User login
Handheld device highly sensitive in detecting amblyopia; can be used in children as young as 2 years of age
A handheld vision screening device to test for amblyopia and strabismus has been found to have a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 85%, and a median acquisition time of 28 seconds, according to a study published in the Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus.
The prospective study involved 300 children recruited from two Kaiser Permanente Southern California pediatric clinics. The patients, aged 24-72 months, were first screened by trained research staff for amblyopia and strabismus using the device, called the Pediatric Vision Scanner (PVS). They were subsequently screened by a pediatric ophthalmologist who was masked to the previous screening results and who then performed a comprehensive eye examination.
With the gold-standard ophthalmologist examination, six children (2%) were identified as having amblyopia and/or strabismus. Using the PVS, all six children with amblyopia and/or strabismus were identified, yielding 100% sensitivity. PVS findings were normal for 45 children (15%), yielding a specificity rate of 85%. The positive predictive value was 26.0% (95% confidence interval, 12.4%-32.4%), and the negative predictive value was 100% (95% CI, 97.1%-100%).
The findings suggest that the device could be used to screen for amblyopia, according to Shaival S. Shah, MD, the study’s first author, who is a pediatric ophthalmologist and regional section lead of pediatric ophthalmology, Southern California Permanente Medical Group.
“A strength of this device is that it is user friendly and easy to use and very quick, which is essential when working with young children,” said Dr. Shah in an interview. He noted that the device could be used for children as young as 2 years.
Dr. Shah pointed out that the children were recruited from a pediatrician’s office and reflect more of a “real-world setting” than had they been recruited from a pediatric ophthalmology clinic.
Dr. Shah added that, with a negative predictive value of 100%, the device is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present. “It did have a positive predictive value of 26%, which needs to be considered when deciding one’s vision screening strategy,” he said.
A limitation of the study is that there was no head-to-head comparison with another screening device, noted Dr. Shah. “While it may have been more useful to include another vision screening device to have a head-to-head comparison, we did not do this to limit complexity and cost.”
Michael J. Wan, MD, FRCSC, pediatric ophthalmologist, Sick Kids Hospital, Toronto, and assistant professor at the University of Toronto, told this news organization that the device has multiple strengths, including quick acquisition time and excellent detection rate of amblyopia and strabismus in children as young as 2 years.
“It is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present,” said Dr. Wan, who was not involved in the study. “The PVS uses an elegant mechanism to test for amblyopia directly (as opposed to other screening devices, which only detect risk factors). This study demonstrates the impressive diagnostic accuracy of this approach. With a study population of 300 children, the PVS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 85% (over 90% in cooperative children). This means that the PVS would detect essentially all cases of amblyopia and strabismus while minimizing the number of unnecessary referrals and examinations.”
He added that, although the study included children as young as 2 years, only 2.5% of the children were unable to complete the PVS test. “Detecting amblyopia in children at an age when treatment is still effective has been a longstanding goal in pediatric ophthalmology,” said Dr. Wan, who described the technology as user friendly. “Based on this study, the search for an accurate and practical pediatric vision screening device appears to be over.”
Dr. Wan said it would be useful to replicate this study with a different population to confirm the findings.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Wan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handheld vision screening device to test for amblyopia and strabismus has been found to have a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 85%, and a median acquisition time of 28 seconds, according to a study published in the Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus.
The prospective study involved 300 children recruited from two Kaiser Permanente Southern California pediatric clinics. The patients, aged 24-72 months, were first screened by trained research staff for amblyopia and strabismus using the device, called the Pediatric Vision Scanner (PVS). They were subsequently screened by a pediatric ophthalmologist who was masked to the previous screening results and who then performed a comprehensive eye examination.
With the gold-standard ophthalmologist examination, six children (2%) were identified as having amblyopia and/or strabismus. Using the PVS, all six children with amblyopia and/or strabismus were identified, yielding 100% sensitivity. PVS findings were normal for 45 children (15%), yielding a specificity rate of 85%. The positive predictive value was 26.0% (95% confidence interval, 12.4%-32.4%), and the negative predictive value was 100% (95% CI, 97.1%-100%).
The findings suggest that the device could be used to screen for amblyopia, according to Shaival S. Shah, MD, the study’s first author, who is a pediatric ophthalmologist and regional section lead of pediatric ophthalmology, Southern California Permanente Medical Group.
“A strength of this device is that it is user friendly and easy to use and very quick, which is essential when working with young children,” said Dr. Shah in an interview. He noted that the device could be used for children as young as 2 years.
Dr. Shah pointed out that the children were recruited from a pediatrician’s office and reflect more of a “real-world setting” than had they been recruited from a pediatric ophthalmology clinic.
Dr. Shah added that, with a negative predictive value of 100%, the device is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present. “It did have a positive predictive value of 26%, which needs to be considered when deciding one’s vision screening strategy,” he said.
A limitation of the study is that there was no head-to-head comparison with another screening device, noted Dr. Shah. “While it may have been more useful to include another vision screening device to have a head-to-head comparison, we did not do this to limit complexity and cost.”
Michael J. Wan, MD, FRCSC, pediatric ophthalmologist, Sick Kids Hospital, Toronto, and assistant professor at the University of Toronto, told this news organization that the device has multiple strengths, including quick acquisition time and excellent detection rate of amblyopia and strabismus in children as young as 2 years.
“It is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present,” said Dr. Wan, who was not involved in the study. “The PVS uses an elegant mechanism to test for amblyopia directly (as opposed to other screening devices, which only detect risk factors). This study demonstrates the impressive diagnostic accuracy of this approach. With a study population of 300 children, the PVS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 85% (over 90% in cooperative children). This means that the PVS would detect essentially all cases of amblyopia and strabismus while minimizing the number of unnecessary referrals and examinations.”
He added that, although the study included children as young as 2 years, only 2.5% of the children were unable to complete the PVS test. “Detecting amblyopia in children at an age when treatment is still effective has been a longstanding goal in pediatric ophthalmology,” said Dr. Wan, who described the technology as user friendly. “Based on this study, the search for an accurate and practical pediatric vision screening device appears to be over.”
Dr. Wan said it would be useful to replicate this study with a different population to confirm the findings.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Wan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handheld vision screening device to test for amblyopia and strabismus has been found to have a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 85%, and a median acquisition time of 28 seconds, according to a study published in the Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus.
The prospective study involved 300 children recruited from two Kaiser Permanente Southern California pediatric clinics. The patients, aged 24-72 months, were first screened by trained research staff for amblyopia and strabismus using the device, called the Pediatric Vision Scanner (PVS). They were subsequently screened by a pediatric ophthalmologist who was masked to the previous screening results and who then performed a comprehensive eye examination.
With the gold-standard ophthalmologist examination, six children (2%) were identified as having amblyopia and/or strabismus. Using the PVS, all six children with amblyopia and/or strabismus were identified, yielding 100% sensitivity. PVS findings were normal for 45 children (15%), yielding a specificity rate of 85%. The positive predictive value was 26.0% (95% confidence interval, 12.4%-32.4%), and the negative predictive value was 100% (95% CI, 97.1%-100%).
The findings suggest that the device could be used to screen for amblyopia, according to Shaival S. Shah, MD, the study’s first author, who is a pediatric ophthalmologist and regional section lead of pediatric ophthalmology, Southern California Permanente Medical Group.
“A strength of this device is that it is user friendly and easy to use and very quick, which is essential when working with young children,” said Dr. Shah in an interview. He noted that the device could be used for children as young as 2 years.
Dr. Shah pointed out that the children were recruited from a pediatrician’s office and reflect more of a “real-world setting” than had they been recruited from a pediatric ophthalmology clinic.
Dr. Shah added that, with a negative predictive value of 100%, the device is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present. “It did have a positive predictive value of 26%, which needs to be considered when deciding one’s vision screening strategy,” he said.
A limitation of the study is that there was no head-to-head comparison with another screening device, noted Dr. Shah. “While it may have been more useful to include another vision screening device to have a head-to-head comparison, we did not do this to limit complexity and cost.”
Michael J. Wan, MD, FRCSC, pediatric ophthalmologist, Sick Kids Hospital, Toronto, and assistant professor at the University of Toronto, told this news organization that the device has multiple strengths, including quick acquisition time and excellent detection rate of amblyopia and strabismus in children as young as 2 years.
“It is highly reliable at informing the clinician that amblyopia is not present,” said Dr. Wan, who was not involved in the study. “The PVS uses an elegant mechanism to test for amblyopia directly (as opposed to other screening devices, which only detect risk factors). This study demonstrates the impressive diagnostic accuracy of this approach. With a study population of 300 children, the PVS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 85% (over 90% in cooperative children). This means that the PVS would detect essentially all cases of amblyopia and strabismus while minimizing the number of unnecessary referrals and examinations.”
He added that, although the study included children as young as 2 years, only 2.5% of the children were unable to complete the PVS test. “Detecting amblyopia in children at an age when treatment is still effective has been a longstanding goal in pediatric ophthalmology,” said Dr. Wan, who described the technology as user friendly. “Based on this study, the search for an accurate and practical pediatric vision screening device appears to be over.”
Dr. Wan said it would be useful to replicate this study with a different population to confirm the findings.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Wan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA clears first mobile rapid test for concussion
, the company has announced.
Eye-Sync is a virtual reality eye-tracking platform that provides objective measurements to aid in the assessment of concussion. It’s the first mobile, rapid test for concussion that has been cleared by the FDA, the company said.
As reported by this news organization, Eye-Sync received breakthrough designation from the FDA for this indication in March 2019.
The FDA initially cleared the Eye-Sync platform for recording, viewing, and analyzing eye movements to help clinicians identify visual tracking impairment.
The Eye-Sync technology uses a series of 60-second eye tracking assessments, neurocognitive batteries, symptom inventories, and standardized patient inventories to identify the type and severity of impairment after concussion.
“The platform generates customizable and interpretive reports that support clinical decision making and offers visual and vestibular therapies to remedy deficits and monitor improvement over time,” the company said.
In support of the application for use in concussion, SyncThink enrolled 1,655 children and adults into a clinical study that collected comprehensive patient and concussion-related data for over 12 months.
The company used these data to develop proprietary algorithms and deep learning models to identify a positive or negative indication of concussion.
The study showed that Eye-Sinc had sensitivity greater than 82% and specificity greater than 93%, “thereby providing clinicians with significant and actionable data when evaluating individuals with concussion,” the company said in a news release.
“The outcome of this study very clearly shows the effectiveness of our technology at detecting concussion and definitively demonstrates the clinical utility of Eye-Sinc,” SyncThink Chief Clinical Officer Scott Anderson said in the release.
“It also shows that the future of concussion diagnosis is no longer purely symptom-based but that of a technology driven multi-modal approach,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, the company has announced.
Eye-Sync is a virtual reality eye-tracking platform that provides objective measurements to aid in the assessment of concussion. It’s the first mobile, rapid test for concussion that has been cleared by the FDA, the company said.
As reported by this news organization, Eye-Sync received breakthrough designation from the FDA for this indication in March 2019.
The FDA initially cleared the Eye-Sync platform for recording, viewing, and analyzing eye movements to help clinicians identify visual tracking impairment.
The Eye-Sync technology uses a series of 60-second eye tracking assessments, neurocognitive batteries, symptom inventories, and standardized patient inventories to identify the type and severity of impairment after concussion.
“The platform generates customizable and interpretive reports that support clinical decision making and offers visual and vestibular therapies to remedy deficits and monitor improvement over time,” the company said.
In support of the application for use in concussion, SyncThink enrolled 1,655 children and adults into a clinical study that collected comprehensive patient and concussion-related data for over 12 months.
The company used these data to develop proprietary algorithms and deep learning models to identify a positive or negative indication of concussion.
The study showed that Eye-Sinc had sensitivity greater than 82% and specificity greater than 93%, “thereby providing clinicians with significant and actionable data when evaluating individuals with concussion,” the company said in a news release.
“The outcome of this study very clearly shows the effectiveness of our technology at detecting concussion and definitively demonstrates the clinical utility of Eye-Sinc,” SyncThink Chief Clinical Officer Scott Anderson said in the release.
“It also shows that the future of concussion diagnosis is no longer purely symptom-based but that of a technology driven multi-modal approach,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, the company has announced.
Eye-Sync is a virtual reality eye-tracking platform that provides objective measurements to aid in the assessment of concussion. It’s the first mobile, rapid test for concussion that has been cleared by the FDA, the company said.
As reported by this news organization, Eye-Sync received breakthrough designation from the FDA for this indication in March 2019.
The FDA initially cleared the Eye-Sync platform for recording, viewing, and analyzing eye movements to help clinicians identify visual tracking impairment.
The Eye-Sync technology uses a series of 60-second eye tracking assessments, neurocognitive batteries, symptom inventories, and standardized patient inventories to identify the type and severity of impairment after concussion.
“The platform generates customizable and interpretive reports that support clinical decision making and offers visual and vestibular therapies to remedy deficits and monitor improvement over time,” the company said.
In support of the application for use in concussion, SyncThink enrolled 1,655 children and adults into a clinical study that collected comprehensive patient and concussion-related data for over 12 months.
The company used these data to develop proprietary algorithms and deep learning models to identify a positive or negative indication of concussion.
The study showed that Eye-Sinc had sensitivity greater than 82% and specificity greater than 93%, “thereby providing clinicians with significant and actionable data when evaluating individuals with concussion,” the company said in a news release.
“The outcome of this study very clearly shows the effectiveness of our technology at detecting concussion and definitively demonstrates the clinical utility of Eye-Sinc,” SyncThink Chief Clinical Officer Scott Anderson said in the release.
“It also shows that the future of concussion diagnosis is no longer purely symptom-based but that of a technology driven multi-modal approach,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Racism a strong factor in Black women’s high rate of premature births, study finds
Dr. Paula Braveman, director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, says her latest research revealed an “astounding” level of evidence that racism is a decisive “upstream” cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women.
The tipping point for Dr. Paula Braveman came when a longtime patient of hers at a community clinic in San Francisco’s Mission District slipped past the front desk and knocked on her office door to say goodbye. He wouldn’t be coming to the clinic anymore, he told her, because he could no longer afford it.
It was a decisive moment for Dr. Braveman, who decided she wanted not only to heal ailing patients but also to advocate for policies that would help them be healthier when they arrived at her clinic. In the nearly four decades since, Dr. Braveman has dedicated herself to studying the “social determinants of health” – how the spaces where we live, work, play and learn, and the relationships we have in those places influence how healthy we are.
As director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Braveman has studied the link between neighborhood wealth and children’s health, and how access to insurance influences prenatal care. A longtime advocate of translating research into policy, she has collaborated on major health initiatives with the health department in San Francisco, the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the World Health Organization.
Dr. Braveman has a particular interest in maternal and infant health. Her latest research reviews what’s known about the persistent gap in preterm birth rates between Black and White women in the United States. Black women are about 1.6 times as likely as White women to give birth more than three weeks before the due date. That statistic bears alarming and costly health consequences, as infants born prematurely are at higher risk for breathing, heart, and brain abnormalities, among other complications.
Dr. Braveman coauthored the review with a group of experts convened by the March of Dimes that included geneticists, clinicians, epidemiologists, biomedical experts, and neurologists. They examined more than two dozen suspected causes of preterm births – including quality of prenatal care, environmental toxics, chronic stress, poverty and obesity – and determined that racism, directly or indirectly, best explained the racial disparities in preterm birth rates.
(Note: In the review, the authors make extensive use of the terms “upstream” and “downstream” to describe what determines people’s health. A downstream risk is the condition or factor most directly responsible for a health outcome, while an upstream factor is what causes or fuels the downstream risk – and often what needs to change to prevent someone from becoming sick. For example, a person living near drinking water polluted with toxic chemicals might get sick from drinking the water. The downstream fix would be telling individuals to use filters. The upstream solution would be to stop the dumping of toxic chemicals.)
KHN spoke with Dr. Braveman about the study and its findings. The excerpts have been edited for length and style.
Q: You have been studying the issue of preterm birth and racial disparities for so long. Were there any findings from this review that surprised you?
The process of systematically going through all of the risk factors that are written about in the literature and then seeing how the story of racism was an upstream determinant for virtually all of them. That was kind of astounding.
The other thing that was very impressive: When we looked at the idea that genetic factors could be the cause of the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. The genetics experts in the group, and there were three or four of them, concluded from the evidence that genetic factors might influence the disparity in preterm birth, but at most the effect would be very small, very small indeed. This could not account for the greater rate of preterm birth among Black women compared to White women.
Q: You were looking to identify not just what causes preterm birth but also to explain racial differences in rates of preterm birth. Are there examples of factors that can influence preterm birth that don’t explain racial disparities?
It does look like there are genetic components to preterm birth, but they don’t explain the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. Another example is having an early elective C-section. That’s one of the problems contributing to avoidable preterm birth, but it doesn’t look like that’s really contributing to the Black-White disparity in preterm birth.
Q: You and your colleagues listed exactly one upstream cause of preterm birth: racism. How would you characterize the certainty that racism is a decisive upstream cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women?
It makes me think of this saying: A randomized clinical trial wouldn’t be necessary to give certainty about the importance of having a parachute on if you jump from a plane. To me, at this point, it is close to that.
Going through that paper – and we worked on that paper over a three- or four-year period, so there was a lot of time to think about it – I don’t see how the evidence that we have could be explained otherwise.
Q: What did you learn about how a mother’s broader lifetime experience of racism might affect birth outcomes versus what she experienced within the medical establishment during pregnancy?
There were many ways that experiencing racial discrimination would affect a woman’s pregnancy, but one major way would be through pathways and biological mechanisms involved in stress and stress physiology. In neuroscience, what’s been clear is that a chronic stressor seems to be more damaging to health than an acute stressor.
So it doesn’t make much sense to be looking only during pregnancy. But that’s where most of that research has been done: stress during pregnancy and racial discrimination, and its role in birth outcomes. Very few studies have looked at experiences of racial discrimination across the life course.
My colleagues and I have published a paper where we asked African American women about their experiences of racism, and we didn’t even define what we meant. Women did not talk a lot about the experiences of racism during pregnancy from their medical providers; they talked about the lifetime experience and particularly experiences going back to childhood. And they talked about having to worry, and constant vigilance, so that even if they’re not experiencing an incident, their antennae have to be out to be prepared in case an incident does occur.
Putting all of it together with what we know about stress physiology, I would put my money on the lifetime experiences being so much more important than experiences during pregnancy. There isn’t enough known about preterm birth, but from what is known, inflammation is involved, immune dysfunction, and that’s what stress leads to. The neuroscientists have shown us that chronic stress produces inflammation and immune system dysfunction.
Q: What policies do you think are most important at this stage for reducing preterm birth for Black women?
I wish I could just say one policy or two policies, but I think it does get back to the need to dismantle racism in our society. In all of its manifestations. That’s unfortunate, not to be able to say, “Oh, here, I have this magic bullet, and if you just go with that, that will solve the problem.”
If you take the conclusions of this study seriously, you say, well, policies to just go after these downstream factors are not going to work. It’s up to the upstream investment in trying to achieve a more equitable and less racist society. Ultimately, I think that’s the take-home, and it’s a tall, tall order.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Dr. Paula Braveman, director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, says her latest research revealed an “astounding” level of evidence that racism is a decisive “upstream” cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women.
The tipping point for Dr. Paula Braveman came when a longtime patient of hers at a community clinic in San Francisco’s Mission District slipped past the front desk and knocked on her office door to say goodbye. He wouldn’t be coming to the clinic anymore, he told her, because he could no longer afford it.
It was a decisive moment for Dr. Braveman, who decided she wanted not only to heal ailing patients but also to advocate for policies that would help them be healthier when they arrived at her clinic. In the nearly four decades since, Dr. Braveman has dedicated herself to studying the “social determinants of health” – how the spaces where we live, work, play and learn, and the relationships we have in those places influence how healthy we are.
As director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Braveman has studied the link between neighborhood wealth and children’s health, and how access to insurance influences prenatal care. A longtime advocate of translating research into policy, she has collaborated on major health initiatives with the health department in San Francisco, the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the World Health Organization.
Dr. Braveman has a particular interest in maternal and infant health. Her latest research reviews what’s known about the persistent gap in preterm birth rates between Black and White women in the United States. Black women are about 1.6 times as likely as White women to give birth more than three weeks before the due date. That statistic bears alarming and costly health consequences, as infants born prematurely are at higher risk for breathing, heart, and brain abnormalities, among other complications.
Dr. Braveman coauthored the review with a group of experts convened by the March of Dimes that included geneticists, clinicians, epidemiologists, biomedical experts, and neurologists. They examined more than two dozen suspected causes of preterm births – including quality of prenatal care, environmental toxics, chronic stress, poverty and obesity – and determined that racism, directly or indirectly, best explained the racial disparities in preterm birth rates.
(Note: In the review, the authors make extensive use of the terms “upstream” and “downstream” to describe what determines people’s health. A downstream risk is the condition or factor most directly responsible for a health outcome, while an upstream factor is what causes or fuels the downstream risk – and often what needs to change to prevent someone from becoming sick. For example, a person living near drinking water polluted with toxic chemicals might get sick from drinking the water. The downstream fix would be telling individuals to use filters. The upstream solution would be to stop the dumping of toxic chemicals.)
KHN spoke with Dr. Braveman about the study and its findings. The excerpts have been edited for length and style.
Q: You have been studying the issue of preterm birth and racial disparities for so long. Were there any findings from this review that surprised you?
The process of systematically going through all of the risk factors that are written about in the literature and then seeing how the story of racism was an upstream determinant for virtually all of them. That was kind of astounding.
The other thing that was very impressive: When we looked at the idea that genetic factors could be the cause of the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. The genetics experts in the group, and there were three or four of them, concluded from the evidence that genetic factors might influence the disparity in preterm birth, but at most the effect would be very small, very small indeed. This could not account for the greater rate of preterm birth among Black women compared to White women.
Q: You were looking to identify not just what causes preterm birth but also to explain racial differences in rates of preterm birth. Are there examples of factors that can influence preterm birth that don’t explain racial disparities?
It does look like there are genetic components to preterm birth, but they don’t explain the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. Another example is having an early elective C-section. That’s one of the problems contributing to avoidable preterm birth, but it doesn’t look like that’s really contributing to the Black-White disparity in preterm birth.
Q: You and your colleagues listed exactly one upstream cause of preterm birth: racism. How would you characterize the certainty that racism is a decisive upstream cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women?
It makes me think of this saying: A randomized clinical trial wouldn’t be necessary to give certainty about the importance of having a parachute on if you jump from a plane. To me, at this point, it is close to that.
Going through that paper – and we worked on that paper over a three- or four-year period, so there was a lot of time to think about it – I don’t see how the evidence that we have could be explained otherwise.
Q: What did you learn about how a mother’s broader lifetime experience of racism might affect birth outcomes versus what she experienced within the medical establishment during pregnancy?
There were many ways that experiencing racial discrimination would affect a woman’s pregnancy, but one major way would be through pathways and biological mechanisms involved in stress and stress physiology. In neuroscience, what’s been clear is that a chronic stressor seems to be more damaging to health than an acute stressor.
So it doesn’t make much sense to be looking only during pregnancy. But that’s where most of that research has been done: stress during pregnancy and racial discrimination, and its role in birth outcomes. Very few studies have looked at experiences of racial discrimination across the life course.
My colleagues and I have published a paper where we asked African American women about their experiences of racism, and we didn’t even define what we meant. Women did not talk a lot about the experiences of racism during pregnancy from their medical providers; they talked about the lifetime experience and particularly experiences going back to childhood. And they talked about having to worry, and constant vigilance, so that even if they’re not experiencing an incident, their antennae have to be out to be prepared in case an incident does occur.
Putting all of it together with what we know about stress physiology, I would put my money on the lifetime experiences being so much more important than experiences during pregnancy. There isn’t enough known about preterm birth, but from what is known, inflammation is involved, immune dysfunction, and that’s what stress leads to. The neuroscientists have shown us that chronic stress produces inflammation and immune system dysfunction.
Q: What policies do you think are most important at this stage for reducing preterm birth for Black women?
I wish I could just say one policy or two policies, but I think it does get back to the need to dismantle racism in our society. In all of its manifestations. That’s unfortunate, not to be able to say, “Oh, here, I have this magic bullet, and if you just go with that, that will solve the problem.”
If you take the conclusions of this study seriously, you say, well, policies to just go after these downstream factors are not going to work. It’s up to the upstream investment in trying to achieve a more equitable and less racist society. Ultimately, I think that’s the take-home, and it’s a tall, tall order.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Dr. Paula Braveman, director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, says her latest research revealed an “astounding” level of evidence that racism is a decisive “upstream” cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women.
The tipping point for Dr. Paula Braveman came when a longtime patient of hers at a community clinic in San Francisco’s Mission District slipped past the front desk and knocked on her office door to say goodbye. He wouldn’t be coming to the clinic anymore, he told her, because he could no longer afford it.
It was a decisive moment for Dr. Braveman, who decided she wanted not only to heal ailing patients but also to advocate for policies that would help them be healthier when they arrived at her clinic. In the nearly four decades since, Dr. Braveman has dedicated herself to studying the “social determinants of health” – how the spaces where we live, work, play and learn, and the relationships we have in those places influence how healthy we are.
As director of the Center on Social Disparities in Health at the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Braveman has studied the link between neighborhood wealth and children’s health, and how access to insurance influences prenatal care. A longtime advocate of translating research into policy, she has collaborated on major health initiatives with the health department in San Francisco, the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the World Health Organization.
Dr. Braveman has a particular interest in maternal and infant health. Her latest research reviews what’s known about the persistent gap in preterm birth rates between Black and White women in the United States. Black women are about 1.6 times as likely as White women to give birth more than three weeks before the due date. That statistic bears alarming and costly health consequences, as infants born prematurely are at higher risk for breathing, heart, and brain abnormalities, among other complications.
Dr. Braveman coauthored the review with a group of experts convened by the March of Dimes that included geneticists, clinicians, epidemiologists, biomedical experts, and neurologists. They examined more than two dozen suspected causes of preterm births – including quality of prenatal care, environmental toxics, chronic stress, poverty and obesity – and determined that racism, directly or indirectly, best explained the racial disparities in preterm birth rates.
(Note: In the review, the authors make extensive use of the terms “upstream” and “downstream” to describe what determines people’s health. A downstream risk is the condition or factor most directly responsible for a health outcome, while an upstream factor is what causes or fuels the downstream risk – and often what needs to change to prevent someone from becoming sick. For example, a person living near drinking water polluted with toxic chemicals might get sick from drinking the water. The downstream fix would be telling individuals to use filters. The upstream solution would be to stop the dumping of toxic chemicals.)
KHN spoke with Dr. Braveman about the study and its findings. The excerpts have been edited for length and style.
Q: You have been studying the issue of preterm birth and racial disparities for so long. Were there any findings from this review that surprised you?
The process of systematically going through all of the risk factors that are written about in the literature and then seeing how the story of racism was an upstream determinant for virtually all of them. That was kind of astounding.
The other thing that was very impressive: When we looked at the idea that genetic factors could be the cause of the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. The genetics experts in the group, and there were three or four of them, concluded from the evidence that genetic factors might influence the disparity in preterm birth, but at most the effect would be very small, very small indeed. This could not account for the greater rate of preterm birth among Black women compared to White women.
Q: You were looking to identify not just what causes preterm birth but also to explain racial differences in rates of preterm birth. Are there examples of factors that can influence preterm birth that don’t explain racial disparities?
It does look like there are genetic components to preterm birth, but they don’t explain the Black-White disparity in preterm birth. Another example is having an early elective C-section. That’s one of the problems contributing to avoidable preterm birth, but it doesn’t look like that’s really contributing to the Black-White disparity in preterm birth.
Q: You and your colleagues listed exactly one upstream cause of preterm birth: racism. How would you characterize the certainty that racism is a decisive upstream cause of higher rates of preterm birth among Black women?
It makes me think of this saying: A randomized clinical trial wouldn’t be necessary to give certainty about the importance of having a parachute on if you jump from a plane. To me, at this point, it is close to that.
Going through that paper – and we worked on that paper over a three- or four-year period, so there was a lot of time to think about it – I don’t see how the evidence that we have could be explained otherwise.
Q: What did you learn about how a mother’s broader lifetime experience of racism might affect birth outcomes versus what she experienced within the medical establishment during pregnancy?
There were many ways that experiencing racial discrimination would affect a woman’s pregnancy, but one major way would be through pathways and biological mechanisms involved in stress and stress physiology. In neuroscience, what’s been clear is that a chronic stressor seems to be more damaging to health than an acute stressor.
So it doesn’t make much sense to be looking only during pregnancy. But that’s where most of that research has been done: stress during pregnancy and racial discrimination, and its role in birth outcomes. Very few studies have looked at experiences of racial discrimination across the life course.
My colleagues and I have published a paper where we asked African American women about their experiences of racism, and we didn’t even define what we meant. Women did not talk a lot about the experiences of racism during pregnancy from their medical providers; they talked about the lifetime experience and particularly experiences going back to childhood. And they talked about having to worry, and constant vigilance, so that even if they’re not experiencing an incident, their antennae have to be out to be prepared in case an incident does occur.
Putting all of it together with what we know about stress physiology, I would put my money on the lifetime experiences being so much more important than experiences during pregnancy. There isn’t enough known about preterm birth, but from what is known, inflammation is involved, immune dysfunction, and that’s what stress leads to. The neuroscientists have shown us that chronic stress produces inflammation and immune system dysfunction.
Q: What policies do you think are most important at this stage for reducing preterm birth for Black women?
I wish I could just say one policy or two policies, but I think it does get back to the need to dismantle racism in our society. In all of its manifestations. That’s unfortunate, not to be able to say, “Oh, here, I have this magic bullet, and if you just go with that, that will solve the problem.”
If you take the conclusions of this study seriously, you say, well, policies to just go after these downstream factors are not going to work. It’s up to the upstream investment in trying to achieve a more equitable and less racist society. Ultimately, I think that’s the take-home, and it’s a tall, tall order.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
FDA approves first CAR T-cell for adult ALL: For patients with R/R B-cell disease
The therapy is the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment approved for adults with ALL.
This is a “meaningful advance,” because “roughly half of all adults with B-ALL will relapse on currently available therapies,” said Bijal Shah, MD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Fla., in a press statement from the manufacturer, Kite.
“A single infusion of Tecartus has demonstrated durable responses, suggesting the potential for long-term remission and a new approach to care,” he added.
“Roughly half of all cases actually occur in adults, and unlike pediatric ALL, adult ALL has historically had a poor prognosis,” said Lee Greenberger, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, in the statement. The median overall survival (OS) is only about 8 months in this setting with current treatments, according to the company.
The new FDA approval, which is the fourth indication for brexucabtagene autoleucel, is based on results from ZUMA-3, a multicenter, single-arm study of 71 patients, with 54 efficacy-evaluable patients.
Efficacy was established on the basis of complete remission (CR) rate within 3 months after infusion and the duration of CR (DOCR). Twenty-eight (51.9%) of evaluable patients achieved CR, with a median follow-up for responders of 7.1 months. The median DOCR was not reached.
The median time to CR was 56 days. All 54 efficacy-evaluable patients had potential follow-up for 10 or more months with a median actual follow-up time of 12.3 months.
Among the 54 patients, the median time from leukapheresis to product delivery was 16 days and the median time from leukapheresis to infusion was 29 days.
Of the 17 study patients who did reach efficacy evaluation, 6 did not receive the agent because of manufacturing failure, 8 were not treated because of adverse events following leukapheresis, 2 underwent leukapheresis and received lymphodepleting chemotherapy but were not treated with the drug, and 1 treated patient was not evaluable for efficacy, per the prescribing information.
Among all patients treated with brexucabtagene autoleucel at its target dose, grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic events occurred in 26% and 35% of patients, respectively, and were generally well managed, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) among ALL patients are fever, CRS, hypotension, encephalopathy, tachycardia, nausea, chills, headache, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, hypoxia, rash, edema, tremor, infection with pathogen unspecified, constipation, decreased appetite, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning about the risks of CRS and neurologic toxicities; the drug is approved with a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) because of these risks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The therapy is the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment approved for adults with ALL.
This is a “meaningful advance,” because “roughly half of all adults with B-ALL will relapse on currently available therapies,” said Bijal Shah, MD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Fla., in a press statement from the manufacturer, Kite.
“A single infusion of Tecartus has demonstrated durable responses, suggesting the potential for long-term remission and a new approach to care,” he added.
“Roughly half of all cases actually occur in adults, and unlike pediatric ALL, adult ALL has historically had a poor prognosis,” said Lee Greenberger, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, in the statement. The median overall survival (OS) is only about 8 months in this setting with current treatments, according to the company.
The new FDA approval, which is the fourth indication for brexucabtagene autoleucel, is based on results from ZUMA-3, a multicenter, single-arm study of 71 patients, with 54 efficacy-evaluable patients.
Efficacy was established on the basis of complete remission (CR) rate within 3 months after infusion and the duration of CR (DOCR). Twenty-eight (51.9%) of evaluable patients achieved CR, with a median follow-up for responders of 7.1 months. The median DOCR was not reached.
The median time to CR was 56 days. All 54 efficacy-evaluable patients had potential follow-up for 10 or more months with a median actual follow-up time of 12.3 months.
Among the 54 patients, the median time from leukapheresis to product delivery was 16 days and the median time from leukapheresis to infusion was 29 days.
Of the 17 study patients who did reach efficacy evaluation, 6 did not receive the agent because of manufacturing failure, 8 were not treated because of adverse events following leukapheresis, 2 underwent leukapheresis and received lymphodepleting chemotherapy but were not treated with the drug, and 1 treated patient was not evaluable for efficacy, per the prescribing information.
Among all patients treated with brexucabtagene autoleucel at its target dose, grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic events occurred in 26% and 35% of patients, respectively, and were generally well managed, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) among ALL patients are fever, CRS, hypotension, encephalopathy, tachycardia, nausea, chills, headache, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, hypoxia, rash, edema, tremor, infection with pathogen unspecified, constipation, decreased appetite, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning about the risks of CRS and neurologic toxicities; the drug is approved with a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) because of these risks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The therapy is the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment approved for adults with ALL.
This is a “meaningful advance,” because “roughly half of all adults with B-ALL will relapse on currently available therapies,” said Bijal Shah, MD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Fla., in a press statement from the manufacturer, Kite.
“A single infusion of Tecartus has demonstrated durable responses, suggesting the potential for long-term remission and a new approach to care,” he added.
“Roughly half of all cases actually occur in adults, and unlike pediatric ALL, adult ALL has historically had a poor prognosis,” said Lee Greenberger, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, in the statement. The median overall survival (OS) is only about 8 months in this setting with current treatments, according to the company.
The new FDA approval, which is the fourth indication for brexucabtagene autoleucel, is based on results from ZUMA-3, a multicenter, single-arm study of 71 patients, with 54 efficacy-evaluable patients.
Efficacy was established on the basis of complete remission (CR) rate within 3 months after infusion and the duration of CR (DOCR). Twenty-eight (51.9%) of evaluable patients achieved CR, with a median follow-up for responders of 7.1 months. The median DOCR was not reached.
The median time to CR was 56 days. All 54 efficacy-evaluable patients had potential follow-up for 10 or more months with a median actual follow-up time of 12.3 months.
Among the 54 patients, the median time from leukapheresis to product delivery was 16 days and the median time from leukapheresis to infusion was 29 days.
Of the 17 study patients who did reach efficacy evaluation, 6 did not receive the agent because of manufacturing failure, 8 were not treated because of adverse events following leukapheresis, 2 underwent leukapheresis and received lymphodepleting chemotherapy but were not treated with the drug, and 1 treated patient was not evaluable for efficacy, per the prescribing information.
Among all patients treated with brexucabtagene autoleucel at its target dose, grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic events occurred in 26% and 35% of patients, respectively, and were generally well managed, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) among ALL patients are fever, CRS, hypotension, encephalopathy, tachycardia, nausea, chills, headache, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, hypoxia, rash, edema, tremor, infection with pathogen unspecified, constipation, decreased appetite, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning about the risks of CRS and neurologic toxicities; the drug is approved with a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) because of these risks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic Hyperpigmented Patches on the Legs
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
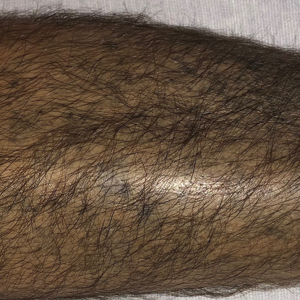
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
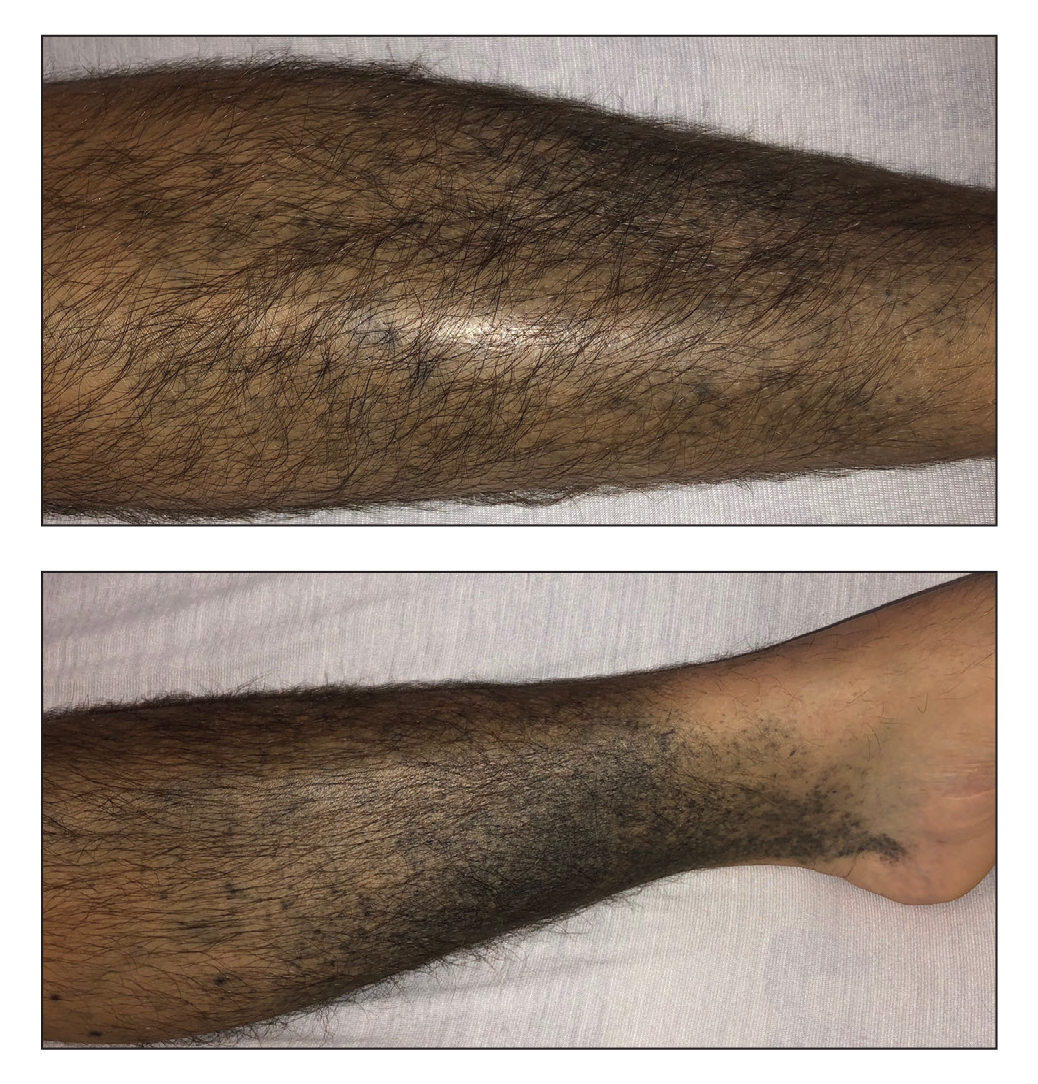
A 37-year-old man with a history of cerebral palsy, bipolar disorder, and impulse control disorder presented to the emergency department with breathing difficulty and worsening malaise. The patient subsequently was intubated due to hypoxic respiratory failure and was found to be positive for SARS-CoV-2. He was admitted to the intensive care unit, and dermatology was consulted due to concern that the cutaneous findings were demonstrative of a vasculitic process. Physical examination revealed diffuse, symmetric, dark brown to blue-gray macules coalescing into patches on the anterior tibia (top) and covering the entire lower leg (bottom). The patches were mottled and did not blanch with pressure. According to the patient’s caretaker, the leg hyperpigmentation had been present for 2 years.
Increased risk for early-onset colorectal cancer extends to third-degree relatives
Among first-degree relatives, there was a sixfold increased risk of developing the malignancy before age 50 in comparison with the general population. Among second- and third-degree relatives, the risk was 1.5 times higher.
Family history is a recognized risk factor for CRC. Roughly 1 in 10 cases of CRC in the United States occurs in people younger than 50 years. It has not been clear to what extent having relatives with early-onset CRC contributes to risk beyond familial syndromes and whether risk extends beyond first-degree relatives, according to study author Lisa A. Cannon-Albright, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
The new findings suggest “that extended family history should be part of the discussion when making cancer screening decisions,” the researchers write. Their study appears in the August issue of Cancer Epidemiology.
The authors used the Utah Population Data Base (UPDB) to examine genealogies in which more than three generations were linked to the Utah Cancer Registry. The analysis comprised all CRC cases for which there were linked genealogy data.
Of the 1,510 cases of early-onset CRC that the team identified, the risk for CRC was 6.00, 3.09, and 1.56 times higher than expected on the basis of UPDB disease rates for first-, second-, and third-degree relatives, respectively. All results were statistically significant.
The authors also found that individuals with a first-degree relative with early-onset CRC were at 2.64-fold higher risk for CRC at any age. The risk was 1.96-fold higher risk with a second-degree relative and 1.3-fold higher with a third-degree relative. In other words, “the risk for [early-onset] CRC is higher than the risk for CRC at any age, for all degrees of relatives shown,” the team writes.
“Significantly elevated risk for CRC at both locations (left or right) was observed for all degrees of relationship; however the confidence intervals are overlapping, suggesting no difference in risk of left- vs. right-sided CRC,” they state.
The findings held up when the researchers used a genealogic index of familiality test instead of calculating relative risk. Although the authors were unable to exclude from the analysis people with inherited syndromes, they say that it is not likely that Lynch syndrome is driving the results, given that more than three-quarters of the early-onset CRC cases were left-sided, “and Lynch primarily occurs in the proximal colon.”
The authors caution, however, that the majority of the study population were of Northern European ancestry, which could limit generalizability to other groups.
Currently, there are no screening guidelines for second- or third-degree relatives of persons with early-onset CRC unless Lynch syndrome or another genetic condition is identified, the researchers write.
The authors note that their findings suggest that early colonoscopy screening may be considered not only for first-degree relatives, but also for second- and possibly third-degree relatives of persons who have early-onset CRC and that the findings could “influence future CRC screening recommendations.
“Relatives may also benefit from an evaluation with genetic counseling to assess underlying inherited conditions,” they write. “However, we note that there are important considerations in the need for resources to accomplish earlier population-based CRC screening.”
The study was supported by the Utah Cancer Registry, which is funded by the National Cancer Institute’s SEER Program, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries. Additional support was provided by the University of Utah and Huntsman Cancer Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among first-degree relatives, there was a sixfold increased risk of developing the malignancy before age 50 in comparison with the general population. Among second- and third-degree relatives, the risk was 1.5 times higher.
Family history is a recognized risk factor for CRC. Roughly 1 in 10 cases of CRC in the United States occurs in people younger than 50 years. It has not been clear to what extent having relatives with early-onset CRC contributes to risk beyond familial syndromes and whether risk extends beyond first-degree relatives, according to study author Lisa A. Cannon-Albright, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
The new findings suggest “that extended family history should be part of the discussion when making cancer screening decisions,” the researchers write. Their study appears in the August issue of Cancer Epidemiology.
The authors used the Utah Population Data Base (UPDB) to examine genealogies in which more than three generations were linked to the Utah Cancer Registry. The analysis comprised all CRC cases for which there were linked genealogy data.
Of the 1,510 cases of early-onset CRC that the team identified, the risk for CRC was 6.00, 3.09, and 1.56 times higher than expected on the basis of UPDB disease rates for first-, second-, and third-degree relatives, respectively. All results were statistically significant.
The authors also found that individuals with a first-degree relative with early-onset CRC were at 2.64-fold higher risk for CRC at any age. The risk was 1.96-fold higher risk with a second-degree relative and 1.3-fold higher with a third-degree relative. In other words, “the risk for [early-onset] CRC is higher than the risk for CRC at any age, for all degrees of relatives shown,” the team writes.
“Significantly elevated risk for CRC at both locations (left or right) was observed for all degrees of relationship; however the confidence intervals are overlapping, suggesting no difference in risk of left- vs. right-sided CRC,” they state.
The findings held up when the researchers used a genealogic index of familiality test instead of calculating relative risk. Although the authors were unable to exclude from the analysis people with inherited syndromes, they say that it is not likely that Lynch syndrome is driving the results, given that more than three-quarters of the early-onset CRC cases were left-sided, “and Lynch primarily occurs in the proximal colon.”
The authors caution, however, that the majority of the study population were of Northern European ancestry, which could limit generalizability to other groups.
Currently, there are no screening guidelines for second- or third-degree relatives of persons with early-onset CRC unless Lynch syndrome or another genetic condition is identified, the researchers write.
The authors note that their findings suggest that early colonoscopy screening may be considered not only for first-degree relatives, but also for second- and possibly third-degree relatives of persons who have early-onset CRC and that the findings could “influence future CRC screening recommendations.
“Relatives may also benefit from an evaluation with genetic counseling to assess underlying inherited conditions,” they write. “However, we note that there are important considerations in the need for resources to accomplish earlier population-based CRC screening.”
The study was supported by the Utah Cancer Registry, which is funded by the National Cancer Institute’s SEER Program, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries. Additional support was provided by the University of Utah and Huntsman Cancer Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among first-degree relatives, there was a sixfold increased risk of developing the malignancy before age 50 in comparison with the general population. Among second- and third-degree relatives, the risk was 1.5 times higher.
Family history is a recognized risk factor for CRC. Roughly 1 in 10 cases of CRC in the United States occurs in people younger than 50 years. It has not been clear to what extent having relatives with early-onset CRC contributes to risk beyond familial syndromes and whether risk extends beyond first-degree relatives, according to study author Lisa A. Cannon-Albright, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
The new findings suggest “that extended family history should be part of the discussion when making cancer screening decisions,” the researchers write. Their study appears in the August issue of Cancer Epidemiology.
The authors used the Utah Population Data Base (UPDB) to examine genealogies in which more than three generations were linked to the Utah Cancer Registry. The analysis comprised all CRC cases for which there were linked genealogy data.
Of the 1,510 cases of early-onset CRC that the team identified, the risk for CRC was 6.00, 3.09, and 1.56 times higher than expected on the basis of UPDB disease rates for first-, second-, and third-degree relatives, respectively. All results were statistically significant.
The authors also found that individuals with a first-degree relative with early-onset CRC were at 2.64-fold higher risk for CRC at any age. The risk was 1.96-fold higher risk with a second-degree relative and 1.3-fold higher with a third-degree relative. In other words, “the risk for [early-onset] CRC is higher than the risk for CRC at any age, for all degrees of relatives shown,” the team writes.
“Significantly elevated risk for CRC at both locations (left or right) was observed for all degrees of relationship; however the confidence intervals are overlapping, suggesting no difference in risk of left- vs. right-sided CRC,” they state.
The findings held up when the researchers used a genealogic index of familiality test instead of calculating relative risk. Although the authors were unable to exclude from the analysis people with inherited syndromes, they say that it is not likely that Lynch syndrome is driving the results, given that more than three-quarters of the early-onset CRC cases were left-sided, “and Lynch primarily occurs in the proximal colon.”
The authors caution, however, that the majority of the study population were of Northern European ancestry, which could limit generalizability to other groups.
Currently, there are no screening guidelines for second- or third-degree relatives of persons with early-onset CRC unless Lynch syndrome or another genetic condition is identified, the researchers write.
The authors note that their findings suggest that early colonoscopy screening may be considered not only for first-degree relatives, but also for second- and possibly third-degree relatives of persons who have early-onset CRC and that the findings could “influence future CRC screening recommendations.
“Relatives may also benefit from an evaluation with genetic counseling to assess underlying inherited conditions,” they write. “However, we note that there are important considerations in the need for resources to accomplish earlier population-based CRC screening.”
The study was supported by the Utah Cancer Registry, which is funded by the National Cancer Institute’s SEER Program, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries. Additional support was provided by the University of Utah and Huntsman Cancer Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is AFib a stroke cause or innocent bystander? The debate continues
Discovery of substantial atrial fibrillation (AFib) is usually an indication to start oral anticoagulation (OAC) for stroke prevention, but it’s far from settled whether such AFib is actually a direct cause of thromboembolic stroke. And that has implications for whether patients with occasional bouts of the arrhythmia need to be on continuous OAC.
It’s possible that some with infrequent paroxysmal AFib can get away with OAC maintained only about as long as the arrhythmia persists, and then go off the drugs, say researchers based on their study, which, they caution, would need the support of prospective trials before such a strategy could be considered.
But importantly, in their patients who had been continuously monitored by their cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) prior to experiencing a stroke, the 30-day risk of that stroke more than tripled if their AFib burden on 1 day reached at least 5-6 hours. The risk jumped especially high within the first few days after accumulating that amount of AFib in a day, but then fell off sharply over the next few days.
Based on the study, “Your risk of stroke goes up acutely when you have an episode of AFib, and it decreases rapidly, back to baseline – certainly by 30 days and it looked like in our data by 5 days,” Daniel E. Singer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Increasingly, he noted, “there’s a widespread belief that AFib is a risk marker, not a causal risk factor.” In that scenario, most embolic strokes are caused by thrombi formed as a result of an atrial myopathy, characterized by fibrosis and inflammation, that also happens to trigger AFib.
But said Dr. Singer, who is lead author on the analysis published online Sept. 29 in JAMA Cardiology.
Some studies have “shown that anticoagulants seem to lower stroke risk even in patients without atrial fib, and even from sources not likely to be coming from the atrium,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, Palo Alto, said in an interview. Collectively they point to “atrial fibrillation as a cause of and a noncausal marker for stroke.”
For example, Dr. Turakhia pointed out in an editorial accompanying the current report that stroke in patients with CIEDs “may occur during prolonged periods of sinus rhythm.”
The current study, he said in an interview, doesn’t preclude atrial myopathy as one direct cause of stroke-associated thrombus, because probably both the myopathy and AFib can be culprits. Still, AFib itself it may bear more responsibility for strokes in patients with fewer competing risks for stroke.
In such patients at lower vascular risk, who may have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of only 1 or 2, for example, “AFib can become a more important cause” of ischemic stroke, Dr. Turakhia said. That’s when AFib is more likely to be temporally related to stroke as the likely culprit, the mechanism addressed by Dr. Singer and associates.
“I think we’re all trying to grapple with what the truth is,” Dr. Singer observed. Still, the current study was unusual for primarily looking at the temporal relationship between AFib and stroke, rather than stroke risk. “And once again, as we found in our earlier study, but now a much larger study, it’s a tight relationship.”
Based on the current results, he said, the risk is “high when you have AFib, and it decreases very rapidly after the AFib is over.” And, “it takes multiple hours of AFib to raise stroke risk.” Inclusion in the analysis required accumulation of at least 5.5 hours of AFib on at least 1 day in a month, the cut point at which stroke risk started to climb significantly in an earlier trial.
In the current analysis, however, the 30-day odds ratio for stroke was a nonsignificant 2.75 for an AFib burden of 6-23 hours in a day and jumped to a significant 5.0 for a burden in excess of 23 hours in a day. “That’s a lot of AFib” before the risk actually goes up, and supports AFib as causative, Dr. Singer said. If it were the myopathy itself triggering stroke in these particular patients, the risk would be ongoing and not subject to a threshold of AFib burden.
Implications for noncontinuous OAC
“The hope is that there are people who have very little AFib: They may have several hours, and then they have nothing for 6 months. Do they have to be anticoagulated or not?” Dr. Singer asked.
“If you believe the risk-marker story, you might say they have to be anticoagulated. But if you believe our results, you would certainly think there’s a good chance they don’t have to be anticoagulated,” he said.
“So it is logical to think, if you have the right people and continuous monitoring, that you could have time-delimited anticoagulation.” That is, patients might start right away on a direct OAC once reaching the AFib threshold in a day, Dr. Singer said, “going on and off anticoagulants in parallel with their episodes of AFib.”
The strategy wouldn’t be feasible in patients who often experience AFib, Dr. Singer noted, “but it might work for people who have infrequent paroxysmal AFib.” It certainly would first have to be tested in prospective trials, he said. Such trials would be more practical than ever to carry out given the growing availability of continuous AFib monitoring by wearables.
“We need a trial to make the case whether it’s safe or not,” Dr. Turakhia said of such a rhythm-guided approach to OAC for AFib. The population to start with, he said, would be patients with paroxysmal AFib and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores. “If you think CHA2DS2-VASc as an integrated score of vascular risk, such patients would have a lot fewer reasons to have strokes. And if they do have a stroke, it’s more reasonable to assume that it’s likely caused by atrial fib and not just a marker.”
Importantly, such a strategy could well be safer than continuous OAC for some patients – those at the lowest vascular risk and with the most occasional AFib and lowest AFib burden “who are otherwise doing fine,” Dr. Turakhia said. In such patients on continuous OAC, he proposed, the risks of bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage could potentially exceed the expected degree of protection from ischemic events.
Discordant periods of AFib burden
Dr. Singer and his colleagues linked a national electronic health record database with Medtronic CareLink records covering 10 years to identify 891 patients who experienced an ischemic stroke preceded by at least 120 days of continuous heart-rhythm monitoring.
The patients were then categorized by their pattern of AFib, if any, within each of two prestroke periods: the most recent 30 days, which was the test period, and the preceding 91-120 days, the control period.
The analysis then excluded any patients who reached an AFib-burden threshold of at least 5.5 hours on any day during both the test and control periods, and those who did not attain that threshold in either period.
“The ones who had AFib in both periods mostly had permanent AFib, and ones that didn’t have AFib in either period mostly were in sinus rhythm,” Dr. Singer said. It was “close to 100%” in both cases.
Those exclusions left 66 patients, 7.4% of the total, who reached the AFib-burden threshold on at least 1 day during either the test or control periods, but not both. They included 52 and 14 patients, respectively, with “discordant” periods, that is, at least that burden of AFib in a day during either the test or control period, but not both.
Comparing AFib burden at test versus control periods among patients for whom the two periods were discordant yielded an OR for stroke of 3.71 (95% confidence interval, 2.06-6.70).
Stroke risk levels were not evenly spread throughout the 24-hour periods that met the AFib-burden threshold or the 30 days preceding the patients’ strokes. The OR for stroke was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.62-9.55) during days 1-5 following the day in which the AFib-burden threshold was met. And it was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.08-12.01) over 30 days if the AFib burden exceeded 23 hours on any day of the test period.
The study’s case-crossover design, in which each patient served as their own control, is one of its advantages, Dr. Singer observed. Most patient features, including CHA2DS2-VASc score and comorbidities, did not change appreciably from earliest to the latest 30-day period, which strengthens the comparison of the two because “you don’t have to worry about long-term confounding.”
Dr. Singer was supported by the Eliot B. and Edith C. Shoolman fund of the Massachusetts General Hospital. He discloses receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol-Myers Squibb; personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Fitbit, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer; and royalties from UpToDate.
Dr. Turakhia discloses personal fees from Medtronic, Abbott, Sanofi, Pfizer, Myokardia, Johnson & Johnson, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, InCarda Therapeutics, 100Plus, Forward Pharma, and AliveCor; and grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, the American Heart Association, Apple, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Discovery of substantial atrial fibrillation (AFib) is usually an indication to start oral anticoagulation (OAC) for stroke prevention, but it’s far from settled whether such AFib is actually a direct cause of thromboembolic stroke. And that has implications for whether patients with occasional bouts of the arrhythmia need to be on continuous OAC.
It’s possible that some with infrequent paroxysmal AFib can get away with OAC maintained only about as long as the arrhythmia persists, and then go off the drugs, say researchers based on their study, which, they caution, would need the support of prospective trials before such a strategy could be considered.
But importantly, in their patients who had been continuously monitored by their cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) prior to experiencing a stroke, the 30-day risk of that stroke more than tripled if their AFib burden on 1 day reached at least 5-6 hours. The risk jumped especially high within the first few days after accumulating that amount of AFib in a day, but then fell off sharply over the next few days.
Based on the study, “Your risk of stroke goes up acutely when you have an episode of AFib, and it decreases rapidly, back to baseline – certainly by 30 days and it looked like in our data by 5 days,” Daniel E. Singer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Increasingly, he noted, “there’s a widespread belief that AFib is a risk marker, not a causal risk factor.” In that scenario, most embolic strokes are caused by thrombi formed as a result of an atrial myopathy, characterized by fibrosis and inflammation, that also happens to trigger AFib.
But said Dr. Singer, who is lead author on the analysis published online Sept. 29 in JAMA Cardiology.
Some studies have “shown that anticoagulants seem to lower stroke risk even in patients without atrial fib, and even from sources not likely to be coming from the atrium,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, Palo Alto, said in an interview. Collectively they point to “atrial fibrillation as a cause of and a noncausal marker for stroke.”
For example, Dr. Turakhia pointed out in an editorial accompanying the current report that stroke in patients with CIEDs “may occur during prolonged periods of sinus rhythm.”
The current study, he said in an interview, doesn’t preclude atrial myopathy as one direct cause of stroke-associated thrombus, because probably both the myopathy and AFib can be culprits. Still, AFib itself it may bear more responsibility for strokes in patients with fewer competing risks for stroke.
In such patients at lower vascular risk, who may have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of only 1 or 2, for example, “AFib can become a more important cause” of ischemic stroke, Dr. Turakhia said. That’s when AFib is more likely to be temporally related to stroke as the likely culprit, the mechanism addressed by Dr. Singer and associates.
“I think we’re all trying to grapple with what the truth is,” Dr. Singer observed. Still, the current study was unusual for primarily looking at the temporal relationship between AFib and stroke, rather than stroke risk. “And once again, as we found in our earlier study, but now a much larger study, it’s a tight relationship.”
Based on the current results, he said, the risk is “high when you have AFib, and it decreases very rapidly after the AFib is over.” And, “it takes multiple hours of AFib to raise stroke risk.” Inclusion in the analysis required accumulation of at least 5.5 hours of AFib on at least 1 day in a month, the cut point at which stroke risk started to climb significantly in an earlier trial.
In the current analysis, however, the 30-day odds ratio for stroke was a nonsignificant 2.75 for an AFib burden of 6-23 hours in a day and jumped to a significant 5.0 for a burden in excess of 23 hours in a day. “That’s a lot of AFib” before the risk actually goes up, and supports AFib as causative, Dr. Singer said. If it were the myopathy itself triggering stroke in these particular patients, the risk would be ongoing and not subject to a threshold of AFib burden.
Implications for noncontinuous OAC
“The hope is that there are people who have very little AFib: They may have several hours, and then they have nothing for 6 months. Do they have to be anticoagulated or not?” Dr. Singer asked.
“If you believe the risk-marker story, you might say they have to be anticoagulated. But if you believe our results, you would certainly think there’s a good chance they don’t have to be anticoagulated,” he said.
“So it is logical to think, if you have the right people and continuous monitoring, that you could have time-delimited anticoagulation.” That is, patients might start right away on a direct OAC once reaching the AFib threshold in a day, Dr. Singer said, “going on and off anticoagulants in parallel with their episodes of AFib.”
The strategy wouldn’t be feasible in patients who often experience AFib, Dr. Singer noted, “but it might work for people who have infrequent paroxysmal AFib.” It certainly would first have to be tested in prospective trials, he said. Such trials would be more practical than ever to carry out given the growing availability of continuous AFib monitoring by wearables.
“We need a trial to make the case whether it’s safe or not,” Dr. Turakhia said of such a rhythm-guided approach to OAC for AFib. The population to start with, he said, would be patients with paroxysmal AFib and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores. “If you think CHA2DS2-VASc as an integrated score of vascular risk, such patients would have a lot fewer reasons to have strokes. And if they do have a stroke, it’s more reasonable to assume that it’s likely caused by atrial fib and not just a marker.”
Importantly, such a strategy could well be safer than continuous OAC for some patients – those at the lowest vascular risk and with the most occasional AFib and lowest AFib burden “who are otherwise doing fine,” Dr. Turakhia said. In such patients on continuous OAC, he proposed, the risks of bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage could potentially exceed the expected degree of protection from ischemic events.
Discordant periods of AFib burden
Dr. Singer and his colleagues linked a national electronic health record database with Medtronic CareLink records covering 10 years to identify 891 patients who experienced an ischemic stroke preceded by at least 120 days of continuous heart-rhythm monitoring.
The patients were then categorized by their pattern of AFib, if any, within each of two prestroke periods: the most recent 30 days, which was the test period, and the preceding 91-120 days, the control period.
The analysis then excluded any patients who reached an AFib-burden threshold of at least 5.5 hours on any day during both the test and control periods, and those who did not attain that threshold in either period.
“The ones who had AFib in both periods mostly had permanent AFib, and ones that didn’t have AFib in either period mostly were in sinus rhythm,” Dr. Singer said. It was “close to 100%” in both cases.
Those exclusions left 66 patients, 7.4% of the total, who reached the AFib-burden threshold on at least 1 day during either the test or control periods, but not both. They included 52 and 14 patients, respectively, with “discordant” periods, that is, at least that burden of AFib in a day during either the test or control period, but not both.
Comparing AFib burden at test versus control periods among patients for whom the two periods were discordant yielded an OR for stroke of 3.71 (95% confidence interval, 2.06-6.70).
Stroke risk levels were not evenly spread throughout the 24-hour periods that met the AFib-burden threshold or the 30 days preceding the patients’ strokes. The OR for stroke was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.62-9.55) during days 1-5 following the day in which the AFib-burden threshold was met. And it was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.08-12.01) over 30 days if the AFib burden exceeded 23 hours on any day of the test period.
The study’s case-crossover design, in which each patient served as their own control, is one of its advantages, Dr. Singer observed. Most patient features, including CHA2DS2-VASc score and comorbidities, did not change appreciably from earliest to the latest 30-day period, which strengthens the comparison of the two because “you don’t have to worry about long-term confounding.”
Dr. Singer was supported by the Eliot B. and Edith C. Shoolman fund of the Massachusetts General Hospital. He discloses receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol-Myers Squibb; personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Fitbit, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer; and royalties from UpToDate.
Dr. Turakhia discloses personal fees from Medtronic, Abbott, Sanofi, Pfizer, Myokardia, Johnson & Johnson, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, InCarda Therapeutics, 100Plus, Forward Pharma, and AliveCor; and grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, the American Heart Association, Apple, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Discovery of substantial atrial fibrillation (AFib) is usually an indication to start oral anticoagulation (OAC) for stroke prevention, but it’s far from settled whether such AFib is actually a direct cause of thromboembolic stroke. And that has implications for whether patients with occasional bouts of the arrhythmia need to be on continuous OAC.
It’s possible that some with infrequent paroxysmal AFib can get away with OAC maintained only about as long as the arrhythmia persists, and then go off the drugs, say researchers based on their study, which, they caution, would need the support of prospective trials before such a strategy could be considered.
But importantly, in their patients who had been continuously monitored by their cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) prior to experiencing a stroke, the 30-day risk of that stroke more than tripled if their AFib burden on 1 day reached at least 5-6 hours. The risk jumped especially high within the first few days after accumulating that amount of AFib in a day, but then fell off sharply over the next few days.
Based on the study, “Your risk of stroke goes up acutely when you have an episode of AFib, and it decreases rapidly, back to baseline – certainly by 30 days and it looked like in our data by 5 days,” Daniel E. Singer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Increasingly, he noted, “there’s a widespread belief that AFib is a risk marker, not a causal risk factor.” In that scenario, most embolic strokes are caused by thrombi formed as a result of an atrial myopathy, characterized by fibrosis and inflammation, that also happens to trigger AFib.
But said Dr. Singer, who is lead author on the analysis published online Sept. 29 in JAMA Cardiology.
Some studies have “shown that anticoagulants seem to lower stroke risk even in patients without atrial fib, and even from sources not likely to be coming from the atrium,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, Palo Alto, said in an interview. Collectively they point to “atrial fibrillation as a cause of and a noncausal marker for stroke.”
For example, Dr. Turakhia pointed out in an editorial accompanying the current report that stroke in patients with CIEDs “may occur during prolonged periods of sinus rhythm.”
The current study, he said in an interview, doesn’t preclude atrial myopathy as one direct cause of stroke-associated thrombus, because probably both the myopathy and AFib can be culprits. Still, AFib itself it may bear more responsibility for strokes in patients with fewer competing risks for stroke.
In such patients at lower vascular risk, who may have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of only 1 or 2, for example, “AFib can become a more important cause” of ischemic stroke, Dr. Turakhia said. That’s when AFib is more likely to be temporally related to stroke as the likely culprit, the mechanism addressed by Dr. Singer and associates.
“I think we’re all trying to grapple with what the truth is,” Dr. Singer observed. Still, the current study was unusual for primarily looking at the temporal relationship between AFib and stroke, rather than stroke risk. “And once again, as we found in our earlier study, but now a much larger study, it’s a tight relationship.”
Based on the current results, he said, the risk is “high when you have AFib, and it decreases very rapidly after the AFib is over.” And, “it takes multiple hours of AFib to raise stroke risk.” Inclusion in the analysis required accumulation of at least 5.5 hours of AFib on at least 1 day in a month, the cut point at which stroke risk started to climb significantly in an earlier trial.
In the current analysis, however, the 30-day odds ratio for stroke was a nonsignificant 2.75 for an AFib burden of 6-23 hours in a day and jumped to a significant 5.0 for a burden in excess of 23 hours in a day. “That’s a lot of AFib” before the risk actually goes up, and supports AFib as causative, Dr. Singer said. If it were the myopathy itself triggering stroke in these particular patients, the risk would be ongoing and not subject to a threshold of AFib burden.
Implications for noncontinuous OAC
“The hope is that there are people who have very little AFib: They may have several hours, and then they have nothing for 6 months. Do they have to be anticoagulated or not?” Dr. Singer asked.
“If you believe the risk-marker story, you might say they have to be anticoagulated. But if you believe our results, you would certainly think there’s a good chance they don’t have to be anticoagulated,” he said.
“So it is logical to think, if you have the right people and continuous monitoring, that you could have time-delimited anticoagulation.” That is, patients might start right away on a direct OAC once reaching the AFib threshold in a day, Dr. Singer said, “going on and off anticoagulants in parallel with their episodes of AFib.”
The strategy wouldn’t be feasible in patients who often experience AFib, Dr. Singer noted, “but it might work for people who have infrequent paroxysmal AFib.” It certainly would first have to be tested in prospective trials, he said. Such trials would be more practical than ever to carry out given the growing availability of continuous AFib monitoring by wearables.
“We need a trial to make the case whether it’s safe or not,” Dr. Turakhia said of such a rhythm-guided approach to OAC for AFib. The population to start with, he said, would be patients with paroxysmal AFib and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores. “If you think CHA2DS2-VASc as an integrated score of vascular risk, such patients would have a lot fewer reasons to have strokes. And if they do have a stroke, it’s more reasonable to assume that it’s likely caused by atrial fib and not just a marker.”
Importantly, such a strategy could well be safer than continuous OAC for some patients – those at the lowest vascular risk and with the most occasional AFib and lowest AFib burden “who are otherwise doing fine,” Dr. Turakhia said. In such patients on continuous OAC, he proposed, the risks of bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage could potentially exceed the expected degree of protection from ischemic events.
Discordant periods of AFib burden
Dr. Singer and his colleagues linked a national electronic health record database with Medtronic CareLink records covering 10 years to identify 891 patients who experienced an ischemic stroke preceded by at least 120 days of continuous heart-rhythm monitoring.
The patients were then categorized by their pattern of AFib, if any, within each of two prestroke periods: the most recent 30 days, which was the test period, and the preceding 91-120 days, the control period.
The analysis then excluded any patients who reached an AFib-burden threshold of at least 5.5 hours on any day during both the test and control periods, and those who did not attain that threshold in either period.
“The ones who had AFib in both periods mostly had permanent AFib, and ones that didn’t have AFib in either period mostly were in sinus rhythm,” Dr. Singer said. It was “close to 100%” in both cases.
Those exclusions left 66 patients, 7.4% of the total, who reached the AFib-burden threshold on at least 1 day during either the test or control periods, but not both. They included 52 and 14 patients, respectively, with “discordant” periods, that is, at least that burden of AFib in a day during either the test or control period, but not both.
Comparing AFib burden at test versus control periods among patients for whom the two periods were discordant yielded an OR for stroke of 3.71 (95% confidence interval, 2.06-6.70).
Stroke risk levels were not evenly spread throughout the 24-hour periods that met the AFib-burden threshold or the 30 days preceding the patients’ strokes. The OR for stroke was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.62-9.55) during days 1-5 following the day in which the AFib-burden threshold was met. And it was 5.00 (95% CI, 2.08-12.01) over 30 days if the AFib burden exceeded 23 hours on any day of the test period.
The study’s case-crossover design, in which each patient served as their own control, is one of its advantages, Dr. Singer observed. Most patient features, including CHA2DS2-VASc score and comorbidities, did not change appreciably from earliest to the latest 30-day period, which strengthens the comparison of the two because “you don’t have to worry about long-term confounding.”
Dr. Singer was supported by the Eliot B. and Edith C. Shoolman fund of the Massachusetts General Hospital. He discloses receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol-Myers Squibb; personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Fitbit, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer; and royalties from UpToDate.
Dr. Turakhia discloses personal fees from Medtronic, Abbott, Sanofi, Pfizer, Myokardia, Johnson & Johnson, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, InCarda Therapeutics, 100Plus, Forward Pharma, and AliveCor; and grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, the American Heart Association, Apple, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medtronic expands recall of MiniMed 600 insulin pumps
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
ADHD med may reduce apathy in Alzheimer’s disease
Methylphenidate is safe and effective for treating apathy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), new research suggests.
Results from a phase 3 randomized trial showed that, after 6 months of treatment, mean score on the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) apathy subscale decreased by 4.5 points for patients who received methylphenidate vs. a decrease of 3.1 points for those who received placebo.
In addition, the safety profile showed no significant between-group differences.
“Methylphenidate offers a treatment approach providing a modest but potentially clinically significant benefit for patients and caregivers,” said the investigators, led by Jacobo E. Mintzer, MD, MBA, professor of health studies at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston.
The findings were published online Sept. 27 in JAMA Neurology.
Common problem
Apathy, which is common among patients with AD, is associated with increased risk for mortality, financial burden, and caregiver burden. No treatment has proved effective for apathy in this population.
Two trials of methylphenidate, a catecholaminergic agent, have provided preliminary evidence of efficacy. Findings from the Apathy in Dementia Methylphenidate trial (ADMET) suggested the drug was associated with improved cognition and few adverse events. However, both trials had small patient populations and short durations.
The current investigators conducted ADMET 2, a 6-month, phase 3 trial, to investigate methylphenidate further. They recruited 200 patients (mean age, 76 years; 66% men; 90% White) at nine clinical centers that specialized in dementia care in the United States and one in Canada.
Eligible patients had a diagnosis of possible or probable AD and a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 10 and 28. They also had clinically significant apathy for at least 4 weeks and an available caregiver who spent more than 10 hours a week with the patient.
The researchers randomly assigned patients to receive methylphenidate (n = 99) or placebo (n = 101). For 3 days, participants in the active group received 10 mg/day of methylphenidate. After that point, they received 20 mg/day of methylphenidate for the rest of the study.
Patients in both treatment groups were given the same number of identical-appearing capsules each day.
In-person follow-up visits took place monthly for 6 months. Participants also were contacted by telephone at days 15, 45, and 75 after treatment assignment.
Participants underwent cognitive testing at baseline and at 2, 4, and 6 months. The battery of tests included the MMSE, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test, and Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised Digit Span.
The trial’s two primary outcomes were mean change in NPI apathy score from baseline to 6 months and the odds of an improved rating on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC) between baseline and 6 months.
Significant change on either outcome was to be considered a signal of effective treatment.
Treatment-specific benefit
Ten patients in the methylphenidate group and seven in the placebo group withdrew during the study.
Mean baseline score on the NPI apathy subscale was 8.0 vs. 7.6, respectively.
In an adjusted, longitudinal model, mean between-group difference in change in NPI apathy score at 6 months was –1.25 (P = .002). The mean NPI apathy score decreased by 4.5 points in the methylphenidate group vs. 3.1 points in the placebo group.
The largest change in apathy score occurred during the first 2 months of treatment. At 6 months, 27% of the methylphenidate group vs. 14% of the placebo group had an NPI apathy score of 0.
In addition, 43.8% of the methylphenidate group had improvement on the ADCS-CGIC compared with 35.2% of the placebo group. The odds ratio (OR) for improvement on ADCS-CGIC for methylphenidate vs. placebo was 1.90 (P = .07).
There was also a strong association between score improvement on the NPI apathy subscale and improvement on the ADCS-CGIC subscale (OR, 2.95; P = .002).
“It is important to note that there were no group differences in any of the cognitive measures, suggesting that the effect of the treatment is specific to the treatment of apathy and not a secondary effect of improvement in cognition,” the researchers wrote.
In all, 17 serious adverse events occurred in the methylphenidate group and 10 occurred in the placebo group. However, all events were found to be hospitalizations for events not related to treatment.
‘Enduring effect’
Commenting on the findings, Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, professor of brain sciences at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, noted that the reduction in NPI apathy subscale score of more than 50% was clinically meaningful.
A more robust outcome on the ADCS-CGIC would have been desirable, he added, although that instrument is not designed specifically for apathy.
Methylphenidate’s effect on apathy observed at 2 months and remaining stable throughout the study makes it appear to be “an enduring effect, and not something that the patient accommodates to,” said Dr. Cummings, who was not involved with the research. Such a change may manifest itself in a patient’s greater willingness to help voluntarily with housework or to suggest going for a walk, he noted.
“These are not dramatic changes in cognition, of course, but they are changes in initiative and that is very important,” Dr. Cummings said. Decreased apathy also may improve quality of life for the patient’s caregiver, he added.
Overall, the findings raise the question of whether the Food and Drug Administration should recognize apathy as an indication for which drugs can be approved, said Dr. Cummings.
“For me, that would be the next major step in this line of investigation,” he concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Mintzer has served as an adviser to Praxis Bioresearch and Cerevel Therapeutics on matters unrelated to this study. Dr. Cummings is the author of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory but does not receive payments for it from academic trials such as ADMET 2.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Methylphenidate is safe and effective for treating apathy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), new research suggests.
Results from a phase 3 randomized trial showed that, after 6 months of treatment, mean score on the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) apathy subscale decreased by 4.5 points for patients who received methylphenidate vs. a decrease of 3.1 points for those who received placebo.
In addition, the safety profile showed no significant between-group differences.
“Methylphenidate offers a treatment approach providing a modest but potentially clinically significant benefit for patients and caregivers,” said the investigators, led by Jacobo E. Mintzer, MD, MBA, professor of health studies at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston.
The findings were published online Sept. 27 in JAMA Neurology.
Common problem
Apathy, which is common among patients with AD, is associated with increased risk for mortality, financial burden, and caregiver burden. No treatment has proved effective for apathy in this population.
Two trials of methylphenidate, a catecholaminergic agent, have provided preliminary evidence of efficacy. Findings from the Apathy in Dementia Methylphenidate trial (ADMET) suggested the drug was associated with improved cognition and few adverse events. However, both trials had small patient populations and short durations.
The current investigators conducted ADMET 2, a 6-month, phase 3 trial, to investigate methylphenidate further. They recruited 200 patients (mean age, 76 years; 66% men; 90% White) at nine clinical centers that specialized in dementia care in the United States and one in Canada.
Eligible patients had a diagnosis of possible or probable AD and a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 10 and 28. They also had clinically significant apathy for at least 4 weeks and an available caregiver who spent more than 10 hours a week with the patient.
The researchers randomly assigned patients to receive methylphenidate (n = 99) or placebo (n = 101). For 3 days, participants in the active group received 10 mg/day of methylphenidate. After that point, they received 20 mg/day of methylphenidate for the rest of the study.
Patients in both treatment groups were given the same number of identical-appearing capsules each day.
In-person follow-up visits took place monthly for 6 months. Participants also were contacted by telephone at days 15, 45, and 75 after treatment assignment.
Participants underwent cognitive testing at baseline and at 2, 4, and 6 months. The battery of tests included the MMSE, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test, and Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised Digit Span.
The trial’s two primary outcomes were mean change in NPI apathy score from baseline to 6 months and the odds of an improved rating on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC) between baseline and 6 months.
Significant change on either outcome was to be considered a signal of effective treatment.
Treatment-specific benefit
Ten patients in the methylphenidate group and seven in the placebo group withdrew during the study.
Mean baseline score on the NPI apathy subscale was 8.0 vs. 7.6, respectively.
In an adjusted, longitudinal model, mean between-group difference in change in NPI apathy score at 6 months was –1.25 (P = .002). The mean NPI apathy score decreased by 4.5 points in the methylphenidate group vs. 3.1 points in the placebo group.
The largest change in apathy score occurred during the first 2 months of treatment. At 6 months, 27% of the methylphenidate group vs. 14% of the placebo group had an NPI apathy score of 0.
In addition, 43.8% of the methylphenidate group had improvement on the ADCS-CGIC compared with 35.2% of the placebo group. The odds ratio (OR) for improvement on ADCS-CGIC for methylphenidate vs. placebo was 1.90 (P = .07).
There was also a strong association between score improvement on the NPI apathy subscale and improvement on the ADCS-CGIC subscale (OR, 2.95; P = .002).
“It is important to note that there were no group differences in any of the cognitive measures, suggesting that the effect of the treatment is specific to the treatment of apathy and not a secondary effect of improvement in cognition,” the researchers wrote.
In all, 17 serious adverse events occurred in the methylphenidate group and 10 occurred in the placebo group. However, all events were found to be hospitalizations for events not related to treatment.
‘Enduring effect’
Commenting on the findings, Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, professor of brain sciences at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, noted that the reduction in NPI apathy subscale score of more than 50% was clinically meaningful.
A more robust outcome on the ADCS-CGIC would have been desirable, he added, although that instrument is not designed specifically for apathy.
Methylphenidate’s effect on apathy observed at 2 months and remaining stable throughout the study makes it appear to be “an enduring effect, and not something that the patient accommodates to,” said Dr. Cummings, who was not involved with the research. Such a change may manifest itself in a patient’s greater willingness to help voluntarily with housework or to suggest going for a walk, he noted.
“These are not dramatic changes in cognition, of course, but they are changes in initiative and that is very important,” Dr. Cummings said. Decreased apathy also may improve quality of life for the patient’s caregiver, he added.
Overall, the findings raise the question of whether the Food and Drug Administration should recognize apathy as an indication for which drugs can be approved, said Dr. Cummings.
“For me, that would be the next major step in this line of investigation,” he concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Mintzer has served as an adviser to Praxis Bioresearch and Cerevel Therapeutics on matters unrelated to this study. Dr. Cummings is the author of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory but does not receive payments for it from academic trials such as ADMET 2.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Methylphenidate is safe and effective for treating apathy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), new research suggests.
Results from a phase 3 randomized trial showed that, after 6 months of treatment, mean score on the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) apathy subscale decreased by 4.5 points for patients who received methylphenidate vs. a decrease of 3.1 points for those who received placebo.
In addition, the safety profile showed no significant between-group differences.
“Methylphenidate offers a treatment approach providing a modest but potentially clinically significant benefit for patients and caregivers,” said the investigators, led by Jacobo E. Mintzer, MD, MBA, professor of health studies at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston.
The findings were published online Sept. 27 in JAMA Neurology.
Common problem
Apathy, which is common among patients with AD, is associated with increased risk for mortality, financial burden, and caregiver burden. No treatment has proved effective for apathy in this population.
Two trials of methylphenidate, a catecholaminergic agent, have provided preliminary evidence of efficacy. Findings from the Apathy in Dementia Methylphenidate trial (ADMET) suggested the drug was associated with improved cognition and few adverse events. However, both trials had small patient populations and short durations.
The current investigators conducted ADMET 2, a 6-month, phase 3 trial, to investigate methylphenidate further. They recruited 200 patients (mean age, 76 years; 66% men; 90% White) at nine clinical centers that specialized in dementia care in the United States and one in Canada.
Eligible patients had a diagnosis of possible or probable AD and a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 10 and 28. They also had clinically significant apathy for at least 4 weeks and an available caregiver who spent more than 10 hours a week with the patient.
The researchers randomly assigned patients to receive methylphenidate (n = 99) or placebo (n = 101). For 3 days, participants in the active group received 10 mg/day of methylphenidate. After that point, they received 20 mg/day of methylphenidate for the rest of the study.
Patients in both treatment groups were given the same number of identical-appearing capsules each day.
In-person follow-up visits took place monthly for 6 months. Participants also were contacted by telephone at days 15, 45, and 75 after treatment assignment.
Participants underwent cognitive testing at baseline and at 2, 4, and 6 months. The battery of tests included the MMSE, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test, and Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised Digit Span.
The trial’s two primary outcomes were mean change in NPI apathy score from baseline to 6 months and the odds of an improved rating on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC) between baseline and 6 months.
Significant change on either outcome was to be considered a signal of effective treatment.
Treatment-specific benefit
Ten patients in the methylphenidate group and seven in the placebo group withdrew during the study.
Mean baseline score on the NPI apathy subscale was 8.0 vs. 7.6, respectively.
In an adjusted, longitudinal model, mean between-group difference in change in NPI apathy score at 6 months was –1.25 (P = .002). The mean NPI apathy score decreased by 4.5 points in the methylphenidate group vs. 3.1 points in the placebo group.
The largest change in apathy score occurred during the first 2 months of treatment. At 6 months, 27% of the methylphenidate group vs. 14% of the placebo group had an NPI apathy score of 0.
In addition, 43.8% of the methylphenidate group had improvement on the ADCS-CGIC compared with 35.2% of the placebo group. The odds ratio (OR) for improvement on ADCS-CGIC for methylphenidate vs. placebo was 1.90 (P = .07).
There was also a strong association between score improvement on the NPI apathy subscale and improvement on the ADCS-CGIC subscale (OR, 2.95; P = .002).
“It is important to note that there were no group differences in any of the cognitive measures, suggesting that the effect of the treatment is specific to the treatment of apathy and not a secondary effect of improvement in cognition,” the researchers wrote.
In all, 17 serious adverse events occurred in the methylphenidate group and 10 occurred in the placebo group. However, all events were found to be hospitalizations for events not related to treatment.
‘Enduring effect’
Commenting on the findings, Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, professor of brain sciences at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, noted that the reduction in NPI apathy subscale score of more than 50% was clinically meaningful.
A more robust outcome on the ADCS-CGIC would have been desirable, he added, although that instrument is not designed specifically for apathy.
Methylphenidate’s effect on apathy observed at 2 months and remaining stable throughout the study makes it appear to be “an enduring effect, and not something that the patient accommodates to,” said Dr. Cummings, who was not involved with the research. Such a change may manifest itself in a patient’s greater willingness to help voluntarily with housework or to suggest going for a walk, he noted.
“These are not dramatic changes in cognition, of course, but they are changes in initiative and that is very important,” Dr. Cummings said. Decreased apathy also may improve quality of life for the patient’s caregiver, he added.
Overall, the findings raise the question of whether the Food and Drug Administration should recognize apathy as an indication for which drugs can be approved, said Dr. Cummings.
“For me, that would be the next major step in this line of investigation,” he concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Mintzer has served as an adviser to Praxis Bioresearch and Cerevel Therapeutics on matters unrelated to this study. Dr. Cummings is the author of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory but does not receive payments for it from academic trials such as ADMET 2.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Decline of summer surge continues
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.