User login
Mechanistic link between herpes virus, Alzheimer’s revealed?
, new research suggests.
“Our results suggest one pathway to Alzheimer’s disease, caused by a VZV infection which creates inflammatory triggers that awaken HSV in the brain,” lead author Dana Cairns, PhD, research associate, department of biomedical engineering at Tufts University, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
‘One-two punch’
Previous research has suggested a correlation between HSV-1 and AD and involvement of VZV. However, the sequence of events that the viruses create to set the disease in motion has been unclear.
“We think we now have evidence of those events,” co–senior author David Kaplan, PhD, chair of the department of biomedical engineering at Tufts, said in the release.
Working with co–senior author Ruth Itzhaki, PhD, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, the researchers infected human-induced neural stem cells (hiNSCs) and 3D brain tissue models with HSV-1 and/or VZV. Dr. Itzhaki was one of the first to hypothesize a connection between herpes virus and AD.
The investigators found that HSV-1 infection of hiNSCs induces amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation: the main components of AD plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, respectively.
On the other hand, VZV infection of cultured hiNSCs did not lead to amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation but instead resulted in gliosis and increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines.
“Strikingly,” VZV infection of cells quiescently infected with HSV-1 caused reactivation of HSV-1, leading to AD-like changes, including amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation, the investigators report.
This suggests that VZV is unlikely to be a direct cause of AD but rather acts indirectly via reactivation of HSV-1, they add.
Similar findings emerged in similar experiments using 3D human brain tissue models.
“It’s a one-two punch of two viruses that are very common and usually harmless, but the lab studies suggest that if a new exposure to VZV wakes up dormant HSV-1, they could cause trouble,” Dr. Cairns said.
The researchers note that vaccination against VZV has been shown previously to reduce risk for dementia. It is possible, they add, that the vaccine is helping to stop the cycle of viral reactivation, inflammation, and neuronal damage.
‘A first step’
Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, said that the study “is using artificial systems with the goal of more clearly and more deeply understanding” the assessed associations.
She added that although it is a first step, it may provide valuable direction for follow-up research.
“This is preliminary work that first needs replication, validation, and further development to understand if any association that is uncovered between viruses and Alzheimer’s/dementia has a mechanistic link,” said Dr. Snyder.
She noted that several past studies have sought to help the research field better understand the links between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
“There have been some challenges in evaluating these associations in our current model systems or in individuals for a number of reasons,” said Dr. Snyder.
However, “the COVID-19 pandemic has created an opportunity to examine and investigate the relationships between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other dementias by following individuals in more common and well-established ways,” she added.
She reported that her organization is “leading and working with a large global network of studies and investigators to address some of these questions” from during and after the COVID pandemic.
“The lessons we learn and share may inform our understanding of how other viruses are, or are not, connected to Alzheimer’s and other dementia,” Dr. Snyder said.
More information on the Alzheimer’s Association International Cohort Study of Chronic Neurological Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 is available online.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cairns, Dr. Kaplan, Dr. Itzhaki, and Dr. Snyder have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
“Our results suggest one pathway to Alzheimer’s disease, caused by a VZV infection which creates inflammatory triggers that awaken HSV in the brain,” lead author Dana Cairns, PhD, research associate, department of biomedical engineering at Tufts University, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
‘One-two punch’
Previous research has suggested a correlation between HSV-1 and AD and involvement of VZV. However, the sequence of events that the viruses create to set the disease in motion has been unclear.
“We think we now have evidence of those events,” co–senior author David Kaplan, PhD, chair of the department of biomedical engineering at Tufts, said in the release.
Working with co–senior author Ruth Itzhaki, PhD, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, the researchers infected human-induced neural stem cells (hiNSCs) and 3D brain tissue models with HSV-1 and/or VZV. Dr. Itzhaki was one of the first to hypothesize a connection between herpes virus and AD.
The investigators found that HSV-1 infection of hiNSCs induces amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation: the main components of AD plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, respectively.
On the other hand, VZV infection of cultured hiNSCs did not lead to amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation but instead resulted in gliosis and increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines.
“Strikingly,” VZV infection of cells quiescently infected with HSV-1 caused reactivation of HSV-1, leading to AD-like changes, including amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation, the investigators report.
This suggests that VZV is unlikely to be a direct cause of AD but rather acts indirectly via reactivation of HSV-1, they add.
Similar findings emerged in similar experiments using 3D human brain tissue models.
“It’s a one-two punch of two viruses that are very common and usually harmless, but the lab studies suggest that if a new exposure to VZV wakes up dormant HSV-1, they could cause trouble,” Dr. Cairns said.
The researchers note that vaccination against VZV has been shown previously to reduce risk for dementia. It is possible, they add, that the vaccine is helping to stop the cycle of viral reactivation, inflammation, and neuronal damage.
‘A first step’
Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, said that the study “is using artificial systems with the goal of more clearly and more deeply understanding” the assessed associations.
She added that although it is a first step, it may provide valuable direction for follow-up research.
“This is preliminary work that first needs replication, validation, and further development to understand if any association that is uncovered between viruses and Alzheimer’s/dementia has a mechanistic link,” said Dr. Snyder.
She noted that several past studies have sought to help the research field better understand the links between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
“There have been some challenges in evaluating these associations in our current model systems or in individuals for a number of reasons,” said Dr. Snyder.
However, “the COVID-19 pandemic has created an opportunity to examine and investigate the relationships between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other dementias by following individuals in more common and well-established ways,” she added.
She reported that her organization is “leading and working with a large global network of studies and investigators to address some of these questions” from during and after the COVID pandemic.
“The lessons we learn and share may inform our understanding of how other viruses are, or are not, connected to Alzheimer’s and other dementia,” Dr. Snyder said.
More information on the Alzheimer’s Association International Cohort Study of Chronic Neurological Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 is available online.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cairns, Dr. Kaplan, Dr. Itzhaki, and Dr. Snyder have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
“Our results suggest one pathway to Alzheimer’s disease, caused by a VZV infection which creates inflammatory triggers that awaken HSV in the brain,” lead author Dana Cairns, PhD, research associate, department of biomedical engineering at Tufts University, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
‘One-two punch’
Previous research has suggested a correlation between HSV-1 and AD and involvement of VZV. However, the sequence of events that the viruses create to set the disease in motion has been unclear.
“We think we now have evidence of those events,” co–senior author David Kaplan, PhD, chair of the department of biomedical engineering at Tufts, said in the release.
Working with co–senior author Ruth Itzhaki, PhD, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, the researchers infected human-induced neural stem cells (hiNSCs) and 3D brain tissue models with HSV-1 and/or VZV. Dr. Itzhaki was one of the first to hypothesize a connection between herpes virus and AD.
The investigators found that HSV-1 infection of hiNSCs induces amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation: the main components of AD plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, respectively.
On the other hand, VZV infection of cultured hiNSCs did not lead to amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation but instead resulted in gliosis and increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines.
“Strikingly,” VZV infection of cells quiescently infected with HSV-1 caused reactivation of HSV-1, leading to AD-like changes, including amyloid-beta and P-tau accumulation, the investigators report.
This suggests that VZV is unlikely to be a direct cause of AD but rather acts indirectly via reactivation of HSV-1, they add.
Similar findings emerged in similar experiments using 3D human brain tissue models.
“It’s a one-two punch of two viruses that are very common and usually harmless, but the lab studies suggest that if a new exposure to VZV wakes up dormant HSV-1, they could cause trouble,” Dr. Cairns said.
The researchers note that vaccination against VZV has been shown previously to reduce risk for dementia. It is possible, they add, that the vaccine is helping to stop the cycle of viral reactivation, inflammation, and neuronal damage.
‘A first step’
Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, said that the study “is using artificial systems with the goal of more clearly and more deeply understanding” the assessed associations.
She added that although it is a first step, it may provide valuable direction for follow-up research.
“This is preliminary work that first needs replication, validation, and further development to understand if any association that is uncovered between viruses and Alzheimer’s/dementia has a mechanistic link,” said Dr. Snyder.
She noted that several past studies have sought to help the research field better understand the links between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
“There have been some challenges in evaluating these associations in our current model systems or in individuals for a number of reasons,” said Dr. Snyder.
However, “the COVID-19 pandemic has created an opportunity to examine and investigate the relationships between different viruses and Alzheimer’s and other dementias by following individuals in more common and well-established ways,” she added.
She reported that her organization is “leading and working with a large global network of studies and investigators to address some of these questions” from during and after the COVID pandemic.
“The lessons we learn and share may inform our understanding of how other viruses are, or are not, connected to Alzheimer’s and other dementia,” Dr. Snyder said.
More information on the Alzheimer’s Association International Cohort Study of Chronic Neurological Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 is available online.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cairns, Dr. Kaplan, Dr. Itzhaki, and Dr. Snyder have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
Oncologists’ wealth and debt: COVID had little impact
concludes the latest Medscape Oncologist Wealth & Debt Report 2022.
Comparing the findings with those in the larger Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2022, which surveyed more than 13,000 physicians in 29 specialties, the findings for oncologists show how they compare with those who chose other paths in medicine.
Oncologists’ income rose, on average, by 2% in the past year and now stands at an average of $411,000 annually, up from $403,000 in the 2021 report.
This puts oncologists in the top third of specialties, with plastic surgeons again in the top slot (with average income of $576,000 in 2022).
One-fifth (20%) of oncologists surveyed reported a family worth of more than $5 million, which represents substantial family wealth, the report comments.
However, 22% of oncologists reported that their family net worth was less than $500,000, and another 10% estimated that it to fall between $500,000 and $1 million.
For comparison, the average U.S. family net worth is about $749,000, according to data from the Federal Reserve.
Most live ‘within their means’
Most oncologists (94%) and also most (94%) of all of the physicians surveyed said that they live within or below their means.
How does one do this? Just paying off credit cards each month and contributing enough to a 401(k) account to receive an employer match does not meet this standard, said Joel Greenwald MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians. To live within or below your means, you also need to be saving at least 20% toward retirement, pay down student loans, contribute to your kids’ college savings, and set aside rainy day cash, he explained.
When physicians were asked about their favorite cost-cutting tactics, replies included bringing lunch to work, keeping a car for 15 years, and carrying out their own household maintenance and repairs. One doctor described a “24-hour rule” when it comes to shopping: “Revisit the desired purchase after 24 hours to see if it’s still desired.”
But how well do these tactics go down with ‘the other half’ and the rest of the household? Two-thirds (66%) of oncologists, and a similar proportion of all physicians, said that they argue with their significant other about spending. This appears to be high in comparison with the finding from a recent survey that across the United States, about one in four couples (25%) argue about money at least once a month.
Regarding spending, the top expense among oncologists was for childcare (16%), private tuition for offspring (14%), mortgage on a second home (14%), college tuition for offspring (14%), and a car lease (12%).
Around 17% of oncologists reported that they are still paying off their own college or medical school loans. For this statistic, they are about in the middle of all specialties.
The report notes that freeing oneself from medical school debt is very costly. Physicians in the United States pay an average of $356,000-$440,000, about half of which is interest.
Little change over 2021
The COVID pandemic had much less of an impact on physicians than it had on the general population when it comes to keeping up with payments, and most physicians were not affected. Only 3% of oncologists said they fell behind with payments for mortgage; 6% fell behind with payments for other bills.
In comparison, nearly half (46%) of Americans missed one or more payments of rent or mortgage because of COVID, according to a 2021 industry survey.
Over the past year, most oncologists (70%) did not change their spending habits, and only 11% cut expenses by deferring or refinancing loans. Also, most oncologists (75%) avoided major financial loses. Only 8% reported financial losses because of problems at their medical practice.
However, a slightly higher percentage of oncologists reported a stock or company investment that had turned sour in 2022 (37%) in comparison with 2021 (28%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
concludes the latest Medscape Oncologist Wealth & Debt Report 2022.
Comparing the findings with those in the larger Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2022, which surveyed more than 13,000 physicians in 29 specialties, the findings for oncologists show how they compare with those who chose other paths in medicine.
Oncologists’ income rose, on average, by 2% in the past year and now stands at an average of $411,000 annually, up from $403,000 in the 2021 report.
This puts oncologists in the top third of specialties, with plastic surgeons again in the top slot (with average income of $576,000 in 2022).
One-fifth (20%) of oncologists surveyed reported a family worth of more than $5 million, which represents substantial family wealth, the report comments.
However, 22% of oncologists reported that their family net worth was less than $500,000, and another 10% estimated that it to fall between $500,000 and $1 million.
For comparison, the average U.S. family net worth is about $749,000, according to data from the Federal Reserve.
Most live ‘within their means’
Most oncologists (94%) and also most (94%) of all of the physicians surveyed said that they live within or below their means.
How does one do this? Just paying off credit cards each month and contributing enough to a 401(k) account to receive an employer match does not meet this standard, said Joel Greenwald MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians. To live within or below your means, you also need to be saving at least 20% toward retirement, pay down student loans, contribute to your kids’ college savings, and set aside rainy day cash, he explained.
When physicians were asked about their favorite cost-cutting tactics, replies included bringing lunch to work, keeping a car for 15 years, and carrying out their own household maintenance and repairs. One doctor described a “24-hour rule” when it comes to shopping: “Revisit the desired purchase after 24 hours to see if it’s still desired.”
But how well do these tactics go down with ‘the other half’ and the rest of the household? Two-thirds (66%) of oncologists, and a similar proportion of all physicians, said that they argue with their significant other about spending. This appears to be high in comparison with the finding from a recent survey that across the United States, about one in four couples (25%) argue about money at least once a month.
Regarding spending, the top expense among oncologists was for childcare (16%), private tuition for offspring (14%), mortgage on a second home (14%), college tuition for offspring (14%), and a car lease (12%).
Around 17% of oncologists reported that they are still paying off their own college or medical school loans. For this statistic, they are about in the middle of all specialties.
The report notes that freeing oneself from medical school debt is very costly. Physicians in the United States pay an average of $356,000-$440,000, about half of which is interest.
Little change over 2021
The COVID pandemic had much less of an impact on physicians than it had on the general population when it comes to keeping up with payments, and most physicians were not affected. Only 3% of oncologists said they fell behind with payments for mortgage; 6% fell behind with payments for other bills.
In comparison, nearly half (46%) of Americans missed one or more payments of rent or mortgage because of COVID, according to a 2021 industry survey.
Over the past year, most oncologists (70%) did not change their spending habits, and only 11% cut expenses by deferring or refinancing loans. Also, most oncologists (75%) avoided major financial loses. Only 8% reported financial losses because of problems at their medical practice.
However, a slightly higher percentage of oncologists reported a stock or company investment that had turned sour in 2022 (37%) in comparison with 2021 (28%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
concludes the latest Medscape Oncologist Wealth & Debt Report 2022.
Comparing the findings with those in the larger Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2022, which surveyed more than 13,000 physicians in 29 specialties, the findings for oncologists show how they compare with those who chose other paths in medicine.
Oncologists’ income rose, on average, by 2% in the past year and now stands at an average of $411,000 annually, up from $403,000 in the 2021 report.
This puts oncologists in the top third of specialties, with plastic surgeons again in the top slot (with average income of $576,000 in 2022).
One-fifth (20%) of oncologists surveyed reported a family worth of more than $5 million, which represents substantial family wealth, the report comments.
However, 22% of oncologists reported that their family net worth was less than $500,000, and another 10% estimated that it to fall between $500,000 and $1 million.
For comparison, the average U.S. family net worth is about $749,000, according to data from the Federal Reserve.
Most live ‘within their means’
Most oncologists (94%) and also most (94%) of all of the physicians surveyed said that they live within or below their means.
How does one do this? Just paying off credit cards each month and contributing enough to a 401(k) account to receive an employer match does not meet this standard, said Joel Greenwald MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians. To live within or below your means, you also need to be saving at least 20% toward retirement, pay down student loans, contribute to your kids’ college savings, and set aside rainy day cash, he explained.
When physicians were asked about their favorite cost-cutting tactics, replies included bringing lunch to work, keeping a car for 15 years, and carrying out their own household maintenance and repairs. One doctor described a “24-hour rule” when it comes to shopping: “Revisit the desired purchase after 24 hours to see if it’s still desired.”
But how well do these tactics go down with ‘the other half’ and the rest of the household? Two-thirds (66%) of oncologists, and a similar proportion of all physicians, said that they argue with their significant other about spending. This appears to be high in comparison with the finding from a recent survey that across the United States, about one in four couples (25%) argue about money at least once a month.
Regarding spending, the top expense among oncologists was for childcare (16%), private tuition for offspring (14%), mortgage on a second home (14%), college tuition for offspring (14%), and a car lease (12%).
Around 17% of oncologists reported that they are still paying off their own college or medical school loans. For this statistic, they are about in the middle of all specialties.
The report notes that freeing oneself from medical school debt is very costly. Physicians in the United States pay an average of $356,000-$440,000, about half of which is interest.
Little change over 2021
The COVID pandemic had much less of an impact on physicians than it had on the general population when it comes to keeping up with payments, and most physicians were not affected. Only 3% of oncologists said they fell behind with payments for mortgage; 6% fell behind with payments for other bills.
In comparison, nearly half (46%) of Americans missed one or more payments of rent or mortgage because of COVID, according to a 2021 industry survey.
Over the past year, most oncologists (70%) did not change their spending habits, and only 11% cut expenses by deferring or refinancing loans. Also, most oncologists (75%) avoided major financial loses. Only 8% reported financial losses because of problems at their medical practice.
However, a slightly higher percentage of oncologists reported a stock or company investment that had turned sour in 2022 (37%) in comparison with 2021 (28%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
IV nutrition becoming the norm for athletes despite no evidence it works
In their editorial, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, experts urged the “food first” and “no needle” messages – that are taught in sports nutrition courses around the world – need to be amplified among all athletes and their support teams to “stop this trend in its tracks”.
The international group of authors, including experts from St Mary’s University, London; University College London; and University of Bath (England), who regularly interact with professional team players in European and American leagues and their support teams, said they have become increasingly aware of the practice.
Although it’s not known exactly how common the practice is, they pointed out that, anecdotally, some players are hooked up to intravenous nutrition drips as often as every week as part of a pre- or postgame routine.
‘Drip-bars’ easily accessible but devoid of regulation
Intravenous nutrition has traditionally been reserved for serious clinical conditions – such as anaemia – symptoms caused by nutrient deficiencies, or to correct severe dehydration caused by marathon running in, for example, a desert.
A ban on needle use by athletes at the Olympic Games has been in place for all recent Games except for appropriate medical use, and where a therapeutic use exemption is obtained, explained the authors.
However, “so-called ‘drip bars’ and concierge IV nutrition services are now easily accessible,” they said. These claim to boost health and performance, restore hydration, and speed up recovery, by offering a menu of B vitamins, amino acids, glutathione, vitamin C, and electrolytes, and potentially boosting levels beyond any therapeutic range.
However, they are “devoid of regulation” and for players or practitioners there is no official guidance on their use.
Physical and reputational risks
Bypassing the gut-liver axis risks nutrient toxicity warned the authors, and “appears foolhardy” unless there is a “significant clinical rationale.” They highlighted that they had noted vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 levels often “beyond the measurement range of the laboratory” in a subgroup of professional players. They pointed out how long-term effects of too much vitamin B6 include peripheral neuropathy, and that athletes regularly receiving parenteral iron “risk liver disease.”
“Given that the long-term effects of supratherapeutic doses of B vitamins and other nutrients are unknown in athletes, it does not appear to be worth the risk, especially given the lack of evidence-based benefits,” they said. They added that there is also the risk related to venous access, including “infection and thromboembolic complications.”
Additionally, a shift away from “what works” according to scientific standards to that which is “unproven” puts the reputation of sport at risk, and also puts athletes at risk of antidoping violation, they cautioned.
Figures on the prevalence of intravenous nutrition need to be gathered in tandem with governing bodies and players’ associations in the professional leagues providing guidance on the potential risks of intravenous nutrition use, recommended the authors.
The ‘food first’ and ‘no needle’ messages need to be amplified among all athletes and multidisciplinary support teams, they emphasised, to avoid what was previously a ‘last resort’ treatment becoming “normal without scientific evidence of benefit”.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
In their editorial, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, experts urged the “food first” and “no needle” messages – that are taught in sports nutrition courses around the world – need to be amplified among all athletes and their support teams to “stop this trend in its tracks”.
The international group of authors, including experts from St Mary’s University, London; University College London; and University of Bath (England), who regularly interact with professional team players in European and American leagues and their support teams, said they have become increasingly aware of the practice.
Although it’s not known exactly how common the practice is, they pointed out that, anecdotally, some players are hooked up to intravenous nutrition drips as often as every week as part of a pre- or postgame routine.
‘Drip-bars’ easily accessible but devoid of regulation
Intravenous nutrition has traditionally been reserved for serious clinical conditions – such as anaemia – symptoms caused by nutrient deficiencies, or to correct severe dehydration caused by marathon running in, for example, a desert.
A ban on needle use by athletes at the Olympic Games has been in place for all recent Games except for appropriate medical use, and where a therapeutic use exemption is obtained, explained the authors.
However, “so-called ‘drip bars’ and concierge IV nutrition services are now easily accessible,” they said. These claim to boost health and performance, restore hydration, and speed up recovery, by offering a menu of B vitamins, amino acids, glutathione, vitamin C, and electrolytes, and potentially boosting levels beyond any therapeutic range.
However, they are “devoid of regulation” and for players or practitioners there is no official guidance on their use.
Physical and reputational risks
Bypassing the gut-liver axis risks nutrient toxicity warned the authors, and “appears foolhardy” unless there is a “significant clinical rationale.” They highlighted that they had noted vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 levels often “beyond the measurement range of the laboratory” in a subgroup of professional players. They pointed out how long-term effects of too much vitamin B6 include peripheral neuropathy, and that athletes regularly receiving parenteral iron “risk liver disease.”
“Given that the long-term effects of supratherapeutic doses of B vitamins and other nutrients are unknown in athletes, it does not appear to be worth the risk, especially given the lack of evidence-based benefits,” they said. They added that there is also the risk related to venous access, including “infection and thromboembolic complications.”
Additionally, a shift away from “what works” according to scientific standards to that which is “unproven” puts the reputation of sport at risk, and also puts athletes at risk of antidoping violation, they cautioned.
Figures on the prevalence of intravenous nutrition need to be gathered in tandem with governing bodies and players’ associations in the professional leagues providing guidance on the potential risks of intravenous nutrition use, recommended the authors.
The ‘food first’ and ‘no needle’ messages need to be amplified among all athletes and multidisciplinary support teams, they emphasised, to avoid what was previously a ‘last resort’ treatment becoming “normal without scientific evidence of benefit”.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
In their editorial, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, experts urged the “food first” and “no needle” messages – that are taught in sports nutrition courses around the world – need to be amplified among all athletes and their support teams to “stop this trend in its tracks”.
The international group of authors, including experts from St Mary’s University, London; University College London; and University of Bath (England), who regularly interact with professional team players in European and American leagues and their support teams, said they have become increasingly aware of the practice.
Although it’s not known exactly how common the practice is, they pointed out that, anecdotally, some players are hooked up to intravenous nutrition drips as often as every week as part of a pre- or postgame routine.
‘Drip-bars’ easily accessible but devoid of regulation
Intravenous nutrition has traditionally been reserved for serious clinical conditions – such as anaemia – symptoms caused by nutrient deficiencies, or to correct severe dehydration caused by marathon running in, for example, a desert.
A ban on needle use by athletes at the Olympic Games has been in place for all recent Games except for appropriate medical use, and where a therapeutic use exemption is obtained, explained the authors.
However, “so-called ‘drip bars’ and concierge IV nutrition services are now easily accessible,” they said. These claim to boost health and performance, restore hydration, and speed up recovery, by offering a menu of B vitamins, amino acids, glutathione, vitamin C, and electrolytes, and potentially boosting levels beyond any therapeutic range.
However, they are “devoid of regulation” and for players or practitioners there is no official guidance on their use.
Physical and reputational risks
Bypassing the gut-liver axis risks nutrient toxicity warned the authors, and “appears foolhardy” unless there is a “significant clinical rationale.” They highlighted that they had noted vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 levels often “beyond the measurement range of the laboratory” in a subgroup of professional players. They pointed out how long-term effects of too much vitamin B6 include peripheral neuropathy, and that athletes regularly receiving parenteral iron “risk liver disease.”
“Given that the long-term effects of supratherapeutic doses of B vitamins and other nutrients are unknown in athletes, it does not appear to be worth the risk, especially given the lack of evidence-based benefits,” they said. They added that there is also the risk related to venous access, including “infection and thromboembolic complications.”
Additionally, a shift away from “what works” according to scientific standards to that which is “unproven” puts the reputation of sport at risk, and also puts athletes at risk of antidoping violation, they cautioned.
Figures on the prevalence of intravenous nutrition need to be gathered in tandem with governing bodies and players’ associations in the professional leagues providing guidance on the potential risks of intravenous nutrition use, recommended the authors.
The ‘food first’ and ‘no needle’ messages need to be amplified among all athletes and multidisciplinary support teams, they emphasised, to avoid what was previously a ‘last resort’ treatment becoming “normal without scientific evidence of benefit”.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Medications
Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks improve fracture pain
results from a meta-analysis published in BMC Anesthesiology show.
With the caveat that the quality of evidence in most trials in the analysis is low owing to a lack of blinding and other factors, “our review suggests that, among patients suffering from a hip fracture, a preoperative ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block is associated with a significant pain reduction and reduced need for systemic analgesics compared to conventional analgesia,” reported the authors.
“Our results may also indicate a lower risk of delirium, serious adverse events and higher patient satisfaction in patients receiving an ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block,” they added.
Because hip fractures commonly affect older populations and those who are frail, treatment of the substantial pain that can occur perioperatively is a challenge.
Peripheral nerve blocks have been shown to reduce pain within 30 minutes of the block placement; however, most studies have primarily included blocks that use anatomic landmarks or nerve stimulation for guidance. However, the use of ultrasound guidance with the nerve block should improve efficacy, the authors noted.
“It seems intuitive that using ultrasound-guidance should be more effective than using a blind technique, since it allows a trained physician to deposit the local anesthetic with much more precision,” they wrote.
To evaluate the data from studies that have looked at ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, Oskar Wilborg Exsteen, of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, Copenhagen University Hospital and Nordsjællands Hospital, Hillerød, Denmark, and colleagues identified 12 randomized controlled trials, involving a combined total of 976 participants, for the meta-analysis.
The studies included 509 participants who received ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, specifically the femoral nerve block and fascia iliaca block, and 476 who were randomly assigned to control groups.
Overall, those treated with the nerve blocks showed significantly greater reductions in pain measured closest to 2 hours of block placement, compared with conventional analgesia, with a mean reduction of 2.26 points on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) (range, 0-10; P < .001).
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block use was associated with lower preoperative usage of analgesic intravenous morphine equivalents in milligram, reported in four of the trials (random effects model mean difference, –5.34; P = .003).
Delirium was also significantly lower with the nerve blocks (risk ratio, 0.6; P = 0.03), as were serious adverse events, compared with standard analgesia (RR, 0.33; P = .006), whereas patient satisfaction was significantly higher with the nerve blocks (mean VAS difference, 25.9 [score 0-100]; P < .001).
Seven of the studies had monitored for serious adverse events or complications related to the nerve blocks, but none reported any complications directly related to the ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks.
Owing to the inability to conduct blinded comparisons, clinical heterogeneity, and other caveats, the quality of evidence was ultimately judged to be “low” or “very low”; however, the observed benefits are nevertheless relevant, the authors concluded.
“Despite the low quality of evidence, ultrasound-guided blocks were associated with benefits compared to conventional systemic analgesia,” they said.
Key caveats include that the morphine reductions observed with the nerve blocks were not substantial, they noted. “The opioid-sparing effect seems small and may be of less clinical importance.” The decreases in opioid consumption, as well as pain reduction in the analysis, are in fact similar to those observed with conventional, peripheral nerve blocks that did not use ultrasound guidance, compared with standard pain management.
No trials were identified that directly compared ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks with nerve block techniques that didn’t use ultrasound.
However, the other noted improvements carry more weight, the authors said.
“The potential for higher patient satisfaction and reduction in serious adverse events and delirium may be of clinical importance,” they wrote.
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks not always accessible
Of note, the use of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks appears to be somewhat low, with one observational trend study of national data in the United States showing that, among patients receiving a peripheral nerve block for hip arthroplasty, only 3.2% of the procedures were performed using ultrasound guidance.
Stephen C. Haskins, MD, a coauthor on that study, said that the low utilization underscores that, in real-world practice, an ultrasound-guided approach isn’t always convenient.
“I think our findings demonstrate a common misconception that exists for those of us that work at academic institutions and/or within the ivory towers of regional anesthesia, which is that everyone is performing cutting edge ultrasound-guided techniques for all procedures,” Dr. Haskins, an associate attending anesthesiologist and chief medical diversity officer with the department of anesthesiology, critical care & pain management at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
However, “there are many limitations to use of ultrasound for these blocks, including limited access to machines, limited access to training, and limited interest and support from our surgical colleagues,” he explained.
“Ultimately, the best nerve block is the one performed in a timely and successful fashion, regardless of technique,” he said. “But we will continue to see a trend towards ultrasound use in the future due to increasing access in the form of portability and affordability.”
Haskins noted that newer ultrasound-guided nerve blocks that were not reviewed in the study, such as the pericapsular nerve group block, regional block, and supra-inguinal fascia iliaca block, which provide additional benefits such as avoiding quadriceps weakness.
Jeff Gadsden, MD, chief of the orthopedics, plastic, and regional anesthesiology division at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., agreed, noting that much has changed since some of the older studies in the analysis, that date back to 2010.
“A fascia iliaca block done in 2022 looks a lot different than it did in 2012, and we would expect it to be more consistent, reliable and longer-lasting with current techniques and technology,” he said in an interview. “So, if anything, I would expect the findings of this analysis to undersell the benefits of peripheral nerve blocks in this population.”
Although the quality of evidence in the meta-analysis is described as “low,” the downsides of the procedures are few, and “the potential benefits [of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks] are just too good to ignore,” Dr. Gadsden emphasized.
“If we can avoid or reduce opioids in this population and at the same time reduce the acute pain from the injury, there is no question that the incidence of delirium will go down,” he said. “Delirium is associated with a number of poor outcomes following hip fracture, including increased mortality.
“The bottom line is that the risk/benefit ratio is so far in favor of performing the blocks that even in the face of ‘modest’ levels of evidence, we should all be doing these.”
The authors, Dr. Haskins, and Dr. Gadsden had no disclosures relating to the study to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a meta-analysis published in BMC Anesthesiology show.
With the caveat that the quality of evidence in most trials in the analysis is low owing to a lack of blinding and other factors, “our review suggests that, among patients suffering from a hip fracture, a preoperative ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block is associated with a significant pain reduction and reduced need for systemic analgesics compared to conventional analgesia,” reported the authors.
“Our results may also indicate a lower risk of delirium, serious adverse events and higher patient satisfaction in patients receiving an ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block,” they added.
Because hip fractures commonly affect older populations and those who are frail, treatment of the substantial pain that can occur perioperatively is a challenge.
Peripheral nerve blocks have been shown to reduce pain within 30 minutes of the block placement; however, most studies have primarily included blocks that use anatomic landmarks or nerve stimulation for guidance. However, the use of ultrasound guidance with the nerve block should improve efficacy, the authors noted.
“It seems intuitive that using ultrasound-guidance should be more effective than using a blind technique, since it allows a trained physician to deposit the local anesthetic with much more precision,” they wrote.
To evaluate the data from studies that have looked at ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, Oskar Wilborg Exsteen, of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, Copenhagen University Hospital and Nordsjællands Hospital, Hillerød, Denmark, and colleagues identified 12 randomized controlled trials, involving a combined total of 976 participants, for the meta-analysis.
The studies included 509 participants who received ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, specifically the femoral nerve block and fascia iliaca block, and 476 who were randomly assigned to control groups.
Overall, those treated with the nerve blocks showed significantly greater reductions in pain measured closest to 2 hours of block placement, compared with conventional analgesia, with a mean reduction of 2.26 points on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) (range, 0-10; P < .001).
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block use was associated with lower preoperative usage of analgesic intravenous morphine equivalents in milligram, reported in four of the trials (random effects model mean difference, –5.34; P = .003).
Delirium was also significantly lower with the nerve blocks (risk ratio, 0.6; P = 0.03), as were serious adverse events, compared with standard analgesia (RR, 0.33; P = .006), whereas patient satisfaction was significantly higher with the nerve blocks (mean VAS difference, 25.9 [score 0-100]; P < .001).
Seven of the studies had monitored for serious adverse events or complications related to the nerve blocks, but none reported any complications directly related to the ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks.
Owing to the inability to conduct blinded comparisons, clinical heterogeneity, and other caveats, the quality of evidence was ultimately judged to be “low” or “very low”; however, the observed benefits are nevertheless relevant, the authors concluded.
“Despite the low quality of evidence, ultrasound-guided blocks were associated with benefits compared to conventional systemic analgesia,” they said.
Key caveats include that the morphine reductions observed with the nerve blocks were not substantial, they noted. “The opioid-sparing effect seems small and may be of less clinical importance.” The decreases in opioid consumption, as well as pain reduction in the analysis, are in fact similar to those observed with conventional, peripheral nerve blocks that did not use ultrasound guidance, compared with standard pain management.
No trials were identified that directly compared ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks with nerve block techniques that didn’t use ultrasound.
However, the other noted improvements carry more weight, the authors said.
“The potential for higher patient satisfaction and reduction in serious adverse events and delirium may be of clinical importance,” they wrote.
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks not always accessible
Of note, the use of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks appears to be somewhat low, with one observational trend study of national data in the United States showing that, among patients receiving a peripheral nerve block for hip arthroplasty, only 3.2% of the procedures were performed using ultrasound guidance.
Stephen C. Haskins, MD, a coauthor on that study, said that the low utilization underscores that, in real-world practice, an ultrasound-guided approach isn’t always convenient.
“I think our findings demonstrate a common misconception that exists for those of us that work at academic institutions and/or within the ivory towers of regional anesthesia, which is that everyone is performing cutting edge ultrasound-guided techniques for all procedures,” Dr. Haskins, an associate attending anesthesiologist and chief medical diversity officer with the department of anesthesiology, critical care & pain management at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
However, “there are many limitations to use of ultrasound for these blocks, including limited access to machines, limited access to training, and limited interest and support from our surgical colleagues,” he explained.
“Ultimately, the best nerve block is the one performed in a timely and successful fashion, regardless of technique,” he said. “But we will continue to see a trend towards ultrasound use in the future due to increasing access in the form of portability and affordability.”
Haskins noted that newer ultrasound-guided nerve blocks that were not reviewed in the study, such as the pericapsular nerve group block, regional block, and supra-inguinal fascia iliaca block, which provide additional benefits such as avoiding quadriceps weakness.
Jeff Gadsden, MD, chief of the orthopedics, plastic, and regional anesthesiology division at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., agreed, noting that much has changed since some of the older studies in the analysis, that date back to 2010.
“A fascia iliaca block done in 2022 looks a lot different than it did in 2012, and we would expect it to be more consistent, reliable and longer-lasting with current techniques and technology,” he said in an interview. “So, if anything, I would expect the findings of this analysis to undersell the benefits of peripheral nerve blocks in this population.”
Although the quality of evidence in the meta-analysis is described as “low,” the downsides of the procedures are few, and “the potential benefits [of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks] are just too good to ignore,” Dr. Gadsden emphasized.
“If we can avoid or reduce opioids in this population and at the same time reduce the acute pain from the injury, there is no question that the incidence of delirium will go down,” he said. “Delirium is associated with a number of poor outcomes following hip fracture, including increased mortality.
“The bottom line is that the risk/benefit ratio is so far in favor of performing the blocks that even in the face of ‘modest’ levels of evidence, we should all be doing these.”
The authors, Dr. Haskins, and Dr. Gadsden had no disclosures relating to the study to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a meta-analysis published in BMC Anesthesiology show.
With the caveat that the quality of evidence in most trials in the analysis is low owing to a lack of blinding and other factors, “our review suggests that, among patients suffering from a hip fracture, a preoperative ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block is associated with a significant pain reduction and reduced need for systemic analgesics compared to conventional analgesia,” reported the authors.
“Our results may also indicate a lower risk of delirium, serious adverse events and higher patient satisfaction in patients receiving an ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block,” they added.
Because hip fractures commonly affect older populations and those who are frail, treatment of the substantial pain that can occur perioperatively is a challenge.
Peripheral nerve blocks have been shown to reduce pain within 30 minutes of the block placement; however, most studies have primarily included blocks that use anatomic landmarks or nerve stimulation for guidance. However, the use of ultrasound guidance with the nerve block should improve efficacy, the authors noted.
“It seems intuitive that using ultrasound-guidance should be more effective than using a blind technique, since it allows a trained physician to deposit the local anesthetic with much more precision,” they wrote.
To evaluate the data from studies that have looked at ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, Oskar Wilborg Exsteen, of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, Copenhagen University Hospital and Nordsjællands Hospital, Hillerød, Denmark, and colleagues identified 12 randomized controlled trials, involving a combined total of 976 participants, for the meta-analysis.
The studies included 509 participants who received ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks, specifically the femoral nerve block and fascia iliaca block, and 476 who were randomly assigned to control groups.
Overall, those treated with the nerve blocks showed significantly greater reductions in pain measured closest to 2 hours of block placement, compared with conventional analgesia, with a mean reduction of 2.26 points on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) (range, 0-10; P < .001).
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block use was associated with lower preoperative usage of analgesic intravenous morphine equivalents in milligram, reported in four of the trials (random effects model mean difference, –5.34; P = .003).
Delirium was also significantly lower with the nerve blocks (risk ratio, 0.6; P = 0.03), as were serious adverse events, compared with standard analgesia (RR, 0.33; P = .006), whereas patient satisfaction was significantly higher with the nerve blocks (mean VAS difference, 25.9 [score 0-100]; P < .001).
Seven of the studies had monitored for serious adverse events or complications related to the nerve blocks, but none reported any complications directly related to the ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks.
Owing to the inability to conduct blinded comparisons, clinical heterogeneity, and other caveats, the quality of evidence was ultimately judged to be “low” or “very low”; however, the observed benefits are nevertheless relevant, the authors concluded.
“Despite the low quality of evidence, ultrasound-guided blocks were associated with benefits compared to conventional systemic analgesia,” they said.
Key caveats include that the morphine reductions observed with the nerve blocks were not substantial, they noted. “The opioid-sparing effect seems small and may be of less clinical importance.” The decreases in opioid consumption, as well as pain reduction in the analysis, are in fact similar to those observed with conventional, peripheral nerve blocks that did not use ultrasound guidance, compared with standard pain management.
No trials were identified that directly compared ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks with nerve block techniques that didn’t use ultrasound.
However, the other noted improvements carry more weight, the authors said.
“The potential for higher patient satisfaction and reduction in serious adverse events and delirium may be of clinical importance,” they wrote.
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks not always accessible
Of note, the use of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks appears to be somewhat low, with one observational trend study of national data in the United States showing that, among patients receiving a peripheral nerve block for hip arthroplasty, only 3.2% of the procedures were performed using ultrasound guidance.
Stephen C. Haskins, MD, a coauthor on that study, said that the low utilization underscores that, in real-world practice, an ultrasound-guided approach isn’t always convenient.
“I think our findings demonstrate a common misconception that exists for those of us that work at academic institutions and/or within the ivory towers of regional anesthesia, which is that everyone is performing cutting edge ultrasound-guided techniques for all procedures,” Dr. Haskins, an associate attending anesthesiologist and chief medical diversity officer with the department of anesthesiology, critical care & pain management at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
However, “there are many limitations to use of ultrasound for these blocks, including limited access to machines, limited access to training, and limited interest and support from our surgical colleagues,” he explained.
“Ultimately, the best nerve block is the one performed in a timely and successful fashion, regardless of technique,” he said. “But we will continue to see a trend towards ultrasound use in the future due to increasing access in the form of portability and affordability.”
Haskins noted that newer ultrasound-guided nerve blocks that were not reviewed in the study, such as the pericapsular nerve group block, regional block, and supra-inguinal fascia iliaca block, which provide additional benefits such as avoiding quadriceps weakness.
Jeff Gadsden, MD, chief of the orthopedics, plastic, and regional anesthesiology division at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., agreed, noting that much has changed since some of the older studies in the analysis, that date back to 2010.
“A fascia iliaca block done in 2022 looks a lot different than it did in 2012, and we would expect it to be more consistent, reliable and longer-lasting with current techniques and technology,” he said in an interview. “So, if anything, I would expect the findings of this analysis to undersell the benefits of peripheral nerve blocks in this population.”
Although the quality of evidence in the meta-analysis is described as “low,” the downsides of the procedures are few, and “the potential benefits [of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks] are just too good to ignore,” Dr. Gadsden emphasized.
“If we can avoid or reduce opioids in this population and at the same time reduce the acute pain from the injury, there is no question that the incidence of delirium will go down,” he said. “Delirium is associated with a number of poor outcomes following hip fracture, including increased mortality.
“The bottom line is that the risk/benefit ratio is so far in favor of performing the blocks that even in the face of ‘modest’ levels of evidence, we should all be doing these.”
The authors, Dr. Haskins, and Dr. Gadsden had no disclosures relating to the study to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMC ANESTHESIOLOGY
Doctors using fake positive reviews to boost business
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why our brains wear out at the end of the day
The transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Once again, we’re doing an informal journal club to talk about a really interesting study, “A Neuro-metabolic Account of Why Daylong Cognitive Work Alters the Control of Economic Decisions,” that just came out. It tries to answer the question of why our brains wear out. I’m going to put myself in the corner here. Let’s walk through this study, which appears in Current Biology, by lead author Antonius Wiehler from Paris.
The big question is what’s going on with cognitive fatigue. If you look at chess players who are exerting a lot of cognitive effort, it’s well documented that over hours of play, they get worse and make more mistakes. It takes them longer to make decisions. The question is, why?
Why does your brain get tired?
To date, it’s been a little bit hard to tease that out. Now, there is some suggestion of what is responsible for this. The cognitive control center of the brain is probably somewhere in the left lateral prefrontal cortex (LLPC).
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher-level thinking. It’s what causes you to be inhibited. It gets shut off by alcohol and leads to impulsive behaviors. The LLPC, according to functional MRI studies, has reduced activity as people become more and more cognitively fatigued. The LLPC helps you think through choices. As you become more fatigued, this area of the brain isn’t working as well. But why would it not work as well? What is going on in that particular part of the brain? It doesn’t seem to be something simple, like glucose levels; that’s been investigated and glucose levels are pretty constant throughout the brain, regardless of cognitive task. This paper seeks to tease out what is actually going on in the LLPC when you are becoming cognitively tired.
They did an experiment where they induced cognitive fatigue, and it sounds like a painful experiment. For more than 6 hours, volunteers completed sessions during which they had to perform cognitive switching tasks. Investigators showed participants a letter, in either red or green, and the participant would respond with whether it was a vowel or a consonant or whether it was a capital or lowercase letter, based on the color. If it’s red, say whether it’s a consonant or vowel. If it’s green, say whether it’s upper- or lowercase.
It’s hard, and doing it for 6 hours is likely to induce a lot of cognitive fatigue. They had a control group as well, which is really important here. The control group also did a task like this for 6 hours, but for them, investigators didn’t change the color as often – perhaps only once per session. For the study group, they were switching colors back and forth quite a lot. They also incorporated a memory challenge that worked in a similar way.
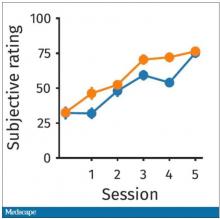
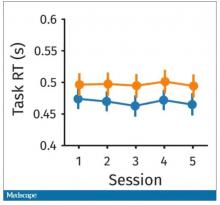
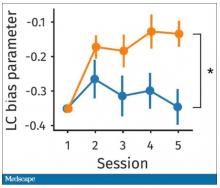
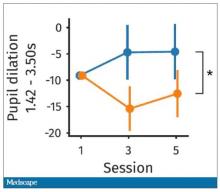
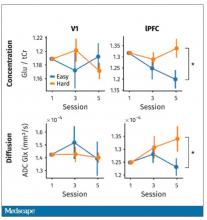
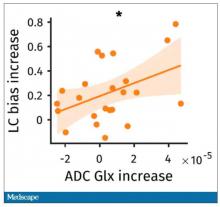
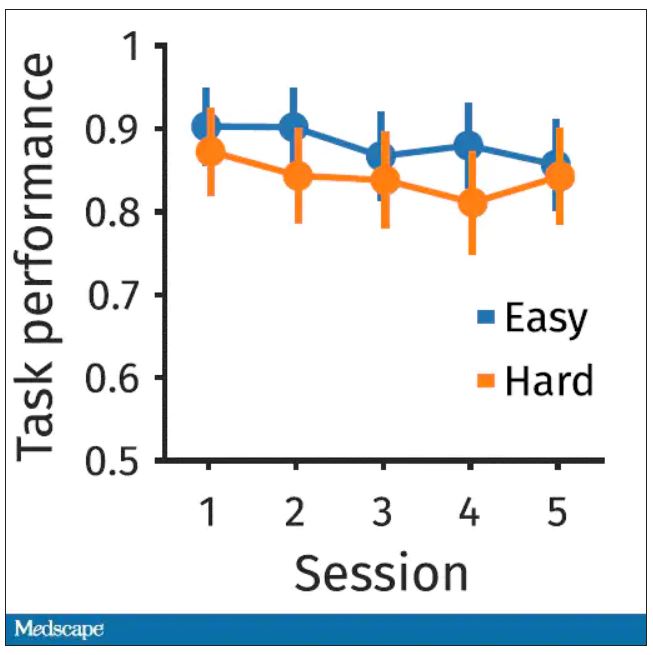
So, what are the readouts of this study? They had a group who went through the hard cognitive challenge and a group who went through the easy cognitive challenge. They looked at a variety of metrics. I’ll describe a few.
The first is performance decrement. Did they get it wrong? What percentage of the time did the participant say “consonant” when they should have said “lowercase?”
You can see here that the hard group did a little bit worse overall. It was harder, so they don’t do as well. That makes sense. But both groups kind of waned over time a little bit. It’s not as though the hard group declines much more. The slopes of those lines are pretty similar. So, not very robust findings there.
What about subjective fatigue? They asked the participants how exhausted they were from doing the tasks.
Both groups were worn out. It was a long day. There was a suggestion that the hard group became worn out a little bit sooner, but I don’t think this achieves statistical significance. Everyone was getting tired by hour 6 here.
What about response time? How quickly could the participant say “consonant,” “vowel,” “lowercase,” or “uppercase?”
The hard group took longer to respond because it was a harder task. But over time, the response times were pretty flat.
So far there isn’t a robust readout that would make us say, oh, yeah, that is a good marker of cognitive fatigue. That’s how you measure cognitive fatigue. It’s not what people say. It’s not how quick they are. It’s not even how accurate they are.
But then the investigators got a little bit clever. Participants were asked to play a “would you rather” game, a reward game. Here are two examples.
Would you rather:
- Have a 25% chance of earning $50 OR a 95% chance of earning $17.30?
- Earn $50, but your next task session will be hard or earn $40 and your next task session will be easy?
Participants had to figure out the better odds – what should they be choosing here? They had to tease out whether they preferred lower cost lower-risk choices – when they are cognitively fatigued, which has been shown in prior studies.
This showed a pretty dramatic difference between the groups in terms of the low-cost bias – how much more likely they were to pick the low-cost, easier choice as they became more and more cognitively fatigued. The hard group participants were more likely to pick the easy thing rather than the potentially more lucrative thing, which is really interesting when we think about how our own cognitive fatigue happens at the end of a difficult workday, how you may just be likely to go with the flow and do something easy because you just don’t have that much decision-making power left.
It would be nice to have some objective physiologic measurements for this, and they do. This is pupil dilation.
When you’re paying attention to something, your pupils dilate a little bit. They were able to show that as the hard group became more and more fatigued, pupil dilation sort of went away. In fact, if anything, their pupils constricted a little bit. But basically there was a significant difference here. The easy group’s pupils were still fine; they were still dilating. The hard group’s pupils got more sluggish. This is a physiologic correlate of what’s going on.
But again, these are all downstream of whatever is happening in the LLPC. So the real meat of this study is a functional MRI analysis, and the way they did this is pretty clever. They were looking for metabolites in the various parts of the brain using a labeled hydrogen MRI, which is even fancier than a functional MRI. It’s like MRI spectroscopy, and it can measure the levels of certain chemicals in the brain. They hypothesized that if there is a chemical that builds up when you are tired, it should build up preferentially in the LLPC.
Whereas in the rest of the brain, there shouldn’t be that much difference because we know the action is happening in the LLPC. The control part of the brain is a section called V1. They looked at a variety of metabolites, but the only one that behaved the way they expected was glutamate and glutamic acid (glutamate metabolites). In the hard group, the glutamate is building up over time, so there is a higher concentration of glutamate in the LLPC but not the rest of the brain. There is also a greater diffusion of glutamate from the intracellular to the extracellular space, which suggests that it’s kind of leaking out of the cells.
So the signal here is that the thing that’s impacting that part of the brain is this buildup of glutamate. To tie this together, they showed in the scatterplot the relationship between the increase in glutamate and the low-cost bias from the decision fatigue example.
It’s not the strongest correlation, but it is statistically significant that the more glutamate in your LLPC, the more likely you are to just take the easy decision as opposed to really thinking things through. That is pretty powerful. It’s telling us that your brain making you fatigued, and making you less likely to continue to use your LLPC, may be a self-defense mechanism against a buildup of glutamate, which may be neurotoxic. And that’s a fascinating bit of homeostasis.
Of course, it makes you wonder how we might adjust glutamate levels in the brain, although maybe we should let the brain be tired if the brain wants to be tired. It reminds me of that old Far Side cartoon where the guy is raising his hand and asking: “Can I be excused? My brain is full.” That is essentially what’s happening. This part of your brain is becoming taxed and building up glutamate. There’s some kind of negative feedback loop. The authors don’t know what the receptor pathway is that down-regulates that part of the brain based on the glutamate buildup, but some kind of negative feedback loop is saying, okay, give this part of the brain a rest. Things have gone on too far here.
It’s a fascinating study, although it’s not clear what we can do with this information. It’s not clear whether we can manipulate glutamate levels in this particular part of the brain or not. But it’s nice to see some biologic correlates of a psychological phenomenon that is incredibly well described – the phenomenon of decision fatigue. I think we all feel it at the end of a hard workday. If you’ve been doing a lot of cognitively intensive tasks, you just don’t have it in you anymore. And maybe the act of a good night’s sleep is clearing out some of that glutamate in the LLPC, which lets you start over and make some good decisions again. So I hope you all make some good decisions and keep your glutamate levels low. And I’ll see you next time.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Once again, we’re doing an informal journal club to talk about a really interesting study, “A Neuro-metabolic Account of Why Daylong Cognitive Work Alters the Control of Economic Decisions,” that just came out. It tries to answer the question of why our brains wear out. I’m going to put myself in the corner here. Let’s walk through this study, which appears in Current Biology, by lead author Antonius Wiehler from Paris.
The big question is what’s going on with cognitive fatigue. If you look at chess players who are exerting a lot of cognitive effort, it’s well documented that over hours of play, they get worse and make more mistakes. It takes them longer to make decisions. The question is, why?
Why does your brain get tired?
To date, it’s been a little bit hard to tease that out. Now, there is some suggestion of what is responsible for this. The cognitive control center of the brain is probably somewhere in the left lateral prefrontal cortex (LLPC).
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher-level thinking. It’s what causes you to be inhibited. It gets shut off by alcohol and leads to impulsive behaviors. The LLPC, according to functional MRI studies, has reduced activity as people become more and more cognitively fatigued. The LLPC helps you think through choices. As you become more fatigued, this area of the brain isn’t working as well. But why would it not work as well? What is going on in that particular part of the brain? It doesn’t seem to be something simple, like glucose levels; that’s been investigated and glucose levels are pretty constant throughout the brain, regardless of cognitive task. This paper seeks to tease out what is actually going on in the LLPC when you are becoming cognitively tired.
They did an experiment where they induced cognitive fatigue, and it sounds like a painful experiment. For more than 6 hours, volunteers completed sessions during which they had to perform cognitive switching tasks. Investigators showed participants a letter, in either red or green, and the participant would respond with whether it was a vowel or a consonant or whether it was a capital or lowercase letter, based on the color. If it’s red, say whether it’s a consonant or vowel. If it’s green, say whether it’s upper- or lowercase.
It’s hard, and doing it for 6 hours is likely to induce a lot of cognitive fatigue. They had a control group as well, which is really important here. The control group also did a task like this for 6 hours, but for them, investigators didn’t change the color as often – perhaps only once per session. For the study group, they were switching colors back and forth quite a lot. They also incorporated a memory challenge that worked in a similar way.
So, what are the readouts of this study? They had a group who went through the hard cognitive challenge and a group who went through the easy cognitive challenge. They looked at a variety of metrics. I’ll describe a few.
The first is performance decrement. Did they get it wrong? What percentage of the time did the participant say “consonant” when they should have said “lowercase?”
You can see here that the hard group did a little bit worse overall. It was harder, so they don’t do as well. That makes sense. But both groups kind of waned over time a little bit. It’s not as though the hard group declines much more. The slopes of those lines are pretty similar. So, not very robust findings there.
What about subjective fatigue? They asked the participants how exhausted they were from doing the tasks.
Both groups were worn out. It was a long day. There was a suggestion that the hard group became worn out a little bit sooner, but I don’t think this achieves statistical significance. Everyone was getting tired by hour 6 here.
What about response time? How quickly could the participant say “consonant,” “vowel,” “lowercase,” or “uppercase?”
The hard group took longer to respond because it was a harder task. But over time, the response times were pretty flat.
So far there isn’t a robust readout that would make us say, oh, yeah, that is a good marker of cognitive fatigue. That’s how you measure cognitive fatigue. It’s not what people say. It’s not how quick they are. It’s not even how accurate they are.
But then the investigators got a little bit clever. Participants were asked to play a “would you rather” game, a reward game. Here are two examples.
Would you rather:
- Have a 25% chance of earning $50 OR a 95% chance of earning $17.30?
- Earn $50, but your next task session will be hard or earn $40 and your next task session will be easy?
Participants had to figure out the better odds – what should they be choosing here? They had to tease out whether they preferred lower cost lower-risk choices – when they are cognitively fatigued, which has been shown in prior studies.
This showed a pretty dramatic difference between the groups in terms of the low-cost bias – how much more likely they were to pick the low-cost, easier choice as they became more and more cognitively fatigued. The hard group participants were more likely to pick the easy thing rather than the potentially more lucrative thing, which is really interesting when we think about how our own cognitive fatigue happens at the end of a difficult workday, how you may just be likely to go with the flow and do something easy because you just don’t have that much decision-making power left.
It would be nice to have some objective physiologic measurements for this, and they do. This is pupil dilation.
When you’re paying attention to something, your pupils dilate a little bit. They were able to show that as the hard group became more and more fatigued, pupil dilation sort of went away. In fact, if anything, their pupils constricted a little bit. But basically there was a significant difference here. The easy group’s pupils were still fine; they were still dilating. The hard group’s pupils got more sluggish. This is a physiologic correlate of what’s going on.
But again, these are all downstream of whatever is happening in the LLPC. So the real meat of this study is a functional MRI analysis, and the way they did this is pretty clever. They were looking for metabolites in the various parts of the brain using a labeled hydrogen MRI, which is even fancier than a functional MRI. It’s like MRI spectroscopy, and it can measure the levels of certain chemicals in the brain. They hypothesized that if there is a chemical that builds up when you are tired, it should build up preferentially in the LLPC.
Whereas in the rest of the brain, there shouldn’t be that much difference because we know the action is happening in the LLPC. The control part of the brain is a section called V1. They looked at a variety of metabolites, but the only one that behaved the way they expected was glutamate and glutamic acid (glutamate metabolites). In the hard group, the glutamate is building up over time, so there is a higher concentration of glutamate in the LLPC but not the rest of the brain. There is also a greater diffusion of glutamate from the intracellular to the extracellular space, which suggests that it’s kind of leaking out of the cells.
So the signal here is that the thing that’s impacting that part of the brain is this buildup of glutamate. To tie this together, they showed in the scatterplot the relationship between the increase in glutamate and the low-cost bias from the decision fatigue example.
It’s not the strongest correlation, but it is statistically significant that the more glutamate in your LLPC, the more likely you are to just take the easy decision as opposed to really thinking things through. That is pretty powerful. It’s telling us that your brain making you fatigued, and making you less likely to continue to use your LLPC, may be a self-defense mechanism against a buildup of glutamate, which may be neurotoxic. And that’s a fascinating bit of homeostasis.
Of course, it makes you wonder how we might adjust glutamate levels in the brain, although maybe we should let the brain be tired if the brain wants to be tired. It reminds me of that old Far Side cartoon where the guy is raising his hand and asking: “Can I be excused? My brain is full.” That is essentially what’s happening. This part of your brain is becoming taxed and building up glutamate. There’s some kind of negative feedback loop. The authors don’t know what the receptor pathway is that down-regulates that part of the brain based on the glutamate buildup, but some kind of negative feedback loop is saying, okay, give this part of the brain a rest. Things have gone on too far here.
It’s a fascinating study, although it’s not clear what we can do with this information. It’s not clear whether we can manipulate glutamate levels in this particular part of the brain or not. But it’s nice to see some biologic correlates of a psychological phenomenon that is incredibly well described – the phenomenon of decision fatigue. I think we all feel it at the end of a hard workday. If you’ve been doing a lot of cognitively intensive tasks, you just don’t have it in you anymore. And maybe the act of a good night’s sleep is clearing out some of that glutamate in the LLPC, which lets you start over and make some good decisions again. So I hope you all make some good decisions and keep your glutamate levels low. And I’ll see you next time.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Once again, we’re doing an informal journal club to talk about a really interesting study, “A Neuro-metabolic Account of Why Daylong Cognitive Work Alters the Control of Economic Decisions,” that just came out. It tries to answer the question of why our brains wear out. I’m going to put myself in the corner here. Let’s walk through this study, which appears in Current Biology, by lead author Antonius Wiehler from Paris.
The big question is what’s going on with cognitive fatigue. If you look at chess players who are exerting a lot of cognitive effort, it’s well documented that over hours of play, they get worse and make more mistakes. It takes them longer to make decisions. The question is, why?
Why does your brain get tired?
To date, it’s been a little bit hard to tease that out. Now, there is some suggestion of what is responsible for this. The cognitive control center of the brain is probably somewhere in the left lateral prefrontal cortex (LLPC).
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher-level thinking. It’s what causes you to be inhibited. It gets shut off by alcohol and leads to impulsive behaviors. The LLPC, according to functional MRI studies, has reduced activity as people become more and more cognitively fatigued. The LLPC helps you think through choices. As you become more fatigued, this area of the brain isn’t working as well. But why would it not work as well? What is going on in that particular part of the brain? It doesn’t seem to be something simple, like glucose levels; that’s been investigated and glucose levels are pretty constant throughout the brain, regardless of cognitive task. This paper seeks to tease out what is actually going on in the LLPC when you are becoming cognitively tired.
They did an experiment where they induced cognitive fatigue, and it sounds like a painful experiment. For more than 6 hours, volunteers completed sessions during which they had to perform cognitive switching tasks. Investigators showed participants a letter, in either red or green, and the participant would respond with whether it was a vowel or a consonant or whether it was a capital or lowercase letter, based on the color. If it’s red, say whether it’s a consonant or vowel. If it’s green, say whether it’s upper- or lowercase.
It’s hard, and doing it for 6 hours is likely to induce a lot of cognitive fatigue. They had a control group as well, which is really important here. The control group also did a task like this for 6 hours, but for them, investigators didn’t change the color as often – perhaps only once per session. For the study group, they were switching colors back and forth quite a lot. They also incorporated a memory challenge that worked in a similar way.
So, what are the readouts of this study? They had a group who went through the hard cognitive challenge and a group who went through the easy cognitive challenge. They looked at a variety of metrics. I’ll describe a few.
The first is performance decrement. Did they get it wrong? What percentage of the time did the participant say “consonant” when they should have said “lowercase?”
You can see here that the hard group did a little bit worse overall. It was harder, so they don’t do as well. That makes sense. But both groups kind of waned over time a little bit. It’s not as though the hard group declines much more. The slopes of those lines are pretty similar. So, not very robust findings there.
What about subjective fatigue? They asked the participants how exhausted they were from doing the tasks.
Both groups were worn out. It was a long day. There was a suggestion that the hard group became worn out a little bit sooner, but I don’t think this achieves statistical significance. Everyone was getting tired by hour 6 here.
What about response time? How quickly could the participant say “consonant,” “vowel,” “lowercase,” or “uppercase?”
The hard group took longer to respond because it was a harder task. But over time, the response times were pretty flat.
So far there isn’t a robust readout that would make us say, oh, yeah, that is a good marker of cognitive fatigue. That’s how you measure cognitive fatigue. It’s not what people say. It’s not how quick they are. It’s not even how accurate they are.
But then the investigators got a little bit clever. Participants were asked to play a “would you rather” game, a reward game. Here are two examples.
Would you rather:
- Have a 25% chance of earning $50 OR a 95% chance of earning $17.30?
- Earn $50, but your next task session will be hard or earn $40 and your next task session will be easy?
Participants had to figure out the better odds – what should they be choosing here? They had to tease out whether they preferred lower cost lower-risk choices – when they are cognitively fatigued, which has been shown in prior studies.
This showed a pretty dramatic difference between the groups in terms of the low-cost bias – how much more likely they were to pick the low-cost, easier choice as they became more and more cognitively fatigued. The hard group participants were more likely to pick the easy thing rather than the potentially more lucrative thing, which is really interesting when we think about how our own cognitive fatigue happens at the end of a difficult workday, how you may just be likely to go with the flow and do something easy because you just don’t have that much decision-making power left.
It would be nice to have some objective physiologic measurements for this, and they do. This is pupil dilation.
When you’re paying attention to something, your pupils dilate a little bit. They were able to show that as the hard group became more and more fatigued, pupil dilation sort of went away. In fact, if anything, their pupils constricted a little bit. But basically there was a significant difference here. The easy group’s pupils were still fine; they were still dilating. The hard group’s pupils got more sluggish. This is a physiologic correlate of what’s going on.
But again, these are all downstream of whatever is happening in the LLPC. So the real meat of this study is a functional MRI analysis, and the way they did this is pretty clever. They were looking for metabolites in the various parts of the brain using a labeled hydrogen MRI, which is even fancier than a functional MRI. It’s like MRI spectroscopy, and it can measure the levels of certain chemicals in the brain. They hypothesized that if there is a chemical that builds up when you are tired, it should build up preferentially in the LLPC.
Whereas in the rest of the brain, there shouldn’t be that much difference because we know the action is happening in the LLPC. The control part of the brain is a section called V1. They looked at a variety of metabolites, but the only one that behaved the way they expected was glutamate and glutamic acid (glutamate metabolites). In the hard group, the glutamate is building up over time, so there is a higher concentration of glutamate in the LLPC but not the rest of the brain. There is also a greater diffusion of glutamate from the intracellular to the extracellular space, which suggests that it’s kind of leaking out of the cells.
So the signal here is that the thing that’s impacting that part of the brain is this buildup of glutamate. To tie this together, they showed in the scatterplot the relationship between the increase in glutamate and the low-cost bias from the decision fatigue example.
It’s not the strongest correlation, but it is statistically significant that the more glutamate in your LLPC, the more likely you are to just take the easy decision as opposed to really thinking things through. That is pretty powerful. It’s telling us that your brain making you fatigued, and making you less likely to continue to use your LLPC, may be a self-defense mechanism against a buildup of glutamate, which may be neurotoxic. And that’s a fascinating bit of homeostasis.
Of course, it makes you wonder how we might adjust glutamate levels in the brain, although maybe we should let the brain be tired if the brain wants to be tired. It reminds me of that old Far Side cartoon where the guy is raising his hand and asking: “Can I be excused? My brain is full.” That is essentially what’s happening. This part of your brain is becoming taxed and building up glutamate. There’s some kind of negative feedback loop. The authors don’t know what the receptor pathway is that down-regulates that part of the brain based on the glutamate buildup, but some kind of negative feedback loop is saying, okay, give this part of the brain a rest. Things have gone on too far here.
It’s a fascinating study, although it’s not clear what we can do with this information. It’s not clear whether we can manipulate glutamate levels in this particular part of the brain or not. But it’s nice to see some biologic correlates of a psychological phenomenon that is incredibly well described – the phenomenon of decision fatigue. I think we all feel it at the end of a hard workday. If you’ve been doing a lot of cognitively intensive tasks, you just don’t have it in you anymore. And maybe the act of a good night’s sleep is clearing out some of that glutamate in the LLPC, which lets you start over and make some good decisions again. So I hope you all make some good decisions and keep your glutamate levels low. And I’ll see you next time.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New international dermatology registry tracks monkeypox cases
The American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) have created a new registry that now accepts reports from health care providers worldwide about monkeypox cases and monkeypox vaccine reactions.
Patient data such as names and dates of birth will not be collected.
“As with our joint COVID-19 registry, we will be doing real-time data analysis during the outbreak,” dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a member of the AAD’s monkeypox task force, said in an interview. “We will to try to feed information back to our front line in terms of clinical characteristics of cases, morphology, and any unexpected findings.”
According to Dr. Freeman, the principal investigator for the COVID-19 registry, this registry has allowed the quick gathering of information about dermatologic findings of COVID-19 from over 53 countries. “We have published over 15 papers, and we share data with outside investigators wishing to do their own analysis of registry-related data,” she said. “Our most-cited paper on COVID vaccine skin reactions has been cited almost 500 times since 2021. It has been used to educate the public on vaccine side effects and to combat vaccine hesitancy.”
The monkeypox registry “doesn’t belong to any one group or person,” Dr. Freeman said. “The idea with rapid data analysis is to be able to give back to the dermatologic community what is hard for us to see with any single case: Patterns and new findings that can be helpful to share with dermatologists and other physicians worldwide, all working together to stop an outbreak.”
The American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) have created a new registry that now accepts reports from health care providers worldwide about monkeypox cases and monkeypox vaccine reactions.
Patient data such as names and dates of birth will not be collected.
“As with our joint COVID-19 registry, we will be doing real-time data analysis during the outbreak,” dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a member of the AAD’s monkeypox task force, said in an interview. “We will to try to feed information back to our front line in terms of clinical characteristics of cases, morphology, and any unexpected findings.”
According to Dr. Freeman, the principal investigator for the COVID-19 registry, this registry has allowed the quick gathering of information about dermatologic findings of COVID-19 from over 53 countries. “We have published over 15 papers, and we share data with outside investigators wishing to do their own analysis of registry-related data,” she said. “Our most-cited paper on COVID vaccine skin reactions has been cited almost 500 times since 2021. It has been used to educate the public on vaccine side effects and to combat vaccine hesitancy.”
The monkeypox registry “doesn’t belong to any one group or person,” Dr. Freeman said. “The idea with rapid data analysis is to be able to give back to the dermatologic community what is hard for us to see with any single case: Patterns and new findings that can be helpful to share with dermatologists and other physicians worldwide, all working together to stop an outbreak.”
The American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) have created a new registry that now accepts reports from health care providers worldwide about monkeypox cases and monkeypox vaccine reactions.
Patient data such as names and dates of birth will not be collected.
“As with our joint COVID-19 registry, we will be doing real-time data analysis during the outbreak,” dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a member of the AAD’s monkeypox task force, said in an interview. “We will to try to feed information back to our front line in terms of clinical characteristics of cases, morphology, and any unexpected findings.”
According to Dr. Freeman, the principal investigator for the COVID-19 registry, this registry has allowed the quick gathering of information about dermatologic findings of COVID-19 from over 53 countries. “We have published over 15 papers, and we share data with outside investigators wishing to do their own analysis of registry-related data,” she said. “Our most-cited paper on COVID vaccine skin reactions has been cited almost 500 times since 2021. It has been used to educate the public on vaccine side effects and to combat vaccine hesitancy.”
The monkeypox registry “doesn’t belong to any one group or person,” Dr. Freeman said. “The idea with rapid data analysis is to be able to give back to the dermatologic community what is hard for us to see with any single case: Patterns and new findings that can be helpful to share with dermatologists and other physicians worldwide, all working together to stop an outbreak.”
Dermatology and monkeypox: What you need to know
.
Diagnosing cases “can be hard and folks should keep a very open mind and consider monkeypox virus,” said Misha Rosenbach, MD, a University of Pennsylvania dermatologist and member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s ad hoc task force to develop monkeypox content.
Although it’s named after a primate, it turns out that monkeypox is quite the copycat. As dermatologists have learned, its lesions can look like those caused by a long list of other diseases including herpes, varicella, and syphilis. In small numbers, they can even appear to be insect bites.
To make things more complicated, a patient can have one or two lesions – or dozens. They often cluster in the anogenital area, likely reflecting transmission via sexual intercourse, unlike previous outbreaks in which lesions appeared all over the body. “We have to let go of some of our conceptions about what monkeypox might look like,” said dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Harvard University, Boston, and a member of the AAD task force.
To make things even more complicated, “the spectrum of illness that we are seeing has ranged from limited, subtle lesions to dramatic, widespread, ulcerative/necrotic lesions,” said Dr. Rosenbach, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
But monkeypox has unique traits that can set it apart and pave the way toward a diagnosis, dermatologists say. And important patient data can help dermatologists gauge the likelihood of a case: Almost 99% of cases with data available have been in men, and among men with available information, 94% reported male-to-male sexual or close intimate contact during the 3 weeks before developing symptoms, according to a CDC report tracking cases from May through late July. So far, cases in women and children are extremely rare, although there have been some reported in the United States.
Are dermatologists likely to see monkeypox in the clinic? It’s unclear so far. Of four dermatologists interviewed for this article, only one has seen patients with monkeypox in person. But others say they’ve been sought for consultations. “I have been asked by infectious disease colleagues for advice remotely but have not seen it,” said dermatologist Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “Most of the time, they’re catching all the symptomatic cases before any need for dermatology in-person referrals.”
Still, the rapid rate of growth of the outbreak – up from 3,487 in the United States on July 25 to 12,689 as of Aug.16 – suggests that more dermatologists will see cases, and consultations may become more common too.
Know your lesions
Lesions are the telltale signs of symptomatic monkeypox. According to a recent New England Journal of Medicine study of 528 monkeypox cases from 16 nations, diagnosed between April 27 and June 24, 2022, 95% had skin lesions (58% were vesiculopustular), most commonly in the anogenital area (73%), and on the trunk/arms/or legs (55%) and face (25%), and the palms/soles (10%).
However, “the current monkeypox outbreak often presents differently from the multiple classic vesiculopustules on the skin we see in textbooks,” Dr. Yeung said. “Sometimes people can present with throat pain or rectal pain, with isolated pharyngitis or proctitis. Sometimes there are so few lesions on the skin that it can be easily confused with a bug bite, folliculitis, herpes, dyshidrotic eczema, or other skin problems. This is where dermatologists will get consulted to clarify the diagnosis while the monkeypox PCR test is pending.”
Dr. Rosenbach, who has provided consultation services to other physicians about cases, said the lesions often appear to be vesicles or pustules, “but if you go to ‘pop’ it – e.g., for testing – it’s firm and without fluid. This is likely due to pox virus inclusion, similar to other diseases such as molluscum,” caused by another pox virus, he said. Molluscum lesions are “characteristically umbilicated, with a dimple in the center, and monkeypox lesions seem to be showing a roughly similar morphology with many bowl- or caldera-shaped lesions that are donut-like in appearance,” he added.
Over time, Dr. Rosenbach said, “lesions tend to evolve slowly from smaller flesh-colored or vaguely white firm papules to broader more umbilicated/donut-shaped lesions which may erode, ulcerate, develop a crust or scab, and then heal. The amount of scarring is not yet clear, but we anticipate it to be significant, especially in patients with more widespread or severe disease.”
Jon Peebles, MD, a dermatologist at Kaiser Permanente in Largo, Md., who has treated a few in-person monkeypox cases, said the lesions can be “exquisitely painful,” although he’s also seen patients with asymptomatic lesions. “Lesions are showing a predilection for the anogenital skin, though they can occur anywhere and not uncommonly involve the oral mucosa,” said Dr. Peebles, also a member of the AAD monkeypox task force.
Dr. Yeung said it’s important to ask patients about their sexual orientation, gender identity, and sexual behaviors. “That is the only way to know who your patients are and the only way to understand who else may be at risks and can benefit from contact tracing and additional prevention measures, such as vaccination for asymptomatic sex partners.” (The Jynneos smallpox vaccine is Food and Drug Administration–approved to prevent monkeypox, although its efficacy is not entirely clear, and there’s controversy over expanding its limited availability by administering the vaccine intradermally.)
It’s also important to keep in mind that sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common in gay and bisexual men. “Just because the patient is diagnosed with gonorrhea or syphilis does not mean the patient cannot also have monkeypox,” Dr. Rosenbach said. Indeed, the NEJM study reported that of 377 patients screened, 29% had an STI other than HIV, mostly syphilis (9%) and gonorrhea (8%). Of all 528 patients in the study (all male or transgender/nonbinary), 41% were HIV-positive, and the median number of sex partners in the last 3 months was 5 (range, 3-15).
Testing is crucial to rule monkeypox in – or out
While monkeypox lesions can be confused for other diseases, Dr. Rosenbach said that a diagnosis can be confirmed through various tests. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV) have distinct findings on Tzanck smears (nuclear molding, multinucleated cells), and have widely available fairly rapid tests (PCR, or in some places, DFA). “Staph and bacterial folliculitis can usually be cultured quickly,” he said. “If you have someone with no risk factors/exposure, and you test for VZV, HSV, folliculitis, and it’s negative – you should know within 24 hours in most places – then you can broaden your differential diagnosis and consider alternate explanations, including monkeypox.”
Quest Diagnostics and Labcorp, two of the largest commercial labs in the United States, are now offering monkeypox tests. Labcorp says its test has a 2- to 3-day turnaround time.
As for treatment, some physicians are prescribing off-label use of tecovirimat (also known as TPOXX or ST-246), a smallpox antiviral treatment. The CDC offers guidelines about its use. “It seems to work very fast, with patients improving in 24-72 hours,” Dr. Rosenbach said. However, “it is still very challenging to give and get. There’s a cumbersome system to prescribe it, and it needs to be shipped from the national stockpile. Dermatologists should be working with their state health department, infection control, and infectious disease doctors.”
It’s likely that dermatologists are not comfortable with the process to access the drug, he said, “but if we do not act quickly to control the current outbreak, we will all – unfortunately – need to learn to be comfortable prescribing it.”
In regard to pain control, an over-the-counter painkiller approach may be appropriate depending on comorbidities, Dr. Rosenbach said. “Some patients with very severe disease, such as perianal involvement and proctitis, have such severe pain they need to be hospitalized. This is less common.”
Recommendations pending on scarring prevention
There’s limited high-quality evidence about the prevention of scarring in diseases like monkeypox, Dr. Rosenbach noted. “Any recommendations are usually based on very small, limited, uncontrolled studies. In the case of monkeypox, truly we are off the edge of the map.”
He advises cleaning lesions with gentle soap and water – keeping in mind that contaminated towels may spread disease – and potentially using a topical ointment-based dressing such as a Vaseline/nonstick dressing or Vaseline-impregnated gauze. If there’s concern about superinfection, as can occur with staph infections, topical antibiotics such as mupirocin 2% ointment may be appropriate, he said.
“Some folks like to try silica gel sheets to prevent scarring,” Dr. Rosenbach said. “There’s not a lot of evidence to support that, but they’re unlikely to be harmful. I would personally consider them, but it really depends on the extent of disease, anatomic sites involved, and access to care.”
Emory University’s Dr. Yeung also suggested using silicone gel or sheets to optimize the scar appearance once the lesions have crusted over. “People have used lasers, microneedling, etc., to improve smallpox scar appearance,” he added, “and I’m sure dermatologists will be the ones to study what works best for treating monkeypox scars.”
As for the big picture, Dr. Yeung said that dermatologists are critical in the fight to control monkeypox: “We can help our colleagues and patients manage symptoms and wound care, advocate for vaccination and treatment, treat long-term scarring sequelae, and destigmatize LGBTQ health care.”
The dermatologists interviewed for this article report no disclosures.
.
Diagnosing cases “can be hard and folks should keep a very open mind and consider monkeypox virus,” said Misha Rosenbach, MD, a University of Pennsylvania dermatologist and member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s ad hoc task force to develop monkeypox content.
Although it’s named after a primate, it turns out that monkeypox is quite the copycat. As dermatologists have learned, its lesions can look like those caused by a long list of other diseases including herpes, varicella, and syphilis. In small numbers, they can even appear to be insect bites.
To make things more complicated, a patient can have one or two lesions – or dozens. They often cluster in the anogenital area, likely reflecting transmission via sexual intercourse, unlike previous outbreaks in which lesions appeared all over the body. “We have to let go of some of our conceptions about what monkeypox might look like,” said dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Harvard University, Boston, and a member of the AAD task force.
To make things even more complicated, “the spectrum of illness that we are seeing has ranged from limited, subtle lesions to dramatic, widespread, ulcerative/necrotic lesions,” said Dr. Rosenbach, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
But monkeypox has unique traits that can set it apart and pave the way toward a diagnosis, dermatologists say. And important patient data can help dermatologists gauge the likelihood of a case: Almost 99% of cases with data available have been in men, and among men with available information, 94% reported male-to-male sexual or close intimate contact during the 3 weeks before developing symptoms, according to a CDC report tracking cases from May through late July. So far, cases in women and children are extremely rare, although there have been some reported in the United States.
Are dermatologists likely to see monkeypox in the clinic? It’s unclear so far. Of four dermatologists interviewed for this article, only one has seen patients with monkeypox in person. But others say they’ve been sought for consultations. “I have been asked by infectious disease colleagues for advice remotely but have not seen it,” said dermatologist Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “Most of the time, they’re catching all the symptomatic cases before any need for dermatology in-person referrals.”
Still, the rapid rate of growth of the outbreak – up from 3,487 in the United States on July 25 to 12,689 as of Aug.16 – suggests that more dermatologists will see cases, and consultations may become more common too.
Know your lesions
Lesions are the telltale signs of symptomatic monkeypox. According to a recent New England Journal of Medicine study of 528 monkeypox cases from 16 nations, diagnosed between April 27 and June 24, 2022, 95% had skin lesions (58% were vesiculopustular), most commonly in the anogenital area (73%), and on the trunk/arms/or legs (55%) and face (25%), and the palms/soles (10%).
However, “the current monkeypox outbreak often presents differently from the multiple classic vesiculopustules on the skin we see in textbooks,” Dr. Yeung said. “Sometimes people can present with throat pain or rectal pain, with isolated pharyngitis or proctitis. Sometimes there are so few lesions on the skin that it can be easily confused with a bug bite, folliculitis, herpes, dyshidrotic eczema, or other skin problems. This is where dermatologists will get consulted to clarify the diagnosis while the monkeypox PCR test is pending.”
Dr. Rosenbach, who has provided consultation services to other physicians about cases, said the lesions often appear to be vesicles or pustules, “but if you go to ‘pop’ it – e.g., for testing – it’s firm and without fluid. This is likely due to pox virus inclusion, similar to other diseases such as molluscum,” caused by another pox virus, he said. Molluscum lesions are “characteristically umbilicated, with a dimple in the center, and monkeypox lesions seem to be showing a roughly similar morphology with many bowl- or caldera-shaped lesions that are donut-like in appearance,” he added.
Over time, Dr. Rosenbach said, “lesions tend to evolve slowly from smaller flesh-colored or vaguely white firm papules to broader more umbilicated/donut-shaped lesions which may erode, ulcerate, develop a crust or scab, and then heal. The amount of scarring is not yet clear, but we anticipate it to be significant, especially in patients with more widespread or severe disease.”
Jon Peebles, MD, a dermatologist at Kaiser Permanente in Largo, Md., who has treated a few in-person monkeypox cases, said the lesions can be “exquisitely painful,” although he’s also seen patients with asymptomatic lesions. “Lesions are showing a predilection for the anogenital skin, though they can occur anywhere and not uncommonly involve the oral mucosa,” said Dr. Peebles, also a member of the AAD monkeypox task force.
Dr. Yeung said it’s important to ask patients about their sexual orientation, gender identity, and sexual behaviors. “That is the only way to know who your patients are and the only way to understand who else may be at risks and can benefit from contact tracing and additional prevention measures, such as vaccination for asymptomatic sex partners.” (The Jynneos smallpox vaccine is Food and Drug Administration–approved to prevent monkeypox, although its efficacy is not entirely clear, and there’s controversy over expanding its limited availability by administering the vaccine intradermally.)
It’s also important to keep in mind that sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common in gay and bisexual men. “Just because the patient is diagnosed with gonorrhea or syphilis does not mean the patient cannot also have monkeypox,” Dr. Rosenbach said. Indeed, the NEJM study reported that of 377 patients screened, 29% had an STI other than HIV, mostly syphilis (9%) and gonorrhea (8%). Of all 528 patients in the study (all male or transgender/nonbinary), 41% were HIV-positive, and the median number of sex partners in the last 3 months was 5 (range, 3-15).
Testing is crucial to rule monkeypox in – or out
While monkeypox lesions can be confused for other diseases, Dr. Rosenbach said that a diagnosis can be confirmed through various tests. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV) have distinct findings on Tzanck smears (nuclear molding, multinucleated cells), and have widely available fairly rapid tests (PCR, or in some places, DFA). “Staph and bacterial folliculitis can usually be cultured quickly,” he said. “If you have someone with no risk factors/exposure, and you test for VZV, HSV, folliculitis, and it’s negative – you should know within 24 hours in most places – then you can broaden your differential diagnosis and consider alternate explanations, including monkeypox.”
Quest Diagnostics and Labcorp, two of the largest commercial labs in the United States, are now offering monkeypox tests. Labcorp says its test has a 2- to 3-day turnaround time.
As for treatment, some physicians are prescribing off-label use of tecovirimat (also known as TPOXX or ST-246), a smallpox antiviral treatment. The CDC offers guidelines about its use. “It seems to work very fast, with patients improving in 24-72 hours,” Dr. Rosenbach said. However, “it is still very challenging to give and get. There’s a cumbersome system to prescribe it, and it needs to be shipped from the national stockpile. Dermatologists should be working with their state health department, infection control, and infectious disease doctors.”
It’s likely that dermatologists are not comfortable with the process to access the drug, he said, “but if we do not act quickly to control the current outbreak, we will all – unfortunately – need to learn to be comfortable prescribing it.”
In regard to pain control, an over-the-counter painkiller approach may be appropriate depending on comorbidities, Dr. Rosenbach said. “Some patients with very severe disease, such as perianal involvement and proctitis, have such severe pain they need to be hospitalized. This is less common.”
Recommendations pending on scarring prevention
There’s limited high-quality evidence about the prevention of scarring in diseases like monkeypox, Dr. Rosenbach noted. “Any recommendations are usually based on very small, limited, uncontrolled studies. In the case of monkeypox, truly we are off the edge of the map.”
He advises cleaning lesions with gentle soap and water – keeping in mind that contaminated towels may spread disease – and potentially using a topical ointment-based dressing such as a Vaseline/nonstick dressing or Vaseline-impregnated gauze. If there’s concern about superinfection, as can occur with staph infections, topical antibiotics such as mupirocin 2% ointment may be appropriate, he said.
“Some folks like to try silica gel sheets to prevent scarring,” Dr. Rosenbach said. “There’s not a lot of evidence to support that, but they’re unlikely to be harmful. I would personally consider them, but it really depends on the extent of disease, anatomic sites involved, and access to care.”
Emory University’s Dr. Yeung also suggested using silicone gel or sheets to optimize the scar appearance once the lesions have crusted over. “People have used lasers, microneedling, etc., to improve smallpox scar appearance,” he added, “and I’m sure dermatologists will be the ones to study what works best for treating monkeypox scars.”
As for the big picture, Dr. Yeung said that dermatologists are critical in the fight to control monkeypox: “We can help our colleagues and patients manage symptoms and wound care, advocate for vaccination and treatment, treat long-term scarring sequelae, and destigmatize LGBTQ health care.”
The dermatologists interviewed for this article report no disclosures.
.
Diagnosing cases “can be hard and folks should keep a very open mind and consider monkeypox virus,” said Misha Rosenbach, MD, a University of Pennsylvania dermatologist and member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s ad hoc task force to develop monkeypox content.
Although it’s named after a primate, it turns out that monkeypox is quite the copycat. As dermatologists have learned, its lesions can look like those caused by a long list of other diseases including herpes, varicella, and syphilis. In small numbers, they can even appear to be insect bites.
To make things more complicated, a patient can have one or two lesions – or dozens. They often cluster in the anogenital area, likely reflecting transmission via sexual intercourse, unlike previous outbreaks in which lesions appeared all over the body. “We have to let go of some of our conceptions about what monkeypox might look like,” said dermatologist Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Harvard University, Boston, and a member of the AAD task force.
To make things even more complicated, “the spectrum of illness that we are seeing has ranged from limited, subtle lesions to dramatic, widespread, ulcerative/necrotic lesions,” said Dr. Rosenbach, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
But monkeypox has unique traits that can set it apart and pave the way toward a diagnosis, dermatologists say. And important patient data can help dermatologists gauge the likelihood of a case: Almost 99% of cases with data available have been in men, and among men with available information, 94% reported male-to-male sexual or close intimate contact during the 3 weeks before developing symptoms, according to a CDC report tracking cases from May through late July. So far, cases in women and children are extremely rare, although there have been some reported in the United States.
Are dermatologists likely to see monkeypox in the clinic? It’s unclear so far. Of four dermatologists interviewed for this article, only one has seen patients with monkeypox in person. But others say they’ve been sought for consultations. “I have been asked by infectious disease colleagues for advice remotely but have not seen it,” said dermatologist Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “Most of the time, they’re catching all the symptomatic cases before any need for dermatology in-person referrals.”
Still, the rapid rate of growth of the outbreak – up from 3,487 in the United States on July 25 to 12,689 as of Aug.16 – suggests that more dermatologists will see cases, and consultations may become more common too.
Know your lesions
Lesions are the telltale signs of symptomatic monkeypox. According to a recent New England Journal of Medicine study of 528 monkeypox cases from 16 nations, diagnosed between April 27 and June 24, 2022, 95% had skin lesions (58% were vesiculopustular), most commonly in the anogenital area (73%), and on the trunk/arms/or legs (55%) and face (25%), and the palms/soles (10%).
However, “the current monkeypox outbreak often presents differently from the multiple classic vesiculopustules on the skin we see in textbooks,” Dr. Yeung said. “Sometimes people can present with throat pain or rectal pain, with isolated pharyngitis or proctitis. Sometimes there are so few lesions on the skin that it can be easily confused with a bug bite, folliculitis, herpes, dyshidrotic eczema, or other skin problems. This is where dermatologists will get consulted to clarify the diagnosis while the monkeypox PCR test is pending.”
Dr. Rosenbach, who has provided consultation services to other physicians about cases, said the lesions often appear to be vesicles or pustules, “but if you go to ‘pop’ it – e.g., for testing – it’s firm and without fluid. This is likely due to pox virus inclusion, similar to other diseases such as molluscum,” caused by another pox virus, he said. Molluscum lesions are “characteristically umbilicated, with a dimple in the center, and monkeypox lesions seem to be showing a roughly similar morphology with many bowl- or caldera-shaped lesions that are donut-like in appearance,” he added.
Over time, Dr. Rosenbach said, “lesions tend to evolve slowly from smaller flesh-colored or vaguely white firm papules to broader more umbilicated/donut-shaped lesions which may erode, ulcerate, develop a crust or scab, and then heal. The amount of scarring is not yet clear, but we anticipate it to be significant, especially in patients with more widespread or severe disease.”
Jon Peebles, MD, a dermatologist at Kaiser Permanente in Largo, Md., who has treated a few in-person monkeypox cases, said the lesions can be “exquisitely painful,” although he’s also seen patients with asymptomatic lesions. “Lesions are showing a predilection for the anogenital skin, though they can occur anywhere and not uncommonly involve the oral mucosa,” said Dr. Peebles, also a member of the AAD monkeypox task force.
Dr. Yeung said it’s important to ask patients about their sexual orientation, gender identity, and sexual behaviors. “That is the only way to know who your patients are and the only way to understand who else may be at risks and can benefit from contact tracing and additional prevention measures, such as vaccination for asymptomatic sex partners.” (The Jynneos smallpox vaccine is Food and Drug Administration–approved to prevent monkeypox, although its efficacy is not entirely clear, and there’s controversy over expanding its limited availability by administering the vaccine intradermally.)
It’s also important to keep in mind that sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common in gay and bisexual men. “Just because the patient is diagnosed with gonorrhea or syphilis does not mean the patient cannot also have monkeypox,” Dr. Rosenbach said. Indeed, the NEJM study reported that of 377 patients screened, 29% had an STI other than HIV, mostly syphilis (9%) and gonorrhea (8%). Of all 528 patients in the study (all male or transgender/nonbinary), 41% were HIV-positive, and the median number of sex partners in the last 3 months was 5 (range, 3-15).
Testing is crucial to rule monkeypox in – or out
While monkeypox lesions can be confused for other diseases, Dr. Rosenbach said that a diagnosis can be confirmed through various tests. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV) have distinct findings on Tzanck smears (nuclear molding, multinucleated cells), and have widely available fairly rapid tests (PCR, or in some places, DFA). “Staph and bacterial folliculitis can usually be cultured quickly,” he said. “If you have someone with no risk factors/exposure, and you test for VZV, HSV, folliculitis, and it’s negative – you should know within 24 hours in most places – then you can broaden your differential diagnosis and consider alternate explanations, including monkeypox.”
Quest Diagnostics and Labcorp, two of the largest commercial labs in the United States, are now offering monkeypox tests. Labcorp says its test has a 2- to 3-day turnaround time.
As for treatment, some physicians are prescribing off-label use of tecovirimat (also known as TPOXX or ST-246), a smallpox antiviral treatment. The CDC offers guidelines about its use. “It seems to work very fast, with patients improving in 24-72 hours,” Dr. Rosenbach said. However, “it is still very challenging to give and get. There’s a cumbersome system to prescribe it, and it needs to be shipped from the national stockpile. Dermatologists should be working with their state health department, infection control, and infectious disease doctors.”
It’s likely that dermatologists are not comfortable with the process to access the drug, he said, “but if we do not act quickly to control the current outbreak, we will all – unfortunately – need to learn to be comfortable prescribing it.”
In regard to pain control, an over-the-counter painkiller approach may be appropriate depending on comorbidities, Dr. Rosenbach said. “Some patients with very severe disease, such as perianal involvement and proctitis, have such severe pain they need to be hospitalized. This is less common.”
Recommendations pending on scarring prevention
There’s limited high-quality evidence about the prevention of scarring in diseases like monkeypox, Dr. Rosenbach noted. “Any recommendations are usually based on very small, limited, uncontrolled studies. In the case of monkeypox, truly we are off the edge of the map.”
He advises cleaning lesions with gentle soap and water – keeping in mind that contaminated towels may spread disease – and potentially using a topical ointment-based dressing such as a Vaseline/nonstick dressing or Vaseline-impregnated gauze. If there’s concern about superinfection, as can occur with staph infections, topical antibiotics such as mupirocin 2% ointment may be appropriate, he said.
“Some folks like to try silica gel sheets to prevent scarring,” Dr. Rosenbach said. “There’s not a lot of evidence to support that, but they’re unlikely to be harmful. I would personally consider them, but it really depends on the extent of disease, anatomic sites involved, and access to care.”
Emory University’s Dr. Yeung also suggested using silicone gel or sheets to optimize the scar appearance once the lesions have crusted over. “People have used lasers, microneedling, etc., to improve smallpox scar appearance,” he added, “and I’m sure dermatologists will be the ones to study what works best for treating monkeypox scars.”
As for the big picture, Dr. Yeung said that dermatologists are critical in the fight to control monkeypox: “We can help our colleagues and patients manage symptoms and wound care, advocate for vaccination and treatment, treat long-term scarring sequelae, and destigmatize LGBTQ health care.”
The dermatologists interviewed for this article report no disclosures.
Exaggerated Facial Lines on the Forehead and Cheeks
The Diagnosis: Pachydermoperiostosis
Histopathology of the forehead punch biopsy demonstrated sebaceous hyperplasia with an occupation rate of greater than 40%, increased mucin, elastic fiber degeneration, and fibrosis. Pachydermia is graded from 0 to 3 depending on the degree of these changes; our patient met criteria for grade 3 pachydermia (Figure 1). Radiography revealed diffuse cortical thickening of the long bones that was most marked in the left femur (Figure 2); however, no other findings were demonstrative of Paget disease.
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP)(also known as Touraine-Solente-Golé syndrome or primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy) is a rare genetic condition that affects both the dermatologic and skeletal systems. Clinical features of the disease include progressive thickening and furrowing of the skin on the scalp and face (known as pachydermia), digital clubbing, and periostosis. Other potential cutaneous features include seborrhea, acne, hyperhidrosis of the palms and soles, cutis verticis gyrata, eczema, and a burning sensation of the hands and feet. Myelofibrosis and gastrointestinal abnormalities also have been reported.1
The disease typically affects males (7:1 ratio); also, men typically display a more severe phenotype of the disease.2 It most commonly begins during puberty and follows a generally progressive course of 5 to 20 years before eventually stabilizing. Both autosomal-dominant with incomplete penetrance and recessive inheritance versions of PDP can occur. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PDP; PGE2 is important in the inflammatory response and may evolve from disrupted protein degradation pathways.3 Sasaki et al4 additionally reported that the severity of pachydermia clinically and histologically appeared to correlate with the serum PGE2 levels in affected patients. Prostaglandin E2 causes a vasodilatory effect, perhaps explaining the clubbing observed in PDP, and also modifies the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, causing the bone remodeling observed in the disease.4
In our patient, the initial differential diagnosis included PDP, as well as lepromatous leprosy, acromegaly, Paget disease of the bone, amyloidosis, scleromyxedema, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, the time course of the disease, lack of numerous symmetric thickened plaques and madarosis, and pathology argued against lepromatous leprosy. Acromegaly was ruled out due to lack of macroglossia as well as laboratory analysis within reference range including IGF-1 levels and thyroid function tests. Biopsy findings ultimately ruled out amyloidosis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The bone scan revealed diffuse cortical thickening consistent with PDP, and there were no other radiologic findings suggestive of Paget disease. Pachydermoperiostosis is diagnosed using the Borochowitz criteria, which entails that 2 of the following 4 fulfillment criteria must be met: familial transmission, pachydermia, digital clubbing, and/or bony involvement with evidence of radiologic alterations or pain. Our patient met all 4 criteria. The clinical manifestations of PDP are variable with respect to skin and bone changes. The various clinical expressions include the complete form (ie, pachydermia, cutis verticis gyrata, periostosis), the incomplete form (ie, absence of cutis verticis gyrata), and forme fruste (ie, pachydermia with minimal or absent periostosis).5
Management for PDP involves surgical correction for cosmesis as well as for functional concerns if present. Symptoms secondary to periostosis should be managed with symptomatic treatment such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Patients managed with etoricoxib, a COX-2–selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, have had normalized inflammatory markers that resulted in the lessening of forehead skin folds. Oral aescin has been shown to relieve joint pain due to its antiedematous effect.6 Our patient received treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for symptomatic management of the associated joint pain but unfortunately was lost to follow-up.
- Castori M, Sinibaldi L, Mingarelli R, et al. Pachydermoperiostosis: an update. Clin Genet. 2005;68:477-486.
- Reginato AJ, Shipachasse V, Guerrero R. Familial idiopathic hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and cranial suture defects in children. Skel Radiol. 1982;8:105-109.
- Coggins KG, Coffman TM, Koller BH. The Hippocratic finger points the blame at PGE2. Nat Genet. 2008;40:691-692.
- Sasaki T, Niizeki H, Shimizu A, et al. Identification of mutations in the prostaglandin transporter gene SLCO2A1 and its phenotype-genotype correlation in Japanese patients with pachydermoperiostosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;68:36-44.
- Bhaskaranand K, Shetty RR, Bhat AK. Pachydermoperiostosis: three case reports. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2001;9:61-66.
- Zhang H, Yang B. Successful treatment of pachydermoperiostosis patients with etoricoxib, aescin, and arthroscopic synovectomy: two case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:E8865.
The Diagnosis: Pachydermoperiostosis
Histopathology of the forehead punch biopsy demonstrated sebaceous hyperplasia with an occupation rate of greater than 40%, increased mucin, elastic fiber degeneration, and fibrosis. Pachydermia is graded from 0 to 3 depending on the degree of these changes; our patient met criteria for grade 3 pachydermia (Figure 1). Radiography revealed diffuse cortical thickening of the long bones that was most marked in the left femur (Figure 2); however, no other findings were demonstrative of Paget disease.

Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP)(also known as Touraine-Solente-Golé syndrome or primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy) is a rare genetic condition that affects both the dermatologic and skeletal systems. Clinical features of the disease include progressive thickening and furrowing of the skin on the scalp and face (known as pachydermia), digital clubbing, and periostosis. Other potential cutaneous features include seborrhea, acne, hyperhidrosis of the palms and soles, cutis verticis gyrata, eczema, and a burning sensation of the hands and feet. Myelofibrosis and gastrointestinal abnormalities also have been reported.1

The disease typically affects males (7:1 ratio); also, men typically display a more severe phenotype of the disease.2 It most commonly begins during puberty and follows a generally progressive course of 5 to 20 years before eventually stabilizing. Both autosomal-dominant with incomplete penetrance and recessive inheritance versions of PDP can occur. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PDP; PGE2 is important in the inflammatory response and may evolve from disrupted protein degradation pathways.3 Sasaki et al4 additionally reported that the severity of pachydermia clinically and histologically appeared to correlate with the serum PGE2 levels in affected patients. Prostaglandin E2 causes a vasodilatory effect, perhaps explaining the clubbing observed in PDP, and also modifies the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, causing the bone remodeling observed in the disease.4
In our patient, the initial differential diagnosis included PDP, as well as lepromatous leprosy, acromegaly, Paget disease of the bone, amyloidosis, scleromyxedema, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, the time course of the disease, lack of numerous symmetric thickened plaques and madarosis, and pathology argued against lepromatous leprosy. Acromegaly was ruled out due to lack of macroglossia as well as laboratory analysis within reference range including IGF-1 levels and thyroid function tests. Biopsy findings ultimately ruled out amyloidosis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The bone scan revealed diffuse cortical thickening consistent with PDP, and there were no other radiologic findings suggestive of Paget disease. Pachydermoperiostosis is diagnosed using the Borochowitz criteria, which entails that 2 of the following 4 fulfillment criteria must be met: familial transmission, pachydermia, digital clubbing, and/or bony involvement with evidence of radiologic alterations or pain. Our patient met all 4 criteria. The clinical manifestations of PDP are variable with respect to skin and bone changes. The various clinical expressions include the complete form (ie, pachydermia, cutis verticis gyrata, periostosis), the incomplete form (ie, absence of cutis verticis gyrata), and forme fruste (ie, pachydermia with minimal or absent periostosis).5
Management for PDP involves surgical correction for cosmesis as well as for functional concerns if present. Symptoms secondary to periostosis should be managed with symptomatic treatment such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Patients managed with etoricoxib, a COX-2–selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, have had normalized inflammatory markers that resulted in the lessening of forehead skin folds. Oral aescin has been shown to relieve joint pain due to its antiedematous effect.6 Our patient received treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for symptomatic management of the associated joint pain but unfortunately was lost to follow-up.
The Diagnosis: Pachydermoperiostosis
Histopathology of the forehead punch biopsy demonstrated sebaceous hyperplasia with an occupation rate of greater than 40%, increased mucin, elastic fiber degeneration, and fibrosis. Pachydermia is graded from 0 to 3 depending on the degree of these changes; our patient met criteria for grade 3 pachydermia (Figure 1). Radiography revealed diffuse cortical thickening of the long bones that was most marked in the left femur (Figure 2); however, no other findings were demonstrative of Paget disease.

Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP)(also known as Touraine-Solente-Golé syndrome or primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy) is a rare genetic condition that affects both the dermatologic and skeletal systems. Clinical features of the disease include progressive thickening and furrowing of the skin on the scalp and face (known as pachydermia), digital clubbing, and periostosis. Other potential cutaneous features include seborrhea, acne, hyperhidrosis of the palms and soles, cutis verticis gyrata, eczema, and a burning sensation of the hands and feet. Myelofibrosis and gastrointestinal abnormalities also have been reported.1

The disease typically affects males (7:1 ratio); also, men typically display a more severe phenotype of the disease.2 It most commonly begins during puberty and follows a generally progressive course of 5 to 20 years before eventually stabilizing. Both autosomal-dominant with incomplete penetrance and recessive inheritance versions of PDP can occur. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PDP; PGE2 is important in the inflammatory response and may evolve from disrupted protein degradation pathways.3 Sasaki et al4 additionally reported that the severity of pachydermia clinically and histologically appeared to correlate with the serum PGE2 levels in affected patients. Prostaglandin E2 causes a vasodilatory effect, perhaps explaining the clubbing observed in PDP, and also modifies the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, causing the bone remodeling observed in the disease.4
In our patient, the initial differential diagnosis included PDP, as well as lepromatous leprosy, acromegaly, Paget disease of the bone, amyloidosis, scleromyxedema, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, the time course of the disease, lack of numerous symmetric thickened plaques and madarosis, and pathology argued against lepromatous leprosy. Acromegaly was ruled out due to lack of macroglossia as well as laboratory analysis within reference range including IGF-1 levels and thyroid function tests. Biopsy findings ultimately ruled out amyloidosis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The bone scan revealed diffuse cortical thickening consistent with PDP, and there were no other radiologic findings suggestive of Paget disease. Pachydermoperiostosis is diagnosed using the Borochowitz criteria, which entails that 2 of the following 4 fulfillment criteria must be met: familial transmission, pachydermia, digital clubbing, and/or bony involvement with evidence of radiologic alterations or pain. Our patient met all 4 criteria. The clinical manifestations of PDP are variable with respect to skin and bone changes. The various clinical expressions include the complete form (ie, pachydermia, cutis verticis gyrata, periostosis), the incomplete form (ie, absence of cutis verticis gyrata), and forme fruste (ie, pachydermia with minimal or absent periostosis).5
Management for PDP involves surgical correction for cosmesis as well as for functional concerns if present. Symptoms secondary to periostosis should be managed with symptomatic treatment such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Patients managed with etoricoxib, a COX-2–selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, have had normalized inflammatory markers that resulted in the lessening of forehead skin folds. Oral aescin has been shown to relieve joint pain due to its antiedematous effect.6 Our patient received treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for symptomatic management of the associated joint pain but unfortunately was lost to follow-up.
- Castori M, Sinibaldi L, Mingarelli R, et al. Pachydermoperiostosis: an update. Clin Genet. 2005;68:477-486.
- Reginato AJ, Shipachasse V, Guerrero R. Familial idiopathic hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and cranial suture defects in children. Skel Radiol. 1982;8:105-109.
- Coggins KG, Coffman TM, Koller BH. The Hippocratic finger points the blame at PGE2. Nat Genet. 2008;40:691-692.
- Sasaki T, Niizeki H, Shimizu A, et al. Identification of mutations in the prostaglandin transporter gene SLCO2A1 and its phenotype-genotype correlation in Japanese patients with pachydermoperiostosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;68:36-44.
- Bhaskaranand K, Shetty RR, Bhat AK. Pachydermoperiostosis: three case reports. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2001;9:61-66.
- Zhang H, Yang B. Successful treatment of pachydermoperiostosis patients with etoricoxib, aescin, and arthroscopic synovectomy: two case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:E8865.
- Castori M, Sinibaldi L, Mingarelli R, et al. Pachydermoperiostosis: an update. Clin Genet. 2005;68:477-486.
- Reginato AJ, Shipachasse V, Guerrero R. Familial idiopathic hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and cranial suture defects in children. Skel Radiol. 1982;8:105-109.
- Coggins KG, Coffman TM, Koller BH. The Hippocratic finger points the blame at PGE2. Nat Genet. 2008;40:691-692.
- Sasaki T, Niizeki H, Shimizu A, et al. Identification of mutations in the prostaglandin transporter gene SLCO2A1 and its phenotype-genotype correlation in Japanese patients with pachydermoperiostosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;68:36-44.
- Bhaskaranand K, Shetty RR, Bhat AK. Pachydermoperiostosis: three case reports. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2001;9:61-66.
- Zhang H, Yang B. Successful treatment of pachydermoperiostosis patients with etoricoxib, aescin, and arthroscopic synovectomy: two case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:E8865.
A 36-year-old man presented to the emergency department with an olecranon fracture after falling from a tree. The patient had a medical history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and a surgical history of facial cosmetic surgery. He underwent internal fixation with orthopedic surgery for the olecranon fracture, and dermatology subsequently was consulted due to diffuse skin changes on the face. He reported that these dermatologic changes began around 17 years of age and had progressed to the current presentation. He denied itching, burning, pain, or contact with armadillos. A family history revealed the patient’s brother also had a similar appearance. Physical examination revealed exaggerated facial lines on the forehead (top) and cheeks. Digital clubbing and skin thickening were noted on the hands (bottom) and feet; examination of the back revealed multiple hypopigmented patches. Observation of the scalp showed multiple symmetric ridges and grooves with sparse overlying hair consistent with cutis verticis gyrata. A punch biopsy of the forehead was obtained as well as bone radiography taken previously by the primary team.