User login
Time to consider topical capsaicin for acute trauma pain?
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 23-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to an urgent care center after a fall on his right arm while playing football. He reports a pain level of 6 using the visual analog scale (VAS). Physical exam reveals minor erythema and edema of his forearm with pain to palpation. Range of motion, strength, and sensation are intact. No lacerations are present. His vital signs are normal. No fracture is found on imaging. The physician decides that treatment with a topical analgesic is reasonable for this uncomplicated contusion of the right forearm. Is there a role for topical capsaicin in the treatment of this patient’s pain?
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for the treatment of acute non–low back pain musculoskeletal injuries.2 They are generally well tolerated and just as effective as oral NSAIDS or acetaminophen for localized injuries. Their ubiquitous availability, affordability, and low adverse effect profile make them an attractive first-line treatment option for acute musculoskeletal pain.
Capsaicin, a topical agent derived from a genus of red peppers, has been used for the treatment of neuropathic and chronic pain via its interactions with substance P, transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1), and nociceptive nerve fibers.3,4 It has demonstrated effectiveness in the management of diabetic neuropathy, knee osteoarthritis, and postherpetic neuralgia, as well as various causes of pruritus.5,6
Although many studies have compared oral and topical NSAIDs, opiates, and acetaminophen, few studies have directly compared topical NSAIDs and capsaicin. This study compared the topical NSAID piroxicam with topical capsaicin.
STUDY SUMMARY
Topical capsaicin demonstrated superior pain reduction
This prospective, double-blind RCT compared the efficacy of topical capsaicin vs topical piroxicam for the treatment of acute pain following upper extremity blunt trauma. Patients (ages ≥ 18 years) who presented to a Turkish emergency department within 2 hours of upper extremity injury were randomized to receive either 0.05% capsaicin gel (n = 69) or 0.5% piroxicam gel (n = 67). Patients reported level 5 or higher pain on the VAS. Those with fractures, dislocations, skin disruption, or other trauma were excluded. Age, gender, pain duration, and mechanism of injury did not differ significantly between study groups.1
Blinding was ensured by placing the gels in opaque containers containing 30 mg of either capsaicin or piroxicam and dyeing the medicine with red and yellow food coloring. A thin layer of medication was applied to an area no larger than 5 × 5 cm on the upper extremity and rubbed for 1 minute. Patients were observed in the emergency department for 2 hours and discharged with instructions to apply the medication 3 times daily for 72 hours.
The investigators measured pain using VAS scores at 1 hour, 2 hours, 24 hours, and 72 hours after treatment. Topical capsaicin was superior to topical piroxicam at achieving both primary outcomes: a VAS score of ≤ 4 (85.5% vs 50.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 2.9; P < .001) and a > 50% reduction in VAS score (87% vs 62.7%; NNT = 4.1; P < .01) at the end of treatment.1 (These outcomes were based on earlier determinations of the minimal clinically important difference.7,8)
Additionally, capsaicin was more effective than piroxicam at each time interval. This difference was most pronounced at 72 hours, with a mean difference of delta VAS scores of 1.53 (95% CI, 0.85-2.221) and a mean percentage of the reduction in VAS scores of 19.7% (95% CI, 12.4%-27.2%) (P < .001).1
Reported adverse effects, such as burning, itching, and rash, were mild and infrequent and showed no significant difference between the treatment groups.
WHAT’S NEW
First study comparing topical capsaicin and a topical NSAID in acute trauma
Although both capsaicin and topical piroxicam have proven efficacy for the treatment of pain, this RCT is the first study to directly compare these agents in the setting of acute upper extremity blunt trauma. Capsaicin is currently more commonly prescribed as a treatment for chronic neuropathic pain.4,9 In this study, capsaicin demonstrated superior results in pain reduction at each assessed time interval and at the primary end point of 72 hours.
CAVEATS
Limited generalizability to lower extremity and truncal trauma
This RCT included a relatively small sample size (136 patients). Researchers evaluated only blunt upper extremity injuries; as such, the generalizability of the effectiveness of topical capsaicin in blunt lower extremity and truncal trauma is limited, especially over larger surface areas.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No major challenges found
There are no major challenges to implementing this inexpensive treatment.
1. Kocak AO, Dogruyol S, Akbas I, et al. Comparison of topical capsaicin and topical piroxicam in the treatment of acute trauma-induced pain: a randomized double-blind trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:1767-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.104
2. Busse JW, Sadeghirad B, Oparin Y, et al. Management of acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:730-738. doi: 10.7326/M19-3601
3. Chrubasik S, Weiser T, Beime B. Effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin cream in the treatment of chronic soft tissue pain. Phytother Res. 2010;24:1877-1885. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3335
4. Derry S, Moore RA. Topical capsaicin (low concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012(9):CD010111. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010111
5. Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
6. Papoiu ADP, Yosipovitch G. Topical capsaicin. The fire of a ‘hot’ medicine is reignited. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11:1359-1371. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.481670
7. Kulkantrakorn K, Lorsuwansiri C, Meesawatsom P. 0.025% capsaicin gel for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2013;13:497-503. doi: 10.1111/papr.12013
8. Kocak AO, Ahiskalioglu A, Sengun E, et al. Comparison of intravenous NSAIDs and trigger point injection for low back pain in ED: a prospective randomized study. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37:1927-1931. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.01.015
9. Derry S, Rice ASC, Cole P, et al. Topical capsaicin (high concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1(1):CD007393. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007393.pub4
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 23-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to an urgent care center after a fall on his right arm while playing football. He reports a pain level of 6 using the visual analog scale (VAS). Physical exam reveals minor erythema and edema of his forearm with pain to palpation. Range of motion, strength, and sensation are intact. No lacerations are present. His vital signs are normal. No fracture is found on imaging. The physician decides that treatment with a topical analgesic is reasonable for this uncomplicated contusion of the right forearm. Is there a role for topical capsaicin in the treatment of this patient’s pain?
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for the treatment of acute non–low back pain musculoskeletal injuries.2 They are generally well tolerated and just as effective as oral NSAIDS or acetaminophen for localized injuries. Their ubiquitous availability, affordability, and low adverse effect profile make them an attractive first-line treatment option for acute musculoskeletal pain.
Capsaicin, a topical agent derived from a genus of red peppers, has been used for the treatment of neuropathic and chronic pain via its interactions with substance P, transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1), and nociceptive nerve fibers.3,4 It has demonstrated effectiveness in the management of diabetic neuropathy, knee osteoarthritis, and postherpetic neuralgia, as well as various causes of pruritus.5,6
Although many studies have compared oral and topical NSAIDs, opiates, and acetaminophen, few studies have directly compared topical NSAIDs and capsaicin. This study compared the topical NSAID piroxicam with topical capsaicin.
STUDY SUMMARY
Topical capsaicin demonstrated superior pain reduction
This prospective, double-blind RCT compared the efficacy of topical capsaicin vs topical piroxicam for the treatment of acute pain following upper extremity blunt trauma. Patients (ages ≥ 18 years) who presented to a Turkish emergency department within 2 hours of upper extremity injury were randomized to receive either 0.05% capsaicin gel (n = 69) or 0.5% piroxicam gel (n = 67). Patients reported level 5 or higher pain on the VAS. Those with fractures, dislocations, skin disruption, or other trauma were excluded. Age, gender, pain duration, and mechanism of injury did not differ significantly between study groups.1
Blinding was ensured by placing the gels in opaque containers containing 30 mg of either capsaicin or piroxicam and dyeing the medicine with red and yellow food coloring. A thin layer of medication was applied to an area no larger than 5 × 5 cm on the upper extremity and rubbed for 1 minute. Patients were observed in the emergency department for 2 hours and discharged with instructions to apply the medication 3 times daily for 72 hours.
The investigators measured pain using VAS scores at 1 hour, 2 hours, 24 hours, and 72 hours after treatment. Topical capsaicin was superior to topical piroxicam at achieving both primary outcomes: a VAS score of ≤ 4 (85.5% vs 50.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 2.9; P < .001) and a > 50% reduction in VAS score (87% vs 62.7%; NNT = 4.1; P < .01) at the end of treatment.1 (These outcomes were based on earlier determinations of the minimal clinically important difference.7,8)
Additionally, capsaicin was more effective than piroxicam at each time interval. This difference was most pronounced at 72 hours, with a mean difference of delta VAS scores of 1.53 (95% CI, 0.85-2.221) and a mean percentage of the reduction in VAS scores of 19.7% (95% CI, 12.4%-27.2%) (P < .001).1
Reported adverse effects, such as burning, itching, and rash, were mild and infrequent and showed no significant difference between the treatment groups.
WHAT’S NEW
First study comparing topical capsaicin and a topical NSAID in acute trauma
Although both capsaicin and topical piroxicam have proven efficacy for the treatment of pain, this RCT is the first study to directly compare these agents in the setting of acute upper extremity blunt trauma. Capsaicin is currently more commonly prescribed as a treatment for chronic neuropathic pain.4,9 In this study, capsaicin demonstrated superior results in pain reduction at each assessed time interval and at the primary end point of 72 hours.
CAVEATS
Limited generalizability to lower extremity and truncal trauma
This RCT included a relatively small sample size (136 patients). Researchers evaluated only blunt upper extremity injuries; as such, the generalizability of the effectiveness of topical capsaicin in blunt lower extremity and truncal trauma is limited, especially over larger surface areas.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No major challenges found
There are no major challenges to implementing this inexpensive treatment.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 23-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to an urgent care center after a fall on his right arm while playing football. He reports a pain level of 6 using the visual analog scale (VAS). Physical exam reveals minor erythema and edema of his forearm with pain to palpation. Range of motion, strength, and sensation are intact. No lacerations are present. His vital signs are normal. No fracture is found on imaging. The physician decides that treatment with a topical analgesic is reasonable for this uncomplicated contusion of the right forearm. Is there a role for topical capsaicin in the treatment of this patient’s pain?
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for the treatment of acute non–low back pain musculoskeletal injuries.2 They are generally well tolerated and just as effective as oral NSAIDS or acetaminophen for localized injuries. Their ubiquitous availability, affordability, and low adverse effect profile make them an attractive first-line treatment option for acute musculoskeletal pain.
Capsaicin, a topical agent derived from a genus of red peppers, has been used for the treatment of neuropathic and chronic pain via its interactions with substance P, transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1), and nociceptive nerve fibers.3,4 It has demonstrated effectiveness in the management of diabetic neuropathy, knee osteoarthritis, and postherpetic neuralgia, as well as various causes of pruritus.5,6
Although many studies have compared oral and topical NSAIDs, opiates, and acetaminophen, few studies have directly compared topical NSAIDs and capsaicin. This study compared the topical NSAID piroxicam with topical capsaicin.
STUDY SUMMARY
Topical capsaicin demonstrated superior pain reduction
This prospective, double-blind RCT compared the efficacy of topical capsaicin vs topical piroxicam for the treatment of acute pain following upper extremity blunt trauma. Patients (ages ≥ 18 years) who presented to a Turkish emergency department within 2 hours of upper extremity injury were randomized to receive either 0.05% capsaicin gel (n = 69) or 0.5% piroxicam gel (n = 67). Patients reported level 5 or higher pain on the VAS. Those with fractures, dislocations, skin disruption, or other trauma were excluded. Age, gender, pain duration, and mechanism of injury did not differ significantly between study groups.1
Blinding was ensured by placing the gels in opaque containers containing 30 mg of either capsaicin or piroxicam and dyeing the medicine with red and yellow food coloring. A thin layer of medication was applied to an area no larger than 5 × 5 cm on the upper extremity and rubbed for 1 minute. Patients were observed in the emergency department for 2 hours and discharged with instructions to apply the medication 3 times daily for 72 hours.
The investigators measured pain using VAS scores at 1 hour, 2 hours, 24 hours, and 72 hours after treatment. Topical capsaicin was superior to topical piroxicam at achieving both primary outcomes: a VAS score of ≤ 4 (85.5% vs 50.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 2.9; P < .001) and a > 50% reduction in VAS score (87% vs 62.7%; NNT = 4.1; P < .01) at the end of treatment.1 (These outcomes were based on earlier determinations of the minimal clinically important difference.7,8)
Additionally, capsaicin was more effective than piroxicam at each time interval. This difference was most pronounced at 72 hours, with a mean difference of delta VAS scores of 1.53 (95% CI, 0.85-2.221) and a mean percentage of the reduction in VAS scores of 19.7% (95% CI, 12.4%-27.2%) (P < .001).1
Reported adverse effects, such as burning, itching, and rash, were mild and infrequent and showed no significant difference between the treatment groups.
WHAT’S NEW
First study comparing topical capsaicin and a topical NSAID in acute trauma
Although both capsaicin and topical piroxicam have proven efficacy for the treatment of pain, this RCT is the first study to directly compare these agents in the setting of acute upper extremity blunt trauma. Capsaicin is currently more commonly prescribed as a treatment for chronic neuropathic pain.4,9 In this study, capsaicin demonstrated superior results in pain reduction at each assessed time interval and at the primary end point of 72 hours.
CAVEATS
Limited generalizability to lower extremity and truncal trauma
This RCT included a relatively small sample size (136 patients). Researchers evaluated only blunt upper extremity injuries; as such, the generalizability of the effectiveness of topical capsaicin in blunt lower extremity and truncal trauma is limited, especially over larger surface areas.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No major challenges found
There are no major challenges to implementing this inexpensive treatment.
1. Kocak AO, Dogruyol S, Akbas I, et al. Comparison of topical capsaicin and topical piroxicam in the treatment of acute trauma-induced pain: a randomized double-blind trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:1767-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.104
2. Busse JW, Sadeghirad B, Oparin Y, et al. Management of acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:730-738. doi: 10.7326/M19-3601
3. Chrubasik S, Weiser T, Beime B. Effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin cream in the treatment of chronic soft tissue pain. Phytother Res. 2010;24:1877-1885. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3335
4. Derry S, Moore RA. Topical capsaicin (low concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012(9):CD010111. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010111
5. Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
6. Papoiu ADP, Yosipovitch G. Topical capsaicin. The fire of a ‘hot’ medicine is reignited. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11:1359-1371. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.481670
7. Kulkantrakorn K, Lorsuwansiri C, Meesawatsom P. 0.025% capsaicin gel for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2013;13:497-503. doi: 10.1111/papr.12013
8. Kocak AO, Ahiskalioglu A, Sengun E, et al. Comparison of intravenous NSAIDs and trigger point injection for low back pain in ED: a prospective randomized study. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37:1927-1931. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.01.015
9. Derry S, Rice ASC, Cole P, et al. Topical capsaicin (high concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1(1):CD007393. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007393.pub4
1. Kocak AO, Dogruyol S, Akbas I, et al. Comparison of topical capsaicin and topical piroxicam in the treatment of acute trauma-induced pain: a randomized double-blind trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:1767-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.104
2. Busse JW, Sadeghirad B, Oparin Y, et al. Management of acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:730-738. doi: 10.7326/M19-3601
3. Chrubasik S, Weiser T, Beime B. Effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin cream in the treatment of chronic soft tissue pain. Phytother Res. 2010;24:1877-1885. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3335
4. Derry S, Moore RA. Topical capsaicin (low concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012(9):CD010111. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010111
5. Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
6. Papoiu ADP, Yosipovitch G. Topical capsaicin. The fire of a ‘hot’ medicine is reignited. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11:1359-1371. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.481670
7. Kulkantrakorn K, Lorsuwansiri C, Meesawatsom P. 0.025% capsaicin gel for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2013;13:497-503. doi: 10.1111/papr.12013
8. Kocak AO, Ahiskalioglu A, Sengun E, et al. Comparison of intravenous NSAIDs and trigger point injection for low back pain in ED: a prospective randomized study. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37:1927-1931. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.01.015
9. Derry S, Rice ASC, Cole P, et al. Topical capsaicin (high concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1(1):CD007393. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007393.pub4
PRACTICE CHANGER
Use topical capsaicin gel 0.05% for pain reduction in patients with isolated blunt injuries of the upper extremity without fracture.
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
B: Based on a single randomized controlled trial (RCT)1
Kocak AO, Dogruyol S, Akbas I, et al. Comparison of topical capsaicin and topical piroxicam in the treatment of acute trauma-induced pain: a randomized double-blind trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:1767-1771.
Managing TIA: Early action and essential risk-reduction steps
As many as 240,000 people per year in the United States experience a transient ischemic attack (TIA),1,2 which is now defined by the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association as a “transient episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord, or retinal ischemia, without acute infarction.”3 An older definition of TIA was based on the duration of the event (ie, resolution of symptoms at 24 hours); in the updated (2009) definition, the diagnostic criterion is the extent of focal tissue damage.3 Using the 2009 definition might mean a decrease in the number of patients who have a diagnosis of a TIA and an increase in the number who are determined to have had a stroke because an infarction is found on initial imaging.
Guided by the 2009 revised definition of a TIA, we review here the work-up and treatment of TIA, emphasizing immediacy of management to (1) prevent further tissue damage and (2) decrease the risk of a second event.
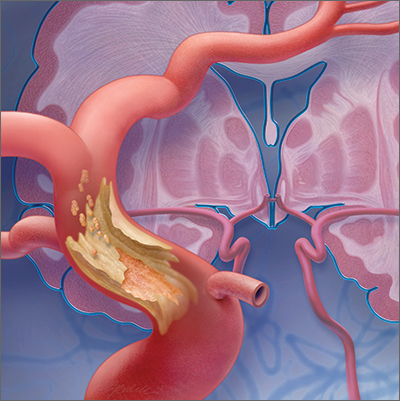
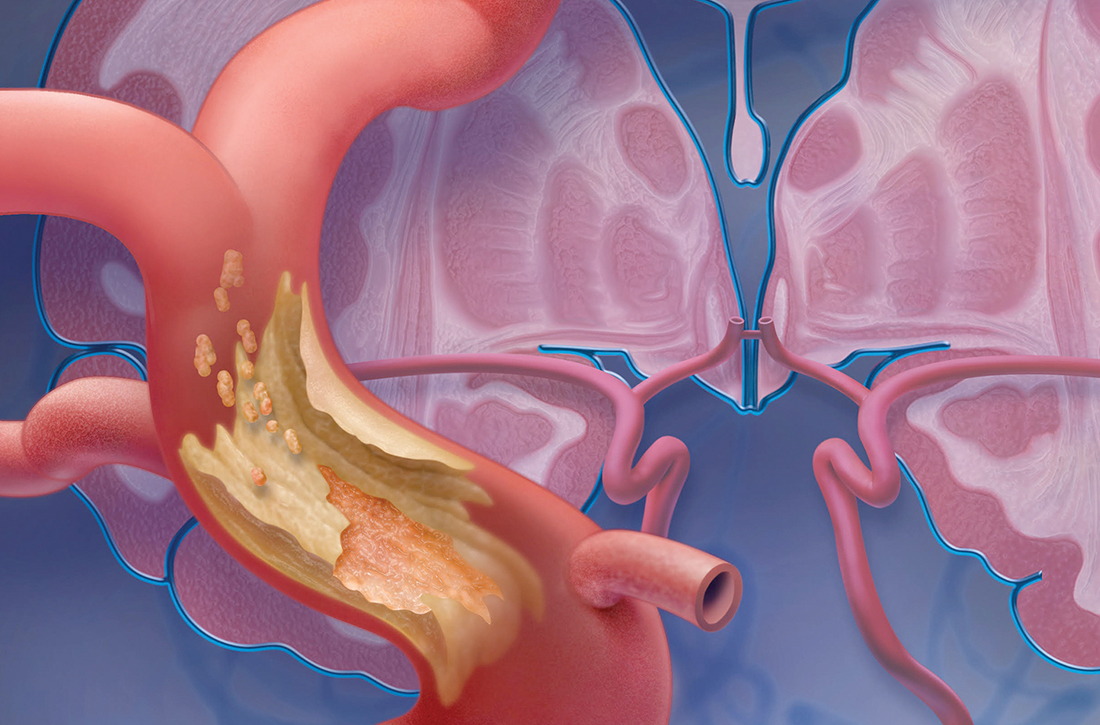
CASE
Martin L, 69 years old, retired, a nonsmoker, and with a history of peripheral arterial disease and hypercholesterolemia, presents to the emergency department (ED) of a rural hospital complaining of slurred speech and left-side facial numbness. He had an episode of facial numbness that lasted 30 minutes, then resolved, each of the 2 previous evenings; he did not seek care at those times. Now, in the ED, Mr. L is normotensive.
The patient’s medication history includes a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin to improve sleep. He reports having discontinued a statin because he could not tolerate its adverse effects.
What immediate steps are recommended for Mr. L’s care?
Common event callsfor quick action
A TIA is the strongest predictor of subsequent stroke and stroke-related death; the highest period of risk of these devastating outcomes is immediately following a TIA.1,2,4,5 It is essential, therefore, for the physician who sees a patient with a current complaint or recent history of suspected focal neurologic deficits to direct that patient to an ED for an accurate diagnosis and, as appropriate, early treatment for the best possible outcome.
Imaging—preferably, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI), the gold standard for diagnosing stroke (see “Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics”)2,3—should be performed as soon as the patient with a suspected TIA arrives in the ED. Imaging should not be held while waiting for a stroke to declare itself—ie, by allowing symptoms to persist for longer than 24 hours. 6
Continue to: Late presentation
Late presentation. Some patients present ≥ 48 hours after onset of early symptoms of a TIA; for them, the work-up is the same as for prompt presentation but can be completed in the outpatient clinic—as long as the patient is stable clinically and imaging is accessible there. DW-MRI should be completed within 48 hours after late presentation. In such cases, the patient should be cautioned regarding risks and any recurrence of symptoms.7,8
Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics
All patients in whom a stroke is suspected should be evaluated on an emergency basis with brain imaging upon arrival at the hospital, before any therapy is initiated. As noted, DW-MRI is the preferred modality; noncontrast computed tomography (CT) or CT angiography can be used if MRI is unavailable.2,3
Mimics. Stroke has many mimics; quickly eliminating them from the differential diagnosis is important so that appropriate therapy can be initiated. Mimics usually have a prolonged presentation of symptoms, whereas the presentation of a TIA is usually abrupt. The 3 more common diagnoses that mimic a TIA are migraine with aura, seizure, and syncope.9,10 Symptoms that generally are not associated with a TIA are chest pain, generalized weakness, and confusion.11 A complete history and physical exam provide the path to the imaging, laboratory, and cardiac testing that is needed to differentiate these diagnoses from a TIA.
A thorough history is best obtained from the patient and a witness, if available, and should include identification of any focal neurologic deficits and the duration and time to resolution of symptoms. Obtain a history of risk factors for ischemia—tobacco use, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, previous TIA or stroke, atrial fibrillation, and any coagulopathy. Ask questions about a family history of TIA, stroke, and coagulopathy.11
A comprehensive physical exam, including vital signs, cardiac exam, a check for carotid bruits, and complete neurologic exam, should be performed. Most patients present with concerns for unilateral weakness and changes in speech, which are usually associated with infarction on DW-MRI.12 The most common findings on physical exam include cranial nerve abnormalities, such as diplopia, hemianopia, monocular blindness, disconjugate gaze, facial drooping, lateral tongue movement, dysphagia, and vestibular dysfunction. Cerebellar abnormalities are also often noted, including past pointing, dystaxia, ataxia, nystagmus, and motor abnormalities (eg, spasticity, clonus, or unilateral weakness in the face or extremities).11
Electrocardiography at the bedside can confirm atrial fibrillation or another arrhythmia quickly.
Essential laboratory testing includes measurement of blood glucose and serum electrolytes to determine if these particular imbalances are the cause of symptoms. The presence of a hypercoaguable state is determined by a complete blood count and coagulation studies.3,13 Urine toxicology should also be obtained to rule out other causes of symptoms. A lipid profile is beneficial for making long-term treatment decisions.
Continue to: ABCD2 score
ABCD2 score. Patients who have had a TIA and present within 72 hours after symptoms have resolved should be hospitalized if they have an ABCD2 (Age, Blood pressure [BP], Clinical presentation, Diabetes mellitus [type 1 or 2], Duration of symptoms) prediction system score > 3.14 ABCD2 criteria can be used to help identify patients who are at higher risk of stroke or need further therapy (TABLE 1).14,15
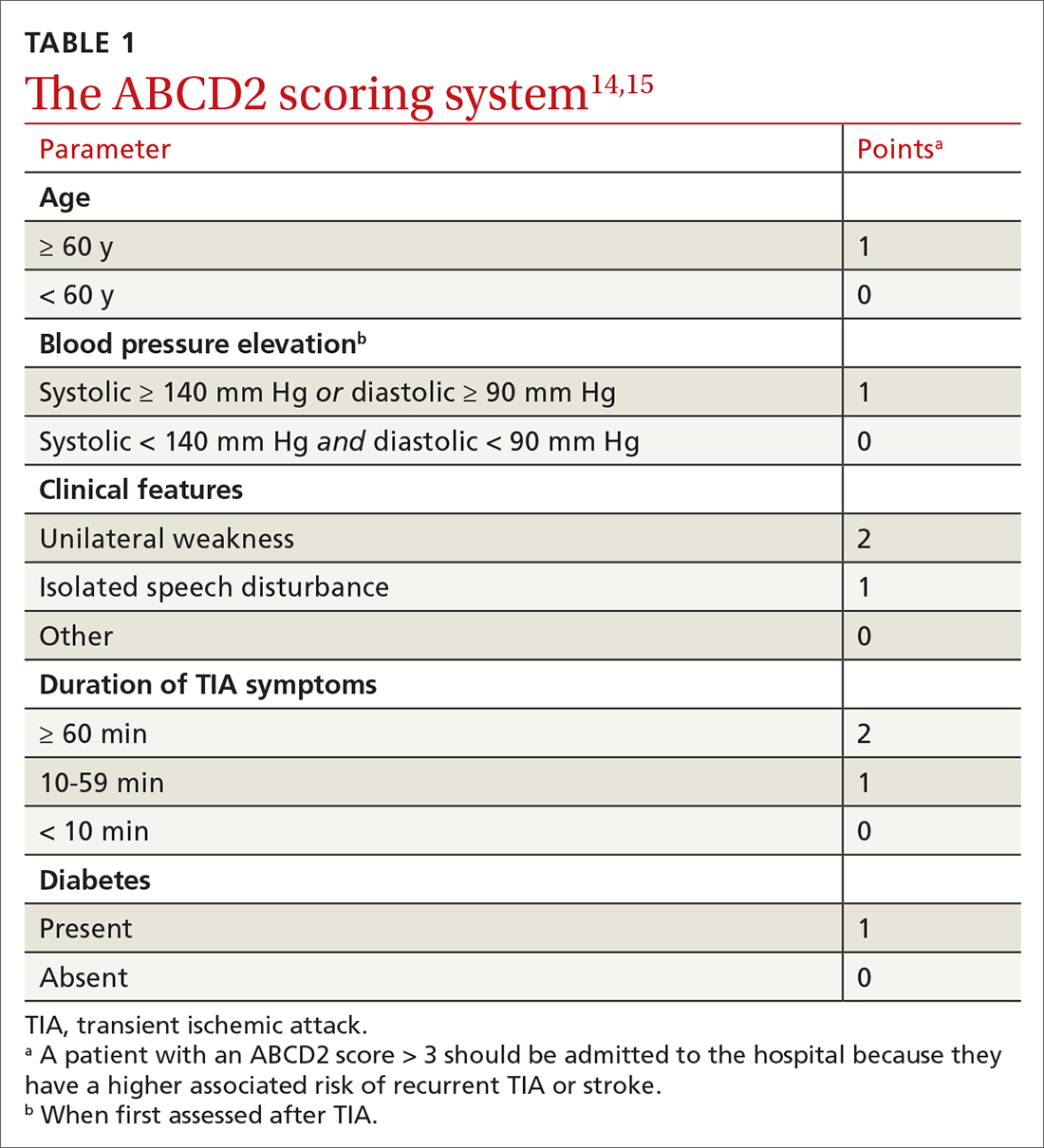
The ABCD2 score is also used to determine whether a patient needs dual antiplatelet therapy. Patients who score at the higher end of the ABCD2 system usually have an increased risk of stroke, longer hospitalization, and greater disability.
CASE
In the ED, Mr. L is immediately assessed and airlifted to a larger regional medical center, where MRI confirms a stroke.
Management
Initial management of a TIA is aimed at reducing the risk of recurrent TIA or stroke. Early medical and possibly surgical treatment are key for preventing stroke and improving outcomes. The first 48 hours after a TIA are the most critical because the incidence of recurrent TIA or stroke is highest during this period.16-18
What is the accepted strategy for early treatment?
Initial treatment must include antiplatelet therapy, BP management, anticoagulation, statin therapy, and carotid endarterectomy as indicated.2,19,20 Control of hypertension and anticoagulation decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by the largest margin20; both are “A”-level Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy interventions.2,3
Step 1: Antiplatelet therapy. After initial imaging is complete and if there are no contraindications, antiplatelet agents are recommended for patients who have had a noncardioembolic TIA. The American Heart Association and American Stroke Association recommend either aspirin, clopidogrel, dipyridamole + aspirin (available in a single capsule [Aggrenox]), or clopidogrel + aspirin as first-line therapy.2,20 The choice of agent needs to be individualized, based on tolerability and adverse effects (TABLE 22,20,21).
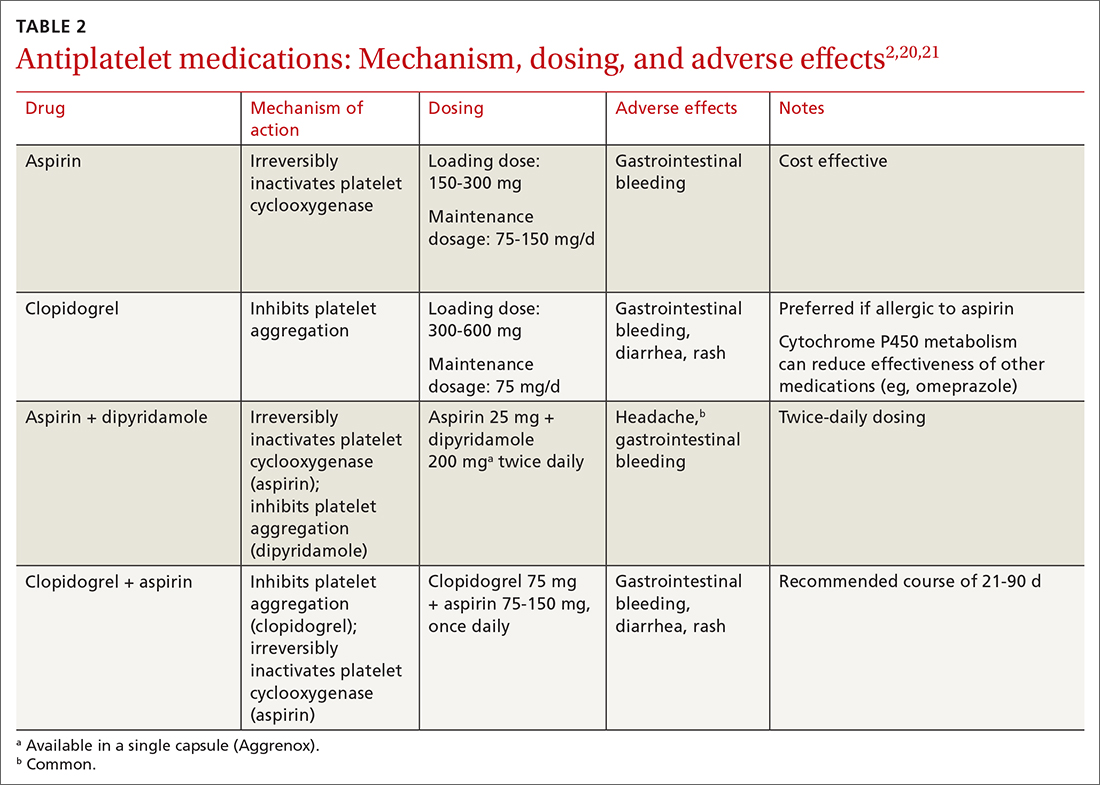
A meta-analysis of antiplatelet therapy reviewed the optimum dosing of each medication.21,22 Reduction of the risk of ischemic stroke with aspirin is 21% to 22% at the optimal dosing of 75 to 150 mg/d, which also reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Continue to: For a patient who has...
For a patient who has an ABCD2 score ≥ 4, has had a prior TIA, or has large-vessel disease, dual antiplatelet therapy is recommended for the first 21 days, with a subsequent return to monotherapy. Dual antiplatelet therapy of clopidogrel + aspirin increases the risk of adverse reactions and has not been shown to have greater long-term benefit23-25 (TABLE 22,20,21).
Step 2: BP management. This is the next immediate step. As many as 80% of patients who present with a TIA have elevated BP upon admission. BP needs to be treated and carefully monitored during this early treatment phase. The recommendation is for a systolic BP < 185 mm Hg and a diastolic BP < 110 mm Hg.24
Step 3: Anticoagulation. Treatment with warfarin or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) is recommended for patients who have the potential for forming emboli—eg, in the setting of atrial fibrillation, ventricular thrombus, mechanical heart valve, or venous thromboembolism.
Step 4. High-intensity statin. A statin agent is recommended as part of immediate and long-term medical management, regardless of the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, to reduce the risk of stroke.2,24
Carotid artery management. Surgical intervention is not always considered a component of immediate medical management. However, guidelines recommend that carotid endarterectomy or stenting be considered in patients who have stenosis > 70%.2
CASE
Mr. L is admitted to the hospital and undergoes neurosurgical intervention. Medical management is instituted.
Long-term management and secondary prevention
The main risk factors for stroke can be divided into modifiable, vascular, and unmodifiable. Addressing both modifiable and vascular risks is important for secondary prevention.
Continue to: Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable risk factors for stroke include hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, and physical activity; the most important of these, for preventing subsequent stroke after an initial TIA, is hypertension.26
The 2 more significant vascular risk factors for stroke are carotid artery stenosis and atrial fibrillation.
Hypertension. Improving control of hypertension can improve secondary risk reduction for recurrent stroke. Control of both systolic and diastolic BP is important in this regard, with larger systolic BP reductions having a greater impact on decreasing the risk of recurrent stroke.24 Evidence supports lowering BP to improve secondary risk reduction in people with and without diagnosed hypertension: The goal is to lower systolic BP by ≥ 10 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 5 mm Hg.24 No particular class of antihypertensive is recommended in the first line, although preliminary evidence shows that a diuretic, with or without an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, might be more beneficial than other options.24
Diabetes. The risk of cardiovascular disease, including stroke, is higher in people with diabetes. Evidence shows that various (but not all) agents in 2 pharmaceutical classes—glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the sodium glucose-2 cotransporter (SGLT2) inhibitors—reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events and improve secondary prevention of recurrent stroke:
- EMPA-REG OUTCOME (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01131676) was the first trial to show cardiovascular benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin); subsequent studies confirmed the cardiovascular benefits found in EMPA-REG OUTCOME.27,28
- The ELIXA trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01147250) was the first to show cardiovascular benefit from a GLP-1 receptor agonist (lixisenatide); subsequent studies supported this finding.29,30
Appropriate agents in these 2 classes should be considered as first-line or adjunctive in patients with both diabetes and known cardiovascular disease, as long as there are no contraindications.27,28
Pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione-class antidiabetic agent, was once considered a potential option to improve secondary prevention of stroke. However, the thiazolidinediones are generally no longer considered; instead, the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are favored.31
Evidence demonstrates the effect of hyperglycemia on cardiovascular events; however, it is important to note that hypoglycemia can result in symptoms and focal changes that mimic a stroke. In addition, some evidence suggests that hypoglycemia can increase cardiovascular risk—thereby supporting the importance of strict control of diabetes and maintenance of euglycemia in reducing overall cardiovascular risk.32
Continue to: Lipids
Lipids. The SPARCL trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00147602) was the first study to demonstrate the benefit of high-intensity statin therapy—specifically, atorvastatin 80 mg/d—for secondary prevention for recurrent stroke.33 The recommendation is to use high-intensity statin therapy to decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by reducing the level of LDL-C—by ≥ 50% or to < 70 mg/dL, for maximum risk reduction.24,34
The IMPROVE-IT trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00202878) demonstrated the benefit of adding ezetimibe, 10 mg/d, to a moderate-to-high-intensity statin (simvastatin, 40-80 mg/d) to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke.35
Results of recent studies support the use of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors for regulating levels of LDL-C, as an additional option to consider—if needed to further reduce the LDL-C level or if statins are contraindicated in a particular patient.34
Smoking cessation. Cigarette smoking is known to increase the risk of ischemic stroke; newer evidence shows that second-hand exposure to smoke also increases the risk of ischemic stroke.36,37 Although these studies focused on primary prevention of ischemic stroke, the data can reasonably be applied to secondary prevention.38 The recommendation for secondary prevention is to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.24
Alcohol. Evidence demonstrates that heavy alcohol consumption and alcoholism increase the risk of stroke; similar to what is known about smoking, most available data relate to primary prevention.38 The recommendation for providing secondary stroke prevention is to stop or decrease alcohol intake.24
Weight reduction. Obesity (body mass index > 30) increases the risk of ischemic stroke. However, there is, as yet, no evidence that weight loss diminishes the risk of subsequent stroke for secondary prevention.24
Physical activity. Aerobic exercise and strength-training programs after a stroke improve cardiovascular health and mobility. There is no evidence that exercise leads to a reduction in the risk of subsequent stroke.24
Continue to: Nutrition
Nutrition. No current randomized controlled trials are focused on the relationship between diet and recurrent stroke for purposes of prevention; however, evidence for both BP and lipid control incorporate dietary guidance. Recommendations include reducing intake of saturated fats and of sodium (the latter, to < 2.3 g/d) and increasing intake of fruits and vegetables, both of which are beneficial for controlling BP and lipid levels and promoting overall cardiovascular health.38
Carotid artery stenosis. Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated benefit from treating carotid stenosis (> 70% stenosis but not < 50%) with carotid endarterectomy to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA.2 The ideal timing of carotid endarterectomy is still being studied; however, available evidence supports intervention within 2 to 6 weeks after TIA or stroke.25 Studies are ongoing that compare carotid angioplasty and stenting against carotid endarterectomy. Medical therapy, with antiplatelet agents and statins, is recommended after carotid endarterectomy.25
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of recurrent stroke after a TIA, and is the most important indication for secondary stroke prevention with anticoagulation therapy:
- Warfarin. Several studies have shown that warfarin provides a 68% relative risk reduction and a 1.4% absolute risk reduction in the annual stroke rate.24 To achieve this reduction in risk, the optimal international normalized ratio is 2.5 (range, 2-3).24
- Aspirin provides a 13% relative risk reduction for recurrent stroke, although there is evidence that long-term anticoagulation provides more benefit than aspirin after a TIA.39-41 Optimal dosing of aspirin ranges from 75-100 mg/d; greatest benefit is likely in the 12 weeks after stroke, when the risk of recurrent stroke is highest.31,41,42
- DOACs have similar efficacy to warfarin but more rapid onset, lower risk of bleeding, fewer drug interactions, and no requirement for monitoring—often making them a more tolerable long-term choice. Options are rivaroxaban 20 mg/d, dabigatran 150 mg twice daily, apixaban 5 mg twice daily, and edoxaban 60 mg/d.39
When to start anticoagulation and the choice of agent should be weighed against a risk of bleeding, which is highest after the initial stroke. Cost is also a consideration: DOACs are more expensive than warfarin.
CASE
Mr. L is discharged 3 days after carotid endarterectomy and free of residual deficits. He is started on dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin + clopidogrel) for 21 days, to be followed by a return to monotherapy. He is restarted on a high-intensity statin. He is instructed to resume taking the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin for sleep, as needed. Last, he is told to schedule follow-up with his primary care physician in 7 to 10 days to begin post-stroke care.
Final thoughts
Primary care physicians are often the first point of contact for patients with current or remote TIA symptoms. Based on that provider–patient relationship, evidence supports several recommendations for diagnosing and treating a TIA and for reducing the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA. Addressing each of these areas, in this order, is imperative to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke and improve overall cardiovascular outcomes:
- Obtain an accurate diagnosis of a TIA, using DW-MRI or comparable brain imaging, to allow for prompt intervention.
- Initiate BP management promptly in the acute setting and establish optimal BP control over the long term.
- Begin appropriate antiplatelet therapy.
- When indicated (eg, atrial fibrillation), begin anticoagulation therapy with a DOAC or warfarin.
- Begin high-intensity statin therapy.
- Consider treating patients with diabetes using an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1 receptor agonist.
- Encourage smoking cessation, prescribe quit-smoking medications, or refer a smoker for behavioral support.
Education. Last, it is important to educate patients—especially those who have risk factors for a TIA or stroke—about the presentation of events, so that they know to seek immediate medical attention.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kristen Rundell, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, 655 North Alvernon Way, Suite 228, Tucson, AZ 85711; [email protected]
1. Kleindorfer D, Panagos P, Pancioli A, et al. Incidence and short-term prognosis of transient ischemic attack in a population-based study. Stroke. 2005;36:720-723. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000158917.59233.b7
2. Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52:e364-e467. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000375
3. Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2009;40:2276-2293. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.192218
4. Thacker EL, Wiggins KL, Rice KM, et al. Short-term and long-term risk of incident ischemic stroke after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2010;41:239-243. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.569707
5. Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T, et al. The high risk of stroke immediately after transient ischemic attack: a population-based study. Neurology. 2004;62:2015-2020. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000129482.70315.2f
6. Giles MF, Albers GW, Amarenco P, et al. Early stroke risk and ABCD2 score performance in tissue- vs time-defined TIA: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2011;77:1222-1228. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182309f91
7. Cucchiara BL, Kasner SE. All patients should be admitted to the hospital after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1446-1447. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636746
8. Amarenco P. Not all patients should be admitted to the hospital for observation after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1448-1449. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636753
9. Amort M, Fluri F, Schäfer J, et al. Transient ischemic attack versus transient ischemic attack mimics: frequency, clinical characteristics and outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:57-64. doi: 10.1159/000327034
10. Hand PJ, Kwan J, Lindley RI, et al. Distinguishing between stroke and mimic at the bedside: The Brain Attack Study. Stroke. 2006;37:769-775. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000204041.13466.4c
11. Shah KH, Edlow JA. Transient ischemic attack: review for the emergency physician. Ann Emerg Med. 2004;43:592-604. doi: 10.1016/S0196064404000058
12. Crisostomo RA, Garcia MM, Tong DC. Detection of diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities in patients with transient ischemic attack: correlation with clinical characteristics. Stroke. 2003;34:932-937. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000061496.00669.5E
13. Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al; ; ; ; ; . Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007;38:1655-1711. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.181486
14. Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN, et al. Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet. 2007;369:283-292. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60150-0
15. Cucchiara BL, Messe SR, Taylor RA, et al. Is the ABCD score useful for risk stratification of patients with acute transient ischemic attack? Stroke. 2006;37:1710-1714. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000227195.46336.93
16. Amarenco P, Lavallée PC, Labreuche J, et al; . One-year risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1533-1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412981
17. Wu CM, McLaughlin K, Lorenzetti DL, et al. Early risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:2417-2422. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.22.2417
18. Rothwell PM, Warlow CP. Timing of TIAs preceding stroke: time window for prevention is very short. Neurology. 2005;64:817-820. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000152985.32732.EE
19. Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160-2236. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000024
20. Rothwell PM, Giles MF, Chandratheva A, et al. Effect of urgent treatment of transient ischaemic attack and minor stroke on early recurrent stroke (EXPRESS study): a prospective population-based sequential comparison. Lancet. 2007;370:1432-1442. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61448-2
21. Hackam DG, Spence JD. Antiplatelet therapy in ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: an overview of major trials and meta-analyses. Stroke. 2019;50:773-778. doi: c10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023954
22. Bhatia K, Jain V, Aggarwal D, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy versus aspirin in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2021;52:e217-e223. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.033033
23. Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhao X, et al; CHANCE Investigators. Clopidogrel with aspirin in acute minor stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHANCE) trial: one-year outcomes. Circulation. 2015;132:40-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014791
24. Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, et al; . Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:227-276. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3181f7d043
25. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49:e46-e110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158
26. O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, et al; INTERSTROKE Investigators. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet. 2016;388:761-775. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30506-2
27. Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:776-785. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9
28. Bertoccini L, Baroni MG. GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: new insights and opportunities for cardiovascular protection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1307:193-212. doi:10.1007/5584_2020_494
29. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al; ELIXA Investigators. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2247-2257. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509225
30. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP-1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J. 2020;96:156-161. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-137186
31. Kim AS. Medical management for secondary stroke prevention. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2020;26:435-456. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000849
32. Smith L, Chakraborty D, Bhattacharya P, et al. Exposure to hypoglycemia and risk of stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1431:25-34. doi:10.1111/nyas.13872
33. Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A 3rd, et al; . High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:549-559. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061894
34. Castilla-Guerra, L, Fernandez-Moreno M, Leon-Jimenez D, et al. Statins in ischemic stroke prevention: what have we learned in the post-SPARCL (The Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels) decade? Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21:22. doi: 10.1007/s11940-019-0563-4
35. Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, Giugliano RP, et al. Prevention of stroke with the addition of ezetimibe to statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome in IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation. 2017;136:2440-2450. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029095
36. Moritsugu KP. The 2006 report of the Surgeon General: the health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke. Am J Prev Med. 20067;32:542-543. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.02.026
37. Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Kannel WB, et al. Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. JAMA. 1988;259:1025-1029.
38. Goldstein LB, Adams R, Alberts MJ, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council: cosponsored by the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Interdisciplinary Working Group; Cardiovascular Nursing Council; Clinical Cardiology Council; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Council; and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke. 2006;37:1583-1633. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000223048.70103.F1
39. Klijn CJ, Paciaroni M, Berge E, et al. Antithrombotic treatment for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack and non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A European Stroke Organisation guideline. Eur Stroke J. 2019;4:198-223. doi:10.1177/2396987319841187
40. Antithrombotic Trialists’ (ATT) Collaboration; Baigent C, Blackwell L, Collins R, et al. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2009;373:1849-1860. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1
41. Singer DE, Albers GW, Dalen JE, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 suppl):546S–592S. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0678
42. Rothwell PM, Algra A, Chen Z, et al. Effects of aspirin on risk and severity of early recurrent stroke after transient ischaemic attack and ischaemic stroke: time-course analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;388:365-375. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30468-8
As many as 240,000 people per year in the United States experience a transient ischemic attack (TIA),1,2 which is now defined by the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association as a “transient episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord, or retinal ischemia, without acute infarction.”3 An older definition of TIA was based on the duration of the event (ie, resolution of symptoms at 24 hours); in the updated (2009) definition, the diagnostic criterion is the extent of focal tissue damage.3 Using the 2009 definition might mean a decrease in the number of patients who have a diagnosis of a TIA and an increase in the number who are determined to have had a stroke because an infarction is found on initial imaging.
Guided by the 2009 revised definition of a TIA, we review here the work-up and treatment of TIA, emphasizing immediacy of management to (1) prevent further tissue damage and (2) decrease the risk of a second event.

CASE
Martin L, 69 years old, retired, a nonsmoker, and with a history of peripheral arterial disease and hypercholesterolemia, presents to the emergency department (ED) of a rural hospital complaining of slurred speech and left-side facial numbness. He had an episode of facial numbness that lasted 30 minutes, then resolved, each of the 2 previous evenings; he did not seek care at those times. Now, in the ED, Mr. L is normotensive.
The patient’s medication history includes a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin to improve sleep. He reports having discontinued a statin because he could not tolerate its adverse effects.
What immediate steps are recommended for Mr. L’s care?
Common event callsfor quick action
A TIA is the strongest predictor of subsequent stroke and stroke-related death; the highest period of risk of these devastating outcomes is immediately following a TIA.1,2,4,5 It is essential, therefore, for the physician who sees a patient with a current complaint or recent history of suspected focal neurologic deficits to direct that patient to an ED for an accurate diagnosis and, as appropriate, early treatment for the best possible outcome.
Imaging—preferably, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI), the gold standard for diagnosing stroke (see “Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics”)2,3—should be performed as soon as the patient with a suspected TIA arrives in the ED. Imaging should not be held while waiting for a stroke to declare itself—ie, by allowing symptoms to persist for longer than 24 hours. 6
Continue to: Late presentation
Late presentation. Some patients present ≥ 48 hours after onset of early symptoms of a TIA; for them, the work-up is the same as for prompt presentation but can be completed in the outpatient clinic—as long as the patient is stable clinically and imaging is accessible there. DW-MRI should be completed within 48 hours after late presentation. In such cases, the patient should be cautioned regarding risks and any recurrence of symptoms.7,8
Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics
All patients in whom a stroke is suspected should be evaluated on an emergency basis with brain imaging upon arrival at the hospital, before any therapy is initiated. As noted, DW-MRI is the preferred modality; noncontrast computed tomography (CT) or CT angiography can be used if MRI is unavailable.2,3
Mimics. Stroke has many mimics; quickly eliminating them from the differential diagnosis is important so that appropriate therapy can be initiated. Mimics usually have a prolonged presentation of symptoms, whereas the presentation of a TIA is usually abrupt. The 3 more common diagnoses that mimic a TIA are migraine with aura, seizure, and syncope.9,10 Symptoms that generally are not associated with a TIA are chest pain, generalized weakness, and confusion.11 A complete history and physical exam provide the path to the imaging, laboratory, and cardiac testing that is needed to differentiate these diagnoses from a TIA.
A thorough history is best obtained from the patient and a witness, if available, and should include identification of any focal neurologic deficits and the duration and time to resolution of symptoms. Obtain a history of risk factors for ischemia—tobacco use, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, previous TIA or stroke, atrial fibrillation, and any coagulopathy. Ask questions about a family history of TIA, stroke, and coagulopathy.11
A comprehensive physical exam, including vital signs, cardiac exam, a check for carotid bruits, and complete neurologic exam, should be performed. Most patients present with concerns for unilateral weakness and changes in speech, which are usually associated with infarction on DW-MRI.12 The most common findings on physical exam include cranial nerve abnormalities, such as diplopia, hemianopia, monocular blindness, disconjugate gaze, facial drooping, lateral tongue movement, dysphagia, and vestibular dysfunction. Cerebellar abnormalities are also often noted, including past pointing, dystaxia, ataxia, nystagmus, and motor abnormalities (eg, spasticity, clonus, or unilateral weakness in the face or extremities).11
Electrocardiography at the bedside can confirm atrial fibrillation or another arrhythmia quickly.
Essential laboratory testing includes measurement of blood glucose and serum electrolytes to determine if these particular imbalances are the cause of symptoms. The presence of a hypercoaguable state is determined by a complete blood count and coagulation studies.3,13 Urine toxicology should also be obtained to rule out other causes of symptoms. A lipid profile is beneficial for making long-term treatment decisions.
Continue to: ABCD2 score
ABCD2 score. Patients who have had a TIA and present within 72 hours after symptoms have resolved should be hospitalized if they have an ABCD2 (Age, Blood pressure [BP], Clinical presentation, Diabetes mellitus [type 1 or 2], Duration of symptoms) prediction system score > 3.14 ABCD2 criteria can be used to help identify patients who are at higher risk of stroke or need further therapy (TABLE 1).14,15

The ABCD2 score is also used to determine whether a patient needs dual antiplatelet therapy. Patients who score at the higher end of the ABCD2 system usually have an increased risk of stroke, longer hospitalization, and greater disability.
CASE
In the ED, Mr. L is immediately assessed and airlifted to a larger regional medical center, where MRI confirms a stroke.
Management
Initial management of a TIA is aimed at reducing the risk of recurrent TIA or stroke. Early medical and possibly surgical treatment are key for preventing stroke and improving outcomes. The first 48 hours after a TIA are the most critical because the incidence of recurrent TIA or stroke is highest during this period.16-18
What is the accepted strategy for early treatment?
Initial treatment must include antiplatelet therapy, BP management, anticoagulation, statin therapy, and carotid endarterectomy as indicated.2,19,20 Control of hypertension and anticoagulation decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by the largest margin20; both are “A”-level Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy interventions.2,3
Step 1: Antiplatelet therapy. After initial imaging is complete and if there are no contraindications, antiplatelet agents are recommended for patients who have had a noncardioembolic TIA. The American Heart Association and American Stroke Association recommend either aspirin, clopidogrel, dipyridamole + aspirin (available in a single capsule [Aggrenox]), or clopidogrel + aspirin as first-line therapy.2,20 The choice of agent needs to be individualized, based on tolerability and adverse effects (TABLE 22,20,21).

A meta-analysis of antiplatelet therapy reviewed the optimum dosing of each medication.21,22 Reduction of the risk of ischemic stroke with aspirin is 21% to 22% at the optimal dosing of 75 to 150 mg/d, which also reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Continue to: For a patient who has...
For a patient who has an ABCD2 score ≥ 4, has had a prior TIA, or has large-vessel disease, dual antiplatelet therapy is recommended for the first 21 days, with a subsequent return to monotherapy. Dual antiplatelet therapy of clopidogrel + aspirin increases the risk of adverse reactions and has not been shown to have greater long-term benefit23-25 (TABLE 22,20,21).
Step 2: BP management. This is the next immediate step. As many as 80% of patients who present with a TIA have elevated BP upon admission. BP needs to be treated and carefully monitored during this early treatment phase. The recommendation is for a systolic BP < 185 mm Hg and a diastolic BP < 110 mm Hg.24
Step 3: Anticoagulation. Treatment with warfarin or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) is recommended for patients who have the potential for forming emboli—eg, in the setting of atrial fibrillation, ventricular thrombus, mechanical heart valve, or venous thromboembolism.
Step 4. High-intensity statin. A statin agent is recommended as part of immediate and long-term medical management, regardless of the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, to reduce the risk of stroke.2,24
Carotid artery management. Surgical intervention is not always considered a component of immediate medical management. However, guidelines recommend that carotid endarterectomy or stenting be considered in patients who have stenosis > 70%.2
CASE
Mr. L is admitted to the hospital and undergoes neurosurgical intervention. Medical management is instituted.
Long-term management and secondary prevention
The main risk factors for stroke can be divided into modifiable, vascular, and unmodifiable. Addressing both modifiable and vascular risks is important for secondary prevention.
Continue to: Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable risk factors for stroke include hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, and physical activity; the most important of these, for preventing subsequent stroke after an initial TIA, is hypertension.26
The 2 more significant vascular risk factors for stroke are carotid artery stenosis and atrial fibrillation.
Hypertension. Improving control of hypertension can improve secondary risk reduction for recurrent stroke. Control of both systolic and diastolic BP is important in this regard, with larger systolic BP reductions having a greater impact on decreasing the risk of recurrent stroke.24 Evidence supports lowering BP to improve secondary risk reduction in people with and without diagnosed hypertension: The goal is to lower systolic BP by ≥ 10 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 5 mm Hg.24 No particular class of antihypertensive is recommended in the first line, although preliminary evidence shows that a diuretic, with or without an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, might be more beneficial than other options.24
Diabetes. The risk of cardiovascular disease, including stroke, is higher in people with diabetes. Evidence shows that various (but not all) agents in 2 pharmaceutical classes—glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the sodium glucose-2 cotransporter (SGLT2) inhibitors—reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events and improve secondary prevention of recurrent stroke:
- EMPA-REG OUTCOME (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01131676) was the first trial to show cardiovascular benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin); subsequent studies confirmed the cardiovascular benefits found in EMPA-REG OUTCOME.27,28
- The ELIXA trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01147250) was the first to show cardiovascular benefit from a GLP-1 receptor agonist (lixisenatide); subsequent studies supported this finding.29,30
Appropriate agents in these 2 classes should be considered as first-line or adjunctive in patients with both diabetes and known cardiovascular disease, as long as there are no contraindications.27,28
Pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione-class antidiabetic agent, was once considered a potential option to improve secondary prevention of stroke. However, the thiazolidinediones are generally no longer considered; instead, the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are favored.31
Evidence demonstrates the effect of hyperglycemia on cardiovascular events; however, it is important to note that hypoglycemia can result in symptoms and focal changes that mimic a stroke. In addition, some evidence suggests that hypoglycemia can increase cardiovascular risk—thereby supporting the importance of strict control of diabetes and maintenance of euglycemia in reducing overall cardiovascular risk.32
Continue to: Lipids
Lipids. The SPARCL trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00147602) was the first study to demonstrate the benefit of high-intensity statin therapy—specifically, atorvastatin 80 mg/d—for secondary prevention for recurrent stroke.33 The recommendation is to use high-intensity statin therapy to decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by reducing the level of LDL-C—by ≥ 50% or to < 70 mg/dL, for maximum risk reduction.24,34
The IMPROVE-IT trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00202878) demonstrated the benefit of adding ezetimibe, 10 mg/d, to a moderate-to-high-intensity statin (simvastatin, 40-80 mg/d) to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke.35
Results of recent studies support the use of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors for regulating levels of LDL-C, as an additional option to consider—if needed to further reduce the LDL-C level or if statins are contraindicated in a particular patient.34
Smoking cessation. Cigarette smoking is known to increase the risk of ischemic stroke; newer evidence shows that second-hand exposure to smoke also increases the risk of ischemic stroke.36,37 Although these studies focused on primary prevention of ischemic stroke, the data can reasonably be applied to secondary prevention.38 The recommendation for secondary prevention is to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.24
Alcohol. Evidence demonstrates that heavy alcohol consumption and alcoholism increase the risk of stroke; similar to what is known about smoking, most available data relate to primary prevention.38 The recommendation for providing secondary stroke prevention is to stop or decrease alcohol intake.24
Weight reduction. Obesity (body mass index > 30) increases the risk of ischemic stroke. However, there is, as yet, no evidence that weight loss diminishes the risk of subsequent stroke for secondary prevention.24
Physical activity. Aerobic exercise and strength-training programs after a stroke improve cardiovascular health and mobility. There is no evidence that exercise leads to a reduction in the risk of subsequent stroke.24
Continue to: Nutrition
Nutrition. No current randomized controlled trials are focused on the relationship between diet and recurrent stroke for purposes of prevention; however, evidence for both BP and lipid control incorporate dietary guidance. Recommendations include reducing intake of saturated fats and of sodium (the latter, to < 2.3 g/d) and increasing intake of fruits and vegetables, both of which are beneficial for controlling BP and lipid levels and promoting overall cardiovascular health.38
Carotid artery stenosis. Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated benefit from treating carotid stenosis (> 70% stenosis but not < 50%) with carotid endarterectomy to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA.2 The ideal timing of carotid endarterectomy is still being studied; however, available evidence supports intervention within 2 to 6 weeks after TIA or stroke.25 Studies are ongoing that compare carotid angioplasty and stenting against carotid endarterectomy. Medical therapy, with antiplatelet agents and statins, is recommended after carotid endarterectomy.25
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of recurrent stroke after a TIA, and is the most important indication for secondary stroke prevention with anticoagulation therapy:
- Warfarin. Several studies have shown that warfarin provides a 68% relative risk reduction and a 1.4% absolute risk reduction in the annual stroke rate.24 To achieve this reduction in risk, the optimal international normalized ratio is 2.5 (range, 2-3).24
- Aspirin provides a 13% relative risk reduction for recurrent stroke, although there is evidence that long-term anticoagulation provides more benefit than aspirin after a TIA.39-41 Optimal dosing of aspirin ranges from 75-100 mg/d; greatest benefit is likely in the 12 weeks after stroke, when the risk of recurrent stroke is highest.31,41,42
- DOACs have similar efficacy to warfarin but more rapid onset, lower risk of bleeding, fewer drug interactions, and no requirement for monitoring—often making them a more tolerable long-term choice. Options are rivaroxaban 20 mg/d, dabigatran 150 mg twice daily, apixaban 5 mg twice daily, and edoxaban 60 mg/d.39
When to start anticoagulation and the choice of agent should be weighed against a risk of bleeding, which is highest after the initial stroke. Cost is also a consideration: DOACs are more expensive than warfarin.
CASE
Mr. L is discharged 3 days after carotid endarterectomy and free of residual deficits. He is started on dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin + clopidogrel) for 21 days, to be followed by a return to monotherapy. He is restarted on a high-intensity statin. He is instructed to resume taking the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin for sleep, as needed. Last, he is told to schedule follow-up with his primary care physician in 7 to 10 days to begin post-stroke care.
Final thoughts
Primary care physicians are often the first point of contact for patients with current or remote TIA symptoms. Based on that provider–patient relationship, evidence supports several recommendations for diagnosing and treating a TIA and for reducing the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA. Addressing each of these areas, in this order, is imperative to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke and improve overall cardiovascular outcomes:
- Obtain an accurate diagnosis of a TIA, using DW-MRI or comparable brain imaging, to allow for prompt intervention.
- Initiate BP management promptly in the acute setting and establish optimal BP control over the long term.
- Begin appropriate antiplatelet therapy.
- When indicated (eg, atrial fibrillation), begin anticoagulation therapy with a DOAC or warfarin.
- Begin high-intensity statin therapy.
- Consider treating patients with diabetes using an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1 receptor agonist.
- Encourage smoking cessation, prescribe quit-smoking medications, or refer a smoker for behavioral support.
Education. Last, it is important to educate patients—especially those who have risk factors for a TIA or stroke—about the presentation of events, so that they know to seek immediate medical attention.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kristen Rundell, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, 655 North Alvernon Way, Suite 228, Tucson, AZ 85711; [email protected]
As many as 240,000 people per year in the United States experience a transient ischemic attack (TIA),1,2 which is now defined by the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association as a “transient episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord, or retinal ischemia, without acute infarction.”3 An older definition of TIA was based on the duration of the event (ie, resolution of symptoms at 24 hours); in the updated (2009) definition, the diagnostic criterion is the extent of focal tissue damage.3 Using the 2009 definition might mean a decrease in the number of patients who have a diagnosis of a TIA and an increase in the number who are determined to have had a stroke because an infarction is found on initial imaging.
Guided by the 2009 revised definition of a TIA, we review here the work-up and treatment of TIA, emphasizing immediacy of management to (1) prevent further tissue damage and (2) decrease the risk of a second event.

CASE
Martin L, 69 years old, retired, a nonsmoker, and with a history of peripheral arterial disease and hypercholesterolemia, presents to the emergency department (ED) of a rural hospital complaining of slurred speech and left-side facial numbness. He had an episode of facial numbness that lasted 30 minutes, then resolved, each of the 2 previous evenings; he did not seek care at those times. Now, in the ED, Mr. L is normotensive.
The patient’s medication history includes a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin to improve sleep. He reports having discontinued a statin because he could not tolerate its adverse effects.
What immediate steps are recommended for Mr. L’s care?
Common event callsfor quick action
A TIA is the strongest predictor of subsequent stroke and stroke-related death; the highest period of risk of these devastating outcomes is immediately following a TIA.1,2,4,5 It is essential, therefore, for the physician who sees a patient with a current complaint or recent history of suspected focal neurologic deficits to direct that patient to an ED for an accurate diagnosis and, as appropriate, early treatment for the best possible outcome.
Imaging—preferably, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI), the gold standard for diagnosing stroke (see “Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics”)2,3—should be performed as soon as the patient with a suspected TIA arrives in the ED. Imaging should not be held while waiting for a stroke to declare itself—ie, by allowing symptoms to persist for longer than 24 hours. 6
Continue to: Late presentation
Late presentation. Some patients present ≥ 48 hours after onset of early symptoms of a TIA; for them, the work-up is the same as for prompt presentation but can be completed in the outpatient clinic—as long as the patient is stable clinically and imaging is accessible there. DW-MRI should be completed within 48 hours after late presentation. In such cases, the patient should be cautioned regarding risks and any recurrence of symptoms.7,8
Diagnosis includes ruling out mimics
All patients in whom a stroke is suspected should be evaluated on an emergency basis with brain imaging upon arrival at the hospital, before any therapy is initiated. As noted, DW-MRI is the preferred modality; noncontrast computed tomography (CT) or CT angiography can be used if MRI is unavailable.2,3
Mimics. Stroke has many mimics; quickly eliminating them from the differential diagnosis is important so that appropriate therapy can be initiated. Mimics usually have a prolonged presentation of symptoms, whereas the presentation of a TIA is usually abrupt. The 3 more common diagnoses that mimic a TIA are migraine with aura, seizure, and syncope.9,10 Symptoms that generally are not associated with a TIA are chest pain, generalized weakness, and confusion.11 A complete history and physical exam provide the path to the imaging, laboratory, and cardiac testing that is needed to differentiate these diagnoses from a TIA.
A thorough history is best obtained from the patient and a witness, if available, and should include identification of any focal neurologic deficits and the duration and time to resolution of symptoms. Obtain a history of risk factors for ischemia—tobacco use, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, previous TIA or stroke, atrial fibrillation, and any coagulopathy. Ask questions about a family history of TIA, stroke, and coagulopathy.11
A comprehensive physical exam, including vital signs, cardiac exam, a check for carotid bruits, and complete neurologic exam, should be performed. Most patients present with concerns for unilateral weakness and changes in speech, which are usually associated with infarction on DW-MRI.12 The most common findings on physical exam include cranial nerve abnormalities, such as diplopia, hemianopia, monocular blindness, disconjugate gaze, facial drooping, lateral tongue movement, dysphagia, and vestibular dysfunction. Cerebellar abnormalities are also often noted, including past pointing, dystaxia, ataxia, nystagmus, and motor abnormalities (eg, spasticity, clonus, or unilateral weakness in the face or extremities).11
Electrocardiography at the bedside can confirm atrial fibrillation or another arrhythmia quickly.
Essential laboratory testing includes measurement of blood glucose and serum electrolytes to determine if these particular imbalances are the cause of symptoms. The presence of a hypercoaguable state is determined by a complete blood count and coagulation studies.3,13 Urine toxicology should also be obtained to rule out other causes of symptoms. A lipid profile is beneficial for making long-term treatment decisions.
Continue to: ABCD2 score
ABCD2 score. Patients who have had a TIA and present within 72 hours after symptoms have resolved should be hospitalized if they have an ABCD2 (Age, Blood pressure [BP], Clinical presentation, Diabetes mellitus [type 1 or 2], Duration of symptoms) prediction system score > 3.14 ABCD2 criteria can be used to help identify patients who are at higher risk of stroke or need further therapy (TABLE 1).14,15

The ABCD2 score is also used to determine whether a patient needs dual antiplatelet therapy. Patients who score at the higher end of the ABCD2 system usually have an increased risk of stroke, longer hospitalization, and greater disability.
CASE
In the ED, Mr. L is immediately assessed and airlifted to a larger regional medical center, where MRI confirms a stroke.
Management
Initial management of a TIA is aimed at reducing the risk of recurrent TIA or stroke. Early medical and possibly surgical treatment are key for preventing stroke and improving outcomes. The first 48 hours after a TIA are the most critical because the incidence of recurrent TIA or stroke is highest during this period.16-18
What is the accepted strategy for early treatment?
Initial treatment must include antiplatelet therapy, BP management, anticoagulation, statin therapy, and carotid endarterectomy as indicated.2,19,20 Control of hypertension and anticoagulation decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by the largest margin20; both are “A”-level Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy interventions.2,3
Step 1: Antiplatelet therapy. After initial imaging is complete and if there are no contraindications, antiplatelet agents are recommended for patients who have had a noncardioembolic TIA. The American Heart Association and American Stroke Association recommend either aspirin, clopidogrel, dipyridamole + aspirin (available in a single capsule [Aggrenox]), or clopidogrel + aspirin as first-line therapy.2,20 The choice of agent needs to be individualized, based on tolerability and adverse effects (TABLE 22,20,21).

A meta-analysis of antiplatelet therapy reviewed the optimum dosing of each medication.21,22 Reduction of the risk of ischemic stroke with aspirin is 21% to 22% at the optimal dosing of 75 to 150 mg/d, which also reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Continue to: For a patient who has...
For a patient who has an ABCD2 score ≥ 4, has had a prior TIA, or has large-vessel disease, dual antiplatelet therapy is recommended for the first 21 days, with a subsequent return to monotherapy. Dual antiplatelet therapy of clopidogrel + aspirin increases the risk of adverse reactions and has not been shown to have greater long-term benefit23-25 (TABLE 22,20,21).
Step 2: BP management. This is the next immediate step. As many as 80% of patients who present with a TIA have elevated BP upon admission. BP needs to be treated and carefully monitored during this early treatment phase. The recommendation is for a systolic BP < 185 mm Hg and a diastolic BP < 110 mm Hg.24
Step 3: Anticoagulation. Treatment with warfarin or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) is recommended for patients who have the potential for forming emboli—eg, in the setting of atrial fibrillation, ventricular thrombus, mechanical heart valve, or venous thromboembolism.
Step 4. High-intensity statin. A statin agent is recommended as part of immediate and long-term medical management, regardless of the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, to reduce the risk of stroke.2,24
Carotid artery management. Surgical intervention is not always considered a component of immediate medical management. However, guidelines recommend that carotid endarterectomy or stenting be considered in patients who have stenosis > 70%.2
CASE
Mr. L is admitted to the hospital and undergoes neurosurgical intervention. Medical management is instituted.
Long-term management and secondary prevention
The main risk factors for stroke can be divided into modifiable, vascular, and unmodifiable. Addressing both modifiable and vascular risks is important for secondary prevention.
Continue to: Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable and vascular risk factors
Modifiable risk factors for stroke include hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, and physical activity; the most important of these, for preventing subsequent stroke after an initial TIA, is hypertension.26
The 2 more significant vascular risk factors for stroke are carotid artery stenosis and atrial fibrillation.
Hypertension. Improving control of hypertension can improve secondary risk reduction for recurrent stroke. Control of both systolic and diastolic BP is important in this regard, with larger systolic BP reductions having a greater impact on decreasing the risk of recurrent stroke.24 Evidence supports lowering BP to improve secondary risk reduction in people with and without diagnosed hypertension: The goal is to lower systolic BP by ≥ 10 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 5 mm Hg.24 No particular class of antihypertensive is recommended in the first line, although preliminary evidence shows that a diuretic, with or without an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, might be more beneficial than other options.24
Diabetes. The risk of cardiovascular disease, including stroke, is higher in people with diabetes. Evidence shows that various (but not all) agents in 2 pharmaceutical classes—glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the sodium glucose-2 cotransporter (SGLT2) inhibitors—reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events and improve secondary prevention of recurrent stroke:
- EMPA-REG OUTCOME (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01131676) was the first trial to show cardiovascular benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin); subsequent studies confirmed the cardiovascular benefits found in EMPA-REG OUTCOME.27,28
- The ELIXA trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01147250) was the first to show cardiovascular benefit from a GLP-1 receptor agonist (lixisenatide); subsequent studies supported this finding.29,30
Appropriate agents in these 2 classes should be considered as first-line or adjunctive in patients with both diabetes and known cardiovascular disease, as long as there are no contraindications.27,28
Pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione-class antidiabetic agent, was once considered a potential option to improve secondary prevention of stroke. However, the thiazolidinediones are generally no longer considered; instead, the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are favored.31
Evidence demonstrates the effect of hyperglycemia on cardiovascular events; however, it is important to note that hypoglycemia can result in symptoms and focal changes that mimic a stroke. In addition, some evidence suggests that hypoglycemia can increase cardiovascular risk—thereby supporting the importance of strict control of diabetes and maintenance of euglycemia in reducing overall cardiovascular risk.32
Continue to: Lipids
Lipids. The SPARCL trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00147602) was the first study to demonstrate the benefit of high-intensity statin therapy—specifically, atorvastatin 80 mg/d—for secondary prevention for recurrent stroke.33 The recommendation is to use high-intensity statin therapy to decrease the risk of recurrent stroke by reducing the level of LDL-C—by ≥ 50% or to < 70 mg/dL, for maximum risk reduction.24,34
The IMPROVE-IT trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00202878) demonstrated the benefit of adding ezetimibe, 10 mg/d, to a moderate-to-high-intensity statin (simvastatin, 40-80 mg/d) to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke.35
Results of recent studies support the use of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors for regulating levels of LDL-C, as an additional option to consider—if needed to further reduce the LDL-C level or if statins are contraindicated in a particular patient.34
Smoking cessation. Cigarette smoking is known to increase the risk of ischemic stroke; newer evidence shows that second-hand exposure to smoke also increases the risk of ischemic stroke.36,37 Although these studies focused on primary prevention of ischemic stroke, the data can reasonably be applied to secondary prevention.38 The recommendation for secondary prevention is to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.24
Alcohol. Evidence demonstrates that heavy alcohol consumption and alcoholism increase the risk of stroke; similar to what is known about smoking, most available data relate to primary prevention.38 The recommendation for providing secondary stroke prevention is to stop or decrease alcohol intake.24
Weight reduction. Obesity (body mass index > 30) increases the risk of ischemic stroke. However, there is, as yet, no evidence that weight loss diminishes the risk of subsequent stroke for secondary prevention.24
Physical activity. Aerobic exercise and strength-training programs after a stroke improve cardiovascular health and mobility. There is no evidence that exercise leads to a reduction in the risk of subsequent stroke.24
Continue to: Nutrition
Nutrition. No current randomized controlled trials are focused on the relationship between diet and recurrent stroke for purposes of prevention; however, evidence for both BP and lipid control incorporate dietary guidance. Recommendations include reducing intake of saturated fats and of sodium (the latter, to < 2.3 g/d) and increasing intake of fruits and vegetables, both of which are beneficial for controlling BP and lipid levels and promoting overall cardiovascular health.38
Carotid artery stenosis. Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated benefit from treating carotid stenosis (> 70% stenosis but not < 50%) with carotid endarterectomy to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA.2 The ideal timing of carotid endarterectomy is still being studied; however, available evidence supports intervention within 2 to 6 weeks after TIA or stroke.25 Studies are ongoing that compare carotid angioplasty and stenting against carotid endarterectomy. Medical therapy, with antiplatelet agents and statins, is recommended after carotid endarterectomy.25
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of recurrent stroke after a TIA, and is the most important indication for secondary stroke prevention with anticoagulation therapy:
- Warfarin. Several studies have shown that warfarin provides a 68% relative risk reduction and a 1.4% absolute risk reduction in the annual stroke rate.24 To achieve this reduction in risk, the optimal international normalized ratio is 2.5 (range, 2-3).24
- Aspirin provides a 13% relative risk reduction for recurrent stroke, although there is evidence that long-term anticoagulation provides more benefit than aspirin after a TIA.39-41 Optimal dosing of aspirin ranges from 75-100 mg/d; greatest benefit is likely in the 12 weeks after stroke, when the risk of recurrent stroke is highest.31,41,42
- DOACs have similar efficacy to warfarin but more rapid onset, lower risk of bleeding, fewer drug interactions, and no requirement for monitoring—often making them a more tolerable long-term choice. Options are rivaroxaban 20 mg/d, dabigatran 150 mg twice daily, apixaban 5 mg twice daily, and edoxaban 60 mg/d.39
When to start anticoagulation and the choice of agent should be weighed against a risk of bleeding, which is highest after the initial stroke. Cost is also a consideration: DOACs are more expensive than warfarin.
CASE
Mr. L is discharged 3 days after carotid endarterectomy and free of residual deficits. He is started on dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin + clopidogrel) for 21 days, to be followed by a return to monotherapy. He is restarted on a high-intensity statin. He is instructed to resume taking the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and melatonin for sleep, as needed. Last, he is told to schedule follow-up with his primary care physician in 7 to 10 days to begin post-stroke care.
Final thoughts
Primary care physicians are often the first point of contact for patients with current or remote TIA symptoms. Based on that provider–patient relationship, evidence supports several recommendations for diagnosing and treating a TIA and for reducing the risk of recurrent stroke after TIA. Addressing each of these areas, in this order, is imperative to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke and improve overall cardiovascular outcomes:
- Obtain an accurate diagnosis of a TIA, using DW-MRI or comparable brain imaging, to allow for prompt intervention.
- Initiate BP management promptly in the acute setting and establish optimal BP control over the long term.
- Begin appropriate antiplatelet therapy.
- When indicated (eg, atrial fibrillation), begin anticoagulation therapy with a DOAC or warfarin.
- Begin high-intensity statin therapy.
- Consider treating patients with diabetes using an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1 receptor agonist.
- Encourage smoking cessation, prescribe quit-smoking medications, or refer a smoker for behavioral support.
Education. Last, it is important to educate patients—especially those who have risk factors for a TIA or stroke—about the presentation of events, so that they know to seek immediate medical attention.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kristen Rundell, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, 655 North Alvernon Way, Suite 228, Tucson, AZ 85711; [email protected]
1. Kleindorfer D, Panagos P, Pancioli A, et al. Incidence and short-term prognosis of transient ischemic attack in a population-based study. Stroke. 2005;36:720-723. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000158917.59233.b7
2. Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52:e364-e467. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000375
3. Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2009;40:2276-2293. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.192218
4. Thacker EL, Wiggins KL, Rice KM, et al. Short-term and long-term risk of incident ischemic stroke after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2010;41:239-243. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.569707
5. Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T, et al. The high risk of stroke immediately after transient ischemic attack: a population-based study. Neurology. 2004;62:2015-2020. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000129482.70315.2f
6. Giles MF, Albers GW, Amarenco P, et al. Early stroke risk and ABCD2 score performance in tissue- vs time-defined TIA: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2011;77:1222-1228. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182309f91
7. Cucchiara BL, Kasner SE. All patients should be admitted to the hospital after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1446-1447. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636746
8. Amarenco P. Not all patients should be admitted to the hospital for observation after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1448-1449. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636753
9. Amort M, Fluri F, Schäfer J, et al. Transient ischemic attack versus transient ischemic attack mimics: frequency, clinical characteristics and outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:57-64. doi: 10.1159/000327034
10. Hand PJ, Kwan J, Lindley RI, et al. Distinguishing between stroke and mimic at the bedside: The Brain Attack Study. Stroke. 2006;37:769-775. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000204041.13466.4c
11. Shah KH, Edlow JA. Transient ischemic attack: review for the emergency physician. Ann Emerg Med. 2004;43:592-604. doi: 10.1016/S0196064404000058
12. Crisostomo RA, Garcia MM, Tong DC. Detection of diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities in patients with transient ischemic attack: correlation with clinical characteristics. Stroke. 2003;34:932-937. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000061496.00669.5E
13. Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al; ; ; ; ; . Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007;38:1655-1711. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.181486
14. Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN, et al. Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet. 2007;369:283-292. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60150-0
15. Cucchiara BL, Messe SR, Taylor RA, et al. Is the ABCD score useful for risk stratification of patients with acute transient ischemic attack? Stroke. 2006;37:1710-1714. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000227195.46336.93
16. Amarenco P, Lavallée PC, Labreuche J, et al; . One-year risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1533-1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412981
17. Wu CM, McLaughlin K, Lorenzetti DL, et al. Early risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:2417-2422. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.22.2417
18. Rothwell PM, Warlow CP. Timing of TIAs preceding stroke: time window for prevention is very short. Neurology. 2005;64:817-820. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000152985.32732.EE
19. Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160-2236. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000024
20. Rothwell PM, Giles MF, Chandratheva A, et al. Effect of urgent treatment of transient ischaemic attack and minor stroke on early recurrent stroke (EXPRESS study): a prospective population-based sequential comparison. Lancet. 2007;370:1432-1442. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61448-2
21. Hackam DG, Spence JD. Antiplatelet therapy in ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: an overview of major trials and meta-analyses. Stroke. 2019;50:773-778. doi: c10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023954
22. Bhatia K, Jain V, Aggarwal D, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy versus aspirin in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2021;52:e217-e223. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.033033
23. Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhao X, et al; CHANCE Investigators. Clopidogrel with aspirin in acute minor stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHANCE) trial: one-year outcomes. Circulation. 2015;132:40-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014791
24. Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, et al; . Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:227-276. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3181f7d043
25. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49:e46-e110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158
26. O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, et al; INTERSTROKE Investigators. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet. 2016;388:761-775. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30506-2
27. Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:776-785. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9
28. Bertoccini L, Baroni MG. GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: new insights and opportunities for cardiovascular protection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1307:193-212. doi:10.1007/5584_2020_494
29. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al; ELIXA Investigators. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2247-2257. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509225
30. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP-1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J. 2020;96:156-161. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-137186
31. Kim AS. Medical management for secondary stroke prevention. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2020;26:435-456. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000849
32. Smith L, Chakraborty D, Bhattacharya P, et al. Exposure to hypoglycemia and risk of stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1431:25-34. doi:10.1111/nyas.13872
33. Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A 3rd, et al; . High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:549-559. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061894
34. Castilla-Guerra, L, Fernandez-Moreno M, Leon-Jimenez D, et al. Statins in ischemic stroke prevention: what have we learned in the post-SPARCL (The Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels) decade? Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21:22. doi: 10.1007/s11940-019-0563-4
35. Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, Giugliano RP, et al. Prevention of stroke with the addition of ezetimibe to statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome in IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation. 2017;136:2440-2450. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029095
36. Moritsugu KP. The 2006 report of the Surgeon General: the health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke. Am J Prev Med. 20067;32:542-543. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.02.026
37. Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Kannel WB, et al. Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. JAMA. 1988;259:1025-1029.
38. Goldstein LB, Adams R, Alberts MJ, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council: cosponsored by the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Interdisciplinary Working Group; Cardiovascular Nursing Council; Clinical Cardiology Council; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Council; and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke. 2006;37:1583-1633. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000223048.70103.F1
39. Klijn CJ, Paciaroni M, Berge E, et al. Antithrombotic treatment for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack and non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A European Stroke Organisation guideline. Eur Stroke J. 2019;4:198-223. doi:10.1177/2396987319841187
40. Antithrombotic Trialists’ (ATT) Collaboration; Baigent C, Blackwell L, Collins R, et al. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2009;373:1849-1860. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1
41. Singer DE, Albers GW, Dalen JE, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 suppl):546S–592S. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0678
42. Rothwell PM, Algra A, Chen Z, et al. Effects of aspirin on risk and severity of early recurrent stroke after transient ischaemic attack and ischaemic stroke: time-course analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;388:365-375. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30468-8
1. Kleindorfer D, Panagos P, Pancioli A, et al. Incidence and short-term prognosis of transient ischemic attack in a population-based study. Stroke. 2005;36:720-723. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000158917.59233.b7
2. Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52:e364-e467. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000375
3. Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2009;40:2276-2293. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.192218
4. Thacker EL, Wiggins KL, Rice KM, et al. Short-term and long-term risk of incident ischemic stroke after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2010;41:239-243. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.569707
5. Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T, et al. The high risk of stroke immediately after transient ischemic attack: a population-based study. Neurology. 2004;62:2015-2020. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000129482.70315.2f
6. Giles MF, Albers GW, Amarenco P, et al. Early stroke risk and ABCD2 score performance in tissue- vs time-defined TIA: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2011;77:1222-1228. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182309f91
7. Cucchiara BL, Kasner SE. All patients should be admitted to the hospital after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1446-1447. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636746
8. Amarenco P. Not all patients should be admitted to the hospital for observation after a transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2012;43:1448-1449. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636753
9. Amort M, Fluri F, Schäfer J, et al. Transient ischemic attack versus transient ischemic attack mimics: frequency, clinical characteristics and outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:57-64. doi: 10.1159/000327034
10. Hand PJ, Kwan J, Lindley RI, et al. Distinguishing between stroke and mimic at the bedside: The Brain Attack Study. Stroke. 2006;37:769-775. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000204041.13466.4c
11. Shah KH, Edlow JA. Transient ischemic attack: review for the emergency physician. Ann Emerg Med. 2004;43:592-604. doi: 10.1016/S0196064404000058
12. Crisostomo RA, Garcia MM, Tong DC. Detection of diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities in patients with transient ischemic attack: correlation with clinical characteristics. Stroke. 2003;34:932-937. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000061496.00669.5E
13. Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al; ; ; ; ; . Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007;38:1655-1711. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.181486
14. Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN, et al. Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet. 2007;369:283-292. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60150-0
15. Cucchiara BL, Messe SR, Taylor RA, et al. Is the ABCD score useful for risk stratification of patients with acute transient ischemic attack? Stroke. 2006;37:1710-1714. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000227195.46336.93
16. Amarenco P, Lavallée PC, Labreuche J, et al; . One-year risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1533-1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412981
17. Wu CM, McLaughlin K, Lorenzetti DL, et al. Early risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:2417-2422. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.22.2417
18. Rothwell PM, Warlow CP. Timing of TIAs preceding stroke: time window for prevention is very short. Neurology. 2005;64:817-820. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000152985.32732.EE
19. Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160-2236. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000024
20. Rothwell PM, Giles MF, Chandratheva A, et al. Effect of urgent treatment of transient ischaemic attack and minor stroke on early recurrent stroke (EXPRESS study): a prospective population-based sequential comparison. Lancet. 2007;370:1432-1442. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61448-2
21. Hackam DG, Spence JD. Antiplatelet therapy in ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: an overview of major trials and meta-analyses. Stroke. 2019;50:773-778. doi: c10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023954
22. Bhatia K, Jain V, Aggarwal D, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy versus aspirin in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2021;52:e217-e223. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.033033
23. Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhao X, et al; CHANCE Investigators. Clopidogrel with aspirin in acute minor stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHANCE) trial: one-year outcomes. Circulation. 2015;132:40-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014791
24. Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, et al; . Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:227-276. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3181f7d043
25. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al; American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49:e46-e110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158
26. O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, et al; INTERSTROKE Investigators. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet. 2016;388:761-775. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30506-2
27. Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:776-785. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9
28. Bertoccini L, Baroni MG. GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: new insights and opportunities for cardiovascular protection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1307:193-212. doi:10.1007/5584_2020_494
29. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al; ELIXA Investigators. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2247-2257. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509225
30. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP-1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J. 2020;96:156-161. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-137186
31. Kim AS. Medical management for secondary stroke prevention. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2020;26:435-456. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000849
32. Smith L, Chakraborty D, Bhattacharya P, et al. Exposure to hypoglycemia and risk of stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1431:25-34. doi:10.1111/nyas.13872
33. Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A 3rd, et al; . High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:549-559. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061894
34. Castilla-Guerra, L, Fernandez-Moreno M, Leon-Jimenez D, et al. Statins in ischemic stroke prevention: what have we learned in the post-SPARCL (The Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels) decade? Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21:22. doi: 10.1007/s11940-019-0563-4
35. Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, Giugliano RP, et al. Prevention of stroke with the addition of ezetimibe to statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome in IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation. 2017;136:2440-2450. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029095
36. Moritsugu KP. The 2006 report of the Surgeon General: the health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke. Am J Prev Med. 20067;32:542-543. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.02.026
37. Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Kannel WB, et al. Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. JAMA. 1988;259:1025-1029.
38. Goldstein LB, Adams R, Alberts MJ, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council: cosponsored by the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Interdisciplinary Working Group; Cardiovascular Nursing Council; Clinical Cardiology Council; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Council; and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke. 2006;37:1583-1633. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000223048.70103.F1
39. Klijn CJ, Paciaroni M, Berge E, et al. Antithrombotic treatment for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack and non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A European Stroke Organisation guideline. Eur Stroke J. 2019;4:198-223. doi:10.1177/2396987319841187
40. Antithrombotic Trialists’ (ATT) Collaboration; Baigent C, Blackwell L, Collins R, et al. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2009;373:1849-1860. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1
41. Singer DE, Albers GW, Dalen JE, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 suppl):546S–592S. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0678
42. Rothwell PM, Algra A, Chen Z, et al. Effects of aspirin on risk and severity of early recurrent stroke after transient ischaemic attack and ischaemic stroke: time-course analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;388:365-375. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30468-8
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
In the hospital, the treating physician should:
› Immediately initiate brain imaging with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging when TIA is suspected, upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital. A
› Control blood pressure when a TIA is confirmed, to decrease the risk of recurrent stroke. A
› Initiate antiplatelet therapy, to decrease the risk of recurrent stroke. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Mechanical touch therapy device promising for anxiety
An at-home investigational device is a promising noninvasive therapeutic approach for anxiety disorders, results from an open-label pilot trial suggest.
The small study showed
“MATT is part of a large movement toward developing therapeutic devices that patients can self-administer at home,” study author Linda L. Carpenter, MD, professor of psychiatry at Brown University and director of the Neuromodulation & Neuroimaging Core at Butler Hospital, both in Providence, R.I., told this news organization, adding that the new study is a step in the right direction of improving the technology used to treat anxiety disorders.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Psychiatry.
Robust safety profile
Therapeutic noninvasive peripheral nerve stimulation is under investigation for anxiety as well as pain and depression. Nerve activation is achieved by delivering electrical or mechanical energy, although most devices to date have used electrical stimulation.
Although electrical stimulation is considered low risk, mechanical stimulation that activates somatosensory pathways has an even more robust safety profile, the investigators note.
The MATT device targets C-tactile fibers (CT) specialized unmyelinated Group C peripheral nerve fibers that fire when stroked at velocities perceived as pleasurable or comforting.
To use the device, participants wear a headset with a small vibrating piece that sits on the mastoid bone behind each ear. These pieces deliver gentle vibrations that can be adjusted by patients.
During development of the MATT stimulation, researchers noted that an isochronic 10 Hz wave, cycling 2 seconds on and 2 seconds off, induced a state of relaxation and increased occipital alpha oscillations in pilot study participants.
The current study was designed to confirm preliminary efficacy and feasibility signals. The sample included 22 patients (mean age 37.3 years, 72.7% female, 77.3% White). All study participants were diagnosed with an anxiety disorder and had at least moderately severe anxiety symptoms. Some also had symptoms of panic or depression.
Many participants were on medications that weren’t effective, and they wanted to find a nondrug method of relieving their symptoms, said Dr. Carpenter.
What’s the mechanism?
Participants learned how to administer the stimulation and adjust the intensity of vibrations to a level where it was consistently detectable but not uncomfortable. Then they received a MATT device to use at home at least twice daily for 20 minutes.
Patients kept daily diaries documenting device use, adverse effects, and technological problems. In-person assessments were held at 2 and 4 weeks.
Researchers collected resting EEG immediately before, and after, the second stimulation session and again following 4 weeks of MATT use.
At baseline and after 2 and 4 weeks, patients self-reported anxiety using the 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) scale, depression with the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and stress using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). They also reported symptoms with the Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale (DASS).
Researchers also investigated “interoceptive awareness” or being mindful of your body and internal feelings. For this, they had participants complete the 32-item Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness pre- and post treatment.
Interoceptive awareness “is a whole new area of interest in neuroscience and brain health,” said Dr. Carpenter. “The hypothesis was that one way this device might work is that vibrations would travel to the insular cortex, the part of the brain that involves mindfulness and self-awareness.”
Symptom reduction
In the completer sample of 17 participants, mean scores on anxiety and depression symptoms fell significantly from baseline to 4 weeks (all P < .01). For example, the GAD-7 mean score fell from 14.3 to 7.1 and the BDI mean score from 30.6 to 14.8.
The study also showed that mindfulness was enhanced. The MAIA total score increased from 83.1 to 93.5 (P = .014).
Device users had increased alpha and theta brainwave activity, findings that “go along with the concept of decreased anxiety,” said Dr. Carpenter. She noted a recent study of the same patient population showed the device enhanced functional brain connectivity.
This current study was too small to pick up signals showing the device was effective in any particular subpopulation, said Dr. Carpenter.
Unlike other stimulation interventions that require clinic visits, patients use the MATT in the comfort of their own home and at their own convenience.
However, there are still questions surrounding the use of the noninvasive device. For example, said Dr. Carpenter, it’s unclear if it would be more effective if combined with psychotherapy or whether patients can use it while sleeping and driving. A next step could be a sham-controlled trial, she said.
The study was supported by Affect Neuro, developer of MATT therapy, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Carpenter reports receiving a consultancy fee from Affect Neuro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An at-home investigational device is a promising noninvasive therapeutic approach for anxiety disorders, results from an open-label pilot trial suggest.
The small study showed
“MATT is part of a large movement toward developing therapeutic devices that patients can self-administer at home,” study author Linda L. Carpenter, MD, professor of psychiatry at Brown University and director of the Neuromodulation & Neuroimaging Core at Butler Hospital, both in Providence, R.I., told this news organization, adding that the new study is a step in the right direction of improving the technology used to treat anxiety disorders.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Psychiatry.
Robust safety profile
Therapeutic noninvasive peripheral nerve stimulation is under investigation for anxiety as well as pain and depression. Nerve activation is achieved by delivering electrical or mechanical energy, although most devices to date have used electrical stimulation.
Although electrical stimulation is considered low risk, mechanical stimulation that activates somatosensory pathways has an even more robust safety profile, the investigators note.
The MATT device targets C-tactile fibers (CT) specialized unmyelinated Group C peripheral nerve fibers that fire when stroked at velocities perceived as pleasurable or comforting.
To use the device, participants wear a headset with a small vibrating piece that sits on the mastoid bone behind each ear. These pieces deliver gentle vibrations that can be adjusted by patients.
During development of the MATT stimulation, researchers noted that an isochronic 10 Hz wave, cycling 2 seconds on and 2 seconds off, induced a state of relaxation and increased occipital alpha oscillations in pilot study participants.
The current study was designed to confirm preliminary efficacy and feasibility signals. The sample included 22 patients (mean age 37.3 years, 72.7% female, 77.3% White). All study participants were diagnosed with an anxiety disorder and had at least moderately severe anxiety symptoms. Some also had symptoms of panic or depression.
Many participants were on medications that weren’t effective, and they wanted to find a nondrug method of relieving their symptoms, said Dr. Carpenter.
What’s the mechanism?
Participants learned how to administer the stimulation and adjust the intensity of vibrations to a level where it was consistently detectable but not uncomfortable. Then they received a MATT device to use at home at least twice daily for 20 minutes.
Patients kept daily diaries documenting device use, adverse effects, and technological problems. In-person assessments were held at 2 and 4 weeks.
Researchers collected resting EEG immediately before, and after, the second stimulation session and again following 4 weeks of MATT use.
At baseline and after 2 and 4 weeks, patients self-reported anxiety using the 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) scale, depression with the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and stress using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). They also reported symptoms with the Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale (DASS).
Researchers also investigated “interoceptive awareness” or being mindful of your body and internal feelings. For this, they had participants complete the 32-item Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness pre- and post treatment.
Interoceptive awareness “is a whole new area of interest in neuroscience and brain health,” said Dr. Carpenter. “The hypothesis was that one way this device might work is that vibrations would travel to the insular cortex, the part of the brain that involves mindfulness and self-awareness.”
Symptom reduction
In the completer sample of 17 participants, mean scores on anxiety and depression symptoms fell significantly from baseline to 4 weeks (all P < .01). For example, the GAD-7 mean score fell from 14.3 to 7.1 and the BDI mean score from 30.6 to 14.8.
The study also showed that mindfulness was enhanced. The MAIA total score increased from 83.1 to 93.5 (P = .014).
Device users had increased alpha and theta brainwave activity, findings that “go along with the concept of decreased anxiety,” said Dr. Carpenter. She noted a recent study of the same patient population showed the device enhanced functional brain connectivity.
This current study was too small to pick up signals showing the device was effective in any particular subpopulation, said Dr. Carpenter.
Unlike other stimulation interventions that require clinic visits, patients use the MATT in the comfort of their own home and at their own convenience.
However, there are still questions surrounding the use of the noninvasive device. For example, said Dr. Carpenter, it’s unclear if it would be more effective if combined with psychotherapy or whether patients can use it while sleeping and driving. A next step could be a sham-controlled trial, she said.
The study was supported by Affect Neuro, developer of MATT therapy, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Carpenter reports receiving a consultancy fee from Affect Neuro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An at-home investigational device is a promising noninvasive therapeutic approach for anxiety disorders, results from an open-label pilot trial suggest.
The small study showed
“MATT is part of a large movement toward developing therapeutic devices that patients can self-administer at home,” study author Linda L. Carpenter, MD, professor of psychiatry at Brown University and director of the Neuromodulation & Neuroimaging Core at Butler Hospital, both in Providence, R.I., told this news organization, adding that the new study is a step in the right direction of improving the technology used to treat anxiety disorders.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Psychiatry.
Robust safety profile
Therapeutic noninvasive peripheral nerve stimulation is under investigation for anxiety as well as pain and depression. Nerve activation is achieved by delivering electrical or mechanical energy, although most devices to date have used electrical stimulation.
Although electrical stimulation is considered low risk, mechanical stimulation that activates somatosensory pathways has an even more robust safety profile, the investigators note.
The MATT device targets C-tactile fibers (CT) specialized unmyelinated Group C peripheral nerve fibers that fire when stroked at velocities perceived as pleasurable or comforting.
To use the device, participants wear a headset with a small vibrating piece that sits on the mastoid bone behind each ear. These pieces deliver gentle vibrations that can be adjusted by patients.
During development of the MATT stimulation, researchers noted that an isochronic 10 Hz wave, cycling 2 seconds on and 2 seconds off, induced a state of relaxation and increased occipital alpha oscillations in pilot study participants.
The current study was designed to confirm preliminary efficacy and feasibility signals. The sample included 22 patients (mean age 37.3 years, 72.7% female, 77.3% White). All study participants were diagnosed with an anxiety disorder and had at least moderately severe anxiety symptoms. Some also had symptoms of panic or depression.
Many participants were on medications that weren’t effective, and they wanted to find a nondrug method of relieving their symptoms, said Dr. Carpenter.
What’s the mechanism?
Participants learned how to administer the stimulation and adjust the intensity of vibrations to a level where it was consistently detectable but not uncomfortable. Then they received a MATT device to use at home at least twice daily for 20 minutes.
Patients kept daily diaries documenting device use, adverse effects, and technological problems. In-person assessments were held at 2 and 4 weeks.
Researchers collected resting EEG immediately before, and after, the second stimulation session and again following 4 weeks of MATT use.
At baseline and after 2 and 4 weeks, patients self-reported anxiety using the 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) scale, depression with the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and stress using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). They also reported symptoms with the Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale (DASS).
Researchers also investigated “interoceptive awareness” or being mindful of your body and internal feelings. For this, they had participants complete the 32-item Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness pre- and post treatment.
Interoceptive awareness “is a whole new area of interest in neuroscience and brain health,” said Dr. Carpenter. “The hypothesis was that one way this device might work is that vibrations would travel to the insular cortex, the part of the brain that involves mindfulness and self-awareness.”
Symptom reduction
In the completer sample of 17 participants, mean scores on anxiety and depression symptoms fell significantly from baseline to 4 weeks (all P < .01). For example, the GAD-7 mean score fell from 14.3 to 7.1 and the BDI mean score from 30.6 to 14.8.
The study also showed that mindfulness was enhanced. The MAIA total score increased from 83.1 to 93.5 (P = .014).
Device users had increased alpha and theta brainwave activity, findings that “go along with the concept of decreased anxiety,” said Dr. Carpenter. She noted a recent study of the same patient population showed the device enhanced functional brain connectivity.
This current study was too small to pick up signals showing the device was effective in any particular subpopulation, said Dr. Carpenter.
Unlike other stimulation interventions that require clinic visits, patients use the MATT in the comfort of their own home and at their own convenience.
However, there are still questions surrounding the use of the noninvasive device. For example, said Dr. Carpenter, it’s unclear if it would be more effective if combined with psychotherapy or whether patients can use it while sleeping and driving. A next step could be a sham-controlled trial, she said.
The study was supported by Affect Neuro, developer of MATT therapy, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Carpenter reports receiving a consultancy fee from Affect Neuro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy is often incomplete
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Early-onset colon cancer projected to double by 2030
from 7.9 to 12.9 cases in 2015 per 100,000 people. The reason for the increase isn’t well understood.
The findings were highlighted in a recent review article published online in the New England Journal of Medicine. “It’s a national phenomenon and it’s also occurring in other parts of the developed world. We’re used to seeing mostly older people who have this diagnosis. Now we’re seeing a lot of younger people with this disease. It’s rather alarming,” said author Frank Sinicrope, MD, a medical oncologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The trend contrasts with a decline in later-onset CRC likely attributable to increases in screening. As a result of the two trends, but especially the increased number of early-onset cases, the median age of diagnosis dropped from 72 in the early 2000s to 66 today.
“Although patients with early-onset colorectal cancer are more likely to have a hereditary syndrome than those who have later-onset disease, most cases are sporadic, with no identifiable cause. Furthermore, somatic mutational profiling of early-onset colorectal cancers has not revealed previously unidentified or actionable alterations to inform our understanding of the pathogenesis of these cancers or to guide treatment,” he wrote in the review.
“Early-onset colorectal cancers are most commonly detected in the rectum, followed by the distal colon; more than 70% of early-onset colorectal cancers are in the left colon at presentation,” he wrote in the review. Younger patients tend to be unfamiliar with CRC symptoms, which are often mistaken for benign conditions.
“We’ve moved the screening age down to 45, but that still is not going to capture a lot of these patients,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He estimates that 25% of rectal cancers and 10%-12% of colon cancers diagnosed in the next 10 years will be early onset.
Although the direct cause of the increased incidence isn’t clear, Dr. Sinicrope suggested it may reflect changing dietary habits and rising obesity among adolescents. “The sugar-containing beverages, the processed sugar and a lot of red meat in the diet and refined grains … reflect changes in the diet over the last 50 years. We may now be seeing the end result of many of these dietary changes that have occurred,” he said, calling for a greater emphasis on plant-based diets, which promote a healthier gut microbiome that may reduce CRC risk. Western-style diets can change the gut microbiome leading to inflammation which increases the risk of CRC.
Most patients with early CRC present with advanced disease in the left colon. And, pathogenic germline variants are present in one in six patients – half of which are associated with Lynch syndrome which increases the risk for CRC.
Dr. Sinicrope highlighted the need for more risk-based intervention, which in turn requires a better knowledge of family history.
“We need to do better job to risk stratify, and that will help us figure out who’s best to target our screening efforts toward,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He pointed out guidelines from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the American Cancer Society that can help physicians identify patients who might benefit from earlier screening. The American Cancer Society recommends that CRC screening be conducted at 45 years for average-risk individuals.
“The best screening test is the one that the patient will do,” Dr. Sinicrope said.
from 7.9 to 12.9 cases in 2015 per 100,000 people. The reason for the increase isn’t well understood.
The findings were highlighted in a recent review article published online in the New England Journal of Medicine. “It’s a national phenomenon and it’s also occurring in other parts of the developed world. We’re used to seeing mostly older people who have this diagnosis. Now we’re seeing a lot of younger people with this disease. It’s rather alarming,” said author Frank Sinicrope, MD, a medical oncologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The trend contrasts with a decline in later-onset CRC likely attributable to increases in screening. As a result of the two trends, but especially the increased number of early-onset cases, the median age of diagnosis dropped from 72 in the early 2000s to 66 today.
“Although patients with early-onset colorectal cancer are more likely to have a hereditary syndrome than those who have later-onset disease, most cases are sporadic, with no identifiable cause. Furthermore, somatic mutational profiling of early-onset colorectal cancers has not revealed previously unidentified or actionable alterations to inform our understanding of the pathogenesis of these cancers or to guide treatment,” he wrote in the review.
“Early-onset colorectal cancers are most commonly detected in the rectum, followed by the distal colon; more than 70% of early-onset colorectal cancers are in the left colon at presentation,” he wrote in the review. Younger patients tend to be unfamiliar with CRC symptoms, which are often mistaken for benign conditions.
“We’ve moved the screening age down to 45, but that still is not going to capture a lot of these patients,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He estimates that 25% of rectal cancers and 10%-12% of colon cancers diagnosed in the next 10 years will be early onset.
Although the direct cause of the increased incidence isn’t clear, Dr. Sinicrope suggested it may reflect changing dietary habits and rising obesity among adolescents. “The sugar-containing beverages, the processed sugar and a lot of red meat in the diet and refined grains … reflect changes in the diet over the last 50 years. We may now be seeing the end result of many of these dietary changes that have occurred,” he said, calling for a greater emphasis on plant-based diets, which promote a healthier gut microbiome that may reduce CRC risk. Western-style diets can change the gut microbiome leading to inflammation which increases the risk of CRC.
Most patients with early CRC present with advanced disease in the left colon. And, pathogenic germline variants are present in one in six patients – half of which are associated with Lynch syndrome which increases the risk for CRC.
Dr. Sinicrope highlighted the need for more risk-based intervention, which in turn requires a better knowledge of family history.
“We need to do better job to risk stratify, and that will help us figure out who’s best to target our screening efforts toward,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He pointed out guidelines from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the American Cancer Society that can help physicians identify patients who might benefit from earlier screening. The American Cancer Society recommends that CRC screening be conducted at 45 years for average-risk individuals.
“The best screening test is the one that the patient will do,” Dr. Sinicrope said.
from 7.9 to 12.9 cases in 2015 per 100,000 people. The reason for the increase isn’t well understood.
The findings were highlighted in a recent review article published online in the New England Journal of Medicine. “It’s a national phenomenon and it’s also occurring in other parts of the developed world. We’re used to seeing mostly older people who have this diagnosis. Now we’re seeing a lot of younger people with this disease. It’s rather alarming,” said author Frank Sinicrope, MD, a medical oncologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The trend contrasts with a decline in later-onset CRC likely attributable to increases in screening. As a result of the two trends, but especially the increased number of early-onset cases, the median age of diagnosis dropped from 72 in the early 2000s to 66 today.
“Although patients with early-onset colorectal cancer are more likely to have a hereditary syndrome than those who have later-onset disease, most cases are sporadic, with no identifiable cause. Furthermore, somatic mutational profiling of early-onset colorectal cancers has not revealed previously unidentified or actionable alterations to inform our understanding of the pathogenesis of these cancers or to guide treatment,” he wrote in the review.
“Early-onset colorectal cancers are most commonly detected in the rectum, followed by the distal colon; more than 70% of early-onset colorectal cancers are in the left colon at presentation,” he wrote in the review. Younger patients tend to be unfamiliar with CRC symptoms, which are often mistaken for benign conditions.
“We’ve moved the screening age down to 45, but that still is not going to capture a lot of these patients,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He estimates that 25% of rectal cancers and 10%-12% of colon cancers diagnosed in the next 10 years will be early onset.
Although the direct cause of the increased incidence isn’t clear, Dr. Sinicrope suggested it may reflect changing dietary habits and rising obesity among adolescents. “The sugar-containing beverages, the processed sugar and a lot of red meat in the diet and refined grains … reflect changes in the diet over the last 50 years. We may now be seeing the end result of many of these dietary changes that have occurred,” he said, calling for a greater emphasis on plant-based diets, which promote a healthier gut microbiome that may reduce CRC risk. Western-style diets can change the gut microbiome leading to inflammation which increases the risk of CRC.
Most patients with early CRC present with advanced disease in the left colon. And, pathogenic germline variants are present in one in six patients – half of which are associated with Lynch syndrome which increases the risk for CRC.
Dr. Sinicrope highlighted the need for more risk-based intervention, which in turn requires a better knowledge of family history.
“We need to do better job to risk stratify, and that will help us figure out who’s best to target our screening efforts toward,” Dr. Sinicrope said. He pointed out guidelines from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the American Cancer Society that can help physicians identify patients who might benefit from earlier screening. The American Cancer Society recommends that CRC screening be conducted at 45 years for average-risk individuals.
“The best screening test is the one that the patient will do,” Dr. Sinicrope said.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Head and neck cancer patients recommend 11 needed improvements in health care
HNC has a high burden of treatment-related adverse events, along with frequent trouble with speech, swallowing, facial disfigurement, and psychological distress.
Among cancer patients, “they have the highest rates of emergency department use and hospitalization during treatment. They also have the highest rates of psychological distress. We have some Ontario data that shows they’ve got the highest rates of suicide and self-harm. So I think this is a really special population that we need to support,” Christopher Noel, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Noel was the lead author of the study, which was published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
These issues can strongly affect quality of life, and even patient outcomes. “Even a 1-day interruption in treatment has been shown to impact oncologic outcomes. This is a very big issue whether you’re a surgeon, a medical oncologist, or a radiation oncologist,” said Dr. Noel, who is a resident physician at the University of Toronto.
He advocates that physicians interview patients and review the results in a structured way and then act on it. “If we just rely on patient [provided] communication, we’re going to miss about 50% of patient symptoms,” he said.
The researchers aimed for the patient’s perspective on treatment. “What is the patient’s perception of going through head neck cancer and their treatment, and managing their symptoms at home? And where do they think that we could do better?” Dr. Noel asked.
The most pressing issue was that patients felt their emotional and informational needs often were not met. That challenge is even harder for patients who have trouble communicating, which in turn makes them more prone to isolation and loneliness. Many felt that they had to get the information on their own. “They wanted it to be a more effortless process,” said Dr. Noel.
He described one patient with oropharynx cancer who was able to talk to people about her grief over her diagnosis, but treatment led to her throat becoming swollen and she lost the ability to communicate. “She felt very isolated and lonely. She really highlighted the emotional and psychosocial barriers in cancer care. Her treatment inherently leaves her feeling very isolated and lonely, and she had such a hard time connecting with a psychotherapist,” Dr. Noel said.
Another common issue revolved around efforts to communicate about symptoms and adverse effects of treatment. Resources often aren’t available on evenings or weekends, and it can take time for a nurse to call them back. Patients wanted to see more modern approaches, such as use of email or apps.
The patients in the study recommended 11 health care improvements.
- 1. Nurse navigator teams should have hours extended to evenings and weekends.
- 2. Patient communication methods should be expanded, using methods like email or apps.
- 3. HNC resources should be more broadly disseminated.
- 4. Education and information approaches should be individualized to the patient.
- 5. All HNC patients should be offered psychological resources.
- 6. Mental health needs should be assessed repeatedly throughout treatment and extended care.
- 7. Physicians should recognize the added symptom burden often faced by patients who travel extensively for treatment.
- 8. Partners and caregivers should be included as part of the treatment team.
- 9. Share symptom data with patients, which can improve engagement.
- 10. Review symptom scores and act on them regularly.
- 11. A member of the care team should be identified to oversee symptom management.
Dr. Noel had no relevant financial disclosures.
HNC has a high burden of treatment-related adverse events, along with frequent trouble with speech, swallowing, facial disfigurement, and psychological distress.
Among cancer patients, “they have the highest rates of emergency department use and hospitalization during treatment. They also have the highest rates of psychological distress. We have some Ontario data that shows they’ve got the highest rates of suicide and self-harm. So I think this is a really special population that we need to support,” Christopher Noel, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Noel was the lead author of the study, which was published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
These issues can strongly affect quality of life, and even patient outcomes. “Even a 1-day interruption in treatment has been shown to impact oncologic outcomes. This is a very big issue whether you’re a surgeon, a medical oncologist, or a radiation oncologist,” said Dr. Noel, who is a resident physician at the University of Toronto.
He advocates that physicians interview patients and review the results in a structured way and then act on it. “If we just rely on patient [provided] communication, we’re going to miss about 50% of patient symptoms,” he said.
The researchers aimed for the patient’s perspective on treatment. “What is the patient’s perception of going through head neck cancer and their treatment, and managing their symptoms at home? And where do they think that we could do better?” Dr. Noel asked.
The most pressing issue was that patients felt their emotional and informational needs often were not met. That challenge is even harder for patients who have trouble communicating, which in turn makes them more prone to isolation and loneliness. Many felt that they had to get the information on their own. “They wanted it to be a more effortless process,” said Dr. Noel.
He described one patient with oropharynx cancer who was able to talk to people about her grief over her diagnosis, but treatment led to her throat becoming swollen and she lost the ability to communicate. “She felt very isolated and lonely. She really highlighted the emotional and psychosocial barriers in cancer care. Her treatment inherently leaves her feeling very isolated and lonely, and she had such a hard time connecting with a psychotherapist,” Dr. Noel said.
Another common issue revolved around efforts to communicate about symptoms and adverse effects of treatment. Resources often aren’t available on evenings or weekends, and it can take time for a nurse to call them back. Patients wanted to see more modern approaches, such as use of email or apps.
The patients in the study recommended 11 health care improvements.
- 1. Nurse navigator teams should have hours extended to evenings and weekends.
- 2. Patient communication methods should be expanded, using methods like email or apps.
- 3. HNC resources should be more broadly disseminated.
- 4. Education and information approaches should be individualized to the patient.
- 5. All HNC patients should be offered psychological resources.
- 6. Mental health needs should be assessed repeatedly throughout treatment and extended care.
- 7. Physicians should recognize the added symptom burden often faced by patients who travel extensively for treatment.
- 8. Partners and caregivers should be included as part of the treatment team.
- 9. Share symptom data with patients, which can improve engagement.
- 10. Review symptom scores and act on them regularly.
- 11. A member of the care team should be identified to oversee symptom management.
Dr. Noel had no relevant financial disclosures.
HNC has a high burden of treatment-related adverse events, along with frequent trouble with speech, swallowing, facial disfigurement, and psychological distress.
Among cancer patients, “they have the highest rates of emergency department use and hospitalization during treatment. They also have the highest rates of psychological distress. We have some Ontario data that shows they’ve got the highest rates of suicide and self-harm. So I think this is a really special population that we need to support,” Christopher Noel, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Noel was the lead author of the study, which was published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
These issues can strongly affect quality of life, and even patient outcomes. “Even a 1-day interruption in treatment has been shown to impact oncologic outcomes. This is a very big issue whether you’re a surgeon, a medical oncologist, or a radiation oncologist,” said Dr. Noel, who is a resident physician at the University of Toronto.
He advocates that physicians interview patients and review the results in a structured way and then act on it. “If we just rely on patient [provided] communication, we’re going to miss about 50% of patient symptoms,” he said.
The researchers aimed for the patient’s perspective on treatment. “What is the patient’s perception of going through head neck cancer and their treatment, and managing their symptoms at home? And where do they think that we could do better?” Dr. Noel asked.
The most pressing issue was that patients felt their emotional and informational needs often were not met. That challenge is even harder for patients who have trouble communicating, which in turn makes them more prone to isolation and loneliness. Many felt that they had to get the information on their own. “They wanted it to be a more effortless process,” said Dr. Noel.
He described one patient with oropharynx cancer who was able to talk to people about her grief over her diagnosis, but treatment led to her throat becoming swollen and she lost the ability to communicate. “She felt very isolated and lonely. She really highlighted the emotional and psychosocial barriers in cancer care. Her treatment inherently leaves her feeling very isolated and lonely, and she had such a hard time connecting with a psychotherapist,” Dr. Noel said.
Another common issue revolved around efforts to communicate about symptoms and adverse effects of treatment. Resources often aren’t available on evenings or weekends, and it can take time for a nurse to call them back. Patients wanted to see more modern approaches, such as use of email or apps.
The patients in the study recommended 11 health care improvements.
- 1. Nurse navigator teams should have hours extended to evenings and weekends.
- 2. Patient communication methods should be expanded, using methods like email or apps.
- 3. HNC resources should be more broadly disseminated.
- 4. Education and information approaches should be individualized to the patient.
- 5. All HNC patients should be offered psychological resources.
- 6. Mental health needs should be assessed repeatedly throughout treatment and extended care.
- 7. Physicians should recognize the added symptom burden often faced by patients who travel extensively for treatment.
- 8. Partners and caregivers should be included as part of the treatment team.
- 9. Share symptom data with patients, which can improve engagement.
- 10. Review symptom scores and act on them regularly.
- 11. A member of the care team should be identified to oversee symptom management.
Dr. Noel had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM JAMA OTOLARYNGOLOGY – HEAD & NECK SURGERY
Study hints at a mechanism behind aggressive melanoma
that combined in vitro and animal model data.
The gene, ARID2, is a part of the switch/sucrose nonfermentable (SWI/SNF) complex, which maneuvers cellular structures called nucleosomes to make cellular DNA accessible. About 20% of human cancers have a mutation within the SWI/SNF complex.
In the new study, published in Cell Reports, researchers reported that the ARID2 subunit was mutated in about 13% of melanoma patients identified through the Cancer Genome Atlas.
ARID2 mutations have been found in early melanoma lesions, which the authors suggested may play a role in early cancer cell dissemination. Other studies have shown SWI/SNF mutations, including ARID2 mutations, in melanoma metastases, especially the brain.
The researchers also found an up-regulation of synaptic pathways in melanoma cells as well as the Cancer Genome Atlas, which also suggests a potential role of ARID2 loss in metastasis or targeting the brain, since synaptic activation in cancer cells has been shown elsewhere to influence cell migration and survival in the brain.
“We look forward to future studies that investigate the role of the PBAF complex ... in order to better tailor treatments for melanoma patients,” wrote the study authors, who were led by Emily Bernstein, PhD, a professor in oncological sciences with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The SWI/SNF complex includes a subcomplex that targets specific DNA sequences or chromatin reader domains. There are multiple versions of the targeting subcomplex, but two of the most frequently occurring are BAF and PBAF. The most commonly mutated subunit in melanoma is ARID2, which is part of PBAF, and contains an AT-rich region responsible for non–sequence-specific DNA interactions. There is evidence that it plays a role in tumor suppression. In mouse tumors, depletion of ARID2 is associated with increased sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibition and destruction by T cells.
To better understand the role of ARID2 in tumor suppression, the researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 to create ARID2 deficiency in a known human metastatic melanoma cell line. They found there was reduced chromatin accessibility and accompanying gene expression among some PBAF and shared BAF-PBAF–occupied regions. There was also increased chromatin accessibility and gene expression in BAF-occupied regions, and these changes were associated with tumor aggression. In mice, they led to metastasis of distal organs.
This mechanism appears to be conserved between different melanoma cell lines, but deregulated transcriptional targets were different depending on the dominant transcription factors in the cell line. That suggests that the effect of ARID2 mutation or loss may be different depending on the stage of melanoma progression or level of invasiveness. “As melanoma comprises transcriptionally distinct, heterogeneous cell populations, we envision future studies utilizing single-cell methodologies to better understand the nuanced effects of ARID2 loss within subpopulations of cells in human melanoma tumors,” the authors wrote.
The study is limited by the fact that not all ARID2 mutations lead to complete loss of protein, and may lead instead to aberrant complexes.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
that combined in vitro and animal model data.
The gene, ARID2, is a part of the switch/sucrose nonfermentable (SWI/SNF) complex, which maneuvers cellular structures called nucleosomes to make cellular DNA accessible. About 20% of human cancers have a mutation within the SWI/SNF complex.
In the new study, published in Cell Reports, researchers reported that the ARID2 subunit was mutated in about 13% of melanoma patients identified through the Cancer Genome Atlas.
ARID2 mutations have been found in early melanoma lesions, which the authors suggested may play a role in early cancer cell dissemination. Other studies have shown SWI/SNF mutations, including ARID2 mutations, in melanoma metastases, especially the brain.
The researchers also found an up-regulation of synaptic pathways in melanoma cells as well as the Cancer Genome Atlas, which also suggests a potential role of ARID2 loss in metastasis or targeting the brain, since synaptic activation in cancer cells has been shown elsewhere to influence cell migration and survival in the brain.
“We look forward to future studies that investigate the role of the PBAF complex ... in order to better tailor treatments for melanoma patients,” wrote the study authors, who were led by Emily Bernstein, PhD, a professor in oncological sciences with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The SWI/SNF complex includes a subcomplex that targets specific DNA sequences or chromatin reader domains. There are multiple versions of the targeting subcomplex, but two of the most frequently occurring are BAF and PBAF. The most commonly mutated subunit in melanoma is ARID2, which is part of PBAF, and contains an AT-rich region responsible for non–sequence-specific DNA interactions. There is evidence that it plays a role in tumor suppression. In mouse tumors, depletion of ARID2 is associated with increased sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibition and destruction by T cells.
To better understand the role of ARID2 in tumor suppression, the researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 to create ARID2 deficiency in a known human metastatic melanoma cell line. They found there was reduced chromatin accessibility and accompanying gene expression among some PBAF and shared BAF-PBAF–occupied regions. There was also increased chromatin accessibility and gene expression in BAF-occupied regions, and these changes were associated with tumor aggression. In mice, they led to metastasis of distal organs.
This mechanism appears to be conserved between different melanoma cell lines, but deregulated transcriptional targets were different depending on the dominant transcription factors in the cell line. That suggests that the effect of ARID2 mutation or loss may be different depending on the stage of melanoma progression or level of invasiveness. “As melanoma comprises transcriptionally distinct, heterogeneous cell populations, we envision future studies utilizing single-cell methodologies to better understand the nuanced effects of ARID2 loss within subpopulations of cells in human melanoma tumors,” the authors wrote.
The study is limited by the fact that not all ARID2 mutations lead to complete loss of protein, and may lead instead to aberrant complexes.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
that combined in vitro and animal model data.
The gene, ARID2, is a part of the switch/sucrose nonfermentable (SWI/SNF) complex, which maneuvers cellular structures called nucleosomes to make cellular DNA accessible. About 20% of human cancers have a mutation within the SWI/SNF complex.
In the new study, published in Cell Reports, researchers reported that the ARID2 subunit was mutated in about 13% of melanoma patients identified through the Cancer Genome Atlas.
ARID2 mutations have been found in early melanoma lesions, which the authors suggested may play a role in early cancer cell dissemination. Other studies have shown SWI/SNF mutations, including ARID2 mutations, in melanoma metastases, especially the brain.
The researchers also found an up-regulation of synaptic pathways in melanoma cells as well as the Cancer Genome Atlas, which also suggests a potential role of ARID2 loss in metastasis or targeting the brain, since synaptic activation in cancer cells has been shown elsewhere to influence cell migration and survival in the brain.
“We look forward to future studies that investigate the role of the PBAF complex ... in order to better tailor treatments for melanoma patients,” wrote the study authors, who were led by Emily Bernstein, PhD, a professor in oncological sciences with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The SWI/SNF complex includes a subcomplex that targets specific DNA sequences or chromatin reader domains. There are multiple versions of the targeting subcomplex, but two of the most frequently occurring are BAF and PBAF. The most commonly mutated subunit in melanoma is ARID2, which is part of PBAF, and contains an AT-rich region responsible for non–sequence-specific DNA interactions. There is evidence that it plays a role in tumor suppression. In mouse tumors, depletion of ARID2 is associated with increased sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibition and destruction by T cells.
To better understand the role of ARID2 in tumor suppression, the researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 to create ARID2 deficiency in a known human metastatic melanoma cell line. They found there was reduced chromatin accessibility and accompanying gene expression among some PBAF and shared BAF-PBAF–occupied regions. There was also increased chromatin accessibility and gene expression in BAF-occupied regions, and these changes were associated with tumor aggression. In mice, they led to metastasis of distal organs.
This mechanism appears to be conserved between different melanoma cell lines, but deregulated transcriptional targets were different depending on the dominant transcription factors in the cell line. That suggests that the effect of ARID2 mutation or loss may be different depending on the stage of melanoma progression or level of invasiveness. “As melanoma comprises transcriptionally distinct, heterogeneous cell populations, we envision future studies utilizing single-cell methodologies to better understand the nuanced effects of ARID2 loss within subpopulations of cells in human melanoma tumors,” the authors wrote.
The study is limited by the fact that not all ARID2 mutations lead to complete loss of protein, and may lead instead to aberrant complexes.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
FROM CELL REPORTS
Steroid phobia drives weaker prescribing, nonadherence for AD
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
FROM RAD 2022
Flu vaccine linked to lower risk for stroke: INTERSTROKE
in a large new case-control study.
“While influenza vaccination is a cost-effective method to prevent influenza, it is also an effective way to reduce the burden of stroke,” said study author Christopher Schwarzbach, MD, of Ludwigshafen (Germany) Hospital.
“Our results therefore encourage the wider use of influenza vaccination,” he concluded.
Dr. Schwarzbach presented these data from the INTERSTROKE study at the 2022 European Stroke Organisation Conference.
He explained that acute inflammatory disease is thought to increase the risk for cerebrovascular events, and the seasonality of influenza-like illness appears to be associated with the seasonality of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Previous observational studies have also shown a link between influenza vaccination and a reduced risk for stroke.
The current INTERSTROKE study was a large international case-control study conducted between 2007 and 2015 that involved 13,447 cases (patients within 5 days of their first stroke) and a similar number of age- and gender-matched people from 32 countries across the world.
All cases and control subjects were systematically asked whether they had acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks and whether they had received an influenza vaccination within the previous year.
Conditional logistical regression was used to quantify the results, with adjustment for 13 different possible confounding factors, including hypertension, activity, smoking, cardiovascular risk factors, and socioeconomic factors.
Results showed that having had an acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks was more commonly reported in the patients with an acute ischemic stroke (8.7%) than in control patients (5.6%). After adjustment for confounding factors, this gives an adjusted risk ratio of 1.18, which was of borderline statistical significance (95% confidence limits, 1.01-1.39), Dr. Schwarzbach reported.
The association between recent febrile illness and acute ischemic stroke was stronger when compared with community control subjects (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0), but it was absent when compared with hospital control subjects.
The association was also only apparent in Australia, China, North America, and Western Europe; it was not seen in other parts of the world.
There was no association between acute febrile illness and acute cerebral hemorrhage.
Flu vaccine linked to halving of stroke risk
Having received a flu vaccine in the previous year was strongly associated with a lower risk for any type of stroke (aOR, 0.53), ischemic stroke (aOR, 0.57), and hemorrhagic stroke (aOR, 0.34).
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that these results were also consistent in an extended statistical model that included variables that might reflect a willingness to be vaccinated and when compared with both community and hospital-based control subjects.
The strength of the association between influenza vaccination and reduced risk for stroke was similar when compared with either community or hospital control subjects, and was only moderately stronger during than outside the influenza season.
The association was also seen in all regions of the world apart from Africa and South Asia, Dr. Schwarzbach reported, but he noted that vaccination rates in these two regions were extremely low.
The researchers also found that the magnitude of the associations between flu vaccination and lower risk for stroke were stronger in individuals who had multiple annual vaccinations, with an odds ratio of 0.54 in those who had received a vaccine every year for the previous 5 years, and of 0.79 in those who had received one to four vaccinations in the previous 5 years.
Mechanism: Immune stimulation?
Discussing possible mechanisms behind these results, Dr. Schwarzbach noted that the finding that the association with influenza vaccination and reduced stroke risk was independent of seasonality was surprising. “We had expected the protective effect of vaccination to be bigger during the influenza season, but this wasn’t the case.”
He suggested that one explanation might be the inclusion of regions of the world where this seasonality doesn’t exist.
But he pointed out that the finding of a stronger association between flu vaccination and lower stroke risk in those who had received more vaccinations has given rise to another theory: that it is the stimulation of the immune system rather than the protection of infection against influenza that is the key factor.
In an interview with Dr. Schwarzbach, Guillaume Turk, MD, professor of neurology at GHU Paris, pointed out that causal inferences are always difficult in case-control studies and in clinical epidemiology in general.
“What makes you think that this association between influenza vaccination and decreased risk is causal rather than due to unmeasured confounders? For example, patients who received vaccination may have received more medical attention and may have been more aware of the risk factors for stroke,” he asked.
Dr. Schwarzbach replied: “Yes, this is the issue of healthy user bias, which is always a problem in this type of research and is hard to address.”
“What we tried to do here is to adjust for variables that might influence the willingness of people to get vaccinated,” he added. “These were mainly socioeconomic factors. But, of course, this is something that we can’t rule out.”
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that, for more reliable information on this association, prospective studies are needed.
‘A plausible effect’
Discussing the study after the presentation, William Whiteley, BM, PhD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Edinburgh and a consultant neurologist in NHS Lothian, said vaccination was a potentially important way to reduce stroke.
“In this study, there was a plausible effect on reducing stroke incidence from vaccination against influenza, and also a plausible increase in the risk of stroke from having a recent febrile illness, which we have seen in other studies,” he commented.
Dr. Whiteley noted that this observation was particularly relevant now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been worried about the risk of heart attack and stroke after COVID, where we’ve seen quite early high risks, and we are also optimistic about the effect of vaccination on reducing those incidences. We’ve seen data from the U.K. that there may be around a 20% reduction in risk of stroke from vaccination. So, it’s all quite plausible, but at the moment it’s all based on observational evidence and we really need some randomized evidence,” he said.
“Vaccination and infections have all sorts of odd confounders,” he added. “People who get vaccines tend to be more healthy than those who don’t get vaccines, so you can start to see quite implausible effects of vaccination on overall mortality, which probably aren’t real, and you probably can’t get rid of that totally with statistical methods.”
Alastair Webb, MD, University of Oxford (England), asked how reliable the current findings were, given that the occurrence of febrile illnesses and receipt of vaccines were all self-reported, and although there was an association for ischemic stroke and febrile illness, this seemed to go in the opposite direction for hemorrhagic stroke. He also noted that the 50% reduction in stroke risk with vaccination in this study seemed “quite a large magnitude of effect.”
Dr. Whiteley replied: “Yes, it is large, but it is promising.” He cited a previous meta-analysis of randomized studies that showed a roughly 25%-35% reduction in vascular events after flu vaccination, but noted that there was a lot of heterogeneity between studies.
“I’m not sure we’re going to see much more randomized evidence, but I think we can probably all agree that having a vaccine against flu or COVID is a good thing for all of us,” Dr. Whiteley concluded.
The INTERSTROKE study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Canadian Stroke Network, Health Research Board Ireland, Swedish Research Council, Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, The Health & Medical Care Committee of the Regional Executive Board, Region Vastra Gotaland (Sweden), AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, MSD, Chest, Heart and Stroke Scotland, and The Stroke Association, with support from The UK Stroke Research Network. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a large new case-control study.
“While influenza vaccination is a cost-effective method to prevent influenza, it is also an effective way to reduce the burden of stroke,” said study author Christopher Schwarzbach, MD, of Ludwigshafen (Germany) Hospital.
“Our results therefore encourage the wider use of influenza vaccination,” he concluded.
Dr. Schwarzbach presented these data from the INTERSTROKE study at the 2022 European Stroke Organisation Conference.
He explained that acute inflammatory disease is thought to increase the risk for cerebrovascular events, and the seasonality of influenza-like illness appears to be associated with the seasonality of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Previous observational studies have also shown a link between influenza vaccination and a reduced risk for stroke.
The current INTERSTROKE study was a large international case-control study conducted between 2007 and 2015 that involved 13,447 cases (patients within 5 days of their first stroke) and a similar number of age- and gender-matched people from 32 countries across the world.
All cases and control subjects were systematically asked whether they had acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks and whether they had received an influenza vaccination within the previous year.
Conditional logistical regression was used to quantify the results, with adjustment for 13 different possible confounding factors, including hypertension, activity, smoking, cardiovascular risk factors, and socioeconomic factors.
Results showed that having had an acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks was more commonly reported in the patients with an acute ischemic stroke (8.7%) than in control patients (5.6%). After adjustment for confounding factors, this gives an adjusted risk ratio of 1.18, which was of borderline statistical significance (95% confidence limits, 1.01-1.39), Dr. Schwarzbach reported.
The association between recent febrile illness and acute ischemic stroke was stronger when compared with community control subjects (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0), but it was absent when compared with hospital control subjects.
The association was also only apparent in Australia, China, North America, and Western Europe; it was not seen in other parts of the world.
There was no association between acute febrile illness and acute cerebral hemorrhage.
Flu vaccine linked to halving of stroke risk
Having received a flu vaccine in the previous year was strongly associated with a lower risk for any type of stroke (aOR, 0.53), ischemic stroke (aOR, 0.57), and hemorrhagic stroke (aOR, 0.34).
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that these results were also consistent in an extended statistical model that included variables that might reflect a willingness to be vaccinated and when compared with both community and hospital-based control subjects.
The strength of the association between influenza vaccination and reduced risk for stroke was similar when compared with either community or hospital control subjects, and was only moderately stronger during than outside the influenza season.
The association was also seen in all regions of the world apart from Africa and South Asia, Dr. Schwarzbach reported, but he noted that vaccination rates in these two regions were extremely low.
The researchers also found that the magnitude of the associations between flu vaccination and lower risk for stroke were stronger in individuals who had multiple annual vaccinations, with an odds ratio of 0.54 in those who had received a vaccine every year for the previous 5 years, and of 0.79 in those who had received one to four vaccinations in the previous 5 years.
Mechanism: Immune stimulation?
Discussing possible mechanisms behind these results, Dr. Schwarzbach noted that the finding that the association with influenza vaccination and reduced stroke risk was independent of seasonality was surprising. “We had expected the protective effect of vaccination to be bigger during the influenza season, but this wasn’t the case.”
He suggested that one explanation might be the inclusion of regions of the world where this seasonality doesn’t exist.
But he pointed out that the finding of a stronger association between flu vaccination and lower stroke risk in those who had received more vaccinations has given rise to another theory: that it is the stimulation of the immune system rather than the protection of infection against influenza that is the key factor.
In an interview with Dr. Schwarzbach, Guillaume Turk, MD, professor of neurology at GHU Paris, pointed out that causal inferences are always difficult in case-control studies and in clinical epidemiology in general.
“What makes you think that this association between influenza vaccination and decreased risk is causal rather than due to unmeasured confounders? For example, patients who received vaccination may have received more medical attention and may have been more aware of the risk factors for stroke,” he asked.
Dr. Schwarzbach replied: “Yes, this is the issue of healthy user bias, which is always a problem in this type of research and is hard to address.”
“What we tried to do here is to adjust for variables that might influence the willingness of people to get vaccinated,” he added. “These were mainly socioeconomic factors. But, of course, this is something that we can’t rule out.”
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that, for more reliable information on this association, prospective studies are needed.
‘A plausible effect’
Discussing the study after the presentation, William Whiteley, BM, PhD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Edinburgh and a consultant neurologist in NHS Lothian, said vaccination was a potentially important way to reduce stroke.
“In this study, there was a plausible effect on reducing stroke incidence from vaccination against influenza, and also a plausible increase in the risk of stroke from having a recent febrile illness, which we have seen in other studies,” he commented.
Dr. Whiteley noted that this observation was particularly relevant now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been worried about the risk of heart attack and stroke after COVID, where we’ve seen quite early high risks, and we are also optimistic about the effect of vaccination on reducing those incidences. We’ve seen data from the U.K. that there may be around a 20% reduction in risk of stroke from vaccination. So, it’s all quite plausible, but at the moment it’s all based on observational evidence and we really need some randomized evidence,” he said.
“Vaccination and infections have all sorts of odd confounders,” he added. “People who get vaccines tend to be more healthy than those who don’t get vaccines, so you can start to see quite implausible effects of vaccination on overall mortality, which probably aren’t real, and you probably can’t get rid of that totally with statistical methods.”
Alastair Webb, MD, University of Oxford (England), asked how reliable the current findings were, given that the occurrence of febrile illnesses and receipt of vaccines were all self-reported, and although there was an association for ischemic stroke and febrile illness, this seemed to go in the opposite direction for hemorrhagic stroke. He also noted that the 50% reduction in stroke risk with vaccination in this study seemed “quite a large magnitude of effect.”
Dr. Whiteley replied: “Yes, it is large, but it is promising.” He cited a previous meta-analysis of randomized studies that showed a roughly 25%-35% reduction in vascular events after flu vaccination, but noted that there was a lot of heterogeneity between studies.
“I’m not sure we’re going to see much more randomized evidence, but I think we can probably all agree that having a vaccine against flu or COVID is a good thing for all of us,” Dr. Whiteley concluded.
The INTERSTROKE study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Canadian Stroke Network, Health Research Board Ireland, Swedish Research Council, Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, The Health & Medical Care Committee of the Regional Executive Board, Region Vastra Gotaland (Sweden), AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, MSD, Chest, Heart and Stroke Scotland, and The Stroke Association, with support from The UK Stroke Research Network. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a large new case-control study.
“While influenza vaccination is a cost-effective method to prevent influenza, it is also an effective way to reduce the burden of stroke,” said study author Christopher Schwarzbach, MD, of Ludwigshafen (Germany) Hospital.
“Our results therefore encourage the wider use of influenza vaccination,” he concluded.
Dr. Schwarzbach presented these data from the INTERSTROKE study at the 2022 European Stroke Organisation Conference.
He explained that acute inflammatory disease is thought to increase the risk for cerebrovascular events, and the seasonality of influenza-like illness appears to be associated with the seasonality of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Previous observational studies have also shown a link between influenza vaccination and a reduced risk for stroke.
The current INTERSTROKE study was a large international case-control study conducted between 2007 and 2015 that involved 13,447 cases (patients within 5 days of their first stroke) and a similar number of age- and gender-matched people from 32 countries across the world.
All cases and control subjects were systematically asked whether they had acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks and whether they had received an influenza vaccination within the previous year.
Conditional logistical regression was used to quantify the results, with adjustment for 13 different possible confounding factors, including hypertension, activity, smoking, cardiovascular risk factors, and socioeconomic factors.
Results showed that having had an acute febrile illness in the previous 4 weeks was more commonly reported in the patients with an acute ischemic stroke (8.7%) than in control patients (5.6%). After adjustment for confounding factors, this gives an adjusted risk ratio of 1.18, which was of borderline statistical significance (95% confidence limits, 1.01-1.39), Dr. Schwarzbach reported.
The association between recent febrile illness and acute ischemic stroke was stronger when compared with community control subjects (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0), but it was absent when compared with hospital control subjects.
The association was also only apparent in Australia, China, North America, and Western Europe; it was not seen in other parts of the world.
There was no association between acute febrile illness and acute cerebral hemorrhage.
Flu vaccine linked to halving of stroke risk
Having received a flu vaccine in the previous year was strongly associated with a lower risk for any type of stroke (aOR, 0.53), ischemic stroke (aOR, 0.57), and hemorrhagic stroke (aOR, 0.34).
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that these results were also consistent in an extended statistical model that included variables that might reflect a willingness to be vaccinated and when compared with both community and hospital-based control subjects.
The strength of the association between influenza vaccination and reduced risk for stroke was similar when compared with either community or hospital control subjects, and was only moderately stronger during than outside the influenza season.
The association was also seen in all regions of the world apart from Africa and South Asia, Dr. Schwarzbach reported, but he noted that vaccination rates in these two regions were extremely low.
The researchers also found that the magnitude of the associations between flu vaccination and lower risk for stroke were stronger in individuals who had multiple annual vaccinations, with an odds ratio of 0.54 in those who had received a vaccine every year for the previous 5 years, and of 0.79 in those who had received one to four vaccinations in the previous 5 years.
Mechanism: Immune stimulation?
Discussing possible mechanisms behind these results, Dr. Schwarzbach noted that the finding that the association with influenza vaccination and reduced stroke risk was independent of seasonality was surprising. “We had expected the protective effect of vaccination to be bigger during the influenza season, but this wasn’t the case.”
He suggested that one explanation might be the inclusion of regions of the world where this seasonality doesn’t exist.
But he pointed out that the finding of a stronger association between flu vaccination and lower stroke risk in those who had received more vaccinations has given rise to another theory: that it is the stimulation of the immune system rather than the protection of infection against influenza that is the key factor.
In an interview with Dr. Schwarzbach, Guillaume Turk, MD, professor of neurology at GHU Paris, pointed out that causal inferences are always difficult in case-control studies and in clinical epidemiology in general.
“What makes you think that this association between influenza vaccination and decreased risk is causal rather than due to unmeasured confounders? For example, patients who received vaccination may have received more medical attention and may have been more aware of the risk factors for stroke,” he asked.
Dr. Schwarzbach replied: “Yes, this is the issue of healthy user bias, which is always a problem in this type of research and is hard to address.”
“What we tried to do here is to adjust for variables that might influence the willingness of people to get vaccinated,” he added. “These were mainly socioeconomic factors. But, of course, this is something that we can’t rule out.”
Dr. Schwarzbach noted that, for more reliable information on this association, prospective studies are needed.
‘A plausible effect’
Discussing the study after the presentation, William Whiteley, BM, PhD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Edinburgh and a consultant neurologist in NHS Lothian, said vaccination was a potentially important way to reduce stroke.
“In this study, there was a plausible effect on reducing stroke incidence from vaccination against influenza, and also a plausible increase in the risk of stroke from having a recent febrile illness, which we have seen in other studies,” he commented.
Dr. Whiteley noted that this observation was particularly relevant now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been worried about the risk of heart attack and stroke after COVID, where we’ve seen quite early high risks, and we are also optimistic about the effect of vaccination on reducing those incidences. We’ve seen data from the U.K. that there may be around a 20% reduction in risk of stroke from vaccination. So, it’s all quite plausible, but at the moment it’s all based on observational evidence and we really need some randomized evidence,” he said.
“Vaccination and infections have all sorts of odd confounders,” he added. “People who get vaccines tend to be more healthy than those who don’t get vaccines, so you can start to see quite implausible effects of vaccination on overall mortality, which probably aren’t real, and you probably can’t get rid of that totally with statistical methods.”
Alastair Webb, MD, University of Oxford (England), asked how reliable the current findings were, given that the occurrence of febrile illnesses and receipt of vaccines were all self-reported, and although there was an association for ischemic stroke and febrile illness, this seemed to go in the opposite direction for hemorrhagic stroke. He also noted that the 50% reduction in stroke risk with vaccination in this study seemed “quite a large magnitude of effect.”
Dr. Whiteley replied: “Yes, it is large, but it is promising.” He cited a previous meta-analysis of randomized studies that showed a roughly 25%-35% reduction in vascular events after flu vaccination, but noted that there was a lot of heterogeneity between studies.
“I’m not sure we’re going to see much more randomized evidence, but I think we can probably all agree that having a vaccine against flu or COVID is a good thing for all of us,” Dr. Whiteley concluded.
The INTERSTROKE study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Canadian Stroke Network, Health Research Board Ireland, Swedish Research Council, Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, The Health & Medical Care Committee of the Regional Executive Board, Region Vastra Gotaland (Sweden), AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, MSD, Chest, Heart and Stroke Scotland, and The Stroke Association, with support from The UK Stroke Research Network. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. docs at double the risk of postpartum depression
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.