User login
ACST-2: Carotid stenting, surgery on par in asymptomatic patients
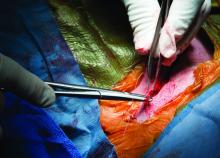
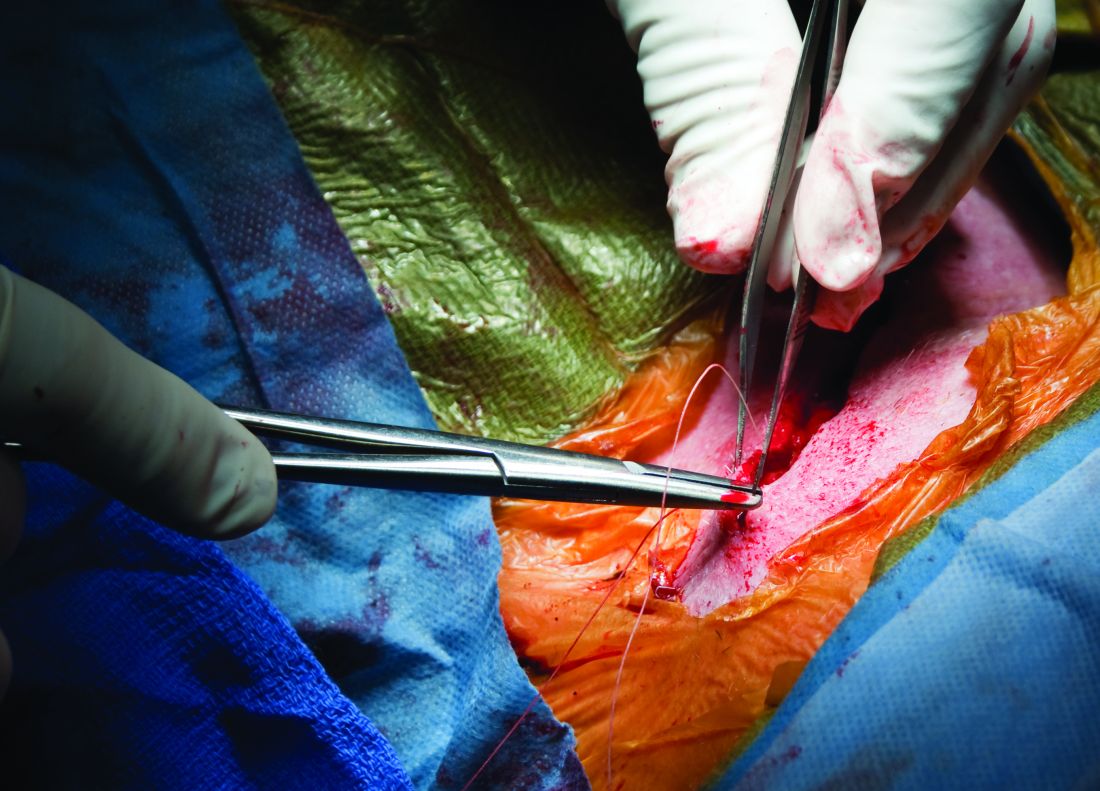
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) and carotid endarterectomy (CEA) provided comparable outcomes over time in asymptomatic patients receiving good medical therapy in the largest trial to date of what to do with severe carotid artery narrowing that is yet to cause a stroke.
Among more than 3,600 patients, stenting and surgery performed by experienced physicians involved a 1.0% risk for causing disabling stroke or death within 30 days.
The annual rate of fatal or disabling strokes was about 0.5% with either procedure over an average 5 years’ follow-up – essentially halving the annual stroke risk had neither procedure been performed, according to Alison Halliday, MD, principal investigator of the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2).
The results were reported Aug. 29 in a Hot Line session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously online in The Lancet.
Session chair Gilles Montalescot, MD, Sorbonne University, Paris, noted that ACST-2 doubled the number of randomly assigned patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis studied in previous trials, “so, a huge contribution to the evidence base in this field and apparently good news for both revascularization techniques.”
Thirty-day and 5-year outcomes
The trial was conducted in 33 countries between January 2008 and December 2020, enrolling 3,625 patients (70% were male; mean age, 70 years) with carotid stenosis of at least 60% on ultrasonography, in whom stenting or surgery was suitable but both the doctor and patient were “substantially uncertain” which procedure to prefer.
Among the 1,811 patients assigned to stenting, 87% underwent the procedure at a median of 14 days; 6% crossed over to surgery, typically because of a highly calcified lesion or a more tortuous carotid than anticipated; and 6% had no intervention.
Among the 1,814 patients assigned to surgery, 92% had the procedure at a median of 14 days; 3% crossed over to stenting, typically because of patient or doctor preference or reluctance to undergo general anesthesia; and 4% had no intervention.
Patients without complications who had stenting stayed on average 1 day less than did those undergoing surgery.
During an earlier press briefing, Dr. Halliday highlighted the need for procedural competency and said doctors had to submit a record of their CEA or CAS experience and, consistent with current guidelines, had to demonstrate an independently verified stroke or death rate of 6% or less for symptomatic patients and 3% or lower for asymptomatic patients.
The results showed the 30-day risk for death, myocardial infarction (MI), or any stroke was 3.9% with carotid stenting and 3.2% with surgery (P = .26).
But with stenting, there was a slightly higher risk for procedural nondisabling strokes (48 vs. 29; P = .03), including 15 strokes vs. 5 strokes, respectively, that left patients with no residual symptoms. This is “consistent with large, recent nationally representative registry data,” observed Dr. Halliday, of the University of Oxford (England).
For those undergoing surgery, cranial nerve palsies were reported in 5.4% vs. no patients undergoing stenting.
At 5 years, the nonprocedural fatal or disabling stroke rate was 2.5% in each group (rate ratio [RR], 0.98; P = .91), with any nonprocedural stroke occurring in 5.3% of patients with stenting vs. 4.5% with surgery (RR, 1.16; P = .33).
The investigators performed a meta-analysis combining the ACST-2 results with those of eight prior trials (four in asymptomatic and four in symptomatic patients) that yielded a similar nonsignificant result for any nonprocedural stroke (RR, 1.11; P = .21).
Based on the results from ACST-2 plus the major trials, stenting and surgery involve “similar risks and similar benefits,” Dr. Halliday concluded.
Discussant Marco Roffi, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, said, “In centers with documented expertise, carotid artery stenting should be offered as an alternative to carotid endarterectomy in patients with asymptomatic stenosis and suitable anatomy.”
While the trial provides “good news” for patients, he pointed out that a reduction in the sample size from 5,000 to 3,625 limited the statistical power and that enrollment over a long period of time may have introduced confounders, such as changes in equipment technique, and medical therapy.
Also, many centers enrolled few patients, raising the concern over low-volume centers and operators, Dr. Roffi said. “We know that 8% of the centers enrolled 39% of the patients,” and “information on the credentialing and experience of the interventionalists was limited.”
Further, a lack of systematic MI assessment may have favored the surgery group, and more recent developments in stenting with the potential of reducing periprocedural stroke were rarely used, such as proximal emboli protection in only 15% and double-layer stents in 11%.
Friedhelm Beyersdorf, MD, University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany, said that, as a vascular surgeon, he finds it understandable that there might be a higher incidence of nonfatal strokes when treating carotid stenosis with stents, given the vulnerability of these lesions.
“Nevertheless, the main conclusion from the entire study is that carotid artery treatment is extremely safe, it has to be done in order to avoid strokes, and, obviously, there seems to be an advantage for surgery in terms of nondisabling stroke,” he said.
Session chair Dr. Montalescot, however, said that what the study cannot address – and what was the subject of many online audience comments – is whether either intervention should be performed in these patients.
Unlike earlier trials comparing interventions to medical therapy, Dr. Halliday said ACST-2 enrolled patients for whom the decision had been made that revascularization was needed. In addition, 99%-100% were receiving antithrombotic therapy at baseline, 85%-90% were receiving antihypertensives, and about 85% were taking statins.
Longer-term follow-up should provide a better picture of the nonprocedural stroke risk, with patients asked annually about exactly what medications and doses they are taking, she said.
“We will have an enormous list of exactly what’s gone on and the intensity of that therapy, which is, of course, much more intense than when we carried out our first trial. But these were people in whom a procedure was thought to be necessary,” she noted.
When asked during the press conference which procedure she would choose, Dr. Halliday, a surgeon, observed that patient preference is important but that the nature of the lesion itself often determines the optimal choice.
“If you know the competence of the people doing it is equal, then the less invasive procedure – providing it has good long-term viability, and that’s why we’re following for 10 years – is the more important,” she added.
The study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council and Health Technology Assessment Programme. Dr. Halliday reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) and carotid endarterectomy (CEA) provided comparable outcomes over time in asymptomatic patients receiving good medical therapy in the largest trial to date of what to do with severe carotid artery narrowing that is yet to cause a stroke.
Among more than 3,600 patients, stenting and surgery performed by experienced physicians involved a 1.0% risk for causing disabling stroke or death within 30 days.
The annual rate of fatal or disabling strokes was about 0.5% with either procedure over an average 5 years’ follow-up – essentially halving the annual stroke risk had neither procedure been performed, according to Alison Halliday, MD, principal investigator of the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2).
The results were reported Aug. 29 in a Hot Line session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously online in The Lancet.
Session chair Gilles Montalescot, MD, Sorbonne University, Paris, noted that ACST-2 doubled the number of randomly assigned patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis studied in previous trials, “so, a huge contribution to the evidence base in this field and apparently good news for both revascularization techniques.”
Thirty-day and 5-year outcomes
The trial was conducted in 33 countries between January 2008 and December 2020, enrolling 3,625 patients (70% were male; mean age, 70 years) with carotid stenosis of at least 60% on ultrasonography, in whom stenting or surgery was suitable but both the doctor and patient were “substantially uncertain” which procedure to prefer.
Among the 1,811 patients assigned to stenting, 87% underwent the procedure at a median of 14 days; 6% crossed over to surgery, typically because of a highly calcified lesion or a more tortuous carotid than anticipated; and 6% had no intervention.
Among the 1,814 patients assigned to surgery, 92% had the procedure at a median of 14 days; 3% crossed over to stenting, typically because of patient or doctor preference or reluctance to undergo general anesthesia; and 4% had no intervention.
Patients without complications who had stenting stayed on average 1 day less than did those undergoing surgery.
During an earlier press briefing, Dr. Halliday highlighted the need for procedural competency and said doctors had to submit a record of their CEA or CAS experience and, consistent with current guidelines, had to demonstrate an independently verified stroke or death rate of 6% or less for symptomatic patients and 3% or lower for asymptomatic patients.
The results showed the 30-day risk for death, myocardial infarction (MI), or any stroke was 3.9% with carotid stenting and 3.2% with surgery (P = .26).
But with stenting, there was a slightly higher risk for procedural nondisabling strokes (48 vs. 29; P = .03), including 15 strokes vs. 5 strokes, respectively, that left patients with no residual symptoms. This is “consistent with large, recent nationally representative registry data,” observed Dr. Halliday, of the University of Oxford (England).
For those undergoing surgery, cranial nerve palsies were reported in 5.4% vs. no patients undergoing stenting.
At 5 years, the nonprocedural fatal or disabling stroke rate was 2.5% in each group (rate ratio [RR], 0.98; P = .91), with any nonprocedural stroke occurring in 5.3% of patients with stenting vs. 4.5% with surgery (RR, 1.16; P = .33).
The investigators performed a meta-analysis combining the ACST-2 results with those of eight prior trials (four in asymptomatic and four in symptomatic patients) that yielded a similar nonsignificant result for any nonprocedural stroke (RR, 1.11; P = .21).
Based on the results from ACST-2 plus the major trials, stenting and surgery involve “similar risks and similar benefits,” Dr. Halliday concluded.
Discussant Marco Roffi, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, said, “In centers with documented expertise, carotid artery stenting should be offered as an alternative to carotid endarterectomy in patients with asymptomatic stenosis and suitable anatomy.”
While the trial provides “good news” for patients, he pointed out that a reduction in the sample size from 5,000 to 3,625 limited the statistical power and that enrollment over a long period of time may have introduced confounders, such as changes in equipment technique, and medical therapy.
Also, many centers enrolled few patients, raising the concern over low-volume centers and operators, Dr. Roffi said. “We know that 8% of the centers enrolled 39% of the patients,” and “information on the credentialing and experience of the interventionalists was limited.”
Further, a lack of systematic MI assessment may have favored the surgery group, and more recent developments in stenting with the potential of reducing periprocedural stroke were rarely used, such as proximal emboli protection in only 15% and double-layer stents in 11%.
Friedhelm Beyersdorf, MD, University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany, said that, as a vascular surgeon, he finds it understandable that there might be a higher incidence of nonfatal strokes when treating carotid stenosis with stents, given the vulnerability of these lesions.
“Nevertheless, the main conclusion from the entire study is that carotid artery treatment is extremely safe, it has to be done in order to avoid strokes, and, obviously, there seems to be an advantage for surgery in terms of nondisabling stroke,” he said.
Session chair Dr. Montalescot, however, said that what the study cannot address – and what was the subject of many online audience comments – is whether either intervention should be performed in these patients.
Unlike earlier trials comparing interventions to medical therapy, Dr. Halliday said ACST-2 enrolled patients for whom the decision had been made that revascularization was needed. In addition, 99%-100% were receiving antithrombotic therapy at baseline, 85%-90% were receiving antihypertensives, and about 85% were taking statins.
Longer-term follow-up should provide a better picture of the nonprocedural stroke risk, with patients asked annually about exactly what medications and doses they are taking, she said.
“We will have an enormous list of exactly what’s gone on and the intensity of that therapy, which is, of course, much more intense than when we carried out our first trial. But these were people in whom a procedure was thought to be necessary,” she noted.
When asked during the press conference which procedure she would choose, Dr. Halliday, a surgeon, observed that patient preference is important but that the nature of the lesion itself often determines the optimal choice.
“If you know the competence of the people doing it is equal, then the less invasive procedure – providing it has good long-term viability, and that’s why we’re following for 10 years – is the more important,” she added.
The study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council and Health Technology Assessment Programme. Dr. Halliday reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) and carotid endarterectomy (CEA) provided comparable outcomes over time in asymptomatic patients receiving good medical therapy in the largest trial to date of what to do with severe carotid artery narrowing that is yet to cause a stroke.
Among more than 3,600 patients, stenting and surgery performed by experienced physicians involved a 1.0% risk for causing disabling stroke or death within 30 days.
The annual rate of fatal or disabling strokes was about 0.5% with either procedure over an average 5 years’ follow-up – essentially halving the annual stroke risk had neither procedure been performed, according to Alison Halliday, MD, principal investigator of the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2).
The results were reported Aug. 29 in a Hot Line session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously online in The Lancet.
Session chair Gilles Montalescot, MD, Sorbonne University, Paris, noted that ACST-2 doubled the number of randomly assigned patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis studied in previous trials, “so, a huge contribution to the evidence base in this field and apparently good news for both revascularization techniques.”
Thirty-day and 5-year outcomes
The trial was conducted in 33 countries between January 2008 and December 2020, enrolling 3,625 patients (70% were male; mean age, 70 years) with carotid stenosis of at least 60% on ultrasonography, in whom stenting or surgery was suitable but both the doctor and patient were “substantially uncertain” which procedure to prefer.
Among the 1,811 patients assigned to stenting, 87% underwent the procedure at a median of 14 days; 6% crossed over to surgery, typically because of a highly calcified lesion or a more tortuous carotid than anticipated; and 6% had no intervention.
Among the 1,814 patients assigned to surgery, 92% had the procedure at a median of 14 days; 3% crossed over to stenting, typically because of patient or doctor preference or reluctance to undergo general anesthesia; and 4% had no intervention.
Patients without complications who had stenting stayed on average 1 day less than did those undergoing surgery.
During an earlier press briefing, Dr. Halliday highlighted the need for procedural competency and said doctors had to submit a record of their CEA or CAS experience and, consistent with current guidelines, had to demonstrate an independently verified stroke or death rate of 6% or less for symptomatic patients and 3% or lower for asymptomatic patients.
The results showed the 30-day risk for death, myocardial infarction (MI), or any stroke was 3.9% with carotid stenting and 3.2% with surgery (P = .26).
But with stenting, there was a slightly higher risk for procedural nondisabling strokes (48 vs. 29; P = .03), including 15 strokes vs. 5 strokes, respectively, that left patients with no residual symptoms. This is “consistent with large, recent nationally representative registry data,” observed Dr. Halliday, of the University of Oxford (England).
For those undergoing surgery, cranial nerve palsies were reported in 5.4% vs. no patients undergoing stenting.
At 5 years, the nonprocedural fatal or disabling stroke rate was 2.5% in each group (rate ratio [RR], 0.98; P = .91), with any nonprocedural stroke occurring in 5.3% of patients with stenting vs. 4.5% with surgery (RR, 1.16; P = .33).
The investigators performed a meta-analysis combining the ACST-2 results with those of eight prior trials (four in asymptomatic and four in symptomatic patients) that yielded a similar nonsignificant result for any nonprocedural stroke (RR, 1.11; P = .21).
Based on the results from ACST-2 plus the major trials, stenting and surgery involve “similar risks and similar benefits,” Dr. Halliday concluded.
Discussant Marco Roffi, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, said, “In centers with documented expertise, carotid artery stenting should be offered as an alternative to carotid endarterectomy in patients with asymptomatic stenosis and suitable anatomy.”
While the trial provides “good news” for patients, he pointed out that a reduction in the sample size from 5,000 to 3,625 limited the statistical power and that enrollment over a long period of time may have introduced confounders, such as changes in equipment technique, and medical therapy.
Also, many centers enrolled few patients, raising the concern over low-volume centers and operators, Dr. Roffi said. “We know that 8% of the centers enrolled 39% of the patients,” and “information on the credentialing and experience of the interventionalists was limited.”
Further, a lack of systematic MI assessment may have favored the surgery group, and more recent developments in stenting with the potential of reducing periprocedural stroke were rarely used, such as proximal emboli protection in only 15% and double-layer stents in 11%.
Friedhelm Beyersdorf, MD, University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany, said that, as a vascular surgeon, he finds it understandable that there might be a higher incidence of nonfatal strokes when treating carotid stenosis with stents, given the vulnerability of these lesions.
“Nevertheless, the main conclusion from the entire study is that carotid artery treatment is extremely safe, it has to be done in order to avoid strokes, and, obviously, there seems to be an advantage for surgery in terms of nondisabling stroke,” he said.
Session chair Dr. Montalescot, however, said that what the study cannot address – and what was the subject of many online audience comments – is whether either intervention should be performed in these patients.
Unlike earlier trials comparing interventions to medical therapy, Dr. Halliday said ACST-2 enrolled patients for whom the decision had been made that revascularization was needed. In addition, 99%-100% were receiving antithrombotic therapy at baseline, 85%-90% were receiving antihypertensives, and about 85% were taking statins.
Longer-term follow-up should provide a better picture of the nonprocedural stroke risk, with patients asked annually about exactly what medications and doses they are taking, she said.
“We will have an enormous list of exactly what’s gone on and the intensity of that therapy, which is, of course, much more intense than when we carried out our first trial. But these were people in whom a procedure was thought to be necessary,” she noted.
When asked during the press conference which procedure she would choose, Dr. Halliday, a surgeon, observed that patient preference is important but that the nature of the lesion itself often determines the optimal choice.
“If you know the competence of the people doing it is equal, then the less invasive procedure – providing it has good long-term viability, and that’s why we’re following for 10 years – is the more important,” she added.
The study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council and Health Technology Assessment Programme. Dr. Halliday reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Verrucous Scalp Plaque and Widespread Eruption
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
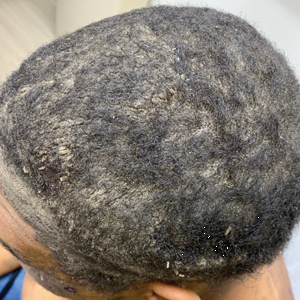
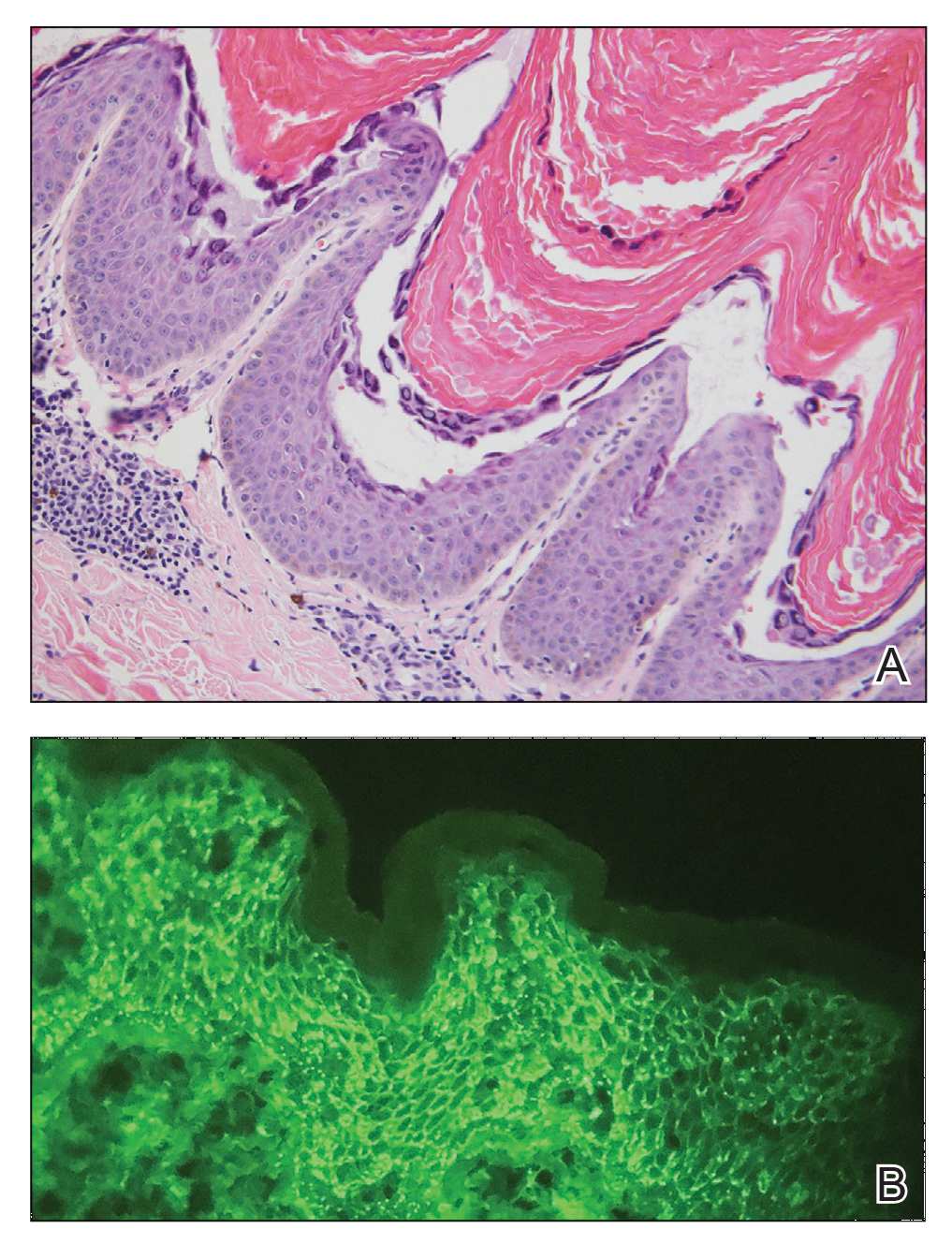
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.
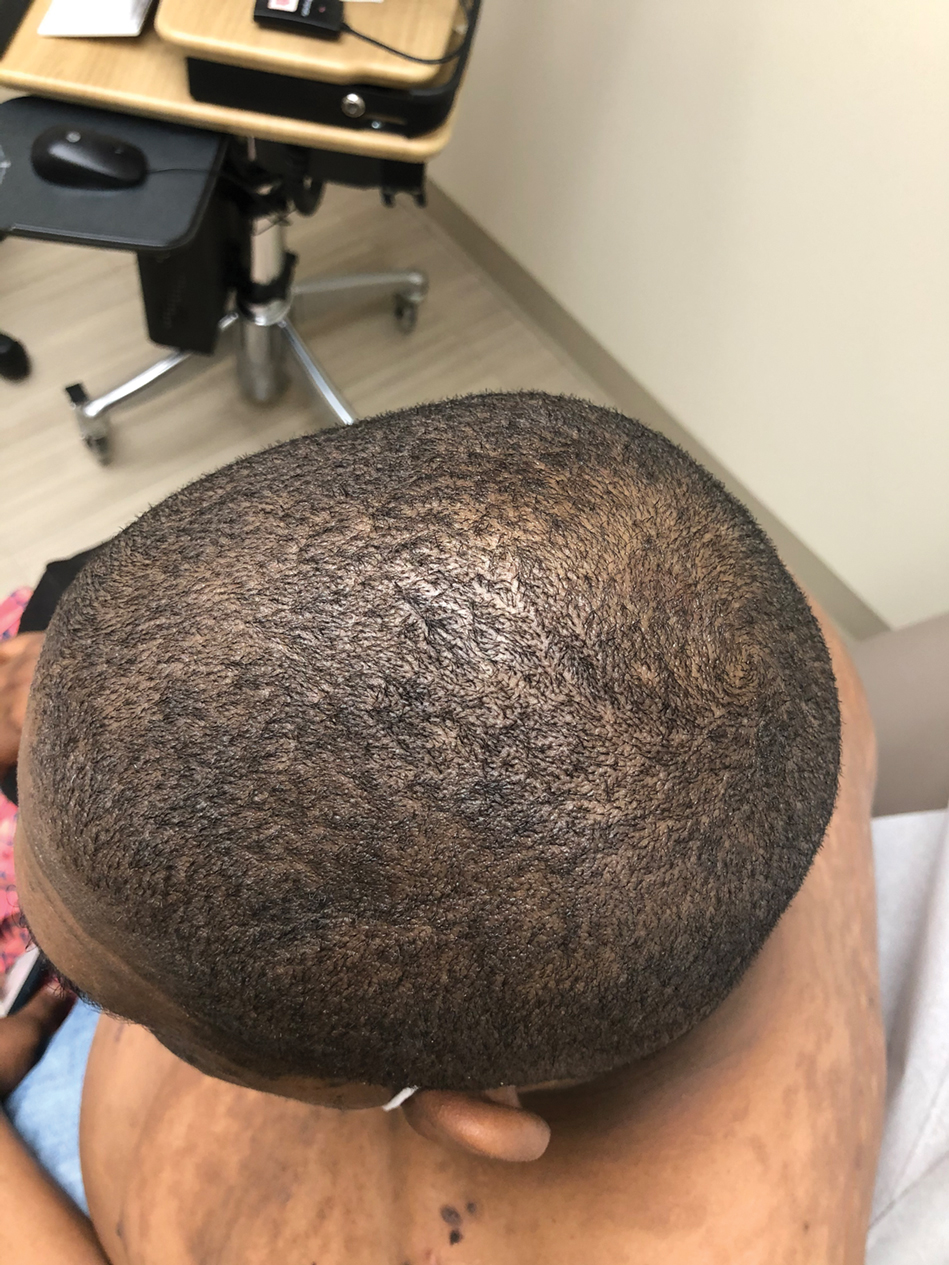
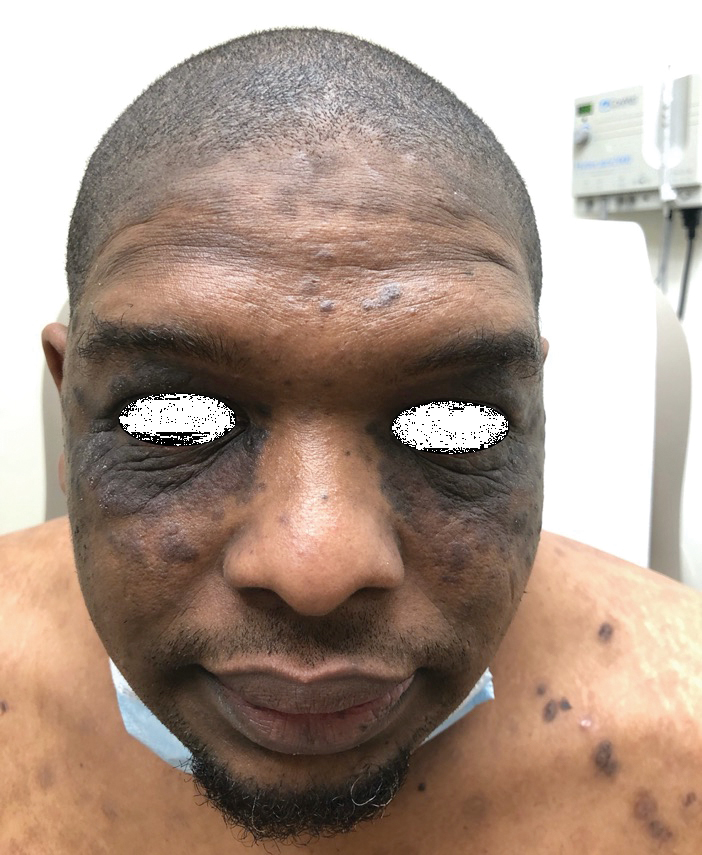
The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.

The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.


Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.

The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.


Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
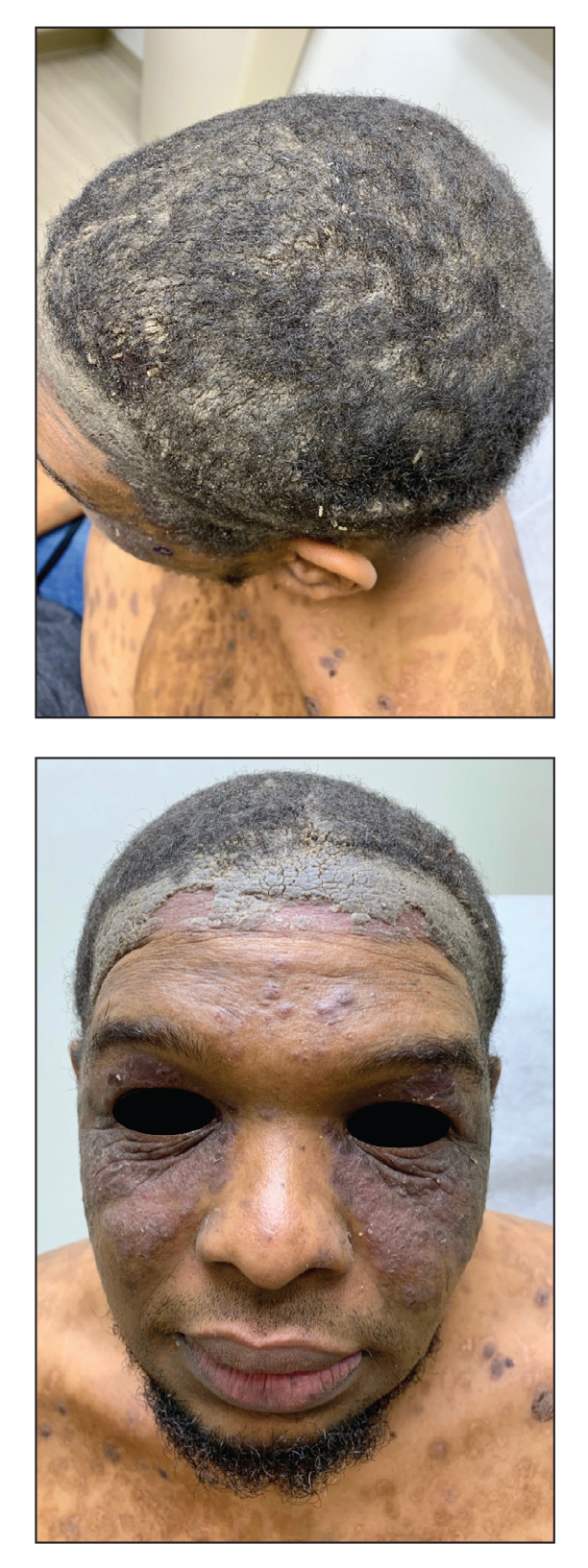
A 40-year-old Black man presented for evaluation of a thick plaque throughout the scalp (top), scaly plaques on the cheeks (bottom), and a spreading rash on the trunk that had progressed over the last few months. He had no relevant medical history, took no medications, and was in a monogamous relationship with a female partner. He previously saw an outside dermatologist who gave him triamcinolone cream, which was mildly helpful. Physical examination revealed a thick verrucous plaque throughout the scalp extending onto the forehead; thick plaques on the cheeks; and numerous, thinly eroded lesions on the trunk. Biopsies and a laboratory workup were performed.
Angiography can wait for cardiac arrest without ST-elevation
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
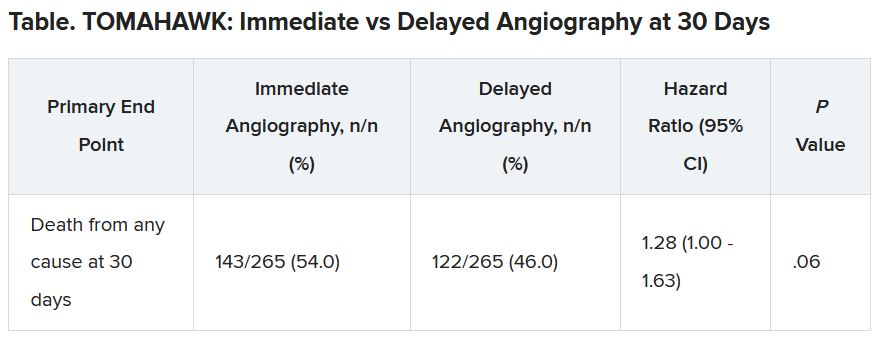
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.
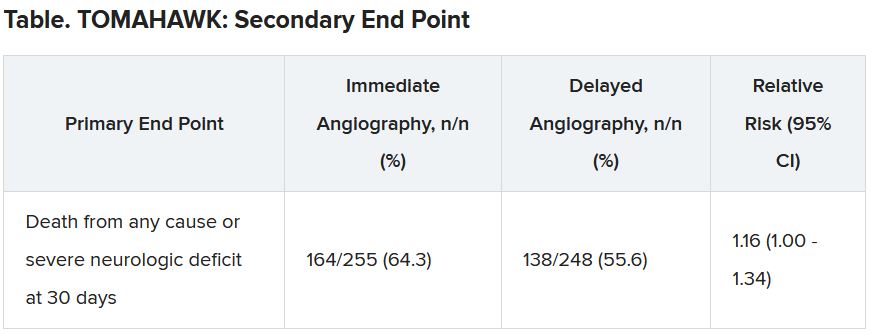
The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”
There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.

The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”

There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.

The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”

There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alcohol use by young adolescents drops during pandemic
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ADOLESCENT HEALTH
CDC panel unanimously backs Pfizer vax, fortifying FDA approval
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Biologic benefit in psoriasis might extend to arthritis prevention
Receiving treatment with a biologic medication, compared with no biologic treatment, appeared to be associated with a lower risk for developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with psoriasis.
That’s according to the results of a nested case-control study involving electronic medical record data from an Israeli health maintenance organization in Arthritis & Rheumatology. Compared with no biologic treatment, the risk for developing PsA among PsO patients was reduced by 39%.
This study shows “a statistically and clinically significant lower risk for developing PsA among patients receiving biologic medications for psoriasis treatment,” wrote Yael Shalev Rosenthal, MPH, of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University and colleagues. “The results suggest considering treatment with biologic medications in patients [who] present with significant risk factors for PsA at an earlier stage of treatment.”
“It would be nice to believe this story, but I don’t think we can based on the evidence we’ve got so far,” commented Philip Helliwell, PhD, DM, in an interview.
Dr. Helliwell, who is professor of clinical rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and an Honorary Consultant Rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals and Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, noted that there were several issues with the current evidence.
Aside from their often retrospective or nonrandomized nature, prior analyses, including the current one, were based on EMR data.
“There’s actually no face-to-face patient contact going on here. It’s all done on coding, and coding can be unreliable,” Dr. Helliwell said.
While the study’s findings are “in line with other studies that have looked at this, and suggest that if you get a biologic, you’re less likely to get PsA with your psoriasis, there could be lots of reasons why.”
The big problem here is confounding by indication. “You don’t get on a biologic unless you’ve got bad psoriasis,” Dr. Helliwell explained. The Israeli criteria for starting a biologic are much higher than in the United Kingdom, he added, requiring more than 50% of patients’ body surface area to be affected, or a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score of more than 50. Moreover, people with bad psoriasis are more likely to get PsA. This, however, makes the results more impressive.
Confounding by indication is an issue with this study, agreed consultant rheumatologist Adewale Adebajo, PhD, in a separate interview. He acknowledged, however, that the study’s authors did try to account for this by limiting the timescale of their analysis to the first 10 years of biologic therapy. They also used the usual methods of propensity score matching and multivariate Cox regression analysis to hopefully iron out any differences between the two groups of patients.
Study details and results
Ms. Rosenthal and coauthors analyzed EMR data on patients with psoriasis but not PsA that were logged in the Maccabi Healthcare Services (MHS) database. The MHS is the second-largest health maintenance organization in Israel, insuring over 2 million members, the researchers said.
In all, 663 patients with psoriasis but not PsA before or at initiation of biologic treatment were included in their analysis and matched to a control group of 663 patients with psoriasis who had not received biologic treatment. Propensity score matching was used to iron out some differences in baseline characteristics that had been seen between the groups, such as older age at diagnosis, higher body mass index, and a longer time between diagnosis and treatment seen in patients treated without biologics.
After adjusting for multiple risk factors and confounders, “the control group still had a significantly higher risk for PsA, compared to the biological treatment group,” the researchers wrote. Indeed, the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.39, with a 95% confidence interval between 1.03 and 1.87.
An ‘intriguing study’
“This is a retrospective study, and it has all the faults of a retrospective study,” said Dr. Adebajo, associate medical director for research and development at Barnsley (England) NHS Foundation Trust. But “these were patients who hopefully hadn’t yet developed psoriatic arthritis, although it is difficult to exclude subclinical psoriatic arthritis.”
The ideal would of course be to look at patients prospectively, but a randomized clinical trial would be unlikely to ever be conducted, Dr. Helliwell noted. “It would be unfair to randomize people who have got bad psoriasis and need a biologic to placebo just to prove the point really,” he said. “Getting control groups in this arena is very difficult.”
That doesn’t mean that prospective evaluation is not possible. Dr. Adebajo noted that there were already cohorts of newly diagnosed patients who were being prospectively followed up and those could perhaps be used to look at the question again in the future.
“You’re then looking at the natural history, the natural outcome, and you don’t need to worry about confounding because you’re just collecting all of the information as you go along.”
The idea that biologics might slow or even prevent the onset of PsA is “an interesting and enchanting hypothesis,” Dr. Adebajo said. “The study doesn’t prove the hypothesis, but it’s an intriguing study because it doesn’t disprove the hypothesis either.
“It gives us food for thought and a basis for further studies,” as well as some “encouragement to perhaps use biologics earlier because there may be additional benefits of doing so.”
That’s still to be proven of course, as it has been reported that patients with psoriasis can develop PsA while taking biologics.
“Clinically, that’s what we see in the combined clinic. We get people referred with psoriasis [who are] already on a biologic who developed musculoskeletal problems,” Dr. Helliwell said.
“It would be nice to believe” that biologics prevent or slow PsA in patients with psoriasis, Dr. Helliwell added, but I’m not sure these data are conclusive. From this study we know nothing about the phenotype of psoriasis, which is important in the development of PsA. In addition, we know that of the 30% of people with psoriasis who develop PsA, about half of these are undiagnosed at the time of such studies. In that case, what the biologic is doing is just treating preexisting PsA. If you count those numbers up, some of the differences between the two groups seen in this study are accounted for. From registry data there is no way of checking this.”
No external funding was used for the study. One author acknowledged acting as an investigator, adviser, or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Coherus, Dexcel Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer. All other authors had nothing to disclose.
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Adebajo had no conflicts of interest.
Receiving treatment with a biologic medication, compared with no biologic treatment, appeared to be associated with a lower risk for developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with psoriasis.
That’s according to the results of a nested case-control study involving electronic medical record data from an Israeli health maintenance organization in Arthritis & Rheumatology. Compared with no biologic treatment, the risk for developing PsA among PsO patients was reduced by 39%.
This study shows “a statistically and clinically significant lower risk for developing PsA among patients receiving biologic medications for psoriasis treatment,” wrote Yael Shalev Rosenthal, MPH, of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University and colleagues. “The results suggest considering treatment with biologic medications in patients [who] present with significant risk factors for PsA at an earlier stage of treatment.”
“It would be nice to believe this story, but I don’t think we can based on the evidence we’ve got so far,” commented Philip Helliwell, PhD, DM, in an interview.
Dr. Helliwell, who is professor of clinical rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and an Honorary Consultant Rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals and Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, noted that there were several issues with the current evidence.
Aside from their often retrospective or nonrandomized nature, prior analyses, including the current one, were based on EMR data.
“There’s actually no face-to-face patient contact going on here. It’s all done on coding, and coding can be unreliable,” Dr. Helliwell said.
While the study’s findings are “in line with other studies that have looked at this, and suggest that if you get a biologic, you’re less likely to get PsA with your psoriasis, there could be lots of reasons why.”
The big problem here is confounding by indication. “You don’t get on a biologic unless you’ve got bad psoriasis,” Dr. Helliwell explained. The Israeli criteria for starting a biologic are much higher than in the United Kingdom, he added, requiring more than 50% of patients’ body surface area to be affected, or a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score of more than 50. Moreover, people with bad psoriasis are more likely to get PsA. This, however, makes the results more impressive.
Confounding by indication is an issue with this study, agreed consultant rheumatologist Adewale Adebajo, PhD, in a separate interview. He acknowledged, however, that the study’s authors did try to account for this by limiting the timescale of their analysis to the first 10 years of biologic therapy. They also used the usual methods of propensity score matching and multivariate Cox regression analysis to hopefully iron out any differences between the two groups of patients.
Study details and results
Ms. Rosenthal and coauthors analyzed EMR data on patients with psoriasis but not PsA that were logged in the Maccabi Healthcare Services (MHS) database. The MHS is the second-largest health maintenance organization in Israel, insuring over 2 million members, the researchers said.
In all, 663 patients with psoriasis but not PsA before or at initiation of biologic treatment were included in their analysis and matched to a control group of 663 patients with psoriasis who had not received biologic treatment. Propensity score matching was used to iron out some differences in baseline characteristics that had been seen between the groups, such as older age at diagnosis, higher body mass index, and a longer time between diagnosis and treatment seen in patients treated without biologics.
After adjusting for multiple risk factors and confounders, “the control group still had a significantly higher risk for PsA, compared to the biological treatment group,” the researchers wrote. Indeed, the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.39, with a 95% confidence interval between 1.03 and 1.87.
An ‘intriguing study’
“This is a retrospective study, and it has all the faults of a retrospective study,” said Dr. Adebajo, associate medical director for research and development at Barnsley (England) NHS Foundation Trust. But “these were patients who hopefully hadn’t yet developed psoriatic arthritis, although it is difficult to exclude subclinical psoriatic arthritis.”
The ideal would of course be to look at patients prospectively, but a randomized clinical trial would be unlikely to ever be conducted, Dr. Helliwell noted. “It would be unfair to randomize people who have got bad psoriasis and need a biologic to placebo just to prove the point really,” he said. “Getting control groups in this arena is very difficult.”
That doesn’t mean that prospective evaluation is not possible. Dr. Adebajo noted that there were already cohorts of newly diagnosed patients who were being prospectively followed up and those could perhaps be used to look at the question again in the future.
“You’re then looking at the natural history, the natural outcome, and you don’t need to worry about confounding because you’re just collecting all of the information as you go along.”
The idea that biologics might slow or even prevent the onset of PsA is “an interesting and enchanting hypothesis,” Dr. Adebajo said. “The study doesn’t prove the hypothesis, but it’s an intriguing study because it doesn’t disprove the hypothesis either.
“It gives us food for thought and a basis for further studies,” as well as some “encouragement to perhaps use biologics earlier because there may be additional benefits of doing so.”
That’s still to be proven of course, as it has been reported that patients with psoriasis can develop PsA while taking biologics.
“Clinically, that’s what we see in the combined clinic. We get people referred with psoriasis [who are] already on a biologic who developed musculoskeletal problems,” Dr. Helliwell said.
“It would be nice to believe” that biologics prevent or slow PsA in patients with psoriasis, Dr. Helliwell added, but I’m not sure these data are conclusive. From this study we know nothing about the phenotype of psoriasis, which is important in the development of PsA. In addition, we know that of the 30% of people with psoriasis who develop PsA, about half of these are undiagnosed at the time of such studies. In that case, what the biologic is doing is just treating preexisting PsA. If you count those numbers up, some of the differences between the two groups seen in this study are accounted for. From registry data there is no way of checking this.”
No external funding was used for the study. One author acknowledged acting as an investigator, adviser, or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Coherus, Dexcel Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer. All other authors had nothing to disclose.
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Adebajo had no conflicts of interest.
Receiving treatment with a biologic medication, compared with no biologic treatment, appeared to be associated with a lower risk for developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with psoriasis.
That’s according to the results of a nested case-control study involving electronic medical record data from an Israeli health maintenance organization in Arthritis & Rheumatology. Compared with no biologic treatment, the risk for developing PsA among PsO patients was reduced by 39%.
This study shows “a statistically and clinically significant lower risk for developing PsA among patients receiving biologic medications for psoriasis treatment,” wrote Yael Shalev Rosenthal, MPH, of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University and colleagues. “The results suggest considering treatment with biologic medications in patients [who] present with significant risk factors for PsA at an earlier stage of treatment.”
“It would be nice to believe this story, but I don’t think we can based on the evidence we’ve got so far,” commented Philip Helliwell, PhD, DM, in an interview.
Dr. Helliwell, who is professor of clinical rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and an Honorary Consultant Rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals and Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, noted that there were several issues with the current evidence.
Aside from their often retrospective or nonrandomized nature, prior analyses, including the current one, were based on EMR data.
“There’s actually no face-to-face patient contact going on here. It’s all done on coding, and coding can be unreliable,” Dr. Helliwell said.
While the study’s findings are “in line with other studies that have looked at this, and suggest that if you get a biologic, you’re less likely to get PsA with your psoriasis, there could be lots of reasons why.”
The big problem here is confounding by indication. “You don’t get on a biologic unless you’ve got bad psoriasis,” Dr. Helliwell explained. The Israeli criteria for starting a biologic are much higher than in the United Kingdom, he added, requiring more than 50% of patients’ body surface area to be affected, or a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score of more than 50. Moreover, people with bad psoriasis are more likely to get PsA. This, however, makes the results more impressive.
Confounding by indication is an issue with this study, agreed consultant rheumatologist Adewale Adebajo, PhD, in a separate interview. He acknowledged, however, that the study’s authors did try to account for this by limiting the timescale of their analysis to the first 10 years of biologic therapy. They also used the usual methods of propensity score matching and multivariate Cox regression analysis to hopefully iron out any differences between the two groups of patients.
Study details and results
Ms. Rosenthal and coauthors analyzed EMR data on patients with psoriasis but not PsA that were logged in the Maccabi Healthcare Services (MHS) database. The MHS is the second-largest health maintenance organization in Israel, insuring over 2 million members, the researchers said.
In all, 663 patients with psoriasis but not PsA before or at initiation of biologic treatment were included in their analysis and matched to a control group of 663 patients with psoriasis who had not received biologic treatment. Propensity score matching was used to iron out some differences in baseline characteristics that had been seen between the groups, such as older age at diagnosis, higher body mass index, and a longer time between diagnosis and treatment seen in patients treated without biologics.
After adjusting for multiple risk factors and confounders, “the control group still had a significantly higher risk for PsA, compared to the biological treatment group,” the researchers wrote. Indeed, the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.39, with a 95% confidence interval between 1.03 and 1.87.
An ‘intriguing study’
“This is a retrospective study, and it has all the faults of a retrospective study,” said Dr. Adebajo, associate medical director for research and development at Barnsley (England) NHS Foundation Trust. But “these were patients who hopefully hadn’t yet developed psoriatic arthritis, although it is difficult to exclude subclinical psoriatic arthritis.”
The ideal would of course be to look at patients prospectively, but a randomized clinical trial would be unlikely to ever be conducted, Dr. Helliwell noted. “It would be unfair to randomize people who have got bad psoriasis and need a biologic to placebo just to prove the point really,” he said. “Getting control groups in this arena is very difficult.”
That doesn’t mean that prospective evaluation is not possible. Dr. Adebajo noted that there were already cohorts of newly diagnosed patients who were being prospectively followed up and those could perhaps be used to look at the question again in the future.
“You’re then looking at the natural history, the natural outcome, and you don’t need to worry about confounding because you’re just collecting all of the information as you go along.”
The idea that biologics might slow or even prevent the onset of PsA is “an interesting and enchanting hypothesis,” Dr. Adebajo said. “The study doesn’t prove the hypothesis, but it’s an intriguing study because it doesn’t disprove the hypothesis either.
“It gives us food for thought and a basis for further studies,” as well as some “encouragement to perhaps use biologics earlier because there may be additional benefits of doing so.”
That’s still to be proven of course, as it has been reported that patients with psoriasis can develop PsA while taking biologics.
“Clinically, that’s what we see in the combined clinic. We get people referred with psoriasis [who are] already on a biologic who developed musculoskeletal problems,” Dr. Helliwell said.
“It would be nice to believe” that biologics prevent or slow PsA in patients with psoriasis, Dr. Helliwell added, but I’m not sure these data are conclusive. From this study we know nothing about the phenotype of psoriasis, which is important in the development of PsA. In addition, we know that of the 30% of people with psoriasis who develop PsA, about half of these are undiagnosed at the time of such studies. In that case, what the biologic is doing is just treating preexisting PsA. If you count those numbers up, some of the differences between the two groups seen in this study are accounted for. From registry data there is no way of checking this.”
No external funding was used for the study. One author acknowledged acting as an investigator, adviser, or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Coherus, Dexcel Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer. All other authors had nothing to disclose.
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Adebajo had no conflicts of interest.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Children’s upper airways primed to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antidepressant helps prevent hospitalization in COVID patients: Study
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although inconclusive, CV safety study of cancer therapy attracts attention
The first global trial to compare the cardiovascular (CV) safety of two therapies for prostate cancer proved inconclusive because of inadequate enrollment and events, but the study is a harbinger of growth in the emerging specialty of cardio-oncology, according to experts.
“Many new cancer agents have extended patient survival, yet some of these agents have significant potential cardiovascular toxicity,” said Renato D. Lopes, MD, in presenting a study at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
In the context of improving survival in patients with or at risk for both cancer and cardiovascular disease, he suggested that the prostate cancer study he led could be “a model for interdisciplinary collaboration” needed to address the relative and sometimes competing risks of these disease states.
This point was seconded by several pioneers in cardio-oncology who participated in the discussion of the results of the trial, called PRONOUNCE.
“We know many drugs in oncology increase cardiovascular risk, so these are the types of trials we need,” according Thomas M. Suter, MD, who leads the cardio-oncology service at the University Hospital, Berne, Switzerland. He was the ESC-invited discussant for PRONOUNCE.
More than 100 centers in 12 countries involved
In PRONOUNCE, 545 patients with prostate cancer and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to degarelix, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist, or leuprolide, a GnRH agonist. The patients were enrolled at 113 participating centers in 12 countries. All of the patients had an indication for an androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT).
In numerous previous studies, “ADT has been associated with higher CV morbidity and mortality, particularly in men with preexisting CV disease,” explained Dr. Lopes, but the relative cardiovascular safety of GnRH agonists relative to GnRH antagonists has been “controversial.”
The PRONOUNCE study was designed to resolve this issue, but the study was terminated early because of slow enrollment (not related to the COVID-19 pandemic). The planned enrollment was 900 patients.
In addition, the rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as myocardial infarction, stroke, or death, was lower over the course of follow-up than anticipated in the study design.
No significant difference on primary endpoint
At the end of 12 months, MACE occurred in 11 (4.1%) of patients randomized to leuprolide and 15 (5.5%) of those randomized to degarelix. The greater hazard ratio for MACE in the degarelix group did not approach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 1.28; P = .53).
As a result, the question of the relative CV safety of these drugs “remains unresolved,” according to Dr. Lopes, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.
This does not diminish the need to answer this question. In the addition to the fact that cancer is a malignancy primarily of advancing age when CV disease is prevalent – the mean age in this study was 73 years and 44% were over age 75 – it is often an indolent disease with long periods of survival, according to Dr. Lopes. About half of prostate cancer patients have concomitant CV disease, and about half will receive ADT at some point in their treatment.
In patients receiving ADT, leuprolide is far more commonly used than GnRH antagonists, which are offered in only about 4% of patients, according to data cited by Dr. Lopes. The underlying hypothesis of this study was that leuprolide is associated with greater CV risk, which might have been relevant to a risk-benefit calculation, if the hypothesis had been confirmed.
Cancer drugs can increase CV risk
Based on experimental data, “there is concern the leuprolide is involved in plaque destabilization,” said Dr. Lopes, but he noted that ADTs in general are associated with adverse metabolic changes, including increases in LDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, and body fat, all of which could be relevant to CV risk.
It is the improving rates of survival for prostate cancer as well for other types of cancer that have increased attention to the potential for cancer drugs to increase CV risk, another major cause of early mortality. For these competing risks, objective data are needed to evaluate a relative risk-to-benefit ratio for treatment choices.
This dilemma led the ESC to recently establish its Council on Cardio-Oncology, and many centers around the world are also creating interdisciplinary groups to guide treatment choices for patients with both diseases.
“You will certainly get a lot of referrals,” said Rudolf de Boer, MD, professor of translational cardiology, University Medical Center, Groningen, Netherlands. Basing his remark on his own experience starting a cardio-oncology clinic at his institution, he called this work challenging and agreed that the need for objective data is urgent.
“We need data to provide common ground on which to judge relative risks,” Dr. de Boer said. He also praised the PRONOUNCE investigators for their efforts even if the data failed to answer the question posed.
The PRONOUNCE results were published online in Circulation at the time of Dr. Lopes’s presentation.
The study received funding from Ferring Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Lopes reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Dr. Suter reports financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Roche. Dr. de Boer reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche.
The first global trial to compare the cardiovascular (CV) safety of two therapies for prostate cancer proved inconclusive because of inadequate enrollment and events, but the study is a harbinger of growth in the emerging specialty of cardio-oncology, according to experts.
“Many new cancer agents have extended patient survival, yet some of these agents have significant potential cardiovascular toxicity,” said Renato D. Lopes, MD, in presenting a study at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
In the context of improving survival in patients with or at risk for both cancer and cardiovascular disease, he suggested that the prostate cancer study he led could be “a model for interdisciplinary collaboration” needed to address the relative and sometimes competing risks of these disease states.
This point was seconded by several pioneers in cardio-oncology who participated in the discussion of the results of the trial, called PRONOUNCE.
“We know many drugs in oncology increase cardiovascular risk, so these are the types of trials we need,” according Thomas M. Suter, MD, who leads the cardio-oncology service at the University Hospital, Berne, Switzerland. He was the ESC-invited discussant for PRONOUNCE.
More than 100 centers in 12 countries involved
In PRONOUNCE, 545 patients with prostate cancer and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to degarelix, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist, or leuprolide, a GnRH agonist. The patients were enrolled at 113 participating centers in 12 countries. All of the patients had an indication for an androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT).
In numerous previous studies, “ADT has been associated with higher CV morbidity and mortality, particularly in men with preexisting CV disease,” explained Dr. Lopes, but the relative cardiovascular safety of GnRH agonists relative to GnRH antagonists has been “controversial.”
The PRONOUNCE study was designed to resolve this issue, but the study was terminated early because of slow enrollment (not related to the COVID-19 pandemic). The planned enrollment was 900 patients.
In addition, the rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as myocardial infarction, stroke, or death, was lower over the course of follow-up than anticipated in the study design.
No significant difference on primary endpoint
At the end of 12 months, MACE occurred in 11 (4.1%) of patients randomized to leuprolide and 15 (5.5%) of those randomized to degarelix. The greater hazard ratio for MACE in the degarelix group did not approach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 1.28; P = .53).
As a result, the question of the relative CV safety of these drugs “remains unresolved,” according to Dr. Lopes, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.
This does not diminish the need to answer this question. In the addition to the fact that cancer is a malignancy primarily of advancing age when CV disease is prevalent – the mean age in this study was 73 years and 44% were over age 75 – it is often an indolent disease with long periods of survival, according to Dr. Lopes. About half of prostate cancer patients have concomitant CV disease, and about half will receive ADT at some point in their treatment.
In patients receiving ADT, leuprolide is far more commonly used than GnRH antagonists, which are offered in only about 4% of patients, according to data cited by Dr. Lopes. The underlying hypothesis of this study was that leuprolide is associated with greater CV risk, which might have been relevant to a risk-benefit calculation, if the hypothesis had been confirmed.
Cancer drugs can increase CV risk
Based on experimental data, “there is concern the leuprolide is involved in plaque destabilization,” said Dr. Lopes, but he noted that ADTs in general are associated with adverse metabolic changes, including increases in LDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, and body fat, all of which could be relevant to CV risk.
It is the improving rates of survival for prostate cancer as well for other types of cancer that have increased attention to the potential for cancer drugs to increase CV risk, another major cause of early mortality. For these competing risks, objective data are needed to evaluate a relative risk-to-benefit ratio for treatment choices.
This dilemma led the ESC to recently establish its Council on Cardio-Oncology, and many centers around the world are also creating interdisciplinary groups to guide treatment choices for patients with both diseases.
“You will certainly get a lot of referrals,” said Rudolf de Boer, MD, professor of translational cardiology, University Medical Center, Groningen, Netherlands. Basing his remark on his own experience starting a cardio-oncology clinic at his institution, he called this work challenging and agreed that the need for objective data is urgent.
“We need data to provide common ground on which to judge relative risks,” Dr. de Boer said. He also praised the PRONOUNCE investigators for their efforts even if the data failed to answer the question posed.
The PRONOUNCE results were published online in Circulation at the time of Dr. Lopes’s presentation.
The study received funding from Ferring Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Lopes reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Dr. Suter reports financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Roche. Dr. de Boer reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche.
The first global trial to compare the cardiovascular (CV) safety of two therapies for prostate cancer proved inconclusive because of inadequate enrollment and events, but the study is a harbinger of growth in the emerging specialty of cardio-oncology, according to experts.
“Many new cancer agents have extended patient survival, yet some of these agents have significant potential cardiovascular toxicity,” said Renato D. Lopes, MD, in presenting a study at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
In the context of improving survival in patients with or at risk for both cancer and cardiovascular disease, he suggested that the prostate cancer study he led could be “a model for interdisciplinary collaboration” needed to address the relative and sometimes competing risks of these disease states.
This point was seconded by several pioneers in cardio-oncology who participated in the discussion of the results of the trial, called PRONOUNCE.
“We know many drugs in oncology increase cardiovascular risk, so these are the types of trials we need,” according Thomas M. Suter, MD, who leads the cardio-oncology service at the University Hospital, Berne, Switzerland. He was the ESC-invited discussant for PRONOUNCE.
More than 100 centers in 12 countries involved
In PRONOUNCE, 545 patients with prostate cancer and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to degarelix, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist, or leuprolide, a GnRH agonist. The patients were enrolled at 113 participating centers in 12 countries. All of the patients had an indication for an androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT).
In numerous previous studies, “ADT has been associated with higher CV morbidity and mortality, particularly in men with preexisting CV disease,” explained Dr. Lopes, but the relative cardiovascular safety of GnRH agonists relative to GnRH antagonists has been “controversial.”
The PRONOUNCE study was designed to resolve this issue, but the study was terminated early because of slow enrollment (not related to the COVID-19 pandemic). The planned enrollment was 900 patients.
In addition, the rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as myocardial infarction, stroke, or death, was lower over the course of follow-up than anticipated in the study design.
No significant difference on primary endpoint
At the end of 12 months, MACE occurred in 11 (4.1%) of patients randomized to leuprolide and 15 (5.5%) of those randomized to degarelix. The greater hazard ratio for MACE in the degarelix group did not approach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 1.28; P = .53).
As a result, the question of the relative CV safety of these drugs “remains unresolved,” according to Dr. Lopes, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.
This does not diminish the need to answer this question. In the addition to the fact that cancer is a malignancy primarily of advancing age when CV disease is prevalent – the mean age in this study was 73 years and 44% were over age 75 – it is often an indolent disease with long periods of survival, according to Dr. Lopes. About half of prostate cancer patients have concomitant CV disease, and about half will receive ADT at some point in their treatment.
In patients receiving ADT, leuprolide is far more commonly used than GnRH antagonists, which are offered in only about 4% of patients, according to data cited by Dr. Lopes. The underlying hypothesis of this study was that leuprolide is associated with greater CV risk, which might have been relevant to a risk-benefit calculation, if the hypothesis had been confirmed.
Cancer drugs can increase CV risk
Based on experimental data, “there is concern the leuprolide is involved in plaque destabilization,” said Dr. Lopes, but he noted that ADTs in general are associated with adverse metabolic changes, including increases in LDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, and body fat, all of which could be relevant to CV risk.
It is the improving rates of survival for prostate cancer as well for other types of cancer that have increased attention to the potential for cancer drugs to increase CV risk, another major cause of early mortality. For these competing risks, objective data are needed to evaluate a relative risk-to-benefit ratio for treatment choices.
This dilemma led the ESC to recently establish its Council on Cardio-Oncology, and many centers around the world are also creating interdisciplinary groups to guide treatment choices for patients with both diseases.
“You will certainly get a lot of referrals,” said Rudolf de Boer, MD, professor of translational cardiology, University Medical Center, Groningen, Netherlands. Basing his remark on his own experience starting a cardio-oncology clinic at his institution, he called this work challenging and agreed that the need for objective data is urgent.
“We need data to provide common ground on which to judge relative risks,” Dr. de Boer said. He also praised the PRONOUNCE investigators for their efforts even if the data failed to answer the question posed.
The PRONOUNCE results were published online in Circulation at the time of Dr. Lopes’s presentation.
The study received funding from Ferring Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Lopes reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Dr. Suter reports financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Roche. Dr. de Boer reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche.
FROM ESC 2021
Pandemic-related drops in breast cancer screening hit hardest among medically underserved
Breast cancer screening rates at community health centers (CHCs) in the United States declined during the pandemic, particularly among Black and uninsured individuals, based on a retrospective look at 32 sites.
Still, drops in screening were less dramatic than national declines previously reported, possibly because of the American Cancer Society–directed CHANGE program, which was simultaneously underway at the CHCs involved, reported lead author Stacey A. Fedewa, PhD, senior principal scientist at the ACS in Atlanta, and colleagues.
“This is one of the first studies to examine breast cancer screening rates during the pandemic specifically among clinics providing care to communities of color and lower income populations, a group with lower utilization of and greater barriers to [breast cancer] screening,” the investigators wrote in Cancer. “This is important because these populations have longstanding barriers to accessing care, lower breast screening rates, higher breast cancer mortality rates, and are especially vulnerable to health care disruptions.”
According to a previous analysis of electronic health records by Mast and Munoz del Rio, breast cancer screening rates in the United States dropped 94% in March/April 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic was declared a national emergency. Although a recent follow-up report showed a rebound in breast cancer screening, the estimated rate remains 13% below average.
The present study evaluated data from 32 out of 1,385 CHCs in the United States. All centers were involved in the ACS-run CHANGE grant program, which funded the clinics for 2 years, during which time they implemented at least three evidence-based provider and client interventions, such as patient navigation or electronic medical record enhancements. The clinics reported breast cancer screening rates on a routine basis throughout the 2-year period, beginning August 2018.
Breast cancer screening rate was defined as the percentage of women aged 50-74 years who had a screening mammogram within the past 27 months, out of a total pool of women who had a medical visit within the past year. For 2018, 2019, and 2020, respectively, 142,207; 142,003; and 150,630 women had a medical visit. Screening rates were compared across years in either June or July. Findings were further characterized by demographic characteristics, urban/rural status, and clinic region.
From 2018 to 2019 breast cancer screening rates rose 18%, from 45.8% to 53.9%. This increase was followed by an 8% decline during the 2019-2020 period, from 53.9% to 49.6%.
The investigators estimated the number of missed mammograms and breast cancer diagnoses for two comparative, hypothetical scenarios: first, if the rising trend from 2018 to 2019 had continued through 2020, and second, if the rate had plateaued at 53.9%.
The rising trend model suggested that 47,517 fewer mammograms than normal were conducted during 2019-2020, resulting in 242 missed breast cancer diagnoses, of which 166 were invasive and 76 were ductal carcinoma in situ. The plateau model suggested that 6,477 fewer mammograms were conducted, leading to 33 missed diagnoses.
Compared with the 8% decline in screening overall, the rate among Black patients dropped 12%, while rates at clinics with a lower proportion of uninsured patients dropped an average of 15%. In contrast, clinics in the South did not have a significant reduction in screening, “possibly reflecting lower baseline rates or impact of stay-at-home orders,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Fedewa and colleagues also noted that their findings were less dramatic than those reported by Mast and Munoz del Rio. They suggested that the CHANGE program may have softened the blow dealt by the pandemic.
“The CHANGE program–funded interventions – that were established before and continued through 2020 – may have mitigated the pandemic’s effects on breast cancer screening services among the 32 CHCs that were studied,” they wrote. “Further investigation of breast cancer screening rates among additional CHCs will further inform where targeted interventions (e.g., client reminders, education on return to screening) are most needed.”
According to Madeline Sutton, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, “Progress seen with the CHANGE program should be duplicated in other clinical venues based on improvements seen in numbers of mammograms and breast cancers detected.”
Still, Dr. Sutton noted that the racial/ethnic disparities remain cause for concern.
“This study has implications for persons served at CHCs, especially if breast cancer racial/ethnic disparities are unintentionally widened during this pandemic,” Dr. Sutton said in a written comment. “Policy-level changes that decrease BCSR [breast cancer screen rate] gaps for women are warranted.”
Ana Velázquez Mañana, MD, a medical oncology fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, suggested that the effects of the pandemic may have been even more pronounced among medically underserved patients in whom interventions to increase screening were not being conducted, as they were through the CHANGE program.
“One must wonder to what degree these interventions reduced the decline in screening mammography rates observed during the pandemic and to what degree could disparities in screening be magnified in community health centers with less resources,” Dr. Velázquez said in a written comment. “Therefore, understanding barriers to breast cancer screening among our specific health care systems is key to guide resource allocation and the development of evidence-based multilevel interventions that can address these barriers, and ultimately increase screening rates.”
Dr. Velázquez also noted that the study by Dr. Fedewa and colleagues may have missed drops in screening among vulnerable populations that occurred later in the pandemic and in geographic hotspots. In a recent JAMA Network Open study, Dr. Velázquez reported a 41% drop in breast cancer screening at a safety-net hospital in San Francisco during the first stay-at-home order, which lasted from Feb. 1, 2020 to May 31, 2020.
The Breast Health Equity CHANGE grant was funded by the National Football League in partnership with the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported employment by the American Cancer Society. Dr. Wehling and Dr. Wysocki disclosed grants from Pfizer unrelated to this research. Dr. Sutton and Dr. Velázquez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Breast cancer screening rates at community health centers (CHCs) in the United States declined during the pandemic, particularly among Black and uninsured individuals, based on a retrospective look at 32 sites.
Still, drops in screening were less dramatic than national declines previously reported, possibly because of the American Cancer Society–directed CHANGE program, which was simultaneously underway at the CHCs involved, reported lead author Stacey A. Fedewa, PhD, senior principal scientist at the ACS in Atlanta, and colleagues.
“This is one of the first studies to examine breast cancer screening rates during the pandemic specifically among clinics providing care to communities of color and lower income populations, a group with lower utilization of and greater barriers to [breast cancer] screening,” the investigators wrote in Cancer. “This is important because these populations have longstanding barriers to accessing care, lower breast screening rates, higher breast cancer mortality rates, and are especially vulnerable to health care disruptions.”
According to a previous analysis of electronic health records by Mast and Munoz del Rio, breast cancer screening rates in the United States dropped 94% in March/April 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic was declared a national emergency. Although a recent follow-up report showed a rebound in breast cancer screening, the estimated rate remains 13% below average.
The present study evaluated data from 32 out of 1,385 CHCs in the United States. All centers were involved in the ACS-run CHANGE grant program, which funded the clinics for 2 years, during which time they implemented at least three evidence-based provider and client interventions, such as patient navigation or electronic medical record enhancements. The clinics reported breast cancer screening rates on a routine basis throughout the 2-year period, beginning August 2018.
Breast cancer screening rate was defined as the percentage of women aged 50-74 years who had a screening mammogram within the past 27 months, out of a total pool of women who had a medical visit within the past year. For 2018, 2019, and 2020, respectively, 142,207; 142,003; and 150,630 women had a medical visit. Screening rates were compared across years in either June or July. Findings were further characterized by demographic characteristics, urban/rural status, and clinic region.
From 2018 to 2019 breast cancer screening rates rose 18%, from 45.8% to 53.9%. This increase was followed by an 8% decline during the 2019-2020 period, from 53.9% to 49.6%.
The investigators estimated the number of missed mammograms and breast cancer diagnoses for two comparative, hypothetical scenarios: first, if the rising trend from 2018 to 2019 had continued through 2020, and second, if the rate had plateaued at 53.9%.
The rising trend model suggested that 47,517 fewer mammograms than normal were conducted during 2019-2020, resulting in 242 missed breast cancer diagnoses, of which 166 were invasive and 76 were ductal carcinoma in situ. The plateau model suggested that 6,477 fewer mammograms were conducted, leading to 33 missed diagnoses.
Compared with the 8% decline in screening overall, the rate among Black patients dropped 12%, while rates at clinics with a lower proportion of uninsured patients dropped an average of 15%. In contrast, clinics in the South did not have a significant reduction in screening, “possibly reflecting lower baseline rates or impact of stay-at-home orders,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Fedewa and colleagues also noted that their findings were less dramatic than those reported by Mast and Munoz del Rio. They suggested that the CHANGE program may have softened the blow dealt by the pandemic.
“The CHANGE program–funded interventions – that were established before and continued through 2020 – may have mitigated the pandemic’s effects on breast cancer screening services among the 32 CHCs that were studied,” they wrote. “Further investigation of breast cancer screening rates among additional CHCs will further inform where targeted interventions (e.g., client reminders, education on return to screening) are most needed.”
According to Madeline Sutton, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, “Progress seen with the CHANGE program should be duplicated in other clinical venues based on improvements seen in numbers of mammograms and breast cancers detected.”
Still, Dr. Sutton noted that the racial/ethnic disparities remain cause for concern.
“This study has implications for persons served at CHCs, especially if breast cancer racial/ethnic disparities are unintentionally widened during this pandemic,” Dr. Sutton said in a written comment. “Policy-level changes that decrease BCSR [breast cancer screen rate] gaps for women are warranted.”
Ana Velázquez Mañana, MD, a medical oncology fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, suggested that the effects of the pandemic may have been even more pronounced among medically underserved patients in whom interventions to increase screening were not being conducted, as they were through the CHANGE program.
“One must wonder to what degree these interventions reduced the decline in screening mammography rates observed during the pandemic and to what degree could disparities in screening be magnified in community health centers with less resources,” Dr. Velázquez said in a written comment. “Therefore, understanding barriers to breast cancer screening among our specific health care systems is key to guide resource allocation and the development of evidence-based multilevel interventions that can address these barriers, and ultimately increase screening rates.”
Dr. Velázquez also noted that the study by Dr. Fedewa and colleagues may have missed drops in screening among vulnerable populations that occurred later in the pandemic and in geographic hotspots. In a recent JAMA Network Open study, Dr. Velázquez reported a 41% drop in breast cancer screening at a safety-net hospital in San Francisco during the first stay-at-home order, which lasted from Feb. 1, 2020 to May 31, 2020.
The Breast Health Equity CHANGE grant was funded by the National Football League in partnership with the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported employment by the American Cancer Society. Dr. Wehling and Dr. Wysocki disclosed grants from Pfizer unrelated to this research. Dr. Sutton and Dr. Velázquez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Breast cancer screening rates at community health centers (CHCs) in the United States declined during the pandemic, particularly among Black and uninsured individuals, based on a retrospective look at 32 sites.
Still, drops in screening were less dramatic than national declines previously reported, possibly because of the American Cancer Society–directed CHANGE program, which was simultaneously underway at the CHCs involved, reported lead author Stacey A. Fedewa, PhD, senior principal scientist at the ACS in Atlanta, and colleagues.
“This is one of the first studies to examine breast cancer screening rates during the pandemic specifically among clinics providing care to communities of color and lower income populations, a group with lower utilization of and greater barriers to [breast cancer] screening,” the investigators wrote in Cancer. “This is important because these populations have longstanding barriers to accessing care, lower breast screening rates, higher breast cancer mortality rates, and are especially vulnerable to health care disruptions.”
According to a previous analysis of electronic health records by Mast and Munoz del Rio, breast cancer screening rates in the United States dropped 94% in March/April 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic was declared a national emergency. Although a recent follow-up report showed a rebound in breast cancer screening, the estimated rate remains 13% below average.
The present study evaluated data from 32 out of 1,385 CHCs in the United States. All centers were involved in the ACS-run CHANGE grant program, which funded the clinics for 2 years, during which time they implemented at least three evidence-based provider and client interventions, such as patient navigation or electronic medical record enhancements. The clinics reported breast cancer screening rates on a routine basis throughout the 2-year period, beginning August 2018.
Breast cancer screening rate was defined as the percentage of women aged 50-74 years who had a screening mammogram within the past 27 months, out of a total pool of women who had a medical visit within the past year. For 2018, 2019, and 2020, respectively, 142,207; 142,003; and 150,630 women had a medical visit. Screening rates were compared across years in either June or July. Findings were further characterized by demographic characteristics, urban/rural status, and clinic region.
From 2018 to 2019 breast cancer screening rates rose 18%, from 45.8% to 53.9%. This increase was followed by an 8% decline during the 2019-2020 period, from 53.9% to 49.6%.
The investigators estimated the number of missed mammograms and breast cancer diagnoses for two comparative, hypothetical scenarios: first, if the rising trend from 2018 to 2019 had continued through 2020, and second, if the rate had plateaued at 53.9%.
The rising trend model suggested that 47,517 fewer mammograms than normal were conducted during 2019-2020, resulting in 242 missed breast cancer diagnoses, of which 166 were invasive and 76 were ductal carcinoma in situ. The plateau model suggested that 6,477 fewer mammograms were conducted, leading to 33 missed diagnoses.
Compared with the 8% decline in screening overall, the rate among Black patients dropped 12%, while rates at clinics with a lower proportion of uninsured patients dropped an average of 15%. In contrast, clinics in the South did not have a significant reduction in screening, “possibly reflecting lower baseline rates or impact of stay-at-home orders,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Fedewa and colleagues also noted that their findings were less dramatic than those reported by Mast and Munoz del Rio. They suggested that the CHANGE program may have softened the blow dealt by the pandemic.
“The CHANGE program–funded interventions – that were established before and continued through 2020 – may have mitigated the pandemic’s effects on breast cancer screening services among the 32 CHCs that were studied,” they wrote. “Further investigation of breast cancer screening rates among additional CHCs will further inform where targeted interventions (e.g., client reminders, education on return to screening) are most needed.”
According to Madeline Sutton, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, “Progress seen with the CHANGE program should be duplicated in other clinical venues based on improvements seen in numbers of mammograms and breast cancers detected.”
Still, Dr. Sutton noted that the racial/ethnic disparities remain cause for concern.
“This study has implications for persons served at CHCs, especially if breast cancer racial/ethnic disparities are unintentionally widened during this pandemic,” Dr. Sutton said in a written comment. “Policy-level changes that decrease BCSR [breast cancer screen rate] gaps for women are warranted.”
Ana Velázquez Mañana, MD, a medical oncology fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, suggested that the effects of the pandemic may have been even more pronounced among medically underserved patients in whom interventions to increase screening were not being conducted, as they were through the CHANGE program.
“One must wonder to what degree these interventions reduced the decline in screening mammography rates observed during the pandemic and to what degree could disparities in screening be magnified in community health centers with less resources,” Dr. Velázquez said in a written comment. “Therefore, understanding barriers to breast cancer screening among our specific health care systems is key to guide resource allocation and the development of evidence-based multilevel interventions that can address these barriers, and ultimately increase screening rates.”
Dr. Velázquez also noted that the study by Dr. Fedewa and colleagues may have missed drops in screening among vulnerable populations that occurred later in the pandemic and in geographic hotspots. In a recent JAMA Network Open study, Dr. Velázquez reported a 41% drop in breast cancer screening at a safety-net hospital in San Francisco during the first stay-at-home order, which lasted from Feb. 1, 2020 to May 31, 2020.
The Breast Health Equity CHANGE grant was funded by the National Football League in partnership with the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported employment by the American Cancer Society. Dr. Wehling and Dr. Wysocki disclosed grants from Pfizer unrelated to this research. Dr. Sutton and Dr. Velázquez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM CANCER