User login
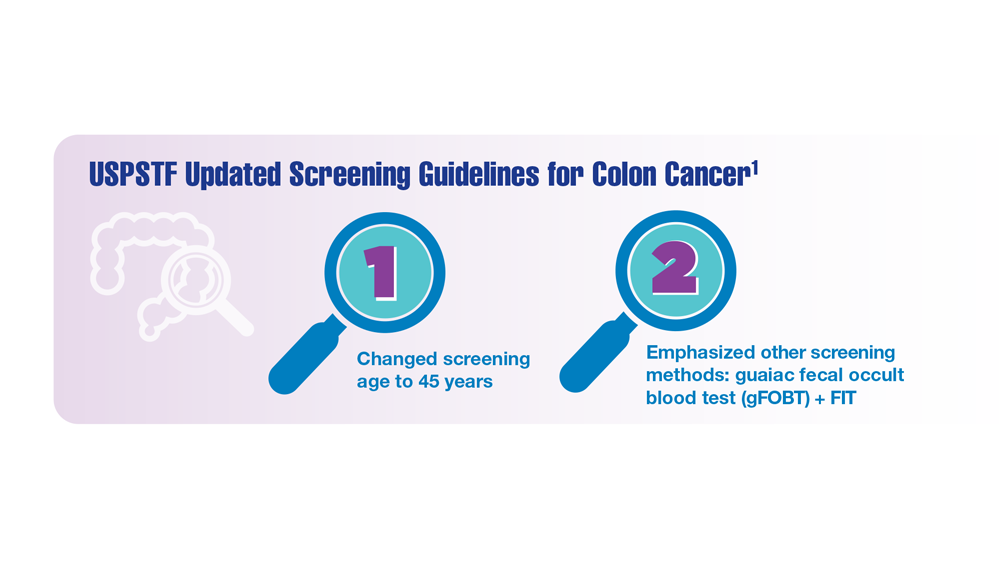
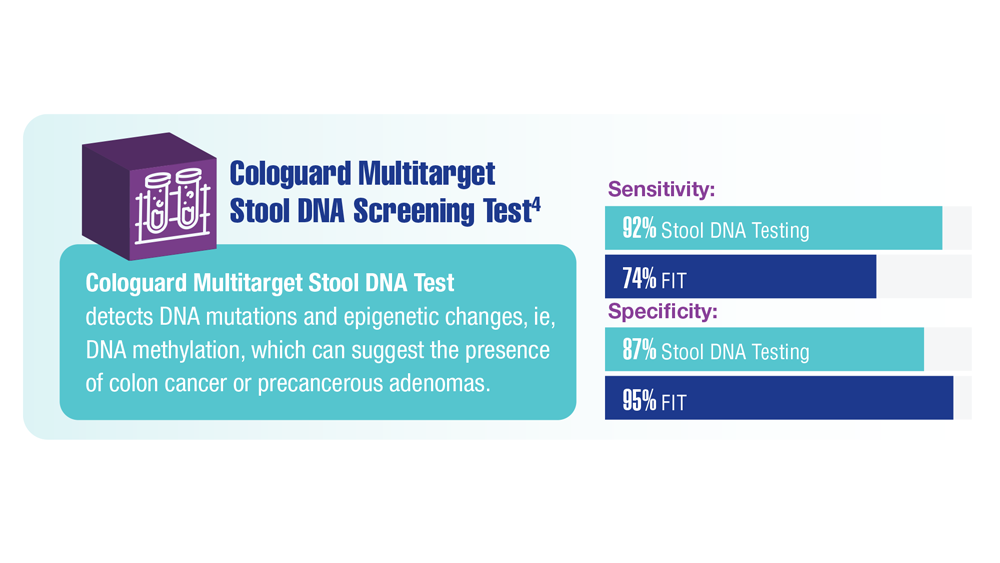
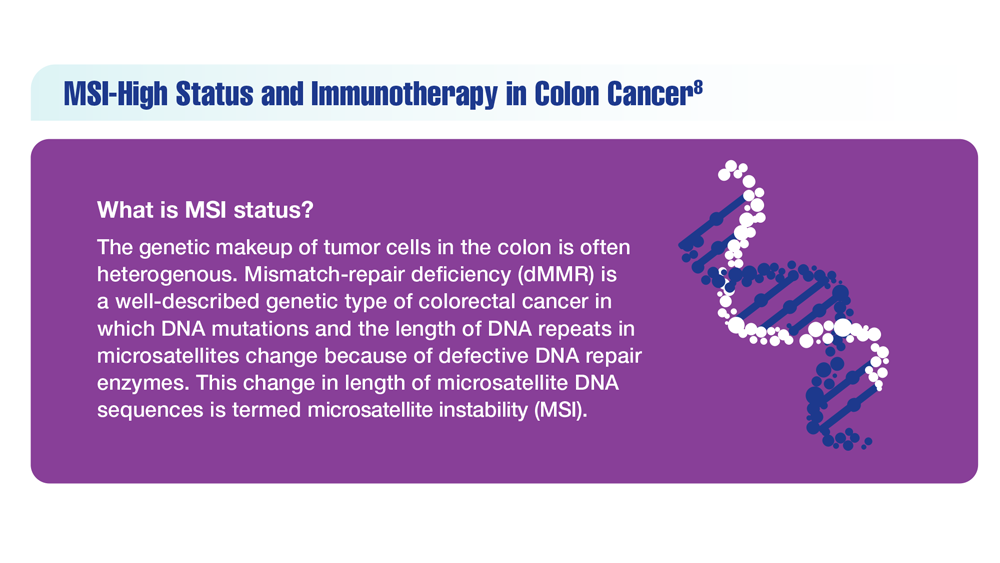
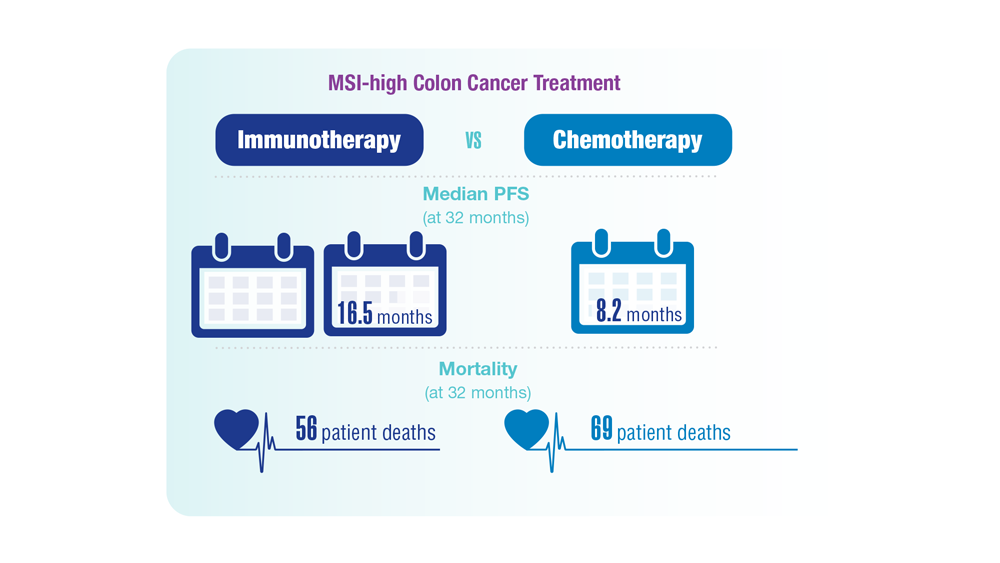
Screening Guideline Updates and New Treatments in Colon Cancer
- Ng K et al. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1943-1945. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4133
- Xie YH et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):22. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0116-z
- Muller C et al. Cells. 2021;10(5):1018. doi:10.3390/cells10051018
- Clebak KT et al. Am Fam Physician. 2022;105(2):198-200.
- May FP et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(8):1923-1932. doi:10.1007/s10620-017-4607-x
- May FP et al. Med Care. 2019;57(10):773-780. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001186
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Oncology Program Office. National Precision Oncology Program (NPOP). Updated June 24, 2022. Accessed December 14, 2022. http://www.cancer.va.gov/CANCER/NPOP.asp
- André T et al; KEYNOTE-177 Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2207-2218. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
- Naidoo M et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):346. doi:10.3390/cancers13020346
- Kasi PM et al. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047831. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047831
- Jin S et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(5):e2017421118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2017421118
- Ng K et al. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1943-1945. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4133
- Xie YH et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):22. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0116-z
- Muller C et al. Cells. 2021;10(5):1018. doi:10.3390/cells10051018
- Clebak KT et al. Am Fam Physician. 2022;105(2):198-200.
- May FP et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(8):1923-1932. doi:10.1007/s10620-017-4607-x
- May FP et al. Med Care. 2019;57(10):773-780. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001186
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Oncology Program Office. National Precision Oncology Program (NPOP). Updated June 24, 2022. Accessed December 14, 2022. http://www.cancer.va.gov/CANCER/NPOP.asp
- André T et al; KEYNOTE-177 Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2207-2218. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
- Naidoo M et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):346. doi:10.3390/cancers13020346
- Kasi PM et al. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047831. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047831
- Jin S et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(5):e2017421118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2017421118
- Ng K et al. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1943-1945. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4133
- Xie YH et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):22. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0116-z
- Muller C et al. Cells. 2021;10(5):1018. doi:10.3390/cells10051018
- Clebak KT et al. Am Fam Physician. 2022;105(2):198-200.
- May FP et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(8):1923-1932. doi:10.1007/s10620-017-4607-x
- May FP et al. Med Care. 2019;57(10):773-780. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001186
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Oncology Program Office. National Precision Oncology Program (NPOP). Updated June 24, 2022. Accessed December 14, 2022. http://www.cancer.va.gov/CANCER/NPOP.asp
- André T et al; KEYNOTE-177 Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2207-2218. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
- Naidoo M et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):346. doi:10.3390/cancers13020346
- Kasi PM et al. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047831. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047831
- Jin S et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(5):e2017421118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2017421118
Cancer Data Trends 2023
Federal Practitioner and the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) present the 2023 edition of Cancer Data Trends (click to view the digital edition). This special issue provides updates on some of the top cancers and related concerns affecting veterans through original infographics and visual storytelling.
In this issue:
- COVID-19 Outcomes in Veterans With Hematologic Cancers
- Promising New Approaches for Testicular and Prostate Cancer
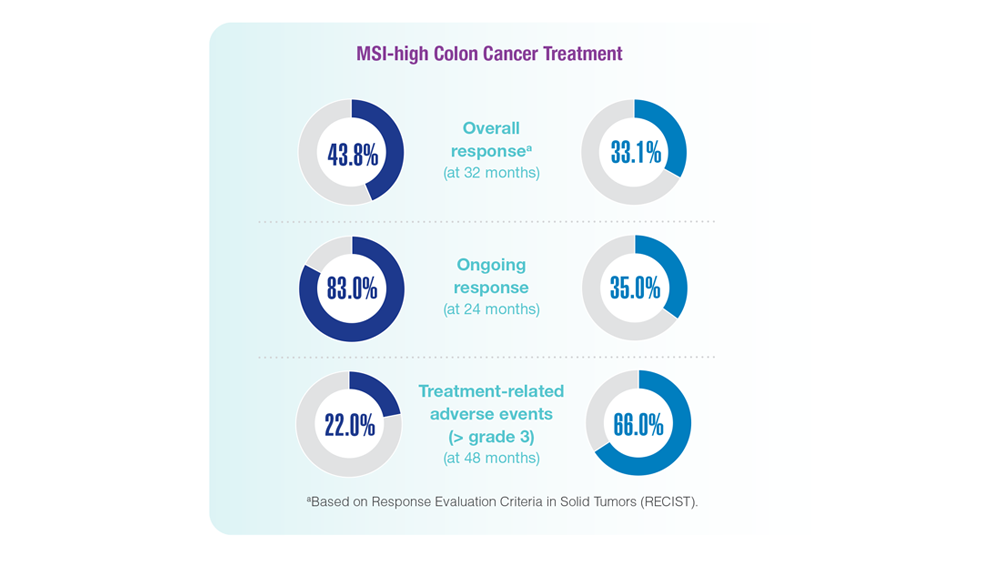
- Screening Guideline Updates and New Treatments in Colon Cancer
- Exposure-Related Cancers: A Look at the PACT Act
- New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
- Gender Disparity in Breast Cancer Among US Veterans
- Lung Cancer Screening in Veterans
- Necessary Updates to Skin Cancer Risk Stratification
- Innovation in Cancer Treatment
Federal Practitioner and the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) present the 2023 edition of Cancer Data Trends (click to view the digital edition). This special issue provides updates on some of the top cancers and related concerns affecting veterans through original infographics and visual storytelling.
In this issue:
- COVID-19 Outcomes in Veterans With Hematologic Cancers
- Promising New Approaches for Testicular and Prostate Cancer
- Screening Guideline Updates and New Treatments in Colon Cancer
- Exposure-Related Cancers: A Look at the PACT Act
- New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
- Gender Disparity in Breast Cancer Among US Veterans
- Lung Cancer Screening in Veterans
- Necessary Updates to Skin Cancer Risk Stratification
- Innovation in Cancer Treatment
Federal Practitioner and the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) present the 2023 edition of Cancer Data Trends (click to view the digital edition). This special issue provides updates on some of the top cancers and related concerns affecting veterans through original infographics and visual storytelling.
In this issue:
- COVID-19 Outcomes in Veterans With Hematologic Cancers
- Promising New Approaches for Testicular and Prostate Cancer
- Screening Guideline Updates and New Treatments in Colon Cancer
- Exposure-Related Cancers: A Look at the PACT Act
- New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
- Gender Disparity in Breast Cancer Among US Veterans
- Lung Cancer Screening in Veterans
- Necessary Updates to Skin Cancer Risk Stratification
- Innovation in Cancer Treatment
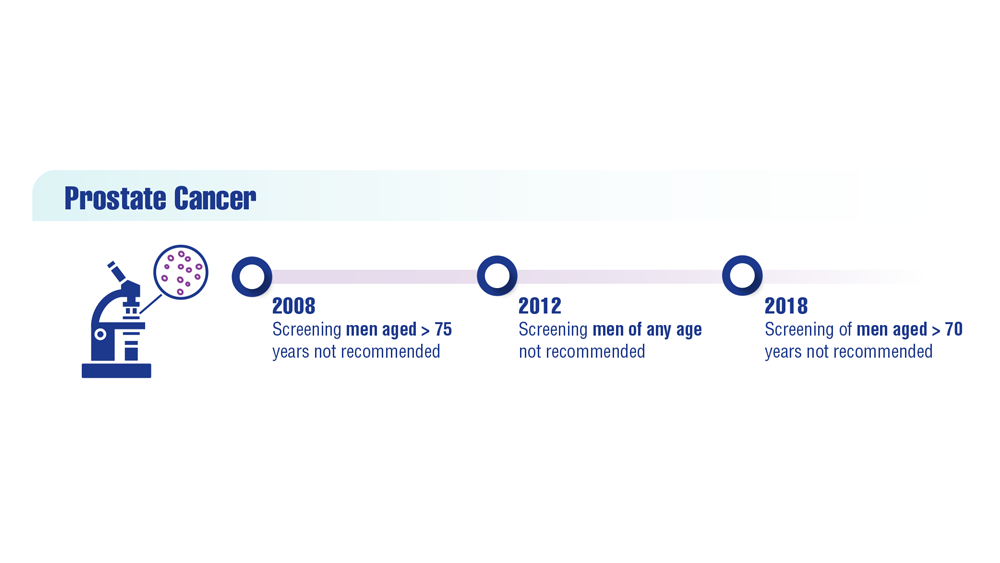
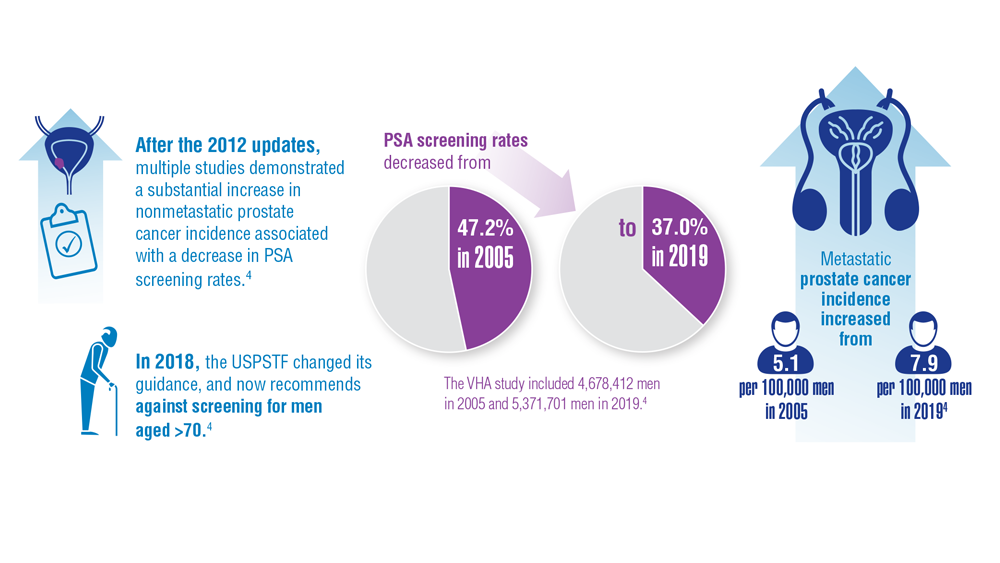
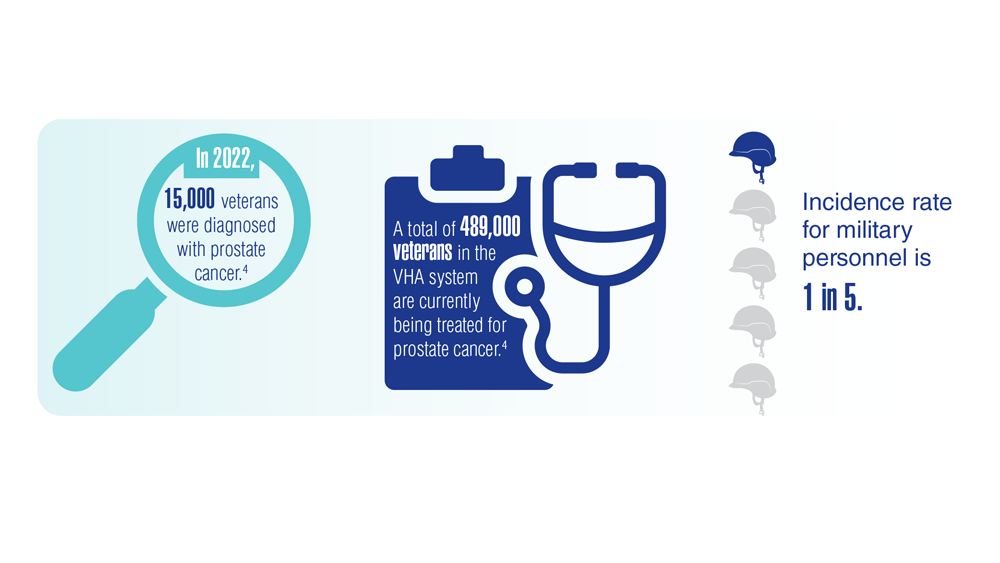
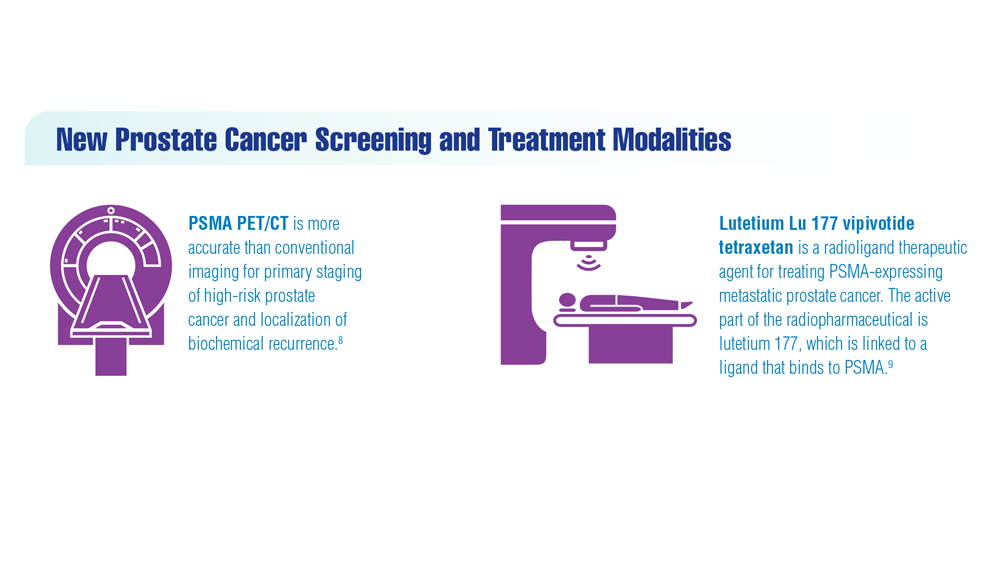
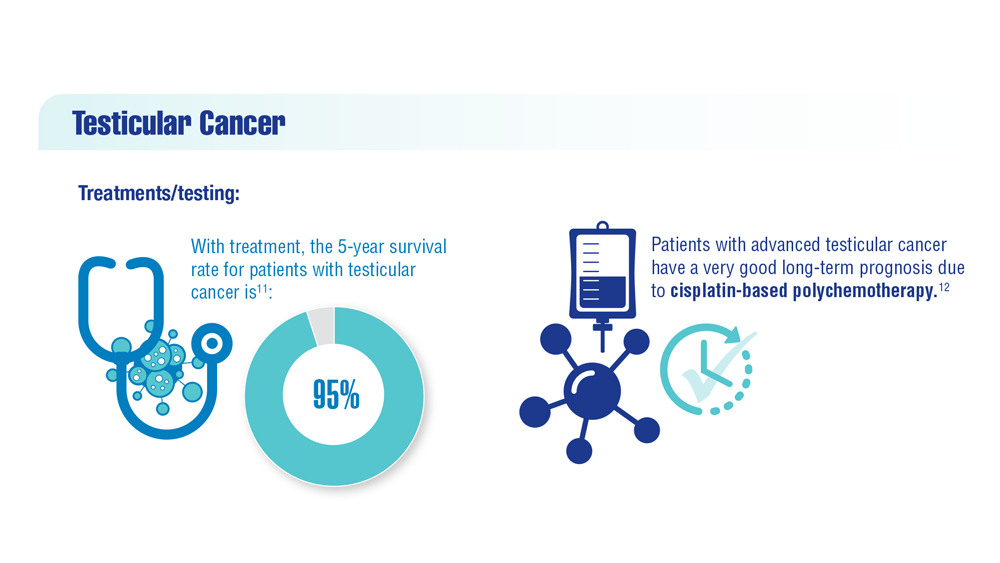
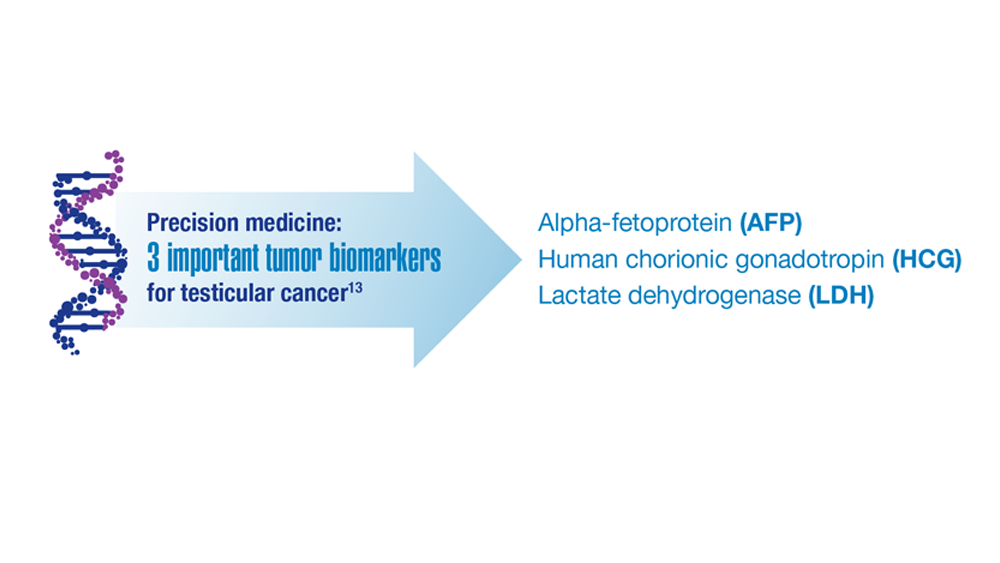
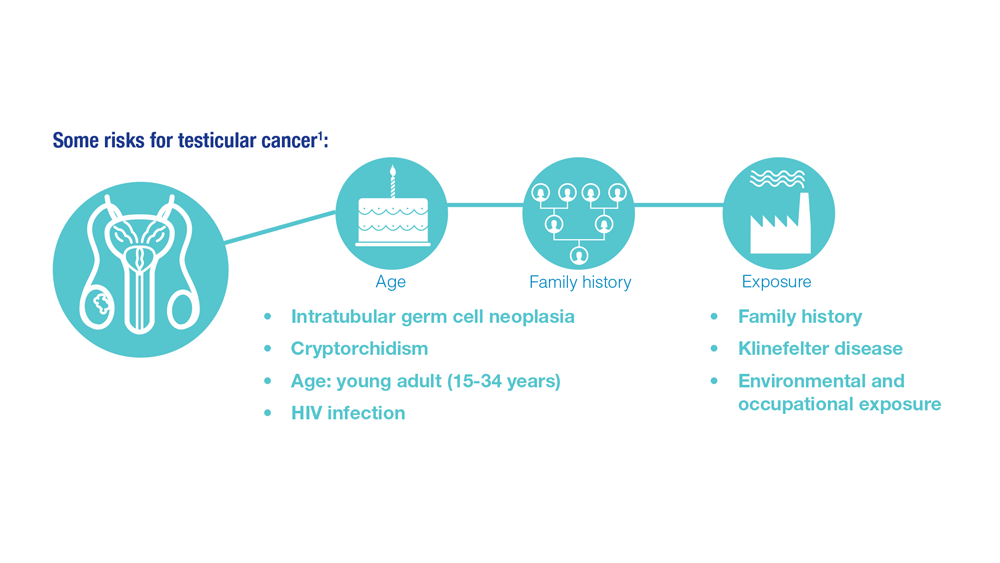
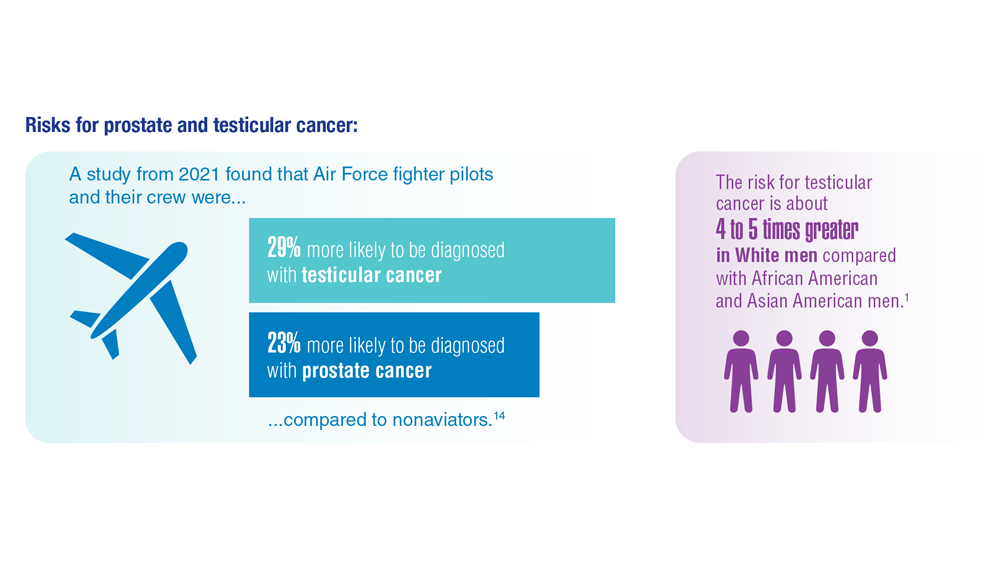
Promising New Approaches for Testicular and Prostate Cancer
- Risk factors for testicular cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 17, 2018. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/testicular-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
- Chovanec M, Cheng L. BMJ. 2022;379:e070499. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-070499
- Tavares NT et al. J Pathol. 2022. doi:10.1002/path.6037
- Bryant AK et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;e224319. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4319
- Kabasakal L et al. Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38(2):149-155. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000617
- Sartor O et al; VISION Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(12):1091-1103. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107322
- Rowe SP et al. Annu Rev Med. 2019;70:461-477. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-062117-073027
- Pomykala KL et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022;S2588-9311(22)00177-8. doi:10.1016/j.euo.2022.10.007
- Keam SJ. Mol Diagn Ther. 2022;26(4):467-475. doi:10.1007/s40291-022-00594-2
- Lovejoy LA et al. Mil Med. 2022:usac297. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac297
- Smith ZL et al. Med Clin North Am. 2018;102(2):251-264. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2017.10.003
- Hohnloser JH et al. Eur J Med Res.1996;1(11):509-514.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine website. Testicular Cancer tumor Markers. Accessed December 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/testicular-cancer/testicular-cancer-tumor-markers
- Webber BJ et al. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(1):71-78. doi:10.1097/JOM.0000000000002353
- Risk factors for testicular cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 17, 2018. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/testicular-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
- Chovanec M, Cheng L. BMJ. 2022;379:e070499. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-070499
- Tavares NT et al. J Pathol. 2022. doi:10.1002/path.6037
- Bryant AK et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;e224319. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4319
- Kabasakal L et al. Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38(2):149-155. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000617
- Sartor O et al; VISION Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(12):1091-1103. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107322
- Rowe SP et al. Annu Rev Med. 2019;70:461-477. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-062117-073027
- Pomykala KL et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022;S2588-9311(22)00177-8. doi:10.1016/j.euo.2022.10.007
- Keam SJ. Mol Diagn Ther. 2022;26(4):467-475. doi:10.1007/s40291-022-00594-2
- Lovejoy LA et al. Mil Med. 2022:usac297. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac297
- Smith ZL et al. Med Clin North Am. 2018;102(2):251-264. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2017.10.003
- Hohnloser JH et al. Eur J Med Res.1996;1(11):509-514.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine website. Testicular Cancer tumor Markers. Accessed December 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/testicular-cancer/testicular-cancer-tumor-markers
- Webber BJ et al. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(1):71-78. doi:10.1097/JOM.0000000000002353
- Risk factors for testicular cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 17, 2018. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/testicular-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
- Chovanec M, Cheng L. BMJ. 2022;379:e070499. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-070499
- Tavares NT et al. J Pathol. 2022. doi:10.1002/path.6037
- Bryant AK et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;e224319. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4319
- Kabasakal L et al. Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38(2):149-155. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000617
- Sartor O et al; VISION Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(12):1091-1103. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107322
- Rowe SP et al. Annu Rev Med. 2019;70:461-477. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-062117-073027
- Pomykala KL et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022;S2588-9311(22)00177-8. doi:10.1016/j.euo.2022.10.007
- Keam SJ. Mol Diagn Ther. 2022;26(4):467-475. doi:10.1007/s40291-022-00594-2
- Lovejoy LA et al. Mil Med. 2022:usac297. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac297
- Smith ZL et al. Med Clin North Am. 2018;102(2):251-264. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2017.10.003
- Hohnloser JH et al. Eur J Med Res.1996;1(11):509-514.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine website. Testicular Cancer tumor Markers. Accessed December 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/testicular-cancer/testicular-cancer-tumor-markers
- Webber BJ et al. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(1):71-78. doi:10.1097/JOM.0000000000002353
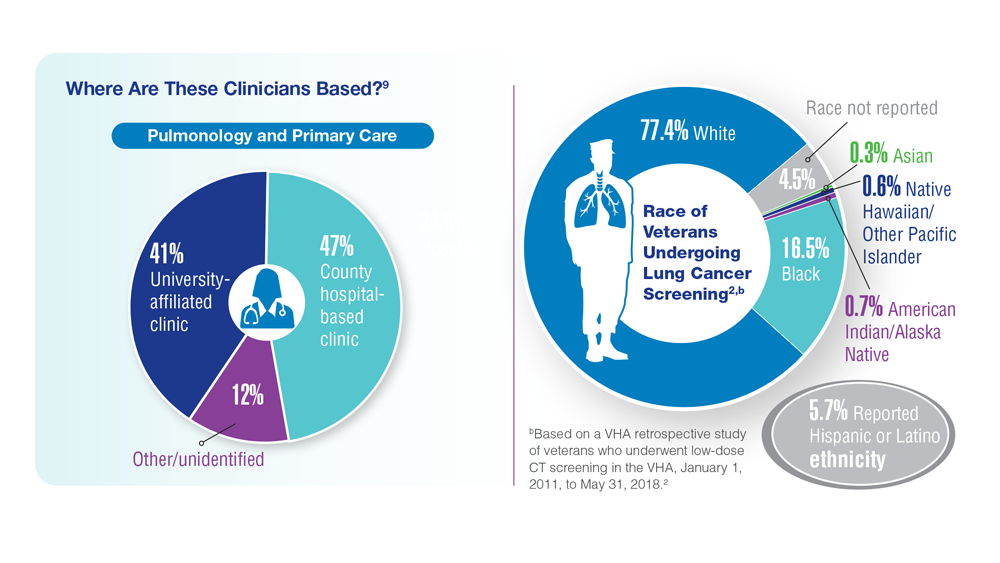
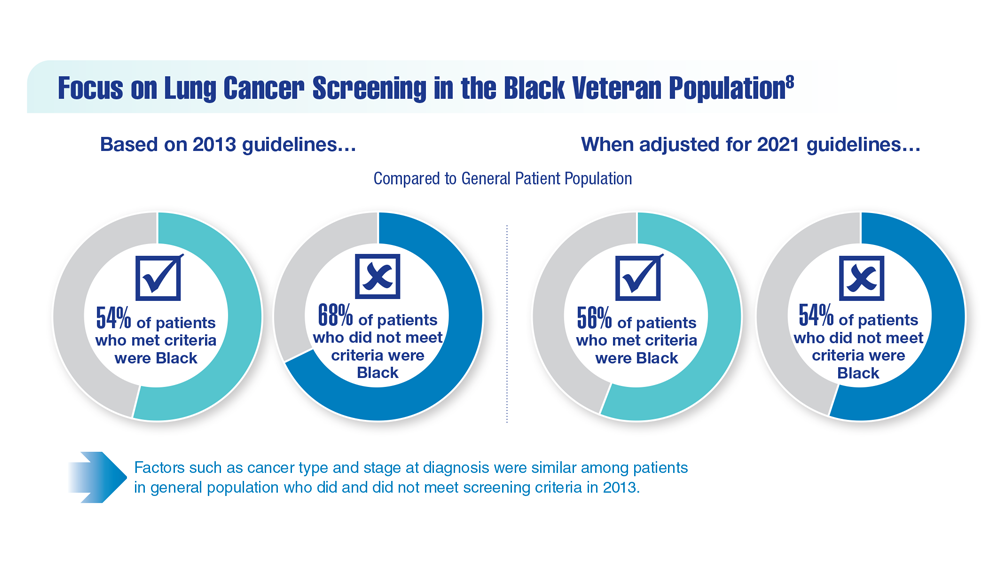
Lung Cancer Screening in Veterans
- Spalluto LB et al. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18(6):809-819. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.12.010
- Lewis JA et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020;4(5):pkaa053. doi:10.1093/jncics/pkaa053
- Wallace C. Largest-ever lung cancer screening study reveals ways to increase screening outreach. Medical University of South Carolina. November 22, 2022. Accessed January 4, 202 https://hollingscancercenter.musc.edu/news/archive/2022/11/22/largest-ever-lung-cancer-screening-study-reveals-ways-to-increase-screening-outreach
- Screening facts & figures. Go2 For Lung Cancer. 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://go2.org/risk-early-detection/screening-facts-figures/
- Dyer O. BMJ. 2021;372:n698. doi:10.1136/bmj.n698
- Boudreau JH et al. Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
- Maurice NM, Tanner NT. Semin Oncol. 2022;S0093-7754(22)00041-0. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.06.001
- Rusher TN et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 2):S48-S51. doi:10.12788/fp.0269
- Núñez ER et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):e2116233. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16233
- Lake M et al. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):561. doi:1186/s12885-020-06923-0
- Spalluto LB et al. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18(6):809-819. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.12.010
- Lewis JA et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020;4(5):pkaa053. doi:10.1093/jncics/pkaa053
- Wallace C. Largest-ever lung cancer screening study reveals ways to increase screening outreach. Medical University of South Carolina. November 22, 2022. Accessed January 4, 202 https://hollingscancercenter.musc.edu/news/archive/2022/11/22/largest-ever-lung-cancer-screening-study-reveals-ways-to-increase-screening-outreach
- Screening facts & figures. Go2 For Lung Cancer. 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://go2.org/risk-early-detection/screening-facts-figures/
- Dyer O. BMJ. 2021;372:n698. doi:10.1136/bmj.n698
- Boudreau JH et al. Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
- Maurice NM, Tanner NT. Semin Oncol. 2022;S0093-7754(22)00041-0. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.06.001
- Rusher TN et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 2):S48-S51. doi:10.12788/fp.0269
- Núñez ER et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):e2116233. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16233
- Lake M et al. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):561. doi:1186/s12885-020-06923-0
- Spalluto LB et al. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18(6):809-819. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.12.010
- Lewis JA et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020;4(5):pkaa053. doi:10.1093/jncics/pkaa053
- Wallace C. Largest-ever lung cancer screening study reveals ways to increase screening outreach. Medical University of South Carolina. November 22, 2022. Accessed January 4, 202 https://hollingscancercenter.musc.edu/news/archive/2022/11/22/largest-ever-lung-cancer-screening-study-reveals-ways-to-increase-screening-outreach
- Screening facts & figures. Go2 For Lung Cancer. 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://go2.org/risk-early-detection/screening-facts-figures/
- Dyer O. BMJ. 2021;372:n698. doi:10.1136/bmj.n698
- Boudreau JH et al. Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
- Maurice NM, Tanner NT. Semin Oncol. 2022;S0093-7754(22)00041-0. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.06.001
- Rusher TN et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 2):S48-S51. doi:10.12788/fp.0269
- Núñez ER et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):e2116233. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16233
- Lake M et al. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):561. doi:1186/s12885-020-06923-0
AGA Research Scholar Awards advance the GI field
AGA’s flagship award is the Research Scholar Award (RSA), which provides career development support for young investigators in gastroenterology and hepatology research.
The AGA Research Awards program has a significant impact on digestive disease research.
- More than $58 million has been awarded in research grants.
- More than 1,000 scientists have been awarded grants.
- Over the first 30 years of the Research Scholar Awards program, 57% of RSA recipients subsequently received at least one NIH R01 award, with 5 years on average between the RSA and first R01. Collectively, this group of investigators has secured 280 distinct R01 or equivalent awards.
Funded by the generosity of donors, the AGA Research Foundation’s research award program ensures that we are building a community of researchers whose work serves the greater community and benefits patients.
“In order to produce truly innovative work at the forefront of current discoveries, donations to research in GI are essential and cannot be replaced by other funding sources,” states Kathleen Curtius, PhD, MS, 2022 AGA Foundation Research Scholar Award recipient.
Join others in supporting the AGA Research Foundation. You will ensure that young researchers have opportunities to continue their lifesaving work. Your tax-deductible contribution supports the Foundation’s research award program, including the RSA, which ensures that studies are funded, discoveries are made, and patients are treated.
To learn more or to make a contribution, visit www.foundation.gastro.org.
AGA’s flagship award is the Research Scholar Award (RSA), which provides career development support for young investigators in gastroenterology and hepatology research.
The AGA Research Awards program has a significant impact on digestive disease research.
- More than $58 million has been awarded in research grants.
- More than 1,000 scientists have been awarded grants.
- Over the first 30 years of the Research Scholar Awards program, 57% of RSA recipients subsequently received at least one NIH R01 award, with 5 years on average between the RSA and first R01. Collectively, this group of investigators has secured 280 distinct R01 or equivalent awards.
Funded by the generosity of donors, the AGA Research Foundation’s research award program ensures that we are building a community of researchers whose work serves the greater community and benefits patients.
“In order to produce truly innovative work at the forefront of current discoveries, donations to research in GI are essential and cannot be replaced by other funding sources,” states Kathleen Curtius, PhD, MS, 2022 AGA Foundation Research Scholar Award recipient.
Join others in supporting the AGA Research Foundation. You will ensure that young researchers have opportunities to continue their lifesaving work. Your tax-deductible contribution supports the Foundation’s research award program, including the RSA, which ensures that studies are funded, discoveries are made, and patients are treated.
To learn more or to make a contribution, visit www.foundation.gastro.org.
AGA’s flagship award is the Research Scholar Award (RSA), which provides career development support for young investigators in gastroenterology and hepatology research.
The AGA Research Awards program has a significant impact on digestive disease research.
- More than $58 million has been awarded in research grants.
- More than 1,000 scientists have been awarded grants.
- Over the first 30 years of the Research Scholar Awards program, 57% of RSA recipients subsequently received at least one NIH R01 award, with 5 years on average between the RSA and first R01. Collectively, this group of investigators has secured 280 distinct R01 or equivalent awards.
Funded by the generosity of donors, the AGA Research Foundation’s research award program ensures that we are building a community of researchers whose work serves the greater community and benefits patients.
“In order to produce truly innovative work at the forefront of current discoveries, donations to research in GI are essential and cannot be replaced by other funding sources,” states Kathleen Curtius, PhD, MS, 2022 AGA Foundation Research Scholar Award recipient.
Join others in supporting the AGA Research Foundation. You will ensure that young researchers have opportunities to continue their lifesaving work. Your tax-deductible contribution supports the Foundation’s research award program, including the RSA, which ensures that studies are funded, discoveries are made, and patients are treated.
To learn more or to make a contribution, visit www.foundation.gastro.org.
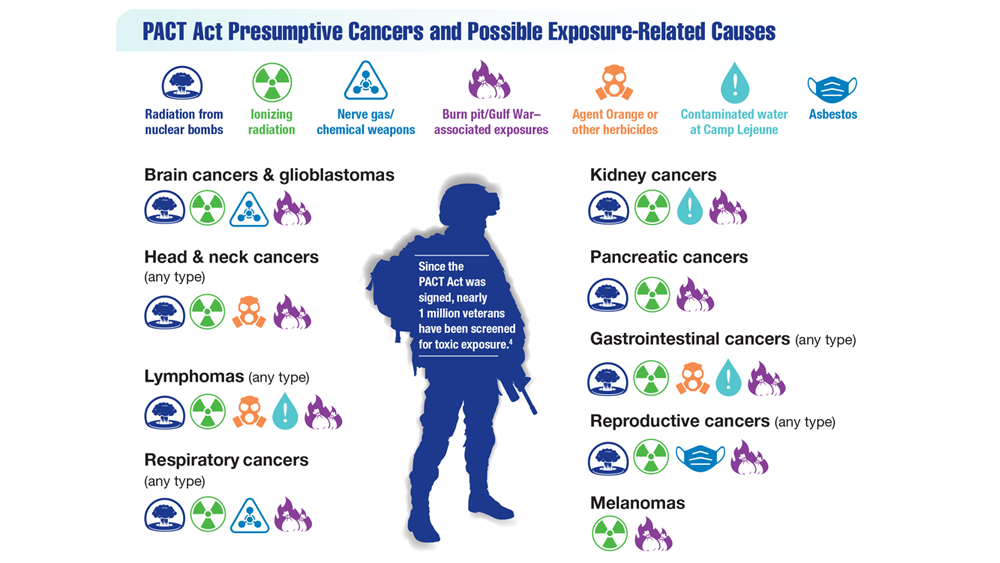
Exposure-Related Cancers: A Look at the PACT Act
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. PACT Act. Updated November 4, 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://www.publichealth.va.gov/exposures/benefits/PACT_Act.asp
- The White House. FACT SHEET: President Biden signs the PACT Act and delivers on his promise to America’s veterans. August 10, 202 Accessed January 10, 2023. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2022/08/10/fact-sheet-president-biden-signs-the-pact-act-and-delivers-on-his-promise-to-americas-veterans/
- US House of Representatives. Honoring our promise to address Comprehensive Toxics Act of 2021. Title I – Expansion of health care eligibility for toxic exposed veterans. House report 117-249. February 22, 2022. Accessed January 19, 202 https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CRPT-117hrpt249/html/CRPT-117hrpt249-pt1.htm
- VA News. Cancer Moonshot week of action sees VA deploying new clinical pathways. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 19, 2023. https://news.va.gov/111925/cancer-moonshot-clinical-pathways/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. PACT Act. Updated November 4, 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://www.publichealth.va.gov/exposures/benefits/PACT_Act.asp
- The White House. FACT SHEET: President Biden signs the PACT Act and delivers on his promise to America’s veterans. August 10, 202 Accessed January 10, 2023. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2022/08/10/fact-sheet-president-biden-signs-the-pact-act-and-delivers-on-his-promise-to-americas-veterans/
- US House of Representatives. Honoring our promise to address Comprehensive Toxics Act of 2021. Title I – Expansion of health care eligibility for toxic exposed veterans. House report 117-249. February 22, 2022. Accessed January 19, 202 https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CRPT-117hrpt249/html/CRPT-117hrpt249-pt1.htm
- VA News. Cancer Moonshot week of action sees VA deploying new clinical pathways. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 19, 2023. https://news.va.gov/111925/cancer-moonshot-clinical-pathways/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. PACT Act. Updated November 4, 2022. Accessed January 4, 2023. https://www.publichealth.va.gov/exposures/benefits/PACT_Act.asp
- The White House. FACT SHEET: President Biden signs the PACT Act and delivers on his promise to America’s veterans. August 10, 202 Accessed January 10, 2023. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2022/08/10/fact-sheet-president-biden-signs-the-pact-act-and-delivers-on-his-promise-to-americas-veterans/
- US House of Representatives. Honoring our promise to address Comprehensive Toxics Act of 2021. Title I – Expansion of health care eligibility for toxic exposed veterans. House report 117-249. February 22, 2022. Accessed January 19, 202 https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CRPT-117hrpt249/html/CRPT-117hrpt249-pt1.htm
- VA News. Cancer Moonshot week of action sees VA deploying new clinical pathways. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 19, 2023. https://news.va.gov/111925/cancer-moonshot-clinical-pathways/
New definition for iron deficiency in CV disease proposed
with implications that may extend to cardiovascular disease in general.
In the study involving more than 900 patients with PH, investigators at seven U.S. centers determined the prevalence of iron deficiency by two separate definitions and assessed its associations with functional measures and quality of life (QoL) scores.
An iron deficiency definition used conventionally in heart failure (HF) – ferritin less than 100 g/mL or 100-299 ng/mL with transferrin saturation (TSAT) less than 20% – failed to discriminate patients with reduced peak oxygen consumption (peakVO2), 6-minute walk test (6MWT) results, and QoL scores on the 36-item Short Form Survey (SF-36).
But an alternative definition for iron deficiency, simply a TSAT less than 21%, did predict such patients with reduced peakVO2, 6MWT, and QoL. It was also associated with an increased mortality risk. The study was published in the European Heart Journal.
“A low TSAT, less than 21%, is key in the pathophysiology of iron deficiency in pulmonary hypertension” and is associated with those important clinical and functional characteristics, lead author Pieter Martens MD, PhD, said in an interview. The study “underscores the importance of these criteria in future intervention studies in the field of pulmonary hypertension testing iron therapies.”
A broader implication is that “we should revise how we define iron deficiency in heart failure and cardiovascular disease in general and how we select patients for iron therapies,” said Dr. Martens, of the Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute of the Cleveland Clinic.
Iron’s role in pulmonary vascular disease
“Iron deficiency is associated with an energetic deficit, especially in high energy–demanding tissue, leading to early skeletal muscle acidification and diminished left and right ventricular (RV) contractile reserve during exercise,” the published report states. It can lead to “maladaptive RV remodeling,” which is a “hallmark feature” predictive of morbidity and mortality in patients with pulmonary vascular disease (PVD).
Some studies have suggested that iron deficiency is a common comorbidity in patients with PVD, their estimates of its prevalence ranging widely due in part to the “absence of a uniform definition,” write the authors.
Dr. Martens said the current study was conducted partly in response to the increasingly common observation that the HF-associated definition of iron deficiency “has limitations.” Yet, “without validation in the field of pulmonary hypertension, the 2022 pulmonary hypertension guidelines endorse this definition.”
As iron deficiency is a causal risk factor for HF progression, Dr. Martens added, the HF field has “taught us the importance of using validated definitions for iron deficiency when selecting patients for iron treatment in randomized controlled trials.”
Moreover, some evidence suggests that iron deficiency by some definitions may be associated with diminished exercise capacity and QoL in patients with PVD, which are associations that have not been confirmed in large studies, the report notes.
Therefore, it continues, the study sought to “determine and validate” the optimal definition of iron deficiency in patients with PVD; document its prevalence; and explore associations between iron deficiency and exercise capacity, QoL, and cardiac and pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Evaluating definitions of iron deficiency
The prospective study, called PVDOMICS, entered 1,195 subjects with available iron levels. After exclusion of 38 patients with sarcoidosis, myeloproliferative disease, or hemoglobinopathy, there remained 693 patients with “overt” PH, 225 with a milder form of PH who served as PVD comparators, and 90 age-, sex-, race/ethnicity- matched “healthy” adults who served as controls.
According to the conventional HF definition of iron deficiency – that is, ferritin 100-299 ng/mL and TSAT less than 20% – the prevalences were 74% in patients with overt PH and 72% of those “across the PVD spectrum.”
But by that definition, iron deficient and non-iron deficient patients didn’t differ significantly in peakVO2, 6MWT distance, or SF-36 physical component scores.
In contrast, patients meeting the alternative definition of iron deficiency of TSAT less than 21% showed significantly reduced functional and QoL measures, compared with those with TSAT greater than or equal to 21%.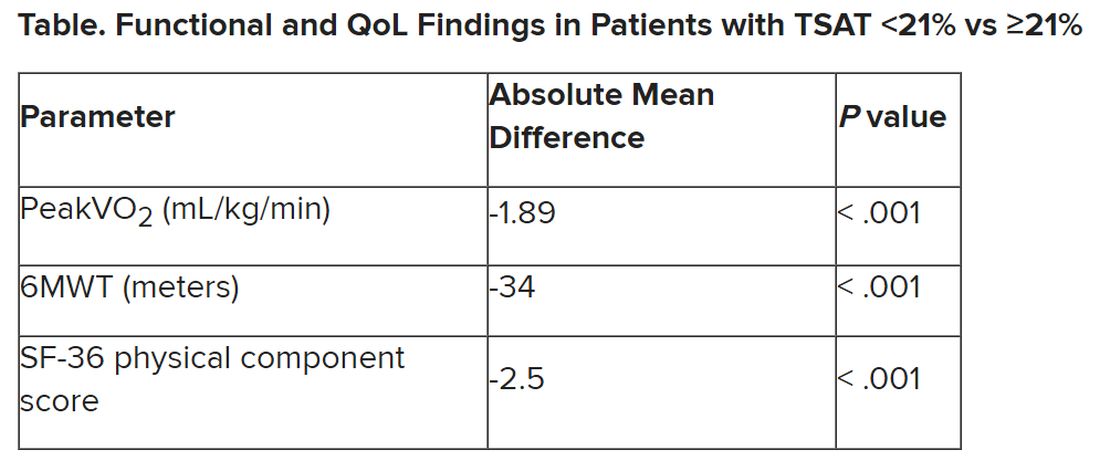
The group with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly more RV remodeling at cardiac MRI, compared with those who had TSAT greater than or equal to 21%, but their invasively measured pulmonary vascular resistance was comparable.
Of note, those with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly increased all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.13-2.34; P = .009) after adjustment for age, sex, hemoglobin, and natriuretic peptide levels.
“Proper validation of the definition of iron deficiency is important for prognostication,” the published report states, “but also for providing a working definition that can be used to identify suitable patients for inclusion in randomized controlled trials” of drugs for iron deficiency.
Additionally, the finding that TSAT less than 21% points to patients with diminished functional and exercise capacity is “consistent with more recent studies in the field of heart failure” that suggest “functional abnormalities and adverse cardiac remodeling are worse in patients with a low TSAT.” Indeed, the report states, such treatment effects have been “the most convincing” in HF trials.
Broader implications
An accompanying editorial agrees that the study’s implications apply well beyond PH. It highlights that iron deficiency is common in PH, while such PH is “not substantially different from the problem in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease in general,” lead editorialist John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, said in an interview. “It’s also common as people get older, even in those without these diseases.”
Dr. Cleland said the anemia definition currently used in cardiovascular research and practice is based on a hemoglobin concentration below the 5th percentile of age and sex in primarily young, healthy people, and not on its association with clinical outcomes.
“We recently analyzed data on a large population in the United Kingdom with a broad range of cardiovascular diseases and found that unless anemia is severe, [other] markers of iron deficiency are usually not measured,” he said. A low hemoglobin and TSAT, but not low ferritin levels, are associated with worse prognosis.
Dr. Cleland agreed that the HF-oriented definition is “poor,” with profound implications for the conduct of clinical trials. “If the definition of iron deficiency lacks specificity, then clinical trials will include many patients without iron deficiency who are unlikely to benefit from and might be harmed by IV iron.” Inclusion of such patients may also “dilute” any benefit that might emerge and render the outcome inaccurate.
But if the definition of iron deficiency lacks sensitivity, “then in clinical practice, many patients with iron deficiency may be denied a simple and effective treatment.”
Measuring serum iron could potentially be useful, but it’s usually not done in randomized trials “especially since taking an iron tablet can give a temporary ‘blip’ in serum iron,” Dr. Cleland said. “So TSAT is a reasonable compromise.” He said he “looks forward” to any further data on serum iron as a way of assessing iron deficiency and anemia.
Half full vs. half empty
Dr. Cleland likened the question of whom to treat with iron supplementation as a “glass half full versus half empty” clinical dilemma. “One approach is to give iron to everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re overloaded,” he said, “while the other is to withhold iron from everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re iron depleted.”
Recent evidence from the IRONMAN trial suggested that its patients with HF who received intravenous iron were less likely to be hospitalized for infections, particularly COVID-19, than a usual-care group. The treatment may also help reduce frailty.
“So should we be offering IV iron specifically to people considered iron deficient, or should we be ensuring that everyone over age 70 get iron supplements?” Dr. Cleland mused rhetorically. On a cautionary note, he added, perhaps iron supplementation will be harmful if it’s not necessary.
Dr. Cleland proposed “focusing for the moment on people who are iron deficient but investigating the possibility that we are being overly restrictive and should be giving iron to a much broader population.” That course, however, would require large population-based studies.
“We need more experience,” Dr. Cleland said, “to make sure that the benefits outweigh any risks before we can just give iron to everyone.”
Dr. Martens has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Cleland declares grant support, support for travel, and personal honoraria from Pharmacosmos and Vifor. Disclosures for other authors are in the published report and editorial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
with implications that may extend to cardiovascular disease in general.
In the study involving more than 900 patients with PH, investigators at seven U.S. centers determined the prevalence of iron deficiency by two separate definitions and assessed its associations with functional measures and quality of life (QoL) scores.
An iron deficiency definition used conventionally in heart failure (HF) – ferritin less than 100 g/mL or 100-299 ng/mL with transferrin saturation (TSAT) less than 20% – failed to discriminate patients with reduced peak oxygen consumption (peakVO2), 6-minute walk test (6MWT) results, and QoL scores on the 36-item Short Form Survey (SF-36).
But an alternative definition for iron deficiency, simply a TSAT less than 21%, did predict such patients with reduced peakVO2, 6MWT, and QoL. It was also associated with an increased mortality risk. The study was published in the European Heart Journal.
“A low TSAT, less than 21%, is key in the pathophysiology of iron deficiency in pulmonary hypertension” and is associated with those important clinical and functional characteristics, lead author Pieter Martens MD, PhD, said in an interview. The study “underscores the importance of these criteria in future intervention studies in the field of pulmonary hypertension testing iron therapies.”
A broader implication is that “we should revise how we define iron deficiency in heart failure and cardiovascular disease in general and how we select patients for iron therapies,” said Dr. Martens, of the Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute of the Cleveland Clinic.
Iron’s role in pulmonary vascular disease
“Iron deficiency is associated with an energetic deficit, especially in high energy–demanding tissue, leading to early skeletal muscle acidification and diminished left and right ventricular (RV) contractile reserve during exercise,” the published report states. It can lead to “maladaptive RV remodeling,” which is a “hallmark feature” predictive of morbidity and mortality in patients with pulmonary vascular disease (PVD).
Some studies have suggested that iron deficiency is a common comorbidity in patients with PVD, their estimates of its prevalence ranging widely due in part to the “absence of a uniform definition,” write the authors.
Dr. Martens said the current study was conducted partly in response to the increasingly common observation that the HF-associated definition of iron deficiency “has limitations.” Yet, “without validation in the field of pulmonary hypertension, the 2022 pulmonary hypertension guidelines endorse this definition.”
As iron deficiency is a causal risk factor for HF progression, Dr. Martens added, the HF field has “taught us the importance of using validated definitions for iron deficiency when selecting patients for iron treatment in randomized controlled trials.”
Moreover, some evidence suggests that iron deficiency by some definitions may be associated with diminished exercise capacity and QoL in patients with PVD, which are associations that have not been confirmed in large studies, the report notes.
Therefore, it continues, the study sought to “determine and validate” the optimal definition of iron deficiency in patients with PVD; document its prevalence; and explore associations between iron deficiency and exercise capacity, QoL, and cardiac and pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Evaluating definitions of iron deficiency
The prospective study, called PVDOMICS, entered 1,195 subjects with available iron levels. After exclusion of 38 patients with sarcoidosis, myeloproliferative disease, or hemoglobinopathy, there remained 693 patients with “overt” PH, 225 with a milder form of PH who served as PVD comparators, and 90 age-, sex-, race/ethnicity- matched “healthy” adults who served as controls.
According to the conventional HF definition of iron deficiency – that is, ferritin 100-299 ng/mL and TSAT less than 20% – the prevalences were 74% in patients with overt PH and 72% of those “across the PVD spectrum.”
But by that definition, iron deficient and non-iron deficient patients didn’t differ significantly in peakVO2, 6MWT distance, or SF-36 physical component scores.
In contrast, patients meeting the alternative definition of iron deficiency of TSAT less than 21% showed significantly reduced functional and QoL measures, compared with those with TSAT greater than or equal to 21%.
The group with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly more RV remodeling at cardiac MRI, compared with those who had TSAT greater than or equal to 21%, but their invasively measured pulmonary vascular resistance was comparable.
Of note, those with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly increased all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.13-2.34; P = .009) after adjustment for age, sex, hemoglobin, and natriuretic peptide levels.
“Proper validation of the definition of iron deficiency is important for prognostication,” the published report states, “but also for providing a working definition that can be used to identify suitable patients for inclusion in randomized controlled trials” of drugs for iron deficiency.
Additionally, the finding that TSAT less than 21% points to patients with diminished functional and exercise capacity is “consistent with more recent studies in the field of heart failure” that suggest “functional abnormalities and adverse cardiac remodeling are worse in patients with a low TSAT.” Indeed, the report states, such treatment effects have been “the most convincing” in HF trials.
Broader implications
An accompanying editorial agrees that the study’s implications apply well beyond PH. It highlights that iron deficiency is common in PH, while such PH is “not substantially different from the problem in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease in general,” lead editorialist John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, said in an interview. “It’s also common as people get older, even in those without these diseases.”
Dr. Cleland said the anemia definition currently used in cardiovascular research and practice is based on a hemoglobin concentration below the 5th percentile of age and sex in primarily young, healthy people, and not on its association with clinical outcomes.
“We recently analyzed data on a large population in the United Kingdom with a broad range of cardiovascular diseases and found that unless anemia is severe, [other] markers of iron deficiency are usually not measured,” he said. A low hemoglobin and TSAT, but not low ferritin levels, are associated with worse prognosis.
Dr. Cleland agreed that the HF-oriented definition is “poor,” with profound implications for the conduct of clinical trials. “If the definition of iron deficiency lacks specificity, then clinical trials will include many patients without iron deficiency who are unlikely to benefit from and might be harmed by IV iron.” Inclusion of such patients may also “dilute” any benefit that might emerge and render the outcome inaccurate.
But if the definition of iron deficiency lacks sensitivity, “then in clinical practice, many patients with iron deficiency may be denied a simple and effective treatment.”
Measuring serum iron could potentially be useful, but it’s usually not done in randomized trials “especially since taking an iron tablet can give a temporary ‘blip’ in serum iron,” Dr. Cleland said. “So TSAT is a reasonable compromise.” He said he “looks forward” to any further data on serum iron as a way of assessing iron deficiency and anemia.
Half full vs. half empty
Dr. Cleland likened the question of whom to treat with iron supplementation as a “glass half full versus half empty” clinical dilemma. “One approach is to give iron to everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re overloaded,” he said, “while the other is to withhold iron from everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re iron depleted.”
Recent evidence from the IRONMAN trial suggested that its patients with HF who received intravenous iron were less likely to be hospitalized for infections, particularly COVID-19, than a usual-care group. The treatment may also help reduce frailty.
“So should we be offering IV iron specifically to people considered iron deficient, or should we be ensuring that everyone over age 70 get iron supplements?” Dr. Cleland mused rhetorically. On a cautionary note, he added, perhaps iron supplementation will be harmful if it’s not necessary.
Dr. Cleland proposed “focusing for the moment on people who are iron deficient but investigating the possibility that we are being overly restrictive and should be giving iron to a much broader population.” That course, however, would require large population-based studies.
“We need more experience,” Dr. Cleland said, “to make sure that the benefits outweigh any risks before we can just give iron to everyone.”
Dr. Martens has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Cleland declares grant support, support for travel, and personal honoraria from Pharmacosmos and Vifor. Disclosures for other authors are in the published report and editorial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
with implications that may extend to cardiovascular disease in general.
In the study involving more than 900 patients with PH, investigators at seven U.S. centers determined the prevalence of iron deficiency by two separate definitions and assessed its associations with functional measures and quality of life (QoL) scores.
An iron deficiency definition used conventionally in heart failure (HF) – ferritin less than 100 g/mL or 100-299 ng/mL with transferrin saturation (TSAT) less than 20% – failed to discriminate patients with reduced peak oxygen consumption (peakVO2), 6-minute walk test (6MWT) results, and QoL scores on the 36-item Short Form Survey (SF-36).
But an alternative definition for iron deficiency, simply a TSAT less than 21%, did predict such patients with reduced peakVO2, 6MWT, and QoL. It was also associated with an increased mortality risk. The study was published in the European Heart Journal.
“A low TSAT, less than 21%, is key in the pathophysiology of iron deficiency in pulmonary hypertension” and is associated with those important clinical and functional characteristics, lead author Pieter Martens MD, PhD, said in an interview. The study “underscores the importance of these criteria in future intervention studies in the field of pulmonary hypertension testing iron therapies.”
A broader implication is that “we should revise how we define iron deficiency in heart failure and cardiovascular disease in general and how we select patients for iron therapies,” said Dr. Martens, of the Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute of the Cleveland Clinic.
Iron’s role in pulmonary vascular disease
“Iron deficiency is associated with an energetic deficit, especially in high energy–demanding tissue, leading to early skeletal muscle acidification and diminished left and right ventricular (RV) contractile reserve during exercise,” the published report states. It can lead to “maladaptive RV remodeling,” which is a “hallmark feature” predictive of morbidity and mortality in patients with pulmonary vascular disease (PVD).
Some studies have suggested that iron deficiency is a common comorbidity in patients with PVD, their estimates of its prevalence ranging widely due in part to the “absence of a uniform definition,” write the authors.
Dr. Martens said the current study was conducted partly in response to the increasingly common observation that the HF-associated definition of iron deficiency “has limitations.” Yet, “without validation in the field of pulmonary hypertension, the 2022 pulmonary hypertension guidelines endorse this definition.”
As iron deficiency is a causal risk factor for HF progression, Dr. Martens added, the HF field has “taught us the importance of using validated definitions for iron deficiency when selecting patients for iron treatment in randomized controlled trials.”
Moreover, some evidence suggests that iron deficiency by some definitions may be associated with diminished exercise capacity and QoL in patients with PVD, which are associations that have not been confirmed in large studies, the report notes.
Therefore, it continues, the study sought to “determine and validate” the optimal definition of iron deficiency in patients with PVD; document its prevalence; and explore associations between iron deficiency and exercise capacity, QoL, and cardiac and pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Evaluating definitions of iron deficiency
The prospective study, called PVDOMICS, entered 1,195 subjects with available iron levels. After exclusion of 38 patients with sarcoidosis, myeloproliferative disease, or hemoglobinopathy, there remained 693 patients with “overt” PH, 225 with a milder form of PH who served as PVD comparators, and 90 age-, sex-, race/ethnicity- matched “healthy” adults who served as controls.
According to the conventional HF definition of iron deficiency – that is, ferritin 100-299 ng/mL and TSAT less than 20% – the prevalences were 74% in patients with overt PH and 72% of those “across the PVD spectrum.”
But by that definition, iron deficient and non-iron deficient patients didn’t differ significantly in peakVO2, 6MWT distance, or SF-36 physical component scores.
In contrast, patients meeting the alternative definition of iron deficiency of TSAT less than 21% showed significantly reduced functional and QoL measures, compared with those with TSAT greater than or equal to 21%.
The group with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly more RV remodeling at cardiac MRI, compared with those who had TSAT greater than or equal to 21%, but their invasively measured pulmonary vascular resistance was comparable.
Of note, those with TSAT less than 21% also showed significantly increased all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.13-2.34; P = .009) after adjustment for age, sex, hemoglobin, and natriuretic peptide levels.
“Proper validation of the definition of iron deficiency is important for prognostication,” the published report states, “but also for providing a working definition that can be used to identify suitable patients for inclusion in randomized controlled trials” of drugs for iron deficiency.
Additionally, the finding that TSAT less than 21% points to patients with diminished functional and exercise capacity is “consistent with more recent studies in the field of heart failure” that suggest “functional abnormalities and adverse cardiac remodeling are worse in patients with a low TSAT.” Indeed, the report states, such treatment effects have been “the most convincing” in HF trials.
Broader implications
An accompanying editorial agrees that the study’s implications apply well beyond PH. It highlights that iron deficiency is common in PH, while such PH is “not substantially different from the problem in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease in general,” lead editorialist John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, said in an interview. “It’s also common as people get older, even in those without these diseases.”
Dr. Cleland said the anemia definition currently used in cardiovascular research and practice is based on a hemoglobin concentration below the 5th percentile of age and sex in primarily young, healthy people, and not on its association with clinical outcomes.
“We recently analyzed data on a large population in the United Kingdom with a broad range of cardiovascular diseases and found that unless anemia is severe, [other] markers of iron deficiency are usually not measured,” he said. A low hemoglobin and TSAT, but not low ferritin levels, are associated with worse prognosis.
Dr. Cleland agreed that the HF-oriented definition is “poor,” with profound implications for the conduct of clinical trials. “If the definition of iron deficiency lacks specificity, then clinical trials will include many patients without iron deficiency who are unlikely to benefit from and might be harmed by IV iron.” Inclusion of such patients may also “dilute” any benefit that might emerge and render the outcome inaccurate.
But if the definition of iron deficiency lacks sensitivity, “then in clinical practice, many patients with iron deficiency may be denied a simple and effective treatment.”
Measuring serum iron could potentially be useful, but it’s usually not done in randomized trials “especially since taking an iron tablet can give a temporary ‘blip’ in serum iron,” Dr. Cleland said. “So TSAT is a reasonable compromise.” He said he “looks forward” to any further data on serum iron as a way of assessing iron deficiency and anemia.
Half full vs. half empty
Dr. Cleland likened the question of whom to treat with iron supplementation as a “glass half full versus half empty” clinical dilemma. “One approach is to give iron to everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re overloaded,” he said, “while the other is to withhold iron from everyone unless there’s evidence that they’re iron depleted.”
Recent evidence from the IRONMAN trial suggested that its patients with HF who received intravenous iron were less likely to be hospitalized for infections, particularly COVID-19, than a usual-care group. The treatment may also help reduce frailty.
“So should we be offering IV iron specifically to people considered iron deficient, or should we be ensuring that everyone over age 70 get iron supplements?” Dr. Cleland mused rhetorically. On a cautionary note, he added, perhaps iron supplementation will be harmful if it’s not necessary.
Dr. Cleland proposed “focusing for the moment on people who are iron deficient but investigating the possibility that we are being overly restrictive and should be giving iron to a much broader population.” That course, however, would require large population-based studies.
“We need more experience,” Dr. Cleland said, “to make sure that the benefits outweigh any risks before we can just give iron to everyone.”
Dr. Martens has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Cleland declares grant support, support for travel, and personal honoraria from Pharmacosmos and Vifor. Disclosures for other authors are in the published report and editorial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL
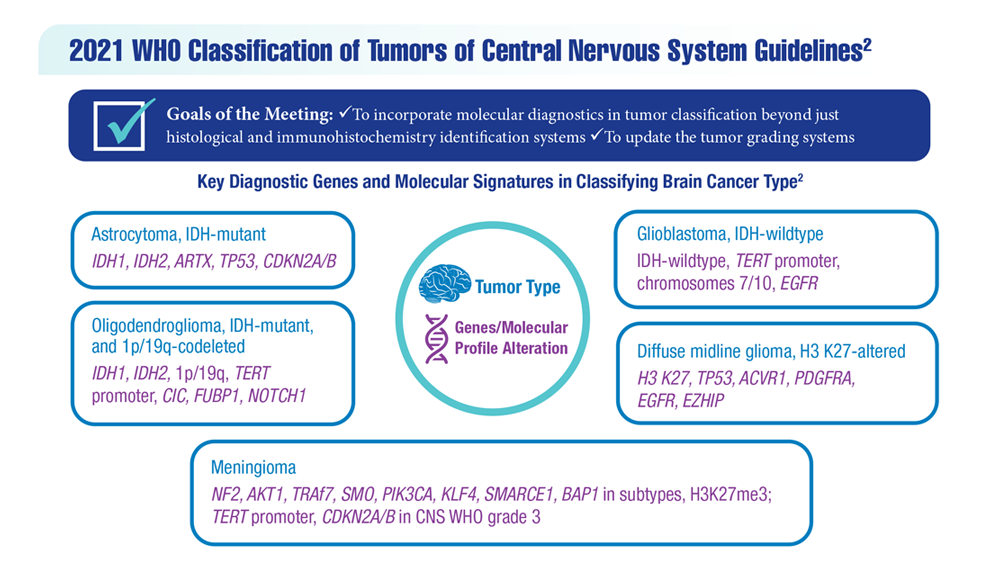
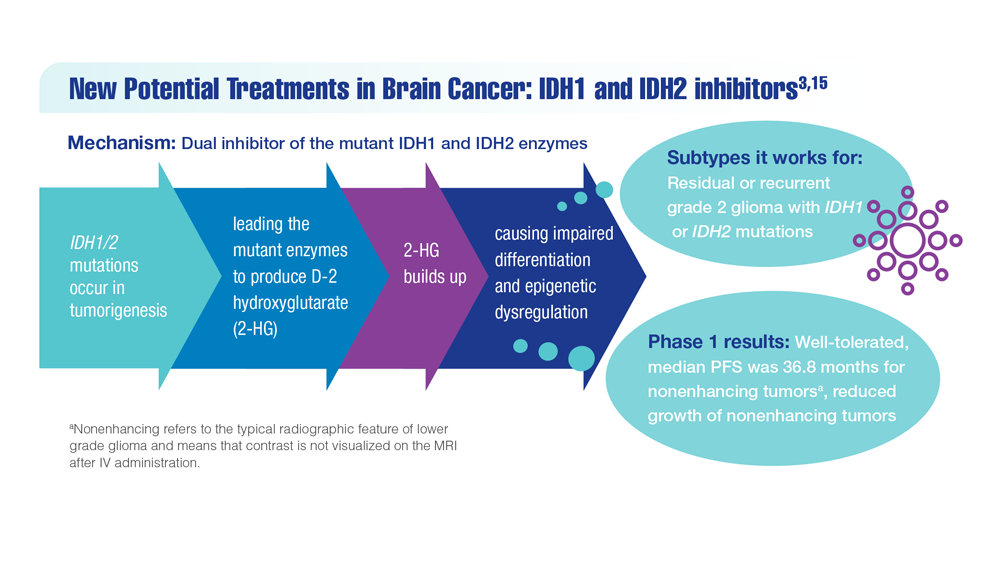
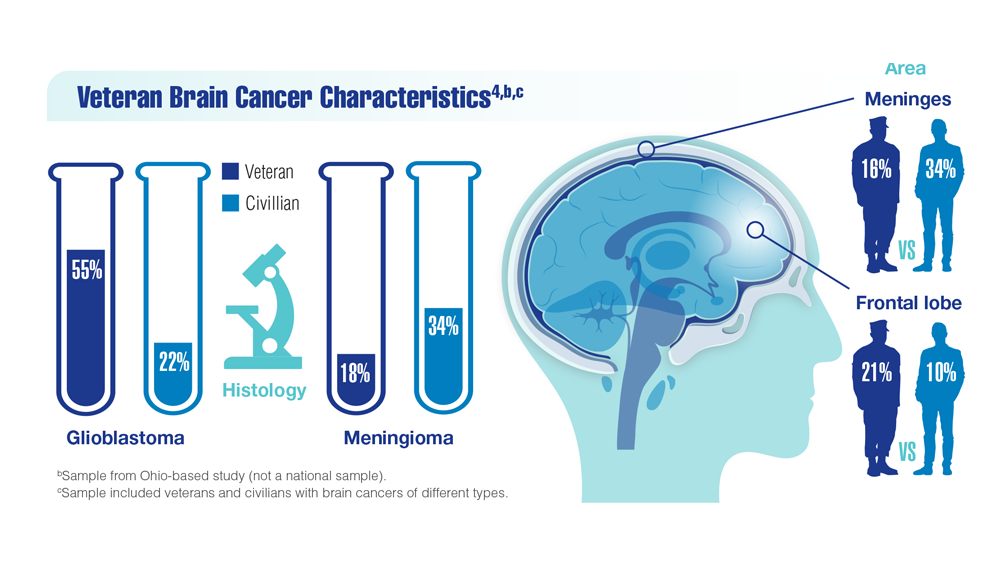
New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
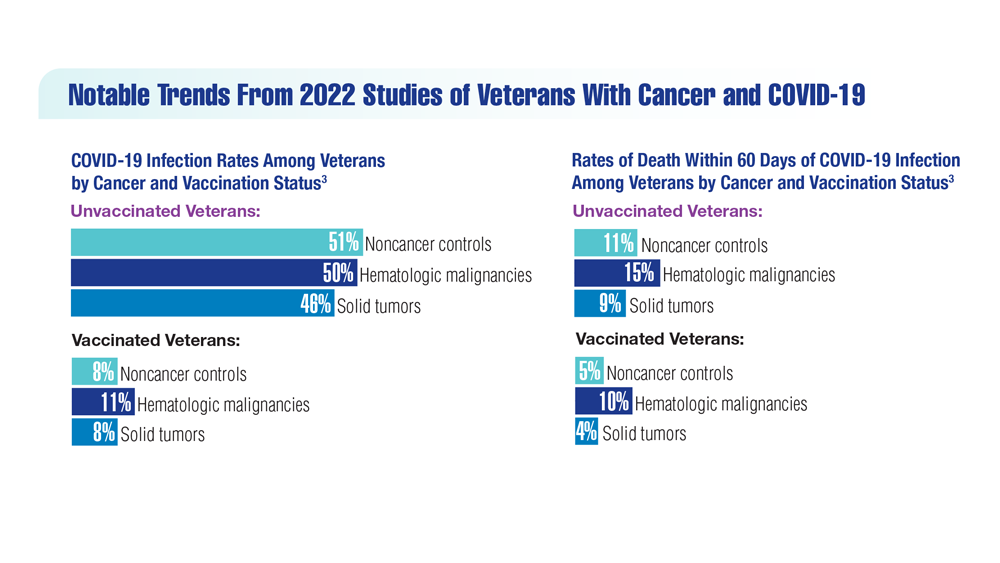
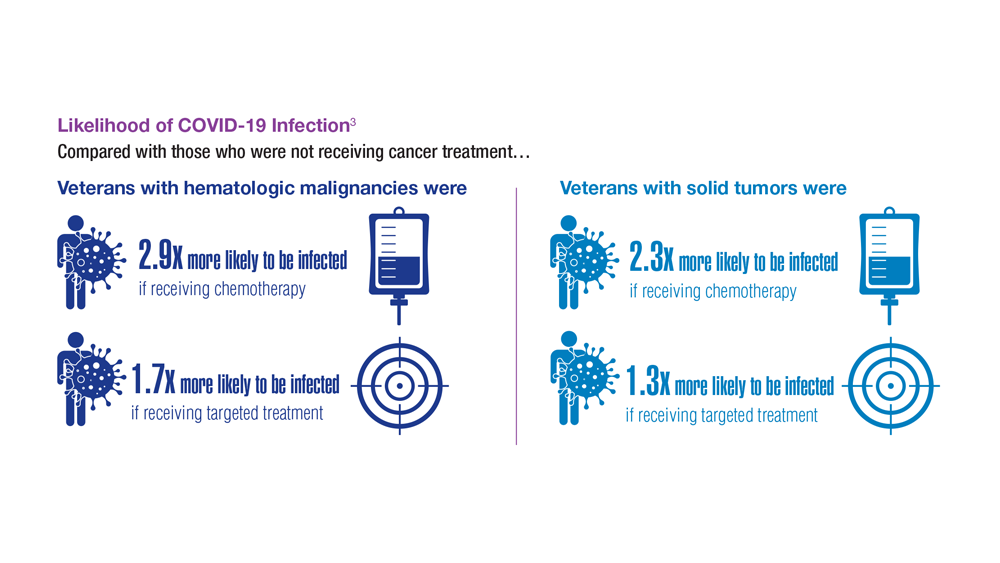
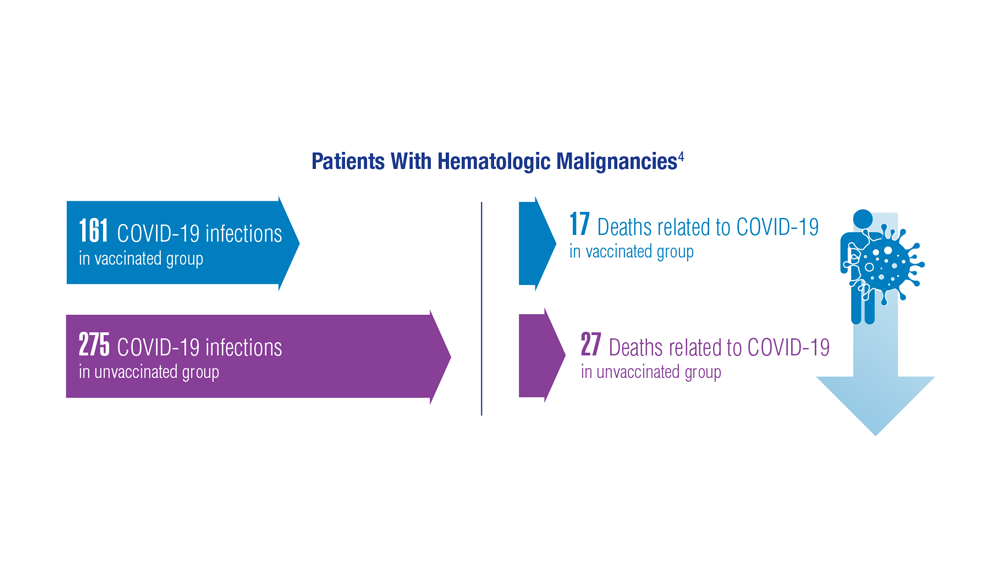
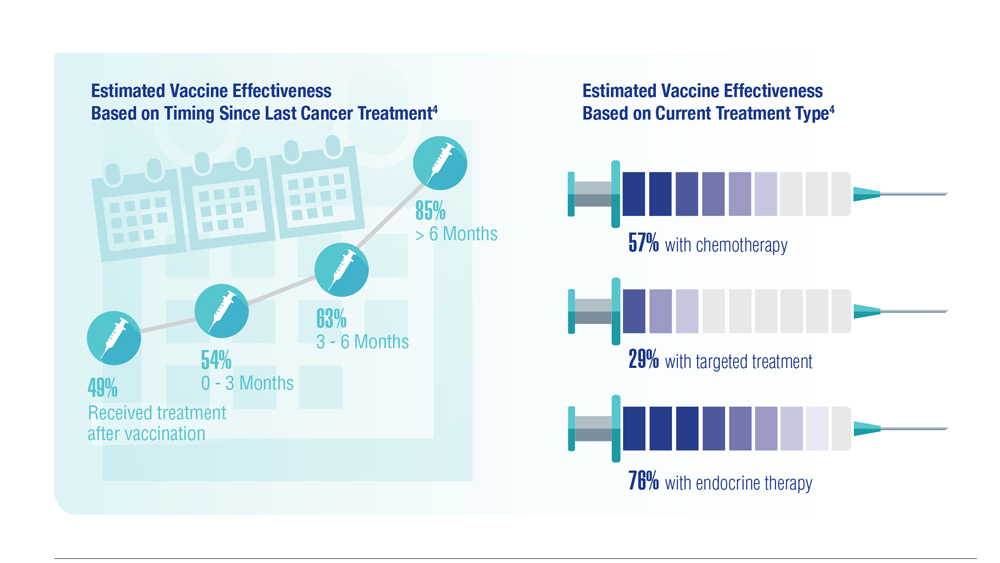
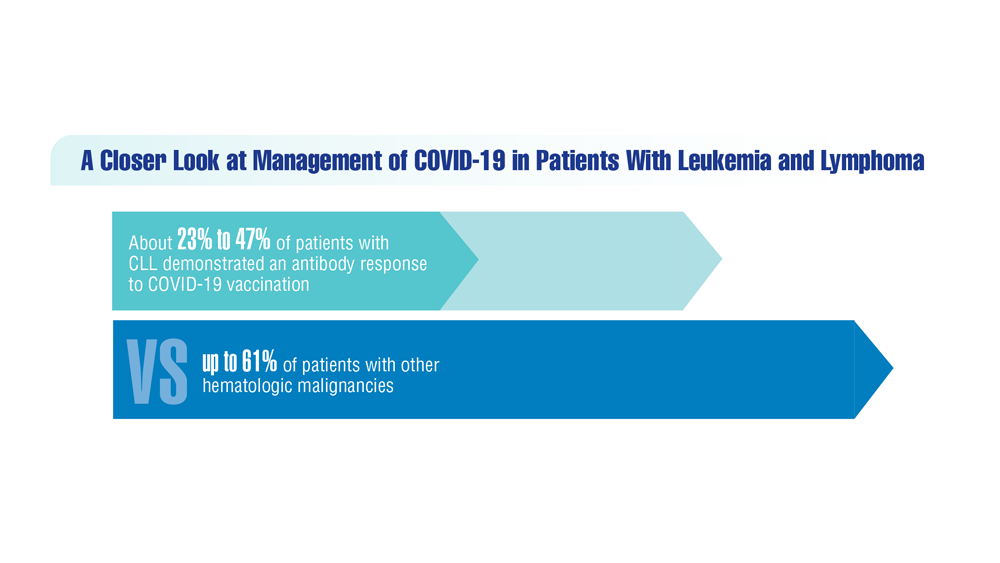
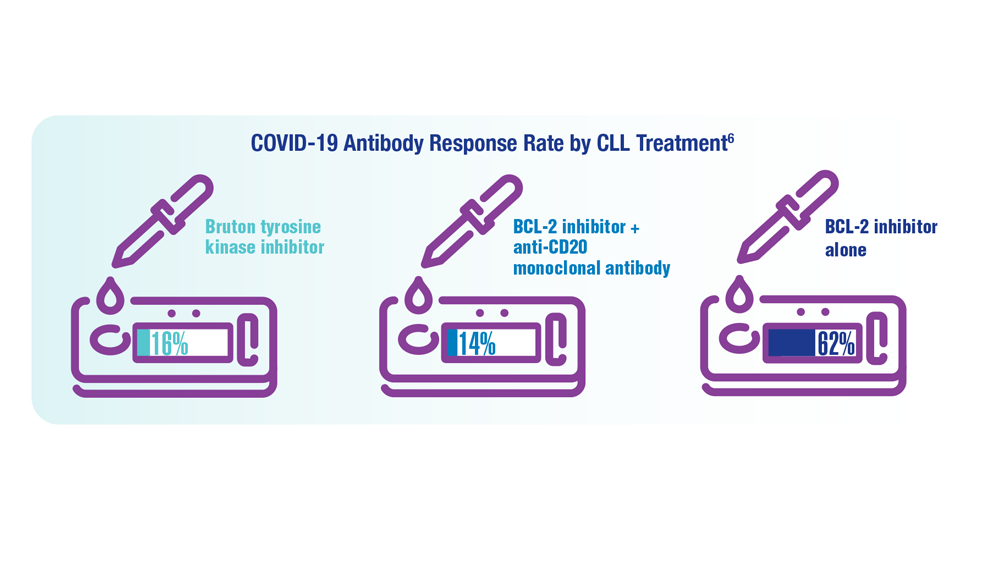
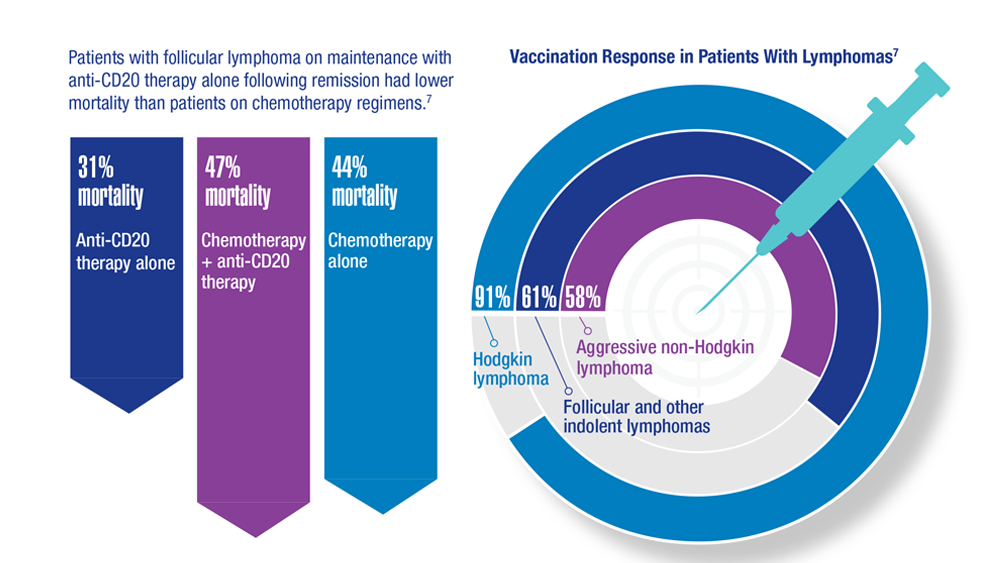
COVID-19 Outcomes in Veterans With Hematologic Malignancies
- Parker S. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(1):2 doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00713-0
- Englum BR et al. Cancer. 2022;128(5):1048-1056. doi:10.1002/cncr.34011
- Leuva H et al. Semin Oncol. 2022:49(5):363-370. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.07.005
- Wu JTY et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(2):281-286. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5771
- Fillmore NR et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021;113(6):691-698. doi:10.1093/jnci/djaa159
- Morawska M. Eur J Haematol. 2022;108(2):91-98. doi:10.1111/ejh.13722
- Passamonti F et al. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(1):3-15. doi:10.1002/hon.3086
- Parker S. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(1):2 doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00713-0
- Englum BR et al. Cancer. 2022;128(5):1048-1056. doi:10.1002/cncr.34011
- Leuva H et al. Semin Oncol. 2022:49(5):363-370. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.07.005
- Wu JTY et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(2):281-286. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5771
- Fillmore NR et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021;113(6):691-698. doi:10.1093/jnci/djaa159
- Morawska M. Eur J Haematol. 2022;108(2):91-98. doi:10.1111/ejh.13722
- Passamonti F et al. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(1):3-15. doi:10.1002/hon.3086
- Parker S. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(1):2 doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00713-0
- Englum BR et al. Cancer. 2022;128(5):1048-1056. doi:10.1002/cncr.34011
- Leuva H et al. Semin Oncol. 2022:49(5):363-370. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2022.07.005
- Wu JTY et al. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(2):281-286. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5771
- Fillmore NR et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021;113(6):691-698. doi:10.1093/jnci/djaa159
- Morawska M. Eur J Haematol. 2022;108(2):91-98. doi:10.1111/ejh.13722
- Passamonti F et al. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(1):3-15. doi:10.1002/hon.3086
Association Between Psoriasis and Obesity Among US Adults in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated dermatologic condition that is associated with various comorbidities, including obesity.1 The underlying pathophysiology of psoriasis has been extensively studied, and recent research has discussed the role of obesity in IL-17 secretion.2 The relationship between being overweight/obese and having psoriasis has been documented in the literature.1,2 However, this association in a recent population is lacking. We sought to investigate the association between psoriasis and obesity utilizing a representative US population of adults—the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data,3 which contains the most recent psoriasis data.
We conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study focused on patients 20 years and older with psoriasis from the 2009-2014 NHANES database. Three 2-year cycles of NHANES data were combined to create our 2009 to 2014 dataset. In the Table, numerous variables including age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, education, diabetes status, tobacco use, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and being called overweight by a health care provider were analyzed using χ2 or t test analyses to evaluate for differences among those with and without psoriasis. Diabetes status was assessed by the question “Other than during pregnancy, have you ever been told by a doctor or health professional that you have diabetes or sugar diabetes?” Tobacco use was assessed by the question “Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your entire life?” Psoriasis status was assessed by a self-reported response to the question “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health care professional that you had psoriasis?” Three different outcome variables were used to determine if patients were overweight or obese: BMI, waist circumference, and response to the question “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?” Obesity was defined as having a BMI of 30 or higher or waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females.4 Being overweight was defined as having a BMI of 25 to 29.99 or response of Yes to “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?”
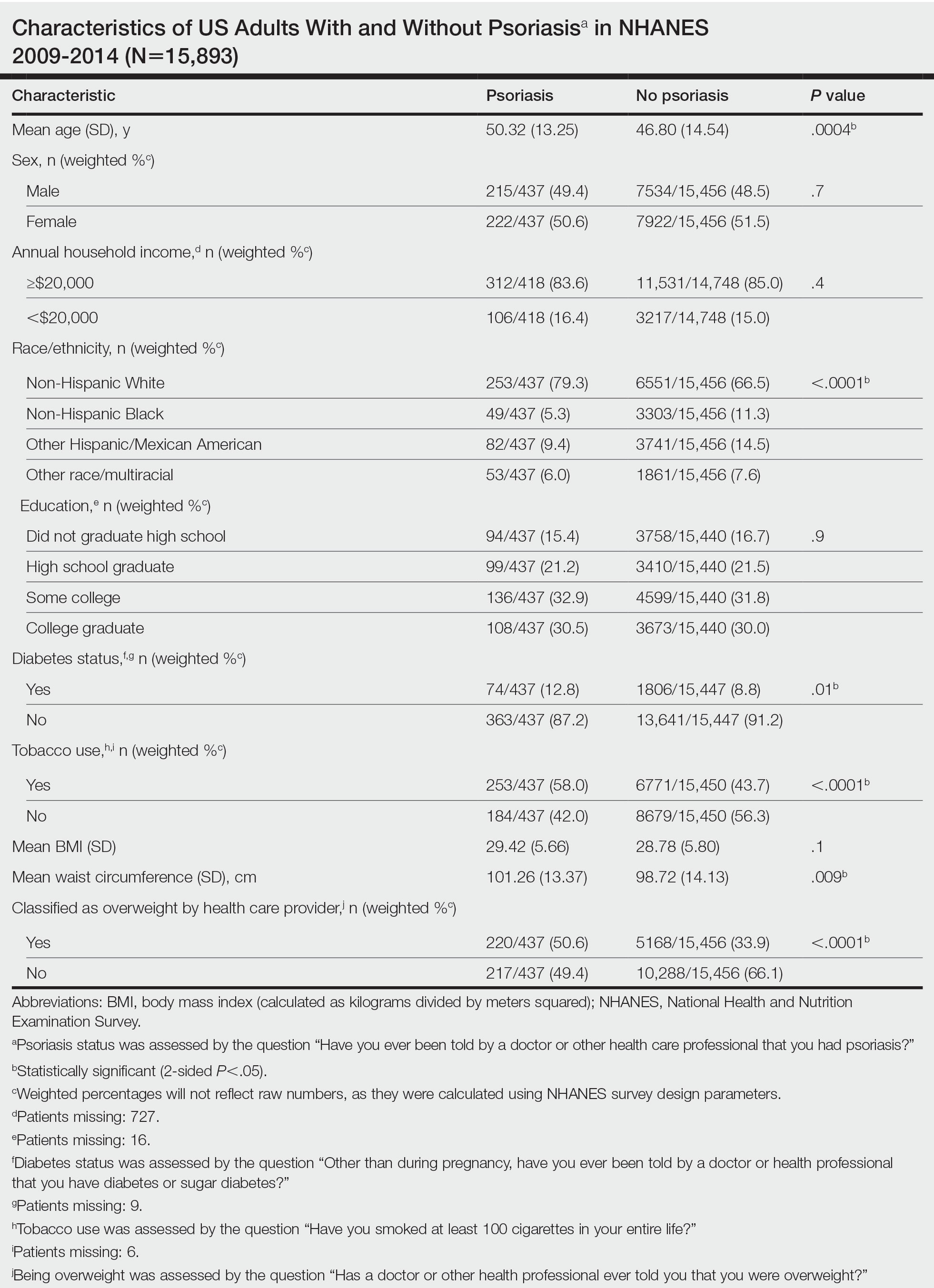
Initially, there were 17,547 participants 20 years and older from 2009 to 2014, but 1654 participants were excluded because of missing data for obesity or psoriasis; therefore, 15,893 patients were included in our analysis. Multivariable logistic regressions were utilized to examine the association between psoriasis and being overweight/obese (eTable). Additionally, the models were adjusted based on age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, diabetes status, and tobacco use. All data processing and analysis were performed in Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
The Table shows characteristics of US adults with and without psoriasis in NHANES 2009-2014. We found that the variables of interest evaluating body weight that were significantly different on analysis between patients with and without psoriasis included waist circumference—patients with psoriasis had a significantly higher waist circumference (P=.009)—and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (P<.0001), which supports the findings by Love et al,5 who reported abdominal obesity was the most common feature of metabolic syndrome exhibited among patients with psoriasis.
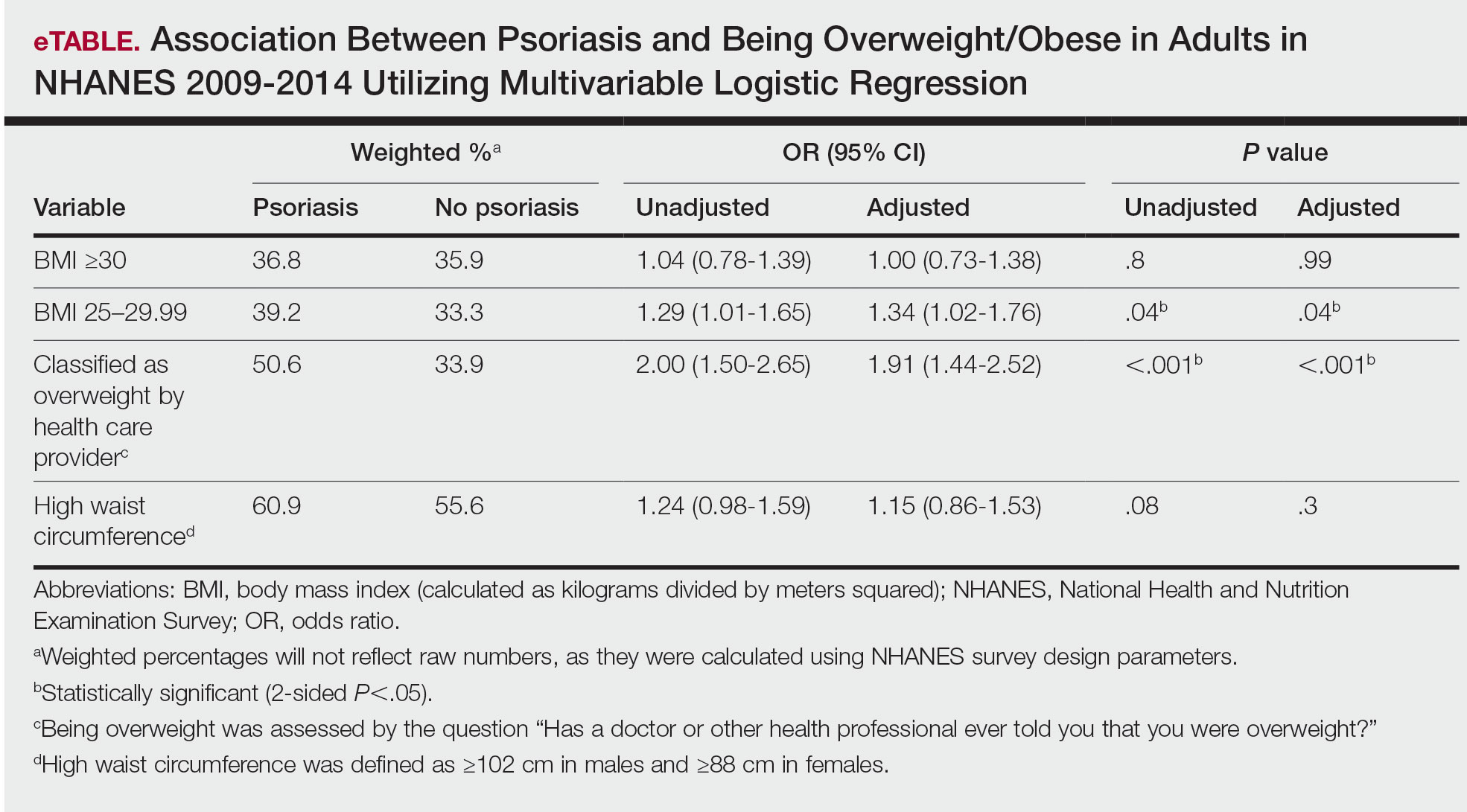
Multivariable logistic regression analysis (eTable) revealed that there was a significant association between psoriasis and BMI of 25 to 29.99 (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.34; 95% CI, 1.02-1.76; P=.04) and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (AOR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.44-2.52; P<.001). After adjusting for confounding variables, there was no significant association between psoriasis and a BMI of 30 or higher (AOR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.73-1.38; P=.99) or a waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females (AOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.86-1.53; P=.3).
Our findings suggest that a few variables indicative of being overweight or obese are associated with psoriasis. This relationship most likely is due to increased adipokine, including resistin, levels in overweight individuals, resulting in a proinflammatory state.6 It has been suggested that BMI alone is not a definitive marker for measuring fat storage levels in individuals. People can have a normal or slightly elevated BMI but possess excessive adiposity, resulting in chronic inflammation.6 Therefore, our findings of a significant association between psoriasis and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight might be a stronger measurement for possessing excessive fat, as this is likely due to clinical judgment rather than BMI measurement.
Moreover, it should be noted that the potential reason for the lack of association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis in our analysis may be a result of BMI serving as a poor measurement for adiposity. Additionally, Armstrong and colleagues7 discussed that the association between BMI and psoriasis was stronger for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Our study consisted of NHANES data for self-reported psoriasis diagnoses without a psoriasis severity index, making it difficult to extrapolate which individuals had mild or moderate to severe psoriasis, which may have contributed to our finding of no association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis.
The self-reported nature of the survey questions and lack of questions regarding psoriasis severity serve as limitations to the study. Both obesity and psoriasis can have various systemic consequences, such as cardiovascular disease, due to the development of an inflammatory state.8 Future studies may explore other body measurements that indicate being overweight or obese and the potential synergistic relationship of obesity and psoriasis severity, optimizing the development of effective treatment plans.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Xu C, Ji J, Su T, et al. The association of psoriasis and obesity: focusing on IL-17A-related immunological mechanisms. Int J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;4:116-121.
- National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.govnchs/nhanes/Default.aspx
- Ross R, Neeland IJ, Yamashita S, et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:177-189.
- Love TJ, Qureshi AA, Karlson EW, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in psoriasis: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003-2006. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:419-424.
- Paroutoglou K, Papadavid E, Christodoulatos GS, et al. Deciphering the association between psoriasis and obesity: current evidence and treatment considerations. Curr Obes Rep. 2020;9:165-178.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Hamminga EA, van der Lely AJ, Neumann HAM, et al. Chronic inflammation in psoriasis and obesity: implications for therapy. Med Hypotheses. 2006;67:768-773.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated dermatologic condition that is associated with various comorbidities, including obesity.1 The underlying pathophysiology of psoriasis has been extensively studied, and recent research has discussed the role of obesity in IL-17 secretion.2 The relationship between being overweight/obese and having psoriasis has been documented in the literature.1,2 However, this association in a recent population is lacking. We sought to investigate the association between psoriasis and obesity utilizing a representative US population of adults—the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data,3 which contains the most recent psoriasis data.
We conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study focused on patients 20 years and older with psoriasis from the 2009-2014 NHANES database. Three 2-year cycles of NHANES data were combined to create our 2009 to 2014 dataset. In the Table, numerous variables including age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, education, diabetes status, tobacco use, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and being called overweight by a health care provider were analyzed using χ2 or t test analyses to evaluate for differences among those with and without psoriasis. Diabetes status was assessed by the question “Other than during pregnancy, have you ever been told by a doctor or health professional that you have diabetes or sugar diabetes?” Tobacco use was assessed by the question “Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your entire life?” Psoriasis status was assessed by a self-reported response to the question “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health care professional that you had psoriasis?” Three different outcome variables were used to determine if patients were overweight or obese: BMI, waist circumference, and response to the question “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?” Obesity was defined as having a BMI of 30 or higher or waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females.4 Being overweight was defined as having a BMI of 25 to 29.99 or response of Yes to “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?”

Initially, there were 17,547 participants 20 years and older from 2009 to 2014, but 1654 participants were excluded because of missing data for obesity or psoriasis; therefore, 15,893 patients were included in our analysis. Multivariable logistic regressions were utilized to examine the association between psoriasis and being overweight/obese (eTable). Additionally, the models were adjusted based on age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, diabetes status, and tobacco use. All data processing and analysis were performed in Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). P<.05 was considered statistically significant.

The Table shows characteristics of US adults with and without psoriasis in NHANES 2009-2014. We found that the variables of interest evaluating body weight that were significantly different on analysis between patients with and without psoriasis included waist circumference—patients with psoriasis had a significantly higher waist circumference (P=.009)—and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (P<.0001), which supports the findings by Love et al,5 who reported abdominal obesity was the most common feature of metabolic syndrome exhibited among patients with psoriasis.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis (eTable) revealed that there was a significant association between psoriasis and BMI of 25 to 29.99 (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.34; 95% CI, 1.02-1.76; P=.04) and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (AOR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.44-2.52; P<.001). After adjusting for confounding variables, there was no significant association between psoriasis and a BMI of 30 or higher (AOR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.73-1.38; P=.99) or a waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females (AOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.86-1.53; P=.3).
Our findings suggest that a few variables indicative of being overweight or obese are associated with psoriasis. This relationship most likely is due to increased adipokine, including resistin, levels in overweight individuals, resulting in a proinflammatory state.6 It has been suggested that BMI alone is not a definitive marker for measuring fat storage levels in individuals. People can have a normal or slightly elevated BMI but possess excessive adiposity, resulting in chronic inflammation.6 Therefore, our findings of a significant association between psoriasis and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight might be a stronger measurement for possessing excessive fat, as this is likely due to clinical judgment rather than BMI measurement.
Moreover, it should be noted that the potential reason for the lack of association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis in our analysis may be a result of BMI serving as a poor measurement for adiposity. Additionally, Armstrong and colleagues7 discussed that the association between BMI and psoriasis was stronger for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Our study consisted of NHANES data for self-reported psoriasis diagnoses without a psoriasis severity index, making it difficult to extrapolate which individuals had mild or moderate to severe psoriasis, which may have contributed to our finding of no association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis.
The self-reported nature of the survey questions and lack of questions regarding psoriasis severity serve as limitations to the study. Both obesity and psoriasis can have various systemic consequences, such as cardiovascular disease, due to the development of an inflammatory state.8 Future studies may explore other body measurements that indicate being overweight or obese and the potential synergistic relationship of obesity and psoriasis severity, optimizing the development of effective treatment plans.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated dermatologic condition that is associated with various comorbidities, including obesity.1 The underlying pathophysiology of psoriasis has been extensively studied, and recent research has discussed the role of obesity in IL-17 secretion.2 The relationship between being overweight/obese and having psoriasis has been documented in the literature.1,2 However, this association in a recent population is lacking. We sought to investigate the association between psoriasis and obesity utilizing a representative US population of adults—the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data,3 which contains the most recent psoriasis data.
We conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study focused on patients 20 years and older with psoriasis from the 2009-2014 NHANES database. Three 2-year cycles of NHANES data were combined to create our 2009 to 2014 dataset. In the Table, numerous variables including age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, education, diabetes status, tobacco use, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and being called overweight by a health care provider were analyzed using χ2 or t test analyses to evaluate for differences among those with and without psoriasis. Diabetes status was assessed by the question “Other than during pregnancy, have you ever been told by a doctor or health professional that you have diabetes or sugar diabetes?” Tobacco use was assessed by the question “Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your entire life?” Psoriasis status was assessed by a self-reported response to the question “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health care professional that you had psoriasis?” Three different outcome variables were used to determine if patients were overweight or obese: BMI, waist circumference, and response to the question “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?” Obesity was defined as having a BMI of 30 or higher or waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females.4 Being overweight was defined as having a BMI of 25 to 29.99 or response of Yes to “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you were overweight?”

Initially, there were 17,547 participants 20 years and older from 2009 to 2014, but 1654 participants were excluded because of missing data for obesity or psoriasis; therefore, 15,893 patients were included in our analysis. Multivariable logistic regressions were utilized to examine the association between psoriasis and being overweight/obese (eTable). Additionally, the models were adjusted based on age, sex, household income, race/ethnicity, diabetes status, and tobacco use. All data processing and analysis were performed in Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). P<.05 was considered statistically significant.

The Table shows characteristics of US adults with and without psoriasis in NHANES 2009-2014. We found that the variables of interest evaluating body weight that were significantly different on analysis between patients with and without psoriasis included waist circumference—patients with psoriasis had a significantly higher waist circumference (P=.009)—and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (P<.0001), which supports the findings by Love et al,5 who reported abdominal obesity was the most common feature of metabolic syndrome exhibited among patients with psoriasis.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis (eTable) revealed that there was a significant association between psoriasis and BMI of 25 to 29.99 (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.34; 95% CI, 1.02-1.76; P=.04) and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight (AOR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.44-2.52; P<.001). After adjusting for confounding variables, there was no significant association between psoriasis and a BMI of 30 or higher (AOR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.73-1.38; P=.99) or a waist circumference of 102 cm or more in males and 88 cm or more in females (AOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.86-1.53; P=.3).
Our findings suggest that a few variables indicative of being overweight or obese are associated with psoriasis. This relationship most likely is due to increased adipokine, including resistin, levels in overweight individuals, resulting in a proinflammatory state.6 It has been suggested that BMI alone is not a definitive marker for measuring fat storage levels in individuals. People can have a normal or slightly elevated BMI but possess excessive adiposity, resulting in chronic inflammation.6 Therefore, our findings of a significant association between psoriasis and being told by a health care provider that they are overweight might be a stronger measurement for possessing excessive fat, as this is likely due to clinical judgment rather than BMI measurement.
Moreover, it should be noted that the potential reason for the lack of association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis in our analysis may be a result of BMI serving as a poor measurement for adiposity. Additionally, Armstrong and colleagues7 discussed that the association between BMI and psoriasis was stronger for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Our study consisted of NHANES data for self-reported psoriasis diagnoses without a psoriasis severity index, making it difficult to extrapolate which individuals had mild or moderate to severe psoriasis, which may have contributed to our finding of no association between BMI of 30 or higher and psoriasis.
The self-reported nature of the survey questions and lack of questions regarding psoriasis severity serve as limitations to the study. Both obesity and psoriasis can have various systemic consequences, such as cardiovascular disease, due to the development of an inflammatory state.8 Future studies may explore other body measurements that indicate being overweight or obese and the potential synergistic relationship of obesity and psoriasis severity, optimizing the development of effective treatment plans.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Xu C, Ji J, Su T, et al. The association of psoriasis and obesity: focusing on IL-17A-related immunological mechanisms. Int J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;4:116-121.
- National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.govnchs/nhanes/Default.aspx
- Ross R, Neeland IJ, Yamashita S, et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:177-189.
- Love TJ, Qureshi AA, Karlson EW, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in psoriasis: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003-2006. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:419-424.
- Paroutoglou K, Papadavid E, Christodoulatos GS, et al. Deciphering the association between psoriasis and obesity: current evidence and treatment considerations. Curr Obes Rep. 2020;9:165-178.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Hamminga EA, van der Lely AJ, Neumann HAM, et al. Chronic inflammation in psoriasis and obesity: implications for therapy. Med Hypotheses. 2006;67:768-773.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Xu C, Ji J, Su T, et al. The association of psoriasis and obesity: focusing on IL-17A-related immunological mechanisms. Int J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;4:116-121.
- National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.govnchs/nhanes/Default.aspx
- Ross R, Neeland IJ, Yamashita S, et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:177-189.
- Love TJ, Qureshi AA, Karlson EW, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in psoriasis: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003-2006. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:419-424.
- Paroutoglou K, Papadavid E, Christodoulatos GS, et al. Deciphering the association between psoriasis and obesity: current evidence and treatment considerations. Curr Obes Rep. 2020;9:165-178.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Hamminga EA, van der Lely AJ, Neumann HAM, et al. Chronic inflammation in psoriasis and obesity: implications for therapy. Med Hypotheses. 2006;67:768-773.
Practice Points
- There are many comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis, making it crucial to evaluate for these diseases in patients with psoriasis.
- Obesity may be a contributing factor to psoriasis development due to the role of IL-17 secretion.