User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Deoxycholic Acid for Dercum Disease: Repurposing a Cosmetic Agent to Treat a Rare Disease
Dercum disease (or adiposis dolorosa) is a rare condition of unknown etiology characterized by multiple painful lipomas localized throughout the body.1,2 It typically presents in adults aged 35 to 50 years and is at least 5 times more common in women.3 It often is associated with comorbidities such as obesity, fatigue and weakness.1 There currently are no approved treatments for Dercum disease, only therapies tried with little to no efficacy for symptom management, including analgesics, excision, liposuction,1 lymphatic drainage,4 hypobaric pressure,5 and frequency rhythmic electrical modulation systems.6 For patients who continually develop widespread lesions, surgical excision is not feasible, which poses a therapeutic challenge. Deoxycholic acid (DCA), a bile acid that is approved to treat submental fat, disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, induces adipocyte lysis, and solubilizes fat when injected subcutaneously.7 We used DCA to mitigate pain and reduce lipoma size in patients with Dercum disease, which demonstrated lipoma reduction via ultrasonography in 3 patients.
Case Reports
Three patients presented to clinic with multiple painful subcutaneous nodules throughout several areas of the body and were screened using radiography. Ultrasonography demonstrated numerous lipomas consistent with Dercum disease. The lipomas were measured by ultrasonography to obtain 3-dimensional measurements of each lesion. The most painful lipomas identified by the patients were either treated with 2 mL of DCA (10 mg/mL) or served as a control with no treatment. Patients returned for symptom monitoring and repeat measurements of both treated and untreated lipomas. Two physicians with expertise in ultrasonography measured lesions in a blinded fashion. Photographs were obtained with patient consent.
Patient 1—A 45-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease that was confirmed via ultrasonography. A painful 1.63×1.64×0.55-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the left forearm, and a 1.17×1.26×0.39-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the right wrist. At a follow-up visit 11 months later, 2 mL of DCA was administered to the lipoma on the volar aspect of the left forearm, while the lipoma on the volar aspect of the right wrist was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported 1 week of swelling and tenderness of the treated area. Repeat imaging 4 months after administration of DCA revealed reduction of the treated lesion to 0.80×1.48×0.60 cm and growth of the untreated lesion to 1.32×2.17×0.52 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 34.55%, while the lipoma in the untreated control increased in volume from its original measurement by 111.11% (Table). The patient also reported decreased pain in the treated area at all follow-up visits in the 1 year following the procedure.
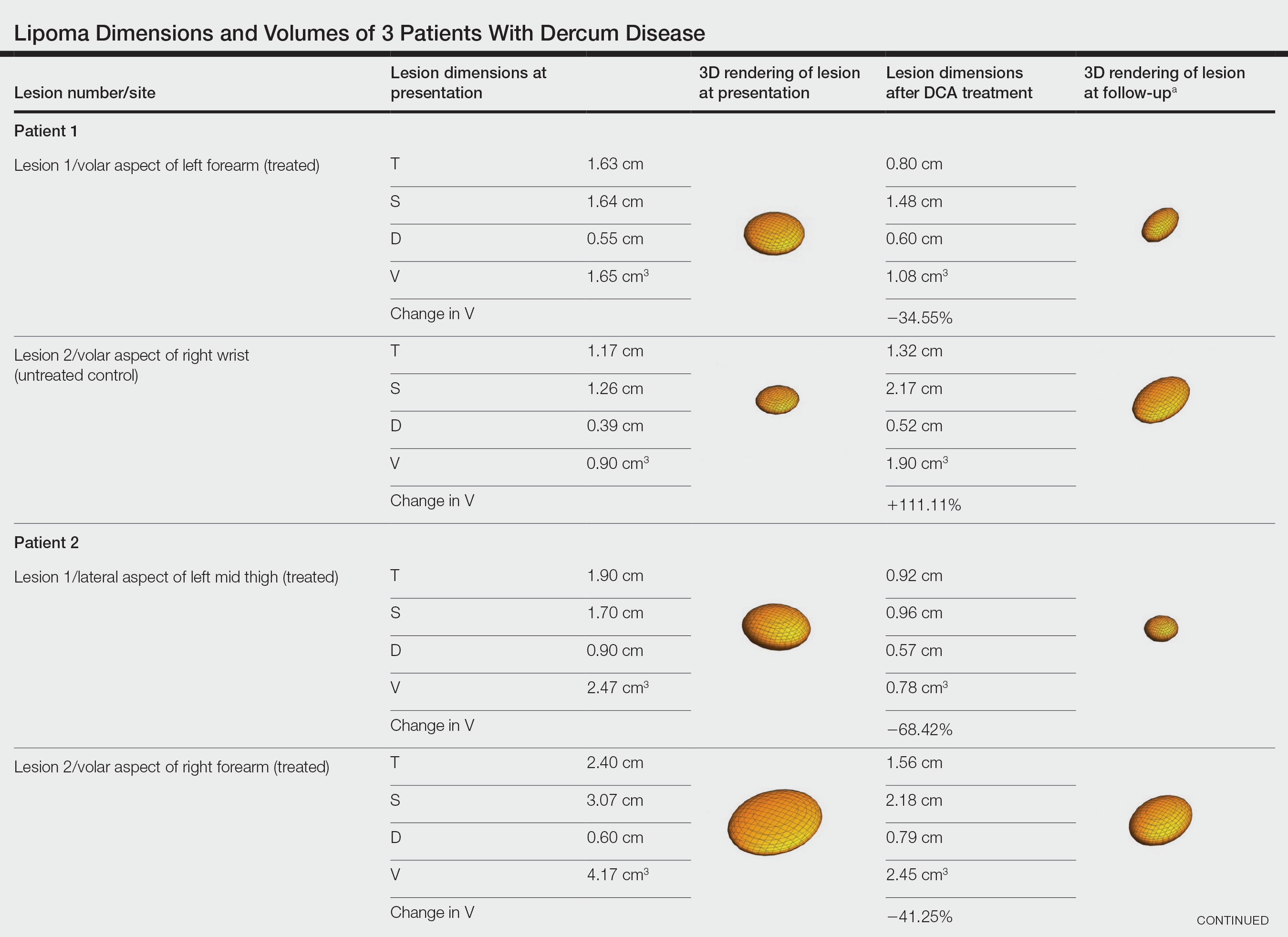
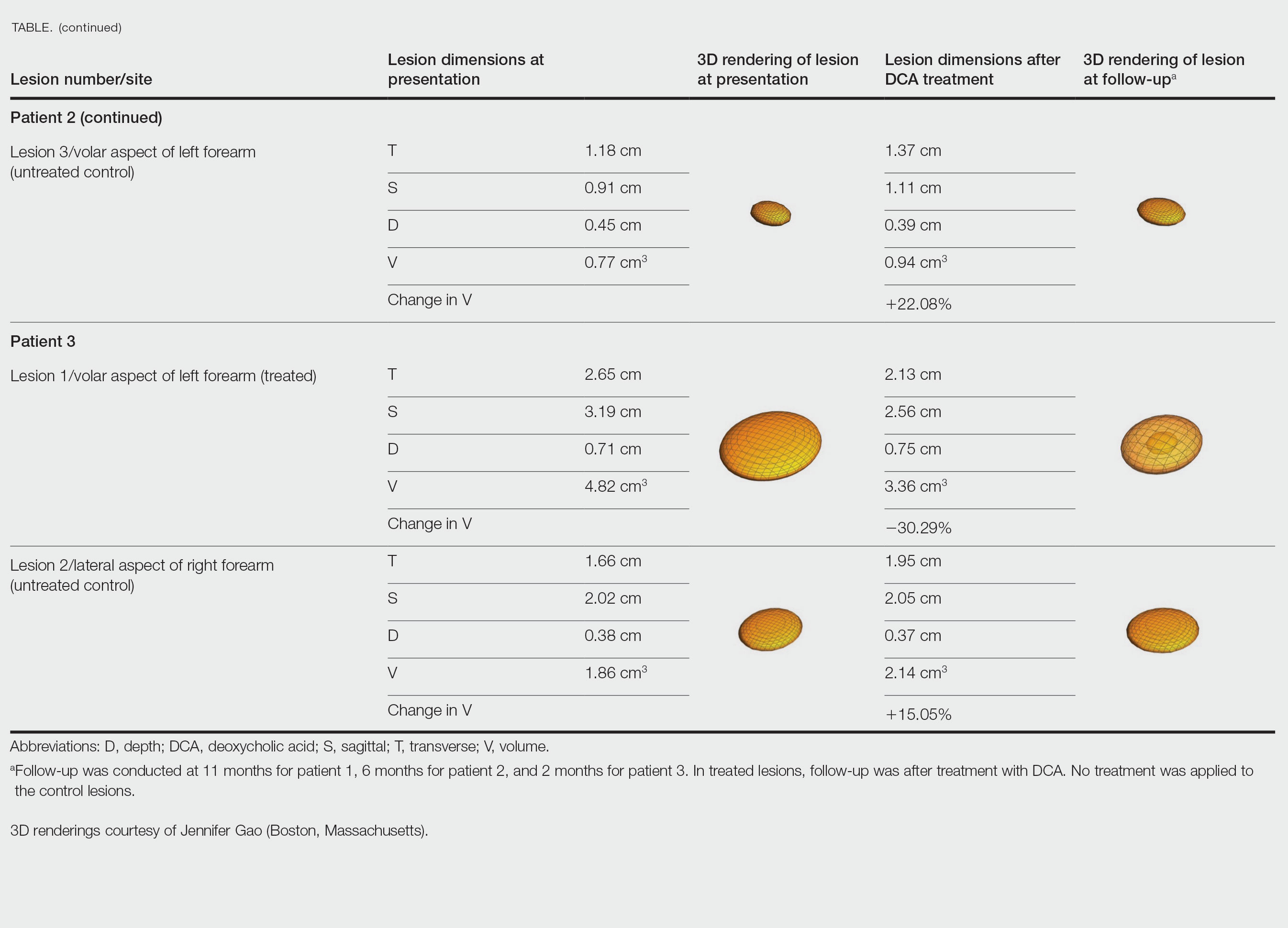
Patient 2—A 42-year-old woman with Dercum disease received administration of 2 mL of DCA to a 1.90×1.70×0.90-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh and 2 mL of DCA to a 2.40×3.07×0.60-cm lipoma on the volar aspect of the right forearm 2 weeks later. A 1.18×0.91×0.45-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm was monitored as an untreated control. The patient reported bruising and discoloration a few weeks following the procedure. At subsequent 1-month and 3-month follow-ups, the patient reported induration in the volar aspect of the right forearm and noticeable reduction in size of the lesion in the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh. At the 6-month follow-up, the patient reported reduction in size of both lesions and improvement of the previously noted side effects. Repeat ultrasonography approximately 6 months after administration of DCA demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh to 0.92×0.96×0.57 cm and the volar aspect of the right forearm to 1.56×2.18×0.79 cm, with growth of the untreated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 1.37×1.11×0.39 cm. The treated lipomas reduced in volume by 68.42% and 41.25%, respectively, and the untreated control increased in volume by 22.08% (Table).
Patient 3—A 75-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease verified by ultrasonography. The patient was administered 2 mL of DCA to a 2.65×3.19×0.71-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm. A 1.66×2.02×0.38-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the right forearm was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported initial swelling that persisted for a few weeks followed by notable pain relief and a decrease in lipoma size. At 2-month follow-up, the patient reported no pain or other adverse effects, while repeat imaging demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 2.13×2.56×0.75 cm and growth of the untreated lesion on the lateral aspect of the right forearm to 1.95×2.05×0.37 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 30.29%, and the untreated control increased in volume by 15.05% (Table).
Comment
Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally found in the body that helps to emulsify and solubilize fats in the intestines. When injected subcutaneously, DCA becomes an adipolytic agent that induces inflammation and targets adipose degradation by macrophages, and it has been manufactured to reduce submental fat.7 Off-label use of DCA has been explored for nonsurgical body contouring and lipomas with promising results in some cases; however, these prior studies have been limited by the lack of quantitative objective measurements to effectively demonstrate the impact of treatment.8,9
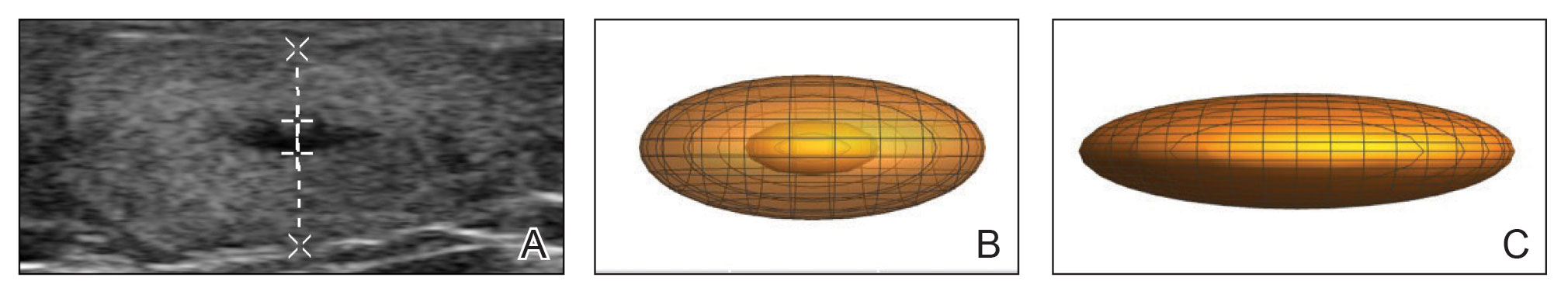
We present 3 patients who requested treatment for numerous painful lipomas. Given the extent of their disease, surgical options were not feasible, and the patients opted to try a nonsurgical alternative. In each case, the painful lipomas that were chosen for treatment were injected with 2 mL of DCA. Injection-associated symptoms included swelling, tenderness, discoloration, and induration, which resolved over a period of months. Patient 1 had a treated lipoma that reduced in volume by approximately 35%, while the control continued to grow and doubled in volume. In patient 2, the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the mid thigh reduced in volume by almost 70%, and the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the right forearm reduced in volume by more than 40%, while the control grew by more than 20%. In patient 3, the volume of the treated lipoma decreased by 30%, and the control increased by 15%. The follow-up interval was shortest in patient 3—2 months as opposed to 11 months and 6 months for patients 1 and 2, respectively; therefore, more progress may be seen in patient 3 with more time. Interestingly, a change in shape of the lipoma was noted in patient 3 (Figure)—an increase in its depth while the center became anechoic, which is a sign of hollowing in the center due to the saponification of fat and a possible cause for the change from an elliptical to a more spherical or doughnutlike shape. Intralesional administration of DCA may offer patients with extensive lipomas, such as those seen in patients with Dercum disease, an alternative, less-invasive option to assist with pain and tumor burden when excision is not feasible. Although treatments with DCA can be associated with side effects, including pain, swelling, bruising, erythema, induration, and numbness, all 3 of our patients had ultimate mitigation of pain and reduction in lipoma size within months of the injection. Additional studies should be explored to determine the optimal dose and frequency of administration of DCA that could benefit patients with Dercum disease.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Dercum’s disease. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2023. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dercums-disease/.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛drek M, Kramza J, et al. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): a review of clinical presentation and management. Reumatologia. 2019;57:281-287. doi:10.5114/reum.2019.89521
- Hansson E, Svensson H, Brorson H. Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7:23. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-23
- Lange U, Oelzner P, Uhlemann C. Dercum’s disease (Lipomatosis dolorosa): successful therapy with pregabalin and manual lymphatic drainage and a current overview. Rheumatol Int. 2008;29:17-22. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0635-3
- Herbst KL, Rutledge T. Pilot study: rapidly cycling hypobaric pressure improves pain after 5 days in adiposis dolorosa. J Pain Res. 2010;3:147-153. doi:10.2147/JPR.S12351
- Martinenghi S, Caretto A, Losio C, et al. Successful treatment of Dercum’s disease by transcutaneous electrical stimulation: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e950. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000950
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary for CID 222528, deoxycholic acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Deoxycholic-acid. Accessed November 11, 2021.
- Liu C, Li MK, Alster TS. Alternative cosmetic and medical applications of injectable deoxycholic acid: a systematic review. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1466-1472. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003159
- Santiago-Vázquez M, Michelen-Gómez EA, Carrasquillo-Bonilla D, et al. Intralesional deoxycholic acid: a potential therapeutic alternative for the treatment of lipomas arising in the face. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;13:112-114. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.037
Dercum disease (or adiposis dolorosa) is a rare condition of unknown etiology characterized by multiple painful lipomas localized throughout the body.1,2 It typically presents in adults aged 35 to 50 years and is at least 5 times more common in women.3 It often is associated with comorbidities such as obesity, fatigue and weakness.1 There currently are no approved treatments for Dercum disease, only therapies tried with little to no efficacy for symptom management, including analgesics, excision, liposuction,1 lymphatic drainage,4 hypobaric pressure,5 and frequency rhythmic electrical modulation systems.6 For patients who continually develop widespread lesions, surgical excision is not feasible, which poses a therapeutic challenge. Deoxycholic acid (DCA), a bile acid that is approved to treat submental fat, disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, induces adipocyte lysis, and solubilizes fat when injected subcutaneously.7 We used DCA to mitigate pain and reduce lipoma size in patients with Dercum disease, which demonstrated lipoma reduction via ultrasonography in 3 patients.
Case Reports
Three patients presented to clinic with multiple painful subcutaneous nodules throughout several areas of the body and were screened using radiography. Ultrasonography demonstrated numerous lipomas consistent with Dercum disease. The lipomas were measured by ultrasonography to obtain 3-dimensional measurements of each lesion. The most painful lipomas identified by the patients were either treated with 2 mL of DCA (10 mg/mL) or served as a control with no treatment. Patients returned for symptom monitoring and repeat measurements of both treated and untreated lipomas. Two physicians with expertise in ultrasonography measured lesions in a blinded fashion. Photographs were obtained with patient consent.
Patient 1—A 45-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease that was confirmed via ultrasonography. A painful 1.63×1.64×0.55-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the left forearm, and a 1.17×1.26×0.39-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the right wrist. At a follow-up visit 11 months later, 2 mL of DCA was administered to the lipoma on the volar aspect of the left forearm, while the lipoma on the volar aspect of the right wrist was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported 1 week of swelling and tenderness of the treated area. Repeat imaging 4 months after administration of DCA revealed reduction of the treated lesion to 0.80×1.48×0.60 cm and growth of the untreated lesion to 1.32×2.17×0.52 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 34.55%, while the lipoma in the untreated control increased in volume from its original measurement by 111.11% (Table). The patient also reported decreased pain in the treated area at all follow-up visits in the 1 year following the procedure.


Patient 2—A 42-year-old woman with Dercum disease received administration of 2 mL of DCA to a 1.90×1.70×0.90-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh and 2 mL of DCA to a 2.40×3.07×0.60-cm lipoma on the volar aspect of the right forearm 2 weeks later. A 1.18×0.91×0.45-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm was monitored as an untreated control. The patient reported bruising and discoloration a few weeks following the procedure. At subsequent 1-month and 3-month follow-ups, the patient reported induration in the volar aspect of the right forearm and noticeable reduction in size of the lesion in the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh. At the 6-month follow-up, the patient reported reduction in size of both lesions and improvement of the previously noted side effects. Repeat ultrasonography approximately 6 months after administration of DCA demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh to 0.92×0.96×0.57 cm and the volar aspect of the right forearm to 1.56×2.18×0.79 cm, with growth of the untreated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 1.37×1.11×0.39 cm. The treated lipomas reduced in volume by 68.42% and 41.25%, respectively, and the untreated control increased in volume by 22.08% (Table).
Patient 3—A 75-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease verified by ultrasonography. The patient was administered 2 mL of DCA to a 2.65×3.19×0.71-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm. A 1.66×2.02×0.38-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the right forearm was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported initial swelling that persisted for a few weeks followed by notable pain relief and a decrease in lipoma size. At 2-month follow-up, the patient reported no pain or other adverse effects, while repeat imaging demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 2.13×2.56×0.75 cm and growth of the untreated lesion on the lateral aspect of the right forearm to 1.95×2.05×0.37 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 30.29%, and the untreated control increased in volume by 15.05% (Table).
Comment
Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally found in the body that helps to emulsify and solubilize fats in the intestines. When injected subcutaneously, DCA becomes an adipolytic agent that induces inflammation and targets adipose degradation by macrophages, and it has been manufactured to reduce submental fat.7 Off-label use of DCA has been explored for nonsurgical body contouring and lipomas with promising results in some cases; however, these prior studies have been limited by the lack of quantitative objective measurements to effectively demonstrate the impact of treatment.8,9
We present 3 patients who requested treatment for numerous painful lipomas. Given the extent of their disease, surgical options were not feasible, and the patients opted to try a nonsurgical alternative. In each case, the painful lipomas that were chosen for treatment were injected with 2 mL of DCA. Injection-associated symptoms included swelling, tenderness, discoloration, and induration, which resolved over a period of months. Patient 1 had a treated lipoma that reduced in volume by approximately 35%, while the control continued to grow and doubled in volume. In patient 2, the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the mid thigh reduced in volume by almost 70%, and the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the right forearm reduced in volume by more than 40%, while the control grew by more than 20%. In patient 3, the volume of the treated lipoma decreased by 30%, and the control increased by 15%. The follow-up interval was shortest in patient 3—2 months as opposed to 11 months and 6 months for patients 1 and 2, respectively; therefore, more progress may be seen in patient 3 with more time. Interestingly, a change in shape of the lipoma was noted in patient 3 (Figure)—an increase in its depth while the center became anechoic, which is a sign of hollowing in the center due to the saponification of fat and a possible cause for the change from an elliptical to a more spherical or doughnutlike shape. Intralesional administration of DCA may offer patients with extensive lipomas, such as those seen in patients with Dercum disease, an alternative, less-invasive option to assist with pain and tumor burden when excision is not feasible. Although treatments with DCA can be associated with side effects, including pain, swelling, bruising, erythema, induration, and numbness, all 3 of our patients had ultimate mitigation of pain and reduction in lipoma size within months of the injection. Additional studies should be explored to determine the optimal dose and frequency of administration of DCA that could benefit patients with Dercum disease.

Dercum disease (or adiposis dolorosa) is a rare condition of unknown etiology characterized by multiple painful lipomas localized throughout the body.1,2 It typically presents in adults aged 35 to 50 years and is at least 5 times more common in women.3 It often is associated with comorbidities such as obesity, fatigue and weakness.1 There currently are no approved treatments for Dercum disease, only therapies tried with little to no efficacy for symptom management, including analgesics, excision, liposuction,1 lymphatic drainage,4 hypobaric pressure,5 and frequency rhythmic electrical modulation systems.6 For patients who continually develop widespread lesions, surgical excision is not feasible, which poses a therapeutic challenge. Deoxycholic acid (DCA), a bile acid that is approved to treat submental fat, disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, induces adipocyte lysis, and solubilizes fat when injected subcutaneously.7 We used DCA to mitigate pain and reduce lipoma size in patients with Dercum disease, which demonstrated lipoma reduction via ultrasonography in 3 patients.
Case Reports
Three patients presented to clinic with multiple painful subcutaneous nodules throughout several areas of the body and were screened using radiography. Ultrasonography demonstrated numerous lipomas consistent with Dercum disease. The lipomas were measured by ultrasonography to obtain 3-dimensional measurements of each lesion. The most painful lipomas identified by the patients were either treated with 2 mL of DCA (10 mg/mL) or served as a control with no treatment. Patients returned for symptom monitoring and repeat measurements of both treated and untreated lipomas. Two physicians with expertise in ultrasonography measured lesions in a blinded fashion. Photographs were obtained with patient consent.
Patient 1—A 45-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease that was confirmed via ultrasonography. A painful 1.63×1.64×0.55-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the left forearm, and a 1.17×1.26×0.39-cm lipoma was measured on the volar aspect of the right wrist. At a follow-up visit 11 months later, 2 mL of DCA was administered to the lipoma on the volar aspect of the left forearm, while the lipoma on the volar aspect of the right wrist was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported 1 week of swelling and tenderness of the treated area. Repeat imaging 4 months after administration of DCA revealed reduction of the treated lesion to 0.80×1.48×0.60 cm and growth of the untreated lesion to 1.32×2.17×0.52 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 34.55%, while the lipoma in the untreated control increased in volume from its original measurement by 111.11% (Table). The patient also reported decreased pain in the treated area at all follow-up visits in the 1 year following the procedure.


Patient 2—A 42-year-old woman with Dercum disease received administration of 2 mL of DCA to a 1.90×1.70×0.90-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh and 2 mL of DCA to a 2.40×3.07×0.60-cm lipoma on the volar aspect of the right forearm 2 weeks later. A 1.18×0.91×0.45-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm was monitored as an untreated control. The patient reported bruising and discoloration a few weeks following the procedure. At subsequent 1-month and 3-month follow-ups, the patient reported induration in the volar aspect of the right forearm and noticeable reduction in size of the lesion in the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh. At the 6-month follow-up, the patient reported reduction in size of both lesions and improvement of the previously noted side effects. Repeat ultrasonography approximately 6 months after administration of DCA demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the left mid thigh to 0.92×0.96×0.57 cm and the volar aspect of the right forearm to 1.56×2.18×0.79 cm, with growth of the untreated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 1.37×1.11×0.39 cm. The treated lipomas reduced in volume by 68.42% and 41.25%, respectively, and the untreated control increased in volume by 22.08% (Table).
Patient 3—A 75-year-old woman with a family history of lipomas was diagnosed with Dercum disease verified by ultrasonography. The patient was administered 2 mL of DCA to a 2.65×3.19×0.71-cm lipoma of the volar aspect of the left forearm. A 1.66×2.02×0.38-cm lipoma of the lateral aspect of the right forearm was monitored as an untreated control. Following the procedure, the patient reported initial swelling that persisted for a few weeks followed by notable pain relief and a decrease in lipoma size. At 2-month follow-up, the patient reported no pain or other adverse effects, while repeat imaging demonstrated reduction of the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the left forearm to 2.13×2.56×0.75 cm and growth of the untreated lesion on the lateral aspect of the right forearm to 1.95×2.05×0.37 cm. The treated lipoma reduced in volume by 30.29%, and the untreated control increased in volume by 15.05% (Table).
Comment
Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally found in the body that helps to emulsify and solubilize fats in the intestines. When injected subcutaneously, DCA becomes an adipolytic agent that induces inflammation and targets adipose degradation by macrophages, and it has been manufactured to reduce submental fat.7 Off-label use of DCA has been explored for nonsurgical body contouring and lipomas with promising results in some cases; however, these prior studies have been limited by the lack of quantitative objective measurements to effectively demonstrate the impact of treatment.8,9
We present 3 patients who requested treatment for numerous painful lipomas. Given the extent of their disease, surgical options were not feasible, and the patients opted to try a nonsurgical alternative. In each case, the painful lipomas that were chosen for treatment were injected with 2 mL of DCA. Injection-associated symptoms included swelling, tenderness, discoloration, and induration, which resolved over a period of months. Patient 1 had a treated lipoma that reduced in volume by approximately 35%, while the control continued to grow and doubled in volume. In patient 2, the treated lesion on the lateral aspect of the mid thigh reduced in volume by almost 70%, and the treated lesion on the volar aspect of the right forearm reduced in volume by more than 40%, while the control grew by more than 20%. In patient 3, the volume of the treated lipoma decreased by 30%, and the control increased by 15%. The follow-up interval was shortest in patient 3—2 months as opposed to 11 months and 6 months for patients 1 and 2, respectively; therefore, more progress may be seen in patient 3 with more time. Interestingly, a change in shape of the lipoma was noted in patient 3 (Figure)—an increase in its depth while the center became anechoic, which is a sign of hollowing in the center due to the saponification of fat and a possible cause for the change from an elliptical to a more spherical or doughnutlike shape. Intralesional administration of DCA may offer patients with extensive lipomas, such as those seen in patients with Dercum disease, an alternative, less-invasive option to assist with pain and tumor burden when excision is not feasible. Although treatments with DCA can be associated with side effects, including pain, swelling, bruising, erythema, induration, and numbness, all 3 of our patients had ultimate mitigation of pain and reduction in lipoma size within months of the injection. Additional studies should be explored to determine the optimal dose and frequency of administration of DCA that could benefit patients with Dercum disease.

- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Dercum’s disease. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2023. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dercums-disease/.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛drek M, Kramza J, et al. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): a review of clinical presentation and management. Reumatologia. 2019;57:281-287. doi:10.5114/reum.2019.89521
- Hansson E, Svensson H, Brorson H. Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7:23. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-23
- Lange U, Oelzner P, Uhlemann C. Dercum’s disease (Lipomatosis dolorosa): successful therapy with pregabalin and manual lymphatic drainage and a current overview. Rheumatol Int. 2008;29:17-22. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0635-3
- Herbst KL, Rutledge T. Pilot study: rapidly cycling hypobaric pressure improves pain after 5 days in adiposis dolorosa. J Pain Res. 2010;3:147-153. doi:10.2147/JPR.S12351
- Martinenghi S, Caretto A, Losio C, et al. Successful treatment of Dercum’s disease by transcutaneous electrical stimulation: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e950. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000950
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary for CID 222528, deoxycholic acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Deoxycholic-acid. Accessed November 11, 2021.
- Liu C, Li MK, Alster TS. Alternative cosmetic and medical applications of injectable deoxycholic acid: a systematic review. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1466-1472. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003159
- Santiago-Vázquez M, Michelen-Gómez EA, Carrasquillo-Bonilla D, et al. Intralesional deoxycholic acid: a potential therapeutic alternative for the treatment of lipomas arising in the face. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;13:112-114. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.037
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Dercum’s disease. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2023. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dercums-disease/.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛drek M, Kramza J, et al. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): a review of clinical presentation and management. Reumatologia. 2019;57:281-287. doi:10.5114/reum.2019.89521
- Hansson E, Svensson H, Brorson H. Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7:23. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-23
- Lange U, Oelzner P, Uhlemann C. Dercum’s disease (Lipomatosis dolorosa): successful therapy with pregabalin and manual lymphatic drainage and a current overview. Rheumatol Int. 2008;29:17-22. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0635-3
- Herbst KL, Rutledge T. Pilot study: rapidly cycling hypobaric pressure improves pain after 5 days in adiposis dolorosa. J Pain Res. 2010;3:147-153. doi:10.2147/JPR.S12351
- Martinenghi S, Caretto A, Losio C, et al. Successful treatment of Dercum’s disease by transcutaneous electrical stimulation: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e950. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000950
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary for CID 222528, deoxycholic acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Deoxycholic-acid. Accessed November 11, 2021.
- Liu C, Li MK, Alster TS. Alternative cosmetic and medical applications of injectable deoxycholic acid: a systematic review. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1466-1472. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003159
- Santiago-Vázquez M, Michelen-Gómez EA, Carrasquillo-Bonilla D, et al. Intralesional deoxycholic acid: a potential therapeutic alternative for the treatment of lipomas arising in the face. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;13:112-114. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.037
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should consider Dercum disease when encountering a patient with numerous painful lipomas.
- Subcutaneous administration of deoxycholic acid resulted in a notable reduction in pain and size of lipomas by 30% to 68% per radiographic review.
- Deoxycholic acid may provide an alternative therapeutic option for patients who have Dercum disease with substantial tumor burden.
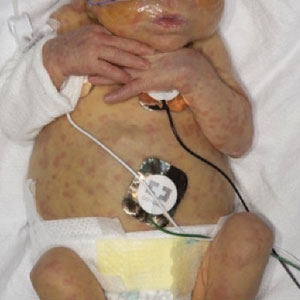
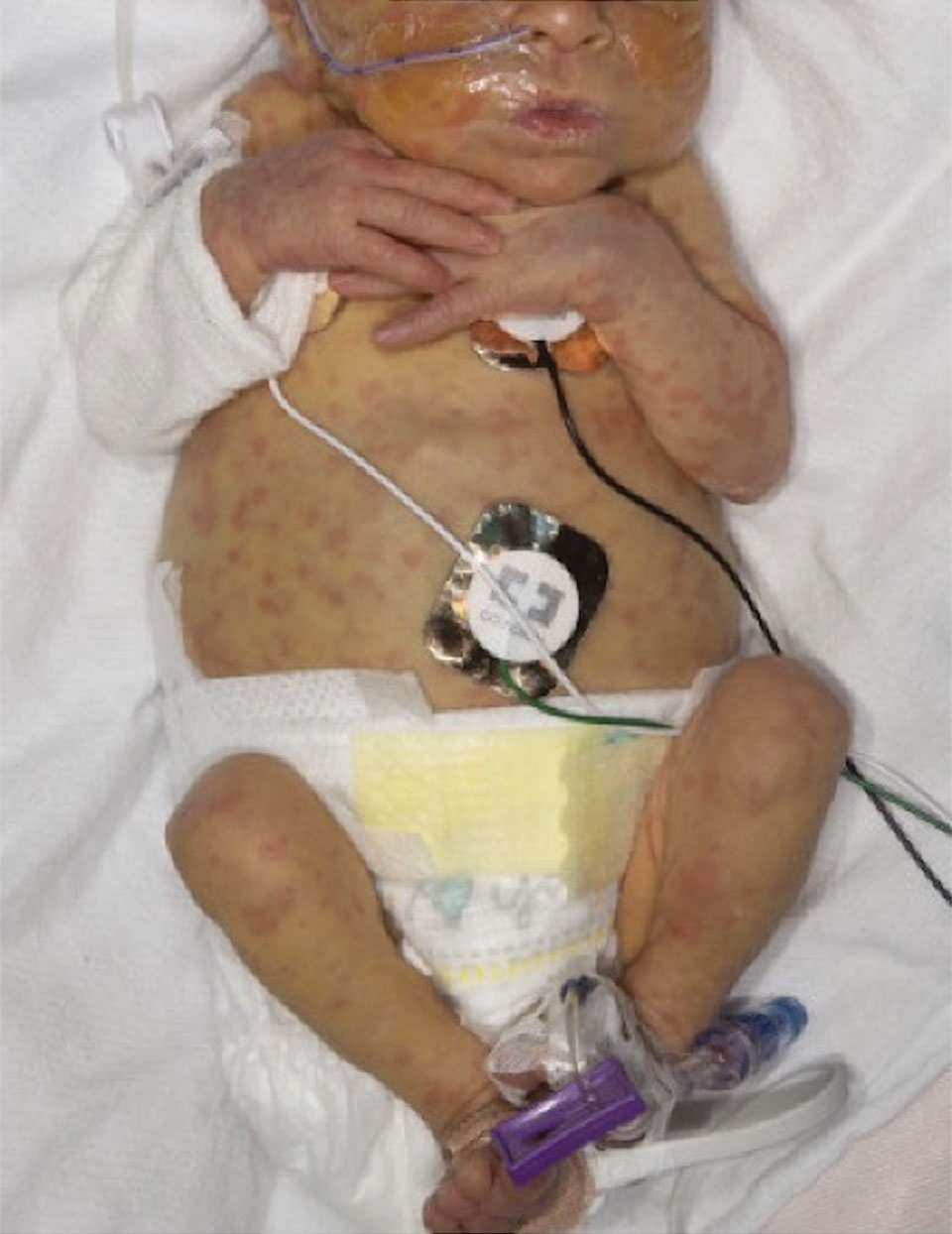
Scattered Red-Brown, Centrally Violaceous, Blanching Papules on an Infant
The Diagnosis: Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disorder (NOMID)
The punch biopsy demonstrated a predominantly deep but somewhat superficial, periadnexal, neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltrate (Figure). The eruption resolved 3 days later with supportive treatment, including appropriate wound care. Genetic analysis revealed an autosomal-dominant NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 gene, NLRP3, de novo variant associated with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disorder (NOMID). Additional workup to characterize our patient’s inflammatory profile revealed elevated IL-18, CD3, CD4, S100A12, and S100A8/A9 levels. On day 48 of life, she was started on anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, at a dose of 1 mg/kg subcutaneously, which eventually was titrated to 10 mg/kg at hospital discharge. Hearing screenings were within normal limits.
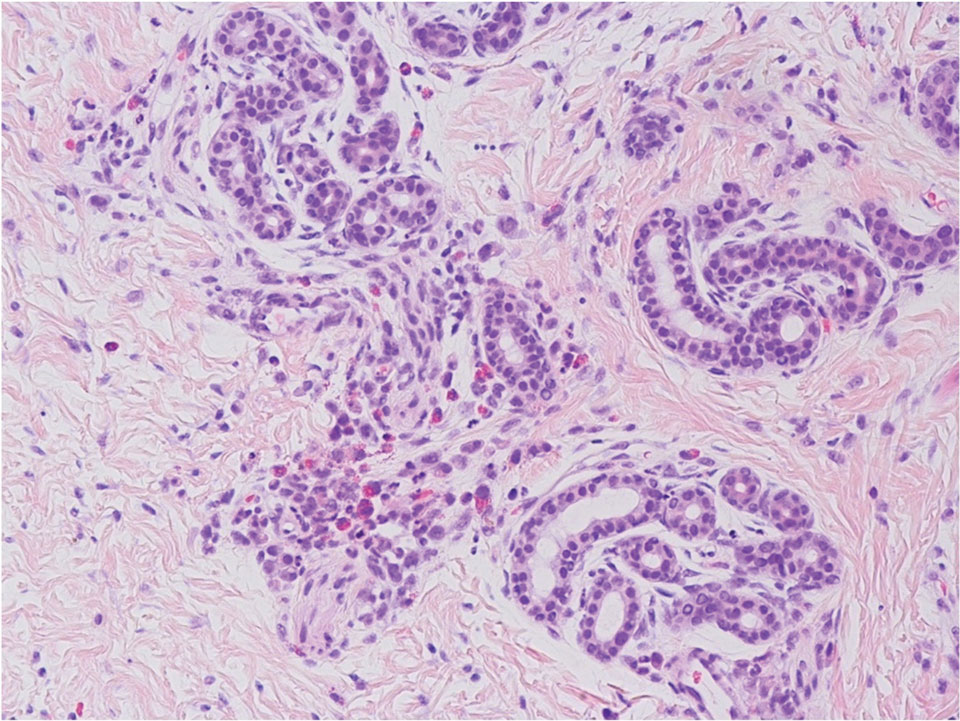
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) consist of 3 rare, IL-1–associated, autoinflammatory disorders, including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS), Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS), and NOMID (also known as chronic infantile neurologic cutaneous and articular syndrome). These conditions result from a sporadic or autosomal-dominant gain-of-function mutations in a single gene, NLRP3, on chromosome 1q44. NLRP3 encodes for cryopyrin, an important component of an IL-1 and IL-18 activating inflammasome.1 The most severe manifestation of CAPS is NOMID, which typically presents at birth as a migratory urticarial eruption, growth failure, myalgia, fever, and abnormal facial features, including frontal bossing, saddle-shaped nose, and protruding eyes.2 The illness also can manifest with hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, uveitis, sensorineural hearing loss, cerebral atrophy, and other neurologic manifestations.3 A diagnosis of chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperature (CANDLE) syndrome was less likely given that our patient remained afebrile and did not show signs of lipodystrophy and persistent violaceous eyelid swelling. Both FCAS and MWS are less severe forms of CAPS when compared to NOMID. Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome was less likely given the absence of the typical periodic fever pattern associated with the condition and severity of our patient’s symptoms. Muckle-Wells syndrome typically presents in adolescence with symptoms of FCAS, painful urticarial plaques, and progressive sensorinueral hearing loss. Tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated periodic fever (TRAPS) usually is associated with episodic fevers, abdominal pain, periorbital edema, migratory erythema, and arthralgia.1,3,4
Diagnostic criteria for CAPS include elevated inflammatory markers and serum amyloid, plus at least 2 of the typical CAPS symptoms: urticarial rash, cold-triggered episodes, sensorineural hearing loss, musculoskeletal symptoms, chronic aseptic meningitis, and skeletal abnormalities.4 The sensitivity and specificity of these diagnostic criteria are 84% and 91%, respectively. Additional findings that can be seen but are not part of the diagnostic criteria include intermittent fever, transient joint swelling, bony overgrowths, uveitis, optic disc edema, impaired growth, and hepatosplenomegaly.5 Laboratory findings may reveal leukocytosis, eosinophilia, anemia, and/or thrombocytopenia.3,5
Genetic testing, skin biopsies, ophthalmic examinations, neuroimaging, joint radiography, cerebrospinal fluid tests, and hearing examinations can be performed for confirmation of diagnosis and evaluation of systemic complications.4 A skin biopsy may reveal a neutrophilic infiltrate. Ophthalmic examination can demonstrate uveitis and optic disk edema. Neuroimaging may reveal cerebral atrophy or ventricular dilation. Lastly, joint radiography can be used to evaluate for the presence of premature long bone ossification or osseous overgrowth.4
In summary, NOMID is a multisystemic disorder with cutaneous manifestations. Early recognition of this entity is important given the severe sequelae and available efficacious therapy. Dermatologists should be aware of these manifestations, as dermatologic consultation and a skin biopsy may aid in diagnosis.
- Lachmann HJ. Periodic fever syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31:596-609. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2017.12.001
- Hull KM, Shoham N, Jin Chae J, et al. The expanding spectrum of systemic autoinflammatory disorders and their rheumatic manifestations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:61-69. doi:10.1097/00002281-200301000-00011
- Ahmadi N, Brewer CC, Zalewski C, et al. Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes: otolaryngologic and audiologic manifestations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145:295-302. doi:10.1177/0194599811402296
- Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Ozen S, Tyrrell PN, et al. Diagnostic criteria for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:942-947. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209686
- Aksentijevich I, Nowak M, Mallah M, et al. De novo CIAS1 mutations, cytokine activation, and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID): a new member of the expanding family of pyrinassociated autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:3340-3348. doi:10.1002/art.10688
The Diagnosis: Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disorder (NOMID)
The punch biopsy demonstrated a predominantly deep but somewhat superficial, periadnexal, neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltrate (Figure). The eruption resolved 3 days later with supportive treatment, including appropriate wound care. Genetic analysis revealed an autosomal-dominant NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 gene, NLRP3, de novo variant associated with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disorder (NOMID). Additional workup to characterize our patient’s inflammatory profile revealed elevated IL-18, CD3, CD4, S100A12, and S100A8/A9 levels. On day 48 of life, she was started on anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, at a dose of 1 mg/kg subcutaneously, which eventually was titrated to 10 mg/kg at hospital discharge. Hearing screenings were within normal limits.

Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) consist of 3 rare, IL-1–associated, autoinflammatory disorders, including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS), Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS), and NOMID (also known as chronic infantile neurologic cutaneous and articular syndrome). These conditions result from a sporadic or autosomal-dominant gain-of-function mutations in a single gene, NLRP3, on chromosome 1q44. NLRP3 encodes for cryopyrin, an important component of an IL-1 and IL-18 activating inflammasome.1 The most severe manifestation of CAPS is NOMID, which typically presents at birth as a migratory urticarial eruption, growth failure, myalgia, fever, and abnormal facial features, including frontal bossing, saddle-shaped nose, and protruding eyes.2 The illness also can manifest with hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, uveitis, sensorineural hearing loss, cerebral atrophy, and other neurologic manifestations.3 A diagnosis of chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperature (CANDLE) syndrome was less likely given that our patient remained afebrile and did not show signs of lipodystrophy and persistent violaceous eyelid swelling. Both FCAS and MWS are less severe forms of CAPS when compared to NOMID. Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome was less likely given the absence of the typical periodic fever pattern associated with the condition and severity of our patient’s symptoms. Muckle-Wells syndrome typically presents in adolescence with symptoms of FCAS, painful urticarial plaques, and progressive sensorinueral hearing loss. Tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated periodic fever (TRAPS) usually is associated with episodic fevers, abdominal pain, periorbital edema, migratory erythema, and arthralgia.1,3,4
Diagnostic criteria for CAPS include elevated inflammatory markers and serum amyloid, plus at least 2 of the typical CAPS symptoms: urticarial rash, cold-triggered episodes, sensorineural hearing loss, musculoskeletal symptoms, chronic aseptic meningitis, and skeletal abnormalities.4 The sensitivity and specificity of these diagnostic criteria are 84% and 91%, respectively. Additional findings that can be seen but are not part of the diagnostic criteria include intermittent fever, transient joint swelling, bony overgrowths, uveitis, optic disc edema, impaired growth, and hepatosplenomegaly.5 Laboratory findings may reveal leukocytosis, eosinophilia, anemia, and/or thrombocytopenia.3,5
Genetic testing, skin biopsies, ophthalmic examinations, neuroimaging, joint radiography, cerebrospinal fluid tests, and hearing examinations can be performed for confirmation of diagnosis and evaluation of systemic complications.4 A skin biopsy may reveal a neutrophilic infiltrate. Ophthalmic examination can demonstrate uveitis and optic disk edema. Neuroimaging may reveal cerebral atrophy or ventricular dilation. Lastly, joint radiography can be used to evaluate for the presence of premature long bone ossification or osseous overgrowth.4
In summary, NOMID is a multisystemic disorder with cutaneous manifestations. Early recognition of this entity is important given the severe sequelae and available efficacious therapy. Dermatologists should be aware of these manifestations, as dermatologic consultation and a skin biopsy may aid in diagnosis.
The Diagnosis: Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disorder (NOMID)
The punch biopsy demonstrated a predominantly deep but somewhat superficial, periadnexal, neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltrate (Figure). The eruption resolved 3 days later with supportive treatment, including appropriate wound care. Genetic analysis revealed an autosomal-dominant NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 gene, NLRP3, de novo variant associated with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disorder (NOMID). Additional workup to characterize our patient’s inflammatory profile revealed elevated IL-18, CD3, CD4, S100A12, and S100A8/A9 levels. On day 48 of life, she was started on anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, at a dose of 1 mg/kg subcutaneously, which eventually was titrated to 10 mg/kg at hospital discharge. Hearing screenings were within normal limits.

Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) consist of 3 rare, IL-1–associated, autoinflammatory disorders, including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS), Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS), and NOMID (also known as chronic infantile neurologic cutaneous and articular syndrome). These conditions result from a sporadic or autosomal-dominant gain-of-function mutations in a single gene, NLRP3, on chromosome 1q44. NLRP3 encodes for cryopyrin, an important component of an IL-1 and IL-18 activating inflammasome.1 The most severe manifestation of CAPS is NOMID, which typically presents at birth as a migratory urticarial eruption, growth failure, myalgia, fever, and abnormal facial features, including frontal bossing, saddle-shaped nose, and protruding eyes.2 The illness also can manifest with hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, uveitis, sensorineural hearing loss, cerebral atrophy, and other neurologic manifestations.3 A diagnosis of chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperature (CANDLE) syndrome was less likely given that our patient remained afebrile and did not show signs of lipodystrophy and persistent violaceous eyelid swelling. Both FCAS and MWS are less severe forms of CAPS when compared to NOMID. Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome was less likely given the absence of the typical periodic fever pattern associated with the condition and severity of our patient’s symptoms. Muckle-Wells syndrome typically presents in adolescence with symptoms of FCAS, painful urticarial plaques, and progressive sensorinueral hearing loss. Tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated periodic fever (TRAPS) usually is associated with episodic fevers, abdominal pain, periorbital edema, migratory erythema, and arthralgia.1,3,4
Diagnostic criteria for CAPS include elevated inflammatory markers and serum amyloid, plus at least 2 of the typical CAPS symptoms: urticarial rash, cold-triggered episodes, sensorineural hearing loss, musculoskeletal symptoms, chronic aseptic meningitis, and skeletal abnormalities.4 The sensitivity and specificity of these diagnostic criteria are 84% and 91%, respectively. Additional findings that can be seen but are not part of the diagnostic criteria include intermittent fever, transient joint swelling, bony overgrowths, uveitis, optic disc edema, impaired growth, and hepatosplenomegaly.5 Laboratory findings may reveal leukocytosis, eosinophilia, anemia, and/or thrombocytopenia.3,5
Genetic testing, skin biopsies, ophthalmic examinations, neuroimaging, joint radiography, cerebrospinal fluid tests, and hearing examinations can be performed for confirmation of diagnosis and evaluation of systemic complications.4 A skin biopsy may reveal a neutrophilic infiltrate. Ophthalmic examination can demonstrate uveitis and optic disk edema. Neuroimaging may reveal cerebral atrophy or ventricular dilation. Lastly, joint radiography can be used to evaluate for the presence of premature long bone ossification or osseous overgrowth.4
In summary, NOMID is a multisystemic disorder with cutaneous manifestations. Early recognition of this entity is important given the severe sequelae and available efficacious therapy. Dermatologists should be aware of these manifestations, as dermatologic consultation and a skin biopsy may aid in diagnosis.
- Lachmann HJ. Periodic fever syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31:596-609. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2017.12.001
- Hull KM, Shoham N, Jin Chae J, et al. The expanding spectrum of systemic autoinflammatory disorders and their rheumatic manifestations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:61-69. doi:10.1097/00002281-200301000-00011
- Ahmadi N, Brewer CC, Zalewski C, et al. Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes: otolaryngologic and audiologic manifestations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145:295-302. doi:10.1177/0194599811402296
- Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Ozen S, Tyrrell PN, et al. Diagnostic criteria for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:942-947. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209686
- Aksentijevich I, Nowak M, Mallah M, et al. De novo CIAS1 mutations, cytokine activation, and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID): a new member of the expanding family of pyrinassociated autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:3340-3348. doi:10.1002/art.10688
- Lachmann HJ. Periodic fever syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31:596-609. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2017.12.001
- Hull KM, Shoham N, Jin Chae J, et al. The expanding spectrum of systemic autoinflammatory disorders and their rheumatic manifestations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:61-69. doi:10.1097/00002281-200301000-00011
- Ahmadi N, Brewer CC, Zalewski C, et al. Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes: otolaryngologic and audiologic manifestations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145:295-302. doi:10.1177/0194599811402296
- Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Ozen S, Tyrrell PN, et al. Diagnostic criteria for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:942-947. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209686
- Aksentijevich I, Nowak M, Mallah M, et al. De novo CIAS1 mutations, cytokine activation, and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID): a new member of the expanding family of pyrinassociated autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:3340-3348. doi:10.1002/art.10688
A 2-week-old infant girl was transferred to a specialty pediatric hospital where dermatology was consulted for evaluation of a diffuse eruption triggered by cold that was similar to an eruption present at birth. She was born at 31 weeks and 2 days’ gestation at an outside hospital via caesarean delivery. Early delivery was prompted by superimposed pre-eclampsia with severe hypertension after administration of antenatal steroids. At birth, the infant was cyanotic and apneic and had a documented skin eruption, according to the medical record. She had thrombocytopenia, elevated C-reactive protein, and an elevated temperature without fever. Extensive septic workup, including blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid cultures; herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus screening; and Toxoplasma polymerase chain reaction were negative. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed no evidence of intracranial congenital infection. Ampicillinsulbactam was initiated for presumed culture-negative sepsis. On day 2 of hospitalization, she developed conjunctival icterus, hepatomegaly, and jaundice. Direct hyperbilirubinemia; anemia; and elevated triglycerides, ferritin, and ammonia all were present. Coagulation studies were normal. Subsequent workup, including abdominal ultrasonography and hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan, was concerning for biliary atresia. Despite appropriate treatment, her condition did not improve and she was transferred. Repeat abdominal ultrasonography on day 24 of life confirmed hepatomegaly but did not demonstrate other findings of biliary atresia. At the current presentation, physical examination revealed many scattered, redbrown and centrally violaceous, blanching papules measuring a few millimeters involving the trunk, arms, buttocks, and legs. A punch biopsy was obtained.
Cleansing balms
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
Get action! – Teddy Roosevelt
“Papa! Where donut?” asks my 2½ year-old sitting with her legs dangling and hands folded in a bustling Starbucks. We’ve been waiting for 8 minutes and we’ve reached her limit of tolerance. She’s unimpressed by the queued customers who compliment her curly blonde hair, many of whom have come and gone since we’ve been waiting. I agree – how long does it take to pour a kiddie milk and grab a donut? We can both see it in the case right there!
No one likes to wait. Truly, one of the great benefits of the modern world is that wait times are now incredibly short. Many Starbucks customers, unlike my daughter, ordered their drink ahead and waited exactly 0 minutes to get their drink. What about Amazon? I ordered a bird feeder this morning and it’s already hanging in the yard. It’s still daylight. Feel like Himalayan Momo Dumplings tonight? Your food could arrive in 37 minutes. The modern wait standard has been set impossibly high for us.
Yes, for some. We created a whole room just for waiting. Airlines call theirs “The Platinum Executive Lounge.” Ours is “The waiting room.”
Excess waiting is a significant reason why health care gets beat up in reviews. We’re unable to keep up with the new expectations. Waiting is also a significant cause of distress. Many patients report the most difficult part of their cancer diagnosis was the waiting for results, not the treatment. It’s because when under stress, we are hardwired to take action. Binding patients into inaction while they wait is very uncomfortable.
Fortunately, the psychology of waiting is well understood and there are best practices that can help. First, anxiety makes waiting much worse. Conveying confidence and reassuring patients they are in the right place and that everything will be OK makes the wait time feel shorter for them. Uncertainty also compounds their apprehension. If you believe the diagnosis will be melanoma, tell them that at the time of the biopsy and tell them what you expect next. This is better than saying, “Well, that could be cancer. We’ll see.”
Knowing a wait time is also much better than not. Have your staff advise patients on how much longer they can expect before seeing you (telling them they’re next isn’t as effective). Advise that test results should be back by the end of next week. Of course, under promise and over deliver. When the results are back on Tuesday, you’ve got a pleased patient.
Explaining that you had to add in an urgent patient helps. Even if it’s not your fault, it’s still better to apologize. For example, the 78 highway, the left anterior descending artery to our office, has been closed because of a sinkhole this month (not kidding). I’ve been apologizing to a lot of patients saying that all our patients are arriving late, which is putting us behind. As they can envision the linear parking lot that used to be a highway, it helps.
Lastly, as any child can tell you, waiting has to not only be, but to also appear, fair. The only thing worse than waiting for an appointment, or donut, is seeing someone who came in after you get their donut before you do. If you’re pulling both Mohs and cosmetics patients from the same waiting area, then your surgery patients will see a lot of patients come and go while they are sitting. Demarcating one sitting area for Mohs and one for clinics might help. So does ordering ahead. I’d show my daughter how to use the app so we don’t have to wait so long next week, but she’s 2 and I’m quite sure she already knows.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“Papa! Where donut?” asks my 2½ year-old sitting with her legs dangling and hands folded in a bustling Starbucks. We’ve been waiting for 8 minutes and we’ve reached her limit of tolerance. She’s unimpressed by the queued customers who compliment her curly blonde hair, many of whom have come and gone since we’ve been waiting. I agree – how long does it take to pour a kiddie milk and grab a donut? We can both see it in the case right there!
No one likes to wait. Truly, one of the great benefits of the modern world is that wait times are now incredibly short. Many Starbucks customers, unlike my daughter, ordered their drink ahead and waited exactly 0 minutes to get their drink. What about Amazon? I ordered a bird feeder this morning and it’s already hanging in the yard. It’s still daylight. Feel like Himalayan Momo Dumplings tonight? Your food could arrive in 37 minutes. The modern wait standard has been set impossibly high for us.
Yes, for some. We created a whole room just for waiting. Airlines call theirs “The Platinum Executive Lounge.” Ours is “The waiting room.”
Excess waiting is a significant reason why health care gets beat up in reviews. We’re unable to keep up with the new expectations. Waiting is also a significant cause of distress. Many patients report the most difficult part of their cancer diagnosis was the waiting for results, not the treatment. It’s because when under stress, we are hardwired to take action. Binding patients into inaction while they wait is very uncomfortable.
Fortunately, the psychology of waiting is well understood and there are best practices that can help. First, anxiety makes waiting much worse. Conveying confidence and reassuring patients they are in the right place and that everything will be OK makes the wait time feel shorter for them. Uncertainty also compounds their apprehension. If you believe the diagnosis will be melanoma, tell them that at the time of the biopsy and tell them what you expect next. This is better than saying, “Well, that could be cancer. We’ll see.”
Knowing a wait time is also much better than not. Have your staff advise patients on how much longer they can expect before seeing you (telling them they’re next isn’t as effective). Advise that test results should be back by the end of next week. Of course, under promise and over deliver. When the results are back on Tuesday, you’ve got a pleased patient.
Explaining that you had to add in an urgent patient helps. Even if it’s not your fault, it’s still better to apologize. For example, the 78 highway, the left anterior descending artery to our office, has been closed because of a sinkhole this month (not kidding). I’ve been apologizing to a lot of patients saying that all our patients are arriving late, which is putting us behind. As they can envision the linear parking lot that used to be a highway, it helps.
Lastly, as any child can tell you, waiting has to not only be, but to also appear, fair. The only thing worse than waiting for an appointment, or donut, is seeing someone who came in after you get their donut before you do. If you’re pulling both Mohs and cosmetics patients from the same waiting area, then your surgery patients will see a lot of patients come and go while they are sitting. Demarcating one sitting area for Mohs and one for clinics might help. So does ordering ahead. I’d show my daughter how to use the app so we don’t have to wait so long next week, but she’s 2 and I’m quite sure she already knows.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“Papa! Where donut?” asks my 2½ year-old sitting with her legs dangling and hands folded in a bustling Starbucks. We’ve been waiting for 8 minutes and we’ve reached her limit of tolerance. She’s unimpressed by the queued customers who compliment her curly blonde hair, many of whom have come and gone since we’ve been waiting. I agree – how long does it take to pour a kiddie milk and grab a donut? We can both see it in the case right there!
No one likes to wait. Truly, one of the great benefits of the modern world is that wait times are now incredibly short. Many Starbucks customers, unlike my daughter, ordered their drink ahead and waited exactly 0 minutes to get their drink. What about Amazon? I ordered a bird feeder this morning and it’s already hanging in the yard. It’s still daylight. Feel like Himalayan Momo Dumplings tonight? Your food could arrive in 37 minutes. The modern wait standard has been set impossibly high for us.
Yes, for some. We created a whole room just for waiting. Airlines call theirs “The Platinum Executive Lounge.” Ours is “The waiting room.”
Excess waiting is a significant reason why health care gets beat up in reviews. We’re unable to keep up with the new expectations. Waiting is also a significant cause of distress. Many patients report the most difficult part of their cancer diagnosis was the waiting for results, not the treatment. It’s because when under stress, we are hardwired to take action. Binding patients into inaction while they wait is very uncomfortable.
Fortunately, the psychology of waiting is well understood and there are best practices that can help. First, anxiety makes waiting much worse. Conveying confidence and reassuring patients they are in the right place and that everything will be OK makes the wait time feel shorter for them. Uncertainty also compounds their apprehension. If you believe the diagnosis will be melanoma, tell them that at the time of the biopsy and tell them what you expect next. This is better than saying, “Well, that could be cancer. We’ll see.”
Knowing a wait time is also much better than not. Have your staff advise patients on how much longer they can expect before seeing you (telling them they’re next isn’t as effective). Advise that test results should be back by the end of next week. Of course, under promise and over deliver. When the results are back on Tuesday, you’ve got a pleased patient.
Explaining that you had to add in an urgent patient helps. Even if it’s not your fault, it’s still better to apologize. For example, the 78 highway, the left anterior descending artery to our office, has been closed because of a sinkhole this month (not kidding). I’ve been apologizing to a lot of patients saying that all our patients are arriving late, which is putting us behind. As they can envision the linear parking lot that used to be a highway, it helps.
Lastly, as any child can tell you, waiting has to not only be, but to also appear, fair. The only thing worse than waiting for an appointment, or donut, is seeing someone who came in after you get their donut before you do. If you’re pulling both Mohs and cosmetics patients from the same waiting area, then your surgery patients will see a lot of patients come and go while they are sitting. Demarcating one sitting area for Mohs and one for clinics might help. So does ordering ahead. I’d show my daughter how to use the app so we don’t have to wait so long next week, but she’s 2 and I’m quite sure she already knows.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
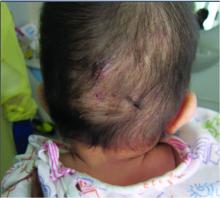
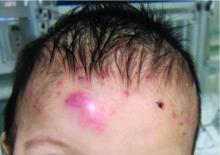
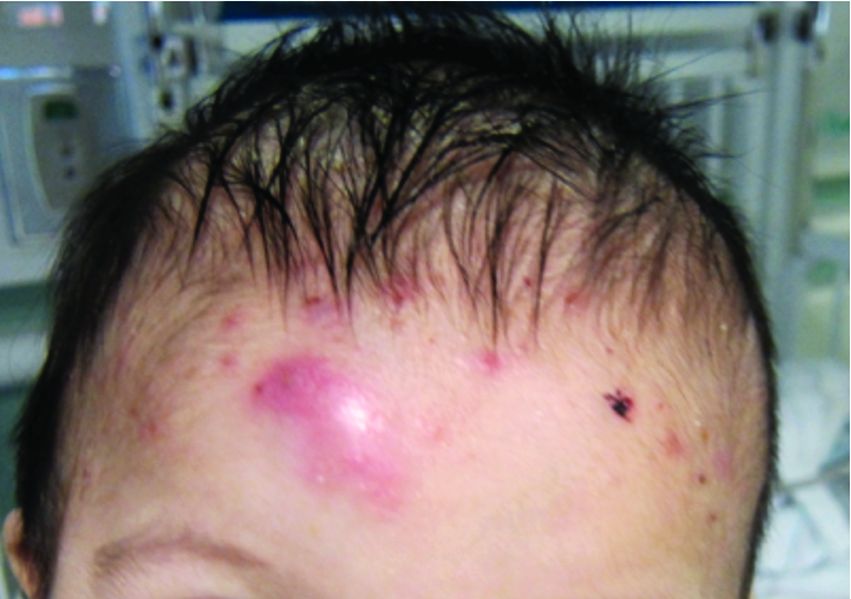
A 7-month-old male presents with pustules and inflamed papules on the scalp and extremities
The bacterial, fungal, and atypical mycobacterial cultures from the lesions performed at the emergency department were all negative.
Pediatric dermatology was consulted and a punch biopsy of one of the lesions was done. Histopathologic examination showed a mixed perifollicular infiltrate of predominantly eosinophils with some neutrophils and associated microabscesses. Periodic acid Schiff and Fite stains failed to reveal any organisms. CD1 immunostain was negative. Fresh tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative.
Given the clinical presentation of chronic recurrent sterile pustules on an infant with associated eosinophilia and the reported histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with eosinophilic pustular folliculitis of infancy (EPFI).
EPFI is a rare and idiopathic cutaneous disorder present in children. About 70% of the cases reported occur in the first 6 month of life and rarely present past 3 years of age. EPF encompasses a group of conditions including the classic adult form, or Ofuji disease. EPF is seen in immunosuppressed patients, mainly HIV positive, and EPF is also seen in infants and children.
In EPFI, males are most commonly affected. The condition presents, as it did in our patient, with recurrent crops of sterile papules and pustules mainly on the scalp, but they can occur in other parts of the body. The lesions go away within a few weeks to months without leaving any scars but it can take months to years to resolve. Histopathologic analysis of the lesions show an eosinophilic infiltrate which can be follicular, perifollicular, or periadnexal with associated flame figures in about 26% of cases.
Aggressive treatment is usually not needed as lesions are self-limited. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamine medications like cetirizine if symptomatic.
If the lesions start to present during the neonatal period, one may consider in the differential diagnosis, neonatal rashes like transient neonatal pustular melanosis and erythema toxicum neonatorum. Both of these neonatal conditions tend to resolve in the first month of life, compared with EPFI where lesions can come and go for months to years. EPFI lesions can be described as pustules and inflammatory papules, as well as furuncles and vesicles. All of the lesions may be seen in one patient at one time, which will not be typical for transient neonatal pustular melanosis or erythema toxicum. Eosinophils can be seen in erythema toxicum but folliculitis is not present. The inflammatory infiltrate seen in transient neonatal pustular melanosis is polymorphonuclear, not eosinophilic.
Early in the presentation, infectious conditions like staphylococcal or streptococcal folliculitis, cellulitis and furunculosis, tinea capitis, atypical mycobacterial infections, herpes simplex, and parasitic infections like scabies should be considered. In young infants, empiric antibiotic treatment may be started until cultures are finalized. If there is a family history of pruritic papules and pustules, scabies should be considered. A scabies prep can be done to rule out this entity.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis can also present with pustules and papules in early infancy and also has a predilection for the scalp. When this condition is in question, a skin biopsy should be performed which shows a CD1 positive histiocytic infiltrate.
In conclusion, EPFI is a benign rare condition that can present in infants as recurrent pustules and papules, mainly on the scalp, which are self-limited and if symptomatic can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.
References
Alonso-Castro L et al. Dermatol Online J. 2012 Oct 15;18(10):6.
Frølunde AS et al. Clin Case Rep. 2021 May 11;9(5):e04167.
Hernández-Martín Á et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Jan;68(1):150-5.
The bacterial, fungal, and atypical mycobacterial cultures from the lesions performed at the emergency department were all negative.
Pediatric dermatology was consulted and a punch biopsy of one of the lesions was done. Histopathologic examination showed a mixed perifollicular infiltrate of predominantly eosinophils with some neutrophils and associated microabscesses. Periodic acid Schiff and Fite stains failed to reveal any organisms. CD1 immunostain was negative. Fresh tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative.
Given the clinical presentation of chronic recurrent sterile pustules on an infant with associated eosinophilia and the reported histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with eosinophilic pustular folliculitis of infancy (EPFI).
EPFI is a rare and idiopathic cutaneous disorder present in children. About 70% of the cases reported occur in the first 6 month of life and rarely present past 3 years of age. EPF encompasses a group of conditions including the classic adult form, or Ofuji disease. EPF is seen in immunosuppressed patients, mainly HIV positive, and EPF is also seen in infants and children.
In EPFI, males are most commonly affected. The condition presents, as it did in our patient, with recurrent crops of sterile papules and pustules mainly on the scalp, but they can occur in other parts of the body. The lesions go away within a few weeks to months without leaving any scars but it can take months to years to resolve. Histopathologic analysis of the lesions show an eosinophilic infiltrate which can be follicular, perifollicular, or periadnexal with associated flame figures in about 26% of cases.
Aggressive treatment is usually not needed as lesions are self-limited. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamine medications like cetirizine if symptomatic.
If the lesions start to present during the neonatal period, one may consider in the differential diagnosis, neonatal rashes like transient neonatal pustular melanosis and erythema toxicum neonatorum. Both of these neonatal conditions tend to resolve in the first month of life, compared with EPFI where lesions can come and go for months to years. EPFI lesions can be described as pustules and inflammatory papules, as well as furuncles and vesicles. All of the lesions may be seen in one patient at one time, which will not be typical for transient neonatal pustular melanosis or erythema toxicum. Eosinophils can be seen in erythema toxicum but folliculitis is not present. The inflammatory infiltrate seen in transient neonatal pustular melanosis is polymorphonuclear, not eosinophilic.
Early in the presentation, infectious conditions like staphylococcal or streptococcal folliculitis, cellulitis and furunculosis, tinea capitis, atypical mycobacterial infections, herpes simplex, and parasitic infections like scabies should be considered. In young infants, empiric antibiotic treatment may be started until cultures are finalized. If there is a family history of pruritic papules and pustules, scabies should be considered. A scabies prep can be done to rule out this entity.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis can also present with pustules and papules in early infancy and also has a predilection for the scalp. When this condition is in question, a skin biopsy should be performed which shows a CD1 positive histiocytic infiltrate.
In conclusion, EPFI is a benign rare condition that can present in infants as recurrent pustules and papules, mainly on the scalp, which are self-limited and if symptomatic can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.
References
Alonso-Castro L et al. Dermatol Online J. 2012 Oct 15;18(10):6.
Frølunde AS et al. Clin Case Rep. 2021 May 11;9(5):e04167.
Hernández-Martín Á et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Jan;68(1):150-5.
The bacterial, fungal, and atypical mycobacterial cultures from the lesions performed at the emergency department were all negative.
Pediatric dermatology was consulted and a punch biopsy of one of the lesions was done. Histopathologic examination showed a mixed perifollicular infiltrate of predominantly eosinophils with some neutrophils and associated microabscesses. Periodic acid Schiff and Fite stains failed to reveal any organisms. CD1 immunostain was negative. Fresh tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative.
Given the clinical presentation of chronic recurrent sterile pustules on an infant with associated eosinophilia and the reported histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with eosinophilic pustular folliculitis of infancy (EPFI).
EPFI is a rare and idiopathic cutaneous disorder present in children. About 70% of the cases reported occur in the first 6 month of life and rarely present past 3 years of age. EPF encompasses a group of conditions including the classic adult form, or Ofuji disease. EPF is seen in immunosuppressed patients, mainly HIV positive, and EPF is also seen in infants and children.
In EPFI, males are most commonly affected. The condition presents, as it did in our patient, with recurrent crops of sterile papules and pustules mainly on the scalp, but they can occur in other parts of the body. The lesions go away within a few weeks to months without leaving any scars but it can take months to years to resolve. Histopathologic analysis of the lesions show an eosinophilic infiltrate which can be follicular, perifollicular, or periadnexal with associated flame figures in about 26% of cases.
Aggressive treatment is usually not needed as lesions are self-limited. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamine medications like cetirizine if symptomatic.
If the lesions start to present during the neonatal period, one may consider in the differential diagnosis, neonatal rashes like transient neonatal pustular melanosis and erythema toxicum neonatorum. Both of these neonatal conditions tend to resolve in the first month of life, compared with EPFI where lesions can come and go for months to years. EPFI lesions can be described as pustules and inflammatory papules, as well as furuncles and vesicles. All of the lesions may be seen in one patient at one time, which will not be typical for transient neonatal pustular melanosis or erythema toxicum. Eosinophils can be seen in erythema toxicum but folliculitis is not present. The inflammatory infiltrate seen in transient neonatal pustular melanosis is polymorphonuclear, not eosinophilic.
Early in the presentation, infectious conditions like staphylococcal or streptococcal folliculitis, cellulitis and furunculosis, tinea capitis, atypical mycobacterial infections, herpes simplex, and parasitic infections like scabies should be considered. In young infants, empiric antibiotic treatment may be started until cultures are finalized. If there is a family history of pruritic papules and pustules, scabies should be considered. A scabies prep can be done to rule out this entity.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis can also present with pustules and papules in early infancy and also has a predilection for the scalp. When this condition is in question, a skin biopsy should be performed which shows a CD1 positive histiocytic infiltrate.
In conclusion, EPFI is a benign rare condition that can present in infants as recurrent pustules and papules, mainly on the scalp, which are self-limited and if symptomatic can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.
References
Alonso-Castro L et al. Dermatol Online J. 2012 Oct 15;18(10):6.
Frølunde AS et al. Clin Case Rep. 2021 May 11;9(5):e04167.
Hernández-Martín Á et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Jan;68(1):150-5.
A 7-month-old male is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of pustules and inflamed papules on the scalp and extremities for several weeks of duration. The parents report the lesions started about a month prior and he has already been treated with cephalexin, clindamycin, and sulfamethoxazole without any improvement. Cultures sent prior by the child's pediatrician did not reveal any fungus or bacteria. The parents report a low-grade fever for about 3 days.
He was born via natural vaginal delivery with no instrumentation or external monitoring. Mom had prenatal care. Besides the skin lesions, the baby has been healthy and growing well. He has no history of eczema or severe infections. He has not been hospitalized before.
On physical examination the baby was not febrile. On the scalp and forehead, he had diffusely distributed pustules, erythematous papules, and nodules. He also presented with scattered, fine, small, crusted 1-2-mm pink papules on the trunk and extremities. He had no adenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly.
At the emergency department, samples from one of the pustules were sent for bacterial, fungal, and atypical mycobacteria cultures. Laboratory test showed a normal blood count with associated eosinophilia (2.8 x 109 L), and normal liver and kidney function. A head ultrasound showed three ill-defined hypoechoic foci within the scalp.
The patient was admitted for treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics and dermatology was consulted.
USPSTF releases updated recommendations on skin cancer screening
.
This final recommendation applies to the general public and is not meant for those at higher risk, such as people with a family history of skin cancer or who have any signs or symptoms, such as irregular moles.
“The new recommendations are consistent with those from 2016, and we are unable to balance benefits and harms,” said Task Force member Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, professor and vice chair of research in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “Unfortunately, there is not enough evidence to recommend for or against screening, and health care professionals should use their judgment when deciding whether or not to screen.”
Dr. Donahue told this news organization that this is a call for more research: “Our recommendations are for patients who present to primary care without symptoms, and after a careful assessment of benefit and harms, we didn’t have evidence to push us towards screening as a benefit. We did look at data from two large screening programs, but they were from Europe and not representative of the U.S. population. They also did not show a benefit for reducing melanoma-related mortality.”
The USPSTF final recommendation statement and corresponding evidence summary have been published online in JAMA, as well as on the USPSTF website.
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, but there are different types that vary in their incidence and severity. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common types of skin cancer, but they infrequently lead to death or substantial morbidity, notes the USPTSF. Melanomas represent about 1% of skin cancer and cause the most skin cancer deaths. An estimated 8,000 individuals in the United States will die of melanoma in 2023.
There are racial differences in melanoma incidence; it is about 30 times more common in White versus Black persons, but disease in persons with darker skin color tends to be diagnosed at a later stage. These disparities may be due to differences in risk factors, access to care, and clinical presentation.
In an accompanying editorial, Maryam M. Asgari, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Lori A. Crane, PhD, MPH, of the Colorado School of Public Health, University of Colorado, Aurora, point out that people with darker skin phenotypes also tend to be affected by skin cancers that are not associated with UV radiation, such as acral melanoma, which arises on the palms and soles, and skin cancers that arise in areas of chronic inflammation, such as wounds.
Thus, differences in anatomical distribution of skin cancers in in the various subpopulations needs to be considered when performing skin screening, they write. “Furthermore, while skin cancer risk is lower among people with darker skin pigmentation, survival is often worse for cancers like melanoma, highlighting the potential need for screening.”
“More data are needed, particularly regarding genetic and environmental risk factors for skin cancer in people with darker pigmentation, to help inform guidelines that can be broadly applied to the U.S. population,” add Dr. Asgari and Dr. Crane. “The diversity of the U.S. population extends also to geography, culture, and socioeconomic status, all of which affect skin cancer risk.”
Review of evidence
The USPSTF commissioned a systematic review to evaluate the benefits and harms of screening for skin cancer in asymptomatic adolescents and adults, including evidence for both keratinocyte carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) and cutaneous melanoma.
Foundational evidence showed that the sensitivity of visual skin examination by a clinician to detect melanoma ranged from 40% to 70% and specificity ranged from 86% to 98%. Evidence that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of visual skin examination to detect keratinocyte carcinoma was limited and inconsistent. There were no new studies reporting on diagnostic accuracy for an asymptomatic screening population.
The USPSTF also reviewed 20 studies in 29 articles (n = 6,053,411). This included three nonrandomized studies evaluating two skin cancer screening programs in Germany, but results were inconsistent. In addition, the ecological and nonrandomized design of the studies limited the conclusions that could be drawn and the applicability to a U.S. population was difficult to assess because of differences in population diversity and health care delivery in the United States.
Other nonrandomized studies that looked at various outcomes, such as harms and stage at diagnosis and melanoma or all-cause mortality, also did not provide sufficient evidence to support screening.
Research is needed
In a second accompanying editorial published in JAMA Dermatology, Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP, of the division of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Texas, Austin, pointed out that unlike other cancer screening programs, such as those for breast, colon, and prostate cancer, skin cancer screening programs are somewhat less organized.
The other programs focus on defined groups of the population, generally with easily identifiable characteristics such as age, sex, and family history, and importantly, there are always defined ages for initiation and halting of screening and intervals for screening frequency. None of these basic screening parameters have been widely adopted among dermatologists in the United States, he wrote. “One important reason why skin cancer screening has remained inconsistent is that it is not covered by Medicare or by many commercial insurance companies,” Dr. Adamson told this news organization. “The test, in this case the skin exam, is often performed as part of a routine dermatology visit.”
Dermatologists should take the lead on this, he said. “Dermatologists should push for a high quality prospective clinical trial of skin cancer screening, preferably in a high-risk population.”
Dr. Donahue agrees that research is needed, as noted in the recommendation. For example, studies are needed demonstrating consistent data of the effects of screening on morbidity and mortality or early detection of skin cancer, and clearer descriptions of skin color and inclusion of a full spectrum of skin colors in study participants. Clinical research is also needed on outcomes in participants that reflect the diversity of the U.S. population.
“I hope funding agencies will be interested in this area of study,” she said. “We put out the whole systematic review and point out the gaps. We need consistent evidence in detecting cancer early and reducing complications from skin cancer.”
The U.S. Congress mandates that the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality support the operations of the USPSTF.
None of the USPSTF authors report any disclosures. Dr. Asgari reported receiving royalties from UpToDate. Dr. Crane did not make any disclosures. Dr. Adamson reported serving as an expert reviewer for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force skin cancer screening report, as well as support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Dermatology Foundation Public Health Career Development Award, the National Institutes of Health, the American Cancer Society, and Meredith’s Mission for Melanoma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
This final recommendation applies to the general public and is not meant for those at higher risk, such as people with a family history of skin cancer or who have any signs or symptoms, such as irregular moles.
“The new recommendations are consistent with those from 2016, and we are unable to balance benefits and harms,” said Task Force member Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, professor and vice chair of research in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “Unfortunately, there is not enough evidence to recommend for or against screening, and health care professionals should use their judgment when deciding whether or not to screen.”
Dr. Donahue told this news organization that this is a call for more research: “Our recommendations are for patients who present to primary care without symptoms, and after a careful assessment of benefit and harms, we didn’t have evidence to push us towards screening as a benefit. We did look at data from two large screening programs, but they were from Europe and not representative of the U.S. population. They also did not show a benefit for reducing melanoma-related mortality.”
The USPSTF final recommendation statement and corresponding evidence summary have been published online in JAMA, as well as on the USPSTF website.
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, but there are different types that vary in their incidence and severity. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common types of skin cancer, but they infrequently lead to death or substantial morbidity, notes the USPTSF. Melanomas represent about 1% of skin cancer and cause the most skin cancer deaths. An estimated 8,000 individuals in the United States will die of melanoma in 2023.
There are racial differences in melanoma incidence; it is about 30 times more common in White versus Black persons, but disease in persons with darker skin color tends to be diagnosed at a later stage. These disparities may be due to differences in risk factors, access to care, and clinical presentation.
In an accompanying editorial, Maryam M. Asgari, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Lori A. Crane, PhD, MPH, of the Colorado School of Public Health, University of Colorado, Aurora, point out that people with darker skin phenotypes also tend to be affected by skin cancers that are not associated with UV radiation, such as acral melanoma, which arises on the palms and soles, and skin cancers that arise in areas of chronic inflammation, such as wounds.
Thus, differences in anatomical distribution of skin cancers in in the various subpopulations needs to be considered when performing skin screening, they write. “Furthermore, while skin cancer risk is lower among people with darker skin pigmentation, survival is often worse for cancers like melanoma, highlighting the potential need for screening.”
“More data are needed, particularly regarding genetic and environmental risk factors for skin cancer in people with darker pigmentation, to help inform guidelines that can be broadly applied to the U.S. population,” add Dr. Asgari and Dr. Crane. “The diversity of the U.S. population extends also to geography, culture, and socioeconomic status, all of which affect skin cancer risk.”
Review of evidence
The USPSTF commissioned a systematic review to evaluate the benefits and harms of screening for skin cancer in asymptomatic adolescents and adults, including evidence for both keratinocyte carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) and cutaneous melanoma.
Foundational evidence showed that the sensitivity of visual skin examination by a clinician to detect melanoma ranged from 40% to 70% and specificity ranged from 86% to 98%. Evidence that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of visual skin examination to detect keratinocyte carcinoma was limited and inconsistent. There were no new studies reporting on diagnostic accuracy for an asymptomatic screening population.
The USPSTF also reviewed 20 studies in 29 articles (n = 6,053,411). This included three nonrandomized studies evaluating two skin cancer screening programs in Germany, but results were inconsistent. In addition, the ecological and nonrandomized design of the studies limited the conclusions that could be drawn and the applicability to a U.S. population was difficult to assess because of differences in population diversity and health care delivery in the United States.
Other nonrandomized studies that looked at various outcomes, such as harms and stage at diagnosis and melanoma or all-cause mortality, also did not provide sufficient evidence to support screening.
Research is needed
In a second accompanying editorial published in JAMA Dermatology, Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP, of the division of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Texas, Austin, pointed out that unlike other cancer screening programs, such as those for breast, colon, and prostate cancer, skin cancer screening programs are somewhat less organized.
The other programs focus on defined groups of the population, generally with easily identifiable characteristics such as age, sex, and family history, and importantly, there are always defined ages for initiation and halting of screening and intervals for screening frequency. None of these basic screening parameters have been widely adopted among dermatologists in the United States, he wrote. “One important reason why skin cancer screening has remained inconsistent is that it is not covered by Medicare or by many commercial insurance companies,” Dr. Adamson told this news organization. “The test, in this case the skin exam, is often performed as part of a routine dermatology visit.”
Dermatologists should take the lead on this, he said. “Dermatologists should push for a high quality prospective clinical trial of skin cancer screening, preferably in a high-risk population.”
Dr. Donahue agrees that research is needed, as noted in the recommendation. For example, studies are needed demonstrating consistent data of the effects of screening on morbidity and mortality or early detection of skin cancer, and clearer descriptions of skin color and inclusion of a full spectrum of skin colors in study participants. Clinical research is also needed on outcomes in participants that reflect the diversity of the U.S. population.
“I hope funding agencies will be interested in this area of study,” she said. “We put out the whole systematic review and point out the gaps. We need consistent evidence in detecting cancer early and reducing complications from skin cancer.”
The U.S. Congress mandates that the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality support the operations of the USPSTF.
None of the USPSTF authors report any disclosures. Dr. Asgari reported receiving royalties from UpToDate. Dr. Crane did not make any disclosures. Dr. Adamson reported serving as an expert reviewer for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force skin cancer screening report, as well as support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Dermatology Foundation Public Health Career Development Award, the National Institutes of Health, the American Cancer Society, and Meredith’s Mission for Melanoma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
This final recommendation applies to the general public and is not meant for those at higher risk, such as people with a family history of skin cancer or who have any signs or symptoms, such as irregular moles.
“The new recommendations are consistent with those from 2016, and we are unable to balance benefits and harms,” said Task Force member Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, professor and vice chair of research in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “Unfortunately, there is not enough evidence to recommend for or against screening, and health care professionals should use their judgment when deciding whether or not to screen.”
Dr. Donahue told this news organization that this is a call for more research: “Our recommendations are for patients who present to primary care without symptoms, and after a careful assessment of benefit and harms, we didn’t have evidence to push us towards screening as a benefit. We did look at data from two large screening programs, but they were from Europe and not representative of the U.S. population. They also did not show a benefit for reducing melanoma-related mortality.”
The USPSTF final recommendation statement and corresponding evidence summary have been published online in JAMA, as well as on the USPSTF website.
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, but there are different types that vary in their incidence and severity. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common types of skin cancer, but they infrequently lead to death or substantial morbidity, notes the USPTSF. Melanomas represent about 1% of skin cancer and cause the most skin cancer deaths. An estimated 8,000 individuals in the United States will die of melanoma in 2023.
There are racial differences in melanoma incidence; it is about 30 times more common in White versus Black persons, but disease in persons with darker skin color tends to be diagnosed at a later stage. These disparities may be due to differences in risk factors, access to care, and clinical presentation.
In an accompanying editorial, Maryam M. Asgari, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Lori A. Crane, PhD, MPH, of the Colorado School of Public Health, University of Colorado, Aurora, point out that people with darker skin phenotypes also tend to be affected by skin cancers that are not associated with UV radiation, such as acral melanoma, which arises on the palms and soles, and skin cancers that arise in areas of chronic inflammation, such as wounds.
Thus, differences in anatomical distribution of skin cancers in in the various subpopulations needs to be considered when performing skin screening, they write. “Furthermore, while skin cancer risk is lower among people with darker skin pigmentation, survival is often worse for cancers like melanoma, highlighting the potential need for screening.”
“More data are needed, particularly regarding genetic and environmental risk factors for skin cancer in people with darker pigmentation, to help inform guidelines that can be broadly applied to the U.S. population,” add Dr. Asgari and Dr. Crane. “The diversity of the U.S. population extends also to geography, culture, and socioeconomic status, all of which affect skin cancer risk.”
Review of evidence
The USPSTF commissioned a systematic review to evaluate the benefits and harms of screening for skin cancer in asymptomatic adolescents and adults, including evidence for both keratinocyte carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) and cutaneous melanoma.
Foundational evidence showed that the sensitivity of visual skin examination by a clinician to detect melanoma ranged from 40% to 70% and specificity ranged from 86% to 98%. Evidence that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of visual skin examination to detect keratinocyte carcinoma was limited and inconsistent. There were no new studies reporting on diagnostic accuracy for an asymptomatic screening population.
The USPSTF also reviewed 20 studies in 29 articles (n = 6,053,411). This included three nonrandomized studies evaluating two skin cancer screening programs in Germany, but results were inconsistent. In addition, the ecological and nonrandomized design of the studies limited the conclusions that could be drawn and the applicability to a U.S. population was difficult to assess because of differences in population diversity and health care delivery in the United States.
Other nonrandomized studies that looked at various outcomes, such as harms and stage at diagnosis and melanoma or all-cause mortality, also did not provide sufficient evidence to support screening.
Research is needed
In a second accompanying editorial published in JAMA Dermatology, Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP, of the division of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Texas, Austin, pointed out that unlike other cancer screening programs, such as those for breast, colon, and prostate cancer, skin cancer screening programs are somewhat less organized.
The other programs focus on defined groups of the population, generally with easily identifiable characteristics such as age, sex, and family history, and importantly, there are always defined ages for initiation and halting of screening and intervals for screening frequency. None of these basic screening parameters have been widely adopted among dermatologists in the United States, he wrote. “One important reason why skin cancer screening has remained inconsistent is that it is not covered by Medicare or by many commercial insurance companies,” Dr. Adamson told this news organization. “The test, in this case the skin exam, is often performed as part of a routine dermatology visit.”
Dermatologists should take the lead on this, he said. “Dermatologists should push for a high quality prospective clinical trial of skin cancer screening, preferably in a high-risk population.”
Dr. Donahue agrees that research is needed, as noted in the recommendation. For example, studies are needed demonstrating consistent data of the effects of screening on morbidity and mortality or early detection of skin cancer, and clearer descriptions of skin color and inclusion of a full spectrum of skin colors in study participants. Clinical research is also needed on outcomes in participants that reflect the diversity of the U.S. population.
“I hope funding agencies will be interested in this area of study,” she said. “We put out the whole systematic review and point out the gaps. We need consistent evidence in detecting cancer early and reducing complications from skin cancer.”
The U.S. Congress mandates that the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality support the operations of the USPSTF.
None of the USPSTF authors report any disclosures. Dr. Asgari reported receiving royalties from UpToDate. Dr. Crane did not make any disclosures. Dr. Adamson reported serving as an expert reviewer for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force skin cancer screening report, as well as support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Dermatology Foundation Public Health Career Development Award, the National Institutes of Health, the American Cancer Society, and Meredith’s Mission for Melanoma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Atopic dermatitis positively linked with the risk for acne
Key clinical point: The overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne is significantly higher in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), highlighting the need to address comorbid skin diseases simultaneously along with the management of AD.
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a 3-fold higher overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne at ≤18 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.44; 95% CI 3.13-3.78) and ≤30 years (aOR 3.15; 95% CI 2.90-3.42) of age.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective registry study that included 70,584 patients with AD aged ≤18 years at the time of their first AD diagnosis and 270,783 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as investigators and receiving educational grants, consulting fees, or speaker honoraria from various organizations.
Source: Sinikumpu SP et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and acne: A retrospective Finnish nationwide registry study. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad086
Key clinical point: The overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne is significantly higher in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), highlighting the need to address comorbid skin diseases simultaneously along with the management of AD.
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a 3-fold higher overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne at ≤18 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.44; 95% CI 3.13-3.78) and ≤30 years (aOR 3.15; 95% CI 2.90-3.42) of age.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective registry study that included 70,584 patients with AD aged ≤18 years at the time of their first AD diagnosis and 270,783 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as investigators and receiving educational grants, consulting fees, or speaker honoraria from various organizations.
Source: Sinikumpu SP et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and acne: A retrospective Finnish nationwide registry study. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad086
Key clinical point: The overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne is significantly higher in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), highlighting the need to address comorbid skin diseases simultaneously along with the management of AD.
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a 3-fold higher overall risk for hospital-diagnosed acne at ≤18 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.44; 95% CI 3.13-3.78) and ≤30 years (aOR 3.15; 95% CI 2.90-3.42) of age.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective registry study that included 70,584 patients with AD aged ≤18 years at the time of their first AD diagnosis and 270,783 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as investigators and receiving educational grants, consulting fees, or speaker honoraria from various organizations.
Source: Sinikumpu SP et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and acne: A retrospective Finnish nationwide registry study. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad086
Moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis patients most likely to develop NMSC vs other malignancies
Key clinical point: Among malignancies, including breast cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, and non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) had the highest incidence rate (IR) for NMSC followed by breast cancer and melanoma; NMSC incidence increased with age among patients with moderate but not severe AD.
Major finding: In patients with moderate and severe AD, the IR per 1000 person-years were 4.6 (95% CI 3.9-5.5) and 5.9 (95% CI 3.8-9.2) for NMSC, 2.2 (95% CI 1.6-3.0) and 0.5 (95% CI 0.1-3.9) for breast cancer, and 0.4 (95% CI 0.2-0.7) and 0.6 (95% CI 0.1-2.3) for melanoma, respectively. The NMSC IR increased with increasing age in patients with moderate AD (18-39 vs ≥65 years: 0.1 [95% CI 0.0-0.7] vs 18.0 [95% CI 13.9-23.2]).
Study details: This retrospective study analyzed the data of 7050 adults with moderate-to-severe AD from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California database.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pfizer.
Source: Hedderson MM et al. Rates of malignancies among patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(3):e071172 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-071172
Key clinical point: Among malignancies, including breast cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, and non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) had the highest incidence rate (IR) for NMSC followed by breast cancer and melanoma; NMSC incidence increased with age among patients with moderate but not severe AD.
Major finding: In patients with moderate and severe AD, the IR per 1000 person-years were 4.6 (95% CI 3.9-5.5) and 5.9 (95% CI 3.8-9.2) for NMSC, 2.2 (95% CI 1.6-3.0) and 0.5 (95% CI 0.1-3.9) for breast cancer, and 0.4 (95% CI 0.2-0.7) and 0.6 (95% CI 0.1-2.3) for melanoma, respectively. The NMSC IR increased with increasing age in patients with moderate AD (18-39 vs ≥65 years: 0.1 [95% CI 0.0-0.7] vs 18.0 [95% CI 13.9-23.2]).
Study details: This retrospective study analyzed the data of 7050 adults with moderate-to-severe AD from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California database.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pfizer.
Source: Hedderson MM et al. Rates of malignancies among patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(3):e071172 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-071172
Key clinical point: Among malignancies, including breast cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, and non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) had the highest incidence rate (IR) for NMSC followed by breast cancer and melanoma; NMSC incidence increased with age among patients with moderate but not severe AD.
Major finding: In patients with moderate and severe AD, the IR per 1000 person-years were 4.6 (95% CI 3.9-5.5) and 5.9 (95% CI 3.8-9.2) for NMSC, 2.2 (95% CI 1.6-3.0) and 0.5 (95% CI 0.1-3.9) for breast cancer, and 0.4 (95% CI 0.2-0.7) and 0.6 (95% CI 0.1-2.3) for melanoma, respectively. The NMSC IR increased with increasing age in patients with moderate AD (18-39 vs ≥65 years: 0.1 [95% CI 0.0-0.7] vs 18.0 [95% CI 13.9-23.2]).
Study details: This retrospective study analyzed the data of 7050 adults with moderate-to-severe AD from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California database.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pfizer.
Source: Hedderson MM et al. Rates of malignancies among patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(3):e071172 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-071172
Enhanced topical treatment of infant atopic dermatitis prevents food allergy
Key clinical point: Compared with conventional treatment, enhanced treatment with topical corticosteroids (TCS) significantly reduced the incidence of hen’s egg allergy among infants with atopic dermatitis (AD) but retarded their growth.
Major finding: Infants receiving enhanced vs conventional treatment had a significantly lower incidence of hen’s egg allergy (31.4% vs 41.9%; P = .0028), but demonstrated lower body weight (mean difference −422 g; 95% CI −553 to −292 g) and height (mean difference −0.8 cm; 95% CI −1.22 to −0.33 cm) at 28 weeks of age.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial included 640 infants aged 7-13 weeks with AD who were randomly assigned to receive enhanced therapy (alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for whole body except face and scalp) followed by maintenance therapy (n = 318) or conventional therapy (alclometasone dipropionate and betamethasone valerate for the affected skin; n = 322).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED). Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including AMED.
Source: Yamamoto-Hanada K et al on behalf of PACI Study Collaborators. Enhanced early skin treatment for atopic dermatitis in infants reduces food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.03.008
Key clinical point: Compared with conventional treatment, enhanced treatment with topical corticosteroids (TCS) significantly reduced the incidence of hen’s egg allergy among infants with atopic dermatitis (AD) but retarded their growth.
Major finding: Infants receiving enhanced vs conventional treatment had a significantly lower incidence of hen’s egg allergy (31.4% vs 41.9%; P = .0028), but demonstrated lower body weight (mean difference −422 g; 95% CI −553 to −292 g) and height (mean difference −0.8 cm; 95% CI −1.22 to −0.33 cm) at 28 weeks of age.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial included 640 infants aged 7-13 weeks with AD who were randomly assigned to receive enhanced therapy (alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for whole body except face and scalp) followed by maintenance therapy (n = 318) or conventional therapy (alclometasone dipropionate and betamethasone valerate for the affected skin; n = 322).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED). Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including AMED.
Source: Yamamoto-Hanada K et al on behalf of PACI Study Collaborators. Enhanced early skin treatment for atopic dermatitis in infants reduces food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.03.008
Key clinical point: Compared with conventional treatment, enhanced treatment with topical corticosteroids (TCS) significantly reduced the incidence of hen’s egg allergy among infants with atopic dermatitis (AD) but retarded their growth.
Major finding: Infants receiving enhanced vs conventional treatment had a significantly lower incidence of hen’s egg allergy (31.4% vs 41.9%; P = .0028), but demonstrated lower body weight (mean difference −422 g; 95% CI −553 to −292 g) and height (mean difference −0.8 cm; 95% CI −1.22 to −0.33 cm) at 28 weeks of age.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial included 640 infants aged 7-13 weeks with AD who were randomly assigned to receive enhanced therapy (alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for whole body except face and scalp) followed by maintenance therapy (n = 318) or conventional therapy (alclometasone dipropionate and betamethasone valerate for the affected skin; n = 322).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED). Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including AMED.
Source: Yamamoto-Hanada K et al on behalf of PACI Study Collaborators. Enhanced early skin treatment for atopic dermatitis in infants reduces food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 (Mar 22). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.03.008
Atopic dermatitis risk in children associated with residential distance from highly trafficked segments
Key clinical point: Children living closer to highly trafficked segments (HTS) are at a greater risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Children living at ≥1,000 vs <500 m from an HTS had 27% lower odds of developing AD (P = .0009). The odds of AD decreased by 21% (P = .0002) with each factor of 10 increase in the distance from an HTS.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 7247 children aged 0-18 years with AD and 7247 age- and sex-matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, National Jewish Health, Denver, Colorado, and Eugene F and Easton M Crawford Charitable Lead Unitrust, Chicago, Illinois. D Leung reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Nevid MZ et al. The association of residential distance from highly trafficked roads with atopic dermatitis risk. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023 (Mar 20). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.03.021
Key clinical point: Children living closer to highly trafficked segments (HTS) are at a greater risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Children living at ≥1,000 vs <500 m from an HTS had 27% lower odds of developing AD (P = .0009). The odds of AD decreased by 21% (P = .0002) with each factor of 10 increase in the distance from an HTS.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 7247 children aged 0-18 years with AD and 7247 age- and sex-matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, National Jewish Health, Denver, Colorado, and Eugene F and Easton M Crawford Charitable Lead Unitrust, Chicago, Illinois. D Leung reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Nevid MZ et al. The association of residential distance from highly trafficked roads with atopic dermatitis risk. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023 (Mar 20). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.03.021
Key clinical point: Children living closer to highly trafficked segments (HTS) are at a greater risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Children living at ≥1,000 vs <500 m from an HTS had 27% lower odds of developing AD (P = .0009). The odds of AD decreased by 21% (P = .0002) with each factor of 10 increase in the distance from an HTS.
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 7247 children aged 0-18 years with AD and 7247 age- and sex-matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, National Jewish Health, Denver, Colorado, and Eugene F and Easton M Crawford Charitable Lead Unitrust, Chicago, Illinois. D Leung reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Nevid MZ et al. The association of residential distance from highly trafficked roads with atopic dermatitis risk. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023 (Mar 20). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.03.021