User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
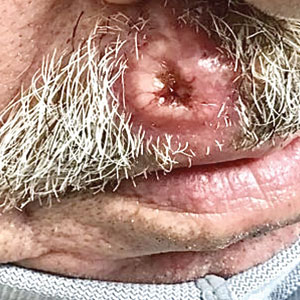
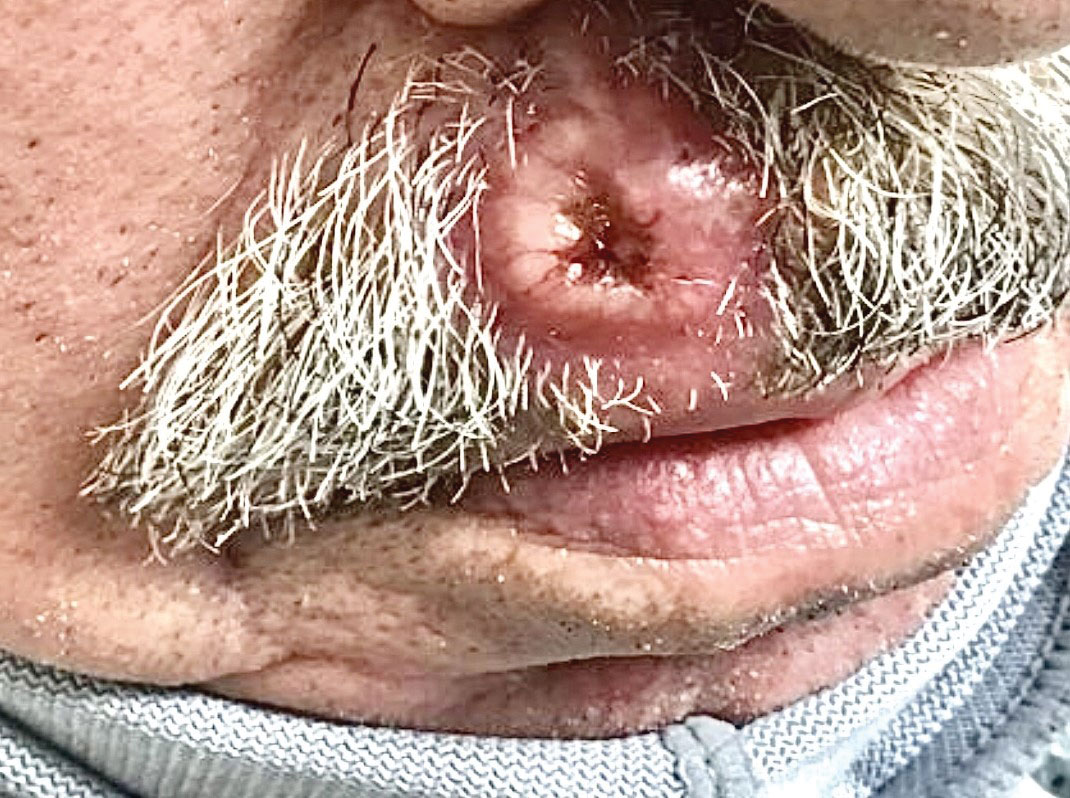
Ulcerated Nodule on the Lip
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
A shave biopsy of the lip revealed a diffuse cellular infiltrate filling the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). Morphologically, the cells had abundant clear cytoplasm with eccentrically located, pleomorphic, hyperchromatic nuclei with occasional prominent nucleoli (Figure 1B). The cells stained positive for AE1/ AE3 on immunohistochemistry (Figure 2). A punch biopsy of the nodule in the right axillary vault revealed a morphologically similar proliferation of cells. A colonoscopy revealed a completely obstructing circumferential mass in the distal ascending colon. A biopsy of the mass confirmed invasive adenocarcinoma, supporting a diagnosis of cutaneous metastases from adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient underwent resection of the lip tumor and started multiagent chemotherapy for his newly diagnosed stage IV adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient died, despite therapy.

Cutaneous metastasis from solid malignancies is uncommon, as only 1.3% of them exhibit cutaneous manifestations at presentation.1 Cutaneous metastasis from signet ring cell adenocarcinoma (SRCA) of the colon is uncommon, and cutaneous metastasis of colorectal SRCA rarely precedes the diagnosis of the primary lesion.2 Among the colorectal cancers that metastasize to the skin, metastasis to the face occurs in only 0.5% of patients.3

Signet ring cell adenocarcinomas are poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas histologically characterized by the neoplastic cells’ circular to ovoid appearance with a flattened top.4,5 This distinctive shape is from the displacement of the nucleus to the periphery of the cell due to the accumulation of intracytoplasmic mucin.4 Classically, malignancies are characterized as an SRCA if more than 50% of the cells have a signet ring cell morphology; if the signet ring cells comprise less than 50% of the neoplasm, the tumor is designated as an adenocarcinoma with signet ring morphology.4 The most common cause of cutaneous metastasis with signet ring morphology is gastric cancer, while colorectal carcinoma is less common.1 Colorectal SRCAs usually are found in the right colon or the rectum in comparison to other colonic sites.6
Clinically, cutaneous metastasis can present in a variety of ways. The most common presentation is nodular lesions that may coalesce to become zosteriform in configuration or lesions that mimic inflammatory dermatoses.7 Cutaneous metastasis is more common in breast and lung cancer, and when it occurs secondary to colorectal cancer, cutaneous metastasis rarely predates the detection of the primary neoplasm.2
The clinical appearance of metastasis is not specific and can mimic many entities8; therefore, a high index of suspicion must be employed when managing patients, even those without a history of internal malignancy. In our patient, the smooth nodular lesion appeared similar to a basal cell carcinoma; however, basal cell carcinomas appear more pearly, and arborizing telangiectasia often is seen.9 Merkel cell carcinoma is common on sundamaged skin of the head and neck but clinically appears more violaceous than the lesion seen in our patient.10 Paracoccidioidomycosis may form ulcerated papulonodules or plaques, especially around the nose and mouth. In many of these cases, lesions develop from contiguous lesions of the oral mucosa; therefore, the presence of oral lesions will help distinguish this infectious entity from cutaneous metastasis. Multiple lesions usually are identified when there is hematogenous dissemination.11 Mycosis fungoides is a subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and is characterized by multiple patches, plaques, and nodules on sun-protected areas. Involvement of the head and neck is not common, except in the folliculotropic subtype, which has a separate and distinct clinical morphology.12
The development of signet ring morphology from an adenocarcinoma can be attributed to the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), which leads to downstream activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the subsequent loss of intercellular tight junctions. The mucin 4 gene, MUC4, also is upregulated by PI3K activation and possesses antiapoptotic and mitogenic effects in addition to its mucin secretory function.13
The neoplastic cells in SRCAs stain positive for mucicarmine, Alcian blue, and periodic acid–Schiff, which highlights the mucinous component of the cells.7 Immunohistochemical stains with CK7, CK20, AE1/AE3, and epithelial membrane antigen can be implemented to confirm an epithelial origin of the primary cancer.7,13 CK20 is a low-molecular-weight cytokeratin normally expressed by Merkel cells and by the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and urothelium, whereas CK7 expression typically is expressed in the lungs, ovaries, endometrium, and breasts, but not in the lower gastrointestinal tract.14 Differentiating primary cutaneous adenocarcinoma from cutaneous metastasis can be accomplished with a thorough clinical history; however, p63 positivity supports a primary cutaneous lesion and may be useful in certain situations.7 CDX2 stains can be utilized to aid in localizing the primary neoplasm when it is unknown, and when positive, it suggests a lower gastrointestinal tract origin. However, special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) recently has been proposed as a replacement immunohistochemical marker for CDX2, as it has greater specificity for SRCA of the lower gastrointestinal tract.15 Benign entities with signet ring cell morphology are difficult to distinguish from SRCA; however, malignant lesions are more likely to demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern, frequent mitotic figures, and apoptosis. Immunohistochemistry also can be utilized to support the diagnosis of benign proliferation with signet ring morphology, as benign lesions often will demonstrate E-cadherin positivity and negativity for p53 and Ki-67.13
Cutaneous metastasis usually correlates to advanced disease and generally indicates a worse prognosis.13 Signet ring cell morphology in both gastric and colorectal cancer portends a poor prognosis, and there is a lower overall survival in patients with these malignancies compared to cancers of the same organ with non–signet ring cell morphology.4,8
- Mandzhieva B, Jalil A, Nadeem M, et al. Most common pathway of metastasis of rectal signet ring cell carcinoma to the skin: hematogenous. Cureus. 2020;12:E6890.
- Parente P, Ciardiello D, Reggiani Bonetti L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from colorectal cancer: making light on an unusual and misdiagnosed event. Life. 2021;11:954.
- Picciariello A, Tomasicchio G, Lantone G, et al. Synchronous “skip” facial metastases from colorectal adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:68.
- Benesch MGK, Mathieson A. Epidemiology of signet ring cell adenocarcinomas. Cancers. 2020;12:1544.
- Xu Q, Karouji Y, Kobayashi M, et al. The PI 3-kinase-Rac-p38 MAP kinase pathway is involved in the formation of signet-ring cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5537-5544.
- Morales-Cruz M, Salgado-Nesme N, Trolle-Silva AM, et al. Signet ring cell carcinoma of the rectum: atypical metastatic presentation. BMJ Case Rep CP. 2019;12:E229135.
- Demirciog˘lu D, Öztürk Durmaz E, Demirkesen C, et al. Livedoid cutaneous metastasis of signet‐ring cell gastric carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:785-788.
- Dong X, Sun G, Qu H, et al. Prognostic significance of signet-ring cell components in patients with gastric carcinoma of different stages. Front Surg. 2021;8:642468.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Nguyen AH, Tahseen AI, Vaudreuil AM, et al. Clinical features and treatment of vulvar Merkel cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Gynecol Oncol Res Pract. 2017;4:2.
- Marques, SA. Paracoccidioidomycosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:610-615.
- Larocca C, Kupper T. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Hematol Oncol Clin. 2019;33:103-120.
- Gündüz Ö, Emeksiz MC, Atasoy P, et al. Signet-ring cells in the skin: a case of late-onset cutaneous metastasis of gastric carcinoma and a brief review of histological approach. Dermatol Rep. 2017;8:6819.
- Al-Taee A, Almukhtar R, Lai J, et al. Metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma of unknown primary origin: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4:283.
- Ma C, Lowenthal BM, Pai RK. SATB2 is superior to CDX2 in distinguishing signet ring cell carcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract and lower gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018; 42:1715-1722.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
A shave biopsy of the lip revealed a diffuse cellular infiltrate filling the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). Morphologically, the cells had abundant clear cytoplasm with eccentrically located, pleomorphic, hyperchromatic nuclei with occasional prominent nucleoli (Figure 1B). The cells stained positive for AE1/ AE3 on immunohistochemistry (Figure 2). A punch biopsy of the nodule in the right axillary vault revealed a morphologically similar proliferation of cells. A colonoscopy revealed a completely obstructing circumferential mass in the distal ascending colon. A biopsy of the mass confirmed invasive adenocarcinoma, supporting a diagnosis of cutaneous metastases from adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient underwent resection of the lip tumor and started multiagent chemotherapy for his newly diagnosed stage IV adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient died, despite therapy.

Cutaneous metastasis from solid malignancies is uncommon, as only 1.3% of them exhibit cutaneous manifestations at presentation.1 Cutaneous metastasis from signet ring cell adenocarcinoma (SRCA) of the colon is uncommon, and cutaneous metastasis of colorectal SRCA rarely precedes the diagnosis of the primary lesion.2 Among the colorectal cancers that metastasize to the skin, metastasis to the face occurs in only 0.5% of patients.3

Signet ring cell adenocarcinomas are poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas histologically characterized by the neoplastic cells’ circular to ovoid appearance with a flattened top.4,5 This distinctive shape is from the displacement of the nucleus to the periphery of the cell due to the accumulation of intracytoplasmic mucin.4 Classically, malignancies are characterized as an SRCA if more than 50% of the cells have a signet ring cell morphology; if the signet ring cells comprise less than 50% of the neoplasm, the tumor is designated as an adenocarcinoma with signet ring morphology.4 The most common cause of cutaneous metastasis with signet ring morphology is gastric cancer, while colorectal carcinoma is less common.1 Colorectal SRCAs usually are found in the right colon or the rectum in comparison to other colonic sites.6
Clinically, cutaneous metastasis can present in a variety of ways. The most common presentation is nodular lesions that may coalesce to become zosteriform in configuration or lesions that mimic inflammatory dermatoses.7 Cutaneous metastasis is more common in breast and lung cancer, and when it occurs secondary to colorectal cancer, cutaneous metastasis rarely predates the detection of the primary neoplasm.2
The clinical appearance of metastasis is not specific and can mimic many entities8; therefore, a high index of suspicion must be employed when managing patients, even those without a history of internal malignancy. In our patient, the smooth nodular lesion appeared similar to a basal cell carcinoma; however, basal cell carcinomas appear more pearly, and arborizing telangiectasia often is seen.9 Merkel cell carcinoma is common on sundamaged skin of the head and neck but clinically appears more violaceous than the lesion seen in our patient.10 Paracoccidioidomycosis may form ulcerated papulonodules or plaques, especially around the nose and mouth. In many of these cases, lesions develop from contiguous lesions of the oral mucosa; therefore, the presence of oral lesions will help distinguish this infectious entity from cutaneous metastasis. Multiple lesions usually are identified when there is hematogenous dissemination.11 Mycosis fungoides is a subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and is characterized by multiple patches, plaques, and nodules on sun-protected areas. Involvement of the head and neck is not common, except in the folliculotropic subtype, which has a separate and distinct clinical morphology.12
The development of signet ring morphology from an adenocarcinoma can be attributed to the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), which leads to downstream activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the subsequent loss of intercellular tight junctions. The mucin 4 gene, MUC4, also is upregulated by PI3K activation and possesses antiapoptotic and mitogenic effects in addition to its mucin secretory function.13
The neoplastic cells in SRCAs stain positive for mucicarmine, Alcian blue, and periodic acid–Schiff, which highlights the mucinous component of the cells.7 Immunohistochemical stains with CK7, CK20, AE1/AE3, and epithelial membrane antigen can be implemented to confirm an epithelial origin of the primary cancer.7,13 CK20 is a low-molecular-weight cytokeratin normally expressed by Merkel cells and by the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and urothelium, whereas CK7 expression typically is expressed in the lungs, ovaries, endometrium, and breasts, but not in the lower gastrointestinal tract.14 Differentiating primary cutaneous adenocarcinoma from cutaneous metastasis can be accomplished with a thorough clinical history; however, p63 positivity supports a primary cutaneous lesion and may be useful in certain situations.7 CDX2 stains can be utilized to aid in localizing the primary neoplasm when it is unknown, and when positive, it suggests a lower gastrointestinal tract origin. However, special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) recently has been proposed as a replacement immunohistochemical marker for CDX2, as it has greater specificity for SRCA of the lower gastrointestinal tract.15 Benign entities with signet ring cell morphology are difficult to distinguish from SRCA; however, malignant lesions are more likely to demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern, frequent mitotic figures, and apoptosis. Immunohistochemistry also can be utilized to support the diagnosis of benign proliferation with signet ring morphology, as benign lesions often will demonstrate E-cadherin positivity and negativity for p53 and Ki-67.13
Cutaneous metastasis usually correlates to advanced disease and generally indicates a worse prognosis.13 Signet ring cell morphology in both gastric and colorectal cancer portends a poor prognosis, and there is a lower overall survival in patients with these malignancies compared to cancers of the same organ with non–signet ring cell morphology.4,8
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
A shave biopsy of the lip revealed a diffuse cellular infiltrate filling the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). Morphologically, the cells had abundant clear cytoplasm with eccentrically located, pleomorphic, hyperchromatic nuclei with occasional prominent nucleoli (Figure 1B). The cells stained positive for AE1/ AE3 on immunohistochemistry (Figure 2). A punch biopsy of the nodule in the right axillary vault revealed a morphologically similar proliferation of cells. A colonoscopy revealed a completely obstructing circumferential mass in the distal ascending colon. A biopsy of the mass confirmed invasive adenocarcinoma, supporting a diagnosis of cutaneous metastases from adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient underwent resection of the lip tumor and started multiagent chemotherapy for his newly diagnosed stage IV adenocarcinoma of the colon. The patient died, despite therapy.

Cutaneous metastasis from solid malignancies is uncommon, as only 1.3% of them exhibit cutaneous manifestations at presentation.1 Cutaneous metastasis from signet ring cell adenocarcinoma (SRCA) of the colon is uncommon, and cutaneous metastasis of colorectal SRCA rarely precedes the diagnosis of the primary lesion.2 Among the colorectal cancers that metastasize to the skin, metastasis to the face occurs in only 0.5% of patients.3

Signet ring cell adenocarcinomas are poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas histologically characterized by the neoplastic cells’ circular to ovoid appearance with a flattened top.4,5 This distinctive shape is from the displacement of the nucleus to the periphery of the cell due to the accumulation of intracytoplasmic mucin.4 Classically, malignancies are characterized as an SRCA if more than 50% of the cells have a signet ring cell morphology; if the signet ring cells comprise less than 50% of the neoplasm, the tumor is designated as an adenocarcinoma with signet ring morphology.4 The most common cause of cutaneous metastasis with signet ring morphology is gastric cancer, while colorectal carcinoma is less common.1 Colorectal SRCAs usually are found in the right colon or the rectum in comparison to other colonic sites.6
Clinically, cutaneous metastasis can present in a variety of ways. The most common presentation is nodular lesions that may coalesce to become zosteriform in configuration or lesions that mimic inflammatory dermatoses.7 Cutaneous metastasis is more common in breast and lung cancer, and when it occurs secondary to colorectal cancer, cutaneous metastasis rarely predates the detection of the primary neoplasm.2
The clinical appearance of metastasis is not specific and can mimic many entities8; therefore, a high index of suspicion must be employed when managing patients, even those without a history of internal malignancy. In our patient, the smooth nodular lesion appeared similar to a basal cell carcinoma; however, basal cell carcinomas appear more pearly, and arborizing telangiectasia often is seen.9 Merkel cell carcinoma is common on sundamaged skin of the head and neck but clinically appears more violaceous than the lesion seen in our patient.10 Paracoccidioidomycosis may form ulcerated papulonodules or plaques, especially around the nose and mouth. In many of these cases, lesions develop from contiguous lesions of the oral mucosa; therefore, the presence of oral lesions will help distinguish this infectious entity from cutaneous metastasis. Multiple lesions usually are identified when there is hematogenous dissemination.11 Mycosis fungoides is a subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and is characterized by multiple patches, plaques, and nodules on sun-protected areas. Involvement of the head and neck is not common, except in the folliculotropic subtype, which has a separate and distinct clinical morphology.12
The development of signet ring morphology from an adenocarcinoma can be attributed to the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), which leads to downstream activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the subsequent loss of intercellular tight junctions. The mucin 4 gene, MUC4, also is upregulated by PI3K activation and possesses antiapoptotic and mitogenic effects in addition to its mucin secretory function.13
The neoplastic cells in SRCAs stain positive for mucicarmine, Alcian blue, and periodic acid–Schiff, which highlights the mucinous component of the cells.7 Immunohistochemical stains with CK7, CK20, AE1/AE3, and epithelial membrane antigen can be implemented to confirm an epithelial origin of the primary cancer.7,13 CK20 is a low-molecular-weight cytokeratin normally expressed by Merkel cells and by the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and urothelium, whereas CK7 expression typically is expressed in the lungs, ovaries, endometrium, and breasts, but not in the lower gastrointestinal tract.14 Differentiating primary cutaneous adenocarcinoma from cutaneous metastasis can be accomplished with a thorough clinical history; however, p63 positivity supports a primary cutaneous lesion and may be useful in certain situations.7 CDX2 stains can be utilized to aid in localizing the primary neoplasm when it is unknown, and when positive, it suggests a lower gastrointestinal tract origin. However, special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) recently has been proposed as a replacement immunohistochemical marker for CDX2, as it has greater specificity for SRCA of the lower gastrointestinal tract.15 Benign entities with signet ring cell morphology are difficult to distinguish from SRCA; however, malignant lesions are more likely to demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern, frequent mitotic figures, and apoptosis. Immunohistochemistry also can be utilized to support the diagnosis of benign proliferation with signet ring morphology, as benign lesions often will demonstrate E-cadherin positivity and negativity for p53 and Ki-67.13
Cutaneous metastasis usually correlates to advanced disease and generally indicates a worse prognosis.13 Signet ring cell morphology in both gastric and colorectal cancer portends a poor prognosis, and there is a lower overall survival in patients with these malignancies compared to cancers of the same organ with non–signet ring cell morphology.4,8
- Mandzhieva B, Jalil A, Nadeem M, et al. Most common pathway of metastasis of rectal signet ring cell carcinoma to the skin: hematogenous. Cureus. 2020;12:E6890.
- Parente P, Ciardiello D, Reggiani Bonetti L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from colorectal cancer: making light on an unusual and misdiagnosed event. Life. 2021;11:954.
- Picciariello A, Tomasicchio G, Lantone G, et al. Synchronous “skip” facial metastases from colorectal adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:68.
- Benesch MGK, Mathieson A. Epidemiology of signet ring cell adenocarcinomas. Cancers. 2020;12:1544.
- Xu Q, Karouji Y, Kobayashi M, et al. The PI 3-kinase-Rac-p38 MAP kinase pathway is involved in the formation of signet-ring cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5537-5544.
- Morales-Cruz M, Salgado-Nesme N, Trolle-Silva AM, et al. Signet ring cell carcinoma of the rectum: atypical metastatic presentation. BMJ Case Rep CP. 2019;12:E229135.
- Demirciog˘lu D, Öztürk Durmaz E, Demirkesen C, et al. Livedoid cutaneous metastasis of signet‐ring cell gastric carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:785-788.
- Dong X, Sun G, Qu H, et al. Prognostic significance of signet-ring cell components in patients with gastric carcinoma of different stages. Front Surg. 2021;8:642468.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Nguyen AH, Tahseen AI, Vaudreuil AM, et al. Clinical features and treatment of vulvar Merkel cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Gynecol Oncol Res Pract. 2017;4:2.
- Marques, SA. Paracoccidioidomycosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:610-615.
- Larocca C, Kupper T. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Hematol Oncol Clin. 2019;33:103-120.
- Gündüz Ö, Emeksiz MC, Atasoy P, et al. Signet-ring cells in the skin: a case of late-onset cutaneous metastasis of gastric carcinoma and a brief review of histological approach. Dermatol Rep. 2017;8:6819.
- Al-Taee A, Almukhtar R, Lai J, et al. Metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma of unknown primary origin: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4:283.
- Ma C, Lowenthal BM, Pai RK. SATB2 is superior to CDX2 in distinguishing signet ring cell carcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract and lower gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018; 42:1715-1722.
- Mandzhieva B, Jalil A, Nadeem M, et al. Most common pathway of metastasis of rectal signet ring cell carcinoma to the skin: hematogenous. Cureus. 2020;12:E6890.
- Parente P, Ciardiello D, Reggiani Bonetti L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from colorectal cancer: making light on an unusual and misdiagnosed event. Life. 2021;11:954.
- Picciariello A, Tomasicchio G, Lantone G, et al. Synchronous “skip” facial metastases from colorectal adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:68.
- Benesch MGK, Mathieson A. Epidemiology of signet ring cell adenocarcinomas. Cancers. 2020;12:1544.
- Xu Q, Karouji Y, Kobayashi M, et al. The PI 3-kinase-Rac-p38 MAP kinase pathway is involved in the formation of signet-ring cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5537-5544.
- Morales-Cruz M, Salgado-Nesme N, Trolle-Silva AM, et al. Signet ring cell carcinoma of the rectum: atypical metastatic presentation. BMJ Case Rep CP. 2019;12:E229135.
- Demirciog˘lu D, Öztürk Durmaz E, Demirkesen C, et al. Livedoid cutaneous metastasis of signet‐ring cell gastric carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:785-788.
- Dong X, Sun G, Qu H, et al. Prognostic significance of signet-ring cell components in patients with gastric carcinoma of different stages. Front Surg. 2021;8:642468.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Nguyen AH, Tahseen AI, Vaudreuil AM, et al. Clinical features and treatment of vulvar Merkel cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Gynecol Oncol Res Pract. 2017;4:2.
- Marques, SA. Paracoccidioidomycosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:610-615.
- Larocca C, Kupper T. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Hematol Oncol Clin. 2019;33:103-120.
- Gündüz Ö, Emeksiz MC, Atasoy P, et al. Signet-ring cells in the skin: a case of late-onset cutaneous metastasis of gastric carcinoma and a brief review of histological approach. Dermatol Rep. 2017;8:6819.
- Al-Taee A, Almukhtar R, Lai J, et al. Metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma of unknown primary origin: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4:283.
- Ma C, Lowenthal BM, Pai RK. SATB2 is superior to CDX2 in distinguishing signet ring cell carcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract and lower gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018; 42:1715-1722.
A 79-year-old man with a medical history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, and atrial fibrillation presented with an enlarging lesion on the right side of the upper cutaneous lip of 5 weeks’ duration. He had no personal history of skin cancer or other malignancy and was up to date on all routine cancer screenings. He reported associated lip and oral cavity tenderness, weakness, and a 13.6-kg (30-lb) unintentional weight loss over the last 6 months. He had used over-the-counter bacitracin ointment on the lesion without relief. A full-body skin examination revealed a firm, mobile, flesh-colored, nondraining nodule in the right axillary vault.
‘Landmark’ trial shows opioids for back, neck pain no better than placebo
Opioids do not relieve acute low back or neck pain in the short term and lead to worse outcomes in the long term, results of the first randomized controlled trial testing the efficacy and safety of a short course of opioids for acute nonspecific low back/neck pain suggest.
After 6 weeks, there was no significant difference in pain scores of patients who took opioids, compared with those who took placebo. After 1 year, patients given the placebo had slightly lower pain scores. Also, patients using opioids were at greater risk of opioid misuse after 1 year.
This is a “landmark” trial with “practice-changing” results, senior author Christine Lin, PhD, with the University of Sydney, told this news organization.
“Before this trial, we did not have good evidence on whether opioids were effective for acute low back pain or neck pain, yet opioids were one of the most commonly used medicines for these conditions,” Dr. Lin explained.
On the basis of these results, “opioids should not be recommended at all for acute low back pain and neck pain,” Dr. Lin said.
Results of the OPAL study were published online in The Lancet.
Rigorous trial
The trial was conducted in 157 primary care or emergency department sites in Australia and involved 347 adults who had been experiencing low back pain, neck pain, or both for 12 weeks or less.
They were randomly allocated (1:1) to receive guideline-recommended care (reassurance and advice to stay active) plus an opioid (oxycodone up to 20 mg daily) or identical placebo for up to 6 weeks. Naloxone was provided to help prevent opioid-induced constipation and improve blinding.
The primary outcome was pain severity at 6 weeks, measured with the pain severity subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (10-point scale).
After 6 weeks, opioid therapy offered no more relief for acute back/neck pain or functional improvement than placebo.
The mean pain score at 6 weeks was 2.78 in the opioid group, versus 2.25 in the placebo group (adjusted mean difference, 0.53; 95% confidence interval, –0.00 to 1.07; P = .051). At 1 year, mean pain scores in the placebo group were slightly lower than in the opioid group (1.8 vs. 2.4).
In addition, there was a doubling of the risk of opioid misuse at 1 year among patients randomly allocated to receive opioid therapy for 6 weeks, compared with those allocated to receive placebo for 6 weeks.
At 1 year, 24 (20%) of 123 of the patients who received opioids were at risk of misuse, as indicated by the Current Opioid Misuse Measure scale, compared with 13 (10%) of 128 patients in the placebo group (P = .049). The COMM is a widely used measure of current aberrant drug-related behavior among patients with chronic pain who are being prescribed opioid therapy.
Results raise ‘serious questions’
“I believe the findings of the study will need to be disseminated to the doctors and patients, so they receive this latest evidence on opioids,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
“We need to reassure doctors and patients that most people with acute low back pain and neck pain recover well with time (usually by 6 weeks), so management is simple – staying active, avoiding bed rest, and, if necessary, using a heat pack for short term pain relief. If drugs are required, consider anti-inflammatory drugs,” Dr. Lin added.
The authors of a linked comment say the OPAL trial “raises serious questions about the use of opioid therapy for acute low back and neck pain.”
Mark Sullivan, MD, PhD, and Jane Ballantyne, MD, with the University of Washington, Seattle, note that current clinical guidelines recommend opioids for patients with acute back and neck pain when other drug treatments fail or are contraindicated.
“As many as two-thirds of patients might receive an opioid when presenting for care of back or neck pain. It is time to re-examine these guidelines and these practices,” Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne conclude.
Funding for the OPAL study was provided by the National Health and Medical Research Council, the University of Sydney Faculty of Medicine and Health, and SafeWork SA. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne are board members (unpaid) of Physicians for Responsible Opioid Prescribing and have been paid consultants in opioid litigation.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioids do not relieve acute low back or neck pain in the short term and lead to worse outcomes in the long term, results of the first randomized controlled trial testing the efficacy and safety of a short course of opioids for acute nonspecific low back/neck pain suggest.
After 6 weeks, there was no significant difference in pain scores of patients who took opioids, compared with those who took placebo. After 1 year, patients given the placebo had slightly lower pain scores. Also, patients using opioids were at greater risk of opioid misuse after 1 year.
This is a “landmark” trial with “practice-changing” results, senior author Christine Lin, PhD, with the University of Sydney, told this news organization.
“Before this trial, we did not have good evidence on whether opioids were effective for acute low back pain or neck pain, yet opioids were one of the most commonly used medicines for these conditions,” Dr. Lin explained.
On the basis of these results, “opioids should not be recommended at all for acute low back pain and neck pain,” Dr. Lin said.
Results of the OPAL study were published online in The Lancet.
Rigorous trial
The trial was conducted in 157 primary care or emergency department sites in Australia and involved 347 adults who had been experiencing low back pain, neck pain, or both for 12 weeks or less.
They were randomly allocated (1:1) to receive guideline-recommended care (reassurance and advice to stay active) plus an opioid (oxycodone up to 20 mg daily) or identical placebo for up to 6 weeks. Naloxone was provided to help prevent opioid-induced constipation and improve blinding.
The primary outcome was pain severity at 6 weeks, measured with the pain severity subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (10-point scale).
After 6 weeks, opioid therapy offered no more relief for acute back/neck pain or functional improvement than placebo.
The mean pain score at 6 weeks was 2.78 in the opioid group, versus 2.25 in the placebo group (adjusted mean difference, 0.53; 95% confidence interval, –0.00 to 1.07; P = .051). At 1 year, mean pain scores in the placebo group were slightly lower than in the opioid group (1.8 vs. 2.4).
In addition, there was a doubling of the risk of opioid misuse at 1 year among patients randomly allocated to receive opioid therapy for 6 weeks, compared with those allocated to receive placebo for 6 weeks.
At 1 year, 24 (20%) of 123 of the patients who received opioids were at risk of misuse, as indicated by the Current Opioid Misuse Measure scale, compared with 13 (10%) of 128 patients in the placebo group (P = .049). The COMM is a widely used measure of current aberrant drug-related behavior among patients with chronic pain who are being prescribed opioid therapy.
Results raise ‘serious questions’
“I believe the findings of the study will need to be disseminated to the doctors and patients, so they receive this latest evidence on opioids,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
“We need to reassure doctors and patients that most people with acute low back pain and neck pain recover well with time (usually by 6 weeks), so management is simple – staying active, avoiding bed rest, and, if necessary, using a heat pack for short term pain relief. If drugs are required, consider anti-inflammatory drugs,” Dr. Lin added.
The authors of a linked comment say the OPAL trial “raises serious questions about the use of opioid therapy for acute low back and neck pain.”
Mark Sullivan, MD, PhD, and Jane Ballantyne, MD, with the University of Washington, Seattle, note that current clinical guidelines recommend opioids for patients with acute back and neck pain when other drug treatments fail or are contraindicated.
“As many as two-thirds of patients might receive an opioid when presenting for care of back or neck pain. It is time to re-examine these guidelines and these practices,” Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne conclude.
Funding for the OPAL study was provided by the National Health and Medical Research Council, the University of Sydney Faculty of Medicine and Health, and SafeWork SA. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne are board members (unpaid) of Physicians for Responsible Opioid Prescribing and have been paid consultants in opioid litigation.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioids do not relieve acute low back or neck pain in the short term and lead to worse outcomes in the long term, results of the first randomized controlled trial testing the efficacy and safety of a short course of opioids for acute nonspecific low back/neck pain suggest.
After 6 weeks, there was no significant difference in pain scores of patients who took opioids, compared with those who took placebo. After 1 year, patients given the placebo had slightly lower pain scores. Also, patients using opioids were at greater risk of opioid misuse after 1 year.
This is a “landmark” trial with “practice-changing” results, senior author Christine Lin, PhD, with the University of Sydney, told this news organization.
“Before this trial, we did not have good evidence on whether opioids were effective for acute low back pain or neck pain, yet opioids were one of the most commonly used medicines for these conditions,” Dr. Lin explained.
On the basis of these results, “opioids should not be recommended at all for acute low back pain and neck pain,” Dr. Lin said.
Results of the OPAL study were published online in The Lancet.
Rigorous trial
The trial was conducted in 157 primary care or emergency department sites in Australia and involved 347 adults who had been experiencing low back pain, neck pain, or both for 12 weeks or less.
They were randomly allocated (1:1) to receive guideline-recommended care (reassurance and advice to stay active) plus an opioid (oxycodone up to 20 mg daily) or identical placebo for up to 6 weeks. Naloxone was provided to help prevent opioid-induced constipation and improve blinding.
The primary outcome was pain severity at 6 weeks, measured with the pain severity subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (10-point scale).
After 6 weeks, opioid therapy offered no more relief for acute back/neck pain or functional improvement than placebo.
The mean pain score at 6 weeks was 2.78 in the opioid group, versus 2.25 in the placebo group (adjusted mean difference, 0.53; 95% confidence interval, –0.00 to 1.07; P = .051). At 1 year, mean pain scores in the placebo group were slightly lower than in the opioid group (1.8 vs. 2.4).
In addition, there was a doubling of the risk of opioid misuse at 1 year among patients randomly allocated to receive opioid therapy for 6 weeks, compared with those allocated to receive placebo for 6 weeks.
At 1 year, 24 (20%) of 123 of the patients who received opioids were at risk of misuse, as indicated by the Current Opioid Misuse Measure scale, compared with 13 (10%) of 128 patients in the placebo group (P = .049). The COMM is a widely used measure of current aberrant drug-related behavior among patients with chronic pain who are being prescribed opioid therapy.
Results raise ‘serious questions’
“I believe the findings of the study will need to be disseminated to the doctors and patients, so they receive this latest evidence on opioids,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
“We need to reassure doctors and patients that most people with acute low back pain and neck pain recover well with time (usually by 6 weeks), so management is simple – staying active, avoiding bed rest, and, if necessary, using a heat pack for short term pain relief. If drugs are required, consider anti-inflammatory drugs,” Dr. Lin added.
The authors of a linked comment say the OPAL trial “raises serious questions about the use of opioid therapy for acute low back and neck pain.”
Mark Sullivan, MD, PhD, and Jane Ballantyne, MD, with the University of Washington, Seattle, note that current clinical guidelines recommend opioids for patients with acute back and neck pain when other drug treatments fail or are contraindicated.
“As many as two-thirds of patients might receive an opioid when presenting for care of back or neck pain. It is time to re-examine these guidelines and these practices,” Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne conclude.
Funding for the OPAL study was provided by the National Health and Medical Research Council, the University of Sydney Faculty of Medicine and Health, and SafeWork SA. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sullivan and Dr. Ballantyne are board members (unpaid) of Physicians for Responsible Opioid Prescribing and have been paid consultants in opioid litigation.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs Suflave, a lower-volume colonoscopy prep drink
, the manufacturer, Sebela Pharmaceuticals, has announced.
Suflave comes in a carton containing two bottles and two flavor packets. Each bottle contains 178.7 g polyethylene glycol 3350, 7.3 g sodium sulfate, 1.12 g potassium chloride, 0.9 g magnesium sulfate, and 0.5 g sodium chloride. One bottle and one flavor packet are equivalent to one dose.
Administration of both doses is required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. After each dose, an additional 16 ounces of water must be consumed.
In a clinical trial, 94% of patients achieved successful bowel cleansing with Suflave, the company said in a news release.
Most patients reported that Suflave tastes like a sports drink and described the taste as “neutral to very pleasant.” Most patients also reported that Suflave was “tolerable to very easy” to consume and indicated they would request it for a subsequent colonoscopy.
“Patients frequently struggle with the taste and volume of traditional bowel preparations – and fear related to the preparation can also negatively affect patient willingness to undergo follow-up colonoscopy if it is indicated,” Douglas K. Rex, MD, gastroenterologist and distinguished professor emeritus at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said in the release.
“I believe the palatable lemon-lime flavor of Suflave will be a welcomed option for patients – reducing preparation hesitancy and giving more people the chance to feel comfortable during preparation and getting a successful and effective procedure,” Dr. Rex added.
Suflave will be available by prescription to patients in the United States in early August.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, the manufacturer, Sebela Pharmaceuticals, has announced.
Suflave comes in a carton containing two bottles and two flavor packets. Each bottle contains 178.7 g polyethylene glycol 3350, 7.3 g sodium sulfate, 1.12 g potassium chloride, 0.9 g magnesium sulfate, and 0.5 g sodium chloride. One bottle and one flavor packet are equivalent to one dose.
Administration of both doses is required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. After each dose, an additional 16 ounces of water must be consumed.
In a clinical trial, 94% of patients achieved successful bowel cleansing with Suflave, the company said in a news release.
Most patients reported that Suflave tastes like a sports drink and described the taste as “neutral to very pleasant.” Most patients also reported that Suflave was “tolerable to very easy” to consume and indicated they would request it for a subsequent colonoscopy.
“Patients frequently struggle with the taste and volume of traditional bowel preparations – and fear related to the preparation can also negatively affect patient willingness to undergo follow-up colonoscopy if it is indicated,” Douglas K. Rex, MD, gastroenterologist and distinguished professor emeritus at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said in the release.
“I believe the palatable lemon-lime flavor of Suflave will be a welcomed option for patients – reducing preparation hesitancy and giving more people the chance to feel comfortable during preparation and getting a successful and effective procedure,” Dr. Rex added.
Suflave will be available by prescription to patients in the United States in early August.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, the manufacturer, Sebela Pharmaceuticals, has announced.
Suflave comes in a carton containing two bottles and two flavor packets. Each bottle contains 178.7 g polyethylene glycol 3350, 7.3 g sodium sulfate, 1.12 g potassium chloride, 0.9 g magnesium sulfate, and 0.5 g sodium chloride. One bottle and one flavor packet are equivalent to one dose.
Administration of both doses is required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. After each dose, an additional 16 ounces of water must be consumed.
In a clinical trial, 94% of patients achieved successful bowel cleansing with Suflave, the company said in a news release.
Most patients reported that Suflave tastes like a sports drink and described the taste as “neutral to very pleasant.” Most patients also reported that Suflave was “tolerable to very easy” to consume and indicated they would request it for a subsequent colonoscopy.
“Patients frequently struggle with the taste and volume of traditional bowel preparations – and fear related to the preparation can also negatively affect patient willingness to undergo follow-up colonoscopy if it is indicated,” Douglas K. Rex, MD, gastroenterologist and distinguished professor emeritus at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said in the release.
“I believe the palatable lemon-lime flavor of Suflave will be a welcomed option for patients – reducing preparation hesitancy and giving more people the chance to feel comfortable during preparation and getting a successful and effective procedure,” Dr. Rex added.
Suflave will be available by prescription to patients in the United States in early August.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO plans to declare common sweetener as possible carcinogen
The World Health Organization is set to list the artificial sweetener aspartame as a possible carcinogen.
The move, reported by multiple media sources, is expected during a July 14 meeting of WHO research experts – the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Reuters cited two unnamed sources “with knowledge of the process,” noting that aspartame is one of the world’s most commonly used sweeteners.
Aspartame is 200 times sweeter than sugar and was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1974 for use as a tabletop sweetener and in chewing gum and cold breakfast cereals, as well as instant coffee, gelatins, puddings and fillings, and dairy products. Up to 95% of carbonated soft drinks that have a sweetener use aspartame, and the substance is often added by consumers to beverages (it’s the blue packet of sweetener in the array of packets that appear on diner and restaurant tables), The Washington Post reported.
The WHO currently lists 126 agents as known to be carcinogenic to humans, ranging from alcohol and tobacco to outdoor air pollution. The WHO also lists 94 agents as “probably” carcinogenic to humans and 322 agents as “possibly” carcinogenic to humans. Aspartame would join the “possibly” group, which includes gasoline engine exhaust and working as a dry cleaner.
Earlier this year, the WHO warned that people should not use nonsugar sweeteners to control their weight because of potential health risks.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization is set to list the artificial sweetener aspartame as a possible carcinogen.
The move, reported by multiple media sources, is expected during a July 14 meeting of WHO research experts – the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Reuters cited two unnamed sources “with knowledge of the process,” noting that aspartame is one of the world’s most commonly used sweeteners.
Aspartame is 200 times sweeter than sugar and was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1974 for use as a tabletop sweetener and in chewing gum and cold breakfast cereals, as well as instant coffee, gelatins, puddings and fillings, and dairy products. Up to 95% of carbonated soft drinks that have a sweetener use aspartame, and the substance is often added by consumers to beverages (it’s the blue packet of sweetener in the array of packets that appear on diner and restaurant tables), The Washington Post reported.
The WHO currently lists 126 agents as known to be carcinogenic to humans, ranging from alcohol and tobacco to outdoor air pollution. The WHO also lists 94 agents as “probably” carcinogenic to humans and 322 agents as “possibly” carcinogenic to humans. Aspartame would join the “possibly” group, which includes gasoline engine exhaust and working as a dry cleaner.
Earlier this year, the WHO warned that people should not use nonsugar sweeteners to control their weight because of potential health risks.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization is set to list the artificial sweetener aspartame as a possible carcinogen.
The move, reported by multiple media sources, is expected during a July 14 meeting of WHO research experts – the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Reuters cited two unnamed sources “with knowledge of the process,” noting that aspartame is one of the world’s most commonly used sweeteners.
Aspartame is 200 times sweeter than sugar and was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1974 for use as a tabletop sweetener and in chewing gum and cold breakfast cereals, as well as instant coffee, gelatins, puddings and fillings, and dairy products. Up to 95% of carbonated soft drinks that have a sweetener use aspartame, and the substance is often added by consumers to beverages (it’s the blue packet of sweetener in the array of packets that appear on diner and restaurant tables), The Washington Post reported.
The WHO currently lists 126 agents as known to be carcinogenic to humans, ranging from alcohol and tobacco to outdoor air pollution. The WHO also lists 94 agents as “probably” carcinogenic to humans and 322 agents as “possibly” carcinogenic to humans. Aspartame would join the “possibly” group, which includes gasoline engine exhaust and working as a dry cleaner.
Earlier this year, the WHO warned that people should not use nonsugar sweeteners to control their weight because of potential health risks.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Does colchicine have a role in treating excess ASCVD risk in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions?
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
What’s new in the new jaundice guidelines?
More than 15 years in the making, the revised AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation was released in 2022. A key driving force for this revision was the expanded evidence base regarding monitoring and treatment of newborns 35 or more weeks’ gestation to prevent bilirubin encephalopathy and kernicterus.
Here, we summarize the highlights of the new guidelines and point out practical ways to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
What has changed?
If you are familiar with the previous guidelines (2004 or the 2009 update) for the management of newborn jaundice, you’ll note that the treatment graphs for phototherapy and exchange transfusion have been updated with new, slightly higher thresholds.
Bilirubin thresholds for starting phototherapy are about 2 mg/dL higher overall than indicated in previous iterations of the guidelines.
This change reflects new evidence that infants don’t typically develop bilirubin neurotoxicity until the total serum bilirubin (TSB) reaches levels well above the previous exchange transfusion threshold, justifying a narrow increase in the bilirubin level for starting phototherapy. Also, phototherapy treatment thresholds are now risk-adjusted, with separate curves for each gestational age from 35 weeks to > 38 weeks.
To find the applicable phototherapy threshold, use the infant’s gestational age (rounding down) and determine whether the infant has even a single neurotoxicity risk factor other than prematurity. Neurotoxicity risk factors include a low albumin level, isoimmune hemolytic disease, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, or other hemolytic conditions; sepsis; or any significant clinical instability in the previous 24 hours.
For example, a 384/7 weeks’ gestation newborn has a TSB of 12 mg/dL at 48 hours of age but no neurotoxicity risk factors. Using the graph Phototherapy Thresholds: No Hyperbilirubinemia Neurotoxicity Risk Factors, should the infant be placed under phototherapy at this time? (Answer: No. The threshold for starting phototherapy on this infant is approximately 16 mg/dL.)
When hyperbilirubinemia becomes a medical emergency
A new term, “escalation of care,” has been adopted to describe actions to take when the newborn’s TSB climbs to within 2 mg/dL of the exchange transfusion threshold – a medical emergency. Instructions on how to ensure intensive phototherapy, and when to initiate an urgent exchange transfusion, are given, including the critical need to maintain intensive phototherapy continuously during infant transport and admission to another facility.
Transcutaneous vs. serum bilirubin
Either a serum TSB or a transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) should be measured in all infants between 24 and 48 hours after birth or before discharge if that occurs earlier. TcB measurements are valid and reliable when used as a screening test to identify infants who require a TSB measurement. Although the two tests are generally correlated, they are not identical, and treatment decisions should be based on TSB levels. A TSB should be obtained if the TcB exceeds or is within 3 mg/dL of the phototherapy treatment threshold, or if the TcB is ≥ 15 mg/dL.
Following up: When to check another bilirubin level
Prior to these new guidelines, the question of when to get the next bilirubin level was based on Vinod Bhutani, MD’s risk nomogram, which classified newborn bilirubin levels within high-, intermediate-, or low-risk zones for needing phototherapy. A bilirubin level in the high-risk zone indicated the need for earlier follow-up. These risk zones have been replaced with a more specific table that provides recommended postdischarge follow-up based on how close the newborn’s bilirubin level is to the hour-specific threshold for treatment. The closer the latest TSB or TcB level is to the newborn’s risk-based phototherapy threshold, the sooner the follow-up to check another bilirubin level will need to be.
Most infants discharged before 72 hours of age will need follow-up within 2 days. Newborns with TSB levels nearing the level for phototherapy (within 2 mg/dL or less) should remain in the hospital.
Five tips for using the new guidelines
Bilitool.org, a popular and useful app, has already been updated to reflect the changes in the new guidelines, making it easy to apply the new thresholds and create a follow-up plan for each patient.
The guidelines provide recommendations for when to check rebound bilirubin levels after stopping phototherapy (hint: babies with neurotoxic risk factors). A TcB device should not be used while the infant is being treated with phototherapy. However, a TcB can be measured once the baby has been off phototherapy for at least 24 hours.
If you have at least two bilirubin measurements, you can calculate the “rate of rise” in bilirubin level. A rapid rate of rise, which serves as a clinical indicator of hemolysis, is defined as ≥ 0.3 mg/dL per hour in the first 24 hours or ≥ 0.2 mg/dL per hour after the first 24 hours of life. This is especially helpful when hemolysis is suspected even if the newborn’s direct antibody test (DAT) is negative. In this scenario, the infant is considered to have a neurotoxic risk factor.
When you initiate phototherapy, be aware of the infant’s bilirubin level threshold for stopping phototherapy (2 mg/dL below the starting phototherapy threshold), as well as the threshold for escalation of care (2 mg/dL below the exchange transfusion threshold).
Because the thresholds for starting phototherapy and initiating exchange transfusion are slightly higher and specific to gestational age, clinicians can more confidently use less phototherapy.
Other guideline highlights
The neurotoxic risk factors and corresponding thresholds are important. If the newborn has one or more neurotoxic risk factors other than prematurity, the neurotoxic risk threshold graph should be used when assessing the need for treatment. Neurotoxic risk thresholds should also be used for newborns whose bilirubin levels continue rising on phototherapy.
The guidelines emphasize that G6PD is one of the most important causes of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia leading to kernicterus in the United States and worldwide. Overall, 13% of African American males and about 4% of African American females have G6PD deficiency.
Finally, the guidelines remind clinicians that an important way to reduce the chances that phototherapy will be needed is to encourage early and frequent feeding (8-12 times in 24 hours).
The AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation contains a great deal more information, but these basic principles should allow practitioners to begin to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
Dr. Amaya is associate professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and medical director, level 1 nursery, department of pediatrics, MUSC general academic pediatrics. She disclosed ties with Medical University of South Carolina. Dr. Balog is clinical associate professor of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She has no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Basco is professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; director, division of general pediatrics, department of pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 15 years in the making, the revised AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation was released in 2022. A key driving force for this revision was the expanded evidence base regarding monitoring and treatment of newborns 35 or more weeks’ gestation to prevent bilirubin encephalopathy and kernicterus.
Here, we summarize the highlights of the new guidelines and point out practical ways to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
What has changed?
If you are familiar with the previous guidelines (2004 or the 2009 update) for the management of newborn jaundice, you’ll note that the treatment graphs for phototherapy and exchange transfusion have been updated with new, slightly higher thresholds.
Bilirubin thresholds for starting phototherapy are about 2 mg/dL higher overall than indicated in previous iterations of the guidelines.
This change reflects new evidence that infants don’t typically develop bilirubin neurotoxicity until the total serum bilirubin (TSB) reaches levels well above the previous exchange transfusion threshold, justifying a narrow increase in the bilirubin level for starting phototherapy. Also, phototherapy treatment thresholds are now risk-adjusted, with separate curves for each gestational age from 35 weeks to > 38 weeks.
To find the applicable phototherapy threshold, use the infant’s gestational age (rounding down) and determine whether the infant has even a single neurotoxicity risk factor other than prematurity. Neurotoxicity risk factors include a low albumin level, isoimmune hemolytic disease, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, or other hemolytic conditions; sepsis; or any significant clinical instability in the previous 24 hours.
For example, a 384/7 weeks’ gestation newborn has a TSB of 12 mg/dL at 48 hours of age but no neurotoxicity risk factors. Using the graph Phototherapy Thresholds: No Hyperbilirubinemia Neurotoxicity Risk Factors, should the infant be placed under phototherapy at this time? (Answer: No. The threshold for starting phototherapy on this infant is approximately 16 mg/dL.)
When hyperbilirubinemia becomes a medical emergency
A new term, “escalation of care,” has been adopted to describe actions to take when the newborn’s TSB climbs to within 2 mg/dL of the exchange transfusion threshold – a medical emergency. Instructions on how to ensure intensive phototherapy, and when to initiate an urgent exchange transfusion, are given, including the critical need to maintain intensive phototherapy continuously during infant transport and admission to another facility.
Transcutaneous vs. serum bilirubin
Either a serum TSB or a transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) should be measured in all infants between 24 and 48 hours after birth or before discharge if that occurs earlier. TcB measurements are valid and reliable when used as a screening test to identify infants who require a TSB measurement. Although the two tests are generally correlated, they are not identical, and treatment decisions should be based on TSB levels. A TSB should be obtained if the TcB exceeds or is within 3 mg/dL of the phototherapy treatment threshold, or if the TcB is ≥ 15 mg/dL.
Following up: When to check another bilirubin level
Prior to these new guidelines, the question of when to get the next bilirubin level was based on Vinod Bhutani, MD’s risk nomogram, which classified newborn bilirubin levels within high-, intermediate-, or low-risk zones for needing phototherapy. A bilirubin level in the high-risk zone indicated the need for earlier follow-up. These risk zones have been replaced with a more specific table that provides recommended postdischarge follow-up based on how close the newborn’s bilirubin level is to the hour-specific threshold for treatment. The closer the latest TSB or TcB level is to the newborn’s risk-based phototherapy threshold, the sooner the follow-up to check another bilirubin level will need to be.
Most infants discharged before 72 hours of age will need follow-up within 2 days. Newborns with TSB levels nearing the level for phototherapy (within 2 mg/dL or less) should remain in the hospital.
Five tips for using the new guidelines
Bilitool.org, a popular and useful app, has already been updated to reflect the changes in the new guidelines, making it easy to apply the new thresholds and create a follow-up plan for each patient.
The guidelines provide recommendations for when to check rebound bilirubin levels after stopping phototherapy (hint: babies with neurotoxic risk factors). A TcB device should not be used while the infant is being treated with phototherapy. However, a TcB can be measured once the baby has been off phototherapy for at least 24 hours.
If you have at least two bilirubin measurements, you can calculate the “rate of rise” in bilirubin level. A rapid rate of rise, which serves as a clinical indicator of hemolysis, is defined as ≥ 0.3 mg/dL per hour in the first 24 hours or ≥ 0.2 mg/dL per hour after the first 24 hours of life. This is especially helpful when hemolysis is suspected even if the newborn’s direct antibody test (DAT) is negative. In this scenario, the infant is considered to have a neurotoxic risk factor.
When you initiate phototherapy, be aware of the infant’s bilirubin level threshold for stopping phototherapy (2 mg/dL below the starting phototherapy threshold), as well as the threshold for escalation of care (2 mg/dL below the exchange transfusion threshold).
Because the thresholds for starting phototherapy and initiating exchange transfusion are slightly higher and specific to gestational age, clinicians can more confidently use less phototherapy.
Other guideline highlights
The neurotoxic risk factors and corresponding thresholds are important. If the newborn has one or more neurotoxic risk factors other than prematurity, the neurotoxic risk threshold graph should be used when assessing the need for treatment. Neurotoxic risk thresholds should also be used for newborns whose bilirubin levels continue rising on phototherapy.
The guidelines emphasize that G6PD is one of the most important causes of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia leading to kernicterus in the United States and worldwide. Overall, 13% of African American males and about 4% of African American females have G6PD deficiency.
Finally, the guidelines remind clinicians that an important way to reduce the chances that phototherapy will be needed is to encourage early and frequent feeding (8-12 times in 24 hours).
The AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation contains a great deal more information, but these basic principles should allow practitioners to begin to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
Dr. Amaya is associate professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and medical director, level 1 nursery, department of pediatrics, MUSC general academic pediatrics. She disclosed ties with Medical University of South Carolina. Dr. Balog is clinical associate professor of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She has no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Basco is professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; director, division of general pediatrics, department of pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 15 years in the making, the revised AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation was released in 2022. A key driving force for this revision was the expanded evidence base regarding monitoring and treatment of newborns 35 or more weeks’ gestation to prevent bilirubin encephalopathy and kernicterus.
Here, we summarize the highlights of the new guidelines and point out practical ways to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
What has changed?
If you are familiar with the previous guidelines (2004 or the 2009 update) for the management of newborn jaundice, you’ll note that the treatment graphs for phototherapy and exchange transfusion have been updated with new, slightly higher thresholds.
Bilirubin thresholds for starting phototherapy are about 2 mg/dL higher overall than indicated in previous iterations of the guidelines.
This change reflects new evidence that infants don’t typically develop bilirubin neurotoxicity until the total serum bilirubin (TSB) reaches levels well above the previous exchange transfusion threshold, justifying a narrow increase in the bilirubin level for starting phototherapy. Also, phototherapy treatment thresholds are now risk-adjusted, with separate curves for each gestational age from 35 weeks to > 38 weeks.
To find the applicable phototherapy threshold, use the infant’s gestational age (rounding down) and determine whether the infant has even a single neurotoxicity risk factor other than prematurity. Neurotoxicity risk factors include a low albumin level, isoimmune hemolytic disease, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, or other hemolytic conditions; sepsis; or any significant clinical instability in the previous 24 hours.
For example, a 384/7 weeks’ gestation newborn has a TSB of 12 mg/dL at 48 hours of age but no neurotoxicity risk factors. Using the graph Phototherapy Thresholds: No Hyperbilirubinemia Neurotoxicity Risk Factors, should the infant be placed under phototherapy at this time? (Answer: No. The threshold for starting phototherapy on this infant is approximately 16 mg/dL.)
When hyperbilirubinemia becomes a medical emergency
A new term, “escalation of care,” has been adopted to describe actions to take when the newborn’s TSB climbs to within 2 mg/dL of the exchange transfusion threshold – a medical emergency. Instructions on how to ensure intensive phototherapy, and when to initiate an urgent exchange transfusion, are given, including the critical need to maintain intensive phototherapy continuously during infant transport and admission to another facility.
Transcutaneous vs. serum bilirubin
Either a serum TSB or a transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) should be measured in all infants between 24 and 48 hours after birth or before discharge if that occurs earlier. TcB measurements are valid and reliable when used as a screening test to identify infants who require a TSB measurement. Although the two tests are generally correlated, they are not identical, and treatment decisions should be based on TSB levels. A TSB should be obtained if the TcB exceeds or is within 3 mg/dL of the phototherapy treatment threshold, or if the TcB is ≥ 15 mg/dL.
Following up: When to check another bilirubin level
Prior to these new guidelines, the question of when to get the next bilirubin level was based on Vinod Bhutani, MD’s risk nomogram, which classified newborn bilirubin levels within high-, intermediate-, or low-risk zones for needing phototherapy. A bilirubin level in the high-risk zone indicated the need for earlier follow-up. These risk zones have been replaced with a more specific table that provides recommended postdischarge follow-up based on how close the newborn’s bilirubin level is to the hour-specific threshold for treatment. The closer the latest TSB or TcB level is to the newborn’s risk-based phototherapy threshold, the sooner the follow-up to check another bilirubin level will need to be.
Most infants discharged before 72 hours of age will need follow-up within 2 days. Newborns with TSB levels nearing the level for phototherapy (within 2 mg/dL or less) should remain in the hospital.
Five tips for using the new guidelines
Bilitool.org, a popular and useful app, has already been updated to reflect the changes in the new guidelines, making it easy to apply the new thresholds and create a follow-up plan for each patient.
The guidelines provide recommendations for when to check rebound bilirubin levels after stopping phototherapy (hint: babies with neurotoxic risk factors). A TcB device should not be used while the infant is being treated with phototherapy. However, a TcB can be measured once the baby has been off phototherapy for at least 24 hours.
If you have at least two bilirubin measurements, you can calculate the “rate of rise” in bilirubin level. A rapid rate of rise, which serves as a clinical indicator of hemolysis, is defined as ≥ 0.3 mg/dL per hour in the first 24 hours or ≥ 0.2 mg/dL per hour after the first 24 hours of life. This is especially helpful when hemolysis is suspected even if the newborn’s direct antibody test (DAT) is negative. In this scenario, the infant is considered to have a neurotoxic risk factor.
When you initiate phototherapy, be aware of the infant’s bilirubin level threshold for stopping phototherapy (2 mg/dL below the starting phototherapy threshold), as well as the threshold for escalation of care (2 mg/dL below the exchange transfusion threshold).
Because the thresholds for starting phototherapy and initiating exchange transfusion are slightly higher and specific to gestational age, clinicians can more confidently use less phototherapy.
Other guideline highlights
The neurotoxic risk factors and corresponding thresholds are important. If the newborn has one or more neurotoxic risk factors other than prematurity, the neurotoxic risk threshold graph should be used when assessing the need for treatment. Neurotoxic risk thresholds should also be used for newborns whose bilirubin levels continue rising on phototherapy.
The guidelines emphasize that G6PD is one of the most important causes of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia leading to kernicterus in the United States and worldwide. Overall, 13% of African American males and about 4% of African American females have G6PD deficiency.
Finally, the guidelines remind clinicians that an important way to reduce the chances that phototherapy will be needed is to encourage early and frequent feeding (8-12 times in 24 hours).
The AAP Clinical Practice Guideline Revision: Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation contains a great deal more information, but these basic principles should allow practitioners to begin to incorporate these guidelines into daily practice.
Dr. Amaya is associate professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and medical director, level 1 nursery, department of pediatrics, MUSC general academic pediatrics. She disclosed ties with Medical University of South Carolina. Dr. Balog is clinical associate professor of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She has no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Basco is professor, department of pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; director, division of general pediatrics, department of pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Tirzepatide: Therapeutic titan or costly cure?
As a general practitioner with a specialist interest in diabetes, I am increasingly diagnosing younger people living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Sadly, my youngest patient living with type 2 diabetes and obesity is only in her early 20s.
In fact, in England, there are now more people under the age of 40 years living with type 2 diabetes than type 1 diabetes. These younger individuals tend to present with very high hemoglobin A1c levels; I am routinely seeing double-digit A1c percentage levels in my practice. Indeed, the patient mentioned above presented with an A1c of more than 13%.
The lifetime cardiometabolic risk of individuals like her is considerable and very worrying: Younger adults with type 2 diabetes often have adverse cardiometabolic risk profiles at diagnosis, with higher body mass indices, marked dyslipidemia, hypertension, and abnormal liver profiles suggesting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The cumulative impact of this risk profile is a significant impact on quality and quantity of life. Evidence tells us that a younger age of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk for premature death, especially from cardiovascular disease.
Early treatment intensification is warranted in younger individuals living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. My patient above is now on triple therapy with metformin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, and a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. I gave her an urgent referral to my local weight management service for weight, nutritional, and psychological support. I have also issued her a real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) device: Whilst she does not meet any current U.K. criteria for using rt-CGM, I feel that the role of CGM as an educational tool for her is invaluable and equally important to her pharmacologic therapies. We are in desperate need of effective pharmacologic and lifestyle interventions to tackle this epidemic of cardiometabolic disease in the young.
I attended the recent ADA 2023 congress in San Diego, including the presentation of the SURMOUNT-2 trial data. SURMOUNT-2 explored the efficacy and safety of the dual GLP-GIP agonist tirzepatide for weight management in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide was associated with significant reductions in weight (average weight loss, 14-16 kg after 72 weeks) and glycemia (2.1% reduction in A1c after 72 weeks), as well as reductions in clinically meaningful cardiometabolic risk factors, including systolic blood pressure, liver enzymes, and fasting non–HDL cholesterol levels. The overall safety profile of tirzepatide was also reassuring and consistent with the GLP-1 class. Most adverse effects were gastrointestinal and of mild to moderate severity. These adverse effects decreased over time.
These results perfectly position tirzepatide for my younger patients like the young woman mentioned above. The significant improvements in weight, glycemia, and cardiometabolic risk factors will not only help mitigate her future cardiometabolic risk but also help the sustainability of the U.K.’s National Health System. The cost of diabetes to the NHS in the United Kingdom is more than 10% of the entire NHS budget for England and Wales. More than 80% of this cost, however, is related not to the medications and devices we prescribe for diabetes but to the downstream complications of diabetes, such as hospital admissions for cardiovascular events and amputations, as well as regular hospital attendance for dialysis for end-stage kidney disease.
There is no doubt, however, that modern obesity medications such as semaglutide and tirzepatide are expensive, and demand has been astronomical. This demand has been driven by private weight-management services and celebrity influencers, and has resulted in major U.K.-wide GLP-1 shortages.
This situation is tragically widening health inequalities, as many of my patients who have been on GLP-1 receptor agonists for many years are unable to obtain them. I am having to consider switching therapies, often to less efficacious options without the compelling cardiorenal benefits. Furthermore, the GLP-1 shortages have prevented GLP-1 initiation for my other high-risk younger patients, potentially increasing future cardiometabolic risk.
There remain unanswered questions for tirzepatide: What is the durability of effect of tirzepatide after 72 weeks (that is, the trial duration of SURMOUNT-2)? Crucially, what is the effect of withdrawal of tirzepatide on weight loss maintenance? Previous evidence has suggested weight regain after discontinuation of a GLP-1 receptor agonist for obesity. This, of course, has further financial and sustainability implications for health care systems such as the NHS.
Finally, we are increasingly seeing younger women of childbearing age with or at risk for cardiometabolic disease. Again, my patient above is one example. Many of the therapies we use for cardiometabolic disease management, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and tirzepatide, have not been studied, and hence have not been licensed in pregnant women. Therefore, frank discussions are required with patients about future family plans and the importance of contraception. Often, the significant weight loss seen with GLP-1 receptor agonists can improve hormonal profiles and fertility in women and result in unexpected pregnancies if robust contraception is not in place.
Tirzepatide has yet to be made commercially available in the United Kingdom, and its price has also yet to be set. But I already envision a clear role for tirzepatide in my treatment armamentarium. I will be positioning tirzepatide as my first injectable of choice after oral treatment escalation with metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor in all my patients who require treatment intensification – not just my younger, higher-risk individuals. This may remain an aspirational goal until supply chains and cost are defined. There is no doubt, however, that the compelling weight and glycemic benefits of tirzepatide alongside individualized lifestyle interventions can help improve the quality and quantity of life of my patients living with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Dr. Fernando is a general practitioner near Edinburgh. He reported receiving speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk..
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a general practitioner with a specialist interest in diabetes, I am increasingly diagnosing younger people living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Sadly, my youngest patient living with type 2 diabetes and obesity is only in her early 20s.
In fact, in England, there are now more people under the age of 40 years living with type 2 diabetes than type 1 diabetes. These younger individuals tend to present with very high hemoglobin A1c levels; I am routinely seeing double-digit A1c percentage levels in my practice. Indeed, the patient mentioned above presented with an A1c of more than 13%.
The lifetime cardiometabolic risk of individuals like her is considerable and very worrying: Younger adults with type 2 diabetes often have adverse cardiometabolic risk profiles at diagnosis, with higher body mass indices, marked dyslipidemia, hypertension, and abnormal liver profiles suggesting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The cumulative impact of this risk profile is a significant impact on quality and quantity of life. Evidence tells us that a younger age of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk for premature death, especially from cardiovascular disease.
Early treatment intensification is warranted in younger individuals living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. My patient above is now on triple therapy with metformin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, and a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. I gave her an urgent referral to my local weight management service for weight, nutritional, and psychological support. I have also issued her a real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) device: Whilst she does not meet any current U.K. criteria for using rt-CGM, I feel that the role of CGM as an educational tool for her is invaluable and equally important to her pharmacologic therapies. We are in desperate need of effective pharmacologic and lifestyle interventions to tackle this epidemic of cardiometabolic disease in the young.
I attended the recent ADA 2023 congress in San Diego, including the presentation of the SURMOUNT-2 trial data. SURMOUNT-2 explored the efficacy and safety of the dual GLP-GIP agonist tirzepatide for weight management in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide was associated with significant reductions in weight (average weight loss, 14-16 kg after 72 weeks) and glycemia (2.1% reduction in A1c after 72 weeks), as well as reductions in clinically meaningful cardiometabolic risk factors, including systolic blood pressure, liver enzymes, and fasting non–HDL cholesterol levels. The overall safety profile of tirzepatide was also reassuring and consistent with the GLP-1 class. Most adverse effects were gastrointestinal and of mild to moderate severity. These adverse effects decreased over time.
These results perfectly position tirzepatide for my younger patients like the young woman mentioned above. The significant improvements in weight, glycemia, and cardiometabolic risk factors will not only help mitigate her future cardiometabolic risk but also help the sustainability of the U.K.’s National Health System. The cost of diabetes to the NHS in the United Kingdom is more than 10% of the entire NHS budget for England and Wales. More than 80% of this cost, however, is related not to the medications and devices we prescribe for diabetes but to the downstream complications of diabetes, such as hospital admissions for cardiovascular events and amputations, as well as regular hospital attendance for dialysis for end-stage kidney disease.
There is no doubt, however, that modern obesity medications such as semaglutide and tirzepatide are expensive, and demand has been astronomical. This demand has been driven by private weight-management services and celebrity influencers, and has resulted in major U.K.-wide GLP-1 shortages.
This situation is tragically widening health inequalities, as many of my patients who have been on GLP-1 receptor agonists for many years are unable to obtain them. I am having to consider switching therapies, often to less efficacious options without the compelling cardiorenal benefits. Furthermore, the GLP-1 shortages have prevented GLP-1 initiation for my other high-risk younger patients, potentially increasing future cardiometabolic risk.
There remain unanswered questions for tirzepatide: What is the durability of effect of tirzepatide after 72 weeks (that is, the trial duration of SURMOUNT-2)? Crucially, what is the effect of withdrawal of tirzepatide on weight loss maintenance? Previous evidence has suggested weight regain after discontinuation of a GLP-1 receptor agonist for obesity. This, of course, has further financial and sustainability implications for health care systems such as the NHS.
Finally, we are increasingly seeing younger women of childbearing age with or at risk for cardiometabolic disease. Again, my patient above is one example. Many of the therapies we use for cardiometabolic disease management, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and tirzepatide, have not been studied, and hence have not been licensed in pregnant women. Therefore, frank discussions are required with patients about future family plans and the importance of contraception. Often, the significant weight loss seen with GLP-1 receptor agonists can improve hormonal profiles and fertility in women and result in unexpected pregnancies if robust contraception is not in place.
Tirzepatide has yet to be made commercially available in the United Kingdom, and its price has also yet to be set. But I already envision a clear role for tirzepatide in my treatment armamentarium. I will be positioning tirzepatide as my first injectable of choice after oral treatment escalation with metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor in all my patients who require treatment intensification – not just my younger, higher-risk individuals. This may remain an aspirational goal until supply chains and cost are defined. There is no doubt, however, that the compelling weight and glycemic benefits of tirzepatide alongside individualized lifestyle interventions can help improve the quality and quantity of life of my patients living with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Dr. Fernando is a general practitioner near Edinburgh. He reported receiving speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk..
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a general practitioner with a specialist interest in diabetes, I am increasingly diagnosing younger people living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Sadly, my youngest patient living with type 2 diabetes and obesity is only in her early 20s.
In fact, in England, there are now more people under the age of 40 years living with type 2 diabetes than type 1 diabetes. These younger individuals tend to present with very high hemoglobin A1c levels; I am routinely seeing double-digit A1c percentage levels in my practice. Indeed, the patient mentioned above presented with an A1c of more than 13%.
The lifetime cardiometabolic risk of individuals like her is considerable and very worrying: Younger adults with type 2 diabetes often have adverse cardiometabolic risk profiles at diagnosis, with higher body mass indices, marked dyslipidemia, hypertension, and abnormal liver profiles suggesting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The cumulative impact of this risk profile is a significant impact on quality and quantity of life. Evidence tells us that a younger age of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk for premature death, especially from cardiovascular disease.
Early treatment intensification is warranted in younger individuals living with type 2 diabetes and obesity. My patient above is now on triple therapy with metformin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, and a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. I gave her an urgent referral to my local weight management service for weight, nutritional, and psychological support. I have also issued her a real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) device: Whilst she does not meet any current U.K. criteria for using rt-CGM, I feel that the role of CGM as an educational tool for her is invaluable and equally important to her pharmacologic therapies. We are in desperate need of effective pharmacologic and lifestyle interventions to tackle this epidemic of cardiometabolic disease in the young.
I attended the recent ADA 2023 congress in San Diego, including the presentation of the SURMOUNT-2 trial data. SURMOUNT-2 explored the efficacy and safety of the dual GLP-GIP agonist tirzepatide for weight management in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide was associated with significant reductions in weight (average weight loss, 14-16 kg after 72 weeks) and glycemia (2.1% reduction in A1c after 72 weeks), as well as reductions in clinically meaningful cardiometabolic risk factors, including systolic blood pressure, liver enzymes, and fasting non–HDL cholesterol levels. The overall safety profile of tirzepatide was also reassuring and consistent with the GLP-1 class. Most adverse effects were gastrointestinal and of mild to moderate severity. These adverse effects decreased over time.
These results perfectly position tirzepatide for my younger patients like the young woman mentioned above. The significant improvements in weight, glycemia, and cardiometabolic risk factors will not only help mitigate her future cardiometabolic risk but also help the sustainability of the U.K.’s National Health System. The cost of diabetes to the NHS in the United Kingdom is more than 10% of the entire NHS budget for England and Wales. More than 80% of this cost, however, is related not to the medications and devices we prescribe for diabetes but to the downstream complications of diabetes, such as hospital admissions for cardiovascular events and amputations, as well as regular hospital attendance for dialysis for end-stage kidney disease.
There is no doubt, however, that modern obesity medications such as semaglutide and tirzepatide are expensive, and demand has been astronomical. This demand has been driven by private weight-management services and celebrity influencers, and has resulted in major U.K.-wide GLP-1 shortages.
This situation is tragically widening health inequalities, as many of my patients who have been on GLP-1 receptor agonists for many years are unable to obtain them. I am having to consider switching therapies, often to less efficacious options without the compelling cardiorenal benefits. Furthermore, the GLP-1 shortages have prevented GLP-1 initiation for my other high-risk younger patients, potentially increasing future cardiometabolic risk.
There remain unanswered questions for tirzepatide: What is the durability of effect of tirzepatide after 72 weeks (that is, the trial duration of SURMOUNT-2)? Crucially, what is the effect of withdrawal of tirzepatide on weight loss maintenance? Previous evidence has suggested weight regain after discontinuation of a GLP-1 receptor agonist for obesity. This, of course, has further financial and sustainability implications for health care systems such as the NHS.
Finally, we are increasingly seeing younger women of childbearing age with or at risk for cardiometabolic disease. Again, my patient above is one example. Many of the therapies we use for cardiometabolic disease management, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and tirzepatide, have not been studied, and hence have not been licensed in pregnant women. Therefore, frank discussions are required with patients about future family plans and the importance of contraception. Often, the significant weight loss seen with GLP-1 receptor agonists can improve hormonal profiles and fertility in women and result in unexpected pregnancies if robust contraception is not in place.
Tirzepatide has yet to be made commercially available in the United Kingdom, and its price has also yet to be set. But I already envision a clear role for tirzepatide in my treatment armamentarium. I will be positioning tirzepatide as my first injectable of choice after oral treatment escalation with metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor in all my patients who require treatment intensification – not just my younger, higher-risk individuals. This may remain an aspirational goal until supply chains and cost are defined. There is no doubt, however, that the compelling weight and glycemic benefits of tirzepatide alongside individualized lifestyle interventions can help improve the quality and quantity of life of my patients living with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Dr. Fernando is a general practitioner near Edinburgh. He reported receiving speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk..
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA statement addresses equity in cardio-oncology care
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association focuses on equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
A “growing body of evidence” suggests that women and people from underrepresented patient groups experience disproportionately higher cardiovascular effects from new and emerging anticancer therapies, the writing group, led by Daniel Addison, MD, with the Ohio State University, Columbus, pointed out.
For example, women appear to be at higher risk of immune checkpoint inhibitor–related toxicities, whereas Black patients with cancer face up to a threefold higher risk of cardiotoxicity with anticancer therapies.
With reduced screening and delayed preventive measures, Hispanic patients have more complex heart disease, cancer is diagnosed at later stages, and they receive more cardiotoxic regimens because of a lack of eligibility for novel treatments. Ultimately, this contributes to a higher incidence of treatment complications, cardiac dysfunction, and adverse patient outcomes for this patient group, they write.
Although no studies have specifically addressed cardio-oncology disparities in the LGBTQIA+ population, such disparities can be inferred from known cardiovascular disease and oncology disparities, the writing group noted.
These disparities are supported by “disparately high” risk of death after a cancer diagnosis among women and individuals from underrepresented groups, even after accounting for socioeconomic and behavioral patterns, they pointed out.
The scientific statement was published online in Circulation.
Evidence gaps and the path forward
“Despite advances in strategies to limit the risks of cardiovascular events among cancer survivors, relatively limited guidance is available to address the rapidly growing problem of disparate cardiotoxic risks among women and underrepresented patient populations,” the writing group said.
Decentralized and sporadic evaluations have led to a lack of consensus on the definitions, investigations, and potential optimal strategies to address disparate cardiotoxicity with contemporary cancer immunotherapy, as well as biologic and cytotoxic therapies, they noted.
They said caution is needed when interpreting clinical trial data about cardiotoxicity and in generalizing the results because people from diverse racial and ethnic groups have not been well represented in many trials.
The writing group outlined key evidence gaps and future research directions for addressing cardio-oncology disparities, as well as strategies to improve equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
These include the following:
- Identifying specific predictive factors of long-term cardiotoxic risk with targeted and immune-based cancer therapies in women and underrepresented populations.
- Investigating biological mechanisms that may underlie differences in cardiotoxicities between different patient groups.
- Developing personalized cardioprotection strategies that integrate biological, genetic, and social determinant markers.
- Intentionally diversifying clinical trials and identifying optimal strategies to improve representation in cancer clinical trials.
- Determining the role of technology, such as artificial intelligence, in improving cardiotoxicity disparities.
“Conscientiously leveraging technology and designing trials with outcomes related to these issues in practice (considering feasibility and cost) will critically accelerate the field of cardio-oncology in the 21st century. With tangible goals, we can improve health inequities in cardio-oncology,” the writing group said.
The research had no commercial funding. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association focuses on equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
A “growing body of evidence” suggests that women and people from underrepresented patient groups experience disproportionately higher cardiovascular effects from new and emerging anticancer therapies, the writing group, led by Daniel Addison, MD, with the Ohio State University, Columbus, pointed out.
For example, women appear to be at higher risk of immune checkpoint inhibitor–related toxicities, whereas Black patients with cancer face up to a threefold higher risk of cardiotoxicity with anticancer therapies.
With reduced screening and delayed preventive measures, Hispanic patients have more complex heart disease, cancer is diagnosed at later stages, and they receive more cardiotoxic regimens because of a lack of eligibility for novel treatments. Ultimately, this contributes to a higher incidence of treatment complications, cardiac dysfunction, and adverse patient outcomes for this patient group, they write.
Although no studies have specifically addressed cardio-oncology disparities in the LGBTQIA+ population, such disparities can be inferred from known cardiovascular disease and oncology disparities, the writing group noted.
These disparities are supported by “disparately high” risk of death after a cancer diagnosis among women and individuals from underrepresented groups, even after accounting for socioeconomic and behavioral patterns, they pointed out.
The scientific statement was published online in Circulation.
Evidence gaps and the path forward
“Despite advances in strategies to limit the risks of cardiovascular events among cancer survivors, relatively limited guidance is available to address the rapidly growing problem of disparate cardiotoxic risks among women and underrepresented patient populations,” the writing group said.
Decentralized and sporadic evaluations have led to a lack of consensus on the definitions, investigations, and potential optimal strategies to address disparate cardiotoxicity with contemporary cancer immunotherapy, as well as biologic and cytotoxic therapies, they noted.
They said caution is needed when interpreting clinical trial data about cardiotoxicity and in generalizing the results because people from diverse racial and ethnic groups have not been well represented in many trials.
The writing group outlined key evidence gaps and future research directions for addressing cardio-oncology disparities, as well as strategies to improve equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
These include the following:
- Identifying specific predictive factors of long-term cardiotoxic risk with targeted and immune-based cancer therapies in women and underrepresented populations.
- Investigating biological mechanisms that may underlie differences in cardiotoxicities between different patient groups.
- Developing personalized cardioprotection strategies that integrate biological, genetic, and social determinant markers.
- Intentionally diversifying clinical trials and identifying optimal strategies to improve representation in cancer clinical trials.
- Determining the role of technology, such as artificial intelligence, in improving cardiotoxicity disparities.
“Conscientiously leveraging technology and designing trials with outcomes related to these issues in practice (considering feasibility and cost) will critically accelerate the field of cardio-oncology in the 21st century. With tangible goals, we can improve health inequities in cardio-oncology,” the writing group said.
The research had no commercial funding. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association focuses on equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
A “growing body of evidence” suggests that women and people from underrepresented patient groups experience disproportionately higher cardiovascular effects from new and emerging anticancer therapies, the writing group, led by Daniel Addison, MD, with the Ohio State University, Columbus, pointed out.
For example, women appear to be at higher risk of immune checkpoint inhibitor–related toxicities, whereas Black patients with cancer face up to a threefold higher risk of cardiotoxicity with anticancer therapies.
With reduced screening and delayed preventive measures, Hispanic patients have more complex heart disease, cancer is diagnosed at later stages, and they receive more cardiotoxic regimens because of a lack of eligibility for novel treatments. Ultimately, this contributes to a higher incidence of treatment complications, cardiac dysfunction, and adverse patient outcomes for this patient group, they write.
Although no studies have specifically addressed cardio-oncology disparities in the LGBTQIA+ population, such disparities can be inferred from known cardiovascular disease and oncology disparities, the writing group noted.
These disparities are supported by “disparately high” risk of death after a cancer diagnosis among women and individuals from underrepresented groups, even after accounting for socioeconomic and behavioral patterns, they pointed out.
The scientific statement was published online in Circulation.
Evidence gaps and the path forward
“Despite advances in strategies to limit the risks of cardiovascular events among cancer survivors, relatively limited guidance is available to address the rapidly growing problem of disparate cardiotoxic risks among women and underrepresented patient populations,” the writing group said.
Decentralized and sporadic evaluations have led to a lack of consensus on the definitions, investigations, and potential optimal strategies to address disparate cardiotoxicity with contemporary cancer immunotherapy, as well as biologic and cytotoxic therapies, they noted.
They said caution is needed when interpreting clinical trial data about cardiotoxicity and in generalizing the results because people from diverse racial and ethnic groups have not been well represented in many trials.
The writing group outlined key evidence gaps and future research directions for addressing cardio-oncology disparities, as well as strategies to improve equity in cardio-oncology care and research.
These include the following:
- Identifying specific predictive factors of long-term cardiotoxic risk with targeted and immune-based cancer therapies in women and underrepresented populations.
- Investigating biological mechanisms that may underlie differences in cardiotoxicities between different patient groups.
- Developing personalized cardioprotection strategies that integrate biological, genetic, and social determinant markers.
- Intentionally diversifying clinical trials and identifying optimal strategies to improve representation in cancer clinical trials.
- Determining the role of technology, such as artificial intelligence, in improving cardiotoxicity disparities.
“Conscientiously leveraging technology and designing trials with outcomes related to these issues in practice (considering feasibility and cost) will critically accelerate the field of cardio-oncology in the 21st century. With tangible goals, we can improve health inequities in cardio-oncology,” the writing group said.
The research had no commercial funding. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
CGM alarm fatigue in youth?
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Indefinite anticoagulation likely not cost effective after unprovoked VTE
Continuing anticoagulation indefinitely in patients with a first unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) may have benefits for certain patients but is unlikely to be cost effective, say authors of a new study.
Continued anticoagulation for such patients “has little chance of improving life expectancy but might provide a mortality benefit in certain subgroups including patients with an initial PE (pulmonary embolism) or those at a very low risk for major bleeding,” wrote the authors, led by Faizan Khan, PhD, with the O’Brien Institute for Public Health, University of Calgary (Alta.).
Therefore, shared decision-making between patients with unprovoked VTE and physicians that includes discussion of preferences and values and use of validated prediction tools is important.
The authors noted that some patients might value avoiding morbidities of recurrent VTE the most and want to have lifelong anticoagulation. Some might be more fearful of major bleeding than VTE repercussions or don’t want the inconveniences of taking anticoagulants for a lifetime.
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Current guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation
Clinical practice guidelines now recommend indefinite anticoagulation for a first unprovoked VTE.
The authors did a modeling study in a hypothetical cohort of 1,000 patients aged 55 years with a first unprovoked VTE who had completed 3-6 months of initial anticoagulation. The study found indefinite anticoagulation, compared with discontinuing anticoagulation, on average, resulted in 368 fewer recurrent VTE events and 14 fewer fatal PE events.
At the same time, indefinite coagulation in the hypothetical group induced an additional 114 major bleeding events, 30 intracerebral hemorrhages, and 11 fatal bleeding events over 40 years.
As for cost effectiveness, from the perspective of Canada’s health care system, continuing anticoagulation indefinitely, on average, increased costs by $16,014 Canadian dollars per person ($12,140 USD) without improving quality-adjusted life-years (incremental difference, 0.075 per person; 95% uncertainty interval, –0.192 to 0.017).
The authors noted that cost is a prime consideration as the estimated annual health care costs of VTE and its complications is $600 Canadian dollars ($7 billion–$10 billion USD).
High probability of small benefit
The authors spelled out the small benefit in patients with an initial PE.
According to the study, indefinite anticoagulation would result in an 80% probability of a marginal added clinical benefit (average increase of 57 days of perfect health over a lifetime) in patients with an initial PE (but with only a 24% chance of being cost effective).
“This high probability of an additional clinical benefit is plausible due to the higher proportion of recurrent VTE events presenting as PE (approximately 70% of episodes) in patients initially presenting with PE, in turn, resulting in a two- to threefold higher case-fatality rate of recurrent VTE in this patient subgroup.”
Tools to estimate bleeding risk imprecise
Scott Woller, MD, an internal medicine specialist and chair of medicine at Intermountain Medical Center, Murray, Utah, said in an interview that these results should help physicians’ discuss with their patients about duration of anticoagulation after the treatment phase.
He noted that the authors suggest that a low estimated annual risk for major bleeding should be assumed (< 0.67%) to make the choice for indefinite anticoagulation.
“This is a sticky wicket,” he said, “as tools to estimate bleeding risk among VTE patients are presently imprecise. For these reasons PCPs should take into account patient risk estimates – and the limitations that exist surrounding how we calculate these estimates – in addition to their values and preferences. This is really key in electing duration of anticoagulation.”
A limitation of the study is that the model assumed that risks for recurrent VTE and major bleeding in clinical trials at 1 year remained constant during extended anticoagulation.
Dr. Woller said about that limitation: “One might argue that this is unlikely; age is a risk factor for major bleeding and therefore risks may be underestimated. However, in the ‘real world’ those that are perceived at lowest risk and demonstrate good tolerance to anticoagulation might likely preferentially continue anticoagulants and therefore risks may be overestimated.”
One coauthor reported being a clinical investigator for trials sponsored by Pfizer and Bristol-Myers Squibb and receiving honoraria from Pfizer, Sanofi and Aspen Pharma. The other authors disclosed no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. Woller is cochair of the CHEST guidelines on the treatment of venous thromboembolic disease.
Continuing anticoagulation indefinitely in patients with a first unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) may have benefits for certain patients but is unlikely to be cost effective, say authors of a new study.
Continued anticoagulation for such patients “has little chance of improving life expectancy but might provide a mortality benefit in certain subgroups including patients with an initial PE (pulmonary embolism) or those at a very low risk for major bleeding,” wrote the authors, led by Faizan Khan, PhD, with the O’Brien Institute for Public Health, University of Calgary (Alta.).
Therefore, shared decision-making between patients with unprovoked VTE and physicians that includes discussion of preferences and values and use of validated prediction tools is important.
The authors noted that some patients might value avoiding morbidities of recurrent VTE the most and want to have lifelong anticoagulation. Some might be more fearful of major bleeding than VTE repercussions or don’t want the inconveniences of taking anticoagulants for a lifetime.
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Current guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation
Clinical practice guidelines now recommend indefinite anticoagulation for a first unprovoked VTE.
The authors did a modeling study in a hypothetical cohort of 1,000 patients aged 55 years with a first unprovoked VTE who had completed 3-6 months of initial anticoagulation. The study found indefinite anticoagulation, compared with discontinuing anticoagulation, on average, resulted in 368 fewer recurrent VTE events and 14 fewer fatal PE events.
At the same time, indefinite coagulation in the hypothetical group induced an additional 114 major bleeding events, 30 intracerebral hemorrhages, and 11 fatal bleeding events over 40 years.
As for cost effectiveness, from the perspective of Canada’s health care system, continuing anticoagulation indefinitely, on average, increased costs by $16,014 Canadian dollars per person ($12,140 USD) without improving quality-adjusted life-years (incremental difference, 0.075 per person; 95% uncertainty interval, –0.192 to 0.017).
The authors noted that cost is a prime consideration as the estimated annual health care costs of VTE and its complications is $600 Canadian dollars ($7 billion–$10 billion USD).
High probability of small benefit
The authors spelled out the small benefit in patients with an initial PE.
According to the study, indefinite anticoagulation would result in an 80% probability of a marginal added clinical benefit (average increase of 57 days of perfect health over a lifetime) in patients with an initial PE (but with only a 24% chance of being cost effective).
“This high probability of an additional clinical benefit is plausible due to the higher proportion of recurrent VTE events presenting as PE (approximately 70% of episodes) in patients initially presenting with PE, in turn, resulting in a two- to threefold higher case-fatality rate of recurrent VTE in this patient subgroup.”
Tools to estimate bleeding risk imprecise
Scott Woller, MD, an internal medicine specialist and chair of medicine at Intermountain Medical Center, Murray, Utah, said in an interview that these results should help physicians’ discuss with their patients about duration of anticoagulation after the treatment phase.
He noted that the authors suggest that a low estimated annual risk for major bleeding should be assumed (< 0.67%) to make the choice for indefinite anticoagulation.
“This is a sticky wicket,” he said, “as tools to estimate bleeding risk among VTE patients are presently imprecise. For these reasons PCPs should take into account patient risk estimates – and the limitations that exist surrounding how we calculate these estimates – in addition to their values and preferences. This is really key in electing duration of anticoagulation.”
A limitation of the study is that the model assumed that risks for recurrent VTE and major bleeding in clinical trials at 1 year remained constant during extended anticoagulation.
Dr. Woller said about that limitation: “One might argue that this is unlikely; age is a risk factor for major bleeding and therefore risks may be underestimated. However, in the ‘real world’ those that are perceived at lowest risk and demonstrate good tolerance to anticoagulation might likely preferentially continue anticoagulants and therefore risks may be overestimated.”
One coauthor reported being a clinical investigator for trials sponsored by Pfizer and Bristol-Myers Squibb and receiving honoraria from Pfizer, Sanofi and Aspen Pharma. The other authors disclosed no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. Woller is cochair of the CHEST guidelines on the treatment of venous thromboembolic disease.
Continuing anticoagulation indefinitely in patients with a first unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) may have benefits for certain patients but is unlikely to be cost effective, say authors of a new study.
Continued anticoagulation for such patients “has little chance of improving life expectancy but might provide a mortality benefit in certain subgroups including patients with an initial PE (pulmonary embolism) or those at a very low risk for major bleeding,” wrote the authors, led by Faizan Khan, PhD, with the O’Brien Institute for Public Health, University of Calgary (Alta.).
Therefore, shared decision-making between patients with unprovoked VTE and physicians that includes discussion of preferences and values and use of validated prediction tools is important.
The authors noted that some patients might value avoiding morbidities of recurrent VTE the most and want to have lifelong anticoagulation. Some might be more fearful of major bleeding than VTE repercussions or don’t want the inconveniences of taking anticoagulants for a lifetime.
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Current guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation
Clinical practice guidelines now recommend indefinite anticoagulation for a first unprovoked VTE.
The authors did a modeling study in a hypothetical cohort of 1,000 patients aged 55 years with a first unprovoked VTE who had completed 3-6 months of initial anticoagulation. The study found indefinite anticoagulation, compared with discontinuing anticoagulation, on average, resulted in 368 fewer recurrent VTE events and 14 fewer fatal PE events.
At the same time, indefinite coagulation in the hypothetical group induced an additional 114 major bleeding events, 30 intracerebral hemorrhages, and 11 fatal bleeding events over 40 years.
As for cost effectiveness, from the perspective of Canada’s health care system, continuing anticoagulation indefinitely, on average, increased costs by $16,014 Canadian dollars per person ($12,140 USD) without improving quality-adjusted life-years (incremental difference, 0.075 per person; 95% uncertainty interval, –0.192 to 0.017).
The authors noted that cost is a prime consideration as the estimated annual health care costs of VTE and its complications is $600 Canadian dollars ($7 billion–$10 billion USD).
High probability of small benefit
The authors spelled out the small benefit in patients with an initial PE.
According to the study, indefinite anticoagulation would result in an 80% probability of a marginal added clinical benefit (average increase of 57 days of perfect health over a lifetime) in patients with an initial PE (but with only a 24% chance of being cost effective).
“This high probability of an additional clinical benefit is plausible due to the higher proportion of recurrent VTE events presenting as PE (approximately 70% of episodes) in patients initially presenting with PE, in turn, resulting in a two- to threefold higher case-fatality rate of recurrent VTE in this patient subgroup.”
Tools to estimate bleeding risk imprecise
Scott Woller, MD, an internal medicine specialist and chair of medicine at Intermountain Medical Center, Murray, Utah, said in an interview that these results should help physicians’ discuss with their patients about duration of anticoagulation after the treatment phase.
He noted that the authors suggest that a low estimated annual risk for major bleeding should be assumed (< 0.67%) to make the choice for indefinite anticoagulation.
“This is a sticky wicket,” he said, “as tools to estimate bleeding risk among VTE patients are presently imprecise. For these reasons PCPs should take into account patient risk estimates – and the limitations that exist surrounding how we calculate these estimates – in addition to their values and preferences. This is really key in electing duration of anticoagulation.”
A limitation of the study is that the model assumed that risks for recurrent VTE and major bleeding in clinical trials at 1 year remained constant during extended anticoagulation.
Dr. Woller said about that limitation: “One might argue that this is unlikely; age is a risk factor for major bleeding and therefore risks may be underestimated. However, in the ‘real world’ those that are perceived at lowest risk and demonstrate good tolerance to anticoagulation might likely preferentially continue anticoagulants and therefore risks may be overestimated.”
One coauthor reported being a clinical investigator for trials sponsored by Pfizer and Bristol-Myers Squibb and receiving honoraria from Pfizer, Sanofi and Aspen Pharma. The other authors disclosed no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. Woller is cochair of the CHEST guidelines on the treatment of venous thromboembolic disease.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE