User login
Medication-assisted recovery for opioid use disorder: A guide
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.
Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
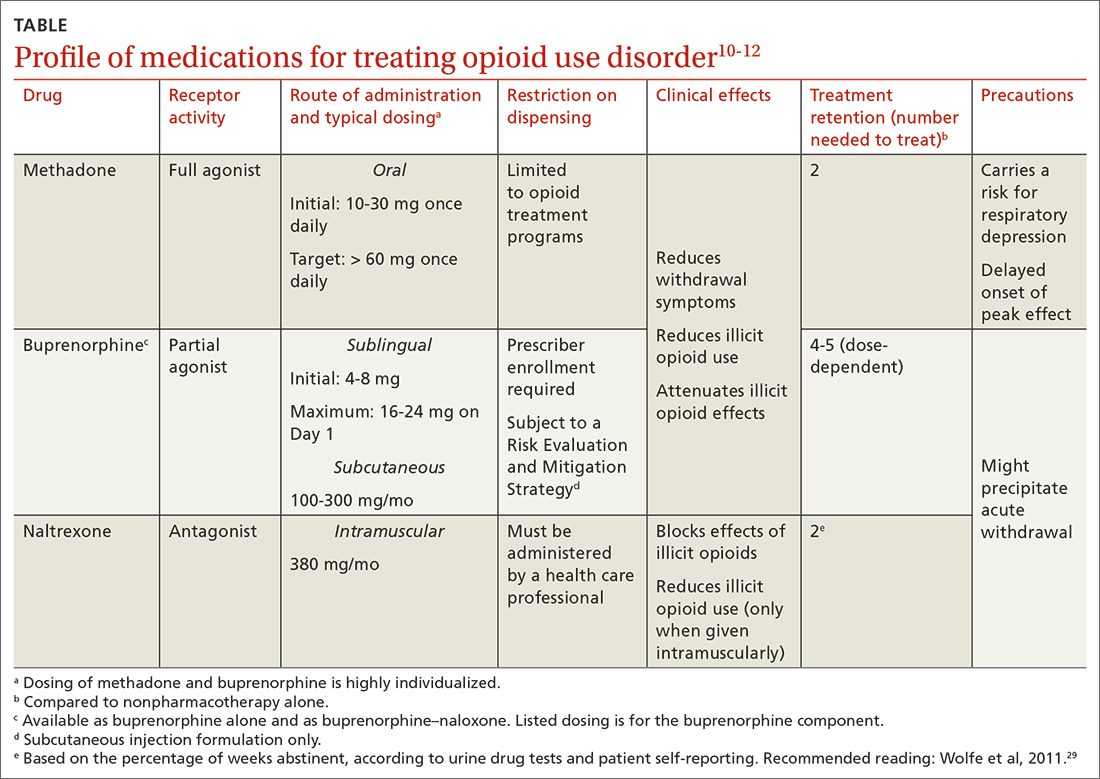
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13
The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.

Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13

The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.

Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13

The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Consider resource availability (eg, treatment programs and regulatory barriers), in addition to patient- and medicationspecific factors, when designing the most individualized, advantageous medication-assisted recovery plan, to reduce the risk for mortality. B
› Schedule early (< 2 weeks) and frequent follow-up with patients who are starting medications for opioid use disorder (particularly methadone), to manage risk when mortality is highest and to support recovery. C
› Set and manage patient expectations for control of withdrawal symptoms when initiating medications for opioid use disorder (particularly buprenorphine). B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Thoughts on the CDC update on opioid prescribing guidelines
The media is filled with stories about the opioid crisis. We have all heard the horror stories of addiction and overdose, as well as “pill mill” doctors. In fact, more than 932,000 people have died of drug overdose since 1999 and, in recent years, approximately 75% of drug overdoses involved opioids.
Yet, they still have their place in the treatment of pain.
The CDC updated the 2016 guidelines for prescribing opioids for pain in 2022. They cover when to initiate prescribing of opioids, selecting appropriate opioids and doses, and deciding the duration of therapy. The guidelines do a great job providing evidence-based recommendations while at the same time keeping the problems with opioids in the picture.
For primary care doctors, pain is one of the most common complaints we see – from broken bones to low back pain to cancer pain. It is important to note that the current guidelines exclude pain from sickle cell disease, cancer-related pain, palliative care, and end-of-life care. The guidelines apply to acute, subacute, and chronic pain. Pain is a complex symptom and often needs a multipronged approach. We make a mistake if we just prescribe a pain medication without understanding the root cause of the pain.
The guidelines suggest starting with nonopioid medications and incorporating nonmedicinal modes of treatments, such as physical therapy, as well. Opioids should be started at the lowest dose and for the shortest duration. Immediate-release medications are preferred over long-acting or extended-release ones. The patient should always be informed of the risks and benefits.
While the guidelines do a great job recommending how to prescribe opioids, they do not go into any depth discussing other treatment options. Perhaps knowledge of other treatment modalities would help primary care physicians avoid opioid prescribing. When treating our patients, it is important to educate them on how to manage their own symptoms.
The guidelines also advise tapering patients who may have been on high-dose opioids for long periods of time. Doctors know this is a very difficult task. However, resources to help with this are often lacking. For example, rehab may not be covered under a patient’s insurance, or it may be cheaper to take an opioid than to go to physical therapy. Although the recommendation is to taper, community assets may not support this. Guidelines are one thing, but the rest of the health care system needs to catch up to them and make them practical.
Primary care doctors often utilize our physical medicine, rehabilitation, and pain management specialists to assist in managing our patients’ pain. Here too, access to this resource is often difficult to come by. Depending on a patient’s insurance, it can take months to get an appointment.
In general, the current guidelines offer 12 key recommendations when prescribing opioids. They are a great reference; however, we need more real-life tools. For many of us in primary care, these guidelines support what we’ve been doing all along.
Primary care doctors will surely play a huge role in addressing the opioid crisis. We can prescribe opioids appropriately, but it doesn’t erase the problems of those patients who were overprescribed in the past. Many still seek out these medications whether for monetary reasons or just for the high. It is often easy to blame the patient but the one in control is the one with the prescription pad. Yet, it is important to remember that many of these patients are in real pain and need help.
Often, it is simpler to just prescribe a pain medication than it is to explain why one is not appropriate. As primary care doctors, we need to be effective ambassadors of appropriate opioid prescribing and often that means doing the hard thing and saying no to a patient.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
The media is filled with stories about the opioid crisis. We have all heard the horror stories of addiction and overdose, as well as “pill mill” doctors. In fact, more than 932,000 people have died of drug overdose since 1999 and, in recent years, approximately 75% of drug overdoses involved opioids.
Yet, they still have their place in the treatment of pain.
The CDC updated the 2016 guidelines for prescribing opioids for pain in 2022. They cover when to initiate prescribing of opioids, selecting appropriate opioids and doses, and deciding the duration of therapy. The guidelines do a great job providing evidence-based recommendations while at the same time keeping the problems with opioids in the picture.
For primary care doctors, pain is one of the most common complaints we see – from broken bones to low back pain to cancer pain. It is important to note that the current guidelines exclude pain from sickle cell disease, cancer-related pain, palliative care, and end-of-life care. The guidelines apply to acute, subacute, and chronic pain. Pain is a complex symptom and often needs a multipronged approach. We make a mistake if we just prescribe a pain medication without understanding the root cause of the pain.
The guidelines suggest starting with nonopioid medications and incorporating nonmedicinal modes of treatments, such as physical therapy, as well. Opioids should be started at the lowest dose and for the shortest duration. Immediate-release medications are preferred over long-acting or extended-release ones. The patient should always be informed of the risks and benefits.
While the guidelines do a great job recommending how to prescribe opioids, they do not go into any depth discussing other treatment options. Perhaps knowledge of other treatment modalities would help primary care physicians avoid opioid prescribing. When treating our patients, it is important to educate them on how to manage their own symptoms.
The guidelines also advise tapering patients who may have been on high-dose opioids for long periods of time. Doctors know this is a very difficult task. However, resources to help with this are often lacking. For example, rehab may not be covered under a patient’s insurance, or it may be cheaper to take an opioid than to go to physical therapy. Although the recommendation is to taper, community assets may not support this. Guidelines are one thing, but the rest of the health care system needs to catch up to them and make them practical.
Primary care doctors often utilize our physical medicine, rehabilitation, and pain management specialists to assist in managing our patients’ pain. Here too, access to this resource is often difficult to come by. Depending on a patient’s insurance, it can take months to get an appointment.
In general, the current guidelines offer 12 key recommendations when prescribing opioids. They are a great reference; however, we need more real-life tools. For many of us in primary care, these guidelines support what we’ve been doing all along.
Primary care doctors will surely play a huge role in addressing the opioid crisis. We can prescribe opioids appropriately, but it doesn’t erase the problems of those patients who were overprescribed in the past. Many still seek out these medications whether for monetary reasons or just for the high. It is often easy to blame the patient but the one in control is the one with the prescription pad. Yet, it is important to remember that many of these patients are in real pain and need help.
Often, it is simpler to just prescribe a pain medication than it is to explain why one is not appropriate. As primary care doctors, we need to be effective ambassadors of appropriate opioid prescribing and often that means doing the hard thing and saying no to a patient.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
The media is filled with stories about the opioid crisis. We have all heard the horror stories of addiction and overdose, as well as “pill mill” doctors. In fact, more than 932,000 people have died of drug overdose since 1999 and, in recent years, approximately 75% of drug overdoses involved opioids.
Yet, they still have their place in the treatment of pain.
The CDC updated the 2016 guidelines for prescribing opioids for pain in 2022. They cover when to initiate prescribing of opioids, selecting appropriate opioids and doses, and deciding the duration of therapy. The guidelines do a great job providing evidence-based recommendations while at the same time keeping the problems with opioids in the picture.
For primary care doctors, pain is one of the most common complaints we see – from broken bones to low back pain to cancer pain. It is important to note that the current guidelines exclude pain from sickle cell disease, cancer-related pain, palliative care, and end-of-life care. The guidelines apply to acute, subacute, and chronic pain. Pain is a complex symptom and often needs a multipronged approach. We make a mistake if we just prescribe a pain medication without understanding the root cause of the pain.
The guidelines suggest starting with nonopioid medications and incorporating nonmedicinal modes of treatments, such as physical therapy, as well. Opioids should be started at the lowest dose and for the shortest duration. Immediate-release medications are preferred over long-acting or extended-release ones. The patient should always be informed of the risks and benefits.
While the guidelines do a great job recommending how to prescribe opioids, they do not go into any depth discussing other treatment options. Perhaps knowledge of other treatment modalities would help primary care physicians avoid opioid prescribing. When treating our patients, it is important to educate them on how to manage their own symptoms.
The guidelines also advise tapering patients who may have been on high-dose opioids for long periods of time. Doctors know this is a very difficult task. However, resources to help with this are often lacking. For example, rehab may not be covered under a patient’s insurance, or it may be cheaper to take an opioid than to go to physical therapy. Although the recommendation is to taper, community assets may not support this. Guidelines are one thing, but the rest of the health care system needs to catch up to them and make them practical.
Primary care doctors often utilize our physical medicine, rehabilitation, and pain management specialists to assist in managing our patients’ pain. Here too, access to this resource is often difficult to come by. Depending on a patient’s insurance, it can take months to get an appointment.
In general, the current guidelines offer 12 key recommendations when prescribing opioids. They are a great reference; however, we need more real-life tools. For many of us in primary care, these guidelines support what we’ve been doing all along.
Primary care doctors will surely play a huge role in addressing the opioid crisis. We can prescribe opioids appropriately, but it doesn’t erase the problems of those patients who were overprescribed in the past. Many still seek out these medications whether for monetary reasons or just for the high. It is often easy to blame the patient but the one in control is the one with the prescription pad. Yet, it is important to remember that many of these patients are in real pain and need help.
Often, it is simpler to just prescribe a pain medication than it is to explain why one is not appropriate. As primary care doctors, we need to be effective ambassadors of appropriate opioid prescribing and often that means doing the hard thing and saying no to a patient.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
BMI has greater impact on survival in younger breast cancer patients
new data suggest.
Obesity is a well-known risk factor for breast cancer in postmenopausal women and has been associated with adverse prognosis, said Senna W.M. Lammers, MD, of Maastricht (the Netherlands) University during a presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Breast Cancer annual congress. In addition, some studies suggest that patients with higher body mass index (BMI) experience reduced benefits from endocrine therapy, she said.
Dr. Lammers and colleagues conducted a study to determine the prognostic and predictive effect of BMI on disease-free survival in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer who were treated with extended endocrine therapy.
The study population included participants in the randomized, phase III DATA trial, which evaluated the use of 6 years vs. 3 years of anastrozole in postmenopausal women with HR+ breast cancer who were disease-free after 2-3 years of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy.
Patients were categorized based on BMI as having normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25-29.9 kg/m2), or obese (30 kg/m2 or higher). The primary outcome was disease-free survival (DFS); the median follow-up period was 13.1 years.
DFS for patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity was 66.2%, 59.5%, and 52.4%, with a P value of less than .001 for the trend, Dr. Lammers said. “These results were confirmed in multivariable analysis,” she said. Overall, patients with overweight and obesity had a worse DFS when compared with patients with normal weight (hazard ratio, 1.16; P = .10, for patients with overweight and HR, 1.26; P = .03 for patients with obesity).
“Next, we aimed to determine whether the prognostic effect of BMI differed by age,” Dr. Lammers said.
In women younger than 60 years, overweight and obesity were significantly associated with worse DFS (HR, 1.29; P = .05 and HR 1.83, P less than .001, respectively). However, this effect was not observed in women aged 60 years and older.
The researchers also examined the treatment effect of extended anastrozole on adapted DFS by weight, and found no significant differences among patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity (HR, 1.00; HR, 0.74; and HR, 0.97, respectively), said Dr. Lammers.
In the question and answer session, Dr. Lammers was asked about possible explanations for the difference in DFS by age. Potential explanations include possible survival bias “as only the healthier [patients with obesity] survive to old age,” she said. Other potential explanations are biological, such as the potentially higher levels of bone density in older [patients with obesity], she said.
When asked about additional clinical implications, Dr. Lammers emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy BMI for breast cancer patients of all ages. Other research areas might involve the use of lifestyle interventions, although these are challenging to implement, she noted.
Data draw attention to quality of life and lifestyle factors
The need to “look at drug development with new eyes” is particularly important when reviewing patient-reported outcomes, said Otto Metzger, MD, of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who served as the discussant for the session.
Dr. Metzger brought up the association between age and the effect of BMI on DFS, specifically.
Based on data from multiple studies and meta-analyses, “I do believe that obesity does play a role in prognosis,” he said, but the question is how long will researchers continue to simply record data without acting to add lifestyle interventions while also trying to develop new drugs, he said. Although convincing patients to make lifestyle changes remains a challenge, patients are often more motivated to make such changes after a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Metzger noted.
“I am a firm believer in the use of digital therapeutics in the context of clinical trials,” said Dr. Metzger. Digital technology offers great potential to educate patients on [adverse effects] and also to improve treatment adherence and quality of life, he concluded.
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, and Dr. Lammers disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly. Dr. Metzger disclosed receiving research funding to his institution from Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, and Sanofi, and serving as an adviser/consultant to AstraZeneca, Merck, Oncoclinicas, Resilience, and Roche.
new data suggest.
Obesity is a well-known risk factor for breast cancer in postmenopausal women and has been associated with adverse prognosis, said Senna W.M. Lammers, MD, of Maastricht (the Netherlands) University during a presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Breast Cancer annual congress. In addition, some studies suggest that patients with higher body mass index (BMI) experience reduced benefits from endocrine therapy, she said.
Dr. Lammers and colleagues conducted a study to determine the prognostic and predictive effect of BMI on disease-free survival in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer who were treated with extended endocrine therapy.
The study population included participants in the randomized, phase III DATA trial, which evaluated the use of 6 years vs. 3 years of anastrozole in postmenopausal women with HR+ breast cancer who were disease-free after 2-3 years of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy.
Patients were categorized based on BMI as having normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25-29.9 kg/m2), or obese (30 kg/m2 or higher). The primary outcome was disease-free survival (DFS); the median follow-up period was 13.1 years.
DFS for patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity was 66.2%, 59.5%, and 52.4%, with a P value of less than .001 for the trend, Dr. Lammers said. “These results were confirmed in multivariable analysis,” she said. Overall, patients with overweight and obesity had a worse DFS when compared with patients with normal weight (hazard ratio, 1.16; P = .10, for patients with overweight and HR, 1.26; P = .03 for patients with obesity).
“Next, we aimed to determine whether the prognostic effect of BMI differed by age,” Dr. Lammers said.
In women younger than 60 years, overweight and obesity were significantly associated with worse DFS (HR, 1.29; P = .05 and HR 1.83, P less than .001, respectively). However, this effect was not observed in women aged 60 years and older.
The researchers also examined the treatment effect of extended anastrozole on adapted DFS by weight, and found no significant differences among patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity (HR, 1.00; HR, 0.74; and HR, 0.97, respectively), said Dr. Lammers.
In the question and answer session, Dr. Lammers was asked about possible explanations for the difference in DFS by age. Potential explanations include possible survival bias “as only the healthier [patients with obesity] survive to old age,” she said. Other potential explanations are biological, such as the potentially higher levels of bone density in older [patients with obesity], she said.
When asked about additional clinical implications, Dr. Lammers emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy BMI for breast cancer patients of all ages. Other research areas might involve the use of lifestyle interventions, although these are challenging to implement, she noted.
Data draw attention to quality of life and lifestyle factors
The need to “look at drug development with new eyes” is particularly important when reviewing patient-reported outcomes, said Otto Metzger, MD, of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who served as the discussant for the session.
Dr. Metzger brought up the association between age and the effect of BMI on DFS, specifically.
Based on data from multiple studies and meta-analyses, “I do believe that obesity does play a role in prognosis,” he said, but the question is how long will researchers continue to simply record data without acting to add lifestyle interventions while also trying to develop new drugs, he said. Although convincing patients to make lifestyle changes remains a challenge, patients are often more motivated to make such changes after a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Metzger noted.
“I am a firm believer in the use of digital therapeutics in the context of clinical trials,” said Dr. Metzger. Digital technology offers great potential to educate patients on [adverse effects] and also to improve treatment adherence and quality of life, he concluded.
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, and Dr. Lammers disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly. Dr. Metzger disclosed receiving research funding to his institution from Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, and Sanofi, and serving as an adviser/consultant to AstraZeneca, Merck, Oncoclinicas, Resilience, and Roche.
new data suggest.
Obesity is a well-known risk factor for breast cancer in postmenopausal women and has been associated with adverse prognosis, said Senna W.M. Lammers, MD, of Maastricht (the Netherlands) University during a presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Breast Cancer annual congress. In addition, some studies suggest that patients with higher body mass index (BMI) experience reduced benefits from endocrine therapy, she said.
Dr. Lammers and colleagues conducted a study to determine the prognostic and predictive effect of BMI on disease-free survival in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer who were treated with extended endocrine therapy.
The study population included participants in the randomized, phase III DATA trial, which evaluated the use of 6 years vs. 3 years of anastrozole in postmenopausal women with HR+ breast cancer who were disease-free after 2-3 years of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy.
Patients were categorized based on BMI as having normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25-29.9 kg/m2), or obese (30 kg/m2 or higher). The primary outcome was disease-free survival (DFS); the median follow-up period was 13.1 years.
DFS for patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity was 66.2%, 59.5%, and 52.4%, with a P value of less than .001 for the trend, Dr. Lammers said. “These results were confirmed in multivariable analysis,” she said. Overall, patients with overweight and obesity had a worse DFS when compared with patients with normal weight (hazard ratio, 1.16; P = .10, for patients with overweight and HR, 1.26; P = .03 for patients with obesity).
“Next, we aimed to determine whether the prognostic effect of BMI differed by age,” Dr. Lammers said.
In women younger than 60 years, overweight and obesity were significantly associated with worse DFS (HR, 1.29; P = .05 and HR 1.83, P less than .001, respectively). However, this effect was not observed in women aged 60 years and older.
The researchers also examined the treatment effect of extended anastrozole on adapted DFS by weight, and found no significant differences among patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity (HR, 1.00; HR, 0.74; and HR, 0.97, respectively), said Dr. Lammers.
In the question and answer session, Dr. Lammers was asked about possible explanations for the difference in DFS by age. Potential explanations include possible survival bias “as only the healthier [patients with obesity] survive to old age,” she said. Other potential explanations are biological, such as the potentially higher levels of bone density in older [patients with obesity], she said.
When asked about additional clinical implications, Dr. Lammers emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy BMI for breast cancer patients of all ages. Other research areas might involve the use of lifestyle interventions, although these are challenging to implement, she noted.
Data draw attention to quality of life and lifestyle factors
The need to “look at drug development with new eyes” is particularly important when reviewing patient-reported outcomes, said Otto Metzger, MD, of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who served as the discussant for the session.
Dr. Metzger brought up the association between age and the effect of BMI on DFS, specifically.
Based on data from multiple studies and meta-analyses, “I do believe that obesity does play a role in prognosis,” he said, but the question is how long will researchers continue to simply record data without acting to add lifestyle interventions while also trying to develop new drugs, he said. Although convincing patients to make lifestyle changes remains a challenge, patients are often more motivated to make such changes after a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Metzger noted.
“I am a firm believer in the use of digital therapeutics in the context of clinical trials,” said Dr. Metzger. Digital technology offers great potential to educate patients on [adverse effects] and also to improve treatment adherence and quality of life, he concluded.
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, and Dr. Lammers disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly. Dr. Metzger disclosed receiving research funding to his institution from Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, and Sanofi, and serving as an adviser/consultant to AstraZeneca, Merck, Oncoclinicas, Resilience, and Roche.
FROM ESMO BREAST CANCER 2023
Anxiety high among Americans, national poll shows
results of a national mental health poll conducted by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) show.
“There is a lot of worry in the world right now about economic uncertainty, about violence, about how we’re going to come out of this period of time,” APA President Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, said during an APA press briefing announcing the latest poll results.
Brendel said the results are an important reminder and opportunity for psychiatrists to put their finger on the pulse of Americans’ mental health.
“If 70% of people are feeling unsafe, we need to come up with individual and also society-based solutions to help people move forward so that we can see a brighter future and not experience so much anxiety,” she added.
The poll was conducted between April 20 and 22, 2023, among a nationally representative sample of 2,201 adults. The analysis also tracks data from a poll conducted between April 23 and 24, 2022, among a sample of 2,210 adults.
Overall, nearly two in five adults (37%) reported feeling more anxious than they were at this time last year, which is higher than in 2022 (32%) but lower than in 2021 (41%) and 2020 (62%).
About one-third (30%) of adults said they have consulted a mental health care professional, a slight uptick from 2022.
Other issues keeping Americans up at night include keeping their identity safe (68%), their health (66%), paying bills or expenses (65%), climate change (59%), the opioid epidemic (50%) and the impact of emerging technology on day-to-day life (45%).
Half of respondents reported they would be likely to consider a mental health treatment involving cannabis or marijuana, while most said they would be unlikely to consider a treatment involving psychedelics (59%) or ketamine (56%).
Two-thirds (68%) of American adults reported that their children and teenagers have more mental health problems than they did a decade ago.
More than 50% of parents are concerned about their children’s technology use (59%) and mental state (55%), and 31% have encountered difficulty scheduling appointments with mental health professionals for their children.
More than three-quarters (78%) of U.S. adults believe mental health affects physical health and that untreated mental illness has a significant negative effect on families (78%). About two-thirds (64%) believe untreated mental illness harms the economy.
One in three adults (34%) would not vote for a candidate for elected office who has a mental illness – up 7% from 2022.
“The majority of the public understands something we’ve been saying for a long time: Your mental health is about your health,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director at the American Psychiatric Association, said in the release.
“It’s contingent upon us as a field to continue to spread that message, and that those who are experiencing mental health concerns aren’t alone and that there are ways to receive help,” Dr. Levin added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a national mental health poll conducted by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) show.
“There is a lot of worry in the world right now about economic uncertainty, about violence, about how we’re going to come out of this period of time,” APA President Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, said during an APA press briefing announcing the latest poll results.
Brendel said the results are an important reminder and opportunity for psychiatrists to put their finger on the pulse of Americans’ mental health.
“If 70% of people are feeling unsafe, we need to come up with individual and also society-based solutions to help people move forward so that we can see a brighter future and not experience so much anxiety,” she added.
The poll was conducted between April 20 and 22, 2023, among a nationally representative sample of 2,201 adults. The analysis also tracks data from a poll conducted between April 23 and 24, 2022, among a sample of 2,210 adults.
Overall, nearly two in five adults (37%) reported feeling more anxious than they were at this time last year, which is higher than in 2022 (32%) but lower than in 2021 (41%) and 2020 (62%).
About one-third (30%) of adults said they have consulted a mental health care professional, a slight uptick from 2022.
Other issues keeping Americans up at night include keeping their identity safe (68%), their health (66%), paying bills or expenses (65%), climate change (59%), the opioid epidemic (50%) and the impact of emerging technology on day-to-day life (45%).
Half of respondents reported they would be likely to consider a mental health treatment involving cannabis or marijuana, while most said they would be unlikely to consider a treatment involving psychedelics (59%) or ketamine (56%).
Two-thirds (68%) of American adults reported that their children and teenagers have more mental health problems than they did a decade ago.
More than 50% of parents are concerned about their children’s technology use (59%) and mental state (55%), and 31% have encountered difficulty scheduling appointments with mental health professionals for their children.
More than three-quarters (78%) of U.S. adults believe mental health affects physical health and that untreated mental illness has a significant negative effect on families (78%). About two-thirds (64%) believe untreated mental illness harms the economy.
One in three adults (34%) would not vote for a candidate for elected office who has a mental illness – up 7% from 2022.
“The majority of the public understands something we’ve been saying for a long time: Your mental health is about your health,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director at the American Psychiatric Association, said in the release.
“It’s contingent upon us as a field to continue to spread that message, and that those who are experiencing mental health concerns aren’t alone and that there are ways to receive help,” Dr. Levin added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a national mental health poll conducted by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) show.
“There is a lot of worry in the world right now about economic uncertainty, about violence, about how we’re going to come out of this period of time,” APA President Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, said during an APA press briefing announcing the latest poll results.
Brendel said the results are an important reminder and opportunity for psychiatrists to put their finger on the pulse of Americans’ mental health.
“If 70% of people are feeling unsafe, we need to come up with individual and also society-based solutions to help people move forward so that we can see a brighter future and not experience so much anxiety,” she added.
The poll was conducted between April 20 and 22, 2023, among a nationally representative sample of 2,201 adults. The analysis also tracks data from a poll conducted between April 23 and 24, 2022, among a sample of 2,210 adults.
Overall, nearly two in five adults (37%) reported feeling more anxious than they were at this time last year, which is higher than in 2022 (32%) but lower than in 2021 (41%) and 2020 (62%).
About one-third (30%) of adults said they have consulted a mental health care professional, a slight uptick from 2022.
Other issues keeping Americans up at night include keeping their identity safe (68%), their health (66%), paying bills or expenses (65%), climate change (59%), the opioid epidemic (50%) and the impact of emerging technology on day-to-day life (45%).
Half of respondents reported they would be likely to consider a mental health treatment involving cannabis or marijuana, while most said they would be unlikely to consider a treatment involving psychedelics (59%) or ketamine (56%).
Two-thirds (68%) of American adults reported that their children and teenagers have more mental health problems than they did a decade ago.
More than 50% of parents are concerned about their children’s technology use (59%) and mental state (55%), and 31% have encountered difficulty scheduling appointments with mental health professionals for their children.
More than three-quarters (78%) of U.S. adults believe mental health affects physical health and that untreated mental illness has a significant negative effect on families (78%). About two-thirds (64%) believe untreated mental illness harms the economy.
One in three adults (34%) would not vote for a candidate for elected office who has a mental illness – up 7% from 2022.
“The majority of the public understands something we’ve been saying for a long time: Your mental health is about your health,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director at the American Psychiatric Association, said in the release.
“It’s contingent upon us as a field to continue to spread that message, and that those who are experiencing mental health concerns aren’t alone and that there are ways to receive help,” Dr. Levin added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
One in five brain injury trials shows errors, signs of spin
LOS ANGELES –
“This is concerning result,” said general physician Lucas Piason F. Martins, MD, of the Bahiana School of Medicine and Public Health, Salvador, Brazil. “Many of these trials have been included in clinical guidelines and cited extensively in systematic reviews and meta-analyses, especially those related to hypothermia therapy.”
Dr. Martins presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
Defining spin
In recent years, medical researchers have sought to define and identify spin in medical literature. According to a 2017 report in PLOS Biology, “spin refers to reporting practices that distort the interpretation of results and mislead readers so that results are viewed in a more favorable light.”
Any spin can be dangerous, Dr. Martins said, because it “can potentially mislead readers and affect the interpretation of study results, which in turn can impact clinical decision-making.”
For the new report, a systematic review, Dr. Martins and colleagues examined 150 studies published in 18 top-ranked journals including the Journal of Neurotrauma (26%), the Journal of Neurosurgery (15%), Critical Care Medicine (9%), and the New England Journal of Medicine (8%).
Studies were published between 1960 and 2020. The review protocol was previously published in BMJ Open.
According to the report, most of the 32 studies with spin (75%) had a “focus on statistically significant results not based on primary outcome.”
For example, Dr. Martins said in an interview that the abstract for a study about drug treatment of brain contusions highlighted a secondary result instead of the main finding that the medication had no effect. Another study of treatment for severe closed head injuries focused on a subgroup outcome.
As Dr. Martins noted, it’s potentially problematic for studies to have several outcomes, measure outcomes in different ways, and have multiple time points without a predefined primary outcome. “A positive finding based on such strategies could potentially be explained by chance alone,” he said.
The researchers also reported that 65% of the studies with spin highlighted “the beneficial effect of the treatment despite statistically nonsignificant results” and that 9% had incorrect statistical analysis.
The findings are especially noteworthy because “the trials we analyzed were deemed to have the highest quality of methodology,” Dr. Martins said.
The researchers didn’t identify specific studies that they deemed to have spin, and they won’t do so, Dr. Martins said. The authors do plan to reveal which journals were most spin-heavy but only when these findings are published.
Were the study authors trying to mislead readers? Not necessarily. Researchers “may search for positive results to confirm their beliefs, although with good intentions,” Dr. Martins said, adding that the researchers found that “positive research tends to be more cited.”
They also reported that studies with smaller sample sizes were more likely to have spin (P = .04).
At 21%, the percentage of studies with spin was lower than that found in some previous reports that analyzed medical literature in other specialties.
A 2019 study of 93 randomized clinical studies in cardiology, for example, found spin in 57% of abstracts and 67% of full texts. The lower number in the new study may be due to its especially conservative definition of spin, Dr. Martins said.
Appropriate methodology
Cardiologist Richard Krasuski, MD, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., who coauthored the 2019 study into spin in cardiology studies, told this news organization that the new analysis follows appropriate methodology and appears to be valid.
It makes sense, he said, that smaller studies had more spin: “It is much harder to show statistical significance in small studies and softer endpoints can be harder to predict. Small neutral trials are also much harder to publish in high-level journals. This all increases the tendency to spin the results so the reviewer and eventually the reader is more captivated.”
Why is there so much spin in medical research? “As an investigator, you always hope to positively impact patient health and outcomes, so there is a tendency to look at secondary analyses to have something good to emphasize,” he said. “This is an inherent trait in most of us, to find something good we can focus on. I do believe that much of this is subconscious and perhaps with noble intent.”
Dr. Krasuski said that he advises trainees to look at the methodology of studies, not just the abstract or discussion sections. “You don’t have to be a trained statistician to identify how well the findings match the author’s interpretation.
“Always try to identify what the primary outcome of the study was at the time of the design and whether the investigators achieved their objective. As a reviewer, my own personal experience in research into spin makes me more cognizant of its existence, and I generally require authors to reword and tone down their message if it is not supported by the data.”
What’s next? The investigators want to look for spin in the wider neurosurgery literature, Dr. Martins said, with an eye toward developing “practical strategies to assess spin and give pragmatic recommendations for good practice in clinical research.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Martins has no disclosures, and several study authors reported funding from the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Krasuski has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES –
“This is concerning result,” said general physician Lucas Piason F. Martins, MD, of the Bahiana School of Medicine and Public Health, Salvador, Brazil. “Many of these trials have been included in clinical guidelines and cited extensively in systematic reviews and meta-analyses, especially those related to hypothermia therapy.”
Dr. Martins presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
Defining spin
In recent years, medical researchers have sought to define and identify spin in medical literature. According to a 2017 report in PLOS Biology, “spin refers to reporting practices that distort the interpretation of results and mislead readers so that results are viewed in a more favorable light.”
Any spin can be dangerous, Dr. Martins said, because it “can potentially mislead readers and affect the interpretation of study results, which in turn can impact clinical decision-making.”
For the new report, a systematic review, Dr. Martins and colleagues examined 150 studies published in 18 top-ranked journals including the Journal of Neurotrauma (26%), the Journal of Neurosurgery (15%), Critical Care Medicine (9%), and the New England Journal of Medicine (8%).
Studies were published between 1960 and 2020. The review protocol was previously published in BMJ Open.
According to the report, most of the 32 studies with spin (75%) had a “focus on statistically significant results not based on primary outcome.”
For example, Dr. Martins said in an interview that the abstract for a study about drug treatment of brain contusions highlighted a secondary result instead of the main finding that the medication had no effect. Another study of treatment for severe closed head injuries focused on a subgroup outcome.
As Dr. Martins noted, it’s potentially problematic for studies to have several outcomes, measure outcomes in different ways, and have multiple time points without a predefined primary outcome. “A positive finding based on such strategies could potentially be explained by chance alone,” he said.
The researchers also reported that 65% of the studies with spin highlighted “the beneficial effect of the treatment despite statistically nonsignificant results” and that 9% had incorrect statistical analysis.
The findings are especially noteworthy because “the trials we analyzed were deemed to have the highest quality of methodology,” Dr. Martins said.
The researchers didn’t identify specific studies that they deemed to have spin, and they won’t do so, Dr. Martins said. The authors do plan to reveal which journals were most spin-heavy but only when these findings are published.
Were the study authors trying to mislead readers? Not necessarily. Researchers “may search for positive results to confirm their beliefs, although with good intentions,” Dr. Martins said, adding that the researchers found that “positive research tends to be more cited.”
They also reported that studies with smaller sample sizes were more likely to have spin (P = .04).
At 21%, the percentage of studies with spin was lower than that found in some previous reports that analyzed medical literature in other specialties.
A 2019 study of 93 randomized clinical studies in cardiology, for example, found spin in 57% of abstracts and 67% of full texts. The lower number in the new study may be due to its especially conservative definition of spin, Dr. Martins said.
Appropriate methodology
Cardiologist Richard Krasuski, MD, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., who coauthored the 2019 study into spin in cardiology studies, told this news organization that the new analysis follows appropriate methodology and appears to be valid.
It makes sense, he said, that smaller studies had more spin: “It is much harder to show statistical significance in small studies and softer endpoints can be harder to predict. Small neutral trials are also much harder to publish in high-level journals. This all increases the tendency to spin the results so the reviewer and eventually the reader is more captivated.”
Why is there so much spin in medical research? “As an investigator, you always hope to positively impact patient health and outcomes, so there is a tendency to look at secondary analyses to have something good to emphasize,” he said. “This is an inherent trait in most of us, to find something good we can focus on. I do believe that much of this is subconscious and perhaps with noble intent.”
Dr. Krasuski said that he advises trainees to look at the methodology of studies, not just the abstract or discussion sections. “You don’t have to be a trained statistician to identify how well the findings match the author’s interpretation.
“Always try to identify what the primary outcome of the study was at the time of the design and whether the investigators achieved their objective. As a reviewer, my own personal experience in research into spin makes me more cognizant of its existence, and I generally require authors to reword and tone down their message if it is not supported by the data.”
What’s next? The investigators want to look for spin in the wider neurosurgery literature, Dr. Martins said, with an eye toward developing “practical strategies to assess spin and give pragmatic recommendations for good practice in clinical research.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Martins has no disclosures, and several study authors reported funding from the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Krasuski has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES –
“This is concerning result,” said general physician Lucas Piason F. Martins, MD, of the Bahiana School of Medicine and Public Health, Salvador, Brazil. “Many of these trials have been included in clinical guidelines and cited extensively in systematic reviews and meta-analyses, especially those related to hypothermia therapy.”
Dr. Martins presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
Defining spin
In recent years, medical researchers have sought to define and identify spin in medical literature. According to a 2017 report in PLOS Biology, “spin refers to reporting practices that distort the interpretation of results and mislead readers so that results are viewed in a more favorable light.”
Any spin can be dangerous, Dr. Martins said, because it “can potentially mislead readers and affect the interpretation of study results, which in turn can impact clinical decision-making.”
For the new report, a systematic review, Dr. Martins and colleagues examined 150 studies published in 18 top-ranked journals including the Journal of Neurotrauma (26%), the Journal of Neurosurgery (15%), Critical Care Medicine (9%), and the New England Journal of Medicine (8%).
Studies were published between 1960 and 2020. The review protocol was previously published in BMJ Open.
According to the report, most of the 32 studies with spin (75%) had a “focus on statistically significant results not based on primary outcome.”
For example, Dr. Martins said in an interview that the abstract for a study about drug treatment of brain contusions highlighted a secondary result instead of the main finding that the medication had no effect. Another study of treatment for severe closed head injuries focused on a subgroup outcome.
As Dr. Martins noted, it’s potentially problematic for studies to have several outcomes, measure outcomes in different ways, and have multiple time points without a predefined primary outcome. “A positive finding based on such strategies could potentially be explained by chance alone,” he said.
The researchers also reported that 65% of the studies with spin highlighted “the beneficial effect of the treatment despite statistically nonsignificant results” and that 9% had incorrect statistical analysis.
The findings are especially noteworthy because “the trials we analyzed were deemed to have the highest quality of methodology,” Dr. Martins said.
The researchers didn’t identify specific studies that they deemed to have spin, and they won’t do so, Dr. Martins said. The authors do plan to reveal which journals were most spin-heavy but only when these findings are published.
Were the study authors trying to mislead readers? Not necessarily. Researchers “may search for positive results to confirm their beliefs, although with good intentions,” Dr. Martins said, adding that the researchers found that “positive research tends to be more cited.”
They also reported that studies with smaller sample sizes were more likely to have spin (P = .04).
At 21%, the percentage of studies with spin was lower than that found in some previous reports that analyzed medical literature in other specialties.
A 2019 study of 93 randomized clinical studies in cardiology, for example, found spin in 57% of abstracts and 67% of full texts. The lower number in the new study may be due to its especially conservative definition of spin, Dr. Martins said.
Appropriate methodology
Cardiologist Richard Krasuski, MD, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., who coauthored the 2019 study into spin in cardiology studies, told this news organization that the new analysis follows appropriate methodology and appears to be valid.
It makes sense, he said, that smaller studies had more spin: “It is much harder to show statistical significance in small studies and softer endpoints can be harder to predict. Small neutral trials are also much harder to publish in high-level journals. This all increases the tendency to spin the results so the reviewer and eventually the reader is more captivated.”
Why is there so much spin in medical research? “As an investigator, you always hope to positively impact patient health and outcomes, so there is a tendency to look at secondary analyses to have something good to emphasize,” he said. “This is an inherent trait in most of us, to find something good we can focus on. I do believe that much of this is subconscious and perhaps with noble intent.”
Dr. Krasuski said that he advises trainees to look at the methodology of studies, not just the abstract or discussion sections. “You don’t have to be a trained statistician to identify how well the findings match the author’s interpretation.
“Always try to identify what the primary outcome of the study was at the time of the design and whether the investigators achieved their objective. As a reviewer, my own personal experience in research into spin makes me more cognizant of its existence, and I generally require authors to reword and tone down their message if it is not supported by the data.”
What’s next? The investigators want to look for spin in the wider neurosurgery literature, Dr. Martins said, with an eye toward developing “practical strategies to assess spin and give pragmatic recommendations for good practice in clinical research.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Martins has no disclosures, and several study authors reported funding from the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Krasuski has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANS 2023
Endovascular approach best for below-knee limb-threatening ischemia?
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET
Fatigue is a monster for patients with pulmonary disease
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
American Gastroenterological Association invests in unsedated transnasal endoscopy medical device company EvoEndo®
, a medical device company developing platforms for unsedated transnasal endoscopy (TNE).
“AGA is proud to support EvoEndo® and its innovative technology that has the potential to improve care, save time, resources, and cost for hospitals and the GI community at large,” said Michael L. Kochman, MD, AGAF, MASGE, Wilmott Family Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Center for Endoscopic Innovation, Research and Training, gastroenterology division, University of Pennsylvania Health System; fund manager and adviser, AGA GI Opportunity Fund.
The EvoEndo® Single-Use Endoscopy System received FDA 510(k) clearance in February 2022. The EvoEndo System includes a sterile, single-use, flexible gastroscope designed for unsedated transnasal upper endoscopy and a small portable video controller. The EvoEndo Comfort Kit (not part of the cleared EvoEndo System) includes virtual reality (VR) goggles for patient distraction during the unsedated transnasal endoscopy procedure. Unsedated TNE can be used to evaluate and diagnose a wide range of upper GI conditions that may require frequent monitoring, including eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), dysphagia, celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, malabsorption, and abdominal pain.
“We are grateful for the support of the AGA, which is a testament to our ongoing commitment to improving GI outcomes with our technology,” said Jonathan T. Hartmann, CEO at EvoEndo. “The AGA has always been at the forefront of improving GI care. Our team could not be more excited that they have recognized EvoEndo, and we look forward to continuing to expand adoption of our technology to the GI community, its physicians, and their patients.”
TNE enabled by EvoEndo’s Single-Use Endoscopy System allows hospitals to move endoscopy procedures from an ambulatory procedural suite to an office-based environment and allows the “traditional” sedation procedure rooms to be used for more complex, therapeutic cases.
“Expanding our fund’s portfolio to include technologies that can transform the pediatric GI landscape is particularly exciting for Varia Ventures,” said Andrea Vossler, cofounder and managing director at Varia Ventures. “EvoEndo® has made significant progress in the TNE category, and we are excited for what’s to come in the future.”
The EvoEndo® Model LE Gastroscope is intended for the visualization of the upper digestive tract in adults and pediatric patients, specifically for the observation, diagnosis, and endoscopic treatment of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb in patients over the age of five. The gastroscope is a sterile, single-use device and can be inserted orally or transnasally. The EvoEndo® Controller is intended for use with an EvoEndo® Endoscope for endoscopic diagnosis, treatment, and video observation. The EvoEndo System is only intended for use by medical professionals. Physicians and other medical providers interested in learning more about EvoEndo’s TNE system or scheduling demonstrations and training can contact the company here.
, a medical device company developing platforms for unsedated transnasal endoscopy (TNE).
“AGA is proud to support EvoEndo® and its innovative technology that has the potential to improve care, save time, resources, and cost for hospitals and the GI community at large,” said Michael L. Kochman, MD, AGAF, MASGE, Wilmott Family Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Center for Endoscopic Innovation, Research and Training, gastroenterology division, University of Pennsylvania Health System; fund manager and adviser, AGA GI Opportunity Fund.
The EvoEndo® Single-Use Endoscopy System received FDA 510(k) clearance in February 2022. The EvoEndo System includes a sterile, single-use, flexible gastroscope designed for unsedated transnasal upper endoscopy and a small portable video controller. The EvoEndo Comfort Kit (not part of the cleared EvoEndo System) includes virtual reality (VR) goggles for patient distraction during the unsedated transnasal endoscopy procedure. Unsedated TNE can be used to evaluate and diagnose a wide range of upper GI conditions that may require frequent monitoring, including eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), dysphagia, celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, malabsorption, and abdominal pain.
“We are grateful for the support of the AGA, which is a testament to our ongoing commitment to improving GI outcomes with our technology,” said Jonathan T. Hartmann, CEO at EvoEndo. “The AGA has always been at the forefront of improving GI care. Our team could not be more excited that they have recognized EvoEndo, and we look forward to continuing to expand adoption of our technology to the GI community, its physicians, and their patients.”
TNE enabled by EvoEndo’s Single-Use Endoscopy System allows hospitals to move endoscopy procedures from an ambulatory procedural suite to an office-based environment and allows the “traditional” sedation procedure rooms to be used for more complex, therapeutic cases.
“Expanding our fund’s portfolio to include technologies that can transform the pediatric GI landscape is particularly exciting for Varia Ventures,” said Andrea Vossler, cofounder and managing director at Varia Ventures. “EvoEndo® has made significant progress in the TNE category, and we are excited for what’s to come in the future.”
The EvoEndo® Model LE Gastroscope is intended for the visualization of the upper digestive tract in adults and pediatric patients, specifically for the observation, diagnosis, and endoscopic treatment of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb in patients over the age of five. The gastroscope is a sterile, single-use device and can be inserted orally or transnasally. The EvoEndo® Controller is intended for use with an EvoEndo® Endoscope for endoscopic diagnosis, treatment, and video observation. The EvoEndo System is only intended for use by medical professionals. Physicians and other medical providers interested in learning more about EvoEndo’s TNE system or scheduling demonstrations and training can contact the company here.
, a medical device company developing platforms for unsedated transnasal endoscopy (TNE).
“AGA is proud to support EvoEndo® and its innovative technology that has the potential to improve care, save time, resources, and cost for hospitals and the GI community at large,” said Michael L. Kochman, MD, AGAF, MASGE, Wilmott Family Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Center for Endoscopic Innovation, Research and Training, gastroenterology division, University of Pennsylvania Health System; fund manager and adviser, AGA GI Opportunity Fund.
The EvoEndo® Single-Use Endoscopy System received FDA 510(k) clearance in February 2022. The EvoEndo System includes a sterile, single-use, flexible gastroscope designed for unsedated transnasal upper endoscopy and a small portable video controller. The EvoEndo Comfort Kit (not part of the cleared EvoEndo System) includes virtual reality (VR) goggles for patient distraction during the unsedated transnasal endoscopy procedure. Unsedated TNE can be used to evaluate and diagnose a wide range of upper GI conditions that may require frequent monitoring, including eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), dysphagia, celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, malabsorption, and abdominal pain.
“We are grateful for the support of the AGA, which is a testament to our ongoing commitment to improving GI outcomes with our technology,” said Jonathan T. Hartmann, CEO at EvoEndo. “The AGA has always been at the forefront of improving GI care. Our team could not be more excited that they have recognized EvoEndo, and we look forward to continuing to expand adoption of our technology to the GI community, its physicians, and their patients.”
TNE enabled by EvoEndo’s Single-Use Endoscopy System allows hospitals to move endoscopy procedures from an ambulatory procedural suite to an office-based environment and allows the “traditional” sedation procedure rooms to be used for more complex, therapeutic cases.
“Expanding our fund’s portfolio to include technologies that can transform the pediatric GI landscape is particularly exciting for Varia Ventures,” said Andrea Vossler, cofounder and managing director at Varia Ventures. “EvoEndo® has made significant progress in the TNE category, and we are excited for what’s to come in the future.”
The EvoEndo® Model LE Gastroscope is intended for the visualization of the upper digestive tract in adults and pediatric patients, specifically for the observation, diagnosis, and endoscopic treatment of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb in patients over the age of five. The gastroscope is a sterile, single-use device and can be inserted orally or transnasally. The EvoEndo® Controller is intended for use with an EvoEndo® Endoscope for endoscopic diagnosis, treatment, and video observation. The EvoEndo System is only intended for use by medical professionals. Physicians and other medical providers interested in learning more about EvoEndo’s TNE system or scheduling demonstrations and training can contact the company here.
CLL: Venetoclax combos top first-line chemoimmunotherapy
according to a phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, dubbed GAIA–CLL13, “is a remarkable demonstration of the quality of fixed-duration therapies for younger, fit patients, and it challenges us to continue to work to develop therapeutic strategies that will ultimately cure patients with CLL,” two hematologic cancer specialists said in an accompanying editorial.
In short, “venetoclax-obinutuzumab and venetoclax-obinutuzumab-ibrutinib were superior to chemoimmunotherapy with respect to both the minimal residual disease end point and progression-free survival, but venetoclax-rituximab was not,” Jennifer Woyach, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and John Byrd, MD, University of Cincinnati, said in their commentary.
Noting that randomized trials involving venetoclax combinations in fit CLL patients “have been lacking,” the investigators compared 6 cycles of chemoimmunotherapy (fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab or bendamustine-rituximab) with 12 cycles of venetoclax plus the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab, venetoclax plus the third generation anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab, and venetoclax combined with both obinutuzumab and the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in a novel triple-therapy regimen.
The 926 patients in the study were a mean of 61 years old and split about evenly among the four treatment arms. Ibrutinib was discontinued after two consecutive measurements if patients had undetectable minimal residual disease (uMRD). Subjects did not have TP53 aberrations, a marker of poor prognosis in CLL.
At 15 months, the percentage of patients with uMRD was significantly higher in the triple-therapy arm (92.2%) and the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (86.5%) than in the chemoimmunotherapy group (52.0%), but there was no statistical difference with venetoclax-rituximab (57%, P = .32).
The three-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 90.5% in the triple-therapy arm versus 87.7% with venetoclax-obinutuzumab. The 3-year PFS with venetoclax-rituximab (80.8%) was again not statistically different than the 75.5% with chemoimmunotherapy (P = .18).
Not ready for prime time
The benefits of triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab held only in patients with unmutated IgVH. “The high efficacy of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen in young, fit patients with mutated IgVH may be difficult to improve on,” noted the investigators, led by Barbara Eichhorst, MD, a hematologic malignancy specialist at the University of Cologne (Germany).
Also, although triple-therapy results were impressive, some of the benefits “are neutralized by the need for dose reductions and early treatment discontinuation owing to adverse events,” they said.
For instance, triple therapy had the highest incidence of both grade 3 and 4 infections (21.2%) and atrial fibrillation (7.8%).
The editorialists noted that there has been “a flurry of interest” in trials combining ibrutinib and venetoclax – as was done in the triple-therapy arm – since both emerged as powerful tools against CLL in recent years. However, even with the study results, they said “the use of triplet therapy should be viewed as investigational.”
For one thing, rates of uMRD were not “dramatically different” between triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab, and longer follow-up is better gauge differences in PFS and long-term toxicities.
Also, ibrutinib is being eclipsed by the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib, because they have better safety profiles, and they are being assessed in CLL combination trials. For now, there are too many unknowns for routine use of triple therapy in fit CLL patients, they said.
The investigators and editorialists both noted that improved uMRD in the study translated into superior PFS, raising the possibility that uMRD might be a valid alternative endpoint to PFS in CLL trials.
With “median remissions in CLL lasting far in excess of 5 years, designing studies that take 8-10 years” to reach a PFS endpoint is simply too slow. Moving to an alternative endpoint such a uMRD would preserve “the momentum that has been generated” with recent advances, Dr. Woyach and Dr. Byrd said.
The work was funded by the companies that market venetoclax, ibrutinib, and obinutuzumab: AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Dr. Eichhorst is a consultant and/or speaker for the companies and also reported grants from them. Dr. Byrd is a consultant/adviser for Eilean Therapeutics, Kurome Therapeutics, Newave, and Orbimed. Dr. Woyach disclosed ties with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Lilly, and other companies.
according to a phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, dubbed GAIA–CLL13, “is a remarkable demonstration of the quality of fixed-duration therapies for younger, fit patients, and it challenges us to continue to work to develop therapeutic strategies that will ultimately cure patients with CLL,” two hematologic cancer specialists said in an accompanying editorial.
In short, “venetoclax-obinutuzumab and venetoclax-obinutuzumab-ibrutinib were superior to chemoimmunotherapy with respect to both the minimal residual disease end point and progression-free survival, but venetoclax-rituximab was not,” Jennifer Woyach, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and John Byrd, MD, University of Cincinnati, said in their commentary.
Noting that randomized trials involving venetoclax combinations in fit CLL patients “have been lacking,” the investigators compared 6 cycles of chemoimmunotherapy (fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab or bendamustine-rituximab) with 12 cycles of venetoclax plus the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab, venetoclax plus the third generation anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab, and venetoclax combined with both obinutuzumab and the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in a novel triple-therapy regimen.
The 926 patients in the study were a mean of 61 years old and split about evenly among the four treatment arms. Ibrutinib was discontinued after two consecutive measurements if patients had undetectable minimal residual disease (uMRD). Subjects did not have TP53 aberrations, a marker of poor prognosis in CLL.
At 15 months, the percentage of patients with uMRD was significantly higher in the triple-therapy arm (92.2%) and the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (86.5%) than in the chemoimmunotherapy group (52.0%), but there was no statistical difference with venetoclax-rituximab (57%, P = .32).
The three-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 90.5% in the triple-therapy arm versus 87.7% with venetoclax-obinutuzumab. The 3-year PFS with venetoclax-rituximab (80.8%) was again not statistically different than the 75.5% with chemoimmunotherapy (P = .18).
Not ready for prime time
The benefits of triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab held only in patients with unmutated IgVH. “The high efficacy of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen in young, fit patients with mutated IgVH may be difficult to improve on,” noted the investigators, led by Barbara Eichhorst, MD, a hematologic malignancy specialist at the University of Cologne (Germany).
Also, although triple-therapy results were impressive, some of the benefits “are neutralized by the need for dose reductions and early treatment discontinuation owing to adverse events,” they said.
For instance, triple therapy had the highest incidence of both grade 3 and 4 infections (21.2%) and atrial fibrillation (7.8%).
The editorialists noted that there has been “a flurry of interest” in trials combining ibrutinib and venetoclax – as was done in the triple-therapy arm – since both emerged as powerful tools against CLL in recent years. However, even with the study results, they said “the use of triplet therapy should be viewed as investigational.”
For one thing, rates of uMRD were not “dramatically different” between triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab, and longer follow-up is better gauge differences in PFS and long-term toxicities.
Also, ibrutinib is being eclipsed by the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib, because they have better safety profiles, and they are being assessed in CLL combination trials. For now, there are too many unknowns for routine use of triple therapy in fit CLL patients, they said.
The investigators and editorialists both noted that improved uMRD in the study translated into superior PFS, raising the possibility that uMRD might be a valid alternative endpoint to PFS in CLL trials.
With “median remissions in CLL lasting far in excess of 5 years, designing studies that take 8-10 years” to reach a PFS endpoint is simply too slow. Moving to an alternative endpoint such a uMRD would preserve “the momentum that has been generated” with recent advances, Dr. Woyach and Dr. Byrd said.
The work was funded by the companies that market venetoclax, ibrutinib, and obinutuzumab: AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Dr. Eichhorst is a consultant and/or speaker for the companies and also reported grants from them. Dr. Byrd is a consultant/adviser for Eilean Therapeutics, Kurome Therapeutics, Newave, and Orbimed. Dr. Woyach disclosed ties with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Lilly, and other companies.
according to a phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, dubbed GAIA–CLL13, “is a remarkable demonstration of the quality of fixed-duration therapies for younger, fit patients, and it challenges us to continue to work to develop therapeutic strategies that will ultimately cure patients with CLL,” two hematologic cancer specialists said in an accompanying editorial.
In short, “venetoclax-obinutuzumab and venetoclax-obinutuzumab-ibrutinib were superior to chemoimmunotherapy with respect to both the minimal residual disease end point and progression-free survival, but venetoclax-rituximab was not,” Jennifer Woyach, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and John Byrd, MD, University of Cincinnati, said in their commentary.
Noting that randomized trials involving venetoclax combinations in fit CLL patients “have been lacking,” the investigators compared 6 cycles of chemoimmunotherapy (fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab or bendamustine-rituximab) with 12 cycles of venetoclax plus the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab, venetoclax plus the third generation anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab, and venetoclax combined with both obinutuzumab and the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in a novel triple-therapy regimen.
The 926 patients in the study were a mean of 61 years old and split about evenly among the four treatment arms. Ibrutinib was discontinued after two consecutive measurements if patients had undetectable minimal residual disease (uMRD). Subjects did not have TP53 aberrations, a marker of poor prognosis in CLL.
At 15 months, the percentage of patients with uMRD was significantly higher in the triple-therapy arm (92.2%) and the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (86.5%) than in the chemoimmunotherapy group (52.0%), but there was no statistical difference with venetoclax-rituximab (57%, P = .32).
The three-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 90.5% in the triple-therapy arm versus 87.7% with venetoclax-obinutuzumab. The 3-year PFS with venetoclax-rituximab (80.8%) was again not statistically different than the 75.5% with chemoimmunotherapy (P = .18).
Not ready for prime time
The benefits of triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab held only in patients with unmutated IgVH. “The high efficacy of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen in young, fit patients with mutated IgVH may be difficult to improve on,” noted the investigators, led by Barbara Eichhorst, MD, a hematologic malignancy specialist at the University of Cologne (Germany).
Also, although triple-therapy results were impressive, some of the benefits “are neutralized by the need for dose reductions and early treatment discontinuation owing to adverse events,” they said.
For instance, triple therapy had the highest incidence of both grade 3 and 4 infections (21.2%) and atrial fibrillation (7.8%).
The editorialists noted that there has been “a flurry of interest” in trials combining ibrutinib and venetoclax – as was done in the triple-therapy arm – since both emerged as powerful tools against CLL in recent years. However, even with the study results, they said “the use of triplet therapy should be viewed as investigational.”
For one thing, rates of uMRD were not “dramatically different” between triple therapy and venetoclax-obinutuzumab, and longer follow-up is better gauge differences in PFS and long-term toxicities.
Also, ibrutinib is being eclipsed by the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib, because they have better safety profiles, and they are being assessed in CLL combination trials. For now, there are too many unknowns for routine use of triple therapy in fit CLL patients, they said.
The investigators and editorialists both noted that improved uMRD in the study translated into superior PFS, raising the possibility that uMRD might be a valid alternative endpoint to PFS in CLL trials.
With “median remissions in CLL lasting far in excess of 5 years, designing studies that take 8-10 years” to reach a PFS endpoint is simply too slow. Moving to an alternative endpoint such a uMRD would preserve “the momentum that has been generated” with recent advances, Dr. Woyach and Dr. Byrd said.
The work was funded by the companies that market venetoclax, ibrutinib, and obinutuzumab: AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Dr. Eichhorst is a consultant and/or speaker for the companies and also reported grants from them. Dr. Byrd is a consultant/adviser for Eilean Therapeutics, Kurome Therapeutics, Newave, and Orbimed. Dr. Woyach disclosed ties with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Lilly, and other companies.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty plus obesity drugs add up to more weight loss
CHICAGO – Antiobesity medications and endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) are popular strategies for weight loss on their own. Now researchers are looking at what happens when you combine them.
In a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), they found
Starting medication within 6 months of ESG was more ideal than other timing intervals. Initiating medical therapy more than 6 months before ESG was associated with less weight loss.
In the single-center, retrospective study, 224 patients were enrolled, of whom 34% were on monotherapy (ESG alone), 31% had combination therapy (medication prescribed within 6 months prior to or after ESG), and 35% had sequential therapy (medication more than 6 months prior to or after ESG).
Most patients were female, ranging from 74% to 95% of each group, and baseline BMI ranged from a mean 37.5 kg/m2 to 40.1 kg/m2.
The medications involved in the study were phentermine, phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), orlistat (Xenical, Alli), bupropion/naltrexone ER (Contrave), or the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza) or semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus). Of the patients who underwent combination therapy, 30% were prescribed a regimen that included a GLP-1RA. Of the patients who underwent sequential therapy, 81% were prescribed a medication first and 19% underwent ESG first.
At 1 year, the greatest total weight loss was a mean 23.7% with the combination of ESG and a GLP-1RA. Total weight loss was 18% with ESG plus a non–GLP-1RA medication. ESG alone led to 17.3%. Sequential therapy that began with ESG yielded 14.7% total weight loss, whereas sequential therapy that began with medication first resulted in 12% weight loss.
It’s possible that gastroplasty performed second was less impressive because the medications were very effective, and there was not as much weight to lose, said Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, a bariatric endoscopist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and lead author of the study.
Researchers stopped medication therapy if people did not experience at least 5% total weight loss after 3 months on a maintenance dose.
Waiting for weight loss to start to plateau after gastroplasty might be an ideal time to add weight loss medication, said Dr. Jirapinyo. “Usually when I see them at 3 months, I plot how fast their weight loss has been. If it’s been going down [steadily], we do not offer an antiobesity medication until I see them again at 6 months.”
The serious adverse event (SAE) rate associated with ESG was similar among the three cohorts: 2.6% with monotherapy group, 1.4% with combination therapy, and 1.3% with sequential therapy. SAEs associated with antiobesity medication occurred in 1.3% of the sequential therapy group and was not reported in either of the other two groups.
“I certainly think combination therapy should be more effective than just gastroplasty alone and is probably better,” said Gregory L. Austin, MD, session comoderator and a gastroenterologist at the UCHealth Digestive Health Center, Denver.
“Whether you start immediately or wait 3 months afterwards is a question that still needs to be answered,” he added.
Dr. Austin agreed that taking an antiobesity medicine more than 6 months before gastroplasty might be associated with enough weight loss to make the gastroplasty look less effective.
He also noted that the study “doesn’t really address the question of whether you should offer gastroplasty to somebody who’s been on [medication] for more than 6 months because you probably still should if they haven’t achieved an appropriate weight loss that’s associated with reduced comorbidity risk going forward.”
Different study, similar result
In a second study, also presented at DDW 2023, investigators looked at timing of liraglutide for weight loss in a randomized controlled trial. They found that administration of GLP-1RA right after transoral outlet reduction endoscopy (TORe) in people with a history of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass extended weight loss longer than a placebo injection. This strategy was also favorable versus waiting to give liraglutide 1 year later.
The researchers randomly assigned 51 people to get weekly subcutaneous liraglutide injections following TORe for 12 months, then placebo injections for 12 months. They assigned 58 patients to receive weekly placebo injections following TORe for 12 months, then liraglutide injections for 12 months.
At 12 months following the procedure, total body weight loss (TBWL) among participants receiving liraglutide was about 22%, compared with about 14% among patients receiving placebo. At 24 months following the procedure (12 months after crossover), TBWL among patients in the liraglutide-first group was almost 35%, compared with about 24% in the placebo-first/liraglutide-second group.
There was a durable effect associated with liraglutide even after switching to placebo, said Ali Lahooti, lead study author and second-year medical student at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There did seem to be a better benefit of starting on it for the first year and then stopping it,” Dr. Austin noted.
These two studies come at a time when the debate over the timing of different obesity interventions continues. Some experts believe weight loss medications can help with the rebound in weight that some people experience months after bariatric surgery, for example.
‘Wave of the future’
The study by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues is “really exciting and interesting,” said Linda S. Lee, MD, medical director of endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when asked to comment.
Medication begun within 6 months of the endoscopic procedure “led to superior outcomes, compared to just endoscopy alone,” Dr. Lee said. “I think that’s really the wave of the future as far as treating patients with obesity issues. We clearly know that diet and exercise alone for most people is not good enough. Of course, we have surgery, but we also realize that with surgery sometimes the weight starts to creep back up over time.”
Dr. Lee noted that the study was limited because it was retrospective. Ideally, it would be good if future, prospective research randomly assigns people to endoscopy alone or endoscopy plus medication.
Dr. Lee also noted there is a limited number of bariatric endoscopists. By the time people with obesity get to a specialist, they’ve likely tried diet and exercise and “probably have seen all the commercials for these different medications. I think the reality is that most people will ask their primary care physicians about antiobesity medication.
“From my point of view, as long as the medicine is safe and not harming them, then let’s do both of them together,” Dr. Lee added.
Dr. Lee also mentioned another study (Abstract Mo1898) presented at DDW 2023 that showed total weight loss with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty was durable over 10 years. Follow-up was with only seven patients, however.
Larger numbers are needed to confirm the finding, but it’s “exciting,” she said.
Dr. Jirapinyo receives grant/research support from Apollo Endosurgery, Fractyl, and USGI Medical, and is a consultant for ERBE, GI Dynamics, and Spatz Medical. Dr. Lahooti, Dr. Austin, and Dr. Lee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Antiobesity medications and endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) are popular strategies for weight loss on their own. Now researchers are looking at what happens when you combine them.
In a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), they found
Starting medication within 6 months of ESG was more ideal than other timing intervals. Initiating medical therapy more than 6 months before ESG was associated with less weight loss.
In the single-center, retrospective study, 224 patients were enrolled, of whom 34% were on monotherapy (ESG alone), 31% had combination therapy (medication prescribed within 6 months prior to or after ESG), and 35% had sequential therapy (medication more than 6 months prior to or after ESG).
Most patients were female, ranging from 74% to 95% of each group, and baseline BMI ranged from a mean 37.5 kg/m2 to 40.1 kg/m2.
The medications involved in the study were phentermine, phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), orlistat (Xenical, Alli), bupropion/naltrexone ER (Contrave), or the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza) or semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus). Of the patients who underwent combination therapy, 30% were prescribed a regimen that included a GLP-1RA. Of the patients who underwent sequential therapy, 81% were prescribed a medication first and 19% underwent ESG first.
At 1 year, the greatest total weight loss was a mean 23.7% with the combination of ESG and a GLP-1RA. Total weight loss was 18% with ESG plus a non–GLP-1RA medication. ESG alone led to 17.3%. Sequential therapy that began with ESG yielded 14.7% total weight loss, whereas sequential therapy that began with medication first resulted in 12% weight loss.
It’s possible that gastroplasty performed second was less impressive because the medications were very effective, and there was not as much weight to lose, said Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, a bariatric endoscopist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and lead author of the study.
Researchers stopped medication therapy if people did not experience at least 5% total weight loss after 3 months on a maintenance dose.
Waiting for weight loss to start to plateau after gastroplasty might be an ideal time to add weight loss medication, said Dr. Jirapinyo. “Usually when I see them at 3 months, I plot how fast their weight loss has been. If it’s been going down [steadily], we do not offer an antiobesity medication until I see them again at 6 months.”
The serious adverse event (SAE) rate associated with ESG was similar among the three cohorts: 2.6% with monotherapy group, 1.4% with combination therapy, and 1.3% with sequential therapy. SAEs associated with antiobesity medication occurred in 1.3% of the sequential therapy group and was not reported in either of the other two groups.
“I certainly think combination therapy should be more effective than just gastroplasty alone and is probably better,” said Gregory L. Austin, MD, session comoderator and a gastroenterologist at the UCHealth Digestive Health Center, Denver.
“Whether you start immediately or wait 3 months afterwards is a question that still needs to be answered,” he added.
Dr. Austin agreed that taking an antiobesity medicine more than 6 months before gastroplasty might be associated with enough weight loss to make the gastroplasty look less effective.
He also noted that the study “doesn’t really address the question of whether you should offer gastroplasty to somebody who’s been on [medication] for more than 6 months because you probably still should if they haven’t achieved an appropriate weight loss that’s associated with reduced comorbidity risk going forward.”
Different study, similar result
In a second study, also presented at DDW 2023, investigators looked at timing of liraglutide for weight loss in a randomized controlled trial. They found that administration of GLP-1RA right after transoral outlet reduction endoscopy (TORe) in people with a history of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass extended weight loss longer than a placebo injection. This strategy was also favorable versus waiting to give liraglutide 1 year later.
The researchers randomly assigned 51 people to get weekly subcutaneous liraglutide injections following TORe for 12 months, then placebo injections for 12 months. They assigned 58 patients to receive weekly placebo injections following TORe for 12 months, then liraglutide injections for 12 months.
At 12 months following the procedure, total body weight loss (TBWL) among participants receiving liraglutide was about 22%, compared with about 14% among patients receiving placebo. At 24 months following the procedure (12 months after crossover), TBWL among patients in the liraglutide-first group was almost 35%, compared with about 24% in the placebo-first/liraglutide-second group.
There was a durable effect associated with liraglutide even after switching to placebo, said Ali Lahooti, lead study author and second-year medical student at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There did seem to be a better benefit of starting on it for the first year and then stopping it,” Dr. Austin noted.
These two studies come at a time when the debate over the timing of different obesity interventions continues. Some experts believe weight loss medications can help with the rebound in weight that some people experience months after bariatric surgery, for example.
‘Wave of the future’
The study by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues is “really exciting and interesting,” said Linda S. Lee, MD, medical director of endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when asked to comment.
Medication begun within 6 months of the endoscopic procedure “led to superior outcomes, compared to just endoscopy alone,” Dr. Lee said. “I think that’s really the wave of the future as far as treating patients with obesity issues. We clearly know that diet and exercise alone for most people is not good enough. Of course, we have surgery, but we also realize that with surgery sometimes the weight starts to creep back up over time.”
Dr. Lee noted that the study was limited because it was retrospective. Ideally, it would be good if future, prospective research randomly assigns people to endoscopy alone or endoscopy plus medication.
Dr. Lee also noted there is a limited number of bariatric endoscopists. By the time people with obesity get to a specialist, they’ve likely tried diet and exercise and “probably have seen all the commercials for these different medications. I think the reality is that most people will ask their primary care physicians about antiobesity medication.
“From my point of view, as long as the medicine is safe and not harming them, then let’s do both of them together,” Dr. Lee added.
Dr. Lee also mentioned another study (Abstract Mo1898) presented at DDW 2023 that showed total weight loss with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty was durable over 10 years. Follow-up was with only seven patients, however.
Larger numbers are needed to confirm the finding, but it’s “exciting,” she said.
Dr. Jirapinyo receives grant/research support from Apollo Endosurgery, Fractyl, and USGI Medical, and is a consultant for ERBE, GI Dynamics, and Spatz Medical. Dr. Lahooti, Dr. Austin, and Dr. Lee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Antiobesity medications and endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) are popular strategies for weight loss on their own. Now researchers are looking at what happens when you combine them.
In a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), they found
Starting medication within 6 months of ESG was more ideal than other timing intervals. Initiating medical therapy more than 6 months before ESG was associated with less weight loss.
In the single-center, retrospective study, 224 patients were enrolled, of whom 34% were on monotherapy (ESG alone), 31% had combination therapy (medication prescribed within 6 months prior to or after ESG), and 35% had sequential therapy (medication more than 6 months prior to or after ESG).
Most patients were female, ranging from 74% to 95% of each group, and baseline BMI ranged from a mean 37.5 kg/m2 to 40.1 kg/m2.
The medications involved in the study were phentermine, phentermine/topiramate extended release (Qsymia), orlistat (Xenical, Alli), bupropion/naltrexone ER (Contrave), or the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza) or semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus). Of the patients who underwent combination therapy, 30% were prescribed a regimen that included a GLP-1RA. Of the patients who underwent sequential therapy, 81% were prescribed a medication first and 19% underwent ESG first.
At 1 year, the greatest total weight loss was a mean 23.7% with the combination of ESG and a GLP-1RA. Total weight loss was 18% with ESG plus a non–GLP-1RA medication. ESG alone led to 17.3%. Sequential therapy that began with ESG yielded 14.7% total weight loss, whereas sequential therapy that began with medication first resulted in 12% weight loss.
It’s possible that gastroplasty performed second was less impressive because the medications were very effective, and there was not as much weight to lose, said Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, a bariatric endoscopist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and lead author of the study.
Researchers stopped medication therapy if people did not experience at least 5% total weight loss after 3 months on a maintenance dose.
Waiting for weight loss to start to plateau after gastroplasty might be an ideal time to add weight loss medication, said Dr. Jirapinyo. “Usually when I see them at 3 months, I plot how fast their weight loss has been. If it’s been going down [steadily], we do not offer an antiobesity medication until I see them again at 6 months.”
The serious adverse event (SAE) rate associated with ESG was similar among the three cohorts: 2.6% with monotherapy group, 1.4% with combination therapy, and 1.3% with sequential therapy. SAEs associated with antiobesity medication occurred in 1.3% of the sequential therapy group and was not reported in either of the other two groups.
“I certainly think combination therapy should be more effective than just gastroplasty alone and is probably better,” said Gregory L. Austin, MD, session comoderator and a gastroenterologist at the UCHealth Digestive Health Center, Denver.
“Whether you start immediately or wait 3 months afterwards is a question that still needs to be answered,” he added.
Dr. Austin agreed that taking an antiobesity medicine more than 6 months before gastroplasty might be associated with enough weight loss to make the gastroplasty look less effective.
He also noted that the study “doesn’t really address the question of whether you should offer gastroplasty to somebody who’s been on [medication] for more than 6 months because you probably still should if they haven’t achieved an appropriate weight loss that’s associated with reduced comorbidity risk going forward.”
Different study, similar result
In a second study, also presented at DDW 2023, investigators looked at timing of liraglutide for weight loss in a randomized controlled trial. They found that administration of GLP-1RA right after transoral outlet reduction endoscopy (TORe) in people with a history of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass extended weight loss longer than a placebo injection. This strategy was also favorable versus waiting to give liraglutide 1 year later.
The researchers randomly assigned 51 people to get weekly subcutaneous liraglutide injections following TORe for 12 months, then placebo injections for 12 months. They assigned 58 patients to receive weekly placebo injections following TORe for 12 months, then liraglutide injections for 12 months.
At 12 months following the procedure, total body weight loss (TBWL) among participants receiving liraglutide was about 22%, compared with about 14% among patients receiving placebo. At 24 months following the procedure (12 months after crossover), TBWL among patients in the liraglutide-first group was almost 35%, compared with about 24% in the placebo-first/liraglutide-second group.
There was a durable effect associated with liraglutide even after switching to placebo, said Ali Lahooti, lead study author and second-year medical student at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There did seem to be a better benefit of starting on it for the first year and then stopping it,” Dr. Austin noted.
These two studies come at a time when the debate over the timing of different obesity interventions continues. Some experts believe weight loss medications can help with the rebound in weight that some people experience months after bariatric surgery, for example.
‘Wave of the future’
The study by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues is “really exciting and interesting,” said Linda S. Lee, MD, medical director of endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when asked to comment.
Medication begun within 6 months of the endoscopic procedure “led to superior outcomes, compared to just endoscopy alone,” Dr. Lee said. “I think that’s really the wave of the future as far as treating patients with obesity issues. We clearly know that diet and exercise alone for most people is not good enough. Of course, we have surgery, but we also realize that with surgery sometimes the weight starts to creep back up over time.”
Dr. Lee noted that the study was limited because it was retrospective. Ideally, it would be good if future, prospective research randomly assigns people to endoscopy alone or endoscopy plus medication.
Dr. Lee also noted there is a limited number of bariatric endoscopists. By the time people with obesity get to a specialist, they’ve likely tried diet and exercise and “probably have seen all the commercials for these different medications. I think the reality is that most people will ask their primary care physicians about antiobesity medication.
“From my point of view, as long as the medicine is safe and not harming them, then let’s do both of them together,” Dr. Lee added.
Dr. Lee also mentioned another study (Abstract Mo1898) presented at DDW 2023 that showed total weight loss with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty was durable over 10 years. Follow-up was with only seven patients, however.
Larger numbers are needed to confirm the finding, but it’s “exciting,” she said.
Dr. Jirapinyo receives grant/research support from Apollo Endosurgery, Fractyl, and USGI Medical, and is a consultant for ERBE, GI Dynamics, and Spatz Medical. Dr. Lahooti, Dr. Austin, and Dr. Lee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT DDW 2023