User login
Positive top-line results for cannabinoid-based med for nerve pain
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How a medical recoding may limit cancer patients’ options for breast reconstruction
On June 1, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services plans to reexamine how doctors are paid for a type of breast reconstruction known as DIEP flap, in which skin, fat, and blood vessels are harvested from a woman’s abdomen to create a new breast.
The procedure offers potential advantages over implants and operations that take muscle from the abdomen. But it’s also more expensive. If patients go outside an insurance network for the operation, it can cost more than $50,000. And, if insurers pay significantly less for the surgery as a result of the government’s decision, some in-network surgeons would stop offering it, a plastic surgeons group has argued.
The DIEP flap controversy, spotlighted by CBS News in January, illustrates arcane and indirect ways the federal government can influence which medical options are available – even to people with private insurance. Often, the answers come down to billing codes – which identify specific medical services on forms doctors submit for reimbursement – and the competing pleas of groups whose interests are riding on them.
Medical coding is the backbone for “how business gets done in medicine,” said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, a physician at Washington University in St. Louis who researches health economics and policy.
CMS, the agency overseeing Medicare and Medicaid, maintains a list of codes representing thousands of medical services and products. It regularly evaluates whether to add codes or revise or remove existing ones. In 2022, it decided to eliminate a code that has enabled doctors to collect much more money for DIEP flap operations than for simpler types of breast reconstruction.
In 2006, CMS established an “S” code – S2068 – for what was then a relatively new procedure: breast reconstructions with deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (DIEP flap). S codes temporarily fill gaps in a parallel system of billing codes known as CPT codes, which are maintained by the American Medical Association.
Codes don’t dictate the amounts private insurers pay for medical services; those reimbursements are generally worked out between insurance companies and medical providers. However, using the narrowly targeted S code, doctors and hospitals have been able to distinguish DIEP flap surgeries, which require complex microsurgical skills, from other forms of breast reconstruction that take less time to perform and generally yield lower insurance reimbursements.
CMS announced in 2022 that it planned to eliminate the S code at the end of 2024 – a move some doctors say would slash the amount surgeons are paid. (To be precise, CMS announced it would eliminate a series of three S codes for similar procedures, but some of the more outspoken critics have focused on one of them, S2068.) The agency’s decision is already changing the landscape of reconstructive surgery and creating anxiety for breast cancer patients.
Kate Getz, a single mother in Morton, Ill., learned she had cancer in January at age 30. As she grappled with her diagnosis, it was overwhelming to think about what her body would look like over the long term. She pictured herself getting married one day and wondered “how on earth I would be able to wear a wedding dress with only having one breast left,” she said.
She thought a DIEP flap was her best option and worried about having to undergo repeated surgeries if she got implants instead. Implants generally need to be replaced every 10 years or so. But after she spent more than a month trying to get answers about how her DIEP flap surgery would be covered, Ms. Getz’s insurer, Cigna, informed her it would use a lower-paying CPT code to reimburse her physician, Ms. Getz said. As far as she could see, that would have made it impossible for Ms. Getz to obtain the surgery.
Paying out of pocket was “not even an option.”
“I’m a single mom. We get by, right? But I’m not, not wealthy by any means,” she said.
Cost is not necessarily the only hurdle patients seeking DIEP flaps must overcome. Citing the complexity of the procedure, Ms. Getz said, a local plastic surgeon told her it would be difficult for him to perform. She ended up traveling from Illinois to Texas for the surgery.
The government’s plan to eliminate the three S codes was driven by the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, a major lobbying organization for health insurance companies. In 2021, the group asked CMS to discontinue the codes, arguing that they were no longer needed because the AMA had updated a CPT code to explicitly include DIEP flap surgery and the related operations, according to a CMS document.
For years, the AMA advised doctors that the CPT code was appropriate for DIEP flap procedures. But after the government’s decision, at least two major insurance companies told doctors they would no longer reimburse them under the higher-paying codes, prompting a backlash.
Physicians and advocacy groups for breast cancer patients, such as the nonprofit organization Susan G. Komen, have argued that many plastic surgeons would stop providing DIEP flap procedures for women with private insurance because they wouldn’t get paid enough.
Lawmakers from both parties have asked the agency to keep the S code, including Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-Fla.) and Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), who have had breast cancer, and Sen. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.).
CMS at its June 1 meeting will consider whether to keep the three S codes or delay their expiration.
In a May 30 statement, Blue Cross Blue Shield Association spokesperson Kelly Parsons reiterated the organization’s view that “there is no longer a need to keep the S codes.”
In a profit-driven health care system, there’s a tug of war over reimbursements between providers and insurance companies, often at the expense of patients, said Dr. Joynt Maddox.
“We’re in this sort of constant battle” between hospital chains and insurance companies “about who’s going to wield more power at the bargaining table,” Dr. Joynt Maddox said. “And the clinical piece of that often gets lost, because it’s not often the clinical benefit and the clinical priority and the patient centeredness that’s at the middle of these conversations.”
Elisabeth Potter, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in DIEP flap surgeries, decided to perform Ms. Getz’s surgery at whatever price Cigna would pay.
According to Fair Health, a nonprofit that provides information on health care costs, in Austin, Tex. – where Dr. Potter is based – an insurer might pay an in-network doctor $9,323 for the surgery when it’s billed using the CPT code and $18,037 under the S code. Those amounts are not averages; rather, Fair Health estimated that 80% of payment rates are lower than or equal to those amounts.
Dr. Potter said her Cigna reimbursement “is significantly lower.”
Weeks before her May surgery, Ms. Getz received big news – Cigna had reversed itself and would cover her surgery under the S code. It “felt like a real victory,” she said.
But she still fears for other patients.
“I’m still asking these companies to do right by women,” Ms. Getz said. “I’m still asking them to provide the procedures we need to reimburse them at rates where women have access to them regardless of their wealth.”
In a statement, Cigna spokesperson Justine Sessions said the insurer remains “committed to ensuring that our customers have affordable coverage and access to the full range of breast reconstruction procedures and to quality surgeons who perform these complex surgeries.”
Medical costs that health insurers cover generally are passed along to consumers in the form of premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses.
For any type of breast reconstruction, there are benefits, risks, and trade-offs. A 2018 paper published in JAMA Surgery found that women who underwent DIEP flap surgery had higher odds of developing “reoperative complications” within 2 years than those who received artificial implants. However, DIEP flaps had lower odds of infection than implants.
Implants carry risks of additional surgery, pain, rupture, and even an uncommon type of immune system cancer.
Other flap procedures that take muscle from the abdomen can leave women with weakened abdominal walls and increase their risk of developing a hernia.
Academic research shows that insurance reimbursement affects which women can access DIEP flap breast reconstruction, creating a two-tiered system for private health insurance versus government programs like Medicare and Medicaid. Private insurance generally pays physicians more than government coverage, and Medicare doesn’t use S codes.
Lynn Damitz, a physician and board vice president of health policy and advocacy for the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, said the group supports continuing the S code temporarily or indefinitely. If reimbursements drop, some doctors won’t perform DIEP flaps anymore.
A study published in February found that, of patients who used their own tissue for breast reconstruction, privately insured patients were more likely than publicly insured patients to receive DIEP flap reconstruction.
To Dr. Potter, that shows what will happen if private insurance payments plummet. “If you’re a Medicare provider and you’re not paid to do DIEP flaps, you never tell a patient that it’s an option. You won’t perform it,” Dr. Potter said. “If you take private insurance and all of a sudden your reimbursement rate is cut from $15,000 down to $3,500, you’re not going to do that surgery. And I’m not saying that that’s the right thing to do, but that’s what happens.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
On June 1, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services plans to reexamine how doctors are paid for a type of breast reconstruction known as DIEP flap, in which skin, fat, and blood vessels are harvested from a woman’s abdomen to create a new breast.
The procedure offers potential advantages over implants and operations that take muscle from the abdomen. But it’s also more expensive. If patients go outside an insurance network for the operation, it can cost more than $50,000. And, if insurers pay significantly less for the surgery as a result of the government’s decision, some in-network surgeons would stop offering it, a plastic surgeons group has argued.
The DIEP flap controversy, spotlighted by CBS News in January, illustrates arcane and indirect ways the federal government can influence which medical options are available – even to people with private insurance. Often, the answers come down to billing codes – which identify specific medical services on forms doctors submit for reimbursement – and the competing pleas of groups whose interests are riding on them.
Medical coding is the backbone for “how business gets done in medicine,” said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, a physician at Washington University in St. Louis who researches health economics and policy.
CMS, the agency overseeing Medicare and Medicaid, maintains a list of codes representing thousands of medical services and products. It regularly evaluates whether to add codes or revise or remove existing ones. In 2022, it decided to eliminate a code that has enabled doctors to collect much more money for DIEP flap operations than for simpler types of breast reconstruction.
In 2006, CMS established an “S” code – S2068 – for what was then a relatively new procedure: breast reconstructions with deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (DIEP flap). S codes temporarily fill gaps in a parallel system of billing codes known as CPT codes, which are maintained by the American Medical Association.
Codes don’t dictate the amounts private insurers pay for medical services; those reimbursements are generally worked out between insurance companies and medical providers. However, using the narrowly targeted S code, doctors and hospitals have been able to distinguish DIEP flap surgeries, which require complex microsurgical skills, from other forms of breast reconstruction that take less time to perform and generally yield lower insurance reimbursements.
CMS announced in 2022 that it planned to eliminate the S code at the end of 2024 – a move some doctors say would slash the amount surgeons are paid. (To be precise, CMS announced it would eliminate a series of three S codes for similar procedures, but some of the more outspoken critics have focused on one of them, S2068.) The agency’s decision is already changing the landscape of reconstructive surgery and creating anxiety for breast cancer patients.
Kate Getz, a single mother in Morton, Ill., learned she had cancer in January at age 30. As she grappled with her diagnosis, it was overwhelming to think about what her body would look like over the long term. She pictured herself getting married one day and wondered “how on earth I would be able to wear a wedding dress with only having one breast left,” she said.
She thought a DIEP flap was her best option and worried about having to undergo repeated surgeries if she got implants instead. Implants generally need to be replaced every 10 years or so. But after she spent more than a month trying to get answers about how her DIEP flap surgery would be covered, Ms. Getz’s insurer, Cigna, informed her it would use a lower-paying CPT code to reimburse her physician, Ms. Getz said. As far as she could see, that would have made it impossible for Ms. Getz to obtain the surgery.
Paying out of pocket was “not even an option.”
“I’m a single mom. We get by, right? But I’m not, not wealthy by any means,” she said.
Cost is not necessarily the only hurdle patients seeking DIEP flaps must overcome. Citing the complexity of the procedure, Ms. Getz said, a local plastic surgeon told her it would be difficult for him to perform. She ended up traveling from Illinois to Texas for the surgery.
The government’s plan to eliminate the three S codes was driven by the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, a major lobbying organization for health insurance companies. In 2021, the group asked CMS to discontinue the codes, arguing that they were no longer needed because the AMA had updated a CPT code to explicitly include DIEP flap surgery and the related operations, according to a CMS document.
For years, the AMA advised doctors that the CPT code was appropriate for DIEP flap procedures. But after the government’s decision, at least two major insurance companies told doctors they would no longer reimburse them under the higher-paying codes, prompting a backlash.
Physicians and advocacy groups for breast cancer patients, such as the nonprofit organization Susan G. Komen, have argued that many plastic surgeons would stop providing DIEP flap procedures for women with private insurance because they wouldn’t get paid enough.
Lawmakers from both parties have asked the agency to keep the S code, including Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-Fla.) and Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), who have had breast cancer, and Sen. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.).
CMS at its June 1 meeting will consider whether to keep the three S codes or delay their expiration.
In a May 30 statement, Blue Cross Blue Shield Association spokesperson Kelly Parsons reiterated the organization’s view that “there is no longer a need to keep the S codes.”
In a profit-driven health care system, there’s a tug of war over reimbursements between providers and insurance companies, often at the expense of patients, said Dr. Joynt Maddox.
“We’re in this sort of constant battle” between hospital chains and insurance companies “about who’s going to wield more power at the bargaining table,” Dr. Joynt Maddox said. “And the clinical piece of that often gets lost, because it’s not often the clinical benefit and the clinical priority and the patient centeredness that’s at the middle of these conversations.”
Elisabeth Potter, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in DIEP flap surgeries, decided to perform Ms. Getz’s surgery at whatever price Cigna would pay.
According to Fair Health, a nonprofit that provides information on health care costs, in Austin, Tex. – where Dr. Potter is based – an insurer might pay an in-network doctor $9,323 for the surgery when it’s billed using the CPT code and $18,037 under the S code. Those amounts are not averages; rather, Fair Health estimated that 80% of payment rates are lower than or equal to those amounts.
Dr. Potter said her Cigna reimbursement “is significantly lower.”
Weeks before her May surgery, Ms. Getz received big news – Cigna had reversed itself and would cover her surgery under the S code. It “felt like a real victory,” she said.
But she still fears for other patients.
“I’m still asking these companies to do right by women,” Ms. Getz said. “I’m still asking them to provide the procedures we need to reimburse them at rates where women have access to them regardless of their wealth.”
In a statement, Cigna spokesperson Justine Sessions said the insurer remains “committed to ensuring that our customers have affordable coverage and access to the full range of breast reconstruction procedures and to quality surgeons who perform these complex surgeries.”
Medical costs that health insurers cover generally are passed along to consumers in the form of premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses.
For any type of breast reconstruction, there are benefits, risks, and trade-offs. A 2018 paper published in JAMA Surgery found that women who underwent DIEP flap surgery had higher odds of developing “reoperative complications” within 2 years than those who received artificial implants. However, DIEP flaps had lower odds of infection than implants.
Implants carry risks of additional surgery, pain, rupture, and even an uncommon type of immune system cancer.
Other flap procedures that take muscle from the abdomen can leave women with weakened abdominal walls and increase their risk of developing a hernia.
Academic research shows that insurance reimbursement affects which women can access DIEP flap breast reconstruction, creating a two-tiered system for private health insurance versus government programs like Medicare and Medicaid. Private insurance generally pays physicians more than government coverage, and Medicare doesn’t use S codes.
Lynn Damitz, a physician and board vice president of health policy and advocacy for the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, said the group supports continuing the S code temporarily or indefinitely. If reimbursements drop, some doctors won’t perform DIEP flaps anymore.
A study published in February found that, of patients who used their own tissue for breast reconstruction, privately insured patients were more likely than publicly insured patients to receive DIEP flap reconstruction.
To Dr. Potter, that shows what will happen if private insurance payments plummet. “If you’re a Medicare provider and you’re not paid to do DIEP flaps, you never tell a patient that it’s an option. You won’t perform it,” Dr. Potter said. “If you take private insurance and all of a sudden your reimbursement rate is cut from $15,000 down to $3,500, you’re not going to do that surgery. And I’m not saying that that’s the right thing to do, but that’s what happens.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
On June 1, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services plans to reexamine how doctors are paid for a type of breast reconstruction known as DIEP flap, in which skin, fat, and blood vessels are harvested from a woman’s abdomen to create a new breast.
The procedure offers potential advantages over implants and operations that take muscle from the abdomen. But it’s also more expensive. If patients go outside an insurance network for the operation, it can cost more than $50,000. And, if insurers pay significantly less for the surgery as a result of the government’s decision, some in-network surgeons would stop offering it, a plastic surgeons group has argued.
The DIEP flap controversy, spotlighted by CBS News in January, illustrates arcane and indirect ways the federal government can influence which medical options are available – even to people with private insurance. Often, the answers come down to billing codes – which identify specific medical services on forms doctors submit for reimbursement – and the competing pleas of groups whose interests are riding on them.
Medical coding is the backbone for “how business gets done in medicine,” said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, a physician at Washington University in St. Louis who researches health economics and policy.
CMS, the agency overseeing Medicare and Medicaid, maintains a list of codes representing thousands of medical services and products. It regularly evaluates whether to add codes or revise or remove existing ones. In 2022, it decided to eliminate a code that has enabled doctors to collect much more money for DIEP flap operations than for simpler types of breast reconstruction.
In 2006, CMS established an “S” code – S2068 – for what was then a relatively new procedure: breast reconstructions with deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (DIEP flap). S codes temporarily fill gaps in a parallel system of billing codes known as CPT codes, which are maintained by the American Medical Association.
Codes don’t dictate the amounts private insurers pay for medical services; those reimbursements are generally worked out between insurance companies and medical providers. However, using the narrowly targeted S code, doctors and hospitals have been able to distinguish DIEP flap surgeries, which require complex microsurgical skills, from other forms of breast reconstruction that take less time to perform and generally yield lower insurance reimbursements.
CMS announced in 2022 that it planned to eliminate the S code at the end of 2024 – a move some doctors say would slash the amount surgeons are paid. (To be precise, CMS announced it would eliminate a series of three S codes for similar procedures, but some of the more outspoken critics have focused on one of them, S2068.) The agency’s decision is already changing the landscape of reconstructive surgery and creating anxiety for breast cancer patients.
Kate Getz, a single mother in Morton, Ill., learned she had cancer in January at age 30. As she grappled with her diagnosis, it was overwhelming to think about what her body would look like over the long term. She pictured herself getting married one day and wondered “how on earth I would be able to wear a wedding dress with only having one breast left,” she said.
She thought a DIEP flap was her best option and worried about having to undergo repeated surgeries if she got implants instead. Implants generally need to be replaced every 10 years or so. But after she spent more than a month trying to get answers about how her DIEP flap surgery would be covered, Ms. Getz’s insurer, Cigna, informed her it would use a lower-paying CPT code to reimburse her physician, Ms. Getz said. As far as she could see, that would have made it impossible for Ms. Getz to obtain the surgery.
Paying out of pocket was “not even an option.”
“I’m a single mom. We get by, right? But I’m not, not wealthy by any means,” she said.
Cost is not necessarily the only hurdle patients seeking DIEP flaps must overcome. Citing the complexity of the procedure, Ms. Getz said, a local plastic surgeon told her it would be difficult for him to perform. She ended up traveling from Illinois to Texas for the surgery.
The government’s plan to eliminate the three S codes was driven by the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, a major lobbying organization for health insurance companies. In 2021, the group asked CMS to discontinue the codes, arguing that they were no longer needed because the AMA had updated a CPT code to explicitly include DIEP flap surgery and the related operations, according to a CMS document.
For years, the AMA advised doctors that the CPT code was appropriate for DIEP flap procedures. But after the government’s decision, at least two major insurance companies told doctors they would no longer reimburse them under the higher-paying codes, prompting a backlash.
Physicians and advocacy groups for breast cancer patients, such as the nonprofit organization Susan G. Komen, have argued that many plastic surgeons would stop providing DIEP flap procedures for women with private insurance because they wouldn’t get paid enough.
Lawmakers from both parties have asked the agency to keep the S code, including Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-Fla.) and Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), who have had breast cancer, and Sen. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.).
CMS at its June 1 meeting will consider whether to keep the three S codes or delay their expiration.
In a May 30 statement, Blue Cross Blue Shield Association spokesperson Kelly Parsons reiterated the organization’s view that “there is no longer a need to keep the S codes.”
In a profit-driven health care system, there’s a tug of war over reimbursements between providers and insurance companies, often at the expense of patients, said Dr. Joynt Maddox.
“We’re in this sort of constant battle” between hospital chains and insurance companies “about who’s going to wield more power at the bargaining table,” Dr. Joynt Maddox said. “And the clinical piece of that often gets lost, because it’s not often the clinical benefit and the clinical priority and the patient centeredness that’s at the middle of these conversations.”
Elisabeth Potter, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in DIEP flap surgeries, decided to perform Ms. Getz’s surgery at whatever price Cigna would pay.
According to Fair Health, a nonprofit that provides information on health care costs, in Austin, Tex. – where Dr. Potter is based – an insurer might pay an in-network doctor $9,323 for the surgery when it’s billed using the CPT code and $18,037 under the S code. Those amounts are not averages; rather, Fair Health estimated that 80% of payment rates are lower than or equal to those amounts.
Dr. Potter said her Cigna reimbursement “is significantly lower.”
Weeks before her May surgery, Ms. Getz received big news – Cigna had reversed itself and would cover her surgery under the S code. It “felt like a real victory,” she said.
But she still fears for other patients.
“I’m still asking these companies to do right by women,” Ms. Getz said. “I’m still asking them to provide the procedures we need to reimburse them at rates where women have access to them regardless of their wealth.”
In a statement, Cigna spokesperson Justine Sessions said the insurer remains “committed to ensuring that our customers have affordable coverage and access to the full range of breast reconstruction procedures and to quality surgeons who perform these complex surgeries.”
Medical costs that health insurers cover generally are passed along to consumers in the form of premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses.
For any type of breast reconstruction, there are benefits, risks, and trade-offs. A 2018 paper published in JAMA Surgery found that women who underwent DIEP flap surgery had higher odds of developing “reoperative complications” within 2 years than those who received artificial implants. However, DIEP flaps had lower odds of infection than implants.
Implants carry risks of additional surgery, pain, rupture, and even an uncommon type of immune system cancer.
Other flap procedures that take muscle from the abdomen can leave women with weakened abdominal walls and increase their risk of developing a hernia.
Academic research shows that insurance reimbursement affects which women can access DIEP flap breast reconstruction, creating a two-tiered system for private health insurance versus government programs like Medicare and Medicaid. Private insurance generally pays physicians more than government coverage, and Medicare doesn’t use S codes.
Lynn Damitz, a physician and board vice president of health policy and advocacy for the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, said the group supports continuing the S code temporarily or indefinitely. If reimbursements drop, some doctors won’t perform DIEP flaps anymore.
A study published in February found that, of patients who used their own tissue for breast reconstruction, privately insured patients were more likely than publicly insured patients to receive DIEP flap reconstruction.
To Dr. Potter, that shows what will happen if private insurance payments plummet. “If you’re a Medicare provider and you’re not paid to do DIEP flaps, you never tell a patient that it’s an option. You won’t perform it,” Dr. Potter said. “If you take private insurance and all of a sudden your reimbursement rate is cut from $15,000 down to $3,500, you’re not going to do that surgery. And I’m not saying that that’s the right thing to do, but that’s what happens.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Diagnosis and Management of Recurrent and Complicated UTIs in Women: Controversies and Dilemmas
In this piece, Dr. Mickey Karram & Dr. Roger R. Dmochowski discuss how although UTIs have demonstrated widespread occurrence and significant healthcare costs, there is not yet a “gold standard” definition for complicated UTI. To avoid the overuse of antimicrobial agents and their associated issues, it is vital that clinicians evaluate test results in the context of a patient’s overall risk and history of UTIs and current clinical presentation and utilize testing that enables more informed decisions.

In this piece, Dr. Mickey Karram & Dr. Roger R. Dmochowski discuss how although UTIs have demonstrated widespread occurrence and significant healthcare costs, there is not yet a “gold standard” definition for complicated UTI. To avoid the overuse of antimicrobial agents and their associated issues, it is vital that clinicians evaluate test results in the context of a patient’s overall risk and history of UTIs and current clinical presentation and utilize testing that enables more informed decisions.

In this piece, Dr. Mickey Karram & Dr. Roger R. Dmochowski discuss how although UTIs have demonstrated widespread occurrence and significant healthcare costs, there is not yet a “gold standard” definition for complicated UTI. To avoid the overuse of antimicrobial agents and their associated issues, it is vital that clinicians evaluate test results in the context of a patient’s overall risk and history of UTIs and current clinical presentation and utilize testing that enables more informed decisions.
Family placement better for deprived kids than institutions
SAN FRANCISCO – results of a new study suggest.
The study shows that sustained recovery is possible after severe, early-life adversity, study author Kathryn L. Humphreys, PhD, assistant professor, department of psychology and human development, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Given the strong evidence from the present study, I hope physicians will play a role in promoting family placements as an alternative to institutional care for children who have been orphaned,” she said.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association and were published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Millions of children around the world experience psychosocial deprivation while living in institutions, and many more are neglected in their families of origin. In addition, about 6.7 million children lost a parent or caregiver during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In particular, Romania has a history of institutionalizing children. Through decades of repressive policies from the Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, child abandonment became a national disaster. Families couldn’t afford to keep their children and were encouraged to turn them over to the state.
The current study was part of the Bucharest Early Intervention Project, initiated in 2001 to examine the impact of high-quality, family-based care on development. It included 136 Romanian children (mean age, about 22 months) who were abandoned at or shortly after birth and were placed in an institution.
Researchers randomly assigned each toddler to 1 of 56 foster families or to continue living in an institution (care as usual). The researchers had to create a foster care network, because such care was extremely limited at the start of the study.
Providing stimulating care
Foster parents in the study received regular support from social workers and U.S.-based psychologists. They were encouraged to “make a commitment to treat the child as if it was their own, providing sensitive, stimulating, and nurturing care, not just in the short term but for their whole life,” said Dr. Humphreys.
Foster care programs in the United States have been criticized for focusing on short-term care, she said. “It’s really just a bed to sleep on, clothes to wear, and food to eat rather than the psychological component we think is really important for child development.”
For the study, the researchers assessed the children across multiple developmental domains at baseline and at ages 30, 42, and 54 months. They conducted additional assessments when the kids were aged 8, 12, and 16-18 years.
The primary outcomes were cognitive functioning (IQ), physical growth (height, weight, head circumference), brain electrical activity (relative electroencephalography power in the alpha frequency band), and symptoms of five types of psychopathology (disinhibited social engagement disorder, reactive attachment disorder, ADHD symptoms, externalizing symptoms, and internalizing symptoms).
From over 7,000 observations analyzed across follow-ups, the investigators found that the intervention had an overall significant effect on cognitive, physical, and neural outcomes when considered collectively across waves (beta, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.46; P = .012). Compared to children who received care as usual, those in foster homes had significantly higher average IQ scores (P < .001) and physical size (P = .008).
The intervention had an overall beneficial effect in regard to psychopathology. The greatest impact involved a reduction in symptoms of reactive attachment disorder (P < .001).
“There are a few forms of psychopathology that seem to almost entirely occur after severe neglect, including reactive attachment disorder; we think of these as disorders of social relatedness that derive from aberrant or insufficient early caregiving experiences,” said Dr. Humphreys. “Being placed in a family reduced the symptoms of reactive attachment disorder to pretty much nonexistent.”
To a lesser extent, the intervention reduced symptoms of disinhibited social engagement disorder. The foster care group also had significantly fewer internalizing symptoms than did children in the care-as-usual group.
But there was no significant overall effect of the intervention on symptoms of ADHD or externalizing problems.
Positive effects persisted
For the most part, the positive effects of the intervention on children’s functioning persisted during nearly 2 decades of follow-up. The impact of the intervention “can be described as rapidly apparent by age 30 months and sustained through late adolescence,” wrote the authors.
Regarding the impact of age at the time of placement, the study found that, compared with children placed into foster care later, those who entered foster care earlier (younger than 33 months) had significantly higher IQ scores and relative alpha power, but there was no difference in physical growth.
For some outcomes, the benefits of earlier placement were apparent in early childhood but faded by adolescence. But Dr. Humphreys noted all placements were early by most definitions.
The researchers also assessed stability of foster care placements. Children were considered “stable” if they remained with their original foster family; they were considered “disrupted” if they no longer resided with the family.
Here, the study found some “striking results,” said Dr. Humphreys. The effect of placement stability was largest in adolescence, when, overall, those who had remained with their original foster family had better cognitive and physical outcomes and less severe symptoms of psychopathology compared to those who experienced placement disruptions.
As for sex differences, “it’s a mixed bag,” said Dr. Humphreys, although overall, “we didn’t see strong evidence of sex differences” in terms of outcomes.
The investigators were unable to examine trajectories of children’s functioning, which would have provided important information on aspects such as rate of growth and the shape of growth curves. Specific features of the institutional or foster care environment in Bucharest during the study may limit the generalizability of the findings to other settings.
Absolutely unique project
The study examined an “absolutely unique project” and had “very exciting” results that should have “important clinical implications,” commented the American Journal of Psychiatry editor-in-chief Ned Kalin, MD, Hedberg Professor and chair, department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin–Madison.
The findings are “pretty dramatic,” added Dr. Kalin. “This is probably the study to be thinking about when considering the future of treatment and interventions in children who have suffered from this type of neglect, which is unfortunately extremely common worldwide, including in the U.S.”
In particular, the findings regarding improved psychopathology “bode well for the future,” said Dr. Kalin. “We know these types of problems are risk factors for the later development of depression and anxiety disorders. It will be really interesting to find out, but my guess is these kids will be protected as they mature further.”
The study was supported by the NIH, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the Palix Foundation, and the Jacobs Foundation. Dr. Humphreys has received research funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation, the Caplan Foundation, the Jacobs Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the NIH, the Vanderbilt Institute for Clinical and Translational Research, the Vanderbilt Kennedy Center, and Vanderbilt University; she has received honoraria from the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology Future Directions Forum, Learning Grove, the University of Iowa, the University of Texas at Austin, and ZERO TO THREE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – results of a new study suggest.
The study shows that sustained recovery is possible after severe, early-life adversity, study author Kathryn L. Humphreys, PhD, assistant professor, department of psychology and human development, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Given the strong evidence from the present study, I hope physicians will play a role in promoting family placements as an alternative to institutional care for children who have been orphaned,” she said.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association and were published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Millions of children around the world experience psychosocial deprivation while living in institutions, and many more are neglected in their families of origin. In addition, about 6.7 million children lost a parent or caregiver during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In particular, Romania has a history of institutionalizing children. Through decades of repressive policies from the Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, child abandonment became a national disaster. Families couldn’t afford to keep their children and were encouraged to turn them over to the state.
The current study was part of the Bucharest Early Intervention Project, initiated in 2001 to examine the impact of high-quality, family-based care on development. It included 136 Romanian children (mean age, about 22 months) who were abandoned at or shortly after birth and were placed in an institution.
Researchers randomly assigned each toddler to 1 of 56 foster families or to continue living in an institution (care as usual). The researchers had to create a foster care network, because such care was extremely limited at the start of the study.
Providing stimulating care
Foster parents in the study received regular support from social workers and U.S.-based psychologists. They were encouraged to “make a commitment to treat the child as if it was their own, providing sensitive, stimulating, and nurturing care, not just in the short term but for their whole life,” said Dr. Humphreys.
Foster care programs in the United States have been criticized for focusing on short-term care, she said. “It’s really just a bed to sleep on, clothes to wear, and food to eat rather than the psychological component we think is really important for child development.”
For the study, the researchers assessed the children across multiple developmental domains at baseline and at ages 30, 42, and 54 months. They conducted additional assessments when the kids were aged 8, 12, and 16-18 years.
The primary outcomes were cognitive functioning (IQ), physical growth (height, weight, head circumference), brain electrical activity (relative electroencephalography power in the alpha frequency band), and symptoms of five types of psychopathology (disinhibited social engagement disorder, reactive attachment disorder, ADHD symptoms, externalizing symptoms, and internalizing symptoms).
From over 7,000 observations analyzed across follow-ups, the investigators found that the intervention had an overall significant effect on cognitive, physical, and neural outcomes when considered collectively across waves (beta, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.46; P = .012). Compared to children who received care as usual, those in foster homes had significantly higher average IQ scores (P < .001) and physical size (P = .008).
The intervention had an overall beneficial effect in regard to psychopathology. The greatest impact involved a reduction in symptoms of reactive attachment disorder (P < .001).
“There are a few forms of psychopathology that seem to almost entirely occur after severe neglect, including reactive attachment disorder; we think of these as disorders of social relatedness that derive from aberrant or insufficient early caregiving experiences,” said Dr. Humphreys. “Being placed in a family reduced the symptoms of reactive attachment disorder to pretty much nonexistent.”
To a lesser extent, the intervention reduced symptoms of disinhibited social engagement disorder. The foster care group also had significantly fewer internalizing symptoms than did children in the care-as-usual group.
But there was no significant overall effect of the intervention on symptoms of ADHD or externalizing problems.
Positive effects persisted
For the most part, the positive effects of the intervention on children’s functioning persisted during nearly 2 decades of follow-up. The impact of the intervention “can be described as rapidly apparent by age 30 months and sustained through late adolescence,” wrote the authors.
Regarding the impact of age at the time of placement, the study found that, compared with children placed into foster care later, those who entered foster care earlier (younger than 33 months) had significantly higher IQ scores and relative alpha power, but there was no difference in physical growth.
For some outcomes, the benefits of earlier placement were apparent in early childhood but faded by adolescence. But Dr. Humphreys noted all placements were early by most definitions.
The researchers also assessed stability of foster care placements. Children were considered “stable” if they remained with their original foster family; they were considered “disrupted” if they no longer resided with the family.
Here, the study found some “striking results,” said Dr. Humphreys. The effect of placement stability was largest in adolescence, when, overall, those who had remained with their original foster family had better cognitive and physical outcomes and less severe symptoms of psychopathology compared to those who experienced placement disruptions.
As for sex differences, “it’s a mixed bag,” said Dr. Humphreys, although overall, “we didn’t see strong evidence of sex differences” in terms of outcomes.
The investigators were unable to examine trajectories of children’s functioning, which would have provided important information on aspects such as rate of growth and the shape of growth curves. Specific features of the institutional or foster care environment in Bucharest during the study may limit the generalizability of the findings to other settings.
Absolutely unique project
The study examined an “absolutely unique project” and had “very exciting” results that should have “important clinical implications,” commented the American Journal of Psychiatry editor-in-chief Ned Kalin, MD, Hedberg Professor and chair, department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin–Madison.
The findings are “pretty dramatic,” added Dr. Kalin. “This is probably the study to be thinking about when considering the future of treatment and interventions in children who have suffered from this type of neglect, which is unfortunately extremely common worldwide, including in the U.S.”
In particular, the findings regarding improved psychopathology “bode well for the future,” said Dr. Kalin. “We know these types of problems are risk factors for the later development of depression and anxiety disorders. It will be really interesting to find out, but my guess is these kids will be protected as they mature further.”
The study was supported by the NIH, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the Palix Foundation, and the Jacobs Foundation. Dr. Humphreys has received research funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation, the Caplan Foundation, the Jacobs Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the NIH, the Vanderbilt Institute for Clinical and Translational Research, the Vanderbilt Kennedy Center, and Vanderbilt University; she has received honoraria from the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology Future Directions Forum, Learning Grove, the University of Iowa, the University of Texas at Austin, and ZERO TO THREE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – results of a new study suggest.
The study shows that sustained recovery is possible after severe, early-life adversity, study author Kathryn L. Humphreys, PhD, assistant professor, department of psychology and human development, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Given the strong evidence from the present study, I hope physicians will play a role in promoting family placements as an alternative to institutional care for children who have been orphaned,” she said.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association and were published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Millions of children around the world experience psychosocial deprivation while living in institutions, and many more are neglected in their families of origin. In addition, about 6.7 million children lost a parent or caregiver during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In particular, Romania has a history of institutionalizing children. Through decades of repressive policies from the Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, child abandonment became a national disaster. Families couldn’t afford to keep their children and were encouraged to turn them over to the state.
The current study was part of the Bucharest Early Intervention Project, initiated in 2001 to examine the impact of high-quality, family-based care on development. It included 136 Romanian children (mean age, about 22 months) who were abandoned at or shortly after birth and were placed in an institution.
Researchers randomly assigned each toddler to 1 of 56 foster families or to continue living in an institution (care as usual). The researchers had to create a foster care network, because such care was extremely limited at the start of the study.
Providing stimulating care
Foster parents in the study received regular support from social workers and U.S.-based psychologists. They were encouraged to “make a commitment to treat the child as if it was their own, providing sensitive, stimulating, and nurturing care, not just in the short term but for their whole life,” said Dr. Humphreys.
Foster care programs in the United States have been criticized for focusing on short-term care, she said. “It’s really just a bed to sleep on, clothes to wear, and food to eat rather than the psychological component we think is really important for child development.”
For the study, the researchers assessed the children across multiple developmental domains at baseline and at ages 30, 42, and 54 months. They conducted additional assessments when the kids were aged 8, 12, and 16-18 years.
The primary outcomes were cognitive functioning (IQ), physical growth (height, weight, head circumference), brain electrical activity (relative electroencephalography power in the alpha frequency band), and symptoms of five types of psychopathology (disinhibited social engagement disorder, reactive attachment disorder, ADHD symptoms, externalizing symptoms, and internalizing symptoms).
From over 7,000 observations analyzed across follow-ups, the investigators found that the intervention had an overall significant effect on cognitive, physical, and neural outcomes when considered collectively across waves (beta, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.46; P = .012). Compared to children who received care as usual, those in foster homes had significantly higher average IQ scores (P < .001) and physical size (P = .008).
The intervention had an overall beneficial effect in regard to psychopathology. The greatest impact involved a reduction in symptoms of reactive attachment disorder (P < .001).
“There are a few forms of psychopathology that seem to almost entirely occur after severe neglect, including reactive attachment disorder; we think of these as disorders of social relatedness that derive from aberrant or insufficient early caregiving experiences,” said Dr. Humphreys. “Being placed in a family reduced the symptoms of reactive attachment disorder to pretty much nonexistent.”
To a lesser extent, the intervention reduced symptoms of disinhibited social engagement disorder. The foster care group also had significantly fewer internalizing symptoms than did children in the care-as-usual group.
But there was no significant overall effect of the intervention on symptoms of ADHD or externalizing problems.
Positive effects persisted
For the most part, the positive effects of the intervention on children’s functioning persisted during nearly 2 decades of follow-up. The impact of the intervention “can be described as rapidly apparent by age 30 months and sustained through late adolescence,” wrote the authors.
Regarding the impact of age at the time of placement, the study found that, compared with children placed into foster care later, those who entered foster care earlier (younger than 33 months) had significantly higher IQ scores and relative alpha power, but there was no difference in physical growth.
For some outcomes, the benefits of earlier placement were apparent in early childhood but faded by adolescence. But Dr. Humphreys noted all placements were early by most definitions.
The researchers also assessed stability of foster care placements. Children were considered “stable” if they remained with their original foster family; they were considered “disrupted” if they no longer resided with the family.
Here, the study found some “striking results,” said Dr. Humphreys. The effect of placement stability was largest in adolescence, when, overall, those who had remained with their original foster family had better cognitive and physical outcomes and less severe symptoms of psychopathology compared to those who experienced placement disruptions.
As for sex differences, “it’s a mixed bag,” said Dr. Humphreys, although overall, “we didn’t see strong evidence of sex differences” in terms of outcomes.
The investigators were unable to examine trajectories of children’s functioning, which would have provided important information on aspects such as rate of growth and the shape of growth curves. Specific features of the institutional or foster care environment in Bucharest during the study may limit the generalizability of the findings to other settings.
Absolutely unique project
The study examined an “absolutely unique project” and had “very exciting” results that should have “important clinical implications,” commented the American Journal of Psychiatry editor-in-chief Ned Kalin, MD, Hedberg Professor and chair, department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin–Madison.
The findings are “pretty dramatic,” added Dr. Kalin. “This is probably the study to be thinking about when considering the future of treatment and interventions in children who have suffered from this type of neglect, which is unfortunately extremely common worldwide, including in the U.S.”
In particular, the findings regarding improved psychopathology “bode well for the future,” said Dr. Kalin. “We know these types of problems are risk factors for the later development of depression and anxiety disorders. It will be really interesting to find out, but my guess is these kids will be protected as they mature further.”
The study was supported by the NIH, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the Palix Foundation, and the Jacobs Foundation. Dr. Humphreys has received research funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation, the Caplan Foundation, the Jacobs Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the NIH, the Vanderbilt Institute for Clinical and Translational Research, the Vanderbilt Kennedy Center, and Vanderbilt University; she has received honoraria from the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology Future Directions Forum, Learning Grove, the University of Iowa, the University of Texas at Austin, and ZERO TO THREE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT APA 2023
ECG implant tightens AFib management, improves outcomes in MONITOR-AF
Chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension “often require long-term care through long-term monitoring,” observed a researcher, and “we know that continuous monitoring is superior to intermittent monitoring for long-term outcomes.”
So maybe practice should rely more on continuous ECG monitoring for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), also a chronic condition, proposed Dhanunjaya R. Lakkireddy, MD, of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kan., in presenting a new analysis at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
(ILRs), compared with standard care. The latter could include intermittent 12-lead ECG, Holter, or other intermittent monitoring at physicians’ discretion.
Patients with AFib and the ECG implants in the MONITOR-AF study, which was not randomized and therefore only suggestive, were managed “more efficiently” with greater access to electrophysiologists (P < .01) and adherence to oral anticoagulants (P = .020) and other medications.
Followed for a mean of 2 years, patients with ILRs were more likely to undergo catheter ablation, and their time to a catheter ablation “was impressively shorter, 153 days versus 426 days” (P < .001), Dr. Lakkireddy said.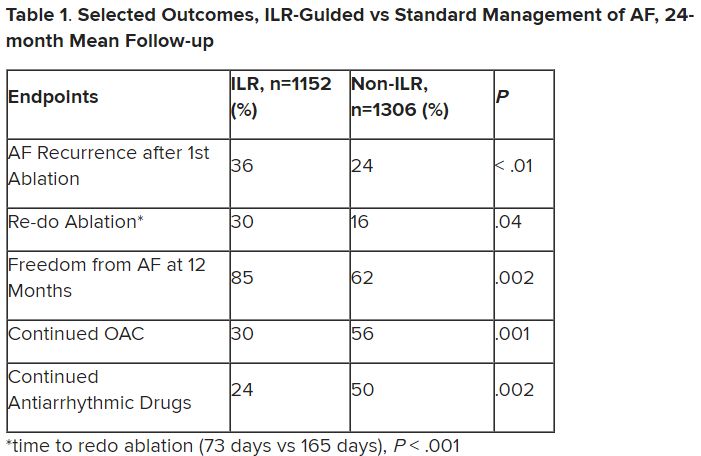
The ILR group also had fewer strokes and bleeding complications and were less likely to be hospitalized for AFib-related reasons, he said, because “a lot of these patients were caught ahead of time through the remote monitoring.”
For example, ILR patients had fewer heart failure (HF) hospitalizations, likely because “you’re not allowing these patients to remain with untreated rapid ventricular rates for a long period of time. You intervene early, thereby mitigating the onset of heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Lakkireddy said, their cumulative rate of any cardiovascular complication was “dramatically lower” – 3.4 versus 10.4 events per 100 person-years (P < .001).
Certainly, a routine recommendation to consider AFib patients for continuous monitoring would require randomized-trial evidence, he acknowledged. “This is an observation registry and proof of concept from a very heterogeneous cohort of patients. There were no obvious set criteria for ILR implantation.”
Nonetheless, “continuous and dynamic monitoring enabled quicker decision-making and patient management,” Dr. Lakkireddy said. “Especially in those patients who may have silent atrial fibrillation, an ILR could significantly mitigate the risk of complications from stroke and heart failure exacerbations.”
Several randomized trials have supported “earlier, more aggressive treatment” for AFib, including EAST-AFNET4, EARLY-AF, and CABANA, observed Daniel Morin, MD, MPH, of Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, as the invited discussant for Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
So, he continued, if the goal is to “get every single AFib patient to ablation just as soon as possible,” then maybe MONITOR-AF supports the use of ILRs in such cases.
Indeed, it is “certainly possible” that the continuous stream of data from ILRs “allows faster progression of therapy and possibly even better outcomes” as MONITOR-AF suggests, said Dr. Morin, who is director of electrophysiology research at his center.
Moreover, ILR data could potentially “support shared decision-making perhaps by convincing the patient, and maybe their insurers, that we should move forward with ablation.”
But given the study’s observational, registry-based nature, the MONITOR-AF analysis is limited by potential confounders that complicate its interpretation.
For example, Dr. Morin continued, all ILR patients but only 60% of those on standard care˙ had access to an electrophysiologist (P = .001). That means “less access to some antiarrhythmic medications and certainly far less access to ablation therapy.”
Moreover, “during shared decision-making, a patient who sees the results of their ILR monitoring may be more prone to seek out or to accept earlier, more definitive therapy via ablation,” he said. “The presence of an ILR may then be a good way to move the needle toward ablation.”
Of note, an overwhelming majority of ILR patients received ablation, 93.5%, compared with 58.6% of standard-care patients. “It’s unclear how much of that association was caused by the ILR’s presence vs. other factors, such as physician availability, physician aggressiveness, or patient willingness for intervention,” Dr. Morin noted.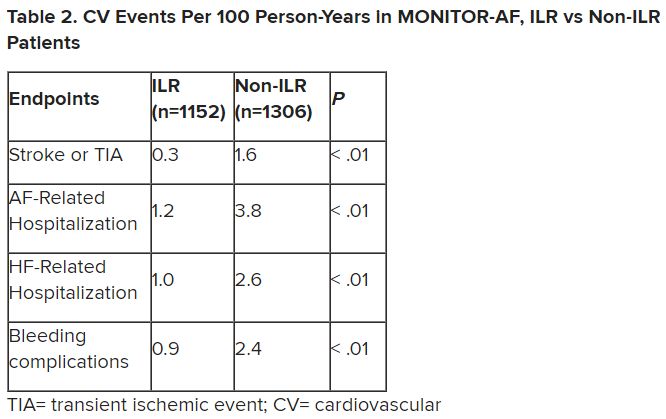
MONITOR-AF included 2,458 patients with paroxysmal or persistent AFib who either were implanted with or did not receive an ILR from 2018 to 2021 and were followed for at least 12 months.
The two groups were similar, Dr. Lakkireddy reported, with respect to demographics and baseline history AFib, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, coronary disease, neurovascular events, peripheral artery disease, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Lakkireddy said a subgroup analysis is forthcoming, but that he’d “intuitively” think that the 15%-20% of AFib patients who are asymptomatic would gain the most from the ILR monitoring approach. There is already evidence that such patients tend to have the worst AFib outcomes, often receiving an AFib diagnosis only after presenting with consequences such as stroke or heart failure.
Dr. Lakkireddy disclosed receiving research grants, modest honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Johnson & Johnson, Biotronik, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Atricure, Northeast Scientific, and Acutus. Dr. Morin disclosed receiving research grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott and serving on a speakers’ bureau for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Zoll Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension “often require long-term care through long-term monitoring,” observed a researcher, and “we know that continuous monitoring is superior to intermittent monitoring for long-term outcomes.”
So maybe practice should rely more on continuous ECG monitoring for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), also a chronic condition, proposed Dhanunjaya R. Lakkireddy, MD, of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kan., in presenting a new analysis at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
(ILRs), compared with standard care. The latter could include intermittent 12-lead ECG, Holter, or other intermittent monitoring at physicians’ discretion.
Patients with AFib and the ECG implants in the MONITOR-AF study, which was not randomized and therefore only suggestive, were managed “more efficiently” with greater access to electrophysiologists (P < .01) and adherence to oral anticoagulants (P = .020) and other medications.
Followed for a mean of 2 years, patients with ILRs were more likely to undergo catheter ablation, and their time to a catheter ablation “was impressively shorter, 153 days versus 426 days” (P < .001), Dr. Lakkireddy said.
The ILR group also had fewer strokes and bleeding complications and were less likely to be hospitalized for AFib-related reasons, he said, because “a lot of these patients were caught ahead of time through the remote monitoring.”
For example, ILR patients had fewer heart failure (HF) hospitalizations, likely because “you’re not allowing these patients to remain with untreated rapid ventricular rates for a long period of time. You intervene early, thereby mitigating the onset of heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Lakkireddy said, their cumulative rate of any cardiovascular complication was “dramatically lower” – 3.4 versus 10.4 events per 100 person-years (P < .001).
Certainly, a routine recommendation to consider AFib patients for continuous monitoring would require randomized-trial evidence, he acknowledged. “This is an observation registry and proof of concept from a very heterogeneous cohort of patients. There were no obvious set criteria for ILR implantation.”
Nonetheless, “continuous and dynamic monitoring enabled quicker decision-making and patient management,” Dr. Lakkireddy said. “Especially in those patients who may have silent atrial fibrillation, an ILR could significantly mitigate the risk of complications from stroke and heart failure exacerbations.”
Several randomized trials have supported “earlier, more aggressive treatment” for AFib, including EAST-AFNET4, EARLY-AF, and CABANA, observed Daniel Morin, MD, MPH, of Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, as the invited discussant for Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
So, he continued, if the goal is to “get every single AFib patient to ablation just as soon as possible,” then maybe MONITOR-AF supports the use of ILRs in such cases.
Indeed, it is “certainly possible” that the continuous stream of data from ILRs “allows faster progression of therapy and possibly even better outcomes” as MONITOR-AF suggests, said Dr. Morin, who is director of electrophysiology research at his center.
Moreover, ILR data could potentially “support shared decision-making perhaps by convincing the patient, and maybe their insurers, that we should move forward with ablation.”
But given the study’s observational, registry-based nature, the MONITOR-AF analysis is limited by potential confounders that complicate its interpretation.
For example, Dr. Morin continued, all ILR patients but only 60% of those on standard care˙ had access to an electrophysiologist (P = .001). That means “less access to some antiarrhythmic medications and certainly far less access to ablation therapy.”
Moreover, “during shared decision-making, a patient who sees the results of their ILR monitoring may be more prone to seek out or to accept earlier, more definitive therapy via ablation,” he said. “The presence of an ILR may then be a good way to move the needle toward ablation.”
Of note, an overwhelming majority of ILR patients received ablation, 93.5%, compared with 58.6% of standard-care patients. “It’s unclear how much of that association was caused by the ILR’s presence vs. other factors, such as physician availability, physician aggressiveness, or patient willingness for intervention,” Dr. Morin noted.
MONITOR-AF included 2,458 patients with paroxysmal or persistent AFib who either were implanted with or did not receive an ILR from 2018 to 2021 and were followed for at least 12 months.
The two groups were similar, Dr. Lakkireddy reported, with respect to demographics and baseline history AFib, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, coronary disease, neurovascular events, peripheral artery disease, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Lakkireddy said a subgroup analysis is forthcoming, but that he’d “intuitively” think that the 15%-20% of AFib patients who are asymptomatic would gain the most from the ILR monitoring approach. There is already evidence that such patients tend to have the worst AFib outcomes, often receiving an AFib diagnosis only after presenting with consequences such as stroke or heart failure.
Dr. Lakkireddy disclosed receiving research grants, modest honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Johnson & Johnson, Biotronik, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Atricure, Northeast Scientific, and Acutus. Dr. Morin disclosed receiving research grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott and serving on a speakers’ bureau for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Zoll Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension “often require long-term care through long-term monitoring,” observed a researcher, and “we know that continuous monitoring is superior to intermittent monitoring for long-term outcomes.”
So maybe practice should rely more on continuous ECG monitoring for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), also a chronic condition, proposed Dhanunjaya R. Lakkireddy, MD, of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kan., in presenting a new analysis at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
(ILRs), compared with standard care. The latter could include intermittent 12-lead ECG, Holter, or other intermittent monitoring at physicians’ discretion.
Patients with AFib and the ECG implants in the MONITOR-AF study, which was not randomized and therefore only suggestive, were managed “more efficiently” with greater access to electrophysiologists (P < .01) and adherence to oral anticoagulants (P = .020) and other medications.
Followed for a mean of 2 years, patients with ILRs were more likely to undergo catheter ablation, and their time to a catheter ablation “was impressively shorter, 153 days versus 426 days” (P < .001), Dr. Lakkireddy said.
The ILR group also had fewer strokes and bleeding complications and were less likely to be hospitalized for AFib-related reasons, he said, because “a lot of these patients were caught ahead of time through the remote monitoring.”
For example, ILR patients had fewer heart failure (HF) hospitalizations, likely because “you’re not allowing these patients to remain with untreated rapid ventricular rates for a long period of time. You intervene early, thereby mitigating the onset of heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Lakkireddy said, their cumulative rate of any cardiovascular complication was “dramatically lower” – 3.4 versus 10.4 events per 100 person-years (P < .001).
Certainly, a routine recommendation to consider AFib patients for continuous monitoring would require randomized-trial evidence, he acknowledged. “This is an observation registry and proof of concept from a very heterogeneous cohort of patients. There were no obvious set criteria for ILR implantation.”
Nonetheless, “continuous and dynamic monitoring enabled quicker decision-making and patient management,” Dr. Lakkireddy said. “Especially in those patients who may have silent atrial fibrillation, an ILR could significantly mitigate the risk of complications from stroke and heart failure exacerbations.”
Several randomized trials have supported “earlier, more aggressive treatment” for AFib, including EAST-AFNET4, EARLY-AF, and CABANA, observed Daniel Morin, MD, MPH, of Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, as the invited discussant for Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
So, he continued, if the goal is to “get every single AFib patient to ablation just as soon as possible,” then maybe MONITOR-AF supports the use of ILRs in such cases.
Indeed, it is “certainly possible” that the continuous stream of data from ILRs “allows faster progression of therapy and possibly even better outcomes” as MONITOR-AF suggests, said Dr. Morin, who is director of electrophysiology research at his center.
Moreover, ILR data could potentially “support shared decision-making perhaps by convincing the patient, and maybe their insurers, that we should move forward with ablation.”
But given the study’s observational, registry-based nature, the MONITOR-AF analysis is limited by potential confounders that complicate its interpretation.
For example, Dr. Morin continued, all ILR patients but only 60% of those on standard care˙ had access to an electrophysiologist (P = .001). That means “less access to some antiarrhythmic medications and certainly far less access to ablation therapy.”
Moreover, “during shared decision-making, a patient who sees the results of their ILR monitoring may be more prone to seek out or to accept earlier, more definitive therapy via ablation,” he said. “The presence of an ILR may then be a good way to move the needle toward ablation.”
Of note, an overwhelming majority of ILR patients received ablation, 93.5%, compared with 58.6% of standard-care patients. “It’s unclear how much of that association was caused by the ILR’s presence vs. other factors, such as physician availability, physician aggressiveness, or patient willingness for intervention,” Dr. Morin noted.
MONITOR-AF included 2,458 patients with paroxysmal or persistent AFib who either were implanted with or did not receive an ILR from 2018 to 2021 and were followed for at least 12 months.
The two groups were similar, Dr. Lakkireddy reported, with respect to demographics and baseline history AFib, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, coronary disease, neurovascular events, peripheral artery disease, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Lakkireddy said a subgroup analysis is forthcoming, but that he’d “intuitively” think that the 15%-20% of AFib patients who are asymptomatic would gain the most from the ILR monitoring approach. There is already evidence that such patients tend to have the worst AFib outcomes, often receiving an AFib diagnosis only after presenting with consequences such as stroke or heart failure.
Dr. Lakkireddy disclosed receiving research grants, modest honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Johnson & Johnson, Biotronik, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Atricure, Northeast Scientific, and Acutus. Dr. Morin disclosed receiving research grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from Abbott and serving on a speakers’ bureau for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Zoll Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEART RHYTHM 2023
Significant increase in vitamin D deficiency in kids with major depressive disorder
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to new findings that suggest spending more time indoors may have fueled this uptick.
“We suspect that this may be due to the COVID lockdowns and kids schooling from home and having less time outside,” study investigator Oluwatomiwa Babade, MD, MPH, with Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, Va., said in an interview.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Anecdotal observation confirmed
During the pandemic, investigators noticed an uptick in the number of children and adolescents attending their clinic for psychiatric hospitalization who had low vitamin D levels.
To investigate, they analyzed the records of all patients aged 6-17 years with psychiatric diagnoses and vitamin D level assessment who were admitted into the inpatient psychiatry unit from March 18, 2020, to June 30, 2021.
Among 599 unique patients, 275 (83% female) had a diagnosis of MDD and 226 of these patients were vitamin D deficient (< 30 ng/mL) – a prevalence rate of roughly 82%. Among 246 patients with psychiatric disorders other than MDD, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was 76%.
“This was very surprising and much higher than prior to the pandemic. Prior to COVID, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was around 14% in similar patients,” Dr. Babade said.
“Now that we are post-lockdown, it would be good to repeat the study. I think the prevalence should drop. That’s my guess,” he added.
Important research, no surprises
In a comment, Cemre Robinson, MD, director of the Mount Sinai Pediatric Bone Health and Calcium Metabolism Clinic, New York, said that although the study’s findings aren’t surprising, “it’s important to present such data in adolescents with major depression.”
“These findings reiterate the importance of screening for vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents, with or without depression, particularly during winter, which is associated with less sun exposure,” Dr. Robinson, assistant professor of pediatrics, endocrinology, and diabetes at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said.
She noted that vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in the general population, and it can be easily corrected with supplementation.
“Vitamin D is important for bone growth, mineralization, and accretion as well as calcium absorption. Adolescence, in particular, is a period of rapid physical, cognitive, and psychosocial growth,” Dr. Robinson said.
“The requirement of all minerals and vitamins changes in this phase of life. Therefore, it is important to have sufficient vitamin D levels during adolescence for several health benefits,” she noted.
Dr. Robinson said that “more research is needed to validate the present findings in adolescents with major depression, and larger studies, including randomized control trials, are required to establish a causal association between MDD and vitamin D deficiency.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Babade and Dr. Robinson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to new findings that suggest spending more time indoors may have fueled this uptick.
“We suspect that this may be due to the COVID lockdowns and kids schooling from home and having less time outside,” study investigator Oluwatomiwa Babade, MD, MPH, with Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, Va., said in an interview.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Anecdotal observation confirmed
During the pandemic, investigators noticed an uptick in the number of children and adolescents attending their clinic for psychiatric hospitalization who had low vitamin D levels.
To investigate, they analyzed the records of all patients aged 6-17 years with psychiatric diagnoses and vitamin D level assessment who were admitted into the inpatient psychiatry unit from March 18, 2020, to June 30, 2021.
Among 599 unique patients, 275 (83% female) had a diagnosis of MDD and 226 of these patients were vitamin D deficient (< 30 ng/mL) – a prevalence rate of roughly 82%. Among 246 patients with psychiatric disorders other than MDD, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was 76%.
“This was very surprising and much higher than prior to the pandemic. Prior to COVID, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was around 14% in similar patients,” Dr. Babade said.
“Now that we are post-lockdown, it would be good to repeat the study. I think the prevalence should drop. That’s my guess,” he added.
Important research, no surprises
In a comment, Cemre Robinson, MD, director of the Mount Sinai Pediatric Bone Health and Calcium Metabolism Clinic, New York, said that although the study’s findings aren’t surprising, “it’s important to present such data in adolescents with major depression.”
“These findings reiterate the importance of screening for vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents, with or without depression, particularly during winter, which is associated with less sun exposure,” Dr. Robinson, assistant professor of pediatrics, endocrinology, and diabetes at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said.
She noted that vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in the general population, and it can be easily corrected with supplementation.
“Vitamin D is important for bone growth, mineralization, and accretion as well as calcium absorption. Adolescence, in particular, is a period of rapid physical, cognitive, and psychosocial growth,” Dr. Robinson said.
“The requirement of all minerals and vitamins changes in this phase of life. Therefore, it is important to have sufficient vitamin D levels during adolescence for several health benefits,” she noted.
Dr. Robinson said that “more research is needed to validate the present findings in adolescents with major depression, and larger studies, including randomized control trials, are required to establish a causal association between MDD and vitamin D deficiency.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Babade and Dr. Robinson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to new findings that suggest spending more time indoors may have fueled this uptick.
“We suspect that this may be due to the COVID lockdowns and kids schooling from home and having less time outside,” study investigator Oluwatomiwa Babade, MD, MPH, with Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, Va., said in an interview.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Anecdotal observation confirmed
During the pandemic, investigators noticed an uptick in the number of children and adolescents attending their clinic for psychiatric hospitalization who had low vitamin D levels.
To investigate, they analyzed the records of all patients aged 6-17 years with psychiatric diagnoses and vitamin D level assessment who were admitted into the inpatient psychiatry unit from March 18, 2020, to June 30, 2021.
Among 599 unique patients, 275 (83% female) had a diagnosis of MDD and 226 of these patients were vitamin D deficient (< 30 ng/mL) – a prevalence rate of roughly 82%. Among 246 patients with psychiatric disorders other than MDD, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was 76%.
“This was very surprising and much higher than prior to the pandemic. Prior to COVID, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was around 14% in similar patients,” Dr. Babade said.
“Now that we are post-lockdown, it would be good to repeat the study. I think the prevalence should drop. That’s my guess,” he added.
Important research, no surprises
In a comment, Cemre Robinson, MD, director of the Mount Sinai Pediatric Bone Health and Calcium Metabolism Clinic, New York, said that although the study’s findings aren’t surprising, “it’s important to present such data in adolescents with major depression.”
“These findings reiterate the importance of screening for vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents, with or without depression, particularly during winter, which is associated with less sun exposure,” Dr. Robinson, assistant professor of pediatrics, endocrinology, and diabetes at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said.
She noted that vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in the general population, and it can be easily corrected with supplementation.
“Vitamin D is important for bone growth, mineralization, and accretion as well as calcium absorption. Adolescence, in particular, is a period of rapid physical, cognitive, and psychosocial growth,” Dr. Robinson said.
“The requirement of all minerals and vitamins changes in this phase of life. Therefore, it is important to have sufficient vitamin D levels during adolescence for several health benefits,” she noted.
Dr. Robinson said that “more research is needed to validate the present findings in adolescents with major depression, and larger studies, including randomized control trials, are required to establish a causal association between MDD and vitamin D deficiency.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Babade and Dr. Robinson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT APA 2023
AI & U: 2
In my most recent column (AI & U), I suggested that artificial intelligence (AI) in its most recent newsworthy iteration, the chatbot, offers some potentially useful opportunities. For example, in the short term the ability of a machine to search for the diagnostic possibilities and treatment options in a matter of seconds sounds very appealing. The skills needed to ask the chatbot the best questions and then interpret the machine’s responses would still require a medical school education. Good news for those of you worried about job security.
However, let’s look further down the road for how AI and other technological advances might change the look and feel of primary care. It is reasonable to expect that a chatbot could engage the patient in a spoken (or written) dialog in the patient’s preferred language and targeted to his/her educational level. You already deal with this kind of interaction in a primitive form when you call the customer service department of even a small company. That is if you were lucky enough to find the number buried in the company’s website.
The “system” could then perform a targeted exam using a variety of sensors. Electronic stethoscopes and tympanographic sensors already exist. While currently most sonograms are performed by trained technicians, one can envision the technology being dumbed down to a point that the patient could operate most of the sensors himself or herself, provided the patient could reach the body part in question. The camera on a basic cell phone can take an image of a skin lesion that can already be compared with a standard set of normals and abnormals. While currently a questionable lesion triggers the provider to perform a biopsy, it is possible that sensors could become so sensitive and the algorithms so clever that the biopsy would be unnecessary. The pandemic has already shown us that patients can obtain sample swabs and accurately perform simple tests in their home.
Once the “system” has made the diagnosis, it would then converse with the patient about the various treatment options and arrange follow up. One would hope that, if the “system’s” diagnosis included a fatal outcome, it would trigger a face-to-face interaction with a counselor and a team of social workers to break the bad news and provide some kind of emotional support.
Those of you who are doubting Dorothys and Thomases may be asking what about scenarios in which the patient’s chief complaint is difficulty breathing or sudden onset of weakness? Remember, I am talking about the usual 8 a.m–6 p.m. primary care office. Any patient with a possibly life-threatening complaint would be triaged by the chatbot and would be seen at some point by a real human. However, it is likely that individual’s training would not require the breadth of the typical medical school education and instead would be targeted at the most common high-risk scenarios. This higher-acuity specialist would, of course, be assisted by a chatbot.
Patients with complaints primarily associated with mental illness would be seen by humans specializing in that area. Although I suspect there are folks somewhere brainstorming on how chatbots could potentially be effective counselors.
Clearly, the future I am suggesting leaves the patient with fewer interactions with a human, and certainly very rarely with a human who has navigated what we think of today as a traditional medical school education.
Would they do it without complaint? Would they have a choice? Do you like it when you are interrogated by the prerecorded voice on the phone tree of some company’s customer service? Do you have a choice? If that interrogation was refined to the point where it saved you time and resulted in the correct answer 99% of the time would you still complain?
If patients found that most of their primary care complaints could be handled more quickly by an AI system with minimal physician intervention and that system offered a success rate of over 90% when measured by the accuracy of the diagnosis and management plan, would they complain? They may have no other choice than to complain if primary care continues to lose favor among recent medical school graduates.
And what would the patients complain about? They already complain about the current system in which they feel that the face-to-face encounters with their physician are becoming less frequent. I often hear complaints that “the doctor just looked at the computer, and he didn’t really examine me.” By which I think they sometimes mean “touched” me.
I suspect we will discover what most of us already suspect and that is there is something special about the eye-to-eye contact and tactile interaction between the physician and the patient. The osteopathic tradition clearly makes this a priority when it utilizes manipulative medicine. It may be that if primary care medicine follows the AI-paved road I have imagined it won’t be able to match the success rate of the current system. Without that human element, with or without the hands-on aspect or even if the diagnosis is correct and the management is spot on, it just won’t work as well.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In my most recent column (AI & U), I suggested that artificial intelligence (AI) in its most recent newsworthy iteration, the chatbot, offers some potentially useful opportunities. For example, in the short term the ability of a machine to search for the diagnostic possibilities and treatment options in a matter of seconds sounds very appealing. The skills needed to ask the chatbot the best questions and then interpret the machine’s responses would still require a medical school education. Good news for those of you worried about job security.
However, let’s look further down the road for how AI and other technological advances might change the look and feel of primary care. It is reasonable to expect that a chatbot could engage the patient in a spoken (or written) dialog in the patient’s preferred language and targeted to his/her educational level. You already deal with this kind of interaction in a primitive form when you call the customer service department of even a small company. That is if you were lucky enough to find the number buried in the company’s website.
The “system” could then perform a targeted exam using a variety of sensors. Electronic stethoscopes and tympanographic sensors already exist. While currently most sonograms are performed by trained technicians, one can envision the technology being dumbed down to a point that the patient could operate most of the sensors himself or herself, provided the patient could reach the body part in question. The camera on a basic cell phone can take an image of a skin lesion that can already be compared with a standard set of normals and abnormals. While currently a questionable lesion triggers the provider to perform a biopsy, it is possible that sensors could become so sensitive and the algorithms so clever that the biopsy would be unnecessary. The pandemic has already shown us that patients can obtain sample swabs and accurately perform simple tests in their home.
Once the “system” has made the diagnosis, it would then converse with the patient about the various treatment options and arrange follow up. One would hope that, if the “system’s” diagnosis included a fatal outcome, it would trigger a face-to-face interaction with a counselor and a team of social workers to break the bad news and provide some kind of emotional support.
Those of you who are doubting Dorothys and Thomases may be asking what about scenarios in which the patient’s chief complaint is difficulty breathing or sudden onset of weakness? Remember, I am talking about the usual 8 a.m–6 p.m. primary care office. Any patient with a possibly life-threatening complaint would be triaged by the chatbot and would be seen at some point by a real human. However, it is likely that individual’s training would not require the breadth of the typical medical school education and instead would be targeted at the most common high-risk scenarios. This higher-acuity specialist would, of course, be assisted by a chatbot.
Patients with complaints primarily associated with mental illness would be seen by humans specializing in that area. Although I suspect there are folks somewhere brainstorming on how chatbots could potentially be effective counselors.
Clearly, the future I am suggesting leaves the patient with fewer interactions with a human, and certainly very rarely with a human who has navigated what we think of today as a traditional medical school education.
Would they do it without complaint? Would they have a choice? Do you like it when you are interrogated by the prerecorded voice on the phone tree of some company’s customer service? Do you have a choice? If that interrogation was refined to the point where it saved you time and resulted in the correct answer 99% of the time would you still complain?
If patients found that most of their primary care complaints could be handled more quickly by an AI system with minimal physician intervention and that system offered a success rate of over 90% when measured by the accuracy of the diagnosis and management plan, would they complain? They may have no other choice than to complain if primary care continues to lose favor among recent medical school graduates.
And what would the patients complain about? They already complain about the current system in which they feel that the face-to-face encounters with their physician are becoming less frequent. I often hear complaints that “the doctor just looked at the computer, and he didn’t really examine me.” By which I think they sometimes mean “touched” me.
I suspect we will discover what most of us already suspect and that is there is something special about the eye-to-eye contact and tactile interaction between the physician and the patient. The osteopathic tradition clearly makes this a priority when it utilizes manipulative medicine. It may be that if primary care medicine follows the AI-paved road I have imagined it won’t be able to match the success rate of the current system. Without that human element, with or without the hands-on aspect or even if the diagnosis is correct and the management is spot on, it just won’t work as well.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In my most recent column (AI & U), I suggested that artificial intelligence (AI) in its most recent newsworthy iteration, the chatbot, offers some potentially useful opportunities. For example, in the short term the ability of a machine to search for the diagnostic possibilities and treatment options in a matter of seconds sounds very appealing. The skills needed to ask the chatbot the best questions and then interpret the machine’s responses would still require a medical school education. Good news for those of you worried about job security.
However, let’s look further down the road for how AI and other technological advances might change the look and feel of primary care. It is reasonable to expect that a chatbot could engage the patient in a spoken (or written) dialog in the patient’s preferred language and targeted to his/her educational level. You already deal with this kind of interaction in a primitive form when you call the customer service department of even a small company. That is if you were lucky enough to find the number buried in the company’s website.
The “system” could then perform a targeted exam using a variety of sensors. Electronic stethoscopes and tympanographic sensors already exist. While currently most sonograms are performed by trained technicians, one can envision the technology being dumbed down to a point that the patient could operate most of the sensors himself or herself, provided the patient could reach the body part in question. The camera on a basic cell phone can take an image of a skin lesion that can already be compared with a standard set of normals and abnormals. While currently a questionable lesion triggers the provider to perform a biopsy, it is possible that sensors could become so sensitive and the algorithms so clever that the biopsy would be unnecessary. The pandemic has already shown us that patients can obtain sample swabs and accurately perform simple tests in their home.
Once the “system” has made the diagnosis, it would then converse with the patient about the various treatment options and arrange follow up. One would hope that, if the “system’s” diagnosis included a fatal outcome, it would trigger a face-to-face interaction with a counselor and a team of social workers to break the bad news and provide some kind of emotional support.
Those of you who are doubting Dorothys and Thomases may be asking what about scenarios in which the patient’s chief complaint is difficulty breathing or sudden onset of weakness? Remember, I am talking about the usual 8 a.m–6 p.m. primary care office. Any patient with a possibly life-threatening complaint would be triaged by the chatbot and would be seen at some point by a real human. However, it is likely that individual’s training would not require the breadth of the typical medical school education and instead would be targeted at the most common high-risk scenarios. This higher-acuity specialist would, of course, be assisted by a chatbot.
Patients with complaints primarily associated with mental illness would be seen by humans specializing in that area. Although I suspect there are folks somewhere brainstorming on how chatbots could potentially be effective counselors.
Clearly, the future I am suggesting leaves the patient with fewer interactions with a human, and certainly very rarely with a human who has navigated what we think of today as a traditional medical school education.
Would they do it without complaint? Would they have a choice? Do you like it when you are interrogated by the prerecorded voice on the phone tree of some company’s customer service? Do you have a choice? If that interrogation was refined to the point where it saved you time and resulted in the correct answer 99% of the time would you still complain?
If patients found that most of their primary care complaints could be handled more quickly by an AI system with minimal physician intervention and that system offered a success rate of over 90% when measured by the accuracy of the diagnosis and management plan, would they complain? They may have no other choice than to complain if primary care continues to lose favor among recent medical school graduates.
And what would the patients complain about? They already complain about the current system in which they feel that the face-to-face encounters with their physician are becoming less frequent. I often hear complaints that “the doctor just looked at the computer, and he didn’t really examine me.” By which I think they sometimes mean “touched” me.
I suspect we will discover what most of us already suspect and that is there is something special about the eye-to-eye contact and tactile interaction between the physician and the patient. The osteopathic tradition clearly makes this a priority when it utilizes manipulative medicine. It may be that if primary care medicine follows the AI-paved road I have imagined it won’t be able to match the success rate of the current system. Without that human element, with or without the hands-on aspect or even if the diagnosis is correct and the management is spot on, it just won’t work as well.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Ancient plague, cyclical pandemics … history lesson?
Even the plague wanted to visit Stonehenge
We’re about to blow your mind: The history you learned in school was often inaccurate. Shocking, we know, so we’ll give you a minute to process this incredible news.
Better? Good. Now, let’s look back at high school European history. The Black Death, specifically. The common narrative is that the Mongols, while besieging a Crimean city belonging to the Genoese, catapulted dead bodies infected with some mystery disease that turned out to be the plague. The Genoese then brought the plague back to Italy, and from there, we all know the rest of the story.
The Black Death was certainly extremely important to the development of modern Europe as we know it, but the history books gloss over the much longer history of the plague. Yersinia pestis did not suddenly appear unbidden in a Mongol war camp in 1347. The Black Death wasn’t even the first horrific, continent-wide pandemic caused by the plague; the Plague of Justinian 800 years earlier crippled the Byzantine Empire during an expansionist phase and killed anywhere between 15 million and 100 million.
Today, though, LOTME looks even deeper into history, nearly beyond even history itself, back into the depths of early Bronze Age northern Europe. Specifically, to two ancient burial sites in England, where researchers have identified three 4,000-year-old cases of Y. pestis, the first recorded incidence of the disease in Britain.
Two of the individuals, identified through analysis of dental pulp, were young children buried at a mass grave in Somerset, while the third, a middle-aged woman, was found in a ring cairn in Cumbria. These sites are hundreds of miles apart, yet carbon dating suggests all three people lived and died at roughly the same time. The strain found is very similar to other samples of plague found across central and western Europe starting around 3,000 BCE, suggesting a single, easily spread disease affecting a large area in a relatively small period of time. In other words, a pandemic. Even in these ancient times, the world was connected. Not even the island of Britain could escape.
Beyond that though, the research helps confirm the cyclical nature of the plague; over time, it loses its effectiveness and goes into hiding, only to mutate and come roaring back. This is a story with absolutely no relevance at all to the modern world. Nope, no plagues or pandemics going around right now, no viruses fading into the background in any way. What a ridiculous inference to make.
Uncovering the invisible with artificial intelligence
This week in “What Else Can AI Do?” new research shows that a computer program can reveal brain injury that couldn’t be seen before with typical MRI.
The hot new AI, birthed by researchers at New York University, could potentially be a game changer by linking repeated head impacts with tiny, structural changes in the brains of athletes who have not been diagnosed with a concussion. By using machine learning to train the AI, the researchers were, for the first time, able to distinguish the brain of athletes who played contact sports (football, soccer, lacrosse) from those participating in noncontact sports such as baseball, basketball, and cross-country.
How did they do it? The investigators “designed statistical techniques that gave their computer program the ability to ‘learn’ how to predict exposure to repeated head impacts using mathematical models,” they explained in a written statement. Adding in data from the MRI scans of 81 male athletes with no known concussion diagnosis and the ability to identify unusual brain features between athletes with and without head trauma allowed the AI to predict results with accuracy even Miss Cleo would envy.
“This method may provide an important diagnostic tool not only for concussion, but also for detecting the damage that stems from subtler and more frequent head impacts,” said lead author Junbo Chen, an engineering doctoral candidate at NYU. That could make this new AI a valuable asset to science and medicine.
There are many things the human brain can do that AI can’t, and delegation could be one of them. Examining the data that represent the human brain in minute detail? Maybe we leave that to the machine.
Talk about your field promotions
If you’re a surgeon doing an amputation, the list of possible assistants pretty much starts and ends in only one place: Not the closest available janitor.
That may seem like an oddly obvious thing for us to say, but there’s at least one former Mainz (Germany) University Hospital physician who really needed to get this bit of advice before he attempted an unassisted toe amputation back in October of 2020. Yes, that does seem like kind of a long time ago for us to be reporting it now, but the details of the incident only just came to light a few days ago, thanks to German public broadcaster SWR.
Since it was just a toe, the surgeon thought he could perform the operation without any help. The toe, unfortunately, had other plans. The partially anesthetized patient got restless in the operating room, but with no actual trained nurse in the vicinity, the surgeon asked the closest available person – that would be the janitor – to lend a hand.
The surgical manager heard about these goings-on and got to the operating room too late to stop the procedure but soon enough to see the cleaning staffer “at the operating table with a bloody suction cup and a bloody compress in their hands,” SWR recently reported.
The incident was reported to the hospital’s medical director and the surgeon was fired, but since the patient experienced no complications not much fuss was made about it at the time.
Well, guess what? It’s toe-tally our job to make a fuss about these kinds of things. Or could it be that our job, much like the surgeon’s employment and the patient’s digit, is here toe-day and gone toe-morrow?
Even the plague wanted to visit Stonehenge
We’re about to blow your mind: The history you learned in school was often inaccurate. Shocking, we know, so we’ll give you a minute to process this incredible news.
Better? Good. Now, let’s look back at high school European history. The Black Death, specifically. The common narrative is that the Mongols, while besieging a Crimean city belonging to the Genoese, catapulted dead bodies infected with some mystery disease that turned out to be the plague. The Genoese then brought the plague back to Italy, and from there, we all know the rest of the story.
The Black Death was certainly extremely important to the development of modern Europe as we know it, but the history books gloss over the much longer history of the plague. Yersinia pestis did not suddenly appear unbidden in a Mongol war camp in 1347. The Black Death wasn’t even the first horrific, continent-wide pandemic caused by the plague; the Plague of Justinian 800 years earlier crippled the Byzantine Empire during an expansionist phase and killed anywhere between 15 million and 100 million.
Today, though, LOTME looks even deeper into history, nearly beyond even history itself, back into the depths of early Bronze Age northern Europe. Specifically, to two ancient burial sites in England, where researchers have identified three 4,000-year-old cases of Y. pestis, the first recorded incidence of the disease in Britain.
Two of the individuals, identified through analysis of dental pulp, were young children buried at a mass grave in Somerset, while the third, a middle-aged woman, was found in a ring cairn in Cumbria. These sites are hundreds of miles apart, yet carbon dating suggests all three people lived and died at roughly the same time. The strain found is very similar to other samples of plague found across central and western Europe starting around 3,000 BCE, suggesting a single, easily spread disease affecting a large area in a relatively small period of time. In other words, a pandemic. Even in these ancient times, the world was connected. Not even the island of Britain could escape.
Beyond that though, the research helps confirm the cyclical nature of the plague; over time, it loses its effectiveness and goes into hiding, only to mutate and come roaring back. This is a story with absolutely no relevance at all to the modern world. Nope, no plagues or pandemics going around right now, no viruses fading into the background in any way. What a ridiculous inference to make.
Uncovering the invisible with artificial intelligence
This week in “What Else Can AI Do?” new research shows that a computer program can reveal brain injury that couldn’t be seen before with typical MRI.
The hot new AI, birthed by researchers at New York University, could potentially be a game changer by linking repeated head impacts with tiny, structural changes in the brains of athletes who have not been diagnosed with a concussion. By using machine learning to train the AI, the researchers were, for the first time, able to distinguish the brain of athletes who played contact sports (football, soccer, lacrosse) from those participating in noncontact sports such as baseball, basketball, and cross-country.
How did they do it? The investigators “designed statistical techniques that gave their computer program the ability to ‘learn’ how to predict exposure to repeated head impacts using mathematical models,” they explained in a written statement. Adding in data from the MRI scans of 81 male athletes with no known concussion diagnosis and the ability to identify unusual brain features between athletes with and without head trauma allowed the AI to predict results with accuracy even Miss Cleo would envy.
“This method may provide an important diagnostic tool not only for concussion, but also for detecting the damage that stems from subtler and more frequent head impacts,” said lead author Junbo Chen, an engineering doctoral candidate at NYU. That could make this new AI a valuable asset to science and medicine.
There are many things the human brain can do that AI can’t, and delegation could be one of them. Examining the data that represent the human brain in minute detail? Maybe we leave that to the machine.
Talk about your field promotions
If you’re a surgeon doing an amputation, the list of possible assistants pretty much starts and ends in only one place: Not the closest available janitor.
That may seem like an oddly obvious thing for us to say, but there’s at least one former Mainz (Germany) University Hospital physician who really needed to get this bit of advice before he attempted an unassisted toe amputation back in October of 2020. Yes, that does seem like kind of a long time ago for us to be reporting it now, but the details of the incident only just came to light a few days ago, thanks to German public broadcaster SWR.
Since it was just a toe, the surgeon thought he could perform the operation without any help. The toe, unfortunately, had other plans. The partially anesthetized patient got restless in the operating room, but with no actual trained nurse in the vicinity, the surgeon asked the closest available person – that would be the janitor – to lend a hand.
The surgical manager heard about these goings-on and got to the operating room too late to stop the procedure but soon enough to see the cleaning staffer “at the operating table with a bloody suction cup and a bloody compress in their hands,” SWR recently reported.
The incident was reported to the hospital’s medical director and the surgeon was fired, but since the patient experienced no complications not much fuss was made about it at the time.
Well, guess what? It’s toe-tally our job to make a fuss about these kinds of things. Or could it be that our job, much like the surgeon’s employment and the patient’s digit, is here toe-day and gone toe-morrow?
Even the plague wanted to visit Stonehenge
We’re about to blow your mind: The history you learned in school was often inaccurate. Shocking, we know, so we’ll give you a minute to process this incredible news.
Better? Good. Now, let’s look back at high school European history. The Black Death, specifically. The common narrative is that the Mongols, while besieging a Crimean city belonging to the Genoese, catapulted dead bodies infected with some mystery disease that turned out to be the plague. The Genoese then brought the plague back to Italy, and from there, we all know the rest of the story.
The Black Death was certainly extremely important to the development of modern Europe as we know it, but the history books gloss over the much longer history of the plague. Yersinia pestis did not suddenly appear unbidden in a Mongol war camp in 1347. The Black Death wasn’t even the first horrific, continent-wide pandemic caused by the plague; the Plague of Justinian 800 years earlier crippled the Byzantine Empire during an expansionist phase and killed anywhere between 15 million and 100 million.
Today, though, LOTME looks even deeper into history, nearly beyond even history itself, back into the depths of early Bronze Age northern Europe. Specifically, to two ancient burial sites in England, where researchers have identified three 4,000-year-old cases of Y. pestis, the first recorded incidence of the disease in Britain.
Two of the individuals, identified through analysis of dental pulp, were young children buried at a mass grave in Somerset, while the third, a middle-aged woman, was found in a ring cairn in Cumbria. These sites are hundreds of miles apart, yet carbon dating suggests all three people lived and died at roughly the same time. The strain found is very similar to other samples of plague found across central and western Europe starting around 3,000 BCE, suggesting a single, easily spread disease affecting a large area in a relatively small period of time. In other words, a pandemic. Even in these ancient times, the world was connected. Not even the island of Britain could escape.
Beyond that though, the research helps confirm the cyclical nature of the plague; over time, it loses its effectiveness and goes into hiding, only to mutate and come roaring back. This is a story with absolutely no relevance at all to the modern world. Nope, no plagues or pandemics going around right now, no viruses fading into the background in any way. What a ridiculous inference to make.
Uncovering the invisible with artificial intelligence
This week in “What Else Can AI Do?” new research shows that a computer program can reveal brain injury that couldn’t be seen before with typical MRI.
The hot new AI, birthed by researchers at New York University, could potentially be a game changer by linking repeated head impacts with tiny, structural changes in the brains of athletes who have not been diagnosed with a concussion. By using machine learning to train the AI, the researchers were, for the first time, able to distinguish the brain of athletes who played contact sports (football, soccer, lacrosse) from those participating in noncontact sports such as baseball, basketball, and cross-country.
How did they do it? The investigators “designed statistical techniques that gave their computer program the ability to ‘learn’ how to predict exposure to repeated head impacts using mathematical models,” they explained in a written statement. Adding in data from the MRI scans of 81 male athletes with no known concussion diagnosis and the ability to identify unusual brain features between athletes with and without head trauma allowed the AI to predict results with accuracy even Miss Cleo would envy.
“This method may provide an important diagnostic tool not only for concussion, but also for detecting the damage that stems from subtler and more frequent head impacts,” said lead author Junbo Chen, an engineering doctoral candidate at NYU. That could make this new AI a valuable asset to science and medicine.
There are many things the human brain can do that AI can’t, and delegation could be one of them. Examining the data that represent the human brain in minute detail? Maybe we leave that to the machine.
Talk about your field promotions
If you’re a surgeon doing an amputation, the list of possible assistants pretty much starts and ends in only one place: Not the closest available janitor.
That may seem like an oddly obvious thing for us to say, but there’s at least one former Mainz (Germany) University Hospital physician who really needed to get this bit of advice before he attempted an unassisted toe amputation back in October of 2020. Yes, that does seem like kind of a long time ago for us to be reporting it now, but the details of the incident only just came to light a few days ago, thanks to German public broadcaster SWR.
Since it was just a toe, the surgeon thought he could perform the operation without any help. The toe, unfortunately, had other plans. The partially anesthetized patient got restless in the operating room, but with no actual trained nurse in the vicinity, the surgeon asked the closest available person – that would be the janitor – to lend a hand.
The surgical manager heard about these goings-on and got to the operating room too late to stop the procedure but soon enough to see the cleaning staffer “at the operating table with a bloody suction cup and a bloody compress in their hands,” SWR recently reported.
The incident was reported to the hospital’s medical director and the surgeon was fired, but since the patient experienced no complications not much fuss was made about it at the time.
Well, guess what? It’s toe-tally our job to make a fuss about these kinds of things. Or could it be that our job, much like the surgeon’s employment and the patient’s digit, is here toe-day and gone toe-morrow?
Optimizing benzodiazepine treatment of anxiety disorders
Though once the main treatment for anxiety disorders—often as monotherapy1—benzodiazepines are now primarily used as adjunctive agents.2-4 Their ability to produce rapid anxiolysis represents a significant therapeutic advantage, but in recent decades their tolerability, class-specific risks, and lack of antidepressant properties contributed to benzodiazepines being largely replaced by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for the pharmacologic treatment of anxiety. This shift within the pharmacologic armamentarium has decreased many clinicians’ familiarity with benzodiazepines.
While benzodiazepines continue to have an important role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly treatment-resistant anxiety,4 clinicians must consider the limitations of these agents. Benzodiazepines can be associated with abuse and dependence, and overdose risk when combined with opiates.5,6 They may cause memory impairment7,8 and conflicting data suggest they may contribute to the risk of developing cognitive disorders.9-11 Benzodiazepines also have been associated with falls and fractures,12 and worse outcomes in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder.13 Some studies of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) found benzodiazepines may increase the risk of COPD exacerbations and accidental overdose,14 though others found that was not always the case.15 Benzodiazepines may be associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion when used early in pregnancy.16 Prospective research in women who were breastfeeding found benzodiazepines may cause sedation in up to 2% of infants.17
Despite the potential for adverse effects, benzodiazepine use remains common.18 These medications have a rapid onset of action, are useful for breakthrough symptoms, may enhance treatment adherence, and alleviate activating symptoms of SSRIs. Like other commonly used medications, benzodiazepines have the potential for both harm and benefit.19 Similar to other medications with tolerability concerns but established efficacy, particularly in treatment-resistant anxiety disorders, it is important to balance “overprescribing … to patients at risk and underusing these effective medications when indicated.”19 Though the use of benzodiazepines has been discouraged and perceptions have shifted, knowledge of benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine pharmacology also has been degraded contemporaneously.
This article provides a synthesis of the clinically relevant pharmacology of benzodiazepines, with a focus on orally administered benzodiazepines, which are more common in outpatient clinical practice. Specifically, this review describes the pharmacology of benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine medication interactions, the relationship between pharmacologic characteristics and treatment response/tolerability, and selection and dosing of oral benzodiazepines (Table20).
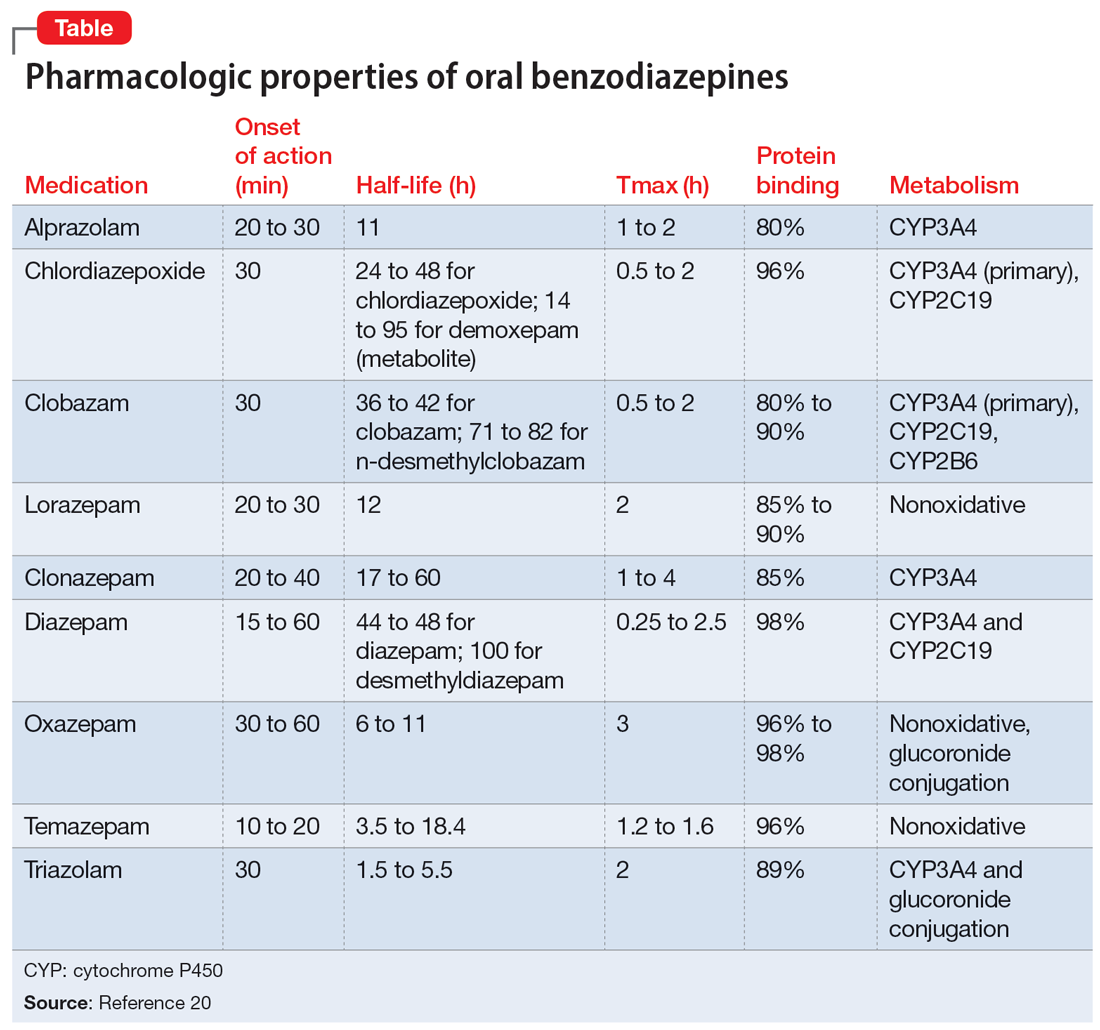
Benzodiazepine pharmacodynamics
Benzodiazepines act at the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptor complex and bind allosterically.21-23 Comprised of 5 glycoprotein subunits (2 alpha subunits, 2 beta subunits, and 1 gamma subunit), the receptor has 2 distinct sites at which the endogenous inhibitory transmitter GABA binds and 1 benzodiazepine binding site. Benzodiazepines bind within a socket created by the alpha and gamma subunits22 and after binding induce a conformational change in the receptor, which enhances GABA binding. There are 2 types of benzodiazepine receptors: BZ1 and BZ2. The subunits play a critical role in driving the pharmacologic characteristics of the receptor.24 BZ1 and BZ2 receptors bind benzodiazepines, although they are differentially distributed within the brain. Binding at BZ1 receptors—which are distributed in cortical, thalamic, and cerebellar regions—contributes to sedation and deleterious effects of benzodiazepines on memory (eg, anterograde amnesia). BZ2 receptors (which contain gamma-2 subunits) are responsible for anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects. They are distributed throughout limbic regions and motor tracts, including motor neurons and neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.24
Benzodiazepines—positive GABA-A receptor allosteric modulators—produce phasic inhibition, largely through the alpha and gamma subunits discussed above. In contrast, newer positive allosteric modulators (eg, zuranolone) bind at the alpha/beta subunits.25 Mechanistically, endogenous neuroactive steroids and nonbenzodiazepine GABA-A–positive allosteric modulators such as zuranolone and ganaxolone also differ in their regulation of GABA-A (downregulated with benzodiazepines and hypothetically upregulated with zuranolone)26 and their synaptic effects (benzodiazepines synaptically vs endogenous neurosteroids and nonbenzodiazpine positive allosteric modulators extrasynaptically).27
From a developmental perspective, benzodiazepines may have less efficacy for anxiolysis and worse tolerability in some pediatric patients,28 although they generally appear effective for immediate use to treat anxiety in acute settings.29 The differences in efficacy and tolerability may be related to pharmacodynamic differences between pediatric populations and adults. GABA receptor expression and function do not reach adult levels until age 14 to 17½ for subcortical regions and age 18 to 22 for cortical regions, although girls reach adult expression of GABA receptors slightly earlier than boys.30 D
Continue to: Pharmacology and clinical effects
Pharmacology and clinical effects
Benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on the route of administration, absorption, and distribution/redistribution.31 In this review, we focus on oral administration as opposed to IV, IM, sublingual, or intranasal administration.
Absorption
Benzodiazepines are rapidly absorbed after oral administration and quickly enter the systemic circulation. However, absorption rates vary depending on specific aspects of the gastrointestinal milieu and intrinsic properties of the benzodiazepine. For example, alprazolam is more rapidly absorbed than most other benzodiazepines, with a Tmax of 1.8 hours compared to lorazepam, which has a Tmax of approximately 2 hours. These pharmacokinetic effects instantiate differences in tolerability and efficacy. Thus, following single doses of alprazolam and diazepam, self-rated sedating effects and impairment on a task of working memory suggest that effects have a more rapid onset for alprazolam relative to lorazepam.32 Food and concomitant medications can significantly affect benzodiazepine absorption. A single-dose, 3-way crossover study demonstrated that taking diazepam concomitantly with an antacid (eg, aluminum hydroxide) decreased peak concentrations and prolonged absorption by approximately 30 minutes. However, total absorption of the medication was unaffected.33 Additionally, administration of diazepam with food significantly slows absorption from 1 hour 15 minutes to approximately 2 hours 30 minutes and increases benzodiazepine absorption by 25% (Figure 134); the fat content of the meal appears important in moderating this effect.35 The impact of food on alprazolam varies by formulation. For example, when administered in an extended-release (XR) formulation with a high-fat meal, alprazolam absorption increases by one-third, while absorption for administration of the orally disintegrating tablet with a high-fat meal increases from 1 hour 30 minutes to 2 hours. Similarly, for lorazepam, administration with a meal delays absorption by approximately 2 hours; however, this effect does not appear present with the XR formulation. Administering benzodiazepines with food can be clinically leveraged to either accelerate the onset of action or decrease peak-associated adverse effects. Thus, when a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine is needed to treat acute anxiety or prior to an expected anxiogenic stimuli, administering the medication without food may produce a faster onset of action.
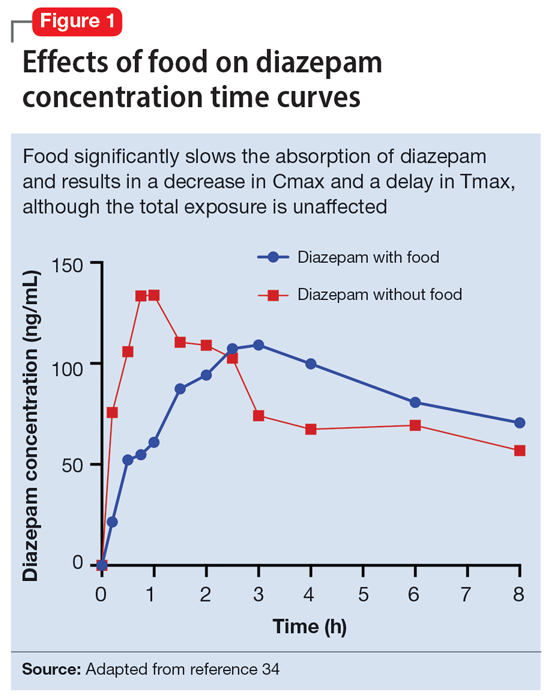
CNS penetration
Benzodiazepines enter the CNS by passive diffusion. Because of this, lipophilicity at physiologic pH influences the rate at which a benzodiazepine crosses the blood-brain barrier. The rate at which benzodiazepines enter the CNS influences their clinical effects and the speed at which both efficacy (ie, anxiolysis) and adverse effects (ie, sedation, slowed cognition) are observed. In general, more lipophilic medications initiate their anxiolytic effect more quickly. However, by quickly leaving the CNS (through the same mechanism that allowed them to enter the CNS at such speed), their effects rapidly cease as they redistribute into fat. Thus, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines produce more intense effects compared to less lipophilic benzodiazepines. For these reasons, lipophilicity is more important than half-life for determining the duration of effect in most patients.
Lipophilicity and duration of effect
Benzodiazepines and their metabolites tend to be highly protein-bound and distributed in fat- and lipid-enriched areas such as the CNS. As a result, the more lipophilic agents generally have the highest rates of absorption and the fastest onset of clinical effects. The duration of action for many benzodiazepines is determined by the rate and extent of distribution (a function of lipophilicity) rather than by the rate of elimination. For example, diazepam has a longer half-life than lorazepam, but its duration of action following a single dose is shorter. This is because diazepam is more lipophilic and therefore more extensively distributed (particularly to adipose tissue). This results in it leaving the brain and blood and distributing to other tissues. In turn, its CNS effect (ie, anxiolytic effects) are more quickly terminated.
By contrast, less lipophilic benzodiazepines maintain their CNS concentrations longer; they have a longer duration of action because of their slower redistribution, which culminates in a shorter half-life, and are less extensively distributed to peripheral tissues. In essence, this means that (other things being equal) a less lipophilic benzodiazepine produces a more sustained anxiolytic effect compared to a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine.36 Lipophilicity is also important in predicting some cognitive adverse effects, including amnesia. Benzodiazepines with high lipophilicity have greater absorption and faster onset of action as well as more rapid amnestic effects.37,38 These effects may relate to overall efficacy differences for oral benzodiazepines. A recent meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 found that less lipophilic benzodiazepines produced a greater response compared to more lipophilic benzodiazepines.
Continue to: Metabolism
Metabolism
Regarding cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism, polymorphic CYP2C19 and CYP3A4/5 are involved in the metabolism of several benzodiazepines39 and CYP2B6 has been recognized as a contributor to diazepam metabolism. CYP3A5 gene polymorphisms may produce variation in alprazolam metabolism; however, the predominant cytochrome involved in the metabolism of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines (ie, benzodiazepines other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam) is primarily CYP3A4, and most effects on CYP3A4 activity are related to concomitant medications and other nongenetic factors.
Drug-drug interactions
Apart from lorazepam,40,41 oxazepam,42,43 and temazepam, most benzodiazepines are metabolized through oxidative mechanisms that involve CYP3A4 (Figure 220).39 As such, their metabolism is influenced by medications that impact CYP3A4, including antifungals (eg, ketoconazole), calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil, diltiazem), nefazodone, some protease inhibitors, and macrolide antibiotics. Research has examined the impact of low-dose estrogen oral contraceptives (OCPs) on exposure (eg, plasma concentrations) of several benzodiazepines. The mechanism for this interaction is likely complex and putatively involves multiple pathways, including inhibition of CYP3A4 by OCPs. The effects of OCPs on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics vary based on the metabolism of the benzodiazepine. In general, medications oxidized and nitroreduced (eg, chlordiazepoxide, alprazolam, diazepam, and nitrazepam) have decreased clearance in patients treated with OCPs. Regarding nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines, data are mixed. Research found no OCP-related effects on the pharmacokinetics of nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines44; another study suggested that clearance of these medications—through increased glucuronidation—may be increased.31 The effect of smoking on benzodiazepine concentration has been well documented. Smoking increases the clearance of orally administered diazepam,45 but not IV diazepam, midazolam, or lorazepam, suggesting that this represents a first-pass effect.46 For alprazolam, plasma concentrations are reduced by 15% to 30% in smokers and total body clearance is 24% greater compared to nonsmokers, which results in an approximately 50% increase in half-life in nonsmokers compared to smokers.47 The most notable interaction between benzodiazepines and SSRIs is seen with fluvoxamine. Because fluvoxamine moderately inhibits CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 and potently inhibits CYP1A2,48 the clearance of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines is reduced.49 Additionally, the effects of grapefruit juice—a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4—has been evaluated for several benzodiazepines. Yasui et al50 found grapefruit juice did not alter alprazolam plasma concentrations. However, in separate research, grapefruit juice tripled diazepam exposure, increased peak concentrations 1.5-fold, and prolonged absorption.51
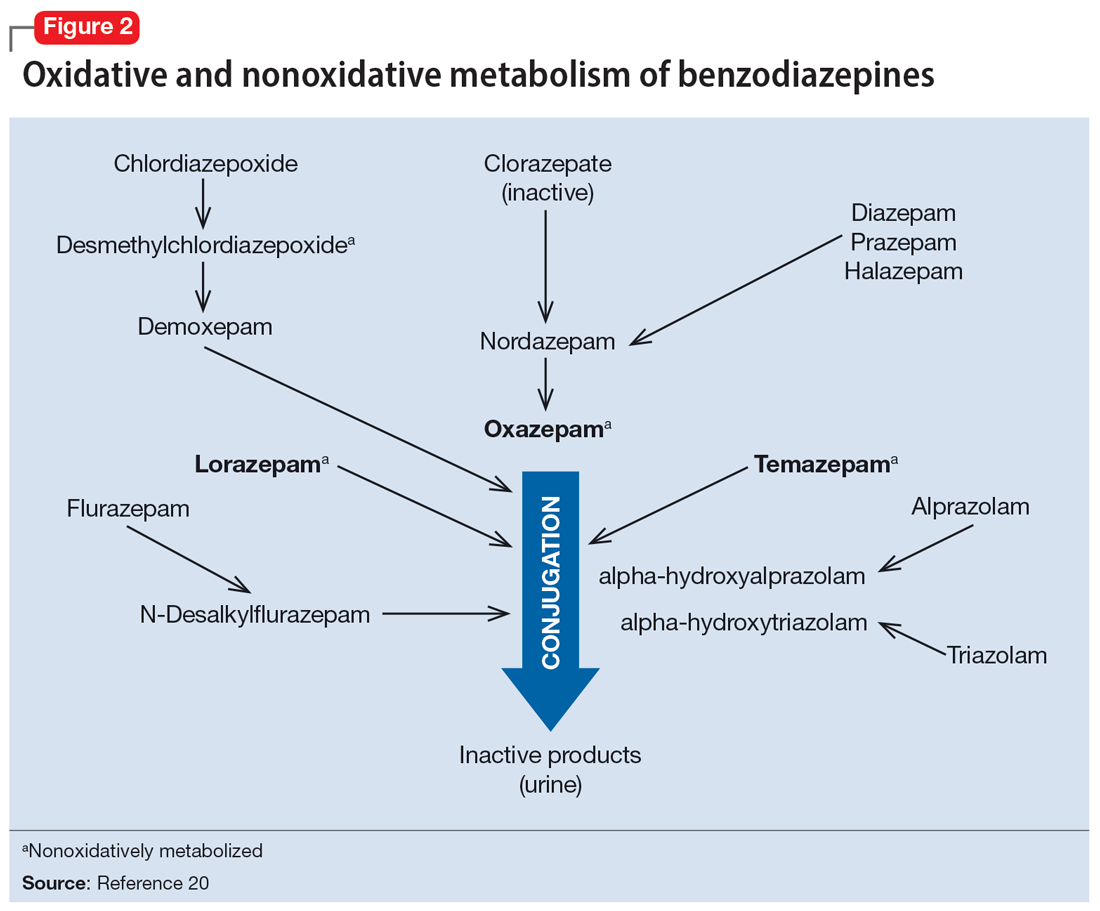
Hepatic disease
Exposure to benzodiazepines—other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam—is influenced by intrinsic hepatic disease and requires dose adjustment in individuals with significant hepatic impairment. The impact of hepatic disease on the clinical pharmacology of benzodiazepines may relate to 2 factors: protein binding and metabolism. In a study of individuals with cirrhosis, lorazepam binding was decreased, although its metabolism and clearance were largely unaffected.40
Aging and benzodiazepine metabolism/clearance
Aging is associated with myriad physiologic changes (eg, decrease in renal clearance after age 40, changes in body fat distribution, changes in activity of cytochromes) that are relevant to benzodiazepine pharmacology. They may underlie differences in the tolerability of benzodiazepines and other clinically relevant characteristics (eg, duration of action, accumulation).
Several studies have evaluated the impact of aging on the clearance and disposition of selected benzodiazepines. The respective half-lives of chlordiazepoxide and diazepam increase from 4- to 6-fold from age 20 to 80. Further, with chronic dosing, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines may require additional attention in geriatric patients. In a study that included individuals up to age 78, steady-state plasma concentrations of diazepam and its metabolite, desmethyldiazepam (DMDZ), were 30% to 35% higher in older patients compared to younger individuals.52 In this study, the half-lives for the young and older patients were 31 hours and 86 hours, respectively, for diazepam, and 40 hours and 80 hours, respectively, for the active metabolite. The half-life of diazepam is increased by “1 hour for each year of age beginning with a half-life of 20 hours at 20 years of age, as the volume of distribution is increased, and clearance is decreased.”52 Clinically, this implies that in older adults, clinicians should expect lower peak concentrations (Cmax), higher trough concentrations (Cmin), and that diazepam will take longer to reach steady-state concentrations. Taken together, these findings raised concern that “slow accumulation and delayed washout of diazepam and DMDZ is probable.”52 These findings—which may have more clinical relevance than those of single-dose studies—suggest that the effects related to diazepam would also take longer to resolve in older patients. Finally, lorazepam clearance or distribution does not appear to be affected by aging, at least in patients age 15 to 73.40 Alprazolam is more slowly cleared in geriatric patients and its effects may be potentiated by reduced protein binding.
Continue to: Obesity
Obesity
The distribution of medications, including benzodiazepines, is altered in patients who are obese because of increased adipose tissue.53,54 This increase in the volume of distribution can attenuate the onset of action, increase medication accumulation in fat, and potentiate the duration of action.55,56
Obesity may also affect hepatic metabolism by induction of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, and inhibition of CYP3A4.57 Triazolam, which is metabolized by CYP3A4, is associated with a greater exposure (ie, plasma concentrations) in individuals who are obese.58 However, when considering differences in benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics in patients who are obese, clinicians must remember that elimination half-life depends on both volume of distribution and clearance. In
How quickly do benzodiazepines work?
Benzodiazepines act quickly. Meta-analyses36 suggest that improvement in anxiety symptoms compared to placebo is greatest initially and then the rate of improvement slows over successive weeks. Research on benzodiazepines reveals statistically significant differences between benzodiazepines and placebo within the first week of treatment, with >80% of the expected improvement by Week 8 of treatment emerging by Week 4 (Figure 336). The rapid reduction in anxiety symptoms seen with benzodiazepines has important treatment implications, given that traditional psychotherapeutic and antidepressant treatments are slow to produce improvements. Consistent data suggesting that benzodiazepines work faster than other treatments support that they may have a role during the initiation of other treatments.
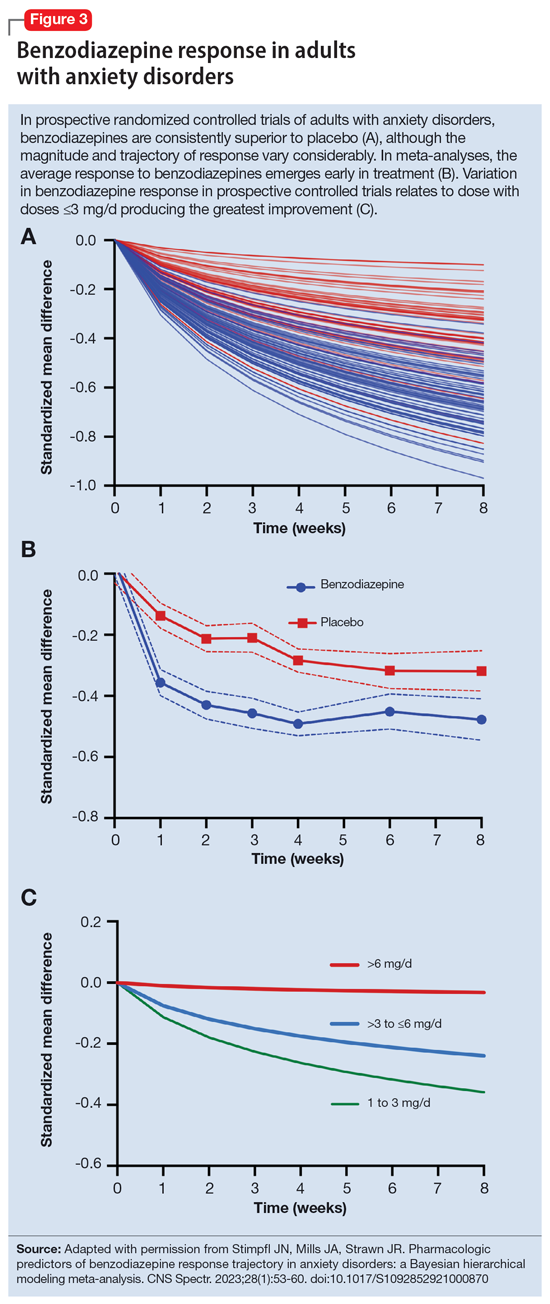
What is the ‘best’ dose?
As seen with other classes of psychotropic medications,4 the relationship between benzodiazepine dose and response is complex. In a recent meta-analysis of 65 placebo-controlled trials of benzodiazepines in adults with anxiety disorders, there was a superior response over time for low-dose benzodiazepines (<3 mg/d in lorazepam equivalents) compared to a medium dose (3 to 6 mg/d; P = .042); high-dose benzodiazepines (>6 mg/d) yielded less improvement compared to medium doses (P = .001).36 A study of adults with panic disorder similarly found the greatest responses with alprazolam plasma concentrations of 20 to 40 ng/mL, with no additional benefit at <20 ng/mL or >40 ng/mL.49 As plasma concentrations increase, adverse effects such as sedation also increase, which may confound the observed loss of a dose-response relationship at higher doses and plasma concentrations.62 This may, in part, account for the observation that higher doses of benzodiazepines are associated with greater depressive symptoms and disrupted sleep.63 As such, low doses may represent a delicate equipoise between efficacy and tolerability, yielding the most optimal clinical response.
Which benzodiazepine should I prescribe?
Comparing benzodiazepines is difficult, given the differences in dosing and disorders studied and differences in how each individual clinical trial was conducted. A meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 that used Bayesian hierarchical modeling, which allowed some of this heterogeneity to be addressed, found that relative to the reference benzodiazepine (lorazepam), clonazepam had the greatest trajectory/magnitude of response (other specific benzodiazepines did not statistically differ from lorazepam) (Figure 436).
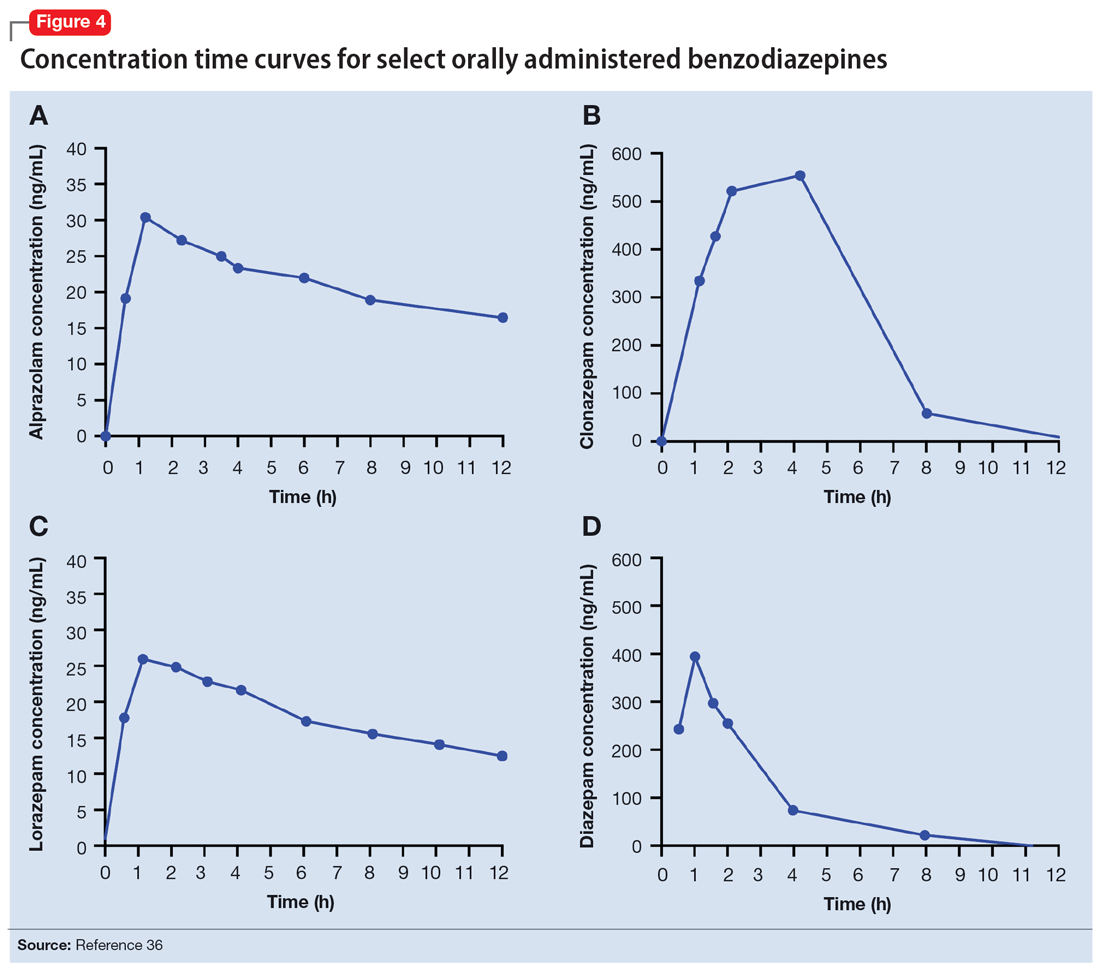
Continue to: Another aspect of the superiority...
Another aspect of the superiority of clonazepam in some research relates to its pharmacokinetic properties, particularly when compared with benzodiazepines that have very short half-lives. Short half-life benzodiazepines have been associated with rebound anxiety, which is defined as “the relative worsening of symptoms on discontinuation of treatment as compared to baseline symptoms” and is distinct from withdrawal.64 While it is difficult to assess this in clinical trials, Herman et al65 provided insight into the contribution of rebound anxiety in a study of patients with panic disorder treated with alprazolam who experienced “interdose anxiety symptoms.” Of the 48 patients in this study, 41 switched to clonazepam, and most who switched (82%) experienced improvement. The improvement was attributed to the decreased frequency of clonazepam (vs alprazolam) administration and lack of interdose anxiety. When selecting an oral benzodiazepine, consider the duration, onset of action, and differences in metabolism that produce varying levels of effectiveness for individual patients. In situations where rapid onset is desired, a short-acting benzodiazepine may be preferable, while a longer-acting benzodiazepine would be preferable in situations where the patient needs sustained effects.
Regarding lipophilicity, differences among benzodiazepines could contribute to differences in psychological dependence and differential utility in some situations. For example, alprazolam rapidly enters the CNS, producing an immediate anxiolytic effect. However, its egress from the CNS is equally rapid, and its anxiolytic effects disappear quickly. This may be desirable for addressing acute, predictable anxiety, but could have unintended consequences in treating chronic anxiety, where it could facilitate psychological dependence.
Practical considerations
When prescribing benzodiazepines, consider a myriad of patient- and medication-specific factors, as these have clinically relevant implications on treatment response. This information, taken together, supports the importance of an individualized approach to benzodiazepine use. Before selecting a benzodiazepine and during treatment, important elements of the patient’s history must be considered, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use (eg, antacids, CYP3A4 inhibitors, OCPs), smoking status, and history of hepatic or renal disease.
Patients age <18 are unlikely to have full expression of GABA receptors in the brain30 and therefore benzodiazepines may not be as efficacious for anxiolysis in this population. Moreover, compared to younger patients, older patients may experience higher steady-state concentrations of benzodiazepines, especially lipophilic agents, due to an increased volume of distribution and decreased clearance. In patients treated with OCPs, some benzodiazepines may take longer to reach steady-state, and dose adjustments may need to be considered. In patients who smoke, clearance of some oral benzodiazepines is also accelerated, potentially decreasing half-life by up to 50%.
When dosing and titrating benzodiazepines, consider the patient’s body weight, particularly if they are obese. The effects of obesity on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are complex. For glucuronidated benzodiazepines, clearance is increased in patients who are obese; however, the volume of distribution is also increased in such patients, meaning it will take longer for benzodiazepines to achieve steady-state in these individuals compared to patients who are not obese. These effects suggest it may take longer to achieve a response at a given dose in patients who are obese compared to individuals who are not obese.
Continue to: The properties of individual benzodiazepines...
The properties of individual benzodiazepines should also be considered when selecting a benzodiazepine treatment. If circumstances necessitate rapid symptom relief, a lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as diazepam, may be preferred for quick onset and offset of action. Onset of action may also be hastened by taking the benzodiazepine without food; conversely, if peak adverse effects are problematic, concurrent consumption of a high-fat meal may help decrease peak concentration and prolonging absorption. In other circumstances, such as if sustained anxiolysis is desired, a clinician may opt for a less lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as clonazepam. Finally, in terms of general treatment response, benzodiazepines separate from placebo in the first week of treatment, which supports the idea they may be useful during the introduction of other medications (eg, SSRIs) that take a longer time to achieve clinical effect.
Bottom Line
The pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on individual absorption and distribution/redistribution. Benzodiazepines’ clinical profile derives from their pharmacokinetic differences and is influenced by many factors, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use, smoking status, and hepatic or renal disease. Consider these factors to individualize the approach to using benzodiazepines and optimize tolerability and efficacy.
Related Resources
- Weber SR, Duchemin AM. Benzodiazepines: sensible prescribing in light of the risks. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):22-27.
- Balon R. Benzodiazepines for anxious depression. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):9-12.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Clobazam • Onfi
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Clorazepate • Gen-Xene
Diazepam • Valium
Diltiazem • Cardizem
Fluvoxamine • Luvox
Ganaxolone • Ztalmy
Ketoconazole • Nizoral
Lorazepam • Ativan
Midazolam • Versed
Temazepam • Restoril
Triazolam • Halcion
Verapamil • Calan
1. Rickels K, Moeller HJ. Benzodiazepines in anxiety disorders: reassessment of usefulness and safety. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019;20(7):514-518. doi:10.1080/15622975.2018.1500031
2. Stevens JC, Pollack MH. Benzodiazepines in clinical practice: consideration of their long-term use and alternative agents. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(Suppl 2):21-27.
3. Pollack MH, van Ameringen M, Simon NM, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of augmentation and switch strategies for refractory social anxiety disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171(1):44-53. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12101353
4. Strawn JR, Geracioti L, Rajdev N, et al. Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adult and pediatric patients: an evidence-based treatment review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19(10):1057-1070. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1491966
5. Karaca-Mandic P, Meara E, Morden NE. The growing problem of co-treatment with opioids and benzodiazepines. BMJ. 2017;356:j1224. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1224
6. Bachhuber MA, Hennessy S, Cunningham CO, et al. Increasing benzodiazepine prescriptions and overdose mortality in the United States, 1996-2013. Am J Public Health. 2016;106(4):686-688. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303061
7. Bentué-Ferrer D, Akwa Y. Benzodiazepines: Effects on memory functioning. In: Pandi-Perumal SR, Verster J, Monti J, et al, eds. Sleep Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapeutics. CRC Press; 2008:104-114. doi:10.3109/9780203091715-15
8. Pomara N, Facelle TM, Roth AE, et al. Dose-dependent retrograde facilitation of verbal memory in healthy elderly after acute oral lorazepam administration.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006;185(4):487-494. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0336-0
9. Gray SL, Dublin S, Yu O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of incident dementia or cognitive decline: prospective population based study. BMJ. 2016;352:i90. doi:10.1136/bmj.i90
10. Biétry FA, Pfeil AM, Reich O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study based on Swiss claims data. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(3):245-251. doi:10.1007/s40263-016-0404-x
11. de Gage SB, Moride Y, Ducruet T, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: case-control study. BMJ. 2014;349g5205. doi:10.1136/bmj.g5205
12. Shah R, Raji MA, Westra J, et al. Association of co-prescribing of opioid and benzodiazepine substitutes with incident falls and fractures among older adults: a cohort study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e052057. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052057
13. Guina J, Rossetter SR, DeRhodes BJ, et al. Benzodiazepines for PTSD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Pract. 2015;21(4):281-303.
14. Ekström MP, Bornefalk-Hermansson A, Abernethy AP, et al. Safety of benzodiazepines and opioids in very severe respiratory disease: national prospective study. BMJ. 2014;348:g445. doi:10.1136/bmj.g445
15. Donovan LM, Malte CA, Spece LJ, et al. Center predictors of long-term benzodiazepine use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and post-traumatic stress disorder. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(9):1151-1157. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-048OC
16. Sheehy O, Zhao JP, Bérard A. Association between incident exposure to benzodiazepines in early pregnancy and risk of spontaneous abortion. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):948-957. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0963
17. Kelly LE, Poon S, Madadi P, et al. Neonatal benzodiazepines exposure during breastfeeding. J Pediatr. 2012;161(3):448-451. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.03.003
18. Agarwal SD, Landon BE. Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(1):e187399. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7399
19. Hirschtritt ME, Olfson M, Kroenke K. Balancing the risks and benefits of benzodiazepines. JAMA. 2021;325(4):347-348. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22106
20. Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
21. Nutt DJ, Malizia AL. New insights into the role of the GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor in psychiatric disorder. British J Psychiatry. 2001;179:390-396. doi:10.1192/bjp.179.5.390
22. Sigel E. Mapping of the benzodiazepine recognition site on GABA(A) receptors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002;2(8):833-839. doi:10.2174/1568026023393444
23. Savic
24. Smith TA. Type A gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor subunits and benzodiazepine binding: significance to clinical syndromes and their treatment. Br J Biomed Sci. 2001;58(2):111-121.
25. Althaus AL, Ackley MA, Belfort GM, et al. Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology. 2020;181:108333. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108333
26. Jacob TC, Michels G, Silayeva L, et al. Benzodiazepine treatment induces subtype-specific changes in GABA(A) receptor trafficking and decreases synaptic inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(45):18595-18600. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204994109
27. Nicholson MW, Sweeney A, Pekle E, et al. Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCδ/ Ca2+/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(9):1851-1867. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0100-y
28. Dobson ET, Bloch MH, Strawn JR. Efficacy and tolerability of pharmacotherapy for pediatric anxiety disorders: a network meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2019;80(1):17r12064. doi:10.4088/JCP.17r12064
29. Kuang H, Johnson JA, Mulqueen JM, et al. The efficacy of benzodiazepines as acute anxiolytics in children: a meta-analysis. Depress Anxiety. 2017;34(10):888-896. doi:10.1002/da.22643
30. Chugani DC, Muzik O, Juhász C, et al. Postnatal maturation of human GABAA receptors measured with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(5):618-626. doi:10.1002/ana.1003
31. Jochemsen R, Breimer DD. Pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines: metabolic pathways and plasma level profiles. Curr Med Res Opin. 1984;8(Suppl 4):60-79. doi:10.1185/03007998409109545
32. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Dorsey C, et al. Comparative single-dose kinetics and dynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam, prazepam, and placebo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988;44(3)326-334. doi:10.1038/clpt.1988.158
33. Shader RI, Georgotas A, Greenblatt DJ, et al. Impaired absorption of desmethydiazepam from clorazepate by magnesium aluminum hydroxide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(3):308-315. doi:10.1002/cpt1978243308
34. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, MacLaughlin DS, et al. Diazepam absorption: effect of antacids and food. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(5):600-609. doi:10.1002/cpt1978245600
35. Yamazaki A, Kumagai Y, Fujita T, et al. Different effects of light food on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of three benzodiazepines, quazepam, nitrazepam and diazepam. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(1):31-39. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00795.x
36. Stimpfl J, Mills JA, Strawn JR. Pharmacologic predictors of benzodiazepine response trajectory in anxiety disorders: a Bayesian hierarchical modeling meta-analysis. CNS Spectr. 2023;28(1):53-60. doi:10.1017/S1092852921000870
37. Griffin CE 3rd, Kaye AM, Bueno FR, et al. Benzodiazepine pharmacology and central nervous system-mediated effects. Ochsner J. 2013;13(2):214-223.
38. Buffett-Jerrott SE, Stewart SH. Cognitive and sedative effects of benzodiazepine use. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;8(1):45-58. doi:10.2174/1381612023396654
39. Fukasawa T, Suzuki A, Otani K. Effects of genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 enzymes on the pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(4):333-341. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00829.x
40. Kraus JW, Desmond PV, Marshall JP, et al. Effects of aging and liver disease on disposition of lorazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(4):411-419. doi:10.1002/cpt1978244411
41. Greenblatt DJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxazepam and lorazepam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981;6(2):89-105. doi:10.2165/00003088-198106020-00001
42. Walkenstein SS, Wiser R, Gudmundsen CH, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of oxazepam and its succinate half‐ester. J Pharm Sci. 1964;53(10):1181-1186. doi:10.1002/jps.2600531010
43. Shull HJ, Wilkinson GR, Johnson R, et al. Normal disposition of oxazepam in acute viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976;84(4):420-425. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-84-4-420
44. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Ochs HR, et al. Lorazepam and oxazepam kinetics in women on low-dose oral contraceptives. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983;33(5):628-632. doi:10.1038/clpt.1983.85
45. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, Harmatz JS, et al. Diazepam disposition determinants. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980;27(3):301-312. doi:10.1038/clpt.1980.40
46. Ochs HR, Greenblatt DJ, Knüchel M. Kinetics of diazepam, midazolam, and lorazepam, in cigarette smokers. Chest. 1985;87(2):223-226. doi:10.1378/chest.87.2.223
47. Smith RB, Gwilt PR, Wright CE 3rd. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam in healthy smoking and nonsmoking men. Clin Pharm. 1983;2(2):139-143.
48. Figgitt DP, McClellan KJ. Fluvoxamine. An updated review of its use in the management of adults with anxiety disorders. Drugs. 2000;60(4):925-954. doi:10.2165/00003495-200060040-00006
49. Greenblatt DJ, Wright CE. Clinical pharmacokinetics of alprazolam. Therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993;24(6):453-471. doi:10.2165/00003088-199324060-00003
50. Yasui N, Kondo T, Furukori H, et al. Effects of repeated ingestion of grapefruit juice on the single and multiple oral-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alprazolam. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000;150(2):185-190. doi:10.1007/s002130000438
51. Özdemir M, Aktan Y, Boydagˇ BS, et al. Interaction between grapefruit juice and diazepam in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1998;23(1):55-59. doi:10.1007/BF03189827
52. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Zhang Q, et al. Slow accumulation and elimination of diazepam and its active metabolite with extended treatment in the elderly. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;61(2):193-203. doi:10.1002/jcph.1726
53. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Drug disposition in obese humans: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986;11(3):199-213. doi:10.2165/00003088-198611030-00002
54. Hanley MJ, Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(2):71-87. doi:10.2165/11318100-000000000-00000
55. Bauer LA. Drug Dosing in special populations: renal and hepatic disease, dialysis, heart failure, obesity, and drug interactions. In: Weitz M, Thomas, CM, eds. Applied Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=1374
56. Kendrick JG, Carr RR, Ensom MHH. Pharmacokinetics and drug dosing in obese children. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2010;15(2):94-109. doi:10.5863/1551-6776-15.2.94
57. Brill MJE, Diepstraten J, van Rongen A, et al. Impact of obesity on drug metabolism and elimination in adults and children. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(5):277-304. doi:10.2165/11599410-000000000-00000
58. Derry CL, Kroboth PD, Pittenger AL, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of triazolam after two intermittent doses in obese and normal-weight men. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;15(3):197-205. doi:10.1097/00004714-199506000-00008
59. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. The influence of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam and triazolam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984;9(2):177-183. doi:10.2165/00003088-198409020-00005
60. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Prolonged accumulation of diazepam in obesity. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;23(8-9):369-376. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1983.tb02750.x
61. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Enhanced glucuronide conjugation of drugs in obesity: studies of lorazepam, oxazepam, and acetaminophen. J Lab Clin Med. 1983;101(6):873-880.
62. Greenblatt DJ, von Moltke LL, Harmatz JS, et al. Alprazolam pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and plasma levels: clinical implications. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54 Suppl:4-11.
63. Chen YT, Liu CY, Chang CM, et al. Perceptions, clinical characteristics, and other factors associated with prolonged and high daily dose of benzodiazepine use among patients with anxiety or depressive disorders. J Affect Disord. 2020;271:215-223. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.077
64. Herman JB, Brotman AW, Rosenbaum JF. Rebound anxiety in panic disorder patients treated with shorter-acting benzodiazepines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1987;48(Suppl):22-28.
65. Herman JB, Rosenbaum JF, Brotman AW. The alprazolam to clonazepam switch for the treatment of panic disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):175-178.
Though once the main treatment for anxiety disorders—often as monotherapy1—benzodiazepines are now primarily used as adjunctive agents.2-4 Their ability to produce rapid anxiolysis represents a significant therapeutic advantage, but in recent decades their tolerability, class-specific risks, and lack of antidepressant properties contributed to benzodiazepines being largely replaced by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for the pharmacologic treatment of anxiety. This shift within the pharmacologic armamentarium has decreased many clinicians’ familiarity with benzodiazepines.
While benzodiazepines continue to have an important role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly treatment-resistant anxiety,4 clinicians must consider the limitations of these agents. Benzodiazepines can be associated with abuse and dependence, and overdose risk when combined with opiates.5,6 They may cause memory impairment7,8 and conflicting data suggest they may contribute to the risk of developing cognitive disorders.9-11 Benzodiazepines also have been associated with falls and fractures,12 and worse outcomes in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder.13 Some studies of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) found benzodiazepines may increase the risk of COPD exacerbations and accidental overdose,14 though others found that was not always the case.15 Benzodiazepines may be associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion when used early in pregnancy.16 Prospective research in women who were breastfeeding found benzodiazepines may cause sedation in up to 2% of infants.17
Despite the potential for adverse effects, benzodiazepine use remains common.18 These medications have a rapid onset of action, are useful for breakthrough symptoms, may enhance treatment adherence, and alleviate activating symptoms of SSRIs. Like other commonly used medications, benzodiazepines have the potential for both harm and benefit.19 Similar to other medications with tolerability concerns but established efficacy, particularly in treatment-resistant anxiety disorders, it is important to balance “overprescribing … to patients at risk and underusing these effective medications when indicated.”19 Though the use of benzodiazepines has been discouraged and perceptions have shifted, knowledge of benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine pharmacology also has been degraded contemporaneously.
This article provides a synthesis of the clinically relevant pharmacology of benzodiazepines, with a focus on orally administered benzodiazepines, which are more common in outpatient clinical practice. Specifically, this review describes the pharmacology of benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine medication interactions, the relationship between pharmacologic characteristics and treatment response/tolerability, and selection and dosing of oral benzodiazepines (Table20).

Benzodiazepine pharmacodynamics
Benzodiazepines act at the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptor complex and bind allosterically.21-23 Comprised of 5 glycoprotein subunits (2 alpha subunits, 2 beta subunits, and 1 gamma subunit), the receptor has 2 distinct sites at which the endogenous inhibitory transmitter GABA binds and 1 benzodiazepine binding site. Benzodiazepines bind within a socket created by the alpha and gamma subunits22 and after binding induce a conformational change in the receptor, which enhances GABA binding. There are 2 types of benzodiazepine receptors: BZ1 and BZ2. The subunits play a critical role in driving the pharmacologic characteristics of the receptor.24 BZ1 and BZ2 receptors bind benzodiazepines, although they are differentially distributed within the brain. Binding at BZ1 receptors—which are distributed in cortical, thalamic, and cerebellar regions—contributes to sedation and deleterious effects of benzodiazepines on memory (eg, anterograde amnesia). BZ2 receptors (which contain gamma-2 subunits) are responsible for anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects. They are distributed throughout limbic regions and motor tracts, including motor neurons and neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.24
Benzodiazepines—positive GABA-A receptor allosteric modulators—produce phasic inhibition, largely through the alpha and gamma subunits discussed above. In contrast, newer positive allosteric modulators (eg, zuranolone) bind at the alpha/beta subunits.25 Mechanistically, endogenous neuroactive steroids and nonbenzodiazepine GABA-A–positive allosteric modulators such as zuranolone and ganaxolone also differ in their regulation of GABA-A (downregulated with benzodiazepines and hypothetically upregulated with zuranolone)26 and their synaptic effects (benzodiazepines synaptically vs endogenous neurosteroids and nonbenzodiazpine positive allosteric modulators extrasynaptically).27
From a developmental perspective, benzodiazepines may have less efficacy for anxiolysis and worse tolerability in some pediatric patients,28 although they generally appear effective for immediate use to treat anxiety in acute settings.29 The differences in efficacy and tolerability may be related to pharmacodynamic differences between pediatric populations and adults. GABA receptor expression and function do not reach adult levels until age 14 to 17½ for subcortical regions and age 18 to 22 for cortical regions, although girls reach adult expression of GABA receptors slightly earlier than boys.30 D
Continue to: Pharmacology and clinical effects
Pharmacology and clinical effects
Benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on the route of administration, absorption, and distribution/redistribution.31 In this review, we focus on oral administration as opposed to IV, IM, sublingual, or intranasal administration.
Absorption
Benzodiazepines are rapidly absorbed after oral administration and quickly enter the systemic circulation. However, absorption rates vary depending on specific aspects of the gastrointestinal milieu and intrinsic properties of the benzodiazepine. For example, alprazolam is more rapidly absorbed than most other benzodiazepines, with a Tmax of 1.8 hours compared to lorazepam, which has a Tmax of approximately 2 hours. These pharmacokinetic effects instantiate differences in tolerability and efficacy. Thus, following single doses of alprazolam and diazepam, self-rated sedating effects and impairment on a task of working memory suggest that effects have a more rapid onset for alprazolam relative to lorazepam.32 Food and concomitant medications can significantly affect benzodiazepine absorption. A single-dose, 3-way crossover study demonstrated that taking diazepam concomitantly with an antacid (eg, aluminum hydroxide) decreased peak concentrations and prolonged absorption by approximately 30 minutes. However, total absorption of the medication was unaffected.33 Additionally, administration of diazepam with food significantly slows absorption from 1 hour 15 minutes to approximately 2 hours 30 minutes and increases benzodiazepine absorption by 25% (Figure 134); the fat content of the meal appears important in moderating this effect.35 The impact of food on alprazolam varies by formulation. For example, when administered in an extended-release (XR) formulation with a high-fat meal, alprazolam absorption increases by one-third, while absorption for administration of the orally disintegrating tablet with a high-fat meal increases from 1 hour 30 minutes to 2 hours. Similarly, for lorazepam, administration with a meal delays absorption by approximately 2 hours; however, this effect does not appear present with the XR formulation. Administering benzodiazepines with food can be clinically leveraged to either accelerate the onset of action or decrease peak-associated adverse effects. Thus, when a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine is needed to treat acute anxiety or prior to an expected anxiogenic stimuli, administering the medication without food may produce a faster onset of action.

CNS penetration
Benzodiazepines enter the CNS by passive diffusion. Because of this, lipophilicity at physiologic pH influences the rate at which a benzodiazepine crosses the blood-brain barrier. The rate at which benzodiazepines enter the CNS influences their clinical effects and the speed at which both efficacy (ie, anxiolysis) and adverse effects (ie, sedation, slowed cognition) are observed. In general, more lipophilic medications initiate their anxiolytic effect more quickly. However, by quickly leaving the CNS (through the same mechanism that allowed them to enter the CNS at such speed), their effects rapidly cease as they redistribute into fat. Thus, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines produce more intense effects compared to less lipophilic benzodiazepines. For these reasons, lipophilicity is more important than half-life for determining the duration of effect in most patients.
Lipophilicity and duration of effect
Benzodiazepines and their metabolites tend to be highly protein-bound and distributed in fat- and lipid-enriched areas such as the CNS. As a result, the more lipophilic agents generally have the highest rates of absorption and the fastest onset of clinical effects. The duration of action for many benzodiazepines is determined by the rate and extent of distribution (a function of lipophilicity) rather than by the rate of elimination. For example, diazepam has a longer half-life than lorazepam, but its duration of action following a single dose is shorter. This is because diazepam is more lipophilic and therefore more extensively distributed (particularly to adipose tissue). This results in it leaving the brain and blood and distributing to other tissues. In turn, its CNS effect (ie, anxiolytic effects) are more quickly terminated.
By contrast, less lipophilic benzodiazepines maintain their CNS concentrations longer; they have a longer duration of action because of their slower redistribution, which culminates in a shorter half-life, and are less extensively distributed to peripheral tissues. In essence, this means that (other things being equal) a less lipophilic benzodiazepine produces a more sustained anxiolytic effect compared to a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine.36 Lipophilicity is also important in predicting some cognitive adverse effects, including amnesia. Benzodiazepines with high lipophilicity have greater absorption and faster onset of action as well as more rapid amnestic effects.37,38 These effects may relate to overall efficacy differences for oral benzodiazepines. A recent meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 found that less lipophilic benzodiazepines produced a greater response compared to more lipophilic benzodiazepines.
Continue to: Metabolism
Metabolism
Regarding cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism, polymorphic CYP2C19 and CYP3A4/5 are involved in the metabolism of several benzodiazepines39 and CYP2B6 has been recognized as a contributor to diazepam metabolism. CYP3A5 gene polymorphisms may produce variation in alprazolam metabolism; however, the predominant cytochrome involved in the metabolism of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines (ie, benzodiazepines other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam) is primarily CYP3A4, and most effects on CYP3A4 activity are related to concomitant medications and other nongenetic factors.
Drug-drug interactions
Apart from lorazepam,40,41 oxazepam,42,43 and temazepam, most benzodiazepines are metabolized through oxidative mechanisms that involve CYP3A4 (Figure 220).39 As such, their metabolism is influenced by medications that impact CYP3A4, including antifungals (eg, ketoconazole), calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil, diltiazem), nefazodone, some protease inhibitors, and macrolide antibiotics. Research has examined the impact of low-dose estrogen oral contraceptives (OCPs) on exposure (eg, plasma concentrations) of several benzodiazepines. The mechanism for this interaction is likely complex and putatively involves multiple pathways, including inhibition of CYP3A4 by OCPs. The effects of OCPs on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics vary based on the metabolism of the benzodiazepine. In general, medications oxidized and nitroreduced (eg, chlordiazepoxide, alprazolam, diazepam, and nitrazepam) have decreased clearance in patients treated with OCPs. Regarding nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines, data are mixed. Research found no OCP-related effects on the pharmacokinetics of nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines44; another study suggested that clearance of these medications—through increased glucuronidation—may be increased.31 The effect of smoking on benzodiazepine concentration has been well documented. Smoking increases the clearance of orally administered diazepam,45 but not IV diazepam, midazolam, or lorazepam, suggesting that this represents a first-pass effect.46 For alprazolam, plasma concentrations are reduced by 15% to 30% in smokers and total body clearance is 24% greater compared to nonsmokers, which results in an approximately 50% increase in half-life in nonsmokers compared to smokers.47 The most notable interaction between benzodiazepines and SSRIs is seen with fluvoxamine. Because fluvoxamine moderately inhibits CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 and potently inhibits CYP1A2,48 the clearance of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines is reduced.49 Additionally, the effects of grapefruit juice—a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4—has been evaluated for several benzodiazepines. Yasui et al50 found grapefruit juice did not alter alprazolam plasma concentrations. However, in separate research, grapefruit juice tripled diazepam exposure, increased peak concentrations 1.5-fold, and prolonged absorption.51

Hepatic disease
Exposure to benzodiazepines—other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam—is influenced by intrinsic hepatic disease and requires dose adjustment in individuals with significant hepatic impairment. The impact of hepatic disease on the clinical pharmacology of benzodiazepines may relate to 2 factors: protein binding and metabolism. In a study of individuals with cirrhosis, lorazepam binding was decreased, although its metabolism and clearance were largely unaffected.40
Aging and benzodiazepine metabolism/clearance
Aging is associated with myriad physiologic changes (eg, decrease in renal clearance after age 40, changes in body fat distribution, changes in activity of cytochromes) that are relevant to benzodiazepine pharmacology. They may underlie differences in the tolerability of benzodiazepines and other clinically relevant characteristics (eg, duration of action, accumulation).
Several studies have evaluated the impact of aging on the clearance and disposition of selected benzodiazepines. The respective half-lives of chlordiazepoxide and diazepam increase from 4- to 6-fold from age 20 to 80. Further, with chronic dosing, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines may require additional attention in geriatric patients. In a study that included individuals up to age 78, steady-state plasma concentrations of diazepam and its metabolite, desmethyldiazepam (DMDZ), were 30% to 35% higher in older patients compared to younger individuals.52 In this study, the half-lives for the young and older patients were 31 hours and 86 hours, respectively, for diazepam, and 40 hours and 80 hours, respectively, for the active metabolite. The half-life of diazepam is increased by “1 hour for each year of age beginning with a half-life of 20 hours at 20 years of age, as the volume of distribution is increased, and clearance is decreased.”52 Clinically, this implies that in older adults, clinicians should expect lower peak concentrations (Cmax), higher trough concentrations (Cmin), and that diazepam will take longer to reach steady-state concentrations. Taken together, these findings raised concern that “slow accumulation and delayed washout of diazepam and DMDZ is probable.”52 These findings—which may have more clinical relevance than those of single-dose studies—suggest that the effects related to diazepam would also take longer to resolve in older patients. Finally, lorazepam clearance or distribution does not appear to be affected by aging, at least in patients age 15 to 73.40 Alprazolam is more slowly cleared in geriatric patients and its effects may be potentiated by reduced protein binding.
Continue to: Obesity
Obesity
The distribution of medications, including benzodiazepines, is altered in patients who are obese because of increased adipose tissue.53,54 This increase in the volume of distribution can attenuate the onset of action, increase medication accumulation in fat, and potentiate the duration of action.55,56
Obesity may also affect hepatic metabolism by induction of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, and inhibition of CYP3A4.57 Triazolam, which is metabolized by CYP3A4, is associated with a greater exposure (ie, plasma concentrations) in individuals who are obese.58 However, when considering differences in benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics in patients who are obese, clinicians must remember that elimination half-life depends on both volume of distribution and clearance. In
How quickly do benzodiazepines work?
Benzodiazepines act quickly. Meta-analyses36 suggest that improvement in anxiety symptoms compared to placebo is greatest initially and then the rate of improvement slows over successive weeks. Research on benzodiazepines reveals statistically significant differences between benzodiazepines and placebo within the first week of treatment, with >80% of the expected improvement by Week 8 of treatment emerging by Week 4 (Figure 336). The rapid reduction in anxiety symptoms seen with benzodiazepines has important treatment implications, given that traditional psychotherapeutic and antidepressant treatments are slow to produce improvements. Consistent data suggesting that benzodiazepines work faster than other treatments support that they may have a role during the initiation of other treatments.

What is the ‘best’ dose?
As seen with other classes of psychotropic medications,4 the relationship between benzodiazepine dose and response is complex. In a recent meta-analysis of 65 placebo-controlled trials of benzodiazepines in adults with anxiety disorders, there was a superior response over time for low-dose benzodiazepines (<3 mg/d in lorazepam equivalents) compared to a medium dose (3 to 6 mg/d; P = .042); high-dose benzodiazepines (>6 mg/d) yielded less improvement compared to medium doses (P = .001).36 A study of adults with panic disorder similarly found the greatest responses with alprazolam plasma concentrations of 20 to 40 ng/mL, with no additional benefit at <20 ng/mL or >40 ng/mL.49 As plasma concentrations increase, adverse effects such as sedation also increase, which may confound the observed loss of a dose-response relationship at higher doses and plasma concentrations.62 This may, in part, account for the observation that higher doses of benzodiazepines are associated with greater depressive symptoms and disrupted sleep.63 As such, low doses may represent a delicate equipoise between efficacy and tolerability, yielding the most optimal clinical response.
Which benzodiazepine should I prescribe?
Comparing benzodiazepines is difficult, given the differences in dosing and disorders studied and differences in how each individual clinical trial was conducted. A meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 that used Bayesian hierarchical modeling, which allowed some of this heterogeneity to be addressed, found that relative to the reference benzodiazepine (lorazepam), clonazepam had the greatest trajectory/magnitude of response (other specific benzodiazepines did not statistically differ from lorazepam) (Figure 436).

Continue to: Another aspect of the superiority...
Another aspect of the superiority of clonazepam in some research relates to its pharmacokinetic properties, particularly when compared with benzodiazepines that have very short half-lives. Short half-life benzodiazepines have been associated with rebound anxiety, which is defined as “the relative worsening of symptoms on discontinuation of treatment as compared to baseline symptoms” and is distinct from withdrawal.64 While it is difficult to assess this in clinical trials, Herman et al65 provided insight into the contribution of rebound anxiety in a study of patients with panic disorder treated with alprazolam who experienced “interdose anxiety symptoms.” Of the 48 patients in this study, 41 switched to clonazepam, and most who switched (82%) experienced improvement. The improvement was attributed to the decreased frequency of clonazepam (vs alprazolam) administration and lack of interdose anxiety. When selecting an oral benzodiazepine, consider the duration, onset of action, and differences in metabolism that produce varying levels of effectiveness for individual patients. In situations where rapid onset is desired, a short-acting benzodiazepine may be preferable, while a longer-acting benzodiazepine would be preferable in situations where the patient needs sustained effects.
Regarding lipophilicity, differences among benzodiazepines could contribute to differences in psychological dependence and differential utility in some situations. For example, alprazolam rapidly enters the CNS, producing an immediate anxiolytic effect. However, its egress from the CNS is equally rapid, and its anxiolytic effects disappear quickly. This may be desirable for addressing acute, predictable anxiety, but could have unintended consequences in treating chronic anxiety, where it could facilitate psychological dependence.
Practical considerations
When prescribing benzodiazepines, consider a myriad of patient- and medication-specific factors, as these have clinically relevant implications on treatment response. This information, taken together, supports the importance of an individualized approach to benzodiazepine use. Before selecting a benzodiazepine and during treatment, important elements of the patient’s history must be considered, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use (eg, antacids, CYP3A4 inhibitors, OCPs), smoking status, and history of hepatic or renal disease.
Patients age <18 are unlikely to have full expression of GABA receptors in the brain30 and therefore benzodiazepines may not be as efficacious for anxiolysis in this population. Moreover, compared to younger patients, older patients may experience higher steady-state concentrations of benzodiazepines, especially lipophilic agents, due to an increased volume of distribution and decreased clearance. In patients treated with OCPs, some benzodiazepines may take longer to reach steady-state, and dose adjustments may need to be considered. In patients who smoke, clearance of some oral benzodiazepines is also accelerated, potentially decreasing half-life by up to 50%.
When dosing and titrating benzodiazepines, consider the patient’s body weight, particularly if they are obese. The effects of obesity on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are complex. For glucuronidated benzodiazepines, clearance is increased in patients who are obese; however, the volume of distribution is also increased in such patients, meaning it will take longer for benzodiazepines to achieve steady-state in these individuals compared to patients who are not obese. These effects suggest it may take longer to achieve a response at a given dose in patients who are obese compared to individuals who are not obese.
Continue to: The properties of individual benzodiazepines...
The properties of individual benzodiazepines should also be considered when selecting a benzodiazepine treatment. If circumstances necessitate rapid symptom relief, a lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as diazepam, may be preferred for quick onset and offset of action. Onset of action may also be hastened by taking the benzodiazepine without food; conversely, if peak adverse effects are problematic, concurrent consumption of a high-fat meal may help decrease peak concentration and prolonging absorption. In other circumstances, such as if sustained anxiolysis is desired, a clinician may opt for a less lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as clonazepam. Finally, in terms of general treatment response, benzodiazepines separate from placebo in the first week of treatment, which supports the idea they may be useful during the introduction of other medications (eg, SSRIs) that take a longer time to achieve clinical effect.
Bottom Line
The pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on individual absorption and distribution/redistribution. Benzodiazepines’ clinical profile derives from their pharmacokinetic differences and is influenced by many factors, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use, smoking status, and hepatic or renal disease. Consider these factors to individualize the approach to using benzodiazepines and optimize tolerability and efficacy.
Related Resources
- Weber SR, Duchemin AM. Benzodiazepines: sensible prescribing in light of the risks. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):22-27.
- Balon R. Benzodiazepines for anxious depression. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):9-12.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Clobazam • Onfi
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Clorazepate • Gen-Xene
Diazepam • Valium
Diltiazem • Cardizem
Fluvoxamine • Luvox
Ganaxolone • Ztalmy
Ketoconazole • Nizoral
Lorazepam • Ativan
Midazolam • Versed
Temazepam • Restoril
Triazolam • Halcion
Verapamil • Calan
Though once the main treatment for anxiety disorders—often as monotherapy1—benzodiazepines are now primarily used as adjunctive agents.2-4 Their ability to produce rapid anxiolysis represents a significant therapeutic advantage, but in recent decades their tolerability, class-specific risks, and lack of antidepressant properties contributed to benzodiazepines being largely replaced by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for the pharmacologic treatment of anxiety. This shift within the pharmacologic armamentarium has decreased many clinicians’ familiarity with benzodiazepines.
While benzodiazepines continue to have an important role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly treatment-resistant anxiety,4 clinicians must consider the limitations of these agents. Benzodiazepines can be associated with abuse and dependence, and overdose risk when combined with opiates.5,6 They may cause memory impairment7,8 and conflicting data suggest they may contribute to the risk of developing cognitive disorders.9-11 Benzodiazepines also have been associated with falls and fractures,12 and worse outcomes in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder.13 Some studies of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) found benzodiazepines may increase the risk of COPD exacerbations and accidental overdose,14 though others found that was not always the case.15 Benzodiazepines may be associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion when used early in pregnancy.16 Prospective research in women who were breastfeeding found benzodiazepines may cause sedation in up to 2% of infants.17
Despite the potential for adverse effects, benzodiazepine use remains common.18 These medications have a rapid onset of action, are useful for breakthrough symptoms, may enhance treatment adherence, and alleviate activating symptoms of SSRIs. Like other commonly used medications, benzodiazepines have the potential for both harm and benefit.19 Similar to other medications with tolerability concerns but established efficacy, particularly in treatment-resistant anxiety disorders, it is important to balance “overprescribing … to patients at risk and underusing these effective medications when indicated.”19 Though the use of benzodiazepines has been discouraged and perceptions have shifted, knowledge of benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine pharmacology also has been degraded contemporaneously.
This article provides a synthesis of the clinically relevant pharmacology of benzodiazepines, with a focus on orally administered benzodiazepines, which are more common in outpatient clinical practice. Specifically, this review describes the pharmacology of benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine medication interactions, the relationship between pharmacologic characteristics and treatment response/tolerability, and selection and dosing of oral benzodiazepines (Table20).

Benzodiazepine pharmacodynamics
Benzodiazepines act at the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptor complex and bind allosterically.21-23 Comprised of 5 glycoprotein subunits (2 alpha subunits, 2 beta subunits, and 1 gamma subunit), the receptor has 2 distinct sites at which the endogenous inhibitory transmitter GABA binds and 1 benzodiazepine binding site. Benzodiazepines bind within a socket created by the alpha and gamma subunits22 and after binding induce a conformational change in the receptor, which enhances GABA binding. There are 2 types of benzodiazepine receptors: BZ1 and BZ2. The subunits play a critical role in driving the pharmacologic characteristics of the receptor.24 BZ1 and BZ2 receptors bind benzodiazepines, although they are differentially distributed within the brain. Binding at BZ1 receptors—which are distributed in cortical, thalamic, and cerebellar regions—contributes to sedation and deleterious effects of benzodiazepines on memory (eg, anterograde amnesia). BZ2 receptors (which contain gamma-2 subunits) are responsible for anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects. They are distributed throughout limbic regions and motor tracts, including motor neurons and neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.24
Benzodiazepines—positive GABA-A receptor allosteric modulators—produce phasic inhibition, largely through the alpha and gamma subunits discussed above. In contrast, newer positive allosteric modulators (eg, zuranolone) bind at the alpha/beta subunits.25 Mechanistically, endogenous neuroactive steroids and nonbenzodiazepine GABA-A–positive allosteric modulators such as zuranolone and ganaxolone also differ in their regulation of GABA-A (downregulated with benzodiazepines and hypothetically upregulated with zuranolone)26 and their synaptic effects (benzodiazepines synaptically vs endogenous neurosteroids and nonbenzodiazpine positive allosteric modulators extrasynaptically).27
From a developmental perspective, benzodiazepines may have less efficacy for anxiolysis and worse tolerability in some pediatric patients,28 although they generally appear effective for immediate use to treat anxiety in acute settings.29 The differences in efficacy and tolerability may be related to pharmacodynamic differences between pediatric populations and adults. GABA receptor expression and function do not reach adult levels until age 14 to 17½ for subcortical regions and age 18 to 22 for cortical regions, although girls reach adult expression of GABA receptors slightly earlier than boys.30 D
Continue to: Pharmacology and clinical effects
Pharmacology and clinical effects
Benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on the route of administration, absorption, and distribution/redistribution.31 In this review, we focus on oral administration as opposed to IV, IM, sublingual, or intranasal administration.
Absorption
Benzodiazepines are rapidly absorbed after oral administration and quickly enter the systemic circulation. However, absorption rates vary depending on specific aspects of the gastrointestinal milieu and intrinsic properties of the benzodiazepine. For example, alprazolam is more rapidly absorbed than most other benzodiazepines, with a Tmax of 1.8 hours compared to lorazepam, which has a Tmax of approximately 2 hours. These pharmacokinetic effects instantiate differences in tolerability and efficacy. Thus, following single doses of alprazolam and diazepam, self-rated sedating effects and impairment on a task of working memory suggest that effects have a more rapid onset for alprazolam relative to lorazepam.32 Food and concomitant medications can significantly affect benzodiazepine absorption. A single-dose, 3-way crossover study demonstrated that taking diazepam concomitantly with an antacid (eg, aluminum hydroxide) decreased peak concentrations and prolonged absorption by approximately 30 minutes. However, total absorption of the medication was unaffected.33 Additionally, administration of diazepam with food significantly slows absorption from 1 hour 15 minutes to approximately 2 hours 30 minutes and increases benzodiazepine absorption by 25% (Figure 134); the fat content of the meal appears important in moderating this effect.35 The impact of food on alprazolam varies by formulation. For example, when administered in an extended-release (XR) formulation with a high-fat meal, alprazolam absorption increases by one-third, while absorption for administration of the orally disintegrating tablet with a high-fat meal increases from 1 hour 30 minutes to 2 hours. Similarly, for lorazepam, administration with a meal delays absorption by approximately 2 hours; however, this effect does not appear present with the XR formulation. Administering benzodiazepines with food can be clinically leveraged to either accelerate the onset of action or decrease peak-associated adverse effects. Thus, when a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine is needed to treat acute anxiety or prior to an expected anxiogenic stimuli, administering the medication without food may produce a faster onset of action.

CNS penetration
Benzodiazepines enter the CNS by passive diffusion. Because of this, lipophilicity at physiologic pH influences the rate at which a benzodiazepine crosses the blood-brain barrier. The rate at which benzodiazepines enter the CNS influences their clinical effects and the speed at which both efficacy (ie, anxiolysis) and adverse effects (ie, sedation, slowed cognition) are observed. In general, more lipophilic medications initiate their anxiolytic effect more quickly. However, by quickly leaving the CNS (through the same mechanism that allowed them to enter the CNS at such speed), their effects rapidly cease as they redistribute into fat. Thus, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines produce more intense effects compared to less lipophilic benzodiazepines. For these reasons, lipophilicity is more important than half-life for determining the duration of effect in most patients.
Lipophilicity and duration of effect
Benzodiazepines and their metabolites tend to be highly protein-bound and distributed in fat- and lipid-enriched areas such as the CNS. As a result, the more lipophilic agents generally have the highest rates of absorption and the fastest onset of clinical effects. The duration of action for many benzodiazepines is determined by the rate and extent of distribution (a function of lipophilicity) rather than by the rate of elimination. For example, diazepam has a longer half-life than lorazepam, but its duration of action following a single dose is shorter. This is because diazepam is more lipophilic and therefore more extensively distributed (particularly to adipose tissue). This results in it leaving the brain and blood and distributing to other tissues. In turn, its CNS effect (ie, anxiolytic effects) are more quickly terminated.
By contrast, less lipophilic benzodiazepines maintain their CNS concentrations longer; they have a longer duration of action because of their slower redistribution, which culminates in a shorter half-life, and are less extensively distributed to peripheral tissues. In essence, this means that (other things being equal) a less lipophilic benzodiazepine produces a more sustained anxiolytic effect compared to a highly lipophilic benzodiazepine.36 Lipophilicity is also important in predicting some cognitive adverse effects, including amnesia. Benzodiazepines with high lipophilicity have greater absorption and faster onset of action as well as more rapid amnestic effects.37,38 These effects may relate to overall efficacy differences for oral benzodiazepines. A recent meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 found that less lipophilic benzodiazepines produced a greater response compared to more lipophilic benzodiazepines.
Continue to: Metabolism
Metabolism
Regarding cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism, polymorphic CYP2C19 and CYP3A4/5 are involved in the metabolism of several benzodiazepines39 and CYP2B6 has been recognized as a contributor to diazepam metabolism. CYP3A5 gene polymorphisms may produce variation in alprazolam metabolism; however, the predominant cytochrome involved in the metabolism of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines (ie, benzodiazepines other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam) is primarily CYP3A4, and most effects on CYP3A4 activity are related to concomitant medications and other nongenetic factors.
Drug-drug interactions
Apart from lorazepam,40,41 oxazepam,42,43 and temazepam, most benzodiazepines are metabolized through oxidative mechanisms that involve CYP3A4 (Figure 220).39 As such, their metabolism is influenced by medications that impact CYP3A4, including antifungals (eg, ketoconazole), calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil, diltiazem), nefazodone, some protease inhibitors, and macrolide antibiotics. Research has examined the impact of low-dose estrogen oral contraceptives (OCPs) on exposure (eg, plasma concentrations) of several benzodiazepines. The mechanism for this interaction is likely complex and putatively involves multiple pathways, including inhibition of CYP3A4 by OCPs. The effects of OCPs on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics vary based on the metabolism of the benzodiazepine. In general, medications oxidized and nitroreduced (eg, chlordiazepoxide, alprazolam, diazepam, and nitrazepam) have decreased clearance in patients treated with OCPs. Regarding nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines, data are mixed. Research found no OCP-related effects on the pharmacokinetics of nonoxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines44; another study suggested that clearance of these medications—through increased glucuronidation—may be increased.31 The effect of smoking on benzodiazepine concentration has been well documented. Smoking increases the clearance of orally administered diazepam,45 but not IV diazepam, midazolam, or lorazepam, suggesting that this represents a first-pass effect.46 For alprazolam, plasma concentrations are reduced by 15% to 30% in smokers and total body clearance is 24% greater compared to nonsmokers, which results in an approximately 50% increase in half-life in nonsmokers compared to smokers.47 The most notable interaction between benzodiazepines and SSRIs is seen with fluvoxamine. Because fluvoxamine moderately inhibits CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 and potently inhibits CYP1A2,48 the clearance of oxidatively metabolized benzodiazepines is reduced.49 Additionally, the effects of grapefruit juice—a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4—has been evaluated for several benzodiazepines. Yasui et al50 found grapefruit juice did not alter alprazolam plasma concentrations. However, in separate research, grapefruit juice tripled diazepam exposure, increased peak concentrations 1.5-fold, and prolonged absorption.51

Hepatic disease
Exposure to benzodiazepines—other than lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam—is influenced by intrinsic hepatic disease and requires dose adjustment in individuals with significant hepatic impairment. The impact of hepatic disease on the clinical pharmacology of benzodiazepines may relate to 2 factors: protein binding and metabolism. In a study of individuals with cirrhosis, lorazepam binding was decreased, although its metabolism and clearance were largely unaffected.40
Aging and benzodiazepine metabolism/clearance
Aging is associated with myriad physiologic changes (eg, decrease in renal clearance after age 40, changes in body fat distribution, changes in activity of cytochromes) that are relevant to benzodiazepine pharmacology. They may underlie differences in the tolerability of benzodiazepines and other clinically relevant characteristics (eg, duration of action, accumulation).
Several studies have evaluated the impact of aging on the clearance and disposition of selected benzodiazepines. The respective half-lives of chlordiazepoxide and diazepam increase from 4- to 6-fold from age 20 to 80. Further, with chronic dosing, highly lipophilic benzodiazepines may require additional attention in geriatric patients. In a study that included individuals up to age 78, steady-state plasma concentrations of diazepam and its metabolite, desmethyldiazepam (DMDZ), were 30% to 35% higher in older patients compared to younger individuals.52 In this study, the half-lives for the young and older patients were 31 hours and 86 hours, respectively, for diazepam, and 40 hours and 80 hours, respectively, for the active metabolite. The half-life of diazepam is increased by “1 hour for each year of age beginning with a half-life of 20 hours at 20 years of age, as the volume of distribution is increased, and clearance is decreased.”52 Clinically, this implies that in older adults, clinicians should expect lower peak concentrations (Cmax), higher trough concentrations (Cmin), and that diazepam will take longer to reach steady-state concentrations. Taken together, these findings raised concern that “slow accumulation and delayed washout of diazepam and DMDZ is probable.”52 These findings—which may have more clinical relevance than those of single-dose studies—suggest that the effects related to diazepam would also take longer to resolve in older patients. Finally, lorazepam clearance or distribution does not appear to be affected by aging, at least in patients age 15 to 73.40 Alprazolam is more slowly cleared in geriatric patients and its effects may be potentiated by reduced protein binding.
Continue to: Obesity
Obesity
The distribution of medications, including benzodiazepines, is altered in patients who are obese because of increased adipose tissue.53,54 This increase in the volume of distribution can attenuate the onset of action, increase medication accumulation in fat, and potentiate the duration of action.55,56
Obesity may also affect hepatic metabolism by induction of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, and inhibition of CYP3A4.57 Triazolam, which is metabolized by CYP3A4, is associated with a greater exposure (ie, plasma concentrations) in individuals who are obese.58 However, when considering differences in benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics in patients who are obese, clinicians must remember that elimination half-life depends on both volume of distribution and clearance. In
How quickly do benzodiazepines work?
Benzodiazepines act quickly. Meta-analyses36 suggest that improvement in anxiety symptoms compared to placebo is greatest initially and then the rate of improvement slows over successive weeks. Research on benzodiazepines reveals statistically significant differences between benzodiazepines and placebo within the first week of treatment, with >80% of the expected improvement by Week 8 of treatment emerging by Week 4 (Figure 336). The rapid reduction in anxiety symptoms seen with benzodiazepines has important treatment implications, given that traditional psychotherapeutic and antidepressant treatments are slow to produce improvements. Consistent data suggesting that benzodiazepines work faster than other treatments support that they may have a role during the initiation of other treatments.

What is the ‘best’ dose?
As seen with other classes of psychotropic medications,4 the relationship between benzodiazepine dose and response is complex. In a recent meta-analysis of 65 placebo-controlled trials of benzodiazepines in adults with anxiety disorders, there was a superior response over time for low-dose benzodiazepines (<3 mg/d in lorazepam equivalents) compared to a medium dose (3 to 6 mg/d; P = .042); high-dose benzodiazepines (>6 mg/d) yielded less improvement compared to medium doses (P = .001).36 A study of adults with panic disorder similarly found the greatest responses with alprazolam plasma concentrations of 20 to 40 ng/mL, with no additional benefit at <20 ng/mL or >40 ng/mL.49 As plasma concentrations increase, adverse effects such as sedation also increase, which may confound the observed loss of a dose-response relationship at higher doses and plasma concentrations.62 This may, in part, account for the observation that higher doses of benzodiazepines are associated with greater depressive symptoms and disrupted sleep.63 As such, low doses may represent a delicate equipoise between efficacy and tolerability, yielding the most optimal clinical response.
Which benzodiazepine should I prescribe?
Comparing benzodiazepines is difficult, given the differences in dosing and disorders studied and differences in how each individual clinical trial was conducted. A meta-analysis by Stimpfl et al36 that used Bayesian hierarchical modeling, which allowed some of this heterogeneity to be addressed, found that relative to the reference benzodiazepine (lorazepam), clonazepam had the greatest trajectory/magnitude of response (other specific benzodiazepines did not statistically differ from lorazepam) (Figure 436).

Continue to: Another aspect of the superiority...
Another aspect of the superiority of clonazepam in some research relates to its pharmacokinetic properties, particularly when compared with benzodiazepines that have very short half-lives. Short half-life benzodiazepines have been associated with rebound anxiety, which is defined as “the relative worsening of symptoms on discontinuation of treatment as compared to baseline symptoms” and is distinct from withdrawal.64 While it is difficult to assess this in clinical trials, Herman et al65 provided insight into the contribution of rebound anxiety in a study of patients with panic disorder treated with alprazolam who experienced “interdose anxiety symptoms.” Of the 48 patients in this study, 41 switched to clonazepam, and most who switched (82%) experienced improvement. The improvement was attributed to the decreased frequency of clonazepam (vs alprazolam) administration and lack of interdose anxiety. When selecting an oral benzodiazepine, consider the duration, onset of action, and differences in metabolism that produce varying levels of effectiveness for individual patients. In situations where rapid onset is desired, a short-acting benzodiazepine may be preferable, while a longer-acting benzodiazepine would be preferable in situations where the patient needs sustained effects.
Regarding lipophilicity, differences among benzodiazepines could contribute to differences in psychological dependence and differential utility in some situations. For example, alprazolam rapidly enters the CNS, producing an immediate anxiolytic effect. However, its egress from the CNS is equally rapid, and its anxiolytic effects disappear quickly. This may be desirable for addressing acute, predictable anxiety, but could have unintended consequences in treating chronic anxiety, where it could facilitate psychological dependence.
Practical considerations
When prescribing benzodiazepines, consider a myriad of patient- and medication-specific factors, as these have clinically relevant implications on treatment response. This information, taken together, supports the importance of an individualized approach to benzodiazepine use. Before selecting a benzodiazepine and during treatment, important elements of the patient’s history must be considered, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use (eg, antacids, CYP3A4 inhibitors, OCPs), smoking status, and history of hepatic or renal disease.
Patients age <18 are unlikely to have full expression of GABA receptors in the brain30 and therefore benzodiazepines may not be as efficacious for anxiolysis in this population. Moreover, compared to younger patients, older patients may experience higher steady-state concentrations of benzodiazepines, especially lipophilic agents, due to an increased volume of distribution and decreased clearance. In patients treated with OCPs, some benzodiazepines may take longer to reach steady-state, and dose adjustments may need to be considered. In patients who smoke, clearance of some oral benzodiazepines is also accelerated, potentially decreasing half-life by up to 50%.
When dosing and titrating benzodiazepines, consider the patient’s body weight, particularly if they are obese. The effects of obesity on benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics are complex. For glucuronidated benzodiazepines, clearance is increased in patients who are obese; however, the volume of distribution is also increased in such patients, meaning it will take longer for benzodiazepines to achieve steady-state in these individuals compared to patients who are not obese. These effects suggest it may take longer to achieve a response at a given dose in patients who are obese compared to individuals who are not obese.
Continue to: The properties of individual benzodiazepines...
The properties of individual benzodiazepines should also be considered when selecting a benzodiazepine treatment. If circumstances necessitate rapid symptom relief, a lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as diazepam, may be preferred for quick onset and offset of action. Onset of action may also be hastened by taking the benzodiazepine without food; conversely, if peak adverse effects are problematic, concurrent consumption of a high-fat meal may help decrease peak concentration and prolonging absorption. In other circumstances, such as if sustained anxiolysis is desired, a clinician may opt for a less lipophilic benzodiazepine, such as clonazepam. Finally, in terms of general treatment response, benzodiazepines separate from placebo in the first week of treatment, which supports the idea they may be useful during the introduction of other medications (eg, SSRIs) that take a longer time to achieve clinical effect.
Bottom Line
The pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines are intimately linked with the onset of action and duration of clinical effect and vary based on individual absorption and distribution/redistribution. Benzodiazepines’ clinical profile derives from their pharmacokinetic differences and is influenced by many factors, including age, body weight, concomitant medication use, smoking status, and hepatic or renal disease. Consider these factors to individualize the approach to using benzodiazepines and optimize tolerability and efficacy.
Related Resources
- Weber SR, Duchemin AM. Benzodiazepines: sensible prescribing in light of the risks. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):22-27.
- Balon R. Benzodiazepines for anxious depression. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):9-12.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Clobazam • Onfi
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Clorazepate • Gen-Xene
Diazepam • Valium
Diltiazem • Cardizem
Fluvoxamine • Luvox
Ganaxolone • Ztalmy
Ketoconazole • Nizoral
Lorazepam • Ativan
Midazolam • Versed
Temazepam • Restoril
Triazolam • Halcion
Verapamil • Calan
1. Rickels K, Moeller HJ. Benzodiazepines in anxiety disorders: reassessment of usefulness and safety. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019;20(7):514-518. doi:10.1080/15622975.2018.1500031
2. Stevens JC, Pollack MH. Benzodiazepines in clinical practice: consideration of their long-term use and alternative agents. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(Suppl 2):21-27.
3. Pollack MH, van Ameringen M, Simon NM, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of augmentation and switch strategies for refractory social anxiety disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171(1):44-53. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12101353
4. Strawn JR, Geracioti L, Rajdev N, et al. Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adult and pediatric patients: an evidence-based treatment review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19(10):1057-1070. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1491966
5. Karaca-Mandic P, Meara E, Morden NE. The growing problem of co-treatment with opioids and benzodiazepines. BMJ. 2017;356:j1224. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1224
6. Bachhuber MA, Hennessy S, Cunningham CO, et al. Increasing benzodiazepine prescriptions and overdose mortality in the United States, 1996-2013. Am J Public Health. 2016;106(4):686-688. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303061
7. Bentué-Ferrer D, Akwa Y. Benzodiazepines: Effects on memory functioning. In: Pandi-Perumal SR, Verster J, Monti J, et al, eds. Sleep Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapeutics. CRC Press; 2008:104-114. doi:10.3109/9780203091715-15
8. Pomara N, Facelle TM, Roth AE, et al. Dose-dependent retrograde facilitation of verbal memory in healthy elderly after acute oral lorazepam administration.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006;185(4):487-494. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0336-0
9. Gray SL, Dublin S, Yu O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of incident dementia or cognitive decline: prospective population based study. BMJ. 2016;352:i90. doi:10.1136/bmj.i90
10. Biétry FA, Pfeil AM, Reich O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study based on Swiss claims data. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(3):245-251. doi:10.1007/s40263-016-0404-x
11. de Gage SB, Moride Y, Ducruet T, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: case-control study. BMJ. 2014;349g5205. doi:10.1136/bmj.g5205
12. Shah R, Raji MA, Westra J, et al. Association of co-prescribing of opioid and benzodiazepine substitutes with incident falls and fractures among older adults: a cohort study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e052057. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052057
13. Guina J, Rossetter SR, DeRhodes BJ, et al. Benzodiazepines for PTSD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Pract. 2015;21(4):281-303.
14. Ekström MP, Bornefalk-Hermansson A, Abernethy AP, et al. Safety of benzodiazepines and opioids in very severe respiratory disease: national prospective study. BMJ. 2014;348:g445. doi:10.1136/bmj.g445
15. Donovan LM, Malte CA, Spece LJ, et al. Center predictors of long-term benzodiazepine use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and post-traumatic stress disorder. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(9):1151-1157. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-048OC
16. Sheehy O, Zhao JP, Bérard A. Association between incident exposure to benzodiazepines in early pregnancy and risk of spontaneous abortion. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):948-957. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0963
17. Kelly LE, Poon S, Madadi P, et al. Neonatal benzodiazepines exposure during breastfeeding. J Pediatr. 2012;161(3):448-451. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.03.003
18. Agarwal SD, Landon BE. Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(1):e187399. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7399
19. Hirschtritt ME, Olfson M, Kroenke K. Balancing the risks and benefits of benzodiazepines. JAMA. 2021;325(4):347-348. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22106
20. Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
21. Nutt DJ, Malizia AL. New insights into the role of the GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor in psychiatric disorder. British J Psychiatry. 2001;179:390-396. doi:10.1192/bjp.179.5.390
22. Sigel E. Mapping of the benzodiazepine recognition site on GABA(A) receptors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002;2(8):833-839. doi:10.2174/1568026023393444
23. Savic
24. Smith TA. Type A gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor subunits and benzodiazepine binding: significance to clinical syndromes and their treatment. Br J Biomed Sci. 2001;58(2):111-121.
25. Althaus AL, Ackley MA, Belfort GM, et al. Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology. 2020;181:108333. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108333
26. Jacob TC, Michels G, Silayeva L, et al. Benzodiazepine treatment induces subtype-specific changes in GABA(A) receptor trafficking and decreases synaptic inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(45):18595-18600. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204994109
27. Nicholson MW, Sweeney A, Pekle E, et al. Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCδ/ Ca2+/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(9):1851-1867. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0100-y
28. Dobson ET, Bloch MH, Strawn JR. Efficacy and tolerability of pharmacotherapy for pediatric anxiety disorders: a network meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2019;80(1):17r12064. doi:10.4088/JCP.17r12064
29. Kuang H, Johnson JA, Mulqueen JM, et al. The efficacy of benzodiazepines as acute anxiolytics in children: a meta-analysis. Depress Anxiety. 2017;34(10):888-896. doi:10.1002/da.22643
30. Chugani DC, Muzik O, Juhász C, et al. Postnatal maturation of human GABAA receptors measured with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(5):618-626. doi:10.1002/ana.1003
31. Jochemsen R, Breimer DD. Pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines: metabolic pathways and plasma level profiles. Curr Med Res Opin. 1984;8(Suppl 4):60-79. doi:10.1185/03007998409109545
32. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Dorsey C, et al. Comparative single-dose kinetics and dynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam, prazepam, and placebo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988;44(3)326-334. doi:10.1038/clpt.1988.158
33. Shader RI, Georgotas A, Greenblatt DJ, et al. Impaired absorption of desmethydiazepam from clorazepate by magnesium aluminum hydroxide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(3):308-315. doi:10.1002/cpt1978243308
34. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, MacLaughlin DS, et al. Diazepam absorption: effect of antacids and food. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(5):600-609. doi:10.1002/cpt1978245600
35. Yamazaki A, Kumagai Y, Fujita T, et al. Different effects of light food on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of three benzodiazepines, quazepam, nitrazepam and diazepam. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(1):31-39. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00795.x
36. Stimpfl J, Mills JA, Strawn JR. Pharmacologic predictors of benzodiazepine response trajectory in anxiety disorders: a Bayesian hierarchical modeling meta-analysis. CNS Spectr. 2023;28(1):53-60. doi:10.1017/S1092852921000870
37. Griffin CE 3rd, Kaye AM, Bueno FR, et al. Benzodiazepine pharmacology and central nervous system-mediated effects. Ochsner J. 2013;13(2):214-223.
38. Buffett-Jerrott SE, Stewart SH. Cognitive and sedative effects of benzodiazepine use. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;8(1):45-58. doi:10.2174/1381612023396654
39. Fukasawa T, Suzuki A, Otani K. Effects of genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 enzymes on the pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(4):333-341. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00829.x
40. Kraus JW, Desmond PV, Marshall JP, et al. Effects of aging and liver disease on disposition of lorazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(4):411-419. doi:10.1002/cpt1978244411
41. Greenblatt DJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxazepam and lorazepam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981;6(2):89-105. doi:10.2165/00003088-198106020-00001
42. Walkenstein SS, Wiser R, Gudmundsen CH, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of oxazepam and its succinate half‐ester. J Pharm Sci. 1964;53(10):1181-1186. doi:10.1002/jps.2600531010
43. Shull HJ, Wilkinson GR, Johnson R, et al. Normal disposition of oxazepam in acute viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976;84(4):420-425. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-84-4-420
44. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Ochs HR, et al. Lorazepam and oxazepam kinetics in women on low-dose oral contraceptives. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983;33(5):628-632. doi:10.1038/clpt.1983.85
45. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, Harmatz JS, et al. Diazepam disposition determinants. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980;27(3):301-312. doi:10.1038/clpt.1980.40
46. Ochs HR, Greenblatt DJ, Knüchel M. Kinetics of diazepam, midazolam, and lorazepam, in cigarette smokers. Chest. 1985;87(2):223-226. doi:10.1378/chest.87.2.223
47. Smith RB, Gwilt PR, Wright CE 3rd. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam in healthy smoking and nonsmoking men. Clin Pharm. 1983;2(2):139-143.
48. Figgitt DP, McClellan KJ. Fluvoxamine. An updated review of its use in the management of adults with anxiety disorders. Drugs. 2000;60(4):925-954. doi:10.2165/00003495-200060040-00006
49. Greenblatt DJ, Wright CE. Clinical pharmacokinetics of alprazolam. Therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993;24(6):453-471. doi:10.2165/00003088-199324060-00003
50. Yasui N, Kondo T, Furukori H, et al. Effects of repeated ingestion of grapefruit juice on the single and multiple oral-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alprazolam. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000;150(2):185-190. doi:10.1007/s002130000438
51. Özdemir M, Aktan Y, Boydagˇ BS, et al. Interaction between grapefruit juice and diazepam in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1998;23(1):55-59. doi:10.1007/BF03189827
52. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Zhang Q, et al. Slow accumulation and elimination of diazepam and its active metabolite with extended treatment in the elderly. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;61(2):193-203. doi:10.1002/jcph.1726
53. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Drug disposition in obese humans: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986;11(3):199-213. doi:10.2165/00003088-198611030-00002
54. Hanley MJ, Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(2):71-87. doi:10.2165/11318100-000000000-00000
55. Bauer LA. Drug Dosing in special populations: renal and hepatic disease, dialysis, heart failure, obesity, and drug interactions. In: Weitz M, Thomas, CM, eds. Applied Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=1374
56. Kendrick JG, Carr RR, Ensom MHH. Pharmacokinetics and drug dosing in obese children. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2010;15(2):94-109. doi:10.5863/1551-6776-15.2.94
57. Brill MJE, Diepstraten J, van Rongen A, et al. Impact of obesity on drug metabolism and elimination in adults and children. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(5):277-304. doi:10.2165/11599410-000000000-00000
58. Derry CL, Kroboth PD, Pittenger AL, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of triazolam after two intermittent doses in obese and normal-weight men. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;15(3):197-205. doi:10.1097/00004714-199506000-00008
59. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. The influence of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam and triazolam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984;9(2):177-183. doi:10.2165/00003088-198409020-00005
60. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Prolonged accumulation of diazepam in obesity. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;23(8-9):369-376. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1983.tb02750.x
61. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Enhanced glucuronide conjugation of drugs in obesity: studies of lorazepam, oxazepam, and acetaminophen. J Lab Clin Med. 1983;101(6):873-880.
62. Greenblatt DJ, von Moltke LL, Harmatz JS, et al. Alprazolam pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and plasma levels: clinical implications. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54 Suppl:4-11.
63. Chen YT, Liu CY, Chang CM, et al. Perceptions, clinical characteristics, and other factors associated with prolonged and high daily dose of benzodiazepine use among patients with anxiety or depressive disorders. J Affect Disord. 2020;271:215-223. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.077
64. Herman JB, Brotman AW, Rosenbaum JF. Rebound anxiety in panic disorder patients treated with shorter-acting benzodiazepines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1987;48(Suppl):22-28.
65. Herman JB, Rosenbaum JF, Brotman AW. The alprazolam to clonazepam switch for the treatment of panic disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):175-178.
1. Rickels K, Moeller HJ. Benzodiazepines in anxiety disorders: reassessment of usefulness and safety. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019;20(7):514-518. doi:10.1080/15622975.2018.1500031
2. Stevens JC, Pollack MH. Benzodiazepines in clinical practice: consideration of their long-term use and alternative agents. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(Suppl 2):21-27.
3. Pollack MH, van Ameringen M, Simon NM, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of augmentation and switch strategies for refractory social anxiety disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171(1):44-53. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12101353
4. Strawn JR, Geracioti L, Rajdev N, et al. Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adult and pediatric patients: an evidence-based treatment review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19(10):1057-1070. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1491966
5. Karaca-Mandic P, Meara E, Morden NE. The growing problem of co-treatment with opioids and benzodiazepines. BMJ. 2017;356:j1224. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1224
6. Bachhuber MA, Hennessy S, Cunningham CO, et al. Increasing benzodiazepine prescriptions and overdose mortality in the United States, 1996-2013. Am J Public Health. 2016;106(4):686-688. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303061
7. Bentué-Ferrer D, Akwa Y. Benzodiazepines: Effects on memory functioning. In: Pandi-Perumal SR, Verster J, Monti J, et al, eds. Sleep Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapeutics. CRC Press; 2008:104-114. doi:10.3109/9780203091715-15
8. Pomara N, Facelle TM, Roth AE, et al. Dose-dependent retrograde facilitation of verbal memory in healthy elderly after acute oral lorazepam administration.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006;185(4):487-494. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0336-0
9. Gray SL, Dublin S, Yu O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of incident dementia or cognitive decline: prospective population based study. BMJ. 2016;352:i90. doi:10.1136/bmj.i90
10. Biétry FA, Pfeil AM, Reich O, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study based on Swiss claims data. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(3):245-251. doi:10.1007/s40263-016-0404-x
11. de Gage SB, Moride Y, Ducruet T, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: case-control study. BMJ. 2014;349g5205. doi:10.1136/bmj.g5205
12. Shah R, Raji MA, Westra J, et al. Association of co-prescribing of opioid and benzodiazepine substitutes with incident falls and fractures among older adults: a cohort study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e052057. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052057
13. Guina J, Rossetter SR, DeRhodes BJ, et al. Benzodiazepines for PTSD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Pract. 2015;21(4):281-303.
14. Ekström MP, Bornefalk-Hermansson A, Abernethy AP, et al. Safety of benzodiazepines and opioids in very severe respiratory disease: national prospective study. BMJ. 2014;348:g445. doi:10.1136/bmj.g445
15. Donovan LM, Malte CA, Spece LJ, et al. Center predictors of long-term benzodiazepine use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and post-traumatic stress disorder. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(9):1151-1157. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-048OC
16. Sheehy O, Zhao JP, Bérard A. Association between incident exposure to benzodiazepines in early pregnancy and risk of spontaneous abortion. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):948-957. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0963
17. Kelly LE, Poon S, Madadi P, et al. Neonatal benzodiazepines exposure during breastfeeding. J Pediatr. 2012;161(3):448-451. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.03.003
18. Agarwal SD, Landon BE. Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(1):e187399. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7399
19. Hirschtritt ME, Olfson M, Kroenke K. Balancing the risks and benefits of benzodiazepines. JAMA. 2021;325(4):347-348. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22106
20. Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
21. Nutt DJ, Malizia AL. New insights into the role of the GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor in psychiatric disorder. British J Psychiatry. 2001;179:390-396. doi:10.1192/bjp.179.5.390
22. Sigel E. Mapping of the benzodiazepine recognition site on GABA(A) receptors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002;2(8):833-839. doi:10.2174/1568026023393444
23. Savic
24. Smith TA. Type A gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor subunits and benzodiazepine binding: significance to clinical syndromes and their treatment. Br J Biomed Sci. 2001;58(2):111-121.
25. Althaus AL, Ackley MA, Belfort GM, et al. Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology. 2020;181:108333. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108333
26. Jacob TC, Michels G, Silayeva L, et al. Benzodiazepine treatment induces subtype-specific changes in GABA(A) receptor trafficking and decreases synaptic inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(45):18595-18600. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204994109
27. Nicholson MW, Sweeney A, Pekle E, et al. Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCδ/ Ca2+/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(9):1851-1867. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0100-y
28. Dobson ET, Bloch MH, Strawn JR. Efficacy and tolerability of pharmacotherapy for pediatric anxiety disorders: a network meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2019;80(1):17r12064. doi:10.4088/JCP.17r12064
29. Kuang H, Johnson JA, Mulqueen JM, et al. The efficacy of benzodiazepines as acute anxiolytics in children: a meta-analysis. Depress Anxiety. 2017;34(10):888-896. doi:10.1002/da.22643
30. Chugani DC, Muzik O, Juhász C, et al. Postnatal maturation of human GABAA receptors measured with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(5):618-626. doi:10.1002/ana.1003
31. Jochemsen R, Breimer DD. Pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines: metabolic pathways and plasma level profiles. Curr Med Res Opin. 1984;8(Suppl 4):60-79. doi:10.1185/03007998409109545
32. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Dorsey C, et al. Comparative single-dose kinetics and dynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam, prazepam, and placebo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988;44(3)326-334. doi:10.1038/clpt.1988.158
33. Shader RI, Georgotas A, Greenblatt DJ, et al. Impaired absorption of desmethydiazepam from clorazepate by magnesium aluminum hydroxide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(3):308-315. doi:10.1002/cpt1978243308
34. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, MacLaughlin DS, et al. Diazepam absorption: effect of antacids and food. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(5):600-609. doi:10.1002/cpt1978245600
35. Yamazaki A, Kumagai Y, Fujita T, et al. Different effects of light food on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of three benzodiazepines, quazepam, nitrazepam and diazepam. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(1):31-39. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00795.x
36. Stimpfl J, Mills JA, Strawn JR. Pharmacologic predictors of benzodiazepine response trajectory in anxiety disorders: a Bayesian hierarchical modeling meta-analysis. CNS Spectr. 2023;28(1):53-60. doi:10.1017/S1092852921000870
37. Griffin CE 3rd, Kaye AM, Bueno FR, et al. Benzodiazepine pharmacology and central nervous system-mediated effects. Ochsner J. 2013;13(2):214-223.
38. Buffett-Jerrott SE, Stewart SH. Cognitive and sedative effects of benzodiazepine use. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;8(1):45-58. doi:10.2174/1381612023396654
39. Fukasawa T, Suzuki A, Otani K. Effects of genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 enzymes on the pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepines. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(4):333-341. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00829.x
40. Kraus JW, Desmond PV, Marshall JP, et al. Effects of aging and liver disease on disposition of lorazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(4):411-419. doi:10.1002/cpt1978244411
41. Greenblatt DJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxazepam and lorazepam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981;6(2):89-105. doi:10.2165/00003088-198106020-00001
42. Walkenstein SS, Wiser R, Gudmundsen CH, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of oxazepam and its succinate half‐ester. J Pharm Sci. 1964;53(10):1181-1186. doi:10.1002/jps.2600531010
43. Shull HJ, Wilkinson GR, Johnson R, et al. Normal disposition of oxazepam in acute viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976;84(4):420-425. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-84-4-420
44. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Ochs HR, et al. Lorazepam and oxazepam kinetics in women on low-dose oral contraceptives. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983;33(5):628-632. doi:10.1038/clpt.1983.85
45. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, Harmatz JS, et al. Diazepam disposition determinants. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980;27(3):301-312. doi:10.1038/clpt.1980.40
46. Ochs HR, Greenblatt DJ, Knüchel M. Kinetics of diazepam, midazolam, and lorazepam, in cigarette smokers. Chest. 1985;87(2):223-226. doi:10.1378/chest.87.2.223
47. Smith RB, Gwilt PR, Wright CE 3rd. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam in healthy smoking and nonsmoking men. Clin Pharm. 1983;2(2):139-143.
48. Figgitt DP, McClellan KJ. Fluvoxamine. An updated review of its use in the management of adults with anxiety disorders. Drugs. 2000;60(4):925-954. doi:10.2165/00003495-200060040-00006
49. Greenblatt DJ, Wright CE. Clinical pharmacokinetics of alprazolam. Therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993;24(6):453-471. doi:10.2165/00003088-199324060-00003
50. Yasui N, Kondo T, Furukori H, et al. Effects of repeated ingestion of grapefruit juice on the single and multiple oral-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alprazolam. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000;150(2):185-190. doi:10.1007/s002130000438
51. Özdemir M, Aktan Y, Boydagˇ BS, et al. Interaction between grapefruit juice and diazepam in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1998;23(1):55-59. doi:10.1007/BF03189827
52. Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Zhang Q, et al. Slow accumulation and elimination of diazepam and its active metabolite with extended treatment in the elderly. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;61(2):193-203. doi:10.1002/jcph.1726
53. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Drug disposition in obese humans: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986;11(3):199-213. doi:10.2165/00003088-198611030-00002
54. Hanley MJ, Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(2):71-87. doi:10.2165/11318100-000000000-00000
55. Bauer LA. Drug Dosing in special populations: renal and hepatic disease, dialysis, heart failure, obesity, and drug interactions. In: Weitz M, Thomas, CM, eds. Applied Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=1374
56. Kendrick JG, Carr RR, Ensom MHH. Pharmacokinetics and drug dosing in obese children. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2010;15(2):94-109. doi:10.5863/1551-6776-15.2.94
57. Brill MJE, Diepstraten J, van Rongen A, et al. Impact of obesity on drug metabolism and elimination in adults and children. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(5):277-304. doi:10.2165/11599410-000000000-00000
58. Derry CL, Kroboth PD, Pittenger AL, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of triazolam after two intermittent doses in obese and normal-weight men. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;15(3):197-205. doi:10.1097/00004714-199506000-00008
59. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. The influence of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam and triazolam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984;9(2):177-183. doi:10.2165/00003088-198409020-00005
60. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Prolonged accumulation of diazepam in obesity. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;23(8-9):369-376. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1983.tb02750.x
61. Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, et al. Enhanced glucuronide conjugation of drugs in obesity: studies of lorazepam, oxazepam, and acetaminophen. J Lab Clin Med. 1983;101(6):873-880.
62. Greenblatt DJ, von Moltke LL, Harmatz JS, et al. Alprazolam pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and plasma levels: clinical implications. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54 Suppl:4-11.
63. Chen YT, Liu CY, Chang CM, et al. Perceptions, clinical characteristics, and other factors associated with prolonged and high daily dose of benzodiazepine use among patients with anxiety or depressive disorders. J Affect Disord. 2020;271:215-223. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.077
64. Herman JB, Brotman AW, Rosenbaum JF. Rebound anxiety in panic disorder patients treated with shorter-acting benzodiazepines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1987;48(Suppl):22-28.
65. Herman JB, Rosenbaum JF, Brotman AW. The alprazolam to clonazepam switch for the treatment of panic disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):175-178.
Child murder by parents: Toward prevention
Deaths of children who are killed by their parents often make the news. Cases of maternal infanticide may be particularly shocking, since women are expected to be selfless nurturers. Yet when a child is murdered, the most common perpetrator is their parent, and mothers and fathers kill at similar rates.1
As psychiatrists, we may see these cases in the news and worry about the risks of our own patients killing their children. In approximately 500 cases annually, an American parent is arrested for the homicide of their child.2 This is not even the entire story, since a large percentage of such cases end in suicide—and no arrest. This article reviews the reasons parents kill their children, and considers common characteristics of these parents, dispelling some myths, before discussing the importance of prevention efforts.
Types of child murder by parents
Child murder by parents is termed filicide. Infanticide has various meanings but often refers to the murder of a child younger than age 1. Approximately 2 dozen nations (but not the United States) have Infanticide Acts that decrease the penalty for mothers who kill their young child.3 Neonaticide refers to murder of the infant at birth or in the first day of life.4
Epidemiology and common characteristics
Approximately 15%—or 1 in 7 murders with an arrest—is a filicide.2 The younger the child, the greater the risk, but older children are killed as well.2 Internationally, fathers and mothers are found to kill at similar rates. For other types of homicide, offenders are overwhelmingly male. This makes child murder by parents the singular type of murder in which women and men perpetrate in equal numbers. Fathers are more likely than mothers to also commit suicide after they kill their children.5 The “Cinderella effect” refers to the elevated risk of a stepchild being killed compared to the risk for a biological child.6
In the general international population, mothers who commit filicide tend to have multiple stressors and limited resources. They may be socially isolated and may be victims themselves as well as potentially experiencing substance abuse.1 Some mothers view the child they killed as abnormal.
Less research has been conducted about fathers who kill. Fathers are more likely to also commit partner homicide.5,7 They are more likely to complete filicide-suicide and use firearms or other violent means.5,7-9 Fathers may have a history of violence, substance abuse, and/or mental illness.7
Neonaticide
Mothers are the most common perpetrator of neonaticide.4 It is unusual for a father to be involved in a neonaticide, or for the father and mother to perpetrate the act together. Rates of neonaticide are considered underestimates because of the number of hidden pregnancies, hidden corpses, and the difficulty that forensic pathologists may have in determining whether a baby was born alive or dead.
Continue to: Perpetrators of neonaticide...
Perpetrators of neonaticide tend to be single, relatively young women acting alone. They often live with their parents and are fearful of the repercussions of being pregnant. Pregnancies are often hidden, with no prenatal care. This includes both denial and concealment of pregnancy.4 Perpetrators of neonaticide commonly lack a premorbid serious mental illness, though after the homicide they may develop anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or adjustment disorder.4 (Individuals who unwittingly find a murdered baby’s corpse may also be at risk of PTSD.)
Hidden pregnancies may be due to concealment or denial of pregnancy.10,11 Concealment of pregnancy involves a woman knowing she is pregnant, but purposely hiding from others. Concealment may occur after a period of denial of pregnancy. Denial of pregnancy has several subtypes: pervasive denial, affective denial, and psychotic denial. In cases of pervasive denial, the existence of the pregnancy and the pregnancy’s emotional significance is outside the woman’s awareness. Alternatively, in affective denial, she is intellectually aware that she is pregnant but makes little emotional or physical preparation. In the rarest form, psychotic denial, a woman with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia may intermittently deny her pregnancy. This may be correlated with a history of custody loss.10,11 Unlike denial of other medical conditions, in cases of denial of pregnancy, there will exist a very specific point in time (delivery) when the reality of the baby confronts the woman. Risks in cases of hidden pregnancies include those from lack of prenatal care and an assisted delivery as well as neonaticide. An FBI study12 of law enforcement files found most neonaticide offenders were single young women with no criminal or psychological history. A caveat is that in the rare cases in which a woman with psychotic illness commits neonaticide, she may have different characteristics from those generally reported.13
Motives
Fathers and mothers have a similar set of motives for killing their child (Table 113-15). Motives are critical to understand not only within forensics, but also for prevention. In performing assessments after a filicide, forensic psychiatrists must be mindful of gender bias.7,16 Resnick15 initially described 5 motives based on his 1969 review of the world literature. Our work5,17 has subsequently further explored these motives.

In child homicides from “fatal maltreatment,” the child has often been a chronic victim of abuse or neglect. National American data indicate that approximately 2 per 100,000 children are killed from child maltreatment annually. Of note in conceptualizing prevention, out of the same population of 100,000, there will be 471 referrals to Child Protective Services and 91 substantiated cases.18 However, only a minority of children who die from maltreatment had previous Child Protective Services involvement. While a child may be killed by fatal maltreatment at any age, one-half are younger than age 1, and three-quarters are younger than age 3.18 In rare cases, a parent who engages in medical child abuse (including factitious disorder imposed upon another) kills the child. Depending on the location and whether or not the death appeared to be intended, parents who kill because of fatal maltreatment might face charges of various levels of murder or manslaughter.
“Unwanted child” homicides occur when the parent has determined that they do not want to have the child, especially in comparison to another need or want. Unwanted child motive is the most common in neonaticide cases, occurring after a hidden pregnancy.4
Continue to: In "partner revenge" cases...
In “partner revenge” cases, parenting disputes, a custody battle, infidelity, or a difficult relationship breakup is often present. The parent wants to make the other parent suffer, and does so by killing their child. A parent may make statements such as “If I can’t have [the child], no one can,” and the child is used as a pawn.
In the final 2 motives—“altruistic” and “acutely psychotic”—mental illness is common. These are the populations we tend to find in samples of filicide-suicide cases where the parent has killed themselves and their child, and those found not guilty by reason of insanity.5,17 Altruistic filicide has been described as “murder out of love.” How can a parent kill their child out of love? Our research has shown several ways. First, the parent may be severely depressed and suicidal. They may be planning their own suicide, and as a parent who loves their child, they plan to take their child with them in death and not leave them alone in the “cruel world” that they themselves are departing. Or the parent may believe they are killing the child out of love to prevent or relieve the child’s suffering. The psychotic parent may believe that a terrible fate will befall their child, and they are killing them “gently.” For example, the parent may believe the child will be tortured or sex trafficked. Some parents may believe that their child has a devastating disease and think they would be better off dead. (Similar thinking of misguided altruism is seen in some cases of intimate partner homicide among older adults.19)
Alternatively, in rare cases of acutely psychotic filicide, parents with psychosis kill their child with no comprehensible motive. For example, they may be in a postictal state or may hear a command hallucination from God in the context of their psychosis.15
Myths vs realities of filicide
Common myths vs the realities of filicide are noted in Table 2. There are issues with believing these myths. For example, if we believe that most parents who kill their child have mental illness, this conflates mental illness and child homicide in our minds as well as the mind of the public. This can lead to further stigmatization of mental illness, and a lack of help-seeking behaviors because parents experiencing psychiatric symptoms may be afraid that if they report their symptoms, their child will be removed by Child Protective Services. However, treated mental illness decreases the risks of child abuse, similar to how treating mental illness decreases risks of other types of violence.20,21
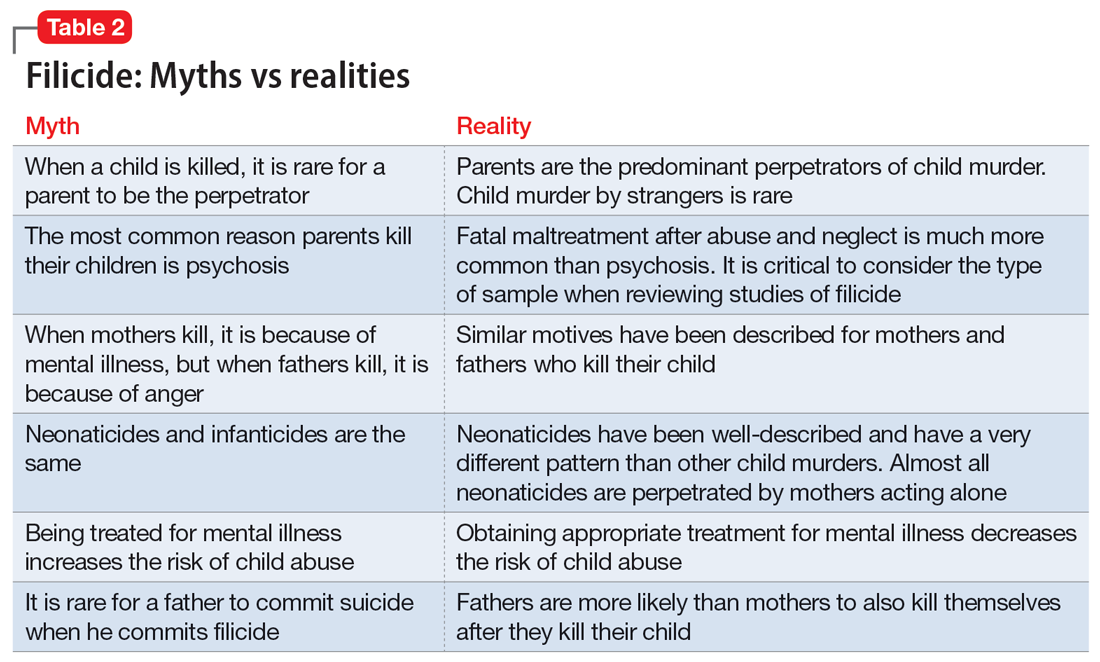
Focusing on prevention
On a local level, we need to understand these tragedies to better understand prevention. To this end, across the United States, counties have Child Fatality Review teams.22 These teams are a partnership across sectors and disciplines, including professionals from health services, law enforcement, and social services—among others—working together to understand cases and consider preventive strategies and additional services needed within our communities.
Continue to: When conceptualizing prevention...
When conceptualizing prevention of child murder by parents, we can think of primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. This means we want to encourage healthy families and healthy relationships within the family, as well as screening for risk and targeting interventions for families that have experienced difficulties, as well as for parents who have mental illness or substance use disorders.
Understanding the motive behind an individual committing filicide is also critical so that we do not conflate filicide and mental illness. Conflating these concepts leads to increased stigmatization and less help-seeking behavior.
Table 33,4,7,18,22,23 describes the importance of understanding the motives for child murder by a parent in order to conceptualize appropriate prevention. Prevention efforts for 1 type of child murder will not necessarily help prevent murders that occur due to the other motives. Regarding prevention for fatal maltreatment cases, poor parenting skills, including inappropriate expressions of discipline, anger, and frustration, are common. In some cases, substance abuse is involved or the parent was acutely mentally unwell. Reporting to Child Protective Services can be helpful, but as previously noted, it is difficult to ascertain which cases will lead to a homicide. Recommendations from Child Fatality Review teams also are valuable.
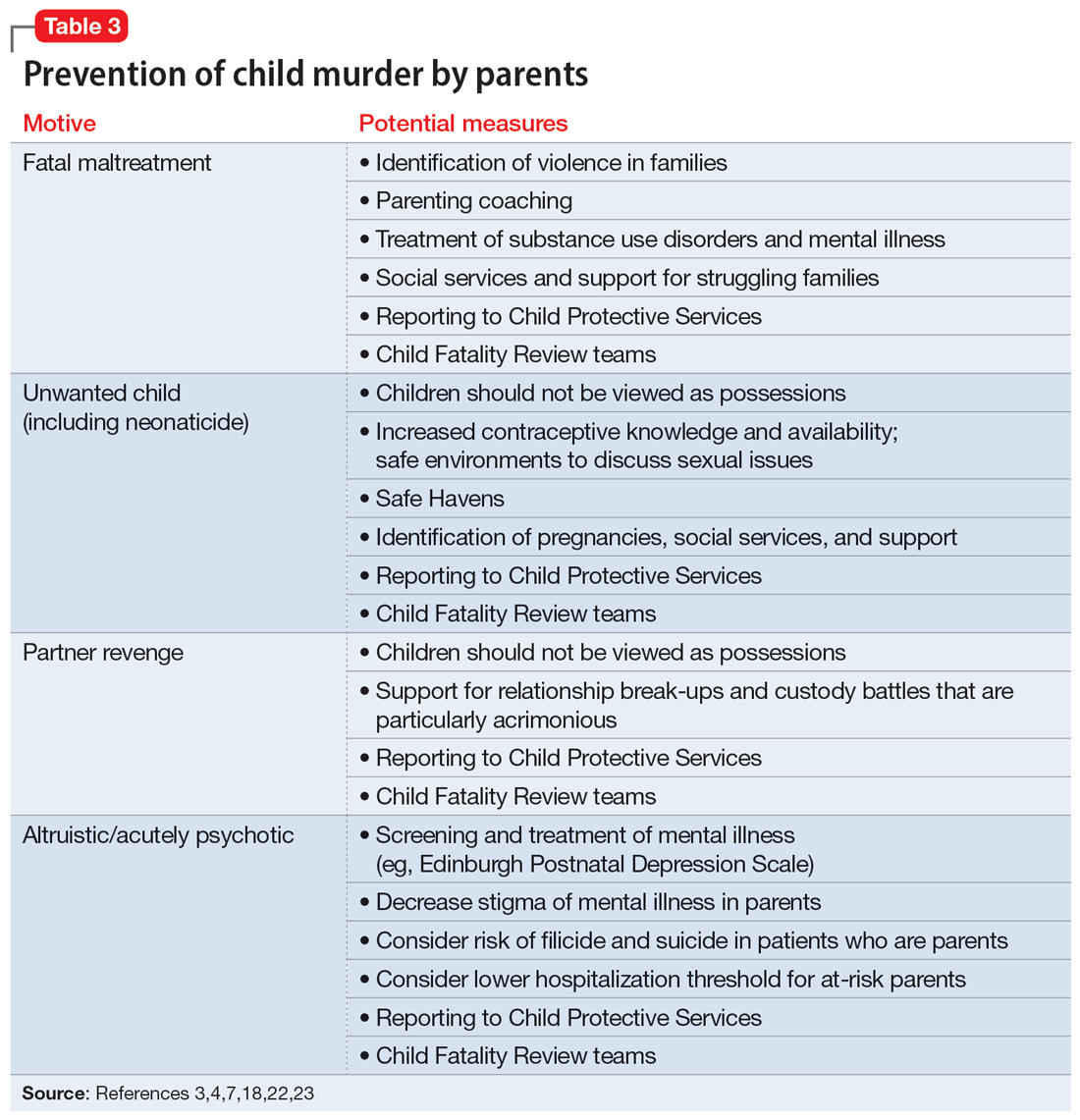
Though many parents have frustrations with their children or thoughts of child harm, the act of filicide is rare, and individual cases may be difficult to predict. Regarding prediction, some mothers who committed filicide saw their psychiatrist within days to weeks before the murders.17 A small New Zealand study found that psychotic mothers reported no plans for killing their children in advance, whereas depressed mothers had contemplated the killing for days to weeks.24
Several studies have asked mothers about thoughts of harming their child. Among mothers with colicky infants, 70% reported “explicit aggressive thoughts and fantasies” while 26% had “infanticidal thoughts” during a colic episode.25 Another study26 found that among depressed mothers of infants and toddlers, 41% revealed thoughts of harming their child. Women with postpartum depression preferred not to share infanticidal thoughts with their doctor but were more likely to disclose that they were having suicidal thoughts in order to get needed help.27 Psychiatrists need to feel comfortable asking mothers about their coping skills, their suicidal thoughts, and their filicidal thoughts.14,23,28 Screening and treatment of mental illness is critical. Postpartum psychosis is well-known to pose an elevated risk of filicide and suicide.23 Obsessive-compulsive disorder may cause a parent to ruminate over ego-dystonic child harm but should be treated and the risk conceptualized very differently than in postpartum psychosis.23,29 Screening for postpartum depression and appropriate treatment of depression during pregnancy and the postpartum period decrease risk.30
Continue to: Regarding prevention of neonaticide...
Regarding prevention of neonaticide, Safe Haven laws, baby boxes, anonymous birth options, and increased contraceptive information and availability can help decrease the risk of this well-defined type of homicide.4 Safe Haven laws originated from Child Fatality Review teams.24 Though each state has its own variation, in general, parents can drop off an unharmed unwanted infant into Safe Havens in their state, which may include hospitals, police stations, or fire stations. In general, the mother remains anonymous and has immunity from prosecution for (safe) abandonment. There are drawbacks, such as lack of information regarding adoption and paternal rights. Safe Haven laws do not prevent all deaths and all unsafe abandonments. Baby boxes and baby hatches are used in various nations, including in Europe, and in some places have been used for centuries. In anonymous birth options, such as in France, a mother is not identified but is able to give birth at a hospital. This can decrease the risk from unattended delivery, but many women with denial of pregnancy report that they did not realize when they were about to give birth.4
Bottom Line
Knowledge about the intersection of mental illness and filicide can help in prevention. Parents who experience mental health concerns should be encouraged to obtain needed treatment, which aids prevention. However, many other factors elevate the risk of child murder by parents.
Related Resources
- National Center for Fatality Review and Prevention. https://ncfrp.org/
- Child Welfare Information Gateway. https://www.childwelfare.gov/topics/preventing/overview/federal-agencies/
1. Friedman SH, Horwitz SM, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: a critical analysis of the current state of knowledge and a research agenda. Am J Psych. 2005;162(9):1578-1587.
2. Mariano TY, Chan HC, Myers WC. Toward a more holistic understanding of filicide: a multidisciplinary analysis of 32 years of US arrest data [published corrections appears in Forensic Sci Int. 2014;245:92-94]. Forensic Sci Int. 2014;236:46-53.
3. Hatters Friedman S, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: patterns and prevention. World Psychiatry. 2007;6(3):137-141.
4. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Neonaticide: phenomenology and considerations for prevention. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2009;32(1):43-47.
5. Hatters Friedman S, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Filicide-suicide: common factors in parents who kill their children and themselves. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2005;33(4):496-504.
6. Daly M, Wilson M. Is the “Cinderella effect” controversial? A case study of evolution-minded research and critiques thereof. In: Crawford C, Krebs D, eds. Foundations of Evolutionary Psychology. Taylor & Francis Group/Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2008:383-400.
7. Friedman SH. Fathers and filicide: Mental illness and outcomes. In: Wong G, Parnham G, eds. Infanticide and Filicide: Foundations in Maternal Mental Health Forensics. 1st ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:85-107.
8. West SG, Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Fathers who kill their children: an analysis of the literature. J Forensic Sci. 2009;54(2):463-468.
9. Putkonen H, Amon S, Eronen M, et al. Gender differences in filicide offense characteristics--a comprehensive register-based study of child murder in two European countries. Child Abuse Neglect. 2011;35(5):319-328.
10. Miller LJ. Denial of pregnancy. In: Spinelli MG, ed. Infanticide: Psychosocial and Legal Perspectives on Mothers Who Kill. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2003:81-104.
11. Friedman SH, Heneghan A, Rosenthal M. Characteristics of women who deny or conceal pregnancy. Psychosomatics. 2007;48(2):117-122.
12. Beyer K, Mack SM, Shelton JL. Investigative analysis of neonaticide: an exploratory study. Criminal Justice and Behavior. 2008;35(4):522-535.
13. Putkonen H, Weizmann-Henelius G, Collander J, et al. Neonaticides may be more preventable and heterogeneous than previously thought--neonaticides in Finland 1980-2000. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2007;10(1):15-23.
14. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Child murder and mental illness in parents: implications for psychiatrists. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(5):587-588.
15. Resnick PJ. Child murder by parents: a psychiatric review of filicide. Am J Psychiatry. 1969;126(3):325-334.
16. Friedman SH. Searching for the whole truth: considering culture and gender in forensic psychiatric practice. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2023;51(1):23-34.
17. Friedman SH, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Child murder committed by severely mentally ill mothers: an examination of mothers found not guilty by reason of insanity. J Forensic Sci. 2005;50(6):1466-1471.
18. Ash P. Fatal maltreatment and child abuse turned to murder. In: Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. Group for the Advancement Psychiatry; 2018.
19. Friedman SH, Appel JM. Murder in the family: intimate partner homicide in the elderly. Psychiatric News. 2018. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://psychnews.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.pn.2018.12a21
20. Friedman SH, McEwan MV. Treated mental illness and the risk of child abuse perpetration. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(2):211-216.
21. McEwan M, Friedman SH. Violence by parents against their children: reporting of maltreatment suspicions, child protection, and risk in mental illness. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2016;39(4):691-700.
22. Hatters Friedman S, Beaman JW, Friedman JB. Fatality review and the role of the forensic psychiatrist. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2021;49(3):396-405.
23. Friedman SH, Prakash C, Nagle-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
24. Stanton J, Simpson AI, Wouldes T. A qualitative study of filicide by mentally ill mothers. Child Abuse Negl. 2000;24(11):1451-1460.
25. Levitzky S, Cooper R. Infant colic syndrome—maternal fantasies of aggression and infanticide. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2000;39(7):395-400.
26. Jennings KD, Ross S, Popper S, et al. Thoughts of harming infants in depressed and nondepressed mothers. J Affect Disord. 1999;54(1-2):21-28.
27. Barr JA, Beck CT. Infanticide secrets: qualitative study on postpartum depression. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(12):1716-1717.e5.
28. Friedman SH, Sorrentino RM, Stankowski JE, et al. Psychiatrists’ knowledge about maternal filicidal thoughts. Compr Psychiatry. 2008;49(1):106-110.
29. Booth BD, Friedman SH, Curry S, et al. Obsessions of child murder: underrecognized manifestations of obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2014;42(1):66-74.
30. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Avoiding malpractice while treating depression in pregnant women. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):30-36.
Deaths of children who are killed by their parents often make the news. Cases of maternal infanticide may be particularly shocking, since women are expected to be selfless nurturers. Yet when a child is murdered, the most common perpetrator is their parent, and mothers and fathers kill at similar rates.1
As psychiatrists, we may see these cases in the news and worry about the risks of our own patients killing their children. In approximately 500 cases annually, an American parent is arrested for the homicide of their child.2 This is not even the entire story, since a large percentage of such cases end in suicide—and no arrest. This article reviews the reasons parents kill their children, and considers common characteristics of these parents, dispelling some myths, before discussing the importance of prevention efforts.
Types of child murder by parents
Child murder by parents is termed filicide. Infanticide has various meanings but often refers to the murder of a child younger than age 1. Approximately 2 dozen nations (but not the United States) have Infanticide Acts that decrease the penalty for mothers who kill their young child.3 Neonaticide refers to murder of the infant at birth or in the first day of life.4
Epidemiology and common characteristics
Approximately 15%—or 1 in 7 murders with an arrest—is a filicide.2 The younger the child, the greater the risk, but older children are killed as well.2 Internationally, fathers and mothers are found to kill at similar rates. For other types of homicide, offenders are overwhelmingly male. This makes child murder by parents the singular type of murder in which women and men perpetrate in equal numbers. Fathers are more likely than mothers to also commit suicide after they kill their children.5 The “Cinderella effect” refers to the elevated risk of a stepchild being killed compared to the risk for a biological child.6
In the general international population, mothers who commit filicide tend to have multiple stressors and limited resources. They may be socially isolated and may be victims themselves as well as potentially experiencing substance abuse.1 Some mothers view the child they killed as abnormal.
Less research has been conducted about fathers who kill. Fathers are more likely to also commit partner homicide.5,7 They are more likely to complete filicide-suicide and use firearms or other violent means.5,7-9 Fathers may have a history of violence, substance abuse, and/or mental illness.7
Neonaticide
Mothers are the most common perpetrator of neonaticide.4 It is unusual for a father to be involved in a neonaticide, or for the father and mother to perpetrate the act together. Rates of neonaticide are considered underestimates because of the number of hidden pregnancies, hidden corpses, and the difficulty that forensic pathologists may have in determining whether a baby was born alive or dead.
Continue to: Perpetrators of neonaticide...
Perpetrators of neonaticide tend to be single, relatively young women acting alone. They often live with their parents and are fearful of the repercussions of being pregnant. Pregnancies are often hidden, with no prenatal care. This includes both denial and concealment of pregnancy.4 Perpetrators of neonaticide commonly lack a premorbid serious mental illness, though after the homicide they may develop anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or adjustment disorder.4 (Individuals who unwittingly find a murdered baby’s corpse may also be at risk of PTSD.)
Hidden pregnancies may be due to concealment or denial of pregnancy.10,11 Concealment of pregnancy involves a woman knowing she is pregnant, but purposely hiding from others. Concealment may occur after a period of denial of pregnancy. Denial of pregnancy has several subtypes: pervasive denial, affective denial, and psychotic denial. In cases of pervasive denial, the existence of the pregnancy and the pregnancy’s emotional significance is outside the woman’s awareness. Alternatively, in affective denial, she is intellectually aware that she is pregnant but makes little emotional or physical preparation. In the rarest form, psychotic denial, a woman with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia may intermittently deny her pregnancy. This may be correlated with a history of custody loss.10,11 Unlike denial of other medical conditions, in cases of denial of pregnancy, there will exist a very specific point in time (delivery) when the reality of the baby confronts the woman. Risks in cases of hidden pregnancies include those from lack of prenatal care and an assisted delivery as well as neonaticide. An FBI study12 of law enforcement files found most neonaticide offenders were single young women with no criminal or psychological history. A caveat is that in the rare cases in which a woman with psychotic illness commits neonaticide, she may have different characteristics from those generally reported.13
Motives
Fathers and mothers have a similar set of motives for killing their child (Table 113-15). Motives are critical to understand not only within forensics, but also for prevention. In performing assessments after a filicide, forensic psychiatrists must be mindful of gender bias.7,16 Resnick15 initially described 5 motives based on his 1969 review of the world literature. Our work5,17 has subsequently further explored these motives.

In child homicides from “fatal maltreatment,” the child has often been a chronic victim of abuse or neglect. National American data indicate that approximately 2 per 100,000 children are killed from child maltreatment annually. Of note in conceptualizing prevention, out of the same population of 100,000, there will be 471 referrals to Child Protective Services and 91 substantiated cases.18 However, only a minority of children who die from maltreatment had previous Child Protective Services involvement. While a child may be killed by fatal maltreatment at any age, one-half are younger than age 1, and three-quarters are younger than age 3.18 In rare cases, a parent who engages in medical child abuse (including factitious disorder imposed upon another) kills the child. Depending on the location and whether or not the death appeared to be intended, parents who kill because of fatal maltreatment might face charges of various levels of murder or manslaughter.
“Unwanted child” homicides occur when the parent has determined that they do not want to have the child, especially in comparison to another need or want. Unwanted child motive is the most common in neonaticide cases, occurring after a hidden pregnancy.4
Continue to: In "partner revenge" cases...
In “partner revenge” cases, parenting disputes, a custody battle, infidelity, or a difficult relationship breakup is often present. The parent wants to make the other parent suffer, and does so by killing their child. A parent may make statements such as “If I can’t have [the child], no one can,” and the child is used as a pawn.
In the final 2 motives—“altruistic” and “acutely psychotic”—mental illness is common. These are the populations we tend to find in samples of filicide-suicide cases where the parent has killed themselves and their child, and those found not guilty by reason of insanity.5,17 Altruistic filicide has been described as “murder out of love.” How can a parent kill their child out of love? Our research has shown several ways. First, the parent may be severely depressed and suicidal. They may be planning their own suicide, and as a parent who loves their child, they plan to take their child with them in death and not leave them alone in the “cruel world” that they themselves are departing. Or the parent may believe they are killing the child out of love to prevent or relieve the child’s suffering. The psychotic parent may believe that a terrible fate will befall their child, and they are killing them “gently.” For example, the parent may believe the child will be tortured or sex trafficked. Some parents may believe that their child has a devastating disease and think they would be better off dead. (Similar thinking of misguided altruism is seen in some cases of intimate partner homicide among older adults.19)
Alternatively, in rare cases of acutely psychotic filicide, parents with psychosis kill their child with no comprehensible motive. For example, they may be in a postictal state or may hear a command hallucination from God in the context of their psychosis.15
Myths vs realities of filicide
Common myths vs the realities of filicide are noted in Table 2. There are issues with believing these myths. For example, if we believe that most parents who kill their child have mental illness, this conflates mental illness and child homicide in our minds as well as the mind of the public. This can lead to further stigmatization of mental illness, and a lack of help-seeking behaviors because parents experiencing psychiatric symptoms may be afraid that if they report their symptoms, their child will be removed by Child Protective Services. However, treated mental illness decreases the risks of child abuse, similar to how treating mental illness decreases risks of other types of violence.20,21

Focusing on prevention
On a local level, we need to understand these tragedies to better understand prevention. To this end, across the United States, counties have Child Fatality Review teams.22 These teams are a partnership across sectors and disciplines, including professionals from health services, law enforcement, and social services—among others—working together to understand cases and consider preventive strategies and additional services needed within our communities.
Continue to: When conceptualizing prevention...
When conceptualizing prevention of child murder by parents, we can think of primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. This means we want to encourage healthy families and healthy relationships within the family, as well as screening for risk and targeting interventions for families that have experienced difficulties, as well as for parents who have mental illness or substance use disorders.
Understanding the motive behind an individual committing filicide is also critical so that we do not conflate filicide and mental illness. Conflating these concepts leads to increased stigmatization and less help-seeking behavior.
Table 33,4,7,18,22,23 describes the importance of understanding the motives for child murder by a parent in order to conceptualize appropriate prevention. Prevention efforts for 1 type of child murder will not necessarily help prevent murders that occur due to the other motives. Regarding prevention for fatal maltreatment cases, poor parenting skills, including inappropriate expressions of discipline, anger, and frustration, are common. In some cases, substance abuse is involved or the parent was acutely mentally unwell. Reporting to Child Protective Services can be helpful, but as previously noted, it is difficult to ascertain which cases will lead to a homicide. Recommendations from Child Fatality Review teams also are valuable.

Though many parents have frustrations with their children or thoughts of child harm, the act of filicide is rare, and individual cases may be difficult to predict. Regarding prediction, some mothers who committed filicide saw their psychiatrist within days to weeks before the murders.17 A small New Zealand study found that psychotic mothers reported no plans for killing their children in advance, whereas depressed mothers had contemplated the killing for days to weeks.24
Several studies have asked mothers about thoughts of harming their child. Among mothers with colicky infants, 70% reported “explicit aggressive thoughts and fantasies” while 26% had “infanticidal thoughts” during a colic episode.25 Another study26 found that among depressed mothers of infants and toddlers, 41% revealed thoughts of harming their child. Women with postpartum depression preferred not to share infanticidal thoughts with their doctor but were more likely to disclose that they were having suicidal thoughts in order to get needed help.27 Psychiatrists need to feel comfortable asking mothers about their coping skills, their suicidal thoughts, and their filicidal thoughts.14,23,28 Screening and treatment of mental illness is critical. Postpartum psychosis is well-known to pose an elevated risk of filicide and suicide.23 Obsessive-compulsive disorder may cause a parent to ruminate over ego-dystonic child harm but should be treated and the risk conceptualized very differently than in postpartum psychosis.23,29 Screening for postpartum depression and appropriate treatment of depression during pregnancy and the postpartum period decrease risk.30
Continue to: Regarding prevention of neonaticide...
Regarding prevention of neonaticide, Safe Haven laws, baby boxes, anonymous birth options, and increased contraceptive information and availability can help decrease the risk of this well-defined type of homicide.4 Safe Haven laws originated from Child Fatality Review teams.24 Though each state has its own variation, in general, parents can drop off an unharmed unwanted infant into Safe Havens in their state, which may include hospitals, police stations, or fire stations. In general, the mother remains anonymous and has immunity from prosecution for (safe) abandonment. There are drawbacks, such as lack of information regarding adoption and paternal rights. Safe Haven laws do not prevent all deaths and all unsafe abandonments. Baby boxes and baby hatches are used in various nations, including in Europe, and in some places have been used for centuries. In anonymous birth options, such as in France, a mother is not identified but is able to give birth at a hospital. This can decrease the risk from unattended delivery, but many women with denial of pregnancy report that they did not realize when they were about to give birth.4
Bottom Line
Knowledge about the intersection of mental illness and filicide can help in prevention. Parents who experience mental health concerns should be encouraged to obtain needed treatment, which aids prevention. However, many other factors elevate the risk of child murder by parents.
Related Resources
- National Center for Fatality Review and Prevention. https://ncfrp.org/
- Child Welfare Information Gateway. https://www.childwelfare.gov/topics/preventing/overview/federal-agencies/
Deaths of children who are killed by their parents often make the news. Cases of maternal infanticide may be particularly shocking, since women are expected to be selfless nurturers. Yet when a child is murdered, the most common perpetrator is their parent, and mothers and fathers kill at similar rates.1
As psychiatrists, we may see these cases in the news and worry about the risks of our own patients killing their children. In approximately 500 cases annually, an American parent is arrested for the homicide of their child.2 This is not even the entire story, since a large percentage of such cases end in suicide—and no arrest. This article reviews the reasons parents kill their children, and considers common characteristics of these parents, dispelling some myths, before discussing the importance of prevention efforts.
Types of child murder by parents
Child murder by parents is termed filicide. Infanticide has various meanings but often refers to the murder of a child younger than age 1. Approximately 2 dozen nations (but not the United States) have Infanticide Acts that decrease the penalty for mothers who kill their young child.3 Neonaticide refers to murder of the infant at birth or in the first day of life.4
Epidemiology and common characteristics
Approximately 15%—or 1 in 7 murders with an arrest—is a filicide.2 The younger the child, the greater the risk, but older children are killed as well.2 Internationally, fathers and mothers are found to kill at similar rates. For other types of homicide, offenders are overwhelmingly male. This makes child murder by parents the singular type of murder in which women and men perpetrate in equal numbers. Fathers are more likely than mothers to also commit suicide after they kill their children.5 The “Cinderella effect” refers to the elevated risk of a stepchild being killed compared to the risk for a biological child.6
In the general international population, mothers who commit filicide tend to have multiple stressors and limited resources. They may be socially isolated and may be victims themselves as well as potentially experiencing substance abuse.1 Some mothers view the child they killed as abnormal.
Less research has been conducted about fathers who kill. Fathers are more likely to also commit partner homicide.5,7 They are more likely to complete filicide-suicide and use firearms or other violent means.5,7-9 Fathers may have a history of violence, substance abuse, and/or mental illness.7
Neonaticide
Mothers are the most common perpetrator of neonaticide.4 It is unusual for a father to be involved in a neonaticide, or for the father and mother to perpetrate the act together. Rates of neonaticide are considered underestimates because of the number of hidden pregnancies, hidden corpses, and the difficulty that forensic pathologists may have in determining whether a baby was born alive or dead.
Continue to: Perpetrators of neonaticide...
Perpetrators of neonaticide tend to be single, relatively young women acting alone. They often live with their parents and are fearful of the repercussions of being pregnant. Pregnancies are often hidden, with no prenatal care. This includes both denial and concealment of pregnancy.4 Perpetrators of neonaticide commonly lack a premorbid serious mental illness, though after the homicide they may develop anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or adjustment disorder.4 (Individuals who unwittingly find a murdered baby’s corpse may also be at risk of PTSD.)
Hidden pregnancies may be due to concealment or denial of pregnancy.10,11 Concealment of pregnancy involves a woman knowing she is pregnant, but purposely hiding from others. Concealment may occur after a period of denial of pregnancy. Denial of pregnancy has several subtypes: pervasive denial, affective denial, and psychotic denial. In cases of pervasive denial, the existence of the pregnancy and the pregnancy’s emotional significance is outside the woman’s awareness. Alternatively, in affective denial, she is intellectually aware that she is pregnant but makes little emotional or physical preparation. In the rarest form, psychotic denial, a woman with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia may intermittently deny her pregnancy. This may be correlated with a history of custody loss.10,11 Unlike denial of other medical conditions, in cases of denial of pregnancy, there will exist a very specific point in time (delivery) when the reality of the baby confronts the woman. Risks in cases of hidden pregnancies include those from lack of prenatal care and an assisted delivery as well as neonaticide. An FBI study12 of law enforcement files found most neonaticide offenders were single young women with no criminal or psychological history. A caveat is that in the rare cases in which a woman with psychotic illness commits neonaticide, she may have different characteristics from those generally reported.13
Motives
Fathers and mothers have a similar set of motives for killing their child (Table 113-15). Motives are critical to understand not only within forensics, but also for prevention. In performing assessments after a filicide, forensic psychiatrists must be mindful of gender bias.7,16 Resnick15 initially described 5 motives based on his 1969 review of the world literature. Our work5,17 has subsequently further explored these motives.

In child homicides from “fatal maltreatment,” the child has often been a chronic victim of abuse or neglect. National American data indicate that approximately 2 per 100,000 children are killed from child maltreatment annually. Of note in conceptualizing prevention, out of the same population of 100,000, there will be 471 referrals to Child Protective Services and 91 substantiated cases.18 However, only a minority of children who die from maltreatment had previous Child Protective Services involvement. While a child may be killed by fatal maltreatment at any age, one-half are younger than age 1, and three-quarters are younger than age 3.18 In rare cases, a parent who engages in medical child abuse (including factitious disorder imposed upon another) kills the child. Depending on the location and whether or not the death appeared to be intended, parents who kill because of fatal maltreatment might face charges of various levels of murder or manslaughter.
“Unwanted child” homicides occur when the parent has determined that they do not want to have the child, especially in comparison to another need or want. Unwanted child motive is the most common in neonaticide cases, occurring after a hidden pregnancy.4
Continue to: In "partner revenge" cases...
In “partner revenge” cases, parenting disputes, a custody battle, infidelity, or a difficult relationship breakup is often present. The parent wants to make the other parent suffer, and does so by killing their child. A parent may make statements such as “If I can’t have [the child], no one can,” and the child is used as a pawn.
In the final 2 motives—“altruistic” and “acutely psychotic”—mental illness is common. These are the populations we tend to find in samples of filicide-suicide cases where the parent has killed themselves and their child, and those found not guilty by reason of insanity.5,17 Altruistic filicide has been described as “murder out of love.” How can a parent kill their child out of love? Our research has shown several ways. First, the parent may be severely depressed and suicidal. They may be planning their own suicide, and as a parent who loves their child, they plan to take their child with them in death and not leave them alone in the “cruel world” that they themselves are departing. Or the parent may believe they are killing the child out of love to prevent or relieve the child’s suffering. The psychotic parent may believe that a terrible fate will befall their child, and they are killing them “gently.” For example, the parent may believe the child will be tortured or sex trafficked. Some parents may believe that their child has a devastating disease and think they would be better off dead. (Similar thinking of misguided altruism is seen in some cases of intimate partner homicide among older adults.19)
Alternatively, in rare cases of acutely psychotic filicide, parents with psychosis kill their child with no comprehensible motive. For example, they may be in a postictal state or may hear a command hallucination from God in the context of their psychosis.15
Myths vs realities of filicide
Common myths vs the realities of filicide are noted in Table 2. There are issues with believing these myths. For example, if we believe that most parents who kill their child have mental illness, this conflates mental illness and child homicide in our minds as well as the mind of the public. This can lead to further stigmatization of mental illness, and a lack of help-seeking behaviors because parents experiencing psychiatric symptoms may be afraid that if they report their symptoms, their child will be removed by Child Protective Services. However, treated mental illness decreases the risks of child abuse, similar to how treating mental illness decreases risks of other types of violence.20,21

Focusing on prevention
On a local level, we need to understand these tragedies to better understand prevention. To this end, across the United States, counties have Child Fatality Review teams.22 These teams are a partnership across sectors and disciplines, including professionals from health services, law enforcement, and social services—among others—working together to understand cases and consider preventive strategies and additional services needed within our communities.
Continue to: When conceptualizing prevention...
When conceptualizing prevention of child murder by parents, we can think of primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. This means we want to encourage healthy families and healthy relationships within the family, as well as screening for risk and targeting interventions for families that have experienced difficulties, as well as for parents who have mental illness or substance use disorders.
Understanding the motive behind an individual committing filicide is also critical so that we do not conflate filicide and mental illness. Conflating these concepts leads to increased stigmatization and less help-seeking behavior.
Table 33,4,7,18,22,23 describes the importance of understanding the motives for child murder by a parent in order to conceptualize appropriate prevention. Prevention efforts for 1 type of child murder will not necessarily help prevent murders that occur due to the other motives. Regarding prevention for fatal maltreatment cases, poor parenting skills, including inappropriate expressions of discipline, anger, and frustration, are common. In some cases, substance abuse is involved or the parent was acutely mentally unwell. Reporting to Child Protective Services can be helpful, but as previously noted, it is difficult to ascertain which cases will lead to a homicide. Recommendations from Child Fatality Review teams also are valuable.

Though many parents have frustrations with their children or thoughts of child harm, the act of filicide is rare, and individual cases may be difficult to predict. Regarding prediction, some mothers who committed filicide saw their psychiatrist within days to weeks before the murders.17 A small New Zealand study found that psychotic mothers reported no plans for killing their children in advance, whereas depressed mothers had contemplated the killing for days to weeks.24
Several studies have asked mothers about thoughts of harming their child. Among mothers with colicky infants, 70% reported “explicit aggressive thoughts and fantasies” while 26% had “infanticidal thoughts” during a colic episode.25 Another study26 found that among depressed mothers of infants and toddlers, 41% revealed thoughts of harming their child. Women with postpartum depression preferred not to share infanticidal thoughts with their doctor but were more likely to disclose that they were having suicidal thoughts in order to get needed help.27 Psychiatrists need to feel comfortable asking mothers about their coping skills, their suicidal thoughts, and their filicidal thoughts.14,23,28 Screening and treatment of mental illness is critical. Postpartum psychosis is well-known to pose an elevated risk of filicide and suicide.23 Obsessive-compulsive disorder may cause a parent to ruminate over ego-dystonic child harm but should be treated and the risk conceptualized very differently than in postpartum psychosis.23,29 Screening for postpartum depression and appropriate treatment of depression during pregnancy and the postpartum period decrease risk.30
Continue to: Regarding prevention of neonaticide...
Regarding prevention of neonaticide, Safe Haven laws, baby boxes, anonymous birth options, and increased contraceptive information and availability can help decrease the risk of this well-defined type of homicide.4 Safe Haven laws originated from Child Fatality Review teams.24 Though each state has its own variation, in general, parents can drop off an unharmed unwanted infant into Safe Havens in their state, which may include hospitals, police stations, or fire stations. In general, the mother remains anonymous and has immunity from prosecution for (safe) abandonment. There are drawbacks, such as lack of information regarding adoption and paternal rights. Safe Haven laws do not prevent all deaths and all unsafe abandonments. Baby boxes and baby hatches are used in various nations, including in Europe, and in some places have been used for centuries. In anonymous birth options, such as in France, a mother is not identified but is able to give birth at a hospital. This can decrease the risk from unattended delivery, but many women with denial of pregnancy report that they did not realize when they were about to give birth.4
Bottom Line
Knowledge about the intersection of mental illness and filicide can help in prevention. Parents who experience mental health concerns should be encouraged to obtain needed treatment, which aids prevention. However, many other factors elevate the risk of child murder by parents.
Related Resources
- National Center for Fatality Review and Prevention. https://ncfrp.org/
- Child Welfare Information Gateway. https://www.childwelfare.gov/topics/preventing/overview/federal-agencies/
1. Friedman SH, Horwitz SM, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: a critical analysis of the current state of knowledge and a research agenda. Am J Psych. 2005;162(9):1578-1587.
2. Mariano TY, Chan HC, Myers WC. Toward a more holistic understanding of filicide: a multidisciplinary analysis of 32 years of US arrest data [published corrections appears in Forensic Sci Int. 2014;245:92-94]. Forensic Sci Int. 2014;236:46-53.
3. Hatters Friedman S, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: patterns and prevention. World Psychiatry. 2007;6(3):137-141.
4. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Neonaticide: phenomenology and considerations for prevention. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2009;32(1):43-47.
5. Hatters Friedman S, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Filicide-suicide: common factors in parents who kill their children and themselves. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2005;33(4):496-504.
6. Daly M, Wilson M. Is the “Cinderella effect” controversial? A case study of evolution-minded research and critiques thereof. In: Crawford C, Krebs D, eds. Foundations of Evolutionary Psychology. Taylor & Francis Group/Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2008:383-400.
7. Friedman SH. Fathers and filicide: Mental illness and outcomes. In: Wong G, Parnham G, eds. Infanticide and Filicide: Foundations in Maternal Mental Health Forensics. 1st ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:85-107.
8. West SG, Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Fathers who kill their children: an analysis of the literature. J Forensic Sci. 2009;54(2):463-468.
9. Putkonen H, Amon S, Eronen M, et al. Gender differences in filicide offense characteristics--a comprehensive register-based study of child murder in two European countries. Child Abuse Neglect. 2011;35(5):319-328.
10. Miller LJ. Denial of pregnancy. In: Spinelli MG, ed. Infanticide: Psychosocial and Legal Perspectives on Mothers Who Kill. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2003:81-104.
11. Friedman SH, Heneghan A, Rosenthal M. Characteristics of women who deny or conceal pregnancy. Psychosomatics. 2007;48(2):117-122.
12. Beyer K, Mack SM, Shelton JL. Investigative analysis of neonaticide: an exploratory study. Criminal Justice and Behavior. 2008;35(4):522-535.
13. Putkonen H, Weizmann-Henelius G, Collander J, et al. Neonaticides may be more preventable and heterogeneous than previously thought--neonaticides in Finland 1980-2000. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2007;10(1):15-23.
14. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Child murder and mental illness in parents: implications for psychiatrists. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(5):587-588.
15. Resnick PJ. Child murder by parents: a psychiatric review of filicide. Am J Psychiatry. 1969;126(3):325-334.
16. Friedman SH. Searching for the whole truth: considering culture and gender in forensic psychiatric practice. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2023;51(1):23-34.
17. Friedman SH, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Child murder committed by severely mentally ill mothers: an examination of mothers found not guilty by reason of insanity. J Forensic Sci. 2005;50(6):1466-1471.
18. Ash P. Fatal maltreatment and child abuse turned to murder. In: Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. Group for the Advancement Psychiatry; 2018.
19. Friedman SH, Appel JM. Murder in the family: intimate partner homicide in the elderly. Psychiatric News. 2018. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://psychnews.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.pn.2018.12a21
20. Friedman SH, McEwan MV. Treated mental illness and the risk of child abuse perpetration. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(2):211-216.
21. McEwan M, Friedman SH. Violence by parents against their children: reporting of maltreatment suspicions, child protection, and risk in mental illness. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2016;39(4):691-700.
22. Hatters Friedman S, Beaman JW, Friedman JB. Fatality review and the role of the forensic psychiatrist. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2021;49(3):396-405.
23. Friedman SH, Prakash C, Nagle-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
24. Stanton J, Simpson AI, Wouldes T. A qualitative study of filicide by mentally ill mothers. Child Abuse Negl. 2000;24(11):1451-1460.
25. Levitzky S, Cooper R. Infant colic syndrome—maternal fantasies of aggression and infanticide. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2000;39(7):395-400.
26. Jennings KD, Ross S, Popper S, et al. Thoughts of harming infants in depressed and nondepressed mothers. J Affect Disord. 1999;54(1-2):21-28.
27. Barr JA, Beck CT. Infanticide secrets: qualitative study on postpartum depression. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(12):1716-1717.e5.
28. Friedman SH, Sorrentino RM, Stankowski JE, et al. Psychiatrists’ knowledge about maternal filicidal thoughts. Compr Psychiatry. 2008;49(1):106-110.
29. Booth BD, Friedman SH, Curry S, et al. Obsessions of child murder: underrecognized manifestations of obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2014;42(1):66-74.
30. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Avoiding malpractice while treating depression in pregnant women. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):30-36.
1. Friedman SH, Horwitz SM, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: a critical analysis of the current state of knowledge and a research agenda. Am J Psych. 2005;162(9):1578-1587.
2. Mariano TY, Chan HC, Myers WC. Toward a more holistic understanding of filicide: a multidisciplinary analysis of 32 years of US arrest data [published corrections appears in Forensic Sci Int. 2014;245:92-94]. Forensic Sci Int. 2014;236:46-53.
3. Hatters Friedman S, Resnick PJ. Child murder by mothers: patterns and prevention. World Psychiatry. 2007;6(3):137-141.
4. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Neonaticide: phenomenology and considerations for prevention. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2009;32(1):43-47.
5. Hatters Friedman S, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Filicide-suicide: common factors in parents who kill their children and themselves. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2005;33(4):496-504.
6. Daly M, Wilson M. Is the “Cinderella effect” controversial? A case study of evolution-minded research and critiques thereof. In: Crawford C, Krebs D, eds. Foundations of Evolutionary Psychology. Taylor & Francis Group/Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2008:383-400.
7. Friedman SH. Fathers and filicide: Mental illness and outcomes. In: Wong G, Parnham G, eds. Infanticide and Filicide: Foundations in Maternal Mental Health Forensics. 1st ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:85-107.
8. West SG, Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Fathers who kill their children: an analysis of the literature. J Forensic Sci. 2009;54(2):463-468.
9. Putkonen H, Amon S, Eronen M, et al. Gender differences in filicide offense characteristics--a comprehensive register-based study of child murder in two European countries. Child Abuse Neglect. 2011;35(5):319-328.
10. Miller LJ. Denial of pregnancy. In: Spinelli MG, ed. Infanticide: Psychosocial and Legal Perspectives on Mothers Who Kill. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2003:81-104.
11. Friedman SH, Heneghan A, Rosenthal M. Characteristics of women who deny or conceal pregnancy. Psychosomatics. 2007;48(2):117-122.
12. Beyer K, Mack SM, Shelton JL. Investigative analysis of neonaticide: an exploratory study. Criminal Justice and Behavior. 2008;35(4):522-535.
13. Putkonen H, Weizmann-Henelius G, Collander J, et al. Neonaticides may be more preventable and heterogeneous than previously thought--neonaticides in Finland 1980-2000. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2007;10(1):15-23.
14. Friedman SH, Resnick PJ. Child murder and mental illness in parents: implications for psychiatrists. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(5):587-588.
15. Resnick PJ. Child murder by parents: a psychiatric review of filicide. Am J Psychiatry. 1969;126(3):325-334.
16. Friedman SH. Searching for the whole truth: considering culture and gender in forensic psychiatric practice. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2023;51(1):23-34.
17. Friedman SH, Hrouda DR, Holden CE, et al. Child murder committed by severely mentally ill mothers: an examination of mothers found not guilty by reason of insanity. J Forensic Sci. 2005;50(6):1466-1471.
18. Ash P. Fatal maltreatment and child abuse turned to murder. In: Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. Group for the Advancement Psychiatry; 2018.
19. Friedman SH, Appel JM. Murder in the family: intimate partner homicide in the elderly. Psychiatric News. 2018. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://psychnews.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.pn.2018.12a21
20. Friedman SH, McEwan MV. Treated mental illness and the risk of child abuse perpetration. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(2):211-216.
21. McEwan M, Friedman SH. Violence by parents against their children: reporting of maltreatment suspicions, child protection, and risk in mental illness. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2016;39(4):691-700.
22. Hatters Friedman S, Beaman JW, Friedman JB. Fatality review and the role of the forensic psychiatrist. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2021;49(3):396-405.
23. Friedman SH, Prakash C, Nagle-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
24. Stanton J, Simpson AI, Wouldes T. A qualitative study of filicide by mentally ill mothers. Child Abuse Negl. 2000;24(11):1451-1460.
25. Levitzky S, Cooper R. Infant colic syndrome—maternal fantasies of aggression and infanticide. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2000;39(7):395-400.
26. Jennings KD, Ross S, Popper S, et al. Thoughts of harming infants in depressed and nondepressed mothers. J Affect Disord. 1999;54(1-2):21-28.
27. Barr JA, Beck CT. Infanticide secrets: qualitative study on postpartum depression. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(12):1716-1717.e5.
28. Friedman SH, Sorrentino RM, Stankowski JE, et al. Psychiatrists’ knowledge about maternal filicidal thoughts. Compr Psychiatry. 2008;49(1):106-110.
29. Booth BD, Friedman SH, Curry S, et al. Obsessions of child murder: underrecognized manifestations of obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2014;42(1):66-74.
30. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Avoiding malpractice while treating depression in pregnant women. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):30-36.











