User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Cases of potentially deadly fungus jump 200%: CDC
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
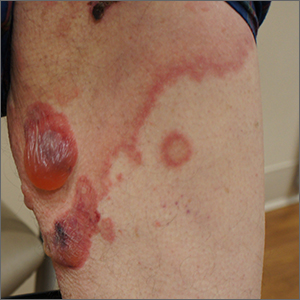
Blisters on arms and legs
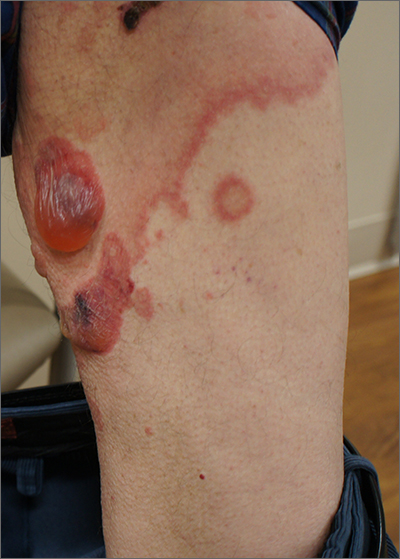
This patient was given a diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid. Although there were a number of clues that pointed to this diagnosis, confirming that this was the case required 2 biopsies and a blood draw. (More on this in a bit.)
Although rare and potentially lethal, bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disease in the elderly. Patients present with tense bullae over limited or widespread areas of the skin. The pathogenesis includes development of autoimmune antibodies that target important proteins (BP180 and BP230) that bind basal epidermal keratinocytes to the dermis. When weakened by inflammation at these sites, the skin delaminates at the dermal-epidermal junction, while the cells of the epidermis continue to bind to each other. This leads to itching, hive-like wheals, and tense fluid-filled bullae.
The differential diagnosis of an acute or semi-acute bullous disease includes bullous pemphigoid, IgA pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and Senear-Usher syndrome. In this case, the large tense bullae suggested bullous pemphigoid over the other diagnoses.
Initial diagnosis requires 2 biopsies be performed: One at the edge of a bulla for a standard pathologic exam to identify the skin level at which the bulla is forming, and another biopsy of skin near the site of inflammation (5-10 mm away) to be sent for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) in Michel’s medium or Zeus medium. In bullous pemphigoid, the separation is at the dermal-epidermal junction, and IgG and C3 are found in the DIF in the same location. There are a couple ways to differentiate this disorder from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita—a similar blistering disorder in which autoantibodies attack collagen at the dermal-epidermal junction. A common approach is to send a patient’s serum for indirect immunofluorescence. This is done because it is impossible to distinguish between the 2 clinically.
While bullous pemphigoid has historically been treated with high-dose prednisone, it is more common now to treat with whole-body topical clobetasol and oral doxycycline 100 mg twice a day to avoid the adverse effects of the prednisone. Other immunosuppressive options, such as mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine, can provide the potency of prednisone with a more favorable long-term safety profile. Rituximab infusions are another very powerful and durable option in refractory or severe cases.1
This patient was treated with topical clobetasol and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day, but he had incomplete clearance after 2 to 3 weeks. At that point, mycophenolate mofetil was added to the regimen and was titrated up to 1000 mg twice daily. When clearance occurred, the clobetasol was discontinued and the mycophenolate mofetil was titrated down to 250 mg/d; the patient continues to maintain clearance at this dose. He continues on doxycycline 100 mg bid.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Ruggiero A, Megna M, Villani A, et al. Strategies to improve outcomes of bullous pemphigoid: a comprehensive review of clinical presentations, diagnosis, and patients' assessment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:661-673. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267573

This patient was given a diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid. Although there were a number of clues that pointed to this diagnosis, confirming that this was the case required 2 biopsies and a blood draw. (More on this in a bit.)
Although rare and potentially lethal, bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disease in the elderly. Patients present with tense bullae over limited or widespread areas of the skin. The pathogenesis includes development of autoimmune antibodies that target important proteins (BP180 and BP230) that bind basal epidermal keratinocytes to the dermis. When weakened by inflammation at these sites, the skin delaminates at the dermal-epidermal junction, while the cells of the epidermis continue to bind to each other. This leads to itching, hive-like wheals, and tense fluid-filled bullae.
The differential diagnosis of an acute or semi-acute bullous disease includes bullous pemphigoid, IgA pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and Senear-Usher syndrome. In this case, the large tense bullae suggested bullous pemphigoid over the other diagnoses.
Initial diagnosis requires 2 biopsies be performed: One at the edge of a bulla for a standard pathologic exam to identify the skin level at which the bulla is forming, and another biopsy of skin near the site of inflammation (5-10 mm away) to be sent for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) in Michel’s medium or Zeus medium. In bullous pemphigoid, the separation is at the dermal-epidermal junction, and IgG and C3 are found in the DIF in the same location. There are a couple ways to differentiate this disorder from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita—a similar blistering disorder in which autoantibodies attack collagen at the dermal-epidermal junction. A common approach is to send a patient’s serum for indirect immunofluorescence. This is done because it is impossible to distinguish between the 2 clinically.
While bullous pemphigoid has historically been treated with high-dose prednisone, it is more common now to treat with whole-body topical clobetasol and oral doxycycline 100 mg twice a day to avoid the adverse effects of the prednisone. Other immunosuppressive options, such as mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine, can provide the potency of prednisone with a more favorable long-term safety profile. Rituximab infusions are another very powerful and durable option in refractory or severe cases.1
This patient was treated with topical clobetasol and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day, but he had incomplete clearance after 2 to 3 weeks. At that point, mycophenolate mofetil was added to the regimen and was titrated up to 1000 mg twice daily. When clearance occurred, the clobetasol was discontinued and the mycophenolate mofetil was titrated down to 250 mg/d; the patient continues to maintain clearance at this dose. He continues on doxycycline 100 mg bid.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

This patient was given a diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid. Although there were a number of clues that pointed to this diagnosis, confirming that this was the case required 2 biopsies and a blood draw. (More on this in a bit.)
Although rare and potentially lethal, bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disease in the elderly. Patients present with tense bullae over limited or widespread areas of the skin. The pathogenesis includes development of autoimmune antibodies that target important proteins (BP180 and BP230) that bind basal epidermal keratinocytes to the dermis. When weakened by inflammation at these sites, the skin delaminates at the dermal-epidermal junction, while the cells of the epidermis continue to bind to each other. This leads to itching, hive-like wheals, and tense fluid-filled bullae.
The differential diagnosis of an acute or semi-acute bullous disease includes bullous pemphigoid, IgA pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and Senear-Usher syndrome. In this case, the large tense bullae suggested bullous pemphigoid over the other diagnoses.
Initial diagnosis requires 2 biopsies be performed: One at the edge of a bulla for a standard pathologic exam to identify the skin level at which the bulla is forming, and another biopsy of skin near the site of inflammation (5-10 mm away) to be sent for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) in Michel’s medium or Zeus medium. In bullous pemphigoid, the separation is at the dermal-epidermal junction, and IgG and C3 are found in the DIF in the same location. There are a couple ways to differentiate this disorder from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita—a similar blistering disorder in which autoantibodies attack collagen at the dermal-epidermal junction. A common approach is to send a patient’s serum for indirect immunofluorescence. This is done because it is impossible to distinguish between the 2 clinically.
While bullous pemphigoid has historically been treated with high-dose prednisone, it is more common now to treat with whole-body topical clobetasol and oral doxycycline 100 mg twice a day to avoid the adverse effects of the prednisone. Other immunosuppressive options, such as mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine, can provide the potency of prednisone with a more favorable long-term safety profile. Rituximab infusions are another very powerful and durable option in refractory or severe cases.1
This patient was treated with topical clobetasol and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day, but he had incomplete clearance after 2 to 3 weeks. At that point, mycophenolate mofetil was added to the regimen and was titrated up to 1000 mg twice daily. When clearance occurred, the clobetasol was discontinued and the mycophenolate mofetil was titrated down to 250 mg/d; the patient continues to maintain clearance at this dose. He continues on doxycycline 100 mg bid.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Ruggiero A, Megna M, Villani A, et al. Strategies to improve outcomes of bullous pemphigoid: a comprehensive review of clinical presentations, diagnosis, and patients' assessment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:661-673. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267573
1. Ruggiero A, Megna M, Villani A, et al. Strategies to improve outcomes of bullous pemphigoid: a comprehensive review of clinical presentations, diagnosis, and patients' assessment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:661-673. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267573
COVID can mimic prostate cancer symptoms
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Like mother, like daughter? Moms pass obesity risk to girls
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s the ‘secret sauce’ to help patients move more?
“Just Do It” is a cute marketing slogan. But let’s face it: Clinically, it doesn’t work well. Most people just don’t exercise. according to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Furthermore, when surveyed about aerobic exercise and strength training, only 24.6% meet these weekly recommendations. These low rates of physical activity are alarming, given the immense benefits of exercise in improving mental and physical health and well-being.
Many people know that exercise is good for them but struggle to go workout consistently. I know firsthand how challenging this can be. In addition to being an integrative obesity specialist, I have gone from 0 minutes of physical activity in 2014 to becoming a fitness enthusiast who’s run more than 5,300 miles over 8 years. I know that as doctors and clinicians, we can profoundly influence our patients’ exercise journey.
Here are five tips to help motivate your patients make the change from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Tip 1: ‘[Clinician], heal thyself’
Data don’t lie. Doctors who move more are more likely to counsel patients on exercise. I’ve been the doctor on both sides of the exercise spectrum. At my heaviest weight and lowest physical activity level, I felt hypocritical counseling patients on exercise.
If and when I counseled my patients on exercise, it was very directive and impersonal. When I started running consistently, I went to the opposite end of the spectrum. In my running zeal, it took a while for me to understand that not everyone wants to run dozens of miles a week. Shocking! Some people can’t handle intense workouts. The “I did it so you can too” perspective wasn’t helpful for long-term change in most patients.
What has been beneficial is recalling the obstacles and emotions I had (and still have) with staying consistent with physical activity. When physicians and clinicians move regularly, we’re more equipped to give our patients genuine counseling based on practicality rather than theory.
Now that self-reflection has been addressed, let’s get to patient counseling.
Tip 2: Motivate, don’t berate
Lectures on why patients should exercise are less helpful than asking, “Why aren›t you able to exercise more often?”
Asking open-ended questions is essential in motivational interviewing. Motivational interviewing promotes behavioral change through collaborative conversation.
Instead of telling the patient what to do, motivational interviewing seeks to establish a person’s why and create an effective plan based on their motivation. Asking open-ended questions is also helpful in determining any challenges to regular exercise, rather than calling these challenges “excuses,” which can be counterproductive.
I encourage patients to embrace challenges as opportunities for improvement. If they say: “I can’t find time to work out,” I suggest that they create time to work out by walking 10-15 minutes during lunch or after dinner. The information gleaned from open-ended questions helps set practical SMARTER goals, which we will discuss next.
Tip 3: Set SMARTER goals
After assessing the patient’s motivation and barriers, use this information to transform their desire to change into an actionable plan through a SMARTER goal. SMARTER stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-Sensitive, Enjoyable, and Rewarding. Practical goals have each of these components. That’s why “Just Do It” or even “Exercise 150 minutes a week” isn’t a clear path for actionable change. SMARTER goals go beyond what to do and help people personalize how to change.
For example, the SMARTER version of “exercise 150 minutes a week” for a busy person who works 50 hours a week may look like this: “My goal is to incorporate 150 minutes of physical activity through 60 minutes of aerobic exercise Monday through Friday (20-minute lunch walks) and 90 minutes of combination resistance training on the weekend (two 45-minute sessions) while listening to my favorite music. To meet my goal, I will reward myself by calling a friend to catch up or buy myself a new workout outfit.”
Exercise prescriptions are another helpful way to empower patients with a realistic exercise strategy. In my practice, I developed my own exercise prescription which focuses on overcoming time barriers to exercise and finding personally enjoyable exercises. To enhance self-directed physical activity, I›ve found it useful to have patients complete part of the “exercise prescription” on their own before or after their visit.
Tip 4: Use accountability tools
Making a SMARTER goal is one thing, but sticking with it takes regular reinforcement. Even with the best plan, once patients leave the office, there are many distractions from their goals. Accountability is the secret sauce to cultivating consistency. Fitness trackers are an affordable form of accountability. Studies show that wearing a fitness tracker can help people get up to 40 minutes of extra walking, compared with people who don’t wear trackers.
Additionally, clinicians can use different ways to offer exercise accountability. For example, more frequent check-ins, individually or in groups, can be helpful. The increase in telehealth has made interval visits easier. Reimbursement and time can limit clinician-level accountability, however. Other options are referring patients to online support groups or programs sponsored by the government or organizations. For years, I coled a Walk With a Doc chapter in Richmond, Va. There are chapters throughout the country.
Tip 5: Prepare and PLAN for setbacks
Breaking news: Most plans don’t go quite as envisioned. Accounting for the potential of setbacks early on helps patients set realistic expectations. As physicians and clinicians, we can help our patients anticipate a few likely obstacles. This may lessen the impact when a setback occurs. Also, it’s helpful to have the patient prepare for a setback with a PLAN for recovering quickly. PLAN stands for Ponder what happened; Learn from it; Adjust the original goal; Now get back on track. Getting back on track as soon as possible is important to keep patients motivated and prevent muscle deconditioning.
Exercise is medicine. Physical inactivity is a leading contributor to many preventable diseases. Although the physical activity statistics are disappointing, improvement is possible. Many systemic changes are needed to increase physical activity on a population level.
While waiting for more extensive changes, we have the power to equip patients with personalized, actionable tools for improving and maintaining physical activity.
We can transform one person at a time through our clinical encounters. Let’s use effective tools to help patients shift from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Sylvia Gonsahn-Bollie, MD, DipABOM, is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness,” was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Just Do It” is a cute marketing slogan. But let’s face it: Clinically, it doesn’t work well. Most people just don’t exercise. according to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Furthermore, when surveyed about aerobic exercise and strength training, only 24.6% meet these weekly recommendations. These low rates of physical activity are alarming, given the immense benefits of exercise in improving mental and physical health and well-being.
Many people know that exercise is good for them but struggle to go workout consistently. I know firsthand how challenging this can be. In addition to being an integrative obesity specialist, I have gone from 0 minutes of physical activity in 2014 to becoming a fitness enthusiast who’s run more than 5,300 miles over 8 years. I know that as doctors and clinicians, we can profoundly influence our patients’ exercise journey.
Here are five tips to help motivate your patients make the change from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Tip 1: ‘[Clinician], heal thyself’
Data don’t lie. Doctors who move more are more likely to counsel patients on exercise. I’ve been the doctor on both sides of the exercise spectrum. At my heaviest weight and lowest physical activity level, I felt hypocritical counseling patients on exercise.
If and when I counseled my patients on exercise, it was very directive and impersonal. When I started running consistently, I went to the opposite end of the spectrum. In my running zeal, it took a while for me to understand that not everyone wants to run dozens of miles a week. Shocking! Some people can’t handle intense workouts. The “I did it so you can too” perspective wasn’t helpful for long-term change in most patients.
What has been beneficial is recalling the obstacles and emotions I had (and still have) with staying consistent with physical activity. When physicians and clinicians move regularly, we’re more equipped to give our patients genuine counseling based on practicality rather than theory.
Now that self-reflection has been addressed, let’s get to patient counseling.
Tip 2: Motivate, don’t berate
Lectures on why patients should exercise are less helpful than asking, “Why aren›t you able to exercise more often?”
Asking open-ended questions is essential in motivational interviewing. Motivational interviewing promotes behavioral change through collaborative conversation.
Instead of telling the patient what to do, motivational interviewing seeks to establish a person’s why and create an effective plan based on their motivation. Asking open-ended questions is also helpful in determining any challenges to regular exercise, rather than calling these challenges “excuses,” which can be counterproductive.
I encourage patients to embrace challenges as opportunities for improvement. If they say: “I can’t find time to work out,” I suggest that they create time to work out by walking 10-15 minutes during lunch or after dinner. The information gleaned from open-ended questions helps set practical SMARTER goals, which we will discuss next.
Tip 3: Set SMARTER goals
After assessing the patient’s motivation and barriers, use this information to transform their desire to change into an actionable plan through a SMARTER goal. SMARTER stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-Sensitive, Enjoyable, and Rewarding. Practical goals have each of these components. That’s why “Just Do It” or even “Exercise 150 minutes a week” isn’t a clear path for actionable change. SMARTER goals go beyond what to do and help people personalize how to change.
For example, the SMARTER version of “exercise 150 minutes a week” for a busy person who works 50 hours a week may look like this: “My goal is to incorporate 150 minutes of physical activity through 60 minutes of aerobic exercise Monday through Friday (20-minute lunch walks) and 90 minutes of combination resistance training on the weekend (two 45-minute sessions) while listening to my favorite music. To meet my goal, I will reward myself by calling a friend to catch up or buy myself a new workout outfit.”
Exercise prescriptions are another helpful way to empower patients with a realistic exercise strategy. In my practice, I developed my own exercise prescription which focuses on overcoming time barriers to exercise and finding personally enjoyable exercises. To enhance self-directed physical activity, I›ve found it useful to have patients complete part of the “exercise prescription” on their own before or after their visit.
Tip 4: Use accountability tools
Making a SMARTER goal is one thing, but sticking with it takes regular reinforcement. Even with the best plan, once patients leave the office, there are many distractions from their goals. Accountability is the secret sauce to cultivating consistency. Fitness trackers are an affordable form of accountability. Studies show that wearing a fitness tracker can help people get up to 40 minutes of extra walking, compared with people who don’t wear trackers.
Additionally, clinicians can use different ways to offer exercise accountability. For example, more frequent check-ins, individually or in groups, can be helpful. The increase in telehealth has made interval visits easier. Reimbursement and time can limit clinician-level accountability, however. Other options are referring patients to online support groups or programs sponsored by the government or organizations. For years, I coled a Walk With a Doc chapter in Richmond, Va. There are chapters throughout the country.
Tip 5: Prepare and PLAN for setbacks
Breaking news: Most plans don’t go quite as envisioned. Accounting for the potential of setbacks early on helps patients set realistic expectations. As physicians and clinicians, we can help our patients anticipate a few likely obstacles. This may lessen the impact when a setback occurs. Also, it’s helpful to have the patient prepare for a setback with a PLAN for recovering quickly. PLAN stands for Ponder what happened; Learn from it; Adjust the original goal; Now get back on track. Getting back on track as soon as possible is important to keep patients motivated and prevent muscle deconditioning.
Exercise is medicine. Physical inactivity is a leading contributor to many preventable diseases. Although the physical activity statistics are disappointing, improvement is possible. Many systemic changes are needed to increase physical activity on a population level.
While waiting for more extensive changes, we have the power to equip patients with personalized, actionable tools for improving and maintaining physical activity.
We can transform one person at a time through our clinical encounters. Let’s use effective tools to help patients shift from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Sylvia Gonsahn-Bollie, MD, DipABOM, is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness,” was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Just Do It” is a cute marketing slogan. But let’s face it: Clinically, it doesn’t work well. Most people just don’t exercise. according to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Furthermore, when surveyed about aerobic exercise and strength training, only 24.6% meet these weekly recommendations. These low rates of physical activity are alarming, given the immense benefits of exercise in improving mental and physical health and well-being.
Many people know that exercise is good for them but struggle to go workout consistently. I know firsthand how challenging this can be. In addition to being an integrative obesity specialist, I have gone from 0 minutes of physical activity in 2014 to becoming a fitness enthusiast who’s run more than 5,300 miles over 8 years. I know that as doctors and clinicians, we can profoundly influence our patients’ exercise journey.
Here are five tips to help motivate your patients make the change from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Tip 1: ‘[Clinician], heal thyself’
Data don’t lie. Doctors who move more are more likely to counsel patients on exercise. I’ve been the doctor on both sides of the exercise spectrum. At my heaviest weight and lowest physical activity level, I felt hypocritical counseling patients on exercise.
If and when I counseled my patients on exercise, it was very directive and impersonal. When I started running consistently, I went to the opposite end of the spectrum. In my running zeal, it took a while for me to understand that not everyone wants to run dozens of miles a week. Shocking! Some people can’t handle intense workouts. The “I did it so you can too” perspective wasn’t helpful for long-term change in most patients.
What has been beneficial is recalling the obstacles and emotions I had (and still have) with staying consistent with physical activity. When physicians and clinicians move regularly, we’re more equipped to give our patients genuine counseling based on practicality rather than theory.
Now that self-reflection has been addressed, let’s get to patient counseling.
Tip 2: Motivate, don’t berate
Lectures on why patients should exercise are less helpful than asking, “Why aren›t you able to exercise more often?”
Asking open-ended questions is essential in motivational interviewing. Motivational interviewing promotes behavioral change through collaborative conversation.
Instead of telling the patient what to do, motivational interviewing seeks to establish a person’s why and create an effective plan based on their motivation. Asking open-ended questions is also helpful in determining any challenges to regular exercise, rather than calling these challenges “excuses,” which can be counterproductive.
I encourage patients to embrace challenges as opportunities for improvement. If they say: “I can’t find time to work out,” I suggest that they create time to work out by walking 10-15 minutes during lunch or after dinner. The information gleaned from open-ended questions helps set practical SMARTER goals, which we will discuss next.
Tip 3: Set SMARTER goals
After assessing the patient’s motivation and barriers, use this information to transform their desire to change into an actionable plan through a SMARTER goal. SMARTER stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-Sensitive, Enjoyable, and Rewarding. Practical goals have each of these components. That’s why “Just Do It” or even “Exercise 150 minutes a week” isn’t a clear path for actionable change. SMARTER goals go beyond what to do and help people personalize how to change.
For example, the SMARTER version of “exercise 150 minutes a week” for a busy person who works 50 hours a week may look like this: “My goal is to incorporate 150 minutes of physical activity through 60 minutes of aerobic exercise Monday through Friday (20-minute lunch walks) and 90 minutes of combination resistance training on the weekend (two 45-minute sessions) while listening to my favorite music. To meet my goal, I will reward myself by calling a friend to catch up or buy myself a new workout outfit.”
Exercise prescriptions are another helpful way to empower patients with a realistic exercise strategy. In my practice, I developed my own exercise prescription which focuses on overcoming time barriers to exercise and finding personally enjoyable exercises. To enhance self-directed physical activity, I›ve found it useful to have patients complete part of the “exercise prescription” on their own before or after their visit.
Tip 4: Use accountability tools
Making a SMARTER goal is one thing, but sticking with it takes regular reinforcement. Even with the best plan, once patients leave the office, there are many distractions from their goals. Accountability is the secret sauce to cultivating consistency. Fitness trackers are an affordable form of accountability. Studies show that wearing a fitness tracker can help people get up to 40 minutes of extra walking, compared with people who don’t wear trackers.
Additionally, clinicians can use different ways to offer exercise accountability. For example, more frequent check-ins, individually or in groups, can be helpful. The increase in telehealth has made interval visits easier. Reimbursement and time can limit clinician-level accountability, however. Other options are referring patients to online support groups or programs sponsored by the government or organizations. For years, I coled a Walk With a Doc chapter in Richmond, Va. There are chapters throughout the country.
Tip 5: Prepare and PLAN for setbacks
Breaking news: Most plans don’t go quite as envisioned. Accounting for the potential of setbacks early on helps patients set realistic expectations. As physicians and clinicians, we can help our patients anticipate a few likely obstacles. This may lessen the impact when a setback occurs. Also, it’s helpful to have the patient prepare for a setback with a PLAN for recovering quickly. PLAN stands for Ponder what happened; Learn from it; Adjust the original goal; Now get back on track. Getting back on track as soon as possible is important to keep patients motivated and prevent muscle deconditioning.
Exercise is medicine. Physical inactivity is a leading contributor to many preventable diseases. Although the physical activity statistics are disappointing, improvement is possible. Many systemic changes are needed to increase physical activity on a population level.
While waiting for more extensive changes, we have the power to equip patients with personalized, actionable tools for improving and maintaining physical activity.
We can transform one person at a time through our clinical encounters. Let’s use effective tools to help patients shift from “I Won’t Do It” to “I’m Doing It.”
Sylvia Gonsahn-Bollie, MD, DipABOM, is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness,” was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
California picks generic drug company Civica to produce low-cost insulin
Gov. Gavin Newsom on March 18 announced the selection of Utah-based generic drug manufacturer Civica to produce low-cost insulin for California, an unprecedented move that makes good on his promise to put state government in direct competition with the brand-name drug companies that dominate the market.
“People should not be forced to go into debt to get lifesaving prescriptions,” Gov. Newsom said. “Californians will have access to some of the most inexpensive insulin available, helping them save thousands of dollars each year.”
The contract, with an initial cost of $50 million that Gov. Newsom and his fellow Democratic lawmakers approved last year, calls for Civica to manufacture state-branded insulin and make the lifesaving drug available to any Californian who needs it, regardless of insurance coverage, by mail order and at local pharmacies. But insulin is just the beginning. Gov. Newsom said the state will also look to produce the opioid overdose reversal drug naloxone.
Allan Coukell, Civica’s senior vice president of public policy, said in an interview that the nonprofit drugmaker is also in talks with the Newsom administration to potentially produce other generic medications, but he declined to elaborate, saying the company is focused on making cheap insulin widely available first.
“We are very excited about this partnership with the state of California,” Mr. Coukell said. “We’re not looking to have 100% of the market, but we do want 100% of people to have access to fair insulin prices.”
As insulin costs for consumers have soared, Democratic lawmakers and activists have called on the industry to rein in prices. Just weeks after President Joe Biden attacked Big Pharma for jacking up insulin prices, the three drugmakers that control the insulin market – Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi – announced they would slash the list prices of some products.
Gov. Newsom, who has previously accused the pharmaceutical industry of gouging Californians with “sky-high prices,” argued that the launch of the state’s generic drug label, CalRx, will add competition and apply pressure on the industry. Administration officials declined to say when California’s insulin products would be available, but experts say it could be as soon as 2025. Mr. Coukell said the state-branded medication will still require approval from the Food and Drug Administration, which can take roughly 10 months.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, which lobbies on behalf of brand-name companies, blasted California’s move. Reid Porter, senior director of state public affairs for PhRMA, said Gov. Newsom just “wants to score political points.”
“If the governor wants to impact what patients pay for insulins and other medicines meaningfully, he should expand his focus to others in the system that often make patients pay more than they do for medicines,” Mr. Porter said, blaming pharmaceutical go-between companies, known as pharmacy benefit managers, that negotiate with manufacturers on behalf of insurers for rebates and discounts on drugs.
The Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, which represents pharmacy benefit managers argued in turn that it’s pharmaceutical companies that are to blame for high prices.
Drug pricing experts, however, say pharmacy benefit managers and drugmakers share the blame.
Gov. Newsom administration officials say that inflated insulin costs force some to pay as much as $300 per vial or $500 for a box of injectable pens, and that too many Californians with diabetes skip or ration their medication. Doing so can lead to blindness, amputations, and life-threatening conditions such as heart disease and kidney failure. Nearly 10% of California adults have diabetes.
Civica is developing three types of generic insulin, known as a biosimilar, which will be available both in vials and in injectable pens. They are expected to be interchangeable with brand-name products including Lantus, Humalog, and NovoLog. Mr. Coukell said the company would make the drug available for no more than $30 a vial, or $55 for five injectable pens.
Gov. Newsom said the state’s insulin will save many patients $2,000-$4,000 a year, though critical questions about how California would get the products into the hands of consumers remain unanswered, including how it would persuade pharmacies, insurers, and retailers to distribute the drugs.
In 2022, Gov. Newsom also secured $50 million in seed money to build a facility to manufacture insulin; Mr. Coukell said Civica is exploring building a plant in California.
California’s move, though never previously tried by a state government, could be blunted by recent industry decisions to lower insulin prices. In March, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi vowed to cut prices, with Lilly offering a vial at $25 per month, Novo Nordisk promising major reductions that would bring the price of a particular generic vial to $48, and Sanofi pegging one vial at $64.
The governor’s office said it will cost the state $30 per vial to manufacture and distribute insulin and it will be sold at that price. Doing so, the administration argued, “will prevent the egregious cost-shifting that happens in traditional pharmaceutical price games.”
Drug pricing experts said generic production in California could further lower costs for insulin, and benefit people with high-deductible health insurance plans or no insurance.
“This is an extraordinary move in the pharmaceutical industry, not just for insulin but potentially for all kinds of drugs,” said Robin Feldman, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s a very difficult industry to disrupt, but California is poised to do just that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Gov. Gavin Newsom on March 18 announced the selection of Utah-based generic drug manufacturer Civica to produce low-cost insulin for California, an unprecedented move that makes good on his promise to put state government in direct competition with the brand-name drug companies that dominate the market.
“People should not be forced to go into debt to get lifesaving prescriptions,” Gov. Newsom said. “Californians will have access to some of the most inexpensive insulin available, helping them save thousands of dollars each year.”
The contract, with an initial cost of $50 million that Gov. Newsom and his fellow Democratic lawmakers approved last year, calls for Civica to manufacture state-branded insulin and make the lifesaving drug available to any Californian who needs it, regardless of insurance coverage, by mail order and at local pharmacies. But insulin is just the beginning. Gov. Newsom said the state will also look to produce the opioid overdose reversal drug naloxone.
Allan Coukell, Civica’s senior vice president of public policy, said in an interview that the nonprofit drugmaker is also in talks with the Newsom administration to potentially produce other generic medications, but he declined to elaborate, saying the company is focused on making cheap insulin widely available first.
“We are very excited about this partnership with the state of California,” Mr. Coukell said. “We’re not looking to have 100% of the market, but we do want 100% of people to have access to fair insulin prices.”
As insulin costs for consumers have soared, Democratic lawmakers and activists have called on the industry to rein in prices. Just weeks after President Joe Biden attacked Big Pharma for jacking up insulin prices, the three drugmakers that control the insulin market – Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi – announced they would slash the list prices of some products.
Gov. Newsom, who has previously accused the pharmaceutical industry of gouging Californians with “sky-high prices,” argued that the launch of the state’s generic drug label, CalRx, will add competition and apply pressure on the industry. Administration officials declined to say when California’s insulin products would be available, but experts say it could be as soon as 2025. Mr. Coukell said the state-branded medication will still require approval from the Food and Drug Administration, which can take roughly 10 months.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, which lobbies on behalf of brand-name companies, blasted California’s move. Reid Porter, senior director of state public affairs for PhRMA, said Gov. Newsom just “wants to score political points.”
“If the governor wants to impact what patients pay for insulins and other medicines meaningfully, he should expand his focus to others in the system that often make patients pay more than they do for medicines,” Mr. Porter said, blaming pharmaceutical go-between companies, known as pharmacy benefit managers, that negotiate with manufacturers on behalf of insurers for rebates and discounts on drugs.
The Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, which represents pharmacy benefit managers argued in turn that it’s pharmaceutical companies that are to blame for high prices.
Drug pricing experts, however, say pharmacy benefit managers and drugmakers share the blame.
Gov. Newsom administration officials say that inflated insulin costs force some to pay as much as $300 per vial or $500 for a box of injectable pens, and that too many Californians with diabetes skip or ration their medication. Doing so can lead to blindness, amputations, and life-threatening conditions such as heart disease and kidney failure. Nearly 10% of California adults have diabetes.
Civica is developing three types of generic insulin, known as a biosimilar, which will be available both in vials and in injectable pens. They are expected to be interchangeable with brand-name products including Lantus, Humalog, and NovoLog. Mr. Coukell said the company would make the drug available for no more than $30 a vial, or $55 for five injectable pens.
Gov. Newsom said the state’s insulin will save many patients $2,000-$4,000 a year, though critical questions about how California would get the products into the hands of consumers remain unanswered, including how it would persuade pharmacies, insurers, and retailers to distribute the drugs.
In 2022, Gov. Newsom also secured $50 million in seed money to build a facility to manufacture insulin; Mr. Coukell said Civica is exploring building a plant in California.
California’s move, though never previously tried by a state government, could be blunted by recent industry decisions to lower insulin prices. In March, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi vowed to cut prices, with Lilly offering a vial at $25 per month, Novo Nordisk promising major reductions that would bring the price of a particular generic vial to $48, and Sanofi pegging one vial at $64.
The governor’s office said it will cost the state $30 per vial to manufacture and distribute insulin and it will be sold at that price. Doing so, the administration argued, “will prevent the egregious cost-shifting that happens in traditional pharmaceutical price games.”
Drug pricing experts said generic production in California could further lower costs for insulin, and benefit people with high-deductible health insurance plans or no insurance.
“This is an extraordinary move in the pharmaceutical industry, not just for insulin but potentially for all kinds of drugs,” said Robin Feldman, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s a very difficult industry to disrupt, but California is poised to do just that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Gov. Gavin Newsom on March 18 announced the selection of Utah-based generic drug manufacturer Civica to produce low-cost insulin for California, an unprecedented move that makes good on his promise to put state government in direct competition with the brand-name drug companies that dominate the market.
“People should not be forced to go into debt to get lifesaving prescriptions,” Gov. Newsom said. “Californians will have access to some of the most inexpensive insulin available, helping them save thousands of dollars each year.”
The contract, with an initial cost of $50 million that Gov. Newsom and his fellow Democratic lawmakers approved last year, calls for Civica to manufacture state-branded insulin and make the lifesaving drug available to any Californian who needs it, regardless of insurance coverage, by mail order and at local pharmacies. But insulin is just the beginning. Gov. Newsom said the state will also look to produce the opioid overdose reversal drug naloxone.
Allan Coukell, Civica’s senior vice president of public policy, said in an interview that the nonprofit drugmaker is also in talks with the Newsom administration to potentially produce other generic medications, but he declined to elaborate, saying the company is focused on making cheap insulin widely available first.
“We are very excited about this partnership with the state of California,” Mr. Coukell said. “We’re not looking to have 100% of the market, but we do want 100% of people to have access to fair insulin prices.”
As insulin costs for consumers have soared, Democratic lawmakers and activists have called on the industry to rein in prices. Just weeks after President Joe Biden attacked Big Pharma for jacking up insulin prices, the three drugmakers that control the insulin market – Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi – announced they would slash the list prices of some products.
Gov. Newsom, who has previously accused the pharmaceutical industry of gouging Californians with “sky-high prices,” argued that the launch of the state’s generic drug label, CalRx, will add competition and apply pressure on the industry. Administration officials declined to say when California’s insulin products would be available, but experts say it could be as soon as 2025. Mr. Coukell said the state-branded medication will still require approval from the Food and Drug Administration, which can take roughly 10 months.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, which lobbies on behalf of brand-name companies, blasted California’s move. Reid Porter, senior director of state public affairs for PhRMA, said Gov. Newsom just “wants to score political points.”
“If the governor wants to impact what patients pay for insulins and other medicines meaningfully, he should expand his focus to others in the system that often make patients pay more than they do for medicines,” Mr. Porter said, blaming pharmaceutical go-between companies, known as pharmacy benefit managers, that negotiate with manufacturers on behalf of insurers for rebates and discounts on drugs.
The Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, which represents pharmacy benefit managers argued in turn that it’s pharmaceutical companies that are to blame for high prices.
Drug pricing experts, however, say pharmacy benefit managers and drugmakers share the blame.
Gov. Newsom administration officials say that inflated insulin costs force some to pay as much as $300 per vial or $500 for a box of injectable pens, and that too many Californians with diabetes skip or ration their medication. Doing so can lead to blindness, amputations, and life-threatening conditions such as heart disease and kidney failure. Nearly 10% of California adults have diabetes.
Civica is developing three types of generic insulin, known as a biosimilar, which will be available both in vials and in injectable pens. They are expected to be interchangeable with brand-name products including Lantus, Humalog, and NovoLog. Mr. Coukell said the company would make the drug available for no more than $30 a vial, or $55 for five injectable pens.
Gov. Newsom said the state’s insulin will save many patients $2,000-$4,000 a year, though critical questions about how California would get the products into the hands of consumers remain unanswered, including how it would persuade pharmacies, insurers, and retailers to distribute the drugs.
In 2022, Gov. Newsom also secured $50 million in seed money to build a facility to manufacture insulin; Mr. Coukell said Civica is exploring building a plant in California.
California’s move, though never previously tried by a state government, could be blunted by recent industry decisions to lower insulin prices. In March, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi vowed to cut prices, with Lilly offering a vial at $25 per month, Novo Nordisk promising major reductions that would bring the price of a particular generic vial to $48, and Sanofi pegging one vial at $64.
The governor’s office said it will cost the state $30 per vial to manufacture and distribute insulin and it will be sold at that price. Doing so, the administration argued, “will prevent the egregious cost-shifting that happens in traditional pharmaceutical price games.”
Drug pricing experts said generic production in California could further lower costs for insulin, and benefit people with high-deductible health insurance plans or no insurance.
“This is an extraordinary move in the pharmaceutical industry, not just for insulin but potentially for all kinds of drugs,” said Robin Feldman, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s a very difficult industry to disrupt, but California is poised to do just that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Mediterranean diet linked to 24% reduction in CVD risk in women
The Mediterranean diet appears to be associated with a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in women, new observational data suggest.
Those who had a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had a 24% lower risk for cardiovascular disease and 23% lower risk for death.
“A healthy diet is a huge factor in preventing heart disease. However, current guidelines on preventing heart disease lack sex-specific recommendations,” said senior author Sarah Zaman, MBBS, PhD, an associate professor of medicine and principal research fellow at the University of Sydney’s Westmead Applied Research Centre.
“Historically, research trials and studies have had predominantly male participants or lacked sex-specific analysis,” she said. “Our results will pave the way to bridge this gap and also highlight the need for more research to ensure health guidelines and policies include diverse perspectives.”
The study was published online in the journal Heart.
Analyzing cardiovascular outcomes
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies published between 2006 and 2021 that reported a Mediterranean diet score and included either all women or had stratified outcomes by sex. They excluded studies that referred to only certain components of the Mediterranean diet or combined it with other lifestyle-related factors.
The studies, which were mainly conducted in the United States and Europe, included 722,495 adult women without previous clinical or subclinical CVD, with a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was defined as the highest category reporting the highest range of Mediterranean diet scores, and lower adherence was defined as the lowest category reporting lowest scores. Incident CVD included coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, cardiovascular death, major adverse cardiovascular events, major adverse cardiac cerebrovascular events, and patient-reported CVD.
Overall, higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet was associated with lower CVD incidence (hazard ratio, 0.76; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.81), total mortality (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.74-0.80), and coronary heart disease (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.87).
Stroke incidence was also lower among women who adhered to the Mediterranean diet, although it wasn’t considered statistically significant (HR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01).
Additional analyses found similar reductions in risk across women of different ethnicities. Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was associated with lower CVD incidence for both women of European descent (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98) and women of non-European descent – Asian, Native Hawaiian, and African American – (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.72-0.87).
The results didn’t materially change in sensitivity analyses, the authors note. Excluding one study at a time, the pooled HRs for the highest versus the lowest Mediterranean diet adherence ranged from 0.76 (95% CI, 0.72-0.80) to 0.83 (95% CI, 0.70-0.98) for incident CVD and from 0.77 (95% CI, 0.75-0.80) to 0.77 (95% CI, 0.74-0.81) for total mortality among women.
At the same time, the authors pointed to several limitations, including the observational nature of all of the studies, the reliance on self-reported food frequency questionnaires, and heterogeneity in the adjustments for influential factors across the studies.
Additional considerations
Dr. Zaman and colleagues called for more sex-specific research in cardiology, including risk factors related to premature menopause, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus.
Future studies should also explore the underlying mechanisms that may explain the links between the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular disease, and death, the authors write. For instance, the diet may reduce inflammation and cardiovascular risk factors through antioxidant and beneficial gut microbiome pathways. Other components of the diet – such as polyphenols, nitrates, omega-3 fatty acids, higher fiber intake, and reduced glycemic load – may also play a role.
“It was striking to see how strong the long-term cardioprotective properties of a Mediterranean-type dietary pattern were,” said Samia Mora, MD, MHS, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Lipid Metabolomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Dr. Mora, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched potential mechanisms related to the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular events, and diabetes in women. She and colleagues have found that women with high adherence to the diet are more likely to have lower inflammation, insulin resistance, body mass index, and blood pressure, as well as improved lipid and metabolic profiles.
“This could represent an opportunity to intervene earlier and more intensively on improving inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiometabolic health through evidence-based dietary approaches such as the Mediterranean diet,” she said. “As health care providers, we should promote the healthy dietary attributes of the Mediterranean diet, especially as many of our patients in the U.S. are less familiar with the Mediterranean diet and how to incorporate its components into daily food intake.”
The study did not receive any funding. Dr. Zaman was supported by a Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mora reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mediterranean diet appears to be associated with a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in women, new observational data suggest.
Those who had a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had a 24% lower risk for cardiovascular disease and 23% lower risk for death.
“A healthy diet is a huge factor in preventing heart disease. However, current guidelines on preventing heart disease lack sex-specific recommendations,” said senior author Sarah Zaman, MBBS, PhD, an associate professor of medicine and principal research fellow at the University of Sydney’s Westmead Applied Research Centre.
“Historically, research trials and studies have had predominantly male participants or lacked sex-specific analysis,” she said. “Our results will pave the way to bridge this gap and also highlight the need for more research to ensure health guidelines and policies include diverse perspectives.”
The study was published online in the journal Heart.
Analyzing cardiovascular outcomes
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies published between 2006 and 2021 that reported a Mediterranean diet score and included either all women or had stratified outcomes by sex. They excluded studies that referred to only certain components of the Mediterranean diet or combined it with other lifestyle-related factors.
The studies, which were mainly conducted in the United States and Europe, included 722,495 adult women without previous clinical or subclinical CVD, with a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was defined as the highest category reporting the highest range of Mediterranean diet scores, and lower adherence was defined as the lowest category reporting lowest scores. Incident CVD included coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, cardiovascular death, major adverse cardiovascular events, major adverse cardiac cerebrovascular events, and patient-reported CVD.
Overall, higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet was associated with lower CVD incidence (hazard ratio, 0.76; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.81), total mortality (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.74-0.80), and coronary heart disease (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.87).
Stroke incidence was also lower among women who adhered to the Mediterranean diet, although it wasn’t considered statistically significant (HR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01).
Additional analyses found similar reductions in risk across women of different ethnicities. Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was associated with lower CVD incidence for both women of European descent (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98) and women of non-European descent – Asian, Native Hawaiian, and African American – (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.72-0.87).
The results didn’t materially change in sensitivity analyses, the authors note. Excluding one study at a time, the pooled HRs for the highest versus the lowest Mediterranean diet adherence ranged from 0.76 (95% CI, 0.72-0.80) to 0.83 (95% CI, 0.70-0.98) for incident CVD and from 0.77 (95% CI, 0.75-0.80) to 0.77 (95% CI, 0.74-0.81) for total mortality among women.
At the same time, the authors pointed to several limitations, including the observational nature of all of the studies, the reliance on self-reported food frequency questionnaires, and heterogeneity in the adjustments for influential factors across the studies.
Additional considerations
Dr. Zaman and colleagues called for more sex-specific research in cardiology, including risk factors related to premature menopause, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus.
Future studies should also explore the underlying mechanisms that may explain the links between the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular disease, and death, the authors write. For instance, the diet may reduce inflammation and cardiovascular risk factors through antioxidant and beneficial gut microbiome pathways. Other components of the diet – such as polyphenols, nitrates, omega-3 fatty acids, higher fiber intake, and reduced glycemic load – may also play a role.
“It was striking to see how strong the long-term cardioprotective properties of a Mediterranean-type dietary pattern were,” said Samia Mora, MD, MHS, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Lipid Metabolomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Dr. Mora, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched potential mechanisms related to the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular events, and diabetes in women. She and colleagues have found that women with high adherence to the diet are more likely to have lower inflammation, insulin resistance, body mass index, and blood pressure, as well as improved lipid and metabolic profiles.
“This could represent an opportunity to intervene earlier and more intensively on improving inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiometabolic health through evidence-based dietary approaches such as the Mediterranean diet,” she said. “As health care providers, we should promote the healthy dietary attributes of the Mediterranean diet, especially as many of our patients in the U.S. are less familiar with the Mediterranean diet and how to incorporate its components into daily food intake.”
The study did not receive any funding. Dr. Zaman was supported by a Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mora reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mediterranean diet appears to be associated with a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in women, new observational data suggest.
Those who had a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had a 24% lower risk for cardiovascular disease and 23% lower risk for death.
“A healthy diet is a huge factor in preventing heart disease. However, current guidelines on preventing heart disease lack sex-specific recommendations,” said senior author Sarah Zaman, MBBS, PhD, an associate professor of medicine and principal research fellow at the University of Sydney’s Westmead Applied Research Centre.
“Historically, research trials and studies have had predominantly male participants or lacked sex-specific analysis,” she said. “Our results will pave the way to bridge this gap and also highlight the need for more research to ensure health guidelines and policies include diverse perspectives.”
The study was published online in the journal Heart.
Analyzing cardiovascular outcomes
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies published between 2006 and 2021 that reported a Mediterranean diet score and included either all women or had stratified outcomes by sex. They excluded studies that referred to only certain components of the Mediterranean diet or combined it with other lifestyle-related factors.
The studies, which were mainly conducted in the United States and Europe, included 722,495 adult women without previous clinical or subclinical CVD, with a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was defined as the highest category reporting the highest range of Mediterranean diet scores, and lower adherence was defined as the lowest category reporting lowest scores. Incident CVD included coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, cardiovascular death, major adverse cardiovascular events, major adverse cardiac cerebrovascular events, and patient-reported CVD.
Overall, higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet was associated with lower CVD incidence (hazard ratio, 0.76; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.81), total mortality (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.74-0.80), and coronary heart disease (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.87).
Stroke incidence was also lower among women who adhered to the Mediterranean diet, although it wasn’t considered statistically significant (HR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01).
Additional analyses found similar reductions in risk across women of different ethnicities. Higher Mediterranean diet adherence was associated with lower CVD incidence for both women of European descent (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98) and women of non-European descent – Asian, Native Hawaiian, and African American – (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.72-0.87).
The results didn’t materially change in sensitivity analyses, the authors note. Excluding one study at a time, the pooled HRs for the highest versus the lowest Mediterranean diet adherence ranged from 0.76 (95% CI, 0.72-0.80) to 0.83 (95% CI, 0.70-0.98) for incident CVD and from 0.77 (95% CI, 0.75-0.80) to 0.77 (95% CI, 0.74-0.81) for total mortality among women.
At the same time, the authors pointed to several limitations, including the observational nature of all of the studies, the reliance on self-reported food frequency questionnaires, and heterogeneity in the adjustments for influential factors across the studies.
Additional considerations
Dr. Zaman and colleagues called for more sex-specific research in cardiology, including risk factors related to premature menopause, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus.
Future studies should also explore the underlying mechanisms that may explain the links between the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular disease, and death, the authors write. For instance, the diet may reduce inflammation and cardiovascular risk factors through antioxidant and beneficial gut microbiome pathways. Other components of the diet – such as polyphenols, nitrates, omega-3 fatty acids, higher fiber intake, and reduced glycemic load – may also play a role.
“It was striking to see how strong the long-term cardioprotective properties of a Mediterranean-type dietary pattern were,” said Samia Mora, MD, MHS, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Lipid Metabolomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Dr. Mora, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched potential mechanisms related to the Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular events, and diabetes in women. She and colleagues have found that women with high adherence to the diet are more likely to have lower inflammation, insulin resistance, body mass index, and blood pressure, as well as improved lipid and metabolic profiles.
“This could represent an opportunity to intervene earlier and more intensively on improving inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiometabolic health through evidence-based dietary approaches such as the Mediterranean diet,” she said. “As health care providers, we should promote the healthy dietary attributes of the Mediterranean diet, especially as many of our patients in the U.S. are less familiar with the Mediterranean diet and how to incorporate its components into daily food intake.”
The study did not receive any funding. Dr. Zaman was supported by a Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mora reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Holy smoke: Air pollution link to bone damage confirmed
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
Ozempic: The latest weight loss craze and how over-prescribing is harming patients
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Marathon running does not increase arthritis risk: Survey
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAOS 2023