User login
New single-button blood glucose monitor available in U.S.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alopecia tied to a threefold increased risk for dementia
Alopecia areata (AA) has been linked to a significantly increased risk for dementia, new research shows.
After controlling for an array of potential confounders, investigators found a threefold higher risk of developing any form of dementia and a fourfold higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in those with AA versus the controls.
“AA shares a similar inflammatory signature with dementia and has great psychological impacts that lead to poor social engagement,” lead author Cheng-Yuan Li, MD, MSc, of the department of dermatology, Taipei (Taiwan) Veterans General Hospital.
“Poor social engagement and shared inflammatory cytokines might both be important links between AA and dementia,” said Dr. Li, who is also affiliated with the School of Medicine and the Institute of Brain Science at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei.
The study was published online Oct. 26, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry (doi: 10.4088/JCP.21m13931).
Significant psychological impact
Patients with AA often experience anxiety and depression, possibly caused by the negative emotional and psychological impact of the hair loss and partial or even complete baldness associated with the disease, the authors noted.
However, AA is also associated with an array of other atopic and autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Epidemiologic research has suggested a link between dementia and autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and SLE, with some evidence suggesting that autoimmune and inflammatory mechanisms may “play a role” in the development of AD.
Dementia in general and AD in particular, “have been shown to include an inflammatory component” that may share some of the same mediators seen in AA (eg, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha).
Moreover, “the great negative psychosocial impact of AA might result in poor social engagement, a typical risk factor for dementia,” said Dr. Li. The investigators sought to investigate whether patients with AA actually do have a higher dementia risk than individuals without AA.
The researchers used data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database, comparing 2,534 patients with AA against 25,340 controls matched for age, sex, residence, income, dementia-related comorbidities, systemic steroid use, and annual outpatient visits. Participants were enrolled between 1998 and 2011 and followed to the end of 2013.
The mean age of the cohort was 53.9 years, and a little over half (57.6%) were female. The most common comorbidity was hypertension (32.3%), followed by dyslipidemia (27%) and diabetes (15.4%).
Dual intervention
After adjusting for potential confounders, those with AA were more likely to develop dementia, AD, and unspecified dementia, compared with controls. They also had a numerically higher risk for vascular dementia, compared with controls, but it was not statistically significant.
When participants were stratified by age, investigators found a significant association between AA and higher risk for any dementia as well as unspecified dementia in individuals of all ages and an increased risk for AD in patients with dementia age at onset of 65 years and older.
The mean age of dementia diagnosis was considerably younger in patients with AA versus controls (73.4 vs. 78.9 years, P = .002). The risk for any dementia and unspecified dementia was higher in patients of both sexes, but the risk for AD was higher only in male patients.
Sensitivity analyses that excluded the first year or first 3 years of observation yielded similar and consistent findings.
“Intervention targeting poor social engagement and inflammatory cytokines may be beneficial to AA-associated dementia,” said Dr. Li.
“Physicians should be more aware of this possible association, help reduce disease discrimination among the public, and encourage more social engagement for AA patients,” he said.
“Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying pathophysiology between AA and dementia risk,” he added.
No cause and effect
Commenting on the study, Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific affairs, Alzheimer’s Association, said, “We continue to learn about and better understand factors that may increase or decrease a person’s risk of dementia.”
“While we know the immune system plays a role in Alzheimer’s and other dementia, we are still investigating links between, and impact of, autoimmune diseases – like alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and others – on our overall health and our brains, [which] may eventually give us important information on risk reduction strategies as well,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the research.
She cautioned that although the study did show a correlation between AA and dementia risk, this does not equate to a demonstration of cause and effect.
At present, “the message for clinicians is that when a patient comes to your office with complaints about their memory, they should, No. 1, be taken seriously; and, No. 2, receive a thorough evaluation that takes into account the many factors that may lead to cognitive decline,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was supported by a grant from Taipei Veterans General Hospital and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. Dr. Li, coauthors, and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alopecia areata (AA) has been linked to a significantly increased risk for dementia, new research shows.
After controlling for an array of potential confounders, investigators found a threefold higher risk of developing any form of dementia and a fourfold higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in those with AA versus the controls.
“AA shares a similar inflammatory signature with dementia and has great psychological impacts that lead to poor social engagement,” lead author Cheng-Yuan Li, MD, MSc, of the department of dermatology, Taipei (Taiwan) Veterans General Hospital.
“Poor social engagement and shared inflammatory cytokines might both be important links between AA and dementia,” said Dr. Li, who is also affiliated with the School of Medicine and the Institute of Brain Science at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei.
The study was published online Oct. 26, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry (doi: 10.4088/JCP.21m13931).
Significant psychological impact
Patients with AA often experience anxiety and depression, possibly caused by the negative emotional and psychological impact of the hair loss and partial or even complete baldness associated with the disease, the authors noted.
However, AA is also associated with an array of other atopic and autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Epidemiologic research has suggested a link between dementia and autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and SLE, with some evidence suggesting that autoimmune and inflammatory mechanisms may “play a role” in the development of AD.
Dementia in general and AD in particular, “have been shown to include an inflammatory component” that may share some of the same mediators seen in AA (eg, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha).
Moreover, “the great negative psychosocial impact of AA might result in poor social engagement, a typical risk factor for dementia,” said Dr. Li. The investigators sought to investigate whether patients with AA actually do have a higher dementia risk than individuals without AA.
The researchers used data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database, comparing 2,534 patients with AA against 25,340 controls matched for age, sex, residence, income, dementia-related comorbidities, systemic steroid use, and annual outpatient visits. Participants were enrolled between 1998 and 2011 and followed to the end of 2013.
The mean age of the cohort was 53.9 years, and a little over half (57.6%) were female. The most common comorbidity was hypertension (32.3%), followed by dyslipidemia (27%) and diabetes (15.4%).
Dual intervention
After adjusting for potential confounders, those with AA were more likely to develop dementia, AD, and unspecified dementia, compared with controls. They also had a numerically higher risk for vascular dementia, compared with controls, but it was not statistically significant.
When participants were stratified by age, investigators found a significant association between AA and higher risk for any dementia as well as unspecified dementia in individuals of all ages and an increased risk for AD in patients with dementia age at onset of 65 years and older.
The mean age of dementia diagnosis was considerably younger in patients with AA versus controls (73.4 vs. 78.9 years, P = .002). The risk for any dementia and unspecified dementia was higher in patients of both sexes, but the risk for AD was higher only in male patients.
Sensitivity analyses that excluded the first year or first 3 years of observation yielded similar and consistent findings.
“Intervention targeting poor social engagement and inflammatory cytokines may be beneficial to AA-associated dementia,” said Dr. Li.
“Physicians should be more aware of this possible association, help reduce disease discrimination among the public, and encourage more social engagement for AA patients,” he said.
“Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying pathophysiology between AA and dementia risk,” he added.
No cause and effect
Commenting on the study, Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific affairs, Alzheimer’s Association, said, “We continue to learn about and better understand factors that may increase or decrease a person’s risk of dementia.”
“While we know the immune system plays a role in Alzheimer’s and other dementia, we are still investigating links between, and impact of, autoimmune diseases – like alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and others – on our overall health and our brains, [which] may eventually give us important information on risk reduction strategies as well,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the research.
She cautioned that although the study did show a correlation between AA and dementia risk, this does not equate to a demonstration of cause and effect.
At present, “the message for clinicians is that when a patient comes to your office with complaints about their memory, they should, No. 1, be taken seriously; and, No. 2, receive a thorough evaluation that takes into account the many factors that may lead to cognitive decline,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was supported by a grant from Taipei Veterans General Hospital and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. Dr. Li, coauthors, and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alopecia areata (AA) has been linked to a significantly increased risk for dementia, new research shows.
After controlling for an array of potential confounders, investigators found a threefold higher risk of developing any form of dementia and a fourfold higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in those with AA versus the controls.
“AA shares a similar inflammatory signature with dementia and has great psychological impacts that lead to poor social engagement,” lead author Cheng-Yuan Li, MD, MSc, of the department of dermatology, Taipei (Taiwan) Veterans General Hospital.
“Poor social engagement and shared inflammatory cytokines might both be important links between AA and dementia,” said Dr. Li, who is also affiliated with the School of Medicine and the Institute of Brain Science at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei.
The study was published online Oct. 26, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry (doi: 10.4088/JCP.21m13931).
Significant psychological impact
Patients with AA often experience anxiety and depression, possibly caused by the negative emotional and psychological impact of the hair loss and partial or even complete baldness associated with the disease, the authors noted.
However, AA is also associated with an array of other atopic and autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Epidemiologic research has suggested a link between dementia and autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and SLE, with some evidence suggesting that autoimmune and inflammatory mechanisms may “play a role” in the development of AD.
Dementia in general and AD in particular, “have been shown to include an inflammatory component” that may share some of the same mediators seen in AA (eg, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha).
Moreover, “the great negative psychosocial impact of AA might result in poor social engagement, a typical risk factor for dementia,” said Dr. Li. The investigators sought to investigate whether patients with AA actually do have a higher dementia risk than individuals without AA.
The researchers used data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database, comparing 2,534 patients with AA against 25,340 controls matched for age, sex, residence, income, dementia-related comorbidities, systemic steroid use, and annual outpatient visits. Participants were enrolled between 1998 and 2011 and followed to the end of 2013.
The mean age of the cohort was 53.9 years, and a little over half (57.6%) were female. The most common comorbidity was hypertension (32.3%), followed by dyslipidemia (27%) and diabetes (15.4%).
Dual intervention
After adjusting for potential confounders, those with AA were more likely to develop dementia, AD, and unspecified dementia, compared with controls. They also had a numerically higher risk for vascular dementia, compared with controls, but it was not statistically significant.
When participants were stratified by age, investigators found a significant association between AA and higher risk for any dementia as well as unspecified dementia in individuals of all ages and an increased risk for AD in patients with dementia age at onset of 65 years and older.
The mean age of dementia diagnosis was considerably younger in patients with AA versus controls (73.4 vs. 78.9 years, P = .002). The risk for any dementia and unspecified dementia was higher in patients of both sexes, but the risk for AD was higher only in male patients.
Sensitivity analyses that excluded the first year or first 3 years of observation yielded similar and consistent findings.
“Intervention targeting poor social engagement and inflammatory cytokines may be beneficial to AA-associated dementia,” said Dr. Li.
“Physicians should be more aware of this possible association, help reduce disease discrimination among the public, and encourage more social engagement for AA patients,” he said.
“Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying pathophysiology between AA and dementia risk,” he added.
No cause and effect
Commenting on the study, Heather M. Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific affairs, Alzheimer’s Association, said, “We continue to learn about and better understand factors that may increase or decrease a person’s risk of dementia.”
“While we know the immune system plays a role in Alzheimer’s and other dementia, we are still investigating links between, and impact of, autoimmune diseases – like alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and others – on our overall health and our brains, [which] may eventually give us important information on risk reduction strategies as well,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the research.
She cautioned that although the study did show a correlation between AA and dementia risk, this does not equate to a demonstration of cause and effect.
At present, “the message for clinicians is that when a patient comes to your office with complaints about their memory, they should, No. 1, be taken seriously; and, No. 2, receive a thorough evaluation that takes into account the many factors that may lead to cognitive decline,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was supported by a grant from Taipei Veterans General Hospital and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. Dr. Li, coauthors, and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ivermectin–COVID-19 study retracted; authors blame file mix-up
The paper, “Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon,” appeared in the journal Viruses in May. According to the abstract: “A randomized controlled trial was conducted in 100 asymptomatic Lebanese subjects that have tested positive for SARS-CoV2. Fifty patients received standard preventive treatment, mainly supplements, and the experimental group received a single dose (according to body weight) of ivermectin, in addition to the same supplements the control group received.”
Results results results … and: “Ivermectin appears to be efficacious in providing clinical benefits in a randomized treatment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects, effectively resulting in fewer symptoms, lower viral load and reduced hospital admissions. However, larger-scale trials are warranted for this conclusion to be further cemented.”
However, in early October, the BBC reported — in a larger piece about the concerns about ivermectin-Covid-19 research — that the study “was found to have blocks of details of 11 patients that had been copied and pasted repeatedly – suggesting many of the trial’s apparent patients didn’t really exist.”
The study’s authors told the BBC that the ‘original set of data was rigged, sabotaged or mistakenly entered in the final file’ and that they have submitted a retraction to the scientific journal which published it.
That’s not quite what the retraction notice states: “The journal retracts the article, Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon [ 1 ], cited above. Following publication, the authors contacted the editorial office regarding an error between files used for the statistical analysis. Adhering to our complaints procedure, an investigation was conducted that confirmed the error reported by the authors.
This retraction was approved by the Editor in Chief of the journal. The authors agreed to this retraction.”
Ali Samaha, of Lebanese University in Beirut, and the lead author of the study, told us: “It was brought to our attention that we have used wrong file for our paper. We informed immediately the journal and we have run investigations. After revising the raw data we realised that a file that was used to train a research assistant was sent by mistake for analysis. Re-analysing the original data , the conclusions of the paper remained valid. For our transparency we asked for retraction.”
About that BBC report? Samaha said: “The BBC article was generated before the report of independent reviewers who confirmed an innocent mistake by using wrong file.”
Samaha added that he and his colleagues are now considering whether to resubmit the paper.
The article has been cited four times, according to Clarivate Analytics’ Web of Science — including in this meta-analysis published in June in the American Journal of Therapeutics , which concluded that: “Moderate-certainty evidence finds that large reductions in COVID-19 deaths are possible using ivermectin. Using ivermectin early in the clinical course may reduce numbers progressing to severe disease. The apparent safety and low cost suggest that ivermectin is likely to have a significant impact on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic globally.”
That article was a social media darling, receiving more than 45,000 tweets and pickups in 90 news outlets, according to Altmetrics, which ranks it No. 7 among all papers published at that time.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
The paper, “Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon,” appeared in the journal Viruses in May. According to the abstract: “A randomized controlled trial was conducted in 100 asymptomatic Lebanese subjects that have tested positive for SARS-CoV2. Fifty patients received standard preventive treatment, mainly supplements, and the experimental group received a single dose (according to body weight) of ivermectin, in addition to the same supplements the control group received.”
Results results results … and: “Ivermectin appears to be efficacious in providing clinical benefits in a randomized treatment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects, effectively resulting in fewer symptoms, lower viral load and reduced hospital admissions. However, larger-scale trials are warranted for this conclusion to be further cemented.”
However, in early October, the BBC reported — in a larger piece about the concerns about ivermectin-Covid-19 research — that the study “was found to have blocks of details of 11 patients that had been copied and pasted repeatedly – suggesting many of the trial’s apparent patients didn’t really exist.”
The study’s authors told the BBC that the ‘original set of data was rigged, sabotaged or mistakenly entered in the final file’ and that they have submitted a retraction to the scientific journal which published it.
That’s not quite what the retraction notice states: “The journal retracts the article, Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon [ 1 ], cited above. Following publication, the authors contacted the editorial office regarding an error between files used for the statistical analysis. Adhering to our complaints procedure, an investigation was conducted that confirmed the error reported by the authors.
This retraction was approved by the Editor in Chief of the journal. The authors agreed to this retraction.”
Ali Samaha, of Lebanese University in Beirut, and the lead author of the study, told us: “It was brought to our attention that we have used wrong file for our paper. We informed immediately the journal and we have run investigations. After revising the raw data we realised that a file that was used to train a research assistant was sent by mistake for analysis. Re-analysing the original data , the conclusions of the paper remained valid. For our transparency we asked for retraction.”
About that BBC report? Samaha said: “The BBC article was generated before the report of independent reviewers who confirmed an innocent mistake by using wrong file.”
Samaha added that he and his colleagues are now considering whether to resubmit the paper.
The article has been cited four times, according to Clarivate Analytics’ Web of Science — including in this meta-analysis published in June in the American Journal of Therapeutics , which concluded that: “Moderate-certainty evidence finds that large reductions in COVID-19 deaths are possible using ivermectin. Using ivermectin early in the clinical course may reduce numbers progressing to severe disease. The apparent safety and low cost suggest that ivermectin is likely to have a significant impact on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic globally.”
That article was a social media darling, receiving more than 45,000 tweets and pickups in 90 news outlets, according to Altmetrics, which ranks it No. 7 among all papers published at that time.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
The paper, “Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon,” appeared in the journal Viruses in May. According to the abstract: “A randomized controlled trial was conducted in 100 asymptomatic Lebanese subjects that have tested positive for SARS-CoV2. Fifty patients received standard preventive treatment, mainly supplements, and the experimental group received a single dose (according to body weight) of ivermectin, in addition to the same supplements the control group received.”
Results results results … and: “Ivermectin appears to be efficacious in providing clinical benefits in a randomized treatment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects, effectively resulting in fewer symptoms, lower viral load and reduced hospital admissions. However, larger-scale trials are warranted for this conclusion to be further cemented.”
However, in early October, the BBC reported — in a larger piece about the concerns about ivermectin-Covid-19 research — that the study “was found to have blocks of details of 11 patients that had been copied and pasted repeatedly – suggesting many of the trial’s apparent patients didn’t really exist.”
The study’s authors told the BBC that the ‘original set of data was rigged, sabotaged or mistakenly entered in the final file’ and that they have submitted a retraction to the scientific journal which published it.
That’s not quite what the retraction notice states: “The journal retracts the article, Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon [ 1 ], cited above. Following publication, the authors contacted the editorial office regarding an error between files used for the statistical analysis. Adhering to our complaints procedure, an investigation was conducted that confirmed the error reported by the authors.
This retraction was approved by the Editor in Chief of the journal. The authors agreed to this retraction.”
Ali Samaha, of Lebanese University in Beirut, and the lead author of the study, told us: “It was brought to our attention that we have used wrong file for our paper. We informed immediately the journal and we have run investigations. After revising the raw data we realised that a file that was used to train a research assistant was sent by mistake for analysis. Re-analysing the original data , the conclusions of the paper remained valid. For our transparency we asked for retraction.”
About that BBC report? Samaha said: “The BBC article was generated before the report of independent reviewers who confirmed an innocent mistake by using wrong file.”
Samaha added that he and his colleagues are now considering whether to resubmit the paper.
The article has been cited four times, according to Clarivate Analytics’ Web of Science — including in this meta-analysis published in June in the American Journal of Therapeutics , which concluded that: “Moderate-certainty evidence finds that large reductions in COVID-19 deaths are possible using ivermectin. Using ivermectin early in the clinical course may reduce numbers progressing to severe disease. The apparent safety and low cost suggest that ivermectin is likely to have a significant impact on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic globally.”
That article was a social media darling, receiving more than 45,000 tweets and pickups in 90 news outlets, according to Altmetrics, which ranks it No. 7 among all papers published at that time.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
Update on the Pediatric Dermatology Workforce Shortage
Pediatric dermatology is a relatively young subspecialty. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology (SPD) was established in 1975, followed by the creation of the journal Pediatric Dermatology in 1982 and the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Dermatology in 1986.1 In 2000, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) officially recognized pediatric dermatology as a unique subspecialty of the American Board of Dermatology (ABD). During that time, informal fellowship experiences emerged, and formal 1-year training programs approved by the ABD evolved by 2006. A subspecialty certification examination was created and has been administered every other year since 2004.1 Data provided by the SPD indicate that approximately 431 US dermatologists have passed the ABD’s pediatric dermatology board certification examination thus far (unpublished data, September 2021).
In 1986, the first systematic evaluation of the US pediatric dermatology workforce revealed a total of 57 practicing pediatric dermatologists and concluded that job opportunities appeared to be limited at that time.2 Since then, the demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to grow steadily, and the number of board-certified pediatric dermatologists practicing in the United States has increased to at least 317 per data from a 2020 survey.3 However, given that there are more than 11,000 board-certified dermatologists in the United States, there continues to be a severe shortage of pediatric dermatologists.1
Increased Demand for Pediatric Dermatologists
Approximately 10% to 30% of almost 200 million annual outpatient pediatric primary care visits involve a skin concern. Although many of these problems can be handled by primary care physicians, more than 80% of pediatricians report having difficulty accessing dermatology services for their patients.4 In surveys of pediatricians, pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate but has consistently ranked third among the specialties deemed most difficult to access.5-7 In addition, it is not uncommon for the wait time to see a pediatric dermatologist to be 6 weeks or longer.5,8
Recent population data estimate that there are 73 million children living in the United States.9 If there are roughly 317 practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists, that translates into approximately 4.3 pediatric dermatologists per million children. This number is far smaller than the 4 general dermatologists per 100,000 individuals recommended by Glazer et al10 in 2017. To meet this suggested ratio goal, the workforce of pediatric dermatologists would have to increase to 2920. In addition to this severe workforce shortage, there is an additional problem with geographic maldistribution of pediatric dermatologists. More than 98% of pediatric dermatologists practice in metropolitan areas. At least 8 states and 95% of counties have no pediatric dermatologist, and there are no pediatric dermatologists practicing in rural counties.9 This disparity has considerable implications for barriers to care and lack of access for children living in underserved areas. Suggestions for attracting pediatric dermatologists to practice in these areas have included loan forgiveness programs as well as remote mentorship programs to provide professional support.8,9
Training in Pediatrics
There currently are 38 ABD-approved pediatric dermatology fellowship training programs in the United States. Beginning in 2009, pediatric dermatology fellowship programs have participated in the SF Match program. Data provided by the SPD show that, since 2012, up to 27 programs have participated in the annual Match, offering a total number of positions ranging from 27 to 38; however, only 11 to 21 positions have been filled each year, leaving a large number of post-Match vacancies (unpublished data, September 2021).
Surveys have explored the reasons behind this lack of interest in pediatric dermatology training among dermatology residents. Factors that have been mentioned include lack of exposure and mentorship in medical school and residency, the financial hardship of an additional year of fellowship training, and historically lower salaries for pediatric dermatologists compared to general dermatologists.3,6
A 2004 survey revealed that more than 75% of dermatology department chairs believed it was important to have a pediatric dermatologist on the faculty; however, at that time only 48% of dermatology programs reported having at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatology faculty member.11 By 2008, a follow-up survey showed an increase to 70% of dermatology training programs reporting at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatologist; however, 43% of departments still had at least 1 open position, and 76% of those programs shared that they had been searching for more than 1 year.2 Currently, the Accreditation Data System of the ACGME shows a total of 144 accredited US dermatology training programs. Of those, 117 programs have 1 or more board-certified pediatric dermatology faculty member, and 27 programs still have none (unpublished data, September 2021).
A shortage of pediatric dermatologists in training programs contributes to the lack of exposure and mentorship for medical students and residents during a critical time in professional development. Studies show that up to 91% of pediatric dermatologists decided to pursue training in pediatric dermatology during medical school, pediatrics residency, or dermatology residency. In one survey, 84% of respondents (N=109) cited early mentorship as the most important factor in their decision to pursue pediatric dermatology.6
A lack of pediatric dermatologists also results in suboptimal dermatology training for residents who care for children in primary care specialties, including pediatrics, combined internal medicine and pediatrics, and family practice. Multiple surveys have shown that many pediatricians feel they received inadequate training in dermatology during residency. Up to 38% have cited a need for more pediatric dermatology education (N=755).5,6 In addition, studies show a wide disparity in diagnostic accuracy between dermatologists and pediatricians, with one concluding that more than one-third of referrals to pediatric dermatologists were initially misdiagnosed and/or incorrectly treated.5,7
Recruitment Efforts for Pediatric Dermatologists
There are multiple strategies for recruiting trainees into the pediatric dermatology workforce. First, given the importance of early exposure to the field and role models/mentors, pediatric dermatologists must take advantage of every opportunity to interact with medical students and residents. They can share their genuine enthusiasm and love for the specialty while encouraging and supporting those who show interest. They also should seek opportunities for teaching, lecturing, and advising at every level of training. In addition, they can enhance visibility of the specialty by participating in career forums and/or assuming leadership roles within their departments or institutions.12 Another suggestion is for dermatology training programs to consider giving priority to qualified applicants who express sincere interest in pursuing pediatric dermatology training (including those who have already completed pediatrics residency). Although a 2008 survey revealed that 39% of dermatology residency programs (N=80) favored giving priority to applicants demonstrating interest in pediatric dermatology, others were against it, citing issues such as lack of funding for additional residency training, lack of pediatric dermatology mentors within the program, and an overall mistrust of applicants’ sincerity.2
Final Thoughts
The subspecialty of pediatric dermatology has experienced remarkable growth over the last 40 years; however, demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to outpace supply, resulting in a persistent and notable workforce shortage. Overall, the current supply of pediatric dermatologists can neither meet the clinical demands of the pediatric population nor fulfill academic needs of existing training programs. We must continue to develop novel strategies for increasing the pool of students and residents who are interested in pursuing careers in pediatric dermatology. Ultimately, we also must create incentives and develop tactics to address the geographic maldistribution that exists within the specialty.
- Prindaville B, Antaya R, Siegfried E. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12.
- Craiglow BG, Resneck JS, Lucky AW, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: perspectives from academia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:986-989.
- Ashrafzadeh S, Peters G, Brandling-Bennett H, et al. The geographic distribution of the US pediatric dermatologist workforce: a national cross-sectional study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:1098-1105.
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897.
- Prindaville B, Simon S, Horii K. Dermatology-related outpatient visits by children: implications for workforce and pediatric education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:228-229.
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim S, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-375.
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. The US pediatric dermatology workforce: an assessment of productivity and practice patterns. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:825-829.
- Prindaville B, Horii K, Siegfried E, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:166-168.
- Ugwu-Dike P, Nambudiri V. Access as equity: addressing the distribution of the pediatric dermatology workforce [published online August 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14665
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Hester EJ, McNealy KM, Kelloff JN, et al. Demand outstrips supply of US pediatric dermatologists: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:431-434.
- Wright TS, Huang JT. Comment on “pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States”. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:177-178.
Pediatric dermatology is a relatively young subspecialty. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology (SPD) was established in 1975, followed by the creation of the journal Pediatric Dermatology in 1982 and the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Dermatology in 1986.1 In 2000, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) officially recognized pediatric dermatology as a unique subspecialty of the American Board of Dermatology (ABD). During that time, informal fellowship experiences emerged, and formal 1-year training programs approved by the ABD evolved by 2006. A subspecialty certification examination was created and has been administered every other year since 2004.1 Data provided by the SPD indicate that approximately 431 US dermatologists have passed the ABD’s pediatric dermatology board certification examination thus far (unpublished data, September 2021).
In 1986, the first systematic evaluation of the US pediatric dermatology workforce revealed a total of 57 practicing pediatric dermatologists and concluded that job opportunities appeared to be limited at that time.2 Since then, the demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to grow steadily, and the number of board-certified pediatric dermatologists practicing in the United States has increased to at least 317 per data from a 2020 survey.3 However, given that there are more than 11,000 board-certified dermatologists in the United States, there continues to be a severe shortage of pediatric dermatologists.1
Increased Demand for Pediatric Dermatologists
Approximately 10% to 30% of almost 200 million annual outpatient pediatric primary care visits involve a skin concern. Although many of these problems can be handled by primary care physicians, more than 80% of pediatricians report having difficulty accessing dermatology services for their patients.4 In surveys of pediatricians, pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate but has consistently ranked third among the specialties deemed most difficult to access.5-7 In addition, it is not uncommon for the wait time to see a pediatric dermatologist to be 6 weeks or longer.5,8
Recent population data estimate that there are 73 million children living in the United States.9 If there are roughly 317 practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists, that translates into approximately 4.3 pediatric dermatologists per million children. This number is far smaller than the 4 general dermatologists per 100,000 individuals recommended by Glazer et al10 in 2017. To meet this suggested ratio goal, the workforce of pediatric dermatologists would have to increase to 2920. In addition to this severe workforce shortage, there is an additional problem with geographic maldistribution of pediatric dermatologists. More than 98% of pediatric dermatologists practice in metropolitan areas. At least 8 states and 95% of counties have no pediatric dermatologist, and there are no pediatric dermatologists practicing in rural counties.9 This disparity has considerable implications for barriers to care and lack of access for children living in underserved areas. Suggestions for attracting pediatric dermatologists to practice in these areas have included loan forgiveness programs as well as remote mentorship programs to provide professional support.8,9
Training in Pediatrics
There currently are 38 ABD-approved pediatric dermatology fellowship training programs in the United States. Beginning in 2009, pediatric dermatology fellowship programs have participated in the SF Match program. Data provided by the SPD show that, since 2012, up to 27 programs have participated in the annual Match, offering a total number of positions ranging from 27 to 38; however, only 11 to 21 positions have been filled each year, leaving a large number of post-Match vacancies (unpublished data, September 2021).
Surveys have explored the reasons behind this lack of interest in pediatric dermatology training among dermatology residents. Factors that have been mentioned include lack of exposure and mentorship in medical school and residency, the financial hardship of an additional year of fellowship training, and historically lower salaries for pediatric dermatologists compared to general dermatologists.3,6
A 2004 survey revealed that more than 75% of dermatology department chairs believed it was important to have a pediatric dermatologist on the faculty; however, at that time only 48% of dermatology programs reported having at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatology faculty member.11 By 2008, a follow-up survey showed an increase to 70% of dermatology training programs reporting at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatologist; however, 43% of departments still had at least 1 open position, and 76% of those programs shared that they had been searching for more than 1 year.2 Currently, the Accreditation Data System of the ACGME shows a total of 144 accredited US dermatology training programs. Of those, 117 programs have 1 or more board-certified pediatric dermatology faculty member, and 27 programs still have none (unpublished data, September 2021).
A shortage of pediatric dermatologists in training programs contributes to the lack of exposure and mentorship for medical students and residents during a critical time in professional development. Studies show that up to 91% of pediatric dermatologists decided to pursue training in pediatric dermatology during medical school, pediatrics residency, or dermatology residency. In one survey, 84% of respondents (N=109) cited early mentorship as the most important factor in their decision to pursue pediatric dermatology.6
A lack of pediatric dermatologists also results in suboptimal dermatology training for residents who care for children in primary care specialties, including pediatrics, combined internal medicine and pediatrics, and family practice. Multiple surveys have shown that many pediatricians feel they received inadequate training in dermatology during residency. Up to 38% have cited a need for more pediatric dermatology education (N=755).5,6 In addition, studies show a wide disparity in diagnostic accuracy between dermatologists and pediatricians, with one concluding that more than one-third of referrals to pediatric dermatologists were initially misdiagnosed and/or incorrectly treated.5,7
Recruitment Efforts for Pediatric Dermatologists
There are multiple strategies for recruiting trainees into the pediatric dermatology workforce. First, given the importance of early exposure to the field and role models/mentors, pediatric dermatologists must take advantage of every opportunity to interact with medical students and residents. They can share their genuine enthusiasm and love for the specialty while encouraging and supporting those who show interest. They also should seek opportunities for teaching, lecturing, and advising at every level of training. In addition, they can enhance visibility of the specialty by participating in career forums and/or assuming leadership roles within their departments or institutions.12 Another suggestion is for dermatology training programs to consider giving priority to qualified applicants who express sincere interest in pursuing pediatric dermatology training (including those who have already completed pediatrics residency). Although a 2008 survey revealed that 39% of dermatology residency programs (N=80) favored giving priority to applicants demonstrating interest in pediatric dermatology, others were against it, citing issues such as lack of funding for additional residency training, lack of pediatric dermatology mentors within the program, and an overall mistrust of applicants’ sincerity.2
Final Thoughts
The subspecialty of pediatric dermatology has experienced remarkable growth over the last 40 years; however, demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to outpace supply, resulting in a persistent and notable workforce shortage. Overall, the current supply of pediatric dermatologists can neither meet the clinical demands of the pediatric population nor fulfill academic needs of existing training programs. We must continue to develop novel strategies for increasing the pool of students and residents who are interested in pursuing careers in pediatric dermatology. Ultimately, we also must create incentives and develop tactics to address the geographic maldistribution that exists within the specialty.
Pediatric dermatology is a relatively young subspecialty. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology (SPD) was established in 1975, followed by the creation of the journal Pediatric Dermatology in 1982 and the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Dermatology in 1986.1 In 2000, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) officially recognized pediatric dermatology as a unique subspecialty of the American Board of Dermatology (ABD). During that time, informal fellowship experiences emerged, and formal 1-year training programs approved by the ABD evolved by 2006. A subspecialty certification examination was created and has been administered every other year since 2004.1 Data provided by the SPD indicate that approximately 431 US dermatologists have passed the ABD’s pediatric dermatology board certification examination thus far (unpublished data, September 2021).
In 1986, the first systematic evaluation of the US pediatric dermatology workforce revealed a total of 57 practicing pediatric dermatologists and concluded that job opportunities appeared to be limited at that time.2 Since then, the demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to grow steadily, and the number of board-certified pediatric dermatologists practicing in the United States has increased to at least 317 per data from a 2020 survey.3 However, given that there are more than 11,000 board-certified dermatologists in the United States, there continues to be a severe shortage of pediatric dermatologists.1
Increased Demand for Pediatric Dermatologists
Approximately 10% to 30% of almost 200 million annual outpatient pediatric primary care visits involve a skin concern. Although many of these problems can be handled by primary care physicians, more than 80% of pediatricians report having difficulty accessing dermatology services for their patients.4 In surveys of pediatricians, pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate but has consistently ranked third among the specialties deemed most difficult to access.5-7 In addition, it is not uncommon for the wait time to see a pediatric dermatologist to be 6 weeks or longer.5,8
Recent population data estimate that there are 73 million children living in the United States.9 If there are roughly 317 practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists, that translates into approximately 4.3 pediatric dermatologists per million children. This number is far smaller than the 4 general dermatologists per 100,000 individuals recommended by Glazer et al10 in 2017. To meet this suggested ratio goal, the workforce of pediatric dermatologists would have to increase to 2920. In addition to this severe workforce shortage, there is an additional problem with geographic maldistribution of pediatric dermatologists. More than 98% of pediatric dermatologists practice in metropolitan areas. At least 8 states and 95% of counties have no pediatric dermatologist, and there are no pediatric dermatologists practicing in rural counties.9 This disparity has considerable implications for barriers to care and lack of access for children living in underserved areas. Suggestions for attracting pediatric dermatologists to practice in these areas have included loan forgiveness programs as well as remote mentorship programs to provide professional support.8,9
Training in Pediatrics
There currently are 38 ABD-approved pediatric dermatology fellowship training programs in the United States. Beginning in 2009, pediatric dermatology fellowship programs have participated in the SF Match program. Data provided by the SPD show that, since 2012, up to 27 programs have participated in the annual Match, offering a total number of positions ranging from 27 to 38; however, only 11 to 21 positions have been filled each year, leaving a large number of post-Match vacancies (unpublished data, September 2021).
Surveys have explored the reasons behind this lack of interest in pediatric dermatology training among dermatology residents. Factors that have been mentioned include lack of exposure and mentorship in medical school and residency, the financial hardship of an additional year of fellowship training, and historically lower salaries for pediatric dermatologists compared to general dermatologists.3,6
A 2004 survey revealed that more than 75% of dermatology department chairs believed it was important to have a pediatric dermatologist on the faculty; however, at that time only 48% of dermatology programs reported having at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatology faculty member.11 By 2008, a follow-up survey showed an increase to 70% of dermatology training programs reporting at least 1 full-time pediatric dermatologist; however, 43% of departments still had at least 1 open position, and 76% of those programs shared that they had been searching for more than 1 year.2 Currently, the Accreditation Data System of the ACGME shows a total of 144 accredited US dermatology training programs. Of those, 117 programs have 1 or more board-certified pediatric dermatology faculty member, and 27 programs still have none (unpublished data, September 2021).
A shortage of pediatric dermatologists in training programs contributes to the lack of exposure and mentorship for medical students and residents during a critical time in professional development. Studies show that up to 91% of pediatric dermatologists decided to pursue training in pediatric dermatology during medical school, pediatrics residency, or dermatology residency. In one survey, 84% of respondents (N=109) cited early mentorship as the most important factor in their decision to pursue pediatric dermatology.6
A lack of pediatric dermatologists also results in suboptimal dermatology training for residents who care for children in primary care specialties, including pediatrics, combined internal medicine and pediatrics, and family practice. Multiple surveys have shown that many pediatricians feel they received inadequate training in dermatology during residency. Up to 38% have cited a need for more pediatric dermatology education (N=755).5,6 In addition, studies show a wide disparity in diagnostic accuracy between dermatologists and pediatricians, with one concluding that more than one-third of referrals to pediatric dermatologists were initially misdiagnosed and/or incorrectly treated.5,7
Recruitment Efforts for Pediatric Dermatologists
There are multiple strategies for recruiting trainees into the pediatric dermatology workforce. First, given the importance of early exposure to the field and role models/mentors, pediatric dermatologists must take advantage of every opportunity to interact with medical students and residents. They can share their genuine enthusiasm and love for the specialty while encouraging and supporting those who show interest. They also should seek opportunities for teaching, lecturing, and advising at every level of training. In addition, they can enhance visibility of the specialty by participating in career forums and/or assuming leadership roles within their departments or institutions.12 Another suggestion is for dermatology training programs to consider giving priority to qualified applicants who express sincere interest in pursuing pediatric dermatology training (including those who have already completed pediatrics residency). Although a 2008 survey revealed that 39% of dermatology residency programs (N=80) favored giving priority to applicants demonstrating interest in pediatric dermatology, others were against it, citing issues such as lack of funding for additional residency training, lack of pediatric dermatology mentors within the program, and an overall mistrust of applicants’ sincerity.2
Final Thoughts
The subspecialty of pediatric dermatology has experienced remarkable growth over the last 40 years; however, demand for pediatric dermatology services has continued to outpace supply, resulting in a persistent and notable workforce shortage. Overall, the current supply of pediatric dermatologists can neither meet the clinical demands of the pediatric population nor fulfill academic needs of existing training programs. We must continue to develop novel strategies for increasing the pool of students and residents who are interested in pursuing careers in pediatric dermatology. Ultimately, we also must create incentives and develop tactics to address the geographic maldistribution that exists within the specialty.
- Prindaville B, Antaya R, Siegfried E. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12.
- Craiglow BG, Resneck JS, Lucky AW, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: perspectives from academia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:986-989.
- Ashrafzadeh S, Peters G, Brandling-Bennett H, et al. The geographic distribution of the US pediatric dermatologist workforce: a national cross-sectional study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:1098-1105.
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897.
- Prindaville B, Simon S, Horii K. Dermatology-related outpatient visits by children: implications for workforce and pediatric education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:228-229.
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim S, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-375.
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. The US pediatric dermatology workforce: an assessment of productivity and practice patterns. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:825-829.
- Prindaville B, Horii K, Siegfried E, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:166-168.
- Ugwu-Dike P, Nambudiri V. Access as equity: addressing the distribution of the pediatric dermatology workforce [published online August 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14665
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Hester EJ, McNealy KM, Kelloff JN, et al. Demand outstrips supply of US pediatric dermatologists: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:431-434.
- Wright TS, Huang JT. Comment on “pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States”. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:177-178.
- Prindaville B, Antaya R, Siegfried E. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12.
- Craiglow BG, Resneck JS, Lucky AW, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: perspectives from academia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:986-989.
- Ashrafzadeh S, Peters G, Brandling-Bennett H, et al. The geographic distribution of the US pediatric dermatologist workforce: a national cross-sectional study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:1098-1105.
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897.
- Prindaville B, Simon S, Horii K. Dermatology-related outpatient visits by children: implications for workforce and pediatric education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:228-229.
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim S, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-375.
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. The US pediatric dermatology workforce: an assessment of productivity and practice patterns. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:825-829.
- Prindaville B, Horii K, Siegfried E, et al. Pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:166-168.
- Ugwu-Dike P, Nambudiri V. Access as equity: addressing the distribution of the pediatric dermatology workforce [published online August 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. doi:10.1111/pde.14665
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Hester EJ, McNealy KM, Kelloff JN, et al. Demand outstrips supply of US pediatric dermatologists: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:431-434.
- Wright TS, Huang JT. Comment on “pediatric dermatology workforce in the United States”. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:177-178.
Not COVID Toes: Pool Palms and Feet in Pediatric Patients
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
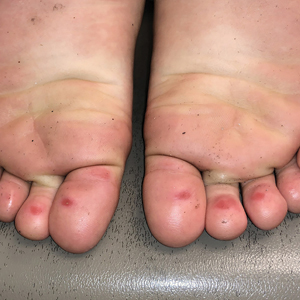
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.
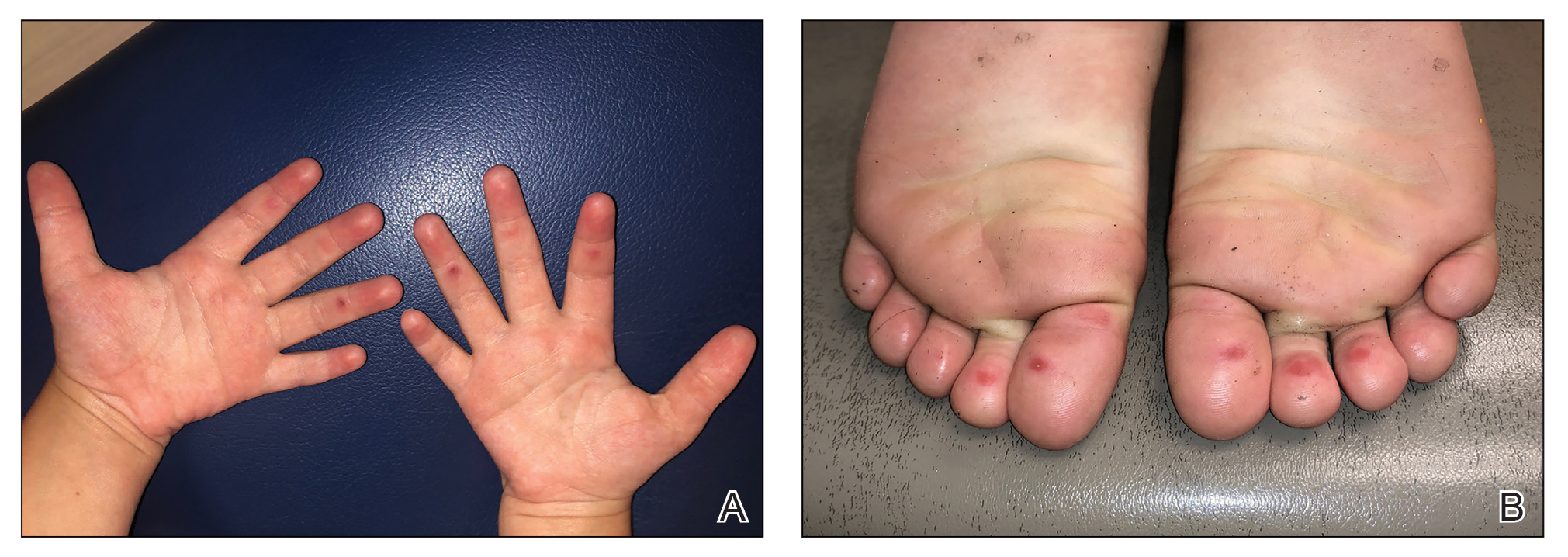
Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.

Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.

Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
AHA dietary guidance cites structural challenges to heart-healthy patterns
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
FROM CIRCULATION
Management of Pediatric Nail Psoriasis
Pediatric nail psoriasis is a condition that has not been extensively studied. The prevalence of nail alterations in pediatric patients with psoriasis varies among different studies, ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail pitting, onycholysis associated with subungual hyperkeratosis, paronychia, and pachyonychia are the most frequent features of psoriatic nail involvement in children.2,3 The management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents is critical due to the quality-of-life impact, from potential functional impairment issues to the obvious cosmetic problems, which can aggravate the psychologic distress and social embarrassment of patients with psoriasis. Despite the emergence of modern potent systemic agents to treat chronic plaque psoriasis, nail psoriasis often is refractory to treatment.4 Coupled with the limited on-label options for psoriasis treatment in children, the management of nail psoriasis in this special patient group constitutes an even greater therapeutic challenge. This report aims to summarize the limited existing data on the successful management of nail psoriasis in the pediatric population.
Reviewing the Literature on Nail Psoriasis
We conducted a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus using the following Medical Subject Headings key terms: nail psoriasis and children, juvenile, pediatric. Additional articles were identified from the reference lists of the retrieved articles and citations. Our search included reports in the English language published from 2000 to 2019. The selection process included the following 2 steps: screening of the titles and abstracts, followed by evaluation of the selected full-text articles.
Topical Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Because most systemic antipsoriatic treatments that can be administered in adult patients have not yet been granted an official license for administration in children, topical treatments are considered by many physicians as the preferred first-line therapy for psoriatic nail involvement in pediatric patients.5,6 However, only scarce data are available in the literature concerning the successful use of local agents in pediatric patients with psoriasis.
The main limitation of local treatments relates mostly to their impaired penetration into the affected area (nails). To optimize drug penetration, some authors suggest the use of potent keratolytic topical preparations to reduce the nail volume and facilitate drug absorption.7 A popular suggestion is trimming the onycholytic nail plate followed by 40% urea avulsion to treat subungual hyperkeratosis8 or simply the use of occlusive 40% urea in petroleum jelly.9 Other approaches include clipping the onycholytic nail over the diseased nail bed or processing the nail plate through grinding or even drilling holes with the use of mechanical burrs or ablative lasers to enhance the penetration of the topical agent.7
A frequent approach in pediatric patients is clipping the detached nails combined with daily application of calcipotriene (calcipotriol) and steroids, such as betamethasone dipropionate.5,8 Reports on the use of regimens with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% under occlusion, with or without the concomitant use of calcipotriol solution 0.005%, also are present in the literature but not always with satisfactory results.10,11 Another successfully administered topical steroid is mometasone furoate cream 0.1%.12 Although the use of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide also has demonstrated encouraging outcomes in isolated reports,13 associated adverse events, such as pain and hematomas, can result in tolerability issues for pediatric patients.7
Piraccini et al14 described the case of an 8-year-old patient with pustular nail psoriasis who showed improvement within 3 to 6 months of treatment with topical calcipotriol 5 μg/g as monotherapy applied to the nail and periungual tissues twice daily. Another approach, described by Diluvio et al,15 is the use of tazarotene gel 0.05% applied once daily to the affected nail plates, nail folds, and periungual skin without occlusion. In a 6-year-old patient with isolated nail psoriasis, this treatment regimen demonstrated notable improvement within 8 weeks.15
Systemic Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Data on the successful administration of systemic agents in pediatric patients also are extremely scarce. Due to the lack of clinical trials, everyday practice is mostly based on isolated case series and case reports.
Methotrexate—Lee11 described the case of an 11-year-old girl with severe, symptomatic, 20-nail psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed a complete response to oral methotrexate 5 mg/wk after topical clobetasol propionate and calcipotriol failed. Improvement was seen as early as 4 weeks after therapy initiation, and complete resolution of the lesions was documented after 9 and 13 months of methotrexate therapy for the fingers and toes, respectively.11 The successful use of methotrexate in the improvement of psoriatic nail dystrophy in a pediatric patient also was documented by Teran et al.16 In this case, a 9-year-old girl with erythrodermic psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and severe onychodystrophy showed notable amelioration of all psoriatic manifestations, including the nail findings, with systemic methotrexate therapy (dose not specified).16 Notably, the authors reported that the improvement of onychodystrophy occurred with considerable delay compared to the other psoriatic lesions,16 indicating the already-known refractoriness of nail psoriasis to the various therapeutic attempts.9-15
Acitretin—Another agent that has been linked with partial improvement of acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau (ACH)–associated onychodystrophy is acitretin. In a case series of 15 pediatric patients with pustular psoriasis, a 5-year-old boy with severe nail involvement presented with partial amelioration of nail changes with acitretin within the first 6 weeks of treatment using the following regimen: initial dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/d for 6 weeks, followed by 0.3 mg/kg/d for 4 weeks.17
Biologics—The emerging use of biologics in pediatric psoriasis also has brought important advances in the successful management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents.18-21 Wells et al18 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with nail psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis who showed complete resolution of all psoriatic manifestations, including nail involvement, within 3 months of treatment with secukinumab 150 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Prior failed treatments included various systemic agents (ie, subcutaneous methotrexate 20 mg/m2, etanercept 0.8 mg/kg weekly, adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks) as well as topical agents (ie, urea, tazarotene, corticosteroids) and intralesional triamcinolone.18
Infliximab also has been successfully used for pediatric nail psoriasis. Watabe et al19 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with psoriatic onychodystrophy in addition to psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis. Prior therapy with adalimumab 20 mg every other week combined with methotrexate 10 mg weekly failed. She experienced notable amelioration of the nail dystrophy within 3 months of using a combination of infliximab and methotrexate (infliximab 5 mg/kg intravenously on weeks 0, 2, and 6, and every 8 weeks thereafter; methotrexate 10 mg/wk).19
Cases in which infliximab has resulted in rapid yet only transient restoration of psoriatic onychodystrophy also are present in the literature. Pereira et al20 reported that a 3-year-old patient with severe 20-digit onychodystrophy in addition to pustular psoriasis had complete resolution of nail lesions within 2 weeks of treatment with infliximab (5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6, and then every 7 weeks thereafter), which was sustained over the course of 1 year. The therapy had to be discontinued because of exacerbation of the cutaneous symptoms; thereafter, etanercept was initiated. Although the patient noted major improvement of all skin lesions under etanercept, only moderate amelioration of the psoriatic nail lesions was demonstrated.20
Dini et al21 described a 9-year-old girl with severe ACH-associated psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed complete clearance of all lesions within 8 weeks of treatment with adalimumab (initially 80 mg, followed by 40 mg after 1 week and then 40 mg every other week). Prior treatment with potent topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine (3 mg/kg/d for 6 months), and etanercept (0.4 mg/kg twice weekly for 3 months) was ineffective.21
Phototherapy—Other systemic agents with reported satisfactory outcomes in the treatment of psoriatic onychodystrophy include thalidomide combined with UVB phototherapy. Kiszewski et al22 described a 2-year-old patient with ACH and severe 19-digit onychodystrophy. Prior failed therapies included occluded clobetasol ointment 0.05%, occluded pimecrolimus 0.1%, and systemic methotrexate, while systemic acitretin (0.8 mg⁄kg⁄d) resulted in elevated cholesterol levels and therefore had to be interrupted. Improvement was seen 2 months after the initiation of a combined broadband UVB and thalidomide (50 mg⁄d) treatment, with no documented relapses after discontinuation of therapy.22
Narrowband UVB (311 nm) also has been used as monotherapy for ACH-associated onychodystrophy, as demonstrated by Bordignon et al.23 They reported a 9-year-old patient who showed partial improvement of isolated onychodystrophy of the fourth nail plate of the left hand after 36 sessions of narrowband UVB using a 311-nm filtering handpiece with a square spot size of 19×19 mm.23
Conclusion
Nail psoriasis constitutes a type of psoriasis that is not only refractory to most treatments but is accompanied by substantial psychological and occasionally functional burden for the affected individuals.24 Data concerning therapeutic options in the pediatric population are extremely limited, and therefore the everyday practice often involves administration of off-label medications, which can constitute a dilemma for many physicians, especially for safety.10 We suggest a simple therapeutic algorithm for the management of pediatric nail psoriasis based on the summarized data that are currently available in the literature. This algorithm is shown in the eFigure.
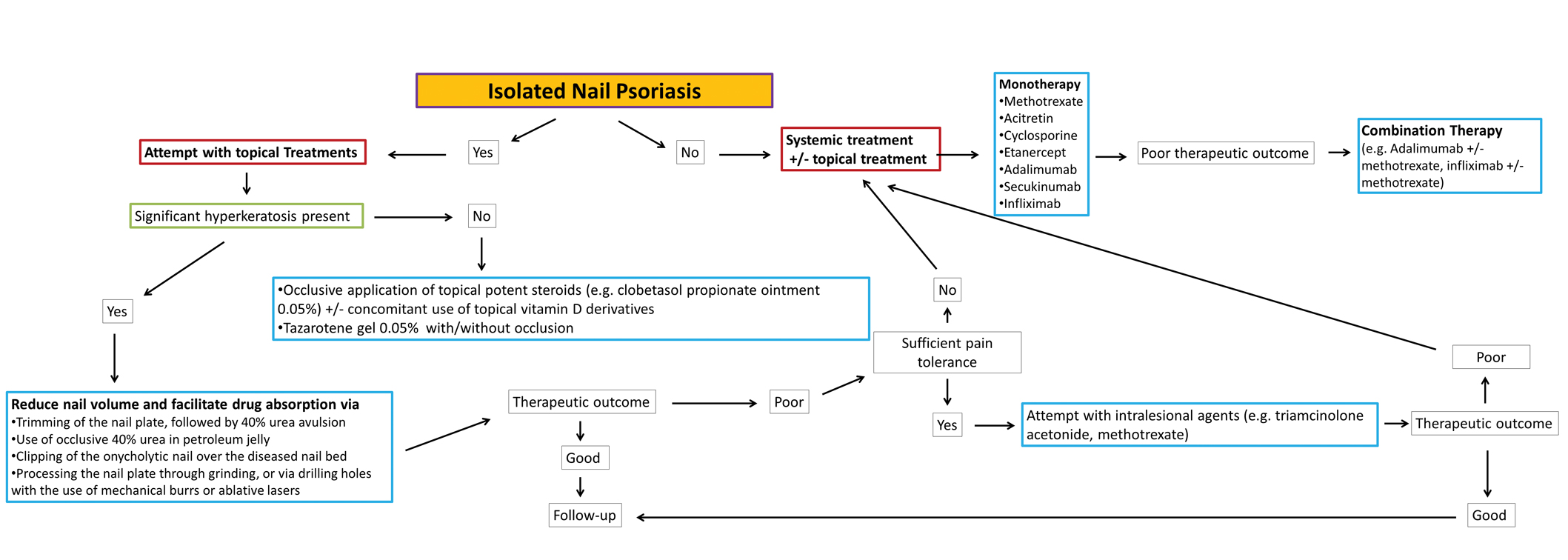
As progressively more agents—especially biologics—receive approval for use in plaque psoriasis in pediatric patients,25 it is expected that gradually more real-life data on their side efficacy for plaque psoriasis of the nails in children also will come to light. Furthermore, their on-label use in pediatric psoriasis patients will facilitate further relevant clinical trials to this target group so that the potential of these medications in the management of nail psoriasis can be fully explored.
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207.
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63.
- Piraccini BM, Triantafyllopoulou I, Prevezas C, et al. Nail psoriasis in children: common or uncommon? results from a 10-year double-center study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:43-48.
- Baran R. The burden of nail psoriasis: an introduction. Dermatology. 2010;221(suppl 1):1-5.
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112.
- Trüeb RM. Therapies for childhood psoriasis. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2009;38:137-159.
- Haneke E. Nail psoriasis: clinical features, pathogenesis, differential diagnoses, and management. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2017;7:51-63.
- Piraccini BM, Starace M. Nail disorders in infants and children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:440-445.
- Duran-McKinster C, Ortiz-Solis D, Granados J, et al. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis with nail psoriasis in the absence of cutaneous lesions. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:32-35.
- Holzberg M, Ruben BS, Baran R. Psoriasis restricted to the nail in a 7-year-old child. should biologics be an appropriate treatment modality when considering quality of life? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:668-670.
- Lee JY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Liao YC, Lee JY. Psoriasis in a 3-month-old infant with Kawasaki disease. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Khoo BP, Giam YC. A pilot study on the role of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of pitted nails in children. Singapore Med J. 2000;41:66-68.
- Piraccini BM, Tosti A, Iorizzo M, et al. Pustular psoriasis of the nails: treatment and long-term follow-up of 46 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:1000-1005.
- Diluvio L, Campione E, Paternò EJ, et al. Childhood nail psoriasis: a useful treatment with tazarotene 0.05%. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:332-333.
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179.
- Chen P, Li C, Xue R, et al. Efficacy and safety of acitretin monotherapy in children with pustular psoriasis: results from 15 cases and a literature review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:353-363.
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385.
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508.
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352.
- Dini V, Barbanera S, Romanelli M. Efficacy of adalimumab for the treatment of refractory paediatric acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:588-589.
- Kiszewski AE, De Villa D, Scheibel I, et al. An infant with acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau: successful treatment with thalidomide and UVB therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:105-106.
- Bordignon M, Zattra E, Albertin C, et al. Successful treatment of a 9-year-old boy affected by acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau with targeted ultraviolet B narrow-band phototherapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:41-43.
- Fabroni C, Gori A, Troiano M, et al. Infliximab efficacy in nail psoriasis. a retrospective study in 48 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:549-553.
- Lilly’s Taltz® (ixekizumab) receives U.S. FDA approval for the treatment of pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Eli Lilly and Company. March 30, 2020. Accessed September 24, 2021. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-taltzr-ixekizumab-receives-us-fda-approval-treatment-1
Pediatric nail psoriasis is a condition that has not been extensively studied. The prevalence of nail alterations in pediatric patients with psoriasis varies among different studies, ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail pitting, onycholysis associated with subungual hyperkeratosis, paronychia, and pachyonychia are the most frequent features of psoriatic nail involvement in children.2,3 The management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents is critical due to the quality-of-life impact, from potential functional impairment issues to the obvious cosmetic problems, which can aggravate the psychologic distress and social embarrassment of patients with psoriasis. Despite the emergence of modern potent systemic agents to treat chronic plaque psoriasis, nail psoriasis often is refractory to treatment.4 Coupled with the limited on-label options for psoriasis treatment in children, the management of nail psoriasis in this special patient group constitutes an even greater therapeutic challenge. This report aims to summarize the limited existing data on the successful management of nail psoriasis in the pediatric population.
Reviewing the Literature on Nail Psoriasis
We conducted a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus using the following Medical Subject Headings key terms: nail psoriasis and children, juvenile, pediatric. Additional articles were identified from the reference lists of the retrieved articles and citations. Our search included reports in the English language published from 2000 to 2019. The selection process included the following 2 steps: screening of the titles and abstracts, followed by evaluation of the selected full-text articles.
Topical Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Because most systemic antipsoriatic treatments that can be administered in adult patients have not yet been granted an official license for administration in children, topical treatments are considered by many physicians as the preferred first-line therapy for psoriatic nail involvement in pediatric patients.5,6 However, only scarce data are available in the literature concerning the successful use of local agents in pediatric patients with psoriasis.
The main limitation of local treatments relates mostly to their impaired penetration into the affected area (nails). To optimize drug penetration, some authors suggest the use of potent keratolytic topical preparations to reduce the nail volume and facilitate drug absorption.7 A popular suggestion is trimming the onycholytic nail plate followed by 40% urea avulsion to treat subungual hyperkeratosis8 or simply the use of occlusive 40% urea in petroleum jelly.9 Other approaches include clipping the onycholytic nail over the diseased nail bed or processing the nail plate through grinding or even drilling holes with the use of mechanical burrs or ablative lasers to enhance the penetration of the topical agent.7
A frequent approach in pediatric patients is clipping the detached nails combined with daily application of calcipotriene (calcipotriol) and steroids, such as betamethasone dipropionate.5,8 Reports on the use of regimens with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% under occlusion, with or without the concomitant use of calcipotriol solution 0.005%, also are present in the literature but not always with satisfactory results.10,11 Another successfully administered topical steroid is mometasone furoate cream 0.1%.12 Although the use of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide also has demonstrated encouraging outcomes in isolated reports,13 associated adverse events, such as pain and hematomas, can result in tolerability issues for pediatric patients.7
Piraccini et al14 described the case of an 8-year-old patient with pustular nail psoriasis who showed improvement within 3 to 6 months of treatment with topical calcipotriol 5 μg/g as monotherapy applied to the nail and periungual tissues twice daily. Another approach, described by Diluvio et al,15 is the use of tazarotene gel 0.05% applied once daily to the affected nail plates, nail folds, and periungual skin without occlusion. In a 6-year-old patient with isolated nail psoriasis, this treatment regimen demonstrated notable improvement within 8 weeks.15
Systemic Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Data on the successful administration of systemic agents in pediatric patients also are extremely scarce. Due to the lack of clinical trials, everyday practice is mostly based on isolated case series and case reports.
Methotrexate—Lee11 described the case of an 11-year-old girl with severe, symptomatic, 20-nail psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed a complete response to oral methotrexate 5 mg/wk after topical clobetasol propionate and calcipotriol failed. Improvement was seen as early as 4 weeks after therapy initiation, and complete resolution of the lesions was documented after 9 and 13 months of methotrexate therapy for the fingers and toes, respectively.11 The successful use of methotrexate in the improvement of psoriatic nail dystrophy in a pediatric patient also was documented by Teran et al.16 In this case, a 9-year-old girl with erythrodermic psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and severe onychodystrophy showed notable amelioration of all psoriatic manifestations, including the nail findings, with systemic methotrexate therapy (dose not specified).16 Notably, the authors reported that the improvement of onychodystrophy occurred with considerable delay compared to the other psoriatic lesions,16 indicating the already-known refractoriness of nail psoriasis to the various therapeutic attempts.9-15
Acitretin—Another agent that has been linked with partial improvement of acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau (ACH)–associated onychodystrophy is acitretin. In a case series of 15 pediatric patients with pustular psoriasis, a 5-year-old boy with severe nail involvement presented with partial amelioration of nail changes with acitretin within the first 6 weeks of treatment using the following regimen: initial dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/d for 6 weeks, followed by 0.3 mg/kg/d for 4 weeks.17
Biologics—The emerging use of biologics in pediatric psoriasis also has brought important advances in the successful management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents.18-21 Wells et al18 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with nail psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis who showed complete resolution of all psoriatic manifestations, including nail involvement, within 3 months of treatment with secukinumab 150 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Prior failed treatments included various systemic agents (ie, subcutaneous methotrexate 20 mg/m2, etanercept 0.8 mg/kg weekly, adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks) as well as topical agents (ie, urea, tazarotene, corticosteroids) and intralesional triamcinolone.18
Infliximab also has been successfully used for pediatric nail psoriasis. Watabe et al19 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with psoriatic onychodystrophy in addition to psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis. Prior therapy with adalimumab 20 mg every other week combined with methotrexate 10 mg weekly failed. She experienced notable amelioration of the nail dystrophy within 3 months of using a combination of infliximab and methotrexate (infliximab 5 mg/kg intravenously on weeks 0, 2, and 6, and every 8 weeks thereafter; methotrexate 10 mg/wk).19
Cases in which infliximab has resulted in rapid yet only transient restoration of psoriatic onychodystrophy also are present in the literature. Pereira et al20 reported that a 3-year-old patient with severe 20-digit onychodystrophy in addition to pustular psoriasis had complete resolution of nail lesions within 2 weeks of treatment with infliximab (5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6, and then every 7 weeks thereafter), which was sustained over the course of 1 year. The therapy had to be discontinued because of exacerbation of the cutaneous symptoms; thereafter, etanercept was initiated. Although the patient noted major improvement of all skin lesions under etanercept, only moderate amelioration of the psoriatic nail lesions was demonstrated.20
Dini et al21 described a 9-year-old girl with severe ACH-associated psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed complete clearance of all lesions within 8 weeks of treatment with adalimumab (initially 80 mg, followed by 40 mg after 1 week and then 40 mg every other week). Prior treatment with potent topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine (3 mg/kg/d for 6 months), and etanercept (0.4 mg/kg twice weekly for 3 months) was ineffective.21
Phototherapy—Other systemic agents with reported satisfactory outcomes in the treatment of psoriatic onychodystrophy include thalidomide combined with UVB phototherapy. Kiszewski et al22 described a 2-year-old patient with ACH and severe 19-digit onychodystrophy. Prior failed therapies included occluded clobetasol ointment 0.05%, occluded pimecrolimus 0.1%, and systemic methotrexate, while systemic acitretin (0.8 mg⁄kg⁄d) resulted in elevated cholesterol levels and therefore had to be interrupted. Improvement was seen 2 months after the initiation of a combined broadband UVB and thalidomide (50 mg⁄d) treatment, with no documented relapses after discontinuation of therapy.22
Narrowband UVB (311 nm) also has been used as monotherapy for ACH-associated onychodystrophy, as demonstrated by Bordignon et al.23 They reported a 9-year-old patient who showed partial improvement of isolated onychodystrophy of the fourth nail plate of the left hand after 36 sessions of narrowband UVB using a 311-nm filtering handpiece with a square spot size of 19×19 mm.23
Conclusion
Nail psoriasis constitutes a type of psoriasis that is not only refractory to most treatments but is accompanied by substantial psychological and occasionally functional burden for the affected individuals.24 Data concerning therapeutic options in the pediatric population are extremely limited, and therefore the everyday practice often involves administration of off-label medications, which can constitute a dilemma for many physicians, especially for safety.10 We suggest a simple therapeutic algorithm for the management of pediatric nail psoriasis based on the summarized data that are currently available in the literature. This algorithm is shown in the eFigure.

As progressively more agents—especially biologics—receive approval for use in plaque psoriasis in pediatric patients,25 it is expected that gradually more real-life data on their side efficacy for plaque psoriasis of the nails in children also will come to light. Furthermore, their on-label use in pediatric psoriasis patients will facilitate further relevant clinical trials to this target group so that the potential of these medications in the management of nail psoriasis can be fully explored.
Pediatric nail psoriasis is a condition that has not been extensively studied. The prevalence of nail alterations in pediatric patients with psoriasis varies among different studies, ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail pitting, onycholysis associated with subungual hyperkeratosis, paronychia, and pachyonychia are the most frequent features of psoriatic nail involvement in children.2,3 The management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents is critical due to the quality-of-life impact, from potential functional impairment issues to the obvious cosmetic problems, which can aggravate the psychologic distress and social embarrassment of patients with psoriasis. Despite the emergence of modern potent systemic agents to treat chronic plaque psoriasis, nail psoriasis often is refractory to treatment.4 Coupled with the limited on-label options for psoriasis treatment in children, the management of nail psoriasis in this special patient group constitutes an even greater therapeutic challenge. This report aims to summarize the limited existing data on the successful management of nail psoriasis in the pediatric population.
Reviewing the Literature on Nail Psoriasis
We conducted a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus using the following Medical Subject Headings key terms: nail psoriasis and children, juvenile, pediatric. Additional articles were identified from the reference lists of the retrieved articles and citations. Our search included reports in the English language published from 2000 to 2019. The selection process included the following 2 steps: screening of the titles and abstracts, followed by evaluation of the selected full-text articles.
Topical Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Because most systemic antipsoriatic treatments that can be administered in adult patients have not yet been granted an official license for administration in children, topical treatments are considered by many physicians as the preferred first-line therapy for psoriatic nail involvement in pediatric patients.5,6 However, only scarce data are available in the literature concerning the successful use of local agents in pediatric patients with psoriasis.
The main limitation of local treatments relates mostly to their impaired penetration into the affected area (nails). To optimize drug penetration, some authors suggest the use of potent keratolytic topical preparations to reduce the nail volume and facilitate drug absorption.7 A popular suggestion is trimming the onycholytic nail plate followed by 40% urea avulsion to treat subungual hyperkeratosis8 or simply the use of occlusive 40% urea in petroleum jelly.9 Other approaches include clipping the onycholytic nail over the diseased nail bed or processing the nail plate through grinding or even drilling holes with the use of mechanical burrs or ablative lasers to enhance the penetration of the topical agent.7
A frequent approach in pediatric patients is clipping the detached nails combined with daily application of calcipotriene (calcipotriol) and steroids, such as betamethasone dipropionate.5,8 Reports on the use of regimens with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% under occlusion, with or without the concomitant use of calcipotriol solution 0.005%, also are present in the literature but not always with satisfactory results.10,11 Another successfully administered topical steroid is mometasone furoate cream 0.1%.12 Although the use of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide also has demonstrated encouraging outcomes in isolated reports,13 associated adverse events, such as pain and hematomas, can result in tolerability issues for pediatric patients.7
Piraccini et al14 described the case of an 8-year-old patient with pustular nail psoriasis who showed improvement within 3 to 6 months of treatment with topical calcipotriol 5 μg/g as monotherapy applied to the nail and periungual tissues twice daily. Another approach, described by Diluvio et al,15 is the use of tazarotene gel 0.05% applied once daily to the affected nail plates, nail folds, and periungual skin without occlusion. In a 6-year-old patient with isolated nail psoriasis, this treatment regimen demonstrated notable improvement within 8 weeks.15
Systemic Treatments for Nail Psoriasis
Data on the successful administration of systemic agents in pediatric patients also are extremely scarce. Due to the lack of clinical trials, everyday practice is mostly based on isolated case series and case reports.
Methotrexate—Lee11 described the case of an 11-year-old girl with severe, symptomatic, 20-nail psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed a complete response to oral methotrexate 5 mg/wk after topical clobetasol propionate and calcipotriol failed. Improvement was seen as early as 4 weeks after therapy initiation, and complete resolution of the lesions was documented after 9 and 13 months of methotrexate therapy for the fingers and toes, respectively.11 The successful use of methotrexate in the improvement of psoriatic nail dystrophy in a pediatric patient also was documented by Teran et al.16 In this case, a 9-year-old girl with erythrodermic psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and severe onychodystrophy showed notable amelioration of all psoriatic manifestations, including the nail findings, with systemic methotrexate therapy (dose not specified).16 Notably, the authors reported that the improvement of onychodystrophy occurred with considerable delay compared to the other psoriatic lesions,16 indicating the already-known refractoriness of nail psoriasis to the various therapeutic attempts.9-15
Acitretin—Another agent that has been linked with partial improvement of acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau (ACH)–associated onychodystrophy is acitretin. In a case series of 15 pediatric patients with pustular psoriasis, a 5-year-old boy with severe nail involvement presented with partial amelioration of nail changes with acitretin within the first 6 weeks of treatment using the following regimen: initial dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/d for 6 weeks, followed by 0.3 mg/kg/d for 4 weeks.17
Biologics—The emerging use of biologics in pediatric psoriasis also has brought important advances in the successful management of nail psoriasis in children and adolescents.18-21 Wells et al18 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with nail psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis who showed complete resolution of all psoriatic manifestations, including nail involvement, within 3 months of treatment with secukinumab 150 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Prior failed treatments included various systemic agents (ie, subcutaneous methotrexate 20 mg/m2, etanercept 0.8 mg/kg weekly, adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks) as well as topical agents (ie, urea, tazarotene, corticosteroids) and intralesional triamcinolone.18
Infliximab also has been successfully used for pediatric nail psoriasis. Watabe et al19 presented the case of an 8-year-old girl with psoriatic onychodystrophy in addition to psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis. Prior therapy with adalimumab 20 mg every other week combined with methotrexate 10 mg weekly failed. She experienced notable amelioration of the nail dystrophy within 3 months of using a combination of infliximab and methotrexate (infliximab 5 mg/kg intravenously on weeks 0, 2, and 6, and every 8 weeks thereafter; methotrexate 10 mg/wk).19
Cases in which infliximab has resulted in rapid yet only transient restoration of psoriatic onychodystrophy also are present in the literature. Pereira et al20 reported that a 3-year-old patient with severe 20-digit onychodystrophy in addition to pustular psoriasis had complete resolution of nail lesions within 2 weeks of treatment with infliximab (5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6, and then every 7 weeks thereafter), which was sustained over the course of 1 year. The therapy had to be discontinued because of exacerbation of the cutaneous symptoms; thereafter, etanercept was initiated. Although the patient noted major improvement of all skin lesions under etanercept, only moderate amelioration of the psoriatic nail lesions was demonstrated.20
Dini et al21 described a 9-year-old girl with severe ACH-associated psoriatic onychodystrophy who showed complete clearance of all lesions within 8 weeks of treatment with adalimumab (initially 80 mg, followed by 40 mg after 1 week and then 40 mg every other week). Prior treatment with potent topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine (3 mg/kg/d for 6 months), and etanercept (0.4 mg/kg twice weekly for 3 months) was ineffective.21
Phototherapy—Other systemic agents with reported satisfactory outcomes in the treatment of psoriatic onychodystrophy include thalidomide combined with UVB phototherapy. Kiszewski et al22 described a 2-year-old patient with ACH and severe 19-digit onychodystrophy. Prior failed therapies included occluded clobetasol ointment 0.05%, occluded pimecrolimus 0.1%, and systemic methotrexate, while systemic acitretin (0.8 mg⁄kg⁄d) resulted in elevated cholesterol levels and therefore had to be interrupted. Improvement was seen 2 months after the initiation of a combined broadband UVB and thalidomide (50 mg⁄d) treatment, with no documented relapses after discontinuation of therapy.22
Narrowband UVB (311 nm) also has been used as monotherapy for ACH-associated onychodystrophy, as demonstrated by Bordignon et al.23 They reported a 9-year-old patient who showed partial improvement of isolated onychodystrophy of the fourth nail plate of the left hand after 36 sessions of narrowband UVB using a 311-nm filtering handpiece with a square spot size of 19×19 mm.23
Conclusion
Nail psoriasis constitutes a type of psoriasis that is not only refractory to most treatments but is accompanied by substantial psychological and occasionally functional burden for the affected individuals.24 Data concerning therapeutic options in the pediatric population are extremely limited, and therefore the everyday practice often involves administration of off-label medications, which can constitute a dilemma for many physicians, especially for safety.10 We suggest a simple therapeutic algorithm for the management of pediatric nail psoriasis based on the summarized data that are currently available in the literature. This algorithm is shown in the eFigure.

As progressively more agents—especially biologics—receive approval for use in plaque psoriasis in pediatric patients,25 it is expected that gradually more real-life data on their side efficacy for plaque psoriasis of the nails in children also will come to light. Furthermore, their on-label use in pediatric psoriasis patients will facilitate further relevant clinical trials to this target group so that the potential of these medications in the management of nail psoriasis can be fully explored.
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207.
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63.
- Piraccini BM, Triantafyllopoulou I, Prevezas C, et al. Nail psoriasis in children: common or uncommon? results from a 10-year double-center study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:43-48.
- Baran R. The burden of nail psoriasis: an introduction. Dermatology. 2010;221(suppl 1):1-5.
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112.
- Trüeb RM. Therapies for childhood psoriasis. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2009;38:137-159.
- Haneke E. Nail psoriasis: clinical features, pathogenesis, differential diagnoses, and management. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2017;7:51-63.
- Piraccini BM, Starace M. Nail disorders in infants and children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:440-445.
- Duran-McKinster C, Ortiz-Solis D, Granados J, et al. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis with nail psoriasis in the absence of cutaneous lesions. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:32-35.
- Holzberg M, Ruben BS, Baran R. Psoriasis restricted to the nail in a 7-year-old child. should biologics be an appropriate treatment modality when considering quality of life? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:668-670.
- Lee JY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Liao YC, Lee JY. Psoriasis in a 3-month-old infant with Kawasaki disease. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Khoo BP, Giam YC. A pilot study on the role of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of pitted nails in children. Singapore Med J. 2000;41:66-68.
- Piraccini BM, Tosti A, Iorizzo M, et al. Pustular psoriasis of the nails: treatment and long-term follow-up of 46 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:1000-1005.
- Diluvio L, Campione E, Paternò EJ, et al. Childhood nail psoriasis: a useful treatment with tazarotene 0.05%. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:332-333.
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179.
- Chen P, Li C, Xue R, et al. Efficacy and safety of acitretin monotherapy in children with pustular psoriasis: results from 15 cases and a literature review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:353-363.
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385.
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508.
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352.
- Dini V, Barbanera S, Romanelli M. Efficacy of adalimumab for the treatment of refractory paediatric acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:588-589.
- Kiszewski AE, De Villa D, Scheibel I, et al. An infant with acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau: successful treatment with thalidomide and UVB therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:105-106.
- Bordignon M, Zattra E, Albertin C, et al. Successful treatment of a 9-year-old boy affected by acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau with targeted ultraviolet B narrow-band phototherapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:41-43.
- Fabroni C, Gori A, Troiano M, et al. Infliximab efficacy in nail psoriasis. a retrospective study in 48 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:549-553.
- Lilly’s Taltz® (ixekizumab) receives U.S. FDA approval for the treatment of pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Eli Lilly and Company. March 30, 2020. Accessed September 24, 2021. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-taltzr-ixekizumab-receives-us-fda-approval-treatment-1
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207.
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63.
- Piraccini BM, Triantafyllopoulou I, Prevezas C, et al. Nail psoriasis in children: common or uncommon? results from a 10-year double-center study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:43-48.
- Baran R. The burden of nail psoriasis: an introduction. Dermatology. 2010;221(suppl 1):1-5.
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112.
- Trüeb RM. Therapies for childhood psoriasis. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2009;38:137-159.
- Haneke E. Nail psoriasis: clinical features, pathogenesis, differential diagnoses, and management. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2017;7:51-63.
- Piraccini BM, Starace M. Nail disorders in infants and children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:440-445.
- Duran-McKinster C, Ortiz-Solis D, Granados J, et al. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis with nail psoriasis in the absence of cutaneous lesions. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:32-35.
- Holzberg M, Ruben BS, Baran R. Psoriasis restricted to the nail in a 7-year-old child. should biologics be an appropriate treatment modality when considering quality of life? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:668-670.
- Lee JY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Liao YC, Lee JY. Psoriasis in a 3-month-old infant with Kawasaki disease. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Khoo BP, Giam YC. A pilot study on the role of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of pitted nails in children. Singapore Med J. 2000;41:66-68.
- Piraccini BM, Tosti A, Iorizzo M, et al. Pustular psoriasis of the nails: treatment and long-term follow-up of 46 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:1000-1005.
- Diluvio L, Campione E, Paternò EJ, et al. Childhood nail psoriasis: a useful treatment with tazarotene 0.05%. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:332-333.
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179.
- Chen P, Li C, Xue R, et al. Efficacy and safety of acitretin monotherapy in children with pustular psoriasis: results from 15 cases and a literature review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:353-363.
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385.
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriatic onycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508.
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352.
- Dini V, Barbanera S, Romanelli M. Efficacy of adalimumab for the treatment of refractory paediatric acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:588-589.
- Kiszewski AE, De Villa D, Scheibel I, et al. An infant with acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau: successful treatment with thalidomide and UVB therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:105-106.
- Bordignon M, Zattra E, Albertin C, et al. Successful treatment of a 9-year-old boy affected by acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau with targeted ultraviolet B narrow-band phototherapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:41-43.
- Fabroni C, Gori A, Troiano M, et al. Infliximab efficacy in nail psoriasis. a retrospective study in 48 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:549-553.
- Lilly’s Taltz® (ixekizumab) receives U.S. FDA approval for the treatment of pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Eli Lilly and Company. March 30, 2020. Accessed September 24, 2021. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-taltzr-ixekizumab-receives-us-fda-approval-treatment-1
Practice Points
- No clinical trials assessing the management of pediatric nail psoriasis currently are present in the literature. Limited information on the treatment of pediatric nail psoriasis exists, mostly in the form of small case series and case reports.
- As more agents are approved for on-label use in plaque psoriasis in pediatric patients, gradually more real-life data on their efficacy for nail psoriasis in children are expected to come to light.
Annular Erythema of Infancy With Reactive Helper T Lymphocytes
Annular erythemas of infancy (AEIs) are rare benign skin eruptions characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques that arise in patients younger than 1 year.1 Annular erythemas of infancy originally were described by Peterson and Jarratt2 in 1981. Relatively few cases of AEIs have been reported in the literature (eTable).2-15
Case Report
An 11-month-old girl presented to dermatology for a rash characterized by annular erythematous patches and plaques on the back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). Three months prior, the rash was more diffuse, monomorphic, and papular. Based on physical examination, the differential diagnosis included a gyrate erythema such as erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC), neonatal lupus, a viral exanthem, leukemia cutis, and AEI. A skin punch biopsy was performed.
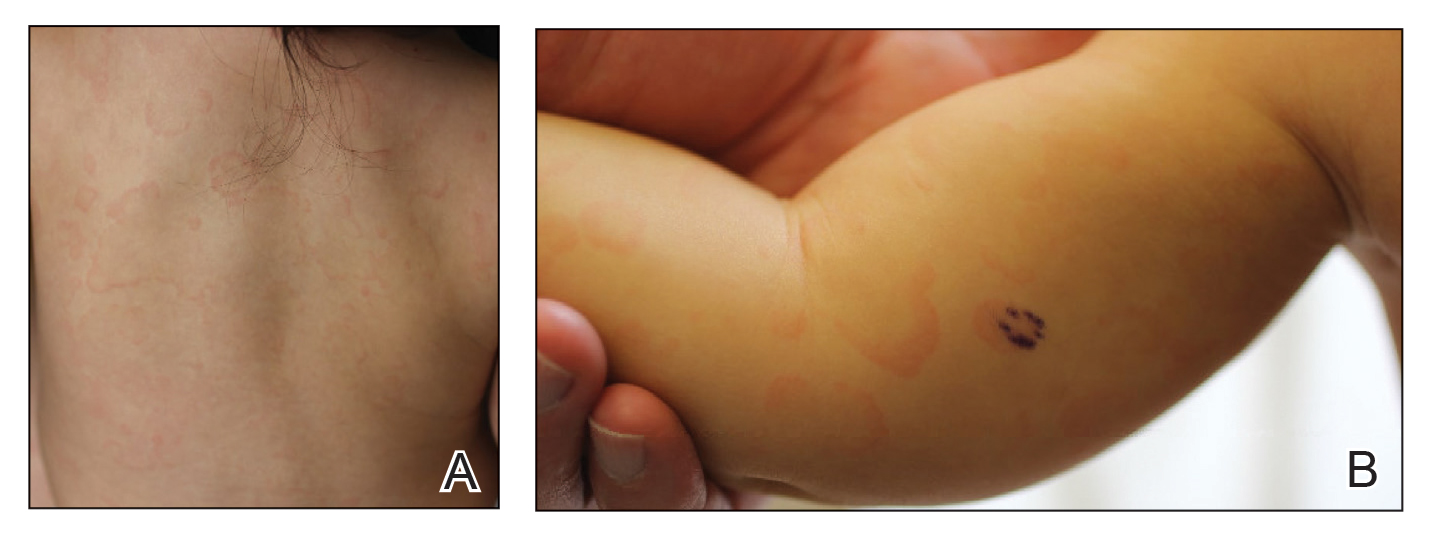
Histologically, the biopsy revealed a superficial to mid dermal, tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate admixed with rare neutrophils in eosinophils within the dermis (Figure 2A). The infiltrate also contained numerous large mononuclear cells with enlarged nuclei, fine loose chromatin, rare nucleoli, and a thin rim of cytoplasm (Figure 2B). There were associated apoptotic bodies with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemistry exhibited enlarged cells that were strong staining with CD3 and CD4, which was consistent with reactive helper T cells (Figure 3). A myeloperoxidase stain highlighted few neutrophils. Stains for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, CD1a, CD117, and CD34 were negative. These findings along with the clinical presentation yielded a diagnosis of AEI with reactive helper T cells.
Comment
Clinical Presentation of AEIs—Annular erythemas of infancy are rare benign skin eruptions that develop in the first few months of life.1,16 Few cases have been reported (eTable). Clinically, AEIs are characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques. They can occur on the face, trunk, and extremities, and they completely resolve by 1 year of age in most cases. One case was reported to persist in a patient from birth until 15 years of age.9 It is thought that AEIs may occur as a hypersensitivity reaction to an unrecognized antigen.
Histopathology—Histologically, AEIs demonstrate a superficial and deep, perivascular, inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis composed of small lymphocytes, some neutrophils, and eosinophils.16 Less common variants of AEI include eosinophilic annular erythema, characterized by a diffuse dermal infiltrate of eosinophils and some lymphocytes, and neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy, characterized by a dermal infiltrate with neutrophils and leukocytoclasis without vasculitis.1
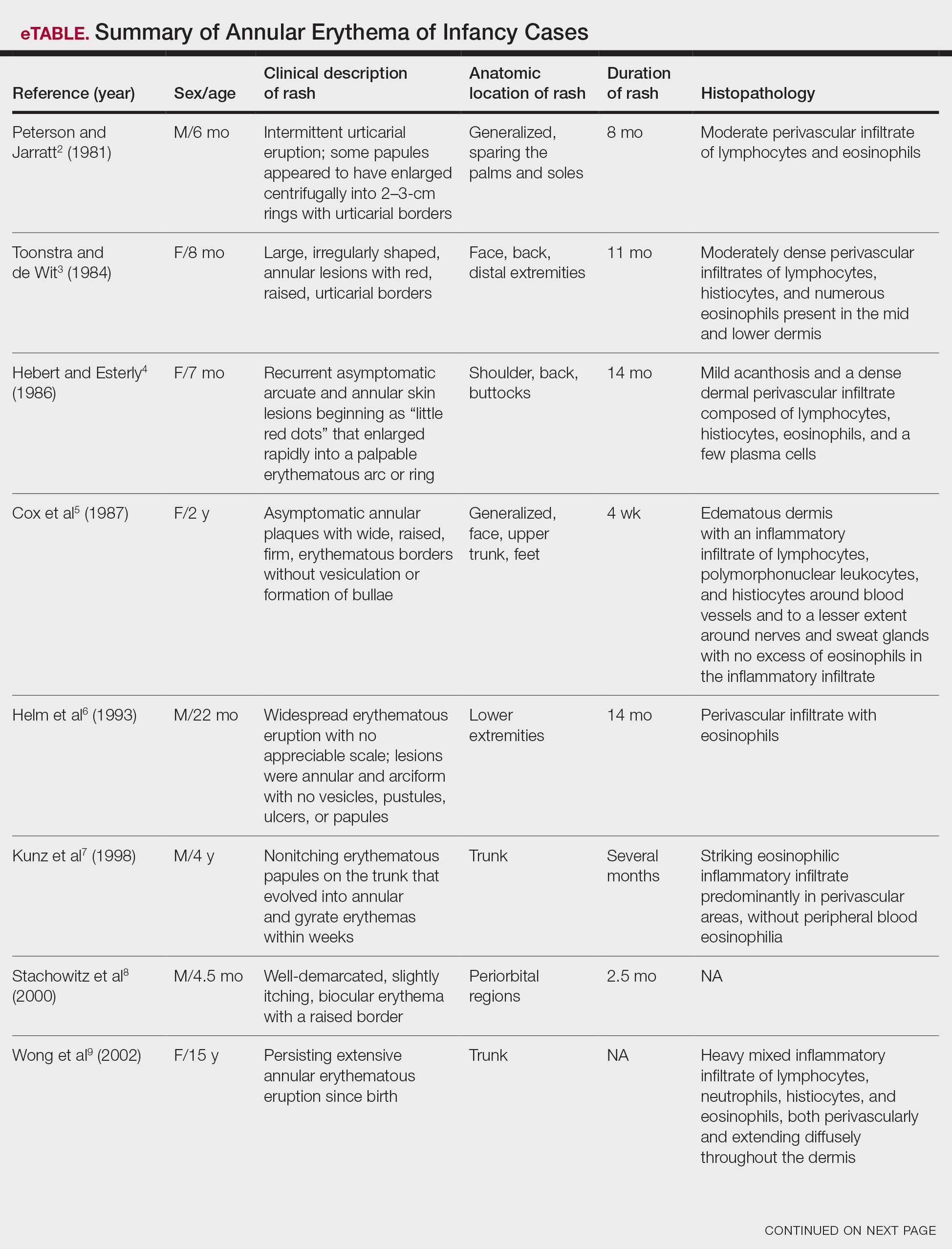
Our patient’s skin rash was unusual in that the biopsy demonstrated few neutrophils, rare eosinophils, and larger mononuclear cells consistent with reactive helper T lymphocytes. Although these cells may raise concern for an atypical lymphoid infiltrate, recognition of areas with more conventional histopathology of AEIs can facilitate the correct diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis—The main considerations in the differential diagnosis for AEIs include the following: EAC, familial annular erythema, erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale, erythema chronicum migrans, urticaria, tinea corporis, neonatal lupus erythematosus, viral exanthems, and leukemia cutis.16
Erythema annulare centrifugum typically begins in middle age and follows a course of 2 or more years.2 It occurs in association with an underlying infection or neoplasm, and it can develop on the trunk and proximal extremities. Morphologically, EAC can present with arcuate or polycyclic lesions with trailing scale. Histologically, a skin biopsy shows a tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with variable epidermal spongiosis and parakeratosis.16 Our patient’s biopsy did show a tight perivascular infiltrate, raising suspicion for EAC. However, the eruption occurred in infancy, and she had no clinical evidence of infection or neoplasm.
Familial annular erythemas can arise within a few days after birth and can present on any part of the body, including the tongue.2 Individual lesions can persist for 4 to 5 days and can accompany congenital malformations. Morphologically, they can present as papules that slowly enlarge to form arcuate lesions with central hyperpigmentation. Histologically, there can be a mild, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis.16 Our patient’s lesions showed no scale or pigmentation and occurred without a family history or associated malformations.
Erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale also can arise in the first few days of life and can affect the trunk, neck, and lips.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate erythematous patches (3–20 mm) with raised borders and central atrophy. Histologically, there is epidermal atrophy with a dermal perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrate with edema. Our patient’s clinical presentation was not classic for this condition, and the lesions showed no atrophy.
Erythema chronicum migrans can arise in children, often with a history of an arthropod bite.13 Morphologically, lesions can evolve over weeks to months and rarely are multiple. Erythema chronicum migrans most commonly occurs in the United States in association with Lyme disease from infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Histologically, erythema chronicum migrans shows a superficial and deep, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis with plasma cells and eosinophils. A silver stain can demonstrate dermal spirochetes. Our patient had no history of an arthropod bite. A Warthin-Starry stain performed on the biopsy was negative for spirochetes, and serologies for Lyme disease were negative.
Urticaria is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.2 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate, erythematous, and polycyclic plaques that wax and wane. Histologically, there is dermal edema with a mild, perivascular and interstitial, mixed inflammatory infiltrate.16 Our patient’s biopsy did not reveal notable edema, and the perivascular infiltrate was coat sleeve–like with few neutrophils and eosinophils. The patient did not respond to initial treatment with antihistamines, making urticaria less likely.
Tinea corporis is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.13 Morphologically, it can present as scaly annular lesions that are fixed and more persistent. Histologically, there are fungal hyphae and/or yeast in the stratum corneum with spongiotic dermatitis and parakeratosis. Our patient’s lesions were not scaly, and the biopsy demonstrated minimal spongiosis. A periodic acid–Schiff special stain was negative for fungal microorganisms.
Neonatal lupus erythematosus can arise at birth or during the first few weeks of life.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions occur on the scalp, forehead, or neck in a periorbital or malar distribution. They can present as erythematous, annular, scaly patches and plaques. Transplacental transmission of material autoantibodies has been implicated in the etiology, and a complication is infantile heart block. Histologically, a skin biopsy typically shows interface/lichenoid dermatitis. However, our patient’s biopsy did not demonstrate interface changes, and serologically she was negative for autoantibodies.
Viral exanthems are skin eruptions that accompany underlying viral infections.17 Morphologically, patients can present with an erythematous maculopapular rash, sometimes with vesicular, petechial, and urticarial lesions. Laboratory confirmation is made by virus-specific serologies. Histologically, viral exanthems can show a superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with reactive T cells and epidermal spongiosis. Our patient was afebrile and had no known sick contacts. A cytomegalovirus immunohistochemical study on the biopsy was negative, and an Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization study was negative.
Leukemia cutis is the infiltration of the skin by leukemic cells, most often in conjunction with systemic leukemia.18 In infants and children, the most common leukemia is B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Morphologically, the skin lesions are characterized by single or multiple violaceous papules, nodules, and plaques. Histologically, there is a perivascular to interstitial infiltrate of atypical mononuclear cells in the dermis and sometimes subcutis. The leukemic cells demonstrate enlarged nuclei with coarse chromatin and prominent nucleoli. Increased mitotic activity may be seen with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells can be positive for myeloperoxidase, CD43, CD68, CD34, and CD117.18 Although our patient’s biopsy demonstrated mononuclear cells with karyorrhexis, the cells did not have striking atypia and were negative for blast markers. A recent complete blood cell count on the patient was normal.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of AEI with mononuclear cells consistent with helper T cells. One must keep these cells in mind when evaluating a biopsy of AEI, as they are benign and not suggestive of an atypical lymphoid infiltrate or leukemia cutis. This will prevent misdiagnosis and ensure that the patient receives appropriate management.
- Ríos-Martín JJ, Ferrándiz-Pulido L, Moreno-Ramírez D. Approaches to the dermatopathologic diagnosis of figurate lesions [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011;102:316-324. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2010.12.009
- Peterson AO, Jarratt M. Annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:145-148.
- Toonstra J, de Wit RF. “Persistent” annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol.1984;120:1069-1072.
- Hebert AA, Esterly NB. Annular erythema of infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:339-343.
- Cox NH, McQueen A, Evans TJ, et al. An annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:510-513.
- Helm TN, Bass J, Chang LW, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:46-48.
- Kunz M, Hamm K, Bröcker EB, et al. Annular erythema in childhood—a new eosinophilic dermatosis [in German]. Hautarzt. 1998;49:131-134.
- Stachowitz S, Abeck D, Schmidt T, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy associated with intestinal Candida colonization. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:404-405.
- Wong L-C, Kakakios A, Rogers M. Congenital annular erythema persisting in a 15-year-old girl. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:55-61.
- Patrizi A, Savoia F, Varotti E, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:255-260. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00646.x
- Saha A, Seth J, Mukherjee S, et al. Annular erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2014;15:147-149. doi:10.4103/2319-7250.143678
- Pfingstler LF, Miller KP, Pride H. Recurring diffuse annular erythematous plaques in a newborn. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:565-566. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.8059
- Del Puerto Troncoso C, Curi Tuma M, González Bombardiere S, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy associated with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:431-433. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2014.09.013
- Hamidi S, Prose NS, Selim MA. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge [published online December 26, 2018]. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:216-220. doi:10.1111/cup.13394
- Patel N, Goldbach H, Hogeling M. An annular eruption in a young child. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1213-1214. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1174
- Palit A, Inamadar AC. Annular, erythematous skin lesions in a neonate. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2012;3:45-47. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93504
- Keighley CL, Saunderson RB, Kok J, et al. Viral exanthems. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015;28:139-150. doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000145
- Cronin DMP, George TI, Sundram UN. An updated approach to the diagnosis of myeloid leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:101-110. doi:10.1309/AJCP6GR8BDEXPKHR
Annular erythemas of infancy (AEIs) are rare benign skin eruptions characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques that arise in patients younger than 1 year.1 Annular erythemas of infancy originally were described by Peterson and Jarratt2 in 1981. Relatively few cases of AEIs have been reported in the literature (eTable).2-15
Case Report
An 11-month-old girl presented to dermatology for a rash characterized by annular erythematous patches and plaques on the back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). Three months prior, the rash was more diffuse, monomorphic, and papular. Based on physical examination, the differential diagnosis included a gyrate erythema such as erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC), neonatal lupus, a viral exanthem, leukemia cutis, and AEI. A skin punch biopsy was performed.

Histologically, the biopsy revealed a superficial to mid dermal, tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate admixed with rare neutrophils in eosinophils within the dermis (Figure 2A). The infiltrate also contained numerous large mononuclear cells with enlarged nuclei, fine loose chromatin, rare nucleoli, and a thin rim of cytoplasm (Figure 2B). There were associated apoptotic bodies with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemistry exhibited enlarged cells that were strong staining with CD3 and CD4, which was consistent with reactive helper T cells (Figure 3). A myeloperoxidase stain highlighted few neutrophils. Stains for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, CD1a, CD117, and CD34 were negative. These findings along with the clinical presentation yielded a diagnosis of AEI with reactive helper T cells.

Comment
Clinical Presentation of AEIs—Annular erythemas of infancy are rare benign skin eruptions that develop in the first few months of life.1,16 Few cases have been reported (eTable). Clinically, AEIs are characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques. They can occur on the face, trunk, and extremities, and they completely resolve by 1 year of age in most cases. One case was reported to persist in a patient from birth until 15 years of age.9 It is thought that AEIs may occur as a hypersensitivity reaction to an unrecognized antigen.

Histopathology—Histologically, AEIs demonstrate a superficial and deep, perivascular, inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis composed of small lymphocytes, some neutrophils, and eosinophils.16 Less common variants of AEI include eosinophilic annular erythema, characterized by a diffuse dermal infiltrate of eosinophils and some lymphocytes, and neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy, characterized by a dermal infiltrate with neutrophils and leukocytoclasis without vasculitis.1

Our patient’s skin rash was unusual in that the biopsy demonstrated few neutrophils, rare eosinophils, and larger mononuclear cells consistent with reactive helper T lymphocytes. Although these cells may raise concern for an atypical lymphoid infiltrate, recognition of areas with more conventional histopathology of AEIs can facilitate the correct diagnosis.

Differential Diagnosis—The main considerations in the differential diagnosis for AEIs include the following: EAC, familial annular erythema, erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale, erythema chronicum migrans, urticaria, tinea corporis, neonatal lupus erythematosus, viral exanthems, and leukemia cutis.16
Erythema annulare centrifugum typically begins in middle age and follows a course of 2 or more years.2 It occurs in association with an underlying infection or neoplasm, and it can develop on the trunk and proximal extremities. Morphologically, EAC can present with arcuate or polycyclic lesions with trailing scale. Histologically, a skin biopsy shows a tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with variable epidermal spongiosis and parakeratosis.16 Our patient’s biopsy did show a tight perivascular infiltrate, raising suspicion for EAC. However, the eruption occurred in infancy, and she had no clinical evidence of infection or neoplasm.
Familial annular erythemas can arise within a few days after birth and can present on any part of the body, including the tongue.2 Individual lesions can persist for 4 to 5 days and can accompany congenital malformations. Morphologically, they can present as papules that slowly enlarge to form arcuate lesions with central hyperpigmentation. Histologically, there can be a mild, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis.16 Our patient’s lesions showed no scale or pigmentation and occurred without a family history or associated malformations.
Erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale also can arise in the first few days of life and can affect the trunk, neck, and lips.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate erythematous patches (3–20 mm) with raised borders and central atrophy. Histologically, there is epidermal atrophy with a dermal perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrate with edema. Our patient’s clinical presentation was not classic for this condition, and the lesions showed no atrophy.
Erythema chronicum migrans can arise in children, often with a history of an arthropod bite.13 Morphologically, lesions can evolve over weeks to months and rarely are multiple. Erythema chronicum migrans most commonly occurs in the United States in association with Lyme disease from infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Histologically, erythema chronicum migrans shows a superficial and deep, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis with plasma cells and eosinophils. A silver stain can demonstrate dermal spirochetes. Our patient had no history of an arthropod bite. A Warthin-Starry stain performed on the biopsy was negative for spirochetes, and serologies for Lyme disease were negative.
Urticaria is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.2 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate, erythematous, and polycyclic plaques that wax and wane. Histologically, there is dermal edema with a mild, perivascular and interstitial, mixed inflammatory infiltrate.16 Our patient’s biopsy did not reveal notable edema, and the perivascular infiltrate was coat sleeve–like with few neutrophils and eosinophils. The patient did not respond to initial treatment with antihistamines, making urticaria less likely.
Tinea corporis is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.13 Morphologically, it can present as scaly annular lesions that are fixed and more persistent. Histologically, there are fungal hyphae and/or yeast in the stratum corneum with spongiotic dermatitis and parakeratosis. Our patient’s lesions were not scaly, and the biopsy demonstrated minimal spongiosis. A periodic acid–Schiff special stain was negative for fungal microorganisms.
Neonatal lupus erythematosus can arise at birth or during the first few weeks of life.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions occur on the scalp, forehead, or neck in a periorbital or malar distribution. They can present as erythematous, annular, scaly patches and plaques. Transplacental transmission of material autoantibodies has been implicated in the etiology, and a complication is infantile heart block. Histologically, a skin biopsy typically shows interface/lichenoid dermatitis. However, our patient’s biopsy did not demonstrate interface changes, and serologically she was negative for autoantibodies.
Viral exanthems are skin eruptions that accompany underlying viral infections.17 Morphologically, patients can present with an erythematous maculopapular rash, sometimes with vesicular, petechial, and urticarial lesions. Laboratory confirmation is made by virus-specific serologies. Histologically, viral exanthems can show a superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with reactive T cells and epidermal spongiosis. Our patient was afebrile and had no known sick contacts. A cytomegalovirus immunohistochemical study on the biopsy was negative, and an Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization study was negative.
Leukemia cutis is the infiltration of the skin by leukemic cells, most often in conjunction with systemic leukemia.18 In infants and children, the most common leukemia is B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Morphologically, the skin lesions are characterized by single or multiple violaceous papules, nodules, and plaques. Histologically, there is a perivascular to interstitial infiltrate of atypical mononuclear cells in the dermis and sometimes subcutis. The leukemic cells demonstrate enlarged nuclei with coarse chromatin and prominent nucleoli. Increased mitotic activity may be seen with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells can be positive for myeloperoxidase, CD43, CD68, CD34, and CD117.18 Although our patient’s biopsy demonstrated mononuclear cells with karyorrhexis, the cells did not have striking atypia and were negative for blast markers. A recent complete blood cell count on the patient was normal.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of AEI with mononuclear cells consistent with helper T cells. One must keep these cells in mind when evaluating a biopsy of AEI, as they are benign and not suggestive of an atypical lymphoid infiltrate or leukemia cutis. This will prevent misdiagnosis and ensure that the patient receives appropriate management.
Annular erythemas of infancy (AEIs) are rare benign skin eruptions characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques that arise in patients younger than 1 year.1 Annular erythemas of infancy originally were described by Peterson and Jarratt2 in 1981. Relatively few cases of AEIs have been reported in the literature (eTable).2-15
Case Report
An 11-month-old girl presented to dermatology for a rash characterized by annular erythematous patches and plaques on the back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). Three months prior, the rash was more diffuse, monomorphic, and papular. Based on physical examination, the differential diagnosis included a gyrate erythema such as erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC), neonatal lupus, a viral exanthem, leukemia cutis, and AEI. A skin punch biopsy was performed.

Histologically, the biopsy revealed a superficial to mid dermal, tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate admixed with rare neutrophils in eosinophils within the dermis (Figure 2A). The infiltrate also contained numerous large mononuclear cells with enlarged nuclei, fine loose chromatin, rare nucleoli, and a thin rim of cytoplasm (Figure 2B). There were associated apoptotic bodies with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemistry exhibited enlarged cells that were strong staining with CD3 and CD4, which was consistent with reactive helper T cells (Figure 3). A myeloperoxidase stain highlighted few neutrophils. Stains for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, CD1a, CD117, and CD34 were negative. These findings along with the clinical presentation yielded a diagnosis of AEI with reactive helper T cells.

Comment
Clinical Presentation of AEIs—Annular erythemas of infancy are rare benign skin eruptions that develop in the first few months of life.1,16 Few cases have been reported (eTable). Clinically, AEIs are characterized by annular or circinate, erythematous patches and plaques. They can occur on the face, trunk, and extremities, and they completely resolve by 1 year of age in most cases. One case was reported to persist in a patient from birth until 15 years of age.9 It is thought that AEIs may occur as a hypersensitivity reaction to an unrecognized antigen.

Histopathology—Histologically, AEIs demonstrate a superficial and deep, perivascular, inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis composed of small lymphocytes, some neutrophils, and eosinophils.16 Less common variants of AEI include eosinophilic annular erythema, characterized by a diffuse dermal infiltrate of eosinophils and some lymphocytes, and neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy, characterized by a dermal infiltrate with neutrophils and leukocytoclasis without vasculitis.1

Our patient’s skin rash was unusual in that the biopsy demonstrated few neutrophils, rare eosinophils, and larger mononuclear cells consistent with reactive helper T lymphocytes. Although these cells may raise concern for an atypical lymphoid infiltrate, recognition of areas with more conventional histopathology of AEIs can facilitate the correct diagnosis.

Differential Diagnosis—The main considerations in the differential diagnosis for AEIs include the following: EAC, familial annular erythema, erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale, erythema chronicum migrans, urticaria, tinea corporis, neonatal lupus erythematosus, viral exanthems, and leukemia cutis.16
Erythema annulare centrifugum typically begins in middle age and follows a course of 2 or more years.2 It occurs in association with an underlying infection or neoplasm, and it can develop on the trunk and proximal extremities. Morphologically, EAC can present with arcuate or polycyclic lesions with trailing scale. Histologically, a skin biopsy shows a tight, coat sleeve–like, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with variable epidermal spongiosis and parakeratosis.16 Our patient’s biopsy did show a tight perivascular infiltrate, raising suspicion for EAC. However, the eruption occurred in infancy, and she had no clinical evidence of infection or neoplasm.
Familial annular erythemas can arise within a few days after birth and can present on any part of the body, including the tongue.2 Individual lesions can persist for 4 to 5 days and can accompany congenital malformations. Morphologically, they can present as papules that slowly enlarge to form arcuate lesions with central hyperpigmentation. Histologically, there can be a mild, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis.16 Our patient’s lesions showed no scale or pigmentation and occurred without a family history or associated malformations.
Erythema gyratum atrophicans transiens neonatale also can arise in the first few days of life and can affect the trunk, neck, and lips.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate erythematous patches (3–20 mm) with raised borders and central atrophy. Histologically, there is epidermal atrophy with a dermal perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrate with edema. Our patient’s clinical presentation was not classic for this condition, and the lesions showed no atrophy.
Erythema chronicum migrans can arise in children, often with a history of an arthropod bite.13 Morphologically, lesions can evolve over weeks to months and rarely are multiple. Erythema chronicum migrans most commonly occurs in the United States in association with Lyme disease from infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Histologically, erythema chronicum migrans shows a superficial and deep, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis with plasma cells and eosinophils. A silver stain can demonstrate dermal spirochetes. Our patient had no history of an arthropod bite. A Warthin-Starry stain performed on the biopsy was negative for spirochetes, and serologies for Lyme disease were negative.
Urticaria is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.2 Morphologically, the skin lesions can present as arcuate, erythematous, and polycyclic plaques that wax and wane. Histologically, there is dermal edema with a mild, perivascular and interstitial, mixed inflammatory infiltrate.16 Our patient’s biopsy did not reveal notable edema, and the perivascular infiltrate was coat sleeve–like with few neutrophils and eosinophils. The patient did not respond to initial treatment with antihistamines, making urticaria less likely.
Tinea corporis is rare in neonates and can occur on any part of the body.13 Morphologically, it can present as scaly annular lesions that are fixed and more persistent. Histologically, there are fungal hyphae and/or yeast in the stratum corneum with spongiotic dermatitis and parakeratosis. Our patient’s lesions were not scaly, and the biopsy demonstrated minimal spongiosis. A periodic acid–Schiff special stain was negative for fungal microorganisms.
Neonatal lupus erythematosus can arise at birth or during the first few weeks of life.16 Morphologically, the skin lesions occur on the scalp, forehead, or neck in a periorbital or malar distribution. They can present as erythematous, annular, scaly patches and plaques. Transplacental transmission of material autoantibodies has been implicated in the etiology, and a complication is infantile heart block. Histologically, a skin biopsy typically shows interface/lichenoid dermatitis. However, our patient’s biopsy did not demonstrate interface changes, and serologically she was negative for autoantibodies.
Viral exanthems are skin eruptions that accompany underlying viral infections.17 Morphologically, patients can present with an erythematous maculopapular rash, sometimes with vesicular, petechial, and urticarial lesions. Laboratory confirmation is made by virus-specific serologies. Histologically, viral exanthems can show a superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis, with reactive T cells and epidermal spongiosis. Our patient was afebrile and had no known sick contacts. A cytomegalovirus immunohistochemical study on the biopsy was negative, and an Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization study was negative.
Leukemia cutis is the infiltration of the skin by leukemic cells, most often in conjunction with systemic leukemia.18 In infants and children, the most common leukemia is B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Morphologically, the skin lesions are characterized by single or multiple violaceous papules, nodules, and plaques. Histologically, there is a perivascular to interstitial infiltrate of atypical mononuclear cells in the dermis and sometimes subcutis. The leukemic cells demonstrate enlarged nuclei with coarse chromatin and prominent nucleoli. Increased mitotic activity may be seen with karyorrhectic debris. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells can be positive for myeloperoxidase, CD43, CD68, CD34, and CD117.18 Although our patient’s biopsy demonstrated mononuclear cells with karyorrhexis, the cells did not have striking atypia and were negative for blast markers. A recent complete blood cell count on the patient was normal.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of AEI with mononuclear cells consistent with helper T cells. One must keep these cells in mind when evaluating a biopsy of AEI, as they are benign and not suggestive of an atypical lymphoid infiltrate or leukemia cutis. This will prevent misdiagnosis and ensure that the patient receives appropriate management.
- Ríos-Martín JJ, Ferrándiz-Pulido L, Moreno-Ramírez D. Approaches to the dermatopathologic diagnosis of figurate lesions [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011;102:316-324. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2010.12.009
- Peterson AO, Jarratt M. Annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:145-148.
- Toonstra J, de Wit RF. “Persistent” annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol.1984;120:1069-1072.
- Hebert AA, Esterly NB. Annular erythema of infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:339-343.
- Cox NH, McQueen A, Evans TJ, et al. An annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:510-513.
- Helm TN, Bass J, Chang LW, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:46-48.
- Kunz M, Hamm K, Bröcker EB, et al. Annular erythema in childhood—a new eosinophilic dermatosis [in German]. Hautarzt. 1998;49:131-134.
- Stachowitz S, Abeck D, Schmidt T, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy associated with intestinal Candida colonization. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:404-405.
- Wong L-C, Kakakios A, Rogers M. Congenital annular erythema persisting in a 15-year-old girl. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:55-61.
- Patrizi A, Savoia F, Varotti E, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:255-260. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00646.x
- Saha A, Seth J, Mukherjee S, et al. Annular erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2014;15:147-149. doi:10.4103/2319-7250.143678
- Pfingstler LF, Miller KP, Pride H. Recurring diffuse annular erythematous plaques in a newborn. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:565-566. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.8059
- Del Puerto Troncoso C, Curi Tuma M, González Bombardiere S, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy associated with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:431-433. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2014.09.013
- Hamidi S, Prose NS, Selim MA. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge [published online December 26, 2018]. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:216-220. doi:10.1111/cup.13394
- Patel N, Goldbach H, Hogeling M. An annular eruption in a young child. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1213-1214. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1174
- Palit A, Inamadar AC. Annular, erythematous skin lesions in a neonate. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2012;3:45-47. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93504
- Keighley CL, Saunderson RB, Kok J, et al. Viral exanthems. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015;28:139-150. doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000145
- Cronin DMP, George TI, Sundram UN. An updated approach to the diagnosis of myeloid leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:101-110. doi:10.1309/AJCP6GR8BDEXPKHR
- Ríos-Martín JJ, Ferrándiz-Pulido L, Moreno-Ramírez D. Approaches to the dermatopathologic diagnosis of figurate lesions [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011;102:316-324. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2010.12.009
- Peterson AO, Jarratt M. Annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:145-148.
- Toonstra J, de Wit RF. “Persistent” annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol.1984;120:1069-1072.
- Hebert AA, Esterly NB. Annular erythema of infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:339-343.
- Cox NH, McQueen A, Evans TJ, et al. An annular erythema of infancy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:510-513.
- Helm TN, Bass J, Chang LW, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:46-48.
- Kunz M, Hamm K, Bröcker EB, et al. Annular erythema in childhood—a new eosinophilic dermatosis [in German]. Hautarzt. 1998;49:131-134.
- Stachowitz S, Abeck D, Schmidt T, et al. Persistent annular erythema of infancy associated with intestinal Candida colonization. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:404-405.
- Wong L-C, Kakakios A, Rogers M. Congenital annular erythema persisting in a 15-year-old girl. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:55-61.
- Patrizi A, Savoia F, Varotti E, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:255-260. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00646.x
- Saha A, Seth J, Mukherjee S, et al. Annular erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2014;15:147-149. doi:10.4103/2319-7250.143678
- Pfingstler LF, Miller KP, Pride H. Recurring diffuse annular erythematous plaques in a newborn. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:565-566. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.8059
- Del Puerto Troncoso C, Curi Tuma M, González Bombardiere S, et al. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy associated with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:431-433. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2014.09.013
- Hamidi S, Prose NS, Selim MA. Neutrophilic figurate erythema of infancy: a diagnostic challenge [published online December 26, 2018]. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:216-220. doi:10.1111/cup.13394
- Patel N, Goldbach H, Hogeling M. An annular eruption in a young child. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1213-1214. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1174
- Palit A, Inamadar AC. Annular, erythematous skin lesions in a neonate. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2012;3:45-47. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93504
- Keighley CL, Saunderson RB, Kok J, et al. Viral exanthems. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015;28:139-150. doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000145
- Cronin DMP, George TI, Sundram UN. An updated approach to the diagnosis of myeloid leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:101-110. doi:10.1309/AJCP6GR8BDEXPKHR
Practice Points
- Annular erythemas of infancy (AEIs) are rare benign skin eruptions characterized by persistent, annular, urticarial, nonpruritic patches and plaques that develop in patients younger than 1 year.
- Although AEIs are benign, lesions with uncommon histologic features such as large mononuclear cells consistent with reactive helper T lymphocytes may pose diagnostic challenges.
Pediatric Subungual Exostosis
Exostosis is a type of benign bone tumor in which trabecular (spongy) bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. 1,2 Histologically, it usually is surrounded by a fibrocartilaginous cap. 3 It is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the foot and is thought to be caused by trauma, either physical pressure or infection. 4 When this lesion is found under the nail bed, it is termed subungual exostosis ( Dupuytren exostosis ) . 3 Sequelae of a subungual exostosis include nail dystrophy and lifting of the nail away from the toe, in addition to infection and possible loss of the toenail (onycholysis). There are only 2 genetic conditions related to exostosis: hereditary multiple exostosis and multiple exostoses-mental retardation syndrome.
An exostosis may appear to be a wart on first inspection. It may present similar to osteochondromas, and the only way to get a true diagnosis is by biopsy of the lesion. The treatment for an exostosis is surgery. The surgeon must remove the lesion at the base of the bone from which it grows to prevent recurrence of the lesion.5
Because exostosis may cause nail bed disruption, the differential diagnosis may include nail deformities, such as traumatic onycholysis, onychogryphosis, verrucae, subungual infection, or nail trauma.6,7
Case Report
A 7-year-old boy presented with changes of the right great toenail over the last 4 months. The patient noted that the affected nail was discolored, dystrophic, painful, and thickened. He did not recall prior trauma to the affected nail, and his mother stated that the lesion was growing and becoming more painful with a throbbing sensation at times. He described the pain as stabbing, which was exacerbated while walking and playing sports. Neither the patient nor his family had ever had any similar condition. He was not taking any medications, only a daily multivitamin. He had a history of eczematous dermatitis and keratosis pilaris without any other medical illnesses. He had a family history of psoriasis; however, no prior instances of exostosis had been reported. He had no medication allergies.
A full-body cutaneous and nail examination showed a well-developed, well-nourished boy who was in no acute distress. A firm, subungual, pink, pearly,hyperkeratotic nodule was appreciated on the right great toe (Figure 1). The lesion was tender to palpation. The rest of the examination and review of systems were normal.
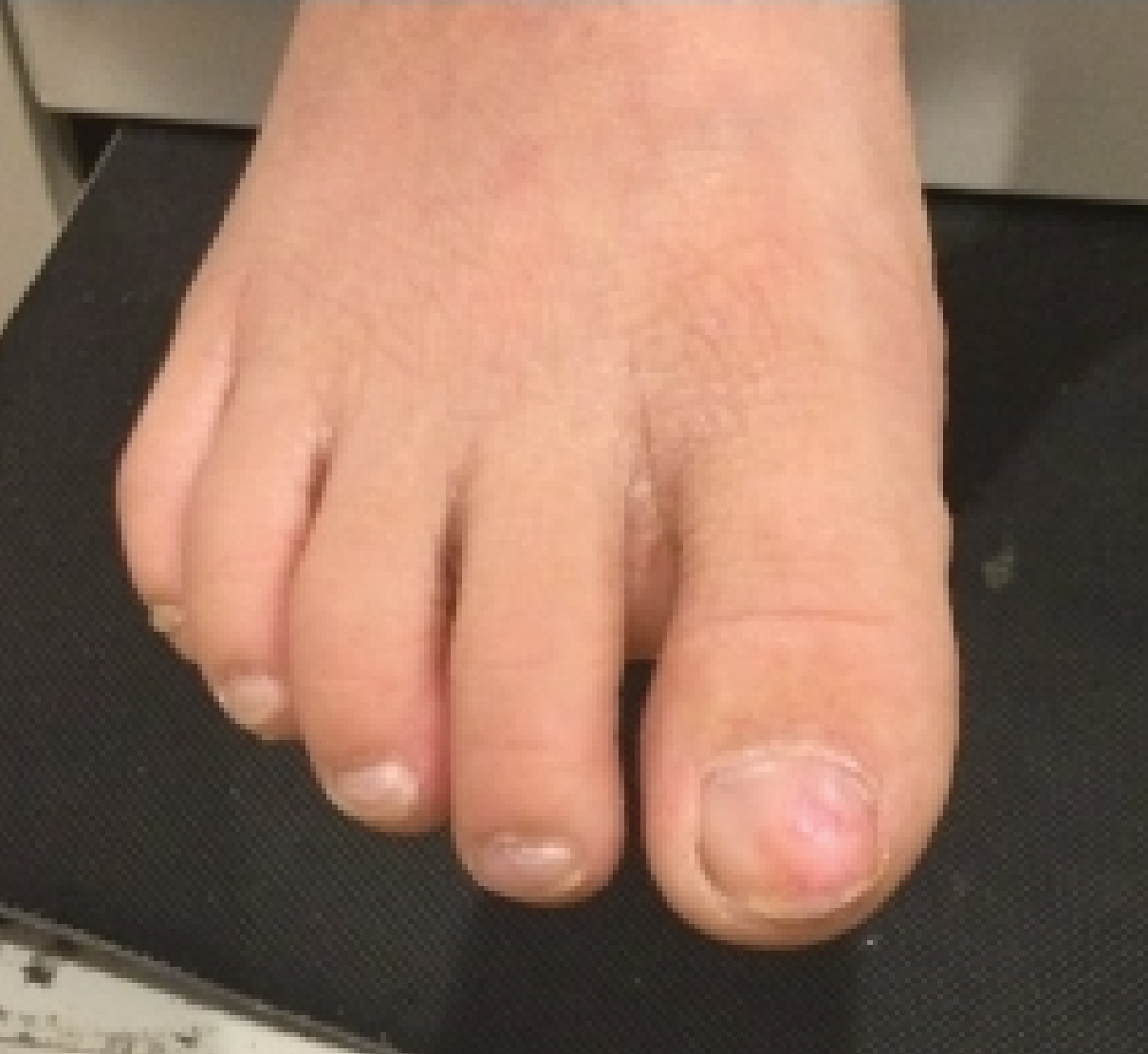
From the clinical findings, a differential diagnosis of glomus tumor, hemangioma, and infection was considered. Periodic acid–Schiff stain was negative, which ruled out fungal infection. Nail avulsion and a shave biopsy were performed under general anesthesia. There was an exostosis arising from the dorsal aspect of the great toe measuring approximately 5 mm in width at the base and approximately 1 mm in height, which endorsed a diagnosis of distal phalanx subungual exostosis. A postsurgery radiograph (Figure 2) showed residual bone below the level of shave removal at the nail bed.
Comment
Exostosis is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the hallux (great toe) in patients younger than 18 years.8 Diagnosis often is obvious, even without a radiograph or biopsy, because the exostosis comes out from under the tip of the nail. Our case was interesting because the patient was a child, and the exostosis did not lift the nail or extrude from the distal tip of the nail bed. Evidence suggests that a greater-than-expected genetic influence contributes to an exostosis, though further investigation is needed to determine all of the causes and risk factors for subungual bony exostosis. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to the prevention of sequelae of the disease, such as toe infection or chronic pain.
- de Palma L, Gigante A, Specchia N. Subungual exostosis of the foot. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17:758-763. doi:10.1177/107110079601701208
- Multhopp-Stephens H, Walling AK. Subungual (Dupuytren’s) exostosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15:582-584. doi:10.1097/01241398-199509000-00006
- Davis DA, Cohen PR. Subungual exostosis: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:212-218.
- Guarneri C, Guarneri F, Risitano G, et al. Solitary asymptomatic nodule of the great toe. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:245-247.
- Letts M, Davidson D, Nizalik E. Subungual exostosis: diagnosis and treatment in children. J Trauma. 1998;44:346-349.
- Hoy NY, Leung AKC, Metelitsa AI, et al. New concepts in median nail dystrophy, onychomycosis, and hand, foot, and mouth disease nail pathology. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:680163.
- Rich P, Scher RK. Examination of the nail and work-up of nail conditions. In: Rich P, Scher RK, eds. An Atlas of Diseases of the Nail. Parthenon Publishing; 2003.
- DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
Exostosis is a type of benign bone tumor in which trabecular (spongy) bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. 1,2 Histologically, it usually is surrounded by a fibrocartilaginous cap. 3 It is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the foot and is thought to be caused by trauma, either physical pressure or infection. 4 When this lesion is found under the nail bed, it is termed subungual exostosis ( Dupuytren exostosis ) . 3 Sequelae of a subungual exostosis include nail dystrophy and lifting of the nail away from the toe, in addition to infection and possible loss of the toenail (onycholysis). There are only 2 genetic conditions related to exostosis: hereditary multiple exostosis and multiple exostoses-mental retardation syndrome.
An exostosis may appear to be a wart on first inspection. It may present similar to osteochondromas, and the only way to get a true diagnosis is by biopsy of the lesion. The treatment for an exostosis is surgery. The surgeon must remove the lesion at the base of the bone from which it grows to prevent recurrence of the lesion.5
Because exostosis may cause nail bed disruption, the differential diagnosis may include nail deformities, such as traumatic onycholysis, onychogryphosis, verrucae, subungual infection, or nail trauma.6,7
Case Report
A 7-year-old boy presented with changes of the right great toenail over the last 4 months. The patient noted that the affected nail was discolored, dystrophic, painful, and thickened. He did not recall prior trauma to the affected nail, and his mother stated that the lesion was growing and becoming more painful with a throbbing sensation at times. He described the pain as stabbing, which was exacerbated while walking and playing sports. Neither the patient nor his family had ever had any similar condition. He was not taking any medications, only a daily multivitamin. He had a history of eczematous dermatitis and keratosis pilaris without any other medical illnesses. He had a family history of psoriasis; however, no prior instances of exostosis had been reported. He had no medication allergies.
A full-body cutaneous and nail examination showed a well-developed, well-nourished boy who was in no acute distress. A firm, subungual, pink, pearly,hyperkeratotic nodule was appreciated on the right great toe (Figure 1). The lesion was tender to palpation. The rest of the examination and review of systems were normal.

From the clinical findings, a differential diagnosis of glomus tumor, hemangioma, and infection was considered. Periodic acid–Schiff stain was negative, which ruled out fungal infection. Nail avulsion and a shave biopsy were performed under general anesthesia. There was an exostosis arising from the dorsal aspect of the great toe measuring approximately 5 mm in width at the base and approximately 1 mm in height, which endorsed a diagnosis of distal phalanx subungual exostosis. A postsurgery radiograph (Figure 2) showed residual bone below the level of shave removal at the nail bed.

Comment
Exostosis is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the hallux (great toe) in patients younger than 18 years.8 Diagnosis often is obvious, even without a radiograph or biopsy, because the exostosis comes out from under the tip of the nail. Our case was interesting because the patient was a child, and the exostosis did not lift the nail or extrude from the distal tip of the nail bed. Evidence suggests that a greater-than-expected genetic influence contributes to an exostosis, though further investigation is needed to determine all of the causes and risk factors for subungual bony exostosis. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to the prevention of sequelae of the disease, such as toe infection or chronic pain.
Exostosis is a type of benign bone tumor in which trabecular (spongy) bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. 1,2 Histologically, it usually is surrounded by a fibrocartilaginous cap. 3 It is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the foot and is thought to be caused by trauma, either physical pressure or infection. 4 When this lesion is found under the nail bed, it is termed subungual exostosis ( Dupuytren exostosis ) . 3 Sequelae of a subungual exostosis include nail dystrophy and lifting of the nail away from the toe, in addition to infection and possible loss of the toenail (onycholysis). There are only 2 genetic conditions related to exostosis: hereditary multiple exostosis and multiple exostoses-mental retardation syndrome.
An exostosis may appear to be a wart on first inspection. It may present similar to osteochondromas, and the only way to get a true diagnosis is by biopsy of the lesion. The treatment for an exostosis is surgery. The surgeon must remove the lesion at the base of the bone from which it grows to prevent recurrence of the lesion.5
Because exostosis may cause nail bed disruption, the differential diagnosis may include nail deformities, such as traumatic onycholysis, onychogryphosis, verrucae, subungual infection, or nail trauma.6,7
Case Report
A 7-year-old boy presented with changes of the right great toenail over the last 4 months. The patient noted that the affected nail was discolored, dystrophic, painful, and thickened. He did not recall prior trauma to the affected nail, and his mother stated that the lesion was growing and becoming more painful with a throbbing sensation at times. He described the pain as stabbing, which was exacerbated while walking and playing sports. Neither the patient nor his family had ever had any similar condition. He was not taking any medications, only a daily multivitamin. He had a history of eczematous dermatitis and keratosis pilaris without any other medical illnesses. He had a family history of psoriasis; however, no prior instances of exostosis had been reported. He had no medication allergies.
A full-body cutaneous and nail examination showed a well-developed, well-nourished boy who was in no acute distress. A firm, subungual, pink, pearly,hyperkeratotic nodule was appreciated on the right great toe (Figure 1). The lesion was tender to palpation. The rest of the examination and review of systems were normal.

From the clinical findings, a differential diagnosis of glomus tumor, hemangioma, and infection was considered. Periodic acid–Schiff stain was negative, which ruled out fungal infection. Nail avulsion and a shave biopsy were performed under general anesthesia. There was an exostosis arising from the dorsal aspect of the great toe measuring approximately 5 mm in width at the base and approximately 1 mm in height, which endorsed a diagnosis of distal phalanx subungual exostosis. A postsurgery radiograph (Figure 2) showed residual bone below the level of shave removal at the nail bed.

Comment
Exostosis is most commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the hallux (great toe) in patients younger than 18 years.8 Diagnosis often is obvious, even without a radiograph or biopsy, because the exostosis comes out from under the tip of the nail. Our case was interesting because the patient was a child, and the exostosis did not lift the nail or extrude from the distal tip of the nail bed. Evidence suggests that a greater-than-expected genetic influence contributes to an exostosis, though further investigation is needed to determine all of the causes and risk factors for subungual bony exostosis. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to the prevention of sequelae of the disease, such as toe infection or chronic pain.
- de Palma L, Gigante A, Specchia N. Subungual exostosis of the foot. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17:758-763. doi:10.1177/107110079601701208
- Multhopp-Stephens H, Walling AK. Subungual (Dupuytren’s) exostosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15:582-584. doi:10.1097/01241398-199509000-00006
- Davis DA, Cohen PR. Subungual exostosis: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:212-218.
- Guarneri C, Guarneri F, Risitano G, et al. Solitary asymptomatic nodule of the great toe. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:245-247.
- Letts M, Davidson D, Nizalik E. Subungual exostosis: diagnosis and treatment in children. J Trauma. 1998;44:346-349.
- Hoy NY, Leung AKC, Metelitsa AI, et al. New concepts in median nail dystrophy, onychomycosis, and hand, foot, and mouth disease nail pathology. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:680163.
- Rich P, Scher RK. Examination of the nail and work-up of nail conditions. In: Rich P, Scher RK, eds. An Atlas of Diseases of the Nail. Parthenon Publishing; 2003.
- DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
- de Palma L, Gigante A, Specchia N. Subungual exostosis of the foot. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17:758-763. doi:10.1177/107110079601701208
- Multhopp-Stephens H, Walling AK. Subungual (Dupuytren’s) exostosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15:582-584. doi:10.1097/01241398-199509000-00006
- Davis DA, Cohen PR. Subungual exostosis: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:212-218.
- Guarneri C, Guarneri F, Risitano G, et al. Solitary asymptomatic nodule of the great toe. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:245-247.
- Letts M, Davidson D, Nizalik E. Subungual exostosis: diagnosis and treatment in children. J Trauma. 1998;44:346-349.
- Hoy NY, Leung AKC, Metelitsa AI, et al. New concepts in median nail dystrophy, onychomycosis, and hand, foot, and mouth disease nail pathology. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:680163.
- Rich P, Scher RK. Examination of the nail and work-up of nail conditions. In: Rich P, Scher RK, eds. An Atlas of Diseases of the Nail. Parthenon Publishing; 2003.
- DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
Practice Points
- Nail dystrophy can have a variety of causes, most commonly trauma, onychomycosis, verrucae, or subungual exostosis.
- Exostosis is a benign osteochondral tumor commonly found on the lateral or medial aspect of the hallux (great toe) in pediatric and young adult patients.
- A radiograph can be used as a preliminary tool for diagnosis, but subungual exostosis must be confirmed by biopsy or tissue histology at the time of excision.
City or country life? Genetic risk for mental illness may decide
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder (BD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), or anorexia nervosa (AN) are significantly more likely to move from a rural to an urban setting, whereas those at high genetic risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder were more likely to do the opposite.
The findings held even in those at high genetic risk who had never been diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, highlighting a genetic factor that previous research linking urban living to mental illness has not explored.
“It’s not as simple as saying that urban environment is responsible for schizophrenia and everyone should move out of urban environments and they will be safe,” study investigator Evangelos Vassos, MD, PhD, senior clinical research fellow at King’s College London, and a consulting psychiatrist, said in an interview. “If you are genetically predisposed to schizophrenia, you will still be predisposed to schizophrenia even if you move.”
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Genetic influence
The study results don’t rule out environmental influence, but offer evidence that the migration pattern researchers have tracked for years may have a multifactorial explanation.
“Our research shows that, at some level, an individual’s genes select their environment and that the relationship between environmental and genetic influences on mental health is interrelated,” Jessye Maxwell, MSc, lead author and a PhD candidate in psychiatry at King’s College, said in a statement. “This overlap needs to be considered when developing models to predict the risk of people developing mental health conditions in the future.”
For the study, the investigators calculated polygenic risk scores (PRS) of different psychiatric illnesses for 385,793 U.K. Biobank participants aged 37-73. PRS analyzes genetic information across a person’s entire genome, rather than by individual genes.
They used address history and U.K. census records from 1931 to 2011 to map population density over time.
PRS analyses showed significant associations with higher population density throughout adulthood, reaching highest significance between age 45 and 55 years for schizophrenia (88 people/km2; 95% confidence interval, 65-98 people/km2), BD (44 people/km2; 95%CI, 34-54 people/km2), AN (36 people/km2; 95%CI, 22-50 people/km2), and ASD (35 people/km2; 95%CI, 25-45 people/km2).
When they compared those who were born and stayed in rural or suburban areas to their counterparts who moved from those areas to cities, they found the odds of moving to urban areas ranged from 5% among people at high genetic risk for schizophrenia to 13% of those with a high risk for BD. Only people at high risk for ADHD were more likely to move to rural areas.
However, the study is not without its limitations. Only people of European descent were included, family medical history was unavailable for some participants, and only about 50,000 people had a lifetime diagnosis of mental illness, which is not representative of the general population.
‘Convincing evidence’
Still, the research adds another piece of the puzzle scientists seek to solve about where people live and mental illness risk, said Jordan DeVylder, PhD, associate professor of social work at Fordham University, New York, who commented on the study for this news organization.
Dr. DeVylder, who has also published research on the topic but was not part of the current study, noted that urban living has long been thought to be among the most consistent environmental risk factors for psychosis. However, he noted, “this association can also be explained by genetic selection, in which the same genes that predispose one to schizophrenia also predispose one to choose urban living.”
“This study presents the most convincing evidence to date that genetics have a major role in this association, at least in the countries where this association between urban living and psychosis exists,” he said.
The study was funded by National Institute for Health Research, Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The authors and Dr. DeVylder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder (BD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), or anorexia nervosa (AN) are significantly more likely to move from a rural to an urban setting, whereas those at high genetic risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder were more likely to do the opposite.
The findings held even in those at high genetic risk who had never been diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, highlighting a genetic factor that previous research linking urban living to mental illness has not explored.
“It’s not as simple as saying that urban environment is responsible for schizophrenia and everyone should move out of urban environments and they will be safe,” study investigator Evangelos Vassos, MD, PhD, senior clinical research fellow at King’s College London, and a consulting psychiatrist, said in an interview. “If you are genetically predisposed to schizophrenia, you will still be predisposed to schizophrenia even if you move.”
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Genetic influence
The study results don’t rule out environmental influence, but offer evidence that the migration pattern researchers have tracked for years may have a multifactorial explanation.
“Our research shows that, at some level, an individual’s genes select their environment and that the relationship between environmental and genetic influences on mental health is interrelated,” Jessye Maxwell, MSc, lead author and a PhD candidate in psychiatry at King’s College, said in a statement. “This overlap needs to be considered when developing models to predict the risk of people developing mental health conditions in the future.”
For the study, the investigators calculated polygenic risk scores (PRS) of different psychiatric illnesses for 385,793 U.K. Biobank participants aged 37-73. PRS analyzes genetic information across a person’s entire genome, rather than by individual genes.
They used address history and U.K. census records from 1931 to 2011 to map population density over time.
PRS analyses showed significant associations with higher population density throughout adulthood, reaching highest significance between age 45 and 55 years for schizophrenia (88 people/km2; 95% confidence interval, 65-98 people/km2), BD (44 people/km2; 95%CI, 34-54 people/km2), AN (36 people/km2; 95%CI, 22-50 people/km2), and ASD (35 people/km2; 95%CI, 25-45 people/km2).
When they compared those who were born and stayed in rural or suburban areas to their counterparts who moved from those areas to cities, they found the odds of moving to urban areas ranged from 5% among people at high genetic risk for schizophrenia to 13% of those with a high risk for BD. Only people at high risk for ADHD were more likely to move to rural areas.
However, the study is not without its limitations. Only people of European descent were included, family medical history was unavailable for some participants, and only about 50,000 people had a lifetime diagnosis of mental illness, which is not representative of the general population.
‘Convincing evidence’
Still, the research adds another piece of the puzzle scientists seek to solve about where people live and mental illness risk, said Jordan DeVylder, PhD, associate professor of social work at Fordham University, New York, who commented on the study for this news organization.
Dr. DeVylder, who has also published research on the topic but was not part of the current study, noted that urban living has long been thought to be among the most consistent environmental risk factors for psychosis. However, he noted, “this association can also be explained by genetic selection, in which the same genes that predispose one to schizophrenia also predispose one to choose urban living.”
“This study presents the most convincing evidence to date that genetics have a major role in this association, at least in the countries where this association between urban living and psychosis exists,” he said.
The study was funded by National Institute for Health Research, Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The authors and Dr. DeVylder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder (BD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), or anorexia nervosa (AN) are significantly more likely to move from a rural to an urban setting, whereas those at high genetic risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder were more likely to do the opposite.
The findings held even in those at high genetic risk who had never been diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, highlighting a genetic factor that previous research linking urban living to mental illness has not explored.
“It’s not as simple as saying that urban environment is responsible for schizophrenia and everyone should move out of urban environments and they will be safe,” study investigator Evangelos Vassos, MD, PhD, senior clinical research fellow at King’s College London, and a consulting psychiatrist, said in an interview. “If you are genetically predisposed to schizophrenia, you will still be predisposed to schizophrenia even if you move.”
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Genetic influence
The study results don’t rule out environmental influence, but offer evidence that the migration pattern researchers have tracked for years may have a multifactorial explanation.
“Our research shows that, at some level, an individual’s genes select their environment and that the relationship between environmental and genetic influences on mental health is interrelated,” Jessye Maxwell, MSc, lead author and a PhD candidate in psychiatry at King’s College, said in a statement. “This overlap needs to be considered when developing models to predict the risk of people developing mental health conditions in the future.”
For the study, the investigators calculated polygenic risk scores (PRS) of different psychiatric illnesses for 385,793 U.K. Biobank participants aged 37-73. PRS analyzes genetic information across a person’s entire genome, rather than by individual genes.
They used address history and U.K. census records from 1931 to 2011 to map population density over time.
PRS analyses showed significant associations with higher population density throughout adulthood, reaching highest significance between age 45 and 55 years for schizophrenia (88 people/km2; 95% confidence interval, 65-98 people/km2), BD (44 people/km2; 95%CI, 34-54 people/km2), AN (36 people/km2; 95%CI, 22-50 people/km2), and ASD (35 people/km2; 95%CI, 25-45 people/km2).
When they compared those who were born and stayed in rural or suburban areas to their counterparts who moved from those areas to cities, they found the odds of moving to urban areas ranged from 5% among people at high genetic risk for schizophrenia to 13% of those with a high risk for BD. Only people at high risk for ADHD were more likely to move to rural areas.
However, the study is not without its limitations. Only people of European descent were included, family medical history was unavailable for some participants, and only about 50,000 people had a lifetime diagnosis of mental illness, which is not representative of the general population.
‘Convincing evidence’
Still, the research adds another piece of the puzzle scientists seek to solve about where people live and mental illness risk, said Jordan DeVylder, PhD, associate professor of social work at Fordham University, New York, who commented on the study for this news organization.
Dr. DeVylder, who has also published research on the topic but was not part of the current study, noted that urban living has long been thought to be among the most consistent environmental risk factors for psychosis. However, he noted, “this association can also be explained by genetic selection, in which the same genes that predispose one to schizophrenia also predispose one to choose urban living.”
“This study presents the most convincing evidence to date that genetics have a major role in this association, at least in the countries where this association between urban living and psychosis exists,” he said.
The study was funded by National Institute for Health Research, Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The authors and Dr. DeVylder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY