User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
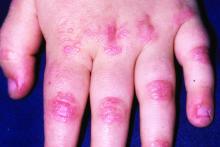
Phase 3 prurigo nodularis trial shows positive results for nemolizumab
NEW ORLEANS – demonstrated.
Nemolizumab is a first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody directed against the interleukin-31 receptor alpha that blocks signaling from IL-31. “From prior studies we know that it modulates pruritus, but also alters keratinocyte differentiation, inflammation, and fibrosis,” one of the investigators, Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said during a late-breaking research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
OLYMPIA 2 was a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind study in adults with PN presenting with 20 or more nodules, and Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 3 or more, and the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 7 or more. Exclusion criteria included chronic pruritus resulting from an active condition other than PN, such as neuropathic and psychogenic pruritus and active atopic dermatitis. In addition, the use of topical steroids, considered a rescue therapy, was not allowed in the trial, Dr. Kwatra said.
After an initial screening period, 274 patients at 73 sites in nine countries were randomized 2:1 either to the nemolizumab monotherapy or placebo. Following an initial 60-mg subcutaneous dose, patients received 30 mg or 60 mg (depending on their baseline weight) every 4 weeks for 16 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS from baseline at week 16 and the proportion of patients with IGA success at week 16.
Selected key secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with a 4 point or greater improvement from baseline in the PP-NRS at week 4, the Sleep Disturbance Numerical Rating Scale at week 4, and the SD-NRS at week 16. Safety endpoints included the incidence and severity of all adverse events.
Of the 274 patients randomized, 183 received nemolizumab and 91 received placebo. A total of 174 patients in the nemolizumab group completed the study, compared with 88 in the placebo group. The mean age of study participants was 53 years, 61% were women, 79% were White, 14% were Asian, and the rest were from other racial groups. More than half (57%) had IGA category 3 disease (moderate) and the remainder had IGA category 4 disease (severe); 63% had 20-100 lesions, and the remainder had more than 100. About one-third of study enrollees (32%) had a history of atopy.
Primary, secondary endpoint results
Dr. Kwatra reported that 56.3% of the patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001), while 37.7% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 16, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001).
As for secondary endpoints, 41% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in PP-NRS at week 4, compared with 7.7% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 37.2% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 4, compared with 9.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001). Almost 52% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 9.8% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 4, compared with 1.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .0074).
Adverse events
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 61.2% of subjects in the nemolizumab group, compared with 52.7% of those in the placebo group. “There were no imbalances overall, [including] no injection-related reactions in either group,” Dr. Kwatra said. There was one case of newly diagnosed asthma in the placebo arm, and none in the treatment arm.
The researchers observed a slightly increased onset of atopic dermatitis in the treatment arm, compared with the placebo arm (5.5% vs. 0%). “Seven out of those 10 patients actually had a history of atopic dermatitis or high IgE [levels] and they were mostly managed with topical steroids without study drug discontinuation,” Dr. Kwatra added. Neurodermatitis, or worsening of PN, occurred in 3.8% of patients in the nemolizumab group, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group.
“The results of this study extend the efficacy and safety findings from the phase 2 study of nemolizumab in patients with PN,” Dr. Kwatra concluded. “I think they also help to usher in a new era of PN [treatment] in prime time.”
Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and was asked to comment on the study, was impressed with nemolizumab’s propensity for blocking IL-31. “To be able to treat PN effectively by simply blocking the itch and not having a significant inflammatory function is really interesting,” he said in an interview at the meeting. If approved, nemolizumab “gives us another treatment option for a disease that is really debilitating. It’s very promising and we hope [the drug] will be available to us in the near future.”
Nemolizumab is being developed by Galderma. According to a press release from the company, nemolizumab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019 for the treatment of pruritus associated with PN, a status that was reconfirmed in February 2023.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Galderma, AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, Cara Therapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Incyte, Johnson and Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Gordon disclosed that he is a consultant to, an investigator for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, but not Galderma.
NEW ORLEANS – demonstrated.
Nemolizumab is a first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody directed against the interleukin-31 receptor alpha that blocks signaling from IL-31. “From prior studies we know that it modulates pruritus, but also alters keratinocyte differentiation, inflammation, and fibrosis,” one of the investigators, Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said during a late-breaking research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
OLYMPIA 2 was a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind study in adults with PN presenting with 20 or more nodules, and Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 3 or more, and the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 7 or more. Exclusion criteria included chronic pruritus resulting from an active condition other than PN, such as neuropathic and psychogenic pruritus and active atopic dermatitis. In addition, the use of topical steroids, considered a rescue therapy, was not allowed in the trial, Dr. Kwatra said.
After an initial screening period, 274 patients at 73 sites in nine countries were randomized 2:1 either to the nemolizumab monotherapy or placebo. Following an initial 60-mg subcutaneous dose, patients received 30 mg or 60 mg (depending on their baseline weight) every 4 weeks for 16 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS from baseline at week 16 and the proportion of patients with IGA success at week 16.
Selected key secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with a 4 point or greater improvement from baseline in the PP-NRS at week 4, the Sleep Disturbance Numerical Rating Scale at week 4, and the SD-NRS at week 16. Safety endpoints included the incidence and severity of all adverse events.
Of the 274 patients randomized, 183 received nemolizumab and 91 received placebo. A total of 174 patients in the nemolizumab group completed the study, compared with 88 in the placebo group. The mean age of study participants was 53 years, 61% were women, 79% were White, 14% were Asian, and the rest were from other racial groups. More than half (57%) had IGA category 3 disease (moderate) and the remainder had IGA category 4 disease (severe); 63% had 20-100 lesions, and the remainder had more than 100. About one-third of study enrollees (32%) had a history of atopy.
Primary, secondary endpoint results
Dr. Kwatra reported that 56.3% of the patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001), while 37.7% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 16, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001).
As for secondary endpoints, 41% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in PP-NRS at week 4, compared with 7.7% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 37.2% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 4, compared with 9.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001). Almost 52% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 9.8% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 4, compared with 1.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .0074).
Adverse events
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 61.2% of subjects in the nemolizumab group, compared with 52.7% of those in the placebo group. “There were no imbalances overall, [including] no injection-related reactions in either group,” Dr. Kwatra said. There was one case of newly diagnosed asthma in the placebo arm, and none in the treatment arm.
The researchers observed a slightly increased onset of atopic dermatitis in the treatment arm, compared with the placebo arm (5.5% vs. 0%). “Seven out of those 10 patients actually had a history of atopic dermatitis or high IgE [levels] and they were mostly managed with topical steroids without study drug discontinuation,” Dr. Kwatra added. Neurodermatitis, or worsening of PN, occurred in 3.8% of patients in the nemolizumab group, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group.
“The results of this study extend the efficacy and safety findings from the phase 2 study of nemolizumab in patients with PN,” Dr. Kwatra concluded. “I think they also help to usher in a new era of PN [treatment] in prime time.”
Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and was asked to comment on the study, was impressed with nemolizumab’s propensity for blocking IL-31. “To be able to treat PN effectively by simply blocking the itch and not having a significant inflammatory function is really interesting,” he said in an interview at the meeting. If approved, nemolizumab “gives us another treatment option for a disease that is really debilitating. It’s very promising and we hope [the drug] will be available to us in the near future.”
Nemolizumab is being developed by Galderma. According to a press release from the company, nemolizumab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019 for the treatment of pruritus associated with PN, a status that was reconfirmed in February 2023.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Galderma, AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, Cara Therapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Incyte, Johnson and Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Gordon disclosed that he is a consultant to, an investigator for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, but not Galderma.
NEW ORLEANS – demonstrated.
Nemolizumab is a first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody directed against the interleukin-31 receptor alpha that blocks signaling from IL-31. “From prior studies we know that it modulates pruritus, but also alters keratinocyte differentiation, inflammation, and fibrosis,” one of the investigators, Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said during a late-breaking research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
OLYMPIA 2 was a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind study in adults with PN presenting with 20 or more nodules, and Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 3 or more, and the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 7 or more. Exclusion criteria included chronic pruritus resulting from an active condition other than PN, such as neuropathic and psychogenic pruritus and active atopic dermatitis. In addition, the use of topical steroids, considered a rescue therapy, was not allowed in the trial, Dr. Kwatra said.
After an initial screening period, 274 patients at 73 sites in nine countries were randomized 2:1 either to the nemolizumab monotherapy or placebo. Following an initial 60-mg subcutaneous dose, patients received 30 mg or 60 mg (depending on their baseline weight) every 4 weeks for 16 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS from baseline at week 16 and the proportion of patients with IGA success at week 16.
Selected key secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with a 4 point or greater improvement from baseline in the PP-NRS at week 4, the Sleep Disturbance Numerical Rating Scale at week 4, and the SD-NRS at week 16. Safety endpoints included the incidence and severity of all adverse events.
Of the 274 patients randomized, 183 received nemolizumab and 91 received placebo. A total of 174 patients in the nemolizumab group completed the study, compared with 88 in the placebo group. The mean age of study participants was 53 years, 61% were women, 79% were White, 14% were Asian, and the rest were from other racial groups. More than half (57%) had IGA category 3 disease (moderate) and the remainder had IGA category 4 disease (severe); 63% had 20-100 lesions, and the remainder had more than 100. About one-third of study enrollees (32%) had a history of atopy.
Primary, secondary endpoint results
Dr. Kwatra reported that 56.3% of the patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in the PP-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001), while 37.7% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 16, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001).
As for secondary endpoints, 41% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in PP-NRS at week 4, compared with 7.7% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 37.2% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 4, compared with 9.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001). Almost 52% of patients in the nemolizumab group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement in SD-NRS at week 16, compared with 20.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .0001); and 9.8% of those in the nemolizumab group achieved IGA success at week 4, compared with 1.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .0074).
Adverse events
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 61.2% of subjects in the nemolizumab group, compared with 52.7% of those in the placebo group. “There were no imbalances overall, [including] no injection-related reactions in either group,” Dr. Kwatra said. There was one case of newly diagnosed asthma in the placebo arm, and none in the treatment arm.
The researchers observed a slightly increased onset of atopic dermatitis in the treatment arm, compared with the placebo arm (5.5% vs. 0%). “Seven out of those 10 patients actually had a history of atopic dermatitis or high IgE [levels] and they were mostly managed with topical steroids without study drug discontinuation,” Dr. Kwatra added. Neurodermatitis, or worsening of PN, occurred in 3.8% of patients in the nemolizumab group, compared with 11% of those in the placebo group.
“The results of this study extend the efficacy and safety findings from the phase 2 study of nemolizumab in patients with PN,” Dr. Kwatra concluded. “I think they also help to usher in a new era of PN [treatment] in prime time.”
Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and was asked to comment on the study, was impressed with nemolizumab’s propensity for blocking IL-31. “To be able to treat PN effectively by simply blocking the itch and not having a significant inflammatory function is really interesting,” he said in an interview at the meeting. If approved, nemolizumab “gives us another treatment option for a disease that is really debilitating. It’s very promising and we hope [the drug] will be available to us in the near future.”
Nemolizumab is being developed by Galderma. According to a press release from the company, nemolizumab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019 for the treatment of pruritus associated with PN, a status that was reconfirmed in February 2023.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Galderma, AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, Cara Therapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Incyte, Johnson and Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Gordon disclosed that he is a consultant to, an investigator for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, but not Galderma.
AT AAD 2023
State medical board chair steps down amid Medicaid fraud accusations
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV testing still suboptimal
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The reasons are complex and could jeopardize goals of ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Patients and doctors alike face system challenges, including stigma, confidentiality concerns, racism, and inequitable access. Yet doctors, public health authorities, and even some patients agree that testing does work: In 2022, 81% of people diagnosed with HIV were linked to care within 30 days. Moreover, many patients are aware of where and how they wish to be tested. So, what would it take to achieve what ostensibly should be the lowest hanging fruit in the HIV care continuum?
“We didn’t look at the reasons for not testing,” Marc Pitasi, MPH, CDC epidemiologist and coauthor of the CDC study said in an interview. But “we found that the majority of people prefer the test in a clinical setting, so that’s a huge important piece of the puzzle,” he said.
The “never-tested” populations (4,334 of 6,072) in the study were predominantly aged 18-29 years (79.7%) and 50 years plus (78.1%). A total of 48% of never-tested adults also indicated that they had engaged in past-year risky behaviors (that is, injection drug use, treated for a sexually transmitted disease, exchanged sex/drugs for money, engaged in condomless anal sex, or had more than four sex partners). However, the difference between never-tested adults who live in EHE (Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.)–designated jurisdictions (comprising 50 areas and 7 U.S. states responsible for more than 50% of new HIV infections) and those residing in non-EHE areas was only about 5 percentage points (69.1% vs. 74.5%, respectively), underscoring the need for broader engagement.
“There’s definitely a lack of testing across the board,” explained Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, MPH, MS, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “There are all sorts of biases on how we make decisions and how we stratify … and these heuristics that we have in our minds to identify who is at risk and who needs testing,” she said.
“If we just look at the need for HIV testing based on who is at risk, I think that we are always going to fall short.”
Conflicting priorities
Seventeen years have passed since the CDC recommended that HIV testing and screening be offered at least once to all people aged 13-64 years in a routine clinical setting, with an opt-out option and without a separate written consent. People at higher risk (sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men) should be rescreened at least annually.
These recommendations were subsequently reinforced by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013 and again in 2019, and the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2021.
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee said that some clinicians remain unaware of the guidelines; for others, they’re usually not top-of-mind because of conflicting priorities.
This is especially true of pediatricians, who, despite data demonstrating that adolescents account for roughly 21% of new HIV diagnoses, rarely recognize or take advantage of HIV-testing opportunities during routine clinical visits.
“Pediatricians want to do the right thing for their patients but at the same time, they want to do the right thing on so many different fronts,” said Sarah Wood, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and attending physician of adolescent medicine at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Wood is coauthor of a study published in Implementation Science Communicationsexamining pediatrician perspectives on implementing HIV testing and prevention. Participants identified confidentiality and time constraints as the most important challenges across every step of their workflow, which in turn, influenced perceptions about patients’ perceived risks for acquiring HIV – perceptions that Dr. Wood believes can be overcome.
“We need to really push pediatricians (through guideline-making societies like AAP and USPSTF) that screening should be universal and not linked to sexual activity or pinned to behavior, so the offer of testing is a universal opt-out,” she said. Additionally, “we need to make it easier for pediatricians to order the test,” for example, “through an office rapid test … and a redesigned workflow that moves the conversation away from physicians and nurse practitioners to medical assistants.”
Dr. Wood also pointed out that any effort would require pediatricians and other types of providers to overcome discomfort around sexual health conversations, noting that, while pediatricians are ideally positioned to work with parents to do education around sexual health, training and impetus are needed.
A fractured system
A fractured, often ill-funded U.S. health care system might also be at play according to Scott Harris, MD, MPH, state health officer of the Alabama Department of Public Health in Montgomery, and Association of State and Territorial Health Officials’ Infectious Disease Policy Committee chair.
“There’s a general consensus among everyone in public health that [HIV testing] is an important issue that we’re not addressing as well as we’d like to,” he said.
Dr. Harris acknowledged that, while COVID diverted attention away from HIV, some states have prioritized HIV more than others.
“We don’t have a national public health program; we have a nationwide public health program,” he said. “Everyone’s different and has different responsibilities and authorities ... depending on where their funding streams come from.”
The White House recently announced that it proposed a measure in its Fiscal Year 2023 budget to increase funding for HIV a further $313 million to accelerate efforts to end HIV by 2030, also adding a mandatory program to increase preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access. Without congressional approval, the measures are doomed to fail, leaving many states without the proper tools to enhance existing programs, and further painting overworked clinicians into a corner.
For patients, the ramifications are even greater.
“The majority of folks [in the CDC study] that were not tested said that if they were to get tested, they’d prefer to do that within the context of their primary care setting,” said Justin C. Smith, MS, MPH, director of the Campaign to End AIDS, Positive Impact Health Centers; a behavioral scientist at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta; and a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS.
“When you create a more responsive system that really speaks to the needs that people are expressing, that can provide better outcomes,” Dr. Smith said.
“It’s vital that we create health care and public health interventions that change the dynamics ... and make sure that we’re designing systems with the people that we’re trying to serve at the center.”
Mr. Pitasi, Dr. Rosengren-Hovee, Dr. Wood, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
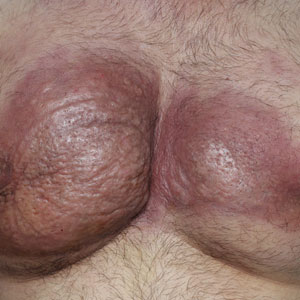
Novel therapy shows promise for treating skin-predominant dermatomyositis
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Treatment of craniofacial hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at [email protected]. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Papular Rash in a New Tattoo
The Diagnosis: Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This patient’s history and physical examination were most consistent with a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, likely from an additive or diluent solution within the tattoo ink. Her history of a similar transient reaction following tattooing 2 weeks prior lent credence to an allergic etiology. She was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1% as well as mupirocin ointment 2% for use as both an emollient and for precautionary antimicrobial coverage. The rash resolved within 2 days, and she reported no recurrence at a 6-month follow-up. The cosmesis of her tattoo was preserved.
Acute cellulitis may follow tattooing, but the absence of warmth, pain, or purulence on physical examination made this diagnosis less likely in this patient. Sarcoidosis or other granulomatous reactions may present as papules or nodules arising within a tattoo but would be unlikely to occur the next day. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection likewise tends to present subacutely or chronically rather than immediately following tattoo application.
Tattooing has existed for millennia and is becoming increasingly popular.1,2 The tattooing process entails introduction of insoluble pigment compounds into the dermis to create a permanent design on the skin, which most often is accomplished via needling. As a result, tattooed skin is susceptible to both acute and chronic complications. Acute complications prominently include allergic hypersensitivity reactions and pyogenic bacterial infections. Chronic granulomatous, inflammatory, or infectious complications also can occur.
Allergic eczematous reactions to tattooing are well documented in the literature and are thought to originate from sensitization to pigment molecules themselves or alternatively to ink diluent compounds.3 Although reactions to ink diluent chemicals typically are self-resolving, allergic reactions to pigment can persist beyond the acute phase, as these insoluble compounds intentionally remain embedded in the dermis. The mechanism of action may involve haptenization of pigment molecules that then induces allergic hypersensitivity.3,4 Black pigment typically is derived from carbon black (ie, amorphous combustion byproducts such as soot). Colored inks historically consisted of inorganic heavy metal–containing salts prior to the modern introduction of synthetic azo and polycyclic dyes. These newer colored pigments appear to be less allergenic than their metallic predecessors; however, epidemiologic studies have suggested that allergic reactions still occur more commonly in colored tattoos than black tattoos.1 Overall, these reactions may occur in as many as one-third of individuals who receive tattoos.2,4
As with any process that disrupts skin integrity, tattooing carries a risk for transmitting various infectious pathogens. Microbes may originate from adjacent skin, contaminated needles, ink bottles, or nonsterile ink diluents. Although tattoo parlors and artists may undergo licensing to demonstrate adherence to hygienic standards, regulations vary between states and do not include testing of ink or ink additives to ensure sterility.4,5 Staphylococci and streptococci commonly are implicated in acute pyogenic skin infections following tattooing.5,6 Nontuberculous mycobacteria increasingly are being recognized as causative organisms for granulomatous lesions developing subacutely or even months after receiving a new tattoo.5,7 Local and systemic viral infections also may be transmitted during tattooing; cases of tattoo-transmitted viral warts, molluscum contagiosum, and hepatitis B and C viruses all have been observed.5,6,8 Herpes simplex virus transmission (colloquially termed herpes compunctorum) and HIV transmission through tattooing also are hypothesized to be possible, though there is a paucity of known cases for each.8,9
Chronic inflammatory, granulomatous, or neoplastic lesions may arise within tattooed skin months or years after tattooing. Foreign body granulomas, sarcoidosis, pseudolymphoma, pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, and keratoacanthoma are some representative entities.3,5 Cases of cancerous lesions in tattooed skin have been documented, but their incidence appears similar to nontattooed skin.3 These broad categories of lesions are clinically diverse but may be difficult to definitively diagnose on examination alone; therefore, a biopsy should be strongly considered for any subacute to chronic skin lesions within a tattoo. Patients may be hesitant to disrupt the cosmesis of a tattoo but should be counseled on the attendant risks and benefits to make an informed decision regarding biopsy.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Liszewski W, Kream E, Helland S, et al. The demographics and rates of tattoo complications, regret, and unsafe tattooing practices: a crosssectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1283-1289.
- Islam PS, Chang C, Selmi C, et al. Medical complications of tattoos: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50:273-286.
- Serup J, Carlsen KH, Sepehri M. Tattoo complaints and complications: diagnosis and clinical spectrum. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2015;48:48-60.
- Simunovic C, Shinohara MM. Complications of decorative tattoos: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:525-536.
- Kazandjieva J, Tsankov N. Tattoos: dermatological complications. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:375-382.
- Sergeant A, Conaglen P, Laurenson IF, et al. Mycobacterium chelonae infection: a complication of tattooing. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:140-142.
- Cohen PR. Tattoo-associated viral infections: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1529-1540.
- Doll DC. Tattooing in prison and HIV infection. Lancet. 1988;1:66-67.
The Diagnosis: Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This patient’s history and physical examination were most consistent with a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, likely from an additive or diluent solution within the tattoo ink. Her history of a similar transient reaction following tattooing 2 weeks prior lent credence to an allergic etiology. She was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1% as well as mupirocin ointment 2% for use as both an emollient and for precautionary antimicrobial coverage. The rash resolved within 2 days, and she reported no recurrence at a 6-month follow-up. The cosmesis of her tattoo was preserved.
Acute cellulitis may follow tattooing, but the absence of warmth, pain, or purulence on physical examination made this diagnosis less likely in this patient. Sarcoidosis or other granulomatous reactions may present as papules or nodules arising within a tattoo but would be unlikely to occur the next day. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection likewise tends to present subacutely or chronically rather than immediately following tattoo application.
Tattooing has existed for millennia and is becoming increasingly popular.1,2 The tattooing process entails introduction of insoluble pigment compounds into the dermis to create a permanent design on the skin, which most often is accomplished via needling. As a result, tattooed skin is susceptible to both acute and chronic complications. Acute complications prominently include allergic hypersensitivity reactions and pyogenic bacterial infections. Chronic granulomatous, inflammatory, or infectious complications also can occur.
Allergic eczematous reactions to tattooing are well documented in the literature and are thought to originate from sensitization to pigment molecules themselves or alternatively to ink diluent compounds.3 Although reactions to ink diluent chemicals typically are self-resolving, allergic reactions to pigment can persist beyond the acute phase, as these insoluble compounds intentionally remain embedded in the dermis. The mechanism of action may involve haptenization of pigment molecules that then induces allergic hypersensitivity.3,4 Black pigment typically is derived from carbon black (ie, amorphous combustion byproducts such as soot). Colored inks historically consisted of inorganic heavy metal–containing salts prior to the modern introduction of synthetic azo and polycyclic dyes. These newer colored pigments appear to be less allergenic than their metallic predecessors; however, epidemiologic studies have suggested that allergic reactions still occur more commonly in colored tattoos than black tattoos.1 Overall, these reactions may occur in as many as one-third of individuals who receive tattoos.2,4
As with any process that disrupts skin integrity, tattooing carries a risk for transmitting various infectious pathogens. Microbes may originate from adjacent skin, contaminated needles, ink bottles, or nonsterile ink diluents. Although tattoo parlors and artists may undergo licensing to demonstrate adherence to hygienic standards, regulations vary between states and do not include testing of ink or ink additives to ensure sterility.4,5 Staphylococci and streptococci commonly are implicated in acute pyogenic skin infections following tattooing.5,6 Nontuberculous mycobacteria increasingly are being recognized as causative organisms for granulomatous lesions developing subacutely or even months after receiving a new tattoo.5,7 Local and systemic viral infections also may be transmitted during tattooing; cases of tattoo-transmitted viral warts, molluscum contagiosum, and hepatitis B and C viruses all have been observed.5,6,8 Herpes simplex virus transmission (colloquially termed herpes compunctorum) and HIV transmission through tattooing also are hypothesized to be possible, though there is a paucity of known cases for each.8,9
Chronic inflammatory, granulomatous, or neoplastic lesions may arise within tattooed skin months or years after tattooing. Foreign body granulomas, sarcoidosis, pseudolymphoma, pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, and keratoacanthoma are some representative entities.3,5 Cases of cancerous lesions in tattooed skin have been documented, but their incidence appears similar to nontattooed skin.3 These broad categories of lesions are clinically diverse but may be difficult to definitively diagnose on examination alone; therefore, a biopsy should be strongly considered for any subacute to chronic skin lesions within a tattoo. Patients may be hesitant to disrupt the cosmesis of a tattoo but should be counseled on the attendant risks and benefits to make an informed decision regarding biopsy.
The Diagnosis: Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This patient’s history and physical examination were most consistent with a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, likely from an additive or diluent solution within the tattoo ink. Her history of a similar transient reaction following tattooing 2 weeks prior lent credence to an allergic etiology. She was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1% as well as mupirocin ointment 2% for use as both an emollient and for precautionary antimicrobial coverage. The rash resolved within 2 days, and she reported no recurrence at a 6-month follow-up. The cosmesis of her tattoo was preserved.
Acute cellulitis may follow tattooing, but the absence of warmth, pain, or purulence on physical examination made this diagnosis less likely in this patient. Sarcoidosis or other granulomatous reactions may present as papules or nodules arising within a tattoo but would be unlikely to occur the next day. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection likewise tends to present subacutely or chronically rather than immediately following tattoo application.
Tattooing has existed for millennia and is becoming increasingly popular.1,2 The tattooing process entails introduction of insoluble pigment compounds into the dermis to create a permanent design on the skin, which most often is accomplished via needling. As a result, tattooed skin is susceptible to both acute and chronic complications. Acute complications prominently include allergic hypersensitivity reactions and pyogenic bacterial infections. Chronic granulomatous, inflammatory, or infectious complications also can occur.
Allergic eczematous reactions to tattooing are well documented in the literature and are thought to originate from sensitization to pigment molecules themselves or alternatively to ink diluent compounds.3 Although reactions to ink diluent chemicals typically are self-resolving, allergic reactions to pigment can persist beyond the acute phase, as these insoluble compounds intentionally remain embedded in the dermis. The mechanism of action may involve haptenization of pigment molecules that then induces allergic hypersensitivity.3,4 Black pigment typically is derived from carbon black (ie, amorphous combustion byproducts such as soot). Colored inks historically consisted of inorganic heavy metal–containing salts prior to the modern introduction of synthetic azo and polycyclic dyes. These newer colored pigments appear to be less allergenic than their metallic predecessors; however, epidemiologic studies have suggested that allergic reactions still occur more commonly in colored tattoos than black tattoos.1 Overall, these reactions may occur in as many as one-third of individuals who receive tattoos.2,4
As with any process that disrupts skin integrity, tattooing carries a risk for transmitting various infectious pathogens. Microbes may originate from adjacent skin, contaminated needles, ink bottles, or nonsterile ink diluents. Although tattoo parlors and artists may undergo licensing to demonstrate adherence to hygienic standards, regulations vary between states and do not include testing of ink or ink additives to ensure sterility.4,5 Staphylococci and streptococci commonly are implicated in acute pyogenic skin infections following tattooing.5,6 Nontuberculous mycobacteria increasingly are being recognized as causative organisms for granulomatous lesions developing subacutely or even months after receiving a new tattoo.5,7 Local and systemic viral infections also may be transmitted during tattooing; cases of tattoo-transmitted viral warts, molluscum contagiosum, and hepatitis B and C viruses all have been observed.5,6,8 Herpes simplex virus transmission (colloquially termed herpes compunctorum) and HIV transmission through tattooing also are hypothesized to be possible, though there is a paucity of known cases for each.8,9
Chronic inflammatory, granulomatous, or neoplastic lesions may arise within tattooed skin months or years after tattooing. Foreign body granulomas, sarcoidosis, pseudolymphoma, pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, and keratoacanthoma are some representative entities.3,5 Cases of cancerous lesions in tattooed skin have been documented, but their incidence appears similar to nontattooed skin.3 These broad categories of lesions are clinically diverse but may be difficult to definitively diagnose on examination alone; therefore, a biopsy should be strongly considered for any subacute to chronic skin lesions within a tattoo. Patients may be hesitant to disrupt the cosmesis of a tattoo but should be counseled on the attendant risks and benefits to make an informed decision regarding biopsy.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Liszewski W, Kream E, Helland S, et al. The demographics and rates of tattoo complications, regret, and unsafe tattooing practices: a crosssectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1283-1289.
- Islam PS, Chang C, Selmi C, et al. Medical complications of tattoos: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50:273-286.
- Serup J, Carlsen KH, Sepehri M. Tattoo complaints and complications: diagnosis and clinical spectrum. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2015;48:48-60.
- Simunovic C, Shinohara MM. Complications of decorative tattoos: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:525-536.
- Kazandjieva J, Tsankov N. Tattoos: dermatological complications. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:375-382.
- Sergeant A, Conaglen P, Laurenson IF, et al. Mycobacterium chelonae infection: a complication of tattooing. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:140-142.
- Cohen PR. Tattoo-associated viral infections: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1529-1540.
- Doll DC. Tattooing in prison and HIV infection. Lancet. 1988;1:66-67.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Liszewski W, Kream E, Helland S, et al. The demographics and rates of tattoo complications, regret, and unsafe tattooing practices: a crosssectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1283-1289.
- Islam PS, Chang C, Selmi C, et al. Medical complications of tattoos: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50:273-286.
- Serup J, Carlsen KH, Sepehri M. Tattoo complaints and complications: diagnosis and clinical spectrum. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2015;48:48-60.
- Simunovic C, Shinohara MM. Complications of decorative tattoos: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:525-536.
- Kazandjieva J, Tsankov N. Tattoos: dermatological complications. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:375-382.
- Sergeant A, Conaglen P, Laurenson IF, et al. Mycobacterium chelonae infection: a complication of tattooing. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:140-142.
- Cohen PR. Tattoo-associated viral infections: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1529-1540.
- Doll DC. Tattooing in prison and HIV infection. Lancet. 1988;1:66-67.
A healthy 21-year-old woman presented with a pruritic papulovesicular rash on the left arm of 2 days’ duration. The day before rash onset, she received a black ink tattoo on the left arm to complete the second half of a monochromatic sleevestyle design. She previously underwent initial tattooing of the left arm by the same artist 2 weeks prior and experienced a similar but less extensive rash that self-resolved after 1 week. She had 8 older tattoos on various other body parts and denied any reactions. Physical examination showed numerous scattered papules and papulovesicles confined to areas of newly tattooed skin throughout the left arm. In the larger swaths of the tattoo, the papules coalesced into well-defined plaques. There was a discrete rim of faint erythema bordering the newly tattooed skin. No erosions, ulcerations, or purulent areas were observed, and there was no tenderness or excess warmth of the affected skin. Adjacent previously tattooed areas of the left arm were unaffected.

Studies validate IL-17 as hidradenitis suppurativa drug target
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Fat Necrosis of the Breast Mimicking Breast Cancer in a Male Patient Following Wax Hair Removal
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.
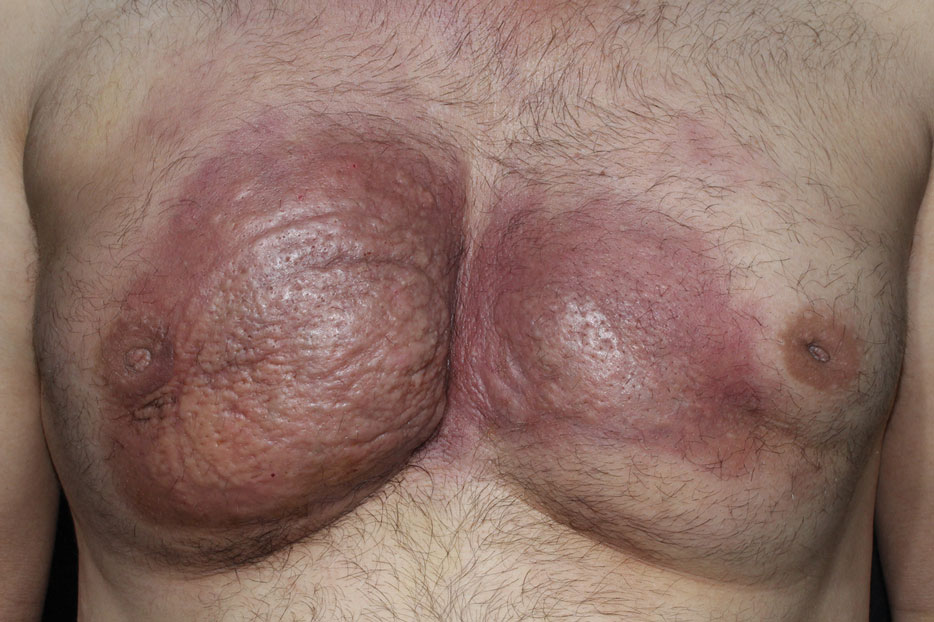
Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).
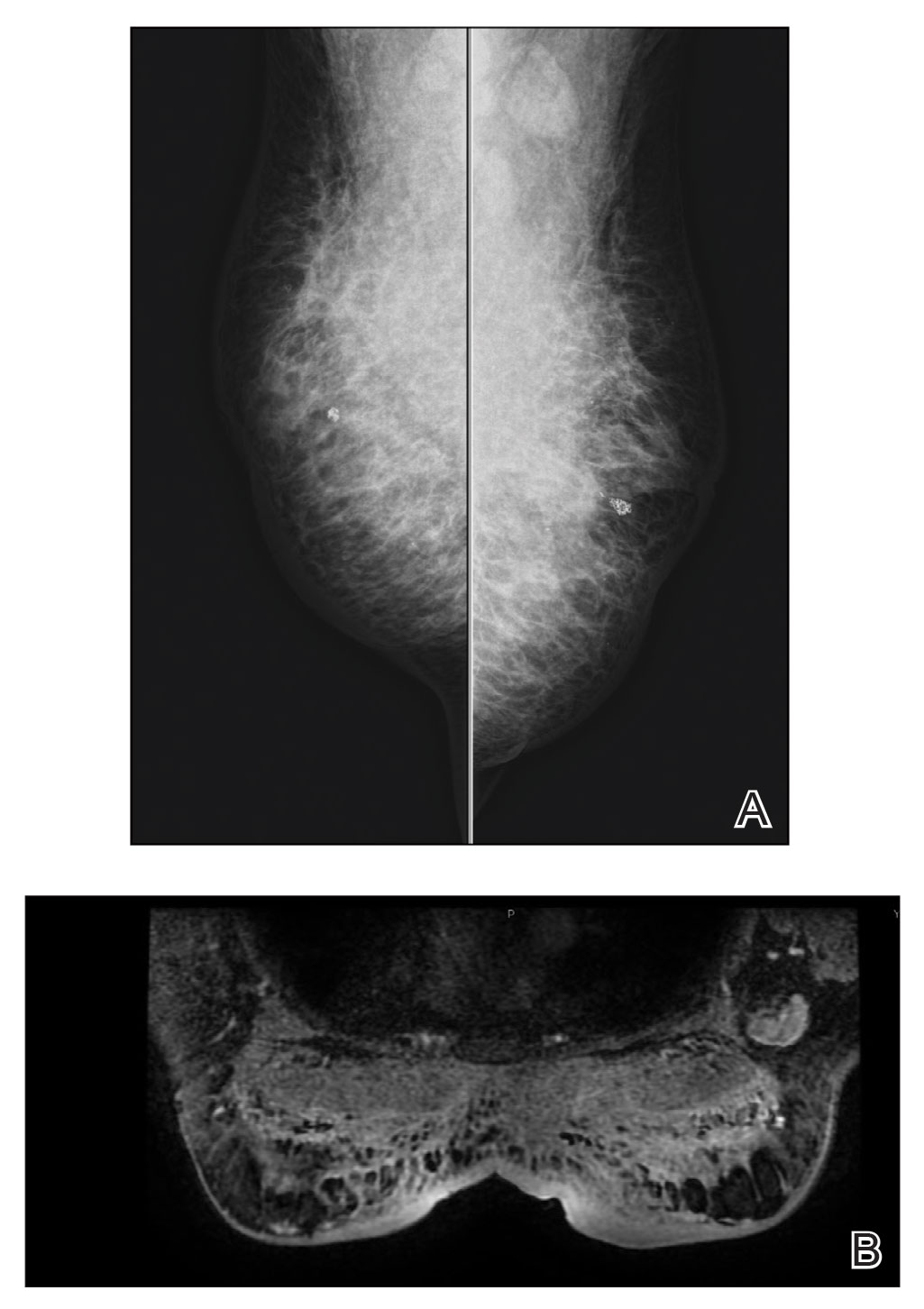
Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.
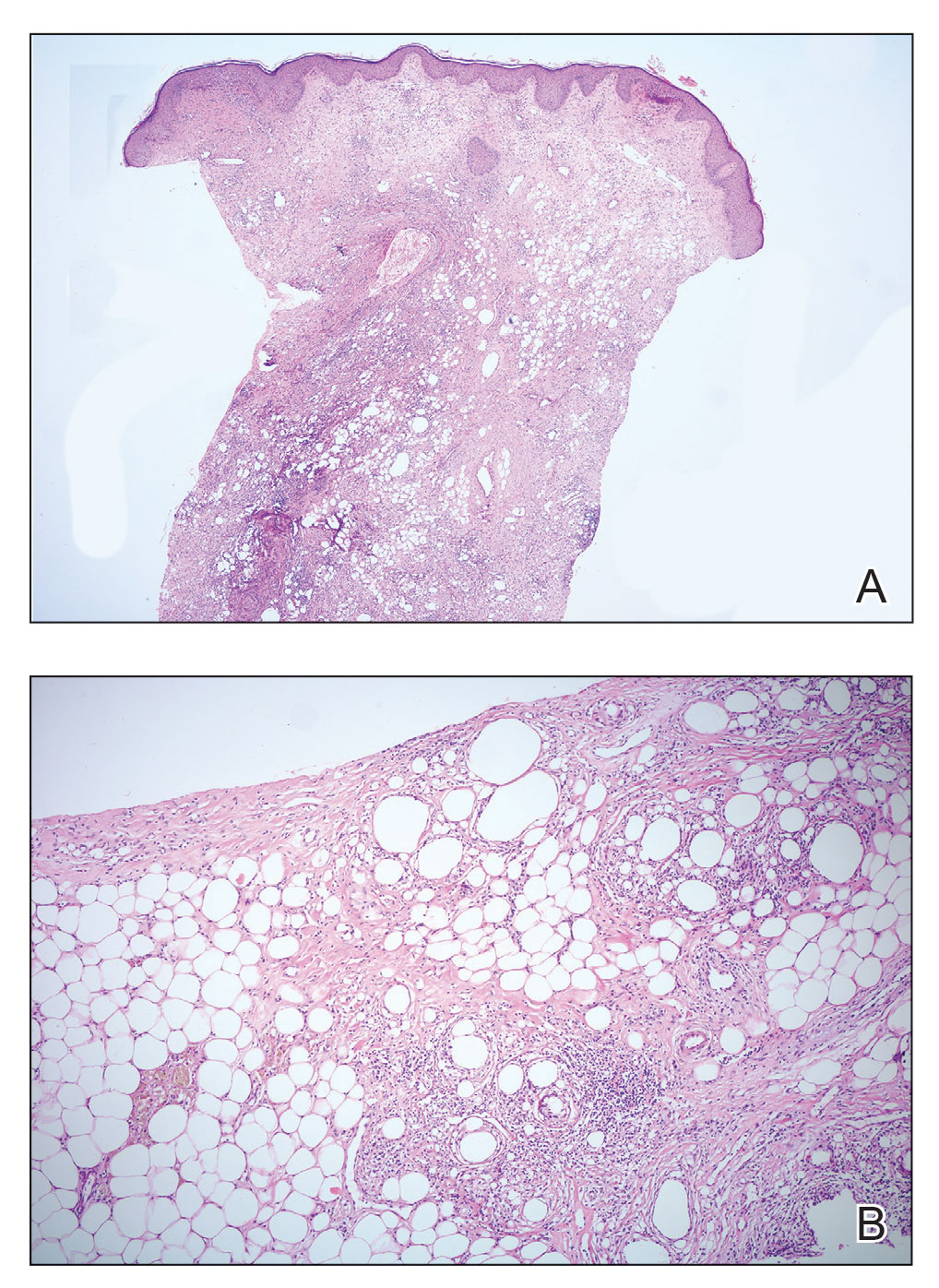
Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
Practice Points
- Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy; therefore, diagnosis should be confirmed by histopathology in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, and hair removal with wax may be a rare cause of the disease.
Match Day: Record number of residencies offered
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.
NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Increased cancer in military pilots and ground crew: Pentagon
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.