User login
Can Cannabis Help to Reduce Diabetes Risk?
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Cold or Flu Virus May Trigger Relapse of Long COVID
researchers have found.
In some cases, they may be experiencing what researchers call viral interference, something also experienced by people with HIV and other infections associated with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Clinical studies on the issue are limited, but patients, doctors, and researchers report many people who previously had long COVID have developed recurring symptoms after consequent viral infections.
Viral persistence — where bits of virus linger in the body — and viral reactivation remain two of the leading suspects for Yale researchers. Viral activation occurs when the immune system responds to an infection by triggering a dormant virus.
Anecdotally, these flare-ups occur more commonly in patients with long COVID with autonomic dysfunction — severe dizziness when standing up — and other symptoms of ME/CFS, said Alba Azola, MD, a Johns Hopkins Medicine rehabilitation specialist in Baltimore, Maryland, who works with patients with long COVID and other “fatiguing illnesses.”
At last count, about 18% of those surveyed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said they had experienced long COVID. Nearly 60% of those surveyed said they had contracted COVID-19 at least once.
Dr. Azola said that very afternoon she had seen a patient with the flu and a recurrence of previous long COVID symptoms. Not much data exist about cases like this.
“I can’t say there is a specific study looking at this, but anecdotally, we see it all the time,” Dr. Azola said.
She has not seen completely different symptoms; more commonly, she sees a flare-up of previously existing symptoms.
David Putrino, PhD, is director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City. He treats and studies patients with long COVID and echoes what others have seen.
Patients can “recover (or feel recovered) from long COVID until the next immune challenge — another COVID infection, flu infection, pregnancy, food poisoning (all examples we have seen in the clinic) — and experience a significant flare-up of your initial COVID infection,” he said.
“Relapse” is a better term than reinfection, said Jeffrey Parsonnet, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and director of the Dartmouth Hitchcock Post-Acute COVID Syndrome Clinic, Lebanon, New Hampshire.
“We see patients who had COVID-19 followed by long COVID who then get better — either completely or mostly better. Then they’ve gotten COVID again, and this is followed by recurrence of long COVID symptoms,” he said.
“Every patient looks different in terms of what gets better and how quickly. And again, some patients are not better (or even minimally so) after a couple of years,” he said.
Patients Tell Their Stories
On the COVID-19 Long Haulers Support Facebook group, many of the 100,000 followers ask about viral reactivation. Delainne “Laney” Bond, RN, who has battled postinfection chronic illness herself, runs the Facebook group. From what she sees, “each time a person is infected or reinfected with SARS-CoV-2, they have a risk of developing long COVID or experiencing worse long COVID. Multiple infections can lead to progressive health complications.”
The posts on her site include many queries about reinfections. A post from December included nearly 80 comments with people describing the full range of symptoms. Some stories relayed how the reinfection symptoms were short lived. Some report returning to their baseline — not completely symptom free but improved.
Doctors and patients say long COVID comes and goes — relapsing-remitting — and shares many features with other complex multisystem chronic conditions, according to a new National Academy of Sciences report. Those include ME/CFS and the Epstein-Barr virus.
As far as how to treat, Dr. Putrino is one of the clinical researchers testing antivirals. One is Paxlovid; the others are drugs developed for the AIDS virus.
“A plausible mechanism for long COVID is persistence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in tissue and/or the reactivation of latent pathogens,” according to an explanation of the research on the PolyBio Institute website, which is involved with the research.
In the meantime, “long COVID appears to be a chronic condition with few patients achieving full remission,” according to a new Academy of Sciences report. The report concludes that long COVID recovery can plateau at 6-12 months. They also note that 18%-22% of people who have long COVID symptoms at 5 months are still ill at 1 year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
In some cases, they may be experiencing what researchers call viral interference, something also experienced by people with HIV and other infections associated with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Clinical studies on the issue are limited, but patients, doctors, and researchers report many people who previously had long COVID have developed recurring symptoms after consequent viral infections.
Viral persistence — where bits of virus linger in the body — and viral reactivation remain two of the leading suspects for Yale researchers. Viral activation occurs when the immune system responds to an infection by triggering a dormant virus.
Anecdotally, these flare-ups occur more commonly in patients with long COVID with autonomic dysfunction — severe dizziness when standing up — and other symptoms of ME/CFS, said Alba Azola, MD, a Johns Hopkins Medicine rehabilitation specialist in Baltimore, Maryland, who works with patients with long COVID and other “fatiguing illnesses.”
At last count, about 18% of those surveyed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said they had experienced long COVID. Nearly 60% of those surveyed said they had contracted COVID-19 at least once.
Dr. Azola said that very afternoon she had seen a patient with the flu and a recurrence of previous long COVID symptoms. Not much data exist about cases like this.
“I can’t say there is a specific study looking at this, but anecdotally, we see it all the time,” Dr. Azola said.
She has not seen completely different symptoms; more commonly, she sees a flare-up of previously existing symptoms.
David Putrino, PhD, is director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City. He treats and studies patients with long COVID and echoes what others have seen.
Patients can “recover (or feel recovered) from long COVID until the next immune challenge — another COVID infection, flu infection, pregnancy, food poisoning (all examples we have seen in the clinic) — and experience a significant flare-up of your initial COVID infection,” he said.
“Relapse” is a better term than reinfection, said Jeffrey Parsonnet, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and director of the Dartmouth Hitchcock Post-Acute COVID Syndrome Clinic, Lebanon, New Hampshire.
“We see patients who had COVID-19 followed by long COVID who then get better — either completely or mostly better. Then they’ve gotten COVID again, and this is followed by recurrence of long COVID symptoms,” he said.
“Every patient looks different in terms of what gets better and how quickly. And again, some patients are not better (or even minimally so) after a couple of years,” he said.
Patients Tell Their Stories
On the COVID-19 Long Haulers Support Facebook group, many of the 100,000 followers ask about viral reactivation. Delainne “Laney” Bond, RN, who has battled postinfection chronic illness herself, runs the Facebook group. From what she sees, “each time a person is infected or reinfected with SARS-CoV-2, they have a risk of developing long COVID or experiencing worse long COVID. Multiple infections can lead to progressive health complications.”
The posts on her site include many queries about reinfections. A post from December included nearly 80 comments with people describing the full range of symptoms. Some stories relayed how the reinfection symptoms were short lived. Some report returning to their baseline — not completely symptom free but improved.
Doctors and patients say long COVID comes and goes — relapsing-remitting — and shares many features with other complex multisystem chronic conditions, according to a new National Academy of Sciences report. Those include ME/CFS and the Epstein-Barr virus.
As far as how to treat, Dr. Putrino is one of the clinical researchers testing antivirals. One is Paxlovid; the others are drugs developed for the AIDS virus.
“A plausible mechanism for long COVID is persistence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in tissue and/or the reactivation of latent pathogens,” according to an explanation of the research on the PolyBio Institute website, which is involved with the research.
In the meantime, “long COVID appears to be a chronic condition with few patients achieving full remission,” according to a new Academy of Sciences report. The report concludes that long COVID recovery can plateau at 6-12 months. They also note that 18%-22% of people who have long COVID symptoms at 5 months are still ill at 1 year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
In some cases, they may be experiencing what researchers call viral interference, something also experienced by people with HIV and other infections associated with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Clinical studies on the issue are limited, but patients, doctors, and researchers report many people who previously had long COVID have developed recurring symptoms after consequent viral infections.
Viral persistence — where bits of virus linger in the body — and viral reactivation remain two of the leading suspects for Yale researchers. Viral activation occurs when the immune system responds to an infection by triggering a dormant virus.
Anecdotally, these flare-ups occur more commonly in patients with long COVID with autonomic dysfunction — severe dizziness when standing up — and other symptoms of ME/CFS, said Alba Azola, MD, a Johns Hopkins Medicine rehabilitation specialist in Baltimore, Maryland, who works with patients with long COVID and other “fatiguing illnesses.”
At last count, about 18% of those surveyed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said they had experienced long COVID. Nearly 60% of those surveyed said they had contracted COVID-19 at least once.
Dr. Azola said that very afternoon she had seen a patient with the flu and a recurrence of previous long COVID symptoms. Not much data exist about cases like this.
“I can’t say there is a specific study looking at this, but anecdotally, we see it all the time,” Dr. Azola said.
She has not seen completely different symptoms; more commonly, she sees a flare-up of previously existing symptoms.
David Putrino, PhD, is director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City. He treats and studies patients with long COVID and echoes what others have seen.
Patients can “recover (or feel recovered) from long COVID until the next immune challenge — another COVID infection, flu infection, pregnancy, food poisoning (all examples we have seen in the clinic) — and experience a significant flare-up of your initial COVID infection,” he said.
“Relapse” is a better term than reinfection, said Jeffrey Parsonnet, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and director of the Dartmouth Hitchcock Post-Acute COVID Syndrome Clinic, Lebanon, New Hampshire.
“We see patients who had COVID-19 followed by long COVID who then get better — either completely or mostly better. Then they’ve gotten COVID again, and this is followed by recurrence of long COVID symptoms,” he said.
“Every patient looks different in terms of what gets better and how quickly. And again, some patients are not better (or even minimally so) after a couple of years,” he said.
Patients Tell Their Stories
On the COVID-19 Long Haulers Support Facebook group, many of the 100,000 followers ask about viral reactivation. Delainne “Laney” Bond, RN, who has battled postinfection chronic illness herself, runs the Facebook group. From what she sees, “each time a person is infected or reinfected with SARS-CoV-2, they have a risk of developing long COVID or experiencing worse long COVID. Multiple infections can lead to progressive health complications.”
The posts on her site include many queries about reinfections. A post from December included nearly 80 comments with people describing the full range of symptoms. Some stories relayed how the reinfection symptoms were short lived. Some report returning to their baseline — not completely symptom free but improved.
Doctors and patients say long COVID comes and goes — relapsing-remitting — and shares many features with other complex multisystem chronic conditions, according to a new National Academy of Sciences report. Those include ME/CFS and the Epstein-Barr virus.
As far as how to treat, Dr. Putrino is one of the clinical researchers testing antivirals. One is Paxlovid; the others are drugs developed for the AIDS virus.
“A plausible mechanism for long COVID is persistence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in tissue and/or the reactivation of latent pathogens,” according to an explanation of the research on the PolyBio Institute website, which is involved with the research.
In the meantime, “long COVID appears to be a chronic condition with few patients achieving full remission,” according to a new Academy of Sciences report. The report concludes that long COVID recovery can plateau at 6-12 months. They also note that 18%-22% of people who have long COVID symptoms at 5 months are still ill at 1 year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Response to Semaglutide Be Predicted With a Genetic Test?
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Adjuvant Avelumab Benefits Seen in High Risk, Triple Negative BC
“The 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, and 34% reduction in the risk of death suggests that avelumab may have a role in early triple negative breast cancer patients at high risk of relapse after primary surgery or with invasive residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy,” Pierfranco Conte, MD, from the department of surgery, oncology, and gastroenterology at the University of Padua, Italy, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
A-BRAVE is the first randomized phase 3 trial patients with TNBC, treated with adjuvant avelumab, explained Dr. Conte. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for stage cT1c or larger, or cN+ disease. However, in case of invasive residual disease at surgery, prognosis is still very poor.”
TNBC is more immunogenic compared with other breast cancer subtypes, suggesting a role for immune checkpoint inhibitors such as avelumab in this setting, he said.
A-BRAVE Methods and Results
The trial enrolled 477 patients, median age 51 years, between June 2016 and October 2020, after their disease had progressed following initial treatment. There were two strata of patients: those who had received upfront surgery and then adjuvant chemotherapy before disease progression (stratum A, 18%); and those who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and then adjuvant chemo, but still had residual disease (stratum B, 82%).
Patients were randomized to either observation (n = 239) or treatment with avelumab (n = 238), at a dose of 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks for one year.
At a median follow-up of 52.1 months, avelumab did not show an advantage for the primary endpoint of 3-year disease-free survival (DFS), with 68.3% of treated patients meeting this endpoint, compared to 63.2% of observed patients (hazard ratio [HR 0.81, P = .172].
However, the treatment did show statistically significant benefits for the secondary 3-year OS endpoint (84.8% vs 76.3%, HR 0.66, P = .035).
“Trying to understand why we did observe a greater benefit with avelumab in overall survival compared to disease-free survival, we also made a post-hoc exploratory analysis on distant disease-free survival,” explained Dr. Conte.
There was a statistically significant 3-year distant disease-free survival (DDFS) benefit for treated patients compared with controls (75.4% vs 67.9%, HR 0.7, P = .0277), translating to a 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, he noted.
Findings Are ‘Hypothesis-Generating’
The results are “hypothesis-generating at this point,” Alexandra Thomas, MD, a breast medical oncologist who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “These results suggest that the story on how to best utilize checkpoint blockade as adjuvant therapy in triple negative breast cancer may not yet be fully written.”
She emphasized the study did not meet its primary endpoint, “though the results for secondary endpoints OS and the exploratory endpoint DDFS are intriguing.
“A-BRAVE is a smaller study, especially relative to Impassion030 (ALEXANDRA), which enrolled over 2,000 patients,” she explained. “It is notable that avelumab has slightly different properties than atezolizumab, which was used in Impassion030.”
“Avelumab is also a weak PD-L2 inhibitor. Could this be important? Notably, today most patients with clinical stage II-III triple negative breast cancer will receive pembrolizumab as per KEYNOTE-522, so the potential for clinical impact is greatly reduced,” added Dr. Thomas, professor and assistant director in the department of internal medicine at Duke Cancer Institute, in Durham, North Carolina.
SWOG1814, which has not been reported yet, “also looks at pembrolizumab in patients with residual disease post neoadjuvant chemotherapy and will provide further important information on in this space,” she said.
Merck KGaA funded the study.
Dr. Conte disclosed consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Reveal Genomics; a HER2Dx patient; and providing expert testimony for AstraZeneca.
Dr. Thomas disclosed research grants from Sanofi and Merck.
“The 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, and 34% reduction in the risk of death suggests that avelumab may have a role in early triple negative breast cancer patients at high risk of relapse after primary surgery or with invasive residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy,” Pierfranco Conte, MD, from the department of surgery, oncology, and gastroenterology at the University of Padua, Italy, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
A-BRAVE is the first randomized phase 3 trial patients with TNBC, treated with adjuvant avelumab, explained Dr. Conte. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for stage cT1c or larger, or cN+ disease. However, in case of invasive residual disease at surgery, prognosis is still very poor.”
TNBC is more immunogenic compared with other breast cancer subtypes, suggesting a role for immune checkpoint inhibitors such as avelumab in this setting, he said.
A-BRAVE Methods and Results
The trial enrolled 477 patients, median age 51 years, between June 2016 and October 2020, after their disease had progressed following initial treatment. There were two strata of patients: those who had received upfront surgery and then adjuvant chemotherapy before disease progression (stratum A, 18%); and those who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and then adjuvant chemo, but still had residual disease (stratum B, 82%).
Patients were randomized to either observation (n = 239) or treatment with avelumab (n = 238), at a dose of 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks for one year.
At a median follow-up of 52.1 months, avelumab did not show an advantage for the primary endpoint of 3-year disease-free survival (DFS), with 68.3% of treated patients meeting this endpoint, compared to 63.2% of observed patients (hazard ratio [HR 0.81, P = .172].
However, the treatment did show statistically significant benefits for the secondary 3-year OS endpoint (84.8% vs 76.3%, HR 0.66, P = .035).
“Trying to understand why we did observe a greater benefit with avelumab in overall survival compared to disease-free survival, we also made a post-hoc exploratory analysis on distant disease-free survival,” explained Dr. Conte.
There was a statistically significant 3-year distant disease-free survival (DDFS) benefit for treated patients compared with controls (75.4% vs 67.9%, HR 0.7, P = .0277), translating to a 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, he noted.
Findings Are ‘Hypothesis-Generating’
The results are “hypothesis-generating at this point,” Alexandra Thomas, MD, a breast medical oncologist who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “These results suggest that the story on how to best utilize checkpoint blockade as adjuvant therapy in triple negative breast cancer may not yet be fully written.”
She emphasized the study did not meet its primary endpoint, “though the results for secondary endpoints OS and the exploratory endpoint DDFS are intriguing.
“A-BRAVE is a smaller study, especially relative to Impassion030 (ALEXANDRA), which enrolled over 2,000 patients,” she explained. “It is notable that avelumab has slightly different properties than atezolizumab, which was used in Impassion030.”
“Avelumab is also a weak PD-L2 inhibitor. Could this be important? Notably, today most patients with clinical stage II-III triple negative breast cancer will receive pembrolizumab as per KEYNOTE-522, so the potential for clinical impact is greatly reduced,” added Dr. Thomas, professor and assistant director in the department of internal medicine at Duke Cancer Institute, in Durham, North Carolina.
SWOG1814, which has not been reported yet, “also looks at pembrolizumab in patients with residual disease post neoadjuvant chemotherapy and will provide further important information on in this space,” she said.
Merck KGaA funded the study.
Dr. Conte disclosed consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Reveal Genomics; a HER2Dx patient; and providing expert testimony for AstraZeneca.
Dr. Thomas disclosed research grants from Sanofi and Merck.
“The 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, and 34% reduction in the risk of death suggests that avelumab may have a role in early triple negative breast cancer patients at high risk of relapse after primary surgery or with invasive residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy,” Pierfranco Conte, MD, from the department of surgery, oncology, and gastroenterology at the University of Padua, Italy, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
A-BRAVE is the first randomized phase 3 trial patients with TNBC, treated with adjuvant avelumab, explained Dr. Conte. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for stage cT1c or larger, or cN+ disease. However, in case of invasive residual disease at surgery, prognosis is still very poor.”
TNBC is more immunogenic compared with other breast cancer subtypes, suggesting a role for immune checkpoint inhibitors such as avelumab in this setting, he said.
A-BRAVE Methods and Results
The trial enrolled 477 patients, median age 51 years, between June 2016 and October 2020, after their disease had progressed following initial treatment. There were two strata of patients: those who had received upfront surgery and then adjuvant chemotherapy before disease progression (stratum A, 18%); and those who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and then adjuvant chemo, but still had residual disease (stratum B, 82%).
Patients were randomized to either observation (n = 239) or treatment with avelumab (n = 238), at a dose of 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks for one year.
At a median follow-up of 52.1 months, avelumab did not show an advantage for the primary endpoint of 3-year disease-free survival (DFS), with 68.3% of treated patients meeting this endpoint, compared to 63.2% of observed patients (hazard ratio [HR 0.81, P = .172].
However, the treatment did show statistically significant benefits for the secondary 3-year OS endpoint (84.8% vs 76.3%, HR 0.66, P = .035).
“Trying to understand why we did observe a greater benefit with avelumab in overall survival compared to disease-free survival, we also made a post-hoc exploratory analysis on distant disease-free survival,” explained Dr. Conte.
There was a statistically significant 3-year distant disease-free survival (DDFS) benefit for treated patients compared with controls (75.4% vs 67.9%, HR 0.7, P = .0277), translating to a 30% reduction in the risk of distant metastasis, he noted.
Findings Are ‘Hypothesis-Generating’
The results are “hypothesis-generating at this point,” Alexandra Thomas, MD, a breast medical oncologist who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “These results suggest that the story on how to best utilize checkpoint blockade as adjuvant therapy in triple negative breast cancer may not yet be fully written.”
She emphasized the study did not meet its primary endpoint, “though the results for secondary endpoints OS and the exploratory endpoint DDFS are intriguing.
“A-BRAVE is a smaller study, especially relative to Impassion030 (ALEXANDRA), which enrolled over 2,000 patients,” she explained. “It is notable that avelumab has slightly different properties than atezolizumab, which was used in Impassion030.”
“Avelumab is also a weak PD-L2 inhibitor. Could this be important? Notably, today most patients with clinical stage II-III triple negative breast cancer will receive pembrolizumab as per KEYNOTE-522, so the potential for clinical impact is greatly reduced,” added Dr. Thomas, professor and assistant director in the department of internal medicine at Duke Cancer Institute, in Durham, North Carolina.
SWOG1814, which has not been reported yet, “also looks at pembrolizumab in patients with residual disease post neoadjuvant chemotherapy and will provide further important information on in this space,” she said.
Merck KGaA funded the study.
Dr. Conte disclosed consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Reveal Genomics; a HER2Dx patient; and providing expert testimony for AstraZeneca.
Dr. Thomas disclosed research grants from Sanofi and Merck.
FROM ASCO 2024
Clinical Controversy: Standard Dose or Baby TAM for Breast Cancer Prevention?
Should 5 mg of tamoxifen — known as “baby TAM” — or the usual 20 mg dose be standard of care for breast cancer prevention in high-risk women?
Research to date clearly shows that tamoxifen can reduce the risk for breast cancer in high-risk individuals by 30%-50%. Recent evidence also indicates that this chemoprevention approach can reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer by as much as 57%.
In 2019, the US Preventive Services Task Force issued updated recommendations that clinicians offer risk-reducing medications, such as tamoxifen, raloxifene, or aromatase inhibitors, to women at an increased risk for breast cancer and a low risk for adverse medication effects.
However, this prophylactic strategy remains underused.
A major roadblock: The drugs’ side effects, which include venous thromboembolic events and endometrial cancer as well as symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and sexual issues, have made uptake and adherence a challenge.
Offering women a lower dose of tamoxifen could allay fears about toxicities and improve uptake as well as reduce side effects and boost long-term adherence among those receiving baby TAM.
However,
The Debate
Years ago, Andrea De Censi, MD, a breast cancer researcher at the Galliera Hospital in Genova, Italy, and his colleagues reasoned that, because tamoxifen is a competitive estrogen receptor inhibitor, it may indeed have a minimal effective dose below 20 mg/d.
The fruits of that line of thought were presented to the world in the TAM-01 trial, first published in 2019, which pitted tamoxifen 5 mg/d for 3 years against placebo in 500 women with high-risk lesions, including lobular and ductal carcinoma in situ.
Dr. De Censi and colleagues found that baby TAM reduced the risk for invasive breast cancer by 52% and the risk for contralateral breast cancer by 75%.
Treatment adherence was slightly higher in the baby TAM group at 65% vs 61% in the placebo group.
A recent 10-year follow-up showed ongoing benefits associated with baby TAM vs placebo — a 42% reduction in breast cancer and a 64% drop in contralateral lesions.
The baby TAM group vs placebo experienced a slight increase in hot flashes but no significant increase in other common side effects.
Regarding serious adverse events, the baby TAM arm had one case of stage 1 endometrial cancer (0.4% of patients) and 20 cases of endometrial polyps (5%) vs 13 cases of endometrial polyps in the placebo arm. But there were no significant differences in thrombosis, cataracts, bone fractures, and other serious events.
Dr. De Censi said he’s surprised the baby TAM vs tamoxifen topic is still being debated. “Baby TAM, in my opinion, is a new standard of care for endocrine prevention of breast cancer in high-risk [women],” and baby TAM over 3 years is enough, said Dr. De Censi during a debate on the topic at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Congress in Berlin.
Gareth Evans, MD, a cancer genetics and prevention specialist at the University of Manchester, Manchester, England, however, isn’t convinced.
During the debate, Dr. Evans explained that his main concern was that the baby TAM trial was limited to women with high-risk lesions, not other common reasons for tamoxifen prophylaxis, such as a positive family history or BRCA mutations.
“In Manchester, we have put over a thousand women on tamoxifen who have a family history or other risk factors, not high-risk lesions,” and there simply isn’t definitive evidence for baby TAM in these women, Dr. Evans said.
The vast weight of evidence for tamoxifen prophylaxis, he added, is in trials involving tens of thousands of women, followed in some cases for 20 years, who received the 20 mg dose for 5 years.
As a result, women in Manchester are started on 20 mg and dropped down to 5 mg only for side effects. That way, Evans explained, we are not taking away the benefit among women who can tolerate 20 mg.
Meanwhile, there’s no evidence that baby TAM improves medication adherence, he noted. Trials have reported similar adherence rates to baby TAM and standard dose tamoxifen as well as no definitive evidence that the risk for cancer and thrombosis is less with baby TAM, he said.
In fact, Dr. Evans noted, “many women take tamoxifen 20 mg for 5 years with no side effects.”
Overall, “I don’t think we’ve got the evidence yet to drop” dosages, particularly in women without high-risk lesions, Dr. Evans said. A real concern, he added, is poor metabolizers for whom 5 mg won’t be enough to have a preventive effect.
Dr. De Censi noted, however, that there will likely never be a definitive answer to the question of baby TAM vs standard dosing because industry has no financial incentive to do a head-to-head trial; tamoxifen went off patent over 30 years ago.
Still, a poll of the audience favored Evans’ approach — 80% said they would start high-risk women on 20 mg for breast cancer prophylaxis and reduce for side effects as needed.
Dr. De Censi didn’t have any disclosures. Dr. Evans is a consultant/advisor for AstraZeneca, SpringWorks, Recursion, Everything Genetic, and Syantra.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should 5 mg of tamoxifen — known as “baby TAM” — or the usual 20 mg dose be standard of care for breast cancer prevention in high-risk women?
Research to date clearly shows that tamoxifen can reduce the risk for breast cancer in high-risk individuals by 30%-50%. Recent evidence also indicates that this chemoprevention approach can reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer by as much as 57%.
In 2019, the US Preventive Services Task Force issued updated recommendations that clinicians offer risk-reducing medications, such as tamoxifen, raloxifene, or aromatase inhibitors, to women at an increased risk for breast cancer and a low risk for adverse medication effects.
However, this prophylactic strategy remains underused.
A major roadblock: The drugs’ side effects, which include venous thromboembolic events and endometrial cancer as well as symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and sexual issues, have made uptake and adherence a challenge.
Offering women a lower dose of tamoxifen could allay fears about toxicities and improve uptake as well as reduce side effects and boost long-term adherence among those receiving baby TAM.
However,
The Debate
Years ago, Andrea De Censi, MD, a breast cancer researcher at the Galliera Hospital in Genova, Italy, and his colleagues reasoned that, because tamoxifen is a competitive estrogen receptor inhibitor, it may indeed have a minimal effective dose below 20 mg/d.
The fruits of that line of thought were presented to the world in the TAM-01 trial, first published in 2019, which pitted tamoxifen 5 mg/d for 3 years against placebo in 500 women with high-risk lesions, including lobular and ductal carcinoma in situ.
Dr. De Censi and colleagues found that baby TAM reduced the risk for invasive breast cancer by 52% and the risk for contralateral breast cancer by 75%.
Treatment adherence was slightly higher in the baby TAM group at 65% vs 61% in the placebo group.
A recent 10-year follow-up showed ongoing benefits associated with baby TAM vs placebo — a 42% reduction in breast cancer and a 64% drop in contralateral lesions.
The baby TAM group vs placebo experienced a slight increase in hot flashes but no significant increase in other common side effects.
Regarding serious adverse events, the baby TAM arm had one case of stage 1 endometrial cancer (0.4% of patients) and 20 cases of endometrial polyps (5%) vs 13 cases of endometrial polyps in the placebo arm. But there were no significant differences in thrombosis, cataracts, bone fractures, and other serious events.
Dr. De Censi said he’s surprised the baby TAM vs tamoxifen topic is still being debated. “Baby TAM, in my opinion, is a new standard of care for endocrine prevention of breast cancer in high-risk [women],” and baby TAM over 3 years is enough, said Dr. De Censi during a debate on the topic at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Congress in Berlin.
Gareth Evans, MD, a cancer genetics and prevention specialist at the University of Manchester, Manchester, England, however, isn’t convinced.
During the debate, Dr. Evans explained that his main concern was that the baby TAM trial was limited to women with high-risk lesions, not other common reasons for tamoxifen prophylaxis, such as a positive family history or BRCA mutations.
“In Manchester, we have put over a thousand women on tamoxifen who have a family history or other risk factors, not high-risk lesions,” and there simply isn’t definitive evidence for baby TAM in these women, Dr. Evans said.
The vast weight of evidence for tamoxifen prophylaxis, he added, is in trials involving tens of thousands of women, followed in some cases for 20 years, who received the 20 mg dose for 5 years.
As a result, women in Manchester are started on 20 mg and dropped down to 5 mg only for side effects. That way, Evans explained, we are not taking away the benefit among women who can tolerate 20 mg.
Meanwhile, there’s no evidence that baby TAM improves medication adherence, he noted. Trials have reported similar adherence rates to baby TAM and standard dose tamoxifen as well as no definitive evidence that the risk for cancer and thrombosis is less with baby TAM, he said.
In fact, Dr. Evans noted, “many women take tamoxifen 20 mg for 5 years with no side effects.”
Overall, “I don’t think we’ve got the evidence yet to drop” dosages, particularly in women without high-risk lesions, Dr. Evans said. A real concern, he added, is poor metabolizers for whom 5 mg won’t be enough to have a preventive effect.
Dr. De Censi noted, however, that there will likely never be a definitive answer to the question of baby TAM vs standard dosing because industry has no financial incentive to do a head-to-head trial; tamoxifen went off patent over 30 years ago.
Still, a poll of the audience favored Evans’ approach — 80% said they would start high-risk women on 20 mg for breast cancer prophylaxis and reduce for side effects as needed.
Dr. De Censi didn’t have any disclosures. Dr. Evans is a consultant/advisor for AstraZeneca, SpringWorks, Recursion, Everything Genetic, and Syantra.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should 5 mg of tamoxifen — known as “baby TAM” — or the usual 20 mg dose be standard of care for breast cancer prevention in high-risk women?
Research to date clearly shows that tamoxifen can reduce the risk for breast cancer in high-risk individuals by 30%-50%. Recent evidence also indicates that this chemoprevention approach can reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer by as much as 57%.
In 2019, the US Preventive Services Task Force issued updated recommendations that clinicians offer risk-reducing medications, such as tamoxifen, raloxifene, or aromatase inhibitors, to women at an increased risk for breast cancer and a low risk for adverse medication effects.
However, this prophylactic strategy remains underused.
A major roadblock: The drugs’ side effects, which include venous thromboembolic events and endometrial cancer as well as symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and sexual issues, have made uptake and adherence a challenge.
Offering women a lower dose of tamoxifen could allay fears about toxicities and improve uptake as well as reduce side effects and boost long-term adherence among those receiving baby TAM.
However,
The Debate
Years ago, Andrea De Censi, MD, a breast cancer researcher at the Galliera Hospital in Genova, Italy, and his colleagues reasoned that, because tamoxifen is a competitive estrogen receptor inhibitor, it may indeed have a minimal effective dose below 20 mg/d.
The fruits of that line of thought were presented to the world in the TAM-01 trial, first published in 2019, which pitted tamoxifen 5 mg/d for 3 years against placebo in 500 women with high-risk lesions, including lobular and ductal carcinoma in situ.
Dr. De Censi and colleagues found that baby TAM reduced the risk for invasive breast cancer by 52% and the risk for contralateral breast cancer by 75%.
Treatment adherence was slightly higher in the baby TAM group at 65% vs 61% in the placebo group.
A recent 10-year follow-up showed ongoing benefits associated with baby TAM vs placebo — a 42% reduction in breast cancer and a 64% drop in contralateral lesions.
The baby TAM group vs placebo experienced a slight increase in hot flashes but no significant increase in other common side effects.
Regarding serious adverse events, the baby TAM arm had one case of stage 1 endometrial cancer (0.4% of patients) and 20 cases of endometrial polyps (5%) vs 13 cases of endometrial polyps in the placebo arm. But there were no significant differences in thrombosis, cataracts, bone fractures, and other serious events.
Dr. De Censi said he’s surprised the baby TAM vs tamoxifen topic is still being debated. “Baby TAM, in my opinion, is a new standard of care for endocrine prevention of breast cancer in high-risk [women],” and baby TAM over 3 years is enough, said Dr. De Censi during a debate on the topic at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Congress in Berlin.
Gareth Evans, MD, a cancer genetics and prevention specialist at the University of Manchester, Manchester, England, however, isn’t convinced.
During the debate, Dr. Evans explained that his main concern was that the baby TAM trial was limited to women with high-risk lesions, not other common reasons for tamoxifen prophylaxis, such as a positive family history or BRCA mutations.
“In Manchester, we have put over a thousand women on tamoxifen who have a family history or other risk factors, not high-risk lesions,” and there simply isn’t definitive evidence for baby TAM in these women, Dr. Evans said.
The vast weight of evidence for tamoxifen prophylaxis, he added, is in trials involving tens of thousands of women, followed in some cases for 20 years, who received the 20 mg dose for 5 years.
As a result, women in Manchester are started on 20 mg and dropped down to 5 mg only for side effects. That way, Evans explained, we are not taking away the benefit among women who can tolerate 20 mg.
Meanwhile, there’s no evidence that baby TAM improves medication adherence, he noted. Trials have reported similar adherence rates to baby TAM and standard dose tamoxifen as well as no definitive evidence that the risk for cancer and thrombosis is less with baby TAM, he said.
In fact, Dr. Evans noted, “many women take tamoxifen 20 mg for 5 years with no side effects.”
Overall, “I don’t think we’ve got the evidence yet to drop” dosages, particularly in women without high-risk lesions, Dr. Evans said. A real concern, he added, is poor metabolizers for whom 5 mg won’t be enough to have a preventive effect.
Dr. De Censi noted, however, that there will likely never be a definitive answer to the question of baby TAM vs standard dosing because industry has no financial incentive to do a head-to-head trial; tamoxifen went off patent over 30 years ago.
Still, a poll of the audience favored Evans’ approach — 80% said they would start high-risk women on 20 mg for breast cancer prophylaxis and reduce for side effects as needed.
Dr. De Censi didn’t have any disclosures. Dr. Evans is a consultant/advisor for AstraZeneca, SpringWorks, Recursion, Everything Genetic, and Syantra.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric Studies Produce Mixed Messages on Relationship Between COVID and Asthma
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Histiocytoid Pyoderma Gangrenosum: A Challenging Case With Features of Sweet Syndrome
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatoses—a group of inflammatory cutaneous conditions—include acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet syndrome), pyoderma gangrenosum, and neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. Histopathology shows a dense dermal infiltrate of mature neutrophils. In 2005, the histiocytoid subtype of Sweet syndrome was introduced with histopathologic findings of a dermal infiltrate composed of immature myeloid cells that resemble histiocytes in appearance but stain strongly with neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.1 We present a case of histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum with histopathology that showed a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate with strong positivity for neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.
An 85-year-old man was seen by dermatology in the inpatient setting for a new-onset painful abdominal wound. He had a medical history of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), high-grade invasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, and a recent diagnosis of low-grade invasive ascending colon adenocarcinoma. Ten days prior he underwent a right colectomy without intraoperative complications that was followed by septic shock. Workup with urinalysis and urine culture showed minimal pyuria with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additional studies, including blood cultures, abdominal wound cultures, computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, renal ultrasound, and chest radiographs, were unremarkable and showed no signs of surgical site infection, intra-abdominal or pelvic abscess formation, or pulmonary embolism. Broad-spectrum antibiotics—vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam—were started. Persistent fever (Tmax of 102.3 °F [39.1 °C]) and leukocytosis (45.3×109/L [4.2–10×109/L]) despite antibiotic therapy, increasing pressor requirements, and progressive painful erythema and purulence at the abdominal surgical site led to debridement of the wound by the general surgery team on day 9 following the initial surgery due to suspected necrotizing infection. Within 24 hours, dermatology was consulted for continued rapid expansion of the wound. Physical examination of the abdomen revealed a large, well-demarcated, pink-red, indurated, ulcerated plaque with clear to purulent exudate and superficial erosions with violaceous undermined borders extending centrifugally from the abdominal surgical incision line (Figure 1A). Two punch biopsies sent for histopathologic evaluation and tissue culture showed dermal edema with a dense histiocytic infiltrate with nodular foci and admixed mature neutrophils to a lesser degree (Figure 2). Special staining was negative for bacteria, fungi, and mycobacteria. Immunohistochemistry revealed positive staining of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate with CD68, myeloperoxidase, and lysozyme, as well as negative staining with CD34 (Figure 3). These findings were suggestive of a histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis such as Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum. Due to the morphology of the solitary lesion and the abrupt exacerbation shortly after surgical intervention, the patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. At the same time, the patient’s septic shock was treated with intravenous hydrocortisone (100 mg 3 times daily) for 2 days and also achieved a prompt response in the cutaneous symptoms (Figure 1B).
Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum are considered distinct neutrophilic dermatoses that rarely coexist but share several clinical and histopathologic features, which can become a diagnostic challenge.2 Both conditions can manifest clinically as abrupt-onset, tender, erythematous papules; vesiculopustular lesions; or bullae with ulcerative changes. They also exhibit pathergy; present with systemic symptoms such as pyrexia, malaise, and joint pain; are associated with underlying systemic conditions such as infections and/or malignancy; demonstrate a dense neutrophilic infiltrate in the dermis on histopathology; and respond promptly to systemic corticosteroids.2-6 Bullous Sweet syndrome, which can present as vesicles, pustules, or bullae that progress to superficial ulcerations, may represent a variant of neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by features seen in both Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum, suggesting that these 2 conditions may be on a spectrum.5Clinical features such as erythema with a blue, gray, or purple hue; undermined and ragged borders; and healing of skin lesions with atrophic or cribriform scarring may favor pyoderma gangrenosum, whereas a dull red or plum color and resolution of lesions without scarring may support the diagnosis of Sweet syndrome.7 Although both conditions can exhibit pathergy secondary to minor skin trauma such as venipuncture and biopsies,2,3,5,8 Sweet syndrome rarely has been described to develop after surgery in a patient without a known history of the condition.9 In contrast, postsurgical pyoderma gangrenosum has been well described as secondary to the pathergy phenomenon.5
Our patient was favored to have pyoderma gangrenosum given the solitary lesion, its abrupt development after surgery, and the morphology of the lesion that exhibited a large violaceous to red ulcerative and exudative plaque with undermined borders with atrophic scarring. In patients with skin disease that cannot be distinguished with certainty as either Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum, it is essential to recognize that, as neutrophilic dermatoses, both conditions can be managed with either the first-line treatment option of high-dose systemic steroids or one of the shared alternative first-line or second-line steroid-sparing treatments, such as dapsone and cyclosporine.2
Although the exact pathogenesis of pyoderma gangrenosum remains to be fully understood, paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum is a frequently described phenomenon.10,11 Our patient’s history of multiple malignancies, both solid and hematologic, supports the likelihood of malignancy-induced pyoderma gangrenosum; however, given his history of MDS, several other conditions were ruled out prior to making the diagnosis of pyoderma gangrenosum.
Classically, neutrophilic dermatoses such as pyoderma gangrenosum have a dense dermal neutrophilic infiltrate. Concurrent myeloproliferative disorders can alter the maturation of leukocytes, subsequently leading to an atypical appearance of the inflammatory cells on histopathology. Further, in the setting of myeloproliferative disorders, conditions such as leukemia cutis, in which there can be a cutaneous infiltrate of immature or mature myeloid or lymphocytic cells, must be considered. To ensure our patient’s abdominal skin changes were not a cutaneous manifestation of hematologic malignancy, immunohistochemical staining with CD20 and CD3 was performed and showed only the rare presence of B and T lymphocytes, respectively. Staining with CD34 for lymphocytic and myeloid progenitor cells was negative in the dermal infiltrate and further reduced the likelihood of leukemia cutis. Alternatively, patients can have aleukemic cutaneous myeloid sarcoma or leukemia cutis without an underlying hematologic condition or with latent peripheral blood or bone marrow myeloproliferative disorder, but our patient’s history of MDS eliminated this possibility.12 After exclusion of cutaneous infiltration by malignant leukocytes, our patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis.
Multiple reports have described histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, in which there is a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate on histopathology that demonstrates myeloid lineage with immunologic staining.1,13 The typical pattern of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome includes a predominantly unaffected epidermis with papillary dermal edema, an absence of vasculitis, and a dense dermal infiltrate primarily composed of immature histiocytelike mononuclear cells with a basophilic elongated, twisted, or kidney-shaped nucleus and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.1,13 In an analogous manner, Morin et al12 described a patient with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia who presented with lesions that clinically resembled pyoderma gangrenosum but revealed a dense dermal infiltrate mostly made of large immature histiocytoid mononuclear cells on histopathology, consistent with the histopathologic features observed in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. The patient ultimately was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. Similarly, we believe that our patient also developed histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. As with histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, this diagnosis is based on histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings of a dense dermal infiltrate composed of histiocyte-resembling immature neutrophils.
Typically, pyoderma gangrenosum responds promptly to treatment with systemic corticosteroids.4 Steroid-sparing agents such as cyclosporine, azathioprine, dapsone, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also may be used.4,10 In the setting of MDS, clearance of pyoderma gangrenosum has been reported upon treatment of the underlying malignancy,14 high-dose systemic corticosteroids,11,15 cyclosporine with systemic steroids,16 thalidomide,17 combination therapy with thalidomide and interferon alfa-2a,18 and ustekinumab with vacuum-assisted closure therapy.19 Our patient’s histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancy cleared rapidly with high-dose systemic hydrocortisone.
In the setting of malignancy, as in our patient, neutrophilic dermatoses may develop from an aberrant immune system or tumor-induced cytokine dysregulation that leads to increased neutrophil production or dysfunction.4,10,11 Although our patient’s MDS may have contributed to the atypical appearance of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate, it is unclear whether the hematologic disorder increased his risk for the histiocytoid variant of neutrophilic dermatoses. Alegría-Landa et al13 reported that histiocytoid Sweet syndrome is associated with hematologic malignancy at a similar frequency as classic Sweet syndrome. It is unknown if histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum would have a strong association with hematologic malignancy. Future reports may elucidate a better understanding of the histiocytoid subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum and its clinical implications.
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses: a review of current treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:301-312.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34.
- Braswell SF, Kostopoulos TC, Ortega-Loayza AG. Pathophysiology of pyoderma gangrenosum (PG): an updated review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:691-698.
- Wallach D, Vignon-Pennamen MD. Pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet syndrome: the prototypic neutrophilic dermatoses. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:595-602.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Lear JT, Atherton MT, Byrne JP. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet’s syndrome. Postgrad Med. 1997;73:65-68.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006.
- Minocha R, Sebaratnam DF, Choi JY. Sweet’s syndrome following surgery: cutaneous trauma as a possible aetiological co-factor in neutrophilic dermatoses. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:E74-E76.
- Shah M, Sachdeva M, Gefri A, et al. Paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum in solid organ malignancy: a literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:154-158.
- Montagnon CM, Fracica EA, Patel AA, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum in hematologic malignancies: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1346-1359.
- Morin CB, Côté B, Belisle A. An interesting case of pyoderma gangrenosum with immature histiocytoid neutrophils. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:63-66.
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659.
- Saleh MFM, Saunthararajah Y. Severe pyoderma gangrenosum caused by myelodysplastic syndrome successfully treated with decitabine administered by a noncytotoxic regimen. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5:2025-2027.
- Yamauchi R, Ishida K, Iwashima Y, et al. Successful treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum that developed in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Infect Chemother. 2003;9:268-271.
- Ha JW, Hahm JE, Kim KS, et al. A case of pyoderma gangrenosum with myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:392-393.
- Malkan UY, Gunes G, Eliacik E, et al. Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum with thalidomide in a myelodysplastic syndrome case. Int J Med Case Rep. 2016;9:61-64.
- Koca E, Duman AE, Cetiner D, et al. Successful treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome-induced pyoderma gangrenosum. Neth J Med. 2006;64:422-424.
- Nieto D, Sendagorta E, Rueda JM, et al. Successful treatment with ustekinumab and vacuum-assisted closure therapy in recalcitrant myelodysplastic syndrome-associated pyoderma gangrenosum: case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:116-119.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatoses—a group of inflammatory cutaneous conditions—include acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet syndrome), pyoderma gangrenosum, and neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. Histopathology shows a dense dermal infiltrate of mature neutrophils. In 2005, the histiocytoid subtype of Sweet syndrome was introduced with histopathologic findings of a dermal infiltrate composed of immature myeloid cells that resemble histiocytes in appearance but stain strongly with neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.1 We present a case of histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum with histopathology that showed a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate with strong positivity for neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.
An 85-year-old man was seen by dermatology in the inpatient setting for a new-onset painful abdominal wound. He had a medical history of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), high-grade invasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, and a recent diagnosis of low-grade invasive ascending colon adenocarcinoma. Ten days prior he underwent a right colectomy without intraoperative complications that was followed by septic shock. Workup with urinalysis and urine culture showed minimal pyuria with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additional studies, including blood cultures, abdominal wound cultures, computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, renal ultrasound, and chest radiographs, were unremarkable and showed no signs of surgical site infection, intra-abdominal or pelvic abscess formation, or pulmonary embolism. Broad-spectrum antibiotics—vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam—were started. Persistent fever (Tmax of 102.3 °F [39.1 °C]) and leukocytosis (45.3×109/L [4.2–10×109/L]) despite antibiotic therapy, increasing pressor requirements, and progressive painful erythema and purulence at the abdominal surgical site led to debridement of the wound by the general surgery team on day 9 following the initial surgery due to suspected necrotizing infection. Within 24 hours, dermatology was consulted for continued rapid expansion of the wound. Physical examination of the abdomen revealed a large, well-demarcated, pink-red, indurated, ulcerated plaque with clear to purulent exudate and superficial erosions with violaceous undermined borders extending centrifugally from the abdominal surgical incision line (Figure 1A). Two punch biopsies sent for histopathologic evaluation and tissue culture showed dermal edema with a dense histiocytic infiltrate with nodular foci and admixed mature neutrophils to a lesser degree (Figure 2). Special staining was negative for bacteria, fungi, and mycobacteria. Immunohistochemistry revealed positive staining of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate with CD68, myeloperoxidase, and lysozyme, as well as negative staining with CD34 (Figure 3). These findings were suggestive of a histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis such as Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum. Due to the morphology of the solitary lesion and the abrupt exacerbation shortly after surgical intervention, the patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. At the same time, the patient’s septic shock was treated with intravenous hydrocortisone (100 mg 3 times daily) for 2 days and also achieved a prompt response in the cutaneous symptoms (Figure 1B).
Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum are considered distinct neutrophilic dermatoses that rarely coexist but share several clinical and histopathologic features, which can become a diagnostic challenge.2 Both conditions can manifest clinically as abrupt-onset, tender, erythematous papules; vesiculopustular lesions; or bullae with ulcerative changes. They also exhibit pathergy; present with systemic symptoms such as pyrexia, malaise, and joint pain; are associated with underlying systemic conditions such as infections and/or malignancy; demonstrate a dense neutrophilic infiltrate in the dermis on histopathology; and respond promptly to systemic corticosteroids.2-6 Bullous Sweet syndrome, which can present as vesicles, pustules, or bullae that progress to superficial ulcerations, may represent a variant of neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by features seen in both Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum, suggesting that these 2 conditions may be on a spectrum.5Clinical features such as erythema with a blue, gray, or purple hue; undermined and ragged borders; and healing of skin lesions with atrophic or cribriform scarring may favor pyoderma gangrenosum, whereas a dull red or plum color and resolution of lesions without scarring may support the diagnosis of Sweet syndrome.7 Although both conditions can exhibit pathergy secondary to minor skin trauma such as venipuncture and biopsies,2,3,5,8 Sweet syndrome rarely has been described to develop after surgery in a patient without a known history of the condition.9 In contrast, postsurgical pyoderma gangrenosum has been well described as secondary to the pathergy phenomenon.5
Our patient was favored to have pyoderma gangrenosum given the solitary lesion, its abrupt development after surgery, and the morphology of the lesion that exhibited a large violaceous to red ulcerative and exudative plaque with undermined borders with atrophic scarring. In patients with skin disease that cannot be distinguished with certainty as either Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum, it is essential to recognize that, as neutrophilic dermatoses, both conditions can be managed with either the first-line treatment option of high-dose systemic steroids or one of the shared alternative first-line or second-line steroid-sparing treatments, such as dapsone and cyclosporine.2
Although the exact pathogenesis of pyoderma gangrenosum remains to be fully understood, paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum is a frequently described phenomenon.10,11 Our patient’s history of multiple malignancies, both solid and hematologic, supports the likelihood of malignancy-induced pyoderma gangrenosum; however, given his history of MDS, several other conditions were ruled out prior to making the diagnosis of pyoderma gangrenosum.
Classically, neutrophilic dermatoses such as pyoderma gangrenosum have a dense dermal neutrophilic infiltrate. Concurrent myeloproliferative disorders can alter the maturation of leukocytes, subsequently leading to an atypical appearance of the inflammatory cells on histopathology. Further, in the setting of myeloproliferative disorders, conditions such as leukemia cutis, in which there can be a cutaneous infiltrate of immature or mature myeloid or lymphocytic cells, must be considered. To ensure our patient’s abdominal skin changes were not a cutaneous manifestation of hematologic malignancy, immunohistochemical staining with CD20 and CD3 was performed and showed only the rare presence of B and T lymphocytes, respectively. Staining with CD34 for lymphocytic and myeloid progenitor cells was negative in the dermal infiltrate and further reduced the likelihood of leukemia cutis. Alternatively, patients can have aleukemic cutaneous myeloid sarcoma or leukemia cutis without an underlying hematologic condition or with latent peripheral blood or bone marrow myeloproliferative disorder, but our patient’s history of MDS eliminated this possibility.12 After exclusion of cutaneous infiltration by malignant leukocytes, our patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis.


Multiple reports have described histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, in which there is a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate on histopathology that demonstrates myeloid lineage with immunologic staining.1,13 The typical pattern of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome includes a predominantly unaffected epidermis with papillary dermal edema, an absence of vasculitis, and a dense dermal infiltrate primarily composed of immature histiocytelike mononuclear cells with a basophilic elongated, twisted, or kidney-shaped nucleus and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.1,13 In an analogous manner, Morin et al12 described a patient with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia who presented with lesions that clinically resembled pyoderma gangrenosum but revealed a dense dermal infiltrate mostly made of large immature histiocytoid mononuclear cells on histopathology, consistent with the histopathologic features observed in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. The patient ultimately was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. Similarly, we believe that our patient also developed histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. As with histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, this diagnosis is based on histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings of a dense dermal infiltrate composed of histiocyte-resembling immature neutrophils.

Typically, pyoderma gangrenosum responds promptly to treatment with systemic corticosteroids.4 Steroid-sparing agents such as cyclosporine, azathioprine, dapsone, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also may be used.4,10 In the setting of MDS, clearance of pyoderma gangrenosum has been reported upon treatment of the underlying malignancy,14 high-dose systemic corticosteroids,11,15 cyclosporine with systemic steroids,16 thalidomide,17 combination therapy with thalidomide and interferon alfa-2a,18 and ustekinumab with vacuum-assisted closure therapy.19 Our patient’s histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancy cleared rapidly with high-dose systemic hydrocortisone.
In the setting of malignancy, as in our patient, neutrophilic dermatoses may develop from an aberrant immune system or tumor-induced cytokine dysregulation that leads to increased neutrophil production or dysfunction.4,10,11 Although our patient’s MDS may have contributed to the atypical appearance of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate, it is unclear whether the hematologic disorder increased his risk for the histiocytoid variant of neutrophilic dermatoses. Alegría-Landa et al13 reported that histiocytoid Sweet syndrome is associated with hematologic malignancy at a similar frequency as classic Sweet syndrome. It is unknown if histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum would have a strong association with hematologic malignancy. Future reports may elucidate a better understanding of the histiocytoid subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum and its clinical implications.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatoses—a group of inflammatory cutaneous conditions—include acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet syndrome), pyoderma gangrenosum, and neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. Histopathology shows a dense dermal infiltrate of mature neutrophils. In 2005, the histiocytoid subtype of Sweet syndrome was introduced with histopathologic findings of a dermal infiltrate composed of immature myeloid cells that resemble histiocytes in appearance but stain strongly with neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.1 We present a case of histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum with histopathology that showed a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate with strong positivity for neutrophil markers on immunohistochemistry.
An 85-year-old man was seen by dermatology in the inpatient setting for a new-onset painful abdominal wound. He had a medical history of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), high-grade invasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, and a recent diagnosis of low-grade invasive ascending colon adenocarcinoma. Ten days prior he underwent a right colectomy without intraoperative complications that was followed by septic shock. Workup with urinalysis and urine culture showed minimal pyuria with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additional studies, including blood cultures, abdominal wound cultures, computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, renal ultrasound, and chest radiographs, were unremarkable and showed no signs of surgical site infection, intra-abdominal or pelvic abscess formation, or pulmonary embolism. Broad-spectrum antibiotics—vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam—were started. Persistent fever (Tmax of 102.3 °F [39.1 °C]) and leukocytosis (45.3×109/L [4.2–10×109/L]) despite antibiotic therapy, increasing pressor requirements, and progressive painful erythema and purulence at the abdominal surgical site led to debridement of the wound by the general surgery team on day 9 following the initial surgery due to suspected necrotizing infection. Within 24 hours, dermatology was consulted for continued rapid expansion of the wound. Physical examination of the abdomen revealed a large, well-demarcated, pink-red, indurated, ulcerated plaque with clear to purulent exudate and superficial erosions with violaceous undermined borders extending centrifugally from the abdominal surgical incision line (Figure 1A). Two punch biopsies sent for histopathologic evaluation and tissue culture showed dermal edema with a dense histiocytic infiltrate with nodular foci and admixed mature neutrophils to a lesser degree (Figure 2). Special staining was negative for bacteria, fungi, and mycobacteria. Immunohistochemistry revealed positive staining of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate with CD68, myeloperoxidase, and lysozyme, as well as negative staining with CD34 (Figure 3). These findings were suggestive of a histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis such as Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum. Due to the morphology of the solitary lesion and the abrupt exacerbation shortly after surgical intervention, the patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. At the same time, the patient’s septic shock was treated with intravenous hydrocortisone (100 mg 3 times daily) for 2 days and also achieved a prompt response in the cutaneous symptoms (Figure 1B).
Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum are considered distinct neutrophilic dermatoses that rarely coexist but share several clinical and histopathologic features, which can become a diagnostic challenge.2 Both conditions can manifest clinically as abrupt-onset, tender, erythematous papules; vesiculopustular lesions; or bullae with ulcerative changes. They also exhibit pathergy; present with systemic symptoms such as pyrexia, malaise, and joint pain; are associated with underlying systemic conditions such as infections and/or malignancy; demonstrate a dense neutrophilic infiltrate in the dermis on histopathology; and respond promptly to systemic corticosteroids.2-6 Bullous Sweet syndrome, which can present as vesicles, pustules, or bullae that progress to superficial ulcerations, may represent a variant of neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by features seen in both Sweet syndrome and pyoderma gangrenosum, suggesting that these 2 conditions may be on a spectrum.5Clinical features such as erythema with a blue, gray, or purple hue; undermined and ragged borders; and healing of skin lesions with atrophic or cribriform scarring may favor pyoderma gangrenosum, whereas a dull red or plum color and resolution of lesions without scarring may support the diagnosis of Sweet syndrome.7 Although both conditions can exhibit pathergy secondary to minor skin trauma such as venipuncture and biopsies,2,3,5,8 Sweet syndrome rarely has been described to develop after surgery in a patient without a known history of the condition.9 In contrast, postsurgical pyoderma gangrenosum has been well described as secondary to the pathergy phenomenon.5
Our patient was favored to have pyoderma gangrenosum given the solitary lesion, its abrupt development after surgery, and the morphology of the lesion that exhibited a large violaceous to red ulcerative and exudative plaque with undermined borders with atrophic scarring. In patients with skin disease that cannot be distinguished with certainty as either Sweet syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum, it is essential to recognize that, as neutrophilic dermatoses, both conditions can be managed with either the first-line treatment option of high-dose systemic steroids or one of the shared alternative first-line or second-line steroid-sparing treatments, such as dapsone and cyclosporine.2
Although the exact pathogenesis of pyoderma gangrenosum remains to be fully understood, paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum is a frequently described phenomenon.10,11 Our patient’s history of multiple malignancies, both solid and hematologic, supports the likelihood of malignancy-induced pyoderma gangrenosum; however, given his history of MDS, several other conditions were ruled out prior to making the diagnosis of pyoderma gangrenosum.
Classically, neutrophilic dermatoses such as pyoderma gangrenosum have a dense dermal neutrophilic infiltrate. Concurrent myeloproliferative disorders can alter the maturation of leukocytes, subsequently leading to an atypical appearance of the inflammatory cells on histopathology. Further, in the setting of myeloproliferative disorders, conditions such as leukemia cutis, in which there can be a cutaneous infiltrate of immature or mature myeloid or lymphocytic cells, must be considered. To ensure our patient’s abdominal skin changes were not a cutaneous manifestation of hematologic malignancy, immunohistochemical staining with CD20 and CD3 was performed and showed only the rare presence of B and T lymphocytes, respectively. Staining with CD34 for lymphocytic and myeloid progenitor cells was negative in the dermal infiltrate and further reduced the likelihood of leukemia cutis. Alternatively, patients can have aleukemic cutaneous myeloid sarcoma or leukemia cutis without an underlying hematologic condition or with latent peripheral blood or bone marrow myeloproliferative disorder, but our patient’s history of MDS eliminated this possibility.12 After exclusion of cutaneous infiltration by malignant leukocytes, our patient was diagnosed with histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatosis.


Multiple reports have described histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, in which there is a dense dermal histiocytoid infiltrate on histopathology that demonstrates myeloid lineage with immunologic staining.1,13 The typical pattern of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome includes a predominantly unaffected epidermis with papillary dermal edema, an absence of vasculitis, and a dense dermal infiltrate primarily composed of immature histiocytelike mononuclear cells with a basophilic elongated, twisted, or kidney-shaped nucleus and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.1,13 In an analogous manner, Morin et al12 described a patient with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia who presented with lesions that clinically resembled pyoderma gangrenosum but revealed a dense dermal infiltrate mostly made of large immature histiocytoid mononuclear cells on histopathology, consistent with the histopathologic features observed in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. The patient ultimately was diagnosed with histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. Similarly, we believe that our patient also developed histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum. As with histiocytoid Sweet syndrome, this diagnosis is based on histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings of a dense dermal infiltrate composed of histiocyte-resembling immature neutrophils.

Typically, pyoderma gangrenosum responds promptly to treatment with systemic corticosteroids.4 Steroid-sparing agents such as cyclosporine, azathioprine, dapsone, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also may be used.4,10 In the setting of MDS, clearance of pyoderma gangrenosum has been reported upon treatment of the underlying malignancy,14 high-dose systemic corticosteroids,11,15 cyclosporine with systemic steroids,16 thalidomide,17 combination therapy with thalidomide and interferon alfa-2a,18 and ustekinumab with vacuum-assisted closure therapy.19 Our patient’s histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancy cleared rapidly with high-dose systemic hydrocortisone.
In the setting of malignancy, as in our patient, neutrophilic dermatoses may develop from an aberrant immune system or tumor-induced cytokine dysregulation that leads to increased neutrophil production or dysfunction.4,10,11 Although our patient’s MDS may have contributed to the atypical appearance of the dermal inflammatory infiltrate, it is unclear whether the hematologic disorder increased his risk for the histiocytoid variant of neutrophilic dermatoses. Alegría-Landa et al13 reported that histiocytoid Sweet syndrome is associated with hematologic malignancy at a similar frequency as classic Sweet syndrome. It is unknown if histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum would have a strong association with hematologic malignancy. Future reports may elucidate a better understanding of the histiocytoid subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum and its clinical implications.
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses: a review of current treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:301-312.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34.
- Braswell SF, Kostopoulos TC, Ortega-Loayza AG. Pathophysiology of pyoderma gangrenosum (PG): an updated review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:691-698.
- Wallach D, Vignon-Pennamen MD. Pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet syndrome: the prototypic neutrophilic dermatoses. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:595-602.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Lear JT, Atherton MT, Byrne JP. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet’s syndrome. Postgrad Med. 1997;73:65-68.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006.
- Minocha R, Sebaratnam DF, Choi JY. Sweet’s syndrome following surgery: cutaneous trauma as a possible aetiological co-factor in neutrophilic dermatoses. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:E74-E76.
- Shah M, Sachdeva M, Gefri A, et al. Paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum in solid organ malignancy: a literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:154-158.
- Montagnon CM, Fracica EA, Patel AA, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum in hematologic malignancies: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1346-1359.
- Morin CB, Côté B, Belisle A. An interesting case of pyoderma gangrenosum with immature histiocytoid neutrophils. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:63-66.
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659.
- Saleh MFM, Saunthararajah Y. Severe pyoderma gangrenosum caused by myelodysplastic syndrome successfully treated with decitabine administered by a noncytotoxic regimen. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5:2025-2027.
- Yamauchi R, Ishida K, Iwashima Y, et al. Successful treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum that developed in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Infect Chemother. 2003;9:268-271.
- Ha JW, Hahm JE, Kim KS, et al. A case of pyoderma gangrenosum with myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:392-393.
- Malkan UY, Gunes G, Eliacik E, et al. Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum with thalidomide in a myelodysplastic syndrome case. Int J Med Case Rep. 2016;9:61-64.
- Koca E, Duman AE, Cetiner D, et al. Successful treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome-induced pyoderma gangrenosum. Neth J Med. 2006;64:422-424.
- Nieto D, Sendagorta E, Rueda JM, et al. Successful treatment with ustekinumab and vacuum-assisted closure therapy in recalcitrant myelodysplastic syndrome-associated pyoderma gangrenosum: case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:116-119.
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses: a review of current treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:301-312.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34.
- Braswell SF, Kostopoulos TC, Ortega-Loayza AG. Pathophysiology of pyoderma gangrenosum (PG): an updated review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:691-698.
- Wallach D, Vignon-Pennamen MD. Pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet syndrome: the prototypic neutrophilic dermatoses. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:595-602.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Lear JT, Atherton MT, Byrne JP. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pyoderma gangrenosum and Sweet’s syndrome. Postgrad Med. 1997;73:65-68.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006.
- Minocha R, Sebaratnam DF, Choi JY. Sweet’s syndrome following surgery: cutaneous trauma as a possible aetiological co-factor in neutrophilic dermatoses. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:E74-E76.
- Shah M, Sachdeva M, Gefri A, et al. Paraneoplastic pyoderma gangrenosum in solid organ malignancy: a literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:154-158.
- Montagnon CM, Fracica EA, Patel AA, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum in hematologic malignancies: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1346-1359.
- Morin CB, Côté B, Belisle A. An interesting case of pyoderma gangrenosum with immature histiocytoid neutrophils. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:63-66.
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659.
- Saleh MFM, Saunthararajah Y. Severe pyoderma gangrenosum caused by myelodysplastic syndrome successfully treated with decitabine administered by a noncytotoxic regimen. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5:2025-2027.
- Yamauchi R, Ishida K, Iwashima Y, et al. Successful treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum that developed in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Infect Chemother. 2003;9:268-271.
- Ha JW, Hahm JE, Kim KS, et al. A case of pyoderma gangrenosum with myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:392-393.
- Malkan UY, Gunes G, Eliacik E, et al. Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum with thalidomide in a myelodysplastic syndrome case. Int J Med Case Rep. 2016;9:61-64.
- Koca E, Duman AE, Cetiner D, et al. Successful treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome-induced pyoderma gangrenosum. Neth J Med. 2006;64:422-424.
- Nieto D, Sendagorta E, Rueda JM, et al. Successful treatment with ustekinumab and vacuum-assisted closure therapy in recalcitrant myelodysplastic syndrome-associated pyoderma gangrenosum: case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:116-119.
Practice Points:
- Dermatologists and dermatopathologists should be aware of the histiocytoid variant of pyoderma gangrenosum, which can clinical and histologic features that overlap with histiocytoid Sweet syndrome.
- When considering a diagnosis of histiocytoid neutrophilic dermatoses, leukemia cutis or aleukemic cutaneous myeloid sarcoma should be ruled out.
- Similar to histiocytoid Sweet syndrome and neutrophilic dermatoses in the setting of hematologic or solid organ malignancy, histiocytoid pyoderma gangrenosum may respond well to high-dose systemic corticosteroids.
Stroke Recurrence Risk Doubles in Patients With AF Who Stop Anticoagulation Therapy
, a new Danish nationwide cohort study finds.
Among 8,119 patients aged 50 years and older (54.1% male, mean age 78.4), 4.3% had a recurrent stroke within 1 year following discharge for the initial stroke, reported David Gaist, PhD, of Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark, and colleagues in JAMA Neurology.
An adjusted analysis found that those who stopped therapy were more than twice as likely to experience another stroke over a mean 2.9 years (13.4% vs 6.8%, adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 2.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57-2.89).
The findings highlight the preventive power of OAC therapy, Dr. Gaist said in an interview, and point to the importance of counseling patients about the benefits of the drugs. “Clinicians can provide balanced information on the pros and cons of discontinuing oral anticoagulants as well as lay out plans on when to restart the medication,” he said.
The researchers launched the study “to provide data on how often recurrent ischemic strokes occur in a large, unselected cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation who had a stroke and started or restarted oral anticoagulants, a situation mirroring what we see in our everyday lives as clinicians,” Dr. Gaist said. “We also wanted to see if patients with breakthrough strokes had particular characteristics compared with patients who did not have a recurrent stroke. Finally, we wanted to quantify a very simple cause of breakthrough stroke by answering the following question: How many of these patients had stopped taking their oral anticoagulant?”
A Large, Unselected Patient Cohort
Dr. Gaist and colleagues tracked 8,119 patients with ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation who started or restarted OAC therapy within 30 days following their discharge between 2014 and 2021. Patients either had atrial fibrillation before their stroke or developed it afterward.
Eighty-one percent of patients had hypertension, 19.7% had diabetes, and 27.3% had ischemic heart disease; 35.3% had never smoked and smoking information was missing for 15.9%. Race/ethnicity information was not provided.
Patients were followed for an average of 2.9 years until 2022, and all were alive at least 30 days after discharge. During that time, 663 patients had a recurrent ischemic stroke (4.3%), of whom 80.4% were on OAC therapy. The percentage who had stroke at 2 years rose to 6.5%.
While the researchers thought the number of strokes was high, Dr. Gaist said, this isn’t a sign that the drugs aren’t working. “Oral anticoagulant use in secondary prevention in atrial fibrillation is guideline-supported as it has been proven to reduce the risk of stroke by roughly two thirds.”
Of study participants at baseline, 37.9% took oral anticoagulants, 23.5% took direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs; dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban), and 15.1% took vitamin K antagonists. In a nested case-control analysis of 663 cases (58.7% men, mean age 80.1) matched to 2,652 controls, at admission for ischemic stroke, 80.4% were on OAC therapy, and 8%-11% of patients stopped OAC therapy after their strokes, the researchers reported.
Patients who stopped OAC therapy had more severe strokes than those who didn’t at 7 days (median recurrent ischemic stroke Scandinavian Stroke Scale [SSS] score = 40.0 vs 46.0, respectively; aOR = 2.10; 95% CI, 1.31-3.36). Those who stopped OAC therapy also had higher mortality rates at 7 days (11.2% vs 3.9%, respectively) and 30 days (28.1% vs 10.9%, respectively).
It’s not clear why some patients discontinued OAC therapy. “We looked for evidence of serious bleeding or surgical procedures around the time of anticoagulant discontinuation but found this only to be the case in roughly 10% of these patients,” Dr. Gaist said.
He added that the study probably “underestimates the issue of anticoagulant discontinuation, particularly for DOACs, where a shorter half-life compared with warfarin means that even a short drug-break of a few days puts the patient at increased risk of stroke.”
The authors noted study limitations, including the lack of data on actual medication usage, alcohol usage, stroke etiology, lesion location, and socioeconomic status. And, they wrote, the study population is mostly of European origin.
No Surprises
Steven R. Messe, MD, professor of neurology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who didn’t take part in the study but is familiar with its findings, said in an interview that the study is a “well-done analysis.”
The findings are not surprising, he said. “The overall risk of stroke recurrence was 4.3% at 1 year while the mortality rate was higher at 15.4%. Given that the median CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4 and the average age was 79, the stroke recurrence rate and mortality rate are in line with prior studies.”
In regard to the power of OAC therapy to prevent recurrent strokes, Dr. Messe noted that patients may not be adhering to prescribed regimens. Also, “while DOACs are clearly safer that vitamin K–dependent anticoagulants, the medications are generally not dose adjusted. It is possible that adjusting the dose based on measured anti-Xa levels to insure therapeutic anticoagulant effects may reduce the stroke risk further.”
He added that “most of these patients with prior stroke and atrial fibrillation are vasculopathic and at risk of additional strokes due to other mechanisms such as small vessel or large vessel disease.”
In the big picture, the study “confirms again that anticoagulation should be prescribed to all patients with atrial fibrillation and prior stroke, unless there is a strong bleeding risk contraindication,” Dr. Messe said. These patients are clearly at high risk of stroke recurrence and mortality, and all risk factors should be aggressively managed.”
Researchers are exploring other options, he said. “For example, there are studies of factor XI inhibitors that could be added to a DOAC for additional reductions in ischemic stroke. In addition, in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, the randomized trial LAOS III demonstrated that surgical left atrial occlusion in addition to anticoagulation may provide additional stroke prevention.”
Dr. Gaist disclosed personal fees from Pfizer and Bristol Myers Squibb, and grants from Bayer. Several other authors reported various relationships with industry. Dr. Messe has no disclosures.
, a new Danish nationwide cohort study finds.
Among 8,119 patients aged 50 years and older (54.1% male, mean age 78.4), 4.3% had a recurrent stroke within 1 year following discharge for the initial stroke, reported David Gaist, PhD, of Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark, and colleagues in JAMA Neurology.
An adjusted analysis found that those who stopped therapy were more than twice as likely to experience another stroke over a mean 2.9 years (13.4% vs 6.8%, adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 2.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57-2.89).
The findings highlight the preventive power of OAC therapy, Dr. Gaist said in an interview, and point to the importance of counseling patients about the benefits of the drugs. “Clinicians can provide balanced information on the pros and cons of discontinuing oral anticoagulants as well as lay out plans on when to restart the medication,” he said.
The researchers launched the study “to provide data on how often recurrent ischemic strokes occur in a large, unselected cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation who had a stroke and started or restarted oral anticoagulants, a situation mirroring what we see in our everyday lives as clinicians,” Dr. Gaist said. “We also wanted to see if patients with breakthrough strokes had particular characteristics compared with patients who did not have a recurrent stroke. Finally, we wanted to quantify a very simple cause of breakthrough stroke by answering the following question: How many of these patients had stopped taking their oral anticoagulant?”
A Large, Unselected Patient Cohort
Dr. Gaist and colleagues tracked 8,119 patients with ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation who started or restarted OAC therapy within 30 days following their discharge between 2014 and 2021. Patients either had atrial fibrillation before their stroke or developed it afterward.
Eighty-one percent of patients had hypertension, 19.7% had diabetes, and 27.3% had ischemic heart disease; 35.3% had never smoked and smoking information was missing for 15.9%. Race/ethnicity information was not provided.
Patients were followed for an average of 2.9 years until 2022, and all were alive at least 30 days after discharge. During that time, 663 patients had a recurrent ischemic stroke (4.3%), of whom 80.4% were on OAC therapy. The percentage who had stroke at 2 years rose to 6.5%.
While the researchers thought the number of strokes was high, Dr. Gaist said, this isn’t a sign that the drugs aren’t working. “Oral anticoagulant use in secondary prevention in atrial fibrillation is guideline-supported as it has been proven to reduce the risk of stroke by roughly two thirds.”
Of study participants at baseline, 37.9% took oral anticoagulants, 23.5% took direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs; dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban), and 15.1% took vitamin K antagonists. In a nested case-control analysis of 663 cases (58.7% men, mean age 80.1) matched to 2,652 controls, at admission for ischemic stroke, 80.4% were on OAC therapy, and 8%-11% of patients stopped OAC therapy after their strokes, the researchers reported.
Patients who stopped OAC therapy had more severe strokes than those who didn’t at 7 days (median recurrent ischemic stroke Scandinavian Stroke Scale [SSS] score = 40.0 vs 46.0, respectively; aOR = 2.10; 95% CI, 1.31-3.36). Those who stopped OAC therapy also had higher mortality rates at 7 days (11.2% vs 3.9%, respectively) and 30 days (28.1% vs 10.9%, respectively).
It’s not clear why some patients discontinued OAC therapy. “We looked for evidence of serious bleeding or surgical procedures around the time of anticoagulant discontinuation but found this only to be the case in roughly 10% of these patients,” Dr. Gaist said.
He added that the study probably “underestimates the issue of anticoagulant discontinuation, particularly for DOACs, where a shorter half-life compared with warfarin means that even a short drug-break of a few days puts the patient at increased risk of stroke.”
The authors noted study limitations, including the lack of data on actual medication usage, alcohol usage, stroke etiology, lesion location, and socioeconomic status. And, they wrote, the study population is mostly of European origin.
No Surprises
Steven R. Messe, MD, professor of neurology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who didn’t take part in the study but is familiar with its findings, said in an interview that the study is a “well-done analysis.”
The findings are not surprising, he said. “The overall risk of stroke recurrence was 4.3% at 1 year while the mortality rate was higher at 15.4%. Given that the median CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4 and the average age was 79, the stroke recurrence rate and mortality rate are in line with prior studies.”
In regard to the power of OAC therapy to prevent recurrent strokes, Dr. Messe noted that patients may not be adhering to prescribed regimens. Also, “while DOACs are clearly safer that vitamin K–dependent anticoagulants, the medications are generally not dose adjusted. It is possible that adjusting the dose based on measured anti-Xa levels to insure therapeutic anticoagulant effects may reduce the stroke risk further.”
He added that “most of these patients with prior stroke and atrial fibrillation are vasculopathic and at risk of additional strokes due to other mechanisms such as small vessel or large vessel disease.”
In the big picture, the study “confirms again that anticoagulation should be prescribed to all patients with atrial fibrillation and prior stroke, unless there is a strong bleeding risk contraindication,” Dr. Messe said. These patients are clearly at high risk of stroke recurrence and mortality, and all risk factors should be aggressively managed.”
Researchers are exploring other options, he said. “For example, there are studies of factor XI inhibitors that could be added to a DOAC for additional reductions in ischemic stroke. In addition, in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, the randomized trial LAOS III demonstrated that surgical left atrial occlusion in addition to anticoagulation may provide additional stroke prevention.”
Dr. Gaist disclosed personal fees from Pfizer and Bristol Myers Squibb, and grants from Bayer. Several other authors reported various relationships with industry. Dr. Messe has no disclosures.
, a new Danish nationwide cohort study finds.
Among 8,119 patients aged 50 years and older (54.1% male, mean age 78.4), 4.3% had a recurrent stroke within 1 year following discharge for the initial stroke, reported David Gaist, PhD, of Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark, and colleagues in JAMA Neurology.
An adjusted analysis found that those who stopped therapy were more than twice as likely to experience another stroke over a mean 2.9 years (13.4% vs 6.8%, adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 2.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57-2.89).
The findings highlight the preventive power of OAC therapy, Dr. Gaist said in an interview, and point to the importance of counseling patients about the benefits of the drugs. “Clinicians can provide balanced information on the pros and cons of discontinuing oral anticoagulants as well as lay out plans on when to restart the medication,” he said.
The researchers launched the study “to provide data on how often recurrent ischemic strokes occur in a large, unselected cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation who had a stroke and started or restarted oral anticoagulants, a situation mirroring what we see in our everyday lives as clinicians,” Dr. Gaist said. “We also wanted to see if patients with breakthrough strokes had particular characteristics compared with patients who did not have a recurrent stroke. Finally, we wanted to quantify a very simple cause of breakthrough stroke by answering the following question: How many of these patients had stopped taking their oral anticoagulant?”
A Large, Unselected Patient Cohort
Dr. Gaist and colleagues tracked 8,119 patients with ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation who started or restarted OAC therapy within 30 days following their discharge between 2014 and 2021. Patients either had atrial fibrillation before their stroke or developed it afterward.
Eighty-one percent of patients had hypertension, 19.7% had diabetes, and 27.3% had ischemic heart disease; 35.3% had never smoked and smoking information was missing for 15.9%. Race/ethnicity information was not provided.
Patients were followed for an average of 2.9 years until 2022, and all were alive at least 30 days after discharge. During that time, 663 patients had a recurrent ischemic stroke (4.3%), of whom 80.4% were on OAC therapy. The percentage who had stroke at 2 years rose to 6.5%.
While the researchers thought the number of strokes was high, Dr. Gaist said, this isn’t a sign that the drugs aren’t working. “Oral anticoagulant use in secondary prevention in atrial fibrillation is guideline-supported as it has been proven to reduce the risk of stroke by roughly two thirds.”
Of study participants at baseline, 37.9% took oral anticoagulants, 23.5% took direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs; dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban), and 15.1% took vitamin K antagonists. In a nested case-control analysis of 663 cases (58.7% men, mean age 80.1) matched to 2,652 controls, at admission for ischemic stroke, 80.4% were on OAC therapy, and 8%-11% of patients stopped OAC therapy after their strokes, the researchers reported.
Patients who stopped OAC therapy had more severe strokes than those who didn’t at 7 days (median recurrent ischemic stroke Scandinavian Stroke Scale [SSS] score = 40.0 vs 46.0, respectively; aOR = 2.10; 95% CI, 1.31-3.36). Those who stopped OAC therapy also had higher mortality rates at 7 days (11.2% vs 3.9%, respectively) and 30 days (28.1% vs 10.9%, respectively).
It’s not clear why some patients discontinued OAC therapy. “We looked for evidence of serious bleeding or surgical procedures around the time of anticoagulant discontinuation but found this only to be the case in roughly 10% of these patients,” Dr. Gaist said.
He added that the study probably “underestimates the issue of anticoagulant discontinuation, particularly for DOACs, where a shorter half-life compared with warfarin means that even a short drug-break of a few days puts the patient at increased risk of stroke.”
The authors noted study limitations, including the lack of data on actual medication usage, alcohol usage, stroke etiology, lesion location, and socioeconomic status. And, they wrote, the study population is mostly of European origin.
No Surprises
Steven R. Messe, MD, professor of neurology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who didn’t take part in the study but is familiar with its findings, said in an interview that the study is a “well-done analysis.”
The findings are not surprising, he said. “The overall risk of stroke recurrence was 4.3% at 1 year while the mortality rate was higher at 15.4%. Given that the median CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4 and the average age was 79, the stroke recurrence rate and mortality rate are in line with prior studies.”
In regard to the power of OAC therapy to prevent recurrent strokes, Dr. Messe noted that patients may not be adhering to prescribed regimens. Also, “while DOACs are clearly safer that vitamin K–dependent anticoagulants, the medications are generally not dose adjusted. It is possible that adjusting the dose based on measured anti-Xa levels to insure therapeutic anticoagulant effects may reduce the stroke risk further.”
He added that “most of these patients with prior stroke and atrial fibrillation are vasculopathic and at risk of additional strokes due to other mechanisms such as small vessel or large vessel disease.”
In the big picture, the study “confirms again that anticoagulation should be prescribed to all patients with atrial fibrillation and prior stroke, unless there is a strong bleeding risk contraindication,” Dr. Messe said. These patients are clearly at high risk of stroke recurrence and mortality, and all risk factors should be aggressively managed.”
Researchers are exploring other options, he said. “For example, there are studies of factor XI inhibitors that could be added to a DOAC for additional reductions in ischemic stroke. In addition, in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, the randomized trial LAOS III demonstrated that surgical left atrial occlusion in addition to anticoagulation may provide additional stroke prevention.”
Dr. Gaist disclosed personal fees from Pfizer and Bristol Myers Squibb, and grants from Bayer. Several other authors reported various relationships with industry. Dr. Messe has no disclosures.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Nail Alterations From Musical Instruments: Insights for Dermatologists Treating Musicians
A variety of skin problems can occur in musicians due to the repetitive movements of playing instruments.1,2 Musicians’ nails are continuously exposed to the mechanical forces and chemical substances characteristic of their instruments.3 Occupational nail alterations in musicians caused by repetitive physical trauma, allergic contact dermatitis, and/or infection may lead to disability and compromise their professional career.
We conducted a systematic review of the literature on the clinical features of musical instrument–related nail alterations to optimize the management and prevention of these conditions.
Methods
We conducted a systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases for eligible publications on instrument-related nail alterations in musicians using the search terms musicians with nail, onychopathy, and Raynaud. No time or language criteria were applied. Reviews, editorials, and articles not related to the topic were excluded. Bibliographies/reference lists were checked to find any additional relevant publications. Relevant articles in English and French were screened by 2 independent reviewers (A.G. and N.L.), and the following data were extracted for qualitative synthesis: sex, age, musical instrument, clinical features, number of years practicing the instrument, laboratory investigations, and disease course.
Results
The literature search yielded 11 publications. Sixteen additional articles were identified by other methods (ie, references, related publications). Overall, 3 full-text articles described general nail alterations but did not describe the clinical data, and 11 publications were editorials, commentaries, reviews, or not relevant. Thirteen contributions fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were eligible for qualitative synthesis. The flow diagram illustrates the screening process (Figure 1).
Twenty-three patients were included. The instruments identified were divided into 2 groups: string instruments (ie, guitar, violin, harp) and percussion instruments (ie, drums, piano, slap bass). Nail alterations were clinically expressed as: (1) modifications of the nail surface; (2) nail bed, soft-tissue, and bone abnormalities; and (3) periungual tissue and distal pulp disorders. All cases are summarized in the Table.4-16 Three articles described occupational Raynaud phenomenon.12-14
Comment
Modifications of the Nail Surface—Onychodystrophy, such as deformity or discoloration of the nail plate, was described in 6 patients among a cohort of 295 musicians and an additional 6 patients among 199 musicians with induced skin lesions. This condition was most common in string instrument players and pianists due to injury and irritation.
One patient, who had been a professional violist for 27 years, presented with lamellar onychoschizia, which corresponds to a horizontal splitting of the nail toward its distal portion (Figure 2). The 3 fingernails of the dominant hand were involved with a V-shaped incision of the distal margin of the nail due to the repetitive friction of the nails with the strings.6
Striations of the nail plate were reported in a guitarist who played for 10 years.7 Physical examination revealed linear transverse ridges alternating with depressions on the central aspect of the nail plate of the right thumbnail, as the patient was right-handed. This condition, attributed to sustained pressure on the string applied by the thumb, also has been called habit tic deformity.7
Nail Bed, Soft-Tissue, and Bone Lesions—Purpura (or hemorrhage) of the nail bed was associated with a percussion instrument (ie, piano) in 1 patient, affecting the second, third, and fourth fingernails of the right hand.8 Especially when performing ascending glissando passages, the pianist applies pressure that may damage the finger and cause fingernail purpura. This condition improved after the patient stopping practicing glissandi.8
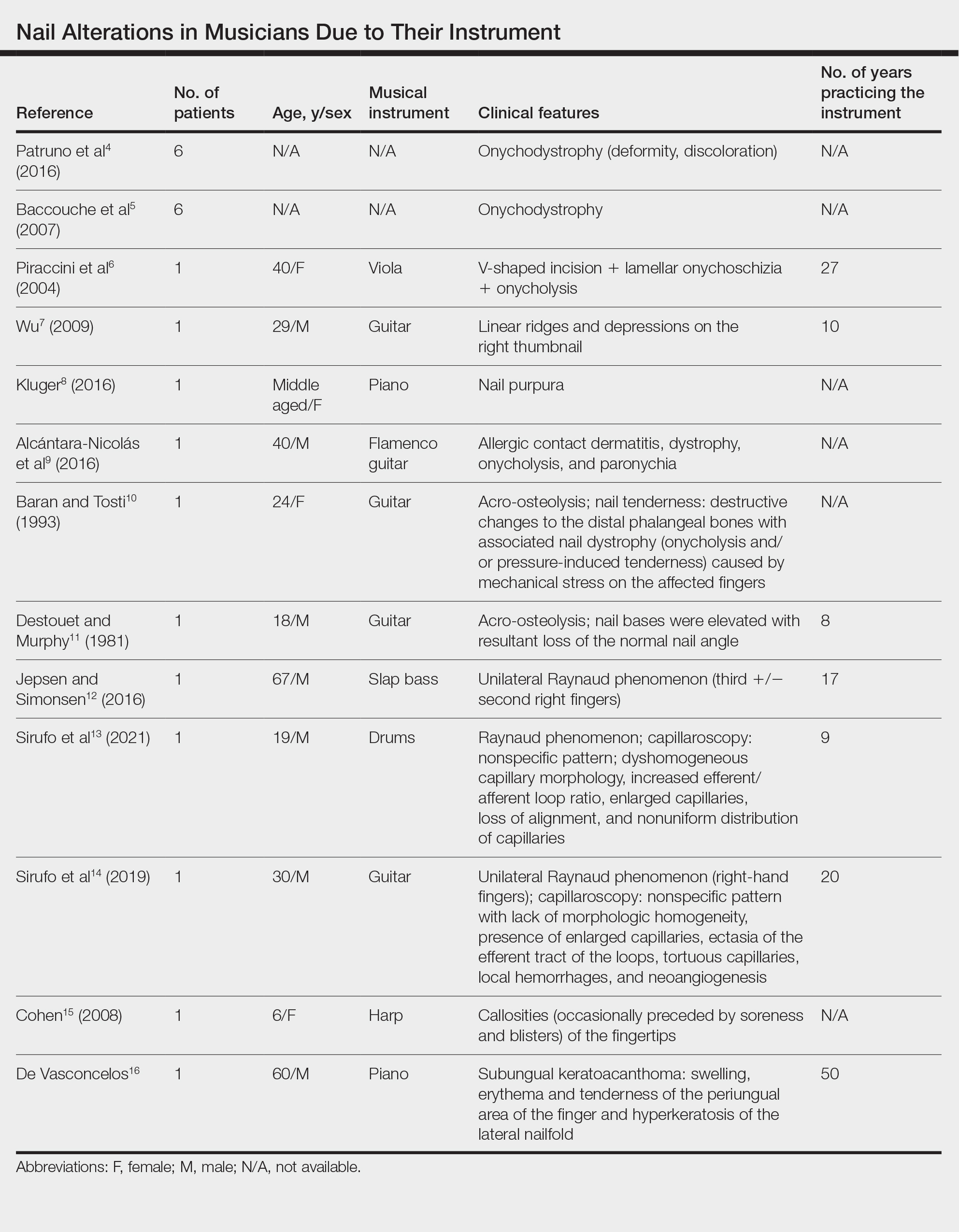
Three patients—2 guitarists and 1 violist—had onycholysis, defined by a loss of the attachment between the nail bed and the nail plate (Figure 3). It may result from repetitive trauma when strings are plucked.6,9,10
Acro-osteolysis associated with pain was reported in 2 guitarists.10,11 This condition is defined as transverse lytic bands in the distal phalanges (Figure 4). Acro-osteolysis may be secondary to multiple causes, such as vinyl chloride exposure, connective tissue diseases, thermal injuries, neuropathic diseases, hyperparathyroidism, nutritional deficiencies, psoriasis, and biomechanical stress.10 In musicians playing instruments, the mechanical stress to the guitar-playing fingers is the causative factor.17
Periungual Tissue and Distal Pulp Disorders—Paronychia is an important occupational hazard of harpists, violists, and pianists.2 It represents an inflammatory condition involving the folds of tissue surrounding fingernails. Pizzicato paronychia is related to infection in the nail fold in string players and secondary to pizzicato playing, whereby the musician plucks the instrument strings with the nails and fingertips.3
Acrylates in artificial nails frequently are used among guitarists to strengthen their nails. A case of occupational allergic contact dermatitis induced by acrylic gel nails in a flamenco guitarist was described.9 The patient developed dystrophy, onycholysis, and paronychia involving the nails of the right hand where acrylic materials were used, which resolved following the removal of the artificial nails. Patch tests were performed and were positive for 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate, supporting the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis to acrylates.9 Therefore, musicians should be aware of the sensitizing potential of acrylates and adopt preventive measures.
Unilateral Raynaud phenomenon of the dominant hand was noted in 3 cases of musicians who played string instruments due to the increased tendency to vasospasm in the digital capillaries from the direct transmission of vibrations of the strings (>100 Hz).12-14 Consequently, the disruption of the digital blood circulation leads to an abnormal reaction to cold, which is called vibration-induced white fingers or vasospastic white finger disease.19 In these 3 patients, capillaroscopy showed a nonspecific pattern with a lack of morphologic homogeneity of capillaries, the presence of enlarged capillaries, ectasia of the efferent tract of the loops, tortuous capillaries, local hemorrhages, and neoangiogenesis.13,14
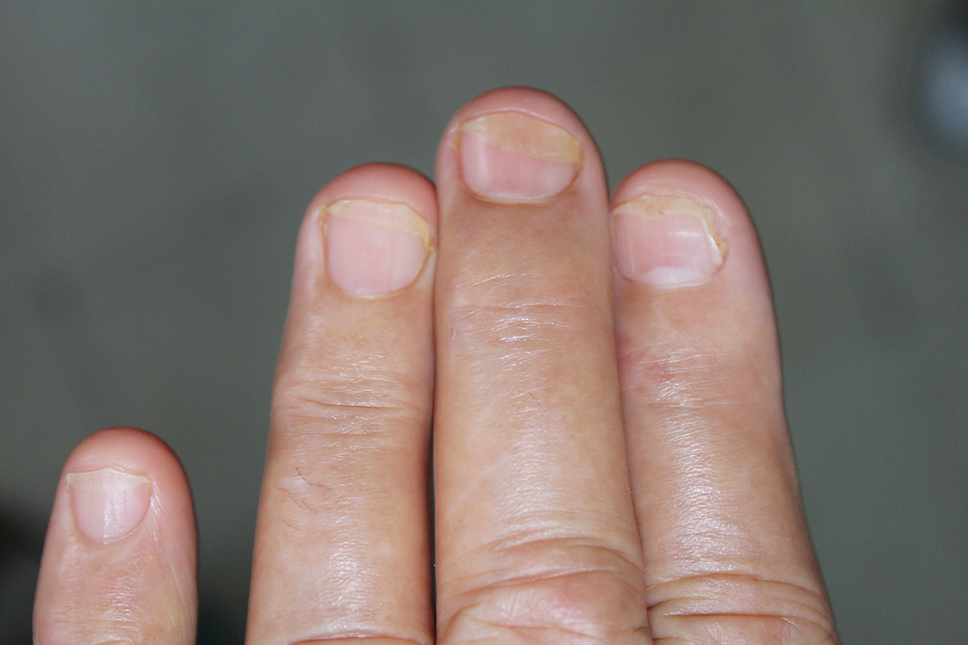
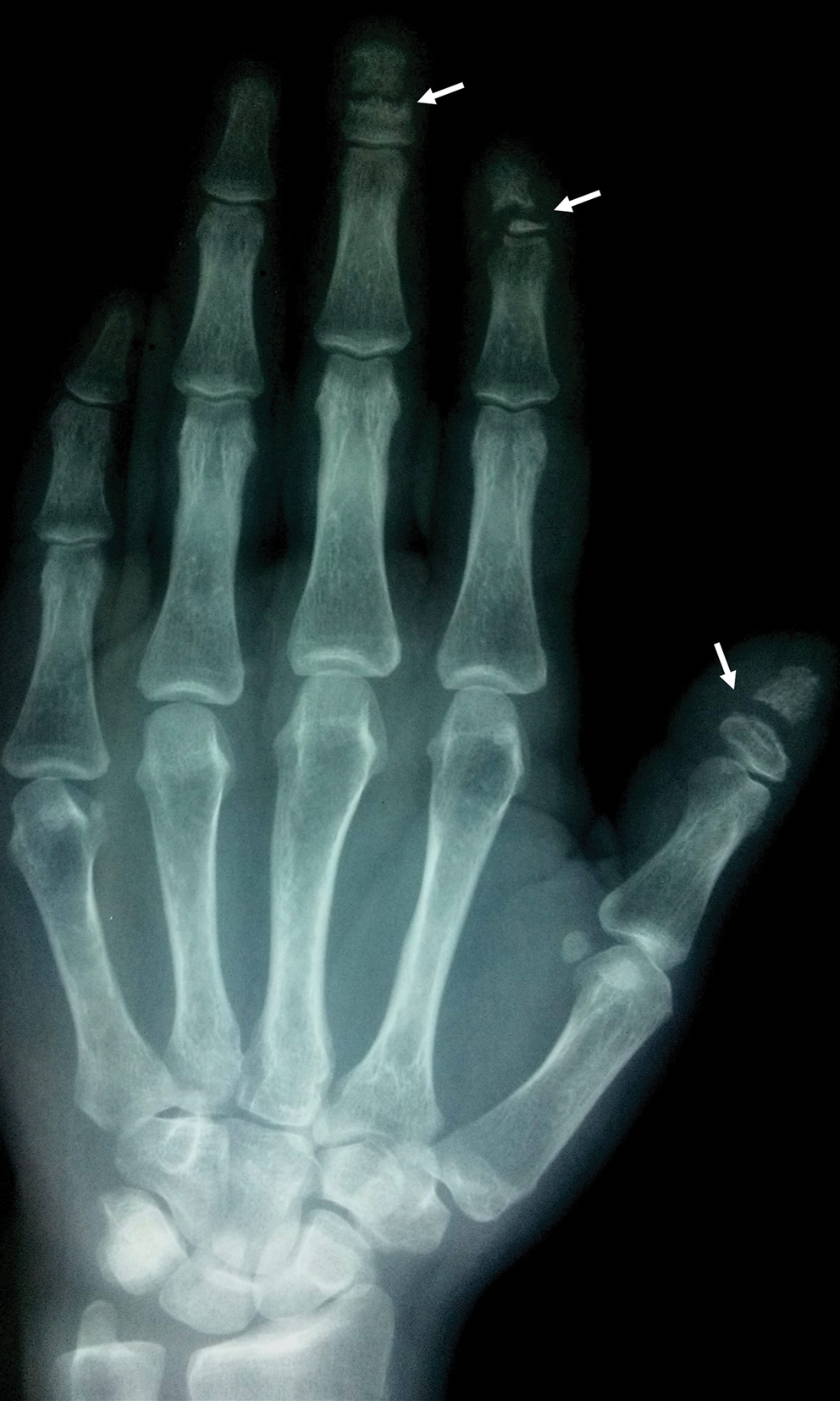
A middle-aged professional concert pianist presented with paronychia with hyperkeratosis of the lateral nail fold. Histopathology revealed a subungual keratoacanthoma eroding the distal phalanx tip, which was removed by surgical excision. The repeated fingertip trauma associated with pianistic activity was suspected to be the causative event.16
Callosities also are common on the fingertips of musicians, including 18.4% of patients in a cohort of 628 musicians, and involving fingers in 64.6% of these patients.4 These callosities are explained by the chronic mechanical forces and characterize the way musicians grasp and hold their instruments. Callosities could be preceded by soreness and blisters of the fingertips in a harpist (harpist’s finger).1,15 Calluses were located on the lateral fourth fingertip of a drummer corresponding to the friction with the drumsticks (drummer’s digit) and on the thumb of a bassoon player. Trumpet calluses generally overlie the proximal interphalangeal joint of the left index finger.
Conclusion
Healthy nails are essential for playing a musical instrument. This review highlights the occurrence of fingertip callosities, paronychia, onycholysis, and subungual hemorrhages among musicians who play instruments. Additionally, the transmission of string-vibratory movements can produce microvascular damage and occupational Raynaud phenomenon in some musicians. These occupational nail disorders are underrecognized and may be underdiagnosed. Thus, musicians and clinicians must be aware of these alterations to adopt preventive measures and to provide adequate treatment.
- Rimmer S, Spielvogel RL. Dermatologic problems of musicians. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:657-663.
- Adams RM. Skin conditions of musicians. Cutis. 2000;65:37-38.
- Vine K, DeLeo V. Dermatologic manifestations of musicians: a case report and review of skin conditions in musicians. Cutis. 2011;87:117-121.
- Patruno C, Napolitano M, La Bella S, et al. Instrument-related skin disorders in musicians. Dermatitis. 2016;27:26-29.
- Baccouche D, Mokni M, Ben Abdelaziz A, et al. Dermatological problems of musicians: a prospective study in musical students . Article in French. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2007;134(5 Pt 1):445-449.
- Piraccini BM, Antonucci A, Iorizzo M, et al. Occupational nail fragility in a professional violist. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:35-36.
- Wu JJ. Habit tic deformity secondary to guitar playing. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:16.
- Kluger N. Piano glissando purpura: another cutaneous curiosity in musicians. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:683.
- Alcántara-Nicolás FA, Pastor-Nieto MA, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acrylic nails in a flamenco guitarist. Occup Med (Lond). 2016;66:751-753.
- Baran R, Tosti A. Occupational acroosteolysis in a guitar player. Acta Derm Venereol. 1993;73:64-65.
- Destouet JM, Murphy WA. Guitar player acro-osteolysis. Skeletal Radiol. 1981;6:275-277.
- Jepsen JR, Simonsen JA. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a slap bass player: a case report. Med Probl Perform Art. 2016;31:51-53.
- Sirufo MM, Catalogna A, De Pietro F, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a drummer player: microvascular disorder and nailfold video capillaroscopic findings. EXCLI J. 2021;20:1526-1531.
- Sirufo MM, Ginaldi L, De Martinis M. Raynaud’s phenomenon and the nailfold capillaroscopic findings in a guitar player. QJM. 2019;112:531-533.
- Cohen PR. Harpist’s finger: case report of a trauma-induced blister in a beginner harpist and review of string instrument-associated skin problems in musicians. Cutis. 2008;82:329-334.
- De Vasconcelos P, Soares-Almeida L, Filipe P. Subungual keratoacanthoma in a pianist. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:455-456.
- Young RS, Bryk D, Ratner H. Selective phalangeal tuft fractures in a guitar player. Br J Radiol. 1977;50:147-148.
- Vázquez-Osorio I, Espasandín-Arias M, García-Gavín J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to acrylates in acrylic gel nails: a report of 3 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:430-432.
- Atashpaz S, Ghabili K. Color triad in guitarist’s fingers: a probable case of Raynaud’s phenomenon due to string vibration phenomenon. Med Probl Perform Art. 2008;23:143.
A variety of skin problems can occur in musicians due to the repetitive movements of playing instruments.1,2 Musicians’ nails are continuously exposed to the mechanical forces and chemical substances characteristic of their instruments.3 Occupational nail alterations in musicians caused by repetitive physical trauma, allergic contact dermatitis, and/or infection may lead to disability and compromise their professional career.
We conducted a systematic review of the literature on the clinical features of musical instrument–related nail alterations to optimize the management and prevention of these conditions.
Methods
We conducted a systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases for eligible publications on instrument-related nail alterations in musicians using the search terms musicians with nail, onychopathy, and Raynaud. No time or language criteria were applied. Reviews, editorials, and articles not related to the topic were excluded. Bibliographies/reference lists were checked to find any additional relevant publications. Relevant articles in English and French were screened by 2 independent reviewers (A.G. and N.L.), and the following data were extracted for qualitative synthesis: sex, age, musical instrument, clinical features, number of years practicing the instrument, laboratory investigations, and disease course.
Results
The literature search yielded 11 publications. Sixteen additional articles were identified by other methods (ie, references, related publications). Overall, 3 full-text articles described general nail alterations but did not describe the clinical data, and 11 publications were editorials, commentaries, reviews, or not relevant. Thirteen contributions fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were eligible for qualitative synthesis. The flow diagram illustrates the screening process (Figure 1).

Twenty-three patients were included. The instruments identified were divided into 2 groups: string instruments (ie, guitar, violin, harp) and percussion instruments (ie, drums, piano, slap bass). Nail alterations were clinically expressed as: (1) modifications of the nail surface; (2) nail bed, soft-tissue, and bone abnormalities; and (3) periungual tissue and distal pulp disorders. All cases are summarized in the Table.4-16 Three articles described occupational Raynaud phenomenon.12-14
Comment
Modifications of the Nail Surface—Onychodystrophy, such as deformity or discoloration of the nail plate, was described in 6 patients among a cohort of 295 musicians and an additional 6 patients among 199 musicians with induced skin lesions. This condition was most common in string instrument players and pianists due to injury and irritation.
One patient, who had been a professional violist for 27 years, presented with lamellar onychoschizia, which corresponds to a horizontal splitting of the nail toward its distal portion (Figure 2). The 3 fingernails of the dominant hand were involved with a V-shaped incision of the distal margin of the nail due to the repetitive friction of the nails with the strings.6
Striations of the nail plate were reported in a guitarist who played for 10 years.7 Physical examination revealed linear transverse ridges alternating with depressions on the central aspect of the nail plate of the right thumbnail, as the patient was right-handed. This condition, attributed to sustained pressure on the string applied by the thumb, also has been called habit tic deformity.7
Nail Bed, Soft-Tissue, and Bone Lesions—Purpura (or hemorrhage) of the nail bed was associated with a percussion instrument (ie, piano) in 1 patient, affecting the second, third, and fourth fingernails of the right hand.8 Especially when performing ascending glissando passages, the pianist applies pressure that may damage the finger and cause fingernail purpura. This condition improved after the patient stopping practicing glissandi.8


Three patients—2 guitarists and 1 violist—had onycholysis, defined by a loss of the attachment between the nail bed and the nail plate (Figure 3). It may result from repetitive trauma when strings are plucked.6,9,10
Acro-osteolysis associated with pain was reported in 2 guitarists.10,11 This condition is defined as transverse lytic bands in the distal phalanges (Figure 4). Acro-osteolysis may be secondary to multiple causes, such as vinyl chloride exposure, connective tissue diseases, thermal injuries, neuropathic diseases, hyperparathyroidism, nutritional deficiencies, psoriasis, and biomechanical stress.10 In musicians playing instruments, the mechanical stress to the guitar-playing fingers is the causative factor.17
Periungual Tissue and Distal Pulp Disorders—Paronychia is an important occupational hazard of harpists, violists, and pianists.2 It represents an inflammatory condition involving the folds of tissue surrounding fingernails. Pizzicato paronychia is related to infection in the nail fold in string players and secondary to pizzicato playing, whereby the musician plucks the instrument strings with the nails and fingertips.3
Acrylates in artificial nails frequently are used among guitarists to strengthen their nails. A case of occupational allergic contact dermatitis induced by acrylic gel nails in a flamenco guitarist was described.9 The patient developed dystrophy, onycholysis, and paronychia involving the nails of the right hand where acrylic materials were used, which resolved following the removal of the artificial nails. Patch tests were performed and were positive for 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate, supporting the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis to acrylates.9 Therefore, musicians should be aware of the sensitizing potential of acrylates and adopt preventive measures.
Unilateral Raynaud phenomenon of the dominant hand was noted in 3 cases of musicians who played string instruments due to the increased tendency to vasospasm in the digital capillaries from the direct transmission of vibrations of the strings (>100 Hz).12-14 Consequently, the disruption of the digital blood circulation leads to an abnormal reaction to cold, which is called vibration-induced white fingers or vasospastic white finger disease.19 In these 3 patients, capillaroscopy showed a nonspecific pattern with a lack of morphologic homogeneity of capillaries, the presence of enlarged capillaries, ectasia of the efferent tract of the loops, tortuous capillaries, local hemorrhages, and neoangiogenesis.13,14


A middle-aged professional concert pianist presented with paronychia with hyperkeratosis of the lateral nail fold. Histopathology revealed a subungual keratoacanthoma eroding the distal phalanx tip, which was removed by surgical excision. The repeated fingertip trauma associated with pianistic activity was suspected to be the causative event.16
Callosities also are common on the fingertips of musicians, including 18.4% of patients in a cohort of 628 musicians, and involving fingers in 64.6% of these patients.4 These callosities are explained by the chronic mechanical forces and characterize the way musicians grasp and hold their instruments. Callosities could be preceded by soreness and blisters of the fingertips in a harpist (harpist’s finger).1,15 Calluses were located on the lateral fourth fingertip of a drummer corresponding to the friction with the drumsticks (drummer’s digit) and on the thumb of a bassoon player. Trumpet calluses generally overlie the proximal interphalangeal joint of the left index finger.
Conclusion
Healthy nails are essential for playing a musical instrument. This review highlights the occurrence of fingertip callosities, paronychia, onycholysis, and subungual hemorrhages among musicians who play instruments. Additionally, the transmission of string-vibratory movements can produce microvascular damage and occupational Raynaud phenomenon in some musicians. These occupational nail disorders are underrecognized and may be underdiagnosed. Thus, musicians and clinicians must be aware of these alterations to adopt preventive measures and to provide adequate treatment.
A variety of skin problems can occur in musicians due to the repetitive movements of playing instruments.1,2 Musicians’ nails are continuously exposed to the mechanical forces and chemical substances characteristic of their instruments.3 Occupational nail alterations in musicians caused by repetitive physical trauma, allergic contact dermatitis, and/or infection may lead to disability and compromise their professional career.
We conducted a systematic review of the literature on the clinical features of musical instrument–related nail alterations to optimize the management and prevention of these conditions.
Methods
We conducted a systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases for eligible publications on instrument-related nail alterations in musicians using the search terms musicians with nail, onychopathy, and Raynaud. No time or language criteria were applied. Reviews, editorials, and articles not related to the topic were excluded. Bibliographies/reference lists were checked to find any additional relevant publications. Relevant articles in English and French were screened by 2 independent reviewers (A.G. and N.L.), and the following data were extracted for qualitative synthesis: sex, age, musical instrument, clinical features, number of years practicing the instrument, laboratory investigations, and disease course.
Results
The literature search yielded 11 publications. Sixteen additional articles were identified by other methods (ie, references, related publications). Overall, 3 full-text articles described general nail alterations but did not describe the clinical data, and 11 publications were editorials, commentaries, reviews, or not relevant. Thirteen contributions fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were eligible for qualitative synthesis. The flow diagram illustrates the screening process (Figure 1).

Twenty-three patients were included. The instruments identified were divided into 2 groups: string instruments (ie, guitar, violin, harp) and percussion instruments (ie, drums, piano, slap bass). Nail alterations were clinically expressed as: (1) modifications of the nail surface; (2) nail bed, soft-tissue, and bone abnormalities; and (3) periungual tissue and distal pulp disorders. All cases are summarized in the Table.4-16 Three articles described occupational Raynaud phenomenon.12-14
Comment
Modifications of the Nail Surface—Onychodystrophy, such as deformity or discoloration of the nail plate, was described in 6 patients among a cohort of 295 musicians and an additional 6 patients among 199 musicians with induced skin lesions. This condition was most common in string instrument players and pianists due to injury and irritation.
One patient, who had been a professional violist for 27 years, presented with lamellar onychoschizia, which corresponds to a horizontal splitting of the nail toward its distal portion (Figure 2). The 3 fingernails of the dominant hand were involved with a V-shaped incision of the distal margin of the nail due to the repetitive friction of the nails with the strings.6
Striations of the nail plate were reported in a guitarist who played for 10 years.7 Physical examination revealed linear transverse ridges alternating with depressions on the central aspect of the nail plate of the right thumbnail, as the patient was right-handed. This condition, attributed to sustained pressure on the string applied by the thumb, also has been called habit tic deformity.7
Nail Bed, Soft-Tissue, and Bone Lesions—Purpura (or hemorrhage) of the nail bed was associated with a percussion instrument (ie, piano) in 1 patient, affecting the second, third, and fourth fingernails of the right hand.8 Especially when performing ascending glissando passages, the pianist applies pressure that may damage the finger and cause fingernail purpura. This condition improved after the patient stopping practicing glissandi.8


Three patients—2 guitarists and 1 violist—had onycholysis, defined by a loss of the attachment between the nail bed and the nail plate (Figure 3). It may result from repetitive trauma when strings are plucked.6,9,10
Acro-osteolysis associated with pain was reported in 2 guitarists.10,11 This condition is defined as transverse lytic bands in the distal phalanges (Figure 4). Acro-osteolysis may be secondary to multiple causes, such as vinyl chloride exposure, connective tissue diseases, thermal injuries, neuropathic diseases, hyperparathyroidism, nutritional deficiencies, psoriasis, and biomechanical stress.10 In musicians playing instruments, the mechanical stress to the guitar-playing fingers is the causative factor.17
Periungual Tissue and Distal Pulp Disorders—Paronychia is an important occupational hazard of harpists, violists, and pianists.2 It represents an inflammatory condition involving the folds of tissue surrounding fingernails. Pizzicato paronychia is related to infection in the nail fold in string players and secondary to pizzicato playing, whereby the musician plucks the instrument strings with the nails and fingertips.3
Acrylates in artificial nails frequently are used among guitarists to strengthen their nails. A case of occupational allergic contact dermatitis induced by acrylic gel nails in a flamenco guitarist was described.9 The patient developed dystrophy, onycholysis, and paronychia involving the nails of the right hand where acrylic materials were used, which resolved following the removal of the artificial nails. Patch tests were performed and were positive for 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate, supporting the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis to acrylates.9 Therefore, musicians should be aware of the sensitizing potential of acrylates and adopt preventive measures.
Unilateral Raynaud phenomenon of the dominant hand was noted in 3 cases of musicians who played string instruments due to the increased tendency to vasospasm in the digital capillaries from the direct transmission of vibrations of the strings (>100 Hz).12-14 Consequently, the disruption of the digital blood circulation leads to an abnormal reaction to cold, which is called vibration-induced white fingers or vasospastic white finger disease.19 In these 3 patients, capillaroscopy showed a nonspecific pattern with a lack of morphologic homogeneity of capillaries, the presence of enlarged capillaries, ectasia of the efferent tract of the loops, tortuous capillaries, local hemorrhages, and neoangiogenesis.13,14


A middle-aged professional concert pianist presented with paronychia with hyperkeratosis of the lateral nail fold. Histopathology revealed a subungual keratoacanthoma eroding the distal phalanx tip, which was removed by surgical excision. The repeated fingertip trauma associated with pianistic activity was suspected to be the causative event.16
Callosities also are common on the fingertips of musicians, including 18.4% of patients in a cohort of 628 musicians, and involving fingers in 64.6% of these patients.4 These callosities are explained by the chronic mechanical forces and characterize the way musicians grasp and hold their instruments. Callosities could be preceded by soreness and blisters of the fingertips in a harpist (harpist’s finger).1,15 Calluses were located on the lateral fourth fingertip of a drummer corresponding to the friction with the drumsticks (drummer’s digit) and on the thumb of a bassoon player. Trumpet calluses generally overlie the proximal interphalangeal joint of the left index finger.
Conclusion
Healthy nails are essential for playing a musical instrument. This review highlights the occurrence of fingertip callosities, paronychia, onycholysis, and subungual hemorrhages among musicians who play instruments. Additionally, the transmission of string-vibratory movements can produce microvascular damage and occupational Raynaud phenomenon in some musicians. These occupational nail disorders are underrecognized and may be underdiagnosed. Thus, musicians and clinicians must be aware of these alterations to adopt preventive measures and to provide adequate treatment.
- Rimmer S, Spielvogel RL. Dermatologic problems of musicians. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:657-663.
- Adams RM. Skin conditions of musicians. Cutis. 2000;65:37-38.
- Vine K, DeLeo V. Dermatologic manifestations of musicians: a case report and review of skin conditions in musicians. Cutis. 2011;87:117-121.
- Patruno C, Napolitano M, La Bella S, et al. Instrument-related skin disorders in musicians. Dermatitis. 2016;27:26-29.
- Baccouche D, Mokni M, Ben Abdelaziz A, et al. Dermatological problems of musicians: a prospective study in musical students . Article in French. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2007;134(5 Pt 1):445-449.
- Piraccini BM, Antonucci A, Iorizzo M, et al. Occupational nail fragility in a professional violist. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:35-36.
- Wu JJ. Habit tic deformity secondary to guitar playing. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:16.
- Kluger N. Piano glissando purpura: another cutaneous curiosity in musicians. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:683.
- Alcántara-Nicolás FA, Pastor-Nieto MA, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acrylic nails in a flamenco guitarist. Occup Med (Lond). 2016;66:751-753.
- Baran R, Tosti A. Occupational acroosteolysis in a guitar player. Acta Derm Venereol. 1993;73:64-65.
- Destouet JM, Murphy WA. Guitar player acro-osteolysis. Skeletal Radiol. 1981;6:275-277.
- Jepsen JR, Simonsen JA. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a slap bass player: a case report. Med Probl Perform Art. 2016;31:51-53.
- Sirufo MM, Catalogna A, De Pietro F, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a drummer player: microvascular disorder and nailfold video capillaroscopic findings. EXCLI J. 2021;20:1526-1531.
- Sirufo MM, Ginaldi L, De Martinis M. Raynaud’s phenomenon and the nailfold capillaroscopic findings in a guitar player. QJM. 2019;112:531-533.
- Cohen PR. Harpist’s finger: case report of a trauma-induced blister in a beginner harpist and review of string instrument-associated skin problems in musicians. Cutis. 2008;82:329-334.
- De Vasconcelos P, Soares-Almeida L, Filipe P. Subungual keratoacanthoma in a pianist. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:455-456.
- Young RS, Bryk D, Ratner H. Selective phalangeal tuft fractures in a guitar player. Br J Radiol. 1977;50:147-148.
- Vázquez-Osorio I, Espasandín-Arias M, García-Gavín J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to acrylates in acrylic gel nails: a report of 3 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:430-432.
- Atashpaz S, Ghabili K. Color triad in guitarist’s fingers: a probable case of Raynaud’s phenomenon due to string vibration phenomenon. Med Probl Perform Art. 2008;23:143.
- Rimmer S, Spielvogel RL. Dermatologic problems of musicians. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:657-663.
- Adams RM. Skin conditions of musicians. Cutis. 2000;65:37-38.
- Vine K, DeLeo V. Dermatologic manifestations of musicians: a case report and review of skin conditions in musicians. Cutis. 2011;87:117-121.
- Patruno C, Napolitano M, La Bella S, et al. Instrument-related skin disorders in musicians. Dermatitis. 2016;27:26-29.
- Baccouche D, Mokni M, Ben Abdelaziz A, et al. Dermatological problems of musicians: a prospective study in musical students . Article in French. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2007;134(5 Pt 1):445-449.
- Piraccini BM, Antonucci A, Iorizzo M, et al. Occupational nail fragility in a professional violist. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:35-36.
- Wu JJ. Habit tic deformity secondary to guitar playing. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:16.
- Kluger N. Piano glissando purpura: another cutaneous curiosity in musicians. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:683.
- Alcántara-Nicolás FA, Pastor-Nieto MA, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acrylic nails in a flamenco guitarist. Occup Med (Lond). 2016;66:751-753.
- Baran R, Tosti A. Occupational acroosteolysis in a guitar player. Acta Derm Venereol. 1993;73:64-65.
- Destouet JM, Murphy WA. Guitar player acro-osteolysis. Skeletal Radiol. 1981;6:275-277.
- Jepsen JR, Simonsen JA. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a slap bass player: a case report. Med Probl Perform Art. 2016;31:51-53.
- Sirufo MM, Catalogna A, De Pietro F, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon in a drummer player: microvascular disorder and nailfold video capillaroscopic findings. EXCLI J. 2021;20:1526-1531.
- Sirufo MM, Ginaldi L, De Martinis M. Raynaud’s phenomenon and the nailfold capillaroscopic findings in a guitar player. QJM. 2019;112:531-533.
- Cohen PR. Harpist’s finger: case report of a trauma-induced blister in a beginner harpist and review of string instrument-associated skin problems in musicians. Cutis. 2008;82:329-334.
- De Vasconcelos P, Soares-Almeida L, Filipe P. Subungual keratoacanthoma in a pianist. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:455-456.
- Young RS, Bryk D, Ratner H. Selective phalangeal tuft fractures in a guitar player. Br J Radiol. 1977;50:147-148.
- Vázquez-Osorio I, Espasandín-Arias M, García-Gavín J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to acrylates in acrylic gel nails: a report of 3 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:430-432.
- Atashpaz S, Ghabili K. Color triad in guitarist’s fingers: a probable case of Raynaud’s phenomenon due to string vibration phenomenon. Med Probl Perform Art. 2008;23:143.
Practice Points
- Long-term practice and performance with a musical instrument predispose musicians to several skin conditions and nail disorders.
- Nail alterations in musicians include onychodystrophy, callosities of the fingertips, paronychia, distal onycholysis, lamellar onychoschizia, striations, subungual hemorrhage, and occupational Raynaud phenomenon.
- Nail lesions in musicians may be caused by localized pressure, friction-induced mechanical forces, allergic or irritant contact dermatitis, or infections.
Act Fast With Traction Alopecia to Avoid Permanent Hair Loss
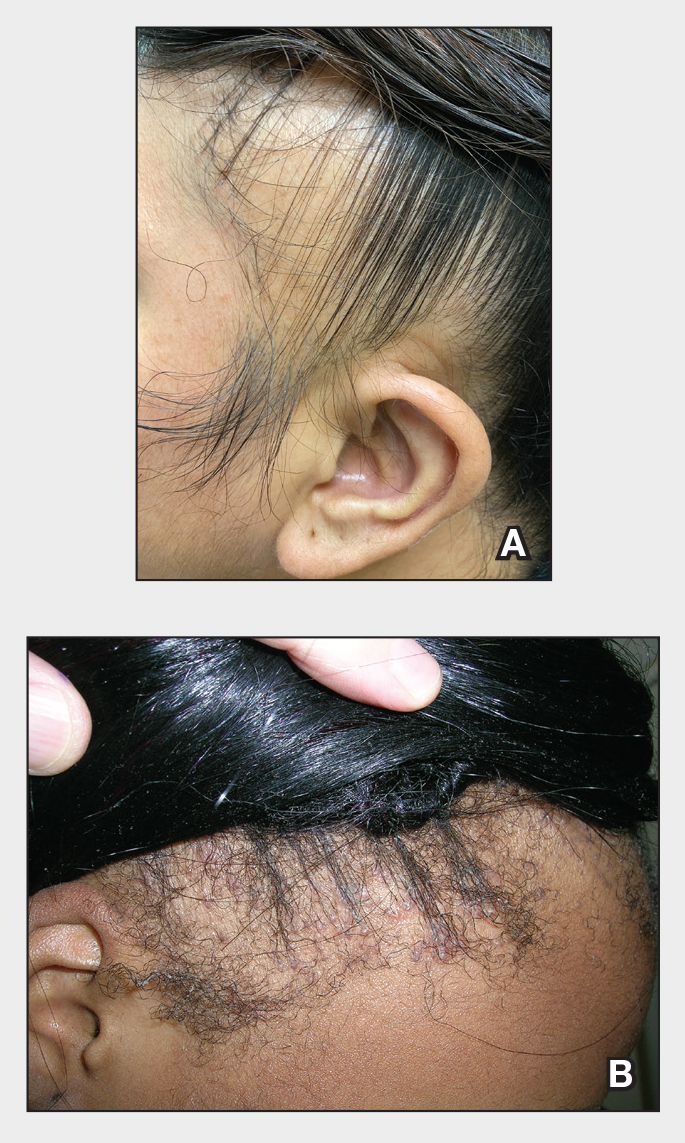
The Comparison
Traction alopecia (TA) is a common type of alopecia that ultimately can result in permanent hair loss. It often is caused or worsened by repetitive and prolonged hairstyling practices such as tight ponytails, braids, or locs, or use of wigs or weaves.1 Use of headwear, as in certain religious or ethnic groups, also can be contributory.2 Individuals participating in or training for occupations involving military service or ballet are at risk for TA due to hairstyling-specific policies. Early stages of TA are reversible with proper treatment and avoidance of exacerbating factors, emphasizing the importance of prompt recognition.3
Epidemiology
Data on the true prevalence of TA are lacking. It can occur in individuals of any race or any hair type. However, it is most common in women of African descent, affecting approximately one-third of this population.4 Other commonly affected groups include ballerinas and active-duty service members due to tight ponytails and buns, as well as the Sikh population due to the use of turbans as a part of their religious practice.2,5,6
Traction alopecia also impacts children, particularly those of African descent. A 2007 study of schoolchildren in South Africa determined that more than 17% of young African girls had evidence of TA—even some as young as 6 years of age.7
Traction alopecia can be caused or exacerbated by the use of hair clips and bobby pins that aid holding styles in place.8
Hair shaft morphology may contribute to the risk for TA, with more tightly coiled hair types being more susceptible.8 Variables such as use of chemical relaxers also increase the risk for disease, especially when combined with high-tension styling methods such as braids.9
Key clinical features
Patients with TA clinically present with hair loss and breakage in areas with tension, most commonly the marginal areas of the scalp as well as the frontal hairline and temporal scalp. Hair loss can result in a “fringe sign,” in which a patient may have preservation of a thin line of hairs at the frontal aspect of the hairline with a band of hair loss behind.10 This presentation may be used to differentiate TA from other forms of alopecia, including frontal fibrosing alopecia and female pattern hair loss. When the hair loss is not marginal, it may mimic other forms of patchy hair loss including alopecia areata and trichotillomania. Other clinical findings in TA may include broken hairs, pustules, and follicular papules.10 Patients also may describe symptoms such as scalp tenderness with specific hairstyles or headaches,11 or they may be completely asymptomatic.
Trichoscopy can be helpful in guiding diagnosis and treatment. Patients with TA often have perifollicular erythema and hair casts (cylindrical structures that encircle the proximal hair shafts) in the earlier stages of the disease, with eventual loss of follicular ostia in the later stages.10,12 Hair casts also may indicate ongoing traction.12 The flambeau sign—white tracks seen on trichoscopy in the direction the hair is pulled—resembles a lit torch.13
Worth noting
Early-stage TA can be reversed by avoiding hair tension. However, patients may not be amenable to this due to personal hairstyling preferences, job duties, or religious practices. Treatment with topical or intralesional steroids or even oral antibiotics such as doxycycline for its anti-inflammatory ability may result in regrowth of lost hair if the follicles are not permanently lost and exacerbating factors are avoided.3,14 Both topical and oral minoxidil have been used with success, with minoxidil thought to increase hair density by extending the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles.3,15 Culturally sensitive patient counseling on the condition and potential exacerbating factors is critical.16
At later stages of the disease—after loss of follicular ostia has occurred—surgical interventions should be considered,17 such as hair transplantation, which can be successful but remains a technical challenge due to variability in hair shaft curvature.18 Additionally, the cost of the procedure can limit use, and some patients may not be optimal candidates due to the extent of their hair loss. Traction alopecia may not be the only hair loss condition present. Examining the scalp is important even if the chief area of concern is the marginal scalp.
Health disparity highlight
Prevention, early identification, and treatment initiated in a timely fashion are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss. There are added societal and cultural pressures that impact hairstyle and hair care practices, especially for those with tightly coiled hair.19 Historically, tightly coiled hair has been unfairly viewed as “unprofessional,” “unkempt,” and a challenge to “manage” by some. Thus, heat, chemical relaxers, and tight hairstyles holding hair in one position have been used to straighten the hair permanently or temporarily or to keep it maintained in a style that did not necessitate excessive manipulation—often contributing to further tension on the hair.
Military service branches have evaluated and changed some hair-related policies to reflect the diverse hair types of military personnel.20 The CROWN Act (www.thecrownact.com/about)—“Creating a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair”—is a model law passed by 26 states that prohibits race-based hair discrimination, which is the denial of employment and educational opportunities because of hair texture. Although the law has not been passed in every state, it may help individuals with tightly coiled hair to embrace natural hairstyles. However, even hairstyles with one’s own natural curl pattern can contribute to tension and thus potential development of TA.
- Larrondo J, McMichael AJ. Traction alopecia. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:676. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.6298
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2007.05.070076
- Callender VD, McMichael AJ, Cohen GF. Medical and surgical therapies for alopecias in black women. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:164-176.
- Loussouarn G, El Rawadi C, Genain G. Diversity of hair growth profiles. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44(suppl 1):6-9.
- Samrao AChen CZedek Det al. Traction alopecia in a ballerina: clinicopathologic features. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:918-935. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.183
- Korona-Bailey J, Banaag A, Nguyen DR, et al. Free the bun: prevalence of alopecia among active duty service women, fiscal years 2010-2019. Mil Med. 2023;188:e492-e496. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab274
- Khumalo NP, Jessop S, Gumedze F, et al. Hairdressing is associated with scalp disease in African schoolchildren. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:106-110. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07987.x
- Billero V, Miteva M. Traction alopecia: the root of the problem. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;11:149-159. doi:10.2147/CCID.S137296
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia (TA). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1162
- Samrao A, Price VH, Zedek D, et al. The “fringe sign”—a useful clinical finding in traction alopecia of the marginal hair line. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Kararizou E, Bougea AM, Giotopoulou D, et al. An update on the less-known group of other primary headaches—a review. Eur Neurol Rev. 2014;9:71-77. doi:10.17925/ENR.2014.09.01.71
- Tosti A, Miteva M, Torres F, et al. Hair casts are a dermoscopic clue for the diagnosis of traction alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1353-1355.
- Agrawal S, Daruwalla SB, Dhurat RS. The flambeau sign—a new dermoscopy finding in a case of marginal traction alopecia. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:49-50. doi:10. 1111/ajd.13187
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Awad A, Chim I, Sharma P, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil improves hair density in traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.024
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.
- Ozçelik D. Extensive traction alopecia attributable to ponytail hairstyle and its treatment with hair transplantation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005;29:325-327. doi:10.1007/s00266-005-0004-5
- Singh MK, Avram MR. Technical considerations for follicular unit extraction in African-American hair. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1282-1284. doi:10.1111/dsu.12229
- Jones NL, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):158-160.
- Franklin JMM, Wohltmann WE, Wong EB. From buns to braids and ponytails: entering a new era of female military hair-grooming standards. Cutis. 2021;108:31-35. doi:10.12788/cutis.0296

The Comparison
Traction alopecia (TA) is a common type of alopecia that ultimately can result in permanent hair loss. It often is caused or worsened by repetitive and prolonged hairstyling practices such as tight ponytails, braids, or locs, or use of wigs or weaves.1 Use of headwear, as in certain religious or ethnic groups, also can be contributory.2 Individuals participating in or training for occupations involving military service or ballet are at risk for TA due to hairstyling-specific policies. Early stages of TA are reversible with proper treatment and avoidance of exacerbating factors, emphasizing the importance of prompt recognition.3
Epidemiology
Data on the true prevalence of TA are lacking. It can occur in individuals of any race or any hair type. However, it is most common in women of African descent, affecting approximately one-third of this population.4 Other commonly affected groups include ballerinas and active-duty service members due to tight ponytails and buns, as well as the Sikh population due to the use of turbans as a part of their religious practice.2,5,6
Traction alopecia also impacts children, particularly those of African descent. A 2007 study of schoolchildren in South Africa determined that more than 17% of young African girls had evidence of TA—even some as young as 6 years of age.7
Traction alopecia can be caused or exacerbated by the use of hair clips and bobby pins that aid holding styles in place.8
Hair shaft morphology may contribute to the risk for TA, with more tightly coiled hair types being more susceptible.8 Variables such as use of chemical relaxers also increase the risk for disease, especially when combined with high-tension styling methods such as braids.9
Key clinical features
Patients with TA clinically present with hair loss and breakage in areas with tension, most commonly the marginal areas of the scalp as well as the frontal hairline and temporal scalp. Hair loss can result in a “fringe sign,” in which a patient may have preservation of a thin line of hairs at the frontal aspect of the hairline with a band of hair loss behind.10 This presentation may be used to differentiate TA from other forms of alopecia, including frontal fibrosing alopecia and female pattern hair loss. When the hair loss is not marginal, it may mimic other forms of patchy hair loss including alopecia areata and trichotillomania. Other clinical findings in TA may include broken hairs, pustules, and follicular papules.10 Patients also may describe symptoms such as scalp tenderness with specific hairstyles or headaches,11 or they may be completely asymptomatic.
Trichoscopy can be helpful in guiding diagnosis and treatment. Patients with TA often have perifollicular erythema and hair casts (cylindrical structures that encircle the proximal hair shafts) in the earlier stages of the disease, with eventual loss of follicular ostia in the later stages.10,12 Hair casts also may indicate ongoing traction.12 The flambeau sign—white tracks seen on trichoscopy in the direction the hair is pulled—resembles a lit torch.13
Worth noting
Early-stage TA can be reversed by avoiding hair tension. However, patients may not be amenable to this due to personal hairstyling preferences, job duties, or religious practices. Treatment with topical or intralesional steroids or even oral antibiotics such as doxycycline for its anti-inflammatory ability may result in regrowth of lost hair if the follicles are not permanently lost and exacerbating factors are avoided.3,14 Both topical and oral minoxidil have been used with success, with minoxidil thought to increase hair density by extending the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles.3,15 Culturally sensitive patient counseling on the condition and potential exacerbating factors is critical.16
At later stages of the disease—after loss of follicular ostia has occurred—surgical interventions should be considered,17 such as hair transplantation, which can be successful but remains a technical challenge due to variability in hair shaft curvature.18 Additionally, the cost of the procedure can limit use, and some patients may not be optimal candidates due to the extent of their hair loss. Traction alopecia may not be the only hair loss condition present. Examining the scalp is important even if the chief area of concern is the marginal scalp.
Health disparity highlight
Prevention, early identification, and treatment initiated in a timely fashion are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss. There are added societal and cultural pressures that impact hairstyle and hair care practices, especially for those with tightly coiled hair.19 Historically, tightly coiled hair has been unfairly viewed as “unprofessional,” “unkempt,” and a challenge to “manage” by some. Thus, heat, chemical relaxers, and tight hairstyles holding hair in one position have been used to straighten the hair permanently or temporarily or to keep it maintained in a style that did not necessitate excessive manipulation—often contributing to further tension on the hair.
Military service branches have evaluated and changed some hair-related policies to reflect the diverse hair types of military personnel.20 The CROWN Act (www.thecrownact.com/about)—“Creating a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair”—is a model law passed by 26 states that prohibits race-based hair discrimination, which is the denial of employment and educational opportunities because of hair texture. Although the law has not been passed in every state, it may help individuals with tightly coiled hair to embrace natural hairstyles. However, even hairstyles with one’s own natural curl pattern can contribute to tension and thus potential development of TA.

The Comparison
Traction alopecia (TA) is a common type of alopecia that ultimately can result in permanent hair loss. It often is caused or worsened by repetitive and prolonged hairstyling practices such as tight ponytails, braids, or locs, or use of wigs or weaves.1 Use of headwear, as in certain religious or ethnic groups, also can be contributory.2 Individuals participating in or training for occupations involving military service or ballet are at risk for TA due to hairstyling-specific policies. Early stages of TA are reversible with proper treatment and avoidance of exacerbating factors, emphasizing the importance of prompt recognition.3
Epidemiology
Data on the true prevalence of TA are lacking. It can occur in individuals of any race or any hair type. However, it is most common in women of African descent, affecting approximately one-third of this population.4 Other commonly affected groups include ballerinas and active-duty service members due to tight ponytails and buns, as well as the Sikh population due to the use of turbans as a part of their religious practice.2,5,6
Traction alopecia also impacts children, particularly those of African descent. A 2007 study of schoolchildren in South Africa determined that more than 17% of young African girls had evidence of TA—even some as young as 6 years of age.7
Traction alopecia can be caused or exacerbated by the use of hair clips and bobby pins that aid holding styles in place.8
Hair shaft morphology may contribute to the risk for TA, with more tightly coiled hair types being more susceptible.8 Variables such as use of chemical relaxers also increase the risk for disease, especially when combined with high-tension styling methods such as braids.9
Key clinical features
Patients with TA clinically present with hair loss and breakage in areas with tension, most commonly the marginal areas of the scalp as well as the frontal hairline and temporal scalp. Hair loss can result in a “fringe sign,” in which a patient may have preservation of a thin line of hairs at the frontal aspect of the hairline with a band of hair loss behind.10 This presentation may be used to differentiate TA from other forms of alopecia, including frontal fibrosing alopecia and female pattern hair loss. When the hair loss is not marginal, it may mimic other forms of patchy hair loss including alopecia areata and trichotillomania. Other clinical findings in TA may include broken hairs, pustules, and follicular papules.10 Patients also may describe symptoms such as scalp tenderness with specific hairstyles or headaches,11 or they may be completely asymptomatic.
Trichoscopy can be helpful in guiding diagnosis and treatment. Patients with TA often have perifollicular erythema and hair casts (cylindrical structures that encircle the proximal hair shafts) in the earlier stages of the disease, with eventual loss of follicular ostia in the later stages.10,12 Hair casts also may indicate ongoing traction.12 The flambeau sign—white tracks seen on trichoscopy in the direction the hair is pulled—resembles a lit torch.13
Worth noting
Early-stage TA can be reversed by avoiding hair tension. However, patients may not be amenable to this due to personal hairstyling preferences, job duties, or religious practices. Treatment with topical or intralesional steroids or even oral antibiotics such as doxycycline for its anti-inflammatory ability may result in regrowth of lost hair if the follicles are not permanently lost and exacerbating factors are avoided.3,14 Both topical and oral minoxidil have been used with success, with minoxidil thought to increase hair density by extending the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles.3,15 Culturally sensitive patient counseling on the condition and potential exacerbating factors is critical.16
At later stages of the disease—after loss of follicular ostia has occurred—surgical interventions should be considered,17 such as hair transplantation, which can be successful but remains a technical challenge due to variability in hair shaft curvature.18 Additionally, the cost of the procedure can limit use, and some patients may not be optimal candidates due to the extent of their hair loss. Traction alopecia may not be the only hair loss condition present. Examining the scalp is important even if the chief area of concern is the marginal scalp.
Health disparity highlight
Prevention, early identification, and treatment initiated in a timely fashion are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss. There are added societal and cultural pressures that impact hairstyle and hair care practices, especially for those with tightly coiled hair.19 Historically, tightly coiled hair has been unfairly viewed as “unprofessional,” “unkempt,” and a challenge to “manage” by some. Thus, heat, chemical relaxers, and tight hairstyles holding hair in one position have been used to straighten the hair permanently or temporarily or to keep it maintained in a style that did not necessitate excessive manipulation—often contributing to further tension on the hair.
Military service branches have evaluated and changed some hair-related policies to reflect the diverse hair types of military personnel.20 The CROWN Act (www.thecrownact.com/about)—“Creating a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair”—is a model law passed by 26 states that prohibits race-based hair discrimination, which is the denial of employment and educational opportunities because of hair texture. Although the law has not been passed in every state, it may help individuals with tightly coiled hair to embrace natural hairstyles. However, even hairstyles with one’s own natural curl pattern can contribute to tension and thus potential development of TA.
- Larrondo J, McMichael AJ. Traction alopecia. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:676. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.6298
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2007.05.070076
- Callender VD, McMichael AJ, Cohen GF. Medical and surgical therapies for alopecias in black women. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:164-176.
- Loussouarn G, El Rawadi C, Genain G. Diversity of hair growth profiles. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44(suppl 1):6-9.
- Samrao AChen CZedek Det al. Traction alopecia in a ballerina: clinicopathologic features. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:918-935. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.183
- Korona-Bailey J, Banaag A, Nguyen DR, et al. Free the bun: prevalence of alopecia among active duty service women, fiscal years 2010-2019. Mil Med. 2023;188:e492-e496. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab274
- Khumalo NP, Jessop S, Gumedze F, et al. Hairdressing is associated with scalp disease in African schoolchildren. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:106-110. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07987.x
- Billero V, Miteva M. Traction alopecia: the root of the problem. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;11:149-159. doi:10.2147/CCID.S137296
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia (TA). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1162
- Samrao A, Price VH, Zedek D, et al. The “fringe sign”—a useful clinical finding in traction alopecia of the marginal hair line. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Kararizou E, Bougea AM, Giotopoulou D, et al. An update on the less-known group of other primary headaches—a review. Eur Neurol Rev. 2014;9:71-77. doi:10.17925/ENR.2014.09.01.71
- Tosti A, Miteva M, Torres F, et al. Hair casts are a dermoscopic clue for the diagnosis of traction alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1353-1355.
- Agrawal S, Daruwalla SB, Dhurat RS. The flambeau sign—a new dermoscopy finding in a case of marginal traction alopecia. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:49-50. doi:10. 1111/ajd.13187
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Awad A, Chim I, Sharma P, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil improves hair density in traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.024
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.
- Ozçelik D. Extensive traction alopecia attributable to ponytail hairstyle and its treatment with hair transplantation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005;29:325-327. doi:10.1007/s00266-005-0004-5
- Singh MK, Avram MR. Technical considerations for follicular unit extraction in African-American hair. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1282-1284. doi:10.1111/dsu.12229
- Jones NL, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):158-160.
- Franklin JMM, Wohltmann WE, Wong EB. From buns to braids and ponytails: entering a new era of female military hair-grooming standards. Cutis. 2021;108:31-35. doi:10.12788/cutis.0296
- Larrondo J, McMichael AJ. Traction alopecia. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:676. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.6298
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2007.05.070076
- Callender VD, McMichael AJ, Cohen GF. Medical and surgical therapies for alopecias in black women. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:164-176.
- Loussouarn G, El Rawadi C, Genain G. Diversity of hair growth profiles. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44(suppl 1):6-9.
- Samrao AChen CZedek Det al. Traction alopecia in a ballerina: clinicopathologic features. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:918-935. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.183
- Korona-Bailey J, Banaag A, Nguyen DR, et al. Free the bun: prevalence of alopecia among active duty service women, fiscal years 2010-2019. Mil Med. 2023;188:e492-e496. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab274
- Khumalo NP, Jessop S, Gumedze F, et al. Hairdressing is associated with scalp disease in African schoolchildren. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:106-110. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07987.x
- Billero V, Miteva M. Traction alopecia: the root of the problem. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;11:149-159. doi:10.2147/CCID.S137296
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia (TA). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1162
- Samrao A, Price VH, Zedek D, et al. The “fringe sign”—a useful clinical finding in traction alopecia of the marginal hair line. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Kararizou E, Bougea AM, Giotopoulou D, et al. An update on the less-known group of other primary headaches—a review. Eur Neurol Rev. 2014;9:71-77. doi:10.17925/ENR.2014.09.01.71
- Tosti A, Miteva M, Torres F, et al. Hair casts are a dermoscopic clue for the diagnosis of traction alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1353-1355.
- Agrawal S, Daruwalla SB, Dhurat RS. The flambeau sign—a new dermoscopy finding in a case of marginal traction alopecia. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:49-50. doi:10. 1111/ajd.13187
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Awad A, Chim I, Sharma P, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil improves hair density in traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.024
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.
- Ozçelik D. Extensive traction alopecia attributable to ponytail hairstyle and its treatment with hair transplantation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005;29:325-327. doi:10.1007/s00266-005-0004-5
- Singh MK, Avram MR. Technical considerations for follicular unit extraction in African-American hair. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1282-1284. doi:10.1111/dsu.12229
- Jones NL, Heath CR. Hair at the intersection of dermatology and anthropology: a conversation on race and relationships. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):158-160.
- Franklin JMM, Wohltmann WE, Wong EB. From buns to braids and ponytails: entering a new era of female military hair-grooming standards. Cutis. 2021;108:31-35. doi:10.12788/cutis.0296