User login
Corticosteroid Injections Don’t Move Blood Sugar for Most
TOPLINE:
Intra-articular corticosteroid (IACS) injections pose a minimal risk of accelerating diabetes for most people, despite temporarily elevating blood glucose levels, according to a study published in Clinical Diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Almost half of Americans with diabetes have arthritis, so glycemic control is a concern for many receiving IACS injections.
- IACS injections are known to cause short-term hyperglycemia, but their long-term effects on glycemic control are not well studied.
- For the retrospective cohort study, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used electronic health records from 1169 adults who had received an IACS injection in one large joint between 2012 and 2018.
- They analyzed data on A1C levels for study participants from 18 months before and after the injections.
- Researchers assessed if participants had a greater-than-expected (defined as an increase of more than 0.5% above expected) concentration of A1C after the injection, and examined rates of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome in the 30 days following an injection.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 16% of people experienced a greater-than-expected A1C level after receiving an injection.
- A1C levels rose by an average of 1.2% in the greater-than-expected group, but decreased by an average of 0.2% in the average group.
- One patient had an episode of severe hyperglycemia that was linked to the injection.
- A baseline level of A1C above 8% was the only factor associated with a greater-than-expected increase in the marker after an IACS injection.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although most patients do not experience an increase in A1C after IACS, clinicians should counsel patients with suboptimally controlled diabetes about risks of further hyperglycemia after IACS administration,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Terin T. Sytsma, MD, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and could not establish causation. In addition, the population was of residents from one county in Minnesota, and was not racially or ethnically diverse. Details about the injection, such as location and total dose, were not available. The study also did not include a control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Mayo Clinic and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Intra-articular corticosteroid (IACS) injections pose a minimal risk of accelerating diabetes for most people, despite temporarily elevating blood glucose levels, according to a study published in Clinical Diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Almost half of Americans with diabetes have arthritis, so glycemic control is a concern for many receiving IACS injections.
- IACS injections are known to cause short-term hyperglycemia, but their long-term effects on glycemic control are not well studied.
- For the retrospective cohort study, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used electronic health records from 1169 adults who had received an IACS injection in one large joint between 2012 and 2018.
- They analyzed data on A1C levels for study participants from 18 months before and after the injections.
- Researchers assessed if participants had a greater-than-expected (defined as an increase of more than 0.5% above expected) concentration of A1C after the injection, and examined rates of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome in the 30 days following an injection.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 16% of people experienced a greater-than-expected A1C level after receiving an injection.
- A1C levels rose by an average of 1.2% in the greater-than-expected group, but decreased by an average of 0.2% in the average group.
- One patient had an episode of severe hyperglycemia that was linked to the injection.
- A baseline level of A1C above 8% was the only factor associated with a greater-than-expected increase in the marker after an IACS injection.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although most patients do not experience an increase in A1C after IACS, clinicians should counsel patients with suboptimally controlled diabetes about risks of further hyperglycemia after IACS administration,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Terin T. Sytsma, MD, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and could not establish causation. In addition, the population was of residents from one county in Minnesota, and was not racially or ethnically diverse. Details about the injection, such as location and total dose, were not available. The study also did not include a control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Mayo Clinic and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Intra-articular corticosteroid (IACS) injections pose a minimal risk of accelerating diabetes for most people, despite temporarily elevating blood glucose levels, according to a study published in Clinical Diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Almost half of Americans with diabetes have arthritis, so glycemic control is a concern for many receiving IACS injections.
- IACS injections are known to cause short-term hyperglycemia, but their long-term effects on glycemic control are not well studied.
- For the retrospective cohort study, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used electronic health records from 1169 adults who had received an IACS injection in one large joint between 2012 and 2018.
- They analyzed data on A1C levels for study participants from 18 months before and after the injections.
- Researchers assessed if participants had a greater-than-expected (defined as an increase of more than 0.5% above expected) concentration of A1C after the injection, and examined rates of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome in the 30 days following an injection.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 16% of people experienced a greater-than-expected A1C level after receiving an injection.
- A1C levels rose by an average of 1.2% in the greater-than-expected group, but decreased by an average of 0.2% in the average group.
- One patient had an episode of severe hyperglycemia that was linked to the injection.
- A baseline level of A1C above 8% was the only factor associated with a greater-than-expected increase in the marker after an IACS injection.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although most patients do not experience an increase in A1C after IACS, clinicians should counsel patients with suboptimally controlled diabetes about risks of further hyperglycemia after IACS administration,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Terin T. Sytsma, MD, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and could not establish causation. In addition, the population was of residents from one county in Minnesota, and was not racially or ethnically diverse. Details about the injection, such as location and total dose, were not available. The study also did not include a control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Mayo Clinic and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No Compelling Evidence of Pancreatic Cancer Risk With GLP-1s
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypocalcemia Risk Warning Added to Osteoporosis Drug
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has added a boxed warning to the label of the osteoporosis drug denosumab (Prolia) about increased risk for severe hypocalcemia in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody, indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at increased risk for fracture for whom other treatments aren’t effective or can’t be tolerated. It’s also indicated to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture, treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women at high risk for fracture, increase bone mass in men at high risk for fracture receiving androgen-deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer, and increase bone mass in women at high risk for fracture receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
This new warning updates a November 2022 alert based on preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for hypocalcemia in patients with CKD on dialysis.
Upon further examination of the data from two trials including more than 500,000 denosumab-treated women with CKD, the FDA concluded that severe hypocalcemia appears to be more common in those with CKD who also have mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). And, for patients with advanced CKD taking denosumab, “severe hypocalcemia resulted in serious harm, including hospitalization, life-threatening events, and death.”
Most of the severe hypocalcemia events occurred 2-10 weeks after denosumab injection, with the greatest risk during weeks 2-5.
The new warning advises healthcare professionals to assess patients’ kidney function before prescribing denosumab, and for those with advanced CKD, “consider the risk of severe hypocalcemia with Prolia in the context of other available treatments for osteoporosis.”
If the drug is still being considered for those patients for initial or continued use, calcium blood levels should be checked, and patients should be evaluated for CKD-MBD. Prior to prescribing denosumab in these patients, CKD-MBD should be properly managed, hypocalcemia corrected, and patients supplemented with calcium and activated vitamin D to decrease the risk for severe hypocalcemia and associated complications.
“Treatment with denosumab in patients with advanced CKD, including those on dialysis, and particularly patients with diagnosed CKD-MBD should involve a health care provider with expertise in the diagnosis and management of CKD-MBD,” the FDA advises.
Once denosumab is administered, close monitoring of blood calcium levels and prompt hypocalcemia management is essential to prevent complications including seizures or arrythmias. Patients should be advised to promptly report symptoms that could be consistent with hypocalcemia, including confusion, seizures, irregular heartbeat, fainting, muscle spasms or weakness, face twitching, tingling, or numbness anywhere in the body.
In 2022, an estimated 2.2 million Prolia prefilled syringes were sold by the manufacturer to US healthcare settings.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has added a boxed warning to the label of the osteoporosis drug denosumab (Prolia) about increased risk for severe hypocalcemia in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody, indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at increased risk for fracture for whom other treatments aren’t effective or can’t be tolerated. It’s also indicated to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture, treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women at high risk for fracture, increase bone mass in men at high risk for fracture receiving androgen-deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer, and increase bone mass in women at high risk for fracture receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
This new warning updates a November 2022 alert based on preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for hypocalcemia in patients with CKD on dialysis.
Upon further examination of the data from two trials including more than 500,000 denosumab-treated women with CKD, the FDA concluded that severe hypocalcemia appears to be more common in those with CKD who also have mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). And, for patients with advanced CKD taking denosumab, “severe hypocalcemia resulted in serious harm, including hospitalization, life-threatening events, and death.”
Most of the severe hypocalcemia events occurred 2-10 weeks after denosumab injection, with the greatest risk during weeks 2-5.
The new warning advises healthcare professionals to assess patients’ kidney function before prescribing denosumab, and for those with advanced CKD, “consider the risk of severe hypocalcemia with Prolia in the context of other available treatments for osteoporosis.”
If the drug is still being considered for those patients for initial or continued use, calcium blood levels should be checked, and patients should be evaluated for CKD-MBD. Prior to prescribing denosumab in these patients, CKD-MBD should be properly managed, hypocalcemia corrected, and patients supplemented with calcium and activated vitamin D to decrease the risk for severe hypocalcemia and associated complications.
“Treatment with denosumab in patients with advanced CKD, including those on dialysis, and particularly patients with diagnosed CKD-MBD should involve a health care provider with expertise in the diagnosis and management of CKD-MBD,” the FDA advises.
Once denosumab is administered, close monitoring of blood calcium levels and prompt hypocalcemia management is essential to prevent complications including seizures or arrythmias. Patients should be advised to promptly report symptoms that could be consistent with hypocalcemia, including confusion, seizures, irregular heartbeat, fainting, muscle spasms or weakness, face twitching, tingling, or numbness anywhere in the body.
In 2022, an estimated 2.2 million Prolia prefilled syringes were sold by the manufacturer to US healthcare settings.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has added a boxed warning to the label of the osteoporosis drug denosumab (Prolia) about increased risk for severe hypocalcemia in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody, indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at increased risk for fracture for whom other treatments aren’t effective or can’t be tolerated. It’s also indicated to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture, treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women at high risk for fracture, increase bone mass in men at high risk for fracture receiving androgen-deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer, and increase bone mass in women at high risk for fracture receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
This new warning updates a November 2022 alert based on preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for hypocalcemia in patients with CKD on dialysis.
Upon further examination of the data from two trials including more than 500,000 denosumab-treated women with CKD, the FDA concluded that severe hypocalcemia appears to be more common in those with CKD who also have mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). And, for patients with advanced CKD taking denosumab, “severe hypocalcemia resulted in serious harm, including hospitalization, life-threatening events, and death.”
Most of the severe hypocalcemia events occurred 2-10 weeks after denosumab injection, with the greatest risk during weeks 2-5.
The new warning advises healthcare professionals to assess patients’ kidney function before prescribing denosumab, and for those with advanced CKD, “consider the risk of severe hypocalcemia with Prolia in the context of other available treatments for osteoporosis.”
If the drug is still being considered for those patients for initial or continued use, calcium blood levels should be checked, and patients should be evaluated for CKD-MBD. Prior to prescribing denosumab in these patients, CKD-MBD should be properly managed, hypocalcemia corrected, and patients supplemented with calcium and activated vitamin D to decrease the risk for severe hypocalcemia and associated complications.
“Treatment with denosumab in patients with advanced CKD, including those on dialysis, and particularly patients with diagnosed CKD-MBD should involve a health care provider with expertise in the diagnosis and management of CKD-MBD,” the FDA advises.
Once denosumab is administered, close monitoring of blood calcium levels and prompt hypocalcemia management is essential to prevent complications including seizures or arrythmias. Patients should be advised to promptly report symptoms that could be consistent with hypocalcemia, including confusion, seizures, irregular heartbeat, fainting, muscle spasms or weakness, face twitching, tingling, or numbness anywhere in the body.
In 2022, an estimated 2.2 million Prolia prefilled syringes were sold by the manufacturer to US healthcare settings.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Continued Caution Needed Combining Nitrates With ED Drugs
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.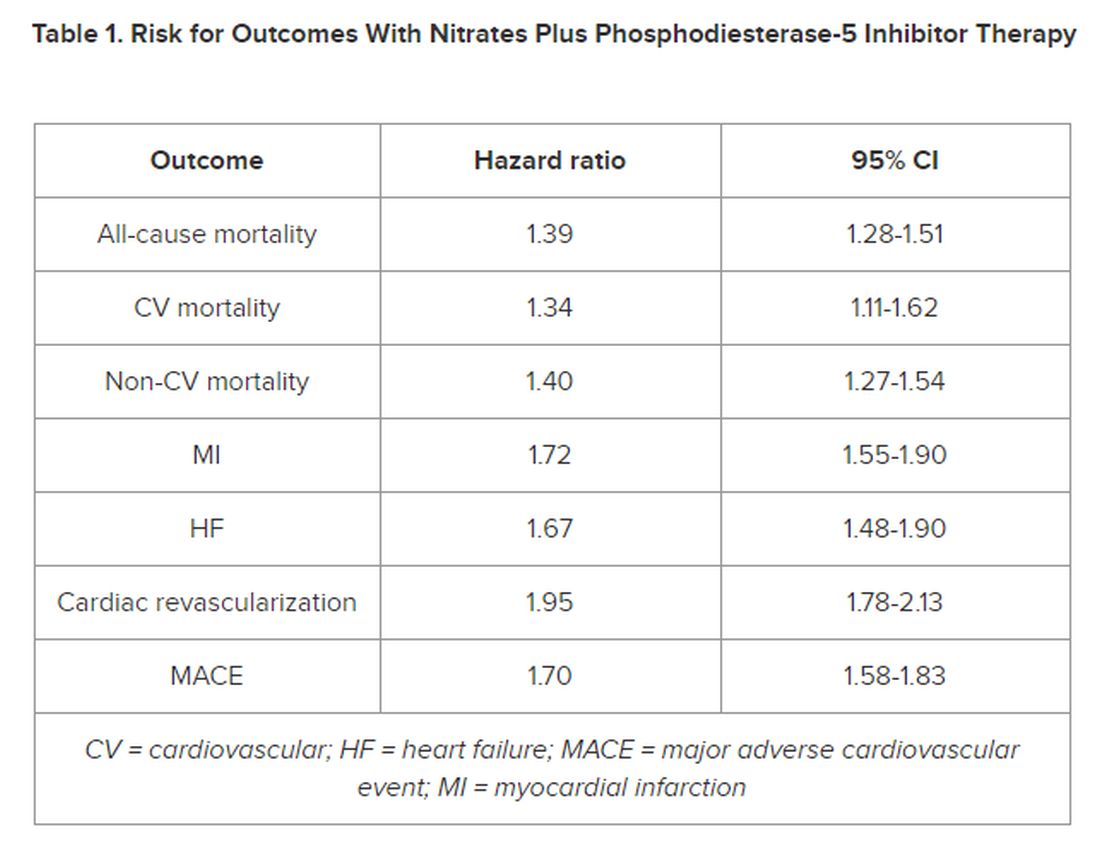
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Plant-based Psychedelics Offer a New Option for TBI Treatment?
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Shingles Vaccine Offers 4 Years of Protection
Two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) are effective against herpes zoster (HZ) for 4 years after vaccination, according to a new study published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Findings from the prospective cohort study showed that people who received two doses of the vaccine, regardless of when they received their second dose, experienced 79% vaccine effectiveness (VE) during the first year, with effectiveness decreasing to 73% by year 4. By contrast, the rate of effectiveness during the first year was 70% for people who received a single dose, falling to 52% effectiveness by year 4.
The findings also showed that the rate of effectiveness was 65% for those taking corticosteroids.
The study was conducted between 2018 and 2022 using data from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, a collaboration between the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and nine healthcare systems across the country.
Researchers evaluated the incidence of HZ, as determined by a diagnosis and prescription for antiviral medication within 7 days of diagnosis, and monitored RZV status over time.
The findings may quell fears that waiting too long for the second dose reduces the effectiveness of the herpes vaccine, according to Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, director of the Vaccine Study Center at Kaiser Permanente in Oakland, California, who led the study.
The long-term efficacy of the vaccine is especially important because older adults are now living much longer than in previous years, according to Alexandra Tien, MD, a family physician at Medical Associates of Rhode Island in Providence.
“People live these days into their 80s and even 90s,” Dr. Tien said. “That’s a large number of years to need protection for, so it’s really important to have a long-lasting vaccine.”
The CDC currently recommends two doses of RZV separated by 2-6 months for patients aged 50 years and older. Adults older than 19 years who are immunocompromised should receive two doses of RZV separated by 1-2 months, the agency said.
According to Dr. Klein, research does not show whether VE for RZV wanes after 4 years. But interim findings from another study following people in clinical trials found VE levels remained high after 7 years.
The risk for HZ increases with age, reaching a lifetime risk of 50% among adults aged 85 years. Complications like postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) — characterized by long-term tingling, numbness, and disabling pain at the site of the rash — can interfere with the quality of life and ability to function in older adults. The CDC estimates that up to 18% of people with shingles experience PHN, and the risk increases with age.
Just like with any other vaccine, patients sometimes have concerns about the potential side effects of RZV, said Dr. Tien. But those effects, such as muscle pain, nausea, and fever, are mild compared to shingles.
“I always tell patients, with any vaccine, immunization is one of the biggest bangs for your buck in healthcare because you’re preventing a problem,” Dr. Tien said.
This study was funded by the CDC through contracts with participating sites. Study authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Tien reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) are effective against herpes zoster (HZ) for 4 years after vaccination, according to a new study published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Findings from the prospective cohort study showed that people who received two doses of the vaccine, regardless of when they received their second dose, experienced 79% vaccine effectiveness (VE) during the first year, with effectiveness decreasing to 73% by year 4. By contrast, the rate of effectiveness during the first year was 70% for people who received a single dose, falling to 52% effectiveness by year 4.
The findings also showed that the rate of effectiveness was 65% for those taking corticosteroids.
The study was conducted between 2018 and 2022 using data from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, a collaboration between the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and nine healthcare systems across the country.
Researchers evaluated the incidence of HZ, as determined by a diagnosis and prescription for antiviral medication within 7 days of diagnosis, and monitored RZV status over time.
The findings may quell fears that waiting too long for the second dose reduces the effectiveness of the herpes vaccine, according to Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, director of the Vaccine Study Center at Kaiser Permanente in Oakland, California, who led the study.
The long-term efficacy of the vaccine is especially important because older adults are now living much longer than in previous years, according to Alexandra Tien, MD, a family physician at Medical Associates of Rhode Island in Providence.
“People live these days into their 80s and even 90s,” Dr. Tien said. “That’s a large number of years to need protection for, so it’s really important to have a long-lasting vaccine.”
The CDC currently recommends two doses of RZV separated by 2-6 months for patients aged 50 years and older. Adults older than 19 years who are immunocompromised should receive two doses of RZV separated by 1-2 months, the agency said.
According to Dr. Klein, research does not show whether VE for RZV wanes after 4 years. But interim findings from another study following people in clinical trials found VE levels remained high after 7 years.
The risk for HZ increases with age, reaching a lifetime risk of 50% among adults aged 85 years. Complications like postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) — characterized by long-term tingling, numbness, and disabling pain at the site of the rash — can interfere with the quality of life and ability to function in older adults. The CDC estimates that up to 18% of people with shingles experience PHN, and the risk increases with age.
Just like with any other vaccine, patients sometimes have concerns about the potential side effects of RZV, said Dr. Tien. But those effects, such as muscle pain, nausea, and fever, are mild compared to shingles.
“I always tell patients, with any vaccine, immunization is one of the biggest bangs for your buck in healthcare because you’re preventing a problem,” Dr. Tien said.
This study was funded by the CDC through contracts with participating sites. Study authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Tien reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) are effective against herpes zoster (HZ) for 4 years after vaccination, according to a new study published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Findings from the prospective cohort study showed that people who received two doses of the vaccine, regardless of when they received their second dose, experienced 79% vaccine effectiveness (VE) during the first year, with effectiveness decreasing to 73% by year 4. By contrast, the rate of effectiveness during the first year was 70% for people who received a single dose, falling to 52% effectiveness by year 4.
The findings also showed that the rate of effectiveness was 65% for those taking corticosteroids.
The study was conducted between 2018 and 2022 using data from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, a collaboration between the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and nine healthcare systems across the country.
Researchers evaluated the incidence of HZ, as determined by a diagnosis and prescription for antiviral medication within 7 days of diagnosis, and monitored RZV status over time.
The findings may quell fears that waiting too long for the second dose reduces the effectiveness of the herpes vaccine, according to Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, director of the Vaccine Study Center at Kaiser Permanente in Oakland, California, who led the study.
The long-term efficacy of the vaccine is especially important because older adults are now living much longer than in previous years, according to Alexandra Tien, MD, a family physician at Medical Associates of Rhode Island in Providence.
“People live these days into their 80s and even 90s,” Dr. Tien said. “That’s a large number of years to need protection for, so it’s really important to have a long-lasting vaccine.”
The CDC currently recommends two doses of RZV separated by 2-6 months for patients aged 50 years and older. Adults older than 19 years who are immunocompromised should receive two doses of RZV separated by 1-2 months, the agency said.
According to Dr. Klein, research does not show whether VE for RZV wanes after 4 years. But interim findings from another study following people in clinical trials found VE levels remained high after 7 years.
The risk for HZ increases with age, reaching a lifetime risk of 50% among adults aged 85 years. Complications like postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) — characterized by long-term tingling, numbness, and disabling pain at the site of the rash — can interfere with the quality of life and ability to function in older adults. The CDC estimates that up to 18% of people with shingles experience PHN, and the risk increases with age.
Just like with any other vaccine, patients sometimes have concerns about the potential side effects of RZV, said Dr. Tien. But those effects, such as muscle pain, nausea, and fever, are mild compared to shingles.
“I always tell patients, with any vaccine, immunization is one of the biggest bangs for your buck in healthcare because you’re preventing a problem,” Dr. Tien said.
This study was funded by the CDC through contracts with participating sites. Study authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Tien reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Common Diabetes Pills Also Protect Kidneys
, according to a study in JAMA Network Open.
These pills, known as sodium-glucose cotransport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, reduce the amount of blood sugar in a kidney by causing more glucose to be excreted in urine.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) cannot be cured and often leads to renal failure. SGLT2 inhibitor drugs can help stave off this possibility. Acute kidney disease (AKD), on the other hand, is potentially reversible. It typically occurs after an acute kidney injury, lasts for up to 90 days, and can progress to CKD if left unchecked.
“There has been a notable absence of targeted pharmacotherapy to offer protection to these patients,” said Vin-Cent Wu, MD, PhD, a nephrologist at National Taiwan University Hospital in Taipei, and an author of the study.
For the retrospective analysis, Dr. Wu and his colleagues looked at data from more than 230,000 adults with type 2 diabetes whose health records were gathered into a research tool called the TriNetX, a global research database. Patients had been treated for AKD between 2002 and 2022. Major adverse kidney events were noted for 5 years after discharge, which were defined as events which required regular dialysis, major adverse cardiovascular events such as a heart attack or stroke, or death.
To determine the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Wu and colleagues compared outcomes among 5317 patients with AKD who received the drugs with 5317 similar patients who did not. Members of both groups had lived for at least 90 days after being discharged from the hospital and did not require dialysis during that period.
After a median follow-up of 2.3 years, more patients who did not receive an SGLT2 inhibitor had died (994 compared with 481) or had endured major stress to their kidneys (1119 compared with 504) or heart (612 compared with 295). The relative reduction in mortality risk for people in the SGLT2-inhibitor arm was 31% (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.77).
Only 2.3% of patients with AKD in the study were prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor.
In the United States, approximately 20% of people with type 2 diabetes and CKD receive a SGLT2 inhibitor, according to 2023 research.
“Our study reveals that the prescription rate of SGLT2 inhibitors remains relatively low in clinical practice among patients with type 2 diabetes and AKD,” Dr. Wu told this news organization. “This underscores the need for increased awareness and greater consideration of this critical issue in clinical decision-making.”
Dr. Wu said that AKD management tends to be conservative and relies on symptom monitoring. He acknowledged that confounders may have influenced the results, and that the use of SGLT2 inhibitors might only be correlated with better results instead of producing a causation effect.
This point was raised by Ayodele Odutayo, MD, DPhil, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. But despite that caution, Dr. Odutayo said that he found the study to be encouraging overall and broadly in line with known benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in CKD.
“The findings are reassuring that the medications work even in people who’ve already had some kidney injury beforehand,” but who are not yet diagnosed with CKD, Dr. Odutayo said.
“There is vast underuse of these medications in people for whom they are indicated,” perhaps due to clinician concern that the drugs will cause side effects such as low blood pressure or loss of salt and fluid, Dr. Odutayo said. Though those concerns are valid, the benefits of these drugs exceed the risks for most patients with CKD.
Dr. Wu and Dr. Odutayo report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a study in JAMA Network Open.
These pills, known as sodium-glucose cotransport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, reduce the amount of blood sugar in a kidney by causing more glucose to be excreted in urine.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) cannot be cured and often leads to renal failure. SGLT2 inhibitor drugs can help stave off this possibility. Acute kidney disease (AKD), on the other hand, is potentially reversible. It typically occurs after an acute kidney injury, lasts for up to 90 days, and can progress to CKD if left unchecked.
“There has been a notable absence of targeted pharmacotherapy to offer protection to these patients,” said Vin-Cent Wu, MD, PhD, a nephrologist at National Taiwan University Hospital in Taipei, and an author of the study.
For the retrospective analysis, Dr. Wu and his colleagues looked at data from more than 230,000 adults with type 2 diabetes whose health records were gathered into a research tool called the TriNetX, a global research database. Patients had been treated for AKD between 2002 and 2022. Major adverse kidney events were noted for 5 years after discharge, which were defined as events which required regular dialysis, major adverse cardiovascular events such as a heart attack or stroke, or death.
To determine the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Wu and colleagues compared outcomes among 5317 patients with AKD who received the drugs with 5317 similar patients who did not. Members of both groups had lived for at least 90 days after being discharged from the hospital and did not require dialysis during that period.
After a median follow-up of 2.3 years, more patients who did not receive an SGLT2 inhibitor had died (994 compared with 481) or had endured major stress to their kidneys (1119 compared with 504) or heart (612 compared with 295). The relative reduction in mortality risk for people in the SGLT2-inhibitor arm was 31% (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.77).
Only 2.3% of patients with AKD in the study were prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor.
In the United States, approximately 20% of people with type 2 diabetes and CKD receive a SGLT2 inhibitor, according to 2023 research.
“Our study reveals that the prescription rate of SGLT2 inhibitors remains relatively low in clinical practice among patients with type 2 diabetes and AKD,” Dr. Wu told this news organization. “This underscores the need for increased awareness and greater consideration of this critical issue in clinical decision-making.”
Dr. Wu said that AKD management tends to be conservative and relies on symptom monitoring. He acknowledged that confounders may have influenced the results, and that the use of SGLT2 inhibitors might only be correlated with better results instead of producing a causation effect.
This point was raised by Ayodele Odutayo, MD, DPhil, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. But despite that caution, Dr. Odutayo said that he found the study to be encouraging overall and broadly in line with known benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in CKD.
“The findings are reassuring that the medications work even in people who’ve already had some kidney injury beforehand,” but who are not yet diagnosed with CKD, Dr. Odutayo said.
“There is vast underuse of these medications in people for whom they are indicated,” perhaps due to clinician concern that the drugs will cause side effects such as low blood pressure or loss of salt and fluid, Dr. Odutayo said. Though those concerns are valid, the benefits of these drugs exceed the risks for most patients with CKD.
Dr. Wu and Dr. Odutayo report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a study in JAMA Network Open.
These pills, known as sodium-glucose cotransport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, reduce the amount of blood sugar in a kidney by causing more glucose to be excreted in urine.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) cannot be cured and often leads to renal failure. SGLT2 inhibitor drugs can help stave off this possibility. Acute kidney disease (AKD), on the other hand, is potentially reversible. It typically occurs after an acute kidney injury, lasts for up to 90 days, and can progress to CKD if left unchecked.
“There has been a notable absence of targeted pharmacotherapy to offer protection to these patients,” said Vin-Cent Wu, MD, PhD, a nephrologist at National Taiwan University Hospital in Taipei, and an author of the study.
For the retrospective analysis, Dr. Wu and his colleagues looked at data from more than 230,000 adults with type 2 diabetes whose health records were gathered into a research tool called the TriNetX, a global research database. Patients had been treated for AKD between 2002 and 2022. Major adverse kidney events were noted for 5 years after discharge, which were defined as events which required regular dialysis, major adverse cardiovascular events such as a heart attack or stroke, or death.
To determine the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Wu and colleagues compared outcomes among 5317 patients with AKD who received the drugs with 5317 similar patients who did not. Members of both groups had lived for at least 90 days after being discharged from the hospital and did not require dialysis during that period.
After a median follow-up of 2.3 years, more patients who did not receive an SGLT2 inhibitor had died (994 compared with 481) or had endured major stress to their kidneys (1119 compared with 504) or heart (612 compared with 295). The relative reduction in mortality risk for people in the SGLT2-inhibitor arm was 31% (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.77).
Only 2.3% of patients with AKD in the study were prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor.
In the United States, approximately 20% of people with type 2 diabetes and CKD receive a SGLT2 inhibitor, according to 2023 research.
“Our study reveals that the prescription rate of SGLT2 inhibitors remains relatively low in clinical practice among patients with type 2 diabetes and AKD,” Dr. Wu told this news organization. “This underscores the need for increased awareness and greater consideration of this critical issue in clinical decision-making.”
Dr. Wu said that AKD management tends to be conservative and relies on symptom monitoring. He acknowledged that confounders may have influenced the results, and that the use of SGLT2 inhibitors might only be correlated with better results instead of producing a causation effect.
This point was raised by Ayodele Odutayo, MD, DPhil, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. But despite that caution, Dr. Odutayo said that he found the study to be encouraging overall and broadly in line with known benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in CKD.
“The findings are reassuring that the medications work even in people who’ve already had some kidney injury beforehand,” but who are not yet diagnosed with CKD, Dr. Odutayo said.
“There is vast underuse of these medications in people for whom they are indicated,” perhaps due to clinician concern that the drugs will cause side effects such as low blood pressure or loss of salt and fluid, Dr. Odutayo said. Though those concerns are valid, the benefits of these drugs exceed the risks for most patients with CKD.
Dr. Wu and Dr. Odutayo report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
‘Fake Xanax’ Tied to Seizures, Coma Is Resistant to Naloxone
Bromazolam, a street drug that has been detected with increasing frequency in the United States, has reportedly caused protracted seizures, myocardial injury, comas, and multiday intensive care stays in three individuals, new data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed.
The substance is one of at least a dozen designer benzodiazepines created in the lab but not approved for any therapeutic use. The Center for Forensic Science Research and Education (CFSRE) reported that bromazolam was first detected in 2016 in recreational drugs in Europe and subsequently appeared in the United States.
It is sold under names such as “XLI-268,” “Xanax,” “Fake Xanax,” and “Dope.” Bromazolam may be sold in tablet or powder form, or sometimes as gummies, and is often taken with fentanyl by users.
The CDC report, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), described three cases of “previously healthy young adults,” two 25-year-old men and a 20-year-old woman, who took tablets believing it was alprazolam, when it was actually bromazolam and were found unresponsive.
They could not be revived with naloxone and continued to be unresponsive upon arrival at the emergency department. One of the men was hypertensive (152/100 mmHg), tachycardic (heart rate of 124 beats per minute), and hyperthermic (101.7 °F [38.7 °C]) and experienced multiple generalized seizures. He was intubated and admitted to intensive care.
The other man also had an elevated temperature (100.4 °F) and was intubated and admitted to the ICU because of unresponsiveness and multiple generalized seizures.
The woman was also intubated and nonresponsive with focal seizures. All three had elevated troponin levels and had urine tests positive for benzodiazepines.
The first man was intubated for 5 days and discharged after 11 days, while the second man was discharged on the fourth day with mild hearing difficulty.
The woman progressed to status epilepticus despite administration of multiple antiepileptic medications and was in a persistent coma. She was transferred to a second hospital after 11 days and was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Toxicology testing by the Drug Enforcement Administration confirmed the presence of bromazolam (range = 31.1-207 ng/mL), without the presence of fentanyl or any other opioid.
The CDC said that “the constellation of findings reported should prompt close involvement with public health officials and regional poison centers, given the more severe findings in these reported cases compared with those expected from routine benzodiazepine overdoses.” In addition, it noted that clinicians and first responders should “consider bromazolam in cases of patients requiring treatment for seizures, myocardial injury, or hyperthermia after illicit drug use.”
Surging Supply, Increased Warnings
In 2022, the CDC warned that the drug was surging in the United States, noting that as of mid-2022, bromazolam was identified in more than 250 toxicology cases submitted to NMS Labs, and that it had been identified in more than 190 toxicology samples tested at CFSRE.
In early 2021, only 1% of samples were positive for bromazolam. By mid-2022, 13% of samples were positive for bromazolam, and 75% of the bromazolam samples were positive for fentanyl.
The combination is sold on the street as benzo-dope.
Health authorities across the globe have been warning about the dangers of designer benzodiazepines, and bromazolam in particular. They’ve noted that the overdose reversal agent naloxone does not combat the effects of a benzodiazepine overdose.
In December 2022, the Canadian province of New Brunswick said that bromazolam had been detected in nine sudden death investigations, and that fentanyl was detected in some of those cases. The provincial government of the Northwest Territories warned in May 2023 that bromazolam had been detected in the region’s drug supply and cautioned against combining it with opioids.
The Indiana Department of Health notified the public, first responders, law enforcement, and clinicians in August 2023 that the drug was increasingly being detected in the state. In the first half of the year, 35 people who had overdosed in Indiana tested positive for bromazolam. The state did not test for the presence of bromazolam before 2023.
According to the MMWR, the law enforcement seizures in the United States of bromazolam increased from no more than three per year during 2016-2018 to 2142 in 2022 and 2913 in 2023.
Illinois has been an area of increased use. Bromazolam-involved deaths increased from 10 in 2021 to 51 in 2022, the CDC researchers reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bromazolam, a street drug that has been detected with increasing frequency in the United States, has reportedly caused protracted seizures, myocardial injury, comas, and multiday intensive care stays in three individuals, new data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed.
The substance is one of at least a dozen designer benzodiazepines created in the lab but not approved for any therapeutic use. The Center for Forensic Science Research and Education (CFSRE) reported that bromazolam was first detected in 2016 in recreational drugs in Europe and subsequently appeared in the United States.
It is sold under names such as “XLI-268,” “Xanax,” “Fake Xanax,” and “Dope.” Bromazolam may be sold in tablet or powder form, or sometimes as gummies, and is often taken with fentanyl by users.
The CDC report, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), described three cases of “previously healthy young adults,” two 25-year-old men and a 20-year-old woman, who took tablets believing it was alprazolam, when it was actually bromazolam and were found unresponsive.
They could not be revived with naloxone and continued to be unresponsive upon arrival at the emergency department. One of the men was hypertensive (152/100 mmHg), tachycardic (heart rate of 124 beats per minute), and hyperthermic (101.7 °F [38.7 °C]) and experienced multiple generalized seizures. He was intubated and admitted to intensive care.
The other man also had an elevated temperature (100.4 °F) and was intubated and admitted to the ICU because of unresponsiveness and multiple generalized seizures.
The woman was also intubated and nonresponsive with focal seizures. All three had elevated troponin levels and had urine tests positive for benzodiazepines.
The first man was intubated for 5 days and discharged after 11 days, while the second man was discharged on the fourth day with mild hearing difficulty.
The woman progressed to status epilepticus despite administration of multiple antiepileptic medications and was in a persistent coma. She was transferred to a second hospital after 11 days and was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Toxicology testing by the Drug Enforcement Administration confirmed the presence of bromazolam (range = 31.1-207 ng/mL), without the presence of fentanyl or any other opioid.
The CDC said that “the constellation of findings reported should prompt close involvement with public health officials and regional poison centers, given the more severe findings in these reported cases compared with those expected from routine benzodiazepine overdoses.” In addition, it noted that clinicians and first responders should “consider bromazolam in cases of patients requiring treatment for seizures, myocardial injury, or hyperthermia after illicit drug use.”
Surging Supply, Increased Warnings
In 2022, the CDC warned that the drug was surging in the United States, noting that as of mid-2022, bromazolam was identified in more than 250 toxicology cases submitted to NMS Labs, and that it had been identified in more than 190 toxicology samples tested at CFSRE.
In early 2021, only 1% of samples were positive for bromazolam. By mid-2022, 13% of samples were positive for bromazolam, and 75% of the bromazolam samples were positive for fentanyl.
The combination is sold on the street as benzo-dope.
Health authorities across the globe have been warning about the dangers of designer benzodiazepines, and bromazolam in particular. They’ve noted that the overdose reversal agent naloxone does not combat the effects of a benzodiazepine overdose.
In December 2022, the Canadian province of New Brunswick said that bromazolam had been detected in nine sudden death investigations, and that fentanyl was detected in some of those cases. The provincial government of the Northwest Territories warned in May 2023 that bromazolam had been detected in the region’s drug supply and cautioned against combining it with opioids.
The Indiana Department of Health notified the public, first responders, law enforcement, and clinicians in August 2023 that the drug was increasingly being detected in the state. In the first half of the year, 35 people who had overdosed in Indiana tested positive for bromazolam. The state did not test for the presence of bromazolam before 2023.
According to the MMWR, the law enforcement seizures in the United States of bromazolam increased from no more than three per year during 2016-2018 to 2142 in 2022 and 2913 in 2023.
Illinois has been an area of increased use. Bromazolam-involved deaths increased from 10 in 2021 to 51 in 2022, the CDC researchers reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bromazolam, a street drug that has been detected with increasing frequency in the United States, has reportedly caused protracted seizures, myocardial injury, comas, and multiday intensive care stays in three individuals, new data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed.
The substance is one of at least a dozen designer benzodiazepines created in the lab but not approved for any therapeutic use. The Center for Forensic Science Research and Education (CFSRE) reported that bromazolam was first detected in 2016 in recreational drugs in Europe and subsequently appeared in the United States.
It is sold under names such as “XLI-268,” “Xanax,” “Fake Xanax,” and “Dope.” Bromazolam may be sold in tablet or powder form, or sometimes as gummies, and is often taken with fentanyl by users.
The CDC report, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), described three cases of “previously healthy young adults,” two 25-year-old men and a 20-year-old woman, who took tablets believing it was alprazolam, when it was actually bromazolam and were found unresponsive.
They could not be revived with naloxone and continued to be unresponsive upon arrival at the emergency department. One of the men was hypertensive (152/100 mmHg), tachycardic (heart rate of 124 beats per minute), and hyperthermic (101.7 °F [38.7 °C]) and experienced multiple generalized seizures. He was intubated and admitted to intensive care.
The other man also had an elevated temperature (100.4 °F) and was intubated and admitted to the ICU because of unresponsiveness and multiple generalized seizures.
The woman was also intubated and nonresponsive with focal seizures. All three had elevated troponin levels and had urine tests positive for benzodiazepines.
The first man was intubated for 5 days and discharged after 11 days, while the second man was discharged on the fourth day with mild hearing difficulty.
The woman progressed to status epilepticus despite administration of multiple antiepileptic medications and was in a persistent coma. She was transferred to a second hospital after 11 days and was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Toxicology testing by the Drug Enforcement Administration confirmed the presence of bromazolam (range = 31.1-207 ng/mL), without the presence of fentanyl or any other opioid.
The CDC said that “the constellation of findings reported should prompt close involvement with public health officials and regional poison centers, given the more severe findings in these reported cases compared with those expected from routine benzodiazepine overdoses.” In addition, it noted that clinicians and first responders should “consider bromazolam in cases of patients requiring treatment for seizures, myocardial injury, or hyperthermia after illicit drug use.”
Surging Supply, Increased Warnings
In 2022, the CDC warned that the drug was surging in the United States, noting that as of mid-2022, bromazolam was identified in more than 250 toxicology cases submitted to NMS Labs, and that it had been identified in more than 190 toxicology samples tested at CFSRE.
In early 2021, only 1% of samples were positive for bromazolam. By mid-2022, 13% of samples were positive for bromazolam, and 75% of the bromazolam samples were positive for fentanyl.
The combination is sold on the street as benzo-dope.
Health authorities across the globe have been warning about the dangers of designer benzodiazepines, and bromazolam in particular. They’ve noted that the overdose reversal agent naloxone does not combat the effects of a benzodiazepine overdose.
In December 2022, the Canadian province of New Brunswick said that bromazolam had been detected in nine sudden death investigations, and that fentanyl was detected in some of those cases. The provincial government of the Northwest Territories warned in May 2023 that bromazolam had been detected in the region’s drug supply and cautioned against combining it with opioids.
The Indiana Department of Health notified the public, first responders, law enforcement, and clinicians in August 2023 that the drug was increasingly being detected in the state. In the first half of the year, 35 people who had overdosed in Indiana tested positive for bromazolam. The state did not test for the presence of bromazolam before 2023.
According to the MMWR, the law enforcement seizures in the United States of bromazolam increased from no more than three per year during 2016-2018 to 2142 in 2022 and 2913 in 2023.
Illinois has been an area of increased use. Bromazolam-involved deaths increased from 10 in 2021 to 51 in 2022, the CDC researchers reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
African Psychedelic Tied to ‘Remarkable’ Improvement in TBI-Related Psych Symptoms, Functional Disability
The plant-based psychoactive compound ibogaine, combined with magnesium to protect the heart, is linked to improvement in severe psychiatric symptoms including depression, anxiety, and functioning in veterans with traumatic brain injury (TBI), early results from a small study showed.
“The most unique findings we observed are the improvements in disability and cognition. At the start of the study, participants had mild to moderate levels of disability. However, a month after treatment, their average disability rating indicated no disability and cognitive testing indicated improvements in concentration and memory,” study investigator Nolan Williams, MD, Stanford University, Stanford, California, told this news organization.
Also noteworthy were improvements across all participants in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety — effects that lasted for at least 1 month after treatment, he said.
“These results are remarkable and exceeded our expectations. There is no drug today that can broadly relieve functional and neuropsychiatric symptoms of TBI as we observed with ibogaine,” Dr. Williams added.
The study was published online on January 5, 2024, in Nature Medicine.
‘The Storm Lifted’
Ibogaine is derived from the root bark of the Tabernanthe iboga shrub and related plants and is traditionally used in African spiritual and healing ceremonies.
It is known to interact with multiple neurotransmitter systems and has been studied primarily as a treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs). Some studies of ibogaine for SUDs have also noted improvements in self-reported measures of mood.
In the United States, ibogaine is classified as a Schedule I substance, but legal ibogaine treatments are offered in clinics in Canada and Mexico.
Dr. Williams noted that a handful of US veterans who went to Mexico for ibogaine treatment anecdotally reported improvements a variety of aspects of their lives.
The goal of the current study was to characterize those improvements with structured clinical and neurobiological assessments.
Participants included 30 US Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) with predominantly mild TBI from combat/blast exposures and psychiatric symptoms and functional limitations. All of them had independently scheduled themselves for treatment with magnesium and ibogaine at a clinic in Mexico.
Before treatment, the veterans had an average disability rating of 30.2 on the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale 2.0, equivalent to mild to moderate disability. One month after ibogaine treatment, that rating improved to 5.1, indicating no disability, the researchers reported.
One month after treatment, participants also experienced average reductions of 88% in PTSD symptoms, 87% in depression symptoms, and 81% in anxiety symptoms relative to before treatment.
Neuropsychological testing revealed improved concentration, information processing, memory, and impulsivity. There was also a substantial reduction in suicidal ideation.
“Before the treatment, I was living life in a blizzard with zero visibility and a cold, hopeless, listless feeling. After ibogaine, the storm lifted,” Sean, a 51-year-old veteran from Arizona with six combat deployments who participated in the study, said in a Stanford news release.
There were no serious side effects of ibogaine, and no instances of heart problems associated with the treatment.
Although the study findings are promising, additional research is needed to address some clear limitations, the researchers noted.
“Most importantly, the study was not controlled and so the relative contribution of any therapeutic benefits from non-ibogaine elements of the experience, such as complementary treatments, group activities, coaching, international travel, expectancy, or other nonspecific effects, cannot be determined,” they wrote.
In addition, follow-up was limited to 1 month, and longer-term data are needed to determine durability of the effects.
“We plan to study this compound further, as well as launch future studies to continue to understand how this drug can be used to treat TBI and possibly as a broader neuro-rehab drug. We will work towards a US-based set of trials to confirm efficacy with a multisite design,” said Dr. Williams.
Promising, but Very Preliminary
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ramon Diaz-Arrastia, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director of the Clinical TBI Research Center, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said the results are “promising, but very preliminary.”
Dr. Diaz-Arrastia noted that this was an open-label, nonrandomized study, early phase 2a study with “highly subjective outcome measures and the likelihood of it being a placebo effect is very high.”
Nonetheless, “there is a lot of interest in these ‘psychedelic’ alkaloids, and ibogaine is a good candidate for further study,” Dr. Diaz-Arrastia said.
Also providing perspective, Alan K. Davis, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State University, Columbus, said “mounting evidence supports the importance of studying this treatment in rigorous clinical trials in the US.”
Dr. Davis and colleagues recently observed that treatment with two naturally occurring psychedelics — ibogaine and 5-MeO-DMT — was associated with reduced depressive and anxiety symptoms in trauma-exposed SOVs, as previously reported by this news organization.
This new study “basically is a replication of what we’ve already published on this topic, and we published data from much larger samples and longer follow up,” said Dr. Davis.
Dr. Davis said it’s “important for the public to know that there are important and serious risks associated with ibogaine therapy, including the possibility of cardiac problems and death. These risks are compounded when people are in clinics or settings where proper screening and medical oversight are not completed.”
“Furthermore, the long-term effectiveness of this treatment is not well established. It may only help in the short term for most people. For many, ongoing clinical aftercare therapy and other forms of treatment may be needed,” Dr. Davis noted.
The study was independently funded by philanthropic gifts from Steve and Genevieve Jurvetson and another anonymous donor. Williams is an inventor on a patent application related to the safety of MISTIC administration as described in the paper and a separate patent related to the use of ibogaine to treat disorders associated with brain aging. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Dr. Diaz-Arrastia has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The plant-based psychoactive compound ibogaine, combined with magnesium to protect the heart, is linked to improvement in severe psychiatric symptoms including depression, anxiety, and functioning in veterans with traumatic brain injury (TBI), early results from a small study showed.
“The most unique findings we observed are the improvements in disability and cognition. At the start of the study, participants had mild to moderate levels of disability. However, a month after treatment, their average disability rating indicated no disability and cognitive testing indicated improvements in concentration and memory,” study investigator Nolan Williams, MD, Stanford University, Stanford, California, told this news organization.
Also noteworthy were improvements across all participants in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety — effects that lasted for at least 1 month after treatment, he said.
“These results are remarkable and exceeded our expectations. There is no drug today that can broadly relieve functional and neuropsychiatric symptoms of TBI as we observed with ibogaine,” Dr. Williams added.
The study was published online on January 5, 2024, in Nature Medicine.
‘The Storm Lifted’
Ibogaine is derived from the root bark of the Tabernanthe iboga shrub and related plants and is traditionally used in African spiritual and healing ceremonies.
It is known to interact with multiple neurotransmitter systems and has been studied primarily as a treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs). Some studies of ibogaine for SUDs have also noted improvements in self-reported measures of mood.
In the United States, ibogaine is classified as a Schedule I substance, but legal ibogaine treatments are offered in clinics in Canada and Mexico.
Dr. Williams noted that a handful of US veterans who went to Mexico for ibogaine treatment anecdotally reported improvements a variety of aspects of their lives.
The goal of the current study was to characterize those improvements with structured clinical and neurobiological assessments.
Participants included 30 US Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) with predominantly mild TBI from combat/blast exposures and psychiatric symptoms and functional limitations. All of them had independently scheduled themselves for treatment with magnesium and ibogaine at a clinic in Mexico.
Before treatment, the veterans had an average disability rating of 30.2 on the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale 2.0, equivalent to mild to moderate disability. One month after ibogaine treatment, that rating improved to 5.1, indicating no disability, the researchers reported.
One month after treatment, participants also experienced average reductions of 88% in PTSD symptoms, 87% in depression symptoms, and 81% in anxiety symptoms relative to before treatment.
Neuropsychological testing revealed improved concentration, information processing, memory, and impulsivity. There was also a substantial reduction in suicidal ideation.
“Before the treatment, I was living life in a blizzard with zero visibility and a cold, hopeless, listless feeling. After ibogaine, the storm lifted,” Sean, a 51-year-old veteran from Arizona with six combat deployments who participated in the study, said in a Stanford news release.
There were no serious side effects of ibogaine, and no instances of heart problems associated with the treatment.
Although the study findings are promising, additional research is needed to address some clear limitations, the researchers noted.
“Most importantly, the study was not controlled and so the relative contribution of any therapeutic benefits from non-ibogaine elements of the experience, such as complementary treatments, group activities, coaching, international travel, expectancy, or other nonspecific effects, cannot be determined,” they wrote.
In addition, follow-up was limited to 1 month, and longer-term data are needed to determine durability of the effects.
“We plan to study this compound further, as well as launch future studies to continue to understand how this drug can be used to treat TBI and possibly as a broader neuro-rehab drug. We will work towards a US-based set of trials to confirm efficacy with a multisite design,” said Dr. Williams.
Promising, but Very Preliminary
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ramon Diaz-Arrastia, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director of the Clinical TBI Research Center, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said the results are “promising, but very preliminary.”
Dr. Diaz-Arrastia noted that this was an open-label, nonrandomized study, early phase 2a study with “highly subjective outcome measures and the likelihood of it being a placebo effect is very high.”
Nonetheless, “there is a lot of interest in these ‘psychedelic’ alkaloids, and ibogaine is a good candidate for further study,” Dr. Diaz-Arrastia said.
Also providing perspective, Alan K. Davis, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State University, Columbus, said “mounting evidence supports the importance of studying this treatment in rigorous clinical trials in the US.”
Dr. Davis and colleagues recently observed that treatment with two naturally occurring psychedelics — ibogaine and 5-MeO-DMT — was associated with reduced depressive and anxiety symptoms in trauma-exposed SOVs, as previously reported by this news organization.
This new study “basically is a replication of what we’ve already published on this topic, and we published data from much larger samples and longer follow up,” said Dr. Davis.
Dr. Davis said it’s “important for the public to know that there are important and serious risks associated with ibogaine therapy, including the possibility of cardiac problems and death. These risks are compounded when people are in clinics or settings where proper screening and medical oversight are not completed.”
“Furthermore, the long-term effectiveness of this treatment is not well established. It may only help in the short term for most people. For many, ongoing clinical aftercare therapy and other forms of treatment may be needed,” Dr. Davis noted.
The study was independently funded by philanthropic gifts from Steve and Genevieve Jurvetson and another anonymous donor. Williams is an inventor on a patent application related to the safety of MISTIC administration as described in the paper and a separate patent related to the use of ibogaine to treat disorders associated with brain aging. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Dr. Diaz-Arrastia has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The plant-based psychoactive compound ibogaine, combined with magnesium to protect the heart, is linked to improvement in severe psychiatric symptoms including depression, anxiety, and functioning in veterans with traumatic brain injury (TBI), early results from a small study showed.
“The most unique findings we observed are the improvements in disability and cognition. At the start of the study, participants had mild to moderate levels of disability. However, a month after treatment, their average disability rating indicated no disability and cognitive testing indicated improvements in concentration and memory,” study investigator Nolan Williams, MD, Stanford University, Stanford, California, told this news organization.
Also noteworthy were improvements across all participants in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety — effects that lasted for at least 1 month after treatment, he said.
“These results are remarkable and exceeded our expectations. There is no drug today that can broadly relieve functional and neuropsychiatric symptoms of TBI as we observed with ibogaine,” Dr. Williams added.
The study was published online on January 5, 2024, in Nature Medicine.
‘The Storm Lifted’
Ibogaine is derived from the root bark of the Tabernanthe iboga shrub and related plants and is traditionally used in African spiritual and healing ceremonies.
It is known to interact with multiple neurotransmitter systems and has been studied primarily as a treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs). Some studies of ibogaine for SUDs have also noted improvements in self-reported measures of mood.
In the United States, ibogaine is classified as a Schedule I substance, but legal ibogaine treatments are offered in clinics in Canada and Mexico.
Dr. Williams noted that a handful of US veterans who went to Mexico for ibogaine treatment anecdotally reported improvements a variety of aspects of their lives.
The goal of the current study was to characterize those improvements with structured clinical and neurobiological assessments.
Participants included 30 US Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) with predominantly mild TBI from combat/blast exposures and psychiatric symptoms and functional limitations. All of them had independently scheduled themselves for treatment with magnesium and ibogaine at a clinic in Mexico.
Before treatment, the veterans had an average disability rating of 30.2 on the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale 2.0, equivalent to mild to moderate disability. One month after ibogaine treatment, that rating improved to 5.1, indicating no disability, the researchers reported.
One month after treatment, participants also experienced average reductions of 88% in PTSD symptoms, 87% in depression symptoms, and 81% in anxiety symptoms relative to before treatment.
Neuropsychological testing revealed improved concentration, information processing, memory, and impulsivity. There was also a substantial reduction in suicidal ideation.
“Before the treatment, I was living life in a blizzard with zero visibility and a cold, hopeless, listless feeling. After ibogaine, the storm lifted,” Sean, a 51-year-old veteran from Arizona with six combat deployments who participated in the study, said in a Stanford news release.
There were no serious side effects of ibogaine, and no instances of heart problems associated with the treatment.
Although the study findings are promising, additional research is needed to address some clear limitations, the researchers noted.
“Most importantly, the study was not controlled and so the relative contribution of any therapeutic benefits from non-ibogaine elements of the experience, such as complementary treatments, group activities, coaching, international travel, expectancy, or other nonspecific effects, cannot be determined,” they wrote.
In addition, follow-up was limited to 1 month, and longer-term data are needed to determine durability of the effects.
“We plan to study this compound further, as well as launch future studies to continue to understand how this drug can be used to treat TBI and possibly as a broader neuro-rehab drug. We will work towards a US-based set of trials to confirm efficacy with a multisite design,” said Dr. Williams.
Promising, but Very Preliminary
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ramon Diaz-Arrastia, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director of the Clinical TBI Research Center, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said the results are “promising, but very preliminary.”
Dr. Diaz-Arrastia noted that this was an open-label, nonrandomized study, early phase 2a study with “highly subjective outcome measures and the likelihood of it being a placebo effect is very high.”
Nonetheless, “there is a lot of interest in these ‘psychedelic’ alkaloids, and ibogaine is a good candidate for further study,” Dr. Diaz-Arrastia said.
Also providing perspective, Alan K. Davis, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State University, Columbus, said “mounting evidence supports the importance of studying this treatment in rigorous clinical trials in the US.”
Dr. Davis and colleagues recently observed that treatment with two naturally occurring psychedelics — ibogaine and 5-MeO-DMT — was associated with reduced depressive and anxiety symptoms in trauma-exposed SOVs, as previously reported by this news organization.
This new study “basically is a replication of what we’ve already published on this topic, and we published data from much larger samples and longer follow up,” said Dr. Davis.
Dr. Davis said it’s “important for the public to know that there are important and serious risks associated with ibogaine therapy, including the possibility of cardiac problems and death. These risks are compounded when people are in clinics or settings where proper screening and medical oversight are not completed.”
“Furthermore, the long-term effectiveness of this treatment is not well established. It may only help in the short term for most people. For many, ongoing clinical aftercare therapy and other forms of treatment may be needed,” Dr. Davis noted.
The study was independently funded by philanthropic gifts from Steve and Genevieve Jurvetson and another anonymous donor. Williams is an inventor on a patent application related to the safety of MISTIC administration as described in the paper and a separate patent related to the use of ibogaine to treat disorders associated with brain aging. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Dr. Diaz-Arrastia has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
FDA Gives Nod to Berdazimer Gel for Molluscum Contagiosum
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.