User login
Old-school printer helps scientists quickly spot bacteria in blood
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID can mimic prostate cancer symptoms
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV testing still suboptimal
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccinations lag in youngest children
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
NOVIDs: Do some have the genes to dodge COVID?
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Spinosad: New kid on the block for treating scabies
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Widespread Erosions in Intertriginous Areas
The Diagnosis: Darier Disease
A clinical diagnosis of Darier disease was made from the skin findings of pruritic, malodorous, keratotic papules in a seborrheic distribution and pathognomonic nail dystrophy, along with a family history that demonstrated autosomal-dominant inheritance. The ulcerations were suspected to be caused by a superimposed herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the form of eczema herpeticum. The clinical diagnosis was later confirmed via punch biopsy. Pathology results demonstrated focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, which was consistent with Darier disease given the focal nature and lack of acanthosis. The patient’s father and sister also were confirmed to have Darier disease by an outside dermatologist.
Darier disease is a rare keratinizing autosomaldominant genodermatosis that occurs due to a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump that decreases cell adhesion between keratinocytes, leading to epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis and ultimately a disrupted skin barrier.1,2 Darier disease often presents in childhood and adolescence with papules in a seborrheic distribution on the central chest and back (Figure, A); the intertriginous folds also may be involved. Darier disease can manifest with palmoplantar pits (Figure, B), a cobblestonelike texture of the oral mucosa, acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf, and nail findings with alternating red and white longitudinal streaks in the nail bed resembling a candy cane along with characteristic V nicking deformities of the nails themselves (Figure, C). Chronic flares may occur throughout one’s lifetime, with patients experiencing more symptoms in the summer months due to heat, sweat, and UV light exposure, as well as infections that irritate the skin and worsen dyskeratosis. Studies have revealed an association between Darier disease and neuropsychiatric conditions, including major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.3,4
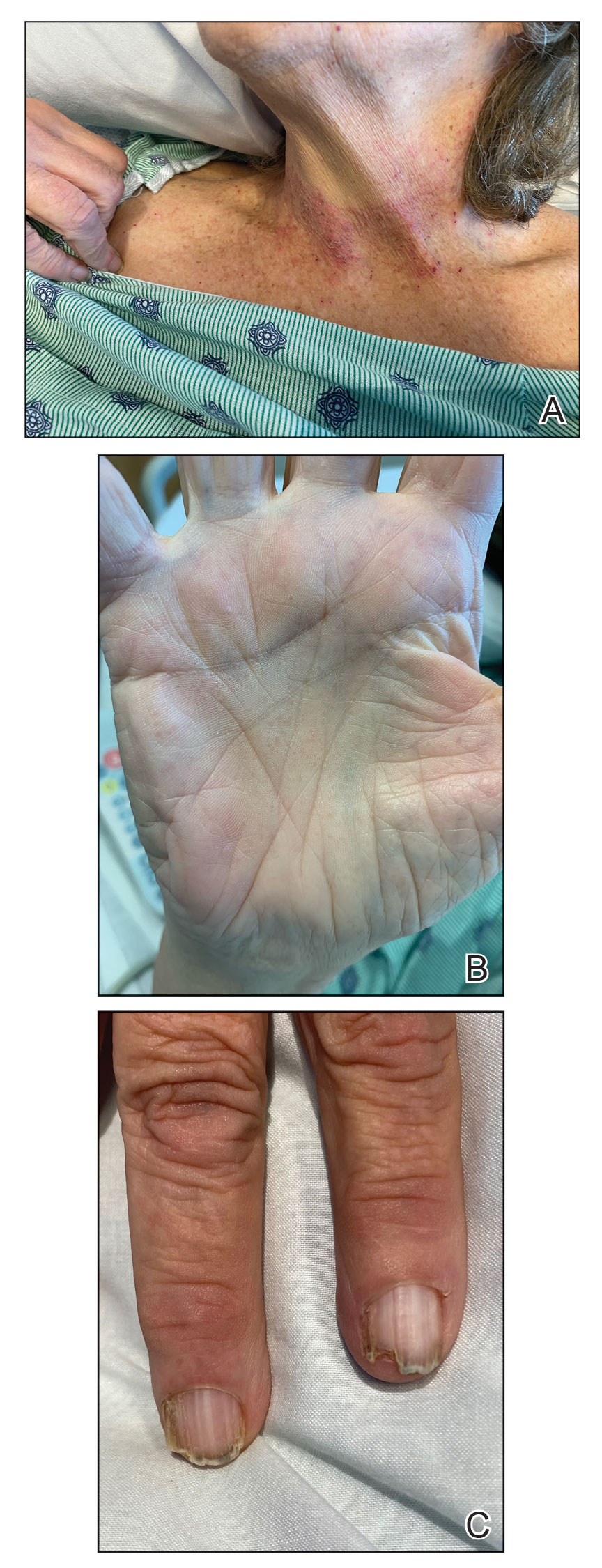
The skin barrier is compromised in patients with Darier disease, thereby making secondary infection more likely to occur. Polymerase chain reaction swabs of our patient’s purulent ulcerations were positive for HSV type 1, further strengthening a diagnosis of secondary eczema herpeticum, which occurs when patients have widespread HSV superinfecting pre-existing skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis, Darier disease, and Hailey-Hailey disease.5-7 The lesions are characterized by a monomorphic eruption of umbilicated vesicles on an erythematous base. Lesions can progress to punched-out ulcers and erosions with hemorrhagic crusts that coalesce, forming scalloped borders, similar to our patient’s presentation.8
Hailey-Hailey disease, a genodermatosis that alters calcium signaling with an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern, was unlikely in our patient due to the presence of nail abnormalities and palmar pits that are characteristic of Darier disease. From a purely histopathologic standpoint, Grover disease was considered with skin biopsy demonstrating acantholytic dyskeratosis but was not compatible with the clinical context. Furthermore, trials of antibiotics with group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus coverage failed in our patient, and she lacked systemic symptoms that would be supportive of a cellulitis diagnosis. The punched-out lesions suggested that an isolated exacerbation of atopic dermatitis was not sufficient to explain all of the clinical findings.
Eczema herpeticum must be considered in the differential diagnosis for patients with underlying Darier disease and widespread ulcerations. Our patient had more recent punched-out ulcerations in the intertriginous regions, with other areas showing later stages of confluent ulcers with scalloped borders. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of eczema herpeticum combined with severe Darier disease can lead to increased risk for hospitalization and rarely fatality.8,9
Our patient was started on intravenous acyclovir until the lesions crusted and then was transitioned to a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir given the widespread distribution. The Darier disease itself was managed with topical steroids and a zinc oxide barrier, serving as protectants to pathogens through microscopic breaks in the skin. Our patient also had a mild case of candidal intertrigo that was exacerbated by obesity and managed with topical ketoconazole. Gabapentin, hydromorphone, and acetaminophen were used for pain. She was discharged 10 days after admission with substantial improvement of both the HSV lesions and the irritation from her Darier disease. At follow-up visits 20 days later and again 6 months after discharge, she had been feeling well without any HSV flares.
The eczema herpeticum likely arose from our patient’s chronic skin barrier impairment attributed to Darier disease, leading to the cutaneous inoculation of HSV. Our patient and her family members had never been evaluated by a dermatologist until late in life during this hospitalization. Medication compliance with a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir and topical steroids is vital to prevent flares of both eczema herpeticum and Darier disease, respectively. This case highlights the importance of dermatology consultation for complex cutaneous findings, as delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
- Cooper SM, Burge SM. Darier’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:97-105. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304020-00003
- Dhitavat J, Cobbold C, Leslie N, et al. Impaired trafficking of the desmoplakins in cultured Darier’s disease keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121:1349-1355. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12557.x
- Nakamura T, Kazuno AA, Nakajima K, et al. Loss of function mutations in ATP2A2 and psychoses: a case report and literature survey. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;70:342-350. doi:10.1111/pcn.12395
- Gordon-Smith K, Jones LA, Burge SM, et al. The neuropsychiatric phenotype in Darier disease. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:515-522. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09834.x
- Hemani SA, Edmond MB, Jaggi P, et al. Frequency and clinical features associated with eczema herpeticum in hospitalized children with presumed atopic dermatitis skin infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39:263-266. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000002542
- Tayabali K, Pothiwalla H, Lowitt M. Eczema herpeticum in Darier’s disease: a topical storm. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2019;9:347-350. doi:10.1080/20009666.2019.1650590
- Lee GH, Kim YM, Lee SY, et al. A case of eczema herpeticum with Hailey-Hailey disease. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:311-314. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.311
- Nikkels AF, Beauthier F, Quatresooz P, et al. Fatal herpes simplex virus infection in Darier disease under corticotherapy. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:293-297.
- Vogt KA, Lohse CM, El-Azhary RA, et al. Kaposi varicelliform eruption in patients with Darier disease: a 20-year retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:481-484. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.12.001
The Diagnosis: Darier Disease
A clinical diagnosis of Darier disease was made from the skin findings of pruritic, malodorous, keratotic papules in a seborrheic distribution and pathognomonic nail dystrophy, along with a family history that demonstrated autosomal-dominant inheritance. The ulcerations were suspected to be caused by a superimposed herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the form of eczema herpeticum. The clinical diagnosis was later confirmed via punch biopsy. Pathology results demonstrated focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, which was consistent with Darier disease given the focal nature and lack of acanthosis. The patient’s father and sister also were confirmed to have Darier disease by an outside dermatologist.
Darier disease is a rare keratinizing autosomaldominant genodermatosis that occurs due to a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump that decreases cell adhesion between keratinocytes, leading to epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis and ultimately a disrupted skin barrier.1,2 Darier disease often presents in childhood and adolescence with papules in a seborrheic distribution on the central chest and back (Figure, A); the intertriginous folds also may be involved. Darier disease can manifest with palmoplantar pits (Figure, B), a cobblestonelike texture of the oral mucosa, acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf, and nail findings with alternating red and white longitudinal streaks in the nail bed resembling a candy cane along with characteristic V nicking deformities of the nails themselves (Figure, C). Chronic flares may occur throughout one’s lifetime, with patients experiencing more symptoms in the summer months due to heat, sweat, and UV light exposure, as well as infections that irritate the skin and worsen dyskeratosis. Studies have revealed an association between Darier disease and neuropsychiatric conditions, including major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.3,4

The skin barrier is compromised in patients with Darier disease, thereby making secondary infection more likely to occur. Polymerase chain reaction swabs of our patient’s purulent ulcerations were positive for HSV type 1, further strengthening a diagnosis of secondary eczema herpeticum, which occurs when patients have widespread HSV superinfecting pre-existing skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis, Darier disease, and Hailey-Hailey disease.5-7 The lesions are characterized by a monomorphic eruption of umbilicated vesicles on an erythematous base. Lesions can progress to punched-out ulcers and erosions with hemorrhagic crusts that coalesce, forming scalloped borders, similar to our patient’s presentation.8
Hailey-Hailey disease, a genodermatosis that alters calcium signaling with an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern, was unlikely in our patient due to the presence of nail abnormalities and palmar pits that are characteristic of Darier disease. From a purely histopathologic standpoint, Grover disease was considered with skin biopsy demonstrating acantholytic dyskeratosis but was not compatible with the clinical context. Furthermore, trials of antibiotics with group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus coverage failed in our patient, and she lacked systemic symptoms that would be supportive of a cellulitis diagnosis. The punched-out lesions suggested that an isolated exacerbation of atopic dermatitis was not sufficient to explain all of the clinical findings.
Eczema herpeticum must be considered in the differential diagnosis for patients with underlying Darier disease and widespread ulcerations. Our patient had more recent punched-out ulcerations in the intertriginous regions, with other areas showing later stages of confluent ulcers with scalloped borders. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of eczema herpeticum combined with severe Darier disease can lead to increased risk for hospitalization and rarely fatality.8,9
Our patient was started on intravenous acyclovir until the lesions crusted and then was transitioned to a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir given the widespread distribution. The Darier disease itself was managed with topical steroids and a zinc oxide barrier, serving as protectants to pathogens through microscopic breaks in the skin. Our patient also had a mild case of candidal intertrigo that was exacerbated by obesity and managed with topical ketoconazole. Gabapentin, hydromorphone, and acetaminophen were used for pain. She was discharged 10 days after admission with substantial improvement of both the HSV lesions and the irritation from her Darier disease. At follow-up visits 20 days later and again 6 months after discharge, she had been feeling well without any HSV flares.
The eczema herpeticum likely arose from our patient’s chronic skin barrier impairment attributed to Darier disease, leading to the cutaneous inoculation of HSV. Our patient and her family members had never been evaluated by a dermatologist until late in life during this hospitalization. Medication compliance with a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir and topical steroids is vital to prevent flares of both eczema herpeticum and Darier disease, respectively. This case highlights the importance of dermatology consultation for complex cutaneous findings, as delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
The Diagnosis: Darier Disease
A clinical diagnosis of Darier disease was made from the skin findings of pruritic, malodorous, keratotic papules in a seborrheic distribution and pathognomonic nail dystrophy, along with a family history that demonstrated autosomal-dominant inheritance. The ulcerations were suspected to be caused by a superimposed herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the form of eczema herpeticum. The clinical diagnosis was later confirmed via punch biopsy. Pathology results demonstrated focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, which was consistent with Darier disease given the focal nature and lack of acanthosis. The patient’s father and sister also were confirmed to have Darier disease by an outside dermatologist.
Darier disease is a rare keratinizing autosomaldominant genodermatosis that occurs due to a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump that decreases cell adhesion between keratinocytes, leading to epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis and ultimately a disrupted skin barrier.1,2 Darier disease often presents in childhood and adolescence with papules in a seborrheic distribution on the central chest and back (Figure, A); the intertriginous folds also may be involved. Darier disease can manifest with palmoplantar pits (Figure, B), a cobblestonelike texture of the oral mucosa, acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf, and nail findings with alternating red and white longitudinal streaks in the nail bed resembling a candy cane along with characteristic V nicking deformities of the nails themselves (Figure, C). Chronic flares may occur throughout one’s lifetime, with patients experiencing more symptoms in the summer months due to heat, sweat, and UV light exposure, as well as infections that irritate the skin and worsen dyskeratosis. Studies have revealed an association between Darier disease and neuropsychiatric conditions, including major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.3,4

The skin barrier is compromised in patients with Darier disease, thereby making secondary infection more likely to occur. Polymerase chain reaction swabs of our patient’s purulent ulcerations were positive for HSV type 1, further strengthening a diagnosis of secondary eczema herpeticum, which occurs when patients have widespread HSV superinfecting pre-existing skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis, Darier disease, and Hailey-Hailey disease.5-7 The lesions are characterized by a monomorphic eruption of umbilicated vesicles on an erythematous base. Lesions can progress to punched-out ulcers and erosions with hemorrhagic crusts that coalesce, forming scalloped borders, similar to our patient’s presentation.8
Hailey-Hailey disease, a genodermatosis that alters calcium signaling with an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern, was unlikely in our patient due to the presence of nail abnormalities and palmar pits that are characteristic of Darier disease. From a purely histopathologic standpoint, Grover disease was considered with skin biopsy demonstrating acantholytic dyskeratosis but was not compatible with the clinical context. Furthermore, trials of antibiotics with group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus coverage failed in our patient, and she lacked systemic symptoms that would be supportive of a cellulitis diagnosis. The punched-out lesions suggested that an isolated exacerbation of atopic dermatitis was not sufficient to explain all of the clinical findings.
Eczema herpeticum must be considered in the differential diagnosis for patients with underlying Darier disease and widespread ulcerations. Our patient had more recent punched-out ulcerations in the intertriginous regions, with other areas showing later stages of confluent ulcers with scalloped borders. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of eczema herpeticum combined with severe Darier disease can lead to increased risk for hospitalization and rarely fatality.8,9
Our patient was started on intravenous acyclovir until the lesions crusted and then was transitioned to a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir given the widespread distribution. The Darier disease itself was managed with topical steroids and a zinc oxide barrier, serving as protectants to pathogens through microscopic breaks in the skin. Our patient also had a mild case of candidal intertrigo that was exacerbated by obesity and managed with topical ketoconazole. Gabapentin, hydromorphone, and acetaminophen were used for pain. She was discharged 10 days after admission with substantial improvement of both the HSV lesions and the irritation from her Darier disease. At follow-up visits 20 days later and again 6 months after discharge, she had been feeling well without any HSV flares.
The eczema herpeticum likely arose from our patient’s chronic skin barrier impairment attributed to Darier disease, leading to the cutaneous inoculation of HSV. Our patient and her family members had never been evaluated by a dermatologist until late in life during this hospitalization. Medication compliance with a suppressive dose of oral valacyclovir and topical steroids is vital to prevent flares of both eczema herpeticum and Darier disease, respectively. This case highlights the importance of dermatology consultation for complex cutaneous findings, as delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
- Cooper SM, Burge SM. Darier’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:97-105. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304020-00003
- Dhitavat J, Cobbold C, Leslie N, et al. Impaired trafficking of the desmoplakins in cultured Darier’s disease keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121:1349-1355. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12557.x
- Nakamura T, Kazuno AA, Nakajima K, et al. Loss of function mutations in ATP2A2 and psychoses: a case report and literature survey. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;70:342-350. doi:10.1111/pcn.12395
- Gordon-Smith K, Jones LA, Burge SM, et al. The neuropsychiatric phenotype in Darier disease. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:515-522. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09834.x
- Hemani SA, Edmond MB, Jaggi P, et al. Frequency and clinical features associated with eczema herpeticum in hospitalized children with presumed atopic dermatitis skin infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39:263-266. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000002542
- Tayabali K, Pothiwalla H, Lowitt M. Eczema herpeticum in Darier’s disease: a topical storm. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2019;9:347-350. doi:10.1080/20009666.2019.1650590
- Lee GH, Kim YM, Lee SY, et al. A case of eczema herpeticum with Hailey-Hailey disease. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:311-314. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.311
- Nikkels AF, Beauthier F, Quatresooz P, et al. Fatal herpes simplex virus infection in Darier disease under corticotherapy. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:293-297.
- Vogt KA, Lohse CM, El-Azhary RA, et al. Kaposi varicelliform eruption in patients with Darier disease: a 20-year retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:481-484. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.12.001
- Cooper SM, Burge SM. Darier’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:97-105. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304020-00003
- Dhitavat J, Cobbold C, Leslie N, et al. Impaired trafficking of the desmoplakins in cultured Darier’s disease keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121:1349-1355. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12557.x
- Nakamura T, Kazuno AA, Nakajima K, et al. Loss of function mutations in ATP2A2 and psychoses: a case report and literature survey. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;70:342-350. doi:10.1111/pcn.12395
- Gordon-Smith K, Jones LA, Burge SM, et al. The neuropsychiatric phenotype in Darier disease. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:515-522. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09834.x
- Hemani SA, Edmond MB, Jaggi P, et al. Frequency and clinical features associated with eczema herpeticum in hospitalized children with presumed atopic dermatitis skin infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39:263-266. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000002542
- Tayabali K, Pothiwalla H, Lowitt M. Eczema herpeticum in Darier’s disease: a topical storm. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2019;9:347-350. doi:10.1080/20009666.2019.1650590
- Lee GH, Kim YM, Lee SY, et al. A case of eczema herpeticum with Hailey-Hailey disease. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:311-314. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.311
- Nikkels AF, Beauthier F, Quatresooz P, et al. Fatal herpes simplex virus infection in Darier disease under corticotherapy. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:293-297.
- Vogt KA, Lohse CM, El-Azhary RA, et al. Kaposi varicelliform eruption in patients with Darier disease: a 20-year retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:481-484. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.12.001
A 72-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with painful, erythematic, pruritic, and purulent lesions in intertriginous regions including the inframammary, infra-abdominal, and inguinal folds with a burning sensation of 1 week’s duration. Her medical history was notable for obesity and major depressive disorder. She was empirically treated for cellulitis, but there was no improvement with cefazolin or clindamycin. Dermatology was consulted. Physical examination revealed gray-brown, slightly umbilicated papules in the inframammary region that were malodorous upon lifting the folds. Grouped, punched-out ulcerations with scalloped borders were superimposed onto these papules. Further examination revealed a macerated erythematous plaque in the infra-abdominal and inguinal regions with punched-out ulcers. Hemecrusted papules were observed in seborrheic areas including the anterior neck, hairline, and trunk. Few subtle keratotic pits were localized on the palms. She reported similar flares in the past but never saw a dermatologist and noted that her father and sister had similar papules in a seborrheic distribution. Nail abnormalities included red and white alternating subungual streaks with irregular texture including V nicking of the distal nails.
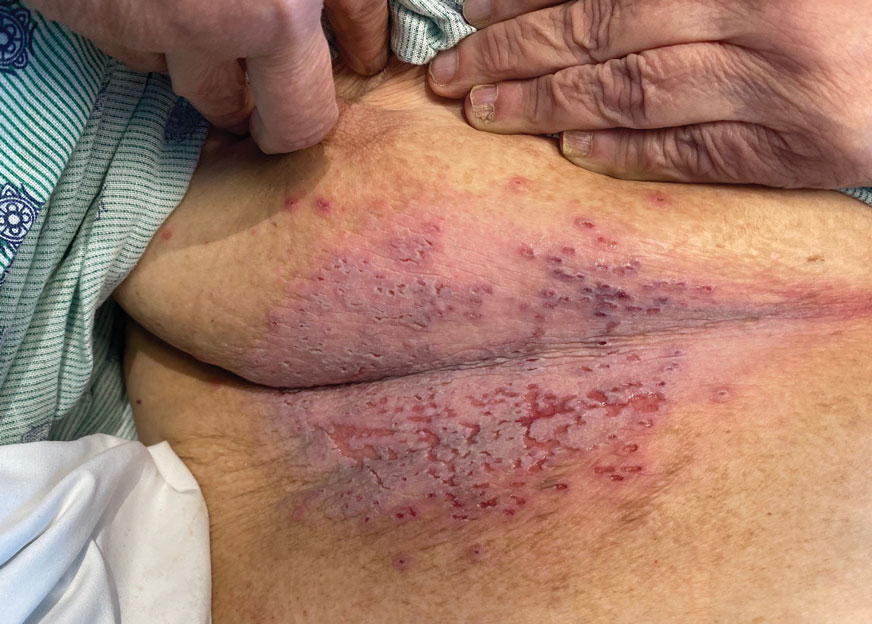
Children and COVID: A look back as the fourth year begins
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?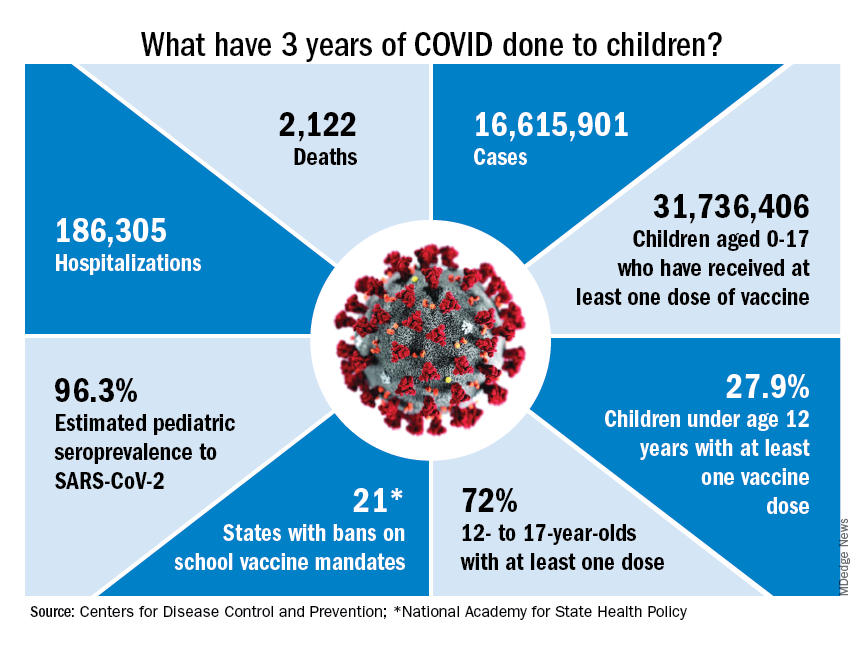
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
Factors linked with increased VTE risk in COVID outpatients
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Can particles in dairy and beef cause cancer and MS?
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.