User login
Pediatric Studies Produce Mixed Messages on Relationship Between COVID and Asthma
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
In one of several recently published studies on the relationship between COVID-19 infection and asthma, according to data drawn from the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH).
The inverse correlation between symptoms and vaccination was strong and statistically significant, according to investigators led by Matthew M. Davis, MD, Physician in Chief and Chief Scientific Officer, Nemours Children’s Health, Wilmington, Delaware.
“With each increase of 10 percentage points in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the parent-reported child asthma symptoms prevalence decreased by 0.36 percentage points (P < .05),” Dr. Davis and his coinvestigators reported in a research letter published in JAMA Network Open.
Studies Explore Relationship of COVID and Asthma
The reduced risk of asthma symptoms with COVID-19 vaccination in children at the population level is just one of several recently published studies exploring the interaction between COVID-19 infection and asthma, but two studies that posed the same question did not reach the same conclusion.
In one, COVID-19 infection in children was not found to be a trigger for new-onset asthma, but the second found that it was. In a third study, the preponderance of evidence from a meta-analysis found that patients with asthma – whether children or adults – did not necessarily experience a more severe course of COVID-19 infection than in those without asthma.
The NSCH database study calculated state-level change in scores for patient-reported childhood asthma symptoms in the years in the years 2018-2019, which preceded the pandemic and the years 2020-2021, when the pandemic began. The hypothesis was that the proportion of the population 5 years of age or older who completed the COVID-19 primary vaccination would be inversely related to asthma symptom prevalence.
Relative to the 2018-2019 years, the mean rate of parent-reported asthma symptoms was 0.85% lower (6.93% vs 7.77%; P < .001) in 2020-2021, when the mean primary series COVID-19 vaccination rate was 72.3%.
The study was not able to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 vaccination specifically in children with asthma, because history of asthma is not captured in the NSCH data, but Dr. Davis contended that the reduction in symptomatic asthma among children with increased vaccination offers validation for the state-level findings.
“Moreover, the absence of an association of COVID-19 vaccination administered predominantly in 2021 with population-level COVID-19 mortality in 2020 serves as a negative control,” he and his colleagues wrote in their research letter.
Protection from Respiratory Viruses Seen for Asthma Patients
In an interview, Dr. Davis reported that these data are consistent with previous evidence that immunization against influenza also reduces risk of asthma symptoms. In a meta-analysis published in 2017, it was estimated that live vaccines reduced risk of influenza by 81% and prevented 59%-72% of asthma attacks leading to hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
“The similarity of our findings regarding COVID-19 vaccination to prior data regarding influenza vaccination underscores the importance of preventing viral illnesses in individuals with a history of asthma,” Dr. Davis said. It is not yet clear if this is true of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Because of the short time that the RSV vaccine has been available, it is too soon to conduct an analysis.
One message from this study is that “clinicians should continue to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for children because of its general benefits in preventing coronavirus-related illness and the apparent specific benefits for children with a history of asthma,” he said.
While vaccination appears to reduce asthmatic symptoms related to COVID-19 infection, one study suggests that COVID-19 does not trigger new-onset asthma. In a retrospective study published in Pediatrics, no association between COVID-19 infection and new-onset asthma could be made in an analysis of 27,423 children (ages, 1-16 years) from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Care Network.
Across all the pediatric age groups evaluated, the consistent finding was “SARS-CoV-2 positivity does not confer an additional risk for asthma diagnosis at least within the first 18 months after a [polymerase chain reaction] test,” concluded the investigators, led by David A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Allergy and Immunology, CHOP, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Risk of Asthma Doubled After COVID-19 Infection
However, the opposite conclusion was reached by investigators evaluating data from two cohorts of children ages 5-18 drawn from the TriNetX database, a global health research network with data on more than 250 million individuals. Cohort 1 included more than 250,000 children. These children had never received COVID-19 vaccination. The 50,000 patients in cohort 2 had all received COVID19 vaccination.
To compare the impact of COVID-19 infection on new-onset asthma, the patients who were infected with COVID-19 were compared with those who were not infected after propensity score matching over 18 months of follow-up.
In cohort 1, the rate of new onset asthma was more than twofold greater among those with COVID-19 infection (4.7% vs 2.0%). The hazard ratio (HR) of 2.25 had tight confidence intervals (95% CI, 2.158-2.367).
In cohort 2, the risk of new-onset asthma at 18 months among those who had a COVID-19 infection relative to those without was even greater (8.3% vs 3.1%). The relative risk approached a 3-fold increase (HR 2.745; 95% CI, 2.521-2.99).
The conclusion of these investigators, led by Chia-Chi Lung, PhD, Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, was that there is “a critical need for ongoing monitoring and customized healthcare strategies to mitigate the long-term respiratory impacts of COVID-19 in children.”
These health risks might not be as significant as once feared. In the recently published study from Environmental Health Insights, the goal of a meta-analysis was to determine if patients with asthma relative to those without asthma face a higher risk of serious disease from COVID-19 infection. The meta-analysis included studies of children and adults. The answer, according an in-depth analysis of 21 articles in a “scoping review,” was a qualified no.
Of the 21 articles, 4 concluded that asthma is a risk factor for serious COVID-19 infection, but 17 did not, according to Chukwudi S. Ubah, PhD, Department of Public Health, Brody School of Medicine, East Caroline University, Greenville, North Carolina.
None of These Questions are Fully Resolved
However, given the disparity in the results and the fact that many of the studies included in this analysis had small sample sizes, Dr. Ubah called for larger studies and studies with better controls. He noted, for example, that the studies did not consistently evaluate mitigating factors, such as used of inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which might affect risk of the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
Rather, “our findings pointed out that the type of medication prescribed for asthma may have implications for the severity of COVID-19 infection in these patients,” Dr. Ubah said in an interview.
Overall, the data do not support a major interaction between asthma and COVID-19, even if the data are not conclusive. Each of the senior authors of these studies called for larger and better investigations to further explore whether COVID-19 infection and preexisting asthma interact. So far, the data indicate that if COVID-19 infection poses a risk of precipitating new-onset asthma or inducing a more severe infection in children with asthma, it is low, but the degree of risk, if any, remains unresolved in subgroups defined by asthma treatment or asthma severity.
Dr. Davis, Dr. Hill, Dr. Lung, and Dr. Ubah reported no potential conflicts of interest. None of these studies received funding from commercial interests.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Urticaria Linked to Higher Cancer Risk, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Time Warp: Fax Machines Still Common in Oncology Practice. Why?
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Drug Shortages Continue in the US, Survey Finds
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Finds Variations in Pediatric Dermatologists Who Accept Medicaid
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified 352 actively practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists using the Society for Pediatric Dermatology database and determined Medicaid acceptance status.
- They collected physician and practice characteristics from the US Census American Community Survey data and a web search.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 275 (78.1%) board-certified pediatric dermatologists accepted Medicaid.
- Academic practices had the highest Medicaid acceptance rate (98.7%), while private practices had the lowest (43.1%), a significant difference (P < .001).
- Acceptance rates were significantly higher in the Midwest (90.9%) than in the Northeast (71.8%) or West (71.4%; P = .005). Regional differences persisted after controlling for practice type: Midwest practice locations had greater odds of Medicaid acceptance than those in the Northeast (odds ratio [OR], 5.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.76-15.65) or West (OR, 5.26; 95% CI, 1.88-14.66).
- Practices in counties with lower median household incomes and greater densities of pediatric dermatologists were associated with higher Medicaid acceptance (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“While most pediatric dermatologists accept Medicaid, this study revealed differential access to care based on practice type, geographic location, and density of pediatric dermatologists per county,” the authors wrote. More research is needed on “the impact on health outcomes when specialty services are unavailable” and on “the role of administrative and reimbursement barriers limiting Medicaid acceptance among pediatric dermatologists,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Madeleine Tessier-Kay, MPH, Department of Dermatology, at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington, Connecticut. It was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include potential incomplete capture of board-certified physicians, as not all board-certified pediatric dermatologists may be members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, and potential inaccurate capture of physician characteristics and Medicaid acceptance status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One author was a consultant for AbbVie. Other authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified 352 actively practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists using the Society for Pediatric Dermatology database and determined Medicaid acceptance status.
- They collected physician and practice characteristics from the US Census American Community Survey data and a web search.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 275 (78.1%) board-certified pediatric dermatologists accepted Medicaid.
- Academic practices had the highest Medicaid acceptance rate (98.7%), while private practices had the lowest (43.1%), a significant difference (P < .001).
- Acceptance rates were significantly higher in the Midwest (90.9%) than in the Northeast (71.8%) or West (71.4%; P = .005). Regional differences persisted after controlling for practice type: Midwest practice locations had greater odds of Medicaid acceptance than those in the Northeast (odds ratio [OR], 5.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.76-15.65) or West (OR, 5.26; 95% CI, 1.88-14.66).
- Practices in counties with lower median household incomes and greater densities of pediatric dermatologists were associated with higher Medicaid acceptance (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“While most pediatric dermatologists accept Medicaid, this study revealed differential access to care based on practice type, geographic location, and density of pediatric dermatologists per county,” the authors wrote. More research is needed on “the impact on health outcomes when specialty services are unavailable” and on “the role of administrative and reimbursement barriers limiting Medicaid acceptance among pediatric dermatologists,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Madeleine Tessier-Kay, MPH, Department of Dermatology, at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington, Connecticut. It was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include potential incomplete capture of board-certified physicians, as not all board-certified pediatric dermatologists may be members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, and potential inaccurate capture of physician characteristics and Medicaid acceptance status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One author was a consultant for AbbVie. Other authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified 352 actively practicing board-certified pediatric dermatologists using the Society for Pediatric Dermatology database and determined Medicaid acceptance status.
- They collected physician and practice characteristics from the US Census American Community Survey data and a web search.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 275 (78.1%) board-certified pediatric dermatologists accepted Medicaid.
- Academic practices had the highest Medicaid acceptance rate (98.7%), while private practices had the lowest (43.1%), a significant difference (P < .001).
- Acceptance rates were significantly higher in the Midwest (90.9%) than in the Northeast (71.8%) or West (71.4%; P = .005). Regional differences persisted after controlling for practice type: Midwest practice locations had greater odds of Medicaid acceptance than those in the Northeast (odds ratio [OR], 5.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.76-15.65) or West (OR, 5.26; 95% CI, 1.88-14.66).
- Practices in counties with lower median household incomes and greater densities of pediatric dermatologists were associated with higher Medicaid acceptance (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“While most pediatric dermatologists accept Medicaid, this study revealed differential access to care based on practice type, geographic location, and density of pediatric dermatologists per county,” the authors wrote. More research is needed on “the impact on health outcomes when specialty services are unavailable” and on “the role of administrative and reimbursement barriers limiting Medicaid acceptance among pediatric dermatologists,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Madeleine Tessier-Kay, MPH, Department of Dermatology, at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington, Connecticut. It was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include potential incomplete capture of board-certified physicians, as not all board-certified pediatric dermatologists may be members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, and potential inaccurate capture of physician characteristics and Medicaid acceptance status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One author was a consultant for AbbVie. Other authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Children on Medicaid With Asthma Receive Less Specialty Care
Primary care clinicians successfully manage many children with asthma, but data on specialist care according to insurance coverage are lacking, wrote Kimberley H. Geissler, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School–Baystate, Springfield, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
Despite many interventions over time, “low-income children insured by Medicaid, many of whom are from minoritized racial and ethnic groups, continue to have worse outcomes and higher rates of poorly controlled asthma than children who are privately insured,” Dr. Geissler said in an interview.
“Because differences in whether a child sees an asthma specialist could contribute to these disparities, better understanding specialist use among both groups of kids may help inform potential solutions,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified children with asthma aged 2-17 years using data from the Massachusetts All-Payer Claims Database for the years 2015-2020. The study population included 198,101 children and 432,455 child-year observations from children with asthma during a year when they met at least one of three criteria with any asthma diagnosis: One or more hospital visits, two or more outpatient visits, or at least one outpatient visit and at least one asthma medication.
Outpatient Visit Outcome
The primary outcome of asthma specialist care was defined as at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis to a clinician with a code of allergy and immunology, pulmonology, or otolaryngology.
A total of 66.2% of the child-year observations involved Medicaid and 33.8% involved private insurance. Approximately 15% of the children received asthma specialist care. However, nearly twice as many children with private insurance received asthma specialty care compared with those with Medicaid (20.6% vs 11.9%). In a full logistic regression analysis, children with Medicaid insurance were 55% less likely to receive asthma specialist treatment than children with private insurance.
Allergy and immunology was the most common specialty used, and the child-years for this specialty among children with Medicaid were less than half of those among children with private insurance (7.1% vs 15.9%).
Rates of persistent asthma were 20.0% and 16.9% in children with Medicaid and private insurance, respectively. Overall, children with persistent asthma were nearly four times as likely to receive asthma specialist care (adjusted odds ratio, 3.96). However, the difference in odds of receiving specialty care based on insurance type in favor of private insurance was greater among children with persistent asthma than among those without persistent asthma (−24.0 percentage points vs −20.8 percentage points).
The researchers found a similar pattern of difference in asthma specialty care in a sensitivity analysis limiting the results to child-year observations with at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis in a calendar year, although they also found a slight narrowing of the difference between the groups over time.
“Contrary to expectations, disparities in specialist care by insurance type were even more striking in children with persistent asthma,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. Notably, the growth of specialty drugs such as biologics for moderate to severe asthma are mainly prescribed by specialists, and ensuring access to specialists for children with Medicaid may reduce disparities in asthma control for those with severe or poorly controlled disease, they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use only of data from Massachusetts, which may not generalize to other states, and the use of completed specialist visits without data on referrals, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on asthma symptom frequency or control and on the setting in which an asthma diagnosis was made.
However, the results suggest a need for more attention to disparities in asthma care by insurance type, and more research is needed to determine whether these disparities persist in subsets of children with asthma, such as those with allergies or chronic medical conditions, they concluded.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“Perhaps unsurprisingly, children with private insurance were more likely to receive asthma specialist care than children with Medicaid,” Dr. Geissler told this news organization. The researchers expected a smaller gap between insurance types among children with persistent asthma, a marker for asthma severity, she said. However, “we found that the gap between those with Medicaid and those with private insurance is actually larger” for children with persistent asthma, she added.
As improved treatments for hard-to-control asthma become more available, pediatricians and primary care clinicians should follow the latest clinical guidelines for referring children to specialists for asthma care, said Dr. Geissler.
“Additionally, asthma specialists should ensure that their practices are accessible to children with Medicaid, as these families may face higher barriers to care; for example, transportation needs or scheduling challenges,” she said. Other strategies to overcome barriers to care might include electronic consultations with specialists or primary care–oriented interdisciplinary asthma clinics, which may be useful for all children with asthma but may particularly benefit those insured by Medicaid, she noted.
“Based on data limitations, we could not examine why we observed such big differences in specialist use by insurance type; for example, whether pediatricians were referring to specialists less for Medicaid-insured kids, or whether kids with Medicaid were less likely to see a specialist after a referral was made,” Dr. Geissler said. More research is needed to examine not only these factors but also the appropriateness of specialty care based on clinical guidelines to ensure high-quality evidence-based care for children with asthma who are insured by Medicaid, she said.
Improve Access and Expand Analysis
Asthma is a chronic and prevalent disease and requires a comprehensive approach that sometimes calls for specialist care, Anne Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist in Portland, Maine, said in an interview.
Dr. Coates said she was surprised by the results of the current study but commended the authors for highlighting the limitations of the study, which illustrate areas for additional research. Notably, “the authors couldn’t observe referrals to specialists from primary care physicians; they used completed visits as a proxy,” Dr. Coates said.
More studies are needed to assess the completion of referral visits regardless of children’s insurance in order to better understand and address the barriers to specialty care, she added.
The current study is important because of the extent of asthma coupled with the significant number of children across the United States who are insured by Medicaid, especially underserved populations, she said.
“The burden of asthma differentially affects people of color who are living in lower resourced areas, and it is important in further research to understanding the barriers to helping people get the care they need,” Dr. Coates told this news organization. Some alternatives might include telehealth visits or even a hybrid visit to a primary care provider (PCP) who has high-speed internet, and the specialist could then conduct a telehealth visit from the PCP’s office, with the PCP acting as on-site eyes and ears, said Dr. Coates, who has used this strategy in her practice in Maine, where many patients live far from specialist care.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the University of Massachusetts Center for Clinical and Translational Science-Biostatistics, Epidemiology & Research Design Component. Dr. Geissler and Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians successfully manage many children with asthma, but data on specialist care according to insurance coverage are lacking, wrote Kimberley H. Geissler, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School–Baystate, Springfield, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
Despite many interventions over time, “low-income children insured by Medicaid, many of whom are from minoritized racial and ethnic groups, continue to have worse outcomes and higher rates of poorly controlled asthma than children who are privately insured,” Dr. Geissler said in an interview.
“Because differences in whether a child sees an asthma specialist could contribute to these disparities, better understanding specialist use among both groups of kids may help inform potential solutions,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified children with asthma aged 2-17 years using data from the Massachusetts All-Payer Claims Database for the years 2015-2020. The study population included 198,101 children and 432,455 child-year observations from children with asthma during a year when they met at least one of three criteria with any asthma diagnosis: One or more hospital visits, two or more outpatient visits, or at least one outpatient visit and at least one asthma medication.
Outpatient Visit Outcome
The primary outcome of asthma specialist care was defined as at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis to a clinician with a code of allergy and immunology, pulmonology, or otolaryngology.
A total of 66.2% of the child-year observations involved Medicaid and 33.8% involved private insurance. Approximately 15% of the children received asthma specialist care. However, nearly twice as many children with private insurance received asthma specialty care compared with those with Medicaid (20.6% vs 11.9%). In a full logistic regression analysis, children with Medicaid insurance were 55% less likely to receive asthma specialist treatment than children with private insurance.
Allergy and immunology was the most common specialty used, and the child-years for this specialty among children with Medicaid were less than half of those among children with private insurance (7.1% vs 15.9%).
Rates of persistent asthma were 20.0% and 16.9% in children with Medicaid and private insurance, respectively. Overall, children with persistent asthma were nearly four times as likely to receive asthma specialist care (adjusted odds ratio, 3.96). However, the difference in odds of receiving specialty care based on insurance type in favor of private insurance was greater among children with persistent asthma than among those without persistent asthma (−24.0 percentage points vs −20.8 percentage points).
The researchers found a similar pattern of difference in asthma specialty care in a sensitivity analysis limiting the results to child-year observations with at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis in a calendar year, although they also found a slight narrowing of the difference between the groups over time.
“Contrary to expectations, disparities in specialist care by insurance type were even more striking in children with persistent asthma,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. Notably, the growth of specialty drugs such as biologics for moderate to severe asthma are mainly prescribed by specialists, and ensuring access to specialists for children with Medicaid may reduce disparities in asthma control for those with severe or poorly controlled disease, they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use only of data from Massachusetts, which may not generalize to other states, and the use of completed specialist visits without data on referrals, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on asthma symptom frequency or control and on the setting in which an asthma diagnosis was made.
However, the results suggest a need for more attention to disparities in asthma care by insurance type, and more research is needed to determine whether these disparities persist in subsets of children with asthma, such as those with allergies or chronic medical conditions, they concluded.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“Perhaps unsurprisingly, children with private insurance were more likely to receive asthma specialist care than children with Medicaid,” Dr. Geissler told this news organization. The researchers expected a smaller gap between insurance types among children with persistent asthma, a marker for asthma severity, she said. However, “we found that the gap between those with Medicaid and those with private insurance is actually larger” for children with persistent asthma, she added.
As improved treatments for hard-to-control asthma become more available, pediatricians and primary care clinicians should follow the latest clinical guidelines for referring children to specialists for asthma care, said Dr. Geissler.
“Additionally, asthma specialists should ensure that their practices are accessible to children with Medicaid, as these families may face higher barriers to care; for example, transportation needs or scheduling challenges,” she said. Other strategies to overcome barriers to care might include electronic consultations with specialists or primary care–oriented interdisciplinary asthma clinics, which may be useful for all children with asthma but may particularly benefit those insured by Medicaid, she noted.
“Based on data limitations, we could not examine why we observed such big differences in specialist use by insurance type; for example, whether pediatricians were referring to specialists less for Medicaid-insured kids, or whether kids with Medicaid were less likely to see a specialist after a referral was made,” Dr. Geissler said. More research is needed to examine not only these factors but also the appropriateness of specialty care based on clinical guidelines to ensure high-quality evidence-based care for children with asthma who are insured by Medicaid, she said.
Improve Access and Expand Analysis
Asthma is a chronic and prevalent disease and requires a comprehensive approach that sometimes calls for specialist care, Anne Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist in Portland, Maine, said in an interview.
Dr. Coates said she was surprised by the results of the current study but commended the authors for highlighting the limitations of the study, which illustrate areas for additional research. Notably, “the authors couldn’t observe referrals to specialists from primary care physicians; they used completed visits as a proxy,” Dr. Coates said.
More studies are needed to assess the completion of referral visits regardless of children’s insurance in order to better understand and address the barriers to specialty care, she added.
The current study is important because of the extent of asthma coupled with the significant number of children across the United States who are insured by Medicaid, especially underserved populations, she said.
“The burden of asthma differentially affects people of color who are living in lower resourced areas, and it is important in further research to understanding the barriers to helping people get the care they need,” Dr. Coates told this news organization. Some alternatives might include telehealth visits or even a hybrid visit to a primary care provider (PCP) who has high-speed internet, and the specialist could then conduct a telehealth visit from the PCP’s office, with the PCP acting as on-site eyes and ears, said Dr. Coates, who has used this strategy in her practice in Maine, where many patients live far from specialist care.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the University of Massachusetts Center for Clinical and Translational Science-Biostatistics, Epidemiology & Research Design Component. Dr. Geissler and Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians successfully manage many children with asthma, but data on specialist care according to insurance coverage are lacking, wrote Kimberley H. Geissler, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School–Baystate, Springfield, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
Despite many interventions over time, “low-income children insured by Medicaid, many of whom are from minoritized racial and ethnic groups, continue to have worse outcomes and higher rates of poorly controlled asthma than children who are privately insured,” Dr. Geissler said in an interview.
“Because differences in whether a child sees an asthma specialist could contribute to these disparities, better understanding specialist use among both groups of kids may help inform potential solutions,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified children with asthma aged 2-17 years using data from the Massachusetts All-Payer Claims Database for the years 2015-2020. The study population included 198,101 children and 432,455 child-year observations from children with asthma during a year when they met at least one of three criteria with any asthma diagnosis: One or more hospital visits, two or more outpatient visits, or at least one outpatient visit and at least one asthma medication.
Outpatient Visit Outcome
The primary outcome of asthma specialist care was defined as at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis to a clinician with a code of allergy and immunology, pulmonology, or otolaryngology.
A total of 66.2% of the child-year observations involved Medicaid and 33.8% involved private insurance. Approximately 15% of the children received asthma specialist care. However, nearly twice as many children with private insurance received asthma specialty care compared with those with Medicaid (20.6% vs 11.9%). In a full logistic regression analysis, children with Medicaid insurance were 55% less likely to receive asthma specialist treatment than children with private insurance.
Allergy and immunology was the most common specialty used, and the child-years for this specialty among children with Medicaid were less than half of those among children with private insurance (7.1% vs 15.9%).
Rates of persistent asthma were 20.0% and 16.9% in children with Medicaid and private insurance, respectively. Overall, children with persistent asthma were nearly four times as likely to receive asthma specialist care (adjusted odds ratio, 3.96). However, the difference in odds of receiving specialty care based on insurance type in favor of private insurance was greater among children with persistent asthma than among those without persistent asthma (−24.0 percentage points vs −20.8 percentage points).
The researchers found a similar pattern of difference in asthma specialty care in a sensitivity analysis limiting the results to child-year observations with at least one outpatient visit with any asthma diagnosis in a calendar year, although they also found a slight narrowing of the difference between the groups over time.
“Contrary to expectations, disparities in specialist care by insurance type were even more striking in children with persistent asthma,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. Notably, the growth of specialty drugs such as biologics for moderate to severe asthma are mainly prescribed by specialists, and ensuring access to specialists for children with Medicaid may reduce disparities in asthma control for those with severe or poorly controlled disease, they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use only of data from Massachusetts, which may not generalize to other states, and the use of completed specialist visits without data on referrals, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on asthma symptom frequency or control and on the setting in which an asthma diagnosis was made.
However, the results suggest a need for more attention to disparities in asthma care by insurance type, and more research is needed to determine whether these disparities persist in subsets of children with asthma, such as those with allergies or chronic medical conditions, they concluded.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“Perhaps unsurprisingly, children with private insurance were more likely to receive asthma specialist care than children with Medicaid,” Dr. Geissler told this news organization. The researchers expected a smaller gap between insurance types among children with persistent asthma, a marker for asthma severity, she said. However, “we found that the gap between those with Medicaid and those with private insurance is actually larger” for children with persistent asthma, she added.
As improved treatments for hard-to-control asthma become more available, pediatricians and primary care clinicians should follow the latest clinical guidelines for referring children to specialists for asthma care, said Dr. Geissler.
“Additionally, asthma specialists should ensure that their practices are accessible to children with Medicaid, as these families may face higher barriers to care; for example, transportation needs or scheduling challenges,” she said. Other strategies to overcome barriers to care might include electronic consultations with specialists or primary care–oriented interdisciplinary asthma clinics, which may be useful for all children with asthma but may particularly benefit those insured by Medicaid, she noted.
“Based on data limitations, we could not examine why we observed such big differences in specialist use by insurance type; for example, whether pediatricians were referring to specialists less for Medicaid-insured kids, or whether kids with Medicaid were less likely to see a specialist after a referral was made,” Dr. Geissler said. More research is needed to examine not only these factors but also the appropriateness of specialty care based on clinical guidelines to ensure high-quality evidence-based care for children with asthma who are insured by Medicaid, she said.
Improve Access and Expand Analysis
Asthma is a chronic and prevalent disease and requires a comprehensive approach that sometimes calls for specialist care, Anne Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist in Portland, Maine, said in an interview.
Dr. Coates said she was surprised by the results of the current study but commended the authors for highlighting the limitations of the study, which illustrate areas for additional research. Notably, “the authors couldn’t observe referrals to specialists from primary care physicians; they used completed visits as a proxy,” Dr. Coates said.
More studies are needed to assess the completion of referral visits regardless of children’s insurance in order to better understand and address the barriers to specialty care, she added.
The current study is important because of the extent of asthma coupled with the significant number of children across the United States who are insured by Medicaid, especially underserved populations, she said.
“The burden of asthma differentially affects people of color who are living in lower resourced areas, and it is important in further research to understanding the barriers to helping people get the care they need,” Dr. Coates told this news organization. Some alternatives might include telehealth visits or even a hybrid visit to a primary care provider (PCP) who has high-speed internet, and the specialist could then conduct a telehealth visit from the PCP’s office, with the PCP acting as on-site eyes and ears, said Dr. Coates, who has used this strategy in her practice in Maine, where many patients live far from specialist care.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the University of Massachusetts Center for Clinical and Translational Science-Biostatistics, Epidemiology & Research Design Component. Dr. Geissler and Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pyzchiva Receives FDA Approval as Third Ustekinumab Biosimilar
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ustekinumab-ttwe (Pyzchiva) as a biosimilar to ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of multiple inflammatory conditions.
In addition, the agency “provisionally determined” that the medication would be interchangeable with the reference product but that designation would not take hold until the interchangeability exclusivity period for the first approved biosimilar ustekinumab-auub (Wezlana) expires, according to a press release. This designation would, depending on state law, allow a pharmacist to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. It’s unclear when ustekinumab-auub’s interchangeability exclusivity ends.
Ustekinumab-ttwe, a human interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, is indicated for the treatment of:
- Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Active psoriatic arthritis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
It is administered via subcutaneous injection in 45 mg/0.5 mL and 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes or via intravenous infusion in 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) single-dose vial.
Developed by Samsung Bioepis, ustekinumab-ttwe will be commercialized by Sandoz in the United States. Besides ustekinumab-auub, the other ustekinumab biosimilar is ustekinumab-aekn (Selarsdi).
Ustekinumab-ttwe is expected to launch in February 2025 “in accordance with the settlement and license agreement with Janssen Biotech,” which manufacturers the reference product, Sandoz said. The other approved ustekinumab biosimilars will launch within a similar time frame.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ustekinumab-ttwe (Pyzchiva) as a biosimilar to ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of multiple inflammatory conditions.
In addition, the agency “provisionally determined” that the medication would be interchangeable with the reference product but that designation would not take hold until the interchangeability exclusivity period for the first approved biosimilar ustekinumab-auub (Wezlana) expires, according to a press release. This designation would, depending on state law, allow a pharmacist to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. It’s unclear when ustekinumab-auub’s interchangeability exclusivity ends.
Ustekinumab-ttwe, a human interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, is indicated for the treatment of:
- Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Active psoriatic arthritis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
It is administered via subcutaneous injection in 45 mg/0.5 mL and 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes or via intravenous infusion in 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) single-dose vial.
Developed by Samsung Bioepis, ustekinumab-ttwe will be commercialized by Sandoz in the United States. Besides ustekinumab-auub, the other ustekinumab biosimilar is ustekinumab-aekn (Selarsdi).
Ustekinumab-ttwe is expected to launch in February 2025 “in accordance with the settlement and license agreement with Janssen Biotech,” which manufacturers the reference product, Sandoz said. The other approved ustekinumab biosimilars will launch within a similar time frame.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ustekinumab-ttwe (Pyzchiva) as a biosimilar to ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of multiple inflammatory conditions.
In addition, the agency “provisionally determined” that the medication would be interchangeable with the reference product but that designation would not take hold until the interchangeability exclusivity period for the first approved biosimilar ustekinumab-auub (Wezlana) expires, according to a press release. This designation would, depending on state law, allow a pharmacist to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. It’s unclear when ustekinumab-auub’s interchangeability exclusivity ends.
Ustekinumab-ttwe, a human interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, is indicated for the treatment of:
- Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Active psoriatic arthritis in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years or older with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
It is administered via subcutaneous injection in 45 mg/0.5 mL and 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes or via intravenous infusion in 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) single-dose vial.
Developed by Samsung Bioepis, ustekinumab-ttwe will be commercialized by Sandoz in the United States. Besides ustekinumab-auub, the other ustekinumab biosimilar is ustekinumab-aekn (Selarsdi).
Ustekinumab-ttwe is expected to launch in February 2025 “in accordance with the settlement and license agreement with Janssen Biotech,” which manufacturers the reference product, Sandoz said. The other approved ustekinumab biosimilars will launch within a similar time frame.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vascular Mass on the Posterior Neck in a Newborn
The Diagnosis: Congenital Hemangioma
Surgical resection of the mass was performed at 4 months of age without complication (Figure 1). Histopathology revealed a lobular endothelial cell proliferation within a densely fibrotic stroma, multiple thin-walled vessels, and negative immunoreactivity to glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT-1)(Figures 2 and 3). Combined with the patient’s clinical history and findings on imaging (Figure 4), the most accurate diagnosis was a congenital hemangioma (CH). The mass was determined to be a noninvoluting congenital hemangioma (NICH).
A variety of vascular anomalies manifest in newborns and can be differentiated by the patient’s clinical history—particularly whether the lesion is present at birth or develops after birth. Imaging and histopathology of the lesion(s) may be utilized when clinical examination alone is not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry further aid in differentiating the type of vascular lesion.
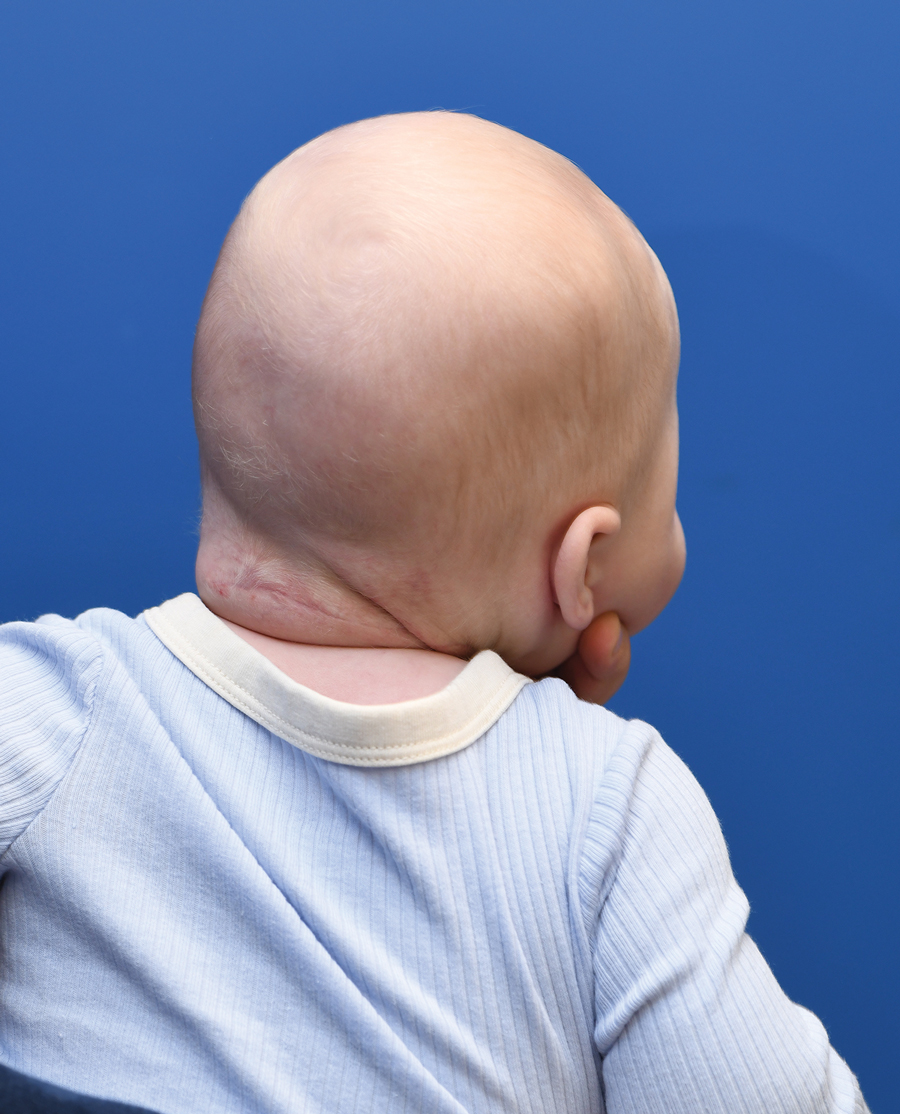

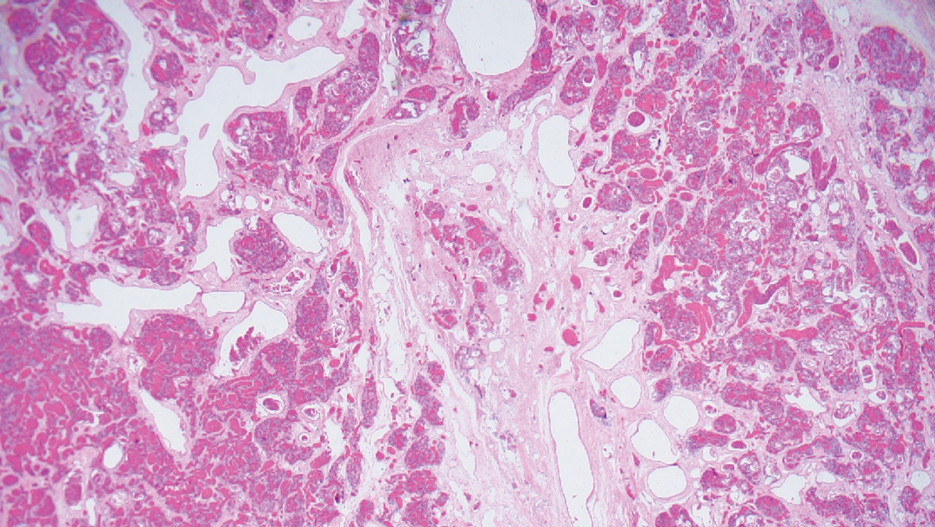
Overall, vascular anomalies are classified broadly into 2 categories based on their pathogenesis: tumors and malformations. Vascular tumors are composed of proliferating endothelial cells that have the potential to resolve spontaneously over time. Examples include CH, infantile hemangioma (IH), kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE), and tufted angioma (TA). In contrast, vascular malformations (ie, arteriovenous malformations) are composed of dysplastic vessels with normal endothelial cell turnover and do not resolve without intervention.1
Congenital hemangiomas are rare vascular tumors that are fully developed at birth. These tumors proliferate in utero, enabling prenatal detection via ultrasonography as early as 12 weeks’ gestation for large heterogeneous vascular masses.2-4 Congenital hemangiomas are described as solitary, well-circumscribed, raised, violaceous lesions most commonly located in the head and neck region.4-6 Histopathologically, they are characterized by lobules of proliferating capillaries surrounded by fibrous stroma and dysplastic vascular channels.6,7
Congenital hemangiomas are categorized based on their postnatal involution patterns.2 Fetally involuting CH both develops and begins regression in utero and often is completely regressed at birth.8 Rapidly involuting CH begins regression in the first few weeks of life and usually is completely involuted by 14 months of age.6,9-11 Conversely, NICH does not regress, often requiring surgical excision due to functional and cosmetic issues.12,13 Partially involuting CH is intermediary, beginning as rapidly involuting but not involuting completely and persisting as lesions that resemble NICH.14-16 Although generally benign and asymptomatic, these tumors can cause transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy at birth, as seen in our patient.17,18
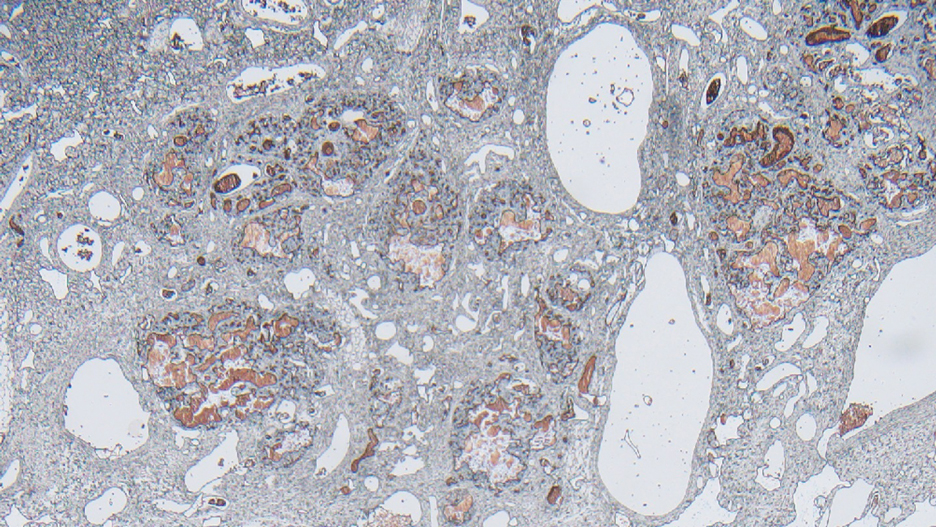
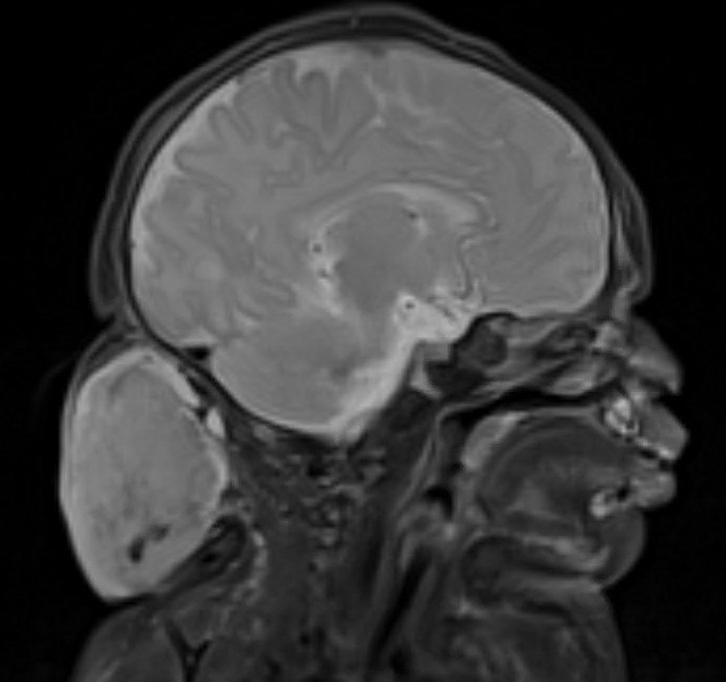
Infantile hemangioma is the most common vascular tumor of infancy.19-21 Although a precursor lesion may be present at birth, generally this tumor becomes apparent after the first few weeks of life as a solitary vascular plaque or nodule with a predilection for the head and neck.22-25 Once it arises, IH quickly enters a period of rapid growth, followed by a period of slower continued growth, with most reaching maximum size by 3 months.22 Thereafter, IH enters a slow period of involution (range, 3–9 years)26; more recent data suggest near resolution by 5 years of age.27 Infantile hemangioma is categorized based on its depth in the skin and subcutaneous tissues and can be classified as superficial, mixed, or deep.22,24,28,29 Superficial IH appears as a red plaque and may exhibit lobulation, while deep IH can be identified as flesh-colored or blue subcutaneous masses. Mixed IH may manifest with both superficial and deep features depending on the extent of its involvement in the dermal and subcutaneous layers. The pattern of involvement may be focal, segmental, or indeterminate.24 In contrast, CH typically is a solitary vascular mass with prominent telangiectases, nodules, and radiating veins.6 Histologically, IH is composed of proliferative plump endothelial cells that form capillaries, and the lesion stains positively for GLUT-1, whereas CH does not.30
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma is classified as a locally aggressive vascular tumor that manifests either prenatally or in early infancy.31 It is described as a solitary, ill-defined, firm, purple plaque most commonly located on the extremities and retroperitoneum.32-34 Histopathologically, these lesions are characterized by dilated lymphatic channels and irregular sheets or lobules of spindle-shaped endothelial cells infiltrating the dermis and subcutaneous fat.33,35 In contrast to CH, KHE lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein.36,37 Notably, 70% of these tumors are complicated by the presence of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, a potentially life-threatening emergency that occurs when platelets are trapped within a vascular tumor, leading to the consumption of clotting factors, intralesional bleeding, and rapid enlargement of the tumor.32 The Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon manifests clinically as microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. 38 Although CH lesions also can be associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy, they generally are mild and self-limited.18
Tufted angioma is a vascular tumor that arises within the first 5 years of life as firm violaceous papules or plaques, often with associated hyperhidrosis or hypertrichosis.39,40 Although TA grows slowly for a period of time, it eventually stabilizes and persists, rarely regressing completely.41 These tumors share many similarities with KHE, and it has been suggested that they may be part of the same spectrum. 42 As with KHE, TA lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein, which are negative in CH.36,37 Although TA also can be complicated by Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, the incidence is much lower (up to 38%).43,44 As such, TAs tend to be recognized as more superficial benign lesions. However, they still can cause notable cosmetic and functional impairment and should be monitored closely, especially in the presence of associated symptoms or complications.
Arteriovenous malformation is a vascular lesion that results from errors during the embryonic development of vascular channels.45 Although present at birth, it may not become clinically apparent until later in life. Arteriovenous malformations enlarge postnatally, and their growth is proportional to the developmental growth of the affected individual rather than the result of endothelial proliferation.46 In infants, AVM may manifest as a faint vascular stain that can evolve over time into a pink patch associated with a palpable thrill during adolescence. 4 On Doppler flow imaging, AVMs are identified as fast-flow anomalies arising from an abnormal communication between high-pressure arterial systems and low-pressure venous systems without the presence of a capillary bed.47 One of the differentiating factors between AVM and CH is that AVMs do not regress spontaneously and tend to have high recurrence rates, even with intervention. 48 In contrast, CH can be categorized based on its postnatal involution pattern. Another distinguishing factor is that AVMs tend to be larger and more invasive than CHs.46 Therefore, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as bleeding, seizures, or neurologic deficits associated with AVMs.1
- Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R. Introduction: ISSVA Classification. In: Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R, eds. Color Atlas of Vascular Tumors and Vascular Malformations. Cambridge University Press; 2007:3-11.
- Fadell MF, Jones BV, Adams DM. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal follow-up of rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma (RICH). Pediatr Radiol. 2011;41:1057-1060.
- Feygin T, Khalek N, Moldenhauer JS. Fetal brain, head, and neck tumors: prenatal imaging and management. Prenat Diagn. 2020;40:1203-1219.
- Foley LS, Kulungowski AM. Vascular anomalies in pediatrics. Adv Pediatr. 2015;62:227-255.
- Bruder E, Alaggio R, Kozakewich HPW, et al. Vascular and perivascular lesions of skin and soft tissues in children and adolescents. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2012;15:26-61.
- Berenguer B, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma: clinical and histopathologic features. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2003;6:495-510.
- North PE, Waner M, James CA, et al. Congenital nonprogressive hemangioma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity unlike infantile hemangioma. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1607-1620.
- Maguiness S, Uihlein LC, Liang MG, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma with fetal involution. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:321-326.
- Keating LJ, Soares GM, Muratore CS. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma. Med Health R I. 2012;95:149-152.
- Schafer F, Tapia M, Pinto C. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99:F422.
- Boon LM, Enjolras O, Mulliken JB. Congenital hemangioma: evidence of accelerated involution. J Pediatr. 1996;128:329-335.
- Liang MG, Frieden IJ. Infantile and congenital hemangiomas. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:162-167.
- Enjolras O, Mulliken JB, Boon LM, et al. Noninvoluting congenital hemangioma: a rare cutaneous vascular anomaly. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1647-1654.
- Nasseri E, Piram M, McCuaig CC, et al. Partially involuting congenital hemangiomas: a report of 8 cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:75-79.
- Wassef M, Blei F, Adams D, et al. Vascular anomalies classification: recommendations from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E203-E214.
- Boull C, Maguiness SM. Congenital hemangiomas. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35:124-127.
- Drolet BA, Frommelt PC, Chamlin SL, et al. Initiation and use of propranolol for infantile hemangioma: report of a consensus conference. Pediatrics. 2013;131:128-140.
- Baselga E, Cordisco MR, Garzon M, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma associated with transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1363-1370.
- Kanada KN, Merin MR, Munden A, et al. A prospective study of cutaneous findings in newborns in the United States: correlation with race, ethnicity, and gestational status using updated classification and nomenclature. J Pediatr. 2012;161:240-245.
- Munden A, Butschek R, Tom WL, et al. Prospective study of infantile haemangiomas: incidence, clinical characteristics and association with placental anomalies. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:907-913.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, et al. Growth characteristics of infantile hemangiomas: implications for management. Pediatrics. 2008;122:360-367.
- Hidano A, Nakajima S. Earliest features of the strawberry mark in the newborn. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:138-144.
- Martinez-Perez D, Fein NA, Boon LM, et al. Not all hemangiomas look like strawberries: uncommon presentations of the most common tumor of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1995;12:1-6.
- Payne MM, Moyer F, Marcks KM, et al. The precursor to the hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966;38:64-67.
- Bowers RE, Graham EA, Tomlinson KM. The natural history of the strawberry nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1960;82:667-680.
- Couto RA, Maclellan RA, Zurakowski D, et al. Infantile hemangioma: clinical assessment of the involuting phase and implications for management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:619-624.
- Drolet BA, Esterly NB, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:173-181.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567-1576.
- North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, et al. GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:11-22.
- Gruman A, Liang MG, Mulliken JB, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma without Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:616-622.
- Croteau SE, Liang MG, Kozakewich HP, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: atypical features and risks of Kasabach- Merritt phenomenon in 107 referrals. J Pediatr. 2013;162:142-147.
- Zukerberg LR, Nickoloff BJ, Weiss SW. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma of infancy and childhood. an aggressive neoplasm associated with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome and lymphangiomatosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17:321-328.
- Mac-Moune Lai F, To KF, Choi PC, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: five patients with cutaneous lesion and long follow-up. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:1087-1092.
- O’Rafferty C, O’Regan GM, Irvine AD, et al. Recent advances in the pathobiology and management of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:38-51.
- Le Huu AR, Jokinen CH, Rubin BP, et al. Expression of prox1, lymphatic endothelial nuclear transcription factor, in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1563-1573.
- Debelenko LV, Perez-Atayde AR, Mulliken JB, et al. D2-40 immuno-histochemical analysis of pediatric vascular tumors reveals positivity in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:1454-1460.
- Haisley-Royster C, Enjolras O, Frieden IJ, et al. Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon: a retrospective study of treatment with vincristine. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002;24:459-462.
- Wilmer A, Kaatz M, Bocker T, et al. Tufted angioma. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:51-53.
- Herron MD, Coffin CM, Vanderhooft SL. Tufted angiomas: variability of the clinical morphology. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19:394-401.
- North PE. Pediatric vascular tumors and malformations. Surg Pathol Clin. 2010,3:455-494.
- Chu CY, Hsiao CH, Chiu HC. Transformation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Dermatology. 2003;206:334-337.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Johnson EF, Davis DM, Tollefson MM, et al. Vascular tumors in infants: case report and review of clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical characteristics of infantile hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma, noninvoluting congenital hemangioma, tufted angioma, and kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:231-239.
- Christison-Lagay ER, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. Surg Clin North Am. 2006;86:393-425.
- Liu AS, Mulliken JB, Zurakowski D, et al. Extracranial arteriovenous malformations: natural progression and recurrence after treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:1185-1194.
- Young AE, Mulliken JB. Arteriovenous malformations. In: Mulliken JB, Young AE, eds. Vascular Birthmarks: Haemangiomas and Malformations. WB Saunders; 1988:228-245.
- Duggan EM, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. In: Holcomb GW III, Murphy JP, St Peter SD, eds. Holcomb and Ashcraft’s Pediatric Surgery. 7th edition. Elsevier; 2019:1147-1170.
The Diagnosis: Congenital Hemangioma
Surgical resection of the mass was performed at 4 months of age without complication (Figure 1). Histopathology revealed a lobular endothelial cell proliferation within a densely fibrotic stroma, multiple thin-walled vessels, and negative immunoreactivity to glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT-1)(Figures 2 and 3). Combined with the patient’s clinical history and findings on imaging (Figure 4), the most accurate diagnosis was a congenital hemangioma (CH). The mass was determined to be a noninvoluting congenital hemangioma (NICH).
A variety of vascular anomalies manifest in newborns and can be differentiated by the patient’s clinical history—particularly whether the lesion is present at birth or develops after birth. Imaging and histopathology of the lesion(s) may be utilized when clinical examination alone is not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry further aid in differentiating the type of vascular lesion.


Overall, vascular anomalies are classified broadly into 2 categories based on their pathogenesis: tumors and malformations. Vascular tumors are composed of proliferating endothelial cells that have the potential to resolve spontaneously over time. Examples include CH, infantile hemangioma (IH), kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE), and tufted angioma (TA). In contrast, vascular malformations (ie, arteriovenous malformations) are composed of dysplastic vessels with normal endothelial cell turnover and do not resolve without intervention.1
Congenital hemangiomas are rare vascular tumors that are fully developed at birth. These tumors proliferate in utero, enabling prenatal detection via ultrasonography as early as 12 weeks’ gestation for large heterogeneous vascular masses.2-4 Congenital hemangiomas are described as solitary, well-circumscribed, raised, violaceous lesions most commonly located in the head and neck region.4-6 Histopathologically, they are characterized by lobules of proliferating capillaries surrounded by fibrous stroma and dysplastic vascular channels.6,7
Congenital hemangiomas are categorized based on their postnatal involution patterns.2 Fetally involuting CH both develops and begins regression in utero and often is completely regressed at birth.8 Rapidly involuting CH begins regression in the first few weeks of life and usually is completely involuted by 14 months of age.6,9-11 Conversely, NICH does not regress, often requiring surgical excision due to functional and cosmetic issues.12,13 Partially involuting CH is intermediary, beginning as rapidly involuting but not involuting completely and persisting as lesions that resemble NICH.14-16 Although generally benign and asymptomatic, these tumors can cause transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy at birth, as seen in our patient.17,18


Infantile hemangioma is the most common vascular tumor of infancy.19-21 Although a precursor lesion may be present at birth, generally this tumor becomes apparent after the first few weeks of life as a solitary vascular plaque or nodule with a predilection for the head and neck.22-25 Once it arises, IH quickly enters a period of rapid growth, followed by a period of slower continued growth, with most reaching maximum size by 3 months.22 Thereafter, IH enters a slow period of involution (range, 3–9 years)26; more recent data suggest near resolution by 5 years of age.27 Infantile hemangioma is categorized based on its depth in the skin and subcutaneous tissues and can be classified as superficial, mixed, or deep.22,24,28,29 Superficial IH appears as a red plaque and may exhibit lobulation, while deep IH can be identified as flesh-colored or blue subcutaneous masses. Mixed IH may manifest with both superficial and deep features depending on the extent of its involvement in the dermal and subcutaneous layers. The pattern of involvement may be focal, segmental, or indeterminate.24 In contrast, CH typically is a solitary vascular mass with prominent telangiectases, nodules, and radiating veins.6 Histologically, IH is composed of proliferative plump endothelial cells that form capillaries, and the lesion stains positively for GLUT-1, whereas CH does not.30
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma is classified as a locally aggressive vascular tumor that manifests either prenatally or in early infancy.31 It is described as a solitary, ill-defined, firm, purple plaque most commonly located on the extremities and retroperitoneum.32-34 Histopathologically, these lesions are characterized by dilated lymphatic channels and irregular sheets or lobules of spindle-shaped endothelial cells infiltrating the dermis and subcutaneous fat.33,35 In contrast to CH, KHE lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein.36,37 Notably, 70% of these tumors are complicated by the presence of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, a potentially life-threatening emergency that occurs when platelets are trapped within a vascular tumor, leading to the consumption of clotting factors, intralesional bleeding, and rapid enlargement of the tumor.32 The Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon manifests clinically as microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. 38 Although CH lesions also can be associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy, they generally are mild and self-limited.18
Tufted angioma is a vascular tumor that arises within the first 5 years of life as firm violaceous papules or plaques, often with associated hyperhidrosis or hypertrichosis.39,40 Although TA grows slowly for a period of time, it eventually stabilizes and persists, rarely regressing completely.41 These tumors share many similarities with KHE, and it has been suggested that they may be part of the same spectrum. 42 As with KHE, TA lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein, which are negative in CH.36,37 Although TA also can be complicated by Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, the incidence is much lower (up to 38%).43,44 As such, TAs tend to be recognized as more superficial benign lesions. However, they still can cause notable cosmetic and functional impairment and should be monitored closely, especially in the presence of associated symptoms or complications.
Arteriovenous malformation is a vascular lesion that results from errors during the embryonic development of vascular channels.45 Although present at birth, it may not become clinically apparent until later in life. Arteriovenous malformations enlarge postnatally, and their growth is proportional to the developmental growth of the affected individual rather than the result of endothelial proliferation.46 In infants, AVM may manifest as a faint vascular stain that can evolve over time into a pink patch associated with a palpable thrill during adolescence. 4 On Doppler flow imaging, AVMs are identified as fast-flow anomalies arising from an abnormal communication between high-pressure arterial systems and low-pressure venous systems without the presence of a capillary bed.47 One of the differentiating factors between AVM and CH is that AVMs do not regress spontaneously and tend to have high recurrence rates, even with intervention. 48 In contrast, CH can be categorized based on its postnatal involution pattern. Another distinguishing factor is that AVMs tend to be larger and more invasive than CHs.46 Therefore, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as bleeding, seizures, or neurologic deficits associated with AVMs.1
The Diagnosis: Congenital Hemangioma
Surgical resection of the mass was performed at 4 months of age without complication (Figure 1). Histopathology revealed a lobular endothelial cell proliferation within a densely fibrotic stroma, multiple thin-walled vessels, and negative immunoreactivity to glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT-1)(Figures 2 and 3). Combined with the patient’s clinical history and findings on imaging (Figure 4), the most accurate diagnosis was a congenital hemangioma (CH). The mass was determined to be a noninvoluting congenital hemangioma (NICH).
A variety of vascular anomalies manifest in newborns and can be differentiated by the patient’s clinical history—particularly whether the lesion is present at birth or develops after birth. Imaging and histopathology of the lesion(s) may be utilized when clinical examination alone is not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry further aid in differentiating the type of vascular lesion.


Overall, vascular anomalies are classified broadly into 2 categories based on their pathogenesis: tumors and malformations. Vascular tumors are composed of proliferating endothelial cells that have the potential to resolve spontaneously over time. Examples include CH, infantile hemangioma (IH), kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE), and tufted angioma (TA). In contrast, vascular malformations (ie, arteriovenous malformations) are composed of dysplastic vessels with normal endothelial cell turnover and do not resolve without intervention.1
Congenital hemangiomas are rare vascular tumors that are fully developed at birth. These tumors proliferate in utero, enabling prenatal detection via ultrasonography as early as 12 weeks’ gestation for large heterogeneous vascular masses.2-4 Congenital hemangiomas are described as solitary, well-circumscribed, raised, violaceous lesions most commonly located in the head and neck region.4-6 Histopathologically, they are characterized by lobules of proliferating capillaries surrounded by fibrous stroma and dysplastic vascular channels.6,7
Congenital hemangiomas are categorized based on their postnatal involution patterns.2 Fetally involuting CH both develops and begins regression in utero and often is completely regressed at birth.8 Rapidly involuting CH begins regression in the first few weeks of life and usually is completely involuted by 14 months of age.6,9-11 Conversely, NICH does not regress, often requiring surgical excision due to functional and cosmetic issues.12,13 Partially involuting CH is intermediary, beginning as rapidly involuting but not involuting completely and persisting as lesions that resemble NICH.14-16 Although generally benign and asymptomatic, these tumors can cause transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy at birth, as seen in our patient.17,18


Infantile hemangioma is the most common vascular tumor of infancy.19-21 Although a precursor lesion may be present at birth, generally this tumor becomes apparent after the first few weeks of life as a solitary vascular plaque or nodule with a predilection for the head and neck.22-25 Once it arises, IH quickly enters a period of rapid growth, followed by a period of slower continued growth, with most reaching maximum size by 3 months.22 Thereafter, IH enters a slow period of involution (range, 3–9 years)26; more recent data suggest near resolution by 5 years of age.27 Infantile hemangioma is categorized based on its depth in the skin and subcutaneous tissues and can be classified as superficial, mixed, or deep.22,24,28,29 Superficial IH appears as a red plaque and may exhibit lobulation, while deep IH can be identified as flesh-colored or blue subcutaneous masses. Mixed IH may manifest with both superficial and deep features depending on the extent of its involvement in the dermal and subcutaneous layers. The pattern of involvement may be focal, segmental, or indeterminate.24 In contrast, CH typically is a solitary vascular mass with prominent telangiectases, nodules, and radiating veins.6 Histologically, IH is composed of proliferative plump endothelial cells that form capillaries, and the lesion stains positively for GLUT-1, whereas CH does not.30
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma is classified as a locally aggressive vascular tumor that manifests either prenatally or in early infancy.31 It is described as a solitary, ill-defined, firm, purple plaque most commonly located on the extremities and retroperitoneum.32-34 Histopathologically, these lesions are characterized by dilated lymphatic channels and irregular sheets or lobules of spindle-shaped endothelial cells infiltrating the dermis and subcutaneous fat.33,35 In contrast to CH, KHE lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein.36,37 Notably, 70% of these tumors are complicated by the presence of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, a potentially life-threatening emergency that occurs when platelets are trapped within a vascular tumor, leading to the consumption of clotting factors, intralesional bleeding, and rapid enlargement of the tumor.32 The Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon manifests clinically as microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. 38 Although CH lesions also can be associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy, they generally are mild and self-limited.18
Tufted angioma is a vascular tumor that arises within the first 5 years of life as firm violaceous papules or plaques, often with associated hyperhidrosis or hypertrichosis.39,40 Although TA grows slowly for a period of time, it eventually stabilizes and persists, rarely regressing completely.41 These tumors share many similarities with KHE, and it has been suggested that they may be part of the same spectrum. 42 As with KHE, TA lesions show immunoreactivity to the markers podoplanin, lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1, and prospero homeobox 1 protein, which are negative in CH.36,37 Although TA also can be complicated by Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon, the incidence is much lower (up to 38%).43,44 As such, TAs tend to be recognized as more superficial benign lesions. However, they still can cause notable cosmetic and functional impairment and should be monitored closely, especially in the presence of associated symptoms or complications.
Arteriovenous malformation is a vascular lesion that results from errors during the embryonic development of vascular channels.45 Although present at birth, it may not become clinically apparent until later in life. Arteriovenous malformations enlarge postnatally, and their growth is proportional to the developmental growth of the affected individual rather than the result of endothelial proliferation.46 In infants, AVM may manifest as a faint vascular stain that can evolve over time into a pink patch associated with a palpable thrill during adolescence. 4 On Doppler flow imaging, AVMs are identified as fast-flow anomalies arising from an abnormal communication between high-pressure arterial systems and low-pressure venous systems without the presence of a capillary bed.47 One of the differentiating factors between AVM and CH is that AVMs do not regress spontaneously and tend to have high recurrence rates, even with intervention. 48 In contrast, CH can be categorized based on its postnatal involution pattern. Another distinguishing factor is that AVMs tend to be larger and more invasive than CHs.46 Therefore, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as bleeding, seizures, or neurologic deficits associated with AVMs.1
- Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R. Introduction: ISSVA Classification. In: Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R, eds. Color Atlas of Vascular Tumors and Vascular Malformations. Cambridge University Press; 2007:3-11.
- Fadell MF, Jones BV, Adams DM. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal follow-up of rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma (RICH). Pediatr Radiol. 2011;41:1057-1060.
- Feygin T, Khalek N, Moldenhauer JS. Fetal brain, head, and neck tumors: prenatal imaging and management. Prenat Diagn. 2020;40:1203-1219.
- Foley LS, Kulungowski AM. Vascular anomalies in pediatrics. Adv Pediatr. 2015;62:227-255.
- Bruder E, Alaggio R, Kozakewich HPW, et al. Vascular and perivascular lesions of skin and soft tissues in children and adolescents. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2012;15:26-61.
- Berenguer B, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma: clinical and histopathologic features. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2003;6:495-510.
- North PE, Waner M, James CA, et al. Congenital nonprogressive hemangioma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity unlike infantile hemangioma. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1607-1620.
- Maguiness S, Uihlein LC, Liang MG, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma with fetal involution. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:321-326.
- Keating LJ, Soares GM, Muratore CS. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma. Med Health R I. 2012;95:149-152.
- Schafer F, Tapia M, Pinto C. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99:F422.
- Boon LM, Enjolras O, Mulliken JB. Congenital hemangioma: evidence of accelerated involution. J Pediatr. 1996;128:329-335.
- Liang MG, Frieden IJ. Infantile and congenital hemangiomas. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:162-167.
- Enjolras O, Mulliken JB, Boon LM, et al. Noninvoluting congenital hemangioma: a rare cutaneous vascular anomaly. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1647-1654.
- Nasseri E, Piram M, McCuaig CC, et al. Partially involuting congenital hemangiomas: a report of 8 cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:75-79.
- Wassef M, Blei F, Adams D, et al. Vascular anomalies classification: recommendations from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E203-E214.
- Boull C, Maguiness SM. Congenital hemangiomas. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35:124-127.
- Drolet BA, Frommelt PC, Chamlin SL, et al. Initiation and use of propranolol for infantile hemangioma: report of a consensus conference. Pediatrics. 2013;131:128-140.
- Baselga E, Cordisco MR, Garzon M, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma associated with transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1363-1370.
- Kanada KN, Merin MR, Munden A, et al. A prospective study of cutaneous findings in newborns in the United States: correlation with race, ethnicity, and gestational status using updated classification and nomenclature. J Pediatr. 2012;161:240-245.
- Munden A, Butschek R, Tom WL, et al. Prospective study of infantile haemangiomas: incidence, clinical characteristics and association with placental anomalies. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:907-913.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, et al. Growth characteristics of infantile hemangiomas: implications for management. Pediatrics. 2008;122:360-367.
- Hidano A, Nakajima S. Earliest features of the strawberry mark in the newborn. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:138-144.
- Martinez-Perez D, Fein NA, Boon LM, et al. Not all hemangiomas look like strawberries: uncommon presentations of the most common tumor of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1995;12:1-6.
- Payne MM, Moyer F, Marcks KM, et al. The precursor to the hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966;38:64-67.
- Bowers RE, Graham EA, Tomlinson KM. The natural history of the strawberry nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1960;82:667-680.
- Couto RA, Maclellan RA, Zurakowski D, et al. Infantile hemangioma: clinical assessment of the involuting phase and implications for management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:619-624.
- Drolet BA, Esterly NB, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:173-181.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567-1576.
- North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, et al. GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:11-22.
- Gruman A, Liang MG, Mulliken JB, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma without Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:616-622.
- Croteau SE, Liang MG, Kozakewich HP, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: atypical features and risks of Kasabach- Merritt phenomenon in 107 referrals. J Pediatr. 2013;162:142-147.
- Zukerberg LR, Nickoloff BJ, Weiss SW. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma of infancy and childhood. an aggressive neoplasm associated with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome and lymphangiomatosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17:321-328.
- Mac-Moune Lai F, To KF, Choi PC, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: five patients with cutaneous lesion and long follow-up. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:1087-1092.
- O’Rafferty C, O’Regan GM, Irvine AD, et al. Recent advances in the pathobiology and management of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:38-51.
- Le Huu AR, Jokinen CH, Rubin BP, et al. Expression of prox1, lymphatic endothelial nuclear transcription factor, in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1563-1573.
- Debelenko LV, Perez-Atayde AR, Mulliken JB, et al. D2-40 immuno-histochemical analysis of pediatric vascular tumors reveals positivity in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:1454-1460.
- Haisley-Royster C, Enjolras O, Frieden IJ, et al. Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon: a retrospective study of treatment with vincristine. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002;24:459-462.
- Wilmer A, Kaatz M, Bocker T, et al. Tufted angioma. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:51-53.
- Herron MD, Coffin CM, Vanderhooft SL. Tufted angiomas: variability of the clinical morphology. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19:394-401.
- North PE. Pediatric vascular tumors and malformations. Surg Pathol Clin. 2010,3:455-494.
- Chu CY, Hsiao CH, Chiu HC. Transformation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Dermatology. 2003;206:334-337.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Johnson EF, Davis DM, Tollefson MM, et al. Vascular tumors in infants: case report and review of clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical characteristics of infantile hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma, noninvoluting congenital hemangioma, tufted angioma, and kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:231-239.
- Christison-Lagay ER, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. Surg Clin North Am. 2006;86:393-425.
- Liu AS, Mulliken JB, Zurakowski D, et al. Extracranial arteriovenous malformations: natural progression and recurrence after treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:1185-1194.
- Young AE, Mulliken JB. Arteriovenous malformations. In: Mulliken JB, Young AE, eds. Vascular Birthmarks: Haemangiomas and Malformations. WB Saunders; 1988:228-245.
- Duggan EM, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. In: Holcomb GW III, Murphy JP, St Peter SD, eds. Holcomb and Ashcraft’s Pediatric Surgery. 7th edition. Elsevier; 2019:1147-1170.
- Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R. Introduction: ISSVA Classification. In: Enjolras O, Wassef M, Chapot R, eds. Color Atlas of Vascular Tumors and Vascular Malformations. Cambridge University Press; 2007:3-11.
- Fadell MF, Jones BV, Adams DM. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal follow-up of rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma (RICH). Pediatr Radiol. 2011;41:1057-1060.
- Feygin T, Khalek N, Moldenhauer JS. Fetal brain, head, and neck tumors: prenatal imaging and management. Prenat Diagn. 2020;40:1203-1219.
- Foley LS, Kulungowski AM. Vascular anomalies in pediatrics. Adv Pediatr. 2015;62:227-255.
- Bruder E, Alaggio R, Kozakewich HPW, et al. Vascular and perivascular lesions of skin and soft tissues in children and adolescents. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2012;15:26-61.
- Berenguer B, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma: clinical and histopathologic features. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2003;6:495-510.
- North PE, Waner M, James CA, et al. Congenital nonprogressive hemangioma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity unlike infantile hemangioma. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1607-1620.
- Maguiness S, Uihlein LC, Liang MG, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma with fetal involution. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:321-326.
- Keating LJ, Soares GM, Muratore CS. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma. Med Health R I. 2012;95:149-152.
- Schafer F, Tapia M, Pinto C. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99:F422.
- Boon LM, Enjolras O, Mulliken JB. Congenital hemangioma: evidence of accelerated involution. J Pediatr. 1996;128:329-335.
- Liang MG, Frieden IJ. Infantile and congenital hemangiomas. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:162-167.
- Enjolras O, Mulliken JB, Boon LM, et al. Noninvoluting congenital hemangioma: a rare cutaneous vascular anomaly. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1647-1654.
- Nasseri E, Piram M, McCuaig CC, et al. Partially involuting congenital hemangiomas: a report of 8 cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:75-79.
- Wassef M, Blei F, Adams D, et al. Vascular anomalies classification: recommendations from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E203-E214.
- Boull C, Maguiness SM. Congenital hemangiomas. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35:124-127.
- Drolet BA, Frommelt PC, Chamlin SL, et al. Initiation and use of propranolol for infantile hemangioma: report of a consensus conference. Pediatrics. 2013;131:128-140.
- Baselga E, Cordisco MR, Garzon M, et al. Rapidly involuting congenital haemangioma associated with transient thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1363-1370.
- Kanada KN, Merin MR, Munden A, et al. A prospective study of cutaneous findings in newborns in the United States: correlation with race, ethnicity, and gestational status using updated classification and nomenclature. J Pediatr. 2012;161:240-245.
- Munden A, Butschek R, Tom WL, et al. Prospective study of infantile haemangiomas: incidence, clinical characteristics and association with placental anomalies. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:907-913.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, et al. Growth characteristics of infantile hemangiomas: implications for management. Pediatrics. 2008;122:360-367.
- Hidano A, Nakajima S. Earliest features of the strawberry mark in the newborn. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:138-144.
- Martinez-Perez D, Fein NA, Boon LM, et al. Not all hemangiomas look like strawberries: uncommon presentations of the most common tumor of infancy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1995;12:1-6.
- Payne MM, Moyer F, Marcks KM, et al. The precursor to the hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966;38:64-67.
- Bowers RE, Graham EA, Tomlinson KM. The natural history of the strawberry nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1960;82:667-680.
- Couto RA, Maclellan RA, Zurakowski D, et al. Infantile hemangioma: clinical assessment of the involuting phase and implications for management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:619-624.
- Drolet BA, Esterly NB, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:173-181.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567-1576.
- North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, et al. GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:11-22.
- Gruman A, Liang MG, Mulliken JB, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma without Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:616-622.
- Croteau SE, Liang MG, Kozakewich HP, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: atypical features and risks of Kasabach- Merritt phenomenon in 107 referrals. J Pediatr. 2013;162:142-147.
- Zukerberg LR, Nickoloff BJ, Weiss SW. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma of infancy and childhood. an aggressive neoplasm associated with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome and lymphangiomatosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17:321-328.
- Mac-Moune Lai F, To KF, Choi PC, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: five patients with cutaneous lesion and long follow-up. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:1087-1092.
- O’Rafferty C, O’Regan GM, Irvine AD, et al. Recent advances in the pathobiology and management of Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:38-51.
- Le Huu AR, Jokinen CH, Rubin BP, et al. Expression of prox1, lymphatic endothelial nuclear transcription factor, in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1563-1573.
- Debelenko LV, Perez-Atayde AR, Mulliken JB, et al. D2-40 immuno-histochemical analysis of pediatric vascular tumors reveals positivity in kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:1454-1460.
- Haisley-Royster C, Enjolras O, Frieden IJ, et al. Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon: a retrospective study of treatment with vincristine. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002;24:459-462.
- Wilmer A, Kaatz M, Bocker T, et al. Tufted angioma. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:51-53.
- Herron MD, Coffin CM, Vanderhooft SL. Tufted angiomas: variability of the clinical morphology. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19:394-401.
- North PE. Pediatric vascular tumors and malformations. Surg Pathol Clin. 2010,3:455-494.
- Chu CY, Hsiao CH, Chiu HC. Transformation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Dermatology. 2003;206:334-337.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Johnson EF, Davis DM, Tollefson MM, et al. Vascular tumors in infants: case report and review of clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical characteristics of infantile hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma, noninvoluting congenital hemangioma, tufted angioma, and kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:231-239.
- Christison-Lagay ER, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. Surg Clin North Am. 2006;86:393-425.
- Liu AS, Mulliken JB, Zurakowski D, et al. Extracranial arteriovenous malformations: natural progression and recurrence after treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:1185-1194.
- Young AE, Mulliken JB. Arteriovenous malformations. In: Mulliken JB, Young AE, eds. Vascular Birthmarks: Haemangiomas and Malformations. WB Saunders; 1988:228-245.
- Duggan EM, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies. In: Holcomb GW III, Murphy JP, St Peter SD, eds. Holcomb and Ashcraft’s Pediatric Surgery. 7th edition. Elsevier; 2019:1147-1170.
A newborn male was delivered via cesarean section at 38 weeks 5 days’ gestation with a large vascular mass on the posterior neck. The mass previously had been identified on a 23-week prenatal ultrasound. Physical examination by dermatology at birth revealed a well-defined violaceous mass measuring 6×5 cm with prominent radiating veins, coarse telangiectases, and a pale rim. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a well-circumscribed mass with avid arterial phase enhancement. The patient experienced transient thrombocytopenia that resolved following administration of methylprednisolone. No evidence of rapid involution was noted after 3 months of observation.
The Future of Obesity
I am not planning on having a headstone on my grave, or even having a grave for that matter. However, if my heirs decide to ignore my wishes and opt for some pithy observation chiseled into a tastefully sized granite block, I suspect they might choose “He always knew which way the wind was blowing ... but wasn’t so sure about the tides.” Which aptly describes both my navigational deficiencies they have observed here over my six decades on the Maine coast as well as my general inability to predict the future. Nonetheless, I am going to throw caution to the wind and take this opportunity to ponder where obesity in this country will go over the next couple of decades.
In March of last year the London-based World Obesity Federation published its World Obesity Atlas. In the summary the authors predict that based on current trends “obesity will cost the global economy of US $4 trillion of potential income in 2035, nearly 3% of current global domestic product (GDP).” They envision the “rising prevalence of obesity to be steepest among children and adolescents rising from 10% to 20% of the world’s boys during the period 2029 to 2035, and rising fro 8% to 18% of the world’s girls.”
These dire predictions assume no significant measures to reverse this trajectory such as universal health coverage. Nor do the authors attempt to predict the effect of the growing use of GLP-1 agonists. This omission is surprising and somewhat refreshing given the fact that the project was funded by an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk, a major producer of one of these drugs.
Unfortunately, I think it is unlikely that over the next couple of decades any large countries who do not already have a functioning universal health care system will find the political will to develop one capable of reversing the trend toward obesity. Certainly, I don’t see it in the cards for this country.
On the other hand, I can foresee the availability and ease of administration for GLP-1 agonists and similar drugs improving over the near term. However, the cost and availability will continue to widen the separation between the haves and the have-nots, both globally and within each country. This will mean that the countries and population subgroups that already experience the bulk of the economic and health consequences of obesity will continue to shoulder an outsized burden of this “disease.”
It is unclear how much this widening of the fat-getting-fatter dynamic will add to the global and national political unrest that already seems to be tracking the effects of climate change. However, I can’t imaging it is going to be a calming or uniting force.
Narrowing our focus from an international to an individual resource-rich country such as the United States, let’s consider what the significant growth in availability and affordability of GLP-1 agonist drugs will mean. There will certainly be short-term improvements in the morbidity and mortality of some of the obesity related diseases. However, for other conditions it may take longer than two decades for us to notice an effect. While it is tempting to consider these declines as a financial boon for the country that already spends a high percentage of its GDP on healthcare. However, as the well-known Saturday Night Live pundit Roseanne Roseannadanna often observed, ”it’s always something ... if it’s not one thing it’s another.” There may be other non-obesity conditions that surge to fill the gap, leaving us still with a substantial financial burden for healthcare.
Patients taking GLP-1 agonists lose weight because they feel full and eat less food. While currently the number of patients taking these drugs is relatively small, the effect on this country’s food consumption is too small to calculate. However, let’s assume that 20 years from now half of the obese patients are taking appetite blunting medication. Using today’s statistics this means that 50 million adults will be eating significantly less food. Will the agriculturists have gradually adjusted to produce less food? Will this mean there is more food for the those experiencing “food insecurity”? I doubt it. Most food insecurity seems to be a problem of distribution and inequality, not supply.
Physicians now caution patients taking GLP-1 agonists to eat a healthy and balanced diet. When the drugs are more commonly available, will this caution be heeded by the majority? Will we see a population that may no longer be obese but nonetheless malnourished because of bad choices?
And, finally, in a similar vein, will previously obese individuals suddenly or gradually begin to be more physically active once the appetite blunting medicines have helped them lose weight? Here, I have my doubts. Of course, some leaner individuals begin to take advantage of their new body morphology. But, I fear that old sedentary habits will die very slowly for most, and not at all for many. We have built a vehicle-centric society in which being physically active requires making a conscious effort. Electronic devices and sedentary entertainment options are not going to disappear just because a significant percentage of the population is no longer obese.
So there you have it. I suspect that I am correct about which way some of the winds are blowing as the obesity becomes moves into its treatable “disease” phase. But, as always, I haven’t a clue which way the tide is running.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I am not planning on having a headstone on my grave, or even having a grave for that matter. However, if my heirs decide to ignore my wishes and opt for some pithy observation chiseled into a tastefully sized granite block, I suspect they might choose “He always knew which way the wind was blowing ... but wasn’t so sure about the tides.” Which aptly describes both my navigational deficiencies they have observed here over my six decades on the Maine coast as well as my general inability to predict the future. Nonetheless, I am going to throw caution to the wind and take this opportunity to ponder where obesity in this country will go over the next couple of decades.
In March of last year the London-based World Obesity Federation published its World Obesity Atlas. In the summary the authors predict that based on current trends “obesity will cost the global economy of US $4 trillion of potential income in 2035, nearly 3% of current global domestic product (GDP).” They envision the “rising prevalence of obesity to be steepest among children and adolescents rising from 10% to 20% of the world’s boys during the period 2029 to 2035, and rising fro 8% to 18% of the world’s girls.”
These dire predictions assume no significant measures to reverse this trajectory such as universal health coverage. Nor do the authors attempt to predict the effect of the growing use of GLP-1 agonists. This omission is surprising and somewhat refreshing given the fact that the project was funded by an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk, a major producer of one of these drugs.
Unfortunately, I think it is unlikely that over the next couple of decades any large countries who do not already have a functioning universal health care system will find the political will to develop one capable of reversing the trend toward obesity. Certainly, I don’t see it in the cards for this country.
On the other hand, I can foresee the availability and ease of administration for GLP-1 agonists and similar drugs improving over the near term. However, the cost and availability will continue to widen the separation between the haves and the have-nots, both globally and within each country. This will mean that the countries and population subgroups that already experience the bulk of the economic and health consequences of obesity will continue to shoulder an outsized burden of this “disease.”
It is unclear how much this widening of the fat-getting-fatter dynamic will add to the global and national political unrest that already seems to be tracking the effects of climate change. However, I can’t imaging it is going to be a calming or uniting force.
Narrowing our focus from an international to an individual resource-rich country such as the United States, let’s consider what the significant growth in availability and affordability of GLP-1 agonist drugs will mean. There will certainly be short-term improvements in the morbidity and mortality of some of the obesity related diseases. However, for other conditions it may take longer than two decades for us to notice an effect. While it is tempting to consider these declines as a financial boon for the country that already spends a high percentage of its GDP on healthcare. However, as the well-known Saturday Night Live pundit Roseanne Roseannadanna often observed, ”it’s always something ... if it’s not one thing it’s another.” There may be other non-obesity conditions that surge to fill the gap, leaving us still with a substantial financial burden for healthcare.
Patients taking GLP-1 agonists lose weight because they feel full and eat less food. While currently the number of patients taking these drugs is relatively small, the effect on this country’s food consumption is too small to calculate. However, let’s assume that 20 years from now half of the obese patients are taking appetite blunting medication. Using today’s statistics this means that 50 million adults will be eating significantly less food. Will the agriculturists have gradually adjusted to produce less food? Will this mean there is more food for the those experiencing “food insecurity”? I doubt it. Most food insecurity seems to be a problem of distribution and inequality, not supply.
Physicians now caution patients taking GLP-1 agonists to eat a healthy and balanced diet. When the drugs are more commonly available, will this caution be heeded by the majority? Will we see a population that may no longer be obese but nonetheless malnourished because of bad choices?
And, finally, in a similar vein, will previously obese individuals suddenly or gradually begin to be more physically active once the appetite blunting medicines have helped them lose weight? Here, I have my doubts. Of course, some leaner individuals begin to take advantage of their new body morphology. But, I fear that old sedentary habits will die very slowly for most, and not at all for many. We have built a vehicle-centric society in which being physically active requires making a conscious effort. Electronic devices and sedentary entertainment options are not going to disappear just because a significant percentage of the population is no longer obese.
So there you have it. I suspect that I am correct about which way some of the winds are blowing as the obesity becomes moves into its treatable “disease” phase. But, as always, I haven’t a clue which way the tide is running.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I am not planning on having a headstone on my grave, or even having a grave for that matter. However, if my heirs decide to ignore my wishes and opt for some pithy observation chiseled into a tastefully sized granite block, I suspect they might choose “He always knew which way the wind was blowing ... but wasn’t so sure about the tides.” Which aptly describes both my navigational deficiencies they have observed here over my six decades on the Maine coast as well as my general inability to predict the future. Nonetheless, I am going to throw caution to the wind and take this opportunity to ponder where obesity in this country will go over the next couple of decades.
In March of last year the London-based World Obesity Federation published its World Obesity Atlas. In the summary the authors predict that based on current trends “obesity will cost the global economy of US $4 trillion of potential income in 2035, nearly 3% of current global domestic product (GDP).” They envision the “rising prevalence of obesity to be steepest among children and adolescents rising from 10% to 20% of the world’s boys during the period 2029 to 2035, and rising fro 8% to 18% of the world’s girls.”
These dire predictions assume no significant measures to reverse this trajectory such as universal health coverage. Nor do the authors attempt to predict the effect of the growing use of GLP-1 agonists. This omission is surprising and somewhat refreshing given the fact that the project was funded by an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk, a major producer of one of these drugs.
Unfortunately, I think it is unlikely that over the next couple of decades any large countries who do not already have a functioning universal health care system will find the political will to develop one capable of reversing the trend toward obesity. Certainly, I don’t see it in the cards for this country.
On the other hand, I can foresee the availability and ease of administration for GLP-1 agonists and similar drugs improving over the near term. However, the cost and availability will continue to widen the separation between the haves and the have-nots, both globally and within each country. This will mean that the countries and population subgroups that already experience the bulk of the economic and health consequences of obesity will continue to shoulder an outsized burden of this “disease.”
It is unclear how much this widening of the fat-getting-fatter dynamic will add to the global and national political unrest that already seems to be tracking the effects of climate change. However, I can’t imaging it is going to be a calming or uniting force.
Narrowing our focus from an international to an individual resource-rich country such as the United States, let’s consider what the significant growth in availability and affordability of GLP-1 agonist drugs will mean. There will certainly be short-term improvements in the morbidity and mortality of some of the obesity related diseases. However, for other conditions it may take longer than two decades for us to notice an effect. While it is tempting to consider these declines as a financial boon for the country that already spends a high percentage of its GDP on healthcare. However, as the well-known Saturday Night Live pundit Roseanne Roseannadanna often observed, ”it’s always something ... if it’s not one thing it’s another.” There may be other non-obesity conditions that surge to fill the gap, leaving us still with a substantial financial burden for healthcare.
Patients taking GLP-1 agonists lose weight because they feel full and eat less food. While currently the number of patients taking these drugs is relatively small, the effect on this country’s food consumption is too small to calculate. However, let’s assume that 20 years from now half of the obese patients are taking appetite blunting medication. Using today’s statistics this means that 50 million adults will be eating significantly less food. Will the agriculturists have gradually adjusted to produce less food? Will this mean there is more food for the those experiencing “food insecurity”? I doubt it. Most food insecurity seems to be a problem of distribution and inequality, not supply.
Physicians now caution patients taking GLP-1 agonists to eat a healthy and balanced diet. When the drugs are more commonly available, will this caution be heeded by the majority? Will we see a population that may no longer be obese but nonetheless malnourished because of bad choices?
And, finally, in a similar vein, will previously obese individuals suddenly or gradually begin to be more physically active once the appetite blunting medicines have helped them lose weight? Here, I have my doubts. Of course, some leaner individuals begin to take advantage of their new body morphology. But, I fear that old sedentary habits will die very slowly for most, and not at all for many. We have built a vehicle-centric society in which being physically active requires making a conscious effort. Electronic devices and sedentary entertainment options are not going to disappear just because a significant percentage of the population is no longer obese.
So there you have it. I suspect that I am correct about which way some of the winds are blowing as the obesity becomes moves into its treatable “disease” phase. But, as always, I haven’t a clue which way the tide is running.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Reducing Unnecessary Antibiotics for Conjunctivitis
TOPLINE:
More than two thirds of children with conjunctivitis received antibiotics within a day of their initial ambulatory care visit; however,
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the frequency of topical antibiotic treatment and its association with subsequent health care use among commercially insured children with acute infectious conjunctivitis in the United States.
- This cohort study analyzed data from the 2021 MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database, including 44,793 children with conjunctivitis (median age, 5 years; 47% girls) and ambulatory care encounters.
- The primary exposure was a topical antibiotic prescription dispensed within 1 day of an ambulatory care visit, with outcomes assessed 2-14 days after the visit.
- The primary outcomes were ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis and same-day dispensation of a new topical antibiotic, and secondary outcomes included emergency department revisits and hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Topical antibiotics were dispensed within a day of an ambulatory care visit in 69% of the cases; however, they were less frequently dispensed following visits to eye clinics (34%), for children aged 6-11 years (66%), and for those with viral conjunctivitis (28%).
- Ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis within 2 weeks occurred in only 3.2% of children who had received antibiotics (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.11; 95% CI, 0.99-1.25).
- Similarly, revisits with same-day dispensation of a new antibiotic were also rare (1.4%), with no significant association between antibiotic treatment and revisits (aOR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.92-1.33).
- Hospitalizations for conjunctivitis occurred in 0.03% of cases, and emergency department revisits occurred in 0.12%, with no differences between children who received antibiotics and those who did not.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given that antibiotics may not be associated with improved outcomes or change in subsequent health care use and are associated with adverse effects and antibiotic resistance, efforts to reduce overtreatment of acute infectious conjunctivitis are warranted,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daniel J. Shapiro, MD, MPH, of the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and published online on June 27, 2024, in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The major limitations of the study included the inability to distinguish scheduled visits from unscheduled revisits, incomplete clinical data such as rare complications of conjunctivitis, and the inability to confirm the accuracy of the coded diagnosis of infectious conjunctivitis, especially in children who did not receive a thorough eye examination.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not declare receiving funding from any sources. One author reported receiving grants from several sources outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
More than two thirds of children with conjunctivitis received antibiotics within a day of their initial ambulatory care visit; however,
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the frequency of topical antibiotic treatment and its association with subsequent health care use among commercially insured children with acute infectious conjunctivitis in the United States.
- This cohort study analyzed data from the 2021 MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database, including 44,793 children with conjunctivitis (median age, 5 years; 47% girls) and ambulatory care encounters.
- The primary exposure was a topical antibiotic prescription dispensed within 1 day of an ambulatory care visit, with outcomes assessed 2-14 days after the visit.
- The primary outcomes were ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis and same-day dispensation of a new topical antibiotic, and secondary outcomes included emergency department revisits and hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Topical antibiotics were dispensed within a day of an ambulatory care visit in 69% of the cases; however, they were less frequently dispensed following visits to eye clinics (34%), for children aged 6-11 years (66%), and for those with viral conjunctivitis (28%).
- Ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis within 2 weeks occurred in only 3.2% of children who had received antibiotics (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.11; 95% CI, 0.99-1.25).
- Similarly, revisits with same-day dispensation of a new antibiotic were also rare (1.4%), with no significant association between antibiotic treatment and revisits (aOR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.92-1.33).
- Hospitalizations for conjunctivitis occurred in 0.03% of cases, and emergency department revisits occurred in 0.12%, with no differences between children who received antibiotics and those who did not.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given that antibiotics may not be associated with improved outcomes or change in subsequent health care use and are associated with adverse effects and antibiotic resistance, efforts to reduce overtreatment of acute infectious conjunctivitis are warranted,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daniel J. Shapiro, MD, MPH, of the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and published online on June 27, 2024, in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The major limitations of the study included the inability to distinguish scheduled visits from unscheduled revisits, incomplete clinical data such as rare complications of conjunctivitis, and the inability to confirm the accuracy of the coded diagnosis of infectious conjunctivitis, especially in children who did not receive a thorough eye examination.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not declare receiving funding from any sources. One author reported receiving grants from several sources outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
More than two thirds of children with conjunctivitis received antibiotics within a day of their initial ambulatory care visit; however,
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the frequency of topical antibiotic treatment and its association with subsequent health care use among commercially insured children with acute infectious conjunctivitis in the United States.
- This cohort study analyzed data from the 2021 MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database, including 44,793 children with conjunctivitis (median age, 5 years; 47% girls) and ambulatory care encounters.
- The primary exposure was a topical antibiotic prescription dispensed within 1 day of an ambulatory care visit, with outcomes assessed 2-14 days after the visit.
- The primary outcomes were ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis and same-day dispensation of a new topical antibiotic, and secondary outcomes included emergency department revisits and hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Topical antibiotics were dispensed within a day of an ambulatory care visit in 69% of the cases; however, they were less frequently dispensed following visits to eye clinics (34%), for children aged 6-11 years (66%), and for those with viral conjunctivitis (28%).
- Ambulatory care revisits for conjunctivitis within 2 weeks occurred in only 3.2% of children who had received antibiotics (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.11; 95% CI, 0.99-1.25).
- Similarly, revisits with same-day dispensation of a new antibiotic were also rare (1.4%), with no significant association between antibiotic treatment and revisits (aOR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.92-1.33).
- Hospitalizations for conjunctivitis occurred in 0.03% of cases, and emergency department revisits occurred in 0.12%, with no differences between children who received antibiotics and those who did not.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given that antibiotics may not be associated with improved outcomes or change in subsequent health care use and are associated with adverse effects and antibiotic resistance, efforts to reduce overtreatment of acute infectious conjunctivitis are warranted,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Daniel J. Shapiro, MD, MPH, of the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and published online on June 27, 2024, in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The major limitations of the study included the inability to distinguish scheduled visits from unscheduled revisits, incomplete clinical data such as rare complications of conjunctivitis, and the inability to confirm the accuracy of the coded diagnosis of infectious conjunctivitis, especially in children who did not receive a thorough eye examination.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not declare receiving funding from any sources. One author reported receiving grants from several sources outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.