User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
The gut microbes have spoken: All fiber is good fiber
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Perceptions of Community Service in Dermatology Residency Training Programs: A Survey-Based Study of Program Directors, Residents, and Recent Dermatology Residency Graduates
Community service (CS) or service learning in dermatology (eg, free skin cancer screenings, providing care through free clinics, free teledermatology consultations) is instrumental in mitigating disparities and improving access to equitable dermatologic care. With the rate of underinsured and uninsured patients on the rise, free and federally qualified clinics frequently are the sole means by which patients access specialty care such as dermatology.1 Contributing to the economic gap in access, the geographic disparity of dermatologists in the United States continues to climb, and many marginalized communities remain without dermatologists.2 Nearly 30% of the total US population resides in geographic areas that are underserved by dermatologists, while there appears to be an oversupply of dermatologists in urban areas.3 Dermatologists practicing in rural areas make up only 10% of the dermatology workforce,4 whereas 40% of all dermatologists practice in the most densely populated US cities.5 Consequently, patients in these underserved communities face longer wait times6 and are less likely to utilize dermatology services than patients in dermatologist-dense geographic areas.7
Service opportunities have become increasingly integrated into graduate medical education.8 These service activities help bridge the health care access gap while fulfilling Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) requirements. Our study assessed the importance of CS to dermatology residency program directors (PDs), dermatology residents, and recent dermatology residency graduates. Herein, we describe the perceptions of CS within dermatology residency training among PDs and residents.
Methods
In this study, CS is defined as participation in activities to increase dermatologic access, education, and resources to underserved communities. Using the approved Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve and direct email communication, we surveyed 142 PDs of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency training programs. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 17-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
We also surveyed current dermatology residents and recent graduates of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs via PDs nationwide. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 19-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
Descriptive statistics were used for data analysis for both Qualtrics surveys. The University of Pittsburgh institutional review board deemed this study exempt.
Results
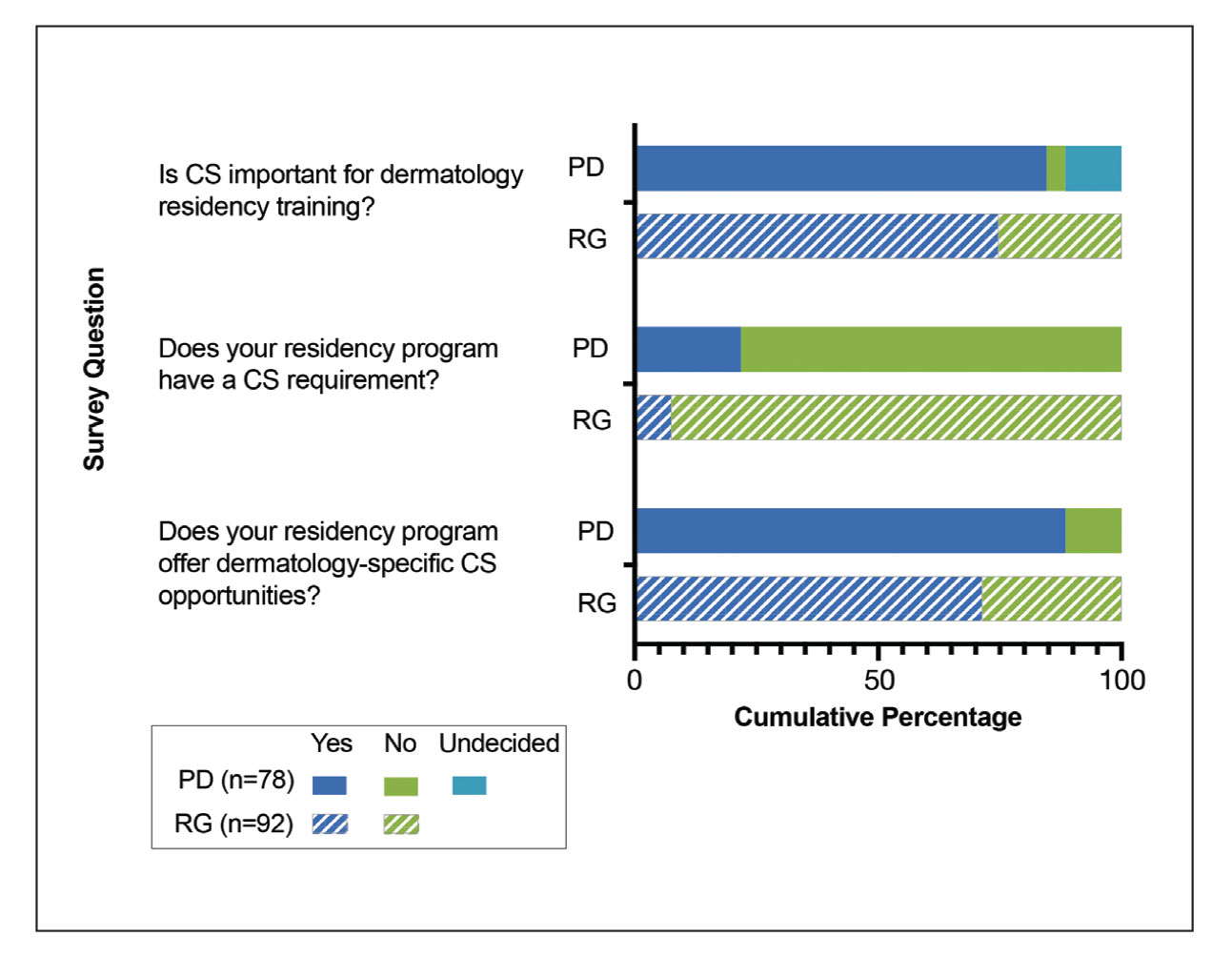
Feedback From PDs—Of the 142 PDs, we received 78 responses (54.9%). For selection of dermatology residents, CS was moderately to extremely important to 64 (82.1%) PDs, and 63 (80.8%) PDs stated CS was moderately to extremely important to their dermatology residency program at large. For dermatology residency training, 66 (84.6%) PDs believed CS is important, whereas 3 (3.8%) believed it is not important, and 9 (11.5%) remained undecided (Figure 1). Notably, 17 (21.8%) programs required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum, with most of these programs requiring 10 hours or less during the 3 years of residency training. Of the programs with required CS, 15 (88.2%) had dermatology-specific CS requirements, with 10 (58.8%) programs involved in CS at free and/or underserved clinics and some programs participating in other CS activities, such as advocacy, mentorship, educational outreach, or sports (Figure 2A).
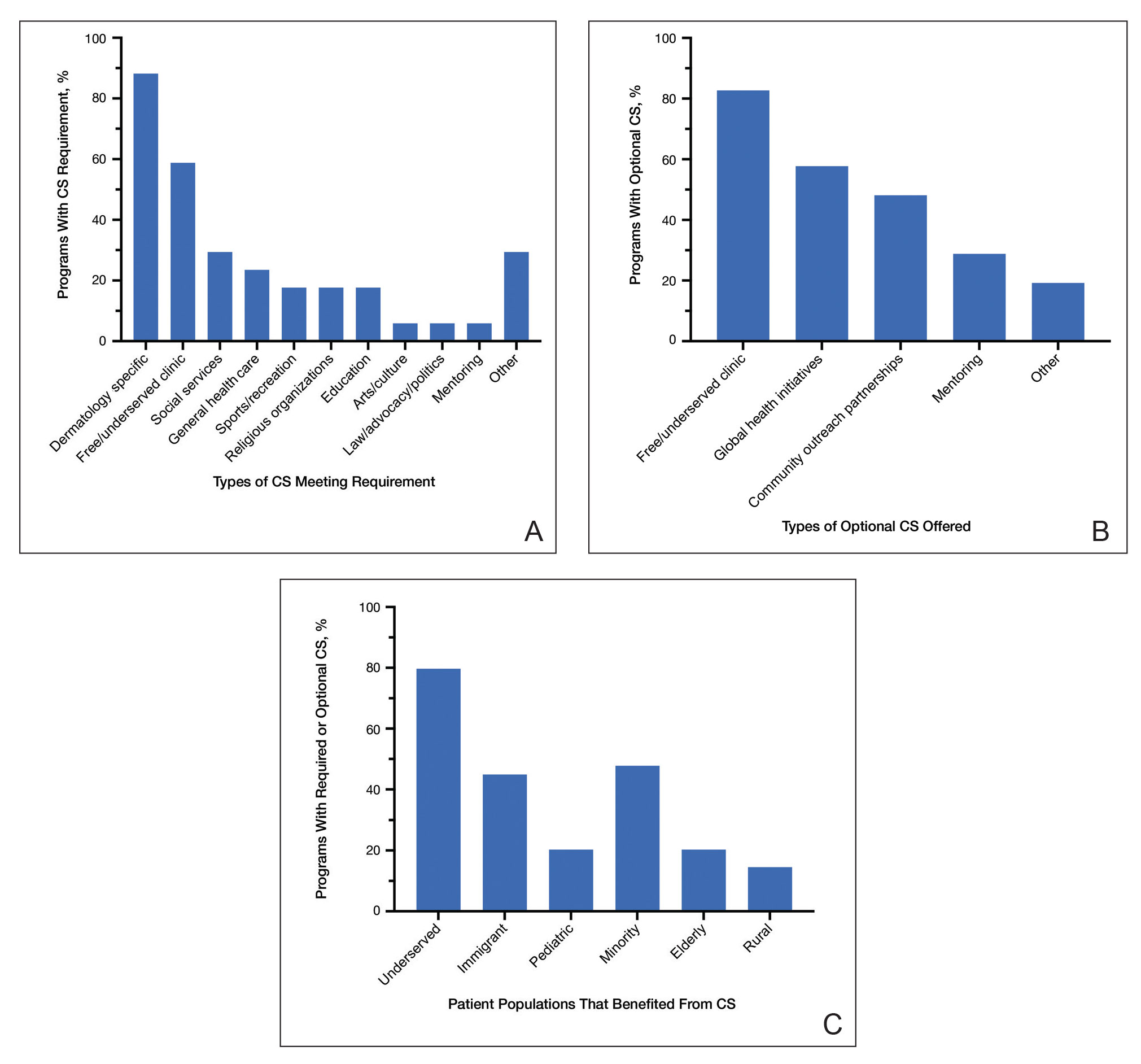
Community service opportunities were offered to dermatology residents by 69 (88.5%) programs, including the 17 programs that required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum. Among these programs with optional CS, 43 (82.7%) PDs reported CS opportunities at free and/or underserved clinics, and 30 (57.7%) reported CS opportunities through global health initiatives (Figure 2B). Other CS opportunities offered included partnerships with community outreach organizations and mentoring underprivileged students. Patient populations that benefit from CS offered by these dermatology residency programs included 55 (79.7%) underserved, 33 (47.8%) minority, 31 (44.9%) immigrant, 14 (20.3%) pediatric, 14 (20.3%) elderly, and 10 (14.5%) rural populations (Figure 2C). At dermatology residency programs with optional CS opportunities, 22 (42.3%) PDs endorsed at least 50% of their residents participating in these activities.
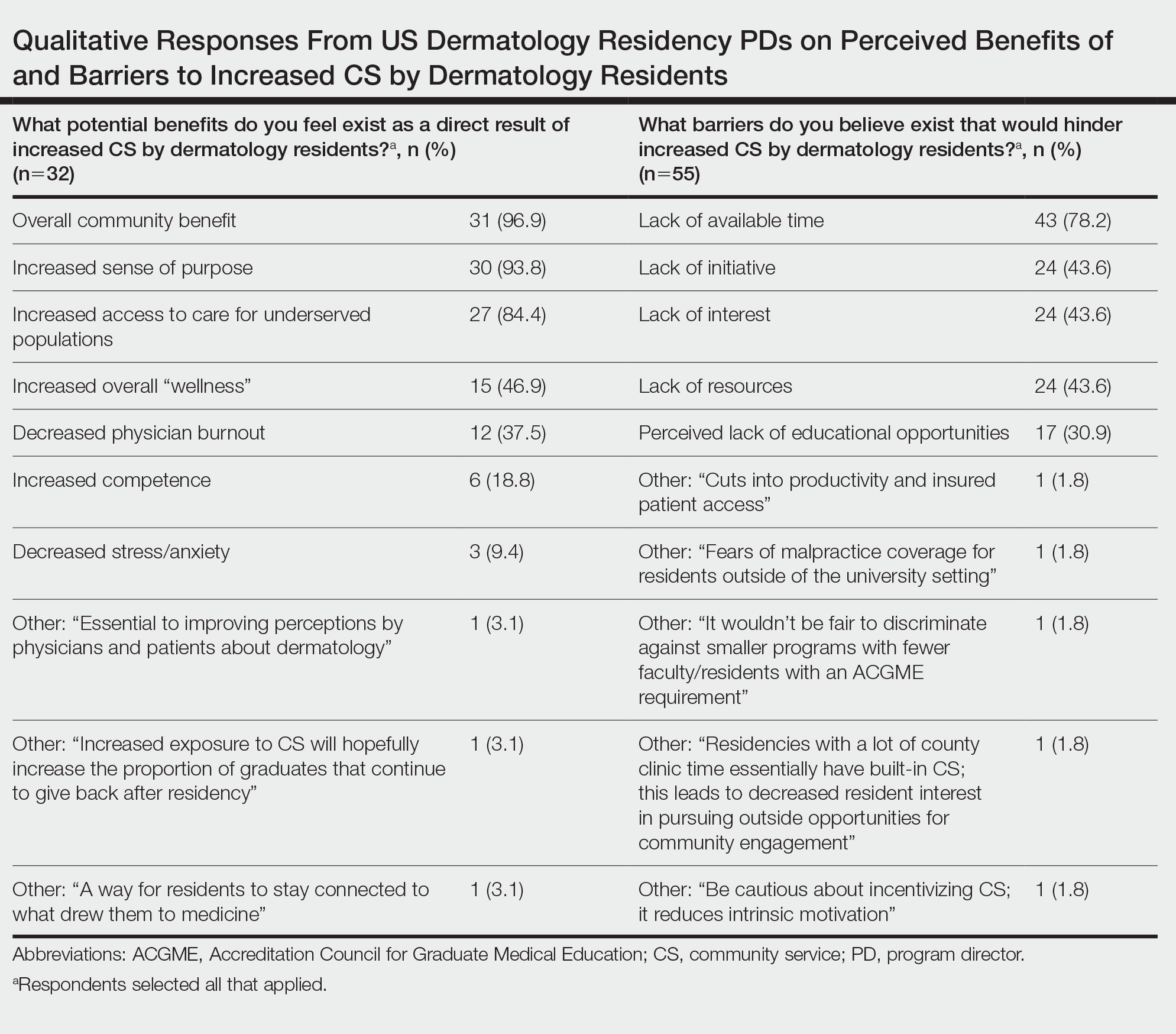
Qualitative responses revealed that some PDs view CS as “a way for residents to stay connected to what drew them to medicine” and “essential to improving perceptions by physicians and patients about dermatology.” Program directors perceived lack of available time, initiative, and resources as well as minimal resident interest, malpractice coverage, and lack of educational opportunities as potential barriers to CS involvement by residents (Table). Forty-six (59.0%) PDs believed that CS should not be an ACGME requirement for dermatology training, 23 (29.5%) believed it should be required, and 9 (11.5%) were undecided.
Feedback From Residents—We received responses from 92 current dermatology residents and recent dermatology residency graduates; 86 (93.5%) respondents were trainees or recent graduates from academic dermatology residency training programs, and 6 (6.5%) were from community-based training programs. Community service was perceived to be an important part of dermatology training by 68 (73.9%) respondents, and dermatology-specific CS opportunities were available to 65 (70.7%) respondents (Figure 1). Although CS was required of only 7 (7.6%) respondents, 36 (39.1%) respondents volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during residency training. Among respondents who were not provided CS opportunities through their residency program, 23 (85.2%) stated they would have participated if given the opportunity.
Dermatology residents listed increased access to care for marginalized populations, increased sense of purpose, increased competence, and decreased burnout as perceived benefits of participation in CS. Of the dermatology residents who volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during training, 27 (75.0%) regarded the experience as a “high-yield learning opportunity.” Additionally, 29 (80.6%) residents stated their participation in a free dermatology clinic increased their awareness of health disparities and societal factors affecting dermatologic care in underserved patient populations. These respondents affirmed that their participation motivated them to become more involved in outreach targeting underserved populations throughout the duration of their careers.
Comment
The results of this nationwide survey have several important implications for dermatology residency programs, with a focus on programs in well-resourced and high socioeconomic status areas. Although most PDs believe that CS is important for dermatology resident training, few programs have CS requirements, and the majority are opposed to ACGME-mandated CS. Dermatology residents and recent graduates overwhelmingly conveyed that participation in a free dermatology clinic during residency training increased their knowledge base surrounding socioeconomic determinants of health and practicing in resource-limited settings. Furthermore, most trainees expressed that CS participation as a resident motivated them to continue to partake in CS for the underserved as an attending physician. The discordance between perceived value of CS by residents and the lack of CS requirements and opportunities by residency programs represents a realistic opportunity for residency training programs to integrate CS into the curriculum.
Residency programs that integrate service for the underserved into their program goals are 3 times more successful in graduating dermatology residents who practice in underserved communities.9 Patients in marginalized communities and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds face many barriers to accessing dermatologic care including longer wait times and higher practice rejection rates than patients with private insurance.6 Through increased CS opportunities, dermatology residency programs can strengthen the local health care infrastructure and bridge the gap in access to dermatologic care.
By establishing a formal CS rotation in dermatology residency programs, residents will experience invaluable first-hand educational opportunities, provide comprehensive care for patients in resource-limited settings, and hopefully continue to serve in marginalized communities. Incorporating service for the underserved into the dermatology residency curriculum not only enhances the cultural competency of trainees but also mandates that skin health equity be made a priority. By exposing dermatology residents to the diverse patient populations often served by free clinics, residents will increase their knowledge of skin disease presentation in patients with darker skin tones, which has historically been deficient in medical education.10,11
The limitations of this survey study included recall bias, the response rate of PDs (54.9%), and the inability to determine response rate of residents, as we were unable to establish the total number of residents who received our survey. Based on geographic location, some dermatology residency programs may treat a high percentage of medically underserved patients, which already improves access to dermatology. For this reason, follow-up studies correlating PD and resident responses with region, program size, and university/community affiliation will increase our understanding of CS participation and perceptions.
Conclusion
Dermatology residency program participation in CS helps reduce barriers to access for patients in marginalized communities. Incorporating CS into the dermatology residency program curriculum creates a rewarding training environment that increases skin health equity, fosters an interest in health disparities, and enhances the cultural competency of its trainees.
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Resneck J, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Resneck J, Pletcher MJ, Lozano N. Medicare, Medicaid, and access to dermatologists: the effect of patient insurance on appointment access and wait times. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:85-92.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Vance MC, Kennedy KG. Developing an advocacy curriculum: lessons learned from a national survey of psychiatric residency programs. Acad Psychiatry. 2020;44:283-288.
- Blanco G, Vasquez R, Nezafati K, et al. How residency programs can foster practice for the underserved. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:158-159.
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
Community service (CS) or service learning in dermatology (eg, free skin cancer screenings, providing care through free clinics, free teledermatology consultations) is instrumental in mitigating disparities and improving access to equitable dermatologic care. With the rate of underinsured and uninsured patients on the rise, free and federally qualified clinics frequently are the sole means by which patients access specialty care such as dermatology.1 Contributing to the economic gap in access, the geographic disparity of dermatologists in the United States continues to climb, and many marginalized communities remain without dermatologists.2 Nearly 30% of the total US population resides in geographic areas that are underserved by dermatologists, while there appears to be an oversupply of dermatologists in urban areas.3 Dermatologists practicing in rural areas make up only 10% of the dermatology workforce,4 whereas 40% of all dermatologists practice in the most densely populated US cities.5 Consequently, patients in these underserved communities face longer wait times6 and are less likely to utilize dermatology services than patients in dermatologist-dense geographic areas.7
Service opportunities have become increasingly integrated into graduate medical education.8 These service activities help bridge the health care access gap while fulfilling Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) requirements. Our study assessed the importance of CS to dermatology residency program directors (PDs), dermatology residents, and recent dermatology residency graduates. Herein, we describe the perceptions of CS within dermatology residency training among PDs and residents.
Methods
In this study, CS is defined as participation in activities to increase dermatologic access, education, and resources to underserved communities. Using the approved Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve and direct email communication, we surveyed 142 PDs of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency training programs. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 17-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
We also surveyed current dermatology residents and recent graduates of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs via PDs nationwide. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 19-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
Descriptive statistics were used for data analysis for both Qualtrics surveys. The University of Pittsburgh institutional review board deemed this study exempt.

Results
Feedback From PDs—Of the 142 PDs, we received 78 responses (54.9%). For selection of dermatology residents, CS was moderately to extremely important to 64 (82.1%) PDs, and 63 (80.8%) PDs stated CS was moderately to extremely important to their dermatology residency program at large. For dermatology residency training, 66 (84.6%) PDs believed CS is important, whereas 3 (3.8%) believed it is not important, and 9 (11.5%) remained undecided (Figure 1). Notably, 17 (21.8%) programs required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum, with most of these programs requiring 10 hours or less during the 3 years of residency training. Of the programs with required CS, 15 (88.2%) had dermatology-specific CS requirements, with 10 (58.8%) programs involved in CS at free and/or underserved clinics and some programs participating in other CS activities, such as advocacy, mentorship, educational outreach, or sports (Figure 2A).

Community service opportunities were offered to dermatology residents by 69 (88.5%) programs, including the 17 programs that required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum. Among these programs with optional CS, 43 (82.7%) PDs reported CS opportunities at free and/or underserved clinics, and 30 (57.7%) reported CS opportunities through global health initiatives (Figure 2B). Other CS opportunities offered included partnerships with community outreach organizations and mentoring underprivileged students. Patient populations that benefit from CS offered by these dermatology residency programs included 55 (79.7%) underserved, 33 (47.8%) minority, 31 (44.9%) immigrant, 14 (20.3%) pediatric, 14 (20.3%) elderly, and 10 (14.5%) rural populations (Figure 2C). At dermatology residency programs with optional CS opportunities, 22 (42.3%) PDs endorsed at least 50% of their residents participating in these activities.
Qualitative responses revealed that some PDs view CS as “a way for residents to stay connected to what drew them to medicine” and “essential to improving perceptions by physicians and patients about dermatology.” Program directors perceived lack of available time, initiative, and resources as well as minimal resident interest, malpractice coverage, and lack of educational opportunities as potential barriers to CS involvement by residents (Table). Forty-six (59.0%) PDs believed that CS should not be an ACGME requirement for dermatology training, 23 (29.5%) believed it should be required, and 9 (11.5%) were undecided.

Feedback From Residents—We received responses from 92 current dermatology residents and recent dermatology residency graduates; 86 (93.5%) respondents were trainees or recent graduates from academic dermatology residency training programs, and 6 (6.5%) were from community-based training programs. Community service was perceived to be an important part of dermatology training by 68 (73.9%) respondents, and dermatology-specific CS opportunities were available to 65 (70.7%) respondents (Figure 1). Although CS was required of only 7 (7.6%) respondents, 36 (39.1%) respondents volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during residency training. Among respondents who were not provided CS opportunities through their residency program, 23 (85.2%) stated they would have participated if given the opportunity.
Dermatology residents listed increased access to care for marginalized populations, increased sense of purpose, increased competence, and decreased burnout as perceived benefits of participation in CS. Of the dermatology residents who volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during training, 27 (75.0%) regarded the experience as a “high-yield learning opportunity.” Additionally, 29 (80.6%) residents stated their participation in a free dermatology clinic increased their awareness of health disparities and societal factors affecting dermatologic care in underserved patient populations. These respondents affirmed that their participation motivated them to become more involved in outreach targeting underserved populations throughout the duration of their careers.
Comment
The results of this nationwide survey have several important implications for dermatology residency programs, with a focus on programs in well-resourced and high socioeconomic status areas. Although most PDs believe that CS is important for dermatology resident training, few programs have CS requirements, and the majority are opposed to ACGME-mandated CS. Dermatology residents and recent graduates overwhelmingly conveyed that participation in a free dermatology clinic during residency training increased their knowledge base surrounding socioeconomic determinants of health and practicing in resource-limited settings. Furthermore, most trainees expressed that CS participation as a resident motivated them to continue to partake in CS for the underserved as an attending physician. The discordance between perceived value of CS by residents and the lack of CS requirements and opportunities by residency programs represents a realistic opportunity for residency training programs to integrate CS into the curriculum.
Residency programs that integrate service for the underserved into their program goals are 3 times more successful in graduating dermatology residents who practice in underserved communities.9 Patients in marginalized communities and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds face many barriers to accessing dermatologic care including longer wait times and higher practice rejection rates than patients with private insurance.6 Through increased CS opportunities, dermatology residency programs can strengthen the local health care infrastructure and bridge the gap in access to dermatologic care.
By establishing a formal CS rotation in dermatology residency programs, residents will experience invaluable first-hand educational opportunities, provide comprehensive care for patients in resource-limited settings, and hopefully continue to serve in marginalized communities. Incorporating service for the underserved into the dermatology residency curriculum not only enhances the cultural competency of trainees but also mandates that skin health equity be made a priority. By exposing dermatology residents to the diverse patient populations often served by free clinics, residents will increase their knowledge of skin disease presentation in patients with darker skin tones, which has historically been deficient in medical education.10,11
The limitations of this survey study included recall bias, the response rate of PDs (54.9%), and the inability to determine response rate of residents, as we were unable to establish the total number of residents who received our survey. Based on geographic location, some dermatology residency programs may treat a high percentage of medically underserved patients, which already improves access to dermatology. For this reason, follow-up studies correlating PD and resident responses with region, program size, and university/community affiliation will increase our understanding of CS participation and perceptions.
Conclusion
Dermatology residency program participation in CS helps reduce barriers to access for patients in marginalized communities. Incorporating CS into the dermatology residency program curriculum creates a rewarding training environment that increases skin health equity, fosters an interest in health disparities, and enhances the cultural competency of its trainees.
Community service (CS) or service learning in dermatology (eg, free skin cancer screenings, providing care through free clinics, free teledermatology consultations) is instrumental in mitigating disparities and improving access to equitable dermatologic care. With the rate of underinsured and uninsured patients on the rise, free and federally qualified clinics frequently are the sole means by which patients access specialty care such as dermatology.1 Contributing to the economic gap in access, the geographic disparity of dermatologists in the United States continues to climb, and many marginalized communities remain without dermatologists.2 Nearly 30% of the total US population resides in geographic areas that are underserved by dermatologists, while there appears to be an oversupply of dermatologists in urban areas.3 Dermatologists practicing in rural areas make up only 10% of the dermatology workforce,4 whereas 40% of all dermatologists practice in the most densely populated US cities.5 Consequently, patients in these underserved communities face longer wait times6 and are less likely to utilize dermatology services than patients in dermatologist-dense geographic areas.7
Service opportunities have become increasingly integrated into graduate medical education.8 These service activities help bridge the health care access gap while fulfilling Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) requirements. Our study assessed the importance of CS to dermatology residency program directors (PDs), dermatology residents, and recent dermatology residency graduates. Herein, we describe the perceptions of CS within dermatology residency training among PDs and residents.
Methods
In this study, CS is defined as participation in activities to increase dermatologic access, education, and resources to underserved communities. Using the approved Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve and direct email communication, we surveyed 142 PDs of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency training programs. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 17-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
We also surveyed current dermatology residents and recent graduates of ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs via PDs nationwide. The deidentified respondents voluntarily completed a 19-question Qualtrics survey with a 5-point Likert scale (extremely, very, moderately, slightly, or not at all), yes/no/undecided, and qualitative responses.
Descriptive statistics were used for data analysis for both Qualtrics surveys. The University of Pittsburgh institutional review board deemed this study exempt.

Results
Feedback From PDs—Of the 142 PDs, we received 78 responses (54.9%). For selection of dermatology residents, CS was moderately to extremely important to 64 (82.1%) PDs, and 63 (80.8%) PDs stated CS was moderately to extremely important to their dermatology residency program at large. For dermatology residency training, 66 (84.6%) PDs believed CS is important, whereas 3 (3.8%) believed it is not important, and 9 (11.5%) remained undecided (Figure 1). Notably, 17 (21.8%) programs required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum, with most of these programs requiring 10 hours or less during the 3 years of residency training. Of the programs with required CS, 15 (88.2%) had dermatology-specific CS requirements, with 10 (58.8%) programs involved in CS at free and/or underserved clinics and some programs participating in other CS activities, such as advocacy, mentorship, educational outreach, or sports (Figure 2A).

Community service opportunities were offered to dermatology residents by 69 (88.5%) programs, including the 17 programs that required CS as part of the dermatology educational curriculum. Among these programs with optional CS, 43 (82.7%) PDs reported CS opportunities at free and/or underserved clinics, and 30 (57.7%) reported CS opportunities through global health initiatives (Figure 2B). Other CS opportunities offered included partnerships with community outreach organizations and mentoring underprivileged students. Patient populations that benefit from CS offered by these dermatology residency programs included 55 (79.7%) underserved, 33 (47.8%) minority, 31 (44.9%) immigrant, 14 (20.3%) pediatric, 14 (20.3%) elderly, and 10 (14.5%) rural populations (Figure 2C). At dermatology residency programs with optional CS opportunities, 22 (42.3%) PDs endorsed at least 50% of their residents participating in these activities.
Qualitative responses revealed that some PDs view CS as “a way for residents to stay connected to what drew them to medicine” and “essential to improving perceptions by physicians and patients about dermatology.” Program directors perceived lack of available time, initiative, and resources as well as minimal resident interest, malpractice coverage, and lack of educational opportunities as potential barriers to CS involvement by residents (Table). Forty-six (59.0%) PDs believed that CS should not be an ACGME requirement for dermatology training, 23 (29.5%) believed it should be required, and 9 (11.5%) were undecided.

Feedback From Residents—We received responses from 92 current dermatology residents and recent dermatology residency graduates; 86 (93.5%) respondents were trainees or recent graduates from academic dermatology residency training programs, and 6 (6.5%) were from community-based training programs. Community service was perceived to be an important part of dermatology training by 68 (73.9%) respondents, and dermatology-specific CS opportunities were available to 65 (70.7%) respondents (Figure 1). Although CS was required of only 7 (7.6%) respondents, 36 (39.1%) respondents volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during residency training. Among respondents who were not provided CS opportunities through their residency program, 23 (85.2%) stated they would have participated if given the opportunity.
Dermatology residents listed increased access to care for marginalized populations, increased sense of purpose, increased competence, and decreased burnout as perceived benefits of participation in CS. Of the dermatology residents who volunteered at a free dermatology clinic during training, 27 (75.0%) regarded the experience as a “high-yield learning opportunity.” Additionally, 29 (80.6%) residents stated their participation in a free dermatology clinic increased their awareness of health disparities and societal factors affecting dermatologic care in underserved patient populations. These respondents affirmed that their participation motivated them to become more involved in outreach targeting underserved populations throughout the duration of their careers.
Comment
The results of this nationwide survey have several important implications for dermatology residency programs, with a focus on programs in well-resourced and high socioeconomic status areas. Although most PDs believe that CS is important for dermatology resident training, few programs have CS requirements, and the majority are opposed to ACGME-mandated CS. Dermatology residents and recent graduates overwhelmingly conveyed that participation in a free dermatology clinic during residency training increased their knowledge base surrounding socioeconomic determinants of health and practicing in resource-limited settings. Furthermore, most trainees expressed that CS participation as a resident motivated them to continue to partake in CS for the underserved as an attending physician. The discordance between perceived value of CS by residents and the lack of CS requirements and opportunities by residency programs represents a realistic opportunity for residency training programs to integrate CS into the curriculum.
Residency programs that integrate service for the underserved into their program goals are 3 times more successful in graduating dermatology residents who practice in underserved communities.9 Patients in marginalized communities and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds face many barriers to accessing dermatologic care including longer wait times and higher practice rejection rates than patients with private insurance.6 Through increased CS opportunities, dermatology residency programs can strengthen the local health care infrastructure and bridge the gap in access to dermatologic care.
By establishing a formal CS rotation in dermatology residency programs, residents will experience invaluable first-hand educational opportunities, provide comprehensive care for patients in resource-limited settings, and hopefully continue to serve in marginalized communities. Incorporating service for the underserved into the dermatology residency curriculum not only enhances the cultural competency of trainees but also mandates that skin health equity be made a priority. By exposing dermatology residents to the diverse patient populations often served by free clinics, residents will increase their knowledge of skin disease presentation in patients with darker skin tones, which has historically been deficient in medical education.10,11
The limitations of this survey study included recall bias, the response rate of PDs (54.9%), and the inability to determine response rate of residents, as we were unable to establish the total number of residents who received our survey. Based on geographic location, some dermatology residency programs may treat a high percentage of medically underserved patients, which already improves access to dermatology. For this reason, follow-up studies correlating PD and resident responses with region, program size, and university/community affiliation will increase our understanding of CS participation and perceptions.
Conclusion
Dermatology residency program participation in CS helps reduce barriers to access for patients in marginalized communities. Incorporating CS into the dermatology residency program curriculum creates a rewarding training environment that increases skin health equity, fosters an interest in health disparities, and enhances the cultural competency of its trainees.
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Resneck J, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Resneck J, Pletcher MJ, Lozano N. Medicare, Medicaid, and access to dermatologists: the effect of patient insurance on appointment access and wait times. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:85-92.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Vance MC, Kennedy KG. Developing an advocacy curriculum: lessons learned from a national survey of psychiatric residency programs. Acad Psychiatry. 2020;44:283-288.
- Blanco G, Vasquez R, Nezafati K, et al. How residency programs can foster practice for the underserved. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:158-159.
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Resneck J, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Resneck J, Pletcher MJ, Lozano N. Medicare, Medicaid, and access to dermatologists: the effect of patient insurance on appointment access and wait times. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:85-92.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Vance MC, Kennedy KG. Developing an advocacy curriculum: lessons learned from a national survey of psychiatric residency programs. Acad Psychiatry. 2020;44:283-288.
- Blanco G, Vasquez R, Nezafati K, et al. How residency programs can foster practice for the underserved. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:158-159.
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
Practice Points
- Participation of dermatology residents in service-learning experiences increases awareness of health disparities and social factors impacting dermatologic care and promotes a lifelong commitment to serving vulnerable populations.
- Integrating service learning into the dermatology residency program curriculum enhances trainees’ cultural sensitivity and encourages the prioritization of skin health equity.
- Service learning will help bridge the gap in access to dermatologic care for patients in medically marginalized communities.
Nail Salon Safety: From Nail Dystrophy to Acrylate Contact Allergies
As residents, it is important to understand the steps of the manicuring process and be able to inform patients on how to maintain optimal nail health while continuing to go to nail salons. Most patients are not aware of the possible allergic, traumatic, and/or infectious complications of manicuring their nails. There are practical steps that can be taken to prevent nail issues, such as avoiding cutting one’s cuticles or using allergen-free nail polishes. These simple fixes can make a big difference in long-term nail health in our patients.
Nail Polish Application Process
The nails are first soaked in a warm soapy solution to soften the nail plate and cuticles.1 Then the nail tips and plates are filed and occasionally are smoothed with a drill. The cuticles are cut with a cuticle cutter. Nail polish—base coat, color enamel, and top coat—is then applied to the nail. Acrylic or sculptured nails and gel and dip manicures are composed of chemical monomers and polymers that harden either at room temperature or through UV or light-emitting diode (LED) exposure. The chemicals in these products can damage nails and cause allergic reactions.
Contact Dermatitis
Approximately 2% of individuals have been found to have allergic or irritant contact dermatitis to nail care products. The top 5 allergens implicated in nail products are (1) 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, (2) methyl methacrylate, (3) ethyl acrylate, (4) ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate, and (5) tosylamide.2 Methyl methacrylate was banned in 1974 by the US Food and Drug Administration due to reports of severe contact dermatitis, paronychia, and nail dystrophy.3 Due to their potent sensitizing effects, acrylates were named the contact allergen of the year in 2012 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.3
Acrylates are plastic products formed by polymerization of acrylic or methacrylic acid.4 Artificial sculptured nails are created by mixing powdered polymethyl methacrylate polymers and liquid ethyl or isobutyl methacrylate monomers and then applying this mixture to the nail plate.5 Gel and powder nails employ a mixture that is similar to acrylic powders, which require UV or LED radiation to polymerize and harden on the nail plate.
Tosylamide, or tosylamide formaldehyde resin, is another potent allergen that promotes adhesion of the enamel to the nail.6 It is important to note that sensitization may develop months to years after using artificial nails.
Clinical features of contact allergy secondary to nail polish can vary. Some patients experience severe periungual dermatitis. Others can present with facial or eyelid dermatitis due to exposure to airborne particles of acrylates or from contact with fingertips bearing acrylic nails.6,7 If inhaled, acrylates also can cause wheezing asthma or allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Common Onychodystrophies
Damage to the natural nail plate is inevitable with continued wear of sculptured nails. With 2 to 4 months of consecutive wear, the natural nails turn yellow, brittle, and weak.5 One study noted that the thickness of an individual’s left thumb nail plate thinned from 0.059 cm to 0.03 cm after a gel manicure was removed from the nail.8 Nail injuries due to manicuring include keratin granulations, onycholysis, pincer nail deformities, pseudopsoriatic nails, lamellar onychoschizia, transverse leukonychia, and ingrown nails.6 One interesting nail dystrophy reported secondary to gel manicures is pterygium inversum unguis or a ventral pterygium that causes an abnormal painful adherence of the hyponychium to the ventral surface of the nail plate. Patients prone to developing pterygium inversum unguis can experience sensitivity, pain, or burning sensations during LED or UVA light exposure.9
Infections
In addition to contact allergies and nail dystrophies, each step of the manicuring process, such as cutting cuticles, presents opportunities for infectious agents to enter the nail fold. Acute or chronic paronychia, or inflammation of the nail fold, most commonly is caused by bacterial infections with Staphylococcus aureus. Green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa also is common.1 Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton rubrum is one of the most frequent fungal infections contracted at nail salons. Mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium fortuitum also have been implicated in infections from salons, as they can be found in the jets of pedicure spas, which are not sanitized regularly.10
Final Thoughts
Nail cosmetics are an integral part of many patients’ lives. Being able to educate yourself and your patients on the hazards of nail salons can help them avoid painful infections, contact allergies, and acute to chronic nail deformities. It is important for residents to be aware of the different dermatoses that can arise in men and women who frequent nail salons as the popularity of the nail beauty industry continues to rise.
- Reinecke JK, Hinshaw MA. Nail health in women. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:73-79. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.01.006
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermatitis. 2020;31:191-201. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000583
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society allergens of the year 2000 to 2020 [published online April 25, 2020]. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.011
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Draelos ZD. Cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:2587-2588.
- Iorizzo M, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. Nail cosmetics in nail disorders.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2007;6:53-58. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2007.00290.x
- Maio P, Carvalho R, Amaro C, et al. Letter: allergic contact dermatitis from sculptured acrylic nails: special presentation with a possible airborne pattern. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:13.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00595.x
- Cervantes J, Sanchez M, Eber AE, et al. Pterygium inversum unguis secondary to gel polish [published online October 16, 2017]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:160-163. doi:10.1111/jdv.14603
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
As residents, it is important to understand the steps of the manicuring process and be able to inform patients on how to maintain optimal nail health while continuing to go to nail salons. Most patients are not aware of the possible allergic, traumatic, and/or infectious complications of manicuring their nails. There are practical steps that can be taken to prevent nail issues, such as avoiding cutting one’s cuticles or using allergen-free nail polishes. These simple fixes can make a big difference in long-term nail health in our patients.
Nail Polish Application Process
The nails are first soaked in a warm soapy solution to soften the nail plate and cuticles.1 Then the nail tips and plates are filed and occasionally are smoothed with a drill. The cuticles are cut with a cuticle cutter. Nail polish—base coat, color enamel, and top coat—is then applied to the nail. Acrylic or sculptured nails and gel and dip manicures are composed of chemical monomers and polymers that harden either at room temperature or through UV or light-emitting diode (LED) exposure. The chemicals in these products can damage nails and cause allergic reactions.
Contact Dermatitis
Approximately 2% of individuals have been found to have allergic or irritant contact dermatitis to nail care products. The top 5 allergens implicated in nail products are (1) 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, (2) methyl methacrylate, (3) ethyl acrylate, (4) ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate, and (5) tosylamide.2 Methyl methacrylate was banned in 1974 by the US Food and Drug Administration due to reports of severe contact dermatitis, paronychia, and nail dystrophy.3 Due to their potent sensitizing effects, acrylates were named the contact allergen of the year in 2012 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.3
Acrylates are plastic products formed by polymerization of acrylic or methacrylic acid.4 Artificial sculptured nails are created by mixing powdered polymethyl methacrylate polymers and liquid ethyl or isobutyl methacrylate monomers and then applying this mixture to the nail plate.5 Gel and powder nails employ a mixture that is similar to acrylic powders, which require UV or LED radiation to polymerize and harden on the nail plate.
Tosylamide, or tosylamide formaldehyde resin, is another potent allergen that promotes adhesion of the enamel to the nail.6 It is important to note that sensitization may develop months to years after using artificial nails.
Clinical features of contact allergy secondary to nail polish can vary. Some patients experience severe periungual dermatitis. Others can present with facial or eyelid dermatitis due to exposure to airborne particles of acrylates or from contact with fingertips bearing acrylic nails.6,7 If inhaled, acrylates also can cause wheezing asthma or allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Common Onychodystrophies
Damage to the natural nail plate is inevitable with continued wear of sculptured nails. With 2 to 4 months of consecutive wear, the natural nails turn yellow, brittle, and weak.5 One study noted that the thickness of an individual’s left thumb nail plate thinned from 0.059 cm to 0.03 cm after a gel manicure was removed from the nail.8 Nail injuries due to manicuring include keratin granulations, onycholysis, pincer nail deformities, pseudopsoriatic nails, lamellar onychoschizia, transverse leukonychia, and ingrown nails.6 One interesting nail dystrophy reported secondary to gel manicures is pterygium inversum unguis or a ventral pterygium that causes an abnormal painful adherence of the hyponychium to the ventral surface of the nail plate. Patients prone to developing pterygium inversum unguis can experience sensitivity, pain, or burning sensations during LED or UVA light exposure.9
Infections
In addition to contact allergies and nail dystrophies, each step of the manicuring process, such as cutting cuticles, presents opportunities for infectious agents to enter the nail fold. Acute or chronic paronychia, or inflammation of the nail fold, most commonly is caused by bacterial infections with Staphylococcus aureus. Green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa also is common.1 Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton rubrum is one of the most frequent fungal infections contracted at nail salons. Mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium fortuitum also have been implicated in infections from salons, as they can be found in the jets of pedicure spas, which are not sanitized regularly.10
Final Thoughts
Nail cosmetics are an integral part of many patients’ lives. Being able to educate yourself and your patients on the hazards of nail salons can help them avoid painful infections, contact allergies, and acute to chronic nail deformities. It is important for residents to be aware of the different dermatoses that can arise in men and women who frequent nail salons as the popularity of the nail beauty industry continues to rise.
As residents, it is important to understand the steps of the manicuring process and be able to inform patients on how to maintain optimal nail health while continuing to go to nail salons. Most patients are not aware of the possible allergic, traumatic, and/or infectious complications of manicuring their nails. There are practical steps that can be taken to prevent nail issues, such as avoiding cutting one’s cuticles or using allergen-free nail polishes. These simple fixes can make a big difference in long-term nail health in our patients.
Nail Polish Application Process
The nails are first soaked in a warm soapy solution to soften the nail plate and cuticles.1 Then the nail tips and plates are filed and occasionally are smoothed with a drill. The cuticles are cut with a cuticle cutter. Nail polish—base coat, color enamel, and top coat—is then applied to the nail. Acrylic or sculptured nails and gel and dip manicures are composed of chemical monomers and polymers that harden either at room temperature or through UV or light-emitting diode (LED) exposure. The chemicals in these products can damage nails and cause allergic reactions.
Contact Dermatitis
Approximately 2% of individuals have been found to have allergic or irritant contact dermatitis to nail care products. The top 5 allergens implicated in nail products are (1) 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, (2) methyl methacrylate, (3) ethyl acrylate, (4) ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate, and (5) tosylamide.2 Methyl methacrylate was banned in 1974 by the US Food and Drug Administration due to reports of severe contact dermatitis, paronychia, and nail dystrophy.3 Due to their potent sensitizing effects, acrylates were named the contact allergen of the year in 2012 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.3
Acrylates are plastic products formed by polymerization of acrylic or methacrylic acid.4 Artificial sculptured nails are created by mixing powdered polymethyl methacrylate polymers and liquid ethyl or isobutyl methacrylate monomers and then applying this mixture to the nail plate.5 Gel and powder nails employ a mixture that is similar to acrylic powders, which require UV or LED radiation to polymerize and harden on the nail plate.
Tosylamide, or tosylamide formaldehyde resin, is another potent allergen that promotes adhesion of the enamel to the nail.6 It is important to note that sensitization may develop months to years after using artificial nails.
Clinical features of contact allergy secondary to nail polish can vary. Some patients experience severe periungual dermatitis. Others can present with facial or eyelid dermatitis due to exposure to airborne particles of acrylates or from contact with fingertips bearing acrylic nails.6,7 If inhaled, acrylates also can cause wheezing asthma or allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Common Onychodystrophies
Damage to the natural nail plate is inevitable with continued wear of sculptured nails. With 2 to 4 months of consecutive wear, the natural nails turn yellow, brittle, and weak.5 One study noted that the thickness of an individual’s left thumb nail plate thinned from 0.059 cm to 0.03 cm after a gel manicure was removed from the nail.8 Nail injuries due to manicuring include keratin granulations, onycholysis, pincer nail deformities, pseudopsoriatic nails, lamellar onychoschizia, transverse leukonychia, and ingrown nails.6 One interesting nail dystrophy reported secondary to gel manicures is pterygium inversum unguis or a ventral pterygium that causes an abnormal painful adherence of the hyponychium to the ventral surface of the nail plate. Patients prone to developing pterygium inversum unguis can experience sensitivity, pain, or burning sensations during LED or UVA light exposure.9
Infections
In addition to contact allergies and nail dystrophies, each step of the manicuring process, such as cutting cuticles, presents opportunities for infectious agents to enter the nail fold. Acute or chronic paronychia, or inflammation of the nail fold, most commonly is caused by bacterial infections with Staphylococcus aureus. Green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa also is common.1 Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton rubrum is one of the most frequent fungal infections contracted at nail salons. Mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium fortuitum also have been implicated in infections from salons, as they can be found in the jets of pedicure spas, which are not sanitized regularly.10
Final Thoughts
Nail cosmetics are an integral part of many patients’ lives. Being able to educate yourself and your patients on the hazards of nail salons can help them avoid painful infections, contact allergies, and acute to chronic nail deformities. It is important for residents to be aware of the different dermatoses that can arise in men and women who frequent nail salons as the popularity of the nail beauty industry continues to rise.
- Reinecke JK, Hinshaw MA. Nail health in women. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:73-79. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.01.006
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermatitis. 2020;31:191-201. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000583
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society allergens of the year 2000 to 2020 [published online April 25, 2020]. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.011
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Draelos ZD. Cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:2587-2588.
- Iorizzo M, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. Nail cosmetics in nail disorders.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2007;6:53-58. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2007.00290.x
- Maio P, Carvalho R, Amaro C, et al. Letter: allergic contact dermatitis from sculptured acrylic nails: special presentation with a possible airborne pattern. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:13.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00595.x
- Cervantes J, Sanchez M, Eber AE, et al. Pterygium inversum unguis secondary to gel polish [published online October 16, 2017]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:160-163. doi:10.1111/jdv.14603
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
- Reinecke JK, Hinshaw MA. Nail health in women. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:73-79. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.01.006
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermatitis. 2020;31:191-201. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000583
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society allergens of the year 2000 to 2020 [published online April 25, 2020]. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.011
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Draelos ZD. Cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:2587-2588.
- Iorizzo M, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. Nail cosmetics in nail disorders.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2007;6:53-58. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2007.00290.x
- Maio P, Carvalho R, Amaro C, et al. Letter: allergic contact dermatitis from sculptured acrylic nails: special presentation with a possible airborne pattern. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:13.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00595.x
- Cervantes J, Sanchez M, Eber AE, et al. Pterygium inversum unguis secondary to gel polish [published online October 16, 2017]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:160-163. doi:10.1111/jdv.14603
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
Resident Pearls
- Every step of the nail manicuring process presents opportunities for nail trauma, infections, and contact dermatitis.
- As residents, it is important to be aware of the hazards associated with nail salons and educate our patients accordingly.
- Nail health is essential to optimizing everyday work for our patients—whether it entails taking care of children, typing, or other hands-on activities.
Haven’t had COVID yet? Wanna bet?
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long COVID comes in three forms: Study
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Burnout and stress of today: How do we cope?
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Cultural humility required to optimize treatment of eczema patients with skin of color
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
AT SPD 2022
Solitary Pink Plaque on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.
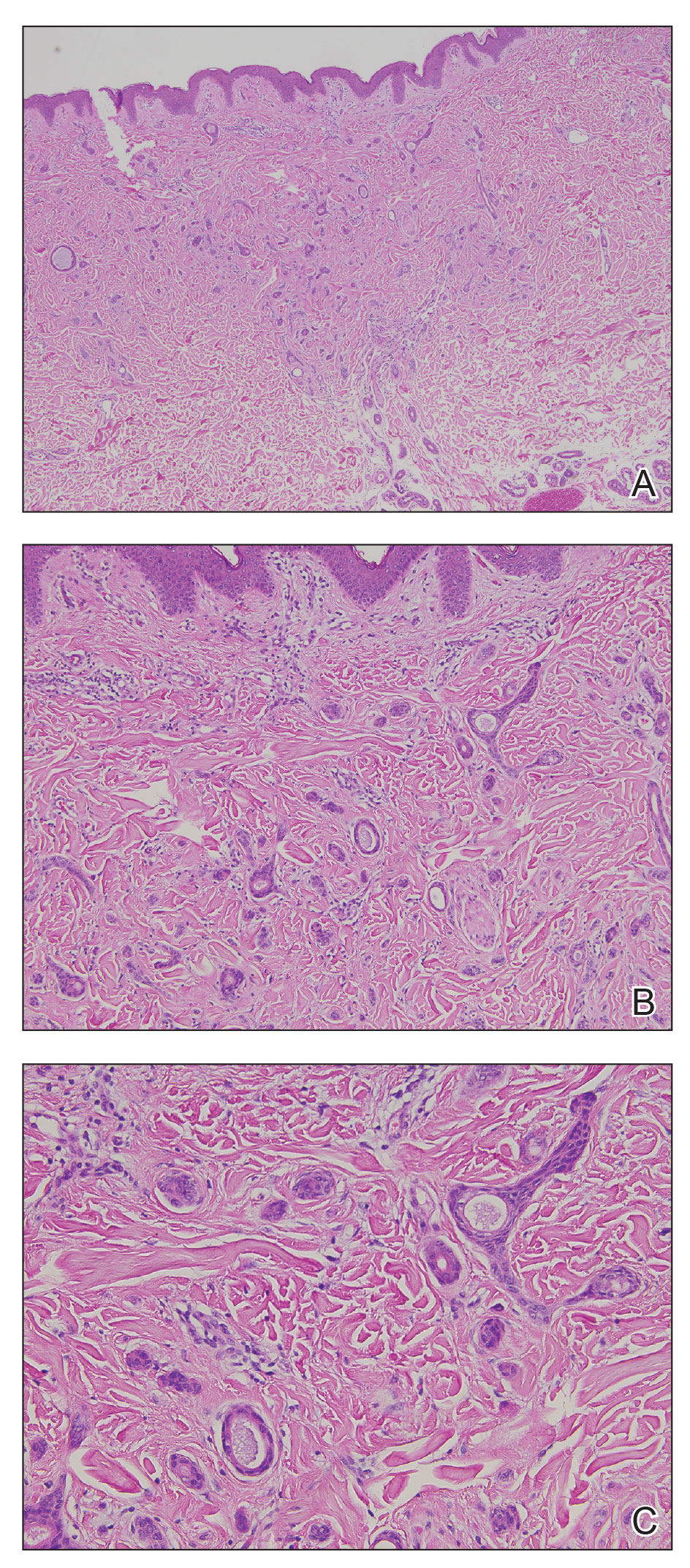
Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6
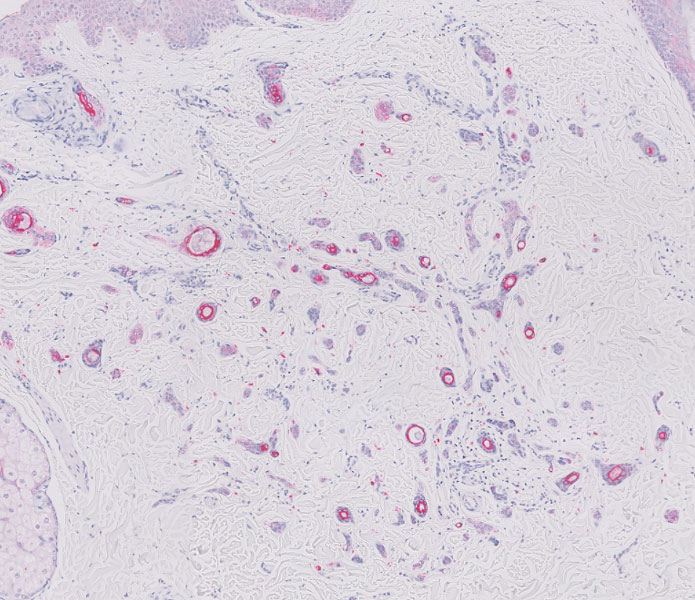
Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
A 17-year-old adolescent girl presented with a solitary, 8-cm, pink plaque on the anterior aspect of the neck of 5 years’ duration. No similar skin findings were present elsewhere on the body. The rash was not painful or pruritic, and she denied prior trauma to the site. The patient previously had tried a salicylic acid bodywash as well as mupirocin cream 2% and mometasone ointment with no improvement. Her medical history was unremarkable, and she had no known allergies. There was no family history of a similar rash. Physical examination revealed no palpable subcutaneous lumps or masses and no lymphadenopathy of the head or neck. An incisional biopsy was performed.
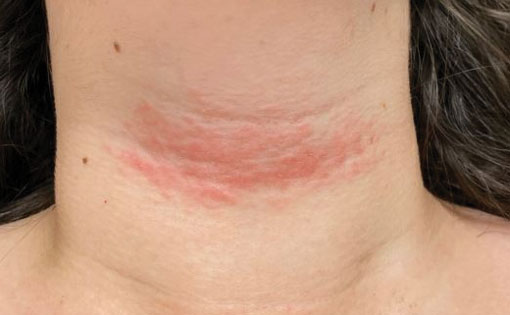
Ustekinumab becomes second biologic approved for PsA in kids
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six specialties attracting the highest private equity acquisitions
While tracking the extent of physician practice acquisition by private equity firms may be difficult, new research highlights what specialties and U.S. regions are most affected by such purchases.
The study, supported by the National Institute for Health Care Management (NIHCM), examined 97,094 physicians practicing in six specialties, 4,738 of whom worked in private equity–acquired practices. Of these specialties, 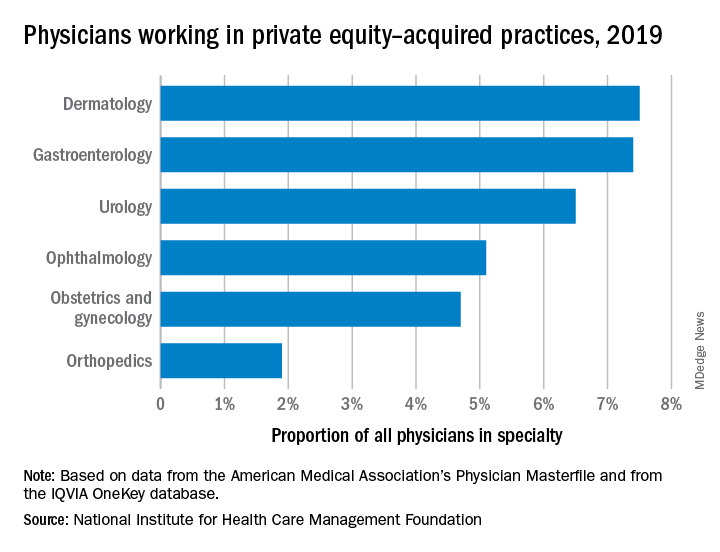
“These specialties offer private equity firms diverse revenue streams. You have a mix of commercially insured individuals with Medicare insurance and self-pay,” said Yashaswini Singh, MPA, a doctoral student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and coauthor of the study, which was published in JAMA Health Forum as a research letter.
“In dermatology, you have a mix of surgical procedures that are covered under insurance, but also a lot of cosmetic procedures that are most likely to be self-pay procedures. This offers private equity several mechanisms to which they can increase their revenues.”
Ms. Singh’s coauthors were part of a previous study looking at private practice penetration by private equity firms. That research found such deals surged from 59 deals in 2013 representing 843 physicians, to 136 private equity acquisition deals representing 1,882 physicians in 2016.
The most recent study notes limited data and use of nondisclosure agreements during early negotiations as part of the difficulty in truly pinpointing private equity’s presence in health care. Monitoring private equity activity has become necessary across all industries, noted the authors of the study. If continued at this rate, long-term private equity acquisition has a multitude of potential pros and cons.
Ms. Singh explained that such specialties are highly fragmented and they allow for economies of scale and scope. In particular, an aging population increases demand for dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology services such as skin biopsies, cataracts, and colonoscopies. This makes these specialties very attractive to private equity firms. The same can be said for obstetrics and gynecology, as fertility clinics have attracted many private equity investments.
“This is another area where understanding changes to physician practice patterns and patient outcomes is critical as women continue to delay motherhood,” said Ms. Singh.
Reducing competition, increasing focus on patient care
Researchers found significant geographical trends for private equity penetration, as it varies across the country. It is highest in the Northeast, Florida, and Arizona in hospital referral regions. Researchers are still analyzing the cause of this occurrence.
Geographic concentration of private equity penetration likely reflects strategic selection of investment opportunities by private equity funds as the decision to invest in a practice does not happen at random, Ms. Singh noted.
Ms. Singh said she hopes that by documenting a variation and geographic concentration that the NIHCM is providing the first foundational step to tackle questions related to incentives and regulations that facilitate investment.
“Understanding the regulatory and economic environments that facilitate private equity activity is an interesting and important question to explore further,” she said in an interview. “This can include supply-side factors that can shape the business environment, e.g., taxation environment, regulatory burden to complete acquisitions, as well as demand-side factors that facilitate growth.”
Researchers found that continued growth of private equity penetration may lead to consolidation among independent practices facing financial pressures, as well as reduced competition and increased prices within each local health care market.
“Localized consolidation in certain markets has the potential for competition to reduce, [and] reduced competition has been shown in a variety of settings to be associated with increases in prices and reduced access for patients,” said Ms. Singh.
Conversely, Ms. Singh addressed several benefits of growing private equity presence. Companies can exploit their full potential through the addition of private equity expertise and contacts. Specifically, health care development of technological infrastructure is likely, along with reduced patient wait times and the expansion of business hours. It could also be a way for practices to offload administrative responsibilities and for physicians to focus more on the care delivery process.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While tracking the extent of physician practice acquisition by private equity firms may be difficult, new research highlights what specialties and U.S. regions are most affected by such purchases.
The study, supported by the National Institute for Health Care Management (NIHCM), examined 97,094 physicians practicing in six specialties, 4,738 of whom worked in private equity–acquired practices. Of these specialties, 
“These specialties offer private equity firms diverse revenue streams. You have a mix of commercially insured individuals with Medicare insurance and self-pay,” said Yashaswini Singh, MPA, a doctoral student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and coauthor of the study, which was published in JAMA Health Forum as a research letter.
“In dermatology, you have a mix of surgical procedures that are covered under insurance, but also a lot of cosmetic procedures that are most likely to be self-pay procedures. This offers private equity several mechanisms to which they can increase their revenues.”
Ms. Singh’s coauthors were part of a previous study looking at private practice penetration by private equity firms. That research found such deals surged from 59 deals in 2013 representing 843 physicians, to 136 private equity acquisition deals representing 1,882 physicians in 2016.
The most recent study notes limited data and use of nondisclosure agreements during early negotiations as part of the difficulty in truly pinpointing private equity’s presence in health care. Monitoring private equity activity has become necessary across all industries, noted the authors of the study. If continued at this rate, long-term private equity acquisition has a multitude of potential pros and cons.
Ms. Singh explained that such specialties are highly fragmented and they allow for economies of scale and scope. In particular, an aging population increases demand for dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology services such as skin biopsies, cataracts, and colonoscopies. This makes these specialties very attractive to private equity firms. The same can be said for obstetrics and gynecology, as fertility clinics have attracted many private equity investments.
“This is another area where understanding changes to physician practice patterns and patient outcomes is critical as women continue to delay motherhood,” said Ms. Singh.
Reducing competition, increasing focus on patient care
Researchers found significant geographical trends for private equity penetration, as it varies across the country. It is highest in the Northeast, Florida, and Arizona in hospital referral regions. Researchers are still analyzing the cause of this occurrence.
Geographic concentration of private equity penetration likely reflects strategic selection of investment opportunities by private equity funds as the decision to invest in a practice does not happen at random, Ms. Singh noted.
Ms. Singh said she hopes that by documenting a variation and geographic concentration that the NIHCM is providing the first foundational step to tackle questions related to incentives and regulations that facilitate investment.
“Understanding the regulatory and economic environments that facilitate private equity activity is an interesting and important question to explore further,” she said in an interview. “This can include supply-side factors that can shape the business environment, e.g., taxation environment, regulatory burden to complete acquisitions, as well as demand-side factors that facilitate growth.”
Researchers found that continued growth of private equity penetration may lead to consolidation among independent practices facing financial pressures, as well as reduced competition and increased prices within each local health care market.
“Localized consolidation in certain markets has the potential for competition to reduce, [and] reduced competition has been shown in a variety of settings to be associated with increases in prices and reduced access for patients,” said Ms. Singh.
Conversely, Ms. Singh addressed several benefits of growing private equity presence. Companies can exploit their full potential through the addition of private equity expertise and contacts. Specifically, health care development of technological infrastructure is likely, along with reduced patient wait times and the expansion of business hours. It could also be a way for practices to offload administrative responsibilities and for physicians to focus more on the care delivery process.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While tracking the extent of physician practice acquisition by private equity firms may be difficult, new research highlights what specialties and U.S. regions are most affected by such purchases.
The study, supported by the National Institute for Health Care Management (NIHCM), examined 97,094 physicians practicing in six specialties, 4,738 of whom worked in private equity–acquired practices. Of these specialties, 
“These specialties offer private equity firms diverse revenue streams. You have a mix of commercially insured individuals with Medicare insurance and self-pay,” said Yashaswini Singh, MPA, a doctoral student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and coauthor of the study, which was published in JAMA Health Forum as a research letter.
“In dermatology, you have a mix of surgical procedures that are covered under insurance, but also a lot of cosmetic procedures that are most likely to be self-pay procedures. This offers private equity several mechanisms to which they can increase their revenues.”
Ms. Singh’s coauthors were part of a previous study looking at private practice penetration by private equity firms. That research found such deals surged from 59 deals in 2013 representing 843 physicians, to 136 private equity acquisition deals representing 1,882 physicians in 2016.
The most recent study notes limited data and use of nondisclosure agreements during early negotiations as part of the difficulty in truly pinpointing private equity’s presence in health care. Monitoring private equity activity has become necessary across all industries, noted the authors of the study. If continued at this rate, long-term private equity acquisition has a multitude of potential pros and cons.
Ms. Singh explained that such specialties are highly fragmented and they allow for economies of scale and scope. In particular, an aging population increases demand for dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology services such as skin biopsies, cataracts, and colonoscopies. This makes these specialties very attractive to private equity firms. The same can be said for obstetrics and gynecology, as fertility clinics have attracted many private equity investments.
“This is another area where understanding changes to physician practice patterns and patient outcomes is critical as women continue to delay motherhood,” said Ms. Singh.
Reducing competition, increasing focus on patient care
Researchers found significant geographical trends for private equity penetration, as it varies across the country. It is highest in the Northeast, Florida, and Arizona in hospital referral regions. Researchers are still analyzing the cause of this occurrence.
Geographic concentration of private equity penetration likely reflects strategic selection of investment opportunities by private equity funds as the decision to invest in a practice does not happen at random, Ms. Singh noted.
Ms. Singh said she hopes that by documenting a variation and geographic concentration that the NIHCM is providing the first foundational step to tackle questions related to incentives and regulations that facilitate investment.
“Understanding the regulatory and economic environments that facilitate private equity activity is an interesting and important question to explore further,” she said in an interview. “This can include supply-side factors that can shape the business environment, e.g., taxation environment, regulatory burden to complete acquisitions, as well as demand-side factors that facilitate growth.”
Researchers found that continued growth of private equity penetration may lead to consolidation among independent practices facing financial pressures, as well as reduced competition and increased prices within each local health care market.
“Localized consolidation in certain markets has the potential for competition to reduce, [and] reduced competition has been shown in a variety of settings to be associated with increases in prices and reduced access for patients,” said Ms. Singh.
Conversely, Ms. Singh addressed several benefits of growing private equity presence. Companies can exploit their full potential through the addition of private equity expertise and contacts. Specifically, health care development of technological infrastructure is likely, along with reduced patient wait times and the expansion of business hours. It could also be a way for practices to offload administrative responsibilities and for physicians to focus more on the care delivery process.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA HEALTH FORUM