User login
Migraine comorbidities rise with increased headache days
PHILADELPHIA – The more days per month a person reported experiencing migraine headaches the greater their prevalence of various comorbidities associated with migraine headaches, including insomnia, depression, anxiety, and gastric ulcer disease, according to results from a survey of more than 92,000 U.S. residents.
“Increasing monthly headache day [MHD] frequency was associated with an increased risk of other health conditions in people with migraine,” Richard B. Lipton, MD, and his associates reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. “The findings may be due to direct causality, reverse causality, shared risk factors, or detection bias.”
Additional analysis of the association with gastric ulcer disease (GUD) showed that it also linked with the number of days per month when a person with migraine used an NSAID. Migraineurs who self-reported having GUD averaged 10.5 days a month using an NSAID, compared with an average NSAID usage of just over 6 days a month among migraineurs without GUD, Dr. Lipton, a professor and vice-chair of neurology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, reported in a separate poster at the meeting.
The Migraine in America Symptoms and Treatment (MAST) study enrolled more than 90,000 U.S. residents starting in 2016. Using a validated diagnostic screening tool, the MAST researchers identified 15,133 of these people as having at least one day with a migraine headache during the 3 months prior to the survey and 77,453 who reported no migraine history (Headache. 2018 Oct;58[9]: 1408-26). The people with migraine averaged 43 years old, compared with an average of 52 years for those without migraine; 73% of the migraineurs were women.
Analysis of the prevalence of various self-reported, physician-diagnosed comorbidities showed a strong correlation between the relative odds of having a comorbidity and the self-reported number of MHDs. For example, the odds ratio for having insomnia, compared with the people without migraine, was nearly 200% among people reporting 1-4 MHDs, more than 300% higher among those reporting 5-9 MHDs, 500% higher with MHDs of 10-14, and nearly 700% higher among people reporting 20 or more MHDs. The researchers saw roughly similar patterns of rising comorbidity prevalence with higher numbers of MHDs for depression, anxiety, and GUD. The prevalence of a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack also increased with increasing numbers of MHDs but less steeply than for the other comorbidities. And while the prevalence of peripheral artery disease and epilepsy was consistently more than 100% greater among the migraineurs, compared with those with no recent migraine history, the prevalence of each of these two comorbidities showed no clear pattern of increasing prevalence as MHDs increased.
The analysis looked specifically at the relationship between GUD and NSAID use among people reporting migraine. Overall, the migraineurs had a greater than 200% increased prevalence of GUD than those without migraine. The odds ratio for GUD among migraineurs with 1-4 MHDs was 2.6, compared with those without migraine, and the odds ratio steadily rose with increasing MHDs to a peak of 490% higher among those who averaged 21 or more MHDs.
This link between the number of MHDs and prevalence of GUD may have some relationship to oral NSAID use, as overall NSAID use was higher among people with recent migraines than in those without migraines. However, the number of days per month of oral NSAID use appeared to plateau at an average of about 19 days once people reported having at least 10 MHDs, the researchers said. Even when people reported having more than twice as many MHDs their NSAID use remained at an average of about 19 days per month.
MAST was sponsored by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories. Dr. Lipton had been a consultant to Dr. Reddy’s and to several other companies.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, P54.
PHILADELPHIA – The more days per month a person reported experiencing migraine headaches the greater their prevalence of various comorbidities associated with migraine headaches, including insomnia, depression, anxiety, and gastric ulcer disease, according to results from a survey of more than 92,000 U.S. residents.
“Increasing monthly headache day [MHD] frequency was associated with an increased risk of other health conditions in people with migraine,” Richard B. Lipton, MD, and his associates reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. “The findings may be due to direct causality, reverse causality, shared risk factors, or detection bias.”
Additional analysis of the association with gastric ulcer disease (GUD) showed that it also linked with the number of days per month when a person with migraine used an NSAID. Migraineurs who self-reported having GUD averaged 10.5 days a month using an NSAID, compared with an average NSAID usage of just over 6 days a month among migraineurs without GUD, Dr. Lipton, a professor and vice-chair of neurology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, reported in a separate poster at the meeting.
The Migraine in America Symptoms and Treatment (MAST) study enrolled more than 90,000 U.S. residents starting in 2016. Using a validated diagnostic screening tool, the MAST researchers identified 15,133 of these people as having at least one day with a migraine headache during the 3 months prior to the survey and 77,453 who reported no migraine history (Headache. 2018 Oct;58[9]: 1408-26). The people with migraine averaged 43 years old, compared with an average of 52 years for those without migraine; 73% of the migraineurs were women.
Analysis of the prevalence of various self-reported, physician-diagnosed comorbidities showed a strong correlation between the relative odds of having a comorbidity and the self-reported number of MHDs. For example, the odds ratio for having insomnia, compared with the people without migraine, was nearly 200% among people reporting 1-4 MHDs, more than 300% higher among those reporting 5-9 MHDs, 500% higher with MHDs of 10-14, and nearly 700% higher among people reporting 20 or more MHDs. The researchers saw roughly similar patterns of rising comorbidity prevalence with higher numbers of MHDs for depression, anxiety, and GUD. The prevalence of a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack also increased with increasing numbers of MHDs but less steeply than for the other comorbidities. And while the prevalence of peripheral artery disease and epilepsy was consistently more than 100% greater among the migraineurs, compared with those with no recent migraine history, the prevalence of each of these two comorbidities showed no clear pattern of increasing prevalence as MHDs increased.
The analysis looked specifically at the relationship between GUD and NSAID use among people reporting migraine. Overall, the migraineurs had a greater than 200% increased prevalence of GUD than those without migraine. The odds ratio for GUD among migraineurs with 1-4 MHDs was 2.6, compared with those without migraine, and the odds ratio steadily rose with increasing MHDs to a peak of 490% higher among those who averaged 21 or more MHDs.
This link between the number of MHDs and prevalence of GUD may have some relationship to oral NSAID use, as overall NSAID use was higher among people with recent migraines than in those without migraines. However, the number of days per month of oral NSAID use appeared to plateau at an average of about 19 days once people reported having at least 10 MHDs, the researchers said. Even when people reported having more than twice as many MHDs their NSAID use remained at an average of about 19 days per month.
MAST was sponsored by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories. Dr. Lipton had been a consultant to Dr. Reddy’s and to several other companies.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, P54.
PHILADELPHIA – The more days per month a person reported experiencing migraine headaches the greater their prevalence of various comorbidities associated with migraine headaches, including insomnia, depression, anxiety, and gastric ulcer disease, according to results from a survey of more than 92,000 U.S. residents.
“Increasing monthly headache day [MHD] frequency was associated with an increased risk of other health conditions in people with migraine,” Richard B. Lipton, MD, and his associates reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. “The findings may be due to direct causality, reverse causality, shared risk factors, or detection bias.”
Additional analysis of the association with gastric ulcer disease (GUD) showed that it also linked with the number of days per month when a person with migraine used an NSAID. Migraineurs who self-reported having GUD averaged 10.5 days a month using an NSAID, compared with an average NSAID usage of just over 6 days a month among migraineurs without GUD, Dr. Lipton, a professor and vice-chair of neurology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, reported in a separate poster at the meeting.
The Migraine in America Symptoms and Treatment (MAST) study enrolled more than 90,000 U.S. residents starting in 2016. Using a validated diagnostic screening tool, the MAST researchers identified 15,133 of these people as having at least one day with a migraine headache during the 3 months prior to the survey and 77,453 who reported no migraine history (Headache. 2018 Oct;58[9]: 1408-26). The people with migraine averaged 43 years old, compared with an average of 52 years for those without migraine; 73% of the migraineurs were women.
Analysis of the prevalence of various self-reported, physician-diagnosed comorbidities showed a strong correlation between the relative odds of having a comorbidity and the self-reported number of MHDs. For example, the odds ratio for having insomnia, compared with the people without migraine, was nearly 200% among people reporting 1-4 MHDs, more than 300% higher among those reporting 5-9 MHDs, 500% higher with MHDs of 10-14, and nearly 700% higher among people reporting 20 or more MHDs. The researchers saw roughly similar patterns of rising comorbidity prevalence with higher numbers of MHDs for depression, anxiety, and GUD. The prevalence of a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack also increased with increasing numbers of MHDs but less steeply than for the other comorbidities. And while the prevalence of peripheral artery disease and epilepsy was consistently more than 100% greater among the migraineurs, compared with those with no recent migraine history, the prevalence of each of these two comorbidities showed no clear pattern of increasing prevalence as MHDs increased.
The analysis looked specifically at the relationship between GUD and NSAID use among people reporting migraine. Overall, the migraineurs had a greater than 200% increased prevalence of GUD than those without migraine. The odds ratio for GUD among migraineurs with 1-4 MHDs was 2.6, compared with those without migraine, and the odds ratio steadily rose with increasing MHDs to a peak of 490% higher among those who averaged 21 or more MHDs.
This link between the number of MHDs and prevalence of GUD may have some relationship to oral NSAID use, as overall NSAID use was higher among people with recent migraines than in those without migraines. However, the number of days per month of oral NSAID use appeared to plateau at an average of about 19 days once people reported having at least 10 MHDs, the researchers said. Even when people reported having more than twice as many MHDs their NSAID use remained at an average of about 19 days per month.
MAST was sponsored by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories. Dr. Lipton had been a consultant to Dr. Reddy’s and to several other companies.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, P54.
REPORTING FROM AHS 2019
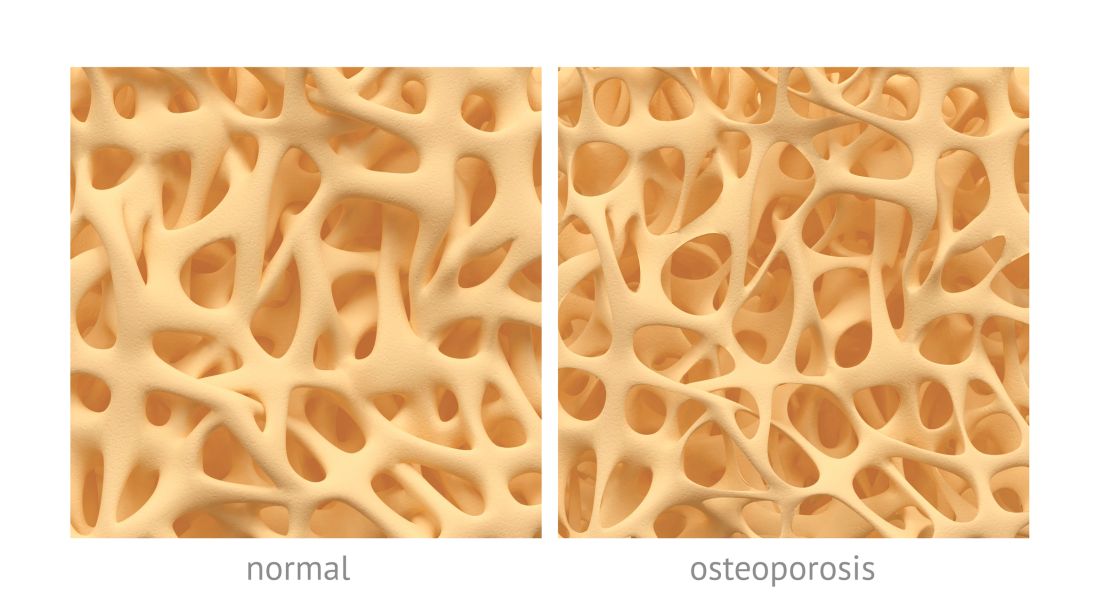
Osteoporosis, osteoarthritis risk high among cerebral palsy patients
compared with adults without the disorder, according to a study published in Bone.
Neil E. O’Connell, PhD, of Brunel University London, and colleagues assessed the risks of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases in a population-based cohort study that used data collected by the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink during 1987-2015. The study included 1,705 patients with CP and 5,115 patients matched for age, sex, and general practices; data on smoking status and alcohol consumption for many of the patients also were gathered.
After adjustment for smoking status, alcohol consumption, and mean yearly general practice visits, investigators found evidence of significantly increased risk for osteoarthritis (hazard ratio, 1.54; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-2.02; P = .002) and osteoporosis (HR, 6.19; 95% CI, 3.37-11.39; P less than .001); they did not see increased risk for inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.45-1.75; P = .731).
One limitation of the study is the risk for residual confounding given the investigators could not account for mobility status or physical activity. Other limitations include potential incompleteness of diagnostic code lists, how identification of cases is depending on quality of original recording in the database, and that data regarding smoking status and alcohol consumption were missing for a substantial proportion of patients.
“Despite previous studies identifying a high prevalence of joint pain and functional deterioration among people with CP, there is a dearth of literature on the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in this population,” they wrote. “Further research is required into effective management of these conditions in adults with CP.”
This study was supported by an interdisciplinary award from Brunel University London’s Research Catalyst Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: O’Connell NE et al. Bone. 2019 Aug;125:30-5.
compared with adults without the disorder, according to a study published in Bone.
Neil E. O’Connell, PhD, of Brunel University London, and colleagues assessed the risks of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases in a population-based cohort study that used data collected by the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink during 1987-2015. The study included 1,705 patients with CP and 5,115 patients matched for age, sex, and general practices; data on smoking status and alcohol consumption for many of the patients also were gathered.
After adjustment for smoking status, alcohol consumption, and mean yearly general practice visits, investigators found evidence of significantly increased risk for osteoarthritis (hazard ratio, 1.54; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-2.02; P = .002) and osteoporosis (HR, 6.19; 95% CI, 3.37-11.39; P less than .001); they did not see increased risk for inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.45-1.75; P = .731).
One limitation of the study is the risk for residual confounding given the investigators could not account for mobility status or physical activity. Other limitations include potential incompleteness of diagnostic code lists, how identification of cases is depending on quality of original recording in the database, and that data regarding smoking status and alcohol consumption were missing for a substantial proportion of patients.
“Despite previous studies identifying a high prevalence of joint pain and functional deterioration among people with CP, there is a dearth of literature on the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in this population,” they wrote. “Further research is required into effective management of these conditions in adults with CP.”
This study was supported by an interdisciplinary award from Brunel University London’s Research Catalyst Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: O’Connell NE et al. Bone. 2019 Aug;125:30-5.
compared with adults without the disorder, according to a study published in Bone.
Neil E. O’Connell, PhD, of Brunel University London, and colleagues assessed the risks of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases in a population-based cohort study that used data collected by the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink during 1987-2015. The study included 1,705 patients with CP and 5,115 patients matched for age, sex, and general practices; data on smoking status and alcohol consumption for many of the patients also were gathered.
After adjustment for smoking status, alcohol consumption, and mean yearly general practice visits, investigators found evidence of significantly increased risk for osteoarthritis (hazard ratio, 1.54; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-2.02; P = .002) and osteoporosis (HR, 6.19; 95% CI, 3.37-11.39; P less than .001); they did not see increased risk for inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.45-1.75; P = .731).
One limitation of the study is the risk for residual confounding given the investigators could not account for mobility status or physical activity. Other limitations include potential incompleteness of diagnostic code lists, how identification of cases is depending on quality of original recording in the database, and that data regarding smoking status and alcohol consumption were missing for a substantial proportion of patients.
“Despite previous studies identifying a high prevalence of joint pain and functional deterioration among people with CP, there is a dearth of literature on the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in this population,” they wrote. “Further research is required into effective management of these conditions in adults with CP.”
This study was supported by an interdisciplinary award from Brunel University London’s Research Catalyst Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: O’Connell NE et al. Bone. 2019 Aug;125:30-5.
FROM BONE
CDC: Look for early symptoms of acute flaccid myelitis, report suspected cases
the CDC said in a telebriefing.
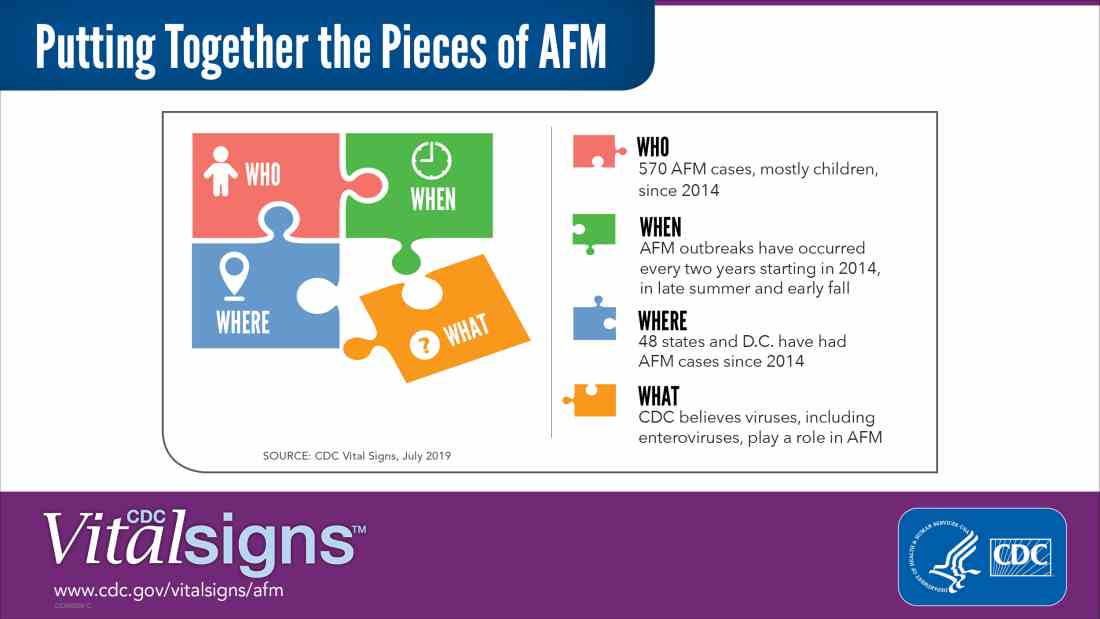
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
the CDC said in a telebriefing.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
the CDC said in a telebriefing.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
NEWS FROM THE FDA/CDC
Metformin linked to lower dementia risk in black patients
Black individuals who develop type 2 diabetes are more likely than their white counterparts to develop dementia. Now, findings from a new study point to a possible preventive strategy: Putting older patients on metformin when they are diagnosed could reduce their risk for dementia by as much as 40%, whereas sulfonylureas do not seem to have such an effect.
The researchers did not examine cause and effect, so their findings are not conclusive, and very few women were included in the study. Still, the authors said that their data showing a 29% lower risk of dementia associated with metformin use in black patients aged 65-74 years, and a 40% lower risk in those aged 50-64 years, suggested that “this inexpensive, widely available treatment could be broadly prescribed to substantially reduce the risk of dementia in younger [black] patients with [type 2 diabetes]” (Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62).
Previous findings have suggested that black patients with type 2 diabetes face a 10%-18% higher risk of dementia, compared with white patients (Diabetes Care. 2014; 37[4]:1009-15). Another study linked type 2 diabetes in middle-aged black patients to a 41% decrease in cognition per test results over 14 years. There was no such decrease in white patients (Neuroepidemiology. 2014;43[3-4]: 220-7).
For the new study, researchers led by Jeffrey F. Scherrer, PhD, of Saint Louis University tracked 73,761 patients aged 50 years or older from 2000-2001 (when they were free of dementia and not taking diabetes) to 2015. Among the patients, 86% were white and 14% were black. In the white and black groups, 97% and 95% were men, respectively, and 61% and 55% were obese, respectively.
All participants began metformin (76%) or sulfonylurea (24%) monotherapy after the baseline period. Guidelines recommend metformin as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, whereas sulfonylureas are considered second-line drugs that should be added to metformin.
After adjustment for confounders such as socioeconomic status and other medical conditions, the researchers found a significantly lower risk of dementia in black patients who took metformin, compared with those taking a sulfonylurea (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.6-0.89). There was no difference between the drugs among white patients (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.9-1.03, both P = .008)
The results were not statistically significant among age groups, but there were trends. In black patients, the dementia-lowering benefit was largest among those aged 50-64 years (HR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.45-0.81), followed by those aged 65-74 years (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.53-0.94), and there was no benefit among those aged at least 75 (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.73-1.85) all P = .055. There was a slight benefit among white patients in one of the age groups – 65-74 years (HR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.82-0.99; P = .315).
The authors suggested that the findings could have been the result of an effect of metformin to reduce vascular disease and chronic inflammation in black patients.
They also noted that further research is needed to identify the demographic and clinical subgroups in which metformin is most strongly associated with a reduction in the risk of dementia. In addition, they emphasized that clinical trials are needed to confirm the study findings.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. The authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Scherrer JF et al. Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62.
Black individuals who develop type 2 diabetes are more likely than their white counterparts to develop dementia. Now, findings from a new study point to a possible preventive strategy: Putting older patients on metformin when they are diagnosed could reduce their risk for dementia by as much as 40%, whereas sulfonylureas do not seem to have such an effect.
The researchers did not examine cause and effect, so their findings are not conclusive, and very few women were included in the study. Still, the authors said that their data showing a 29% lower risk of dementia associated with metformin use in black patients aged 65-74 years, and a 40% lower risk in those aged 50-64 years, suggested that “this inexpensive, widely available treatment could be broadly prescribed to substantially reduce the risk of dementia in younger [black] patients with [type 2 diabetes]” (Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62).
Previous findings have suggested that black patients with type 2 diabetes face a 10%-18% higher risk of dementia, compared with white patients (Diabetes Care. 2014; 37[4]:1009-15). Another study linked type 2 diabetes in middle-aged black patients to a 41% decrease in cognition per test results over 14 years. There was no such decrease in white patients (Neuroepidemiology. 2014;43[3-4]: 220-7).
For the new study, researchers led by Jeffrey F. Scherrer, PhD, of Saint Louis University tracked 73,761 patients aged 50 years or older from 2000-2001 (when they were free of dementia and not taking diabetes) to 2015. Among the patients, 86% were white and 14% were black. In the white and black groups, 97% and 95% were men, respectively, and 61% and 55% were obese, respectively.
All participants began metformin (76%) or sulfonylurea (24%) monotherapy after the baseline period. Guidelines recommend metformin as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, whereas sulfonylureas are considered second-line drugs that should be added to metformin.
After adjustment for confounders such as socioeconomic status and other medical conditions, the researchers found a significantly lower risk of dementia in black patients who took metformin, compared with those taking a sulfonylurea (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.6-0.89). There was no difference between the drugs among white patients (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.9-1.03, both P = .008)
The results were not statistically significant among age groups, but there were trends. In black patients, the dementia-lowering benefit was largest among those aged 50-64 years (HR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.45-0.81), followed by those aged 65-74 years (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.53-0.94), and there was no benefit among those aged at least 75 (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.73-1.85) all P = .055. There was a slight benefit among white patients in one of the age groups – 65-74 years (HR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.82-0.99; P = .315).
The authors suggested that the findings could have been the result of an effect of metformin to reduce vascular disease and chronic inflammation in black patients.
They also noted that further research is needed to identify the demographic and clinical subgroups in which metformin is most strongly associated with a reduction in the risk of dementia. In addition, they emphasized that clinical trials are needed to confirm the study findings.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. The authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Scherrer JF et al. Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62.
Black individuals who develop type 2 diabetes are more likely than their white counterparts to develop dementia. Now, findings from a new study point to a possible preventive strategy: Putting older patients on metformin when they are diagnosed could reduce their risk for dementia by as much as 40%, whereas sulfonylureas do not seem to have such an effect.
The researchers did not examine cause and effect, so their findings are not conclusive, and very few women were included in the study. Still, the authors said that their data showing a 29% lower risk of dementia associated with metformin use in black patients aged 65-74 years, and a 40% lower risk in those aged 50-64 years, suggested that “this inexpensive, widely available treatment could be broadly prescribed to substantially reduce the risk of dementia in younger [black] patients with [type 2 diabetes]” (Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62).
Previous findings have suggested that black patients with type 2 diabetes face a 10%-18% higher risk of dementia, compared with white patients (Diabetes Care. 2014; 37[4]:1009-15). Another study linked type 2 diabetes in middle-aged black patients to a 41% decrease in cognition per test results over 14 years. There was no such decrease in white patients (Neuroepidemiology. 2014;43[3-4]: 220-7).
For the new study, researchers led by Jeffrey F. Scherrer, PhD, of Saint Louis University tracked 73,761 patients aged 50 years or older from 2000-2001 (when they were free of dementia and not taking diabetes) to 2015. Among the patients, 86% were white and 14% were black. In the white and black groups, 97% and 95% were men, respectively, and 61% and 55% were obese, respectively.
All participants began metformin (76%) or sulfonylurea (24%) monotherapy after the baseline period. Guidelines recommend metformin as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, whereas sulfonylureas are considered second-line drugs that should be added to metformin.
After adjustment for confounders such as socioeconomic status and other medical conditions, the researchers found a significantly lower risk of dementia in black patients who took metformin, compared with those taking a sulfonylurea (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.6-0.89). There was no difference between the drugs among white patients (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.9-1.03, both P = .008)
The results were not statistically significant among age groups, but there were trends. In black patients, the dementia-lowering benefit was largest among those aged 50-64 years (HR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.45-0.81), followed by those aged 65-74 years (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.53-0.94), and there was no benefit among those aged at least 75 (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.73-1.85) all P = .055. There was a slight benefit among white patients in one of the age groups – 65-74 years (HR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.82-0.99; P = .315).
The authors suggested that the findings could have been the result of an effect of metformin to reduce vascular disease and chronic inflammation in black patients.
They also noted that further research is needed to identify the demographic and clinical subgroups in which metformin is most strongly associated with a reduction in the risk of dementia. In addition, they emphasized that clinical trials are needed to confirm the study findings.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. The authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Scherrer JF et al. Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62.
FROM ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Metformin monotherapy, compared with sulfonylurea monotherapy, was linked to a significantly lower risk for dementia in black patients (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.6-0.89), but not in white patients (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.9-1.03; P = .008).
Study details: Retrospective analysis of 73,761 patients aged 50 years or older in the Veterans Health Administration system who were tracked from 2000-2001 to 2015 and began metformin or sulfonylurea monotherapy after baseline.
Disclosures: The National Institutes of Health funded the study. The authors report no relevant disclosures.
Source: Scherrer JF et al. Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:352-62.
Almost one-third of ED patients with gout are prescribed opioids
Patients with gout who visit the emergency department are regularly prescribed opioids, based on a review of electronic medical records.
“In addition to regulatory changes, the burden of opioid prescription could be potentially reduced by creating prompts for providers in electronic record systems to avoid prescribing opioids in opioid-naive patients or using lower intensity and shorter duration of prescription,” wrote Deepan S. Dalal, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and coauthors. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To determine frequency, dose, and duration of opioid prescription at ED discharge, the researchers reviewed the records of 456 patients with acute gout who were discharged in Rhode Island between March 30, 2015, and Sept. 30, 2017. All data were gathered via electronic medical system records.
Of the 456 discharged patients, 129 (28.3%) were prescribed opioids; 102 (79%) were not on opioids at the time. A full prescription description was available for 119 of the 129 patients; 96 (81%) were prescribed oxycodone or oxycodone combinations. Hydrocodone was prescribed for 9 patients (8%) and tramadol was prescribed for 11 patients (9%).
The median duration of each prescription was 8 days (interquartile range, 5-14 days) and the average daily dose was 37.9 mg of morphine equivalent. Patients who were prescribed opioids tended to be younger and male. After multivariable analysis, diabetes, polyarticular gout attack, and prior opioid use were all associated with a more than 100% higher odds of receiving an opioid prescription.
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including their inability to determine the physicians’ reasoning behind each prescription or the prescribing habits of each provider. In addition, they were only able to assess the prescriptions as being written and not the number of pills actually taken or not taken.
No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Dalal DS et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jul 3. doi: 10.1002/acr.23928.
Patients with gout who visit the emergency department are regularly prescribed opioids, based on a review of electronic medical records.
“In addition to regulatory changes, the burden of opioid prescription could be potentially reduced by creating prompts for providers in electronic record systems to avoid prescribing opioids in opioid-naive patients or using lower intensity and shorter duration of prescription,” wrote Deepan S. Dalal, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and coauthors. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To determine frequency, dose, and duration of opioid prescription at ED discharge, the researchers reviewed the records of 456 patients with acute gout who were discharged in Rhode Island between March 30, 2015, and Sept. 30, 2017. All data were gathered via electronic medical system records.
Of the 456 discharged patients, 129 (28.3%) were prescribed opioids; 102 (79%) were not on opioids at the time. A full prescription description was available for 119 of the 129 patients; 96 (81%) were prescribed oxycodone or oxycodone combinations. Hydrocodone was prescribed for 9 patients (8%) and tramadol was prescribed for 11 patients (9%).
The median duration of each prescription was 8 days (interquartile range, 5-14 days) and the average daily dose was 37.9 mg of morphine equivalent. Patients who were prescribed opioids tended to be younger and male. After multivariable analysis, diabetes, polyarticular gout attack, and prior opioid use were all associated with a more than 100% higher odds of receiving an opioid prescription.
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including their inability to determine the physicians’ reasoning behind each prescription or the prescribing habits of each provider. In addition, they were only able to assess the prescriptions as being written and not the number of pills actually taken or not taken.
No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Dalal DS et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jul 3. doi: 10.1002/acr.23928.
Patients with gout who visit the emergency department are regularly prescribed opioids, based on a review of electronic medical records.
“In addition to regulatory changes, the burden of opioid prescription could be potentially reduced by creating prompts for providers in electronic record systems to avoid prescribing opioids in opioid-naive patients or using lower intensity and shorter duration of prescription,” wrote Deepan S. Dalal, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and coauthors. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To determine frequency, dose, and duration of opioid prescription at ED discharge, the researchers reviewed the records of 456 patients with acute gout who were discharged in Rhode Island between March 30, 2015, and Sept. 30, 2017. All data were gathered via electronic medical system records.
Of the 456 discharged patients, 129 (28.3%) were prescribed opioids; 102 (79%) were not on opioids at the time. A full prescription description was available for 119 of the 129 patients; 96 (81%) were prescribed oxycodone or oxycodone combinations. Hydrocodone was prescribed for 9 patients (8%) and tramadol was prescribed for 11 patients (9%).
The median duration of each prescription was 8 days (interquartile range, 5-14 days) and the average daily dose was 37.9 mg of morphine equivalent. Patients who were prescribed opioids tended to be younger and male. After multivariable analysis, diabetes, polyarticular gout attack, and prior opioid use were all associated with a more than 100% higher odds of receiving an opioid prescription.
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including their inability to determine the physicians’ reasoning behind each prescription or the prescribing habits of each provider. In addition, they were only able to assess the prescriptions as being written and not the number of pills actually taken or not taken.
No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Dalal DS et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jul 3. doi: 10.1002/acr.23928.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Key clinical point: Though there are other effective conventional treatments, opioids are often prescribed for patients who present to the ED with gout.
Major finding: After multivariable analysis, diabetes, polyarticular gout attack, and prior opioid use were all associated with a more than 100% higher odds of opioid prescription.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 456 patients with acute gout discharged from EDs in Rhode Island.
Disclosures: The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Dalal DS et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jul 3. doi: 10.1002/acr.23928.
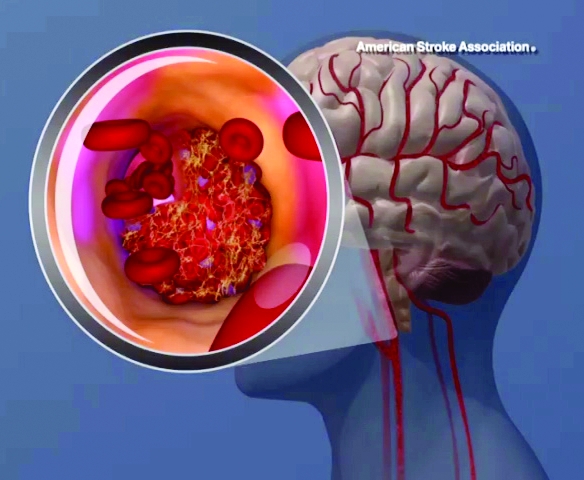
Sleepiest OSA patients have worse CV outcomes
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who complain of feeling tired when they wake up, being sleepy during the day, and have a high score on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale face an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, results from a population-based analysis suggest.
“OSA is a highly heterogeneous disease, with multiple clinical presentations and consequences,” the study’s first author, Diego R. Mazzotti, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “These patients also have diverse comorbidities, and there are arbitrary severity definitions and variable therapeutic responses. It’s difficult to lump these patients together.”
Symptom subtypes of OSA were originally described in the Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort, and defined as excessively sleepy, minimally symptomatic, and disturbed sleep (Eur Respir J. 2014; 44[6]:1600-7). These distinct clusters were identified based on symptom experiences and the existence of major comorbidities. “This concept is more popular today, trying to identify symptom clusters, or groups of individuals, that share similar polysomnographic data, and then compare differences in prevalence or incidence of cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Mazzotti, a research associate at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s a concept that needs to be moving forward.”
Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues set out to determine if OSA symptom subtypes are present in the Sleep Heart Health Study, a multicenter, prospective, community-based cohort of individuals aged 40 years and older designed to assess the cardiovascular (CV) consequences of OSA. They also wanted to know if there is additional evidence of the relevance of OSA symptom subtypes, particularly with respect to cardiovascular disease .
Participant-reported symptoms, such as difficulty falling and staying asleep, snoring, fatigue, drowsy driving and daytime sleepiness, and responses to the Epworth Sleepiness Scale were used to determine the patient’s subtype. Assessments including questionnaires and in-home polysomnography were conducted at baseline (between 1995 and 1998) and follow-up (between 2001 and 2003), while CV outcomes were assessed until the end of follow-up (between 2008 and 2011).
In all, 1,207 patients from the Sleep Heart Health Study met criteria for moderate to severe OSA (apnea-hypopnea index, or AHI, of 15 or greater) and were included in the final analysis. They were followed for a mean of 12 years. Based on the clustering of symptoms, the researchers identified four OSA symptom subtypes: disturbed sleep (12%), minimally symptomatic (33%), excessively sleepy (17%), and moderately sleepy (38%) – proportions that were similar to those observed in prior studies.
The disturbed sleep subtype presented with increased prevalence of “insomnialike” symptoms, such as difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, according to Dr. Mazzotti. “On the other hand, the excessively sleepy subtype presented with a very high prevalence of several symptoms related to excessive daytime sleepiness, while the moderately sleepy showed a moderately high prevalence of such symptoms, but not as much when compared to the excessively sleepy subtype,” he explained. “Finally, the minimally symptomatic subtype was found to have the lowest prevalence of all investigated symptoms, suggesting that these patients have low symptom burden. They do not complain as much, even though they have moderate-to-severe OSA.”
Next, Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models to evaluate whether subtypes were associated with incident coronary heart disease (CHD), heart failure, and CV disease, including CV mortality. Similar analyses were performed comparing each symptom subtype with 2,830 individuals without OSA (AHI less than 5).
Compared with other subtypes, the excessively sleepy group had a more than threefold increased odds of prevalent heart failure, after adjustment for other CV risk factors. They also had a 1.7- to 2.3-fold increased risk for incident CV disease (P less than .001), CHD (P = .015) and heart failure (P = 0.018), after adjustment for other CV risk factors.
“Compared to individuals without OSA, the excessively sleepy subtype is the only subtype with increased risk of incident CV disease and CHD,” Dr. Mazzotti said. “It is possible that excessively sleepy OSA patients are more likely to benefit from CPAP therapy in preventing CV disease.” These results were published online earlier this year (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Feb 15. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201808-1509OC).
Dr. Mazzotti reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mazzotti D et al. SLEEP 2019, Abstract 0586.
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who complain of feeling tired when they wake up, being sleepy during the day, and have a high score on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale face an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, results from a population-based analysis suggest.
“OSA is a highly heterogeneous disease, with multiple clinical presentations and consequences,” the study’s first author, Diego R. Mazzotti, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “These patients also have diverse comorbidities, and there are arbitrary severity definitions and variable therapeutic responses. It’s difficult to lump these patients together.”
Symptom subtypes of OSA were originally described in the Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort, and defined as excessively sleepy, minimally symptomatic, and disturbed sleep (Eur Respir J. 2014; 44[6]:1600-7). These distinct clusters were identified based on symptom experiences and the existence of major comorbidities. “This concept is more popular today, trying to identify symptom clusters, or groups of individuals, that share similar polysomnographic data, and then compare differences in prevalence or incidence of cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Mazzotti, a research associate at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s a concept that needs to be moving forward.”
Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues set out to determine if OSA symptom subtypes are present in the Sleep Heart Health Study, a multicenter, prospective, community-based cohort of individuals aged 40 years and older designed to assess the cardiovascular (CV) consequences of OSA. They also wanted to know if there is additional evidence of the relevance of OSA symptom subtypes, particularly with respect to cardiovascular disease .
Participant-reported symptoms, such as difficulty falling and staying asleep, snoring, fatigue, drowsy driving and daytime sleepiness, and responses to the Epworth Sleepiness Scale were used to determine the patient’s subtype. Assessments including questionnaires and in-home polysomnography were conducted at baseline (between 1995 and 1998) and follow-up (between 2001 and 2003), while CV outcomes were assessed until the end of follow-up (between 2008 and 2011).
In all, 1,207 patients from the Sleep Heart Health Study met criteria for moderate to severe OSA (apnea-hypopnea index, or AHI, of 15 or greater) and were included in the final analysis. They were followed for a mean of 12 years. Based on the clustering of symptoms, the researchers identified four OSA symptom subtypes: disturbed sleep (12%), minimally symptomatic (33%), excessively sleepy (17%), and moderately sleepy (38%) – proportions that were similar to those observed in prior studies.
The disturbed sleep subtype presented with increased prevalence of “insomnialike” symptoms, such as difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, according to Dr. Mazzotti. “On the other hand, the excessively sleepy subtype presented with a very high prevalence of several symptoms related to excessive daytime sleepiness, while the moderately sleepy showed a moderately high prevalence of such symptoms, but not as much when compared to the excessively sleepy subtype,” he explained. “Finally, the minimally symptomatic subtype was found to have the lowest prevalence of all investigated symptoms, suggesting that these patients have low symptom burden. They do not complain as much, even though they have moderate-to-severe OSA.”
Next, Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models to evaluate whether subtypes were associated with incident coronary heart disease (CHD), heart failure, and CV disease, including CV mortality. Similar analyses were performed comparing each symptom subtype with 2,830 individuals without OSA (AHI less than 5).
Compared with other subtypes, the excessively sleepy group had a more than threefold increased odds of prevalent heart failure, after adjustment for other CV risk factors. They also had a 1.7- to 2.3-fold increased risk for incident CV disease (P less than .001), CHD (P = .015) and heart failure (P = 0.018), after adjustment for other CV risk factors.
“Compared to individuals without OSA, the excessively sleepy subtype is the only subtype with increased risk of incident CV disease and CHD,” Dr. Mazzotti said. “It is possible that excessively sleepy OSA patients are more likely to benefit from CPAP therapy in preventing CV disease.” These results were published online earlier this year (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Feb 15. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201808-1509OC).
Dr. Mazzotti reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mazzotti D et al. SLEEP 2019, Abstract 0586.
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who complain of feeling tired when they wake up, being sleepy during the day, and have a high score on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale face an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, results from a population-based analysis suggest.
“OSA is a highly heterogeneous disease, with multiple clinical presentations and consequences,” the study’s first author, Diego R. Mazzotti, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “These patients also have diverse comorbidities, and there are arbitrary severity definitions and variable therapeutic responses. It’s difficult to lump these patients together.”
Symptom subtypes of OSA were originally described in the Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort, and defined as excessively sleepy, minimally symptomatic, and disturbed sleep (Eur Respir J. 2014; 44[6]:1600-7). These distinct clusters were identified based on symptom experiences and the existence of major comorbidities. “This concept is more popular today, trying to identify symptom clusters, or groups of individuals, that share similar polysomnographic data, and then compare differences in prevalence or incidence of cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Mazzotti, a research associate at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s a concept that needs to be moving forward.”
Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues set out to determine if OSA symptom subtypes are present in the Sleep Heart Health Study, a multicenter, prospective, community-based cohort of individuals aged 40 years and older designed to assess the cardiovascular (CV) consequences of OSA. They also wanted to know if there is additional evidence of the relevance of OSA symptom subtypes, particularly with respect to cardiovascular disease .
Participant-reported symptoms, such as difficulty falling and staying asleep, snoring, fatigue, drowsy driving and daytime sleepiness, and responses to the Epworth Sleepiness Scale were used to determine the patient’s subtype. Assessments including questionnaires and in-home polysomnography were conducted at baseline (between 1995 and 1998) and follow-up (between 2001 and 2003), while CV outcomes were assessed until the end of follow-up (between 2008 and 2011).
In all, 1,207 patients from the Sleep Heart Health Study met criteria for moderate to severe OSA (apnea-hypopnea index, or AHI, of 15 or greater) and were included in the final analysis. They were followed for a mean of 12 years. Based on the clustering of symptoms, the researchers identified four OSA symptom subtypes: disturbed sleep (12%), minimally symptomatic (33%), excessively sleepy (17%), and moderately sleepy (38%) – proportions that were similar to those observed in prior studies.
The disturbed sleep subtype presented with increased prevalence of “insomnialike” symptoms, such as difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, according to Dr. Mazzotti. “On the other hand, the excessively sleepy subtype presented with a very high prevalence of several symptoms related to excessive daytime sleepiness, while the moderately sleepy showed a moderately high prevalence of such symptoms, but not as much when compared to the excessively sleepy subtype,” he explained. “Finally, the minimally symptomatic subtype was found to have the lowest prevalence of all investigated symptoms, suggesting that these patients have low symptom burden. They do not complain as much, even though they have moderate-to-severe OSA.”
Next, Dr. Mazzotti and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models to evaluate whether subtypes were associated with incident coronary heart disease (CHD), heart failure, and CV disease, including CV mortality. Similar analyses were performed comparing each symptom subtype with 2,830 individuals without OSA (AHI less than 5).
Compared with other subtypes, the excessively sleepy group had a more than threefold increased odds of prevalent heart failure, after adjustment for other CV risk factors. They also had a 1.7- to 2.3-fold increased risk for incident CV disease (P less than .001), CHD (P = .015) and heart failure (P = 0.018), after adjustment for other CV risk factors.
“Compared to individuals without OSA, the excessively sleepy subtype is the only subtype with increased risk of incident CV disease and CHD,” Dr. Mazzotti said. “It is possible that excessively sleepy OSA patients are more likely to benefit from CPAP therapy in preventing CV disease.” These results were published online earlier this year (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Feb 15. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201808-1509OC).
Dr. Mazzotti reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mazzotti D et al. SLEEP 2019, Abstract 0586.
REPORTING FROM SLEEP 2019
Functional GI disorders are common in MS
SEATTLE – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. Managing patients’ psychiatric comorbidities could effectively reduce the burden of functional GI disorders, the researchers said.
Knowledge about the prevalence of functional GI disorders in the population of patients with MS is limited. For the most part, previous studies in this population have focused on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A 2013 study by Levinthal et al. (Mult Scler Int. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/319201) investigated the prevalence of other functional GI disorders in MS, but the literature contains little information about the clinical and demographic characteristics associated with these disorders. In addition, the extent to which comorbid functional GI disorders influence health-related quality of life in MS is also unknown.
Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and colleagues sought to determine the prevalence of functional bowel disorders, the demographic and clinical characteristics associated with functional bowel disorders, and the effects of these disorders on health-related quality of life in a large, diverse population of persons with MS. In 2014, the investigators used the Rome III questionnaire to survey participants in the North American Research Committee on MS (NARCOMS) registry about functional bowel disorders. Participants also provided information about their sociodemographic characteristics, their disability status (using Patient-Determined Disease Steps), and any comorbid depression or anxiety, their health behaviors, and their health-related quality of life (using the RAND-12).
Dr. Marrie and colleagues used these data to determine the prevalence of IBS, functional bloating, functional constipation, functional diarrhea, and functional dyspepsia. They used multivariable logistic regression models to examine the factors associated with any functional GI disorder, and they used linear regression to analyze the association between functional GI disorders and health-related quality of life using linear regression.
Dr. Marrie and colleagues identified 6,312 eligible respondents. Approximately 77% of the population was female, and the sample’s mean age was 58.3 years. In all, 2,647 respondents (42%) had a functional GI disorder. The most common was IBS, which affected 28.2% of participants. The prevalence of all functional GI disorders increased with increasing disability. Depression and anxiety were associated with increased odds of IBS and functional dyspepsia. After adjustment for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, functional GI disorders were associated with lower physical and mental health-related quality of life.
The research was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Marrie had no disclosures, but other researchers had financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies, such as Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, and Teva.
SOURCE: Marrie RA et al. CMSC 2019, Abstract QOL13.
SEATTLE – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. Managing patients’ psychiatric comorbidities could effectively reduce the burden of functional GI disorders, the researchers said.
Knowledge about the prevalence of functional GI disorders in the population of patients with MS is limited. For the most part, previous studies in this population have focused on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A 2013 study by Levinthal et al. (Mult Scler Int. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/319201) investigated the prevalence of other functional GI disorders in MS, but the literature contains little information about the clinical and demographic characteristics associated with these disorders. In addition, the extent to which comorbid functional GI disorders influence health-related quality of life in MS is also unknown.
Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and colleagues sought to determine the prevalence of functional bowel disorders, the demographic and clinical characteristics associated with functional bowel disorders, and the effects of these disorders on health-related quality of life in a large, diverse population of persons with MS. In 2014, the investigators used the Rome III questionnaire to survey participants in the North American Research Committee on MS (NARCOMS) registry about functional bowel disorders. Participants also provided information about their sociodemographic characteristics, their disability status (using Patient-Determined Disease Steps), and any comorbid depression or anxiety, their health behaviors, and their health-related quality of life (using the RAND-12).
Dr. Marrie and colleagues used these data to determine the prevalence of IBS, functional bloating, functional constipation, functional diarrhea, and functional dyspepsia. They used multivariable logistic regression models to examine the factors associated with any functional GI disorder, and they used linear regression to analyze the association between functional GI disorders and health-related quality of life using linear regression.
Dr. Marrie and colleagues identified 6,312 eligible respondents. Approximately 77% of the population was female, and the sample’s mean age was 58.3 years. In all, 2,647 respondents (42%) had a functional GI disorder. The most common was IBS, which affected 28.2% of participants. The prevalence of all functional GI disorders increased with increasing disability. Depression and anxiety were associated with increased odds of IBS and functional dyspepsia. After adjustment for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, functional GI disorders were associated with lower physical and mental health-related quality of life.
The research was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Marrie had no disclosures, but other researchers had financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies, such as Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, and Teva.
SOURCE: Marrie RA et al. CMSC 2019, Abstract QOL13.
SEATTLE – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. Managing patients’ psychiatric comorbidities could effectively reduce the burden of functional GI disorders, the researchers said.
Knowledge about the prevalence of functional GI disorders in the population of patients with MS is limited. For the most part, previous studies in this population have focused on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A 2013 study by Levinthal et al. (Mult Scler Int. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/319201) investigated the prevalence of other functional GI disorders in MS, but the literature contains little information about the clinical and demographic characteristics associated with these disorders. In addition, the extent to which comorbid functional GI disorders influence health-related quality of life in MS is also unknown.
Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and colleagues sought to determine the prevalence of functional bowel disorders, the demographic and clinical characteristics associated with functional bowel disorders, and the effects of these disorders on health-related quality of life in a large, diverse population of persons with MS. In 2014, the investigators used the Rome III questionnaire to survey participants in the North American Research Committee on MS (NARCOMS) registry about functional bowel disorders. Participants also provided information about their sociodemographic characteristics, their disability status (using Patient-Determined Disease Steps), and any comorbid depression or anxiety, their health behaviors, and their health-related quality of life (using the RAND-12).
Dr. Marrie and colleagues used these data to determine the prevalence of IBS, functional bloating, functional constipation, functional diarrhea, and functional dyspepsia. They used multivariable logistic regression models to examine the factors associated with any functional GI disorder, and they used linear regression to analyze the association between functional GI disorders and health-related quality of life using linear regression.
Dr. Marrie and colleagues identified 6,312 eligible respondents. Approximately 77% of the population was female, and the sample’s mean age was 58.3 years. In all, 2,647 respondents (42%) had a functional GI disorder. The most common was IBS, which affected 28.2% of participants. The prevalence of all functional GI disorders increased with increasing disability. Depression and anxiety were associated with increased odds of IBS and functional dyspepsia. After adjustment for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, functional GI disorders were associated with lower physical and mental health-related quality of life.
The research was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Marrie had no disclosures, but other researchers had financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies, such as Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, and Teva.
SOURCE: Marrie RA et al. CMSC 2019, Abstract QOL13.
REPORTING FROM CMSC 2019
The hospitalist role in treating opioid use disorder
Screen patients at the time of admission
Let’s begin with a brief case. A 25-year-old patient with a history of injection heroin use is in your care. He is admitted for treatment of endocarditis and will remain in the hospital for intravenous antibiotics for several weeks. Over the first few days of hospitalization, he frequently asks for pain medicine, stating that he is in severe pain, withdrawal, and having opioid cravings. On day 3, he leaves the hospital against medical advice. After 2 weeks, he presents to the ED in septic shock and spends several weeks in the ICU. Or, alternatively, he is found down in the community and pronounced dead from a heroin overdose.
These cases occur all too often, and hospitalists across the nation are actively building knowledge and programs to improve care for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). It is evident that opioid misuse is the public health crisis of our time. In 2017, over 70,000 patients died from an overdose, and over 2 million patients in the United States have a diagnosis of OUD.1,2 Many of these patients interact with the hospital at some point during the course of their illness for management of overdose, withdrawal, and other complications of OUD, including endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and skin and soft tissue infections. Moreover, just 20% of the 580,000 patients hospitalized with OUD in 2015 presented as a direct sequelae of the disease.3 Patients with OUD are often admitted for unrelated reasons, but their addiction goes unaddressed.
Opioid use disorder, like many of the other conditions we see, is a chronic relapsing remitting medical disease and a risk factor for premature mortality. When a patient with diabetes is admitted with cellulitis, we might check an A1C, provide diabetic counseling, and offer evidence-based diabetes treatment, including medications like insulin. We rarely build similar systems of care within the walls of our hospitals to treat OUD like we do for diabetes or other commonly encountered diseases like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
We should be intentional about separating prevention from treatment. Significant work has gone into reducing the availability of prescription opioids and increasing utilization of prescription drug monitoring programs. As a result, the average morphine milligram equivalent per opioid prescription has decreased since 2010.4 An unintended consequence of restricting legal opioids is potentially pushing patients with opioid addiction towards heroin and fentanyl. Limiting opioid prescriptions alone will only decrease opioid overdose mortality by 5% through 2025.5 Thus, treatment of OUD is critical and something that hospitalists should be trained and engaged in.
Food and Drug Administration–approved OUD treatment includes buprenorphine, methadone, and extended-release naltrexone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that treats withdrawal and cravings. Buprenorphine started in the hospital reduces mortality, increases time spent in outpatient treatment after discharge, and reduces opioid-related 30-day readmissions by over 50%.6-8 The number needed to treat with buprenorphine to prevent return to illicit opioid use is two.9 While physicians require an 8-hour “x-waiver” training (physician assistants and nurse practitioners require a 24-hour training) to prescribe buprenorphine for the outpatient treatment of OUD, such certification is not required to order the medication as part of an acute hospitalization.
Hospitalization represents a reachable moment and unique opportunity to start treatment for OUD. Patients are away from triggering environments and surrounded by supportive staff. Unfortunately, up to 30% of these patients leave the hospital against medical advice because of inadequately treated withdrawal, unaddressed cravings, and fear of mistreatment.10 Buprenorphine therapy may help tackle the physiological piece of hospital-based treatment, but we also must work on shifting the culture of our institutions. Importantly, OUD is a medical diagnosis. These patients must receive the same dignity, autonomy, and meaningful care afforded to patients with other medical diagnoses. Patients with OUD are not “addicts,” “abusers,” or “frequent fliers.”
Hospitalists have a clear and compelling role in treating OUD. The National Academy of Medicine recently held a workshop where they compared similarities of the HIV crisis with today’s opioid epidemic. The Academy advocated for the development of hospital-based protocols that empower physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners to integrate the treatment of OUD into their practice.11 Some in our field may feel that treating underlying addiction is a role for behavioral health practitioners. This is akin to having said that HIV specialists should be the only providers to treat patients with HIV during its peak. There are simply not enough psychiatrists or addiction medicine specialists to treat all of the patients who need us during this time of national urgency.
There are several examples of institutions that are laying the groundwork for this important work. The University of California, San Francisco; Oregon Health and Science University, Portland; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; Rush Medical College, Boston; Boston Medical Center; the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York; and the University of Texas at Austin – to name a few. Offering OUD treatment in the hospital setting must be our new and only acceptable standard of care.
What is next? We can start by screening patients for OUD at the time of admission. This can be accomplished by asking two questions: Does the patient misuse prescription or nonprescription opioids? And if so, does the patient become sick if they abruptly stop? If the patient says yes to both, steps should be taken to provide direct and purposeful care related to OUD. Hospitalists should become familiar with buprenorphine therapy and work to reduce stigma by using people-first language with patients, staff, and in medical documentation.
As a society, we should balance our past focus on optimizing opioid prescribing with current efforts to bolster treatment. To that end, a group of SHM members applied to establish a Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group, which was recently approved by the SHM board of directors. Details on its rollout will be announced shortly. The intention is that this group will serve as a resource to SHM membership and leadership
As practitioners of hospital medicine, we may not have anticipated playing a direct role in treating patients’ underlying addiction. By empowering hospitalists and wisely using medical hospitalization as a time to treat OUD, we can all have an incredible impact on our patients. Let’s get to work.
Mr. Bottner is a hospitalist at Dell Seton Medical Center, Austin, Texas, and clinical assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin.
References
1. Katz J. You draw it: Just how bad is the drug overdose epidemic? New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2017/04/14/upshot/drug-overdose-epidemic-you-draw-it.html. Published Oct 26, 2017.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Ohio – Opioid summaries by state. 2018. https://d14rmgtrwzf5a.cloudfront.net/sites/default/files/ohio_2018.pdf.
3. Peterson C et al. U.S. hospital discharges documenting patient opioid use disorder without opioid overdose or treatment services, 2011-2015. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018;92:35-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2018.06.008.
4. Guy GP. Vital Signs: Changes in opioid prescribing in the United States, 2006-2015. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6626a4.
5. Chen Q et al. Prevention of prescription opioid misuse and projected overdose deaths in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7621.
6. Liebschutz J et al. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1369-76.
7. Moreno JL et al. Predictors for 30-day and 90-day hospital readmission among patients with opioid use disorder. J Addict Med. 2019. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000499.
8. Larochelle MR et al. Medication for opioid use disorder after nonfatal opioid overdose and association with mortality: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. June 2018. doi: 10.7326/M17-3107.
9. Raleigh MF. Buprenorphine maintenance vs. placebo for opioid dependence. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95(5). https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/0301/od1.html. Accessed May 12, 2019.
10. Ti L et al. Leaving the hospital against medical advice among people who use illicit drugs: A systematic review. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(12):2587. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302885a.
11. Springer SAM et al. Integrating treatment at the intersection of opioid use disorder and infectious disease epidemics in medical settings: A call for action after a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine workshop. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(5):335-6. doi: 10.7326/M18-1203.
Screen patients at the time of admission
Screen patients at the time of admission
Let’s begin with a brief case. A 25-year-old patient with a history of injection heroin use is in your care. He is admitted for treatment of endocarditis and will remain in the hospital for intravenous antibiotics for several weeks. Over the first few days of hospitalization, he frequently asks for pain medicine, stating that he is in severe pain, withdrawal, and having opioid cravings. On day 3, he leaves the hospital against medical advice. After 2 weeks, he presents to the ED in septic shock and spends several weeks in the ICU. Or, alternatively, he is found down in the community and pronounced dead from a heroin overdose.
These cases occur all too often, and hospitalists across the nation are actively building knowledge and programs to improve care for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). It is evident that opioid misuse is the public health crisis of our time. In 2017, over 70,000 patients died from an overdose, and over 2 million patients in the United States have a diagnosis of OUD.1,2 Many of these patients interact with the hospital at some point during the course of their illness for management of overdose, withdrawal, and other complications of OUD, including endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and skin and soft tissue infections. Moreover, just 20% of the 580,000 patients hospitalized with OUD in 2015 presented as a direct sequelae of the disease.3 Patients with OUD are often admitted for unrelated reasons, but their addiction goes unaddressed.
Opioid use disorder, like many of the other conditions we see, is a chronic relapsing remitting medical disease and a risk factor for premature mortality. When a patient with diabetes is admitted with cellulitis, we might check an A1C, provide diabetic counseling, and offer evidence-based diabetes treatment, including medications like insulin. We rarely build similar systems of care within the walls of our hospitals to treat OUD like we do for diabetes or other commonly encountered diseases like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
We should be intentional about separating prevention from treatment. Significant work has gone into reducing the availability of prescription opioids and increasing utilization of prescription drug monitoring programs. As a result, the average morphine milligram equivalent per opioid prescription has decreased since 2010.4 An unintended consequence of restricting legal opioids is potentially pushing patients with opioid addiction towards heroin and fentanyl. Limiting opioid prescriptions alone will only decrease opioid overdose mortality by 5% through 2025.5 Thus, treatment of OUD is critical and something that hospitalists should be trained and engaged in.
Food and Drug Administration–approved OUD treatment includes buprenorphine, methadone, and extended-release naltrexone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that treats withdrawal and cravings. Buprenorphine started in the hospital reduces mortality, increases time spent in outpatient treatment after discharge, and reduces opioid-related 30-day readmissions by over 50%.6-8 The number needed to treat with buprenorphine to prevent return to illicit opioid use is two.9 While physicians require an 8-hour “x-waiver” training (physician assistants and nurse practitioners require a 24-hour training) to prescribe buprenorphine for the outpatient treatment of OUD, such certification is not required to order the medication as part of an acute hospitalization.
Hospitalization represents a reachable moment and unique opportunity to start treatment for OUD. Patients are away from triggering environments and surrounded by supportive staff. Unfortunately, up to 30% of these patients leave the hospital against medical advice because of inadequately treated withdrawal, unaddressed cravings, and fear of mistreatment.10 Buprenorphine therapy may help tackle the physiological piece of hospital-based treatment, but we also must work on shifting the culture of our institutions. Importantly, OUD is a medical diagnosis. These patients must receive the same dignity, autonomy, and meaningful care afforded to patients with other medical diagnoses. Patients with OUD are not “addicts,” “abusers,” or “frequent fliers.”
Hospitalists have a clear and compelling role in treating OUD. The National Academy of Medicine recently held a workshop where they compared similarities of the HIV crisis with today’s opioid epidemic. The Academy advocated for the development of hospital-based protocols that empower physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners to integrate the treatment of OUD into their practice.11 Some in our field may feel that treating underlying addiction is a role for behavioral health practitioners. This is akin to having said that HIV specialists should be the only providers to treat patients with HIV during its peak. There are simply not enough psychiatrists or addiction medicine specialists to treat all of the patients who need us during this time of national urgency.
There are several examples of institutions that are laying the groundwork for this important work. The University of California, San Francisco; Oregon Health and Science University, Portland; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; Rush Medical College, Boston; Boston Medical Center; the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York; and the University of Texas at Austin – to name a few. Offering OUD treatment in the hospital setting must be our new and only acceptable standard of care.
What is next? We can start by screening patients for OUD at the time of admission. This can be accomplished by asking two questions: Does the patient misuse prescription or nonprescription opioids? And if so, does the patient become sick if they abruptly stop? If the patient says yes to both, steps should be taken to provide direct and purposeful care related to OUD. Hospitalists should become familiar with buprenorphine therapy and work to reduce stigma by using people-first language with patients, staff, and in medical documentation.
As a society, we should balance our past focus on optimizing opioid prescribing with current efforts to bolster treatment. To that end, a group of SHM members applied to establish a Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group, which was recently approved by the SHM board of directors. Details on its rollout will be announced shortly. The intention is that this group will serve as a resource to SHM membership and leadership
As practitioners of hospital medicine, we may not have anticipated playing a direct role in treating patients’ underlying addiction. By empowering hospitalists and wisely using medical hospitalization as a time to treat OUD, we can all have an incredible impact on our patients. Let’s get to work.
Mr. Bottner is a hospitalist at Dell Seton Medical Center, Austin, Texas, and clinical assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin.
References
1. Katz J. You draw it: Just how bad is the drug overdose epidemic? New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2017/04/14/upshot/drug-overdose-epidemic-you-draw-it.html. Published Oct 26, 2017.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Ohio – Opioid summaries by state. 2018. https://d14rmgtrwzf5a.cloudfront.net/sites/default/files/ohio_2018.pdf.
3. Peterson C et al. U.S. hospital discharges documenting patient opioid use disorder without opioid overdose or treatment services, 2011-2015. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018;92:35-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2018.06.008.
4. Guy GP. Vital Signs: Changes in opioid prescribing in the United States, 2006-2015. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6626a4.
5. Chen Q et al. Prevention of prescription opioid misuse and projected overdose deaths in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7621.
6. Liebschutz J et al. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1369-76.
7. Moreno JL et al. Predictors for 30-day and 90-day hospital readmission among patients with opioid use disorder. J Addict Med. 2019. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000499.
8. Larochelle MR et al. Medication for opioid use disorder after nonfatal opioid overdose and association with mortality: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. June 2018. doi: 10.7326/M17-3107.
9. Raleigh MF. Buprenorphine maintenance vs. placebo for opioid dependence. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95(5). https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/0301/od1.html. Accessed May 12, 2019.
10. Ti L et al. Leaving the hospital against medical advice among people who use illicit drugs: A systematic review. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(12):2587. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302885a.
11. Springer SAM et al. Integrating treatment at the intersection of opioid use disorder and infectious disease epidemics in medical settings: A call for action after a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine workshop. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(5):335-6. doi: 10.7326/M18-1203.
Let’s begin with a brief case. A 25-year-old patient with a history of injection heroin use is in your care. He is admitted for treatment of endocarditis and will remain in the hospital for intravenous antibiotics for several weeks. Over the first few days of hospitalization, he frequently asks for pain medicine, stating that he is in severe pain, withdrawal, and having opioid cravings. On day 3, he leaves the hospital against medical advice. After 2 weeks, he presents to the ED in septic shock and spends several weeks in the ICU. Or, alternatively, he is found down in the community and pronounced dead from a heroin overdose.
These cases occur all too often, and hospitalists across the nation are actively building knowledge and programs to improve care for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). It is evident that opioid misuse is the public health crisis of our time. In 2017, over 70,000 patients died from an overdose, and over 2 million patients in the United States have a diagnosis of OUD.1,2 Many of these patients interact with the hospital at some point during the course of their illness for management of overdose, withdrawal, and other complications of OUD, including endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and skin and soft tissue infections. Moreover, just 20% of the 580,000 patients hospitalized with OUD in 2015 presented as a direct sequelae of the disease.3 Patients with OUD are often admitted for unrelated reasons, but their addiction goes unaddressed.
Opioid use disorder, like many of the other conditions we see, is a chronic relapsing remitting medical disease and a risk factor for premature mortality. When a patient with diabetes is admitted with cellulitis, we might check an A1C, provide diabetic counseling, and offer evidence-based diabetes treatment, including medications like insulin. We rarely build similar systems of care within the walls of our hospitals to treat OUD like we do for diabetes or other commonly encountered diseases like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
We should be intentional about separating prevention from treatment. Significant work has gone into reducing the availability of prescription opioids and increasing utilization of prescription drug monitoring programs. As a result, the average morphine milligram equivalent per opioid prescription has decreased since 2010.4 An unintended consequence of restricting legal opioids is potentially pushing patients with opioid addiction towards heroin and fentanyl. Limiting opioid prescriptions alone will only decrease opioid overdose mortality by 5% through 2025.5 Thus, treatment of OUD is critical and something that hospitalists should be trained and engaged in.
Food and Drug Administration–approved OUD treatment includes buprenorphine, methadone, and extended-release naltrexone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that treats withdrawal and cravings. Buprenorphine started in the hospital reduces mortality, increases time spent in outpatient treatment after discharge, and reduces opioid-related 30-day readmissions by over 50%.6-8 The number needed to treat with buprenorphine to prevent return to illicit opioid use is two.9 While physicians require an 8-hour “x-waiver” training (physician assistants and nurse practitioners require a 24-hour training) to prescribe buprenorphine for the outpatient treatment of OUD, such certification is not required to order the medication as part of an acute hospitalization.
Hospitalization represents a reachable moment and unique opportunity to start treatment for OUD. Patients are away from triggering environments and surrounded by supportive staff. Unfortunately, up to 30% of these patients leave the hospital against medical advice because of inadequately treated withdrawal, unaddressed cravings, and fear of mistreatment.10 Buprenorphine therapy may help tackle the physiological piece of hospital-based treatment, but we also must work on shifting the culture of our institutions. Importantly, OUD is a medical diagnosis. These patients must receive the same dignity, autonomy, and meaningful care afforded to patients with other medical diagnoses. Patients with OUD are not “addicts,” “abusers,” or “frequent fliers.”
Hospitalists have a clear and compelling role in treating OUD. The National Academy of Medicine recently held a workshop where they compared similarities of the HIV crisis with today’s opioid epidemic. The Academy advocated for the development of hospital-based protocols that empower physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners to integrate the treatment of OUD into their practice.11 Some in our field may feel that treating underlying addiction is a role for behavioral health practitioners. This is akin to having said that HIV specialists should be the only providers to treat patients with HIV during its peak. There are simply not enough psychiatrists or addiction medicine specialists to treat all of the patients who need us during this time of national urgency.
There are several examples of institutions that are laying the groundwork for this important work. The University of California, San Francisco; Oregon Health and Science University, Portland; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; Rush Medical College, Boston; Boston Medical Center; the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York; and the University of Texas at Austin – to name a few. Offering OUD treatment in the hospital setting must be our new and only acceptable standard of care.
What is next? We can start by screening patients for OUD at the time of admission. This can be accomplished by asking two questions: Does the patient misuse prescription or nonprescription opioids? And if so, does the patient become sick if they abruptly stop? If the patient says yes to both, steps should be taken to provide direct and purposeful care related to OUD. Hospitalists should become familiar with buprenorphine therapy and work to reduce stigma by using people-first language with patients, staff, and in medical documentation.
As a society, we should balance our past focus on optimizing opioid prescribing with current efforts to bolster treatment. To that end, a group of SHM members applied to establish a Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group, which was recently approved by the SHM board of directors. Details on its rollout will be announced shortly. The intention is that this group will serve as a resource to SHM membership and leadership
As practitioners of hospital medicine, we may not have anticipated playing a direct role in treating patients’ underlying addiction. By empowering hospitalists and wisely using medical hospitalization as a time to treat OUD, we can all have an incredible impact on our patients. Let’s get to work.
Mr. Bottner is a hospitalist at Dell Seton Medical Center, Austin, Texas, and clinical assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin.
References
1. Katz J. You draw it: Just how bad is the drug overdose epidemic? New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2017/04/14/upshot/drug-overdose-epidemic-you-draw-it.html. Published Oct 26, 2017.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Ohio – Opioid summaries by state. 2018. https://d14rmgtrwzf5a.cloudfront.net/sites/default/files/ohio_2018.pdf.
3. Peterson C et al. U.S. hospital discharges documenting patient opioid use disorder without opioid overdose or treatment services, 2011-2015. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018;92:35-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2018.06.008.
4. Guy GP. Vital Signs: Changes in opioid prescribing in the United States, 2006-2015. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6626a4.
5. Chen Q et al. Prevention of prescription opioid misuse and projected overdose deaths in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7621.
6. Liebschutz J et al. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1369-76.
7. Moreno JL et al. Predictors for 30-day and 90-day hospital readmission among patients with opioid use disorder. J Addict Med. 2019. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000499.
8. Larochelle MR et al. Medication for opioid use disorder after nonfatal opioid overdose and association with mortality: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. June 2018. doi: 10.7326/M17-3107.
9. Raleigh MF. Buprenorphine maintenance vs. placebo for opioid dependence. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95(5). https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/0301/od1.html. Accessed May 12, 2019.
10. Ti L et al. Leaving the hospital against medical advice among people who use illicit drugs: A systematic review. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(12):2587. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302885a.
11. Springer SAM et al. Integrating treatment at the intersection of opioid use disorder and infectious disease epidemics in medical settings: A call for action after a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine workshop. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(5):335-6. doi: 10.7326/M18-1203.
Lipoprotein(a) levels tied to higher ischemic stroke risk
High levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and LPA genotypes were linked to increased ischemic stroke risk in a recent large, contemporary general population study, investigators are reporting in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Anne Langsted, MD, with Copenhagen University Hospital and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and her co-researchers evaluated the impact of high Lp(a) levels in a large contemporary cohort of 49,699 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study, and another 10,813 individuals in the Copenhagen City Heart Study.
Measurements assessed included plasma lipoprotein(a) levels and carrier or noncarrier status for LPA rs10455872. The endpoint of ischemic stroke was ascertained from Danish national health registries and confirmed by physicians.
Although risk estimates were less pronounced than what was reported before regarding the link between Lp(a) for ischemic heart disease and aortic valve stenosis, the risk of stroke was increased by a factor of 1.6 among individuals with high Lp(a) levels as compared to those with lower levels, the investigators said.
Compared with noncarriers of LPA rs1045572, the hazard ratio for ischemic stroke was 1.23 for carriers of LPA rs1045572, which was associated with high levels plasma lipoprotein(a) levels, according to the researchers.
“Our results indicate a causal association of Lp(a) with risk of ischemic stroke, and emphasize the need for randomized, controlled clinical trials on the effect of Lp(a)-lowering to prevent cardiovascular disease including ischemic stroke,” About 20% of the general population have high Lp(a) levels, and some individuals have extremely high levels, Dr. Langsted and co-authors said in their report.
Interest in Lp(a) as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease has been reignited following large studies showing that high Lp(a) levels were linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis, according to the investigators.
However, results of various studies are conflicting as to whether high Lp(a) levels increase risk of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, they said.
Both cohort studies used in the analysis were supported by sources in Denmark including the Danish Medical Research Council and Copenhagen University Hospital. Dr. Langsted had no disclosures. One co-author reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Langsted A, et al. JACC 2019;74[1]: 54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.524
This study linking high lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels to stroke risk, taken together with previous research, provide a sound basis to routinely perform one-time screening so that individuals with inherited high levels can try to avoid adverse cardiovascular outcomes, according to Christie M. Ballantyne, MD.
“As someone in the dual role of preventive cardiologist and patient with a strong family history of cardiovascular disease, I think that we have sufficient evidence that high Lp(a) is strongly associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and aortic valve stenosis,” Dr. Ballantyne wrote in an editorial comment on the study.
Evidence is now “overwhelming” that high Lp(a) is linked to myocardial infarction and stroke, and it’s known that statins and aspirin reduce risk of these outcomes, he said in the commentary.
Despite that, scientific statements do not recommend routine Lp(a) testing due to a lack of clinical trials evidence; as a result, clinical trials are not including Lp(a) as a routine measurement: “We thus have a loop of futility—lack of routine measurement leads to lack of data,” he said.
This most recent study from Langsted and colleagues demonstrates that high Lp(a) levels, and genetic variants associated with Lp(a), are associated with increased ischemic stroke risk. “The genetics strongly supported that high Lp(a) levels were in the causal pathway for ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease,” Dr. Ballantyne said.
One major strength and weakness of the study is its large and relatively homogeneous European population—that bolstered the genetic analyses, but also means the data can’t be extrapolated to other populations, such as Africans and East Asians, who have higher stroke rates compared with Europeans, Dr. Ballantyne said.
Dr. Ballantyne is with the Department of Medicine and Center for Cardiometabolic Disease Prevention, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Tex. His editorial comment appears in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2019;74[1]:67-9. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.05.029 . Dr. Ballantyne reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, and Novartis.
This study linking high lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels to stroke risk, taken together with previous research, provide a sound basis to routinely perform one-time screening so that individuals with inherited high levels can try to avoid adverse cardiovascular outcomes, according to Christie M. Ballantyne, MD.
“As someone in the dual role of preventive cardiologist and patient with a strong family history of cardiovascular disease, I think that we have sufficient evidence that high Lp(a) is strongly associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and aortic valve stenosis,” Dr. Ballantyne wrote in an editorial comment on the study.
Evidence is now “overwhelming” that high Lp(a) is linked to myocardial infarction and stroke, and it’s known that statins and aspirin reduce risk of these outcomes, he said in the commentary.
Despite that, scientific statements do not recommend routine Lp(a) testing due to a lack of clinical trials evidence; as a result, clinical trials are not including Lp(a) as a routine measurement: “We thus have a loop of futility—lack of routine measurement leads to lack of data,” he said.
This most recent study from Langsted and colleagues demonstrates that high Lp(a) levels, and genetic variants associated with Lp(a), are associated with increased ischemic stroke risk. “The genetics strongly supported that high Lp(a) levels were in the causal pathway for ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease,” Dr. Ballantyne said.
One major strength and weakness of the study is its large and relatively homogeneous European population—that bolstered the genetic analyses, but also means the data can’t be extrapolated to other populations, such as Africans and East Asians, who have higher stroke rates compared with Europeans, Dr. Ballantyne said.
Dr. Ballantyne is with the Department of Medicine and Center for Cardiometabolic Disease Prevention, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Tex. His editorial comment appears in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2019;74[1]:67-9. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.05.029 . Dr. Ballantyne reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, and Novartis.
This study linking high lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels to stroke risk, taken together with previous research, provide a sound basis to routinely perform one-time screening so that individuals with inherited high levels can try to avoid adverse cardiovascular outcomes, according to Christie M. Ballantyne, MD.
“As someone in the dual role of preventive cardiologist and patient with a strong family history of cardiovascular disease, I think that we have sufficient evidence that high Lp(a) is strongly associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and aortic valve stenosis,” Dr. Ballantyne wrote in an editorial comment on the study.
Evidence is now “overwhelming” that high Lp(a) is linked to myocardial infarction and stroke, and it’s known that statins and aspirin reduce risk of these outcomes, he said in the commentary.
Despite that, scientific statements do not recommend routine Lp(a) testing due to a lack of clinical trials evidence; as a result, clinical trials are not including Lp(a) as a routine measurement: “We thus have a loop of futility—lack of routine measurement leads to lack of data,” he said.
This most recent study from Langsted and colleagues demonstrates that high Lp(a) levels, and genetic variants associated with Lp(a), are associated with increased ischemic stroke risk. “The genetics strongly supported that high Lp(a) levels were in the causal pathway for ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease,” Dr. Ballantyne said.
One major strength and weakness of the study is its large and relatively homogeneous European population—that bolstered the genetic analyses, but also means the data can’t be extrapolated to other populations, such as Africans and East Asians, who have higher stroke rates compared with Europeans, Dr. Ballantyne said.
Dr. Ballantyne is with the Department of Medicine and Center for Cardiometabolic Disease Prevention, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Tex. His editorial comment appears in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2019;74[1]:67-9. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.05.029 . Dr. Ballantyne reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, and Novartis.
High levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and LPA genotypes were linked to increased ischemic stroke risk in a recent large, contemporary general population study, investigators are reporting in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Anne Langsted, MD, with Copenhagen University Hospital and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and her co-researchers evaluated the impact of high Lp(a) levels in a large contemporary cohort of 49,699 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study, and another 10,813 individuals in the Copenhagen City Heart Study.
Measurements assessed included plasma lipoprotein(a) levels and carrier or noncarrier status for LPA rs10455872. The endpoint of ischemic stroke was ascertained from Danish national health registries and confirmed by physicians.
Although risk estimates were less pronounced than what was reported before regarding the link between Lp(a) for ischemic heart disease and aortic valve stenosis, the risk of stroke was increased by a factor of 1.6 among individuals with high Lp(a) levels as compared to those with lower levels, the investigators said.
Compared with noncarriers of LPA rs1045572, the hazard ratio for ischemic stroke was 1.23 for carriers of LPA rs1045572, which was associated with high levels plasma lipoprotein(a) levels, according to the researchers.
“Our results indicate a causal association of Lp(a) with risk of ischemic stroke, and emphasize the need for randomized, controlled clinical trials on the effect of Lp(a)-lowering to prevent cardiovascular disease including ischemic stroke,” About 20% of the general population have high Lp(a) levels, and some individuals have extremely high levels, Dr. Langsted and co-authors said in their report.
Interest in Lp(a) as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease has been reignited following large studies showing that high Lp(a) levels were linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis, according to the investigators.
However, results of various studies are conflicting as to whether high Lp(a) levels increase risk of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, they said.
Both cohort studies used in the analysis were supported by sources in Denmark including the Danish Medical Research Council and Copenhagen University Hospital. Dr. Langsted had no disclosures. One co-author reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Langsted A, et al. JACC 2019;74[1]: 54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.524
High levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and LPA genotypes were linked to increased ischemic stroke risk in a recent large, contemporary general population study, investigators are reporting in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Anne Langsted, MD, with Copenhagen University Hospital and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and her co-researchers evaluated the impact of high Lp(a) levels in a large contemporary cohort of 49,699 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study, and another 10,813 individuals in the Copenhagen City Heart Study.
Measurements assessed included plasma lipoprotein(a) levels and carrier or noncarrier status for LPA rs10455872. The endpoint of ischemic stroke was ascertained from Danish national health registries and confirmed by physicians.
Although risk estimates were less pronounced than what was reported before regarding the link between Lp(a) for ischemic heart disease and aortic valve stenosis, the risk of stroke was increased by a factor of 1.6 among individuals with high Lp(a) levels as compared to those with lower levels, the investigators said.
Compared with noncarriers of LPA rs1045572, the hazard ratio for ischemic stroke was 1.23 for carriers of LPA rs1045572, which was associated with high levels plasma lipoprotein(a) levels, according to the researchers.
“Our results indicate a causal association of Lp(a) with risk of ischemic stroke, and emphasize the need for randomized, controlled clinical trials on the effect of Lp(a)-lowering to prevent cardiovascular disease including ischemic stroke,” About 20% of the general population have high Lp(a) levels, and some individuals have extremely high levels, Dr. Langsted and co-authors said in their report.
Interest in Lp(a) as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease has been reignited following large studies showing that high Lp(a) levels were linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis, according to the investigators.
However, results of various studies are conflicting as to whether high Lp(a) levels increase risk of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, they said.
Both cohort studies used in the analysis were supported by sources in Denmark including the Danish Medical Research Council and Copenhagen University Hospital. Dr. Langsted had no disclosures. One co-author reported disclosures related to Akcea, Amgen, Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Langsted A, et al. JACC 2019;74[1]: 54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.524
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Stroke risk was 1.6X higher with high Lp(a) levels.
Study details: Analysis of 49,699 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study, and 10,813 individuals in the Copenhagen City Heart Study.
Disclosures: Both studies were supported by the sources in Denmark including the Danish Medical Research Council and Copenhagen University Hospital. Dr. Langsted had no disclosures.
Source: Langsted A, et al. JACC 2019;74[1]: 54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.524
Giant cell arteritis: An updated review of an old disease
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a systemic vasculitis involving medium-sized and large arteries, most commonly the temporal, ophthalmic, occipital, vertebral, posterior ciliary, and proximal vertebral arteries. Moreover, involvement of the ophthalmic artery and its branches results in loss of vision. GCA can also involve the aorta and its proximal branches, especially in the upper extremities.
GCA is the most common systemic vasculitis in adults. It occurs almost exclusively in patients over age 50 and affects women more than men. It is most frequent in populations of northern European ancestry, especially Scandinavian. In a retrospective cohort study in Norway, the average annual cumulative incidence rate of GCA was 16.7 per 100,000 people over age 50.1 Risk factors include older age, history of smoking, current smoking, early menopause, and, possibly, stress-related disorders.2
PATHOGENESIS IS NOT COMPLETELY UNDERSTOOD
The pathogenesis of GCA is not completely understood, but there is evidence of immune activation in the arterial wall leading to activation of macrophages and formation of multinucleated giant cells (which may not always be present in biopsies).
The most relevant cytokines in the ongoing pathogenesis are still being defined, but the presence of interferon gamma and interleukin 6 (IL-6) seem to be critical for the expression of the disease. The primary immunogenic triggers for the elaboration of these cytokines and the arteritis remain elusive.
A SPECTRUM OF PRESENTATIONS
The initial symptoms of GCA may be vague, such as malaise, fever, and night sweats, and are likely due to systemic inflammation. Features of vascular involvement include headache, scalp tenderness, and jaw claudication (cramping pain in the jaw while chewing).
A less common but serious feature associated with GCA is partial or complete vision loss affecting 1 or both eyes.3 Some patients suddenly go completely blind without any visual prodrome.
Overlapping GCA phenotypes exist, with a spectrum of presentations that include classic cranial arteritis, extracranial GCA (also called large-vessel GCA), and polymyalgia rheumatica.2
Cranial GCA, the best-characterized clinical presentation, causes symptoms such as headache or signs such as tenderness of the temporal artery. On examination, the temporal arteries may be tender or nodular, and the pulses may be felt above the zygomatic arch, above and in front of the tragus of the ear. About two-thirds of patients with cranial GCA present with new-onset headache, most often in the temporal area, but possibly anywhere throughout the head.
Visual disturbance, jaw claudication, and tongue pain are less common but, if present, increase the likelihood of this diagnosis.2
Large-vessel involvement in GCA is common and refers to involvement of the aorta and its proximal branches. Imaging methods used in diagnosing large-vessel GCA include color Doppler ultrasonography, computed tomography with angiography, magnetic resonance imaging with angiography, and positron emission tomography. In some centers, such imaging is performed in all patients diagnosed with GCA to survey for large-vessel involvement.
Depending on the imaging study, large-vessel involvement has been found in 30% to 80% of cases of GCA.4,5 It is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, weight loss, chills, and malaise, but it can also cause more specific symptoms such as unilateral extremity claudication. In contrast to patients with cranial GCA, patients with large-vessel GCA were younger at onset, less likely to have headaches, and more likely to have arm claudication at presentation.6 Aortitis of the ascending aorta can occur with a histopathologic pattern of GCA but without the clinical stigmata of GCA.
The finding of aortitis should prompt the clinician to question the patient about other symptoms of GCA and to order imaging of the whole vascular tree. Ultrasonography and biopsy of the temporal arteries can be considered. Whether idiopathic aortitis is part of the GCA spectrum remains to be seen.
Laboratory tests often show anemia, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis. Acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are often elevated. The sedimentation rate often exceeds 50 mm/hour and sometimes 100 mm/hour.
In 2 retrospective studies, the number of patients with GCA whose sedimentation rate was less than 50 mm/hour ranged between 5% and 11%.7,8 However, a small percentage of patients with GCA have normal inflammatory markers. Therefore, if the suspicion for GCA is high, treatment should be started and biopsy pursued.9 In patients with paraproteinemia or other causes of a spuriously elevated or low erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein is a more reliable test.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is another rheumatologic condition that can occur independently or in conjunction with GCA. It is characterized by stiffness and pain in the proximal joints such as the hips and shoulders, typically worse in the morning and better with activity. Although the patient may subjectively feel weak, a close neurologic examination will reveal normal muscle strength.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is observed in 40% to 60% of patients with GCA at the time of diagnosis; 16% to 21% of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica may develop GCA, especially if untreated.2,10
Differential diagnosis
Other vasculitides (eg, Takayasu arteritis) can also present with unexplained fever, anemia, and constitutional symptoms.
Infection should be considered if fever is present. An infectious disease accompanied by fever, headache, and elevated inflammatory markers can mimic GCA.
Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy can present with sudden vision loss, prompting concern for underlying GCA. Risk factors include hypertension and diabetes mellitus; other features of GCA, including elevated inflammatory markers, are generally absent.
TEMPORAL ARTERY BIOPSY: THE GOLD STANDARD FOR DIAGNOSIS
Temporal artery biopsy remains the standard to confirm the diagnosis. However, because inflammation in the temporal arteries can affect some segments but not others, biopsy results on conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining can be falsely negative in patients with GCA. In one study,11 the mean sensitivity of unilateral temporal artery biopsy was 86.9%.
Typical positive histologic findings are inflammation with panarteritis, CD4-positive lymphocytes, macrophages, giant cells, and fragmentation of the internal elastic lamina.12
When GCA is suspected, treatment with glucocorticoids should be started immediately and biopsy performed as soon as possible. Delaying biopsy for 14 days or more may not affect the accuracy of biopsy study.13 Treatment should never be withheld while awaiting the results of biopsy study.
Biopsy is usually performed unilaterally, on the same side as the symptoms or abnormal findings on examination. Bilateral temporal artery biopsy is also performed and compared with unilateral biopsy; this approach increases the diagnostic yield by about 5%.14
IMAGING
In patients with suspected GCA, imaging is recommended early to complement the clinical criteria for the diagnosis of GCA.15 Positron emission tomography, computed tomography angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, or Doppler ultrasonography can reveal inflammation of the arteries in the proximal upper or lower limbs or the aorta.2
In patients with suspected cranial GCA, ultrasonography of the temporal and axillary arteries is recommended first. If ultrasonography is not available or is inconclusive, high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the cranial arteries can be used as an alternative. Computed tomography and positron emission tomography of the cranial arteries are not recommended.
In patients with suspected large-vessel GCA, ultrasonography, positron emission tomography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging may be used to screen for vessel wall inflammation, edema, and luminal narrowing in extracranial arteries. Ultrasonography is of limited value in assessing aortitis.
Color duplex ultrasonography can be applied to assess for vascular inflammation of the temporal or large arteries. The typical finding of the “halo” sign, a hypoechoic ring around the arterial lumen, represents the inflammation-induced thickening of the arterial wall. The “compression sign,” the persistence of the “halo” during compression of the vessel lumen by the ultrasound probe, has high specificity for the diagnosis.16
Ultrasonography of suspected GCA has yielded sensitivities of 55% to 100% and specificities of 78% to 100%. However, its sensitivity depends on the user’s level of expertise, so it should be done only in medical centers with a high number of GCA cases and with highly experienced sonographers. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging is an alternative to ultrasonography and has shown similar sensitivity and specificity.3
TREATMENT WITH GLUCOCORTICOIDS
Glucocorticoids remain the standard for treatment of GCA. The therapeutic effect of glucocorticoids in GCA has been established by years of clinical experience, but has never been proven in a placebo-controlled trial. When started appropriately and expeditiously, glucocorticoids produce exquisite resolution of signs and symptoms and prevent the serious complication of vision loss. Rapid resolution of symptoms is so typical of GCA that if the patient’s symptoms persist more than a few days after starting a glucocorticoid, the diagnosis of GCA should be reconsidered.
In a retrospective study of 245 patients with biopsy-proven GCA treated with glucocorticoids, 34 had permanent loss of sight.17 In 32 (94%) of the 34, the vision loss occurred before glucocorticoids were started. Of the remaining 2 patients, 1 lost vision 8 days into treatment, and the other lost vision 3 years after diagnosis and 1 year after discontinuation of glucocorticoids.
In a series of 144 patients with biopsy-proven GCA, 51 had no vision loss at presentation and no vision loss after starting glucocorticoids, and 93 had vision loss at presentation. In the latter group, symptoms worsened within 5 days of starting glucocorticoids in 9 patients.18 If vision was intact at the time of presentation, prompt initiation of glucocorticoids reduced the risk of vision loss to less than 1%.
High doses, slowly tapered
The European League Against Rheumatism recommends early initiation of high-dose glucocorticoids for patients with large-vessel vasculitis,19 and it also recommends glucocorticoids for patients with polymyalgia rheumatica.20 The optimal initial and tapering dosage has never been formally evaluated, but regimens have been devised on the basis of expert opinion.21
For patients with GCA who do not have vision loss at the time of diagnosis, the initial dose is prednisone 1 mg/kg or its equivalent daily for 2 to 4 weeks, after which it is tapered.21 If the initial dosage is prednisone 60 mg orally daily for 2 to 4 weeks, our practice is to taper it to 50 mg daily for 2 weeks, then 40 mg daily for 2 weeks. Then, it is decreased by 5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 20 mg daily, and then by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 10 mg orally daily. Thereafter, the dosage is decreased by 1 mg every 2 to 4 weeks.
For patients with GCA who experience transient vision loss or diplopia at the time of diagnosis, intravenous pulse glucocorticoid therapy should be initiated to reduce the risk of vision loss as rapidly as possible.22 A typical pulse regimen is methylprednisolone 1 g intravenously daily for 3 days. Though not rigorously validated in studies, such an approach is used to avoid vision impairment due to GCA, which is rarely reversible.
RELAPSE OF DISEASE
Suspect a relapse of GCA if the patient’s initial symptoms recur, if inflammatory markers become elevated, or if classic symptoms of GCA or polymyalgia rheumatica occur. Elevations in inflammatory markers do not definitely indicate a flare of GCA, but they should trigger close monitoring of the patient’s symptoms.
Relapse is treated by increasing the glucocorticoid dosage as appropriate to the nature of the relapse. If vision is affected or the patient has symptoms of GCA, then increments of 30 to 60 mg of prednisone are warranted, whereas if the patient has symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica, then increments of 5 to 10 mg of prednisone are usually used.
The incidence of relapses of GCA in multiple tertiary care centers has been reported to vary between 34% and 75%.23,24 Most relapses occur at prednisone dosages of less than 20 mg orally daily and within the first year after diagnosis. The most common symptoms are limb ischemia, jaw claudication, constitutional symptoms, headaches, and polymyalgia rheumatica. In a review of 286 patients,25 213 (74%) had at least 1 relapse. The first relapse occurred in the first year in 50%, by 2 years in 68%, and by 5 years in 79%.
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS
In high doses, glucocorticoids have well-known adverse effects. In a population-based study of 120 patients, each patient treated with glucocorticoids experienced at least 1 adverse effect (cataract, fracture, infection, osteonecrosis, diabetes, hypertension, weight gain, capillary fragility, or hair loss).26 The effects were related to aging and cumulative dosage of prednisone but not to the initial dosage.
Glucocorticoids can affect many organs and systems:
- Eyes (cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, exophthalmos)
- Heart (premature atherosclerotic disease, hypertension, fluid retention, hyperlipidemia, arrhythmias)
- Gastrointestinal system (ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding, gastritis, visceral perforation, hepatic steatosis, acute pancreatitis)
- Bone and muscle (osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, myopathy)
- Brain (mood disorder, psychosis, memory impairment)
- Endocrine system (hyperglycemia, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression)
- Immune system (immunosuppression, leading to infection and leukocytosis).
Patients receiving a glucocorticoid dose equivalent to 20 mg or more of prednisone daily for 1 month or more who also have another cause of immunocompromise need prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.27 They should also receive appropriate immunizations before starting glucocorticoids. Live-virus vaccines should not be given to these patients until they have been off glucocorticoids for 1 month.
Glucocorticoids and bone loss
Glucocorticoids are associated with bone loss and fracture, which can occur within the first few months of use and with dosages as low as 2.5 to 7.5 mg orally daily.28 Therefore, glucocorticoid-induced bone loss has to be treated aggressively, particularly in patients who are older and have a history of fragility fracture.
For patients with GCA who need glucocorticoids in doses greater than 5 mg orally daily for more than 3 months, the following measures are advised to decrease the risk of bone loss:
- Weight-bearing exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Moderation in alcohol intake
- Measures to prevent falls29
- Supplementation with 1,200 mg of calcium and 800 IU of vitamin D.30
Pharmacologic therapy should be initiated in men over age 50 who have established osteoporosis and in postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis or osteopenia. For men over age 50 with established osteopenia, risk assessment with the glucocorticoid-corrected FRAX score (www.sheffield.ac.uk/FRAX) should be performed to identify those at high risk in whom pharmacologic therapy is warranted.31
Bisphosphonates are the first-line therapy for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.32
Teriparatide is the second-line therapy and is used in patients who cannot tolerate bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis therapies, and in those who have severe osteoporosis, with T scores of –3.5 and below if they have not had a fracture, and –2.5 and below if they have had a fragility fracture.33
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody to an osteoclast differentiating factor, may be beneficial for some patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.34
To assess the efficacy of therapy, measuring bone mineral density at baseline and at 1 year of therapy is recommended. If density is stable or improved, then repeating the measurement at 2- to 3-year intervals is suggested.
TOCILIZUMAB: A STEROID-SPARING MEDICATION
Due to the adverse effects of long-term use of glucocorticoids and high rates of relapse, there is a pressing need for medications that are more efficacious and less toxic to treat GCA.
The European League Against Rheumatism, in its 2009 management guidelines for large-vessel vasculitis, recommend using an adjunctive immunosuppressant agent.19 In the case of GCA, they recommend using methotrexate 10 to 15 mg/week, which has shown modest evidence of reducing the relapse rate and lowering the cumulative doses of glucocorticoids needed.35,36
Studies of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and abatacept have not yielded significant reductions in the relapse rate or decreased cumulative doses of prednisone.37,38
Advances in treatment for GCA have stagnated, but recent trials39,40 have evaluated the IL-6 receptor alpha inhibitor tocilizumab, given the central role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of GCA. Case reports have revealed rapid induction and maintenance of remission in GCA using tocilizumab.41,42
Villiger et al39 performed a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to study the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in induction and maintenance of disease remission in 30 patients with newly diagnosed GCA. The primary outcome, complete remission at 12 weeks, was achieved in 85% of patients who received tocilizumab plus tapered prednisolone, compared with 40% of patients who received placebo plus tapering prednisolone. The tocilizumab group also had favorable results in secondary outcomes including relapse-free survival at 52 weeks, time to first relapse after induction of remission, and cumulative dose of prednisolone.
The GiACTA trial. Stone et al40 studied the effect of tocilizumab on rates of relapse during glucocorticoid tapering in 251 GCA patients over the course of 52 weeks. Patients were randomized in a 2:1:1:1 ratio to 4 treatment groups:
- Tocilizumab weekly plus prednisone, with prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Tocilizumab every other week plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 52 weeks.
The primary outcome was the rate of sustained glucocorticoid-free remission at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included the remission rate, the cumulative glucocorticoid dose, and safety measures. At 52 weeks, the rates of sustained remission were:
- 56% with tocilizumab weekly
- 53% with tocilizumab every other week
- 14% with placebo plus 26-week prednisone taper
- 18% with placebo plus 52-week taper.
Differences between the active treatment groups and the placebo groups were statistically significant (P < .001).
The cumulative dose of prednisone in tocilizumab recipients was significantly less than in placebo recipients. Rates of adverse events were similar. Ultimately, the study showed that tocilizumab, either weekly or every other week, was more effective than prednisone alone at sustaining glucocorticoid-free remission in patients with GCA.
However, the study also raised questions about tocilizumab’s toxic effect profile and its long-term efficacy, as well as who are the optimal candidates for this therapy. Data on long-term use of tocilizumab are primarily taken from its use in rheumatoid arthritis.43 As of this writing, Stone et al are conducting an open-label trial to help provide long-term safety and efficacy data in patients with GCA. In the meantime, we must extrapolate data from the long-term use of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis.
Tocilizumab and lower gastrointestinal tract perforation
One of the major adverse effects of long-term use of tocilizumab is lower gastrointestinal tract perforation.
Xie et al,44 in 2016, reported that the risk of perforation in patients on tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis was more than 2 times higher than in patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. However, the absolute rates of perforation were low overall, roughly 1 to 3 per 1,000 patient-years in the tocilizumab group. Risk factors for perforation included older age, history of diverticulitis or other gastrointestinal tract condition, and prednisone doses of 7.5 mg or more a day.
Does tocilizumab prevent blindness?
Another consideration is that tocilizumab may not prevent optic neuropathy. In the GiACTA trial, 1 patient in the group receiving tocilizumab every other week developed optic neuropathy.40 Prednisone had been completely tapered off at the time, and the condition resolved when glucocorticoids were restarted. Thus, it is unknown if tocilizumab would be effective on its own without concomitant use of glucocorticoids.
Vision loss is one of the most severe complications of GCA, and it is still unclear whether tocilizumab can prevent vision loss in GCA. Also, we still have no data on the effect of tocilizumab on histopathologic findings, and whether biopsy yield diminishes over time. We hope future studies will help guide us in this regard.
No guidelines on tocilizumab yet
Clinical guidelines on the appropriate use of tocilizumab in GCA are lacking. The American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism have yet to publish updated guidelines with comments on use of tocilizumab. Therefore, it is unclear if tocilizumab is a first-line treatment in GCA, as its efficacy alone without glucocorticoids and its long-term safety in GCA patients have not been studied.
Treatment with tocilizumab should be individualized; it should be considered in patients who have had adverse effects from glucocorticoids, and in patients who experience a flare or cannot have their glucocorticoid dose lowered to an appropriate range.
The optimal duration of tocilizumab therapy is also unknown. However, using the GiACTA study as a rough guide, we try to limit its use to 1 year until additional data are available.
Patients on IL-6 inhibition may have suppressed C-reactive protein regardless of disease activity.43 Therefore, this laboratory value may not be reliable in determining active disease in patients on tocilizumab.
The GiACTA trial has shown an impressive improvement in the relapse-free remission period in patients with GCA taking tocilizumab. However, much work needs to be done to define the safety of this medication and determine which patients should be started on it. In the meantime, we recommend starting high-dose glucocorticoid therapy as soon as the diagnosis of GCA is suspected. In patients who do not tolerate glucocorticoids or whose disease flares during glucocorticoid taper, we recommend starting treatment with tocilizumab either once a week or every other week for at least 1 year.
- Brekke LK, Diamantopoulos AP, Fevang BT, Aßmus J, Esperø E, Gjesdal CG. Incidence of giant cell arteritis in Western Norway 1972–2012: a retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2017; 19(1):278. doi:10.1186/s13075-017-1479-6
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017; 56(4):506–515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. N Engl J Med 2014; 371(17):1653. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1409206
- Ghinoi A, Pipitone N, Nicolini A, et al. Large-vessel involvement in recent-onset giant cell arteritis: a case-control colour-Doppler sonography study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012; 51(4):730–734. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ker329
- Prieto-González S, Depetris M, García-Martínez A, et al. Positron emission tomography assessment of large vessel inflammation in patients with newly diagnosed, biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a prospective, case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73(7):1388–1392. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204572
- Brack A, Martinez-Taboada V, Stanson A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Disease pattern in cranial and large-vessel giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1999; 42(2):311–317. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<311::AID-ANR14>3.0.CO;2-F
- Salvarani C, Hunder GG. Giant cell arteritis with low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: frequency of occurence in a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 45(2):140–145. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200104)45:2<140::AID-ANR166>3.0.CO;2-2
- Liozon E, Jauberteau-Marchan MO, Ly K, Loustaud-Ratti V, Soria P, Vidal E. Giant cell arteritis with a low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: comments on the article by Salvarani and Hunder. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 47(6):692–694. doi:10.1002/art.10809
- Yu-Wai-Man P, Dayan MR. Giant cell arteritis with normal inflammatory markers. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007; 85(4):460. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0420.2006.00864.x
- Buttgereit F, Dejaco C, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a systematic review. JAMA 2016; 315(22):2442–2458. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.5444
- Niederkohr RD, Levin LA. Management of the patient with suspected temporal arteritis a decision-analytic approach. Ophthalmology 2005; 112(5):744–756. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.01.031
- Bowling K, Rait J, Atkinson J, Srinivas G. Temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: does the end justify the means? Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2017; 20:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2017.06.020
- Daily B, Dassow P, Haynes J, Nashelsky J. Giant cell arteritis: biopsy after corticosteroid initiation. Am Fam Physician 2017; 95(2):116–117. pmid:28084703
- Durling B, Toren A, Patel V, Gilberg S, Weis E, Jordan D. Incidence of discordant temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Can J Ophthalmol 2014; 49(2):157–161. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.12.008
- Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Duftner C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 2018; 77(5):636–643. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212649
- Aschwanden M, Imfeld S, Staub D, et al. The ultrasound compression sign to diagnose temporal giant cell arteritis shows an excellent interobserver agreement. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015; 33(2 suppl 89):S-113–S-115. pmid:26016760
- Aiello PD, Trautmann JC, McPhee TJ, Kunselman AR, Hunder GG. Visual prognosis in giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology 1993; 100(4):550–555. pmid:8479714
- Hayreh SS, Zimmerman B. Visual deterioration in giant cell arteritis patients while on high doses of corticosteroid therapy. Ophthalmology 2003; 110(6):1204–1215. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00228-8
- Mukhtyar C, Guillevin L, Cid MC, et al; European Vasculitis Study Group. EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68(3):318–323. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.088351
- Dejaco C, Singh YP, Perel P, et al; European League Against Rheumatism; American College of Rheumatology. 2015 recommendations for the management of polymyalgia rheumatica: a European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74(10):1799–1807. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207492
- Bienvenu B, Ly KH, Lambert M, et al; Groupe d’Étude Français des Artérites des gros Vaisseaux, under the Aegis of the Filière des Maladies Auto-Immunes et Auto-Inflammatoires Rares. Management of giant cell arteritis: recommendations of the French Study Group for Large Vessel Vasculitis (GEFA). Rev Med Interne 2016; 37(3):154–165. doi:10.1016/j.revmed.2015.12.015
- Hayreh SS, Biousse V. Treatment of acute visual loss in giant cell arteritis: should we prescribe high-dose intravenous steroids or just oral steroids? J Neuroophthalmol 2012; 32(3):278–287. doi:10.1097/WNO.0b013e3182688218
- Restuccia G, Boiardi L, Cavazza A, et al. Flares in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis in Northern Italy: characteristics and predictors in a long-term follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(19):e3524. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000003524
- Kermani TA, Warrington KJ, Cuthbertson D, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. Disease relapses among patients with giant cell arteritis: a prospective, longitudinal cohort study. J Rheumatol 2015; 42(7):1213–1217. doi:10.3899/jrheum.141347
- Labarca C, Koster MJ, Crowson CS, et al. Predictors of relapse and treatment outcomes in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a retrospective cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016; 55(2):347–356. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev348
- Proven A, Gabriel SE, Orces C, O’Fallon WM, Hunder GG. Glucocorticoid therapy in giant cell arteritis: duration and adverse outcomes. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 49(5):703–708. doi:10.1002/art.11388
- Sepkowitz KA. Opportunistic infections in patients with and patients without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34(8):1098–1107. doi:10.1086/339548
- van Staa TP, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. The epidemiology of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 2002; 13(10):777–787. doi:10.1007/s001980200108
- Heffernan MP, Saag KG, Robinson JK, Callen JP. Prevention of osteoporosis associated with chronic glucocorticoid therapy. JAMA 2006; 295(11):1300–1303. pmid:16541489
- Buckley L, Guyatt G, Fink HA, et al. 2017 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017; 69(8):1095–1110. doi:10.1002/acr.23279
- Grossman JM, Gordon R, Ranganath VK, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2010 recommendations for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res 201; 62(11):1515–1526. doi:10.1002/acr.20295
- Allen CS, Yeung JH, Vandermeer B, Homik J. Bisphosphonates for steroid-induced osteoporosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016; 10:CD001347. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001347.pub2
- Carpinteri R, Porcelli T, Mejia C, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and parathyroid hormone. J Endocrinol Invest 2010; 33(suppl 7):16–21. pmid:20938221
- Saag KG, Wagman RB, Geusens P, et al. Denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, double-dummy, non-inferiority study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018; 6(6):445–454. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30075-5
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Hellmann DB, et al; International Network for the Study of Systemic Vasculitides. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adjuvant methotrexate treatment for giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46(5):1309–1318. doi:10.1002/art.10262
- Spiera RF, Mitnick HJ, Kupersmith M, et al. A prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial of methotrexate in the treatment of giant cell arteritis (GCA). Clin Exp Rheumatol 2001; 19(5):495–501. pmid:11579707
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Rendt-Zagar KE, et al; Infliximab-GCA Study Group. Infliximab for maintenance of glucocorticosteroid-induced remission of giant cell arteritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007; 146(9):621–630. pmid:17470830
- Langford CA, Cuthbertson D, Ytterberg SR, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. A randomized, double-blind trial of abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) for the treatment of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017; 69(4):837–845. doi:10.1002/art.40044
- Villiger PM, Adler S, Kuchen S, et al. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 387(10031):1921–1927. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00560-2
- Stone JH, Tuckwell K, Dimonaco S, et al. Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med 2017; 377(4):317–328. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1613849
- Oliveira F, Butendieck RR, Ginsburg WW, Parikh K, Abril A. Tocilizumab, an effective treatment for relapsing giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014; 32(3 suppl 82):S76–S78. pmid:24854376
- Loricera J, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis: multicenter open-label study of 22 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2015; 44(6):717–723. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.12.005
- Tamaki H, Hajj-Ali RA. Tocilizumab for giant cell arteritis—a new giant step in an old disease. JAMA Neurol 2018; 75(2):145–146. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3811
- Xie F, Yun H, Bernatsky S, Curtis JR. Risk for gastrointestinal perforation among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, tocilizumab, or other biologics. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68(11):2612–2617. doi:10.1002/art.39761
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a systemic vasculitis involving medium-sized and large arteries, most commonly the temporal, ophthalmic, occipital, vertebral, posterior ciliary, and proximal vertebral arteries. Moreover, involvement of the ophthalmic artery and its branches results in loss of vision. GCA can also involve the aorta and its proximal branches, especially in the upper extremities.
GCA is the most common systemic vasculitis in adults. It occurs almost exclusively in patients over age 50 and affects women more than men. It is most frequent in populations of northern European ancestry, especially Scandinavian. In a retrospective cohort study in Norway, the average annual cumulative incidence rate of GCA was 16.7 per 100,000 people over age 50.1 Risk factors include older age, history of smoking, current smoking, early menopause, and, possibly, stress-related disorders.2
PATHOGENESIS IS NOT COMPLETELY UNDERSTOOD
The pathogenesis of GCA is not completely understood, but there is evidence of immune activation in the arterial wall leading to activation of macrophages and formation of multinucleated giant cells (which may not always be present in biopsies).
The most relevant cytokines in the ongoing pathogenesis are still being defined, but the presence of interferon gamma and interleukin 6 (IL-6) seem to be critical for the expression of the disease. The primary immunogenic triggers for the elaboration of these cytokines and the arteritis remain elusive.
A SPECTRUM OF PRESENTATIONS
The initial symptoms of GCA may be vague, such as malaise, fever, and night sweats, and are likely due to systemic inflammation. Features of vascular involvement include headache, scalp tenderness, and jaw claudication (cramping pain in the jaw while chewing).
A less common but serious feature associated with GCA is partial or complete vision loss affecting 1 or both eyes.3 Some patients suddenly go completely blind without any visual prodrome.
Overlapping GCA phenotypes exist, with a spectrum of presentations that include classic cranial arteritis, extracranial GCA (also called large-vessel GCA), and polymyalgia rheumatica.2
Cranial GCA, the best-characterized clinical presentation, causes symptoms such as headache or signs such as tenderness of the temporal artery. On examination, the temporal arteries may be tender or nodular, and the pulses may be felt above the zygomatic arch, above and in front of the tragus of the ear. About two-thirds of patients with cranial GCA present with new-onset headache, most often in the temporal area, but possibly anywhere throughout the head.
Visual disturbance, jaw claudication, and tongue pain are less common but, if present, increase the likelihood of this diagnosis.2
Large-vessel involvement in GCA is common and refers to involvement of the aorta and its proximal branches. Imaging methods used in diagnosing large-vessel GCA include color Doppler ultrasonography, computed tomography with angiography, magnetic resonance imaging with angiography, and positron emission tomography. In some centers, such imaging is performed in all patients diagnosed with GCA to survey for large-vessel involvement.
Depending on the imaging study, large-vessel involvement has been found in 30% to 80% of cases of GCA.4,5 It is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, weight loss, chills, and malaise, but it can also cause more specific symptoms such as unilateral extremity claudication. In contrast to patients with cranial GCA, patients with large-vessel GCA were younger at onset, less likely to have headaches, and more likely to have arm claudication at presentation.6 Aortitis of the ascending aorta can occur with a histopathologic pattern of GCA but without the clinical stigmata of GCA.
The finding of aortitis should prompt the clinician to question the patient about other symptoms of GCA and to order imaging of the whole vascular tree. Ultrasonography and biopsy of the temporal arteries can be considered. Whether idiopathic aortitis is part of the GCA spectrum remains to be seen.
Laboratory tests often show anemia, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis. Acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are often elevated. The sedimentation rate often exceeds 50 mm/hour and sometimes 100 mm/hour.
In 2 retrospective studies, the number of patients with GCA whose sedimentation rate was less than 50 mm/hour ranged between 5% and 11%.7,8 However, a small percentage of patients with GCA have normal inflammatory markers. Therefore, if the suspicion for GCA is high, treatment should be started and biopsy pursued.9 In patients with paraproteinemia or other causes of a spuriously elevated or low erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein is a more reliable test.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is another rheumatologic condition that can occur independently or in conjunction with GCA. It is characterized by stiffness and pain in the proximal joints such as the hips and shoulders, typically worse in the morning and better with activity. Although the patient may subjectively feel weak, a close neurologic examination will reveal normal muscle strength.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is observed in 40% to 60% of patients with GCA at the time of diagnosis; 16% to 21% of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica may develop GCA, especially if untreated.2,10
Differential diagnosis
Other vasculitides (eg, Takayasu arteritis) can also present with unexplained fever, anemia, and constitutional symptoms.
Infection should be considered if fever is present. An infectious disease accompanied by fever, headache, and elevated inflammatory markers can mimic GCA.
Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy can present with sudden vision loss, prompting concern for underlying GCA. Risk factors include hypertension and diabetes mellitus; other features of GCA, including elevated inflammatory markers, are generally absent.
TEMPORAL ARTERY BIOPSY: THE GOLD STANDARD FOR DIAGNOSIS
Temporal artery biopsy remains the standard to confirm the diagnosis. However, because inflammation in the temporal arteries can affect some segments but not others, biopsy results on conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining can be falsely negative in patients with GCA. In one study,11 the mean sensitivity of unilateral temporal artery biopsy was 86.9%.
Typical positive histologic findings are inflammation with panarteritis, CD4-positive lymphocytes, macrophages, giant cells, and fragmentation of the internal elastic lamina.12
When GCA is suspected, treatment with glucocorticoids should be started immediately and biopsy performed as soon as possible. Delaying biopsy for 14 days or more may not affect the accuracy of biopsy study.13 Treatment should never be withheld while awaiting the results of biopsy study.
Biopsy is usually performed unilaterally, on the same side as the symptoms or abnormal findings on examination. Bilateral temporal artery biopsy is also performed and compared with unilateral biopsy; this approach increases the diagnostic yield by about 5%.14
IMAGING
In patients with suspected GCA, imaging is recommended early to complement the clinical criteria for the diagnosis of GCA.15 Positron emission tomography, computed tomography angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, or Doppler ultrasonography can reveal inflammation of the arteries in the proximal upper or lower limbs or the aorta.2
In patients with suspected cranial GCA, ultrasonography of the temporal and axillary arteries is recommended first. If ultrasonography is not available or is inconclusive, high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the cranial arteries can be used as an alternative. Computed tomography and positron emission tomography of the cranial arteries are not recommended.
In patients with suspected large-vessel GCA, ultrasonography, positron emission tomography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging may be used to screen for vessel wall inflammation, edema, and luminal narrowing in extracranial arteries. Ultrasonography is of limited value in assessing aortitis.
Color duplex ultrasonography can be applied to assess for vascular inflammation of the temporal or large arteries. The typical finding of the “halo” sign, a hypoechoic ring around the arterial lumen, represents the inflammation-induced thickening of the arterial wall. The “compression sign,” the persistence of the “halo” during compression of the vessel lumen by the ultrasound probe, has high specificity for the diagnosis.16
Ultrasonography of suspected GCA has yielded sensitivities of 55% to 100% and specificities of 78% to 100%. However, its sensitivity depends on the user’s level of expertise, so it should be done only in medical centers with a high number of GCA cases and with highly experienced sonographers. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging is an alternative to ultrasonography and has shown similar sensitivity and specificity.3
TREATMENT WITH GLUCOCORTICOIDS
Glucocorticoids remain the standard for treatment of GCA. The therapeutic effect of glucocorticoids in GCA has been established by years of clinical experience, but has never been proven in a placebo-controlled trial. When started appropriately and expeditiously, glucocorticoids produce exquisite resolution of signs and symptoms and prevent the serious complication of vision loss. Rapid resolution of symptoms is so typical of GCA that if the patient’s symptoms persist more than a few days after starting a glucocorticoid, the diagnosis of GCA should be reconsidered.
In a retrospective study of 245 patients with biopsy-proven GCA treated with glucocorticoids, 34 had permanent loss of sight.17 In 32 (94%) of the 34, the vision loss occurred before glucocorticoids were started. Of the remaining 2 patients, 1 lost vision 8 days into treatment, and the other lost vision 3 years after diagnosis and 1 year after discontinuation of glucocorticoids.
In a series of 144 patients with biopsy-proven GCA, 51 had no vision loss at presentation and no vision loss after starting glucocorticoids, and 93 had vision loss at presentation. In the latter group, symptoms worsened within 5 days of starting glucocorticoids in 9 patients.18 If vision was intact at the time of presentation, prompt initiation of glucocorticoids reduced the risk of vision loss to less than 1%.
High doses, slowly tapered
The European League Against Rheumatism recommends early initiation of high-dose glucocorticoids for patients with large-vessel vasculitis,19 and it also recommends glucocorticoids for patients with polymyalgia rheumatica.20 The optimal initial and tapering dosage has never been formally evaluated, but regimens have been devised on the basis of expert opinion.21
For patients with GCA who do not have vision loss at the time of diagnosis, the initial dose is prednisone 1 mg/kg or its equivalent daily for 2 to 4 weeks, after which it is tapered.21 If the initial dosage is prednisone 60 mg orally daily for 2 to 4 weeks, our practice is to taper it to 50 mg daily for 2 weeks, then 40 mg daily for 2 weeks. Then, it is decreased by 5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 20 mg daily, and then by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 10 mg orally daily. Thereafter, the dosage is decreased by 1 mg every 2 to 4 weeks.
For patients with GCA who experience transient vision loss or diplopia at the time of diagnosis, intravenous pulse glucocorticoid therapy should be initiated to reduce the risk of vision loss as rapidly as possible.22 A typical pulse regimen is methylprednisolone 1 g intravenously daily for 3 days. Though not rigorously validated in studies, such an approach is used to avoid vision impairment due to GCA, which is rarely reversible.
RELAPSE OF DISEASE
Suspect a relapse of GCA if the patient’s initial symptoms recur, if inflammatory markers become elevated, or if classic symptoms of GCA or polymyalgia rheumatica occur. Elevations in inflammatory markers do not definitely indicate a flare of GCA, but they should trigger close monitoring of the patient’s symptoms.
Relapse is treated by increasing the glucocorticoid dosage as appropriate to the nature of the relapse. If vision is affected or the patient has symptoms of GCA, then increments of 30 to 60 mg of prednisone are warranted, whereas if the patient has symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica, then increments of 5 to 10 mg of prednisone are usually used.
The incidence of relapses of GCA in multiple tertiary care centers has been reported to vary between 34% and 75%.23,24 Most relapses occur at prednisone dosages of less than 20 mg orally daily and within the first year after diagnosis. The most common symptoms are limb ischemia, jaw claudication, constitutional symptoms, headaches, and polymyalgia rheumatica. In a review of 286 patients,25 213 (74%) had at least 1 relapse. The first relapse occurred in the first year in 50%, by 2 years in 68%, and by 5 years in 79%.
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS
In high doses, glucocorticoids have well-known adverse effects. In a population-based study of 120 patients, each patient treated with glucocorticoids experienced at least 1 adverse effect (cataract, fracture, infection, osteonecrosis, diabetes, hypertension, weight gain, capillary fragility, or hair loss).26 The effects were related to aging and cumulative dosage of prednisone but not to the initial dosage.
Glucocorticoids can affect many organs and systems:
- Eyes (cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, exophthalmos)
- Heart (premature atherosclerotic disease, hypertension, fluid retention, hyperlipidemia, arrhythmias)
- Gastrointestinal system (ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding, gastritis, visceral perforation, hepatic steatosis, acute pancreatitis)
- Bone and muscle (osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, myopathy)
- Brain (mood disorder, psychosis, memory impairment)
- Endocrine system (hyperglycemia, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression)
- Immune system (immunosuppression, leading to infection and leukocytosis).
Patients receiving a glucocorticoid dose equivalent to 20 mg or more of prednisone daily for 1 month or more who also have another cause of immunocompromise need prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.27 They should also receive appropriate immunizations before starting glucocorticoids. Live-virus vaccines should not be given to these patients until they have been off glucocorticoids for 1 month.
Glucocorticoids and bone loss
Glucocorticoids are associated with bone loss and fracture, which can occur within the first few months of use and with dosages as low as 2.5 to 7.5 mg orally daily.28 Therefore, glucocorticoid-induced bone loss has to be treated aggressively, particularly in patients who are older and have a history of fragility fracture.
For patients with GCA who need glucocorticoids in doses greater than 5 mg orally daily for more than 3 months, the following measures are advised to decrease the risk of bone loss:
- Weight-bearing exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Moderation in alcohol intake
- Measures to prevent falls29
- Supplementation with 1,200 mg of calcium and 800 IU of vitamin D.30
Pharmacologic therapy should be initiated in men over age 50 who have established osteoporosis and in postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis or osteopenia. For men over age 50 with established osteopenia, risk assessment with the glucocorticoid-corrected FRAX score (www.sheffield.ac.uk/FRAX) should be performed to identify those at high risk in whom pharmacologic therapy is warranted.31
Bisphosphonates are the first-line therapy for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.32
Teriparatide is the second-line therapy and is used in patients who cannot tolerate bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis therapies, and in those who have severe osteoporosis, with T scores of –3.5 and below if they have not had a fracture, and –2.5 and below if they have had a fragility fracture.33
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody to an osteoclast differentiating factor, may be beneficial for some patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.34
To assess the efficacy of therapy, measuring bone mineral density at baseline and at 1 year of therapy is recommended. If density is stable or improved, then repeating the measurement at 2- to 3-year intervals is suggested.
TOCILIZUMAB: A STEROID-SPARING MEDICATION
Due to the adverse effects of long-term use of glucocorticoids and high rates of relapse, there is a pressing need for medications that are more efficacious and less toxic to treat GCA.
The European League Against Rheumatism, in its 2009 management guidelines for large-vessel vasculitis, recommend using an adjunctive immunosuppressant agent.19 In the case of GCA, they recommend using methotrexate 10 to 15 mg/week, which has shown modest evidence of reducing the relapse rate and lowering the cumulative doses of glucocorticoids needed.35,36
Studies of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and abatacept have not yielded significant reductions in the relapse rate or decreased cumulative doses of prednisone.37,38
Advances in treatment for GCA have stagnated, but recent trials39,40 have evaluated the IL-6 receptor alpha inhibitor tocilizumab, given the central role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of GCA. Case reports have revealed rapid induction and maintenance of remission in GCA using tocilizumab.41,42
Villiger et al39 performed a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to study the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in induction and maintenance of disease remission in 30 patients with newly diagnosed GCA. The primary outcome, complete remission at 12 weeks, was achieved in 85% of patients who received tocilizumab plus tapered prednisolone, compared with 40% of patients who received placebo plus tapering prednisolone. The tocilizumab group also had favorable results in secondary outcomes including relapse-free survival at 52 weeks, time to first relapse after induction of remission, and cumulative dose of prednisolone.
The GiACTA trial. Stone et al40 studied the effect of tocilizumab on rates of relapse during glucocorticoid tapering in 251 GCA patients over the course of 52 weeks. Patients were randomized in a 2:1:1:1 ratio to 4 treatment groups:
- Tocilizumab weekly plus prednisone, with prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Tocilizumab every other week plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 52 weeks.
The primary outcome was the rate of sustained glucocorticoid-free remission at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included the remission rate, the cumulative glucocorticoid dose, and safety measures. At 52 weeks, the rates of sustained remission were:
- 56% with tocilizumab weekly
- 53% with tocilizumab every other week
- 14% with placebo plus 26-week prednisone taper
- 18% with placebo plus 52-week taper.
Differences between the active treatment groups and the placebo groups were statistically significant (P < .001).
The cumulative dose of prednisone in tocilizumab recipients was significantly less than in placebo recipients. Rates of adverse events were similar. Ultimately, the study showed that tocilizumab, either weekly or every other week, was more effective than prednisone alone at sustaining glucocorticoid-free remission in patients with GCA.
However, the study also raised questions about tocilizumab’s toxic effect profile and its long-term efficacy, as well as who are the optimal candidates for this therapy. Data on long-term use of tocilizumab are primarily taken from its use in rheumatoid arthritis.43 As of this writing, Stone et al are conducting an open-label trial to help provide long-term safety and efficacy data in patients with GCA. In the meantime, we must extrapolate data from the long-term use of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis.
Tocilizumab and lower gastrointestinal tract perforation
One of the major adverse effects of long-term use of tocilizumab is lower gastrointestinal tract perforation.
Xie et al,44 in 2016, reported that the risk of perforation in patients on tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis was more than 2 times higher than in patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. However, the absolute rates of perforation were low overall, roughly 1 to 3 per 1,000 patient-years in the tocilizumab group. Risk factors for perforation included older age, history of diverticulitis or other gastrointestinal tract condition, and prednisone doses of 7.5 mg or more a day.
Does tocilizumab prevent blindness?
Another consideration is that tocilizumab may not prevent optic neuropathy. In the GiACTA trial, 1 patient in the group receiving tocilizumab every other week developed optic neuropathy.40 Prednisone had been completely tapered off at the time, and the condition resolved when glucocorticoids were restarted. Thus, it is unknown if tocilizumab would be effective on its own without concomitant use of glucocorticoids.
Vision loss is one of the most severe complications of GCA, and it is still unclear whether tocilizumab can prevent vision loss in GCA. Also, we still have no data on the effect of tocilizumab on histopathologic findings, and whether biopsy yield diminishes over time. We hope future studies will help guide us in this regard.
No guidelines on tocilizumab yet
Clinical guidelines on the appropriate use of tocilizumab in GCA are lacking. The American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism have yet to publish updated guidelines with comments on use of tocilizumab. Therefore, it is unclear if tocilizumab is a first-line treatment in GCA, as its efficacy alone without glucocorticoids and its long-term safety in GCA patients have not been studied.
Treatment with tocilizumab should be individualized; it should be considered in patients who have had adverse effects from glucocorticoids, and in patients who experience a flare or cannot have their glucocorticoid dose lowered to an appropriate range.
The optimal duration of tocilizumab therapy is also unknown. However, using the GiACTA study as a rough guide, we try to limit its use to 1 year until additional data are available.
Patients on IL-6 inhibition may have suppressed C-reactive protein regardless of disease activity.43 Therefore, this laboratory value may not be reliable in determining active disease in patients on tocilizumab.
The GiACTA trial has shown an impressive improvement in the relapse-free remission period in patients with GCA taking tocilizumab. However, much work needs to be done to define the safety of this medication and determine which patients should be started on it. In the meantime, we recommend starting high-dose glucocorticoid therapy as soon as the diagnosis of GCA is suspected. In patients who do not tolerate glucocorticoids or whose disease flares during glucocorticoid taper, we recommend starting treatment with tocilizumab either once a week or every other week for at least 1 year.
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a systemic vasculitis involving medium-sized and large arteries, most commonly the temporal, ophthalmic, occipital, vertebral, posterior ciliary, and proximal vertebral arteries. Moreover, involvement of the ophthalmic artery and its branches results in loss of vision. GCA can also involve the aorta and its proximal branches, especially in the upper extremities.
GCA is the most common systemic vasculitis in adults. It occurs almost exclusively in patients over age 50 and affects women more than men. It is most frequent in populations of northern European ancestry, especially Scandinavian. In a retrospective cohort study in Norway, the average annual cumulative incidence rate of GCA was 16.7 per 100,000 people over age 50.1 Risk factors include older age, history of smoking, current smoking, early menopause, and, possibly, stress-related disorders.2
PATHOGENESIS IS NOT COMPLETELY UNDERSTOOD
The pathogenesis of GCA is not completely understood, but there is evidence of immune activation in the arterial wall leading to activation of macrophages and formation of multinucleated giant cells (which may not always be present in biopsies).
The most relevant cytokines in the ongoing pathogenesis are still being defined, but the presence of interferon gamma and interleukin 6 (IL-6) seem to be critical for the expression of the disease. The primary immunogenic triggers for the elaboration of these cytokines and the arteritis remain elusive.
A SPECTRUM OF PRESENTATIONS
The initial symptoms of GCA may be vague, such as malaise, fever, and night sweats, and are likely due to systemic inflammation. Features of vascular involvement include headache, scalp tenderness, and jaw claudication (cramping pain in the jaw while chewing).
A less common but serious feature associated with GCA is partial or complete vision loss affecting 1 or both eyes.3 Some patients suddenly go completely blind without any visual prodrome.
Overlapping GCA phenotypes exist, with a spectrum of presentations that include classic cranial arteritis, extracranial GCA (also called large-vessel GCA), and polymyalgia rheumatica.2
Cranial GCA, the best-characterized clinical presentation, causes symptoms such as headache or signs such as tenderness of the temporal artery. On examination, the temporal arteries may be tender or nodular, and the pulses may be felt above the zygomatic arch, above and in front of the tragus of the ear. About two-thirds of patients with cranial GCA present with new-onset headache, most often in the temporal area, but possibly anywhere throughout the head.
Visual disturbance, jaw claudication, and tongue pain are less common but, if present, increase the likelihood of this diagnosis.2
Large-vessel involvement in GCA is common and refers to involvement of the aorta and its proximal branches. Imaging methods used in diagnosing large-vessel GCA include color Doppler ultrasonography, computed tomography with angiography, magnetic resonance imaging with angiography, and positron emission tomography. In some centers, such imaging is performed in all patients diagnosed with GCA to survey for large-vessel involvement.
Depending on the imaging study, large-vessel involvement has been found in 30% to 80% of cases of GCA.4,5 It is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, weight loss, chills, and malaise, but it can also cause more specific symptoms such as unilateral extremity claudication. In contrast to patients with cranial GCA, patients with large-vessel GCA were younger at onset, less likely to have headaches, and more likely to have arm claudication at presentation.6 Aortitis of the ascending aorta can occur with a histopathologic pattern of GCA but without the clinical stigmata of GCA.
The finding of aortitis should prompt the clinician to question the patient about other symptoms of GCA and to order imaging of the whole vascular tree. Ultrasonography and biopsy of the temporal arteries can be considered. Whether idiopathic aortitis is part of the GCA spectrum remains to be seen.
Laboratory tests often show anemia, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis. Acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are often elevated. The sedimentation rate often exceeds 50 mm/hour and sometimes 100 mm/hour.
In 2 retrospective studies, the number of patients with GCA whose sedimentation rate was less than 50 mm/hour ranged between 5% and 11%.7,8 However, a small percentage of patients with GCA have normal inflammatory markers. Therefore, if the suspicion for GCA is high, treatment should be started and biopsy pursued.9 In patients with paraproteinemia or other causes of a spuriously elevated or low erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein is a more reliable test.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is another rheumatologic condition that can occur independently or in conjunction with GCA. It is characterized by stiffness and pain in the proximal joints such as the hips and shoulders, typically worse in the morning and better with activity. Although the patient may subjectively feel weak, a close neurologic examination will reveal normal muscle strength.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is observed in 40% to 60% of patients with GCA at the time of diagnosis; 16% to 21% of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica may develop GCA, especially if untreated.2,10
Differential diagnosis
Other vasculitides (eg, Takayasu arteritis) can also present with unexplained fever, anemia, and constitutional symptoms.
Infection should be considered if fever is present. An infectious disease accompanied by fever, headache, and elevated inflammatory markers can mimic GCA.
Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy can present with sudden vision loss, prompting concern for underlying GCA. Risk factors include hypertension and diabetes mellitus; other features of GCA, including elevated inflammatory markers, are generally absent.
TEMPORAL ARTERY BIOPSY: THE GOLD STANDARD FOR DIAGNOSIS
Temporal artery biopsy remains the standard to confirm the diagnosis. However, because inflammation in the temporal arteries can affect some segments but not others, biopsy results on conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining can be falsely negative in patients with GCA. In one study,11 the mean sensitivity of unilateral temporal artery biopsy was 86.9%.
Typical positive histologic findings are inflammation with panarteritis, CD4-positive lymphocytes, macrophages, giant cells, and fragmentation of the internal elastic lamina.12
When GCA is suspected, treatment with glucocorticoids should be started immediately and biopsy performed as soon as possible. Delaying biopsy for 14 days or more may not affect the accuracy of biopsy study.13 Treatment should never be withheld while awaiting the results of biopsy study.
Biopsy is usually performed unilaterally, on the same side as the symptoms or abnormal findings on examination. Bilateral temporal artery biopsy is also performed and compared with unilateral biopsy; this approach increases the diagnostic yield by about 5%.14
IMAGING
In patients with suspected GCA, imaging is recommended early to complement the clinical criteria for the diagnosis of GCA.15 Positron emission tomography, computed tomography angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, or Doppler ultrasonography can reveal inflammation of the arteries in the proximal upper or lower limbs or the aorta.2
In patients with suspected cranial GCA, ultrasonography of the temporal and axillary arteries is recommended first. If ultrasonography is not available or is inconclusive, high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the cranial arteries can be used as an alternative. Computed tomography and positron emission tomography of the cranial arteries are not recommended.
In patients with suspected large-vessel GCA, ultrasonography, positron emission tomography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging may be used to screen for vessel wall inflammation, edema, and luminal narrowing in extracranial arteries. Ultrasonography is of limited value in assessing aortitis.
Color duplex ultrasonography can be applied to assess for vascular inflammation of the temporal or large arteries. The typical finding of the “halo” sign, a hypoechoic ring around the arterial lumen, represents the inflammation-induced thickening of the arterial wall. The “compression sign,” the persistence of the “halo” during compression of the vessel lumen by the ultrasound probe, has high specificity for the diagnosis.16
Ultrasonography of suspected GCA has yielded sensitivities of 55% to 100% and specificities of 78% to 100%. However, its sensitivity depends on the user’s level of expertise, so it should be done only in medical centers with a high number of GCA cases and with highly experienced sonographers. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging is an alternative to ultrasonography and has shown similar sensitivity and specificity.3
TREATMENT WITH GLUCOCORTICOIDS
Glucocorticoids remain the standard for treatment of GCA. The therapeutic effect of glucocorticoids in GCA has been established by years of clinical experience, but has never been proven in a placebo-controlled trial. When started appropriately and expeditiously, glucocorticoids produce exquisite resolution of signs and symptoms and prevent the serious complication of vision loss. Rapid resolution of symptoms is so typical of GCA that if the patient’s symptoms persist more than a few days after starting a glucocorticoid, the diagnosis of GCA should be reconsidered.
In a retrospective study of 245 patients with biopsy-proven GCA treated with glucocorticoids, 34 had permanent loss of sight.17 In 32 (94%) of the 34, the vision loss occurred before glucocorticoids were started. Of the remaining 2 patients, 1 lost vision 8 days into treatment, and the other lost vision 3 years after diagnosis and 1 year after discontinuation of glucocorticoids.
In a series of 144 patients with biopsy-proven GCA, 51 had no vision loss at presentation and no vision loss after starting glucocorticoids, and 93 had vision loss at presentation. In the latter group, symptoms worsened within 5 days of starting glucocorticoids in 9 patients.18 If vision was intact at the time of presentation, prompt initiation of glucocorticoids reduced the risk of vision loss to less than 1%.
High doses, slowly tapered
The European League Against Rheumatism recommends early initiation of high-dose glucocorticoids for patients with large-vessel vasculitis,19 and it also recommends glucocorticoids for patients with polymyalgia rheumatica.20 The optimal initial and tapering dosage has never been formally evaluated, but regimens have been devised on the basis of expert opinion.21
For patients with GCA who do not have vision loss at the time of diagnosis, the initial dose is prednisone 1 mg/kg or its equivalent daily for 2 to 4 weeks, after which it is tapered.21 If the initial dosage is prednisone 60 mg orally daily for 2 to 4 weeks, our practice is to taper it to 50 mg daily for 2 weeks, then 40 mg daily for 2 weeks. Then, it is decreased by 5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 20 mg daily, and then by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks until it is 10 mg orally daily. Thereafter, the dosage is decreased by 1 mg every 2 to 4 weeks.
For patients with GCA who experience transient vision loss or diplopia at the time of diagnosis, intravenous pulse glucocorticoid therapy should be initiated to reduce the risk of vision loss as rapidly as possible.22 A typical pulse regimen is methylprednisolone 1 g intravenously daily for 3 days. Though not rigorously validated in studies, such an approach is used to avoid vision impairment due to GCA, which is rarely reversible.
RELAPSE OF DISEASE
Suspect a relapse of GCA if the patient’s initial symptoms recur, if inflammatory markers become elevated, or if classic symptoms of GCA or polymyalgia rheumatica occur. Elevations in inflammatory markers do not definitely indicate a flare of GCA, but they should trigger close monitoring of the patient’s symptoms.
Relapse is treated by increasing the glucocorticoid dosage as appropriate to the nature of the relapse. If vision is affected or the patient has symptoms of GCA, then increments of 30 to 60 mg of prednisone are warranted, whereas if the patient has symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica, then increments of 5 to 10 mg of prednisone are usually used.
The incidence of relapses of GCA in multiple tertiary care centers has been reported to vary between 34% and 75%.23,24 Most relapses occur at prednisone dosages of less than 20 mg orally daily and within the first year after diagnosis. The most common symptoms are limb ischemia, jaw claudication, constitutional symptoms, headaches, and polymyalgia rheumatica. In a review of 286 patients,25 213 (74%) had at least 1 relapse. The first relapse occurred in the first year in 50%, by 2 years in 68%, and by 5 years in 79%.
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS
In high doses, glucocorticoids have well-known adverse effects. In a population-based study of 120 patients, each patient treated with glucocorticoids experienced at least 1 adverse effect (cataract, fracture, infection, osteonecrosis, diabetes, hypertension, weight gain, capillary fragility, or hair loss).26 The effects were related to aging and cumulative dosage of prednisone but not to the initial dosage.
Glucocorticoids can affect many organs and systems:
- Eyes (cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, exophthalmos)
- Heart (premature atherosclerotic disease, hypertension, fluid retention, hyperlipidemia, arrhythmias)
- Gastrointestinal system (ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding, gastritis, visceral perforation, hepatic steatosis, acute pancreatitis)
- Bone and muscle (osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, myopathy)
- Brain (mood disorder, psychosis, memory impairment)
- Endocrine system (hyperglycemia, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression)
- Immune system (immunosuppression, leading to infection and leukocytosis).
Patients receiving a glucocorticoid dose equivalent to 20 mg or more of prednisone daily for 1 month or more who also have another cause of immunocompromise need prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.27 They should also receive appropriate immunizations before starting glucocorticoids. Live-virus vaccines should not be given to these patients until they have been off glucocorticoids for 1 month.
Glucocorticoids and bone loss
Glucocorticoids are associated with bone loss and fracture, which can occur within the first few months of use and with dosages as low as 2.5 to 7.5 mg orally daily.28 Therefore, glucocorticoid-induced bone loss has to be treated aggressively, particularly in patients who are older and have a history of fragility fracture.
For patients with GCA who need glucocorticoids in doses greater than 5 mg orally daily for more than 3 months, the following measures are advised to decrease the risk of bone loss:
- Weight-bearing exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Moderation in alcohol intake
- Measures to prevent falls29
- Supplementation with 1,200 mg of calcium and 800 IU of vitamin D.30
Pharmacologic therapy should be initiated in men over age 50 who have established osteoporosis and in postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis or osteopenia. For men over age 50 with established osteopenia, risk assessment with the glucocorticoid-corrected FRAX score (www.sheffield.ac.uk/FRAX) should be performed to identify those at high risk in whom pharmacologic therapy is warranted.31
Bisphosphonates are the first-line therapy for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.32
Teriparatide is the second-line therapy and is used in patients who cannot tolerate bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis therapies, and in those who have severe osteoporosis, with T scores of –3.5 and below if they have not had a fracture, and –2.5 and below if they have had a fragility fracture.33
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody to an osteoclast differentiating factor, may be beneficial for some patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.34
To assess the efficacy of therapy, measuring bone mineral density at baseline and at 1 year of therapy is recommended. If density is stable or improved, then repeating the measurement at 2- to 3-year intervals is suggested.
TOCILIZUMAB: A STEROID-SPARING MEDICATION
Due to the adverse effects of long-term use of glucocorticoids and high rates of relapse, there is a pressing need for medications that are more efficacious and less toxic to treat GCA.
The European League Against Rheumatism, in its 2009 management guidelines for large-vessel vasculitis, recommend using an adjunctive immunosuppressant agent.19 In the case of GCA, they recommend using methotrexate 10 to 15 mg/week, which has shown modest evidence of reducing the relapse rate and lowering the cumulative doses of glucocorticoids needed.35,36
Studies of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and abatacept have not yielded significant reductions in the relapse rate or decreased cumulative doses of prednisone.37,38
Advances in treatment for GCA have stagnated, but recent trials39,40 have evaluated the IL-6 receptor alpha inhibitor tocilizumab, given the central role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of GCA. Case reports have revealed rapid induction and maintenance of remission in GCA using tocilizumab.41,42
Villiger et al39 performed a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to study the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in induction and maintenance of disease remission in 30 patients with newly diagnosed GCA. The primary outcome, complete remission at 12 weeks, was achieved in 85% of patients who received tocilizumab plus tapered prednisolone, compared with 40% of patients who received placebo plus tapering prednisolone. The tocilizumab group also had favorable results in secondary outcomes including relapse-free survival at 52 weeks, time to first relapse after induction of remission, and cumulative dose of prednisolone.
The GiACTA trial. Stone et al40 studied the effect of tocilizumab on rates of relapse during glucocorticoid tapering in 251 GCA patients over the course of 52 weeks. Patients were randomized in a 2:1:1:1 ratio to 4 treatment groups:
- Tocilizumab weekly plus prednisone, with prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Tocilizumab every other week plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 26 weeks
- Placebo plus prednisone tapered over 52 weeks.
The primary outcome was the rate of sustained glucocorticoid-free remission at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included the remission rate, the cumulative glucocorticoid dose, and safety measures. At 52 weeks, the rates of sustained remission were:
- 56% with tocilizumab weekly
- 53% with tocilizumab every other week
- 14% with placebo plus 26-week prednisone taper
- 18% with placebo plus 52-week taper.
Differences between the active treatment groups and the placebo groups were statistically significant (P < .001).
The cumulative dose of prednisone in tocilizumab recipients was significantly less than in placebo recipients. Rates of adverse events were similar. Ultimately, the study showed that tocilizumab, either weekly or every other week, was more effective than prednisone alone at sustaining glucocorticoid-free remission in patients with GCA.
However, the study also raised questions about tocilizumab’s toxic effect profile and its long-term efficacy, as well as who are the optimal candidates for this therapy. Data on long-term use of tocilizumab are primarily taken from its use in rheumatoid arthritis.43 As of this writing, Stone et al are conducting an open-label trial to help provide long-term safety and efficacy data in patients with GCA. In the meantime, we must extrapolate data from the long-term use of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis.
Tocilizumab and lower gastrointestinal tract perforation
One of the major adverse effects of long-term use of tocilizumab is lower gastrointestinal tract perforation.
Xie et al,44 in 2016, reported that the risk of perforation in patients on tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis was more than 2 times higher than in patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. However, the absolute rates of perforation were low overall, roughly 1 to 3 per 1,000 patient-years in the tocilizumab group. Risk factors for perforation included older age, history of diverticulitis or other gastrointestinal tract condition, and prednisone doses of 7.5 mg or more a day.
Does tocilizumab prevent blindness?
Another consideration is that tocilizumab may not prevent optic neuropathy. In the GiACTA trial, 1 patient in the group receiving tocilizumab every other week developed optic neuropathy.40 Prednisone had been completely tapered off at the time, and the condition resolved when glucocorticoids were restarted. Thus, it is unknown if tocilizumab would be effective on its own without concomitant use of glucocorticoids.
Vision loss is one of the most severe complications of GCA, and it is still unclear whether tocilizumab can prevent vision loss in GCA. Also, we still have no data on the effect of tocilizumab on histopathologic findings, and whether biopsy yield diminishes over time. We hope future studies will help guide us in this regard.
No guidelines on tocilizumab yet
Clinical guidelines on the appropriate use of tocilizumab in GCA are lacking. The American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism have yet to publish updated guidelines with comments on use of tocilizumab. Therefore, it is unclear if tocilizumab is a first-line treatment in GCA, as its efficacy alone without glucocorticoids and its long-term safety in GCA patients have not been studied.
Treatment with tocilizumab should be individualized; it should be considered in patients who have had adverse effects from glucocorticoids, and in patients who experience a flare or cannot have their glucocorticoid dose lowered to an appropriate range.
The optimal duration of tocilizumab therapy is also unknown. However, using the GiACTA study as a rough guide, we try to limit its use to 1 year until additional data are available.
Patients on IL-6 inhibition may have suppressed C-reactive protein regardless of disease activity.43 Therefore, this laboratory value may not be reliable in determining active disease in patients on tocilizumab.
The GiACTA trial has shown an impressive improvement in the relapse-free remission period in patients with GCA taking tocilizumab. However, much work needs to be done to define the safety of this medication and determine which patients should be started on it. In the meantime, we recommend starting high-dose glucocorticoid therapy as soon as the diagnosis of GCA is suspected. In patients who do not tolerate glucocorticoids or whose disease flares during glucocorticoid taper, we recommend starting treatment with tocilizumab either once a week or every other week for at least 1 year.
- Brekke LK, Diamantopoulos AP, Fevang BT, Aßmus J, Esperø E, Gjesdal CG. Incidence of giant cell arteritis in Western Norway 1972–2012: a retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2017; 19(1):278. doi:10.1186/s13075-017-1479-6
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017; 56(4):506–515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. N Engl J Med 2014; 371(17):1653. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1409206
- Ghinoi A, Pipitone N, Nicolini A, et al. Large-vessel involvement in recent-onset giant cell arteritis: a case-control colour-Doppler sonography study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012; 51(4):730–734. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ker329
- Prieto-González S, Depetris M, García-Martínez A, et al. Positron emission tomography assessment of large vessel inflammation in patients with newly diagnosed, biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a prospective, case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73(7):1388–1392. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204572
- Brack A, Martinez-Taboada V, Stanson A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Disease pattern in cranial and large-vessel giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1999; 42(2):311–317. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<311::AID-ANR14>3.0.CO;2-F
- Salvarani C, Hunder GG. Giant cell arteritis with low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: frequency of occurence in a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 45(2):140–145. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200104)45:2<140::AID-ANR166>3.0.CO;2-2
- Liozon E, Jauberteau-Marchan MO, Ly K, Loustaud-Ratti V, Soria P, Vidal E. Giant cell arteritis with a low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: comments on the article by Salvarani and Hunder. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 47(6):692–694. doi:10.1002/art.10809
- Yu-Wai-Man P, Dayan MR. Giant cell arteritis with normal inflammatory markers. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007; 85(4):460. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0420.2006.00864.x
- Buttgereit F, Dejaco C, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a systematic review. JAMA 2016; 315(22):2442–2458. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.5444
- Niederkohr RD, Levin LA. Management of the patient with suspected temporal arteritis a decision-analytic approach. Ophthalmology 2005; 112(5):744–756. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.01.031
- Bowling K, Rait J, Atkinson J, Srinivas G. Temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: does the end justify the means? Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2017; 20:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2017.06.020
- Daily B, Dassow P, Haynes J, Nashelsky J. Giant cell arteritis: biopsy after corticosteroid initiation. Am Fam Physician 2017; 95(2):116–117. pmid:28084703
- Durling B, Toren A, Patel V, Gilberg S, Weis E, Jordan D. Incidence of discordant temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Can J Ophthalmol 2014; 49(2):157–161. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.12.008
- Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Duftner C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 2018; 77(5):636–643. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212649
- Aschwanden M, Imfeld S, Staub D, et al. The ultrasound compression sign to diagnose temporal giant cell arteritis shows an excellent interobserver agreement. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015; 33(2 suppl 89):S-113–S-115. pmid:26016760
- Aiello PD, Trautmann JC, McPhee TJ, Kunselman AR, Hunder GG. Visual prognosis in giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology 1993; 100(4):550–555. pmid:8479714
- Hayreh SS, Zimmerman B. Visual deterioration in giant cell arteritis patients while on high doses of corticosteroid therapy. Ophthalmology 2003; 110(6):1204–1215. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00228-8
- Mukhtyar C, Guillevin L, Cid MC, et al; European Vasculitis Study Group. EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68(3):318–323. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.088351
- Dejaco C, Singh YP, Perel P, et al; European League Against Rheumatism; American College of Rheumatology. 2015 recommendations for the management of polymyalgia rheumatica: a European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74(10):1799–1807. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207492
- Bienvenu B, Ly KH, Lambert M, et al; Groupe d’Étude Français des Artérites des gros Vaisseaux, under the Aegis of the Filière des Maladies Auto-Immunes et Auto-Inflammatoires Rares. Management of giant cell arteritis: recommendations of the French Study Group for Large Vessel Vasculitis (GEFA). Rev Med Interne 2016; 37(3):154–165. doi:10.1016/j.revmed.2015.12.015
- Hayreh SS, Biousse V. Treatment of acute visual loss in giant cell arteritis: should we prescribe high-dose intravenous steroids or just oral steroids? J Neuroophthalmol 2012; 32(3):278–287. doi:10.1097/WNO.0b013e3182688218
- Restuccia G, Boiardi L, Cavazza A, et al. Flares in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis in Northern Italy: characteristics and predictors in a long-term follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(19):e3524. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000003524
- Kermani TA, Warrington KJ, Cuthbertson D, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. Disease relapses among patients with giant cell arteritis: a prospective, longitudinal cohort study. J Rheumatol 2015; 42(7):1213–1217. doi:10.3899/jrheum.141347
- Labarca C, Koster MJ, Crowson CS, et al. Predictors of relapse and treatment outcomes in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a retrospective cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016; 55(2):347–356. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev348
- Proven A, Gabriel SE, Orces C, O’Fallon WM, Hunder GG. Glucocorticoid therapy in giant cell arteritis: duration and adverse outcomes. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 49(5):703–708. doi:10.1002/art.11388
- Sepkowitz KA. Opportunistic infections in patients with and patients without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34(8):1098–1107. doi:10.1086/339548
- van Staa TP, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. The epidemiology of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 2002; 13(10):777–787. doi:10.1007/s001980200108
- Heffernan MP, Saag KG, Robinson JK, Callen JP. Prevention of osteoporosis associated with chronic glucocorticoid therapy. JAMA 2006; 295(11):1300–1303. pmid:16541489
- Buckley L, Guyatt G, Fink HA, et al. 2017 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017; 69(8):1095–1110. doi:10.1002/acr.23279
- Grossman JM, Gordon R, Ranganath VK, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2010 recommendations for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res 201; 62(11):1515–1526. doi:10.1002/acr.20295
- Allen CS, Yeung JH, Vandermeer B, Homik J. Bisphosphonates for steroid-induced osteoporosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016; 10:CD001347. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001347.pub2
- Carpinteri R, Porcelli T, Mejia C, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and parathyroid hormone. J Endocrinol Invest 2010; 33(suppl 7):16–21. pmid:20938221
- Saag KG, Wagman RB, Geusens P, et al. Denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, double-dummy, non-inferiority study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018; 6(6):445–454. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30075-5
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Hellmann DB, et al; International Network for the Study of Systemic Vasculitides. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adjuvant methotrexate treatment for giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46(5):1309–1318. doi:10.1002/art.10262
- Spiera RF, Mitnick HJ, Kupersmith M, et al. A prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial of methotrexate in the treatment of giant cell arteritis (GCA). Clin Exp Rheumatol 2001; 19(5):495–501. pmid:11579707
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Rendt-Zagar KE, et al; Infliximab-GCA Study Group. Infliximab for maintenance of glucocorticosteroid-induced remission of giant cell arteritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007; 146(9):621–630. pmid:17470830
- Langford CA, Cuthbertson D, Ytterberg SR, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. A randomized, double-blind trial of abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) for the treatment of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017; 69(4):837–845. doi:10.1002/art.40044
- Villiger PM, Adler S, Kuchen S, et al. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 387(10031):1921–1927. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00560-2
- Stone JH, Tuckwell K, Dimonaco S, et al. Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med 2017; 377(4):317–328. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1613849
- Oliveira F, Butendieck RR, Ginsburg WW, Parikh K, Abril A. Tocilizumab, an effective treatment for relapsing giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014; 32(3 suppl 82):S76–S78. pmid:24854376
- Loricera J, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis: multicenter open-label study of 22 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2015; 44(6):717–723. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.12.005
- Tamaki H, Hajj-Ali RA. Tocilizumab for giant cell arteritis—a new giant step in an old disease. JAMA Neurol 2018; 75(2):145–146. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3811
- Xie F, Yun H, Bernatsky S, Curtis JR. Risk for gastrointestinal perforation among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, tocilizumab, or other biologics. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68(11):2612–2617. doi:10.1002/art.39761
- Brekke LK, Diamantopoulos AP, Fevang BT, Aßmus J, Esperø E, Gjesdal CG. Incidence of giant cell arteritis in Western Norway 1972–2012: a retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2017; 19(1):278. doi:10.1186/s13075-017-1479-6
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017; 56(4):506–515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. N Engl J Med 2014; 371(17):1653. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1409206
- Ghinoi A, Pipitone N, Nicolini A, et al. Large-vessel involvement in recent-onset giant cell arteritis: a case-control colour-Doppler sonography study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012; 51(4):730–734. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ker329
- Prieto-González S, Depetris M, García-Martínez A, et al. Positron emission tomography assessment of large vessel inflammation in patients with newly diagnosed, biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a prospective, case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73(7):1388–1392. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204572
- Brack A, Martinez-Taboada V, Stanson A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Disease pattern in cranial and large-vessel giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1999; 42(2):311–317. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<311::AID-ANR14>3.0.CO;2-F
- Salvarani C, Hunder GG. Giant cell arteritis with low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: frequency of occurence in a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 45(2):140–145. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200104)45:2<140::AID-ANR166>3.0.CO;2-2
- Liozon E, Jauberteau-Marchan MO, Ly K, Loustaud-Ratti V, Soria P, Vidal E. Giant cell arteritis with a low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: comments on the article by Salvarani and Hunder. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 47(6):692–694. doi:10.1002/art.10809
- Yu-Wai-Man P, Dayan MR. Giant cell arteritis with normal inflammatory markers. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007; 85(4):460. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0420.2006.00864.x
- Buttgereit F, Dejaco C, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a systematic review. JAMA 2016; 315(22):2442–2458. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.5444
- Niederkohr RD, Levin LA. Management of the patient with suspected temporal arteritis a decision-analytic approach. Ophthalmology 2005; 112(5):744–756. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.01.031
- Bowling K, Rait J, Atkinson J, Srinivas G. Temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: does the end justify the means? Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2017; 20:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2017.06.020
- Daily B, Dassow P, Haynes J, Nashelsky J. Giant cell arteritis: biopsy after corticosteroid initiation. Am Fam Physician 2017; 95(2):116–117. pmid:28084703
- Durling B, Toren A, Patel V, Gilberg S, Weis E, Jordan D. Incidence of discordant temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Can J Ophthalmol 2014; 49(2):157–161. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.12.008
- Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Duftner C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 2018; 77(5):636–643. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212649
- Aschwanden M, Imfeld S, Staub D, et al. The ultrasound compression sign to diagnose temporal giant cell arteritis shows an excellent interobserver agreement. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015; 33(2 suppl 89):S-113–S-115. pmid:26016760
- Aiello PD, Trautmann JC, McPhee TJ, Kunselman AR, Hunder GG. Visual prognosis in giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology 1993; 100(4):550–555. pmid:8479714
- Hayreh SS, Zimmerman B. Visual deterioration in giant cell arteritis patients while on high doses of corticosteroid therapy. Ophthalmology 2003; 110(6):1204–1215. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00228-8
- Mukhtyar C, Guillevin L, Cid MC, et al; European Vasculitis Study Group. EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68(3):318–323. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.088351
- Dejaco C, Singh YP, Perel P, et al; European League Against Rheumatism; American College of Rheumatology. 2015 recommendations for the management of polymyalgia rheumatica: a European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74(10):1799–1807. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207492
- Bienvenu B, Ly KH, Lambert M, et al; Groupe d’Étude Français des Artérites des gros Vaisseaux, under the Aegis of the Filière des Maladies Auto-Immunes et Auto-Inflammatoires Rares. Management of giant cell arteritis: recommendations of the French Study Group for Large Vessel Vasculitis (GEFA). Rev Med Interne 2016; 37(3):154–165. doi:10.1016/j.revmed.2015.12.015
- Hayreh SS, Biousse V. Treatment of acute visual loss in giant cell arteritis: should we prescribe high-dose intravenous steroids or just oral steroids? J Neuroophthalmol 2012; 32(3):278–287. doi:10.1097/WNO.0b013e3182688218
- Restuccia G, Boiardi L, Cavazza A, et al. Flares in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis in Northern Italy: characteristics and predictors in a long-term follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(19):e3524. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000003524
- Kermani TA, Warrington KJ, Cuthbertson D, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. Disease relapses among patients with giant cell arteritis: a prospective, longitudinal cohort study. J Rheumatol 2015; 42(7):1213–1217. doi:10.3899/jrheum.141347
- Labarca C, Koster MJ, Crowson CS, et al. Predictors of relapse and treatment outcomes in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: a retrospective cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016; 55(2):347–356. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev348
- Proven A, Gabriel SE, Orces C, O’Fallon WM, Hunder GG. Glucocorticoid therapy in giant cell arteritis: duration and adverse outcomes. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 49(5):703–708. doi:10.1002/art.11388
- Sepkowitz KA. Opportunistic infections in patients with and patients without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34(8):1098–1107. doi:10.1086/339548
- van Staa TP, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. The epidemiology of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 2002; 13(10):777–787. doi:10.1007/s001980200108
- Heffernan MP, Saag KG, Robinson JK, Callen JP. Prevention of osteoporosis associated with chronic glucocorticoid therapy. JAMA 2006; 295(11):1300–1303. pmid:16541489
- Buckley L, Guyatt G, Fink HA, et al. 2017 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017; 69(8):1095–1110. doi:10.1002/acr.23279
- Grossman JM, Gordon R, Ranganath VK, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2010 recommendations for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthritis Care Res 201; 62(11):1515–1526. doi:10.1002/acr.20295
- Allen CS, Yeung JH, Vandermeer B, Homik J. Bisphosphonates for steroid-induced osteoporosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016; 10:CD001347. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001347.pub2
- Carpinteri R, Porcelli T, Mejia C, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and parathyroid hormone. J Endocrinol Invest 2010; 33(suppl 7):16–21. pmid:20938221
- Saag KG, Wagman RB, Geusens P, et al. Denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, double-dummy, non-inferiority study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018; 6(6):445–454. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30075-5
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Hellmann DB, et al; International Network for the Study of Systemic Vasculitides. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adjuvant methotrexate treatment for giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46(5):1309–1318. doi:10.1002/art.10262
- Spiera RF, Mitnick HJ, Kupersmith M, et al. A prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial of methotrexate in the treatment of giant cell arteritis (GCA). Clin Exp Rheumatol 2001; 19(5):495–501. pmid:11579707
- Hoffman GS, Cid MC, Rendt-Zagar KE, et al; Infliximab-GCA Study Group. Infliximab for maintenance of glucocorticosteroid-induced remission of giant cell arteritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007; 146(9):621–630. pmid:17470830
- Langford CA, Cuthbertson D, Ytterberg SR, et al; Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. A randomized, double-blind trial of abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) for the treatment of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017; 69(4):837–845. doi:10.1002/art.40044
- Villiger PM, Adler S, Kuchen S, et al. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 387(10031):1921–1927. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00560-2
- Stone JH, Tuckwell K, Dimonaco S, et al. Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med 2017; 377(4):317–328. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1613849
- Oliveira F, Butendieck RR, Ginsburg WW, Parikh K, Abril A. Tocilizumab, an effective treatment for relapsing giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014; 32(3 suppl 82):S76–S78. pmid:24854376
- Loricera J, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis: multicenter open-label study of 22 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2015; 44(6):717–723. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.12.005
- Tamaki H, Hajj-Ali RA. Tocilizumab for giant cell arteritis—a new giant step in an old disease. JAMA Neurol 2018; 75(2):145–146. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3811
- Xie F, Yun H, Bernatsky S, Curtis JR. Risk for gastrointestinal perforation among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, tocilizumab, or other biologics. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68(11):2612–2617. doi:10.1002/art.39761
KEY POINTS
- Giant cell arteritis can present with cranial symptoms, extracranial large-vessel involvement, or polymyalgia rheumatica.
- Temporal artery biopsy is the standard for diagnosis.
- Adverse effects of glucocorticoid treatment, particularly bone loss, need to be managed.
- In patients treated with glucocorticoids alone, the relapse rate is high when the drugs are tapered; thus, prolonged treatment is required.