User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
The right indoor relative humidity could ward off COVID
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY INTERFACE
Hormonal management of gender-diverse patients: SOC8 updates
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
Nurse practitioner fined $20k for advertising herself as ‘Doctor Sarah’
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More weight loss with surgery than new obesity meds: meta-analysis
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
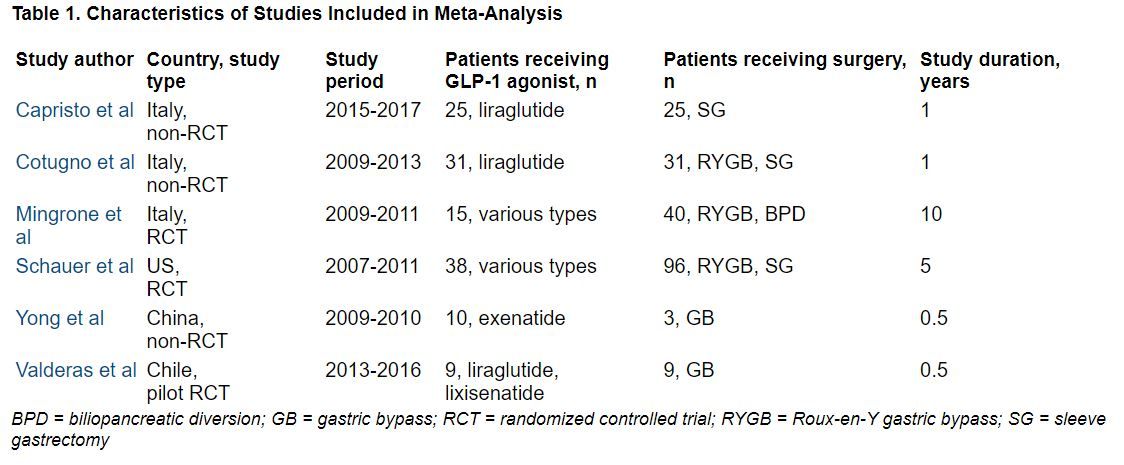
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT OBESITYWEEK®
Balanced crystalloid fluids surpass saline for kidney transplant
ORLANDO – Using a low-chloride, balanced crystalloid solution for all intravenous fluids received by patients who received a deceased donor kidney transplant resulted in significantly fewer episodes of delayed graft function, compared with patients who received saline as their IV fluids, in a new multicenter trial with 807 randomized and evaluable patients called BEST-Fluids.
“The findings suggest that balanced crystalloids should be the standard-of-care IV fluid in deceased donor kidney transplantations,” Michael G. Collins, MBChB, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“Balanced crystalloids are cheap, readily available worldwide, and this simple change in kidney transplant practice can easily be implemented in global practice ... almost immediately,” said Dr. Collins, a nephrologist at Royal Adelaide Hospital, Australia.
A 1-L bag of balanced crystalloid fluid is more expensive; however, it has a U.S. retail cost of about $2-$5 per bag, compared with about $1 per bag of saline fluid, Dr. Collins added.
Various other commentators had mixed views. Some agreed with Dr. Collins and said the switch could be made immediately, although one researcher wanted to see more trials. Another wondered why balanced crystalloid fluid hadn’t seemed to provide benefit in studies in acute kidney injury.
Treating 10 patients prevents one delayed graft function
The incidence of delayed graft function, defined as the need for dialysis during the 7 days following transplantation, occurred in 30.0% of 404 patients who received balanced crystalloid fluids (Plasma-Lyte 148) and in 39.7% of 403 patients who received saline starting at the time of randomization (prior to surgery) until 48 hours post-surgery, Dr. Collins reported.
This translated into a significant, adjusted relative risk reduction of 26% and a number needed to treat of 10 to result in one avoided episode of delayed graft function.
Preventing delayed graft function is important because it is a “major complication” of deceased donor kidney transplantation that usually occurs in about 30%-50% of people who receive these organs, Dr. Collins explained. Incident delayed graft function leads to higher hospitalization costs because of a prolonged need for dialysis and extended hospital days, as well as increased risk for long-term graft failure and death.
A secondary outcome – the number of dialysis sessions required during the 28 days following transplantation – was 406 sessions among those who received balanced crystalloid fluids and 596 sessions among the controls who received saline, a significant adjusted relative decrease of 30%.
Freedom from need for dialysis by 12 weeks after surgery increased by a significant 10% among those treated with balanced crystalloid fluids, compared with controls. The balanced crystalloid fluids were also significantly linked with an average 1-L increase in urine output during the first 2 days after transplantation, compared with controls.
Chloride is the culprit
“I think this is driven by the harmful effects of saline,” which is currently the standard fluid that kidney transplant patients receive worldwide, said Dr. Collins. Specifically, he cited the chloride content of saline – which contains 0.9% sodium chloride – as the culprit by causing reduced kidney perfusion.
“Some data suggest that saline may be harmful because of chloride acidosis producing vasoconstriction and increasing ischemia,” commented Karen A. Griffin, MD, chief of the renal section at the Edward Hines, Jr. VA Medical Center, Hines, Illinois. But Dr. Griffin said she’d like to see further study of balanced crystalloid fluids in this setting before she’d be comfortable using it routinely as a replacement for saline.
However, Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist with Oklahoma University Health, Oklahoma City, predicted that based on these results, “I think it will be rapidly embraced” by U.S. clinicians. Dr. Lane expressed concern about the availability of an adequate supply of balanced crystalloid fluid, but Dr. Collins said he did not believe supply would be an issue based on current availability.
This was “a beautiful study, very well done, with nice results, and a very easy switch to balanced crystalloid fluids without harm,” commented Richard Lafayette, MD, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Success attributed to early treatment
But Dr. Lafayette also wondered, “Why should this work for transplant patients when it did not work for patients who develop acute kidney injury in the ICU?” And he found it hard to understand how the impact of the balanced crystalloid fluid could manifest so quickly, with a change in urine output during the first day following surgery.
Dr. Collins attributed the rapid effects and overall success to the early initiation of balanced crystalloid fluids before the transplant occurred.
The BEST-Fluids trial ran at 16 centers in Australia and New Zealand and enrolled patients from January 2018 to August 2020. It enrolled adults and children scheduled to receive a deceased donor kidney, excluding those who weighed less than 20 kg and those who received multiple organs.
Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, about 63% were men, and their average duration on dialysis prior to surgery was about 30 months. The study randomized 808 patients who received their transplanted kidney, with 807 included in the efficacy analysis. Patients in each of the two groups showed very close balance for all reported parameters of patient and donor characteristics. During the period of randomized fluid treatment, patients in the balanced crystalloid group received an average of just over 8 L of fluid, while those in the control group received an average of just over 7 L.
During follow-up, serious adverse events were rare and balanced, with three in the balanced crystalloid group and four among controls.
The only significant difference in adverse events was the rate of ICU admissions that required ventilation, which occurred in one patient in the balanced crystalloid group and 12 controls.
BEST-Fluids received balanced crystalloid and saline solutions at no charge from Baxter Healthcare, which markets Plasma-Lyte 148. The study received no other commercial funding. Dr. Collins, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Lane have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lafayette has received personal fees and grants from Alexion, Aurinia, Calliditas, Omeros, Pfizer, Roche, Travere, and Vera and has been an advisor to Akahest and Equillium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – Using a low-chloride, balanced crystalloid solution for all intravenous fluids received by patients who received a deceased donor kidney transplant resulted in significantly fewer episodes of delayed graft function, compared with patients who received saline as their IV fluids, in a new multicenter trial with 807 randomized and evaluable patients called BEST-Fluids.
“The findings suggest that balanced crystalloids should be the standard-of-care IV fluid in deceased donor kidney transplantations,” Michael G. Collins, MBChB, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“Balanced crystalloids are cheap, readily available worldwide, and this simple change in kidney transplant practice can easily be implemented in global practice ... almost immediately,” said Dr. Collins, a nephrologist at Royal Adelaide Hospital, Australia.
A 1-L bag of balanced crystalloid fluid is more expensive; however, it has a U.S. retail cost of about $2-$5 per bag, compared with about $1 per bag of saline fluid, Dr. Collins added.
Various other commentators had mixed views. Some agreed with Dr. Collins and said the switch could be made immediately, although one researcher wanted to see more trials. Another wondered why balanced crystalloid fluid hadn’t seemed to provide benefit in studies in acute kidney injury.
Treating 10 patients prevents one delayed graft function
The incidence of delayed graft function, defined as the need for dialysis during the 7 days following transplantation, occurred in 30.0% of 404 patients who received balanced crystalloid fluids (Plasma-Lyte 148) and in 39.7% of 403 patients who received saline starting at the time of randomization (prior to surgery) until 48 hours post-surgery, Dr. Collins reported.
This translated into a significant, adjusted relative risk reduction of 26% and a number needed to treat of 10 to result in one avoided episode of delayed graft function.
Preventing delayed graft function is important because it is a “major complication” of deceased donor kidney transplantation that usually occurs in about 30%-50% of people who receive these organs, Dr. Collins explained. Incident delayed graft function leads to higher hospitalization costs because of a prolonged need for dialysis and extended hospital days, as well as increased risk for long-term graft failure and death.
A secondary outcome – the number of dialysis sessions required during the 28 days following transplantation – was 406 sessions among those who received balanced crystalloid fluids and 596 sessions among the controls who received saline, a significant adjusted relative decrease of 30%.
Freedom from need for dialysis by 12 weeks after surgery increased by a significant 10% among those treated with balanced crystalloid fluids, compared with controls. The balanced crystalloid fluids were also significantly linked with an average 1-L increase in urine output during the first 2 days after transplantation, compared with controls.
Chloride is the culprit
“I think this is driven by the harmful effects of saline,” which is currently the standard fluid that kidney transplant patients receive worldwide, said Dr. Collins. Specifically, he cited the chloride content of saline – which contains 0.9% sodium chloride – as the culprit by causing reduced kidney perfusion.
“Some data suggest that saline may be harmful because of chloride acidosis producing vasoconstriction and increasing ischemia,” commented Karen A. Griffin, MD, chief of the renal section at the Edward Hines, Jr. VA Medical Center, Hines, Illinois. But Dr. Griffin said she’d like to see further study of balanced crystalloid fluids in this setting before she’d be comfortable using it routinely as a replacement for saline.
However, Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist with Oklahoma University Health, Oklahoma City, predicted that based on these results, “I think it will be rapidly embraced” by U.S. clinicians. Dr. Lane expressed concern about the availability of an adequate supply of balanced crystalloid fluid, but Dr. Collins said he did not believe supply would be an issue based on current availability.
This was “a beautiful study, very well done, with nice results, and a very easy switch to balanced crystalloid fluids without harm,” commented Richard Lafayette, MD, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Success attributed to early treatment
But Dr. Lafayette also wondered, “Why should this work for transplant patients when it did not work for patients who develop acute kidney injury in the ICU?” And he found it hard to understand how the impact of the balanced crystalloid fluid could manifest so quickly, with a change in urine output during the first day following surgery.
Dr. Collins attributed the rapid effects and overall success to the early initiation of balanced crystalloid fluids before the transplant occurred.
The BEST-Fluids trial ran at 16 centers in Australia and New Zealand and enrolled patients from January 2018 to August 2020. It enrolled adults and children scheduled to receive a deceased donor kidney, excluding those who weighed less than 20 kg and those who received multiple organs.
Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, about 63% were men, and their average duration on dialysis prior to surgery was about 30 months. The study randomized 808 patients who received their transplanted kidney, with 807 included in the efficacy analysis. Patients in each of the two groups showed very close balance for all reported parameters of patient and donor characteristics. During the period of randomized fluid treatment, patients in the balanced crystalloid group received an average of just over 8 L of fluid, while those in the control group received an average of just over 7 L.
During follow-up, serious adverse events were rare and balanced, with three in the balanced crystalloid group and four among controls.
The only significant difference in adverse events was the rate of ICU admissions that required ventilation, which occurred in one patient in the balanced crystalloid group and 12 controls.
BEST-Fluids received balanced crystalloid and saline solutions at no charge from Baxter Healthcare, which markets Plasma-Lyte 148. The study received no other commercial funding. Dr. Collins, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Lane have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lafayette has received personal fees and grants from Alexion, Aurinia, Calliditas, Omeros, Pfizer, Roche, Travere, and Vera and has been an advisor to Akahest and Equillium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – Using a low-chloride, balanced crystalloid solution for all intravenous fluids received by patients who received a deceased donor kidney transplant resulted in significantly fewer episodes of delayed graft function, compared with patients who received saline as their IV fluids, in a new multicenter trial with 807 randomized and evaluable patients called BEST-Fluids.
“The findings suggest that balanced crystalloids should be the standard-of-care IV fluid in deceased donor kidney transplantations,” Michael G. Collins, MBChB, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“Balanced crystalloids are cheap, readily available worldwide, and this simple change in kidney transplant practice can easily be implemented in global practice ... almost immediately,” said Dr. Collins, a nephrologist at Royal Adelaide Hospital, Australia.
A 1-L bag of balanced crystalloid fluid is more expensive; however, it has a U.S. retail cost of about $2-$5 per bag, compared with about $1 per bag of saline fluid, Dr. Collins added.
Various other commentators had mixed views. Some agreed with Dr. Collins and said the switch could be made immediately, although one researcher wanted to see more trials. Another wondered why balanced crystalloid fluid hadn’t seemed to provide benefit in studies in acute kidney injury.
Treating 10 patients prevents one delayed graft function
The incidence of delayed graft function, defined as the need for dialysis during the 7 days following transplantation, occurred in 30.0% of 404 patients who received balanced crystalloid fluids (Plasma-Lyte 148) and in 39.7% of 403 patients who received saline starting at the time of randomization (prior to surgery) until 48 hours post-surgery, Dr. Collins reported.
This translated into a significant, adjusted relative risk reduction of 26% and a number needed to treat of 10 to result in one avoided episode of delayed graft function.
Preventing delayed graft function is important because it is a “major complication” of deceased donor kidney transplantation that usually occurs in about 30%-50% of people who receive these organs, Dr. Collins explained. Incident delayed graft function leads to higher hospitalization costs because of a prolonged need for dialysis and extended hospital days, as well as increased risk for long-term graft failure and death.
A secondary outcome – the number of dialysis sessions required during the 28 days following transplantation – was 406 sessions among those who received balanced crystalloid fluids and 596 sessions among the controls who received saline, a significant adjusted relative decrease of 30%.
Freedom from need for dialysis by 12 weeks after surgery increased by a significant 10% among those treated with balanced crystalloid fluids, compared with controls. The balanced crystalloid fluids were also significantly linked with an average 1-L increase in urine output during the first 2 days after transplantation, compared with controls.
Chloride is the culprit
“I think this is driven by the harmful effects of saline,” which is currently the standard fluid that kidney transplant patients receive worldwide, said Dr. Collins. Specifically, he cited the chloride content of saline – which contains 0.9% sodium chloride – as the culprit by causing reduced kidney perfusion.
“Some data suggest that saline may be harmful because of chloride acidosis producing vasoconstriction and increasing ischemia,” commented Karen A. Griffin, MD, chief of the renal section at the Edward Hines, Jr. VA Medical Center, Hines, Illinois. But Dr. Griffin said she’d like to see further study of balanced crystalloid fluids in this setting before she’d be comfortable using it routinely as a replacement for saline.
However, Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist with Oklahoma University Health, Oklahoma City, predicted that based on these results, “I think it will be rapidly embraced” by U.S. clinicians. Dr. Lane expressed concern about the availability of an adequate supply of balanced crystalloid fluid, but Dr. Collins said he did not believe supply would be an issue based on current availability.
This was “a beautiful study, very well done, with nice results, and a very easy switch to balanced crystalloid fluids without harm,” commented Richard Lafayette, MD, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Success attributed to early treatment
But Dr. Lafayette also wondered, “Why should this work for transplant patients when it did not work for patients who develop acute kidney injury in the ICU?” And he found it hard to understand how the impact of the balanced crystalloid fluid could manifest so quickly, with a change in urine output during the first day following surgery.
Dr. Collins attributed the rapid effects and overall success to the early initiation of balanced crystalloid fluids before the transplant occurred.
The BEST-Fluids trial ran at 16 centers in Australia and New Zealand and enrolled patients from January 2018 to August 2020. It enrolled adults and children scheduled to receive a deceased donor kidney, excluding those who weighed less than 20 kg and those who received multiple organs.
Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, about 63% were men, and their average duration on dialysis prior to surgery was about 30 months. The study randomized 808 patients who received their transplanted kidney, with 807 included in the efficacy analysis. Patients in each of the two groups showed very close balance for all reported parameters of patient and donor characteristics. During the period of randomized fluid treatment, patients in the balanced crystalloid group received an average of just over 8 L of fluid, while those in the control group received an average of just over 7 L.
During follow-up, serious adverse events were rare and balanced, with three in the balanced crystalloid group and four among controls.
The only significant difference in adverse events was the rate of ICU admissions that required ventilation, which occurred in one patient in the balanced crystalloid group and 12 controls.
BEST-Fluids received balanced crystalloid and saline solutions at no charge from Baxter Healthcare, which markets Plasma-Lyte 148. The study received no other commercial funding. Dr. Collins, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Lane have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lafayette has received personal fees and grants from Alexion, Aurinia, Calliditas, Omeros, Pfizer, Roche, Travere, and Vera and has been an advisor to Akahest and Equillium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT KIDNEY WEEK 2022
Medical school culinary medicine programs grow despite limited funding
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
FROM ACADEMIC MEDICINE
A plane crash interrupts a doctor’s vacation
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Give bacterial diversity a chance: The antibiotic dichotomy
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
Is there a doctor on the plane? Tips for providing in-flight assistance
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
Total replacement and fusion yield similar outcomes for ankle osteoarthritis
Ankle osteoarthritis remains a cause of severe pain and disability. Patients are treated nonoperatively if possible, but surgery is often needed for individuals with end-stage disease, wrote Andrew Goldberg, MBBS, of University College London and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Most patients with ankle arthritis respond to nonoperative treatments, such as weight loss, activity modification, support braces, and analgesia, [but] once the disease has progressed to end-stage osteoarthritis, the main surgical treatments are total ankle re-placement or ankle arthrodesis,” Dr. Goldberg said, in an interview.
In the new study, patients were randomized to receive either a total ankle replacement (TAR) or ankle fusion (AF).
“We showed that, in both treatment groups the clinical scores improved hugely, by more than three times the minimal clinically important difference,” Dr. Goldberg said in an interview.
“Although the ankle replacement arm improved, on average, by more than an extra 4 points over ankle fusion, this was not considered clinically or statistically significant,” he said.
The study is the first randomized trial to show high-quality and robust results, he noted, and findings support data from previous studies.
“Although both TAR and ankle fusion have been shown to be effective, they are very different treatments, with one fusing the bones so that there is no ankle joint movement, and the other replacing the joint with the aim of retaining ankle joint movement. It is difficult for a patient to know which treatment is more suitable for them, with most seeking guidance from their surgeon,” he said.
Generating high-quality evidence
The study, a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial known as TARVA (Total Ankle Replacement Versus Ankle Arthrodesis), aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of the two existing publicly funded U.K. treatment options, the authors wrote.
Patients were recruited at 17 U.K. centers between March 6, 2015, and Jan. 10, 2019. The study enrolled 303 adults aged 50-85 years with end-stage ankle osteoarthritis. The mean age of the participants was 68 years; 71% were men. A total of 137 TAR patients and 144 ankle fusion patients completed their surgeries with clinical scores available for analysis. Baseline characteristics were mainly similar between the groups.
Blinding was not possible because of the nature of the procedures, but the surgeons who screened the patients were not aware of the randomization allocations, the researchers noted. A total of 33 surgeons participated in the trial, with a median number of seven patients per surgeon during the study period.
For TAR, U.K. surgeons use both two-component, fixed-bearing and three-component, mobile-bearing implants, the authors write. Ankle fusion was done using the surgeon’s usual technique of either arthroscopic-assisted or open ankle fusion.
The primary outcome was the change in the Manchester–Oxford Foot Questionnaire walking/standing (MOXFQ-W/S) domain scores from baseline to 52 weeks after surgery. The MOXFQ-W/S uses a scale of 0-100, with lower scores representing better outcomes. Secondary outcomes included change in the MOXFQ-W/S scores at 26 weeks after surgery, as well as measures of patient quality of life.
No statistically significant difference
Overall, the mean MOXFQ-W/S scores improved significantly from baseline to 52 weeks for both groups, with average improvements of 49.9 in the TAR group and 44.4 points in the AF group. The average scores at 52 weeks were 31.4 in the TAR group and 36.8 in the AF group.
The adjusted difference in score change from baseline was –5.56, showing a slightly greater degree of improvement with TAR, but this difference was not clinically or statistically significant, the researchers noted.
Adverse event numbers were similar for both procedures, with 54% of TAR patients and 53% of AF patients experiencing at least 1 adverse event during the study period. Of those, 18% of TAR patients and 24% of AF patients experienced at least 1 serious adverse event.
However, the TAR patients experienced a higher rate of wound healing complications and nerve injuries, while thromboembolism was higher in the AF patients, the researchers noted.
A prespecified subgroup analysis of patients with osteoarthritis in adjacent joints suggested a greater improvement in TAR, compared with AF, a difference that increased when fixed-bearing TAR was compared with AF, the authors wrote.
“This reinforces previous reports that suggest that the presence of adjacent joint arthritis may be an indication for ankle replacement over AF,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
“Many of these patients did not have any symptoms in the adjacent joints,” they noted.
“The presence of adjacent joint arthritis, meaning the wear and tear of the joints around the ankle joint, seemed to favor ankle replacement,” Dr. Goldberg said. Approximately 30 joints in the foot continue to move after the ankle is fused, and if these adjacent joints are not healthy before surgery [as was the case in 42% of the study patients], the results of fusion were less successful, he explained.
A post hoc analysis between TAR subtypes showed that patients who had fixed-bearing TAR had significantly greater improvements, compared with AF patients, but this difference was not observed in patients who had mobile-bearing TAR, the researchers noted.
Dr. Goldberg said it was surprising “that, in a separate analysis, we found that the fixed-bearing ankle replacement patients [who accounted for half of the implants used] improved by a much greater difference when compared to ankle fusion.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short follow-up and study design that allowed surgeons to choose any implant and technique, the researchers noted.
Other limitations include a lack of data on cost-effectiveness and the impact of comorbidities on outcomes, they wrote. However, the study is the first completed multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare TAR and AF procedures for end-stage ankle osteoarthritis and shows that both yield similar clinical improvements, they concluded.
Data can inform treatment discussion
The take-home messages for clinicians are that both ankle replacement and ankle fusion are effective treatments that improve patients’ quality of life, and it is important to establish the health of adjacent joints before making treatment recommendations, Dr. Goldberg said.
“Careful counseling on the relative risks of each procedure should be part of the informed consent process,” he added. Ideally, all patients seeking surgical care for ankle arthritis should have a choice between ankle replacement and ankle fusion, but sometimes there is inequity of provision of the two treatments, he noted.
“We now encourage all surgeons to work in ankle arthritis networks so that every patient, no matter where they live, can have choice about the best treatment for them,” he said.
Researchers met the challenge of surgical RCT
Randomized trials of surgical interventions are challenging to conduct, and therefore limited, wrote Bruce Sangeorzan, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. However, the new study was strengthened by the inclusion of 17 centers for heterogeneity of implant type and surgeon experience level, the editorialists said in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study is especially important, because ankle arthritis treatment is very understudied, compared with hip and knee arthritis, but it has a similar impact on activity, editorial coauthor Dr. Sangeorzan said in an interview.
“Randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for comparing medical therapies,” he said, “but they are very difficult to do in surgical treatments, particularly when the two treatments can be differentiated, in this case by movement of the ankle.”
In addition, there is a strong placebo effect attached to interventions, Dr. Sangeorzan noted. “Determining best-case treatment relies on prospective research, preferably randomized. Since both ankle fusion and ankle replacement are effective therapies, a prospective randomized trial is the best way to help make treatment decisions,” he said.
The current study findings are not surprising, but they are preliminary, and 1 year of follow-up is not enough to determine effectiveness, Dr. Sangeorzan emphasized. However, “the authors have done the hard work of randomizing the patients and collecting the data, and the patients can now be followed for a longer time,” he said.
“In addition, the trial was designed with multiple secondary outcome measures, so the data can be matched up with larger trials that were not randomized to identify key elements of success for each procedure,” he noted.
The key message for clinicians is that ankle arthritis has a significant impact on patients’ lives, but there are two effective treatments that can reduce the impact of the disease, said Dr. Sangeorzan. “The data suggest that there are differences in implant design and differences in comorbidities that should influence decision-making,” he added.
Additional research is needed in the form of a longer study duration with larger cohorts, said Dr. Sangeorzan. In particular, researchers need to determine what comorbidities might drive patients to one type of care vs. another, he said. “The suggestion that [patients receiving implants with two motion segments have better outcomes than those receiving implants with a one-motion segment] also deserves further study,” he added.
The research was supported by the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The trial was sponsored by University College London. Dr. Goldberg disclosed grant support from NIHR HTA, as well as financial relationships with companies including Stryker, Paragon 28, and stock options with Standing CT Company, Elstree Waterfront Outpatients, and X Bolt Orthopedics.
The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Ankle osteoarthritis remains a cause of severe pain and disability. Patients are treated nonoperatively if possible, but surgery is often needed for individuals with end-stage disease, wrote Andrew Goldberg, MBBS, of University College London and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Most patients with ankle arthritis respond to nonoperative treatments, such as weight loss, activity modification, support braces, and analgesia, [but] once the disease has progressed to end-stage osteoarthritis, the main surgical treatments are total ankle re-placement or ankle arthrodesis,” Dr. Goldberg said, in an interview.
In the new study, patients were randomized to receive either a total ankle replacement (TAR) or ankle fusion (AF).
“We showed that, in both treatment groups the clinical scores improved hugely, by more than three times the minimal clinically important difference,” Dr. Goldberg said in an interview.
“Although the ankle replacement arm improved, on average, by more than an extra 4 points over ankle fusion, this was not considered clinically or statistically significant,” he said.
The study is the first randomized trial to show high-quality and robust results, he noted, and findings support data from previous studies.
“Although both TAR and ankle fusion have been shown to be effective, they are very different treatments, with one fusing the bones so that there is no ankle joint movement, and the other replacing the joint with the aim of retaining ankle joint movement. It is difficult for a patient to know which treatment is more suitable for them, with most seeking guidance from their surgeon,” he said.
Generating high-quality evidence
The study, a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial known as TARVA (Total Ankle Replacement Versus Ankle Arthrodesis), aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of the two existing publicly funded U.K. treatment options, the authors wrote.
Patients were recruited at 17 U.K. centers between March 6, 2015, and Jan. 10, 2019. The study enrolled 303 adults aged 50-85 years with end-stage ankle osteoarthritis. The mean age of the participants was 68 years; 71% were men. A total of 137 TAR patients and 144 ankle fusion patients completed their surgeries with clinical scores available for analysis. Baseline characteristics were mainly similar between the groups.
Blinding was not possible because of the nature of the procedures, but the surgeons who screened the patients were not aware of the randomization allocations, the researchers noted. A total of 33 surgeons participated in the trial, with a median number of seven patients per surgeon during the study period.
For TAR, U.K. surgeons use both two-component, fixed-bearing and three-component, mobile-bearing implants, the authors write. Ankle fusion was done using the surgeon’s usual technique of either arthroscopic-assisted or open ankle fusion.
The primary outcome was the change in the Manchester–Oxford Foot Questionnaire walking/standing (MOXFQ-W/S) domain scores from baseline to 52 weeks after surgery. The MOXFQ-W/S uses a scale of 0-100, with lower scores representing better outcomes. Secondary outcomes included change in the MOXFQ-W/S scores at 26 weeks after surgery, as well as measures of patient quality of life.
No statistically significant difference
Overall, the mean MOXFQ-W/S scores improved significantly from baseline to 52 weeks for both groups, with average improvements of 49.9 in the TAR group and 44.4 points in the AF group. The average scores at 52 weeks were 31.4 in the TAR group and 36.8 in the AF group.
The adjusted difference in score change from baseline was –5.56, showing a slightly greater degree of improvement with TAR, but this difference was not clinically or statistically significant, the researchers noted.
Adverse event numbers were similar for both procedures, with 54% of TAR patients and 53% of AF patients experiencing at least 1 adverse event during the study period. Of those, 18% of TAR patients and 24% of AF patients experienced at least 1 serious adverse event.
However, the TAR patients experienced a higher rate of wound healing complications and nerve injuries, while thromboembolism was higher in the AF patients, the researchers noted.
A prespecified subgroup analysis of patients with osteoarthritis in adjacent joints suggested a greater improvement in TAR, compared with AF, a difference that increased when fixed-bearing TAR was compared with AF, the authors wrote.
“This reinforces previous reports that suggest that the presence of adjacent joint arthritis may be an indication for ankle replacement over AF,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
“Many of these patients did not have any symptoms in the adjacent joints,” they noted.
“The presence of adjacent joint arthritis, meaning the wear and tear of the joints around the ankle joint, seemed to favor ankle replacement,” Dr. Goldberg said. Approximately 30 joints in the foot continue to move after the ankle is fused, and if these adjacent joints are not healthy before surgery [as was the case in 42% of the study patients], the results of fusion were less successful, he explained.
A post hoc analysis between TAR subtypes showed that patients who had fixed-bearing TAR had significantly greater improvements, compared with AF patients, but this difference was not observed in patients who had mobile-bearing TAR, the researchers noted.
Dr. Goldberg said it was surprising “that, in a separate analysis, we found that the fixed-bearing ankle replacement patients [who accounted for half of the implants used] improved by a much greater difference when compared to ankle fusion.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short follow-up and study design that allowed surgeons to choose any implant and technique, the researchers noted.
Other limitations include a lack of data on cost-effectiveness and the impact of comorbidities on outcomes, they wrote. However, the study is the first completed multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare TAR and AF procedures for end-stage ankle osteoarthritis and shows that both yield similar clinical improvements, they concluded.
Data can inform treatment discussion
The take-home messages for clinicians are that both ankle replacement and ankle fusion are effective treatments that improve patients’ quality of life, and it is important to establish the health of adjacent joints before making treatment recommendations, Dr. Goldberg said.
“Careful counseling on the relative risks of each procedure should be part of the informed consent process,” he added. Ideally, all patients seeking surgical care for ankle arthritis should have a choice between ankle replacement and ankle fusion, but sometimes there is inequity of provision of the two treatments, he noted.
“We now encourage all surgeons to work in ankle arthritis networks so that every patient, no matter where they live, can have choice about the best treatment for them,” he said.
Researchers met the challenge of surgical RCT
Randomized trials of surgical interventions are challenging to conduct, and therefore limited, wrote Bruce Sangeorzan, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. However, the new study was strengthened by the inclusion of 17 centers for heterogeneity of implant type and surgeon experience level, the editorialists said in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study is especially important, because ankle arthritis treatment is very understudied, compared with hip and knee arthritis, but it has a similar impact on activity, editorial coauthor Dr. Sangeorzan said in an interview.
“Randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for comparing medical therapies,” he said, “but they are very difficult to do in surgical treatments, particularly when the two treatments can be differentiated, in this case by movement of the ankle.”
In addition, there is a strong placebo effect attached to interventions, Dr. Sangeorzan noted. “Determining best-case treatment relies on prospective research, preferably randomized. Since both ankle fusion and ankle replacement are effective therapies, a prospective randomized trial is the best way to help make treatment decisions,” he said.
The current study findings are not surprising, but they are preliminary, and 1 year of follow-up is not enough to determine effectiveness, Dr. Sangeorzan emphasized. However, “the authors have done the hard work of randomizing the patients and collecting the data, and the patients can now be followed for a longer time,” he said.
“In addition, the trial was designed with multiple secondary outcome measures, so the data can be matched up with larger trials that were not randomized to identify key elements of success for each procedure,” he noted.
The key message for clinicians is that ankle arthritis has a significant impact on patients’ lives, but there are two effective treatments that can reduce the impact of the disease, said Dr. Sangeorzan. “The data suggest that there are differences in implant design and differences in comorbidities that should influence decision-making,” he added.
Additional research is needed in the form of a longer study duration with larger cohorts, said Dr. Sangeorzan. In particular, researchers need to determine what comorbidities might drive patients to one type of care vs. another, he said. “The suggestion that [patients receiving implants with two motion segments have better outcomes than those receiving implants with a one-motion segment] also deserves further study,” he added.
The research was supported by the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The trial was sponsored by University College London. Dr. Goldberg disclosed grant support from NIHR HTA, as well as financial relationships with companies including Stryker, Paragon 28, and stock options with Standing CT Company, Elstree Waterfront Outpatients, and X Bolt Orthopedics.
The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Ankle osteoarthritis remains a cause of severe pain and disability. Patients are treated nonoperatively if possible, but surgery is often needed for individuals with end-stage disease, wrote Andrew Goldberg, MBBS, of University College London and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Most patients with ankle arthritis respond to nonoperative treatments, such as weight loss, activity modification, support braces, and analgesia, [but] once the disease has progressed to end-stage osteoarthritis, the main surgical treatments are total ankle re-placement or ankle arthrodesis,” Dr. Goldberg said, in an interview.
In the new study, patients were randomized to receive either a total ankle replacement (TAR) or ankle fusion (AF).
“We showed that, in both treatment groups the clinical scores improved hugely, by more than three times the minimal clinically important difference,” Dr. Goldberg said in an interview.
“Although the ankle replacement arm improved, on average, by more than an extra 4 points over ankle fusion, this was not considered clinically or statistically significant,” he said.
The study is the first randomized trial to show high-quality and robust results, he noted, and findings support data from previous studies.
“Although both TAR and ankle fusion have been shown to be effective, they are very different treatments, with one fusing the bones so that there is no ankle joint movement, and the other replacing the joint with the aim of retaining ankle joint movement. It is difficult for a patient to know which treatment is more suitable for them, with most seeking guidance from their surgeon,” he said.
Generating high-quality evidence
The study, a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial known as TARVA (Total Ankle Replacement Versus Ankle Arthrodesis), aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of the two existing publicly funded U.K. treatment options, the authors wrote.
Patients were recruited at 17 U.K. centers between March 6, 2015, and Jan. 10, 2019. The study enrolled 303 adults aged 50-85 years with end-stage ankle osteoarthritis. The mean age of the participants was 68 years; 71% were men. A total of 137 TAR patients and 144 ankle fusion patients completed their surgeries with clinical scores available for analysis. Baseline characteristics were mainly similar between the groups.
Blinding was not possible because of the nature of the procedures, but the surgeons who screened the patients were not aware of the randomization allocations, the researchers noted. A total of 33 surgeons participated in the trial, with a median number of seven patients per surgeon during the study period.
For TAR, U.K. surgeons use both two-component, fixed-bearing and three-component, mobile-bearing implants, the authors write. Ankle fusion was done using the surgeon’s usual technique of either arthroscopic-assisted or open ankle fusion.
The primary outcome was the change in the Manchester–Oxford Foot Questionnaire walking/standing (MOXFQ-W/S) domain scores from baseline to 52 weeks after surgery. The MOXFQ-W/S uses a scale of 0-100, with lower scores representing better outcomes. Secondary outcomes included change in the MOXFQ-W/S scores at 26 weeks after surgery, as well as measures of patient quality of life.
No statistically significant difference
Overall, the mean MOXFQ-W/S scores improved significantly from baseline to 52 weeks for both groups, with average improvements of 49.9 in the TAR group and 44.4 points in the AF group. The average scores at 52 weeks were 31.4 in the TAR group and 36.8 in the AF group.
The adjusted difference in score change from baseline was –5.56, showing a slightly greater degree of improvement with TAR, but this difference was not clinically or statistically significant, the researchers noted.
Adverse event numbers were similar for both procedures, with 54% of TAR patients and 53% of AF patients experiencing at least 1 adverse event during the study period. Of those, 18% of TAR patients and 24% of AF patients experienced at least 1 serious adverse event.
However, the TAR patients experienced a higher rate of wound healing complications and nerve injuries, while thromboembolism was higher in the AF patients, the researchers noted.
A prespecified subgroup analysis of patients with osteoarthritis in adjacent joints suggested a greater improvement in TAR, compared with AF, a difference that increased when fixed-bearing TAR was compared with AF, the authors wrote.
“This reinforces previous reports that suggest that the presence of adjacent joint arthritis may be an indication for ankle replacement over AF,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
“Many of these patients did not have any symptoms in the adjacent joints,” they noted.
“The presence of adjacent joint arthritis, meaning the wear and tear of the joints around the ankle joint, seemed to favor ankle replacement,” Dr. Goldberg said. Approximately 30 joints in the foot continue to move after the ankle is fused, and if these adjacent joints are not healthy before surgery [as was the case in 42% of the study patients], the results of fusion were less successful, he explained.
A post hoc analysis between TAR subtypes showed that patients who had fixed-bearing TAR had significantly greater improvements, compared with AF patients, but this difference was not observed in patients who had mobile-bearing TAR, the researchers noted.
Dr. Goldberg said it was surprising “that, in a separate analysis, we found that the fixed-bearing ankle replacement patients [who accounted for half of the implants used] improved by a much greater difference when compared to ankle fusion.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short follow-up and study design that allowed surgeons to choose any implant and technique, the researchers noted.
Other limitations include a lack of data on cost-effectiveness and the impact of comorbidities on outcomes, they wrote. However, the study is the first completed multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare TAR and AF procedures for end-stage ankle osteoarthritis and shows that both yield similar clinical improvements, they concluded.
Data can inform treatment discussion
The take-home messages for clinicians are that both ankle replacement and ankle fusion are effective treatments that improve patients’ quality of life, and it is important to establish the health of adjacent joints before making treatment recommendations, Dr. Goldberg said.
“Careful counseling on the relative risks of each procedure should be part of the informed consent process,” he added. Ideally, all patients seeking surgical care for ankle arthritis should have a choice between ankle replacement and ankle fusion, but sometimes there is inequity of provision of the two treatments, he noted.
“We now encourage all surgeons to work in ankle arthritis networks so that every patient, no matter where they live, can have choice about the best treatment for them,” he said.
Researchers met the challenge of surgical RCT
Randomized trials of surgical interventions are challenging to conduct, and therefore limited, wrote Bruce Sangeorzan, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. However, the new study was strengthened by the inclusion of 17 centers for heterogeneity of implant type and surgeon experience level, the editorialists said in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study is especially important, because ankle arthritis treatment is very understudied, compared with hip and knee arthritis, but it has a similar impact on activity, editorial coauthor Dr. Sangeorzan said in an interview.
“Randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for comparing medical therapies,” he said, “but they are very difficult to do in surgical treatments, particularly when the two treatments can be differentiated, in this case by movement of the ankle.”
In addition, there is a strong placebo effect attached to interventions, Dr. Sangeorzan noted. “Determining best-case treatment relies on prospective research, preferably randomized. Since both ankle fusion and ankle replacement are effective therapies, a prospective randomized trial is the best way to help make treatment decisions,” he said.
The current study findings are not surprising, but they are preliminary, and 1 year of follow-up is not enough to determine effectiveness, Dr. Sangeorzan emphasized. However, “the authors have done the hard work of randomizing the patients and collecting the data, and the patients can now be followed for a longer time,” he said.
“In addition, the trial was designed with multiple secondary outcome measures, so the data can be matched up with larger trials that were not randomized to identify key elements of success for each procedure,” he noted.
The key message for clinicians is that ankle arthritis has a significant impact on patients’ lives, but there are two effective treatments that can reduce the impact of the disease, said Dr. Sangeorzan. “The data suggest that there are differences in implant design and differences in comorbidities that should influence decision-making,” he added.
Additional research is needed in the form of a longer study duration with larger cohorts, said Dr. Sangeorzan. In particular, researchers need to determine what comorbidities might drive patients to one type of care vs. another, he said. “The suggestion that [patients receiving implants with two motion segments have better outcomes than those receiving implants with a one-motion segment] also deserves further study,” he added.
The research was supported by the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The trial was sponsored by University College London. Dr. Goldberg disclosed grant support from NIHR HTA, as well as financial relationships with companies including Stryker, Paragon 28, and stock options with Standing CT Company, Elstree Waterfront Outpatients, and X Bolt Orthopedics.
The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.