting was to inspire and guide our next steps toward fellowship, but a discomforting reality loomed over us. It was the first year graduating pediatricians could not choose PHM board certification via the practice pathway – we needed an invitation in the form of a fellowship match.
The “hidden curriculum” was not subtle: People who scored a seat would keep their options open within the field of PHM, and those who did not had a murkier future. This message stood in stark contrast to the PHM inclusivity I had experienced all conference, and planted seeds of doubt: Was I welcome here? Did I “deserve” a seat?
I found the experience as a PHM fellowship applicant to be uncomfortable, and my all-too familiar friend “imposter syndrome” set up camp in my brain and made herself at home. I had no way of knowing how many programs to apply to, how many to interview at, or the chances of my matching at all. Once on the interview trail, I realized I was not alone in my discomfort – most applicants harbored some trepidation, and no one truly knew how the chips would fall on Match Day.
I am thrilled and relieved to have come out the other end in a great position. The team I work with and learn from is phenomenal. I am grateful that ACGME accreditation ensures structures are in place for fellows to be supported in their academic and educational efforts and have full confidence that the skills I gain in fellowship will help me contribute to progression of the field of PHM and improve my performance as a clinician-educator.
Sadly, each year PHM match day celebrations are dampened by the knowledge that a large portion of our colleagues are being left out in the cold with an “unmatched” notification in their inboxes. Approximately 200 graduating pediatricians become pediatric hospitalists each year,1 but only 68 fellowship positions were available in the United States for matriculation in 2020.2 In 2019, PHM fellowship candidates navigated the 6-month application journey with aspirations to further their training in the profession they love. Of the candidates who submitted a rank list committing to 2 or more years in PHM fellowship, 35% were denied.
Unfortunately, despite expansion of PHM fellowship programs and fifteen seats added from last year, we learned this December that there still are not enough positions to welcome qualified applicants with open arms: Thirty-three percent of candidates ranked PHM programs first in the NRMP but did not match – the highest unmatched percentage out of all pediatric subspecialties.3
The NRMP report shared a glimpse of our colleagues who received interview invitations and submitted a rank list, but this is likely an underestimation of pediatric graduates who wanted to obtain PHM board certification and wound up on a different path. Some residents anticipated the stiff competition and delayed their plans to apply for fellowship, while others matched into another subspecialty that was able to accommodate them. Many pediatric graduates joined the workforce directly as pediatric hospitalists knowing the practice pathway to certification is not available to them. Along with other physicians without board certification in PHM, they shoulder concerns of being withheld from professional advancement opportunities.
For the foreseeable future it is clear that pediatric hospitalists without board certification will be a large part of our community, and are crucial to providing high-quality care to hospitalized children nationally. In 2019, a national survey of pediatric hospital medicine groups revealed that 50% of pediatric hospitalist hires came directly out of residency, and only 8% of hires were fellowship trained.4 The same report revealed that 26% of physicians were board-certified.These percentages are likely to change over the next 5 years as the window of practice pathway certification closes and fellowship programs continue to expand. Only time will tell what the national prevalence of board-certified pediatric hospitalists settles out to be.
Historically, PHM fellowship graduates have assumed roles that include teaching and research responsibilities, and ACGME fellowship requirements have ensured that trainees graduate with skills in medical education and scholarship, and need only 4 weeks of training to be done in a community hospital.5 Pediatric hospitalists who do not pursue board certification are seeing the growing pool of PHM fellowship graduates prepared for positions in academic institutions. It is reasonable that they harbor concerns about being siloed toward primarily community hospital roles, and for community hospitalists to feel that this structure undervalues their role within the field of PHM.
At a time when inclusivity and community in medicine are receiving much-needed recognition, the current fellowship application climate has potential to create division within the PHM community. Newly graduating pediatric residents are among the populations disproportionately affected by the practice pathway cutoff. Like other subspecialties with ever-climbing steps up the “ivory tower” of academia and specialization within medicine, the inherent structure of the training pathway makes navigating it more difficult for pediatricians with professional, geographic, and economic diversity or constraints.
Med-Peds–trained colleagues have the added challenge of finding a fellowship position that is willing and able to support their concurrent internal medicine goals. International medical graduates make up about 20% of graduating residents each year, and just 11% of matched PHM fellows.3,6 Similarly, while DO medical graduates make up 20% of pediatric residents in the United States, only 10% of matched PHM fellows were DOs.3,6 New pediatricians with families or financial insecurity may be unable to invest in an expensive application process, move to a new city, and accept less than half of the average starting salary of a pediatric hospitalist for 2-3 years.7
The prevalence of implicit bias in medicine is well documented, and there is growing evidence that it negatively impacts candidate selection in medical education and contributes to minorities being underrepresented in the physician workforce.8 We must recognize the ways that adding a competitive costly hurdle may risk conflict with our mission to encourage diversity of representation within PHM leadership positions.
We have not yet successfully bridged the gap between qualified PHM fellowship candidates and available fellowship positions. I worry that this gap and the lack of transparency surrounding it is resulting in one portion of new pediatricians being welcomed by the subspecialty, and others feeling unsupported and alienated by the larger PHM community as early career physicians.
Right now, the only solution available is expansion of fellowship programs. We see progress with the new addition of fellowship positions every year, but finding funding for each position is often a lengthy endeavor, and the COVID-19 pandemic has tightened the purse strings of many children’s hospitals. It may be many years before the number of available fellowship positions more closely approximates the 200 pediatricians that become hospitalists each year.
The most equitable solution would be offering other avenues to board certification while this gap is being bridged, either by extending the practice pathway option, or making a third pathway that requires less institutional funding per fellow, but still incentivizes institutional investment in fellowship positions and resources (e.g., a pathway requiring some number of years in practice, plus 1 year in fellowship centered around a nonclinical academic curriculum).
In the absence of the solutions above, we collectively hold the responsibility of maintaining inclusivity and support of our PHM colleagues with and without board certification. One important strategy provided by Dr. Gregory Welsh9 is to incorporate community hospital medicine rotations into residency training. Sharing this side of PHM with residents may help some graduates avoid a training pathway they may not want or need. More importantly, it would raise trainee exposure and interest toward a service that is both expansive – approximately 70% of pediatric hospitalists practice in a community hospital – and crucial to children’s health nationally.
Pediatric hospitalists who are not eligible for board certification are vital and valued members of the PHM community, and as such need to maintain representation within PHM leadership. Professional development opportunities need to remain accessible outside of fellowship. The blossoming of virtual conferences and Zoom meet-ups in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic have shown us that with innovation (and a good Internet connection), networking and mentorship can be accomplished across thousands of miles.
While there’s great diversity within PHM, this subspecialty has a history of attracting pediatricians with some common core qualities: Grit, creativity, and the belief that a strong team is far greater than the sum of its parts. I have confidence that if we approach this PHM transition period with transparency about our goals and challenges, this community can emerge from it strong and united.
Dr. Ezzio is a first-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich. Her interests include medical education and advocacy. Dr. Ezzio would like to thank Dr. Jeri Kessenich and Dr. Rachel “Danielle” Fisher for their assistance in revising the article. To submit to, or for inquiries about, our PHM Fellows Column, please contact our Pediatrics Editor, Dr. Anika Kumar ([email protected]).
References
1. Leyenaar JK and Fritner MP. Graduating pediatric residents entering the hospital medicine workforce, 2006-2015. Acad Pediatr. 2018 Mar;18(2):200-7.
2. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2020 appointment year. Washington, DC 2020.
3. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2021 appointment year. Washington, DC 2021.
4. 2020 State of Hospital Medicine report. Society of Hospital Medicine. 2020.
5. Oshimura JM et al. Current roles and perceived needs of pediatric hospital medicine fellowship graduates. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(10):633-7.
6. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: 2020 main residency match. Washington, DC 2020.
7. American Academy of Pediatrics Annual Survey of graduating residents 2003-2020.
8. Quinn Capers IV. How clinicians and educators can mitigate implicit bias in patient care and candidate selection in medical education. American Thoracic Society Scholar. 2020 Jun;1(3):211-17.
9. Welsh G. The importance of community pediatric hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2021 Jan;25(1):27.
A year and a half ago, I found myself seated in a crowded hall at the national Pediatric Hospital Medicine (PHM) conference. Throughout the conference, trainees like me were warmly welcomed into small groups and lunch tables. I tried to keep my cool while PHM “celebrities” chatted with me in the elevator. Most sessions were prepared with plenty of chairs, and those that were not encouraged latecomers to grab a spot on the floor or the back wall – the more the merrier.
The intention of this “advice for applicants” meeting was to inspire and guide our next steps toward fellowship, but a discomforting reality loomed over us. It was the first year graduating pediatricians could not choose PHM board certification via the practice pathway – we needed an invitation in the form of a fellowship match.
The “hidden curriculum” was not subtle: People who scored a seat would keep their options open within the field of PHM, and those who did not had a murkier future. This message stood in stark contrast to the PHM inclusivity I had experienced all conference, and planted seeds of doubt: Was I welcome here? Did I “deserve” a seat?
I found the experience as a PHM fellowship applicant to be uncomfortable, and my all-too familiar friend “imposter syndrome” set up camp in my brain and made herself at home. I had no way of knowing how many programs to apply to, how many to interview at, or the chances of my matching at all. Once on the interview trail, I realized I was not alone in my discomfort – most applicants harbored some trepidation, and no one truly knew how the chips would fall on Match Day.
I am thrilled and relieved to have come out the other end in a great position. The team I work with and learn from is phenomenal. I am grateful that ACGME accreditation ensures structures are in place for fellows to be supported in their academic and educational efforts and have full confidence that the skills I gain in fellowship will help me contribute to progression of the field of PHM and improve my performance as a clinician-educator.
Sadly, each year PHM match day celebrations are dampened by the knowledge that a large portion of our colleagues are being left out in the cold with an “unmatched” notification in their inboxes. Approximately 200 graduating pediatricians become pediatric hospitalists each year,1 but only 68 fellowship positions were available in the United States for matriculation in 2020.2 In 2019, PHM fellowship candidates navigated the 6-month application journey with aspirations to further their training in the profession they love. Of the candidates who submitted a rank list committing to 2 or more years in PHM fellowship, 35% were denied.
Unfortunately, despite expansion of PHM fellowship programs and fifteen seats added from last year, we learned this December that there still are not enough positions to welcome qualified applicants with open arms: Thirty-three percent of candidates ranked PHM programs first in the NRMP but did not match – the highest unmatched percentage out of all pediatric subspecialties.3
The NRMP report shared a glimpse of our colleagues who received interview invitations and submitted a rank list, but this is likely an underestimation of pediatric graduates who wanted to obtain PHM board certification and wound up on a different path. Some residents anticipated the stiff competition and delayed their plans to apply for fellowship, while others matched into another subspecialty that was able to accommodate them. Many pediatric graduates joined the workforce directly as pediatric hospitalists knowing the practice pathway to certification is not available to them. Along with other physicians without board certification in PHM, they shoulder concerns of being withheld from professional advancement opportunities.
For the foreseeable future it is clear that pediatric hospitalists without board certification will be a large part of our community, and are crucial to providing high-quality care to hospitalized children nationally. In 2019, a national survey of pediatric hospital medicine groups revealed that 50% of pediatric hospitalist hires came directly out of residency, and only 8% of hires were fellowship trained.4 The same report revealed that 26% of physicians were board-certified.These percentages are likely to change over the next 5 years as the window of practice pathway certification closes and fellowship programs continue to expand. Only time will tell what the national prevalence of board-certified pediatric hospitalists settles out to be.
Historically, PHM fellowship graduates have assumed roles that include teaching and research responsibilities, and ACGME fellowship requirements have ensured that trainees graduate with skills in medical education and scholarship, and need only 4 weeks of training to be done in a community hospital.5 Pediatric hospitalists who do not pursue board certification are seeing the growing pool of PHM fellowship graduates prepared for positions in academic institutions. It is reasonable that they harbor concerns about being siloed toward primarily community hospital roles, and for community hospitalists to feel that this structure undervalues their role within the field of PHM.
At a time when inclusivity and community in medicine are receiving much-needed recognition, the current fellowship application climate has potential to create division within the PHM community. Newly graduating pediatric residents are among the populations disproportionately affected by the practice pathway cutoff. Like other subspecialties with ever-climbing steps up the “ivory tower” of academia and specialization within medicine, the inherent structure of the training pathway makes navigating it more difficult for pediatricians with professional, geographic, and economic diversity or constraints.
Med-Peds–trained colleagues have the added challenge of finding a fellowship position that is willing and able to support their concurrent internal medicine goals. International medical graduates make up about 20% of graduating residents each year, and just 11% of matched PHM fellows.3,6 Similarly, while DO medical graduates make up 20% of pediatric residents in the United States, only 10% of matched PHM fellows were DOs.3,6 New pediatricians with families or financial insecurity may be unable to invest in an expensive application process, move to a new city, and accept less than half of the average starting salary of a pediatric hospitalist for 2-3 years.7
The prevalence of implicit bias in medicine is well documented, and there is growing evidence that it negatively impacts candidate selection in medical education and contributes to minorities being underrepresented in the physician workforce.8 We must recognize the ways that adding a competitive costly hurdle may risk conflict with our mission to encourage diversity of representation within PHM leadership positions.
We have not yet successfully bridged the gap between qualified PHM fellowship candidates and available fellowship positions. I worry that this gap and the lack of transparency surrounding it is resulting in one portion of new pediatricians being welcomed by the subspecialty, and others feeling unsupported and alienated by the larger PHM community as early career physicians.
Right now, the only solution available is expansion of fellowship programs. We see progress with the new addition of fellowship positions every year, but finding funding for each position is often a lengthy endeavor, and the COVID-19 pandemic has tightened the purse strings of many children’s hospitals. It may be many years before the number of available fellowship positions more closely approximates the 200 pediatricians that become hospitalists each year.
The most equitable solution would be offering other avenues to board certification while this gap is being bridged, either by extending the practice pathway option, or making a third pathway that requires less institutional funding per fellow, but still incentivizes institutional investment in fellowship positions and resources (e.g., a pathway requiring some number of years in practice, plus 1 year in fellowship centered around a nonclinical academic curriculum).
In the absence of the solutions above, we collectively hold the responsibility of maintaining inclusivity and support of our PHM colleagues with and without board certification. One important strategy provided by Dr. Gregory Welsh9 is to incorporate community hospital medicine rotations into residency training. Sharing this side of PHM with residents may help some graduates avoid a training pathway they may not want or need. More importantly, it would raise trainee exposure and interest toward a service that is both expansive – approximately 70% of pediatric hospitalists practice in a community hospital – and crucial to children’s health nationally.
Pediatric hospitalists who are not eligible for board certification are vital and valued members of the PHM community, and as such need to maintain representation within PHM leadership. Professional development opportunities need to remain accessible outside of fellowship. The blossoming of virtual conferences and Zoom meet-ups in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic have shown us that with innovation (and a good Internet connection), networking and mentorship can be accomplished across thousands of miles.
While there’s great diversity within PHM, this subspecialty has a history of attracting pediatricians with some common core qualities: Grit, creativity, and the belief that a strong team is far greater than the sum of its parts. I have confidence that if we approach this PHM transition period with transparency about our goals and challenges, this community can emerge from it strong and united.
Dr. Ezzio is a first-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich. Her interests include medical education and advocacy. Dr. Ezzio would like to thank Dr. Jeri Kessenich and Dr. Rachel “Danielle” Fisher for their assistance in revising the article. To submit to, or for inquiries about, our PHM Fellows Column, please contact our Pediatrics Editor, Dr. Anika Kumar ([email protected]).
References
1. Leyenaar JK and Fritner MP. Graduating pediatric residents entering the hospital medicine workforce, 2006-2015. Acad Pediatr. 2018 Mar;18(2):200-7.
2. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2020 appointment year. Washington, DC 2020.
3. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2021 appointment year. Washington, DC 2021.
4. 2020 State of Hospital Medicine report. Society of Hospital Medicine. 2020.
5. Oshimura JM et al. Current roles and perceived needs of pediatric hospital medicine fellowship graduates. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(10):633-7.
6. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: 2020 main residency match. Washington, DC 2020.
7. American Academy of Pediatrics Annual Survey of graduating residents 2003-2020.
8. Quinn Capers IV. How clinicians and educators can mitigate implicit bias in patient care and candidate selection in medical education. American Thoracic Society Scholar. 2020 Jun;1(3):211-17.
9. Welsh G. The importance of community pediatric hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2021 Jan;25(1):27.
A year and a half ago, I found myself seated in a crowded hall at the national Pediatric Hospital Medicine (PHM) conference. Throughout the conference, trainees like me were warmly welcomed into small groups and lunch tables. I tried to keep my cool while PHM “celebrities” chatted with me in the elevator. Most sessions were prepared with plenty of chairs, and those that were not encouraged latecomers to grab a spot on the floor or the back wall – the more the merrier.
The intention of this “advice for applicants” meeting was to inspire and guide our next steps toward fellowship, but a discomforting reality loomed over us. It was the first year graduating pediatricians could not choose PHM board certification via the practice pathway – we needed an invitation in the form of a fellowship match.
The “hidden curriculum” was not subtle: People who scored a seat would keep their options open within the field of PHM, and those who did not had a murkier future. This message stood in stark contrast to the PHM inclusivity I had experienced all conference, and planted seeds of doubt: Was I welcome here? Did I “deserve” a seat?
I found the experience as a PHM fellowship applicant to be uncomfortable, and my all-too familiar friend “imposter syndrome” set up camp in my brain and made herself at home. I had no way of knowing how many programs to apply to, how many to interview at, or the chances of my matching at all. Once on the interview trail, I realized I was not alone in my discomfort – most applicants harbored some trepidation, and no one truly knew how the chips would fall on Match Day.
I am thrilled and relieved to have come out the other end in a great position. The team I work with and learn from is phenomenal. I am grateful that ACGME accreditation ensures structures are in place for fellows to be supported in their academic and educational efforts and have full confidence that the skills I gain in fellowship will help me contribute to progression of the field of PHM and improve my performance as a clinician-educator.
Sadly, each year PHM match day celebrations are dampened by the knowledge that a large portion of our colleagues are being left out in the cold with an “unmatched” notification in their inboxes. Approximately 200 graduating pediatricians become pediatric hospitalists each year,1 but only 68 fellowship positions were available in the United States for matriculation in 2020.2 In 2019, PHM fellowship candidates navigated the 6-month application journey with aspirations to further their training in the profession they love. Of the candidates who submitted a rank list committing to 2 or more years in PHM fellowship, 35% were denied.
Unfortunately, despite expansion of PHM fellowship programs and fifteen seats added from last year, we learned this December that there still are not enough positions to welcome qualified applicants with open arms: Thirty-three percent of candidates ranked PHM programs first in the NRMP but did not match – the highest unmatched percentage out of all pediatric subspecialties.3
The NRMP report shared a glimpse of our colleagues who received interview invitations and submitted a rank list, but this is likely an underestimation of pediatric graduates who wanted to obtain PHM board certification and wound up on a different path. Some residents anticipated the stiff competition and delayed their plans to apply for fellowship, while others matched into another subspecialty that was able to accommodate them. Many pediatric graduates joined the workforce directly as pediatric hospitalists knowing the practice pathway to certification is not available to them. Along with other physicians without board certification in PHM, they shoulder concerns of being withheld from professional advancement opportunities.
For the foreseeable future it is clear that pediatric hospitalists without board certification will be a large part of our community, and are crucial to providing high-quality care to hospitalized children nationally. In 2019, a national survey of pediatric hospital medicine groups revealed that 50% of pediatric hospitalist hires came directly out of residency, and only 8% of hires were fellowship trained.4 The same report revealed that 26% of physicians were board-certified.These percentages are likely to change over the next 5 years as the window of practice pathway certification closes and fellowship programs continue to expand. Only time will tell what the national prevalence of board-certified pediatric hospitalists settles out to be.
Historically, PHM fellowship graduates have assumed roles that include teaching and research responsibilities, and ACGME fellowship requirements have ensured that trainees graduate with skills in medical education and scholarship, and need only 4 weeks of training to be done in a community hospital.5 Pediatric hospitalists who do not pursue board certification are seeing the growing pool of PHM fellowship graduates prepared for positions in academic institutions. It is reasonable that they harbor concerns about being siloed toward primarily community hospital roles, and for community hospitalists to feel that this structure undervalues their role within the field of PHM.
At a time when inclusivity and community in medicine are receiving much-needed recognition, the current fellowship application climate has potential to create division within the PHM community. Newly graduating pediatric residents are among the populations disproportionately affected by the practice pathway cutoff. Like other subspecialties with ever-climbing steps up the “ivory tower” of academia and specialization within medicine, the inherent structure of the training pathway makes navigating it more difficult for pediatricians with professional, geographic, and economic diversity or constraints.
Med-Peds–trained colleagues have the added challenge of finding a fellowship position that is willing and able to support their concurrent internal medicine goals. International medical graduates make up about 20% of graduating residents each year, and just 11% of matched PHM fellows.3,6 Similarly, while DO medical graduates make up 20% of pediatric residents in the United States, only 10% of matched PHM fellows were DOs.3,6 New pediatricians with families or financial insecurity may be unable to invest in an expensive application process, move to a new city, and accept less than half of the average starting salary of a pediatric hospitalist for 2-3 years.7
The prevalence of implicit bias in medicine is well documented, and there is growing evidence that it negatively impacts candidate selection in medical education and contributes to minorities being underrepresented in the physician workforce.8 We must recognize the ways that adding a competitive costly hurdle may risk conflict with our mission to encourage diversity of representation within PHM leadership positions.
We have not yet successfully bridged the gap between qualified PHM fellowship candidates and available fellowship positions. I worry that this gap and the lack of transparency surrounding it is resulting in one portion of new pediatricians being welcomed by the subspecialty, and others feeling unsupported and alienated by the larger PHM community as early career physicians.
Right now, the only solution available is expansion of fellowship programs. We see progress with the new addition of fellowship positions every year, but finding funding for each position is often a lengthy endeavor, and the COVID-19 pandemic has tightened the purse strings of many children’s hospitals. It may be many years before the number of available fellowship positions more closely approximates the 200 pediatricians that become hospitalists each year.
The most equitable solution would be offering other avenues to board certification while this gap is being bridged, either by extending the practice pathway option, or making a third pathway that requires less institutional funding per fellow, but still incentivizes institutional investment in fellowship positions and resources (e.g., a pathway requiring some number of years in practice, plus 1 year in fellowship centered around a nonclinical academic curriculum).
In the absence of the solutions above, we collectively hold the responsibility of maintaining inclusivity and support of our PHM colleagues with and without board certification. One important strategy provided by Dr. Gregory Welsh9 is to incorporate community hospital medicine rotations into residency training. Sharing this side of PHM with residents may help some graduates avoid a training pathway they may not want or need. More importantly, it would raise trainee exposure and interest toward a service that is both expansive – approximately 70% of pediatric hospitalists practice in a community hospital – and crucial to children’s health nationally.
Pediatric hospitalists who are not eligible for board certification are vital and valued members of the PHM community, and as such need to maintain representation within PHM leadership. Professional development opportunities need to remain accessible outside of fellowship. The blossoming of virtual conferences and Zoom meet-ups in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic have shown us that with innovation (and a good Internet connection), networking and mentorship can be accomplished across thousands of miles.
While there’s great diversity within PHM, this subspecialty has a history of attracting pediatricians with some common core qualities: Grit, creativity, and the belief that a strong team is far greater than the sum of its parts. I have confidence that if we approach this PHM transition period with transparency about our goals and challenges, this community can emerge from it strong and united.
Dr. Ezzio is a first-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich. Her interests include medical education and advocacy. Dr. Ezzio would like to thank Dr. Jeri Kessenich and Dr. Rachel “Danielle” Fisher for their assistance in revising the article. To submit to, or for inquiries about, our PHM Fellows Column, please contact our Pediatrics Editor, Dr. Anika Kumar ([email protected]).
References
1. Leyenaar JK and Fritner MP. Graduating pediatric residents entering the hospital medicine workforce, 2006-2015. Acad Pediatr. 2018 Mar;18(2):200-7.
2. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2020 appointment year. Washington, DC 2020.
3. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: Specialties matching service 2021 appointment year. Washington, DC 2021.
4. 2020 State of Hospital Medicine report. Society of Hospital Medicine. 2020.
5. Oshimura JM et al. Current roles and perceived needs of pediatric hospital medicine fellowship graduates. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(10):633-7.
6. National Resident Matching Program. Results and data: 2020 main residency match. Washington, DC 2020.
7. American Academy of Pediatrics Annual Survey of graduating residents 2003-2020.
8. Quinn Capers IV. How clinicians and educators can mitigate implicit bias in patient care and candidate selection in medical education. American Thoracic Society Scholar. 2020 Jun;1(3):211-17.
9. Welsh G. The importance of community pediatric hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2021 Jan;25(1):27.
Delay surgery by 7 weeks after COVID-19 diagnosis, study shows
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I am the best. Sometimes.
The fifth and last time I was listed as Best of Boston was in 2019, when I shared honors with obstetrics, ice cream, interior design, and kitchenware.
My first time on that list was 10 years earlier, and came as a surprise. Though the magazine that runs the feature said that selections are “peer-generated,” I was never asked to evaluate any colleagues, so I don’t know who my admiring peers were or what they admired.
Three years later I was dropped from the list, for equally mysterious reasons. Maybe my acne patients did worse that year. Be that as it may, I was reinstated several years later. Perhaps my eczema outcomes surged.
How do you know when a doctor is good? I don’t need to remind you how many different ways we are evaluated. Hospitals and insurance companies monitor our prescribing practices and therapeutic outcomes. Many websites rate our performance. Read your own reviews, if you dare, penned by people who range from the totally disgruntled to the charmingly gruntled.
Often, their reasons are either beside the point or just wrong.
An example: (1 star out of 5): “Dr. Rockoff was terrible. He prescribed a very powerful regimen, and when I told him it was drying me out, he just insisted I keep using it.”
In fact – I was able to figure out who the patient was – my “powerful treatment” was over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide along with topical clindamycin. As for my insistence that she continue, she never came back for another visit. But she had called for refills.
You can surely come up with your own review tales.
But if patients don’t really understand how well we do, doctors are not necessarily much better at assessing colleagues. This came to mind recently when a close friend, increasingly hobbled by arthritis (you get more such friends as the years roll by) was looking into getting his knee replaced. He asked friends and family and got several names of orthopedists at respectable institutions. (I don’t know how many of them were Best of Boston, or even Best of Nashua, New Hampshire.)
The patients made these referrals because either they or people they knew had Dr. So-and-So replace their knee and had been pleased. That is nice to hear, but what does it prove? Even backup shortstops get on base sometimes.
So my friend called his rheumatologist, who recommended a knee specialist. My friend consulted that doctor, found her pleasant and personable, and liked what she had to say about the surgery and its expected aftermath.
My friend called back his rheumatologist to report his decision to go with his recommended doctor.
“I’m glad to hear that,” said the rheumatologist. “Three of my friends went to her and were very pleased.”
I am not in any way criticizing the rheumatologist. When people ask me for referrals – to internists, to plastic surgeons – I give them names of people I know or have sent patients to who had good experiences, or whom I just heard good things about. What can I really know about their diagnostic acumen or surgical dexterity?
A useful counterexample is what happened with my cousin who underwent back surgery a while back. He was considering several specialists when he had a discussion with a younger acquaintance who was chief resident in neurosurgery at a local medical center, and had actually operated with several of the surgeons under consideration. “Don’t go to Dr A,” said the young man. “It takes him 7 hours to do that procedure. Better go to Dr. B, who gets it done in under 3. The shorter operative time makes a big difference in speed of recovery.”
That is the kind of specialized and relevant knowledge that actually matters. How many referrals can you think of that you made or heard of about which the same can be said?
In the meantime, I will return to my own Bestness, which has been frequent, though intermittent. I like to think of myself as a vintage Chardonnay. Some years I am the best. Other years, not so much. Your best bet is to consult me in one of the former.
Preferably chilled.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
The fifth and last time I was listed as Best of Boston was in 2019, when I shared honors with obstetrics, ice cream, interior design, and kitchenware.
My first time on that list was 10 years earlier, and came as a surprise. Though the magazine that runs the feature said that selections are “peer-generated,” I was never asked to evaluate any colleagues, so I don’t know who my admiring peers were or what they admired.
Three years later I was dropped from the list, for equally mysterious reasons. Maybe my acne patients did worse that year. Be that as it may, I was reinstated several years later. Perhaps my eczema outcomes surged.
How do you know when a doctor is good? I don’t need to remind you how many different ways we are evaluated. Hospitals and insurance companies monitor our prescribing practices and therapeutic outcomes. Many websites rate our performance. Read your own reviews, if you dare, penned by people who range from the totally disgruntled to the charmingly gruntled.
Often, their reasons are either beside the point or just wrong.
An example: (1 star out of 5): “Dr. Rockoff was terrible. He prescribed a very powerful regimen, and when I told him it was drying me out, he just insisted I keep using it.”
In fact – I was able to figure out who the patient was – my “powerful treatment” was over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide along with topical clindamycin. As for my insistence that she continue, she never came back for another visit. But she had called for refills.
You can surely come up with your own review tales.
But if patients don’t really understand how well we do, doctors are not necessarily much better at assessing colleagues. This came to mind recently when a close friend, increasingly hobbled by arthritis (you get more such friends as the years roll by) was looking into getting his knee replaced. He asked friends and family and got several names of orthopedists at respectable institutions. (I don’t know how many of them were Best of Boston, or even Best of Nashua, New Hampshire.)
The patients made these referrals because either they or people they knew had Dr. So-and-So replace their knee and had been pleased. That is nice to hear, but what does it prove? Even backup shortstops get on base sometimes.
So my friend called his rheumatologist, who recommended a knee specialist. My friend consulted that doctor, found her pleasant and personable, and liked what she had to say about the surgery and its expected aftermath.
My friend called back his rheumatologist to report his decision to go with his recommended doctor.
“I’m glad to hear that,” said the rheumatologist. “Three of my friends went to her and were very pleased.”
I am not in any way criticizing the rheumatologist. When people ask me for referrals – to internists, to plastic surgeons – I give them names of people I know or have sent patients to who had good experiences, or whom I just heard good things about. What can I really know about their diagnostic acumen or surgical dexterity?
A useful counterexample is what happened with my cousin who underwent back surgery a while back. He was considering several specialists when he had a discussion with a younger acquaintance who was chief resident in neurosurgery at a local medical center, and had actually operated with several of the surgeons under consideration. “Don’t go to Dr A,” said the young man. “It takes him 7 hours to do that procedure. Better go to Dr. B, who gets it done in under 3. The shorter operative time makes a big difference in speed of recovery.”
That is the kind of specialized and relevant knowledge that actually matters. How many referrals can you think of that you made or heard of about which the same can be said?
In the meantime, I will return to my own Bestness, which has been frequent, though intermittent. I like to think of myself as a vintage Chardonnay. Some years I am the best. Other years, not so much. Your best bet is to consult me in one of the former.
Preferably chilled.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
The fifth and last time I was listed as Best of Boston was in 2019, when I shared honors with obstetrics, ice cream, interior design, and kitchenware.
My first time on that list was 10 years earlier, and came as a surprise. Though the magazine that runs the feature said that selections are “peer-generated,” I was never asked to evaluate any colleagues, so I don’t know who my admiring peers were or what they admired.
Three years later I was dropped from the list, for equally mysterious reasons. Maybe my acne patients did worse that year. Be that as it may, I was reinstated several years later. Perhaps my eczema outcomes surged.
How do you know when a doctor is good? I don’t need to remind you how many different ways we are evaluated. Hospitals and insurance companies monitor our prescribing practices and therapeutic outcomes. Many websites rate our performance. Read your own reviews, if you dare, penned by people who range from the totally disgruntled to the charmingly gruntled.
Often, their reasons are either beside the point or just wrong.
An example: (1 star out of 5): “Dr. Rockoff was terrible. He prescribed a very powerful regimen, and when I told him it was drying me out, he just insisted I keep using it.”
In fact – I was able to figure out who the patient was – my “powerful treatment” was over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide along with topical clindamycin. As for my insistence that she continue, she never came back for another visit. But she had called for refills.
You can surely come up with your own review tales.
But if patients don’t really understand how well we do, doctors are not necessarily much better at assessing colleagues. This came to mind recently when a close friend, increasingly hobbled by arthritis (you get more such friends as the years roll by) was looking into getting his knee replaced. He asked friends and family and got several names of orthopedists at respectable institutions. (I don’t know how many of them were Best of Boston, or even Best of Nashua, New Hampshire.)
The patients made these referrals because either they or people they knew had Dr. So-and-So replace their knee and had been pleased. That is nice to hear, but what does it prove? Even backup shortstops get on base sometimes.
So my friend called his rheumatologist, who recommended a knee specialist. My friend consulted that doctor, found her pleasant and personable, and liked what she had to say about the surgery and its expected aftermath.
My friend called back his rheumatologist to report his decision to go with his recommended doctor.
“I’m glad to hear that,” said the rheumatologist. “Three of my friends went to her and were very pleased.”
I am not in any way criticizing the rheumatologist. When people ask me for referrals – to internists, to plastic surgeons – I give them names of people I know or have sent patients to who had good experiences, or whom I just heard good things about. What can I really know about their diagnostic acumen or surgical dexterity?
A useful counterexample is what happened with my cousin who underwent back surgery a while back. He was considering several specialists when he had a discussion with a younger acquaintance who was chief resident in neurosurgery at a local medical center, and had actually operated with several of the surgeons under consideration. “Don’t go to Dr A,” said the young man. “It takes him 7 hours to do that procedure. Better go to Dr. B, who gets it done in under 3. The shorter operative time makes a big difference in speed of recovery.”
That is the kind of specialized and relevant knowledge that actually matters. How many referrals can you think of that you made or heard of about which the same can be said?
In the meantime, I will return to my own Bestness, which has been frequent, though intermittent. I like to think of myself as a vintage Chardonnay. Some years I am the best. Other years, not so much. Your best bet is to consult me in one of the former.
Preferably chilled.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
Benefits of bremelanotide to women with HSDD questioned in analysis paper
Dr. Spielmans, professor of psychology at Metropolitan State University in Saint Paul, Minn., examined data from the FDA application for bremelanotide, clinicaltrials.gov entries for two phase 3 trials of the drug, and a 2019 article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology that described results from the 24-week trials.
In Dr. Speilman’s analysis, which was published online March 7 in the Journal of Sex Research, he notes that 42.1% of trial participants who received bremelanotide did not complete the trial, compared with 20.48% of participants who received placebo.
Of those who completed the study, 87.22% who received placebo wanted to continue treatment in an open-label extension, compared with 69.97% who received bremelanotide, he wrote.
Women “should be aware of the small degree of bremelanotide’s efficacy, that the protocol-specified outcomes of bremelanotide are mostly unknown, and that participants would rather take a placebo than bremelanotide,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Anita H. Clayton, MD, an author of the Obstetrics & Gynecology paper addressed in Dr. Spielmans’ analysis, says the Journal of Sex Research article does not provide new information and is a disservice to women because it questions accurate scientific data.
Measuring outcomes in HSDD is an evolving field, Dr. Clayton, a psychiatrist at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, said in an interview. Initial FDA guidance relied on satisfying sexual events as an outcome measure, but this measure was derived from erectile dysfunction studies and is not necessarily adequate for assessing HSDD, she said. The FDA and drug developers agreed to use the desire subscale of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-D) as a coprimary outcome measure instead, she noted.
Dr. Spielmans’ critique of Obstetrics & Gynecology paper
The article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology reporting bremelanotide trial results was noteworthy, although the various issues involved can be seen in reports about other drug trials, Dr. Spielmans said in an interview.
“It is well-established that journal articles reporting clinical trial data overstate benefits and understate harms,” he continued. In this case, “the very incomplete data reporting, reliance on many post-hoc measures of questionable validity, hiding the concerning number of dropouts due to adverse events, and putting a positive spin on efficacy and tolerability is both remarkable and highly problematic,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Dr. Clayton’s reaction
Data about dropout rates due to adverse events have been reported and presented at national meetings, she said in an interview. In addition, a questionnaire found that bremelanotide was superior to placebo in terms of patients feeling that the treatment had provided clinically meaningful benefit, Dr. Clayton said.
The available information enables patients to make informed treatment decisions, Dr. Clayton continued. “There is really this sexist attitude of women needing protection from their own decisions,” she said.
Diagnosing and treating HSDD
Eight of 11 efficacy outcomes in the clinicaltrials.gov study protocols for bremelanotide were not reported in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article in a way that was consistent with the protocols, Dr. Spielmans said. Changing a coprimary outcome to the key secondary outcome “occurred over a year after the trials had begun,” and the authors of the journal article “did not mention that this change occurred,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
For the coprimary outcome measures of mean change on FSFI-D and Female Sexual Distress Scale–Desire/Arousal/Orgasm #13, “bremelanotide offers modest benefits over placebo,” Dr. Spielmans reported.
In addition to outlining his concerns about transparency in the reporting of trial data and raising questions about the outcome measures used in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article, Dr. Spielmans wrote that the diagnosis of HSDD is problematic.
“The lack of specifying symptom duration, questionable validity for the lack of sexual fantasies as a diagnostic criterion, difficulty in disentangling individual sexual problems from relational problems, and the failure to consider cultural influence (including the pressure on women to satisfy the sexual desires of their male partners) in the experience of sexuality all render HSDD as a problematic entity,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
The fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders replaced HSDD and female sexual arousal disorder with the combined condition female sexual interest/arousal disorder. HSDD is in the 11th edition of the International Classification of Diseases and can be applied to men or women, Dr. Spielmans said.
FDA acknowledged HSDD as an unmet medical need
Dr. Clayton pointed out that HSDD was described decades ago and the FDA acknowledged it as an unmet medical need, and she expressed dissatisfaction with the fact the hypoactive sexual desire disorder appears with quotation marks around it in the title of Dr. Spielmans’ article. This way of presenting HSDD indicates that “the author has no concept of sexual health or sexual dysfunction,” Dr. Clayton said. “Basically this is sort of a dramatic tool, I think, to act like this is not a real disorder,” she added.
Carl Spana, PhD, CEO and president of Palatin Technologies, the developer of bremelanotide, defined the article in the Journal of Sex Research as a “retrospective meta-analysis, and not a re-analysis of the data.
“As a meta-analysis, it is open to various interpretations and reflects the author’s interpretations, which appear to have clear biases,” Dr. Spana said in an interview. “We believe several of this author’s interpretations are contrary to the FDA’s positive assessment that led to Vyleesi’s approval as a safe and effective treatment for women suffering from hypoactive sexual desire disorder.”
The author is unaware of the validation that was conducted at the direction of the FDA to establish clinically meaningful cutoffs for patient-reported outcomes and to establish metrics that define clinical benefit, Dr. Spana said
“Vyleesi was approved by the FDA after a thorough analysis of data from two well-controlled phase 3 clinical studies and multiple clinical and preclinical safety studies,” he said. “The analyses in the New Drug Application were prespecified and conducted according to a statistical analysis plan that the sponsor and FDA agreed to prior to database lock.”
Dr. Spielmans disclosed holdings in Vanguard Healthcare, a mutual fund that invests in pharmaceutical firms. Dr. Clayton has received financial support from Palatin and AMAG Pharmaceuticals, the companies that developed bremelanotide, in previous years.
Dr. Spielmans, professor of psychology at Metropolitan State University in Saint Paul, Minn., examined data from the FDA application for bremelanotide, clinicaltrials.gov entries for two phase 3 trials of the drug, and a 2019 article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology that described results from the 24-week trials.
In Dr. Speilman’s analysis, which was published online March 7 in the Journal of Sex Research, he notes that 42.1% of trial participants who received bremelanotide did not complete the trial, compared with 20.48% of participants who received placebo.
Of those who completed the study, 87.22% who received placebo wanted to continue treatment in an open-label extension, compared with 69.97% who received bremelanotide, he wrote.
Women “should be aware of the small degree of bremelanotide’s efficacy, that the protocol-specified outcomes of bremelanotide are mostly unknown, and that participants would rather take a placebo than bremelanotide,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Anita H. Clayton, MD, an author of the Obstetrics & Gynecology paper addressed in Dr. Spielmans’ analysis, says the Journal of Sex Research article does not provide new information and is a disservice to women because it questions accurate scientific data.
Measuring outcomes in HSDD is an evolving field, Dr. Clayton, a psychiatrist at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, said in an interview. Initial FDA guidance relied on satisfying sexual events as an outcome measure, but this measure was derived from erectile dysfunction studies and is not necessarily adequate for assessing HSDD, she said. The FDA and drug developers agreed to use the desire subscale of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-D) as a coprimary outcome measure instead, she noted.
Dr. Spielmans’ critique of Obstetrics & Gynecology paper
The article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology reporting bremelanotide trial results was noteworthy, although the various issues involved can be seen in reports about other drug trials, Dr. Spielmans said in an interview.
“It is well-established that journal articles reporting clinical trial data overstate benefits and understate harms,” he continued. In this case, “the very incomplete data reporting, reliance on many post-hoc measures of questionable validity, hiding the concerning number of dropouts due to adverse events, and putting a positive spin on efficacy and tolerability is both remarkable and highly problematic,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Dr. Clayton’s reaction
Data about dropout rates due to adverse events have been reported and presented at national meetings, she said in an interview. In addition, a questionnaire found that bremelanotide was superior to placebo in terms of patients feeling that the treatment had provided clinically meaningful benefit, Dr. Clayton said.
The available information enables patients to make informed treatment decisions, Dr. Clayton continued. “There is really this sexist attitude of women needing protection from their own decisions,” she said.
Diagnosing and treating HSDD
Eight of 11 efficacy outcomes in the clinicaltrials.gov study protocols for bremelanotide were not reported in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article in a way that was consistent with the protocols, Dr. Spielmans said. Changing a coprimary outcome to the key secondary outcome “occurred over a year after the trials had begun,” and the authors of the journal article “did not mention that this change occurred,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
For the coprimary outcome measures of mean change on FSFI-D and Female Sexual Distress Scale–Desire/Arousal/Orgasm #13, “bremelanotide offers modest benefits over placebo,” Dr. Spielmans reported.
In addition to outlining his concerns about transparency in the reporting of trial data and raising questions about the outcome measures used in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article, Dr. Spielmans wrote that the diagnosis of HSDD is problematic.
“The lack of specifying symptom duration, questionable validity for the lack of sexual fantasies as a diagnostic criterion, difficulty in disentangling individual sexual problems from relational problems, and the failure to consider cultural influence (including the pressure on women to satisfy the sexual desires of their male partners) in the experience of sexuality all render HSDD as a problematic entity,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
The fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders replaced HSDD and female sexual arousal disorder with the combined condition female sexual interest/arousal disorder. HSDD is in the 11th edition of the International Classification of Diseases and can be applied to men or women, Dr. Spielmans said.
FDA acknowledged HSDD as an unmet medical need
Dr. Clayton pointed out that HSDD was described decades ago and the FDA acknowledged it as an unmet medical need, and she expressed dissatisfaction with the fact the hypoactive sexual desire disorder appears with quotation marks around it in the title of Dr. Spielmans’ article. This way of presenting HSDD indicates that “the author has no concept of sexual health or sexual dysfunction,” Dr. Clayton said. “Basically this is sort of a dramatic tool, I think, to act like this is not a real disorder,” she added.
Carl Spana, PhD, CEO and president of Palatin Technologies, the developer of bremelanotide, defined the article in the Journal of Sex Research as a “retrospective meta-analysis, and not a re-analysis of the data.
“As a meta-analysis, it is open to various interpretations and reflects the author’s interpretations, which appear to have clear biases,” Dr. Spana said in an interview. “We believe several of this author’s interpretations are contrary to the FDA’s positive assessment that led to Vyleesi’s approval as a safe and effective treatment for women suffering from hypoactive sexual desire disorder.”
The author is unaware of the validation that was conducted at the direction of the FDA to establish clinically meaningful cutoffs for patient-reported outcomes and to establish metrics that define clinical benefit, Dr. Spana said
“Vyleesi was approved by the FDA after a thorough analysis of data from two well-controlled phase 3 clinical studies and multiple clinical and preclinical safety studies,” he said. “The analyses in the New Drug Application were prespecified and conducted according to a statistical analysis plan that the sponsor and FDA agreed to prior to database lock.”
Dr. Spielmans disclosed holdings in Vanguard Healthcare, a mutual fund that invests in pharmaceutical firms. Dr. Clayton has received financial support from Palatin and AMAG Pharmaceuticals, the companies that developed bremelanotide, in previous years.
Dr. Spielmans, professor of psychology at Metropolitan State University in Saint Paul, Minn., examined data from the FDA application for bremelanotide, clinicaltrials.gov entries for two phase 3 trials of the drug, and a 2019 article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology that described results from the 24-week trials.
In Dr. Speilman’s analysis, which was published online March 7 in the Journal of Sex Research, he notes that 42.1% of trial participants who received bremelanotide did not complete the trial, compared with 20.48% of participants who received placebo.
Of those who completed the study, 87.22% who received placebo wanted to continue treatment in an open-label extension, compared with 69.97% who received bremelanotide, he wrote.
Women “should be aware of the small degree of bremelanotide’s efficacy, that the protocol-specified outcomes of bremelanotide are mostly unknown, and that participants would rather take a placebo than bremelanotide,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Anita H. Clayton, MD, an author of the Obstetrics & Gynecology paper addressed in Dr. Spielmans’ analysis, says the Journal of Sex Research article does not provide new information and is a disservice to women because it questions accurate scientific data.
Measuring outcomes in HSDD is an evolving field, Dr. Clayton, a psychiatrist at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, said in an interview. Initial FDA guidance relied on satisfying sexual events as an outcome measure, but this measure was derived from erectile dysfunction studies and is not necessarily adequate for assessing HSDD, she said. The FDA and drug developers agreed to use the desire subscale of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-D) as a coprimary outcome measure instead, she noted.
Dr. Spielmans’ critique of Obstetrics & Gynecology paper
The article published in Obstetrics & Gynecology reporting bremelanotide trial results was noteworthy, although the various issues involved can be seen in reports about other drug trials, Dr. Spielmans said in an interview.
“It is well-established that journal articles reporting clinical trial data overstate benefits and understate harms,” he continued. In this case, “the very incomplete data reporting, reliance on many post-hoc measures of questionable validity, hiding the concerning number of dropouts due to adverse events, and putting a positive spin on efficacy and tolerability is both remarkable and highly problematic,” Dr. Spielmans said.
Dr. Clayton’s reaction
Data about dropout rates due to adverse events have been reported and presented at national meetings, she said in an interview. In addition, a questionnaire found that bremelanotide was superior to placebo in terms of patients feeling that the treatment had provided clinically meaningful benefit, Dr. Clayton said.
The available information enables patients to make informed treatment decisions, Dr. Clayton continued. “There is really this sexist attitude of women needing protection from their own decisions,” she said.
Diagnosing and treating HSDD
Eight of 11 efficacy outcomes in the clinicaltrials.gov study protocols for bremelanotide were not reported in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article in a way that was consistent with the protocols, Dr. Spielmans said. Changing a coprimary outcome to the key secondary outcome “occurred over a year after the trials had begun,” and the authors of the journal article “did not mention that this change occurred,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
For the coprimary outcome measures of mean change on FSFI-D and Female Sexual Distress Scale–Desire/Arousal/Orgasm #13, “bremelanotide offers modest benefits over placebo,” Dr. Spielmans reported.
In addition to outlining his concerns about transparency in the reporting of trial data and raising questions about the outcome measures used in the Obstetrics & Gynecology article, Dr. Spielmans wrote that the diagnosis of HSDD is problematic.
“The lack of specifying symptom duration, questionable validity for the lack of sexual fantasies as a diagnostic criterion, difficulty in disentangling individual sexual problems from relational problems, and the failure to consider cultural influence (including the pressure on women to satisfy the sexual desires of their male partners) in the experience of sexuality all render HSDD as a problematic entity,” Dr. Spielmans wrote.
The fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders replaced HSDD and female sexual arousal disorder with the combined condition female sexual interest/arousal disorder. HSDD is in the 11th edition of the International Classification of Diseases and can be applied to men or women, Dr. Spielmans said.
FDA acknowledged HSDD as an unmet medical need
Dr. Clayton pointed out that HSDD was described decades ago and the FDA acknowledged it as an unmet medical need, and she expressed dissatisfaction with the fact the hypoactive sexual desire disorder appears with quotation marks around it in the title of Dr. Spielmans’ article. This way of presenting HSDD indicates that “the author has no concept of sexual health or sexual dysfunction,” Dr. Clayton said. “Basically this is sort of a dramatic tool, I think, to act like this is not a real disorder,” she added.
Carl Spana, PhD, CEO and president of Palatin Technologies, the developer of bremelanotide, defined the article in the Journal of Sex Research as a “retrospective meta-analysis, and not a re-analysis of the data.
“As a meta-analysis, it is open to various interpretations and reflects the author’s interpretations, which appear to have clear biases,” Dr. Spana said in an interview. “We believe several of this author’s interpretations are contrary to the FDA’s positive assessment that led to Vyleesi’s approval as a safe and effective treatment for women suffering from hypoactive sexual desire disorder.”
The author is unaware of the validation that was conducted at the direction of the FDA to establish clinically meaningful cutoffs for patient-reported outcomes and to establish metrics that define clinical benefit, Dr. Spana said
“Vyleesi was approved by the FDA after a thorough analysis of data from two well-controlled phase 3 clinical studies and multiple clinical and preclinical safety studies,” he said. “The analyses in the New Drug Application were prespecified and conducted according to a statistical analysis plan that the sponsor and FDA agreed to prior to database lock.”
Dr. Spielmans disclosed holdings in Vanguard Healthcare, a mutual fund that invests in pharmaceutical firms. Dr. Clayton has received financial support from Palatin and AMAG Pharmaceuticals, the companies that developed bremelanotide, in previous years.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF SEX RESEARCH
Novel therapeutic target for depression identified
An antiseizure medication appears to reduce anhedonia in patients with depression via a novel mechanism that may offer a new therapeutic target for the disorder, new research suggests.
Results of a small, randomized trial show those who received ezogabine (Potiga) experienced a significant reduction in key measures of depression and anhedonia versus placebo.
Participants in the treatment group also showed a trend toward increased response to reward anticipation on functional MRI (fMRI), compared with those treated with placebo, although the effect did not reach statistical significance.
“Our study was the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial to show that a drug affecting this kind of ion channel in the brain can improve depression and anhedonia in patients,” senior investigator James Murrough, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Targeting this channel represents a completely different mechanism of action than any currently available antidepressant treatment,” said Dr. Murrough, who is also director of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at Mount Sinai.
The study was published online March 3 in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Need for a novel target
“One of the main issues in treating depression is that many of our current antidepressants have similar mechanisms of action,” Dr. Murrough said in an interview. “Once a patient hasn’t responded to currently available agents, it’s hard think of new medications to fill that need.”
This need for a novel target motivated Dr. Murrough and associates to research the KCNQ2/3 potassium channel, which has not been previously studied as a therapeutic target for depression.
The KCNQ2/3 channel controls brain cell excitability and function by controlling the flow of the electrical charge across the cell membrane in the form of potassium ions, Dr. Murrough explained.
Previous research using a chronic social defeat model of depression in mice showed changes in the KCNQ2/3 channel. “This was key to determining whether a mouse showed depressive behavior in the context of stress, or whether the mice were resistant or resilient to stress,” he said.
Mice resistant to stress showed increased markers in brain regions associated with reward, while the less resilient mice showed excessive excitability and dysfunction. Dysfunction in the brain’s reward system leads to anhedonia, a “core feature” of depressive disorders.
This inspired Dr. Murrough’s group to identify ezogabine, a drug that acts on this channel.
“ for addressing depressive symptoms,” Dr. Murrough said
Nonsignificant trend
The researchers studied 45 adults diagnosed with depression who exhibited significant anhedonia and at least moderate illness severity.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either ezogabine (n = 21, mean age 44 years at enrollment, 28.3% male) or placebo (n = 24, mean age 39 years at enrollment, 50% male). At baseline and following treatment, participants completed the incentive flanker test under fMRI conditions to model brain activity during anticipation of a reward. In addition, clinical measures of depression and anhedonia were assessed at weekly visits.
The study groups did not differ significantly in performance accuracy during the fMRI task at baseline or following treatment. The table below summarizes the percentage of errors in each group, with standard deviation.
Participants in the ezogabine group showed a numerical increase in ventral striatum activation in response to reward anticipation, compared with participants in the placebo group, but this trend was not considered significant.
Heterogeneous condition
In contrast, there were notable improvements from baseline to the final outcome visit in clinical measures of depression and anhedonia in the ezogabine group, compared with the placebo group. Mean (SD) differences in depression scores, based on the MADRS (Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale) from baseline to endpoint as follows: mean difference, –7.9 (3.0); effect size, 0.76; response rate, 61.9% (ezogabine) and 37.5% (placebo); remission rate: 38.1% (ezogabine) and 20.8% (placebo)
Compared with placebo, there were also large improvements in hedonic capacity, as measured by the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale and the anticipatory subscale of the Temporal Experience of Pleasure Scale (t, –4.1; df, 212; P < .001 and t, 3.4; df, 213; P < .001, respectively).
Compared with placebo, ezogabine was associated with “significant benefit” in global illness severity and improvement (Clinical Global Impression–Severity: t, –2.2; df, 214; P = .026 and CGI-Improvement: t, –2.9; d, 214; P = .004, respectively).
Ezogabine was well tolerated. Dizziness and headache were the most common adverse events.
Depression is a “heterogeneous condition” with a single diagnosis encompassing a “large, multifaceted” array of symptoms, Dr. Murrough noted. A growing body of research is focusing on specific components as potential treatment targets. “Our study looked specifically at patients with a diagnosis of depression but high scores on the anhedonia scale and we found that boosting the function of the KCNQ2/3 channel may have a beneficial antidepressant effect by improving anhedonia.”
Potential gain
In a comment, Alan Schatzberg, MD, professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that “anytime there’s a new treatment with a new mechanism of action for a given condition, there’s a potential gain for the field.”
Dr. Schatzberg, who was not involved with the study, said that ezogabine, with its “potentially new mechanism of action, seems to have an effect and reasonable safety and could be important for patients who may not respond to traditional medications. It might also be important for all sorts of patients, depending on findings of later trials.”
Dr. Murrough said that ezogabine in still in “early stages” of research. “We hope that future studies will look at other agents that would also affect this channel,” he added.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. Additional funding was provided by the Friedman Brain Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Ehrenkranz Laboratory for Human Resilience, a component of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Murrough is an inventor of a pending patent application for the use of ezogabine and other KCNQ channel openers to treat depression and related disorders. Dr. Schatzberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An antiseizure medication appears to reduce anhedonia in patients with depression via a novel mechanism that may offer a new therapeutic target for the disorder, new research suggests.
Results of a small, randomized trial show those who received ezogabine (Potiga) experienced a significant reduction in key measures of depression and anhedonia versus placebo.
Participants in the treatment group also showed a trend toward increased response to reward anticipation on functional MRI (fMRI), compared with those treated with placebo, although the effect did not reach statistical significance.
“Our study was the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial to show that a drug affecting this kind of ion channel in the brain can improve depression and anhedonia in patients,” senior investigator James Murrough, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Targeting this channel represents a completely different mechanism of action than any currently available antidepressant treatment,” said Dr. Murrough, who is also director of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at Mount Sinai.
The study was published online March 3 in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Need for a novel target
“One of the main issues in treating depression is that many of our current antidepressants have similar mechanisms of action,” Dr. Murrough said in an interview. “Once a patient hasn’t responded to currently available agents, it’s hard think of new medications to fill that need.”
This need for a novel target motivated Dr. Murrough and associates to research the KCNQ2/3 potassium channel, which has not been previously studied as a therapeutic target for depression.
The KCNQ2/3 channel controls brain cell excitability and function by controlling the flow of the electrical charge across the cell membrane in the form of potassium ions, Dr. Murrough explained.
Previous research using a chronic social defeat model of depression in mice showed changes in the KCNQ2/3 channel. “This was key to determining whether a mouse showed depressive behavior in the context of stress, or whether the mice were resistant or resilient to stress,” he said.
Mice resistant to stress showed increased markers in brain regions associated with reward, while the less resilient mice showed excessive excitability and dysfunction. Dysfunction in the brain’s reward system leads to anhedonia, a “core feature” of depressive disorders.
This inspired Dr. Murrough’s group to identify ezogabine, a drug that acts on this channel.
“ for addressing depressive symptoms,” Dr. Murrough said
Nonsignificant trend
The researchers studied 45 adults diagnosed with depression who exhibited significant anhedonia and at least moderate illness severity.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either ezogabine (n = 21, mean age 44 years at enrollment, 28.3% male) or placebo (n = 24, mean age 39 years at enrollment, 50% male). At baseline and following treatment, participants completed the incentive flanker test under fMRI conditions to model brain activity during anticipation of a reward. In addition, clinical measures of depression and anhedonia were assessed at weekly visits.
The study groups did not differ significantly in performance accuracy during the fMRI task at baseline or following treatment. The table below summarizes the percentage of errors in each group, with standard deviation.
Participants in the ezogabine group showed a numerical increase in ventral striatum activation in response to reward anticipation, compared with participants in the placebo group, but this trend was not considered significant.
Heterogeneous condition
In contrast, there were notable improvements from baseline to the final outcome visit in clinical measures of depression and anhedonia in the ezogabine group, compared with the placebo group. Mean (SD) differences in depression scores, based on the MADRS (Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale) from baseline to endpoint as follows: mean difference, –7.9 (3.0); effect size, 0.76; response rate, 61.9% (ezogabine) and 37.5% (placebo); remission rate: 38.1% (ezogabine) and 20.8% (placebo)
Compared with placebo, there were also large improvements in hedonic capacity, as measured by the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale and the anticipatory subscale of the Temporal Experience of Pleasure Scale (t, –4.1; df, 212; P < .001 and t, 3.4; df, 213; P < .001, respectively).
Compared with placebo, ezogabine was associated with “significant benefit” in global illness severity and improvement (Clinical Global Impression–Severity: t, –2.2; df, 214; P = .026 and CGI-Improvement: t, –2.9; d, 214; P = .004, respectively).
Ezogabine was well tolerated. Dizziness and headache were the most common adverse events.
Depression is a “heterogeneous condition” with a single diagnosis encompassing a “large, multifaceted” array of symptoms, Dr. Murrough noted. A growing body of research is focusing on specific components as potential treatment targets. “Our study looked specifically at patients with a diagnosis of depression but high scores on the anhedonia scale and we found that boosting the function of the KCNQ2/3 channel may have a beneficial antidepressant effect by improving anhedonia.”
Potential gain
In a comment, Alan Schatzberg, MD, professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that “anytime there’s a new treatment with a new mechanism of action for a given condition, there’s a potential gain for the field.”
Dr. Schatzberg, who was not involved with the study, said that ezogabine, with its “potentially new mechanism of action, seems to have an effect and reasonable safety and could be important for patients who may not respond to traditional medications. It might also be important for all sorts of patients, depending on findings of later trials.”
Dr. Murrough said that ezogabine in still in “early stages” of research. “We hope that future studies will look at other agents that would also affect this channel,” he added.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. Additional funding was provided by the Friedman Brain Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Ehrenkranz Laboratory for Human Resilience, a component of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Murrough is an inventor of a pending patent application for the use of ezogabine and other KCNQ channel openers to treat depression and related disorders. Dr. Schatzberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An antiseizure medication appears to reduce anhedonia in patients with depression via a novel mechanism that may offer a new therapeutic target for the disorder, new research suggests.
Results of a small, randomized trial show those who received ezogabine (Potiga) experienced a significant reduction in key measures of depression and anhedonia versus placebo.
Participants in the treatment group also showed a trend toward increased response to reward anticipation on functional MRI (fMRI), compared with those treated with placebo, although the effect did not reach statistical significance.
“Our study was the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial to show that a drug affecting this kind of ion channel in the brain can improve depression and anhedonia in patients,” senior investigator James Murrough, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Targeting this channel represents a completely different mechanism of action than any currently available antidepressant treatment,” said Dr. Murrough, who is also director of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at Mount Sinai.
The study was published online March 3 in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Need for a novel target
“One of the main issues in treating depression is that many of our current antidepressants have similar mechanisms of action,” Dr. Murrough said in an interview. “Once a patient hasn’t responded to currently available agents, it’s hard think of new medications to fill that need.”
This need for a novel target motivated Dr. Murrough and associates to research the KCNQ2/3 potassium channel, which has not been previously studied as a therapeutic target for depression.
The KCNQ2/3 channel controls brain cell excitability and function by controlling the flow of the electrical charge across the cell membrane in the form of potassium ions, Dr. Murrough explained.
Previous research using a chronic social defeat model of depression in mice showed changes in the KCNQ2/3 channel. “This was key to determining whether a mouse showed depressive behavior in the context of stress, or whether the mice were resistant or resilient to stress,” he said.
Mice resistant to stress showed increased markers in brain regions associated with reward, while the less resilient mice showed excessive excitability and dysfunction. Dysfunction in the brain’s reward system leads to anhedonia, a “core feature” of depressive disorders.
This inspired Dr. Murrough’s group to identify ezogabine, a drug that acts on this channel.
“ for addressing depressive symptoms,” Dr. Murrough said
Nonsignificant trend
The researchers studied 45 adults diagnosed with depression who exhibited significant anhedonia and at least moderate illness severity.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either ezogabine (n = 21, mean age 44 years at enrollment, 28.3% male) or placebo (n = 24, mean age 39 years at enrollment, 50% male). At baseline and following treatment, participants completed the incentive flanker test under fMRI conditions to model brain activity during anticipation of a reward. In addition, clinical measures of depression and anhedonia were assessed at weekly visits.
The study groups did not differ significantly in performance accuracy during the fMRI task at baseline or following treatment. The table below summarizes the percentage of errors in each group, with standard deviation.
Participants in the ezogabine group showed a numerical increase in ventral striatum activation in response to reward anticipation, compared with participants in the placebo group, but this trend was not considered significant.
Heterogeneous condition
In contrast, there were notable improvements from baseline to the final outcome visit in clinical measures of depression and anhedonia in the ezogabine group, compared with the placebo group. Mean (SD) differences in depression scores, based on the MADRS (Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale) from baseline to endpoint as follows: mean difference, –7.9 (3.0); effect size, 0.76; response rate, 61.9% (ezogabine) and 37.5% (placebo); remission rate: 38.1% (ezogabine) and 20.8% (placebo)
Compared with placebo, there were also large improvements in hedonic capacity, as measured by the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale and the anticipatory subscale of the Temporal Experience of Pleasure Scale (t, –4.1; df, 212; P < .001 and t, 3.4; df, 213; P < .001, respectively).
Compared with placebo, ezogabine was associated with “significant benefit” in global illness severity and improvement (Clinical Global Impression–Severity: t, –2.2; df, 214; P = .026 and CGI-Improvement: t, –2.9; d, 214; P = .004, respectively).
Ezogabine was well tolerated. Dizziness and headache were the most common adverse events.
Depression is a “heterogeneous condition” with a single diagnosis encompassing a “large, multifaceted” array of symptoms, Dr. Murrough noted. A growing body of research is focusing on specific components as potential treatment targets. “Our study looked specifically at patients with a diagnosis of depression but high scores on the anhedonia scale and we found that boosting the function of the KCNQ2/3 channel may have a beneficial antidepressant effect by improving anhedonia.”
Potential gain
In a comment, Alan Schatzberg, MD, professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that “anytime there’s a new treatment with a new mechanism of action for a given condition, there’s a potential gain for the field.”
Dr. Schatzberg, who was not involved with the study, said that ezogabine, with its “potentially new mechanism of action, seems to have an effect and reasonable safety and could be important for patients who may not respond to traditional medications. It might also be important for all sorts of patients, depending on findings of later trials.”
Dr. Murrough said that ezogabine in still in “early stages” of research. “We hope that future studies will look at other agents that would also affect this channel,” he added.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. Additional funding was provided by the Friedman Brain Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Ehrenkranz Laboratory for Human Resilience, a component of the Depression and Anxiety Center for Discovery and Treatment at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Murrough is an inventor of a pending patent application for the use of ezogabine and other KCNQ channel openers to treat depression and related disorders. Dr. Schatzberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.