User login
AGA News - February 2023
AGA members advocate for GI during Alliance of Specialty Medicine fly-in
In December, six AGA members joined more than 100 specialty doctors organized by the Alliance of Specialty Medicine, a coalition that represents specialty physicians, to meet with House and Senate offices and discuss pressing policy priorities.
Members spoke on behalf of GI and stressed the need for Congress to act immediately on the upcoming Medicare cuts, and discussed step therapy protocols, prior authorization reform, and the role of artificial intelligence in the specialty.
Our members represented GI well throughout the day’s meetings!
AGA PAC Board Member and Congressional Advocate Dr. Sadeea Abbasi spoke to House Leader Kevin McCarthy (R-CA) about challenges specialty doctors are facing and petitioned for Congress to mitigate the nearly 10 percent Medicare payment cuts before the end of the 117th Congress.
Additionally, AGA Government Affairs Committee Chair Dr. Rotonya Carr engaged with several members of Congress on issues impacting specialty care and discussed the future of AI in medicine with Rep. Mariannette Miller-Meeks (R-IA), who is an ophthalmologist.
Thank you to all our members who spoke on behalf of GI! We appreciate our AGA leaders who took time to participate!
- Sadeea Abbasi, MD, PhD
- Dawn B. Beaulieu, MD, AGAF
- Brent Burnette, MD
- Rotonya M. Carr, MD, FACP
- Peter S. Margolis, MD, AGAF
- Suzette Rivera MacMurray, MD
Learn how AGA is advocating for you. Visit gastro.org/advocacy.
AGA workshops champion women in GI
At AGA, we’re committed to supporting, empowering, and amplifying women in GI. As part of our ongoing efforts, we were thrilled to host nearly 250 women at four Women in GI regional workshops this fall. These workshops provided women across the country with opportunities to develop their personal and professional networks, participate in leadership development seminars, receive career mentoring, and engage in various wellness practices.
Following the conclusion of the regional workshops, we hosted the AGA Women’s Leadership Collaboration Conference at the AGA national office in Bethesda, Md.
I can’t stop talking about this weekend! What a profound experience! I continue to be inspired by this group of women, our mission, and the far-reaching impact of this collaboration. Each one of us was absolutely transformed this weekend. And the radius of that impact is immeasurable! – Dr. Bahar Adeli, TJUH–Albert Einstein Medical Center
During the two-day conference, 22 delegates discussed workplace experiences, reported on their region’s workshop, and participated in strategy development exercises to further gender equity in GI, which included identifying tactics and ideas for action.
This unique event brought together delegates from each regional workshop, including 2023 Dr. Maria Leo-Lieber scholarship winners Alyssa Parian and Alexandra Livanos, who attended the Northeast workshop. It was a great time of collaboration and connection with the AGA #WomenInGI community!
Thank you to everyone who participated and made the events a success. We look forward to uplifting all women in GI and identifying ways to support the community in the coming year.
AGA thanks Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Inc. for their support of this program.
Help move innovation forward at the 2023 AGA Tech Summit
Innovative technologies for endoscopy, advanced imaging, and bariatric care are a few of the topics that will headline the 2023 AGA Tech Summit, March 9-10, 2023, at the Grand Hyatt San Francisco. Registration is now open. Visit techsummit.gastro.org to secure your spot.

The Tech Summit is where GI innovators, clinicians, medical device companies, venture capitalists and regulatory agencies meet to foster the development and adoption of GI technologies. It is the perfect venue for:
- All innovators, entrepreneurs and clinicians who want to build their professional networks in the GI space.
- Early-stage GI companies who want to showcase their technologies and find new ideas for further innovations that will improve patient care.
- GI fellows who want an exclusive and immersive behind-the-scenes look into the MedTech world.
Learn more by visiting techsummit.gastro.org.
AGA members advocate for GI during Alliance of Specialty Medicine fly-in
In December, six AGA members joined more than 100 specialty doctors organized by the Alliance of Specialty Medicine, a coalition that represents specialty physicians, to meet with House and Senate offices and discuss pressing policy priorities.
Members spoke on behalf of GI and stressed the need for Congress to act immediately on the upcoming Medicare cuts, and discussed step therapy protocols, prior authorization reform, and the role of artificial intelligence in the specialty.
Our members represented GI well throughout the day’s meetings!
AGA PAC Board Member and Congressional Advocate Dr. Sadeea Abbasi spoke to House Leader Kevin McCarthy (R-CA) about challenges specialty doctors are facing and petitioned for Congress to mitigate the nearly 10 percent Medicare payment cuts before the end of the 117th Congress.
Additionally, AGA Government Affairs Committee Chair Dr. Rotonya Carr engaged with several members of Congress on issues impacting specialty care and discussed the future of AI in medicine with Rep. Mariannette Miller-Meeks (R-IA), who is an ophthalmologist.
Thank you to all our members who spoke on behalf of GI! We appreciate our AGA leaders who took time to participate!
- Sadeea Abbasi, MD, PhD
- Dawn B. Beaulieu, MD, AGAF
- Brent Burnette, MD
- Rotonya M. Carr, MD, FACP
- Peter S. Margolis, MD, AGAF
- Suzette Rivera MacMurray, MD
Learn how AGA is advocating for you. Visit gastro.org/advocacy.
AGA workshops champion women in GI
At AGA, we’re committed to supporting, empowering, and amplifying women in GI. As part of our ongoing efforts, we were thrilled to host nearly 250 women at four Women in GI regional workshops this fall. These workshops provided women across the country with opportunities to develop their personal and professional networks, participate in leadership development seminars, receive career mentoring, and engage in various wellness practices.
Following the conclusion of the regional workshops, we hosted the AGA Women’s Leadership Collaboration Conference at the AGA national office in Bethesda, Md.
I can’t stop talking about this weekend! What a profound experience! I continue to be inspired by this group of women, our mission, and the far-reaching impact of this collaboration. Each one of us was absolutely transformed this weekend. And the radius of that impact is immeasurable! – Dr. Bahar Adeli, TJUH–Albert Einstein Medical Center
During the two-day conference, 22 delegates discussed workplace experiences, reported on their region’s workshop, and participated in strategy development exercises to further gender equity in GI, which included identifying tactics and ideas for action.
This unique event brought together delegates from each regional workshop, including 2023 Dr. Maria Leo-Lieber scholarship winners Alyssa Parian and Alexandra Livanos, who attended the Northeast workshop. It was a great time of collaboration and connection with the AGA #WomenInGI community!
Thank you to everyone who participated and made the events a success. We look forward to uplifting all women in GI and identifying ways to support the community in the coming year.
AGA thanks Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Inc. for their support of this program.
Help move innovation forward at the 2023 AGA Tech Summit
Innovative technologies for endoscopy, advanced imaging, and bariatric care are a few of the topics that will headline the 2023 AGA Tech Summit, March 9-10, 2023, at the Grand Hyatt San Francisco. Registration is now open. Visit techsummit.gastro.org to secure your spot.

The Tech Summit is where GI innovators, clinicians, medical device companies, venture capitalists and regulatory agencies meet to foster the development and adoption of GI technologies. It is the perfect venue for:
- All innovators, entrepreneurs and clinicians who want to build their professional networks in the GI space.
- Early-stage GI companies who want to showcase their technologies and find new ideas for further innovations that will improve patient care.
- GI fellows who want an exclusive and immersive behind-the-scenes look into the MedTech world.
Learn more by visiting techsummit.gastro.org.
AGA members advocate for GI during Alliance of Specialty Medicine fly-in
In December, six AGA members joined more than 100 specialty doctors organized by the Alliance of Specialty Medicine, a coalition that represents specialty physicians, to meet with House and Senate offices and discuss pressing policy priorities.
Members spoke on behalf of GI and stressed the need for Congress to act immediately on the upcoming Medicare cuts, and discussed step therapy protocols, prior authorization reform, and the role of artificial intelligence in the specialty.
Our members represented GI well throughout the day’s meetings!
AGA PAC Board Member and Congressional Advocate Dr. Sadeea Abbasi spoke to House Leader Kevin McCarthy (R-CA) about challenges specialty doctors are facing and petitioned for Congress to mitigate the nearly 10 percent Medicare payment cuts before the end of the 117th Congress.
Additionally, AGA Government Affairs Committee Chair Dr. Rotonya Carr engaged with several members of Congress on issues impacting specialty care and discussed the future of AI in medicine with Rep. Mariannette Miller-Meeks (R-IA), who is an ophthalmologist.
Thank you to all our members who spoke on behalf of GI! We appreciate our AGA leaders who took time to participate!
- Sadeea Abbasi, MD, PhD
- Dawn B. Beaulieu, MD, AGAF
- Brent Burnette, MD
- Rotonya M. Carr, MD, FACP
- Peter S. Margolis, MD, AGAF
- Suzette Rivera MacMurray, MD
Learn how AGA is advocating for you. Visit gastro.org/advocacy.
AGA workshops champion women in GI
At AGA, we’re committed to supporting, empowering, and amplifying women in GI. As part of our ongoing efforts, we were thrilled to host nearly 250 women at four Women in GI regional workshops this fall. These workshops provided women across the country with opportunities to develop their personal and professional networks, participate in leadership development seminars, receive career mentoring, and engage in various wellness practices.
Following the conclusion of the regional workshops, we hosted the AGA Women’s Leadership Collaboration Conference at the AGA national office in Bethesda, Md.
I can’t stop talking about this weekend! What a profound experience! I continue to be inspired by this group of women, our mission, and the far-reaching impact of this collaboration. Each one of us was absolutely transformed this weekend. And the radius of that impact is immeasurable! – Dr. Bahar Adeli, TJUH–Albert Einstein Medical Center
During the two-day conference, 22 delegates discussed workplace experiences, reported on their region’s workshop, and participated in strategy development exercises to further gender equity in GI, which included identifying tactics and ideas for action.
This unique event brought together delegates from each regional workshop, including 2023 Dr. Maria Leo-Lieber scholarship winners Alyssa Parian and Alexandra Livanos, who attended the Northeast workshop. It was a great time of collaboration and connection with the AGA #WomenInGI community!
Thank you to everyone who participated and made the events a success. We look forward to uplifting all women in GI and identifying ways to support the community in the coming year.
AGA thanks Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Inc. for their support of this program.
Help move innovation forward at the 2023 AGA Tech Summit
Innovative technologies for endoscopy, advanced imaging, and bariatric care are a few of the topics that will headline the 2023 AGA Tech Summit, March 9-10, 2023, at the Grand Hyatt San Francisco. Registration is now open. Visit techsummit.gastro.org to secure your spot.

The Tech Summit is where GI innovators, clinicians, medical device companies, venture capitalists and regulatory agencies meet to foster the development and adoption of GI technologies. It is the perfect venue for:
- All innovators, entrepreneurs and clinicians who want to build their professional networks in the GI space.
- Early-stage GI companies who want to showcase their technologies and find new ideas for further innovations that will improve patient care.
- GI fellows who want an exclusive and immersive behind-the-scenes look into the MedTech world.
Learn more by visiting techsummit.gastro.org.
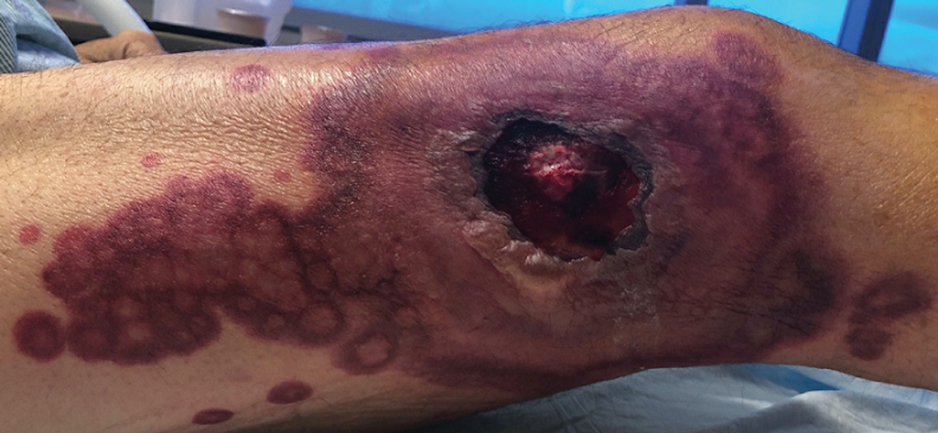
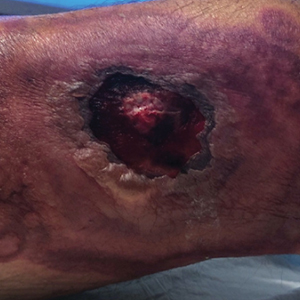
Fatigue and sporadic fever
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of malignant mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
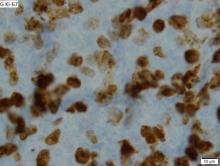
MCL is a rare and aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. MCL has a characteristic immunophenotype (ie, CD5+, CD10−, Bcl-2+, Bcl-6−, CD20+), with the t(11;14)(q13;q32) chromosomal translocation, and expression of cyclin D1. The median age at diagnosis is between 60 and 70 years. Approximately 70% of all cases occur in men.
The clinical presentation of MCL can vary. Patients may have asymptomatic monoclonal MCL type lymphocytosis or nonbulky nodal/extra nodal disease with minimal symptoms, or they may present with significant symptoms, progressive generalized lymphadenopathy, cytopenia, splenomegaly, and extranodal disease, including gastrointestinal involvement (lymphomatous polyposis), kidney involvement, involvement of other organs, or, rarely, central nervous system involvement. Disease involving multiple lymph nodes and other sites of the body is seen in most patients. Approximately 70% of patients present with stage IV disease requiring systemic treatment.
According to 2022 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), essential components in the workup for MCL include:
• Physical examination, with attention to node-bearing areas, including Waldeyer ring, and to size of liver and spleen
• Assessment of performance status and B symptoms (ie, fever > 100.4°F [may be sporadic], drenching night sweats, unintentional weight loss of > 10% of body weight over 6 months or less)
• CBC with differential
• Comprehensive metabolic panel
• Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (an important prognostic marker)
• PET/CT scan (including neck)
• Hepatitis B testing if treatment with rituximab is being contemplated
• Echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan if anthracycline or anthracenedione-based regimen is indicated
• Pregnancy testing in women of childbearing age (if chemotherapy or radiation therapy is planned)
Additional testing may be indicated in specific circumstances, such as colonoscopy/endoscopy.
MCL remains challenging to treat. While 50%-90% of patients with MCL respond to combination chemotherapy, only 30% achieve a complete response. Median time to treatment failure is < 18 months.
When selecting systemic treatment for patients with MCL, clinicians should consider the availability of clinical trials for subsets of patients, eligibility for stem cell transplant (SCT), high-risk status (ie, blastoid MCL, high Ki-67% > 30%, or central nervous system involvement), age, and performance status. The addition of radiation to chemotherapy may be beneficial for patients with limited-stage, nonbulky disease, although this has not been confirmed in large, randomized studies. Outside of clinical trials, the usual approach for frontline treatment of MCL is chemoimmunotherapy with/without autologous SCT and with/without maintenance therapy.
Available options for primary MCL therapy in patients who require systemic therapy include:
• Single alkylating agents
• CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone)
• CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin [hydroxydaunorubicin], vincristine [Oncovin], prednisone)
• Hyper-CVAD (hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) with or without rituximab
• R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)
• Lenalidomide plus rituximab
• Hyper-CVAD with autologous SCT
Options for relapsed or refractory MCL include:
• R-hyper-CVAD
• Hyper-CVAD with or without rituximab followed by autologous SCT
• Nucleoside analogues and combinations
• Salvage chemotherapy combinations followed by autologous SCT
• Bortezomib
• Lenalidomide
• Ibrutinib
• Radioimmunotherapy
• Rituximab
• Rituximab and thalidomide combination
• Acalabrutinib
• High-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow or SCT
• Brexucabtagene autoleucel
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of malignant mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
MCL is a rare and aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. MCL has a characteristic immunophenotype (ie, CD5+, CD10−, Bcl-2+, Bcl-6−, CD20+), with the t(11;14)(q13;q32) chromosomal translocation, and expression of cyclin D1. The median age at diagnosis is between 60 and 70 years. Approximately 70% of all cases occur in men.
The clinical presentation of MCL can vary. Patients may have asymptomatic monoclonal MCL type lymphocytosis or nonbulky nodal/extra nodal disease with minimal symptoms, or they may present with significant symptoms, progressive generalized lymphadenopathy, cytopenia, splenomegaly, and extranodal disease, including gastrointestinal involvement (lymphomatous polyposis), kidney involvement, involvement of other organs, or, rarely, central nervous system involvement. Disease involving multiple lymph nodes and other sites of the body is seen in most patients. Approximately 70% of patients present with stage IV disease requiring systemic treatment.
According to 2022 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), essential components in the workup for MCL include:
• Physical examination, with attention to node-bearing areas, including Waldeyer ring, and to size of liver and spleen
• Assessment of performance status and B symptoms (ie, fever > 100.4°F [may be sporadic], drenching night sweats, unintentional weight loss of > 10% of body weight over 6 months or less)
• CBC with differential
• Comprehensive metabolic panel
• Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (an important prognostic marker)
• PET/CT scan (including neck)
• Hepatitis B testing if treatment with rituximab is being contemplated
• Echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan if anthracycline or anthracenedione-based regimen is indicated
• Pregnancy testing in women of childbearing age (if chemotherapy or radiation therapy is planned)
Additional testing may be indicated in specific circumstances, such as colonoscopy/endoscopy.
MCL remains challenging to treat. While 50%-90% of patients with MCL respond to combination chemotherapy, only 30% achieve a complete response. Median time to treatment failure is < 18 months.
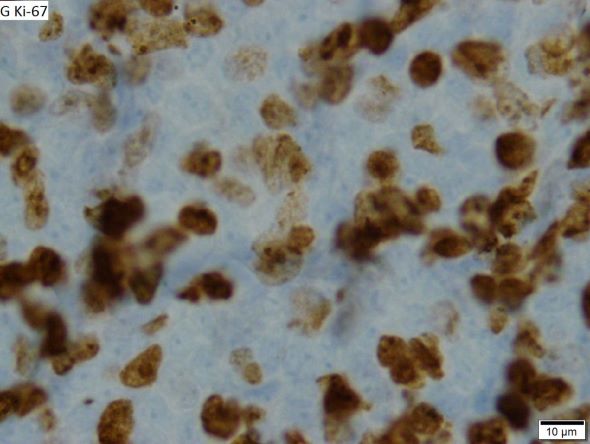
When selecting systemic treatment for patients with MCL, clinicians should consider the availability of clinical trials for subsets of patients, eligibility for stem cell transplant (SCT), high-risk status (ie, blastoid MCL, high Ki-67% > 30%, or central nervous system involvement), age, and performance status. The addition of radiation to chemotherapy may be beneficial for patients with limited-stage, nonbulky disease, although this has not been confirmed in large, randomized studies. Outside of clinical trials, the usual approach for frontline treatment of MCL is chemoimmunotherapy with/without autologous SCT and with/without maintenance therapy.
Available options for primary MCL therapy in patients who require systemic therapy include:
• Single alkylating agents
• CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone)
• CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin [hydroxydaunorubicin], vincristine [Oncovin], prednisone)
• Hyper-CVAD (hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) with or without rituximab
• R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)
• Lenalidomide plus rituximab
• Hyper-CVAD with autologous SCT
Options for relapsed or refractory MCL include:
• R-hyper-CVAD
• Hyper-CVAD with or without rituximab followed by autologous SCT
• Nucleoside analogues and combinations
• Salvage chemotherapy combinations followed by autologous SCT
• Bortezomib
• Lenalidomide
• Ibrutinib
• Radioimmunotherapy
• Rituximab
• Rituximab and thalidomide combination
• Acalabrutinib
• High-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow or SCT
• Brexucabtagene autoleucel
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of malignant mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
MCL is a rare and aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. MCL has a characteristic immunophenotype (ie, CD5+, CD10−, Bcl-2+, Bcl-6−, CD20+), with the t(11;14)(q13;q32) chromosomal translocation, and expression of cyclin D1. The median age at diagnosis is between 60 and 70 years. Approximately 70% of all cases occur in men.
The clinical presentation of MCL can vary. Patients may have asymptomatic monoclonal MCL type lymphocytosis or nonbulky nodal/extra nodal disease with minimal symptoms, or they may present with significant symptoms, progressive generalized lymphadenopathy, cytopenia, splenomegaly, and extranodal disease, including gastrointestinal involvement (lymphomatous polyposis), kidney involvement, involvement of other organs, or, rarely, central nervous system involvement. Disease involving multiple lymph nodes and other sites of the body is seen in most patients. Approximately 70% of patients present with stage IV disease requiring systemic treatment.
According to 2022 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), essential components in the workup for MCL include:
• Physical examination, with attention to node-bearing areas, including Waldeyer ring, and to size of liver and spleen
• Assessment of performance status and B symptoms (ie, fever > 100.4°F [may be sporadic], drenching night sweats, unintentional weight loss of > 10% of body weight over 6 months or less)
• CBC with differential
• Comprehensive metabolic panel
• Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (an important prognostic marker)
• PET/CT scan (including neck)
• Hepatitis B testing if treatment with rituximab is being contemplated
• Echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan if anthracycline or anthracenedione-based regimen is indicated
• Pregnancy testing in women of childbearing age (if chemotherapy or radiation therapy is planned)
Additional testing may be indicated in specific circumstances, such as colonoscopy/endoscopy.
MCL remains challenging to treat. While 50%-90% of patients with MCL respond to combination chemotherapy, only 30% achieve a complete response. Median time to treatment failure is < 18 months.
When selecting systemic treatment for patients with MCL, clinicians should consider the availability of clinical trials for subsets of patients, eligibility for stem cell transplant (SCT), high-risk status (ie, blastoid MCL, high Ki-67% > 30%, or central nervous system involvement), age, and performance status. The addition of radiation to chemotherapy may be beneficial for patients with limited-stage, nonbulky disease, although this has not been confirmed in large, randomized studies. Outside of clinical trials, the usual approach for frontline treatment of MCL is chemoimmunotherapy with/without autologous SCT and with/without maintenance therapy.
Available options for primary MCL therapy in patients who require systemic therapy include:
• Single alkylating agents
• CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone)
• CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin [hydroxydaunorubicin], vincristine [Oncovin], prednisone)
• Hyper-CVAD (hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) with or without rituximab
• R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)
• Lenalidomide plus rituximab
• Hyper-CVAD with autologous SCT
Options for relapsed or refractory MCL include:
• R-hyper-CVAD
• Hyper-CVAD with or without rituximab followed by autologous SCT
• Nucleoside analogues and combinations
• Salvage chemotherapy combinations followed by autologous SCT
• Bortezomib
• Lenalidomide
• Ibrutinib
• Radioimmunotherapy
• Rituximab
• Rituximab and thalidomide combination
• Acalabrutinib
• High-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow or SCT
• Brexucabtagene autoleucel
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 64-year-old Black man with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia presents with complaints of fatigue, sporadic fever > 100.4° F, and mild abdominal pain. The patient has lost 12 lb since he was last seen 9 months earlier. When questioned, he states that he simply doesn't have the appetite he once had. Physical examination reveals pallor; abdominal distension; lymphadenopathy in the anterior cervical, inguinal, and axillary regions; and palpable spleen and liver. CBC findings include RBC 4.4 x 106/µL; WBC 2400/μL; PLT 148,000/dL; MCV 57.8 fL; hematocrit 38%; and ALC 4200/µL. Immunophenotyping by flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry was positive for CD5 and CD19, with no expression of CD10 or CD23. Cyclin D1 was overexpressed.
Ten recommendations for building and growing a cosmetic dermatology practice
SAN DIEGO – When Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, opened his own cosmetic dermatology practice in Stamford, Conn., in 2012, he sensed that he had his work cut out for him.
“I was a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon who wanted to do aesthetics,” Dr. Ibrahimi, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, recalled during the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “I was in a geographic area that was new to me. I didn’t know any referring doctors, but I started to network and tried to grow my practice.”
Someone once told him that the “three As” of being a medical specialist are “Available, Affable, and Ability,” so he applied that principle as he began to cultivate relationships with physicians in his geographic area. “I told my referring doctors, ‘If you’re kind enough to send me Mohs cases, I’ll help you out if there’s something you don’t like doing, whether it’s a nail biopsy or treating male genital warts,’” he said. “You want to make it easy for doctors to refer to you, but you also want to make their lives easier.”
Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, offered . They include:
Know yourself. Do what you love to do, not what you feel like you should do. “Whatever you’re doing in your practice, it should be something that you’re passionate about and excited about,” he said. “I do a mix of Mohs surgery and procedural aesthetic dermatology. Most of my practice is shaped toward energy-based devices and laser procedures. Pick the things that you enjoy doing and try to deliver good results.”
Know your patients. When dermatologists who plan to open their own practice ask Dr. Ibrahimi what kind of laser they should buy, he typically responds by asking them to consider what procedures their patients are asking for. “Depending on where you are geographically and the economic profile of the community in which you practice, it can be a different answer,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “If you practice in the Northeast and do a lot of medical dermatology, it might mean getting a vascular laser to treat rosacea. If you’re in Southern California, treating pigment might be a bigger concern than treating rosacea.” The annual ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures provides a snapshot of trends and can be useful for decision-making, he said.
Know your practice. “Make sure you are capable of entering the aesthetics field,” he advised. “You cannot have a practice that runs like the DMV, with people waiting 30 to 40 minutes to be seen.” Proper training of staff is also key and representatives from device and injectable companies can provide advice and support. As for marketing, some dermatologists hire a public relations agency, but Dr. Ibrahimi finds that the best source of his referrals is word of mouth. “If I do a good job taking care of patients, they will send their friends and family over to me, but social media is also important,” he said. Taking quality before-and-after photos, and obtaining consent from patients to use them online in educational posts is a good approach, he noted.
Know your market. When Dr. Ibrahimi first opened his practice, offering laser hair removal was not a priority because so many other dermatologists and medical spas in his area were already providing it. With time, though, he added laser hair removal to his menu of treatment offerings because “I knew that if my patients weren’t getting that service from me, they would be getting it from somewhere else,” he said. “Initially it wasn’t important for me, but as my practice matured, I wanted to make sure that I was comprehensive.”
Start cautiously. Think safety first. “I tell people that starting a cosmetic practice is like baseball: don’t try to hit home runs,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Just aim for base hits and keep your patients happy. Make sure you deliver safe, good results.” This means knowing everything possible about the devices used in the office, because if the use of a laser is delegated to a staff member and a problem arises, “you have to know everything about how that device works so that you can troubleshoot,” he said. “A lot of problems that arise are from lack of intimacy with your device.”
Seek knowledge. Attend courses in cosmetic dermatology and read literature from journals like Dermatologic Surgery and Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, he advised. “People will see the success, but they won’t know how much hard work it takes to get there,” he said. “You have to develop your reputation to develop the kind of practice that you want.”
Understand the business of aesthetics. Most energy devices carry a steep price tag, and leasing or financing devices come with a monthly payment, he said. “Make sure that what you’re bringing in on that device is going to be sufficient to cover the monthly payment. With something like tissue microcoring, you don’t have to use that five times a day to cover that lease payment. But if you have a vascular laser, you probably need to be treating more than a couple patients per day to make that lease payment. If you can recover the amount the device costs in about a year, that’s going to be a good investment. Many devices come with consumables, so you have to remember that.”
Don’t be afraid to be unique/change directions. Becoming an early adopter of new technologies and procedures can make someone stand out. “Other providers feel more comfortable waiting to allow more data to come out about a new technology before they make a purchase,” he said. “But if you’re established and have a busy practice, that’s an opportunity that can draw people in.”
Have patience and realistic expectations. It’s smart to offer a variety of services, he said, such as medical or surgical dermatology in addition to cosmetic dermatology. “That’s going to help you through any kind of economic downturn,” he said. “Success depends on a lot of factors going right. Make sure you set short- and long-term goals.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – When Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, opened his own cosmetic dermatology practice in Stamford, Conn., in 2012, he sensed that he had his work cut out for him.
“I was a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon who wanted to do aesthetics,” Dr. Ibrahimi, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, recalled during the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “I was in a geographic area that was new to me. I didn’t know any referring doctors, but I started to network and tried to grow my practice.”
Someone once told him that the “three As” of being a medical specialist are “Available, Affable, and Ability,” so he applied that principle as he began to cultivate relationships with physicians in his geographic area. “I told my referring doctors, ‘If you’re kind enough to send me Mohs cases, I’ll help you out if there’s something you don’t like doing, whether it’s a nail biopsy or treating male genital warts,’” he said. “You want to make it easy for doctors to refer to you, but you also want to make their lives easier.”
Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, offered . They include:
Know yourself. Do what you love to do, not what you feel like you should do. “Whatever you’re doing in your practice, it should be something that you’re passionate about and excited about,” he said. “I do a mix of Mohs surgery and procedural aesthetic dermatology. Most of my practice is shaped toward energy-based devices and laser procedures. Pick the things that you enjoy doing and try to deliver good results.”
Know your patients. When dermatologists who plan to open their own practice ask Dr. Ibrahimi what kind of laser they should buy, he typically responds by asking them to consider what procedures their patients are asking for. “Depending on where you are geographically and the economic profile of the community in which you practice, it can be a different answer,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “If you practice in the Northeast and do a lot of medical dermatology, it might mean getting a vascular laser to treat rosacea. If you’re in Southern California, treating pigment might be a bigger concern than treating rosacea.” The annual ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures provides a snapshot of trends and can be useful for decision-making, he said.
Know your practice. “Make sure you are capable of entering the aesthetics field,” he advised. “You cannot have a practice that runs like the DMV, with people waiting 30 to 40 minutes to be seen.” Proper training of staff is also key and representatives from device and injectable companies can provide advice and support. As for marketing, some dermatologists hire a public relations agency, but Dr. Ibrahimi finds that the best source of his referrals is word of mouth. “If I do a good job taking care of patients, they will send their friends and family over to me, but social media is also important,” he said. Taking quality before-and-after photos, and obtaining consent from patients to use them online in educational posts is a good approach, he noted.
Know your market. When Dr. Ibrahimi first opened his practice, offering laser hair removal was not a priority because so many other dermatologists and medical spas in his area were already providing it. With time, though, he added laser hair removal to his menu of treatment offerings because “I knew that if my patients weren’t getting that service from me, they would be getting it from somewhere else,” he said. “Initially it wasn’t important for me, but as my practice matured, I wanted to make sure that I was comprehensive.”
Start cautiously. Think safety first. “I tell people that starting a cosmetic practice is like baseball: don’t try to hit home runs,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Just aim for base hits and keep your patients happy. Make sure you deliver safe, good results.” This means knowing everything possible about the devices used in the office, because if the use of a laser is delegated to a staff member and a problem arises, “you have to know everything about how that device works so that you can troubleshoot,” he said. “A lot of problems that arise are from lack of intimacy with your device.”
Seek knowledge. Attend courses in cosmetic dermatology and read literature from journals like Dermatologic Surgery and Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, he advised. “People will see the success, but they won’t know how much hard work it takes to get there,” he said. “You have to develop your reputation to develop the kind of practice that you want.”
Understand the business of aesthetics. Most energy devices carry a steep price tag, and leasing or financing devices come with a monthly payment, he said. “Make sure that what you’re bringing in on that device is going to be sufficient to cover the monthly payment. With something like tissue microcoring, you don’t have to use that five times a day to cover that lease payment. But if you have a vascular laser, you probably need to be treating more than a couple patients per day to make that lease payment. If you can recover the amount the device costs in about a year, that’s going to be a good investment. Many devices come with consumables, so you have to remember that.”
Don’t be afraid to be unique/change directions. Becoming an early adopter of new technologies and procedures can make someone stand out. “Other providers feel more comfortable waiting to allow more data to come out about a new technology before they make a purchase,” he said. “But if you’re established and have a busy practice, that’s an opportunity that can draw people in.”
Have patience and realistic expectations. It’s smart to offer a variety of services, he said, such as medical or surgical dermatology in addition to cosmetic dermatology. “That’s going to help you through any kind of economic downturn,” he said. “Success depends on a lot of factors going right. Make sure you set short- and long-term goals.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – When Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, opened his own cosmetic dermatology practice in Stamford, Conn., in 2012, he sensed that he had his work cut out for him.
“I was a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon who wanted to do aesthetics,” Dr. Ibrahimi, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, recalled during the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “I was in a geographic area that was new to me. I didn’t know any referring doctors, but I started to network and tried to grow my practice.”
Someone once told him that the “three As” of being a medical specialist are “Available, Affable, and Ability,” so he applied that principle as he began to cultivate relationships with physicians in his geographic area. “I told my referring doctors, ‘If you’re kind enough to send me Mohs cases, I’ll help you out if there’s something you don’t like doing, whether it’s a nail biopsy or treating male genital warts,’” he said. “You want to make it easy for doctors to refer to you, but you also want to make their lives easier.”
Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, offered . They include:
Know yourself. Do what you love to do, not what you feel like you should do. “Whatever you’re doing in your practice, it should be something that you’re passionate about and excited about,” he said. “I do a mix of Mohs surgery and procedural aesthetic dermatology. Most of my practice is shaped toward energy-based devices and laser procedures. Pick the things that you enjoy doing and try to deliver good results.”
Know your patients. When dermatologists who plan to open their own practice ask Dr. Ibrahimi what kind of laser they should buy, he typically responds by asking them to consider what procedures their patients are asking for. “Depending on where you are geographically and the economic profile of the community in which you practice, it can be a different answer,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “If you practice in the Northeast and do a lot of medical dermatology, it might mean getting a vascular laser to treat rosacea. If you’re in Southern California, treating pigment might be a bigger concern than treating rosacea.” The annual ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures provides a snapshot of trends and can be useful for decision-making, he said.
Know your practice. “Make sure you are capable of entering the aesthetics field,” he advised. “You cannot have a practice that runs like the DMV, with people waiting 30 to 40 minutes to be seen.” Proper training of staff is also key and representatives from device and injectable companies can provide advice and support. As for marketing, some dermatologists hire a public relations agency, but Dr. Ibrahimi finds that the best source of his referrals is word of mouth. “If I do a good job taking care of patients, they will send their friends and family over to me, but social media is also important,” he said. Taking quality before-and-after photos, and obtaining consent from patients to use them online in educational posts is a good approach, he noted.
Know your market. When Dr. Ibrahimi first opened his practice, offering laser hair removal was not a priority because so many other dermatologists and medical spas in his area were already providing it. With time, though, he added laser hair removal to his menu of treatment offerings because “I knew that if my patients weren’t getting that service from me, they would be getting it from somewhere else,” he said. “Initially it wasn’t important for me, but as my practice matured, I wanted to make sure that I was comprehensive.”
Start cautiously. Think safety first. “I tell people that starting a cosmetic practice is like baseball: don’t try to hit home runs,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Just aim for base hits and keep your patients happy. Make sure you deliver safe, good results.” This means knowing everything possible about the devices used in the office, because if the use of a laser is delegated to a staff member and a problem arises, “you have to know everything about how that device works so that you can troubleshoot,” he said. “A lot of problems that arise are from lack of intimacy with your device.”
Seek knowledge. Attend courses in cosmetic dermatology and read literature from journals like Dermatologic Surgery and Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, he advised. “People will see the success, but they won’t know how much hard work it takes to get there,” he said. “You have to develop your reputation to develop the kind of practice that you want.”
Understand the business of aesthetics. Most energy devices carry a steep price tag, and leasing or financing devices come with a monthly payment, he said. “Make sure that what you’re bringing in on that device is going to be sufficient to cover the monthly payment. With something like tissue microcoring, you don’t have to use that five times a day to cover that lease payment. But if you have a vascular laser, you probably need to be treating more than a couple patients per day to make that lease payment. If you can recover the amount the device costs in about a year, that’s going to be a good investment. Many devices come with consumables, so you have to remember that.”
Don’t be afraid to be unique/change directions. Becoming an early adopter of new technologies and procedures can make someone stand out. “Other providers feel more comfortable waiting to allow more data to come out about a new technology before they make a purchase,” he said. “But if you’re established and have a busy practice, that’s an opportunity that can draw people in.”
Have patience and realistic expectations. It’s smart to offer a variety of services, he said, such as medical or surgical dermatology in addition to cosmetic dermatology. “That’s going to help you through any kind of economic downturn,” he said. “Success depends on a lot of factors going right. Make sure you set short- and long-term goals.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
AT MOAS 2022
Ohio measles outbreak grows, fueled by vaccine hesitancy
The Ohio measles outbreak continues to expand, with cases now totaling 81 – a 37% increase in the course of just 2 weeks.
. Most of the children infected were unvaccinated but were old enough to get the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) shot, which is 97% effective at preventing measles.
“I think these are individuals who are making a decision not to protect their children against vaccine-preventable diseases, and some of them are making a specific decision not to use the MMR vaccine,” Columbus Public Health Commissioner Mysheika W. Roberts, MD, told JAMA.
She said that parents’ refusal to vaccinate their children was due to a misconception that the vaccine causes autism.
“We’re sounding the alarm that if your child is of age and not vaccinated, they should get vaccinated ASAP,” Dr. Roberts said, noting that she hasn’t seen that happening more.
Health officials have predicted the outbreak, which started in November, will last at least several months. Measles is so contagious that 9 out of 10 unvaccinated people in a room will become infected if exposed.
All of the infections have been in children. According to the Columbus Public Health measles dashboard, of the 81 confirmed cases:
- 29 children have been hospitalized.
- 22 cases are among children under 1 year old.
- No deaths have been reported.
Dr. Roberts said the hospitalized children have had symptoms including dehydration, diarrhea, and pneumonia. Some have had to go to the intensive care unit.
Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, and even death, the CDC says.
One of the most recent cases was an infant too young to be vaccinated who lives 45 miles away from where the outbreak began, the Dayton Daily News reported. That’s the first case in Clark County in more than 20 years. At least 10% of kindergartners’ parents in the region’s elementary schools opted out of vaccines because of religious or moral objections.
“We knew this was coming. It was a matter of when, not if,” Yamini Teegala, MD, chief medical officer at Rocking Horse Community Health Center in Springfield, told the Dayton Daily News.
This is the second measles outbreak this year. Minnesota tallied 22 cases since June in an unrelated outbreak, JAMA reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Ohio measles outbreak continues to expand, with cases now totaling 81 – a 37% increase in the course of just 2 weeks.
. Most of the children infected were unvaccinated but were old enough to get the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) shot, which is 97% effective at preventing measles.
“I think these are individuals who are making a decision not to protect their children against vaccine-preventable diseases, and some of them are making a specific decision not to use the MMR vaccine,” Columbus Public Health Commissioner Mysheika W. Roberts, MD, told JAMA.
She said that parents’ refusal to vaccinate their children was due to a misconception that the vaccine causes autism.
“We’re sounding the alarm that if your child is of age and not vaccinated, they should get vaccinated ASAP,” Dr. Roberts said, noting that she hasn’t seen that happening more.
Health officials have predicted the outbreak, which started in November, will last at least several months. Measles is so contagious that 9 out of 10 unvaccinated people in a room will become infected if exposed.
All of the infections have been in children. According to the Columbus Public Health measles dashboard, of the 81 confirmed cases:
- 29 children have been hospitalized.
- 22 cases are among children under 1 year old.
- No deaths have been reported.
Dr. Roberts said the hospitalized children have had symptoms including dehydration, diarrhea, and pneumonia. Some have had to go to the intensive care unit.
Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, and even death, the CDC says.
One of the most recent cases was an infant too young to be vaccinated who lives 45 miles away from where the outbreak began, the Dayton Daily News reported. That’s the first case in Clark County in more than 20 years. At least 10% of kindergartners’ parents in the region’s elementary schools opted out of vaccines because of religious or moral objections.
“We knew this was coming. It was a matter of when, not if,” Yamini Teegala, MD, chief medical officer at Rocking Horse Community Health Center in Springfield, told the Dayton Daily News.
This is the second measles outbreak this year. Minnesota tallied 22 cases since June in an unrelated outbreak, JAMA reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Ohio measles outbreak continues to expand, with cases now totaling 81 – a 37% increase in the course of just 2 weeks.
. Most of the children infected were unvaccinated but were old enough to get the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) shot, which is 97% effective at preventing measles.
“I think these are individuals who are making a decision not to protect their children against vaccine-preventable diseases, and some of them are making a specific decision not to use the MMR vaccine,” Columbus Public Health Commissioner Mysheika W. Roberts, MD, told JAMA.
She said that parents’ refusal to vaccinate their children was due to a misconception that the vaccine causes autism.
“We’re sounding the alarm that if your child is of age and not vaccinated, they should get vaccinated ASAP,” Dr. Roberts said, noting that she hasn’t seen that happening more.
Health officials have predicted the outbreak, which started in November, will last at least several months. Measles is so contagious that 9 out of 10 unvaccinated people in a room will become infected if exposed.
All of the infections have been in children. According to the Columbus Public Health measles dashboard, of the 81 confirmed cases:
- 29 children have been hospitalized.
- 22 cases are among children under 1 year old.
- No deaths have been reported.
Dr. Roberts said the hospitalized children have had symptoms including dehydration, diarrhea, and pneumonia. Some have had to go to the intensive care unit.
Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, and even death, the CDC says.
One of the most recent cases was an infant too young to be vaccinated who lives 45 miles away from where the outbreak began, the Dayton Daily News reported. That’s the first case in Clark County in more than 20 years. At least 10% of kindergartners’ parents in the region’s elementary schools opted out of vaccines because of religious or moral objections.
“We knew this was coming. It was a matter of when, not if,” Yamini Teegala, MD, chief medical officer at Rocking Horse Community Health Center in Springfield, told the Dayton Daily News.
This is the second measles outbreak this year. Minnesota tallied 22 cases since June in an unrelated outbreak, JAMA reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA
The dark side of online mom groups
I have assumed that being a parent has always been an anxiety-producing experience. Even back when the neonatal mortality rate was orders of magnitude greater than we are experiencing now, I suspect that each birth was still accompanied by a period of angst. However, as families no longer felt the need to produce more children to replace those lost to illness, each surviving child fell under the glare of an ever brightening spotlight.
Raising a child no longer became just something that came naturally, learned from one’s parents. Philosophers and eventually physicians felt obligated to advise parents on the best practices. My parents turned to Dr. Benjamin Spock’s classic work when they had a question, but I never got the feeling that they took his words as gospel.
By the time I started in practice the condition of being a parent was morphing into a verb. Books on “parenting” were beginning to fill the shelves of libraries and bookstores. Frustrated by what I saw as poorly conceived instruction manuals I succumbed to the temptation to spread my “better” advice for anxiety-tormented parents by writing books on how to feed picky eaters, or how to get erratic sleepers to sleep, or how to get a misbehaving child to understand the simple concept of “No!”
Back in the pre-Internet days I was competing for the attention of anxiety-driven parents not just with other self-described experts sitting at word processors, but with grandmothers, aunts, and the ladies next door. The book publishing market has cooled but the demand for advice on how to be the best parent has heated up. Into the void, enabled by the Internet, has erupted the phenomenon of social-media mom groups.
The lady next door and the mothers with strollers meeting informally at the playground are a tiny blip on the radar screen compared with the abundance of other mothers eager to listen and comment on social media–based mom groups unlimited by either geographic or temporal time restraints.
Unfortunately, as a recent article in the Wall Street Journal suggests, these support groups can often have a dark side. Researchers from Pepperdine University found in a small survey of a homogenous population of women that stress, as measured by saliva cortisol levels, increased with increasing use of “mom-centric social media” sites.
Citing anecdotal observations by mothers who did not participate in the study, the WSJ article describes episodes of shaming over topics such as steroid use in eczema and vaccine hesitancy. One mother described how she found group discussions about breastfeeding “particularly anxiety-producing.”
I have limited experience with online support groups but I have been surprised by how rude and condescending some of the contributors can be to what I could consider to be emotionally neutral subjects such as outboard motor oil pressure. I can imagine that when it comes to subjects in which there is no one best answer, the relative anonymity of the Internet provides cover for language that can be hurtful and stress inducing for someone already feeling isolated and anxious about being a parent.
Although this Pepperdine study is small, I suspect that a larger study would support the authors’ observations. For us as providers, it suggests that we need to find where parents are getting their information when we are trying to help those who seem particularly distressed. We should caution them that, while sharing information with peers can be reassuring and helpful at times, mom groups can be toxic as well. It also means that we should be careful in recommending social media sites – even those for which we have had good feedback.
And, most importantly, we must continue to work hard to make ourselves available to provide sensible and sensitive answers to those questions that are anxiety-producing for new parents.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I have assumed that being a parent has always been an anxiety-producing experience. Even back when the neonatal mortality rate was orders of magnitude greater than we are experiencing now, I suspect that each birth was still accompanied by a period of angst. However, as families no longer felt the need to produce more children to replace those lost to illness, each surviving child fell under the glare of an ever brightening spotlight.
Raising a child no longer became just something that came naturally, learned from one’s parents. Philosophers and eventually physicians felt obligated to advise parents on the best practices. My parents turned to Dr. Benjamin Spock’s classic work when they had a question, but I never got the feeling that they took his words as gospel.
By the time I started in practice the condition of being a parent was morphing into a verb. Books on “parenting” were beginning to fill the shelves of libraries and bookstores. Frustrated by what I saw as poorly conceived instruction manuals I succumbed to the temptation to spread my “better” advice for anxiety-tormented parents by writing books on how to feed picky eaters, or how to get erratic sleepers to sleep, or how to get a misbehaving child to understand the simple concept of “No!”
Back in the pre-Internet days I was competing for the attention of anxiety-driven parents not just with other self-described experts sitting at word processors, but with grandmothers, aunts, and the ladies next door. The book publishing market has cooled but the demand for advice on how to be the best parent has heated up. Into the void, enabled by the Internet, has erupted the phenomenon of social-media mom groups.
The lady next door and the mothers with strollers meeting informally at the playground are a tiny blip on the radar screen compared with the abundance of other mothers eager to listen and comment on social media–based mom groups unlimited by either geographic or temporal time restraints.
Unfortunately, as a recent article in the Wall Street Journal suggests, these support groups can often have a dark side. Researchers from Pepperdine University found in a small survey of a homogenous population of women that stress, as measured by saliva cortisol levels, increased with increasing use of “mom-centric social media” sites.
Citing anecdotal observations by mothers who did not participate in the study, the WSJ article describes episodes of shaming over topics such as steroid use in eczema and vaccine hesitancy. One mother described how she found group discussions about breastfeeding “particularly anxiety-producing.”
I have limited experience with online support groups but I have been surprised by how rude and condescending some of the contributors can be to what I could consider to be emotionally neutral subjects such as outboard motor oil pressure. I can imagine that when it comes to subjects in which there is no one best answer, the relative anonymity of the Internet provides cover for language that can be hurtful and stress inducing for someone already feeling isolated and anxious about being a parent.
Although this Pepperdine study is small, I suspect that a larger study would support the authors’ observations. For us as providers, it suggests that we need to find where parents are getting their information when we are trying to help those who seem particularly distressed. We should caution them that, while sharing information with peers can be reassuring and helpful at times, mom groups can be toxic as well. It also means that we should be careful in recommending social media sites – even those for which we have had good feedback.
And, most importantly, we must continue to work hard to make ourselves available to provide sensible and sensitive answers to those questions that are anxiety-producing for new parents.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I have assumed that being a parent has always been an anxiety-producing experience. Even back when the neonatal mortality rate was orders of magnitude greater than we are experiencing now, I suspect that each birth was still accompanied by a period of angst. However, as families no longer felt the need to produce more children to replace those lost to illness, each surviving child fell under the glare of an ever brightening spotlight.
Raising a child no longer became just something that came naturally, learned from one’s parents. Philosophers and eventually physicians felt obligated to advise parents on the best practices. My parents turned to Dr. Benjamin Spock’s classic work when they had a question, but I never got the feeling that they took his words as gospel.
By the time I started in practice the condition of being a parent was morphing into a verb. Books on “parenting” were beginning to fill the shelves of libraries and bookstores. Frustrated by what I saw as poorly conceived instruction manuals I succumbed to the temptation to spread my “better” advice for anxiety-tormented parents by writing books on how to feed picky eaters, or how to get erratic sleepers to sleep, or how to get a misbehaving child to understand the simple concept of “No!”
Back in the pre-Internet days I was competing for the attention of anxiety-driven parents not just with other self-described experts sitting at word processors, but with grandmothers, aunts, and the ladies next door. The book publishing market has cooled but the demand for advice on how to be the best parent has heated up. Into the void, enabled by the Internet, has erupted the phenomenon of social-media mom groups.
The lady next door and the mothers with strollers meeting informally at the playground are a tiny blip on the radar screen compared with the abundance of other mothers eager to listen and comment on social media–based mom groups unlimited by either geographic or temporal time restraints.
Unfortunately, as a recent article in the Wall Street Journal suggests, these support groups can often have a dark side. Researchers from Pepperdine University found in a small survey of a homogenous population of women that stress, as measured by saliva cortisol levels, increased with increasing use of “mom-centric social media” sites.
Citing anecdotal observations by mothers who did not participate in the study, the WSJ article describes episodes of shaming over topics such as steroid use in eczema and vaccine hesitancy. One mother described how she found group discussions about breastfeeding “particularly anxiety-producing.”
I have limited experience with online support groups but I have been surprised by how rude and condescending some of the contributors can be to what I could consider to be emotionally neutral subjects such as outboard motor oil pressure. I can imagine that when it comes to subjects in which there is no one best answer, the relative anonymity of the Internet provides cover for language that can be hurtful and stress inducing for someone already feeling isolated and anxious about being a parent.
Although this Pepperdine study is small, I suspect that a larger study would support the authors’ observations. For us as providers, it suggests that we need to find where parents are getting their information when we are trying to help those who seem particularly distressed. We should caution them that, while sharing information with peers can be reassuring and helpful at times, mom groups can be toxic as well. It also means that we should be careful in recommending social media sites – even those for which we have had good feedback.
And, most importantly, we must continue to work hard to make ourselves available to provide sensible and sensitive answers to those questions that are anxiety-producing for new parents.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Four-gene signature linked to increased PML risk
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
FROM FRONTIERS IN NEUROLOGY
For optimal results, fractional RF microneedling requires multiple treatments
SAN DIEGO – , according to Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD.
Most core fractional RF microneedling indications – acne scars, rhytides, skin tightening – require multiple treatments, Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist who practices in Boston, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “That’s an important expectation to set for your patients,” she said. “You also want to select depth and density parameters based on pathophysiology of the condition being treated, and combination treatments always provide the best results. So, whether you’re treating someone for acne scars or rhytides, you want to treat them for their erythema or their dermatoheliosis. The same goes for skin tightening procedures.”
Many nonpolar and bipolar devices are available for use, most of which feature adjustable depths and energies. Tips can be insulated or noninsulated. Generally, the insulated tips are safer for darker skin types because the energy is not delivered to the epidermis. However, the Sylfirm X device from Benev has a noninsulated tip but is safe for all skin types because the energy is delivered from the tip of a conically shaped needle and moves proximally but never reaches the epidermis, said Dr. DiGiorgio. Continuous wave mode is used for tightening and wrinkles while pulsed mode is used for pigment and vascular lesions.
Treatment with most fractional RF microneedling devices is painful so topical anesthesia is required. Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses topical 23% lidocaine and 7% tetracaine. The downtime varies depending on which device is being used. For anesthesia prior to aggressive fractional microneedle RF treatments such as with the Profound RF for skin tightening, Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses a Mesoram needle with a cocktail of 30 ccs of 2% lidocaine with epinephrine, 15 ccs of bicarbonate, and 5 ccs of saline. “More aggressive RF procedures can result in bruising for 7 to 8 days,” she said. “It can be covered with makeup. Wearing masks during the COVID-19 pandemic have also helped patients cover the bruising.”
In her clinical experience, the ideal patient for skin tightening with fractional RF microneedling has mild to moderate skin laxity that does not require surgical intervention. “Nonsurgical treatments provide nonsurgical results,” she said. “If a patient comes in holding their skin back and there is a lot of laxity, this is not going to be the right treatment for that person.”
Dr. DiGiorgio offers fractional RF microneedling in the context of a full-face rejuvenation. She begins by addressing volume loss and dynamic rhytides with injectables prior to skin tightening devices such as fractional RF microneedling or ultrasound-based tightening devices such as Sofwave or Ulthera (also referred to as Ultherapy). “You can add an ablative fractional to target deeper rhytides or pigment-targeting laser to address their dermatoheliosis, which will enhance their results,” she said. “Finally, you can follow up with a thread lift two weeks after the microneedle RF to achieve greater skin tightening. If the thread lift is performed before the microneedle RF, you want to wait about 2 months because the microneedle RF can damage the thread.”
Despite the limited efficacy for tissue tightening with fractional RF microneedling, “it’s a good alternative to lasers, especially for darker skin types,” she said. “Combination treatments will always enhance your results.”
Dr. DiGiorgio disclosed that she is a member of the advisory board for Quthero. She is also a consultant for Revelle and has received equipment from Acclaro.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD.
Most core fractional RF microneedling indications – acne scars, rhytides, skin tightening – require multiple treatments, Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist who practices in Boston, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “That’s an important expectation to set for your patients,” she said. “You also want to select depth and density parameters based on pathophysiology of the condition being treated, and combination treatments always provide the best results. So, whether you’re treating someone for acne scars or rhytides, you want to treat them for their erythema or their dermatoheliosis. The same goes for skin tightening procedures.”
Many nonpolar and bipolar devices are available for use, most of which feature adjustable depths and energies. Tips can be insulated or noninsulated. Generally, the insulated tips are safer for darker skin types because the energy is not delivered to the epidermis. However, the Sylfirm X device from Benev has a noninsulated tip but is safe for all skin types because the energy is delivered from the tip of a conically shaped needle and moves proximally but never reaches the epidermis, said Dr. DiGiorgio. Continuous wave mode is used for tightening and wrinkles while pulsed mode is used for pigment and vascular lesions.
Treatment with most fractional RF microneedling devices is painful so topical anesthesia is required. Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses topical 23% lidocaine and 7% tetracaine. The downtime varies depending on which device is being used. For anesthesia prior to aggressive fractional microneedle RF treatments such as with the Profound RF for skin tightening, Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses a Mesoram needle with a cocktail of 30 ccs of 2% lidocaine with epinephrine, 15 ccs of bicarbonate, and 5 ccs of saline. “More aggressive RF procedures can result in bruising for 7 to 8 days,” she said. “It can be covered with makeup. Wearing masks during the COVID-19 pandemic have also helped patients cover the bruising.”
In her clinical experience, the ideal patient for skin tightening with fractional RF microneedling has mild to moderate skin laxity that does not require surgical intervention. “Nonsurgical treatments provide nonsurgical results,” she said. “If a patient comes in holding their skin back and there is a lot of laxity, this is not going to be the right treatment for that person.”
Dr. DiGiorgio offers fractional RF microneedling in the context of a full-face rejuvenation. She begins by addressing volume loss and dynamic rhytides with injectables prior to skin tightening devices such as fractional RF microneedling or ultrasound-based tightening devices such as Sofwave or Ulthera (also referred to as Ultherapy). “You can add an ablative fractional to target deeper rhytides or pigment-targeting laser to address their dermatoheliosis, which will enhance their results,” she said. “Finally, you can follow up with a thread lift two weeks after the microneedle RF to achieve greater skin tightening. If the thread lift is performed before the microneedle RF, you want to wait about 2 months because the microneedle RF can damage the thread.”
Despite the limited efficacy for tissue tightening with fractional RF microneedling, “it’s a good alternative to lasers, especially for darker skin types,” she said. “Combination treatments will always enhance your results.”
Dr. DiGiorgio disclosed that she is a member of the advisory board for Quthero. She is also a consultant for Revelle and has received equipment from Acclaro.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD.
Most core fractional RF microneedling indications – acne scars, rhytides, skin tightening – require multiple treatments, Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist who practices in Boston, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “That’s an important expectation to set for your patients,” she said. “You also want to select depth and density parameters based on pathophysiology of the condition being treated, and combination treatments always provide the best results. So, whether you’re treating someone for acne scars or rhytides, you want to treat them for their erythema or their dermatoheliosis. The same goes for skin tightening procedures.”
Many nonpolar and bipolar devices are available for use, most of which feature adjustable depths and energies. Tips can be insulated or noninsulated. Generally, the insulated tips are safer for darker skin types because the energy is not delivered to the epidermis. However, the Sylfirm X device from Benev has a noninsulated tip but is safe for all skin types because the energy is delivered from the tip of a conically shaped needle and moves proximally but never reaches the epidermis, said Dr. DiGiorgio. Continuous wave mode is used for tightening and wrinkles while pulsed mode is used for pigment and vascular lesions.
Treatment with most fractional RF microneedling devices is painful so topical anesthesia is required. Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses topical 23% lidocaine and 7% tetracaine. The downtime varies depending on which device is being used. For anesthesia prior to aggressive fractional microneedle RF treatments such as with the Profound RF for skin tightening, Dr. DiGiorgio typically uses a Mesoram needle with a cocktail of 30 ccs of 2% lidocaine with epinephrine, 15 ccs of bicarbonate, and 5 ccs of saline. “More aggressive RF procedures can result in bruising for 7 to 8 days,” she said. “It can be covered with makeup. Wearing masks during the COVID-19 pandemic have also helped patients cover the bruising.”
In her clinical experience, the ideal patient for skin tightening with fractional RF microneedling has mild to moderate skin laxity that does not require surgical intervention. “Nonsurgical treatments provide nonsurgical results,” she said. “If a patient comes in holding their skin back and there is a lot of laxity, this is not going to be the right treatment for that person.”
Dr. DiGiorgio offers fractional RF microneedling in the context of a full-face rejuvenation. She begins by addressing volume loss and dynamic rhytides with injectables prior to skin tightening devices such as fractional RF microneedling or ultrasound-based tightening devices such as Sofwave or Ulthera (also referred to as Ultherapy). “You can add an ablative fractional to target deeper rhytides or pigment-targeting laser to address their dermatoheliosis, which will enhance their results,” she said. “Finally, you can follow up with a thread lift two weeks after the microneedle RF to achieve greater skin tightening. If the thread lift is performed before the microneedle RF, you want to wait about 2 months because the microneedle RF can damage the thread.”
Despite the limited efficacy for tissue tightening with fractional RF microneedling, “it’s a good alternative to lasers, especially for darker skin types,” she said. “Combination treatments will always enhance your results.”
Dr. DiGiorgio disclosed that she is a member of the advisory board for Quthero. She is also a consultant for Revelle and has received equipment from Acclaro.
AT MOAS 2022
Grateful and hopeful
My year is now over. My staff and I started the habit of closing down mid-December in 2013, when we realized that patients generally didn’t want to come in then, either.
To me a year really ends the day we close up for the holidays. I put away the season’s decorations, send the final batch to my billing company, and lock the door. Not much of a New Year’s, but at my age it’s not a holiday I mark, anyway. It’s more a relief that my office year, at least, is done.
So it’s always a time for reflection, between the more mundane work of returning calls, reviewing the tests that come in, and getting taxes ready. I try to relax as much as I can (given the weird state of our times, I haven’t left town since November 2019, so this is my vacation for now).
Plus, my kids all come home. I have no idea how much longer that’s going to happen, so I’ll enjoy it while I can.
It’s now almost 3 years since I last rounded at a hospital, and I can’t say I miss it. While I usually have plenty to do on my breaks and weekends, and the occasional patient call to return, it’s nice to know that I can stay in my robe, PJs, and slippers through it all.
2022 certainly wasn’t bad for my family and me, though not as good as any of us hoped. The world, already battered by the pandemic, was thrown into greater uncertainty by the war in Europe and its ramifications across the globe. In comparison, I’m very grateful that higher prices are the extent of my suffering as compared with what the people of Ukraine are going through.
But, at the end of it all, my little practice and two wonderful staff are still here, just as we’ve been since 2000. My kids will (hopefully) all be through college by the end of 2023 and moving on with their lives. I love them, and will miss them if they move away, but part of being a parent is accepting that your kids are only visitors and have their own paths to follow.
For my staff I’m glad they’ve stuck with me through good and bad times, and that we still have fun together – even when we haven’t worked under the same roof in a while.
For my patients and their families we’ve seen a few glimmers of optimism in treatments and hopefully they’ll continue to grow and be built upon. Heaven knows my field – and many others – can use them.
And so,
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
My year is now over. My staff and I started the habit of closing down mid-December in 2013, when we realized that patients generally didn’t want to come in then, either.
To me a year really ends the day we close up for the holidays. I put away the season’s decorations, send the final batch to my billing company, and lock the door. Not much of a New Year’s, but at my age it’s not a holiday I mark, anyway. It’s more a relief that my office year, at least, is done.
So it’s always a time for reflection, between the more mundane work of returning calls, reviewing the tests that come in, and getting taxes ready. I try to relax as much as I can (given the weird state of our times, I haven’t left town since November 2019, so this is my vacation for now).
Plus, my kids all come home. I have no idea how much longer that’s going to happen, so I’ll enjoy it while I can.
It’s now almost 3 years since I last rounded at a hospital, and I can’t say I miss it. While I usually have plenty to do on my breaks and weekends, and the occasional patient call to return, it’s nice to know that I can stay in my robe, PJs, and slippers through it all.
2022 certainly wasn’t bad for my family and me, though not as good as any of us hoped. The world, already battered by the pandemic, was thrown into greater uncertainty by the war in Europe and its ramifications across the globe. In comparison, I’m very grateful that higher prices are the extent of my suffering as compared with what the people of Ukraine are going through.
But, at the end of it all, my little practice and two wonderful staff are still here, just as we’ve been since 2000. My kids will (hopefully) all be through college by the end of 2023 and moving on with their lives. I love them, and will miss them if they move away, but part of being a parent is accepting that your kids are only visitors and have their own paths to follow.
For my staff I’m glad they’ve stuck with me through good and bad times, and that we still have fun together – even when we haven’t worked under the same roof in a while.
For my patients and their families we’ve seen a few glimmers of optimism in treatments and hopefully they’ll continue to grow and be built upon. Heaven knows my field – and many others – can use them.
And so,
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
My year is now over. My staff and I started the habit of closing down mid-December in 2013, when we realized that patients generally didn’t want to come in then, either.
To me a year really ends the day we close up for the holidays. I put away the season’s decorations, send the final batch to my billing company, and lock the door. Not much of a New Year’s, but at my age it’s not a holiday I mark, anyway. It’s more a relief that my office year, at least, is done.
So it’s always a time for reflection, between the more mundane work of returning calls, reviewing the tests that come in, and getting taxes ready. I try to relax as much as I can (given the weird state of our times, I haven’t left town since November 2019, so this is my vacation for now).
Plus, my kids all come home. I have no idea how much longer that’s going to happen, so I’ll enjoy it while I can.
It’s now almost 3 years since I last rounded at a hospital, and I can’t say I miss it. While I usually have plenty to do on my breaks and weekends, and the occasional patient call to return, it’s nice to know that I can stay in my robe, PJs, and slippers through it all.
2022 certainly wasn’t bad for my family and me, though not as good as any of us hoped. The world, already battered by the pandemic, was thrown into greater uncertainty by the war in Europe and its ramifications across the globe. In comparison, I’m very grateful that higher prices are the extent of my suffering as compared with what the people of Ukraine are going through.
But, at the end of it all, my little practice and two wonderful staff are still here, just as we’ve been since 2000. My kids will (hopefully) all be through college by the end of 2023 and moving on with their lives. I love them, and will miss them if they move away, but part of being a parent is accepting that your kids are only visitors and have their own paths to follow.
For my staff I’m glad they’ve stuck with me through good and bad times, and that we still have fun together – even when we haven’t worked under the same roof in a while.
For my patients and their families we’ve seen a few glimmers of optimism in treatments and hopefully they’ll continue to grow and be built upon. Heaven knows my field – and many others – can use them.
And so,
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Black HFrEF patients get more empagliflozin benefit in EMPEROR analyses
CHICAGO – Black patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) may receive more benefit from treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor than do White patients, according to a new report.
A secondary analysis of data collected from the pivotal trials that assessed the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients with HFrEF, EMPEROR-Reduced, and in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), EMPEROR-Preserved, was presented by Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The “hypothesis-generating” analysis of data from EMPEROR-Reduced showed “a suggestion of a greater benefit of empagliflozin” in Black, compared with White patients, for the study’s primary endpoint (cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure) as well as for first and total hospitalizations for heart failure, he reported.
However, a similar but separate analysis that compared Black and White patients with heart failure who received treatment with a second agent, dapagliflozin, from the same SGLT2-inhibitor class did not show any suggestion of heterogeneity in the drug’s effect based on race.
Race-linked heterogeneity in empagliflozin’s effect
In EMPEROR-Reduced, which randomized 3,730 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, treatment of White patients with empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced a nonsignificant 16% relative reduction in the rate of the primary endpoint, compared with placebo, during a median 16-month follow-up.
By contrast, among Black patients, treatment with empagliflozin produced a significant 56% reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, a significant heterogeneity (P = .02) in effect between the two race subgroups, said Dr. Verma, a cardiac surgeon and professor at the University of Toronto.
The analysis he reported used combined data from EMPEROR-Reduced and the companion trial EMPEROR-Preserved, which randomized 5,988 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% to treatment with either empagliflozin or placebo and followed them for a median of 26 months.
To assess the effects of the randomized treatments in the two racial subgroups, Dr. Verma and associates used pooled data from both trials, but only from the 3,502 patients enrolled in the Americas, which included 3,024 White patients and 478 Black patients. Analysis of the patients in this subgroup who were randomized to placebo showed a significantly excess rate of the primary outcome among Blacks, who tallied 49% more of the primary outcome events during follow-up than did White patients, Dr. Verma reported. The absolute rate of the primary outcome without empagliflozin treatment was 13.15 events/100 patient-years of follow-up in White patients and 20.83 events/100 patient-years in Black patients.
The impact of empagliflozin was not statistically heterogeneous in the total pool of patients that included both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF. The drug reduced the primary outcome incidence by a significant 20% in White patients, and by a significant 44% among Black patients.
But this point-estimate difference in efficacy, when coupled with the underlying difference in risk for an event between the two racial groups, meant that the number-needed-to-treat to prevent one primary outcome event was 42 among White patients and 12 among Black patients.
Race-linked treatment responses only in HFrEF
This suggestion of an imbalance in treatment efficacy was especially apparent among patients with HFrEF. In addition to the heterogeneity for the primary outcome, the Black and White subgroups also showed significantly divergent results for the outcomes of first hospitalization for heart failure, with a nonsignificant 21% relative reduction with empagliflozin treatment in Whites but a significant 65% relative cut in this endpoint with empagliflozin in Blacks, and for total hospitalizations for heart failure, which showed a similar level of significant heterogeneity between the two race subgroups.
In contrast, the patients with HFpEF showed no signal at all for heterogeneous outcome rates between Black and White subgroups.
One other study outcome, change in symptom burden measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), also showed suggestion of a race-based imbalance. The adjusted mean difference from baseline in the KCCQ clinical summary score was 1.50 points higher with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo among all White patients (those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF), and compared with a 5.25-point increase with empagliflozin over placebo among all Black patients with heart failure in the pooled American EMPEROR dataset, a difference between White and Black patients that just missed significance (P = .06). Again, this difference was especially notable and significant among the patients with HFrEF, where the adjusted mean difference in KCCQ was a 0.77-point increase in White patients and a 6.71-point increase among Black patients (P = .043),
These results also appeared in a report published simultaneously with Dr. Verma’s talk.
But two other analyses that assessed a possible race-based difference in empagliflozin’s effect on renal protection and on functional status showed no suggestion of heterogeneity.
Dr. Verma stressed caution about the limitations of these analyses because they involved a relatively small number of Black patients, and were possibly subject to unadjusted confounding from differences in baseline characteristics between the Black and White patients.
Black patients also had a number-needed-to-treat advantage with dapagliflozin
The finding that Black patients with heart failure potentially get more bang for the buck from treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor by having a lower number needed to treat also showed up in a separate report at the meeting that assessed the treatment effect from dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in Black and White patients in a pooled analysis of the DAPA-HF pivotal trial of patients with HFrEF and the DELIVER pivotal trial of patients with HFpEF. The pooled cohort included a total of 11,007, but for the analysis by race the investigators also limited their focus to patients from the Americas with 2,626 White patients and 381 Black patients.
Assessment of the effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure among all patients, both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF, again showed that event rates among patients treated with placebo were significantly higher in Black, compared with White patients, and this led to a difference in the number needed to treat to prevent one primary outcome event of 12 in Blacks and 17 in Whites, Jawad H. Butt, MD said in a talk at the meeting.
Although treatment with dapagliflozin reduced the rate of the primary outcome in this subgroup of patients from the DAPA-HF trial and the DELIVER trial by similar rates in Black and White patients, event rates were higher in the Black patients resulting in “greater benefit in absolute terms” for Black patients, explained Dr. Butt, a cardiologist at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen.
But in contrast to the empagliflozin findings reported by Dr. Verma, the combined data from the dapagliflozin trials showed no suggestion of heterogeneity in the beneficial effect of dapagliflozin based on left ventricular ejection fraction. In the Black patients, for example, the relative benefit from dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent across the full spectrum of patients with HFrEF and HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). The DAPA-HF and DELIVER trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Verma has received honoraria, research support, or both from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Lilly, and from numerous other companies. Dr. Butt has been a consultant to and received travel grants from AstraZeneca, honoraria from Novartis, and has been an adviser to Bayer.
CHICAGO – Black patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) may receive more benefit from treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor than do White patients, according to a new report.
A secondary analysis of data collected from the pivotal trials that assessed the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients with HFrEF, EMPEROR-Reduced, and in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), EMPEROR-Preserved, was presented by Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The “hypothesis-generating” analysis of data from EMPEROR-Reduced showed “a suggestion of a greater benefit of empagliflozin” in Black, compared with White patients, for the study’s primary endpoint (cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure) as well as for first and total hospitalizations for heart failure, he reported.
However, a similar but separate analysis that compared Black and White patients with heart failure who received treatment with a second agent, dapagliflozin, from the same SGLT2-inhibitor class did not show any suggestion of heterogeneity in the drug’s effect based on race.
Race-linked heterogeneity in empagliflozin’s effect
In EMPEROR-Reduced, which randomized 3,730 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, treatment of White patients with empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced a nonsignificant 16% relative reduction in the rate of the primary endpoint, compared with placebo, during a median 16-month follow-up.
By contrast, among Black patients, treatment with empagliflozin produced a significant 56% reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, a significant heterogeneity (P = .02) in effect between the two race subgroups, said Dr. Verma, a cardiac surgeon and professor at the University of Toronto.
The analysis he reported used combined data from EMPEROR-Reduced and the companion trial EMPEROR-Preserved, which randomized 5,988 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% to treatment with either empagliflozin or placebo and followed them for a median of 26 months.
To assess the effects of the randomized treatments in the two racial subgroups, Dr. Verma and associates used pooled data from both trials, but only from the 3,502 patients enrolled in the Americas, which included 3,024 White patients and 478 Black patients. Analysis of the patients in this subgroup who were randomized to placebo showed a significantly excess rate of the primary outcome among Blacks, who tallied 49% more of the primary outcome events during follow-up than did White patients, Dr. Verma reported. The absolute rate of the primary outcome without empagliflozin treatment was 13.15 events/100 patient-years of follow-up in White patients and 20.83 events/100 patient-years in Black patients.
The impact of empagliflozin was not statistically heterogeneous in the total pool of patients that included both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF. The drug reduced the primary outcome incidence by a significant 20% in White patients, and by a significant 44% among Black patients.
But this point-estimate difference in efficacy, when coupled with the underlying difference in risk for an event between the two racial groups, meant that the number-needed-to-treat to prevent one primary outcome event was 42 among White patients and 12 among Black patients.
Race-linked treatment responses only in HFrEF
This suggestion of an imbalance in treatment efficacy was especially apparent among patients with HFrEF. In addition to the heterogeneity for the primary outcome, the Black and White subgroups also showed significantly divergent results for the outcomes of first hospitalization for heart failure, with a nonsignificant 21% relative reduction with empagliflozin treatment in Whites but a significant 65% relative cut in this endpoint with empagliflozin in Blacks, and for total hospitalizations for heart failure, which showed a similar level of significant heterogeneity between the two race subgroups.
In contrast, the patients with HFpEF showed no signal at all for heterogeneous outcome rates between Black and White subgroups.
One other study outcome, change in symptom burden measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), also showed suggestion of a race-based imbalance. The adjusted mean difference from baseline in the KCCQ clinical summary score was 1.50 points higher with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo among all White patients (those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF), and compared with a 5.25-point increase with empagliflozin over placebo among all Black patients with heart failure in the pooled American EMPEROR dataset, a difference between White and Black patients that just missed significance (P = .06). Again, this difference was especially notable and significant among the patients with HFrEF, where the adjusted mean difference in KCCQ was a 0.77-point increase in White patients and a 6.71-point increase among Black patients (P = .043),
These results also appeared in a report published simultaneously with Dr. Verma’s talk.
But two other analyses that assessed a possible race-based difference in empagliflozin’s effect on renal protection and on functional status showed no suggestion of heterogeneity.
Dr. Verma stressed caution about the limitations of these analyses because they involved a relatively small number of Black patients, and were possibly subject to unadjusted confounding from differences in baseline characteristics between the Black and White patients.
Black patients also had a number-needed-to-treat advantage with dapagliflozin
The finding that Black patients with heart failure potentially get more bang for the buck from treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor by having a lower number needed to treat also showed up in a separate report at the meeting that assessed the treatment effect from dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in Black and White patients in a pooled analysis of the DAPA-HF pivotal trial of patients with HFrEF and the DELIVER pivotal trial of patients with HFpEF. The pooled cohort included a total of 11,007, but for the analysis by race the investigators also limited their focus to patients from the Americas with 2,626 White patients and 381 Black patients.
Assessment of the effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure among all patients, both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF, again showed that event rates among patients treated with placebo were significantly higher in Black, compared with White patients, and this led to a difference in the number needed to treat to prevent one primary outcome event of 12 in Blacks and 17 in Whites, Jawad H. Butt, MD said in a talk at the meeting.
Although treatment with dapagliflozin reduced the rate of the primary outcome in this subgroup of patients from the DAPA-HF trial and the DELIVER trial by similar rates in Black and White patients, event rates were higher in the Black patients resulting in “greater benefit in absolute terms” for Black patients, explained Dr. Butt, a cardiologist at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen.
But in contrast to the empagliflozin findings reported by Dr. Verma, the combined data from the dapagliflozin trials showed no suggestion of heterogeneity in the beneficial effect of dapagliflozin based on left ventricular ejection fraction. In the Black patients, for example, the relative benefit from dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent across the full spectrum of patients with HFrEF and HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). The DAPA-HF and DELIVER trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Verma has received honoraria, research support, or both from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Lilly, and from numerous other companies. Dr. Butt has been a consultant to and received travel grants from AstraZeneca, honoraria from Novartis, and has been an adviser to Bayer.
CHICAGO – Black patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) may receive more benefit from treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor than do White patients, according to a new report.
A secondary analysis of data collected from the pivotal trials that assessed the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients with HFrEF, EMPEROR-Reduced, and in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), EMPEROR-Preserved, was presented by Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The “hypothesis-generating” analysis of data from EMPEROR-Reduced showed “a suggestion of a greater benefit of empagliflozin” in Black, compared with White patients, for the study’s primary endpoint (cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure) as well as for first and total hospitalizations for heart failure, he reported.
However, a similar but separate analysis that compared Black and White patients with heart failure who received treatment with a second agent, dapagliflozin, from the same SGLT2-inhibitor class did not show any suggestion of heterogeneity in the drug’s effect based on race.
Race-linked heterogeneity in empagliflozin’s effect
In EMPEROR-Reduced, which randomized 3,730 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, treatment of White patients with empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced a nonsignificant 16% relative reduction in the rate of the primary endpoint, compared with placebo, during a median 16-month follow-up.
By contrast, among Black patients, treatment with empagliflozin produced a significant 56% reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, a significant heterogeneity (P = .02) in effect between the two race subgroups, said Dr. Verma, a cardiac surgeon and professor at the University of Toronto.
The analysis he reported used combined data from EMPEROR-Reduced and the companion trial EMPEROR-Preserved, which randomized 5,988 patients with heart failure and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% to treatment with either empagliflozin or placebo and followed them for a median of 26 months.
To assess the effects of the randomized treatments in the two racial subgroups, Dr. Verma and associates used pooled data from both trials, but only from the 3,502 patients enrolled in the Americas, which included 3,024 White patients and 478 Black patients. Analysis of the patients in this subgroup who were randomized to placebo showed a significantly excess rate of the primary outcome among Blacks, who tallied 49% more of the primary outcome events during follow-up than did White patients, Dr. Verma reported. The absolute rate of the primary outcome without empagliflozin treatment was 13.15 events/100 patient-years of follow-up in White patients and 20.83 events/100 patient-years in Black patients.
The impact of empagliflozin was not statistically heterogeneous in the total pool of patients that included both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF. The drug reduced the primary outcome incidence by a significant 20% in White patients, and by a significant 44% among Black patients.
But this point-estimate difference in efficacy, when coupled with the underlying difference in risk for an event between the two racial groups, meant that the number-needed-to-treat to prevent one primary outcome event was 42 among White patients and 12 among Black patients.
Race-linked treatment responses only in HFrEF
This suggestion of an imbalance in treatment efficacy was especially apparent among patients with HFrEF. In addition to the heterogeneity for the primary outcome, the Black and White subgroups also showed significantly divergent results for the outcomes of first hospitalization for heart failure, with a nonsignificant 21% relative reduction with empagliflozin treatment in Whites but a significant 65% relative cut in this endpoint with empagliflozin in Blacks, and for total hospitalizations for heart failure, which showed a similar level of significant heterogeneity between the two race subgroups.
In contrast, the patients with HFpEF showed no signal at all for heterogeneous outcome rates between Black and White subgroups.
One other study outcome, change in symptom burden measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), also showed suggestion of a race-based imbalance. The adjusted mean difference from baseline in the KCCQ clinical summary score was 1.50 points higher with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo among all White patients (those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF), and compared with a 5.25-point increase with empagliflozin over placebo among all Black patients with heart failure in the pooled American EMPEROR dataset, a difference between White and Black patients that just missed significance (P = .06). Again, this difference was especially notable and significant among the patients with HFrEF, where the adjusted mean difference in KCCQ was a 0.77-point increase in White patients and a 6.71-point increase among Black patients (P = .043),
These results also appeared in a report published simultaneously with Dr. Verma’s talk.
But two other analyses that assessed a possible race-based difference in empagliflozin’s effect on renal protection and on functional status showed no suggestion of heterogeneity.
Dr. Verma stressed caution about the limitations of these analyses because they involved a relatively small number of Black patients, and were possibly subject to unadjusted confounding from differences in baseline characteristics between the Black and White patients.
Black patients also had a number-needed-to-treat advantage with dapagliflozin
The finding that Black patients with heart failure potentially get more bang for the buck from treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor by having a lower number needed to treat also showed up in a separate report at the meeting that assessed the treatment effect from dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in Black and White patients in a pooled analysis of the DAPA-HF pivotal trial of patients with HFrEF and the DELIVER pivotal trial of patients with HFpEF. The pooled cohort included a total of 11,007, but for the analysis by race the investigators also limited their focus to patients from the Americas with 2,626 White patients and 381 Black patients.
Assessment of the effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure among all patients, both those with HFrEF and those with HFpEF, again showed that event rates among patients treated with placebo were significantly higher in Black, compared with White patients, and this led to a difference in the number needed to treat to prevent one primary outcome event of 12 in Blacks and 17 in Whites, Jawad H. Butt, MD said in a talk at the meeting.
Although treatment with dapagliflozin reduced the rate of the primary outcome in this subgroup of patients from the DAPA-HF trial and the DELIVER trial by similar rates in Black and White patients, event rates were higher in the Black patients resulting in “greater benefit in absolute terms” for Black patients, explained Dr. Butt, a cardiologist at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen.
But in contrast to the empagliflozin findings reported by Dr. Verma, the combined data from the dapagliflozin trials showed no suggestion of heterogeneity in the beneficial effect of dapagliflozin based on left ventricular ejection fraction. In the Black patients, for example, the relative benefit from dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent across the full spectrum of patients with HFrEF and HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). The DAPA-HF and DELIVER trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Verma has received honoraria, research support, or both from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Lilly, and from numerous other companies. Dr. Butt has been a consultant to and received travel grants from AstraZeneca, honoraria from Novartis, and has been an adviser to Bayer.
AT AHA 2022
Violaceous-Purpuric Targetoid Macules and Patches With Bullae and Ulceration
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.
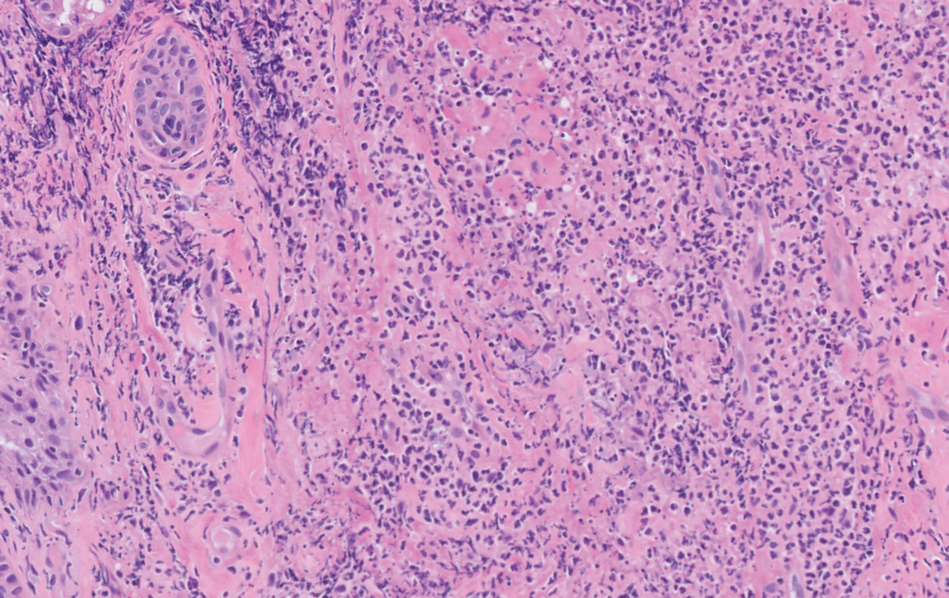
Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1
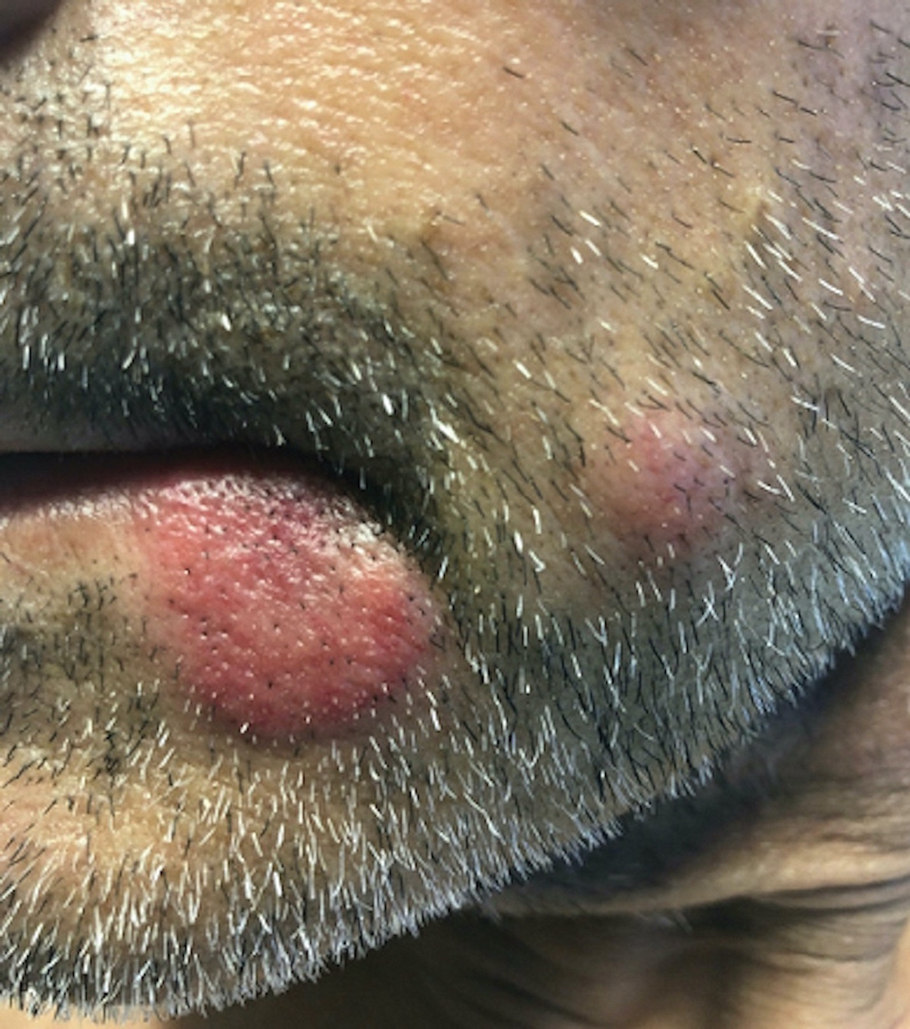
The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.

Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1

The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.

Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1

The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
A 64-year-old man with long-standing myelofibrosis presented with neutropenic fevers as well as progressive painful lesions of 3 days’ duration on the legs. A bone marrow biopsy during this hospitalization demonstrated a recent progression of the patient’s myelofibrosis to acute myeloid leukemia. Physical examination revealed round to oval, violaceous, targetoid plaques. Within a week, new erythematous and nodular lesions appeared on the right arm and left vermilion border. The lesions on the legs enlarged, formed bullae, and ulcerated.