User login
For MD-IQ use only
Crisugabalin Alleviates Postherpetic Neuralgia Symptoms in Phase 3 Study
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter, double-blind study involving 366 patients in China (median age, 63 years; 52.7% men) with PHN with an average daily pain score (ADPS) of 4 or greater on the numeric pain rating scale who were randomly assigned to receive either crisugabalin 40 mg/d (n = 121), 80 mg/d (n = 121), or placebo (n = 124) for 12 weeks.
- Patients who did not experience any serious toxic effects in these 12 weeks entered a 14-week open-label extension phase and received crisugabalin 40 mg twice daily.
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in ADPS from baseline at week 12.
- Secondary efficacy endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving at least 30% and 50% reduction in ADPS at week 12; changes in the Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Visual Analog Scale, and Average Daily Sleep Interference Scale scores at week 12; and change in the SF-MPQ Present Pain Intensity scores at weeks 12 and 26.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, among those on crisugabalin 40 mg/d and 80 mg/d, there were significant reductions in ADPS compared with placebo (least squares mean [LSM] change from baseline, −2.2 and −2.6 vs −1.1, respectively; P < .001).
- A greater proportion of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (61.2%) and 80 mg/d (54.5%) achieved 30% or greater reduction in ADPS (P < .001) than patients who received placebo (35.5%). Similarly, a 50% or greater reduction in ADPS was achieved by 37.2% of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (P = .002) and 38% on 80 mg/d (P < .001), compared with 20.2% for placebo.
- Crisugabalin 40 mg/d and crisugabalin 80 mg/d were associated with greater reductions in the pain intensity at week 12 than placebo (LSM, −1.0 and −1.2 vs −0.5, respectively; P < .001). Similar patterns were noted for other pain-related measures at weeks 12 and 26.
- Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in four patients in each group; only 2.4% of those on 40 mg/d and 1.6% on 80 mg/d discontinued treatment because of side effects.
IN PRACTICE:
“Crisugabalin 40 mg/d or crisugabalin 80 mg/d was well-tolerated and significantly improved ADPS compared to placebo,” the authors wrote, adding that “crisugabalin can be flexibly selected depending on individual patient response and tolerability at 40 mg/d or 80 mg/d.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daying Zhang, PhD, of the Department of Pain Medicine at The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may not be generalizable to the global population as the study population was limited to Chinese patients. The study only provided short-term efficacy and safety data on crisugabalin, lacked an active comparator, and did not reflect the standard of care observed in the United States or Europe, where oral tricyclic antidepressants, pregabalin, and the lidocaine patch are recommended as first-line therapies.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was sponsored and funded by Haisco Pharmaceutical. Dr. Zhang and another author reported receiving support from Haisco. Two authors are company employees.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter, double-blind study involving 366 patients in China (median age, 63 years; 52.7% men) with PHN with an average daily pain score (ADPS) of 4 or greater on the numeric pain rating scale who were randomly assigned to receive either crisugabalin 40 mg/d (n = 121), 80 mg/d (n = 121), or placebo (n = 124) for 12 weeks.
- Patients who did not experience any serious toxic effects in these 12 weeks entered a 14-week open-label extension phase and received crisugabalin 40 mg twice daily.
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in ADPS from baseline at week 12.
- Secondary efficacy endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving at least 30% and 50% reduction in ADPS at week 12; changes in the Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Visual Analog Scale, and Average Daily Sleep Interference Scale scores at week 12; and change in the SF-MPQ Present Pain Intensity scores at weeks 12 and 26.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, among those on crisugabalin 40 mg/d and 80 mg/d, there were significant reductions in ADPS compared with placebo (least squares mean [LSM] change from baseline, −2.2 and −2.6 vs −1.1, respectively; P < .001).
- A greater proportion of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (61.2%) and 80 mg/d (54.5%) achieved 30% or greater reduction in ADPS (P < .001) than patients who received placebo (35.5%). Similarly, a 50% or greater reduction in ADPS was achieved by 37.2% of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (P = .002) and 38% on 80 mg/d (P < .001), compared with 20.2% for placebo.
- Crisugabalin 40 mg/d and crisugabalin 80 mg/d were associated with greater reductions in the pain intensity at week 12 than placebo (LSM, −1.0 and −1.2 vs −0.5, respectively; P < .001). Similar patterns were noted for other pain-related measures at weeks 12 and 26.
- Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in four patients in each group; only 2.4% of those on 40 mg/d and 1.6% on 80 mg/d discontinued treatment because of side effects.
IN PRACTICE:
“Crisugabalin 40 mg/d or crisugabalin 80 mg/d was well-tolerated and significantly improved ADPS compared to placebo,” the authors wrote, adding that “crisugabalin can be flexibly selected depending on individual patient response and tolerability at 40 mg/d or 80 mg/d.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daying Zhang, PhD, of the Department of Pain Medicine at The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may not be generalizable to the global population as the study population was limited to Chinese patients. The study only provided short-term efficacy and safety data on crisugabalin, lacked an active comparator, and did not reflect the standard of care observed in the United States or Europe, where oral tricyclic antidepressants, pregabalin, and the lidocaine patch are recommended as first-line therapies.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was sponsored and funded by Haisco Pharmaceutical. Dr. Zhang and another author reported receiving support from Haisco. Two authors are company employees.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter, double-blind study involving 366 patients in China (median age, 63 years; 52.7% men) with PHN with an average daily pain score (ADPS) of 4 or greater on the numeric pain rating scale who were randomly assigned to receive either crisugabalin 40 mg/d (n = 121), 80 mg/d (n = 121), or placebo (n = 124) for 12 weeks.
- Patients who did not experience any serious toxic effects in these 12 weeks entered a 14-week open-label extension phase and received crisugabalin 40 mg twice daily.
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in ADPS from baseline at week 12.
- Secondary efficacy endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving at least 30% and 50% reduction in ADPS at week 12; changes in the Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Visual Analog Scale, and Average Daily Sleep Interference Scale scores at week 12; and change in the SF-MPQ Present Pain Intensity scores at weeks 12 and 26.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, among those on crisugabalin 40 mg/d and 80 mg/d, there were significant reductions in ADPS compared with placebo (least squares mean [LSM] change from baseline, −2.2 and −2.6 vs −1.1, respectively; P < .001).
- A greater proportion of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (61.2%) and 80 mg/d (54.5%) achieved 30% or greater reduction in ADPS (P < .001) than patients who received placebo (35.5%). Similarly, a 50% or greater reduction in ADPS was achieved by 37.2% of patients on crisugabalin 40 mg/d (P = .002) and 38% on 80 mg/d (P < .001), compared with 20.2% for placebo.
- Crisugabalin 40 mg/d and crisugabalin 80 mg/d were associated with greater reductions in the pain intensity at week 12 than placebo (LSM, −1.0 and −1.2 vs −0.5, respectively; P < .001). Similar patterns were noted for other pain-related measures at weeks 12 and 26.
- Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in four patients in each group; only 2.4% of those on 40 mg/d and 1.6% on 80 mg/d discontinued treatment because of side effects.
IN PRACTICE:
“Crisugabalin 40 mg/d or crisugabalin 80 mg/d was well-tolerated and significantly improved ADPS compared to placebo,” the authors wrote, adding that “crisugabalin can be flexibly selected depending on individual patient response and tolerability at 40 mg/d or 80 mg/d.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daying Zhang, PhD, of the Department of Pain Medicine at The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may not be generalizable to the global population as the study population was limited to Chinese patients. The study only provided short-term efficacy and safety data on crisugabalin, lacked an active comparator, and did not reflect the standard of care observed in the United States or Europe, where oral tricyclic antidepressants, pregabalin, and the lidocaine patch are recommended as first-line therapies.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was sponsored and funded by Haisco Pharmaceutical. Dr. Zhang and another author reported receiving support from Haisco. Two authors are company employees.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Western Pygmy Rattlesnake Envenomation and Bite Management
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
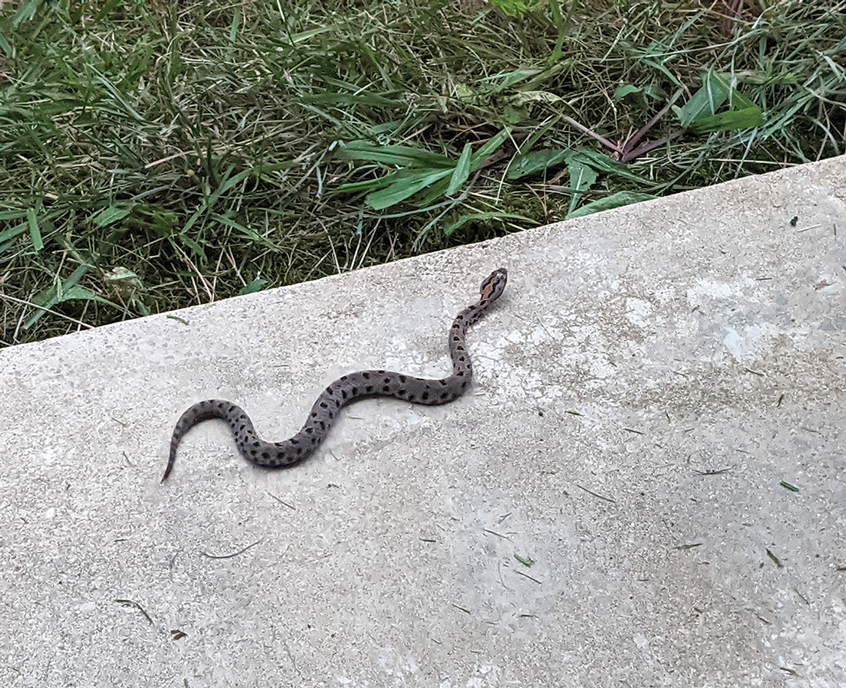
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.
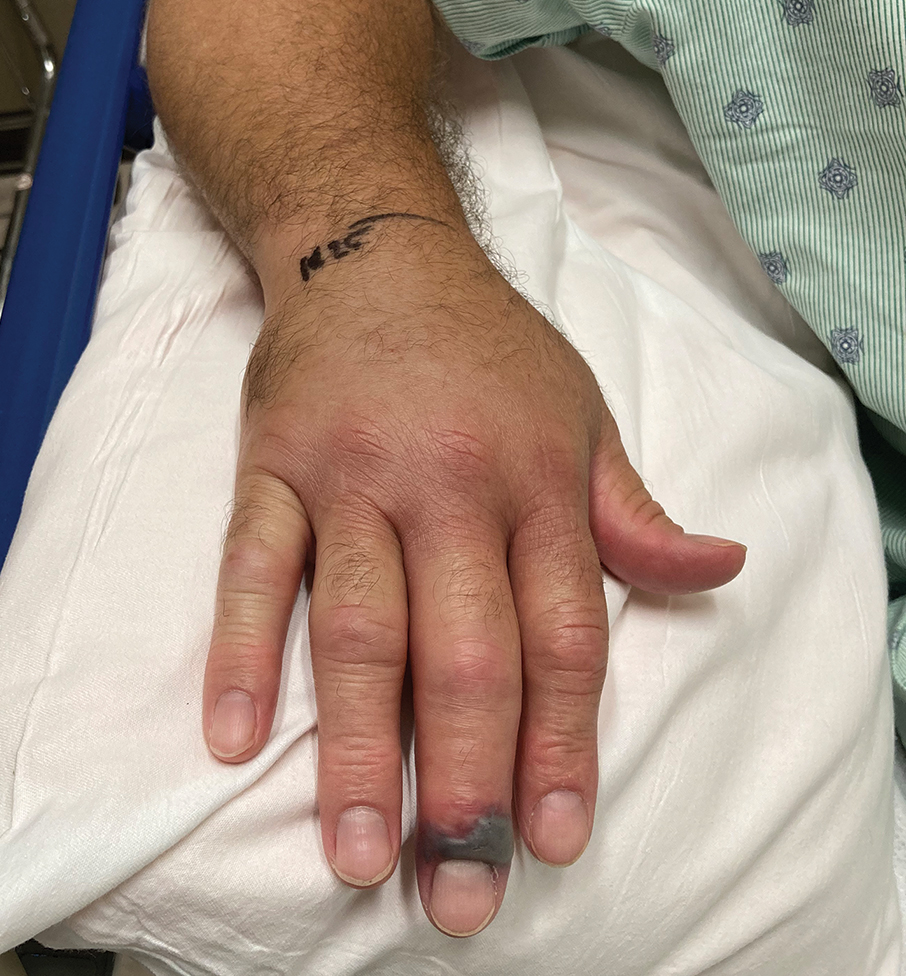

After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
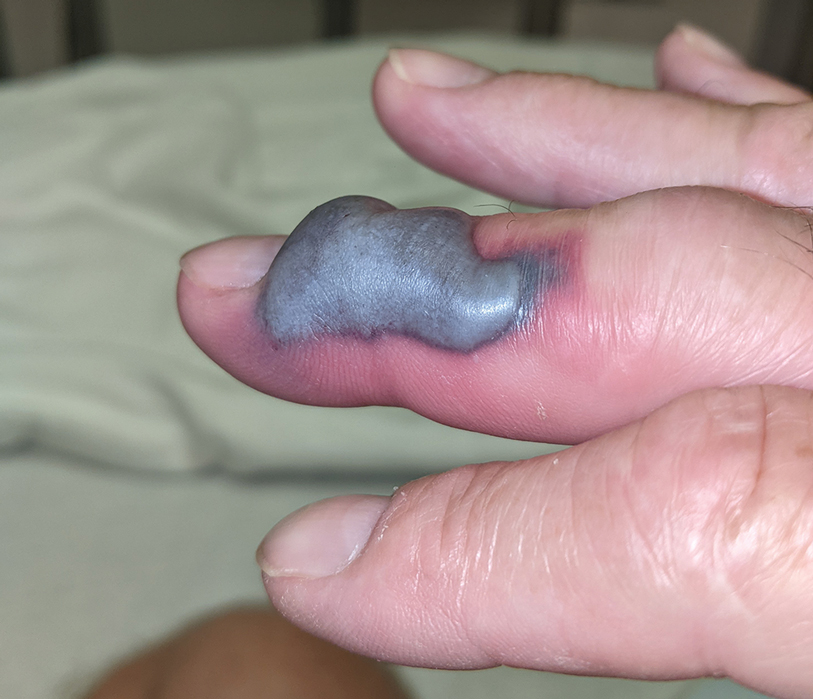
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.
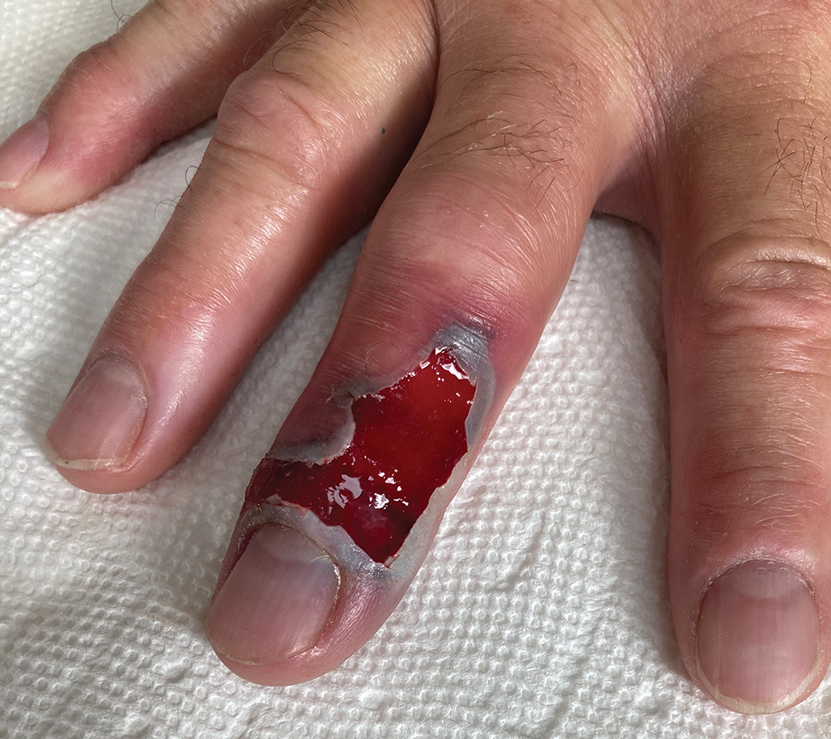
Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.
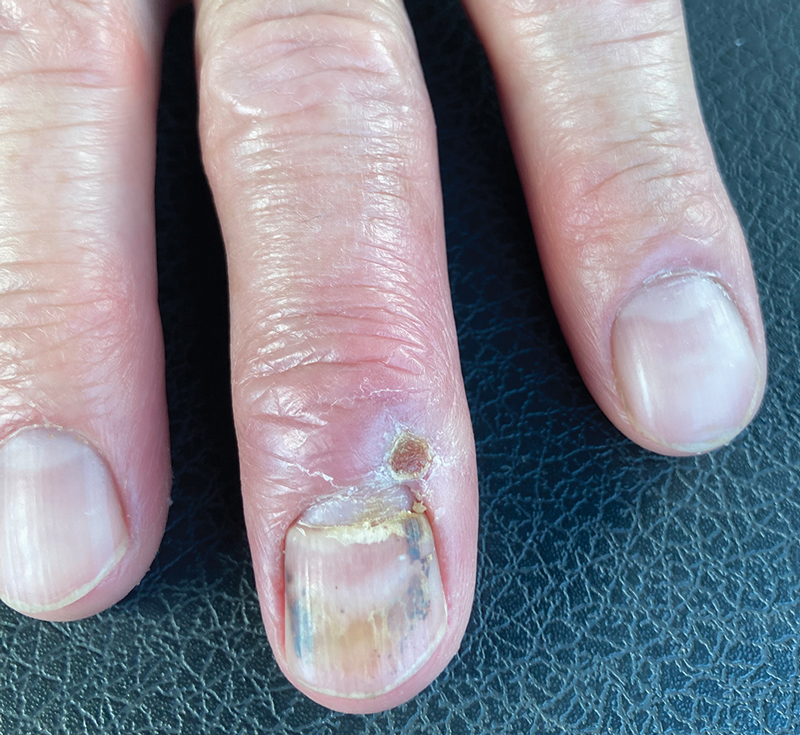
After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.
Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.



After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.

Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.

After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.

Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.



After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.

Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.

After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.

Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
Practice Points
- Patients should seek medical attention immediately for western pygmy rattlesnake bites for early initiation of antivenom treatment.
- Contact the closest emergency department to confirm they are equipped to treat rattlesnake bites and notify them of a pending arrival.
- Consider dermotomy or local debridement of bites involving the digits.
- Monitor the wound in the days and weeks following the bite to ensure adequate healing.
Following the Light
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) was first introduced in the early 1980s by surgeons Michael Gauderer and Jeffrey Ponsky as a less-invasive alternative to surgical gastrostomy via open laparotomy. The concept was born after the pair observed that the light from an endoscope in an infant undergoing endoscopy caused the abdominal wall to glow in the darkened operating room.
In fact, PEG was among the first procedures that defined minimally invasive surgery, a concept that has now revolutionized the surgical field. Since that time, PEG has evolved as a preferred method for patients needing long-term nutritional support for various indications. By 2001, approximately 216,000 PEGs were placed annually in the United States. While the volume of PEG procedures has declined in recent years at some institutions as practice patterns have shifted toward interventional radiology–placed gastrostomy tubes, evaluation of patients for PEG insertion, removal, or management of PEG complications remains a core area of gastroenterology practice.
Among the most important roles of the gastroenterologist in considering potential PEG candidates is to determine whether an appropriate indication exists, a decision that requires a detailed understanding of a patient’s overall clinical condition, goals of care, values, and preferences. a common GI consultation that deserves thoughtful consideration and demands effective communication among members of the multidisciplinary team and with patients.
Also in our October issue, we highlight a recently published large multicohort study from Gastroenterology elucidating clinical, serologic, and genetic factors associated with extraintestinal manifestations in IBD. We also review key updates to colonoscopy quality indicators, including modifications to existing indicators such as ADR and the addition of two new “priority indicators” — rate of inadequate bowel prep and sessile serrated lesion detection rate.
In this month’s Member Spotlight, Dr. Stephanie Pointer of Digestive & Liver Health Specialists in Nashville, Tennessee, shares the many ways in which she has given back to her community through music and mentoring while leading a thriving GI practice. We hope you enjoy this, and all the coverage included in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) was first introduced in the early 1980s by surgeons Michael Gauderer and Jeffrey Ponsky as a less-invasive alternative to surgical gastrostomy via open laparotomy. The concept was born after the pair observed that the light from an endoscope in an infant undergoing endoscopy caused the abdominal wall to glow in the darkened operating room.
In fact, PEG was among the first procedures that defined minimally invasive surgery, a concept that has now revolutionized the surgical field. Since that time, PEG has evolved as a preferred method for patients needing long-term nutritional support for various indications. By 2001, approximately 216,000 PEGs were placed annually in the United States. While the volume of PEG procedures has declined in recent years at some institutions as practice patterns have shifted toward interventional radiology–placed gastrostomy tubes, evaluation of patients for PEG insertion, removal, or management of PEG complications remains a core area of gastroenterology practice.
Among the most important roles of the gastroenterologist in considering potential PEG candidates is to determine whether an appropriate indication exists, a decision that requires a detailed understanding of a patient’s overall clinical condition, goals of care, values, and preferences. a common GI consultation that deserves thoughtful consideration and demands effective communication among members of the multidisciplinary team and with patients.
Also in our October issue, we highlight a recently published large multicohort study from Gastroenterology elucidating clinical, serologic, and genetic factors associated with extraintestinal manifestations in IBD. We also review key updates to colonoscopy quality indicators, including modifications to existing indicators such as ADR and the addition of two new “priority indicators” — rate of inadequate bowel prep and sessile serrated lesion detection rate.
In this month’s Member Spotlight, Dr. Stephanie Pointer of Digestive & Liver Health Specialists in Nashville, Tennessee, shares the many ways in which she has given back to her community through music and mentoring while leading a thriving GI practice. We hope you enjoy this, and all the coverage included in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) was first introduced in the early 1980s by surgeons Michael Gauderer and Jeffrey Ponsky as a less-invasive alternative to surgical gastrostomy via open laparotomy. The concept was born after the pair observed that the light from an endoscope in an infant undergoing endoscopy caused the abdominal wall to glow in the darkened operating room.
In fact, PEG was among the first procedures that defined minimally invasive surgery, a concept that has now revolutionized the surgical field. Since that time, PEG has evolved as a preferred method for patients needing long-term nutritional support for various indications. By 2001, approximately 216,000 PEGs were placed annually in the United States. While the volume of PEG procedures has declined in recent years at some institutions as practice patterns have shifted toward interventional radiology–placed gastrostomy tubes, evaluation of patients for PEG insertion, removal, or management of PEG complications remains a core area of gastroenterology practice.
Among the most important roles of the gastroenterologist in considering potential PEG candidates is to determine whether an appropriate indication exists, a decision that requires a detailed understanding of a patient’s overall clinical condition, goals of care, values, and preferences. a common GI consultation that deserves thoughtful consideration and demands effective communication among members of the multidisciplinary team and with patients.
Also in our October issue, we highlight a recently published large multicohort study from Gastroenterology elucidating clinical, serologic, and genetic factors associated with extraintestinal manifestations in IBD. We also review key updates to colonoscopy quality indicators, including modifications to existing indicators such as ADR and the addition of two new “priority indicators” — rate of inadequate bowel prep and sessile serrated lesion detection rate.
In this month’s Member Spotlight, Dr. Stephanie Pointer of Digestive & Liver Health Specialists in Nashville, Tennessee, shares the many ways in which she has given back to her community through music and mentoring while leading a thriving GI practice. We hope you enjoy this, and all the coverage included in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Childhood-Onset Atopic Dermatitis Adds Burden in Adulthood
AMSTERDAM — There is a mountain of evidence that atopic dermatitis (AD) exerts a large negative impact on quality of life, but a unique study with
These data, drawn from the ambitious Scars of Life (SOL) project, “suggest that childhood AD persisting into adulthood is its own phenotype,” reported Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, director of clinical research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC.
One reasonable message from these data is that the failure to achieve adequate control of AD in children, whether by a late start of systemic agents or other reasons, results in a greater lifetime burden of disease when the burden beyond physical symptoms is measured, according to Dr. Silverberg.
More Than 30,000 From Five Continents Participated
In the SOL project, which was designed to analyze how the age of AD onset affects the severity of symptoms and quality of life, completed questionnaires were collected from 30,801 individuals in 27 countries on five continents. The questions, which elicited data to measure the burden of AD, were developed in association with several professional and patient associations with an interest in AD, including the National Eczema Association.
The SOL project has produced an enormous amount of data in four distinct groups, but Dr. Silverberg, speaking in a late-breaking news session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, focused on a comparison between the 2875 participants who had AD in childhood that has persisted into adulthood and the 7383 adults with adult-onset AD. Data from the other two subsets in SOL — AD in childhood but not in adulthood and no AD in either phase of life — are expected to fuel an extended series of publications.
In the two groups, baseline characteristics were similar with about 60% reporting moderate to severe symptoms and a median age of about 37 years. The proportion of women was 61% in both groups.
Using the PUSH-D questionnaire, which Dr. Silverberg described as a validated tool for gauging a sense of stigmatization, the greater burden of AD was remarkably consistent for those with childhood-onset AD vs adult-onset AD. With higher scores representing a greater sense of stigmatization, the differences in the overall score (23.0 vs 18.1; P < .0001) were highly significant as was every other domain evaluated.
For all five social behavior domains, such as avoiding contact in public and wariness of approaching people spontaneously, having AD onset in childhood persisting into adulthood produced significantly higher scores than having AD onset in adulthood, with no exceptions (P < .001 for all).
AD From Childhood Consistently Results in Worse Outcomes
Providing examples for some of the other 12 domains, Dr. Silverberg maintained that feelings of shame and psychological discomfort were always greater in adults with AD persistent since childhood vs AD starting in adulthood. The P values for these outcomes, such as experiencing bias at work or reporting a sense that others avoided them, were typically highly significant (P < .001).
Compared with those whose AD started in adulthood, “adults with atopic eczema that started during childhood have significantly more difficulties in their life, including occupational relationships, daily life, personal life, and partner or family relationships,” Dr. Silverberg reported.
He said that the data were controlled for multiple confounders, particularly greater severity of AD. He acknowledged that childhood onset might be considered a surrogate for more severe disease, but the data were controlled for this possibility.
Despite the fact that there are “thousands of studies across all age groups showing the burden of AD,” Dr. Silverberg considers these data to be unique by emphasizing the burden of chronicity rather than the impact of AD in any single moment in time.
For those with chronic AD from childhood, “the effect is not just on physical health but a deep negative influence on psychological and social aspects of life,” Dr. Silverberg said, suggesting that the independent effects of chronicity might be worth studying across other dermatologic diseases.
“Regulatory agencies focus on what you can do in that moment of time, losing the bigger picture of how patients are affected chronically,” he said, adding that this is an area of clinical research that should be further explored.
What the data further suggest “is that the earlier we intervene, the more likely patients will do better long term,” he said.
Data Provide Evidence of Systemic Therapy in Kids
For Gudrun Ratzinger, MD, of the Department of Dermatology and Venerology at the Medical University of Innsbruck in Austria, these are valuable data.
“When I prescribe systemic therapies to children, I often get resistance from the healthcare system and even other colleagues,” said Dr. Ratzinger, who was asked to comment on the results. “We are at a teaching hospital, but I often find that when patients return to their home physician, the systemic therapies are stopped.”
In her own practice, she believes the most effective therapies should be introduced in children and adults when complete control is not achieved on first-line drugs. “These data are very helpful for me in explaining to others the importance of effective treatment of atopic dermatitis in children,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make drugs for AD. Dr. Ratzinger reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pelpharma, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — There is a mountain of evidence that atopic dermatitis (AD) exerts a large negative impact on quality of life, but a unique study with
These data, drawn from the ambitious Scars of Life (SOL) project, “suggest that childhood AD persisting into adulthood is its own phenotype,” reported Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, director of clinical research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC.
One reasonable message from these data is that the failure to achieve adequate control of AD in children, whether by a late start of systemic agents or other reasons, results in a greater lifetime burden of disease when the burden beyond physical symptoms is measured, according to Dr. Silverberg.
More Than 30,000 From Five Continents Participated
In the SOL project, which was designed to analyze how the age of AD onset affects the severity of symptoms and quality of life, completed questionnaires were collected from 30,801 individuals in 27 countries on five continents. The questions, which elicited data to measure the burden of AD, were developed in association with several professional and patient associations with an interest in AD, including the National Eczema Association.
The SOL project has produced an enormous amount of data in four distinct groups, but Dr. Silverberg, speaking in a late-breaking news session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, focused on a comparison between the 2875 participants who had AD in childhood that has persisted into adulthood and the 7383 adults with adult-onset AD. Data from the other two subsets in SOL — AD in childhood but not in adulthood and no AD in either phase of life — are expected to fuel an extended series of publications.
In the two groups, baseline characteristics were similar with about 60% reporting moderate to severe symptoms and a median age of about 37 years. The proportion of women was 61% in both groups.
Using the PUSH-D questionnaire, which Dr. Silverberg described as a validated tool for gauging a sense of stigmatization, the greater burden of AD was remarkably consistent for those with childhood-onset AD vs adult-onset AD. With higher scores representing a greater sense of stigmatization, the differences in the overall score (23.0 vs 18.1; P < .0001) were highly significant as was every other domain evaluated.
For all five social behavior domains, such as avoiding contact in public and wariness of approaching people spontaneously, having AD onset in childhood persisting into adulthood produced significantly higher scores than having AD onset in adulthood, with no exceptions (P < .001 for all).
AD From Childhood Consistently Results in Worse Outcomes
Providing examples for some of the other 12 domains, Dr. Silverberg maintained that feelings of shame and psychological discomfort were always greater in adults with AD persistent since childhood vs AD starting in adulthood. The P values for these outcomes, such as experiencing bias at work or reporting a sense that others avoided them, were typically highly significant (P < .001).
Compared with those whose AD started in adulthood, “adults with atopic eczema that started during childhood have significantly more difficulties in their life, including occupational relationships, daily life, personal life, and partner or family relationships,” Dr. Silverberg reported.
He said that the data were controlled for multiple confounders, particularly greater severity of AD. He acknowledged that childhood onset might be considered a surrogate for more severe disease, but the data were controlled for this possibility.
Despite the fact that there are “thousands of studies across all age groups showing the burden of AD,” Dr. Silverberg considers these data to be unique by emphasizing the burden of chronicity rather than the impact of AD in any single moment in time.
For those with chronic AD from childhood, “the effect is not just on physical health but a deep negative influence on psychological and social aspects of life,” Dr. Silverberg said, suggesting that the independent effects of chronicity might be worth studying across other dermatologic diseases.
“Regulatory agencies focus on what you can do in that moment of time, losing the bigger picture of how patients are affected chronically,” he said, adding that this is an area of clinical research that should be further explored.
What the data further suggest “is that the earlier we intervene, the more likely patients will do better long term,” he said.
Data Provide Evidence of Systemic Therapy in Kids
For Gudrun Ratzinger, MD, of the Department of Dermatology and Venerology at the Medical University of Innsbruck in Austria, these are valuable data.
“When I prescribe systemic therapies to children, I often get resistance from the healthcare system and even other colleagues,” said Dr. Ratzinger, who was asked to comment on the results. “We are at a teaching hospital, but I often find that when patients return to their home physician, the systemic therapies are stopped.”
In her own practice, she believes the most effective therapies should be introduced in children and adults when complete control is not achieved on first-line drugs. “These data are very helpful for me in explaining to others the importance of effective treatment of atopic dermatitis in children,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make drugs for AD. Dr. Ratzinger reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pelpharma, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — There is a mountain of evidence that atopic dermatitis (AD) exerts a large negative impact on quality of life, but a unique study with
These data, drawn from the ambitious Scars of Life (SOL) project, “suggest that childhood AD persisting into adulthood is its own phenotype,” reported Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, director of clinical research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC.
One reasonable message from these data is that the failure to achieve adequate control of AD in children, whether by a late start of systemic agents or other reasons, results in a greater lifetime burden of disease when the burden beyond physical symptoms is measured, according to Dr. Silverberg.
More Than 30,000 From Five Continents Participated
In the SOL project, which was designed to analyze how the age of AD onset affects the severity of symptoms and quality of life, completed questionnaires were collected from 30,801 individuals in 27 countries on five continents. The questions, which elicited data to measure the burden of AD, were developed in association with several professional and patient associations with an interest in AD, including the National Eczema Association.
The SOL project has produced an enormous amount of data in four distinct groups, but Dr. Silverberg, speaking in a late-breaking news session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, focused on a comparison between the 2875 participants who had AD in childhood that has persisted into adulthood and the 7383 adults with adult-onset AD. Data from the other two subsets in SOL — AD in childhood but not in adulthood and no AD in either phase of life — are expected to fuel an extended series of publications.
In the two groups, baseline characteristics were similar with about 60% reporting moderate to severe symptoms and a median age of about 37 years. The proportion of women was 61% in both groups.
Using the PUSH-D questionnaire, which Dr. Silverberg described as a validated tool for gauging a sense of stigmatization, the greater burden of AD was remarkably consistent for those with childhood-onset AD vs adult-onset AD. With higher scores representing a greater sense of stigmatization, the differences in the overall score (23.0 vs 18.1; P < .0001) were highly significant as was every other domain evaluated.
For all five social behavior domains, such as avoiding contact in public and wariness of approaching people spontaneously, having AD onset in childhood persisting into adulthood produced significantly higher scores than having AD onset in adulthood, with no exceptions (P < .001 for all).
AD From Childhood Consistently Results in Worse Outcomes
Providing examples for some of the other 12 domains, Dr. Silverberg maintained that feelings of shame and psychological discomfort were always greater in adults with AD persistent since childhood vs AD starting in adulthood. The P values for these outcomes, such as experiencing bias at work or reporting a sense that others avoided them, were typically highly significant (P < .001).
Compared with those whose AD started in adulthood, “adults with atopic eczema that started during childhood have significantly more difficulties in their life, including occupational relationships, daily life, personal life, and partner or family relationships,” Dr. Silverberg reported.
He said that the data were controlled for multiple confounders, particularly greater severity of AD. He acknowledged that childhood onset might be considered a surrogate for more severe disease, but the data were controlled for this possibility.
Despite the fact that there are “thousands of studies across all age groups showing the burden of AD,” Dr. Silverberg considers these data to be unique by emphasizing the burden of chronicity rather than the impact of AD in any single moment in time.
For those with chronic AD from childhood, “the effect is not just on physical health but a deep negative influence on psychological and social aspects of life,” Dr. Silverberg said, suggesting that the independent effects of chronicity might be worth studying across other dermatologic diseases.
“Regulatory agencies focus on what you can do in that moment of time, losing the bigger picture of how patients are affected chronically,” he said, adding that this is an area of clinical research that should be further explored.
What the data further suggest “is that the earlier we intervene, the more likely patients will do better long term,” he said.
Data Provide Evidence of Systemic Therapy in Kids
For Gudrun Ratzinger, MD, of the Department of Dermatology and Venerology at the Medical University of Innsbruck in Austria, these are valuable data.
“When I prescribe systemic therapies to children, I often get resistance from the healthcare system and even other colleagues,” said Dr. Ratzinger, who was asked to comment on the results. “We are at a teaching hospital, but I often find that when patients return to their home physician, the systemic therapies are stopped.”
In her own practice, she believes the most effective therapies should be introduced in children and adults when complete control is not achieved on first-line drugs. “These data are very helpful for me in explaining to others the importance of effective treatment of atopic dermatitis in children,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make drugs for AD. Dr. Ratzinger reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pelpharma, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Does Medicare Advantage Offer Higher-Value Chemotherapy?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AACR Cancer Progress Report: Big Strides and Big Gaps
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Risk: Are Pesticides the New Smoking?
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes Drug Improved Symptoms in Small Study of Women With Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Rebuilding of Military Medicine
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
FDA OKs Subcutaneous Atezolizumab Formulation for Multiple Cancer Indications
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



