User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
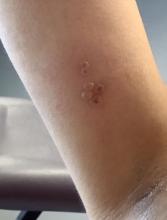
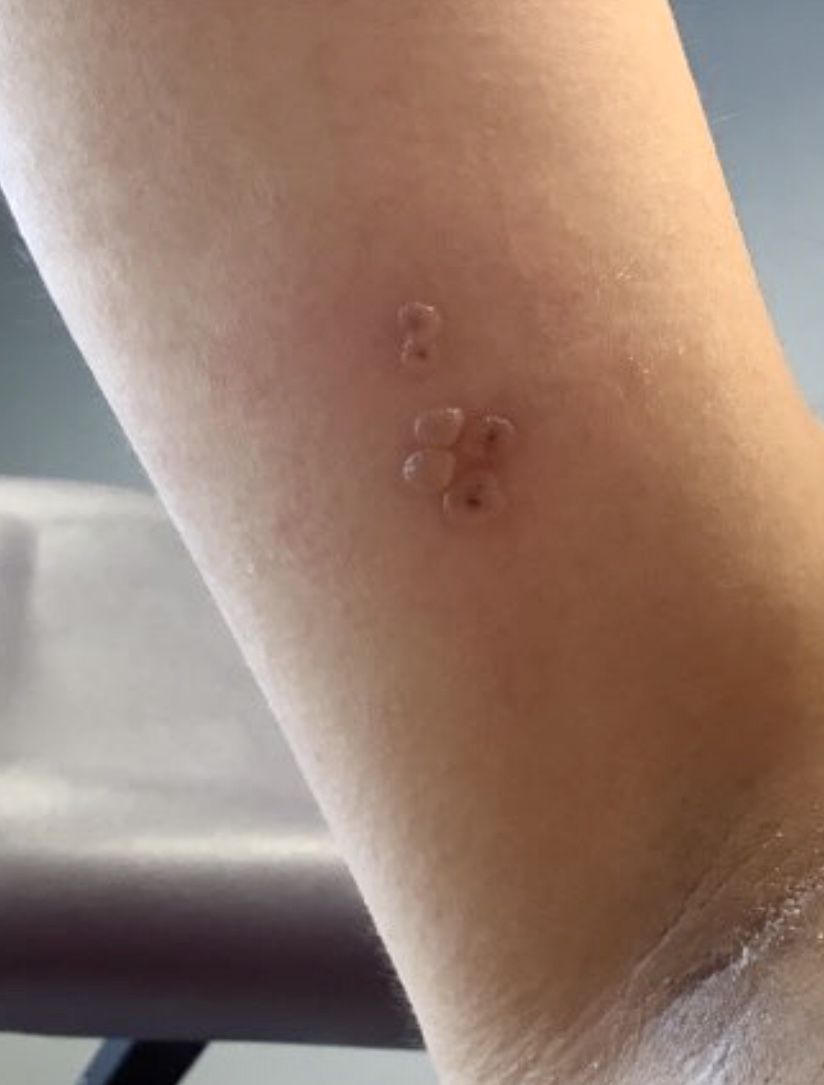
A healthy 36-year-old female presented with 4 days of itchy lesions on the right upper extremity
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Number of cancer survivors with functional limitations doubled in 20 years
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Cutaneous vasculitis curtails quality of life
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
IVIG shows no impact on VTE risk in dermatomyositis patients
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Can this tool forecast peanut allergies?
Pediatricians may have a new aid to better predict peanut allergies among infants with atopic dermatitis.
Their study of the implementation of the scorecard was presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Infants with atopic dermatitis or eczema are six times more likely to have an egg allergy and eleven times more likely to have a peanut allergy at age 12 months than are infants without atopic dermatitis.
The scorecard reflects recent directives from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to help combat the public health problem.
“When the NIAID prevention of peanut allergy guidelines first came out, it asked pediatricians to serve as frontline practitioners in implementing them by identifying children at risk for peanut allergy and guiding families on what to do next,” said Waheeda Samady, MD, professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The impetus for the study was to further support pediatricians in this role.”
Although pediatricians are trained to identify and even treat mild to moderate cases of atopic dermatitis, little emphasis has gone to categorizing the condition on the basis of severity and to correlating peanut allergy risk.
The predictive scorecard captures 14 images from one infant of mixed race, two White infants, two Black infants, and two Hispanic infants.
To create the card, two in-house pediatric dermatologists assessed 58 images from 13 children and categorized images from 0 (no signs of atopic dermatitis) to 4 (severe signs of atopic dermatitis). After a first pass on categorization, the doctors agreed on 84% of images.
Of 189 pediatricians who used the card, fewer than half reported that they “sometimes,” “very often,” or “always” used the scorecard for atopic dermatitis evaluation. A little fewer than three-quarters reported that their ability to diagnose and categorize atopic dermatitis improved.
“Severity staging of atopic dermatitis is not something that the general pediatrician necessarily performs on a day-to-day basis,” said Kawaljit Brar, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital in New York.
Dr. Brar explained that children who are identified as being at high risk are often referred to specialists such as her, who then perform allergy screenings and can determine whether introduction of food at home is safe or whether office feedings supervised by an allergist are necessary. Researchers have found that early introduction to peanuts for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis could prevent peanut allergy.
“This represents a wonderful initiative to educate pediatricians so that they understand which patients require screening for peanut allergy and which patients don’t and can just get introduced to peanuts at home,” Dr. Brar said.
The atopic dermatitis scorecard reflects a growing recognition that varying skin tones show levels of severity incongruously.
“Many of us in clinical practice have recognized that our education has not always been inclusive of patients with varying skin tones,” Dr. Samady said. “When we looked for photos of patients with different skin tones, we simply could not find any that we thought were appropriate. So we decided to take some ourselves, and we’re currently continuing to take photos in order to improve the scorecard we currently have.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Health and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Samady and Dr. Brar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatricians may have a new aid to better predict peanut allergies among infants with atopic dermatitis.
Their study of the implementation of the scorecard was presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Infants with atopic dermatitis or eczema are six times more likely to have an egg allergy and eleven times more likely to have a peanut allergy at age 12 months than are infants without atopic dermatitis.
The scorecard reflects recent directives from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to help combat the public health problem.
“When the NIAID prevention of peanut allergy guidelines first came out, it asked pediatricians to serve as frontline practitioners in implementing them by identifying children at risk for peanut allergy and guiding families on what to do next,” said Waheeda Samady, MD, professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The impetus for the study was to further support pediatricians in this role.”
Although pediatricians are trained to identify and even treat mild to moderate cases of atopic dermatitis, little emphasis has gone to categorizing the condition on the basis of severity and to correlating peanut allergy risk.
The predictive scorecard captures 14 images from one infant of mixed race, two White infants, two Black infants, and two Hispanic infants.
To create the card, two in-house pediatric dermatologists assessed 58 images from 13 children and categorized images from 0 (no signs of atopic dermatitis) to 4 (severe signs of atopic dermatitis). After a first pass on categorization, the doctors agreed on 84% of images.
Of 189 pediatricians who used the card, fewer than half reported that they “sometimes,” “very often,” or “always” used the scorecard for atopic dermatitis evaluation. A little fewer than three-quarters reported that their ability to diagnose and categorize atopic dermatitis improved.
“Severity staging of atopic dermatitis is not something that the general pediatrician necessarily performs on a day-to-day basis,” said Kawaljit Brar, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital in New York.
Dr. Brar explained that children who are identified as being at high risk are often referred to specialists such as her, who then perform allergy screenings and can determine whether introduction of food at home is safe or whether office feedings supervised by an allergist are necessary. Researchers have found that early introduction to peanuts for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis could prevent peanut allergy.
“This represents a wonderful initiative to educate pediatricians so that they understand which patients require screening for peanut allergy and which patients don’t and can just get introduced to peanuts at home,” Dr. Brar said.
The atopic dermatitis scorecard reflects a growing recognition that varying skin tones show levels of severity incongruously.
“Many of us in clinical practice have recognized that our education has not always been inclusive of patients with varying skin tones,” Dr. Samady said. “When we looked for photos of patients with different skin tones, we simply could not find any that we thought were appropriate. So we decided to take some ourselves, and we’re currently continuing to take photos in order to improve the scorecard we currently have.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Health and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Samady and Dr. Brar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatricians may have a new aid to better predict peanut allergies among infants with atopic dermatitis.
Their study of the implementation of the scorecard was presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Infants with atopic dermatitis or eczema are six times more likely to have an egg allergy and eleven times more likely to have a peanut allergy at age 12 months than are infants without atopic dermatitis.
The scorecard reflects recent directives from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to help combat the public health problem.
“When the NIAID prevention of peanut allergy guidelines first came out, it asked pediatricians to serve as frontline practitioners in implementing them by identifying children at risk for peanut allergy and guiding families on what to do next,” said Waheeda Samady, MD, professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The impetus for the study was to further support pediatricians in this role.”
Although pediatricians are trained to identify and even treat mild to moderate cases of atopic dermatitis, little emphasis has gone to categorizing the condition on the basis of severity and to correlating peanut allergy risk.
The predictive scorecard captures 14 images from one infant of mixed race, two White infants, two Black infants, and two Hispanic infants.
To create the card, two in-house pediatric dermatologists assessed 58 images from 13 children and categorized images from 0 (no signs of atopic dermatitis) to 4 (severe signs of atopic dermatitis). After a first pass on categorization, the doctors agreed on 84% of images.
Of 189 pediatricians who used the card, fewer than half reported that they “sometimes,” “very often,” or “always” used the scorecard for atopic dermatitis evaluation. A little fewer than three-quarters reported that their ability to diagnose and categorize atopic dermatitis improved.
“Severity staging of atopic dermatitis is not something that the general pediatrician necessarily performs on a day-to-day basis,” said Kawaljit Brar, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital in New York.
Dr. Brar explained that children who are identified as being at high risk are often referred to specialists such as her, who then perform allergy screenings and can determine whether introduction of food at home is safe or whether office feedings supervised by an allergist are necessary. Researchers have found that early introduction to peanuts for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis could prevent peanut allergy.
“This represents a wonderful initiative to educate pediatricians so that they understand which patients require screening for peanut allergy and which patients don’t and can just get introduced to peanuts at home,” Dr. Brar said.
The atopic dermatitis scorecard reflects a growing recognition that varying skin tones show levels of severity incongruously.
“Many of us in clinical practice have recognized that our education has not always been inclusive of patients with varying skin tones,” Dr. Samady said. “When we looked for photos of patients with different skin tones, we simply could not find any that we thought were appropriate. So we decided to take some ourselves, and we’re currently continuing to take photos in order to improve the scorecard we currently have.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Health and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Samady and Dr. Brar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PAS 2023
Medical students gain momentum in effort to ban legacy admissions
, which they say offer preferential treatment to applicants based on their association with donors or alumni.
While an estimated 25% of public colleges and universities still use legacy admissions, a growing list of top medical schools have moved away from the practice over the last decade, including Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and Tufts University, Medford, Mass.
Legacy admissions contradict schools’ more inclusive policies, Senila Yasmin, MPH, a second-year medical student at Tufts University, said in an interview. While Tufts maintains legacy admissions for its undergraduate applicants, the medical school stopped the practice in 2021, said Ms. Yasmin, a member of a student group that lobbied against the school’s legacy preferences.
Describing herself as a low-income, first-generation Muslim-Pakistani American, Ms. Yasmin wants to use her experience at Tufts to improve accessibility for students like herself.
As a member of the American Medical Association (AMA) Medical Student Section, she coauthored a resolution stating that legacy admissions go against the AMA’s strategic plan to advance racial justice and health equity. The Student Section passed the resolution in November, and in June, the AMA House of Delegates will vote on whether to adopt the policy.
Along with a Supreme Court decision that could strike down race-conscious college admissions, an AMA policy could convince medical schools to rethink legacy admissions and how to maintain diverse student bodies. In June, the court is expected to issue a decision in the Students for Fair Admissions lawsuit against Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., and the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, which alleges that considering race in holistic admissions constitutes racial discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Opponents of legacy admissions, like Ms. Yasmin, say it penalizes students from racial minorities and lower socioeconomic backgrounds, hampering a fair and equitable admissions process that attracts diverse medical school admissions.
Diversity of medical applicants
Diversity in medical schools continued to increase last year with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling, according to a recent report by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). However, universities often include nonacademic criteria in their admission assessments to improve educational access for underrepresented minorities.
Medical schools carefully consider each applicant’s background “to yield a diverse class of students,” Geoffrey Young, PhD, AAMC’s senior director of transforming the health care workforce, told this news organization.
Some schools, such as Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, perform a thorough review of candidates while offering admissions practices designed specifically for legacy applicants. The schools assert that legacy designation doesn’t factor into the student’s likelihood of acceptance.
The arrangement may show that schools want to commit to equity and fairness but have trouble moving away from entrenched traditions, two professors from Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pa., who sit on separate medical admissions subcommittees, wrote last year in Bioethics Today.
Legislation may hasten legacies’ end
In December, Ms. Yasmin and a group of Massachusetts Medical Society student-members presented another resolution to the state medical society, which adopted it.
The society’s new policy opposes the use of legacy status in medical school admissions and supports mechanisms to eliminate its inclusion from the application process, Theodore Calianos II, MD, FACS, president of the Massachusetts Medical Society, said in an interview.
“Legacy preferences limit racial and socioeconomic diversity on campuses, so we asked, ‘What can we do so that everyone has equal access to medical education?’ It is exciting to see the students and young physicians – the future of medicine – become involved in policymaking.”
Proposed laws may also hasten the end of legacy admissions. Last year, the U.S. Senate began considering a bill prohibiting colleges receiving federal financial aid from giving preferential treatment to students based on their relations to donors or alumni. However, the bill allows the Department of Education to make exceptions for institutions serving historically underrepresented groups.
The New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly also are reviewing bills that ban legacy and early admissions policies at public and private universities. Connecticut announced similar legislation last year. Massachusetts legislators are considering two bills: one that would ban the practice at the state’s public universities and another that would require all schools using legacy status to pay a “public service fee” equal to a percentage of its endowment. Colleges with endowment assets exceeding $2 billion must pay at least $2 million, according to the bill’s text.
At schools like Harvard, whose endowment surpasses $50 billion, the option to pay the penalty will make the law moot, Michael Walls, DO, MPH, president of the American Medical Student Association (AMSA), said in an interview. “Smaller schools wouldn’t be able to afford the fine and are less likely to be doing [legacy admissions] anyway,” he said. “The schools that want to continue doing it could just pay the fine.”
Dr. Walls said AMSA supports race-conscious admissions processes and anything that increases fairness for medical school applicants. “Whatever [fair] means is up for interpretation, but it would be great to eliminate legacy admissions,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, which they say offer preferential treatment to applicants based on their association with donors or alumni.
While an estimated 25% of public colleges and universities still use legacy admissions, a growing list of top medical schools have moved away from the practice over the last decade, including Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and Tufts University, Medford, Mass.
Legacy admissions contradict schools’ more inclusive policies, Senila Yasmin, MPH, a second-year medical student at Tufts University, said in an interview. While Tufts maintains legacy admissions for its undergraduate applicants, the medical school stopped the practice in 2021, said Ms. Yasmin, a member of a student group that lobbied against the school’s legacy preferences.
Describing herself as a low-income, first-generation Muslim-Pakistani American, Ms. Yasmin wants to use her experience at Tufts to improve accessibility for students like herself.
As a member of the American Medical Association (AMA) Medical Student Section, she coauthored a resolution stating that legacy admissions go against the AMA’s strategic plan to advance racial justice and health equity. The Student Section passed the resolution in November, and in June, the AMA House of Delegates will vote on whether to adopt the policy.
Along with a Supreme Court decision that could strike down race-conscious college admissions, an AMA policy could convince medical schools to rethink legacy admissions and how to maintain diverse student bodies. In June, the court is expected to issue a decision in the Students for Fair Admissions lawsuit against Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., and the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, which alleges that considering race in holistic admissions constitutes racial discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Opponents of legacy admissions, like Ms. Yasmin, say it penalizes students from racial minorities and lower socioeconomic backgrounds, hampering a fair and equitable admissions process that attracts diverse medical school admissions.
Diversity of medical applicants
Diversity in medical schools continued to increase last year with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling, according to a recent report by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). However, universities often include nonacademic criteria in their admission assessments to improve educational access for underrepresented minorities.
Medical schools carefully consider each applicant’s background “to yield a diverse class of students,” Geoffrey Young, PhD, AAMC’s senior director of transforming the health care workforce, told this news organization.
Some schools, such as Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, perform a thorough review of candidates while offering admissions practices designed specifically for legacy applicants. The schools assert that legacy designation doesn’t factor into the student’s likelihood of acceptance.
The arrangement may show that schools want to commit to equity and fairness but have trouble moving away from entrenched traditions, two professors from Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pa., who sit on separate medical admissions subcommittees, wrote last year in Bioethics Today.
Legislation may hasten legacies’ end
In December, Ms. Yasmin and a group of Massachusetts Medical Society student-members presented another resolution to the state medical society, which adopted it.
The society’s new policy opposes the use of legacy status in medical school admissions and supports mechanisms to eliminate its inclusion from the application process, Theodore Calianos II, MD, FACS, president of the Massachusetts Medical Society, said in an interview.
“Legacy preferences limit racial and socioeconomic diversity on campuses, so we asked, ‘What can we do so that everyone has equal access to medical education?’ It is exciting to see the students and young physicians – the future of medicine – become involved in policymaking.”
Proposed laws may also hasten the end of legacy admissions. Last year, the U.S. Senate began considering a bill prohibiting colleges receiving federal financial aid from giving preferential treatment to students based on their relations to donors or alumni. However, the bill allows the Department of Education to make exceptions for institutions serving historically underrepresented groups.
The New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly also are reviewing bills that ban legacy and early admissions policies at public and private universities. Connecticut announced similar legislation last year. Massachusetts legislators are considering two bills: one that would ban the practice at the state’s public universities and another that would require all schools using legacy status to pay a “public service fee” equal to a percentage of its endowment. Colleges with endowment assets exceeding $2 billion must pay at least $2 million, according to the bill’s text.
At schools like Harvard, whose endowment surpasses $50 billion, the option to pay the penalty will make the law moot, Michael Walls, DO, MPH, president of the American Medical Student Association (AMSA), said in an interview. “Smaller schools wouldn’t be able to afford the fine and are less likely to be doing [legacy admissions] anyway,” he said. “The schools that want to continue doing it could just pay the fine.”
Dr. Walls said AMSA supports race-conscious admissions processes and anything that increases fairness for medical school applicants. “Whatever [fair] means is up for interpretation, but it would be great to eliminate legacy admissions,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, which they say offer preferential treatment to applicants based on their association with donors or alumni.
While an estimated 25% of public colleges and universities still use legacy admissions, a growing list of top medical schools have moved away from the practice over the last decade, including Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and Tufts University, Medford, Mass.
Legacy admissions contradict schools’ more inclusive policies, Senila Yasmin, MPH, a second-year medical student at Tufts University, said in an interview. While Tufts maintains legacy admissions for its undergraduate applicants, the medical school stopped the practice in 2021, said Ms. Yasmin, a member of a student group that lobbied against the school’s legacy preferences.
Describing herself as a low-income, first-generation Muslim-Pakistani American, Ms. Yasmin wants to use her experience at Tufts to improve accessibility for students like herself.
As a member of the American Medical Association (AMA) Medical Student Section, she coauthored a resolution stating that legacy admissions go against the AMA’s strategic plan to advance racial justice and health equity. The Student Section passed the resolution in November, and in June, the AMA House of Delegates will vote on whether to adopt the policy.
Along with a Supreme Court decision that could strike down race-conscious college admissions, an AMA policy could convince medical schools to rethink legacy admissions and how to maintain diverse student bodies. In June, the court is expected to issue a decision in the Students for Fair Admissions lawsuit against Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., and the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, which alleges that considering race in holistic admissions constitutes racial discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Opponents of legacy admissions, like Ms. Yasmin, say it penalizes students from racial minorities and lower socioeconomic backgrounds, hampering a fair and equitable admissions process that attracts diverse medical school admissions.
Diversity of medical applicants
Diversity in medical schools continued to increase last year with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling, according to a recent report by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). However, universities often include nonacademic criteria in their admission assessments to improve educational access for underrepresented minorities.
Medical schools carefully consider each applicant’s background “to yield a diverse class of students,” Geoffrey Young, PhD, AAMC’s senior director of transforming the health care workforce, told this news organization.
Some schools, such as Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, perform a thorough review of candidates while offering admissions practices designed specifically for legacy applicants. The schools assert that legacy designation doesn’t factor into the student’s likelihood of acceptance.
The arrangement may show that schools want to commit to equity and fairness but have trouble moving away from entrenched traditions, two professors from Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pa., who sit on separate medical admissions subcommittees, wrote last year in Bioethics Today.
Legislation may hasten legacies’ end
In December, Ms. Yasmin and a group of Massachusetts Medical Society student-members presented another resolution to the state medical society, which adopted it.
The society’s new policy opposes the use of legacy status in medical school admissions and supports mechanisms to eliminate its inclusion from the application process, Theodore Calianos II, MD, FACS, president of the Massachusetts Medical Society, said in an interview.
“Legacy preferences limit racial and socioeconomic diversity on campuses, so we asked, ‘What can we do so that everyone has equal access to medical education?’ It is exciting to see the students and young physicians – the future of medicine – become involved in policymaking.”
Proposed laws may also hasten the end of legacy admissions. Last year, the U.S. Senate began considering a bill prohibiting colleges receiving federal financial aid from giving preferential treatment to students based on their relations to donors or alumni. However, the bill allows the Department of Education to make exceptions for institutions serving historically underrepresented groups.
The New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly also are reviewing bills that ban legacy and early admissions policies at public and private universities. Connecticut announced similar legislation last year. Massachusetts legislators are considering two bills: one that would ban the practice at the state’s public universities and another that would require all schools using legacy status to pay a “public service fee” equal to a percentage of its endowment. Colleges with endowment assets exceeding $2 billion must pay at least $2 million, according to the bill’s text.
At schools like Harvard, whose endowment surpasses $50 billion, the option to pay the penalty will make the law moot, Michael Walls, DO, MPH, president of the American Medical Student Association (AMSA), said in an interview. “Smaller schools wouldn’t be able to afford the fine and are less likely to be doing [legacy admissions] anyway,” he said. “The schools that want to continue doing it could just pay the fine.”
Dr. Walls said AMSA supports race-conscious admissions processes and anything that increases fairness for medical school applicants. “Whatever [fair] means is up for interpretation, but it would be great to eliminate legacy admissions,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Picosecond laser applications continue to expand
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
FROM ASLMS 2023
Five ways docs may qualify for discounts on medical malpractice premiums
Getting a better deal might simply mean taking advantage of incentives and discounts your insurer may already offer. These include claims-free, new-to-practice, and working part-time discounts.
However, if you decide to shop around, keep in mind that discounts are just one factor that can affect your premium price – insurers look at your specialty, location, and claims history.
One of the most common ways physicians can earn discounts is by participating in risk management programs. With this type of program, physicians evaluate elements of their practice and documentation practices and identify areas that might leave them at risk for a lawsuit. While they save money, physician risk management programs also are designed to reduce malpractice claims, which ultimately minimizes the potential for bigger financial losses, insurance experts say.
“It’s a win-win situation when liability insurers and physicians work together to minimize risk, and it’s a win for patients,” said Gary Price, MD, president of The Physicians Foundation.
Doctors in private practice or employed by small hospitals that are not self-insured can qualify for these discounts, said David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants.
“I do a lot of work with medical malpractice companies trying to find clients policies. All the carriers are transparent about what physicians have to do to lower their premiums. Physicians can receive the discounts if they follow through and meet the insurer’s requirements,” said Mr. Zetter.
State insurance departments regulate medical malpractice insurance, including the premium credits insurers offer. Most states cap discounts at 25%, but some go as high as 70%, according to The Doctors Company, a national physician-owned medical malpractice insurer.
Insurers typically offer doctors several ways to earn discounts. The size of the discount also can depend on whether a doctor is new to a practice, remains claims free, or takes risk management courses.
In addition to the premium discount, some online risk management classes and webinars are eligible for CME credits.
“The credits can add up and they can be used for recertification or relicensure,” said Susan Boisvert, senior patient safety risk manager at The Doctors Company.
Here are five ways you may qualify for discounts with your insurer.
1. Make use of discounts available to new doctors
Doctors can earn hefty discounts on their premiums when they are no longer interns or residents and start practicing medicine. The Doctors Company usually gives a 50% discount on member premiums the first year they’re in practice and a 25% discount credit in their second year. The discounts end after that.
Other insurance carriers offer similar discounts to doctors starting to practice medicine. The deepest one is offered in the first year (at least 50%) and a smaller one (20%-25%) the second year, according to medical malpractice brokers.
“The new-to-practice discount is based solely on when the physician left their formal training to begin their practice for the first time; it is not based on claim-free history,” explained Mr. Zetter.
This is a very common discount used by different insurer carriers, said Dr. Price. “New physicians don’t have the same amount of risk of a lawsuit when they’re starting out. It’s unlikely they will have a claim and most liability actions have a 2-year time limit from the date of injury to be filed.”
2. Take advantage of being claims free
If you’ve been claims free for at least a few years, you may be eligible for a large discount.
“Doctors without claims are a better risk. Once a doctor has one claim, they’re likely to have a second, which the research shows,” said Mr. Zetter.
The most common credit The Doctors Company offers is 3 years of being claim free – this earns doctors up to 25%, he said. Mr. Zetter explained that the criteria and size of The Doctors Company credit may depend on the state where physicians practice.
“We allowed insurance carriers that we acquired to continue with their own claim-free discount program such as Florida’s First Professionals Insurance Company we acquired in 2011,” he said.
Doctors with other medical malpractice insurers may also be eligible for a credit up to 25%. In some instances, they may have to be claims free for 5 or 10 years, say insurance experts.
It pays to shop around before purchasing insurance.
3. If you work part time, make sure your premium reflects that
Physicians who see patients part time can receive up to a 75% discount on their medical liability insurance premiums.
The discounts are based on the hours the physician works per week. The fewer hours worked, the larger the discount. This type of discount does not vary by specialty.
According to The Doctors Company, working 10 hours or less per week may entitle doctors to a 75% discount; working 11-20 hours per week may entitle them to a 50% discount, and working 21-30 hours per week may entitle them to a 25% discount. If you are in this situation, it pays to ask your insurer if there is a discount available to you.
4. Look into your professional medical society insurance company
“I would look at your state medical association [or] state specialty society and talk to your colleagues to learn what premiums they’re paying and about any discounts they’re getting,” advised Mr. Zetter.
Some state medical societies have formed their own liability companies and offer lower premiums to their members because “they’re organized and managed by doctors, which makes their premiums more competitive,” Dr. Price said.
Other state medical societies endorse specific insurance carriers and offer their members a 5% discount for enrolling with them.
5. Enroll in a risk management program
Most insurers offer online educational activities designed to improve patient safety and reduce the risk of a lawsuit. Physicians may be eligible for both premium discounts and CME credits.
Medical Liability Mutual Insurance Company, owned by Berkshire Hathaway, operates in New York and offers physicians a premium discount of up to 5%, CME credit, and maintenance of certification credit for successfully completing its risk management program every other year.
ProAssurance members nationwide can earn 5% in premium discounts if they complete a 2-hour video series called “Back to Basics: Loss Prevention and Navigating Everyday Risks: Using Data to Drive Change.”
They can earn one credit for completing each webinar on topics such as “Medication Management: Minimizing Errors and Improving Safety” and “Opioid Prescribing: Keeping Patients Safe.”
MagMutual offers its insured physicians 1 CME credit for completing their specialty’s risk assessment and courses, which may be applied toward their premium discounts.
The Doctors Company offers its members a 5% premium discount if they complete 4 CME credits. One of its most popular courses is “How To Get Rid of a Difficult Patient.”
“Busy residents like the shorter case studies worth one-quarter credit that they can complete in 15 minutes,” said Ms. Boisvert.
“This is a good bargain from the physician’s standpoint and the fact that risk management education is offered online makes it a lot easier than going to a seminar in person,” said Dr. Price.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Getting a better deal might simply mean taking advantage of incentives and discounts your insurer may already offer. These include claims-free, new-to-practice, and working part-time discounts.
However, if you decide to shop around, keep in mind that discounts are just one factor that can affect your premium price – insurers look at your specialty, location, and claims history.
One of the most common ways physicians can earn discounts is by participating in risk management programs. With this type of program, physicians evaluate elements of their practice and documentation practices and identify areas that might leave them at risk for a lawsuit. While they save money, physician risk management programs also are designed to reduce malpractice claims, which ultimately minimizes the potential for bigger financial losses, insurance experts say.
“It’s a win-win situation when liability insurers and physicians work together to minimize risk, and it’s a win for patients,” said Gary Price, MD, president of The Physicians Foundation.
Doctors in private practice or employed by small hospitals that are not self-insured can qualify for these discounts, said David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants.
“I do a lot of work with medical malpractice companies trying to find clients policies. All the carriers are transparent about what physicians have to do to lower their premiums. Physicians can receive the discounts if they follow through and meet the insurer’s requirements,” said Mr. Zetter.
State insurance departments regulate medical malpractice insurance, including the premium credits insurers offer. Most states cap discounts at 25%, but some go as high as 70%, according to The Doctors Company, a national physician-owned medical malpractice insurer.
Insurers typically offer doctors several ways to earn discounts. The size of the discount also can depend on whether a doctor is new to a practice, remains claims free, or takes risk management courses.
In addition to the premium discount, some online risk management classes and webinars are eligible for CME credits.
“The credits can add up and they can be used for recertification or relicensure,” said Susan Boisvert, senior patient safety risk manager at The Doctors Company.
Here are five ways you may qualify for discounts with your insurer.
1. Make use of discounts available to new doctors
Doctors can earn hefty discounts on their premiums when they are no longer interns or residents and start practicing medicine. The Doctors Company usually gives a 50% discount on member premiums the first year they’re in practice and a 25% discount credit in their second year. The discounts end after that.
Other insurance carriers offer similar discounts to doctors starting to practice medicine. The deepest one is offered in the first year (at least 50%) and a smaller one (20%-25%) the second year, according to medical malpractice brokers.
“The new-to-practice discount is based solely on when the physician left their formal training to begin their practice for the first time; it is not based on claim-free history,” explained Mr. Zetter.
This is a very common discount used by different insurer carriers, said Dr. Price. “New physicians don’t have the same amount of risk of a lawsuit when they’re starting out. It’s unlikely they will have a claim and most liability actions have a 2-year time limit from the date of injury to be filed.”
2. Take advantage of being claims free
If you’ve been claims free for at least a few years, you may be eligible for a large discount.
“Doctors without claims are a better risk. Once a doctor has one claim, they’re likely to have a second, which the research shows,” said Mr. Zetter.
The most common credit The Doctors Company offers is 3 years of being claim free – this earns doctors up to 25%, he said. Mr. Zetter explained that the criteria and size of The Doctors Company credit may depend on the state where physicians practice.
“We allowed insurance carriers that we acquired to continue with their own claim-free discount program such as Florida’s First Professionals Insurance Company we acquired in 2011,” he said.
Doctors with other medical malpractice insurers may also be eligible for a credit up to 25%. In some instances, they may have to be claims free for 5 or 10 years, say insurance experts.
It pays to shop around before purchasing insurance.
3. If you work part time, make sure your premium reflects that
Physicians who see patients part time can receive up to a 75% discount on their medical liability insurance premiums.
The discounts are based on the hours the physician works per week. The fewer hours worked, the larger the discount. This type of discount does not vary by specialty.
According to The Doctors Company, working 10 hours or less per week may entitle doctors to a 75% discount; working 11-20 hours per week may entitle them to a 50% discount, and working 21-30 hours per week may entitle them to a 25% discount. If you are in this situation, it pays to ask your insurer if there is a discount available to you.
4. Look into your professional medical society insurance company
“I would look at your state medical association [or] state specialty society and talk to your colleagues to learn what premiums they’re paying and about any discounts they’re getting,” advised Mr. Zetter.
Some state medical societies have formed their own liability companies and offer lower premiums to their members because “they’re organized and managed by doctors, which makes their premiums more competitive,” Dr. Price said.
Other state medical societies endorse specific insurance carriers and offer their members a 5% discount for enrolling with them.
5. Enroll in a risk management program
Most insurers offer online educational activities designed to improve patient safety and reduce the risk of a lawsuit. Physicians may be eligible for both premium discounts and CME credits.
Medical Liability Mutual Insurance Company, owned by Berkshire Hathaway, operates in New York and offers physicians a premium discount of up to 5%, CME credit, and maintenance of certification credit for successfully completing its risk management program every other year.
ProAssurance members nationwide can earn 5% in premium discounts if they complete a 2-hour video series called “Back to Basics: Loss Prevention and Navigating Everyday Risks: Using Data to Drive Change.”
They can earn one credit for completing each webinar on topics such as “Medication Management: Minimizing Errors and Improving Safety” and “Opioid Prescribing: Keeping Patients Safe.”
MagMutual offers its insured physicians 1 CME credit for completing their specialty’s risk assessment and courses, which may be applied toward their premium discounts.
The Doctors Company offers its members a 5% premium discount if they complete 4 CME credits. One of its most popular courses is “How To Get Rid of a Difficult Patient.”
“Busy residents like the shorter case studies worth one-quarter credit that they can complete in 15 minutes,” said Ms. Boisvert.
“This is a good bargain from the physician’s standpoint and the fact that risk management education is offered online makes it a lot easier than going to a seminar in person,” said Dr. Price.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Getting a better deal might simply mean taking advantage of incentives and discounts your insurer may already offer. These include claims-free, new-to-practice, and working part-time discounts.
However, if you decide to shop around, keep in mind that discounts are just one factor that can affect your premium price – insurers look at your specialty, location, and claims history.
One of the most common ways physicians can earn discounts is by participating in risk management programs. With this type of program, physicians evaluate elements of their practice and documentation practices and identify areas that might leave them at risk for a lawsuit. While they save money, physician risk management programs also are designed to reduce malpractice claims, which ultimately minimizes the potential for bigger financial losses, insurance experts say.
“It’s a win-win situation when liability insurers and physicians work together to minimize risk, and it’s a win for patients,” said Gary Price, MD, president of The Physicians Foundation.
Doctors in private practice or employed by small hospitals that are not self-insured can qualify for these discounts, said David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants.
“I do a lot of work with medical malpractice companies trying to find clients policies. All the carriers are transparent about what physicians have to do to lower their premiums. Physicians can receive the discounts if they follow through and meet the insurer’s requirements,” said Mr. Zetter.
State insurance departments regulate medical malpractice insurance, including the premium credits insurers offer. Most states cap discounts at 25%, but some go as high as 70%, according to The Doctors Company, a national physician-owned medical malpractice insurer.
Insurers typically offer doctors several ways to earn discounts. The size of the discount also can depend on whether a doctor is new to a practice, remains claims free, or takes risk management courses.
In addition to the premium discount, some online risk management classes and webinars are eligible for CME credits.
“The credits can add up and they can be used for recertification or relicensure,” said Susan Boisvert, senior patient safety risk manager at The Doctors Company.
Here are five ways you may qualify for discounts with your insurer.
1. Make use of discounts available to new doctors
Doctors can earn hefty discounts on their premiums when they are no longer interns or residents and start practicing medicine. The Doctors Company usually gives a 50% discount on member premiums the first year they’re in practice and a 25% discount credit in their second year. The discounts end after that.
Other insurance carriers offer similar discounts to doctors starting to practice medicine. The deepest one is offered in the first year (at least 50%) and a smaller one (20%-25%) the second year, according to medical malpractice brokers.
“The new-to-practice discount is based solely on when the physician left their formal training to begin their practice for the first time; it is not based on claim-free history,” explained Mr. Zetter.
This is a very common discount used by different insurer carriers, said Dr. Price. “New physicians don’t have the same amount of risk of a lawsuit when they’re starting out. It’s unlikely they will have a claim and most liability actions have a 2-year time limit from the date of injury to be filed.”
2. Take advantage of being claims free
If you’ve been claims free for at least a few years, you may be eligible for a large discount.
“Doctors without claims are a better risk. Once a doctor has one claim, they’re likely to have a second, which the research shows,” said Mr. Zetter.
The most common credit The Doctors Company offers is 3 years of being claim free – this earns doctors up to 25%, he said. Mr. Zetter explained that the criteria and size of The Doctors Company credit may depend on the state where physicians practice.
“We allowed insurance carriers that we acquired to continue with their own claim-free discount program such as Florida’s First Professionals Insurance Company we acquired in 2011,” he said.
Doctors with other medical malpractice insurers may also be eligible for a credit up to 25%. In some instances, they may have to be claims free for 5 or 10 years, say insurance experts.
It pays to shop around before purchasing insurance.
3. If you work part time, make sure your premium reflects that
Physicians who see patients part time can receive up to a 75% discount on their medical liability insurance premiums.
The discounts are based on the hours the physician works per week. The fewer hours worked, the larger the discount. This type of discount does not vary by specialty.
According to The Doctors Company, working 10 hours or less per week may entitle doctors to a 75% discount; working 11-20 hours per week may entitle them to a 50% discount, and working 21-30 hours per week may entitle them to a 25% discount. If you are in this situation, it pays to ask your insurer if there is a discount available to you.
4. Look into your professional medical society insurance company
“I would look at your state medical association [or] state specialty society and talk to your colleagues to learn what premiums they’re paying and about any discounts they’re getting,” advised Mr. Zetter.
Some state medical societies have formed their own liability companies and offer lower premiums to their members because “they’re organized and managed by doctors, which makes their premiums more competitive,” Dr. Price said.
Other state medical societies endorse specific insurance carriers and offer their members a 5% discount for enrolling with them.
5. Enroll in a risk management program
Most insurers offer online educational activities designed to improve patient safety and reduce the risk of a lawsuit. Physicians may be eligible for both premium discounts and CME credits.
Medical Liability Mutual Insurance Company, owned by Berkshire Hathaway, operates in New York and offers physicians a premium discount of up to 5%, CME credit, and maintenance of certification credit for successfully completing its risk management program every other year.
ProAssurance members nationwide can earn 5% in premium discounts if they complete a 2-hour video series called “Back to Basics: Loss Prevention and Navigating Everyday Risks: Using Data to Drive Change.”
They can earn one credit for completing each webinar on topics such as “Medication Management: Minimizing Errors and Improving Safety” and “Opioid Prescribing: Keeping Patients Safe.”
MagMutual offers its insured physicians 1 CME credit for completing their specialty’s risk assessment and courses, which may be applied toward their premium discounts.
The Doctors Company offers its members a 5% premium discount if they complete 4 CME credits. One of its most popular courses is “How To Get Rid of a Difficult Patient.”
“Busy residents like the shorter case studies worth one-quarter credit that they can complete in 15 minutes,” said Ms. Boisvert.
“This is a good bargain from the physician’s standpoint and the fact that risk management education is offered online makes it a lot easier than going to a seminar in person,” said Dr. Price.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two phase 3 trials show benefits of dupilumab for prurigo nodularis
The results, which were published online in Nature Medicine, were the basis for the FDA approval of dupilumab (Dupixent) for adults with PN in September 2022, the first treatment approved for treating PN in the United States.
“These positive studies support the involvement of type 2 cytokines in driving PN disease pathogenesis and the targeting of the [interleukin]-4/IL-13 axis as a novel therapeutic paradigm for patients with PN,” wrote the researchers, who were led by principal investigator Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Fla. Dupilumab, an IL-4 receptor alpha antagonist, blocks the shared receptor component (IL-4R alpha) for IL-4 and IL-13.
For the two phase 3 trials, which were called LIBERTY-PN PRIME and PRIME2 and were sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, researchers randomized adults with PN with 20 or more nodules and severe itch uncontrolled with topical therapies 1:1 to 300 mg dupilumab or placebo subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was pruritus improvement, which was measured by the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater reduction in Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) from baseline at week 24 (PRIME) or week 12 (PRIME2). Key secondary endpoints included a reduction in the number of nodules to 5 or fewer at week 24.
PRIME and PRIME2 enrolled 151 and 160 patients, respectively. In PRIME, 60% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 24, compared with 18.4% of patients in the placebo arm (P < .001). In PRIME2, 37.2% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 12, compared with 22% of patients in the placebo arm (P = .022).
The researchers also reported that, from an initial baseline of 20 to greater than 100 nodules, 32.0% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 25.6% in PRIME2 showed a reduction to 5 nodules or fewer, which corresponded to a response of “clear” or “almost clear” skin at week 12, compared with 11.8% and 12.2% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. This treatment effect on skin lesions continued to improve after week 12, with 48% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 44.9% in PRIME2 having five nodules or fewer at week 24, compared with 18.4% and 15.9% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. Safety was consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile.
“Validation is the first success of this paper,” said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “While both the safety and efficacy of dupilumab in these two phase 3 programs is the meat of the matter, nuanced highlights for me include the rigid nature of the exclusion criteria to ensure a study population that truly has PN as a stand-alone disease, rather than a secondary finding as we once believed to be the entire story. I think it’s important for us to recognize that it’s not one or the other, rather there is both ‘primary’ prurigo nodularis, and then there is secondary prurigo nodularis associated with something else [a wide range of underlying medical conditions], just like we divide primary and secondary hyperhidrosis.”
Dr. Yosipovitch reported having competing interests with several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron and Sanofi. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant to and a speaker for Regeneron.
The results, which were published online in Nature Medicine, were the basis for the FDA approval of dupilumab (Dupixent) for adults with PN in September 2022, the first treatment approved for treating PN in the United States.
“These positive studies support the involvement of type 2 cytokines in driving PN disease pathogenesis and the targeting of the [interleukin]-4/IL-13 axis as a novel therapeutic paradigm for patients with PN,” wrote the researchers, who were led by principal investigator Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Fla. Dupilumab, an IL-4 receptor alpha antagonist, blocks the shared receptor component (IL-4R alpha) for IL-4 and IL-13.
For the two phase 3 trials, which were called LIBERTY-PN PRIME and PRIME2 and were sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, researchers randomized adults with PN with 20 or more nodules and severe itch uncontrolled with topical therapies 1:1 to 300 mg dupilumab or placebo subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was pruritus improvement, which was measured by the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater reduction in Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) from baseline at week 24 (PRIME) or week 12 (PRIME2). Key secondary endpoints included a reduction in the number of nodules to 5 or fewer at week 24.
PRIME and PRIME2 enrolled 151 and 160 patients, respectively. In PRIME, 60% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 24, compared with 18.4% of patients in the placebo arm (P < .001). In PRIME2, 37.2% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 12, compared with 22% of patients in the placebo arm (P = .022).
The researchers also reported that, from an initial baseline of 20 to greater than 100 nodules, 32.0% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 25.6% in PRIME2 showed a reduction to 5 nodules or fewer, which corresponded to a response of “clear” or “almost clear” skin at week 12, compared with 11.8% and 12.2% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. This treatment effect on skin lesions continued to improve after week 12, with 48% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 44.9% in PRIME2 having five nodules or fewer at week 24, compared with 18.4% and 15.9% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. Safety was consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile.
“Validation is the first success of this paper,” said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “While both the safety and efficacy of dupilumab in these two phase 3 programs is the meat of the matter, nuanced highlights for me include the rigid nature of the exclusion criteria to ensure a study population that truly has PN as a stand-alone disease, rather than a secondary finding as we once believed to be the entire story. I think it’s important for us to recognize that it’s not one or the other, rather there is both ‘primary’ prurigo nodularis, and then there is secondary prurigo nodularis associated with something else [a wide range of underlying medical conditions], just like we divide primary and secondary hyperhidrosis.”
Dr. Yosipovitch reported having competing interests with several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron and Sanofi. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant to and a speaker for Regeneron.
The results, which were published online in Nature Medicine, were the basis for the FDA approval of dupilumab (Dupixent) for adults with PN in September 2022, the first treatment approved for treating PN in the United States.
“These positive studies support the involvement of type 2 cytokines in driving PN disease pathogenesis and the targeting of the [interleukin]-4/IL-13 axis as a novel therapeutic paradigm for patients with PN,” wrote the researchers, who were led by principal investigator Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Fla. Dupilumab, an IL-4 receptor alpha antagonist, blocks the shared receptor component (IL-4R alpha) for IL-4 and IL-13.
For the two phase 3 trials, which were called LIBERTY-PN PRIME and PRIME2 and were sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, researchers randomized adults with PN with 20 or more nodules and severe itch uncontrolled with topical therapies 1:1 to 300 mg dupilumab or placebo subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was pruritus improvement, which was measured by the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater reduction in Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) from baseline at week 24 (PRIME) or week 12 (PRIME2). Key secondary endpoints included a reduction in the number of nodules to 5 or fewer at week 24.
PRIME and PRIME2 enrolled 151 and 160 patients, respectively. In PRIME, 60% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 24, compared with 18.4% of patients in the placebo arm (P < .001). In PRIME2, 37.2% of patients in the dupilumab arm achieved a 4-point or greater reduction in the WI-NRS at week 12, compared with 22% of patients in the placebo arm (P = .022).
The researchers also reported that, from an initial baseline of 20 to greater than 100 nodules, 32.0% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 25.6% in PRIME2 showed a reduction to 5 nodules or fewer, which corresponded to a response of “clear” or “almost clear” skin at week 12, compared with 11.8% and 12.2% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. This treatment effect on skin lesions continued to improve after week 12, with 48% of dupilumab-treated patients in PRIME and 44.9% in PRIME2 having five nodules or fewer at week 24, compared with 18.4% and 15.9% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. Safety was consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile.
“Validation is the first success of this paper,” said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “While both the safety and efficacy of dupilumab in these two phase 3 programs is the meat of the matter, nuanced highlights for me include the rigid nature of the exclusion criteria to ensure a study population that truly has PN as a stand-alone disease, rather than a secondary finding as we once believed to be the entire story. I think it’s important for us to recognize that it’s not one or the other, rather there is both ‘primary’ prurigo nodularis, and then there is secondary prurigo nodularis associated with something else [a wide range of underlying medical conditions], just like we divide primary and secondary hyperhidrosis.”
Dr. Yosipovitch reported having competing interests with several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron and Sanofi. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant to and a speaker for Regeneron.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
Boys may carry the weight, or overweight, of adults’ infertility
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.